EP2104926B1 - Displaying elevation information from a digital map - Google Patents
Displaying elevation information from a digital map Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2104926B1 EP2104926B1 EP08701086A EP08701086A EP2104926B1 EP 2104926 B1 EP2104926 B1 EP 2104926B1 EP 08701086 A EP08701086 A EP 08701086A EP 08701086 A EP08701086 A EP 08701086A EP 2104926 B1 EP2104926 B1 EP 2104926B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- shading
- elevation
- function
- information
- display
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 238000009877 rendering Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 claims description 57
- 238000004422 calculation algorithm Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000012935 Averaging Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007620 mathematical function Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T17/00—Three dimensional [3D] modelling, e.g. data description of 3D objects
- G06T17/05—Geographic models
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/26—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00 specially adapted for navigation in a road network
- G01C21/34—Route searching; Route guidance
- G01C21/36—Input/output arrangements for on-board computers
- G01C21/3626—Details of the output of route guidance instructions
- G01C21/3635—Guidance using 3D or perspective road maps
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T11/00—2D [Two Dimensional] image generation
- G06T11/001—Texturing; Colouring; Generation of texture or colour
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G09—EDUCATION; CRYPTOGRAPHY; DISPLAY; ADVERTISING; SEALS
- G09B—EDUCATIONAL OR DEMONSTRATION APPLIANCES; APPLIANCES FOR TEACHING, OR COMMUNICATING WITH, THE BLIND, DEAF OR MUTE; MODELS; PLANETARIA; GLOBES; MAPS; DIAGRAMS
- G09B29/00—Maps; Plans; Charts; Diagrams, e.g. route diagram
- G09B29/10—Map spot or coordinate position indicators; Map reading aids
- G09B29/106—Map spot or coordinate position indicators; Map reading aids using electronic means
Definitions
- This invention relates to an apparatus and method for generating a display from a digital map, the display including a representation of elevation information.
- the invention is especially suitable for navigation devices, including portable navigation devices (so-called PNDs), but may find utility in any type of processing device for generating a display from digital map information.
- isolines also called contour lines
- shading of the map colour to represent elevation information.
- isolines may provide an accurate representation of elevation
- isolines can clutter the map display and are not intuitive to all users. Map clutter may be a particular problem when displaying the map on a relatively small electronic display device, or when it is also desired to display other map information such as navigation and location information.
- Shading can provide a more intuitive representation of elevation information without cluttering the display.
- shadeing means applying a darkening and/or lightening of the map colour, akin to a positive or negative shadow.
- a conventional technique for shading is to include the shading as a static feature of the map colour in the digital map.
- a digital map 12 is generated by processing map source information 10 that includes elevation data, to create the shading as a static template within the background colour in the digital map 12.
- a rendering process 14 is used to generate an image 18 including the fixed elevation shading template at a desired display scale represented by a display scale input 16.
- the shading is fixed as part of the digital map 12, and is not adaptive.
- the shading pattern also depends on the specific shading technique used when creating the digital map 12. Different shading techniques create different shading patterns based on the same elevation data. While a certain shading technique may be suited to displaying the map at a certain display scale, generating a display at other display scales can require interpolation or averaging of the shading pattern. This can create severe inaccuracies in the elevation shading. For example, as the display scale is varied, peaks and valleys in the elevation may appear to change shape and location as a result of averaging or interpolation inaccuracies.
- the present invention has been devised bearing the above problems in mind.
- a presently preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a method of rendering a display image generated from digital map information.
- the method includes the steps of:
- the shading value varies as a function of the elevation information and the display scale information, whereby the display is generated to represent elevation information by pixel shading that varies with display scale.
- the system may comprise an automomous device, such as a portable navigation device, a portable map viewer, a device including a positioning system (for example, a satellite based positioning system such as a Global Positioning System (GPS)), a portable digital assistant (PDA), a portable computer, or non-portable computer.
- a positioning system for example, a satellite based positioning system such as a Global Positioning System (GPS)
- PDA portable digital assistant
- the system may comprise a server storing the digital map, and a remote terminal or computer configured to generate a display of the digital map based on information received from the server over one or more networks, such as an internet or intranet.
- a remote terminal or computer configured to generate a display of the digital map based on information received from the server over one or more networks, such as an internet or intranet.
- One application for which provision of elevation information is especially useful is for a pedestrian and hiking navigation device or system.
- FIG. 2 illustrates schematically a technique for generating a map display including elevation shading in a preferred embodiment.
- a digital map 20 includes elevation information 20a indicative of elevation at different points in the digital map 20.
- the digital map 20 may be a database of map information stored in any suitable storage medium, for example but not limited to, an optical storage medium, non-volatile electronic memory, volatile electronic memory, a magnetic storage medium, or a magneto-optical storage medium.
- the elevation information 20a may represent a grid of values (a matrix of points). It makes no difference the way the data is stored.
- the surface of the Earth may be divided in some small patches of 3" in latitude and 3" in longitude.
- a map rendering module 22 dynamically renders a display image 24 based on (i) map information 26 received from the digital map 20, (ii) elevation information 26a also received from the digital map 20, and (iii) display scale information 28 indicating the display scale of the image 24, ie. the degree to which the map image is zoomed in towards, or zoomed out from, the map.
- the display scale is represented by a notional viewing (or zoom-out) height value "z" above the map.
- a relatively large display scale is represented by a respectively small value of z, and a relatively small display scale is respresented by a respectively large value of z.
- the map rendering module 22 may comprise dedicated graphics processor circuitry and/or rendering software executed by a general purpose processor.
- the map rendering module 22 is configured to render the map by applying a shading algorithm that darkens and/or lightens the map color to represent elevation in the map image 24.
- the output will be represented by the percentage of shading applied to each pixel on the screen.
- the screen is normally represented by a matrix of pixels, which gives the resolution of the screen.
- Each pixel has a colour associated with, in this case, the form of relief that it represents (for example, different colours for meadow, forest, built area, etc.), as represented by the map information 26.
- shadeing percentage is an indication of the extent that the colour should be darkened or made lighter (whitened). A negative shading percentage takes the colour closer to white, and a positive shading percentage takes the colour closer to black.
- the shading algorithm is a function of (i) the elevation information 20a/26a from the digital map 20, and (ii) the display scale information 28.
- the shading algorithm is configured to vary the shading style based on the same elevation information, as a varying function of the display scale information. In other words, as the display scale is varied, not just the magnification of the shading is varied, but also the style of shading. This enables the style of shading to be adapted to the display scale of the image 24.
- a first shading style is to apply shading that depends on the absolute elevation of an individual point in the image.
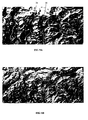
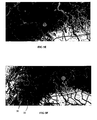
- a typical shading pattern produced using predominantly this style is illustrated in Fig. 5f .
- Darker image shading represents points of higher elevation. For example, peaks 30 are indicated by areas of local maxima in darkness shading, whereas valleys 32 are indicated by areas of local minima in darkness (local maxima in lightness).
- This first type of shading style is suitable for relatively small display scales (high zoom out away from the map), in which there may be significant changes in absolute elevation in close proximity in the map image.
- the first shading style is less suitable for relatively large display scales (zoomed in towards the map), in which the elevation may be substantially the same across the entire display image, leading to almost constant shading that obscures local relief features.
- a very different second shading style is based on elevation slope, namely the difference in elevation between adjacent points in the display image, taken in a certain sampling direction, for example, from North-West to South-East.
- a negative slope is rendered with one type of shading (e.g. with a lighter colour 34), and a positive slope with another type of shading (e.g. a darker colour 36). The steeper the slope the lighter or respective darker the colour that is used.
- a typical shading pattern produced using predominantly this style is illustrated in Fig. 5a .
- This second shading style is suited to large display scales (zoomed in towards the map), it is more responsive to local relief detail even though the absolute elevation may change only fractionally, and can generate intuitive shading for large display scale.
- the second shading style technique is less well suited to small display scale, where two display points on which the slope is calculated may be geographically remote, and so calculating an elevation slope between these points may not provide useful information. For example, if the two display points are of about the same elevation, but on opposite sides of a mountain peak, then the peak will not be represented by any shading using the second technique, because there is little difference between the elevations at the two display points, and important elevation features can easily be lost.
- the shading algorithm preferably combines first and second different shading functions or styles, each weighted by a respective coefficient indicating the respective strength of contribution of each shading function as a component of the shading algorithm.
- the coefficients vary as a function of the display scale information 28 (for example, the zoom out height "z"). More preferably, the coefficients vary as a substantially continuous function of the display scale information.
- a single coefficient l ( z ) may be used, where l ( z ) takes values between zero and 1, ( l ( z ) ⁇ [0,1]), with l ( z ) representing the weight of one shading function, and 1- l ( z ) representing the weight of the other shading function.
- the coefficient l ( z ) could vary linearly as a function of the display scale "z". However, referring to Fig. 3 , it is preferred that l ( z ) vary asymptotically between two limits as a function of the display scale. At large and medium display scales (small and medium “zoom-out” levels “z" away from the map), the predominant shading function is the slope based shading function (second shading function) and at small display scales (high “zoom-out” level "z"), the predominant shading function is the absolute elevation based function (first shading function). The value of l is big in the first case and small in the second.
- the function l (z) is preferably chosen to be composed by a sequence of two Bezier spline curve.
- the main idea behind this approach is to use a function which is "almost" asymptotic towards 0 when z approaches A and "almost” asymptotic towards 1 when z approaches E.
- the zoom value z in A as the lowest zoom level considered in this case and the value in E as the highest.
- Choosing a sequence of two Bezier splines can achieve the freedom to choose different convergence rates for the evolution up to the break even point C and for the one afterwards. It is essentially this type of evolution and the solution chosen which gives to the solution an optimal transition between the two criteria.
- the control points A, B, C, D, E can be tuned to achieve the optimal transition between the two shading criteria.
- the main formula also includes two sub-unitary, or secondary, weight functions for "tuning" the combined shading effect.
- the W 1 (sin( ⁇ )) component is a sub-unitary weight function which tries to attenuate the height values of the slope and has a descending hyperbolic graphic, which "almost” asymptotically approach a minimum value when sin( ⁇ ) approaches 1 (as illustrated in Fig. 4 ).
- W 2 (h) has the same type of evolution but this time as h approaches the conventional maximal value of the altitude.
- Fig. 5 illustrates a range of screenshots for different zoom out levels to illustrate the way the method works.
- the screenshots show how the shading algorithm works for a region in the Alps (around Alagna Valssesia in Italy) starting from the medium zoom levels to the higher ones.
- the elevation information 20a is provided as absolute elevation information for points in the digital map 20, and the rending module 22 performs all of the calculations necessary to calculate a shading percentage to apply to each display pixel.
- the elevation information 20a could, alternatively or additionally, include pre-calculated values (for example of one or more of h, ⁇ , P height ( h ), P slope ( ⁇ ) , and/or l ( z )), for use in the shading algorithm, to reduce the calculation burden within the rendering module.
- the elevation information 20a may be represented directly as the pre-calculated shading percentages according to the first and second different shading functions.
- the shading percentages may be pre-calculated in the digital map 20
- the provision of at least first and second different shading percentages for the same point can enable dynamic rending according to the display scale, by applying a weighted combination of the two pre-calculated percentages using the same principles as described above.
- Fig. 2 such additional elevation information is represented in the digital map 20 at 20b.
- the shading algorithm has been expressed as a mathematical function that may be calculated on demand by a suitable processor
- a function map containing pre-calculated values, for example, as a function of look-up coordinate variables ( ⁇ the angle of the elevation slope, h the current height (elevation), and z the zoom-out level (display scale)).
- ⁇ the angle of the elevation slope
- h the current height
- z the zoom-out level
- Such a pre-calculated function map could be provided within the map display apparatus, or it could be incorporated as an integral part of the data representing the digital map 20 (represented in Fig. 2 at 20c).
- Figs. 6, 7 and 8 represent different types of apparatus that may implement the techniques of the preferred embodiment.
- Fig. 6 illustrates a handheld PND 50
- Fig. 7 illustrates a PND 52 suitable for in-vehicle use.
- the PNDs 50 and 52 typically store the digital map 20 by using semiconductor and/or magnetic memory media.
- the PNDs 50 and 52 typically include a local processor, that implements the rendering module 22 by execution of software.
- Fig. 8 illustrates a networked computer system 60 comprising a server 62 communicating with one or more terminals 64 via a network 66.
- the network 66 may include a local intranet and/or a wider internet (such as the world-wide-web).
- the server 62 stores the digital map 20 and supplies map image generation information upon demand to a requesting terminal 64.
- the server 62 may perform the image calculation, including the function of the map rendering module 22, in order to provide an already-rendered image to the terminal 64 for display.
- the terminal 64 may perform the image calculation, including the function of the map rendering module 22, based on unrendered information received from the server 62.
- the function of the map rendering module 22 may be divided amongst both the server 62 and the terminal 64, to include both server processing and local terminal processing.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Educational Technology (AREA)
- Computer Graphics (AREA)
- Processing Or Creating Images (AREA)
- Instructional Devices (AREA)
- Image Generation (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US87960707P | 2007-01-10 | 2007-01-10 | |
| PCT/EP2008/000182 WO2008083979A1 (en) | 2007-01-10 | 2008-01-09 | Displaying elevation information from a digital map |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2104926A1 EP2104926A1 (en) | 2009-09-30 |
| EP2104926B1 true EP2104926B1 (en) | 2012-07-25 |
Family
ID=39319614
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP08701086A Active EP2104926B1 (en) | 2007-01-10 | 2008-01-09 | Displaying elevation information from a digital map |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8553946B2 (pt) |
| EP (1) | EP2104926B1 (pt) |
| JP (1) | JP2010515941A (pt) |
| CN (1) | CN101578636A (pt) |
| AR (1) | AR064840A1 (pt) |
| AU (1) | AU2008204558A1 (pt) |
| RU (1) | RU2009130385A (pt) |
| TW (1) | TW200839188A (pt) |
| WO (1) | WO2008083979A1 (pt) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2104926B1 (en) * | 2007-01-10 | 2012-07-25 | TomTom International B.V. | Displaying elevation information from a digital map |
| EP2336724A3 (de) * | 2009-12-18 | 2012-01-11 | Navigon AG | Verfahren zum Betrieb eines Navigationssystems |
| KR20130080163A (ko) | 2012-01-04 | 2013-07-12 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 클라이언트의 전자 지도 표시 방법 및 장치 |
| TW201405098A (zh) * | 2012-07-18 | 2014-02-01 | Tian-Min Gao | 地圖及搜尋地圖之方法 |
| US9483846B2 (en) * | 2013-05-29 | 2016-11-01 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Data interpolation and classification method for map data visualization |
| GB201405540D0 (en) * | 2014-03-27 | 2014-05-14 | Tomtom Int Bv | Map Generation |
| AU2014202959B2 (en) * | 2014-05-30 | 2020-10-15 | Caterpillar Of Australia Pty Ltd | Illustrating elevations associated with a mine worksite |
| US10055885B2 (en) * | 2015-09-16 | 2018-08-21 | Raytheon Company | Systems and methods for digital elevation map filters for three dimensional point clouds |
| CN109472864B (zh) * | 2017-09-07 | 2022-12-27 | 广州极飞科技股份有限公司 | 一种高程瓦片地图的生成方法和装置 |
| CN109166307B (zh) * | 2018-06-15 | 2021-11-05 | 中国地质大学(武汉) | 一种交通路网时空可达性的可视化隐喻表达方法及系统 |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2091526B (en) * | 1981-01-13 | 1985-10-02 | Harris Corp | Digital map generator and display system |
| US5542032A (en) * | 1993-10-04 | 1996-07-30 | Loral Federal Systems Company | Fast display of images of three-dimensional surfaces without aliasing |
| EP0723689B1 (en) * | 1993-10-15 | 1998-02-04 | EVANS & SUTHERLAND COMPUTER CORPORATION | Direct rendering of textured height fields |
| GB9717656D0 (en) * | 1997-08-20 | 1997-10-22 | Videologic Ltd | Shading three dimensional images |
| US6654490B2 (en) * | 2000-08-25 | 2003-11-25 | Limbic Systems, Inc. | Method for conducting analysis of two-dimensional images |
| US6288721B1 (en) * | 1999-07-07 | 2001-09-11 | Litton Systems, Inc. | Rendering process and method for digital map illumination intensity shading |
| DE19963764A1 (de) * | 1999-12-30 | 2001-07-05 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Verfahren, Bedienteil, Navigationssystem und Schnittstelle zur Darstellung von Ausschnitten einer digitalen Kartenbasis |
| US6600489B2 (en) * | 2000-12-14 | 2003-07-29 | Harris Corporation | System and method of processing digital terrain information |
| US6765584B1 (en) * | 2002-03-14 | 2004-07-20 | Nvidia Corporation | System and method for creating a vector map in a hardware graphics pipeline |
| EP1498864A4 (en) * | 2002-04-22 | 2006-12-27 | Dgs Comp | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR DRAWING A DIGITAL ALTIMETRIC CARD |
| WO2004042675A1 (ja) * | 2002-11-05 | 2004-05-21 | Asia Air Survey Co.,Ltd. | 視覚化処理システム、視覚化処理方法、及び視覚化処理プログラム |
| US7098809B2 (en) * | 2003-02-18 | 2006-08-29 | Honeywell International, Inc. | Display methodology for encoding simultaneous absolute and relative altitude terrain data |
| US7116806B2 (en) * | 2003-10-23 | 2006-10-03 | Lumeniq, Inc. | Systems and methods relating to AFIS recognition, extraction, and 3-D analysis strategies |
| US7107146B2 (en) * | 2003-12-10 | 2006-09-12 | Honeywell International Inc. | Methods and systems for generating a terrain elevation map in a cartesian format |
| US7242407B2 (en) * | 2004-05-28 | 2007-07-10 | Lockheed Martin Corporation | Reprojecting map images using graphical techniques |
| US7283654B2 (en) * | 2004-08-26 | 2007-10-16 | Lumeniq, Inc. | Dynamic contrast visualization (DCV) |
| US7612775B2 (en) * | 2005-07-28 | 2009-11-03 | The Boeing Company | Real-time conformal terrain rendering |
| US20070146364A1 (en) * | 2005-12-22 | 2007-06-28 | Aspen Sven D | Methods and systems for displaying shaded terrain maps |
| EP2104926B1 (en) * | 2007-01-10 | 2012-07-25 | TomTom International B.V. | Displaying elevation information from a digital map |
-
2008
- 2008-01-09 EP EP08701086A patent/EP2104926B1/en active Active
- 2008-01-09 CN CNA2008800018050A patent/CN101578636A/zh active Pending
- 2008-01-09 JP JP2009545145A patent/JP2010515941A/ja not_active Withdrawn
- 2008-01-09 AU AU2008204558A patent/AU2008204558A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2008-01-09 WO PCT/EP2008/000182 patent/WO2008083979A1/en active Application Filing
- 2008-01-09 RU RU2009130385/08A patent/RU2009130385A/ru not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2008-01-09 US US12/007,375 patent/US8553946B2/en active Active
- 2008-01-10 AR ARP080100098A patent/AR064840A1/es unknown
- 2008-01-10 TW TW097101034A patent/TW200839188A/zh unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW200839188A (en) | 2008-10-01 |
| AR064840A1 (es) | 2009-04-29 |
| RU2009130385A (ru) | 2011-02-20 |
| JP2010515941A (ja) | 2010-05-13 |
| CN101578636A (zh) | 2009-11-11 |
| EP2104926A1 (en) | 2009-09-30 |
| US8553946B2 (en) | 2013-10-08 |
| AU2008204558A1 (en) | 2008-07-17 |
| US20080212893A1 (en) | 2008-09-04 |
| WO2008083979A1 (en) | 2008-07-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2104926B1 (en) | Displaying elevation information from a digital map | |
| AU2014227060B2 (en) | Image processing device, method for image processing, and image processing program | |
| US8274524B1 (en) | Map rendering using interpolation of style parameters across zoom levels | |
| USRE40466E1 (en) | Method for organizing and compressing spatial data | |
| Baltsavias | Digital ortho-images—a powerful tool for the extraction of spatial-and geo-information | |
| EP1986176A1 (en) | Bitmap array for optimally distributing map data content to wireless communications devices | |
| CN106842160B (zh) | 一种雷达回波采样数据的处理方法和装置 | |
| CN109086286B (zh) | 一种彩色地形图生产与发布方法 | |
| WO2011023247A1 (en) | Generating raster image representing road existence probability based on probe measurements | |
| CN105022731B (zh) | 一种地图矢量瓦片缓存的方法 | |
| EP1971827A2 (en) | Methods and systems for displaying shaded terrain maps | |
| CN115631423A (zh) | 顾及气象预测云图和传感器测摆的遥感卫星覆盖预测方法 | |
| US20050146524A1 (en) | System and method for determining a spatial hierarchy for polygonal data by using cube-root scaling | |
| US8224098B2 (en) | Façade rendering system | |
| Gil et al. | DEM shading method for the correction of pseudoscopic effect on multi-platform satellite imagery | |
| US20060285764A1 (en) | Model-based line width control | |
| CN108446303B (zh) | 一种地图节点聚合显示、分层聚合方法及装置 | |
| JP6995912B2 (ja) | 地形図出力装置、地形図出力方法及びプログラム | |
| US20160078651A1 (en) | Proximity-Base Detail Reduction of Geographic Data | |
| US9275481B2 (en) | Viewport-based contrast adjustment for map features | |
| US10546418B2 (en) | Visualization of positional geospatial uncertainty | |
| CN115760578A (zh) | 一种图像处理方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质 | |
| US20100218114A1 (en) | Method for Simplifying the Display of Stationary Members of an Onboard Database | |
| US11056079B2 (en) | Display system and program | |
| CN111429542A (zh) | 一种矢量等值线色斑图生成方法、装置及存储介质 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20090610 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: TOMTOM INTERNATIONAL B.V. |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R079 Ref document number: 602008017391 Country of ref document: DE Free format text: PREVIOUS MAIN CLASS: G06T0017500000 Ipc: G06T0017050000 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: G06T 17/05 20110101AFI20120213BHEP |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 567968 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120815 Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602008017391 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20120920 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 567968 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120725 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D Effective date: 20120725 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121125 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121025 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121026 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121126 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20130426 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121025 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602008017391 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130426 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130131 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121105 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130131 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130109 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120725 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20080109 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130109 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 602008017391 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: TOMTOM NAVIGATION B.V., NL Free format text: FORMER OWNER: TOMTOM INTERNATIONAL B.V., AMSTERDAM, NL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E Free format text: REGISTERED BETWEEN 20200227 AND 20200304 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: PD Owner name: TOMTOM NAVIGATION B.V.; NL Free format text: DETAILS ASSIGNMENT: CHANGE OF OWNER(S), ASSIGNMENT; FORMER OWNER NAME: TOMTOM INTERNATIONAL B.V. Effective date: 20220720 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230520 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20231215 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20231205 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20241205 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20241223 Year of fee payment: 18 |