EP1813402B1 - Plaque en fibres de bois résistant à la moisissure pour toits et murs, et procédé pour sa fabrication - Google Patents
Plaque en fibres de bois résistant à la moisissure pour toits et murs, et procédé pour sa fabrication Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1813402B1 EP1813402B1 EP20070001442 EP07001442A EP1813402B1 EP 1813402 B1 EP1813402 B1 EP 1813402B1 EP 20070001442 EP20070001442 EP 20070001442 EP 07001442 A EP07001442 A EP 07001442A EP 1813402 B1 EP1813402 B1 EP 1813402B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- borates
- wood fibre
- wood fiber
- board
- main side
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B27—WORKING OR PRESERVING WOOD OR SIMILAR MATERIAL; NAILING OR STAPLING MACHINES IN GENERAL
- B27N—MANUFACTURE BY DRY PROCESSES OF ARTICLES, WITH OR WITHOUT ORGANIC BINDING AGENTS, MADE FROM PARTICLES OR FIBRES CONSISTING OF WOOD OR OTHER LIGNOCELLULOSIC OR LIKE ORGANIC MATERIAL
- B27N3/00—Manufacture of substantially flat articles, e.g. boards, from particles or fibres
Definitions
- the invention relates to a wood fiber board for roof and wall construction with the features of the preamble of independent claim 1 and to a method for producing such a wood fiber board with the features of the preamble of independent claim 4.
- a wood fiber board with the features of the preamble of independent claim 1 is z. B. from the WO 94/23914 known. There is also a method for their preparation with the features of the preamble of independent claim 4 is described.
- the known wood fiber board is offered by the applicant as a diffusion-open wall and ceiling plate.
- the wood fiber board can be applied as a second water-bearing layer directly on the rafters.
- the roof is covered, and the windows and doors are installed.
- the screed and the interior plaster are introduced into the new building.
- the heating is usually put into operation to dry out the new building.
- Borates are used as flame retardants for lignocellulosic building materials, such as insulating fillings and are considered environmentally harmless.
- the concentration of borates used as flame retardants is typically 8% atro fibers. Borates are also known to have a fungicidal action which is sufficient for effective mold protection from a concentration of about 1% of atro fibers. Since the binder content of atro fibers in wood fiberboards, which are the subject of the present invention, is typically of the order of magnitude required for mold protection by borates, and even less than the amount in which borates are used as flame retardants, a process must be used for the production of a wood fiber board with such a mold or flame retardant on the presence of relatively large amounts of borate are specially tuned. This is in addition to the cost of borates additional costs associated.
- WO-A-20061065259 From the post-published WO-A-20061065259 are known building materials with bioresistant properties. These building materials, which may be wood fiberboards, have a biocide which, among many other substances, may also be calcium borate, zinc borate, barium bismuth and mixtures thereof. However, particularly preferred is the use of copper oxinate as a biocide, to which the description of the WO-A-2006/065259 concentrated.
- the copper oxinate is sprayed onto a surface of a fiberboard in a mixture with water and solidifying additives such as latex strengthening agent.
- the concentration of the copper oxinate is 0.01 to 2% by weight of the liquid mixture, which is applied in an area concentration of 2 to 12 g of liquid per square foot. This corresponds to 0.0043 to 5.2 g of copper oxinate / m 2 . Corresponding information is not available on any other of the biocides which have a different biotoxicity.
- the US-B-6416789 describes the use of boron-containing fungicides, such as zinc borate, calcium borate and sodium borate, designated as such at typical use levels as providing poor mold protection, in combination with an organo-iodine compound and an amine oxide compound as a mold protection for wood fiberboards.
- This mixture can be sprayed on to treat the wood fiber boards.
- concentration in which the boron-containing compounds should be present in addition to the other fungicidal substances in the wood fiber boards 0.1-5% are given based on the weight of the wood fiber boards.
- boric acid From the GB-A-829407 is a one-sided treatment of fiberboard with boric acid known to improve their sound-absorbing properties.
- the boric acid should be used in an area concentration of 4-15 grams per square foot, which corresponds to 43-161 grams per square meter.
- the invention has for its object to provide a wood fiber board for roof and wall construction and a method for their preparation, by the sufficient mold protection with minimal effort, ie in particular with minimal entry of Foreign material into the fiberboard and minimal increase in the cost of producing the fiberboard is achieved.
- the new fiberboard has borates in an area concentration of not less than one gram and not more than 25 grams per square meter. These borates are in the area of the shoring inward, ie concentrated in the roof down to align main side of the wood fiber board. For this reason, the amount of borates in the new fiberboard is also defined as the area concentration and not the volume concentration. With a board thickness of the wood fiber board of 16 mm and a bulk density of the wood fiber board of 565 kg / m 3 , the amount of borates present in the new wood board is less than 0.3% of atro fibers. This value would be completely inadequate for effective mold protection in the volume of fiberboard.
- borate concentration is still sufficient to provide good mold protection. Due to the relatively small total amount of borates, the cost of the new wood fiber board compared to a wood fiber board without mold protection are only slightly increased. It is also not necessary to significantly change the process for their preparation. Ultimately, the entry of foreign matter in the wood fiber board is so low that it does not lose their safety from an environmental point of view, especially since borates are to be regarded as fundamentally less critical in this respect.
- the borates are not only on the main side of the wood fiber board to be aligned inside, but both as well as below the surface of the fiberboard on this main page.
- abrasion of the borates is prevented in their handling, including the stacking of wood fiber boards, and also a rapid washing away of the borates under the influence of moisture.
- the risk that the borates are washed off and washed off, for example, by water condensing on the inside of the wood fiber boards, so that they become ineffective is relatively low because the water solubility of borates is strongly temperature-dependent and even at a reduced temperature of 10 ° C. only at about 100 g / l.
- weather influences on the construction site are therefore not associated with the immediate danger that the borates are lost from their area at the inboard facing main side of the wood fiber boards.
- the corresponding main page may be provided with a mark.
- the one-sided addition of borates in the area to a main side of the wood fiber boards is usually not visible. He can, however, by dyes that z. B. the borates are struck directly, made visible. It is also possible to provide the main pages with printed instructions on their orientation to be made. In the simplest case, the new wood fiber boards are stacked on pallets, as it corresponds to their subsequent alignment, d. H. e.g. with their roof sides down to be aligned main pages down. If this orientation of the wood fiberboards is maintained, no marking on the fiberboard itself is necessary.
- the borates are applied in an area concentration of not less than 1 gram and not more than 25 grams per square meter to a main side of the fiber cake pressed to the wood fiber board or the wood fiber board itself the lining to be aligned inside the main side of the wood fiber plate forms.
- the borates can thus be applied to the already substantially fiberboard before the hot pressing on the fiber cake or after hot pressing.
- the application to the fiber cake is the application to the fiber cake, because in this way a stronger involvement in the adjacent to the later inner main page volume of wood fiber board is done.
- borates may be applied to the fiber cake or fiberboard by sprinkling the fiber cake with dry borates or by rolling or spraying the borates. It is favorable if the borates are present during application in the form of a solution, in particular a solution in water. The evaporating water leaves the borates back and does not lead to contamination of the fiberboard.
- the borates are sprayed onto the fiber cake from above in the form of a solution in water, whereby the water applied with the borates is vaporized during the hot pressing of the fibreboards.
- the remaining borates are then incorporated into the volume of the fiberboard near their lower main page, which reliably prevents unwanted washing out by condensation water or the handling of the wood fiber boards or direct weather influences on the wood fiber boards on a construction site.
- the fibrous board be turned after hot pressing and further processed downwardly with its main side containing the borates, i. H. packed and transported, for example.
- the wood fiber board is stacked with other identical wood fiber boards to form a stack in which the main side of the wood fiber boards to be aligned downwards in the roof construction lies at the bottom. This alone protects the borates from the effects of the weather, for example rain on the pile.
- Another or additional indication of the meaningful orientation of the new wood fiber boards in the construction can be given in the context of their production, that together with the borates, a dye is applied to the one main side of the fiber cake or the wood fiber board, which is to be aligned inside the main side the fiberboard forms.
- the previously stated upper limit for the boron surface concentration of not more than 25 g / m 2 which corresponds to less than 0.3% of atro fibers for a 16 mm thick fibreboard of 565 kg / m 3 gross density, need not be exhausted in order to obtain the provide desired mold protection. This is also achieved with a maximum of 20 g / m 2 for very long periods. Even with 8 to 10 g / m 2 can not with a mold protection at one insulated roof of about half a year can be expected. A usually completely sufficient mold protection of at least two months is reliably achieved with about 6, ie 5 to 7 g / m 2 . An underlying surface concentration of the borates can only cause a shortened protection. An area concentration of less than 2 g / m 2 is already essentially ineffective.
- Suitable borates for use in the novel wood fiber board and their production are, in particular, inorganic borates, in particular alkali metal, alkaline earth metal and / or ammonium borates. These borates are on the one hand cost-effective and on the other hand largely harmless from an environmental point of view. From an environmental point of view, this means both the influence of the wood fiber board on the living climate in an adjacent living space and the recyclability of the wood fiber board.
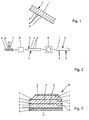
- wood fiber board 1 is provided in addition to the wall construction specifically for use in the roof construction and shown here with a roof pitch.
- the wood fiber board 1 has a typical thickness of 12 to 20 mm and a typical average apparent density of 530 to 600 kg / m 3 .
- the wood fiber board 1 forms a vapor-permeable layer in the roof construction, so that water vapor can pass through it.
- inwardly directed main side 2 of the wood fiber board 1 these can not immediately on the opposite, upwardly, outwardly directed main page 3 diffuse.
- inorganic borates 4 are provided, which has the wood fiber board 1 at and behind its surface 5 at its lower main page 2. The borates 4 are thus on the surface 5, but also within the adjoining volume of the wood fiber board 1 before, but not on the upper main page 3, where no mold protection is needed.
- the concentration of the borates 4 on the lower main side 2 makes it possible to give the wood fiber board 1 sufficient mold protection with respect to atro fibers of the wood fiber board 1 very small amounts of borates 4.
- concentration of about 6 g / m 2 of borates 4 which is less atro fibers 0.1% means sufficient mold protection for a period of at least 3 months.
- Fig. 2 outlined the preparation of the new wood fiber board 1 according to Fig. 1 ,
- a solution 7 of the borates 4 is sprayed from above in water before the fiber cake 6 is pressed in a hot press 8 under the action of elevated pressure and elevated temperature to the wood fiber board 1.
- the main page 2 where the borates 4 are present oriented upwards.
- the wood fiber board 1 is then turned through 180 °, so that the main side 2 with the borates 4 then points downwards.
- the solution 7 could be sprayed even after the hot press 8 on the still warm wood fiber plate 1, before it is turned in the inverter 9.
- Fig. 3 outlines a stack 10 of several wood fiber boards 1 on a base 11.
- the borates 4 are largely protected in the wood fiber boards 1 within the stack 10 from the weather.
- the embedding is also contrary to a simple leaching of borates 4 with rainwater or on the main side 2 condensing water. It is also advantageous that the water solubility of the borates is only slight at reduced temperatures.
- the user of the wood fiber boards 1 can also be pointed out by the necessary orientation of the wood fiber boards 1 in the roof, which together with the borates 4 a dye is applied, which distinguishes the main side 2 of the wood fiber boards from their borate-free main page 3.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Forests & Forestry (AREA)
- Dry Formation Of Fiberboard And The Like (AREA)
Claims (11)
- Plaque en fibres de bois (1) pour toits et murs à base de fibres contenant de la lignocellulose collées avec un liant et comprimées à chaud et comprenant un côté principal (3) à orienter vers l'extérieur lors de l'installation et un côté principal (2) à orienter vers l'intérieur lors de l'installation, caractérisée en ce que la plaque en fibres de bois (1) comprend des borates (4) en une concentration superficielle supérieure ou égale à 1 et inférieure ou égale à 25 g/m2, qui sont concentrés sur le côté principal (2) à orienter vers l'intérieur lors de l'installation de la plaque en fibres de bois (1).
- Plaque en fibres de bois selon la revendication 1, caractérisée en ce que les borates (4) se trouvent sur et sous la surface (5) de la plaque en fibres de bois (1) sur son côté principal inférieur (2) à orienter vers l'intérieur lors de l'installation.
- Plaque en fibres en bois selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisée en ce qu'un des deux côtés principaux (2, 3) de la plaque en fibres de bois (1) comprend un marquage.
- Procédé de fabrication d'une plaque en fibres de bois (1) pour toits et murs, comprenant un côté principal (3) à orienter vers l'extérieur lors de l'installation et un côté principal (2) à orienter vers l'intérieur lors de l'installation, un gâteau de fibres (6) constitué de fibres contenant de la lignocellulose collées avec un liant étant comprimé à chaud, caractérisé en ce que des borates (4) sont appliqués en une concentration superficielle supérieure ou égale à 1 et inférieure ou égale à 25 g/m2 sur un côté principal (2) du gâteau de fibres (6) ou de la plaque en fibres de bois (1), qui forme le côté principal (2) à orienter vers l'intérieur lors de l'installation de la plaque en fibres de bois (1).
- Procédé selon la revendication 4, caractérisé en ce que les borates (4) sont appliqués sous la forme d'une solution (7) dans de l'eau sur le gâteau de fibres (6) ou la plaque en fibres de bois (1).
- Procédé selon la revendication 5, caractérisé en ce que la solution (7) est pulvérisée depuis le haut sur le gâteau de fibres (6).
- Procédé selon la revendication 6, caractérisé en ce que la plaque en fibres de bois (1) est retournée après la compression à chaud.
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 4 à 7, caractérisé en ce que la plaque en fibres de bois (1) est empilée en une pile (10) avec d'autres plaques en fibres de bois (1) identiques, le côté principal (2) à orienter vers l'intérieur lors de l'installation des plaques en fibres de bois (1) se trouvant à chaque fois en bas.
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 4 à 8, caractérisé en ce qu'un colorant est appliqué avec les borates (4) sur le côté principal du gâteau de fibres (6) ou de la plaque en fibres de bois (1).
- Plaque en fibres de bois selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisée en ce que la concentration superficielle des borates (4) est de 2 à 20 g/m2.
- Plaque en fibres de bois selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3 et 10, caractérisée en ce que les borates (4) sont des borates alcalins, alcalino-terreux et/ou d'ammonium.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE200610003699 DE102006003699B3 (de) | 2006-01-26 | 2006-01-26 | Holzfaserplatte mit Schimmelschutz für den Dach- und Wandbau und Verfahren zu deren Herstellung |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1813402A2 EP1813402A2 (fr) | 2007-08-01 |
| EP1813402A3 EP1813402A3 (fr) | 2008-07-16 |
| EP1813402B1 true EP1813402B1 (fr) | 2012-10-31 |
Family
ID=37836863
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20070001442 Active EP1813402B1 (fr) | 2006-01-26 | 2007-01-24 | Plaque en fibres de bois résistant à la moisissure pour toits et murs, et procédé pour sa fabrication |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1813402B1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE102006003699B3 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2396996T3 (fr) |
| PT (1) | PT1813402E (fr) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102009026801B4 (de) * | 2009-06-05 | 2013-10-24 | Glunz Ag | Photolumineszente Faserplatte und Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung |
| DE102013004332B4 (de) * | 2013-03-14 | 2016-05-12 | Fritz Egger Gmbh & Co. Og | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines Lignocellulose enthaltenden, plattenförmigen Werkstoffs |
| DE102016100078B3 (de) | 2016-01-04 | 2017-04-13 | Fritz Egger Gmbh & Co. Og | Faserplatte mit erhöhter Beständigkeit gegen Pilzbefall sowie Verfahren zu deren Herstellung |
| DE102016108551B3 (de) | 2016-05-09 | 2017-11-02 | Fritz Egger Gmbh & Co. Og | Faserplatte mit erhöhter Beständigkeit gegen Pilzbefall sowie Verfahren zu deren Herstellung |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB829407A (en) * | 1955-05-02 | 1960-03-02 | Armstrong Cork Co | Improvements in or relating to sound-absorbing fiberboard |
| US4212675A (en) * | 1978-04-03 | 1980-07-15 | Retroflame International Limited | Fireproofing |
| DE4312564A1 (de) * | 1993-04-17 | 1994-11-10 | Glunz Ag | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Faserplatten |
| US6030562A (en) * | 1995-08-25 | 2000-02-29 | Masonite Corporation | Method of making cellulosic composite articles |
| US5972266A (en) * | 1998-02-26 | 1999-10-26 | Trus Joist Macmillan A Limited Partnership | Composite products |
| US7163974B2 (en) * | 2000-05-14 | 2007-01-16 | U.S. Borax Inc. | Lignocellulosic composites |
| US20050126430A1 (en) * | 2000-10-17 | 2005-06-16 | Lightner James E.Jr. | Building materials with bioresistant properties |
| US6416789B1 (en) * | 2001-01-05 | 2002-07-09 | Kop-Coat, Inc. | Synergistic combination of fungicides to protect wood and wood-based products from fungal decay, mold and mildew damage |
| US6881247B2 (en) * | 2003-01-09 | 2005-04-19 | Vernon H. Batdorf | Protective barrier coating composition |
-
2006
- 2006-01-26 DE DE200610003699 patent/DE102006003699B3/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2007
- 2007-01-24 PT PT07001442T patent/PT1813402E/pt unknown
- 2007-01-24 ES ES07001442T patent/ES2396996T3/es active Active
- 2007-01-24 EP EP20070001442 patent/EP1813402B1/fr active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1813402A2 (fr) | 2007-08-01 |
| PT1813402E (pt) | 2013-01-23 |
| ES2396996T3 (es) | 2013-03-01 |
| EP1813402A3 (fr) | 2008-07-16 |
| DE102006003699B3 (de) | 2007-10-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2277692B2 (fr) | Panneau isolant, mortier adhésif destiné à l'application d'un panneau isolant sur une paroi ou un plafond d'un bâtiment et agencement constitué d'un panneau isolant et mortier adhésif | |
| WO2020211988A1 (fr) | Matériau en forme de plaque et son procédé de fabrication | |
| DD280988A5 (de) | Wasserabweisende aussenbekleidung fuer gebaeude | |
| EP1813402B1 (fr) | Plaque en fibres de bois résistant à la moisissure pour toits et murs, et procédé pour sa fabrication | |
| DE19541626A1 (de) | Dämmstoff und Verfahren zur Herstellung desselben | |
| EP3725481B1 (fr) | Matériau sous forme de plaque et son procédé de fabrication | |
| DE10330298A1 (de) | Paneel, insbesondere Fußboden-Laminatpaneel | |
| EP2112293A1 (fr) | Panneau isolant en fibres de bois | |
| DE202010003580U1 (de) | Feuerfeste und wasserfeste Wabenstruktur | |
| DE4223614A1 (de) | Dämmstoff sowie Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung | |
| DE29624258U1 (de) | Feuerfeste Auskleidungsplatte | |
| DE102008024155A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Formkörpers aus Altpapier und/oder Altpappe, Formkörper und Gebäudeteil | |
| DE29619448U1 (de) | Ein- oder mehrflügelige Brandschutztür | |
| DE1886678U (de) | Tafelfoermiges bauelement, insbesondere dachplatte. | |
| EP1900884B1 (fr) | Panneau de fibres douces en bois pour l'isolation interne | |
| DE202010004204U1 (de) | Zementspanplatte | |
| DE20311928U1 (de) | Dämmplatte für Bauzwecke | |
| EP4090507B1 (fr) | Panneau osb pourvu d'une couche de recouvrement en matériau à base de feuilles de typha | |
| AT515504A1 (de) | Flächiges Bauelement | |
| EP3938158A1 (fr) | Matériau en forme de plaque et son procédé de fabrication | |
| DE9109546U1 (de) | Wärme- und schalldämmendes Bauelement | |
| EP4472817A1 (fr) | Procédé de fabrication d'un panneau de fibres | |
| DE10025193C2 (de) | Fassadenelement | |
| EP0936063A2 (fr) | Elément de construction composite thermo-isolant | |
| DE19702847C2 (de) | Verwendung von Holzflocken als Dämmstoff für Holzhäuser und dergleichen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR MK RS |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: FORSCHNER, DIANA Inventor name: KALWA, NORBERT Inventor name: PFEMETER, ALFRED, DR. |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR MK RS |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20090112 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 581737 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20121115 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: RIEDERER HASLER AND PARTNER PATENTANWAELTE AG, LI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502007010779 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: SC4A Free format text: AVAILABILITY OF NATIONAL TRANSLATION Effective date: 20130102 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2396996 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20130301 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130228 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130201 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: GLUNZ A.G. Effective date: 20130131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20130131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20121031 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130131 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20130801 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130131 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502007010779 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130801 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130124 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20070124 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130124 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230528 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Payment date: 20250122 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20241113 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20250214 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20250201 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20250120 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20250128 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20250131 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20250116 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20250116 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: U11 Free format text: ST27 STATUS EVENT CODE: U-0-0-U10-U11 (AS PROVIDED BY THE NATIONAL OFFICE) Effective date: 20260201 |