EP1558715B1 - Verwendung Schmieröls zur Reduzierung des Kraftstoffverbrauchs - Google Patents
Verwendung Schmieröls zur Reduzierung des Kraftstoffverbrauchs Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1558715B1 EP1558715B1 EP03750716A EP03750716A EP1558715B1 EP 1558715 B1 EP1558715 B1 EP 1558715B1 EP 03750716 A EP03750716 A EP 03750716A EP 03750716 A EP03750716 A EP 03750716A EP 1558715 B1 EP1558715 B1 EP 1558715B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- use according
- general formula
- additives
- ranging
- lubricating
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 title description 16
- 239000010687 lubricating oil Substances 0.000 title description 4
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 84
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims description 56
- 230000001050 lubricating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 34
- 239000003599 detergent Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- 239000007866 anti-wear additive Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000002199 base oil Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- -1 calcium sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 claims description 11
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 9
- WMYJOZQKDZZHAC-UHFFFAOYSA-H trizinc;dioxido-sulfanylidene-sulfido-$l^{5}-phosphane Chemical class [Zn+2].[Zn+2].[Zn+2].[O-]P([O-])([S-])=S.[O-]P([O-])([S-])=S WMYJOZQKDZZHAC-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 claims description 9
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000001342 alkaline earth metals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- AVVIDTZRJBSXML-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium;2-carboxyphenolate;dihydrate Chemical compound O.O.[Ca+2].OC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O.OC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O AVVIDTZRJBSXML-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 37
- BDHFUVZGWQCTTF-UHFFFAOYSA-M sulfonate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)=O BDHFUVZGWQCTTF-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 17
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 16
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 12
- 229960001860 salicylate Drugs 0.000 description 12
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 description 11
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M salicylate Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 11
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 10
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000005461 lubrication Methods 0.000 description 8
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000010705 motor oil Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000002195 synergetic effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butadiene Chemical compound C=CC=C KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- RRHGJUQNOFWUDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isoprene Chemical compound CC(=C)C=C RRHGJUQNOFWUDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 150000003138 primary alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920013639 polyalphaolefin Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004034 viscosity adjusting agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 4
- 150000002989 phenols Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 150000003333 secondary alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formaldehyde Chemical compound O=C WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003831 antifriction material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000003623 enhancer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 3
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 241001239379 Calophysus macropterus Species 0.000 description 2
- 230000032683 aging Effects 0.000 description 2
- XXROGKLTLUQVRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N allyl alcohol Chemical compound OCC=C XXROGKLTLUQVRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000008485 antagonism Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002518 antifoaming agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001427 coherent effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003607 modifier Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000768 polyamine Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000001993 wax Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 2
- RZRNAYUHWVFMIP-KTKRTIGZSA-N 1-oleoylglycerol Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(O)CO RZRNAYUHWVFMIP-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000002918 Fraxinus excelsior Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000272168 Laridae Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920002367 Polyisobutene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000004931 aggregating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000004996 alkyl benzenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002947 alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000013556 antirust agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000149 argon plasma sintering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004982 aromatic amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001491 aromatic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002956 ash Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- OSMZVRQRVPLKTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N calcium;1-nonyl-7-thiabicyclo[4.1.0]hepta-2,4-dien-6-ol Chemical compound [Ca].C1=CC=CC2(CCCCCCCCC)C1(O)S2 OSMZVRQRVPLKTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001735 carboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007859 condensation product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001143 conditioned effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001991 dicarboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000013870 dimethyl polysiloxane Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012990 dithiocarbamate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004659 dithiocarbamates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- HQQADJVZYDDRJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethene;prop-1-ene Chemical group C=C.CC=C HQQADJVZYDDRJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005227 gel permeation chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001519 homopolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- BHEPBYXIRTUNPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydridophosphorus(.) (triplet) Chemical compound [PH] BHEPBYXIRTUNPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000003949 imides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000011835 investigation Methods 0.000 description 1
- JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron(III) oxide Inorganic materials O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000691 measurement method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002734 metacrylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002480 mineral oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005078 molybdenum compound Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002752 molybdenum compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- KHYKFSXXGRUKRE-UHFFFAOYSA-J molybdenum(4+) tetracarbamodithioate Chemical compound C(N)([S-])=S.[Mo+4].C(N)([S-])=S.C(N)([S-])=S.C(N)([S-])=S KHYKFSXXGRUKRE-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 1
- 150000002763 monocarboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000004780 naphthols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008520 organization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000002524 organometallic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000021715 photosynthesis, light harvesting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000435 poly(dimethylsiloxane) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001281 polyalkylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000193 polymethacrylate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005862 polyol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000003077 polyols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000005381 potential energy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene Natural products CC=C QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007670 refining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010008 shearing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003746 surface roughness Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000007970 thio esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010200 validation analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000000391 vinyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000004711 α-olefin Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M169/00—Lubricating compositions characterised by containing as components a mixture of at least two types of ingredient selected from base-materials, thickeners or additives, covered by the preceding groups, each of these compounds being essential
- C10M169/04—Mixtures of base-materials and additives
- C10M169/045—Mixtures of base-materials and additives the additives being a mixture of compounds of unknown or incompletely defined constitution and non-macromolecular compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M157/00—Lubricating compositions characterised by the additive being a mixture of two or more macromolecular compounds covered by more than one of the main groups C10M143/00 - C10M155/00, each of these compounds being essential
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2203/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds and hydrocarbon fractions as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2203/10—Petroleum or coal fractions, e.g. tars, solvents, bitumen
- C10M2203/102—Aliphatic fractions
- C10M2203/1025—Aliphatic fractions used as base material
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2205/00—Organic macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds or fractions, whether or not modified by oxidation as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2205/02—Organic macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds or fractions, whether or not modified by oxidation as ingredients in lubricant compositions containing acyclic monomers
- C10M2205/0206—Organic macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds or fractions, whether or not modified by oxidation as ingredients in lubricant compositions containing acyclic monomers used as base material
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/26—Overbased carboxylic acid salts
- C10M2207/262—Overbased carboxylic acid salts derived from hydroxy substituted aromatic acids, e.g. salicylates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2207/00—Organic non-macromolecular hydrocarbon compounds containing hydrogen, carbon and oxygen as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2207/28—Esters
- C10M2207/287—Partial esters
- C10M2207/289—Partial esters containing free hydroxy groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2219/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2219/04—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions containing sulfur-to-oxygen bonds, i.e. sulfones, sulfoxides
- C10M2219/046—Overbased sulfonic acid salts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2219/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2219/06—Thio-acids; Thiocyanates; Derivatives thereof
- C10M2219/062—Thio-acids; Thiocyanates; Derivatives thereof having carbon-to-sulfur double bonds
- C10M2219/066—Thiocarbamic type compounds
- C10M2219/068—Thiocarbamate metal salts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2219/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing sulfur, selenium or tellurium as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2219/08—Thiols; Sulfides; Polysulfides; Mercaptals
- C10M2219/082—Thiols; Sulfides; Polysulfides; Mercaptals containing sulfur atoms bound to acyclic or cycloaliphatic carbon atoms
- C10M2219/087—Thiols; Sulfides; Polysulfides; Mercaptals containing sulfur atoms bound to acyclic or cycloaliphatic carbon atoms containing hydroxy groups; Derivatives thereof, e.g. sulfurised phenols
- C10M2219/089—Overbased salts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10M—LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS; USE OF CHEMICAL SUBSTANCES EITHER ALONE OR AS LUBRICATING INGREDIENTS IN A LUBRICATING COMPOSITION
- C10M2223/00—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing phosphorus as ingredients in lubricant compositions
- C10M2223/02—Organic non-macromolecular compounds containing phosphorus as ingredients in lubricant compositions having no phosphorus-to-carbon bonds
- C10M2223/04—Phosphate esters
- C10M2223/045—Metal containing thio derivatives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2010/00—Metal present as such or in compounds
- C10N2010/04—Groups 2 or 12
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2010/00—Metal present as such or in compounds
- C10N2010/12—Groups 6 or 16
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2020/00—Specified physical or chemical properties or characteristics, i.e. function, of component of lubricating compositions
- C10N2020/01—Physico-chemical properties
- C10N2020/02—Viscosity; Viscosity index
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2030/00—Specified physical or chemical properties which is improved by the additive characterising the lubricating composition, e.g. multifunctional additives
- C10N2030/06—Oiliness; Film-strength; Anti-wear; Resistance to extreme pressure
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/25—Internal-combustion engines
- C10N2040/252—Diesel engines
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C10—PETROLEUM, GAS OR COKE INDUSTRIES; TECHNICAL GASES CONTAINING CARBON MONOXIDE; FUELS; LUBRICANTS; PEAT
- C10N—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS C10M RELATING TO LUBRICATING COMPOSITIONS
- C10N2040/00—Specified use or application for which the lubricating composition is intended
- C10N2040/25—Internal-combustion engines
- C10N2040/255—Gasoline engines
Definitions
- the present invention relates to lubricating compositions capable of guaranteeing an improvement in the fuel economy performances of internal combustion engines, also without resorting to specific additives conventionally known as friction modifiers or reducers.
- the above compositions envisage the presence of particular deterging additives selected from the group of sulfophenates, preferably superbasic, and particular anti-wear additives having the general formula ZnP 2 S 4 O 4 R 4 .
- lubricants serve to protect metallic surfaces from direct contact, and this role, at hydrodynamic or elasto-hydrodynamic lubrication regimes (hereinafter indicated as H regimes), is effected thanks to a fundamental characteristic of the oil, i.e. its viscosity.
- H regimes hydrodynamic or elasto-hydrodynamic lubrication regimes
- the higher the viscosity the more the presence of thick lubricating layers on the metallic surface, for its protection, is guaranteed.
- high viscosity values which is a representative parameter of intermolecular friction leads to a more difficult flow of the lubricating layers and to the generation of passive friction which dissipates useful mechanical energy.
- the greater fluidity of the oils at H regimes is obtained by improving the characteristics of the base oils and polymeric additives, particularly viscosity modifier and/or viscosity index enhancer additives.
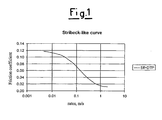
- Measurement of the friction coefficient variations at the various lubrication regimes is a useful method for identifying new and advantageous solutions for the formulation of f.e. products.
- These measurements can be conveniently effected by means of a ball-on-disk tribometer which operates under mixed movement conditions of the rolling/sliding type.
- a ball-on-disk tribometer which operates under mixed movement conditions of the rolling/sliding type.
- SLC Stribeck-Like Curves
- the definitive validation of the above tribological measurements is obtained by means of engine tests required by specifications on the part of European, American and Japanese organisms and manufacturers.
- organometallic additives with Molybdenum for example dithiophosphates, dithiocarbamates, dithioamides
- organometallic additives with Molybdenum for example dithiophosphates, dithiocarbamates, dithioamides
- tribo-reactions chemical reactions in the solid-solid contact area
- EP-A-0913455 discloses a lubricant composition comprising sulfurized phenates and ZnDTP which are P esters, used to improve fuel economy.
- Molybdenum increases the content of ashes, metals, sulfur and (at times) phosphorous of the mixture, and these variations are not coherent with the necessity of improving the compatibility of the oils with post-treatment systems of the exhaust gases of vehicles.
- polar ester products can generally create a negative competition with respect to the solid to defend, obstructing the action of the anti-wear additive.
- Lubricating compositions for engine oils have now been found, which are capable of improving the f.e. performance of an internal combustion engine lubricated with the above lubricating compositions, which overcome the drawbacks indicated above.
- the present invention relates to lubricating compositions for internal combustion engines capable of reducing the fuel consumption of engines lubricated by the compositions themselves, the above lubricating compositions comprising:
- the sulfophenates (I) salified with calcium can be neutral or superbasic, preferably superbasic.
- superbasic means that the above sulfophenates are treated with a quantity of base which is higher than the stoichiometric value. The above excess normally ranges from about 125% to about 220% molar.
- the detergent additives comprise (i) from 60 to 100% by weight of sulfophenates having general formula (I) and may comprise (ii) from 0 to 40% by weight of other detergents selected from calcium sulfonates, calcium alkylbenzene sulfonates, calcium salicylate.
- the anti-wear additives used have a general formula of the type ZnP 2 SgO 4 R 4 , wherein R 4 is an alkyl radical having the formula -CH 2 R 5 , wherein R 5 is a linear and/or branched saturated alkyl radical, having from 2 to 15, preferably from 2 to 7, carbon atoms.
- R 5 is preferably selected from -(CH 2 ) 3 CH 3 , -CH(CH 3 )CH 3 , -C(CH 3 ) 3 , and relative mixtures.
- compositions used in the present invention can also be obtained using compositions which contain, in addition to components (a)-(c), friction modifying or reducing additives, provided they are compatible with the same components (a) - (c).
- the base oils (a) are selected from one or more of mineral or synthetic oils (among synthetic oils, poly ⁇ -olefins (PAO) and ester bases can be mentioned), typically used in lubricating oils for internal combustion engines fed by both gasoline and gas oil.
- the base oils can come from various processings, for example from hydro-refining or conversion processes of heavy waxes. Mixtures of mineral or synthetic oils can obviously be used.
- the viscosity of the above base oils can fall within a range of 2.0 to 10.0 mm 2 /s, preferably from 2.5 to 8.0 mm 2 /s, measured at 100°C.
- These bases, also possibly mixed with each other, are contained in a predominant quantity, reaching, in relation to the remaining group of additives necessary, up to 95-98% w; their concentration is typically equal to about 85% w.
- An object of the invention also relates to the fuel economy upgrading of secondary synergic properties of the above detergent and anti-wear additives, as these additives are typically used in the formulation of lubricating oils for internal combustion engines, to guarantee compliance with various specifications.
- a further object of the invention relates to a method which allows convenient and economical f.e. products to be formulated, without resorting to potentially critical variations to the already complex lubricating mixture.
- Another important object of the invention relates to the possibility of ensuring a high duration of the f.e. performances, due to the fact that said performances are guaranteed by additives traditionally used for long durations, as a much greater duration range of the oil must be guaranteed with respect to the range required by the f.e. engine test.
- the invention is the use of anti-wear additives of the zinc alkyl dithiophosphate type and detergents of the sulfophenate type which, when mixed in suitable ratios in a typical formulation for engine oils, give the mixture an evident fuel economy advantage.
- the f.e. performance can be obtained within a range of concentrations which, for anti-wear, varies from 0.3 to 5.0 %w, preferably from 0.8 to 3.0 %w; for the sulfophenate detergent from 0.5 to 5.0%w, preferably from 1.0 to 4.0%w.
- said mixture significantly reduces the friction coefficient at regimes closest to boundary conditions, and in particular, also the friction coefficient at regimes closest to M and H conditions.
- the lubricating composition used in the present invention can contain one or more components normally used in formulations for engines oils, for example viscosity index enhancers and/or viscosity modifiers, dispersing agents, antioxidants, anti-rust agents, anti-foam agents, demulsifiers, pour point depressants.
- viscosity index enhancers and/or viscosity modifiers for example viscosity index enhancers and/or viscosity modifiers, dispersing agents, antioxidants, anti-rust agents, anti-foam agents, demulsifiers, pour point depressants.
- Ashless nitrogenated dispersing agents typically used normally comprise oil-soluble polymeric structures functionalized with nitrogenated substituents capable of aggregating with polar particles or substances to be dispersed.
- the dispersing agents typically contain one or more nitrogenated parts bound to the polymeric skeleton, often by means of a bridge, and can be selected from all the known oil-soluble derivates, such as salts, amides, imides, amino-esters, oxyazolinic derivatives of mono or dicarboxylic acids with a long hydrocarbon chain and relative hydrocarbon anhydrides; long-chain thiocarboxylates of hydrocarbons to which a polyamine is directly bound; Mannich condensation products formed by condensation between long-chain substituted phenols with formaldehyde and polyalkylene polyamines. Numerous examples of dispersing agents are indicated in patent literature, for example in US-A-5,962,381 .
- Non-nitrogenated dispersing agents also exist, for example esters prepared by reaction between functionalized oil-soluble polymeric hydrocarbons and hydroxyl compounds, such as mono or polycarboxylic alcohols, or with aromatic compounds such as phenols and naphthols. Ester dispersing agents can also be prepared starting from unsaturated alcohols such as allyl alcohol, or starting from ether-alcohols.
- Convenient viscosity modifiers which can be added to the lubricating composition of the present invention comprise oil-soluble polymers having an weight average molecular weight ranging from about 10,000 to about 1,000,000, preferably from about 20,000 to about 500,000, as determined by gel permeation chromatography or light scattering methods.
- Typical examples of these polymers comprise polyisobutene, ethylene/propylene/alphaolefin copolymers, (co)polymethacrylates, copolymers of styrene and acrylic esters, copolymers of vinyl compounds and unsaturated carboxylic acids; partially hydrogenated copolymers of styrene and isoprene, styrene and butadiene, isoprene and butadiene; partially hydrogenated homopolymers of butadiene and isoprene.
- Viscosity modifying compounds also exist, which act as dispersing agents - viscosity modifiers, see for example US-A-4,089,794 ; US-A-4,160,739 and US-A-4,137,185 .
- Other dispersing agents - viscosity modifiers are ethylene or propylene copolymers grafted with nitrogenated compounds, see for example US-A-4,068,056 , US-A-4,146,489 and US-A-4,149,984 .
- the f.e. lubricating composition of the present invention can also contain antioxidants, which reduce the tendency of mineral oils to degrade by thermo-oxidation during their use.
- antioxidants are hindered phenols, variously substituted aromatic amines, salts of alkaline-earth metals of alkylphenol thioesters having C 5 to C 12 side chains, calcium nonylphenol sulfide, oil-soluble phenates, sulfurized phenates.
- Typical anti-rust compounds which can be used in the lubricating composition of the present invention are polyoxyalkylene polyols and relative esters, and polyoxyalkylene phenols.
- demulsifying agents can be obtained by the reaction between an alkylene oxide and an adduct obtained by reacting a bis-epoxide with a polyhydroxyl alcohol (see EP-A-330,522 ).
- Anti-foam agents which can be used are compounds of the polysiloxane type, for example silicon oil or polydimethyl siloxanes.
- additives are pour point depressants which lower the minimum temperature at which the fluid flows and can be poured.
- Typical examples of these additives which improve the fluidity at low temperatures of the lubricating composition are the well-known dialkyl fumarate/vinyl acetate copolymers and polyalkyl methacrylates.
- the lubricating composition of the present invention is prepared by the conventional mixing of the various components, both essential and complementary.
- the lubricating composition of the present invention is characterized by a more favourable SLC with respect to the corresponding formulation without these specific detergent and anti-wear additives. This advantage can be observed along the whole measurement rate range, thus being indifferently apparent in one or more of the "hydrodynamic”, elasto-hydrodynamic", “mixed” and “boundary” conditions.
- a preparative operating sequence of the instrument was prepared, gradual heating from a low to high temperature (from 40 to 135°C), friction coefficient measurements by curves at various S/R values, and the construction of the SLC.
- an SLC curve of this type obtained in the final phase at 135°C), useful for evaluating potential energy dissipations, is indicated in Figure 1 .
- each curve is constructed with average data of at least two tests and the standard deviation is always lower than 10%.
- the friction coefficient values are extracted from these curves at the inlet rates of 0.01 - 0.1 - 1.0 m/sec ( figure 1 ); these values were considered, for the sake of comparison, as being representative of the boundary, mixed and hydrodynamic (or elasto-hydrodynamic) lubrication regimes (B, M, H) respectively.
- the relative comparison between the terns of friction coefficient values thus obtained on the various mixtures, rather than their absolute value, allows a conclusion to be reached as to their fuel economy potentiality.
- the formulations relating to this example (F1-C, F2, F3-C), together with the common complementary components, all envisage the use of an anti-wear additive zinc dithiophosphate of primary alcohols (DTP1-A), as per Table 1.
- DTP1-A zinc dithiophosphate of primary alcohols
- F1-C a sulfonate detergent (SF) however was used, for F2, a sulfophenate (SFF1), and for F3-C a salicylate (SL), all superbasic.
- the formulations of this example all contain a primary zinc alkyl dithiophosphate anti-wear additive, but with a different organic structure from the previous one (DTP1-B, see the Note to Table 1).
- the formulation F7-C contains the detergent SF, F8 the detergent SFF1, F9-C the detergent SL.
- Both of the formulations F10-C and F11 were prepared with PAO bases and with superbasic sulfophenate detergent SFF2, having a different structure with respect to that used in the other examples (see the Note to Table 1). Furthermore:
- the friction coefficient data confirm the synergic action of the sulfophenate/primary dithiophosphate pair, with respect to the analogous sulfophenate/secondary dithiophosphate pair.
- the sulfophenate/primary dithiophosphate pair shows unexpected antifriction performances, it is important to verify that said performances are compatible and coherent with respect to additives specifically commercialized as antifriction agents, particularly with respect to Molybdenum additives and ashless additives of an ester nature (see the state of the art).
- 4 formulations were prepared, all containing an anti-wear agent zinc dithiophosphate of primary alcohols DTP1-A.
- the first two (F12, F13) also contain the other component which serves for the antifriction synergy claimed (a sulfophenate, SFF1).
- the first (F12) also contains a Molybdenum anti-wear additive (MoDTC)
- the second (F13) contains an ashless ester antifriction additive (GMO).
- the further formulations F14-C and F15-C, both containing the antifriction additive GMO, contain a sulfonate (SF) and salicylate (SL) detergent, respectively.
- the addition of the two antifriction additives described allows some of the friction coefficient values to be improved, demonstrating a good compatibility, from this point of view, of the synergic pair towards additives of both species.
- the results obtained from the further comparative formulations F14-C and F15-C show, on the other hand, that the specific addition of the anti-friction additive GMO, in formulations without the pair of synergic additives claimed, does not provide better results with respect to the F2, object of the invention.
- the formulations F16-C and F17 are based on XHVI.
- the formulation F16-C is characterized by a detergent addition to the superbasic sulfonate (SF), anti-wear agent dithiophosphate of secondary alcohols DPT2-A, but with the addition of Molybdenum antifriction agent to try and recuperate a low friction performance on a formulation which does not contain the synergic pair, object of the invention.
- the formulation F17 of the present invention contains the synergic pair (SFF2/DTP1-B) but without antifriction agent.
- compositions with significant SLC friction curves were subjected to engine fuel economy evaluation, according to methods prescribed by performance specifications of engine oils.
- phase II the fuel economy measurement takes place in two distinct phases, one which precedes the aging of the oil (phase I) and the other which follows it (phase II), so that the fuel economy retention can also be evaluated; in the case of the test with an M111 engine, on the other hand, the measurements only refer to the non-aged oil.
- the formulation which in the group of additives contains the superbasic sulfophenate/primary zinc dithiophosphate pair (F8), object of the present invention, with the Mercedes M111 test, has an FEI value which exceeds the limit of the ACEA A1-B1 specifications (2.5%).
- compositions tested in this context containing combinations of detergents/anti-wear agents of a different type (F7-C) from those of the present invention, even with the addition of a molybdenum friction modifying additive (F16-C), provide insufficient results with the Sequence VIB test.
- MoTA Mothioamide
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Lubricants (AREA)
Claims (16)
- Verwendung einer Additivzusammensetzung als reibungsverringerndes Additiv für Schmiermittelzusammensetzungen für Verbrennungsmotoren, umfassend ein Basisöl mit einer Viskosität, die zum Schmieren geeignet ist, wobei die Additivzusammensetzung umfasst:(i) Detergensadditive, wobei mindestens 60 Gew.-% der Detergensadditive ausgewählt sind aus Sulphenaten mit der allgemeinen Struktur (I) RΦ(OH)-Sn-(OH) ΦR', wobei R und R' gleich oder unterschiedlich Alkylreste mit von 1 bis 16 Kohlenstoffatomen sind, n von 1 bis 5 reicht; und wobei beide Hydroxyle mit einem oder mehreren Erdalkalimetallen versalzt sind;(ii) Abriebfeste Additive ausgewählt aus Zinkdithiophosphaten mit der allgemeinen Formel (II) ZnP2S4O4R4, wobei R ein Alkylrest mit der Formel -CH2R5 ist, wobei R5 ein lineares und/oder verzweigtes gesättigtes Alkylrest ist, mit 2 bis 15 Kohlenstoffatomen;wobei die Additivzusammensetzung zu der Schmiermittelzusammensetzung in einer Menge so hinzugefügt wird, dass eine Menge an Detergensadditiven (i) die von 0,5 Gew.-% bis 5,0 Gew.-% bezogen auf das Gesamtgewicht der Schmiermittelzusammensetzung reicht; eine Menge an Abriebfesten Additiven (ii) die von 0,3 Gew.-% bis 5,0 Gew.-% bezogen auf das Gesamtgewicht der Schmiermittelzusammensetzung reicht, zu erhalten.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei die Additivzusammensetzung zu der Schmiermittelzusammensetzung in so einer Menge hinzugefügt wird, um eine Menge an Detergensadditiven (i) von 1,0 bis 4%, bezogen auf das Gesamtgewicht der Schmiermittelzusammensetzung zu erhalten.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei die Additivzusammensetzung zu der Schmiermittelzusammensetzung in so einer Menge hinzugefügt wird, um eine Menge von abriebfesten Additiven (ii) reichend von 0,8 bis 3,0% bezogen auf das Gesamtgewicht der Schmiermittelzusammensetzung zu erhalten.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei mindestens 70 Gew.-% der Detergensadditive (i) ausgewählt ist aus Sulphophenaten mit der allgemeinen Formel (I).
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei bezogen auf die Verbindung mit der allgemeinen Formel (I) n von 1 bis 4 reicht.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei bezogen auf die Verbindung mit der allgemeinen Formel (I) beide Hydroxyle in der Paraposition bezogen auf R und R' sind.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei bezogen auf die Verbindung mit der allgemeinen Formel (I) beide Hydroxyle mit Calcium versalzt sind.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 7, wobei das mit Calcium versalzte Detergensadditiv mit der allgemeinen Formel (I) eine Gesamtbasenzahl (total base number, TBN) die von 50 bis 400 reicht, aufweist.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 8, wobei das mit Calcium versalzte Detergensadditiv mit der allgemeinen Formel (I) eine Gesamtbasenzahl (total base number, TBN) die von 100 bis 300 reicht, aufweist.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei die Detergensadditive (i) von 0 Gew.-% bis 40 Gew.-% an Detergentien, die sich von den Verbindungen mit der allgemeinen Formel (I) unterscheiden, ausgewählt aus Calciumsulphonaten, Calciumalkylbenzolsulphonaten, Calciumsalicylat umfassen.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei in der Verbindung mit der allgemeinen Formel (II), R ein Alkylrest mit der Formel -CH2R5 ist, wobei R5 ein lineares und/oder verzweigtes, gesättigtes Alkylrest mit 2 bis 7 Kohlenstoffatomen ist.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 11, wobei R5 ausgewählt ist aus: -(CH2)3CH3, - CH(CH3)CH3, -C(CH3)3, und relativen Mischungen.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei die Basisöle (a) eine bei 100°C gemessene Viskosität im Bereich von 2,0 bis 10 mm2/s aufweisen.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 13, wobei das Basisöl eine bei 100°C gemessene Viskosität im Bereich von 2,5 bis 8 mm2/s aufweist.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei das Basisöl ausgewählt ist aus einem oder mehreren von Mineralölen oder synthetischen Ölen.
- Verwendung nach Anspruch 1, wobei R und R' gleich oder unterschiedlich Alkylreste mit von 9 bis 12 Kohlenstoffatomen sind.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT002322A ITMI20022322A1 (it) | 2002-10-31 | 2002-10-31 | Olio lubrificante per motori atto a ridurre il consumo di carburante |
| ITMI20022322 | 2002-10-31 | ||
| PCT/EP2003/011419 WO2004039928A1 (en) | 2002-10-31 | 2003-10-15 | Lubricating oil for engines suitable for reducing fuel consumption |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1558715A1 EP1558715A1 (de) | 2005-08-03 |
| EP1558715B1 true EP1558715B1 (de) | 2012-12-26 |
Family
ID=32211394
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP03750716A Expired - Lifetime EP1558715B1 (de) | 2002-10-31 | 2003-10-15 | Verwendung Schmieröls zur Reduzierung des Kraftstoffverbrauchs |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1558715B1 (de) |
| AU (1) | AU2003268940A1 (de) |
| IT (1) | ITMI20022322A1 (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2004039928A1 (de) |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5490945A (en) * | 1991-04-19 | 1996-02-13 | The Lubrizol Corporation | Lubricating compositions and concentrates |
| US5328620A (en) * | 1992-12-21 | 1994-07-12 | The Lubrizol Corporation | Oil additive package useful in diesel engine and transmission lubricants |
| US5744430A (en) * | 1995-04-28 | 1998-04-28 | Nippon Oil Co., Ltd. | Engine oil composition |
| CA2251418C (en) * | 1997-10-30 | 2007-08-14 | The Lubrizol Corporation | A method to improve cu corrosion performance of mo-dtc and active sulfur by adding sunflower oil |
-
2002
- 2002-10-31 IT IT002322A patent/ITMI20022322A1/it unknown
-
2003
- 2003-10-15 WO PCT/EP2003/011419 patent/WO2004039928A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2003-10-15 EP EP03750716A patent/EP1558715B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-10-15 AU AU2003268940A patent/AU2003268940A1/en not_active Abandoned
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ITMI20022322A1 (it) | 2004-05-01 |
| WO2004039928A1 (en) | 2004-05-13 |
| EP1558715A1 (de) | 2005-08-03 |
| AU2003268940A8 (en) | 2004-05-25 |
| AU2003268940A1 (en) | 2004-05-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Pawlak | Tribochemistry of lubricating oils | |
| EP1996683B1 (de) | Stickstoffhaltiges dispergiermittel als aschefreier tbn-booster für schmiermittel | |
| EP1354933B1 (de) | Schierölzusammensetzungen kompatibel mit dem Dichtungselement eines Verbrennungsmotors | |
| US6642191B2 (en) | Lubricating oil additive system particularly useful for natural gas fueled engines | |
| CN103509634B (zh) | 一种用于以甲醇或甲醇汽油为燃料的发动机润滑油组合物 | |
| EP1947164A1 (de) | Motorschmiermittel mit erhöhter Hitzestabilität | |
| RU2615511C2 (ru) | Композиция смазочного масла | |
| EP1458838B1 (de) | Schmieröl mit verbesserter beständigkeit gegen oxidation, nitrierung und viskositätserhöhung | |
| JP4936692B2 (ja) | 潤滑組成物 | |
| WO2003048278A1 (en) | Sulfur containing lubricating oil additive system particularly useful for natural gas fueled engines | |
| CN105008502A (zh) | 由聚甘油醚制得的润滑组合物 | |
| JP2006182986A (ja) | 潤滑油組成物 | |
| US20130137616A1 (en) | Low phosphorus lubricating oil composition having lead corrosion control | |
| EP1558715B1 (de) | Verwendung Schmieröls zur Reduzierung des Kraftstoffverbrauchs | |
| US20230250357A1 (en) | Lubricating oil composition, shock absorber, and method for using lubricating oil composition | |
| EP3940046B1 (de) | Additiv für schmieröl, additivzusammensetzung für schmieröl und herstellung einer schmierölzusammensetzung | |
| EP3234077B1 (de) | Schmierölzusammensetzung | |
| WO2021064059A1 (en) | Non-metallic phosphorus antiwear additives | |
| EP1758971B1 (de) | Schmierölzusammensetzung | |
| US20080277203A1 (en) | Additives and lubricant formulations for improved phosphorus retention properties | |
| CN105296062A (zh) | 一种抗氧化的天然气发动机润滑油的制备方法 | |
| EP4305132B1 (de) | Schmierölzusammensetzung | |
| CN101497842A (zh) | 低沉积省燃料消耗型发动机油组合物 | |
| CA2638534A1 (en) | Engine wear protection in engines operated using ethanol-based fuel | |
| Palekar | Bench scale evaluation of automotive crankcase lubricants |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20050422 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IT LI LU MC NL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK |
|
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20081125 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: ENI S.P.A. |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 60342955 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130307 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20130927 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 60342955 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20130927 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20131017 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20131028 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20131029 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 60342955 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20141015 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150501 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141015 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20150630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20141031 |