EP0750488B1 - Dispositif et procede de melange aseptique de produits liquides - Google Patents
Dispositif et procede de melange aseptique de produits liquides Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0750488B1 EP0750488B1 EP95911514A EP95911514A EP0750488B1 EP 0750488 B1 EP0750488 B1 EP 0750488B1 EP 95911514 A EP95911514 A EP 95911514A EP 95911514 A EP95911514 A EP 95911514A EP 0750488 B1 EP0750488 B1 EP 0750488B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- container
- product
- connection device
- pointed
- pointed part
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61J—CONTAINERS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR MEDICAL OR PHARMACEUTICAL PURPOSES; DEVICES OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR BRINGING PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS INTO PARTICULAR PHYSICAL OR ADMINISTERING FORMS; DEVICES FOR ADMINISTERING FOOD OR MEDICINES ORALLY; BABY COMFORTERS; DEVICES FOR RECEIVING SPITTLE
- A61J1/00—Containers specially adapted for medical or pharmaceutical purposes
- A61J1/14—Details; Accessories therefor
- A61J1/20—Arrangements for transferring or mixing fluids, e.g. from vial to syringe
- A61J1/2089—Containers or vials which are to be joined to each other in order to mix their contents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61J—CONTAINERS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR MEDICAL OR PHARMACEUTICAL PURPOSES; DEVICES OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR BRINGING PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS INTO PARTICULAR PHYSICAL OR ADMINISTERING FORMS; DEVICES FOR ADMINISTERING FOOD OR MEDICINES ORALLY; BABY COMFORTERS; DEVICES FOR RECEIVING SPITTLE
- A61J1/00—Containers specially adapted for medical or pharmaceutical purposes
- A61J1/14—Details; Accessories therefor
- A61J1/20—Arrangements for transferring or mixing fluids, e.g. from vial to syringe
- A61J1/2003—Accessories used in combination with means for transfer or mixing of fluids, e.g. for activating fluid flow, separating fluids, filtering fluid or venting
- A61J1/2006—Piercing means
- A61J1/201—Piercing means having one piercing end
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61J—CONTAINERS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR MEDICAL OR PHARMACEUTICAL PURPOSES; DEVICES OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR BRINGING PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS INTO PARTICULAR PHYSICAL OR ADMINISTERING FORMS; DEVICES FOR ADMINISTERING FOOD OR MEDICINES ORALLY; BABY COMFORTERS; DEVICES FOR RECEIVING SPITTLE
- A61J1/00—Containers specially adapted for medical or pharmaceutical purposes
- A61J1/14—Details; Accessories therefor
- A61J1/20—Arrangements for transferring or mixing fluids, e.g. from vial to syringe
- A61J1/2003—Accessories used in combination with means for transfer or mixing of fluids, e.g. for activating fluid flow, separating fluids, filtering fluid or venting
- A61J1/2006—Piercing means
- A61J1/2013—Piercing means having two piercing ends
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61J—CONTAINERS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR MEDICAL OR PHARMACEUTICAL PURPOSES; DEVICES OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR BRINGING PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS INTO PARTICULAR PHYSICAL OR ADMINISTERING FORMS; DEVICES FOR ADMINISTERING FOOD OR MEDICINES ORALLY; BABY COMFORTERS; DEVICES FOR RECEIVING SPITTLE
- A61J1/00—Containers specially adapted for medical or pharmaceutical purposes
- A61J1/14—Details; Accessories therefor
- A61J1/20—Arrangements for transferring or mixing fluids, e.g. from vial to syringe
- A61J1/2003—Accessories used in combination with means for transfer or mixing of fluids, e.g. for activating fluid flow, separating fluids, filtering fluid or venting
- A61J1/2048—Connecting means
- A61J1/2058—Connecting means having multiple connecting ports
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61J—CONTAINERS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR MEDICAL OR PHARMACEUTICAL PURPOSES; DEVICES OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR BRINGING PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS INTO PARTICULAR PHYSICAL OR ADMINISTERING FORMS; DEVICES FOR ADMINISTERING FOOD OR MEDICINES ORALLY; BABY COMFORTERS; DEVICES FOR RECEIVING SPITTLE
- A61J1/00—Containers specially adapted for medical or pharmaceutical purposes
- A61J1/14—Details; Accessories therefor
- A61J1/20—Arrangements for transferring or mixing fluids, e.g. from vial to syringe
- A61J1/2003—Accessories used in combination with means for transfer or mixing of fluids, e.g. for activating fluid flow, separating fluids, filtering fluid or venting
- A61J1/2068—Venting means
- A61J1/2075—Venting means for external venting
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61J—CONTAINERS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR MEDICAL OR PHARMACEUTICAL PURPOSES; DEVICES OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR BRINGING PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS INTO PARTICULAR PHYSICAL OR ADMINISTERING FORMS; DEVICES FOR ADMINISTERING FOOD OR MEDICINES ORALLY; BABY COMFORTERS; DEVICES FOR RECEIVING SPITTLE
- A61J1/00—Containers specially adapted for medical or pharmaceutical purposes
- A61J1/14—Details; Accessories therefor
- A61J1/20—Arrangements for transferring or mixing fluids, e.g. from vial to syringe
- A61J1/2003—Accessories used in combination with means for transfer or mixing of fluids, e.g. for activating fluid flow, separating fluids, filtering fluid or venting
- A61J1/2079—Filtering means
- A61J1/2082—Filtering means for gas filtration
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for aseptically mixing liquid products.
- the invention particularly relates to an apparatus and a method for mixing aseptically three or more liquid products for pharmaceutical or nutritive use. Even more particularly, the invention relates to an apparatus and to method for mixing aseptically liquid products for inclusion in a preparation for administering nutrient parenterally, particularly intravenously.
- the invention also relates to a connection device and to a system for mixing aseptically three or more liquid products.
- Nutrients are very often administered parenterally to patients who are unable to ingest nutrients in the normal way, for some reason or another.
- the nutrient supply is comprised primarily of three main types of nutrient, namely carbohydrates, amino acids and fat.
- carbohydrates and amino acids are supplied in the form of solutions, and the fat in the form of an emulsion.
- These preparations also contain other necessary nutrients, such as electrolytes, trace elements and water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins.
- the present invention provides an apparatus in accordance with claim 1 for mixing three liquid products aseptically.
- connection device in accordance with claim 2 for mixing together three or more liquid products.
- the invention also relates to a method in accordance with claim 4, using said device for mixing three or more liquid products aseptically.
- At least the product in the last container is pre-packed at a pressure beneath atmospheric pressure and the first product container is caused to communicate with the surrounding atmosphere through the medium of a sterilizing filter, so that the products will be driven or drawn successively through the series of product containers under the influence of the outer atmospheric pressure and mixed mutually together and are finally collected in the last product container as a final mixture.
- all products are packed in their respective containers at a pressure beneath atmospheric pressure.
- the invention also relates to a system in accordance with claim 3 for producing an aseptic mixture of three or more liquid products.
- Figure 1 is a sectioned view of the first pointed connection device according to the invention
- Figure 2 is a side view of the connection device shown in Figure 1
- Figure 3 is a sectioned view of the second pointed connection device according to the invention
- Figure 4 is a side view of the second connection device
- Figure 5 illustrates an additional, intermediate connection device used in accordance with one embodiment of the invention
- Figure 6 illustrates schematically the construction of the inventive system.
- Figs. 1 and 2 illustrate the first connection device, generally referenced 1, which includes a pointed part 2 and two mutually separate and generally parallel through-passing passageways 3 and 4.
- One end of the first passageway 3 opens at 5 into the pointed end 2, while the other end of the first passageway communicates at 6 with the surrounding atmosphere through a sterilizing filter 7.
- the Figure shows the sterilizing filter 7 mounted in a chamber 8 and held in position by a cover member 9 provided with openings 10 in communication with the surrounding atmosphere.
- the sterilizing filter may, of course, be arranged in other ways.
- the second passageway 4 also opens at one end into the pointed part 2, at 11, while the other end of the second passageway 4 is connected at 12 to a connection line (not shown) by means of a connection 13.
- Figs. 3 and 4 illustrate the second connection device, generally referenced 21, which includes a first pointed part 22 and a second pointed part 23, said pointed parts normally extending in mutually opposite directions, although this is not strictly necessary.
- the second connection device 21 includes two mutually separate and generally parallel passageways 24 and 25. One end of the first passageway 24 opens at 26 into the first pointed part 22, while the other end of said passageway is connected at 27 to a connection line (not shown) from the first connection device 1, by means of a connection 28.
- a first end of the second passageway 25 also opens into the first pointed part 22, at 29, and the other end of the passageway opens out adjacent the second pointed part 23, at 30.
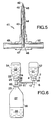
- FIG. 5 is a sectional view of an intermediate, pointed connection device, generally referenced 41, which is used in the embodiment of the invention in which four or more liquids are to be mixed together.
- This intermediate connection device includes a pointed part 42 and two mutually separate and generally parallel through-passing passageways 43 and 44.
- One end 45 and 46 of respective passageways 43 and 44 opens into the pointed end-part 42, while the other ends 47 and 48 of respective passageways connect with connections 49 and 50 for coupling the intermediate connection device in the connection line (not shown) between the first and the second connection devices 1 and 21.
- connection devices 41 may be coupled sequentially in the connection line, one such intermediate connection device being required for each additional liquid product to be mixed in accordance with the invention, over and above the first-mentioned three products.
- connection devices illustrated in Figures 1-5 and the passageways contained therein shall be protected against mechanical damage and primarily against microbial contamination, by means of protective hoods or caps placed over respective points.
- protective hoods will preferably be airtight and may also include a means which is destroyed when the hood is removed, so that the hood cannot subsequently be replaced without it being evident that the hood has been removed (tamper-proof).
- the design of such protective hoods and such safety devices lies within the competence of one of normal skill in this art.
- the protective hood shall not be removed from its respective point until immediately prior to inserting the point through the penetrable product container closure means.
- the protective hoods have not been shown in the drawings, for the sake of clarity.
- Figure 6 is a schematic illustration of an inventive system for mixing three liquid products aseptically.
- the first product 51 is contained in the first product container 52
- the second product 53 is contained in the second product container 54
- the third product 55 is contained in a product container 56 whose empty volume 57 is sufficiently large to accommodate the products 51 and 53 arriving from the containers 52 and 54 respectively.
- the three containers 52, 54 and 56 are closed by means of penetrable closure means 58, 59 and 60 respectively.
- closure means may be of a conventional kind, consisting in a rubber membrane which closes the container opening and which is held in place by a metal capsule.
- This capsule contains in the central region of the closure an opening which exposes the rubber membrane so as to enable said membrane to be pierced by a pointed connection device.
- the opening in the metal capsule can be protected from damage and from bacterial contamination during storage and transportation with the aid of a metal or plastic protective covering. It will be obvious to those skilled in this art that other penetrable closure means are conceivable.
- Figure 6 shows schematically a first pointed connection device 1 according to Figures 1 and 2 inserted through the penetrable closure means 58 of the container 52.
- the passageways 3 and 4 of the connection device 1 connect at one end with the interior of the container 52 at the pointed end 2 of the device.
- the other end of the passageway 3 communicates with the surrounding atmosphere through a sterilizing filter at 6, while the other end of the passageway 4 connects at 12 to a connection line 61 extending to a second connection device 21 of the kind illustrated in Figures 3 and 4.
- connection device 21 The pointed end 22 of the connection device 21 is inserted into the container 54 through the penetrable closure means 59, while the pointed end 23 of said connection device 21 is inserted into the container 56 through the penetrable closure means 60.
- the orifice 27 of the first passageway 24 of said connection device connects with the connection line 61 extending from the first container 52.
- the second passageway 25 connects the interior of the second container 54 with the interior of the third container 56.
- liquid product 51 when subjected to the influence of a suitable driving force, liquid product 51 is able to flow from the container 52 and through the container 54 while mixing with the liquid product 53 contained therein, and finally into the conductor 56 in which all three products are mixed together to form a final mixture.
- connection line 61 When four or more liquid products are to be mixed together, one or more intermediate connection devices of the kind shown in Figure 5 are coupled in the connection line 61 with the aid of their two connectors 49 and 50.
- the pointed part 42 of this connection device which includes the passageways 43 and 44, is then inserted through a penetrable closure means of a product container of similar type to the containers 52 and 54.
- the last container 56 in line which accommodates the final mixture of said liquid products, including the product 55, shall have a volumetric capacity sufficient to accommodate the final mixture.
- the final container 56 will thus have a significant empty volume 57 prior to the mixture components having been transferred to this final container.
- This empty volume shall be under a vacuum or a pressure beneath atmospheric pressure. It is this subpressure that generates the driving force in the mixing process, as will be described in more detail below.
- the products contained in the containers 52 and 54, and also in any other additional container arranged upstream of the final container 56 will also preferably be contained under a vacuum or a subpressure.
- subpressure conditions are not necessary in the case of these containers, and the containers may be under atmospheric pressure or a moderate overpressure.
- an overpressure or subpressure prevails in one or more containers, with the exception of the last container, this overpressure must be equalized through the sterilizing filter.
- the pointed ends of the connection devices In order to achieve this, it is necessary for the pointed ends of the connection devices to lie above the surfaces of the liquid in respective containers.
- the products are often packed under some suitable protective gas, such as nitrogen, and not under air, in order to prevent the oxidation of sensitive components.
- connection line 61 extending between the two connection devices 1 and 21 may have the form of a hose connection between the connectors 13 and 28 of respective connection devices, optionally with additional, intermediate connection devices 41 coupled in the connection line.
- connection line 61 and the two connection devices 1 and 21 are permanently connected together in the manufacture of the mixing apparatus, such as to form a unit.
- This combination of connection devices and connection line can then be combined with a suitable container holding device which functions to hold the three product containers 52, 54 and 56 and their respective connections and connecting line in the form of a unit.
- a suitable container holding device which functions to hold the three product containers 52, 54 and 56 and their respective connections and connecting line in the form of a unit.
- Such a unit can be handled more easily in the mixing process than separate product containers.
- the inventive method of aseptically mixing three liquid products is carried out in the following manner:
- connection devices 1 and 21 will have been connected together by means of the connecting line 61 and all pointed parts 2, 22 and 23 of respective connection devices will have been covered with protective hoods (not shown) which are impervious to air and bacteria and therewith prevent air and bacteria from entering the passageways 3, 4 and 24, 25 of respective devices 1 and 21, as before described.
- the protective hood is now removed from the pointed part 2 of the connection device 1 and the point is inserted through the penetrable closure means 58 of the product container 52. If the product 51 in the container 52 is under subpressure, the interior of the container will now assume atmospheric pressure by virtue of ambient air being able to flow into the device 1, through the sterilizing filter 7 and the passageway 3.
- the protective hood covering the pointed part 22 of the connection device 21 must not be removed before the subpressure in the container 52 has been equalized. This is important in ensuring aseptic conditions in the container 52. If the hood covering the point 22 is removed prematurely while a subpressure still prevails in the container 52, unfiltered air will be sucked in through the passageway 24 and the connection line 61 and enter the container 52 and therewith contaminate the container contents 51.
- the hood covering the point 22 of the connection device 21 is removed and the point is inserted through the penetrable closure means 59 of the container 54.
- the subpressure prevailing in this container is thereafter equalized by air that flows into the connection device 1 through the sterilized filter 7 and from there into the product container 52, while displacing part of its content 51 into the container 54.
- the hood covering the point 23 of the connection device 21 may not be removed before the pressure has been equalized. This is important in preventing unfiltered air from flowing into the product container 54 through the passageway 25 and contaminating the content 53 of said container.
- the hood is removed from the point 23 of the connection device 21 and said point is inserted through the penetrable closure means 60 of the last container 56 in line.
- the subpressure prevailing in the mixing chamber 57 in the container 56 will now draw in product 53 from the container 54 by suction, at the same time as the product 51 from the container 52 will pass through the container 54 and enter the final container 56, in which the three products are mixed.
- the subpressure prevailing in the final container 56 will also be equalized by air drawn by suction through the sterilizing filter 7 and passing through the containers 52 and 54 and the connection line 61.
- the mixing process is analogous with that described above.
- the containers are connected successively by means of the pointed connection devices, it being ensured that the subpressure in a connected container has been equalized before removing the protective hood from the point of the next following connection device and a liquid connection is established with the next following container.
- the container can be removed from the connection device 21 and the finished mixture administered in a conventional manner, for instance by infusion or by injection.
- the mixture is administered as quickly as possible after being produced, in order to reduce the risk of reactions taking place between the component products, these reactions possibly giving rise to undesirable reaction products.
- the finished mixture will preferably be stored in a dark and cool environment, until it can be administered.
- the penetrable closure means will preferably be washed with a disinfectant, e.g. alcohol, prior to inserting the point of a connection device therethrough.
- a disinfectant e.g. alcohol
- the actual connection devices and associated connecting line will preferably be disposable, i.e. intended for one-time use only and stored in a sterilized package prior to use, for instance a package that has been sterilized by ionizing radiation.
- the simple method and apparatus provided by the invention enable the products to be mixed by hospital personnel who have no particular training in this regard without any appreciable risk of bacterial contamination.
- the components of the inventive apparatus may be made of a material that is normally used within known techniques for the aseptic handling of liquids.
- the product containers are conveniently conventional glass or plastic bottles intended for injection or infusion preparations.
- the pointed connection devices are conveniently made of a metal and/or plastic material conventionally used in this field. It is important that the materials can be sterilized, for instance by autoclaving or with the aid of gas or radiation. Since the components will preferably be intended for one-time use only, the cost of the components is also important. A skilled person who has knowledge of the invention will find no difficulty in choosing suitable materials and determining the construction of the components in detail.
- the present invention thus provides a simple technical solution to the problem of mixing three or more liquid products under aseptic conditions without risk of contamination. This is of particular value when, e.g., mixing all of the nutrients required for a complete intravenous nutrient supply.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Medical Preparation Storing Or Oral Administration Devices (AREA)
- Accessories For Mixers (AREA)
- Filling Of Jars Or Cans And Processes For Cleaning And Sealing Jars (AREA)
Claims (7)
- Un appareil pour mélanger trois produits liquides ou plus conjointement de façon aseptique, caractérisé par :a) un premier dispositif de liaison à pointe (1) pour l'insertion au travers d'un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré (58) d'un premier récipient de produit (52) dans lequel le dispositif de liaison comprend deux passages traversants séparés généralement parallèles (3,4) dont le premier (3) débouche dans une extrémité dans la partie en pointe (2) du dispositif de liaison (1) et dont l'autre extrémité communique avec l'atmosphère environnante au moyen d'un filtre de stérilisation (7) et dans lequel le deuxième passage (4) débouche également à une extrémité dans la partie en pointe (2) du dispositif de liaison (1) et est relié à une conduite de liaison à son autre extrémité et,b) un deuxième dispositif de liaison à double pointe (21) dans lequel une première partie en pointe (22) dudit dispositif est agencée pour l'insertion au travers d'un élément de fermeture apte à être pénétré (59) d'un deuxième récipient de produit (54) et comprend deux passages traversants séparés généralement parallèles (24, 25) dont un premier passage (24) débouche à une extrémité dans la première partie en pointe (22) et l'autre extrémité dudit passage (24) est reliée à la conduite de liaison (28) s'étendant à partir du premier dispositif de liaison (1) et dans lequel le deuxième passage (25) débouche également à une extrémité dans la première partie en pointe (22) et au dispositif de liaison (20), cette deuxième partie en pointe (23) étant agencée pour être insérée au travers d'un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré (60) d'un récipient de produit final (56) dans lequel un mélange de tous les produits est recueilli, et, en outre lorsque quatre produits liquides ou plus doivent être mélangés ;c) un ou plusieurs dispositifs de liaison en pointe additionnels, intermédiaires (41) ayant chacun une pointe creuse (42) pour l'insertion au travers d'un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré d'un récipient de produit liquide intermédiaire dans lequel chaque dite pointe (42) comporte deux passages séparés généralement parallèles (43, 49) qui tous deux débouchent dans l'extrémité en pointe (42) du dispositif de liaison et qui sont reliés à leurs autres extrémités ouvertes à une conduite de liaison respective s'étendant à partir d'un dispositif de liaison précédent ou subséquent.
- Un dispositif de liaison (21) pour mélanger trois produits liquides ou plus, caractérisé par une première partie en pointe creuse (22) qui est agencée pour percer un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré d'un récipient de produit liquide, dans lequel la partie en pointe (22) comprend deux passages traversants séparés généralement parallèles (24, 25) dont tous deux débouchent dans l'extrémité de la partie en pointe (22), dans lequel le premier passage (24) est relié à une conduite de liaison (28) pour l'alimentation du produit liquide ou du mélange de produit devant être mélangé avec le produit liquide dans ledit récipient et dans lequel le deuxième passage (25) débouche dans l'extrémité d'une deuxième partie en pointe (23) qui est agencée pour percer un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré d'un récipient final pour un produit liquide supplémentaire avec lequel les autres produits liquides doivent être mélangés finalement pour former un mélange final.
- Un système pour mélanger de façon aseptique trois ou plusieurs produits liquides conjointement, caractérisé en ce que le système comprend :a) un récipient (52) qui renferme un premier produit liquide (51) qui est enfermé dans le récipient avec l'aide d'un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré (58) ;b) un premier dispositif de liaison à pointe (1) qui comprend un premier passage traversant (3) qui débouche à une extrémité (5) dans la partie en pointe (2) du dispositif de liaison et est relié à l'atmosphère ambiante à son autre extrémité par l'intermédiaire du milieu d'un filtre de stérilisation (7) et qui comprend également un deuxième passage traversant (4) qui est généralement parallèle au premier passage (3) et séparé de celui-ci, dans lequel une extrémité du deuxième passage débouche dans la partie en pointe (2) du dispositif de liaison et l'autre extrémité (12) est reliée à une conduite de liaison (13), dans lequel la partie en pointe (2) du premier dispositif de liaison (1) est insérée au travers du moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré (58) du premier récipient (52) pour obtenir une liaison fluidique avec celui-ci ;c) un récipient (54) qui renferme un deuxième produit liquide (53) qui est enfermé dans le récipient au moyen d'un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré (59) ;d) un deuxième dispositif de liaison à pointe double (21) qui comprend un premier passage traversant (24) qui débouche à une extrémité (26) dans la première partie en pointe (22) du dispositif de liaison et est relié à son autre extrémité (27) à la conduite de liaison (28) s'étendant à partir du premier dispositif de liaison (1) et comprend également un deuxième passage traversant (25) qui est généralement parallèle au premier passage (24) et débouche à une extrémité (29) dans la première partie en pointe (22) du dispositif de liaison (21) et débouche à son autre extrémité (30) dans la deuxième partie en pointe (23) dudit dispositif de liaison (21), dans lequel la première partie en pointe (22) est insérée au travers du moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré (59) du deuxième récipient de produit (54) pour obtenir une liaison fluidique avec celui-ci ; ete) un récipient de produit final (56) dans lequel le produit est contenu à une pression en dessous de la pression atmosphérique et qui comprend un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré (60) au travers duquel la deuxième partie en pointe (23) du deuxième dispositif de liaison (21) est insérée pour obtenir une liaison fluidique avec ledit récipient de produit (56), dans lequel la capacité volumétrique du récipient est suffisante pour recevoir le mélange des produits liquides et en outre, lorsque quatre produits liquides ou plus doivent être mélangés ;f) un ou plusieurs dispositifs de liaison à pointe intermédiaires supplémentaires (41) ayant chacun une partie en pointe creuse (42) pour l'insertion au travers d'un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré d'un récipient de produit liquide intermédiaire, dans lequel chaque dite partie en pointe (42) comporte deux passages séparés généralement parallèles (43, 44) qui tous deux débouchent dans la partie en pointe (42) du dispositif de liaison (41) et dont les autres ouvertures d'extrémité (47, 48) sont chacune reliées à une conduite de liaison respective (49, 50) s'étendant à partir d'un dispositif de liaison précédent ou subséquent et dans lequel la partie en pointe (42) de chacun desdits dispositifs de liaison intermédiaires (41) est insérée au travers d'un moyen de fermeture apte à être pénétré d'un récipient de produit liquide intermédiaire supplémentaire pour fournir une liaison liquide avec ledit récipient de produit.
- Un procédé pour mélanger de façon aseptique trois produits liquides ou plus, caractérisé en ce que chacun des produits est contenu dans un récipient de produit individuel (52, 54, 56) dans lequel les récipients sont reliés conjointement en série et le produit ou le mélange de produits à partir de chacun des récipients en commençant avec le premier récipient (52) dans la série, est amené à s'écouler successivement sous des conditions aseptiques au récipient suivant en ligne et là pour être mélangé avec le produit dans ledit récipient jusqu'à ce qu'un mélange final de tous les produits ait été recueilli dans le dernier récipient (56) dans la série, le dernier et le deuxième dernier récipient étant reliés par le dispositif de liaison selon la revendication 2.
- Un procédé selon la revendication 4, caractérisé en ce que, au moins le produit (55), dans le dernier récipient de produit (56) en ligne est pré-conditionné dans le récipient à une pression en dessous de la pression atmosphérique et en ce que le premier récipient de produit (52) est placé en communication avec l'atmosphère environnante par l'intermédiaire d'un filtre de stérilisation (7), si bien que les produits sont entraínés au travers des séries de récipients de produit par l'influence de la pression atmosphérique environnante tout en mélangeant mutuellement les contenus des récipients, lesdits produits étant finalement recueillis comme un mélange final dans le dernier récipient de produit (56) en ligne.
- Un procédé selon la revendication 4 ou 5, caractérisé en ce que le premier récipient de produit (52) est tout d'abord relié à la conduite de liaison (61) s'étendant au deuxième récipient (54) et à l'atmosphère environnante et le premier récipient (52) est amené à la pression atmosphérique tandis que la conduite de liaison (61) audit deuxième récipient (54) est fermée, après quoi la conduite de liaison (61) au deuxième récipient (54) est ouverte après que la pression dans le premier récipient (52) se soit établie à la pression atmosphérique et le deuxième récipient (54) est amené à la pression atmosphérique tandis que la conduite de liaison au troisième récipient est maintenue fermée, après quoi la conduite de liaison au récipient suivant est ouverte quand le deuxième récipient s'est établi à la pression atmosphérique et ledit récipient suivant est amené à la pression atmosphérique, dans lequel le procédé est répété successivement pour chacun des récipients de produit dans les séries jusqu'au dernier récipient de produit (56) en ligne, dans lequel la pression atmosphérique prévaut dans les récipients de produit précédents au récipient de produit final en ligne afin d'obtenir un mélange de produit final dans ledit récipient.
- Un procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 4 à 6, caractérisé par le mélange de trois produits liquides conjointement.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| SE9400681A SE9400681L (sv) | 1994-02-28 | 1994-02-28 | Anordning och förfarande för aseptisk blandning av tre eller flera vätskeformiga produkter samt anslutningsdon och system för åstadkommande av nämnda blandning |
| SE9400681 | 1994-02-28 | ||
| PCT/SE1995/000178 WO1995022954A1 (fr) | 1994-02-28 | 1995-02-21 | Dispositif et procede de melange aseptique de produits liquides |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0750488A1 EP0750488A1 (fr) | 1997-01-02 |
| EP0750488B1 true EP0750488B1 (fr) | 1999-05-06 |
Family
ID=20393107
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP95911514A Expired - Lifetime EP0750488B1 (fr) | 1994-02-28 | 1995-02-21 | Dispositif et procede de melange aseptique de produits liquides |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0750488B1 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN1054279C (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE179589T1 (fr) |
| AU (1) | AU1905295A (fr) |
| CA (1) | CA2184249A1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE69509508T2 (fr) |
| HU (1) | HUT76713A (fr) |
| PL (1) | PL178101B1 (fr) |
| SE (1) | SE9400681L (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO1995022954A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI319984B (en) * | 2003-06-06 | 2010-02-01 | Sterile combined preparation | |
| JP5062639B2 (ja) * | 2006-04-24 | 2012-10-31 | ノボ ノルディスク ヘルス ケア アーゲー | 凍結乾燥薬剤から薬液を形成するための移送システム |
| CN101081192B (zh) * | 2007-07-03 | 2011-10-05 | 王建友 | 一种输液瓶口装置 |
| JP2014504921A (ja) | 2010-12-30 | 2014-02-27 | ジーイー・ヘルスケア・リミテッド | マルチバイアル分注 |
| AU2018319625B2 (en) * | 2017-08-24 | 2023-02-16 | Innatoss Laboratories B.V. | Liquid handling system and method |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE9001271D0 (sv) * | 1990-04-06 | 1990-04-06 | Eric Westberg | Blodpaase foer anvaendning vid separation av blod i komponenter |
| US5154716A (en) * | 1990-11-06 | 1992-10-13 | Miles Inc. | Bottom blood bag separation system |
| JPH05131018A (ja) * | 1991-11-11 | 1993-05-28 | Terumo Corp | バツグ連結体およびその製造方法 |
-
1994
- 1994-02-28 SE SE9400681A patent/SE9400681L/ not_active IP Right Cessation
-
1995
- 1995-02-21 PL PL95316025A patent/PL178101B1/pl unknown
- 1995-02-21 DE DE69509508T patent/DE69509508T2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1995-02-21 EP EP95911514A patent/EP0750488B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-02-21 AU AU19052/95A patent/AU1905295A/en not_active Abandoned
- 1995-02-21 CN CN95190123A patent/CN1054279C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1995-02-21 WO PCT/SE1995/000178 patent/WO1995022954A1/fr not_active Ceased
- 1995-02-21 CA CA 2184249 patent/CA2184249A1/fr not_active Abandoned
- 1995-02-21 HU HU9602344A patent/HUT76713A/hu unknown
- 1995-02-21 AT AT95911514T patent/ATE179589T1/de active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| SE501835C2 (sv) | 1995-05-22 |
| DE69509508D1 (de) | 1999-06-10 |
| ATE179589T1 (de) | 1999-05-15 |
| SE9400681D0 (sv) | 1994-02-28 |
| PL178101B1 (pl) | 2000-02-29 |
| CA2184249A1 (fr) | 1995-08-31 |
| HUT76713A (en) | 1997-10-28 |
| SE9400681L (sv) | 1995-05-22 |
| AU1905295A (en) | 1995-09-11 |
| CN1054279C (zh) | 2000-07-12 |
| HU9602344D0 (en) | 1996-10-28 |
| WO1995022954A1 (fr) | 1995-08-31 |
| PL316025A1 (en) | 1996-12-23 |
| EP0750488A1 (fr) | 1997-01-02 |
| CN1123521A (zh) | 1996-05-29 |
| DE69509508T2 (de) | 1999-09-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4997430A (en) | Method of and apparatus for administering medicament to a patient | |
| US4823833A (en) | Fluid communication device | |
| US5167816A (en) | Sterile coupling device for drug container | |
| AU636060B2 (en) | Sheath for cannula | |
| EP0172836B1 (fr) | Systeme ferme d'administration de medicament | |
| US5334170A (en) | Dye management system including an administration set with an in-line burette | |
| EP0948371B1 (fr) | Appareil permettant d'administrer un fluide toxique | |
| EP0617681B1 (fr) | Systeme de transfert de fluide permettant de tirer du liquide d'une alimentation en vrac | |
| EP0085663B1 (fr) | Appareil pour mélanger une substance avec une autre substance | |
| US5368586A (en) | Closure for a drug-vial | |
| US6379340B1 (en) | Fluid control device | |
| US4325368A (en) | Infusion device | |
| EP0696448A2 (fr) | Récipient pour liquides pour distribuer des solutions médicales | |
| KR20010032470A (ko) | 폐쇄 시스템에서 의약품 용기와 정맥용 백을 연결하는유체 이송 장치 | |
| US20200130873A1 (en) | Methods for preparing autologous blood eye drops | |
| EP3924020A1 (fr) | Dispositif de transfert destiné à être utilisé avec un contenant de liquide de perfusion | |
| TW202348218A (zh) | 用於藉由輸液或注射給予患者的流體藥用或營養物質的劑量重組之具有壓力補償器的無菌軟性包裝 | |
| EP0750488B1 (fr) | Dispositif et procede de melange aseptique de produits liquides | |
| CN111603386A (zh) | 用于施用药物或营养物质的无菌或灭菌包装 | |
| US20200093558A1 (en) | Systems and methods for decontaminated engagement of vessels using a displaceable plate | |
| US5584825A (en) | Closure delivery system | |
| EP0112356B2 (fr) | Dispositif de communication de fluide | |
| EP0379788A1 (fr) | Site d'injection | |
| JPH0414029B2 (fr) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19960930 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19970509 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: AB IMIA DEVELOPMENT |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19990506 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 19990506 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 179589 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19990515 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 69509508 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19990610 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: PATENTANWAELTE SCHAAD, BALASS, MENZL & PARTNER AG |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20010131 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20010131 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20010221 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20010221 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20010226 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020221 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020221 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020228 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020903 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20020221 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20021031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |