EP0182583A2 - Method for cleaning textiles with cyclic siloxanes - Google Patents
Method for cleaning textiles with cyclic siloxanes Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0182583A2 EP0182583A2 EP85308214A EP85308214A EP0182583A2 EP 0182583 A2 EP0182583 A2 EP 0182583A2 EP 85308214 A EP85308214 A EP 85308214A EP 85308214 A EP85308214 A EP 85308214A EP 0182583 A2 EP0182583 A2 EP 0182583A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- cleaning
- cyclic
- percent
- stain
- weight
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/16—Organic compounds
- C11D3/37—Polymers
- C11D3/3703—Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- C11D3/373—Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds containing silicones
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/16—Organic compounds
- C11D3/162—Organic compounds containing Si
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a method for removing soil from textiles using cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes.
- this invention relates to the use of cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes for removal of oily/greasy stains from textiles.
- Textile products such as fabrics, carpets and upholstery often develop prominent stain spots from inadvertent contact with foodstuff and other materials containing grease and oils.
- Various organic solvents such as alcohols, petroleum hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons have been used in cleaning compositions adapted for direct application to fabric as spot removers.
- nonresidue cleaners are formulated with volatile components only. After dissolving, mobilizing, and removing the stained material, such formulations are intended to completely evaporate leaving no residue components on the textile.
- Other cleaning compositions employ a combination of solvent and solid, absorbent particles. The solvent mobilizes the soil and the absorbent solid attracts the soil and solvent to itself. The residue of absorbent solid is intended to be easily removed from the textile by brushing or vacuuming.
- Yet another approach involves liquid detergent compositions which have been adapted as prewash spot removers. These compositions usually contain concentrated synthetic surfactants with alcohol or other solvents.
- the prewash spot remover composition When used as a prewash spot remover, the nonvolatile surfactant components remain on the textile as a residue which is removed by a conventional home laundry operation.
- the prewash spot remover composition additionally functions in the manner of a heavy-duty laundry detergent.
- Stain removing compositions are disclosed in Japanese Patent Publication Kokai No. (1974)-35681, which contain small amounts (0.5 to 10 weight percent) of silicone oil combined with cleaning solvents such as trichlorethane and petroleum hydrocarbons. Although the type of silicone oil employed is not further identified, it is taught that the silicone remains on the fabric after cleaning to provide continuing water repellency and soil resistance for the fabric. Consequently, it is apparent that this publication does not contemplate the use of completely volatile cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes.
- An aerosol type aqueous cleaning composition is disclosed in Japanese Patent Publication Kokai No. (1978)-56203, which contains nonionic surfactant, alkanolamine, glycol ether, alcohol, propellant, and 0.02 to 0.1 weight percent of linear dimethylpolysiloxane with 2 to 7 silicon atoms per molecule.
- This publication discloses only the use of very low amounts of linear dimethylpolysiloxanes and does not contemplate the use of larger, solvent-effective amounts of the cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes.
- tetraethoxysilane as a solvent for removing grease from textiles is disclosed in Russian Patent Publication 979548-A.
- tetraethoxysilane is not stable in contact with water and may hydrolyze forming alcohol and silica solids.
- Liquid cleaning compositions for removing dirt and grit from solid surfaces are disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 2,955,047.
- the compositions contain surfactants, water, water-miscible organic solvent, and an oil-in-water emulsion of dimethylpolysiloxane oil.
- the specified siloxanes are linear polymers with viscosities in the range of 200 to 350 centistokes.
- The. siloxane polymer is said to impart a high glossy polish to the treated surfaces by depositing a monomolecular film on the surface.
- U.S. Patent No. 2,993,866 teaches an aerosol glass cleaner composition containing isopropanol, fluorochlorohydrocarbon propellants, and linear dimethylpolysiloxane having a viscosity of about 200 centistokes.
- An all purpose cleaner composition containing a mixture of surfactants, isopropyl alcohol, and a silicone defoaming agent is disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,311,608.
- the silicone defoaming agent is an oil-in-water emulsion of dimethylsiloxane polymer.
- a cleaner (apparently a wiper type) impregnated with a composition containing mineral oils or alcohols with organopolysiloxanes is disclosed in Japanese Patent Publication Kokai No. (1975)-161059.
- the organopolysiloxanes are characterized by having a viscosity of not more than 30 centipoise at 20°C.
- This invention concerns a method for cleaning textiles which comprises applying to a soiled textile a liquid composition containing an effective amount to aid soil removal of a cyclic siloxane selected from the group consisting of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, and dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane and removing from the textile a combination of soil and cyclic siloxane.
- a cyclic siloxane selected from the group consisting of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, and dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane
- the novel textile cleaning compositions are applied to a soiled area of clothing, carpet, or other textile by spraying, pouring, or from a cloth or sponge applicator.
- the composition may be rubbed or brushed into the textile to facilitate loosening and dissolving the soil components.
- the soil-solvent combination is then removed from the textile by any of the well known methods such as blotting with absorbent material, absorption unto particulate material followed by vacuuming, or a conventional home laundry operation.
- cyclic siloxanes employed in the liquid cleaning and spot removing compositions of this invention are available commercially and are made by well known methods such as, for example, the hydrolysis and condensation of dimethyldichlorosilane.
- cyclic siloxanes employed according to this invention are relatively volatile materials having boiling points below about 250°C at 760 mm Hg.
- a single cyclic siloxane may be used in the liquid cleaning composition or any mixture of two or more of the cyclic siloxanes may be used.
- Specifically preferred cyclic siloxanes for use in this invention are octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, and dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane.
- useful cyclic siloxane mixtures may contain, in addition to the preferred cyclic siloxanes, minor amounts of other cyclic siloxanes including hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane or higher cyclics such as tetradecamethylcycloheptasiloxane. Generally the amount of these other cyclic siloxanes in useful cyclic siloxane mixtures will be less than about 10 percent based on the total weight of the mixture.
- the amount of cyclic siloxane used in the liquid cleaning compositions of this invention is not critical so long as the amount used is effective'to aid soil removal from textiles.
- the cleaning composition may contain, for example, from 1 to 100 percent by weight of the cyclic siloxanes. It is preferred that the cleaning composition contain from 5 to 100, or more preferably 10 to 100, percent by weight of the cyclic siloxanes.
- liquid cleaning compositions of this invention may be included in the liquid cleaning compositions of this invention such as conventional cleaning solvents, absorbent solid particulate materials, synthetic builders, water soluble organic detergent compounds, and cationic antistatic substances.
- nonresidue spot cleaning compositions may contain conventional cleaning solvents mixed with cyclic siloxanes according to the present invention.
- Any conventional cleaning solvent having a boiling point below about 250°C can be mixed with the cyclic siloxanes to prepare a liquid composition useful in the present invention.
- Useful additional cleaning solvents include alcohols such as isopropanol and butanol, petroleum hydrocarbons such as mineral spirits, and chlorinated hydrocarbons such as methylene dichloride, tetrachloroethylene, and trichloroethylene.
- Mixtures of cyclic siloxanes and conventional solvents selected from the group consisting of petroleum hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons are especially effective. Mixtures containing about 30 to 70 percent by weight of conventional cleaning solvent and 30 to 70 percent by weight of the cyclic siloxane are preferred because of their superior ability to mobilize stains.
- Cleaning compositions of the solvent/absorbent class are also useful in the method of this invention.
- Such cleaning compositions may contain in addition to the cyclic siloxane any of the absorbent materials known for such applications.
- Useful absorbent materials include mineral particulates such as silica, talc, diatomaceous earth, kaolinite; organic particulates such as starch and modified starch, nut shell flour, and ground rice hulls; and synthetic porous polymers such as the urea-formaldehyde polymer particles described in U.S. Patent No. 3,910,848, which more fully describes the polymer particles.
- the absorbent material is generally used in amounts of about 5 to 40 percent based on the weight of cleaning solvent in the composition.
- Cleaning compositions of the solvent/absorbent class may also include a cationic antistatic agent to facilitate the removal of the particulate material during brushing or vacuuming of the textile material.
- a cationic antistatic agent to facilitate the removal of the particulate material during brushing or vacuuming of the textile material.
- Useful cationic antistats include quaternary nitrogen salts that contain at least one C 10 to C 24' aliphatic hydrocarbon substituent on the nitrogen such as stearyltrimethylammonium chloride.
- Antistatic agents are typically employed in amounts of about 0.1 to 3 percent by weight based on the total weight of the cleaning composition.
- the method for cleaning textiles of this invention also includes the use of prewash spot remover compositions containing nonvolatile surfactant components in addition to cyclic siloxane solvent.
- Such prewash spot remover compositions will generally include a water soluble organic detergent material and synthetic builders in combination with the cyclic siloxane solvent.
- Detergent compounds useful in prewash spot removers are the anionic, nonionic, zwitterionic and ampholytic surfactant compounds.
- Such detergent compounds are well known to those skilled in the detergent art. Exemplary detergents are described in the well-known books entitled "Surface Active Agents" by Schwartz and Perry and “Surface Active Agents and Detergents” by Schwartz, Perry and Berch, both by Interscience Publishers, New York, N.Y.
- nonionic surfactants which are condensation products of polyethylene oxide with an organic hydrophobic compound which is usually aliphatic or alkylaromatic in nature.
- exemplary nonionic surfactants are polyethylene oxide condensates of nonyl phenol and polyethylene oxide condensates of myristyl alcohol.
- prewash spot removing compositions of this invention from about 10 to 80 percent by weight of surfactants may be used in the prewash spot removing compositions of this invention. More preferred prewash spot removing compositions contain 30 to 70 percent by weight of nonionic surfactants.
- Prewash spot removers of this invention may also contain a variety of builder compounds such as sodium tripolyphosphate, sodium carbonate, sodium silicate, the alkali metal, ammonium and substituted ammonium salts of oxydisuccinic acid, oxydiacetic acid, carboxymethyloxymalonic acid, carboxymethyloxysuccinic acid, lactoxysuccinic acid, citric acid, mellitic acid, tetrahydrofurantetracarboxylic acid, polyacrylic acid, nitrilotriacetic acid, oxidized starches and mixtures thereof.
- Builders are generally added to prewash spot removing compositions in amounts ranging from O.to about 50 percent by weight based on the weight of the . total composition.
- the liquid compositions of the present invention are especially adapted for direct application to stains and soils on fabrics and other textiles.
- the compositions can be applied to soiled textiles by any of the commonly used methods.
- the liquid compositions may be poured or sprayed onto the stains.
- the composition may be brushed or rubbed onto the stained or soiled area using absorbent items such as brushes, paper towels, cloth or sponges that contain the cleaning composition.
- the cyclic siloxane acts to dissolve and/or loosen the soil which it contacts.
- the mobilized soil is then more easily removed from the textile in combination with the cyclic siloxane.
- the cyclic siloxane/soil combination can be removed from the textile by any convenient method such as blotting the textile with a dry absorbent material.
- the textile may be blotted, for example, with sponges, paper towels, or cloth towels.
- the soil/cyclic siloxane combination may be.removed by processes such as brushing, vacuuming, or conventional home laundry operations. Brushing and vacuuming are especially useful if solid, absorbent particles are employed in the liquid cleaning composition.
- Conventional home laundry is the preferred method of removal when nonvolatile surfactants are used in combination with cyclic siloxane in the cleaning composition.
- cyclic siloxanes are sufficiently volatile that any residual cyclic siloxane on the textile, after removal of the soil, readily volatilizes to leave the treated area dry as well as clean.
- the method of the present invention can be used to remove a wide variety of soils and stains.
- the cyclic siloxane is especially effective at removing oil and grease spots or stains.
- One special advantage of the cyclic siloxanes as cleaning solvents is that the formation of a secondary stain ring is either eliminated or greatly reduced in definition.
- Another advantage is that the cyclic siloxanes are essentially nontoxic-and nonharmful in the environment.
- cyclic siloxanes can be used with a wide variety of fabrics without harming or in any way changing the appearance of the fabric.
- the method of cleaning of this invention can be used on all types of textiles including carpets and fabrics used for clothing or upholstery.
- Artificial sebum employed in the following examples was prepared from a base mixture of palmitic acid (5 g), stearic acid (2.5 g), coconut oil (7.5 g), paraffin (5 g), spermaceti (7.5 g), olive oil (10 g), squalene (2.5 g), cholesterol (2.5 g), oleic acid (5 g), and linoleic acid (2.5 g).
- a melted (120°F) 5 g portion of the base mixture was combined with oleic acid (4 g) and triethanolamine (8 g) and agitated at 120°F until homogenous. Then air filter dirt (12 g, +200 mesh) and deionized water (100 ml) were added and the mixture agitated for ten minutes. Additional deionized water (900 ml) was added and the mixture was agitated in a homogenizer for ten minutes. The mixture was stored in a 100°F oven and shaken well before using for staining.
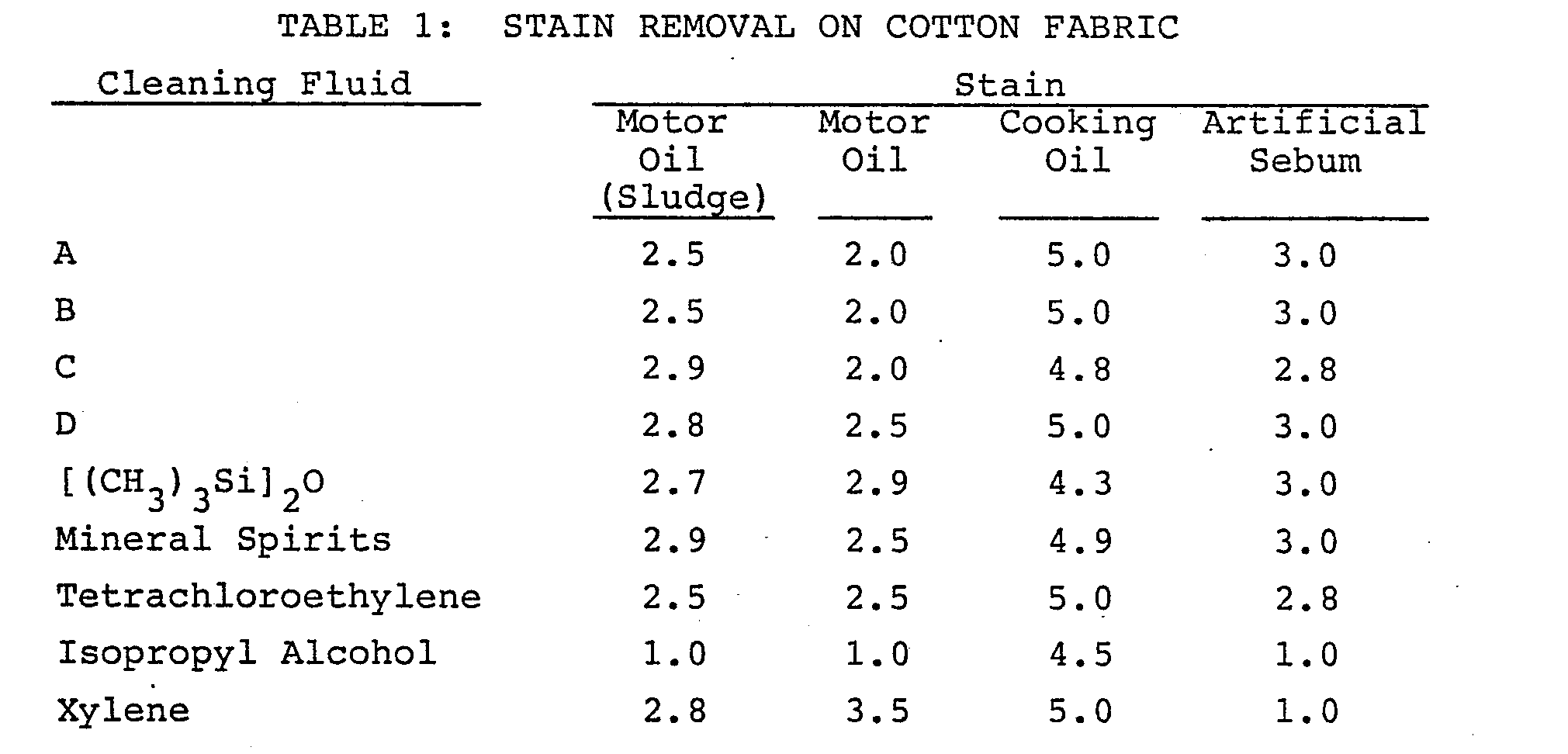
- Cotton fabric test pieces were prepared with approximately 1 inch diameter stains of used motor oil, cooking oil and artificial sebum. The stains were aged at room temperature for 24 hours. Stains were cleaned by placing the fabric pieces on several absorbent paper towels and rubbing the stained area for 20 seconds with a paper towel saturated with the cleaning fluid.
- the cyclic siloxane fluids tested were (A) octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, (B) decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, (C) a cyclic siloxane mixture of about 91 percent by weight octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane and about 8 percent by weight decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, and (D) a cyclic siloxane mixture of about 1.3 percent by weight octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, about 69.3 percent by weight decamethylcyclopentasiloxane and about 29.1 percent by weight dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane.
- hexamethyldisiloxane, mineral spirits, tetrachloroethylene, isopropyl alcohol, and xylene were also used to clean the stains.
- the ratings were made by comparison of the test pieces with a standard series of exemplary stains in a black box using a fluorescent light source. Deviations between the test pieces and the standard stains are indicated by fractional ratings.
- the used motor oil tended to form a dual stain containing a smaller sludge portion nearer the center and a larger oil portion which spread out more from the point of application.
- Example 2 The stain removal testing procedure of Example 1 was repeated using a 65/35 polyester/cotton fabric. The results of the black box visual ratings of the cleaned fabric are presented in Table 2.
- Example 3 The stain removal testing procedure of Example 1 was repeated using a 100 percent polyester fabric. The results of the black box visual ratings of the cleaned fabric are presented in Table 3.
- Example 1 The stain removal testing procedure of Example 1 was modified by heat setting the stain before cleaning. Stains were set by placing the fabric in an automatic clothes dryer at the high temperature setting for two cycles of 60 minutes each. Polyester (100%) fabric was used in these tests. Results of the black box visual ratings of cleaned fabric are presented in Table 4.
- the following experiments demonstrate the relative efficiency of cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes in spreading oil stains on fabric.
- the degree of spreading of the stain relates to the extent of mobilization of the stain by the solvent being tested. Generally, the more effectively a stain can be mobilized, the more easily and completely it can be removed from the fabric.
- Cotton fabric test pieces (8 inch x 8 inch) were placed in an embroidery hoop and approximately 1 ml of cooking oil was applied to the center of the fabric. Stains were aged at room temperature for 24 hours. The fabric was then positioned under a burette filled with the cleaning fluid. With the burette tip just above the center of the stain, a 0.5 ml portion of the cleaning fluid was dropped on the stain. The fabric was allowed to dry at room temperature and the size of the resulting stain was measured. Generally the stains were circular or slightly oval in shape. The approximate areas of the stains after the spreading process with various cleaning fluids are shown in Table 5. In the case of oval shaped stains, approximate areas were calculated as if the stain were circular using a diameter equal to the average of the length and width of the oval. The cyclic siloxane fluids tested are described in Example 1.
- Example 5 The stain spreading procedure of Example 5 was repeated using 100% polyester fabric test pieces. The approximate stain areas after spreading are shown in Table 6.
- Example 7 The stain spreading procedure of Example 5 was repeated using a 65/35 polyester/cotton fabric. Approximate stain areas after spreading are presented in Table 7.
- Cooking oil stains were prepared on 65/35 polyester/cotton fabric and the spreading procedure of Example 5 was repeated except that a 1 ml portion of a blend of cleaning materials was dropped on the stain.
- Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane was blended in various proportions by weight with either mineral spirits or tetrachloroethylene to prepare the cleaning materials.
- the approximate stain areas after spreading are shown in Table 8.
- Example 8 The stain spreading procedure of Example 8 was repeated using decamethylcyclopentasiloxane blended in various proportions by weight with either mineral spirits or tetrachloroethylene. The approximate stain areas after spreading are presented in Table 9.
- Polyester fabric test pieces were prepared with approximately 1 inch diameter stains of used motor oil, cooking oil, and artificial sebum. Stains were heat set by placing the fabric in an automatic clothes dryer at the high temperature setting for two cycles of 60 minutes each. Each stain was treated with 2 ml of the test fluid as described in Example 1. Each fluid was left on the stain for one to two minutes. The test fabric pieces were then washed in a household automatic washer on the normal setting using the recommended level of a powdered nonphosphate detergent. The fabric pieces were dried in an automatic clothes dryer on the permanent press setting.
- the used motor oil tended to form a dual stain containing a smaller sludge portion nearer the center and a larger oil portion which spread out more from the point of application. Some differences in the cleaning of the two portions of these stains were observed and consequently the cleaning of each portion was separately rated. The results of the visual rating are presented in Table 10.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Detergent Compositions (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- The present invention relates to a method for removing soil from textiles using cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes. In particular, this invention relates to the use of cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes for removal of oily/greasy stains from textiles.
- Textile products such as fabrics, carpets and upholstery often develop prominent stain spots from inadvertent contact with foodstuff and other materials containing grease and oils. Various organic solvents such as alcohols, petroleum hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons have been used in cleaning compositions adapted for direct application to fabric as spot removers.
- Several approaches to formulating spot cleaning compositions are known. For instance, nonresidue cleaners are formulated with volatile components only. After dissolving, mobilizing, and removing the stained material, such formulations are intended to completely evaporate leaving no residue components on the textile. Other cleaning compositions employ a combination of solvent and solid, absorbent particles. The solvent mobilizes the soil and the absorbent solid attracts the soil and solvent to itself. The residue of absorbent solid is intended to be easily removed from the textile by brushing or vacuuming. Yet another approach involves liquid detergent compositions which have been adapted as prewash spot removers. These compositions usually contain concentrated synthetic surfactants with alcohol or other solvents. When used as a prewash spot remover, the nonvolatile surfactant components remain on the textile as a residue which is removed by a conventional home laundry operation. In the aqueous wash, the prewash spot remover composition additionally functions in the manner of a heavy-duty laundry detergent.
- While known spot cleaning compositions effectively remove some stains, other types of stains may be unaffected or only incompletely removed by the compositions. In other cases, the cleaning composition itself may damage or leave a residue on the textile in such a way that a visible ring occurs around the treated area. It is an object of the present invention to reduce the problems associated with the prior art cleaning compositions by providing a new method of cleaning stains using volatile silicone fluids that effectively mobilize oil and grease stains, are nondamaging to a wide range of textiles both synthetic and natural, and leave no residue or visible ring on treated textiles.
- It is known from U.S. Patent No. 4,324,595, to remove tacky adhesives from substrates by using octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane fluid to detackify the adhered adhesive. The process is taught to be particularly useful for removing tacky adhesives from human skin, but it is also indicated that the process is applicable to removing tacky adhesives from a wide range of substrates including textiles. However, this patent teaches the removal of only tacky adhesives, it does not suggest removing oil and grease stains with cyclic dimethylsiloxanes.
- Stain removing compositions are disclosed in Japanese Patent Publication Kokai No. (1974)-35681, which contain small amounts (0.5 to 10 weight percent) of silicone oil combined with cleaning solvents such as trichlorethane and petroleum hydrocarbons. Although the type of silicone oil employed is not further identified, it is taught that the silicone remains on the fabric after cleaning to provide continuing water repellency and soil resistance for the fabric. Consequently, it is apparent that this publication does not contemplate the use of completely volatile cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes.
- An aerosol type aqueous cleaning composition is disclosed in Japanese Patent Publication Kokai No. (1978)-56203, which contains nonionic surfactant, alkanolamine, glycol ether, alcohol, propellant, and 0.02 to 0.1 weight percent of linear dimethylpolysiloxane with 2 to 7 silicon atoms per molecule. This publication discloses only the use of very low amounts of linear dimethylpolysiloxanes and does not contemplate the use of larger, solvent-effective amounts of the cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes.
- The use of tetraethoxysilane as a solvent for removing grease from textiles is disclosed in Russian Patent Publication 979548-A. However, tetraethoxysilane is not stable in contact with water and may hydrolyze forming alcohol and silica solids.
- A process for dry cleaning and waterproofing of fabrics is disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 3,123,494 which process employs a silicone composition diluted in typical dry cleaning solvents. The silicone compositions recommended are mixtures of linear dimethylpolysiloxane fluids and crosslinked methylsiloxane resins. Excess liquid cleaning mixture is removed from the textiles by centrifuging but retained silicone provides a continuing waterproofing effect on the textile. Again, it is apparent that this publication does not contemplate the use of completely volatile cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes as a cleaning solvent.
- Liquid cleaning compositions for removing dirt and grit from solid surfaces are disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 2,955,047. The compositions contain surfactants, water, water-miscible organic solvent, and an oil-in-water emulsion of dimethylpolysiloxane oil. The specified siloxanes are linear polymers with viscosities in the range of 200 to 350 centistokes. The. siloxane polymer is said to impart a high glossy polish to the treated surfaces by depositing a monomolecular film on the surface. Somewhat similarly, U.S. Patent No. 2,993,866 teaches an aerosol glass cleaner composition containing isopropanol, fluorochlorohydrocarbon propellants, and linear dimethylpolysiloxane having a viscosity of about 200 centistokes.
- An all purpose cleaner composition containing a mixture of surfactants, isopropyl alcohol, and a silicone defoaming agent is disclosed in U.S. Patent No. 4,311,608. The silicone defoaming agent is an oil-in-water emulsion of dimethylsiloxane polymer.
- A cleaner (apparently a wiper type) impregnated with a composition containing mineral oils or alcohols with organopolysiloxanes is disclosed in Japanese Patent Publication Kokai No. (1975)-161059. The organopolysiloxanes are characterized by having a viscosity of not more than 30 centipoise at 20°C.
- This invention concerns a method for cleaning textiles which comprises applying to a soiled textile a liquid composition containing an effective amount to aid soil removal of a cyclic siloxane selected from the group consisting of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, and dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane and removing from the textile a combination of soil and cyclic siloxane.
- In use, the novel textile cleaning compositions are applied to a soiled area of clothing, carpet, or other textile by spraying, pouring, or from a cloth or sponge applicator. The composition may be rubbed or brushed into the textile to facilitate loosening and dissolving the soil components. The soil-solvent combination is then removed from the textile by any of the well known methods such as blotting with absorbent material, absorption unto particulate material followed by vacuuming, or a conventional home laundry operation.
- The cyclic siloxanes employed in the liquid cleaning and spot removing compositions of this invention are available commercially and are made by well known methods such as, for example, the hydrolysis and condensation of dimethyldichlorosilane.
- Compared with the linear polydimethylsiloxanes the cyclic siloxanes employed according to this invention are relatively volatile materials having boiling points below about 250°C at 760 mm Hg. A single cyclic siloxane may be used in the liquid cleaning composition or any mixture of two or more of the cyclic siloxanes may be used. Specifically preferred cyclic siloxanes for use in this invention are octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, and dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane. It should be understood that useful cyclic siloxane mixtures may contain, in addition to the preferred cyclic siloxanes, minor amounts of other cyclic siloxanes including hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane or higher cyclics such as tetradecamethylcycloheptasiloxane. Generally the amount of these other cyclic siloxanes in useful cyclic siloxane mixtures will be less than about 10 percent based on the total weight of the mixture.
- The amount of cyclic siloxane used in the liquid cleaning compositions of this invention is not critical so long as the amount used is effective'to aid soil removal from textiles. In general, the cleaning composition may contain, for example, from 1 to 100 percent by weight of the cyclic siloxanes. It is preferred that the cleaning composition contain from 5 to 100, or more preferably 10 to 100, percent by weight of the cyclic siloxanes.
- Other adjuvants may be included in the liquid cleaning compositions of this invention such as conventional cleaning solvents, absorbent solid particulate materials, synthetic builders, water soluble organic detergent compounds, and cationic antistatic substances.
- For example, nonresidue spot cleaning compositions may contain conventional cleaning solvents mixed with cyclic siloxanes according to the present invention. Any conventional cleaning solvent having a boiling point below about 250°C can be mixed with the cyclic siloxanes to prepare a liquid composition useful in the present invention. Useful additional cleaning solvents include alcohols such as isopropanol and butanol, petroleum hydrocarbons such as mineral spirits, and chlorinated hydrocarbons such as methylene dichloride, tetrachloroethylene, and trichloroethylene. Surprisingly, it has been found that a mixture of cyclic siloxane and conventional cleaning solvent is more effective at mobilizing stains than is either the cyclic siloxane or the conventional solvent alone.. Mixtures of cyclic siloxanes and conventional solvents selected from the group consisting of petroleum hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons are especially effective. Mixtures containing about 30 to 70 percent by weight of conventional cleaning solvent and 30 to 70 percent by weight of the cyclic siloxane are preferred because of their superior ability to mobilize stains.
- Cleaning compositions of the solvent/absorbent class are also useful in the method of this invention. Such cleaning compositions may contain in addition to the cyclic siloxane any of the absorbent materials known for such applications. Useful absorbent materials include mineral particulates such as silica, talc, diatomaceous earth, kaolinite; organic particulates such as starch and modified starch, nut shell flour, and ground rice hulls; and synthetic porous polymers such as the urea-formaldehyde polymer particles described in U.S. Patent No. 3,910,848, which more fully describes the polymer particles. The absorbent material is generally used in amounts of about 5 to 40 percent based on the weight of cleaning solvent in the composition.
- Cleaning compositions of the solvent/absorbent class may also include a cationic antistatic agent to facilitate the removal of the particulate material during brushing or vacuuming of the textile material. Useful cationic antistats include quaternary nitrogen salts that contain at least one C10 to C24' aliphatic hydrocarbon substituent on the nitrogen such as stearyltrimethylammonium chloride. Antistatic agents are typically employed in amounts of about 0.1 to 3 percent by weight based on the total weight of the cleaning composition.
- The method for cleaning textiles of this invention also includes the use of prewash spot remover compositions containing nonvolatile surfactant components in addition to cyclic siloxane solvent. Such prewash spot remover compositions will generally include a water soluble organic detergent material and synthetic builders in combination with the cyclic siloxane solvent. Detergent compounds useful in prewash spot removers are the anionic, nonionic, zwitterionic and ampholytic surfactant compounds. Such detergent compounds are well known to those skilled in the detergent art. Exemplary detergents are described in the well-known books entitled "Surface Active Agents" by Schwartz and Perry and "Surface Active Agents and Detergents" by Schwartz, Perry and Berch, both by Interscience Publishers, New York, N.Y.
- Especially preferred detergents are the nonionic surfactants which are condensation products of polyethylene oxide with an organic hydrophobic compound which is usually aliphatic or alkylaromatic in nature. Exemplary nonionic surfactants are polyethylene oxide condensates of nonyl phenol and polyethylene oxide condensates of myristyl alcohol.
- Generally, from about 10 to 80 percent by weight of surfactants may be used in the prewash spot removing compositions of this invention. More preferred prewash spot removing compositions contain 30 to 70 percent by weight of nonionic surfactants.
- Prewash spot removers of this invention may also contain a variety of builder compounds such as sodium tripolyphosphate, sodium carbonate, sodium silicate, the alkali metal, ammonium and substituted ammonium salts of oxydisuccinic acid, oxydiacetic acid, carboxymethyloxymalonic acid, carboxymethyloxysuccinic acid, lactoxysuccinic acid, citric acid, mellitic acid, tetrahydrofurantetracarboxylic acid, polyacrylic acid, nitrilotriacetic acid, oxidized starches and mixtures thereof. Builders are generally added to prewash spot removing compositions in amounts ranging from O.to about 50 percent by weight based on the weight of the . total composition.
- The liquid compositions of the present invention are especially adapted for direct application to stains and soils on fabrics and other textiles. The compositions can be applied to soiled textiles by any of the commonly used methods. The liquid compositions may be poured or sprayed onto the stains. Alternatively the composition may be brushed or rubbed onto the stained or soiled area using absorbent items such as brushes, paper towels, cloth or sponges that contain the cleaning composition.
- Once the cleaning composition has been applied to the soiled textile, the cyclic siloxane acts to dissolve and/or loosen the soil which it contacts. The mobilized soil is then more easily removed from the textile in combination with the cyclic siloxane. The cyclic siloxane/soil combination can be removed from the textile by any convenient method such as blotting the textile with a dry absorbent material. The textile may be blotted, for example, with sponges, paper towels, or cloth towels. Alternatively, the soil/cyclic siloxane combination may be.removed by processes such as brushing, vacuuming, or conventional home laundry operations. Brushing and vacuuming are especially useful if solid, absorbent particles are employed in the liquid cleaning composition. Conventional home laundry is the preferred method of removal when nonvolatile surfactants are used in combination with cyclic siloxane in the cleaning composition.
- The cyclic siloxanes are sufficiently volatile that any residual cyclic siloxane on the textile, after removal of the soil, readily volatilizes to leave the treated area dry as well as clean.
- The method of the present invention can be used to remove a wide variety of soils and stains. The cyclic siloxane is especially effective at removing oil and grease spots or stains. One special advantage of the cyclic siloxanes as cleaning solvents is that the formation of a secondary stain ring is either eliminated or greatly reduced in definition. Another advantage is that the cyclic siloxanes are essentially nontoxic-and nonharmful in the environment.
- Furthermore, the cyclic siloxanes can be used with a wide variety of fabrics without harming or in any way changing the appearance of the fabric. The method of cleaning of this invention can be used on all types of textiles including carpets and fabrics used for clothing or upholstery.
- The following examples are presented to illustrate the invention, but the examples in no way limit the scope of the invention as more fully set out in the claims.
- Artificial sebum employed in the following examples was prepared from a base mixture of palmitic acid (5 g), stearic acid (2.5 g), coconut oil (7.5 g), paraffin (5 g), spermaceti (7.5 g), olive oil (10 g), squalene (2.5 g), cholesterol (2.5 g), oleic acid (5 g), and linoleic acid (2.5 g). A melted (120°F) 5 g portion of the base mixture was combined with oleic acid (4 g) and triethanolamine (8 g) and agitated at 120°F until homogenous. Then air filter dirt (12 g, +200 mesh) and deionized water (100 ml) were added and the mixture agitated for ten minutes. Additional deionized water (900 ml) was added and the mixture was agitated in a homogenizer for ten minutes. The mixture was stored in a 100°F oven and shaken well before using for staining.
- The following experiments demonstrate the stain removal ability of cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes on 100 percent cotton fabric.
- Cotton fabric test pieces were prepared with approximately 1 inch diameter stains of used motor oil, cooking oil and artificial sebum. The stains were aged at room temperature for 24 hours. Stains were cleaned by placing the fabric pieces on several absorbent paper towels and rubbing the stained area for 20 seconds with a paper towel saturated with the cleaning fluid.
- The cyclic siloxane fluids tested were (A) octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, (B) decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, (C) a cyclic siloxane mixture of about 91 percent by weight octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane and about 8 percent by weight decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, and (D) a cyclic siloxane mixture of about 1.3 percent by weight octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, about 69.3 percent by weight decamethylcyclopentasiloxane and about 29.1 percent by weight dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane. For comparison, hexamethyldisiloxane, mineral spirits, tetrachloroethylene, isopropyl alcohol, and xylene were also used to clean the stains.
- After drying, the cleaned fabric pieces were rated visually for the degree of stain removal according to the following scale:
- 5 = Complete removal
- 4 = Slight remaining stain
- 3 = Moderate stain remaining
- 2 = Slight removal of stain
- 1 = No change in stain
- The ratings were made by comparison of the test pieces with a standard series of exemplary stains in a black box using a fluorescent light source. Deviations between the test pieces and the standard stains are indicated by fractional ratings.
- The used motor oil tended to form a dual stain containing a smaller sludge portion nearer the center and a larger oil portion which spread out more from the point of application. Some differences in the cleaning of the two portions of these stains were observed and consequently the cleaning of each portion was separately rated. The results of the visual rating are presented in Table 1.
-
-
- The stain removal testing procedure of Example 1 was modified by heat setting the stain before cleaning. Stains were set by placing the fabric in an automatic clothes dryer at the high temperature setting for two cycles of 60 minutes each. Polyester (100%) fabric was used in these tests. Results of the black box visual ratings of cleaned fabric are presented in Table 4.
- The following experiments demonstrate the relative efficiency of cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes in spreading oil stains on fabric. The degree of spreading of the stain relates to the extent of mobilization of the stain by the solvent being tested. Generally, the more effectively a stain can be mobilized, the more easily and completely it can be removed from the fabric.
- Cotton fabric test pieces (8 inch x 8 inch) were placed in an embroidery hoop and approximately 1 ml of cooking oil was applied to the center of the fabric. Stains were aged at room temperature for 24 hours. The fabric was then positioned under a burette filled with the cleaning fluid. With the burette tip just above the center of the stain, a 0.5 ml portion of the cleaning fluid was dropped on the stain. The fabric was allowed to dry at room temperature and the size of the resulting stain was measured. Generally the stains were circular or slightly oval in shape. The approximate areas of the stains after the spreading process with various cleaning fluids are shown in Table 5. In the case of oval shaped stains, approximate areas were calculated as if the stain were circular using a diameter equal to the average of the length and width of the oval. The cyclic siloxane fluids tested are described in Example 1.
-
-
- The following experiments demonstrate the stain spreading efficiency of blends of cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes and conventional cleaning fluids such as mineral spirits and tetrachloroethylene.
- Cooking oil stains were prepared on 65/35 polyester/cotton fabric and the spreading procedure of Example 5 was repeated except that a 1 ml portion of a blend of cleaning materials was dropped on the stain. Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane was blended in various proportions by weight with either mineral spirits or tetrachloroethylene to prepare the cleaning materials. The approximate stain areas after spreading are shown in Table 8.
-
- The following tests demonstrate the use of cyclic dimethylpolysiloxanes as a solvent component in prewash spotting formulations used in home laundering.
- Polyester fabric test pieces were prepared with approximately 1 inch diameter stains of used motor oil, cooking oil, and artificial sebum. Stains were heat set by placing the fabric in an automatic clothes dryer at the high temperature setting for two cycles of 60 minutes each. Each stain was treated with 2 ml of the test fluid as described in Example 1. Each fluid was left on the stain for one to two minutes. The test fabric pieces were then washed in a household automatic washer on the normal setting using the recommended level of a powdered nonphosphate detergent. The fabric pieces were dried in an automatic clothes dryer on the permanent press setting.
- The cleaned fabric pieces were rated visually for the degree of stain removal according to the following scale:
- 5 = Complete removal
- 4 = Slight remaining stain
- 3 = Moderate stain remaining
- 2 = Slight removal of stain
- 1 = No change in stain
- The used motor oil tended to form a dual stain containing a smaller sludge portion nearer the center and a larger oil portion which spread out more from the point of application. Some differences in the cleaning of the two portions of these stains were observed and consequently the cleaning of each portion was separately rated. The results of the visual rating are presented in Table 10.
The ratings were made by comparison of the test pieces with a standard series of exemplary stains in a black box using a fluorescent light source.
Claims (8)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US67019584A | 1984-11-13 | 1984-11-13 | |
| US670195 | 1984-11-13 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0182583A2 true EP0182583A2 (en) | 1986-05-28 |
| EP0182583A3 EP0182583A3 (en) | 1988-04-06 |
| EP0182583B1 EP0182583B1 (en) | 1991-07-03 |
Family
ID=24689398
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19850308214 Expired EP0182583B1 (en) | 1984-11-13 | 1985-11-12 | Method for cleaning textiles with cyclic siloxanes |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0182583B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPS61119765A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU585906B2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA1239326A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE3583377D1 (en) |
Cited By (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2238793A (en) * | 1989-12-09 | 1991-06-12 | Kreussler Chem Fab | Cleaning process |
| GB2240728A (en) * | 1990-02-07 | 1991-08-14 | Ow Corning S A | Method of bonding silicone elastomer to a substrate |
| EP0458969A1 (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1991-12-04 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Detergent composition |
| US5468417A (en) * | 1994-01-07 | 1995-11-21 | Dow Corning Corporation | Silicone containing VOC complaint paint remover |
| US5503681A (en) * | 1990-03-16 | 1996-04-02 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Method of cleaning an object |
| US5593507A (en) * | 1990-08-22 | 1997-01-14 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Cleaning method and cleaning apparatus |
| WO2001094685A1 (en) * | 2000-06-05 | 2001-12-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Bleaching in conjunction with a lipophilic fluid cleaning regimen |
| WO2001094678A1 (en) * | 2000-06-05 | 2001-12-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Domestic fabric article refreshment in integrated cleaning and treatment processes |
| WO2001094681A1 (en) * | 2000-06-05 | 2001-12-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Home laundry method |
| WO2003006733A1 (en) * | 2001-07-10 | 2003-01-23 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Compositions and methods for removal of incidental soils from fabric articles |
| WO2003023125A1 (en) * | 2001-09-10 | 2003-03-20 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Silicone polymers for lipophilic fluid systems |
| US6670317B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2003-12-30 | Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric care compositions and systems for delivering clean, fresh scent in a lipophilic fluid treatment process |
| US6673764B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2004-01-06 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Visual properties for a wash process using a lipophilic fluid based composition containing a colorant |
| US6691536B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2004-02-17 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Washing apparatus |
| US6840069B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2005-01-11 | Procter & Gamble Company | Systems for controlling a drying cycle in a drying apparatus |
| US6855173B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2005-02-15 | Procter & Gamble Company | Use of absorbent materials to separate water from lipophilic fluid |
| US6939837B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2005-09-06 | Procter & Gamble Company | Non-immersive method for treating or cleaning fabrics using a siloxane lipophilic fluid |
| US7018423B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2006-03-28 | Procter & Gamble Company | Method for the use of aqueous vapor and lipophilic fluid during fabric cleaning |
| AU2005200835B2 (en) * | 2000-06-05 | 2006-03-30 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Domestic fabric article refreshment in integrated cleaning and treatment processes |
| US7125831B2 (en) | 2001-05-30 | 2006-10-24 | Nof Corporation | Detergent composition for dry cleaning comprising a cyclic polysiloxane and a polyether modified silicone |
| US7202202B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2007-04-10 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Consumable detergent composition for use in a lipophilic fluid |
| US7318843B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2008-01-15 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric care composition and method for using same |
| US7323014B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2008-01-29 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Down the drain cleaning system |
| US7462589B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2008-12-09 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Delivery system for uniform deposition of fabric care actives in a non-aqueous fabric treatment system |
| US7534304B2 (en) * | 1997-04-29 | 2009-05-19 | Whirlpool Corporation | Non-aqueous washing machine and methods |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0576687B1 (en) * | 1992-01-21 | 2001-08-29 | Olympus Optical Co., Ltd. | Cleaning and drying solvent |
| US6045588A (en) | 1997-04-29 | 2000-04-04 | Whirlpool Corporation | Non-aqueous washing apparatus and method |
| US6059845A (en) * | 1997-08-22 | 2000-05-09 | Greenearth Cleaning, Llc | Dry cleaning apparatus and method capable of utilizing a siloxane composition as a solvent |
| US6310029B1 (en) * | 1999-04-09 | 2001-10-30 | General Electric Company | Cleaning processes and compositions |
| WO2001044256A1 (en) * | 1999-12-17 | 2001-06-21 | General Electric Company | Process for stabilization of siloxanes by contacting them with water |
| US6706076B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2004-03-16 | Procter & Gamble Company | Process for separating lipophilic fluid containing emulsions with electric coalescence |
| US6930079B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2005-08-16 | Procter & Gamble Company | Process for treating a lipophilic fluid |
| US6706677B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2004-03-16 | Procter & Gamble Company | Bleaching in conjunction with a lipophilic fluid cleaning regimen |
| US6564591B2 (en) | 2000-07-21 | 2003-05-20 | Procter & Gamble Company | Methods and apparatus for particulate removal from fabrics |
| JP2004331849A (en) * | 2003-05-08 | 2004-11-25 | Mihama Kk | Detergent composition and washing method for article |
| US7345016B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2008-03-18 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Photo bleach lipophilic fluid cleaning compositions |
| US7365043B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2008-04-29 | The Procter & Gamble Co. | Lipophilic fluid cleaning compositions capable of delivering scent |
| US7695524B2 (en) | 2003-10-31 | 2010-04-13 | Whirlpool Corporation | Non-aqueous washing machine and methods |
| US7739891B2 (en) | 2003-10-31 | 2010-06-22 | Whirlpool Corporation | Fabric laundering apparatus adapted for using a select rinse fluid |
| EP1740757A1 (en) | 2004-04-29 | 2007-01-10 | Unilever N.V. | Dry cleaning method |
| US7966684B2 (en) | 2005-05-23 | 2011-06-28 | Whirlpool Corporation | Methods and apparatus to accelerate the drying of aqueous working fluids |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2074184A (en) * | 1980-04-19 | 1981-10-28 | Dow Corning Ltd | Compositions for Treating Hair and Other Fibrous Materials |
| US4324595A (en) * | 1979-08-31 | 1982-04-13 | Dow Corning Corporation | Method for removing tacky adhesives and articles adhered therewith |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3114969C2 (en) * | 1980-04-19 | 1986-04-03 | Dow Corning Ltd., London | Liquid detergent composition |
-
1985
- 1985-10-23 CA CA000493616A patent/CA1239326A/en not_active Expired
- 1985-11-12 JP JP25360685A patent/JPS61119765A/en active Granted
- 1985-11-12 EP EP19850308214 patent/EP0182583B1/en not_active Expired
- 1985-11-12 AU AU49817/85A patent/AU585906B2/en not_active Ceased
- 1985-11-12 DE DE8585308214T patent/DE3583377D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4324595A (en) * | 1979-08-31 | 1982-04-13 | Dow Corning Corporation | Method for removing tacky adhesives and articles adhered therewith |
| GB2074184A (en) * | 1980-04-19 | 1981-10-28 | Dow Corning Ltd | Compositions for Treating Hair and Other Fibrous Materials |
Cited By (54)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0673996B1 (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 2003-04-16 | Toshiba Silicone Company Limited | Cleaning compositions |
| US5443747A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1995-08-22 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Cleaning compositions |
| US5741365A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1998-04-21 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Continuous method for cleaning industrial parts using a polyorganosiloxane |
| EP0458969A1 (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1991-12-04 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Detergent composition |
| US6136766A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 2000-10-24 | Toshiba Silicone Co., Ltd. | Cleaning compositions |
| US5728228A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1998-03-17 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Method for removing residual liquid from parts using a polyorganosiloxane |
| US5716456A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1998-02-10 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Method for cleaning an object with an agent including water and a polyorganosiloxane |
| US5741367A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1998-04-21 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Method for drying parts using a polyorganosiloxane |
| EP0458969B1 (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1997-07-09 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Non-aqueous cleaning composition comprising a polyorganosiloxane |
| US5985810A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1999-11-16 | Toshiba Silicone Co., Ltd. | Cleaning compositions |
| US5977040A (en) * | 1989-10-26 | 1999-11-02 | Toshiba Silicone Co., Ltd. | Cleaning compositions |
| GB2238793B (en) * | 1989-12-09 | 1993-03-31 | Kreussler Chem Fab | Cleaning process |
| GB2238793A (en) * | 1989-12-09 | 1991-06-12 | Kreussler Chem Fab | Cleaning process |
| DE3940804A1 (en) * | 1989-12-09 | 1991-06-13 | Kreussler Chem Fab | USE OF CYCLOSILOXANES, ISOPARAFFINS AND / OR TEST FUELS |
| GB2240728B (en) * | 1990-02-07 | 1993-12-01 | Ow Corning S A | Method of bonding silicone elastomer to a substrate |
| GB2240728A (en) * | 1990-02-07 | 1991-08-14 | Ow Corning S A | Method of bonding silicone elastomer to a substrate |
| US5772781A (en) * | 1990-03-16 | 1998-06-30 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Method for cleaning an object using an agent that includes a polyorganosiloxane or isoparaffin |
| US5769962A (en) * | 1990-03-16 | 1998-06-23 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Cleaning method |
| US5833761A (en) * | 1990-03-16 | 1998-11-10 | Toshiba Silicone Co., Ltd. | Method of cleaning an object including a cleaning step and a vapor drying step |
| US5888312A (en) * | 1990-03-16 | 1999-03-30 | Toshiba Silicone Co., Ltd. | Cleaning method |
| US5538024A (en) * | 1990-03-16 | 1996-07-23 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Cleaning method and cleaning apparatus |
| US5503681A (en) * | 1990-03-16 | 1996-04-02 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Method of cleaning an object |
| US5690750A (en) * | 1990-08-20 | 1997-11-25 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Cleaning method and cleaning apparatus |
| US5823210A (en) * | 1990-08-22 | 1998-10-20 | Toshiba Silicone Co., Ltd. | Cleaning method and cleaning apparatus |
| US5593507A (en) * | 1990-08-22 | 1997-01-14 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Cleaning method and cleaning apparatus |
| US5468417A (en) * | 1994-01-07 | 1995-11-21 | Dow Corning Corporation | Silicone containing VOC complaint paint remover |
| US7534304B2 (en) * | 1997-04-29 | 2009-05-19 | Whirlpool Corporation | Non-aqueous washing machine and methods |
| WO2001094678A1 (en) * | 2000-06-05 | 2001-12-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Domestic fabric article refreshment in integrated cleaning and treatment processes |
| US6840069B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2005-01-11 | Procter & Gamble Company | Systems for controlling a drying cycle in a drying apparatus |
| US7704937B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2010-04-27 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Composition comprising an organosilicone/diol lipophilic fluid for treating or cleaning fabrics |
| WO2001094681A1 (en) * | 2000-06-05 | 2001-12-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Home laundry method |
| US6670317B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2003-12-30 | Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric care compositions and systems for delivering clean, fresh scent in a lipophilic fluid treatment process |
| US6673764B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2004-01-06 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Visual properties for a wash process using a lipophilic fluid based composition containing a colorant |
| US6691536B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2004-02-17 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Washing apparatus |
| US6828292B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2004-12-07 | Procter & Gamble Company | Domestic fabric article refreshment in integrated cleaning and treatment processes |
| US6840963B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2005-01-11 | Procter & Gamble | Home laundry method |
| US7063750B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2006-06-20 | The Procter & Gamble Co. | Domestic fabric article refreshment in integrated cleaning and treatment processes |
| US6855173B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2005-02-15 | Procter & Gamble Company | Use of absorbent materials to separate water from lipophilic fluid |
| US6939837B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2005-09-06 | Procter & Gamble Company | Non-immersive method for treating or cleaning fabrics using a siloxane lipophilic fluid |
| WO2001094685A1 (en) * | 2000-06-05 | 2001-12-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Bleaching in conjunction with a lipophilic fluid cleaning regimen |
| US7323014B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2008-01-29 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Down the drain cleaning system |
| US7018423B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2006-03-28 | Procter & Gamble Company | Method for the use of aqueous vapor and lipophilic fluid during fabric cleaning |
| AU2005200835B2 (en) * | 2000-06-05 | 2006-03-30 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Domestic fabric article refreshment in integrated cleaning and treatment processes |
| US7033985B2 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2006-04-25 | Procter & Gamble Company | Domestic fabric article refreshment in integrated cleaning and treatment processes |
| US7125831B2 (en) | 2001-05-30 | 2006-10-24 | Nof Corporation | Detergent composition for dry cleaning comprising a cyclic polysiloxane and a polyether modified silicone |
| US6987086B2 (en) | 2001-07-10 | 2006-01-17 | Procter & Gamble Company | Compositions and methods for removal of incidental soils from fabric articles |
| WO2003006733A1 (en) * | 2001-07-10 | 2003-01-23 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Compositions and methods for removal of incidental soils from fabric articles |
| US7244699B2 (en) | 2001-09-10 | 2007-07-17 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Silicone polymers for lipophilic fluid systems |
| US6972279B2 (en) | 2001-09-10 | 2005-12-06 | Procter & Gamble Company | Silicone polymers for lipophilic fluid systems |
| WO2003023125A1 (en) * | 2001-09-10 | 2003-03-20 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Silicone polymers for lipophilic fluid systems |
| US7202202B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2007-04-10 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Consumable detergent composition for use in a lipophilic fluid |
| US7318843B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2008-01-15 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Fabric care composition and method for using same |
| US7462589B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2008-12-09 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Delivery system for uniform deposition of fabric care actives in a non-aqueous fabric treatment system |
| US8148315B2 (en) | 2003-06-27 | 2012-04-03 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method for uniform deposition of fabric care actives in a non-aqueous fabric treatment system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0182583A3 (en) | 1988-04-06 |
| AU585906B2 (en) | 1989-06-29 |
| JPS61119765A (en) | 1986-06-06 |
| EP0182583B1 (en) | 1991-07-03 |
| JPS6350463B2 (en) | 1988-10-07 |
| AU4981785A (en) | 1986-05-22 |
| DE3583377D1 (en) | 1991-08-08 |
| CA1239326A (en) | 1988-07-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0182583B1 (en) | Method for cleaning textiles with cyclic siloxanes | |
| US4685930A (en) | Method for cleaning textiles with cyclic siloxanes | |
| CA2295739C (en) | Moist fabric wipe and method of using it | |
| US3748268A (en) | Spot and stain removing composition | |
| JP3001980B2 (en) | Aqueous composition for rinsing shower equipment and method for keeping shower equipment clean | |
| JPH10501841A (en) | Soft surface cleaning composition containing hydrogen peroxide | |
| JPH057015B2 (en) | ||
| JP2000313900A (en) | Cleaning composition and method | |
| JP2002506924A (en) | Liquid multiphase detergent | |
| JPS6368700A (en) | Washing composition for removing oil contaminant | |
| JPH10501845A (en) | Carpet cleaning and recovery composition | |
| JP4294472B2 (en) | Compositions and methods for removing accidental soils from fabric articles | |
| JPH0631404B2 (en) | Cleaning and / or conditioning agents for glass ceramic surfaces | |
| JP3556806B2 (en) | Detergent composition | |
| JPH04504278A (en) | cleaning composition | |
| US4637892A (en) | Cleaning solution | |
| US3900407A (en) | Composition for cleaning and glazing furs | |
| JP2003105394A (en) | Gel cleaner | |
| US2327495A (en) | Process of removing wax from | |
| CA2460760A1 (en) | Non-toxic cleaning composition | |
| JP3636613B2 (en) | Dry cleaning cleaning method and cleaning composition used in this method | |
| JP3611703B2 (en) | Cleaning composition for dry cleaning | |
| JP2001247899A (en) | Liquid detergent composition | |
| JP2010126561A (en) | Detergent composition for dry cleaning and dry cleaning method | |
| JP6646998B2 (en) | Cleaning solution for dry cleaning, cleaning composition for dry cleaning, and dry cleaning cleaning method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19880907 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19890704 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3583377 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19910808 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19970904 Year of fee payment: 13 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19970904 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19970909 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19981112 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19981112 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990730 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990901 |