EP0165818A2 - Film drive unit - Google Patents
Film drive unit Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0165818A2 EP0165818A2 EP85304419A EP85304419A EP0165818A2 EP 0165818 A2 EP0165818 A2 EP 0165818A2 EP 85304419 A EP85304419 A EP 85304419A EP 85304419 A EP85304419 A EP 85304419A EP 0165818 A2 EP0165818 A2 EP 0165818A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- bag material
- film
- drive unit
- belt
- speed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 63
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 17
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 25
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000002985 plastic film Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920006255 plastic film Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005022 packaging material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B9/00—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, e.g. liquids or semiliquids, in flat, folded, or tubular webs of flexible sheet material; Subdividing filled flexible tubes to form packages
- B65B9/10—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, in preformed tubular webs, or in webs formed into tubes around filling nozzles, e.g. extruded tubular webs
- B65B9/20—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, in preformed tubular webs, or in webs formed into tubes around filling nozzles, e.g. extruded tubular webs the webs being formed into tubes in situ around the filling nozzles
- B65B9/2014—Tube advancing means
- B65B9/2021—Tube advancing means combined with longitudinal welding devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B9/00—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, e.g. liquids or semiliquids, in flat, folded, or tubular webs of flexible sheet material; Subdividing filled flexible tubes to form packages
- B65B9/10—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, in preformed tubular webs, or in webs formed into tubes around filling nozzles, e.g. extruded tubular webs
- B65B9/20—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, in preformed tubular webs, or in webs formed into tubes around filling nozzles, e.g. extruded tubular webs the webs being formed into tubes in situ around the filling nozzles
- B65B9/207—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, in preformed tubular webs, or in webs formed into tubes around filling nozzles, e.g. extruded tubular webs the webs being formed into tubes in situ around the filling nozzles the web advancing continuously
Definitions
- the present invention relates to packaging machinery and more particularly but not exclusively to a film drive for a packaging machine.
- a tubular bag material In the packaging of product which comprises a plurality of discrete units, it is common for a tubular bag material to be formed from sheet material, and the tubular bag material delivered to a filling head whereat the product is delivered to the interior of the tube material.
- the tube material is subsequently sealed at spaced intervals and discrete bags severed from the tubular material.
- the sheet material generally comprises a plastic film which is sealed by heat or other means to form the tubular material.
- the tube material is also sealed transverse of its longitudinal direction of extension, so as to form the discrete bag. This sealed area is also severed by a knife so that the discrete bags are separated from the tubular material.
- the speed of the film through the machine determines the period of time to which the plastic film is exposed to the sealing heads which form the discrete bags.
- the temperature of the sealing heads In order for correct sealing to take place, the temperature of the sealing heads must be adjusted to match the speed of the film material so that proper sealing does take place. More particularly, as the film speed increases the temperature of sealing must also increase since sealing must take place over a shorter interval of time, during which the sealing heads are in contact with the plastic film. It is a disadvantage of these known packaging machines, that it is difficult to adjust the temperature to the duration of time during which the sealing heads are in contact with the plastic film. If the adjustment is incorrect, incorrect sealing takes place with the result that the end product is defective.
- said film drive unit being operable on a continuous basis by comprising, a pair of endless belts having generally parallel co-extensive portions engaging said bag material to move same through said machine, motor means drivingly attached to said endless belts to drive same so that said belt portions have the same velocities and are moving in the same direction, and control means to control said motor means to govern the speed of said endless belts so that said sealing means is engaged with said bag material for a predetermined fixed period of time.
- a method of continuously driving a film material through a packaging machine said machine having means to supply sheet film material, means to form the film material into a tubular bag material, and sealing means to intermittently engage said bag material to sealingly close predetermined length of said bag material to form discrete bags containing product delivered to the interior of said bag material; said method comprising the steps of driving said bag material at a predetermined velocity while said sealing means engages said bag material, and then accelerating or deaccelerating said bag material to determine the production rate of said machine.
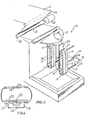
- FIG. 1 there is schematically depicted a drive unit 10 of a packaging machine which unit 10 is operable on a continuous basis.
- the packaging machine includes means to deliver sheet film material 11 to a former 12 which forms the sheet material 11 into a tubular configuration.
- the tubular material is moved through the packaging machine by a pair of endless belts 13 which are provided with a plurality of holes 14 which face the tubular material.
- Located at the rear of the belt 13 is a plennum chamber 15 to which there is delivered a vacuum by means of conduit lb.
- the chamber 15 is open to an inside surface of the belt 13 so that the vacuum is applied to the holes 14 so that the tubular material is held against the belts 13.
- the belts 13 pass around rollers 17 of which two at least are driven.
- rollers 17 could each be driven by a shaft 18 coupled to a worm drive unit 19.
- the drive unit 19 would be connected to an electric motor which would be controlled to vary the peripheral speed of the belt 13.
- the motor could be a stepping, servo, computer controlled or any other motor having suitable control characteristics.
- the speed of the belt 13 would be controlled so that the tubular material delivered to the sealing heads would be travelling at a predetermined velocity so that the sealing heads are in contact with the tubular material for a set period of time. Thereafter, the motors would increase the speed of the endless belts 13 to increase the production rate of the packaging machine or alternatively decrease the speed of the tubular material, to achieve a decrease in the output of the packaging machine. Accordingly, the speed of the endless belt 13 may be adjusted to accommodate different products and/or sheet packaging material 11.
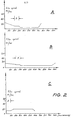
- FIG 2 there is schematically depicted three graphs which illustrate typical velocity profiles of the endless belts 13.
- the period of time D is the period during which the sealing heads are in contact with the tubular film material. Thereafter, the speed of the film is decreased and subsequently increased.
- the period of time D is the same, and the speed of the film is only slightly decreased.
- the period of the interval D is the same with the speed of the film increased after the period D to increase the production rate of the machine. With the period of time D constant, the velocity is also held constant for that time.
- a drive roller 21 is provided around which the film 11 passes.
- the film 11 also passes around an idler roller 23 and is sandwiched between the film drive roller 21 and a further idler roller 22.
- the roller 21 is attached to a servo motor 22 which determines the velocity of the film 11 as required.
- the servo motor 22 could be driven so as to provide the velocity profile of any one of the velocity profiles depicted in Figure 2.
- FIG 4 wherein the tubular material 24 is more fully depicted relative to a backing bar 20 as provided in Figures 1 and 3.
- the tubular material 24 overlaps at portions 25, which portions 25, are heat sealed via heat provided by the sealing head 26.
- the sealing head 26 is located within the chamber 15.
- This particular arrangement in respect of sealingly tubular material 24 is particularly different from the prior art in that the overlap portions 25 are engaged by the belt 13 as well as the opposite side of the tubular material 24. Conventionally, the other two sides of the tubular material are generally engaged. This provides specific advantages in respect of the continuous sealing of the tubular material 24, which is driven in a continuous manner past the heating head 26.
- the shafts 16 would be driven by servo motors so that the velocity of the arms 15, while the heads 14 are engaged with the curved portions 24 of the track 23, is greater than the velocity when the arms 15 are moving through an arc where the heads 14 are moving along the linear portion 25 of the track 23.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Containers And Plastic Fillers For Packaging (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- The present invention relates to packaging machinery and more particularly but not exclusively to a film drive for a packaging machine.
- In the packaging of product which comprises a plurality of discrete units, it is common for a tubular bag material to be formed from sheet material, and the tubular bag material delivered to a filling head whereat the product is delivered to the interior of the tube material. The tube material is subsequently sealed at spaced intervals and discrete bags severed from the tubular material. The sheet material generally comprises a plastic film which is sealed by heat or other means to form the tubular material. The tube material is also sealed transverse of its longitudinal direction of extension, so as to form the discrete bag. This sealed area is also severed by a knife so that the discrete bags are separated from the tubular material. In conventional packaging machines, the speed of the film through the machine determines the period of time to which the plastic film is exposed to the sealing heads which form the discrete bags. In order for correct sealing to take place, the temperature of the sealing heads must be adjusted to match the speed of the film material so that proper sealing does take place. More particularly, as the film speed increases the temperature of sealing must also increase since sealing must take place over a shorter interval of time, during which the sealing heads are in contact with the plastic film. It is a disadvantage of these known packaging machines, that it is difficult to adjust the temperature to the duration of time during which the sealing heads are in contact with the plastic film. If the adjustment is incorrect, incorrect sealing takes place with the result that the end product is defective.
- A still further disadvantage in these previous machines is that their operation is intermittent, and accordingly slow.
- It is the object of the present invention to overcome or substantially ameliorate the above disadvantages.
- There is disclosed herein a film drive unit of a packaging machine using film sheet to form tubular bag material into which a product is delivered, said machine further having sealing heads which intermittently engage the tubular bag material to form discrete bags; said film drive unit being operable on a continuous basis by comprising, a pair of endless belts having generally parallel co-extensive portions engaging said bag material to move same through said machine, motor means drivingly attached to said endless belts to drive same so that said belt portions have the same velocities and are moving in the same direction, and control means to control said motor means to govern the speed of said endless belts so that said sealing means is engaged with said bag material for a predetermined fixed period of time.
- There is further disclosed herein a method of continuously driving a film material through a packaging machine, said machine having means to supply sheet film material, means to form the film material into a tubular bag material, and sealing means to intermittently engage said bag material to sealingly close predetermined length of said bag material to form discrete bags containing product delivered to the interior of said bag material; said method comprising the steps of driving said bag material at a predetermined velocity while said sealing means engages said bag material, and then accelerating or deaccelerating said bag material to determine the production rate of said machine.
- A preferred form of the present invention will now be described by way of example with reference to the accompanying drawings wherein:
- Figure 1 is a schematic perspective view of a film drive unit for a packaging machine; and
- Figure 2 comprises three graphs which schematically depict film velocities for film being driven through a packaging machine by the drive unit of Figure 1.
- Figure 3 is a schematic perspective view of a modification of the drive unit of Figure 1; and
- Figure 4 is a schematic sectioned end view of the sealing assembly of the units of Figures 1 and 3.
- In Figure 1 there is schematically depicted a
drive unit 10 of a packaging machine whichunit 10 is operable on a continuous basis. The packaging machine includes means to deliver sheet film material 11 to a former 12 which forms the sheet material 11 into a tubular configuration. The tubular material is moved through the packaging machine by a pair ofendless belts 13 which are provided with a plurality ofholes 14 which face the tubular material. Located at the rear of thebelt 13 is aplennum chamber 15 to which there is delivered a vacuum by means of conduit lb. Thechamber 15 is open to an inside surface of thebelt 13 so that the vacuum is applied to theholes 14 so that the tubular material is held against thebelts 13. Thebelts 13 pass aroundrollers 17 of which two at least are driven. For example, therollers 17 could each be driven by ashaft 18 coupled to aworm drive unit 19. Thedrive unit 19 would be connected to an electric motor which would be controlled to vary the peripheral speed of thebelt 13. The motor could be a stepping, servo, computer controlled or any other motor having suitable control characteristics. - The speed of the
belt 13 would be controlled so that the tubular material delivered to the sealing heads would be travelling at a predetermined velocity so that the sealing heads are in contact with the tubular material for a set period of time. Thereafter, the motors would increase the speed of theendless belts 13 to increase the production rate of the packaging machine or alternatively decrease the speed of the tubular material, to achieve a decrease in the output of the packaging machine. Accordingly, the speed of theendless belt 13 may be adjusted to accommodate different products and/or sheet packaging material 11. - In Figure 2 there is schematically depicted three graphs which illustrate typical velocity profiles of the
endless belts 13. For example, in graph A, the period of time D is the period during which the sealing heads are in contact with the tubular film material. Thereafter, the speed of the film is decreased and subsequently increased. In the graph B, again the period of time D is the same, and the speed of the film is only slightly decreased. In the graph C, again the period of the interval D is the same with the speed of the film increased after the period D to increase the production rate of the machine. With the period of time D constant, the velocity is also held constant for that time. - Turning now to Figure 3 wherein the
film drive unit 10 is depicted with a modification. In this particular embodiment, adrive roller 21 is provided around which the film 11 passes. The film 11 also passes around anidler roller 23 and is sandwiched between thefilm drive roller 21 and afurther idler roller 22. Theroller 21 is attached to aservo motor 22 which determines the velocity of the film 11 as required. For example, theservo motor 22 could be driven so as to provide the velocity profile of any one of the velocity profiles depicted in Figure 2. However, it is necessary to drive theshafts 18 via constant torque motors which will thus accordingly adjust their speed in a slavish manner to the speed of theroller 21. - Turning now to Figure 4, wherein the
tubular material 24 is more fully depicted relative to abacking bar 20 as provided in Figures 1 and 3. Thetubular material 24 overlaps atportions 25, whichportions 25, are heat sealed via heat provided by the sealinghead 26. The sealinghead 26 is located within thechamber 15. This particular arrangement in respect of sealinglytubular material 24 is particularly different from the prior art in that theoverlap portions 25 are engaged by thebelt 13 as well as the opposite side of thetubular material 24. Conventionally, the other two sides of the tubular material are generally engaged. This provides specific advantages in respect of the continuous sealing of thetubular material 24, which is driven in a continuous manner past theheating head 26. - Preferably the
shafts 16 would be driven by servo motors so that the velocity of thearms 15, while theheads 14 are engaged with thecurved portions 24 of thetrack 23, is greater than the velocity when thearms 15 are moving through an arc where theheads 14 are moving along thelinear portion 25 of thetrack 23.
Claims (9)
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AU5595/84 | 1984-06-20 | ||
| AUPG559584 | 1984-06-20 | ||
| AU43752/85A AU574191B2 (en) | 1984-06-20 | 1985-06-17 | Film drive unit |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0165818A2 true EP0165818A2 (en) | 1985-12-27 |
| EP0165818A3 EP0165818A3 (en) | 1986-12-17 |
| EP0165818B1 EP0165818B1 (en) | 1989-08-30 |
Family
ID=25626475
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19850304419 Expired EP0165818B1 (en) | 1984-06-20 | 1985-06-20 | Film drive unit |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0165818B1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4727707A (en) * | 1986-12-15 | 1988-03-01 | Kliklok Corporation | Packaging film feeding apparatus and method |
| EP0275181A2 (en) * | 1987-01-14 | 1988-07-20 | Alfred Alexander Taylor | A film drive unit for a packaging machine |
| US5753067A (en) * | 1994-12-23 | 1998-05-19 | Ishida Co., Ltd. | Transverse sealer for a bag maker with variable operating speed |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4315067C2 (en) * | 1993-05-06 | 1999-01-21 | Mesoma Hans Guenter Kauck Gmbh | Method and device for forming a weld or sealed seam in a thermoplastic envelope |
| DE19726205A1 (en) * | 1997-06-20 | 1998-12-24 | Rovema Gmbh | Longitudinal welding and transporting unit for film during continuous production of tubular film for packages |
| DE102006025831B4 (en) * | 2006-06-02 | 2013-10-31 | Rovema Gmbh | Device for welding plastic for packaging purposes (torque motor) |
| NL2028931B1 (en) * | 2021-08-05 | 2023-02-17 | Vmi Holland Bv | Packaging device and method for packaging discrete medicaments in pouches |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3762663A (en) * | 1971-11-30 | 1973-10-02 | Ge C | Static means for generating inertia compensation signals in reel drives |
| US4043098A (en) * | 1976-08-26 | 1977-08-23 | Package Machinery Company | Vertical form, fill and seal packaging machine with improved back-up bar for longitudinal sealing |
| US4136505A (en) * | 1977-11-11 | 1979-01-30 | Package Machinery Company | Tubeless vertical form, fill and seal packaging machine with improved feed means |
| US4218863A (en) * | 1978-11-22 | 1980-08-26 | American Can Company | Continuous motion wrapping machine |
| GB2056940A (en) * | 1979-08-27 | 1981-03-25 | Hayssen Mfg Co | Form fill seal packaging |
| GB2096091A (en) * | 1981-04-04 | 1982-10-13 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Form fill seal apparatus |
-
1985
- 1985-06-20 EP EP19850304419 patent/EP0165818B1/en not_active Expired
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3762663A (en) * | 1971-11-30 | 1973-10-02 | Ge C | Static means for generating inertia compensation signals in reel drives |
| US4043098A (en) * | 1976-08-26 | 1977-08-23 | Package Machinery Company | Vertical form, fill and seal packaging machine with improved back-up bar for longitudinal sealing |
| US4136505A (en) * | 1977-11-11 | 1979-01-30 | Package Machinery Company | Tubeless vertical form, fill and seal packaging machine with improved feed means |
| US4218863A (en) * | 1978-11-22 | 1980-08-26 | American Can Company | Continuous motion wrapping machine |
| GB2056940A (en) * | 1979-08-27 | 1981-03-25 | Hayssen Mfg Co | Form fill seal packaging |
| GB2096091A (en) * | 1981-04-04 | 1982-10-13 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Form fill seal apparatus |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4727707A (en) * | 1986-12-15 | 1988-03-01 | Kliklok Corporation | Packaging film feeding apparatus and method |
| EP0275181A2 (en) * | 1987-01-14 | 1988-07-20 | Alfred Alexander Taylor | A film drive unit for a packaging machine |
| EP0275181A3 (en) * | 1987-01-14 | 1989-11-29 | Alfred Alexander Taylor | A film drive unit for a packaging machine |
| US5753067A (en) * | 1994-12-23 | 1998-05-19 | Ishida Co., Ltd. | Transverse sealer for a bag maker with variable operating speed |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0165818B1 (en) | 1989-08-30 |
| EP0165818A3 (en) | 1986-12-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0569628B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for forming and hermetically sealing slices of food items | |
| US4726168A (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling a driving system in a packaging machine | |
| US6854242B2 (en) | Modular shrink-wrap machine | |
| US6247293B1 (en) | Modular packaging machine with web tension control | |
| US6047521A (en) | Vertical form, fill and seal machine for making reclosable bags | |
| US5447486A (en) | Maintaining perforation phasing | |
| US5800851A (en) | Slice of a food item having a heat tack seal | |
| US4947623A (en) | Wrapping method | |
| GB2138381A (en) | Form-fill-seal wrapping apparatus | |
| EP0165818B1 (en) | Film drive unit | |
| GB1480823A (en) | Apparatus and method for continuously expanding and feeding preformed honeycomb material | |
| US6158200A (en) | Apparatus and method for producing packages by vibrating bag material | |
| US3782072A (en) | Apparatus for wrapping articles | |
| GB1487263A (en) | Packaging apparatus | |
| US4744202A (en) | Apparatus and method for maintaining uniform, registration in a packaging machine | |
| AU2001279961B2 (en) | Heat sealing apparatus for packaging machinery | |
| AU2001279961A1 (en) | Heat sealing apparatus for packaging machinery | |
| EP1506087B1 (en) | Application of zippers to film material | |
| US3439471A (en) | Packaging apparatus | |
| ATE52736T1 (en) | LONGITUDINAL SEALING SYSTEM FOR A PACKAGING MACHINE. | |
| JPS6112327A (en) | Method and device for driving film material | |
| JPH0366208B2 (en) | ||
| JP3688310B2 (en) | Raw material feeding method and apparatus in bag making filling and packaging machine | |
| WO1998040202A1 (en) | Packaging machine | |
| JP3027575U (en) | Packaging equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19870526 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19880314 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3572634 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19891005 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PUE Owner name: ALFRED ALEXANDER TAYLOR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP |
|
| ITPR | It: changes in ownership of a european patent |
Owner name: CESSIONE;TAYLOR, ALFRED ALEXANDER |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20020610 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20020619 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20020626 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20020702 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030620 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030630 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040101 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20030620 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040227 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |