EP0069975A1 - Verfahren zur Herstellung von flammwidrigen Polyurethan- und/oder Polyisocyanuratgruppen enthaltenden Schaumstoffen - Google Patents
Verfahren zur Herstellung von flammwidrigen Polyurethan- und/oder Polyisocyanuratgruppen enthaltenden Schaumstoffen Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0069975A1 EP0069975A1 EP82106046A EP82106046A EP0069975A1 EP 0069975 A1 EP0069975 A1 EP 0069975A1 EP 82106046 A EP82106046 A EP 82106046A EP 82106046 A EP82106046 A EP 82106046A EP 0069975 A1 EP0069975 A1 EP 0069975A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- halogen
- und
- organic
- phosphorus
- polyols
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 26
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 9
- 229920000582 polyisocyanurate Polymers 0.000 title claims abstract description 4
- 239000011495 polyisocyanurate Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 4
- 230000000979 retarding effect Effects 0.000 title 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 45
- 229920001228 polyisocyanate Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 45
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 239000005056 polyisocyanate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 229920005862 polyol Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 38
- 150000003077 polyols Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 34
- 239000003063 flame retardant Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphinic acid Chemical class O[PH2]=O ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- RNFJDJUURJAICM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,4,4,6,6-hexaphenoxy-1,3,5-triaza-2$l^{5},4$l^{5},6$l^{5}-triphosphacyclohexa-1,3,5-triene Chemical compound N=1P(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=NP(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=NP=1(OC=1C=CC=CC=1)OC1=CC=CC=C1 RNFJDJUURJAICM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 239000004604 Blowing Agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 239000004970 Chain extender Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 239000003431 cross linking reagent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 230000002195 synergetic effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 18
- ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-M phosphinate Chemical compound [O-][PH2]=O ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 claims description 6
- 229920000877 Melamine resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- JDSHMPZPIAZGSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N melamine Chemical compound NC1=NC(N)=NC(N)=N1 JDSHMPZPIAZGSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910001376 inorganic hypophosphite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 1
- 150000002894 organic compounds Chemical class 0.000 abstract 1
- -1 ZnO Chemical class 0.000 description 32
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCO LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 25
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 24
- MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCOCCO MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 23
- WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N adipic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCC(O)=O WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- ZFSLODLOARCGLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N isocyanuric acid Chemical group OC1=NC(O)=NC(O)=N1 ZFSLODLOARCGLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl urethane Chemical compound CCOC(N)=O JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Chemical compound O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- GOOHAUXETOMSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene oxide Chemical compound CC1CO1 GOOHAUXETOMSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- ZJCCRDAZUWHFQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trimethylolpropane Chemical compound CCC(CO)(CO)CO ZJCCRDAZUWHFQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 125000002947 alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 description 6
- 239000013065 commercial product Substances 0.000 description 6
- 150000002009 diols Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 6
- HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Aminoethan-1-ol Chemical compound NCCO HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- UPMLOUAZCHDJJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-Diphenylmethane Diisocyanate Chemical class C1=CC(N=C=O)=CC=C1CC1=CC=C(N=C=O)C=C1 UPMLOUAZCHDJJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000004721 Polyphenylene oxide Substances 0.000 description 5
- SLINHMUFWFWBMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triisopropanolamine Chemical compound CC(O)CN(CC(C)O)CC(C)O SLINHMUFWFWBMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- XUGISPSHIFXEHZ-GPJXBBLFSA-N [(3r,8s,9s,10r,13r,14s,17r)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2r)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] acetate Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@H](OC(C)=O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 XUGISPSHIFXEHZ-GPJXBBLFSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000001361 adipic acid Substances 0.000 description 5
- 235000011037 adipic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- ADCOVFLJGNWWNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N antimony trioxide Inorganic materials O=[Sb]O[Sb]=O ADCOVFLJGNWWNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- HIFVAOIJYDXIJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzylbenzene;isocyanic acid Chemical class N=C=O.N=C=O.C=1C=CC=CC=1CC1=CC=CC=C1 HIFVAOIJYDXIJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229920000570 polyether Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000005846 sugar alcohols Polymers 0.000 description 5
- CYRMSUTZVYGINF-UHFFFAOYSA-N trichlorofluoromethane Chemical compound FC(Cl)(Cl)Cl CYRMSUTZVYGINF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229940113165 trimethylolpropane Drugs 0.000 description 5
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229930006000 Sucrose Natural products 0.000 description 4
- KKEYFWRCBNTPAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Terephthalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C1 KKEYFWRCBNTPAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethanolamine Chemical compound OCCN(CCO)CCO GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 4
- WERYXYBDKMZEQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N butane-1,4-diol Chemical compound OCCCCO WERYXYBDKMZEQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 150000001991 dicarboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 125000005442 diisocyanate group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 4
- XNGIFLGASWRNHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N phthalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C(O)=O XNGIFLGASWRNHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 4
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium hydroxide Inorganic materials [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- 229960004793 sucrose Drugs 0.000 description 4
- IMNIMPAHZVJRPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N triethylenediamine Chemical class C1CN2CCN1CC2 IMNIMPAHZVJRPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 150000004072 triols Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- PAYRUJLWNCNPSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Aniline Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC=C1 PAYRUJLWNCNPSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Epichlorohydrin Chemical compound ClCC1CO1 BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylenediamine Chemical compound NCCN PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- ABLZXFCXXLZCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorous acid Chemical class OP(O)=O ABLZXFCXXLZCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Succinic acid Natural products OC(=O)CCC(O)=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N Sucrose Chemical compound O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 150000004985 diamines Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 150000005690 diesters Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethanolamine Chemical compound OCCNCCO ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl ether Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1OC1=CC=CC=C1 USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- NIMLQBUJDJZYEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N isophorone diisocyanate Chemical compound CC1(C)CC(N=C=O)CC(C)(CN=C=O)C1 NIMLQBUJDJZYEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WXZMFSXDPGVJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentaerythritol Chemical compound OCC(CO)(CO)CO WXZMFSXDPGVJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000021317 phosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 229920005906 polyester polyol Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000005060 rubber Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000005720 sucrose Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229940029284 trichlorofluoromethane Drugs 0.000 description 3
- XFNJVJPLKCPIBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethylenediamine Chemical compound NCCCN XFNJVJPLKCPIBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- AQPHBYQUCKHJLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3,4,5-pentabromo-6-(2,3,4,5,6-pentabromophenyl)benzene Chemical group BrC1=C(Br)C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1C1=C(Br)C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1Br AQPHBYQUCKHJLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PFUKECZPRROVOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3,5-triisocyanato-2-methylbenzene Chemical compound CC1=C(N=C=O)C=C(N=C=O)C=C1N=C=O PFUKECZPRROVOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SBJCUZQNHOLYMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,5-Naphthalene diisocyanate Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(N=C=O)=CC=CC2=C1N=C=O SBJCUZQNHOLYMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LWMWZNOCSCPBCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[bis[2-[bis(2-hydroxypropyl)amino]ethyl]amino]propan-2-ol Chemical compound CC(O)CN(CC(C)O)CCN(CC(O)C)CCN(CC(C)O)CC(C)O LWMWZNOCSCPBCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RTBFRGCFXZNCOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methylsulfonylpiperidin-4-one Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)N1CCC(=O)CC1 RTBFRGCFXZNCOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VILCJCGEZXAXTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,2-tetramine Chemical compound NCCNCCNCCN VILCJCGEZXAXTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DTFQULSULHRJOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,5,6-tetrabromobenzene-1,4-diol Chemical compound OC1=C(Br)C(Br)=C(O)C(Br)=C1Br DTFQULSULHRJOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FJWGRXKOBIVTFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dibromobutanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(Br)C(Br)C(O)=O FJWGRXKOBIVTFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZMYAKSMZTVWUJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dibromopropanoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(Br)CBr ZMYAKSMZTVWUJB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CYYDNXCYDWWSPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2,2,2-trichloroethyl)oxirane Chemical compound ClC(Cl)(Cl)CC1CO1 CYYDNXCYDWWSPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BYACHAOCSIPLCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[2-[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]ethyl-(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]ethanol Chemical compound OCCN(CCO)CCN(CCO)CCO BYACHAOCSIPLCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XIRDTMSOGDWMOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,4,5,6-tetrabromophthalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=C(Br)C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1C(O)=O XIRDTMSOGDWMOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FKNQCJSGGFJEIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methylpyridine Chemical compound CC1=CC=NC=C1 FKNQCJSGGFJEIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butadiene Chemical compound C=CC=C KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon dioxide Chemical compound O=C=O CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N D-Glucitol Natural products OC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N D-glucitol Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RPNUMPOLZDHAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethylenetriamine Chemical compound NCCNCCN RPNUMPOLZDHAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrazine Chemical compound NN OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium methoxide Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]C WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NSOXQYCFHDMMGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrakis(2-hydroxypropyl)ethylenediamine Chemical compound CC(O)CN(CC(C)O)CCN(CC(C)O)CC(C)O NSOXQYCFHDMMGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005299 abrasion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000013543 active substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000008044 alkali metal hydroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- VSCWAEJMTAWNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium trichloride Chemical compound Cl[Al](Cl)Cl VSCWAEJMTAWNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- JFCQEDHGNNZCLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N anhydrous glutaric acid Natural products OC(=O)CCCC(O)=O JFCQEDHGNNZCLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- TZCXTZWJZNENPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L barium sulfate Chemical compound [Ba+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O TZCXTZWJZNENPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-NUQCWPJISA-N butanedioic acid Chemical compound O[14C](=O)CC[14C](O)=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-NUQCWPJISA-N 0.000 description 2
- VPKDCDLSJZCGKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbodiimide group Chemical group N=C=N VPKDCDLSJZCGKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004359 castor oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019438 castor oil Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanone Chemical compound O=C1CCCCC1 JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZSWFCLXCOIISFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclopentadiene Chemical compound C1C=CC=C1 ZSWFCLXCOIISFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SZXQTJUDPRGNJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N dipropylene glycol Chemical compound OCCCOCCCO SZXQTJUDPRGNJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- TVIDDXQYHWJXFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O TVIDDXQYHWJXFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GKIPXFAANLTWBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N epibromohydrin Chemical compound BrCC1CO1 GKIPXFAANLTWBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 2
- ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N glycerol triricinoleate Natural products CCCCCC[C@@H](O)CC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](COC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@@H](O)CCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@H](O)CCCCCC ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CAYGQBVSOZLICD-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexabromobenzene Chemical compound BrC1=C(Br)C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1Br CAYGQBVSOZLICD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NAQMVNRVTILPCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexane-1,6-diamine Chemical compound NCCCCCCN NAQMVNRVTILPCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XXMIOPMDWAUFGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexane-1,6-diol Chemical compound OCCCCCCO XXMIOPMDWAUFGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001023 inorganic pigment Substances 0.000 description 2
- RBTARNINKXHZNM-UHFFFAOYSA-K iron trichloride Chemical compound Cl[Fe](Cl)Cl RBTARNINKXHZNM-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- 239000012948 isocyanate Substances 0.000 description 2
- IQPQWNKOIGAROB-UHFFFAOYSA-N isocyanate group Chemical group [N-]=C=O IQPQWNKOIGAROB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000002513 isocyanates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- NFHFRUOZVGFOOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N palladium;triphenylphosphane Chemical compound [Pd].C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 NFHFRUOZVGFOOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SVHOVVJFOWGYJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentabromophenol Chemical compound OC1=C(Br)C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1Br SVHOVVJFOWGYJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 2
- UEZVMMHDMIWARA-UHFFFAOYSA-M phosphonate Chemical compound [O-]P(=O)=O UEZVMMHDMIWARA-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- WLJVNTCWHIRURA-UHFFFAOYSA-N pimelic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCCC(O)=O WLJVNTCWHIRURA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920006389 polyphenyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920001451 polypropylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 2
- WQKGAJDYBZOFSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N potassium;propan-2-olate Chemical compound [K+].CC(C)[O-] WQKGAJDYBZOFSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N propane-1,3-diol Chemical compound OCCCO YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KIDHWZJUCRJVML-UHFFFAOYSA-N putrescine Chemical compound NCCCCN KIDHWZJUCRJVML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000600 sorbitol Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000003512 tertiary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- RUELTTOHQODFPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene 2,6-diisocyanate Chemical compound CC1=C(N=C=O)C=CC=C1N=C=O RUELTTOHQODFPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LWBHHRRTOZQPDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N undecanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCC(O)=O LWBHHRRTOZQPDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JIAARYAFYJHUJI-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc dichloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[Cl-].[Zn+2] JIAARYAFYJHUJI-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- HFVMEOPYDLEHBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2-fluorophenyl)-phenylmethanol Chemical compound C=1C=CC=C(F)C=1C(O)C1=CC=CC=C1 HFVMEOPYDLEHBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SHRRVNVEOIKVSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1,2,2,3,3-hexabromocyclododecane Chemical compound BrC1(Br)CCCCCCCCCC(Br)(Br)C1(Br)Br SHRRVNVEOIKVSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AUTSLLHNWAZVLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1,2,2,3-pentabromo-3-chlorocyclohexane Chemical compound ClC1(Br)CCCC(Br)(Br)C1(Br)Br AUTSLLHNWAZVLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AJDIZQLSFPQPEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1,2-Trichlorotrifluoroethane Chemical compound FC(F)(Cl)C(F)(Cl)Cl AJDIZQLSFPQPEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NDRKXFLZSRHAJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3,4,5-pentabromo-6-(2,3,4-tribromophenyl)benzene Chemical group BrC1=C(Br)C(Br)=CC=C1C1=C(Br)C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1Br NDRKXFLZSRHAJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ACRQLFSHISNWRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3,4,5-pentabromo-6-phenoxybenzene Chemical compound BrC1=C(Br)C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1OC1=CC=CC=C1 ACRQLFSHISNWRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JAHJITLFJSDRCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3,4,5-pentachloro-6-(2,3,4-trichlorophenyl)benzene Chemical group ClC1=C(Cl)C(Cl)=CC=C1C1=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1Cl JAHJITLFJSDRCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DDMOUSALMHHKOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-dichloro-1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethane Chemical compound FC(F)(Cl)C(F)(F)Cl DDMOUSALMHHKOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GIWQSPITLQVMSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-dimethylimidazole Chemical compound CC1=NC=CN1C GIWQSPITLQVMSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GEYOCULIXLDCMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-phenylenediamine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC=C1N GEYOCULIXLDCMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FCQPNTOQFPJCMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-bis[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]urea Chemical compound CN(C)CCCNC(=O)NCCCN(C)C FCQPNTOQFPJCMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PMDHMYFSRFZGIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4,7-trioxacyclotridecane-8,13-dione Chemical compound O=C1CCCCC(=O)OCCOCCO1 PMDHMYFSRFZGIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940008841 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- JIABEENURMZTTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-isocyanato-2-[(2-isocyanatophenyl)methyl]benzene Chemical compound O=C=NC1=CC=CC=C1CC1=CC=CC=C1N=C=O JIABEENURMZTTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OUCSIUCEQVCDEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4-tribromophenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=C(Br)C(Br)=C1Br OUCSIUCEQVCDEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CVFRFSNPBJUQMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)benzene-1,4-diol Chemical compound OCCC1=C(O)C=CC(O)=C1CCO CVFRFSNPBJUQMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QKKSKKMOIOGASY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dibromobut-1-ene-1,1-diol Chemical compound CC(Br)C(Br)=C(O)O QKKSKKMOIOGASY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PQXKWPLDPFFDJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3-dimethyloxirane Chemical compound CC1OC1C PQXKWPLDPFFDJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BSWWXRFVMJHFBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4,6-tribromophenol Chemical compound OC1=C(Br)C=C(Br)C=C1Br BSWWXRFVMJHFBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AHDSRXYHVZECER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4,6-tris[(dimethylamino)methyl]phenol Chemical compound CN(C)CC1=CC(CN(C)C)=C(O)C(CN(C)C)=C1 AHDSRXYHVZECER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RLYCRLGLCUXUPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-diaminotoluene Chemical compound CC1=C(N)C=CC=C1N RLYCRLGLCUXUPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BPRJQFIHEGORJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(1-hydroxypropan-2-yloxy)propan-1-ol 1-(2-hydroxypropoxy)propan-2-ol Chemical compound CC(O)COCC(C)O.CC(CO)OC(C)CO BPRJQFIHEGORJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MIJDSYMOBYNHOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(ethylamino)ethanol Chemical compound CCNCCO MIJDSYMOBYNHOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OHKOAJUTRVTYSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[(2-aminophenyl)methyl]aniline Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC=C1CC1=CC=CC=C1N OHKOAJUTRVTYSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CJWBPEYRTPGWPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[bis(2-chloroethoxy)phosphoryloxy]ethyl bis(2-chloroethyl) phosphate Chemical compound ClCCOP(=O)(OCCCl)OCCOP(=O)(OCCCl)OCCCl CJWBPEYRTPGWPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FZZMTSNZRBFGGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-chloro-7-fluoroquinazolin-4-amine Chemical compound FC1=CC=C2C(N)=NC(Cl)=NC2=C1 FZZMTSNZRBFGGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OTOLFQXGRCJFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 2-hydroxypropyl(trimethyl)azanium;formate Chemical compound [O-]C=O.CC(O)C[N+](C)(C)C OTOLFQXGRCJFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- IQUPABOKLQSFBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-nitrophenol Chemical class OC1=CC=CC=C1[N+]([O-])=O IQUPABOKLQSFBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAUWOBSDSJNJQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,4,5,6-tetrabromobenzene-1,2-diol Chemical compound OC1=C(O)C(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1Br OAUWOBSDSJNJQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WUPHOULIZUERAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(oxolan-2-yl)propanoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCC1CCCO1 WUPHOULIZUERAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HVCNXQOWACZAFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-ethylmorpholine Chemical compound CCN1CCOCC1 HVCNXQOWACZAFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CNPURSDMOWDNOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methoxy-7h-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-amine Chemical compound COC1=NC(N)=NC2=C1C=CN2 CNPURSDMOWDNOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MGYGFNQQGAQEON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-tolyl isocyanate Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(N=C=O)C=C1 MGYGFNQQGAQEON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RSWGJHLUYNHPMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Abietic-Saeure Natural products C12CCC(C(C)C)=CC2=CCC2C1(C)CCCC2(C)C(O)=O RSWGJHLUYNHPMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acrylate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)C=C NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000005995 Aluminium silicate Substances 0.000 description 1
- OMNLLLCRKPOACJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N B(O)(O)O.OCC[Na] Chemical compound B(O)(O)O.OCC[Na] OMNLLLCRKPOACJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910015900 BF3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000005711 Benzoic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- KZMGYPLQYOPHEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron trifluoride etherate Chemical compound FB(F)F.CCOCC KZMGYPLQYOPHEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004971 Cross linker Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004338 Dichlorodifluoromethane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052691 Erbium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene oxide Chemical compound C1CO1 IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005727 Friedel-Crafts reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910021578 Iron(III) chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000005058 Isophorone diisocyanate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002841 Lewis acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052765 Lutetium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methacrylic acid Chemical class CC(=C)C(O)=O CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SJRJJKPEHAURKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylmorpholine Chemical compound CN1CCOCC1 SJRJJKPEHAURKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AKNUHUCEWALCOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-ethyldiethanolamine Chemical compound OCCN(CC)CCO AKNUHUCEWALCOI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OPKOKAMJFNKNAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-methylethanolamine Chemical group CNCCO OPKOKAMJFNKNAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QXGBIHFUXMYJEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N N=C=O.N=C=O.N=C=O.N=C=O.C(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1 Chemical compound N=C=O.N=C=O.N=C=O.N=C=O.C(C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1 QXGBIHFUXMYJEF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002292 Nylon 6 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002302 Nylon 6,6 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- ALQSHHUCVQOPAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pentane-1,5-diol Chemical compound OCCCCCO ALQSHHUCVQOPAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920005830 Polyurethane Foam Polymers 0.000 description 1
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KHPCPRHQVVSZAH-HUOMCSJISA-N Rosin Natural products O(C/C=C/c1ccccc1)[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 KHPCPRHQVVSZAH-HUOMCSJISA-N 0.000 description 1
- AWMVMTVKBNGEAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene oxide Chemical compound C1OC1C1=CC=CC=C1 AWMVMTVKBNGEAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052775 Thulium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007983 Tris buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052769 Ytterbium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000005083 Zinc sulfide Substances 0.000 description 1
- UKLDJPRMSDWDSL-UHFFFAOYSA-L [dibutyl(dodecanoyloxy)stannyl] dodecanoate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)O[Sn](CCCC)(CCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCC UKLDJPRMSDWDSL-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 1
- WYTGDNHDOZPMIW-RCBQFDQVSA-N alstonine Natural products C1=CC2=C3C=CC=CC3=NC2=C2N1C[C@H]1[C@H](C)OC=C(C(=O)OC)[C@H]1C2 WYTGDNHDOZPMIW-RCBQFDQVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000012211 aluminium silicate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011114 ammonium hydroxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000010539 anionic addition polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052898 antigorite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052787 antimony Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WATWJIUSRGPENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N antimony atom Chemical compound [Sb] WATWJIUSRGPENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VMPVEPPRYRXYNP-UHFFFAOYSA-I antimony(5+);pentachloride Chemical compound Cl[Sb](Cl)(Cl)(Cl)Cl VMPVEPPRYRXYNP-UHFFFAOYSA-I 0.000 description 1
- 150000005840 aryl radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000022 bacteriostatic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 1
- ADEDSVWTSISPMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid;2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diol Chemical compound OCC(C)(C)CO.OC(=O)C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1 ADEDSVWTSISPMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010233 benzoic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- NDKBVBUGCNGSJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzyltrimethylammonium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].C[N+](C)(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 NDKBVBUGCNGSJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- ITQTTZVARXURQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-methylpyridine Natural products CC1=CC=CN=C1 ITQTTZVARXURQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- OHJMTUPIZMNBFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N biuret Chemical group NC(=O)NC(N)=O OHJMTUPIZMNBFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WTEOIRVLGSZEPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N boron trifluoride Chemical compound FB(F)F WTEOIRVLGSZEPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052793 cadmium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052980 cadmium sulfide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000000711 cancerogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000001569 carbon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002092 carbon dioxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001735 carboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 231100000315 carcinogenic Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 238000010538 cationic polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001768 cations Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004985 dialkyl amino alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- WMWXXXSCZVGQAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N dialuminum;oxygen(2-);hydrate Chemical compound O.[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] WMWXXXSCZVGQAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012975 dibutyltin dilaurate Substances 0.000 description 1
- PXBRQCKWGAHEHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N dichlorodifluoromethane Chemical compound FC(F)(Cl)Cl PXBRQCKWGAHEHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019404 dichlorodifluoromethane Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940087091 dichlorotetrafluoroethane Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000013681 dietary sucrose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940106012 diethylene glycol adipate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000000118 dimethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- XXBDWLFCJWSEKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylbenzylamine Chemical compound CN(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 XXBDWLFCJWSEKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000975 dye Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004185 ester group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000002169 ethanolamines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000002191 fatty alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000001408 fungistatic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000008282 halocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000002366 halogen compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- VUNCWTMEJYMOOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexachlorocyclopentadiene Chemical compound ClC1=C(Cl)C(Cl)(Cl)C(Cl)=C1Cl VUNCWTMEJYMOOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RRAMGCGOFNQTLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexamethylene diisocyanate Chemical compound O=C=NCCCCCCN=C=O RRAMGCGOFNQTLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000000265 homogenisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052892 hornblende Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229940042795 hydrazides for tuberculosis treatment Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011256 inorganic filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910003475 inorganic filler Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron Substances [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron oxide Inorganic materials [Fe]=O UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000013980 iron oxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- VBMVTYDPPZVILR-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron(2+);oxygen(2-) Chemical class [O-2].[Fe+2] VBMVTYDPPZVILR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HLJDOURGTRAFHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N isocyanic acid;3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-one Chemical compound N=C=O.N=C=O.CC1=CC(=O)CC(C)(C)C1 HLJDOURGTRAFHE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BYXYCUABYHCYLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoindole-1,3-dione;potassium Chemical compound [K].C1=CC=C2C(=O)NC(=O)C2=C1 BYXYCUABYHCYLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N kaolin Chemical compound O.O.O=[Al]O[Si](=O)O[Si](=O)O[Al]=O NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052747 lanthanoid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002602 lanthanoids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- VQPKAMAVKYTPLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N lead;octanoic acid Chemical compound [Pb].CCCCCCCC(O)=O VQPKAMAVKYTPLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000007517 lewis acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-NJFSPNSNSA-N methanone Chemical compound O=[14CH2] WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-NJFSPNSNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CRVGTESFCCXCTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl diethanolamine Chemical group OCCN(C)CCO CRVGTESFCCXCTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002763 monocarboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004108 n-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001280 n-hexyl group Chemical group C(CCCCC)* 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N nickel Substances [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 231100000956 nontoxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- OEIJHBUUFURJLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N octane-1,8-diol Chemical compound OCCCCCCCCO OEIJHBUUFURJLI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019198 oils Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012766 organic filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- AHHWIHXENZJRFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxetane Chemical compound C1COC1 AHHWIHXENZJRFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- SOQBVABWOPYFQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);titanium(4+) Chemical class [O-2].[O-2].[Ti+4] SOQBVABWOPYFQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003973 paint Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012188 paraffin wax Substances 0.000 description 1
- UWJJYHHHVWZFEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentane-1,1-diol Chemical compound CCCCC(O)O UWJJYHHHVWZFEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004986 phenylenediamines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- AQSJGOWTSHOLKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphite(3-) Chemical class [O-]P([O-])[O-] AQSJGOWTSHOLKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004714 phosphonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003013 phosphoric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003018 phosphorus compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000233 poly(alkylene oxides) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002685 polymerization catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011496 polyurethane foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002689 polyvinyl acetate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011118 polyvinyl acetate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000915 polyvinyl chloride Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004800 polyvinyl chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011148 porous material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008092 positive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZUFQCVZBBNZMKD-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium 2-ethylhexanoate Chemical compound [K+].CCCCC(CC)C([O-])=O ZUFQCVZBBNZMKD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium benzoate Chemical compound [K+].[O-]C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000004300 potassium benzoate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010235 potassium benzoate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940103091 potassium benzoate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- WFIZEGIEIOHZCP-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium formate Chemical compound [K+].[O-]C=O WFIZEGIEIOHZCP-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- BDAWXSQJJCIFIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N potassium methoxide Chemical compound [K+].[O-]C BDAWXSQJJCIFIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ULWHHBHJGPPBCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N propane-1,1-diol Chemical compound CCC(O)O ULWHHBHJGPPBCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011814 protection agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- ADRDEXBBJTUCND-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrrolizidine Chemical compound C1CCN2CCCC21 ADRDEXBBJTUCND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001453 quaternary ammonium group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012744 reinforcing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007363 ring formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052604 silicate mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004760 silicates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZVUUCUFDAHKLKT-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;2,4,6-trinitrophenolate Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]C1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1[N+]([O-])=O ZVUUCUFDAHKLKT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IUTCEZPPWBHGIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N tin(2+) Chemical class [Sn+2] IUTCEZPPWBHGIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KSBAEPSJVUENNK-UHFFFAOYSA-L tin(ii) 2-ethylhexanoate Chemical compound [Sn+2].CCCCC(CC)C([O-])=O.CCCCC(CC)C([O-])=O KSBAEPSJVUENNK-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium oxide Inorganic materials [Ti]=O OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DVKJHBMWWAPEIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene 2,4-diisocyanate Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(N=C=O)C=C1N=C=O DVKJHBMWWAPEIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002110 toxicologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000723 toxicological property Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- KHPCPRHQVVSZAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-cinnamyl beta-D-glucopyranoside Natural products OC1C(O)C(O)C(CO)OC1OCC=CC1=CC=CC=C1 KHPCPRHQVVSZAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001124 trientine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- RXJKFRMDXUJTEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N triethylphosphine Chemical compound CCP(CC)CC RXJKFRMDXUJTEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N urea group Chemical group NC(=O)N XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AVWRKZWQTYIKIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N urea-1-carboxylic acid Chemical group NC(=O)NC(O)=O AVWRKZWQTYIKIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011592 zinc chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000005074 zinc chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052984 zinc sulfide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- DRDVZXDWVBGGMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N zinc;sulfide Chemical compound [S-2].[Zn+2] DRDVZXDWVBGGMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J9/00—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof
- C08J9/0066—Use of inorganic compounding ingredients
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J9/00—Working-up of macromolecular substances to porous or cellular articles or materials; After-treatment thereof
- C08J9/0014—Use of organic additives
- C08J9/0038—Use of organic additives containing phosphorus
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2375/00—Characterised by the use of polyureas or polyurethanes; Derivatives of such polymers
- C08J2375/04—Polyurethanes
Definitions
- a number of metal oxides such as ZnO, B 2 0 3 , Fe2 0 3 , CaO, S b2 0 3 , can also be added to enhance the flame retardancy. These compounds do not themselves have a flame retardant effect, but they are synergistically active together with the organically bound halogen.
- the most effective system in polyurethane foams has been found to be antimony (III) oxide / halogen (see WC Kuryla and AJ Lapa, Flame Retardancy of Polymeric Materials, Vol. 3 (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1975).
- the object of the present invention was to find a replacement for antimony (III) oxide which has an equivalent synergism with halogen without having its disadvantages.
- This task was surprisingly achieved by using salt-like inorganic and / or organic hypophosphites in combination with the organic halogen or halogen and phosphorus-containing compounds mentioned.
- the hypophosphites themselves have no flame retardant effect.
- hypophosphites are used in foams containing urethane and / or isocyanurate groups together with reactive or additive organic, halogen-containing or halogen- and phosphorus-containing flame retardants, these compounds show a synergistic effect comparable to that of antimony (III) oxide.
- Another advantage is the ease of manufacture of the hypophosphites and, as far as is known, their relative non-toxicity.
- the foams produced in this way have a significantly lower brittleness than corresponding antimony (III) oxide-containing foams. They show good mechanical properties and increased flame resistance.
- the use of the hypophosphite / halogen system according to the invention brings a considerable saving in halogen compounds.
- This saving in flame retardants has a positive effect on the mechanical properties of the foams.
- the additive phosphorus compounds previously used as flame retardants in polyurethane are known to have a certain plasticizing effect in large quantities. This is not the case with the hypophosphites, since only small amounts are necessary to increase the effect of the halogen.
- Organic, organic salt-like and preferably inorganic salt-like hypophosphites can be used for the process according to the invention.
- hypophosphites of mono- and polyhydric alcohols, such as those of the formula R-0-PH 2 0, in which R is a linear or branched alkyl radical having 1 to 20, preferably 4 to 14, carbon atoms, an aryl radical or an oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur-containing heterocyclic radical.
- R is a linear or branched alkyl radical having 1 to 20, preferably 4 to 14, carbon atoms, an aryl radical or an oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur-containing heterocyclic radical.
- R is a linear or branched alkyl radical having 1 to 20, preferably 4 to 14, carbon atoms, an aryl radical or an oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur-containing heterocyclic radical.
- R is a linear or branched alkyl radical having 1 to 20, preferably 4 to 14, carbon atoms, an aryl radical or an oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur-containing heterocyclic radical.
- examples include n-butyl, n-hexyl, n-octyl and 2-ethyl-o
- Hypophos- phite of cellulose and vinyl alcohol polymers Organic salt-like hypophosphites, such as the salts of 1 mole of melamine with 1 to 3, preferably one mole of hypophosphorous acid, have also proven particularly useful.
- Inorganic salt-like hypophosphites, for example hypophosphites of the formula, are preferably used in the Me a metal cation of the valency n of elements of I., II. and III. Main group, which means subgroup I to VII of the periodic table and the lanthanides, the periodic table being defined in accordance with the Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 14th Edition, published by Chemical Rubber Publishing Co, 2310 Superior Ave.
- NaH 2 PO 2 , Mg (H 2 PO 2 ) 2 , Ca (H 2 PO 2 ), Sn (H 2 PO 2 ) 2 and in particular Al (H 2 PO 23 ) have proven particularly useful.
- hypophosphites mentioned are not commercial products, they can be prepared by known processes.
- hypophosphite 5 to 50 parts by weight, preferably 5 to 25 parts by weight, of the compounds containing halogen or halogen and phosphorus for every 100 parts by weight of organic polyisocyanate.
- the amount of hypophosphite required depends on the effectiveness of the halogen or halogen and phosphorus containing compound.
- modified polyfunctional Is o - cyanates ie products which the above by chemical reaction of di- and / or polyisocyanates are obtained, used.
- modified organic di- and polyisocyanates are: polyisocyanates containing carbodiimide groups according to DE-PS 10 92 007, polyisocyanates containing allophanate groups, as described, for example, in GB-PS 994 890, the documents laid out in Belgian patent 761 626 and NL OS 71 02 524 are described, polyisocyanates containing isocyanurate groups as described, for example, in DE-PS 10 22 789, 12 22 067 and 10 27 394 and DE-OS 19 19 034 and 20 04 048, polyisocyanates containing urethane groups, as they are For example, described in the documents laid out in Belgian patent 752 261 or US Pat.
- polyisocyanates containing acylated urea groups for example according to DE-PS 12 30 778, polyisocyanates containing biuret groups, for example according to DE-PS 11 01 394 and GB-PS 889 050;
- Polyisocyanates prepared by telomerization reactions for example in accordance with the documents laid out in Belgian patent 723,640, polyisocyanates containing ester groups, as mentioned, for example, in British Pat. Nos. 965 474 and 10 72 956, US Pat. No. 3,567,765 and German Pat. No. 12 31 688 will.
- polyisocyanates containing urethane groups for example with low molecular weight diols, triols or polypropylene glycols, modified 4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate or tolylene diisocyanate, polyisocyanates containing carbodiimide groups and / or isocyanurate rings, for example on diphenylmethane diisocyanate diisocyanate and / or toluene Basis and in particular tolylene diisocyanates, diphenylmethane diisocyanates, mixtures of
- Diphenylmethane diisocyanates and polyphenyl polymethylene 'polyisocyanates raw MDI
- diphenylmethane diisocyanates and polyphenyl polymethylene 'polyisocyanates raw MDI
- mixtures of tolylene diisocyanates and raw MDI raw MDI
- Polyols polyester instead of the above, alone or can be used as mixtures, can also hanogene, polyols polyester at 10 to 30 0 C liquid mixtures of the above and soluble hard organic components, for example hydroxyl distrronnen polyesters of aromatic dicarboxylic acids and preferably unsubstituted , linear diols, find application.
- the polyols used are preferably polyether polyols with functionalities from 2 to 8, preferably 2 to 4 and hydroxyl numbers from 150 to 800, preferably from 200 to 600, which are prepared by known processes, for example by anionic polymerization with alkali metal hydroxides, such as sodium or Potassium hydroxide or alkali alcoholates, such as sodium or potassium methylate, ethylate or potassium isopropylate as catalysts or by cationic polymerization with Lewis acids, such as antimony pentachloride, boron fluoride etherate and others as catalysts from one or more alkylene oxides having 2 to 4 carbon atoms in the alkylene radical and a starter molecule which contains 2 to 8, preferably 2 to 4 active hydrogen atoms.
- alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium or Potassium hydroxide or alkali alcoholates, such as sodium or potassium methylate, ethylate or potassium isopropylate
- Lewis acids such as antimony pentachloride, boron
- Suitable alkylene oxides are, for example, tetrahydrofuran, 1,3-propylene oxide, 1,2- or 2,3-butylene oxide, styrene oxide, epichlorohydrin and preferably ethylene oxide and 1,2-propylene oxide.
- the alkylene oxides can be used individually, alternately in succession or as mixtures.
- alkanolamines such as ethanolamine, diethanolamine, N-methyl- and N-ethylethanolamine, N-methyl- and N-ethyl-diethanolamine and triethanolamine, ammonia, hydrazine and hydrazides.
- Polyhydric, in particular di- and / or trihydric alcohols such as ethylene glycol, 1,2 and -1,3 propylene glycol, diethylene glycol, dipropylene glycol, 1,4-butylene glycol, 1,6-hexamethylene glycol, glycerol, trimethylol-propane are preferably used. Pentaerythritol, sorbitol and sucrose.
- the polyether polyols can be used individually or in the form of mixtures.
- Crystallite suspensions as described in EP-OS 32980 are also suitable as polyols. They can be used either individually or in the form of mixtures.
- Blowing agents which can be used in the process according to the invention for producing the foams include water which isocyanate groups form to form Carbon dioxide reacts.
- the amounts of water which are expediently used are 0.1 to 3% by weight, based on the weight of polyisocyanate, or 0.1 to 2% by weight, based on the total weight of polyisocyanate and polyol. If necessary, larger quantities of water can also be used.
- blowing agents that can be used are low-boiling liquids which evaporate under the influence of the exothermic polymerization or polyaddition reaction.
- Liquids which are inert to the organic polyisocyanate and have boiling points below 50 ° C. are suitable.
- preferably used liquids are halogenated hydrocarbons, such as methylene chloride, trichlorofluoromethane, dichlorodifluoromethane, dichloromonomofluoromethane, dichlorotetrafluoroethane and 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as methylene chloride, trichlorofluoromethane, dichlorodifluoromethane, dichloromonomofluoromethane, dichlorotetrafluoroethane and 1,1,2-trichloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane.
- low-boiling liquid for the production of the foams depends on the foam density that is to be achieved and, if appropriate, on the use of water. In general, amounts of 5 to 40% by weight, based on organic polyisocyanate, or 2 to 30% by weight, based on the total weight of polyisocyanate and polyol, give satisfactory results.
- Suitable catalysts for accelerating the reaction between the polyols, optionally water and the polyisocyanates are, for example, tertiary amines, such as dimethylbenzylamine, N, N, N ', N' - tetramethyldiaminoethyl ether, bis (dimethylaminopropyl) urea, N-methyl - or N-ethylmorpholine, dimethyl peperazin, 1,2-dimethylimidazole, 1-azabicyclo (3,3,0) octane and preferably triethylenediamine, metal salts such as tin dioctoate, lead octoate, tin diethylhexoate and preferably tin (II) salts and dibutyltin dilaurate as well in particular mixtures of tert. Amines and organic tin salts. 0.1 to 5.0% by weight of catalyst based on tertiary amines and / or 0.
- the usual cyclization and polymerization catalysts for polyisocyanates have proven successful for the production of foams containing isocyanurate groups.
- Examples include: strong bases, such as quaternary ammonium hydroxides, for example benzyltrimethylammonium hydroxide; Alkali metal hydroxides, for example sodium or potassium hydroxide; Alkali metal alkoxides, for example sodium methylate and potassium isopropylate; Trialkylphosphines, for example triethylphosphine; Alkylaminoalkylphenols, for example 2,4,6-tris (dimethylaminomethyl) phenol; 3- and / or 4-substituted pyridines, for example 3- or 4-methylpyridine; metal-organic salts, for example tetrakis (hydroxyethyl) sodium borate; Friedel-Crafts - catalysts, for example aluminum chloride, iron (III) chloride, boron fluoride and zinc chloride and alkali
- the strongly basic N, N ', N "-Tris - (dialkylaminoalkyl) -s-hexahydrotriazines for example the N, N', N" -Tris- (dimethylaminopropyl) -s-hexahydrotriazine, optionally in combination with aliphatic, are used low molecular weight mono- and / or dicarboxylic acids, for example acetic acid and / or adipic acid or aromatic carboxylic acids, such as benzoic acid.
- the suitable amount of catalysts forming isocyanurate groups depends on the effectiveness of the catalyst in question. In general, it has proven advantageous to use 1 to 15 parts by weight, preferably 3.5 to 10 parts by weight, of catalyst for every 100 parts by weight of organic polyisocyanate.
- the catalysts which promote the formation of urethane and isocyanurate groups can also be mixed.
- the rigid foams are produced by the process according to the invention, preferably without the additional use of conventional chain extenders or crosslinking agents. Nevertheless, in some cases, for example for processing reasons, it has proven expedient to use chain extenders or crosslinking agents.
- Suitable chain extenders or crosslinkers have molecular weights of 30 to 600, preferably 60 to 300 and preferably have two active hydrogen atoms.
- aliphatic and / or aromatic diols with 2 to 14, preferably 2 to 6 carbon atoms such as propanediol, pentanediol, 1,6-hexanediol and preferably ethanediol, 1,4-butanediol and bis- (2-hydroxyethyl) hydroquinone
- Diamines such as ethylenediamine and optionally 3,3'- or 3,3 ', 5,5'-di- or tetrasubstituted 4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethanes
- ethanolamines such as triethanolamine and polyhydroxyl compounds, such as glycerol, trimethylolpropane and low molecular weight hydroxyl groups
- Polyalkylene oxides from the aforementioned starting materials are suitable .
- Auxiliaries and additives can also be incorporated into the reaction mixture. Examples include wise stabilizers, hydrolysis protection agents, pore regulators, fungistatic and bacteriostatic substances, dyes, pigments, fillers, surface-active substances and plasticizers.
- organic fillers are: brittle resins as are known as binders for the printing industry, e.g. those based on phenol, rosin or melamine and formaldehyde, polyesters with melting points above 190 ° C., preferably crosslinked polyesters based on di- or higher-functional carboxylic acids with di- or with monomers such as (meth) acrylic acid derivatives, homo- and copolymers of cyclopentadiene, Ketone resins, e.g.
- polyurethane materials based on cyclohexanone and brittle polyurethane materials with melting points greater than 190 ° C, for example crosslinked polyurethanes and polyurethanes containing isocyanurate groups, polyvinyl chloride, polyamide 6 and 6,6, acrylate graft rubbers, butadiene graft rubbers and polyvinyl acetate.
- Inorganic fillers such as the conventional fillers, reinforcing agents, weighting agents, agents for improving the abrasion behavior in paints, coating agents, etc.
- inorganic pigments can also be used.
- silicate minerals for example layered silicates such as antigorite, serpentine, hornblende, amphiboles, chrisotile, talc, metal oxides such as kaolin, aluminum oxide hydrate, titanium oxides, iron oxides, metal salts such as chalk, heavy spar, barium sulfate, inorganic pigments such as cadmium sulfide , Zinc sulfide and glass.
- Auxiliaries which may also be mentioned are, for example, surface-active substances which serve to support the homogenization of the starting materials and, if appropriate, are also suitable for regulating the cell structure of the foams.
- surface-active substances which serve to support the homogenization of the starting materials and, if appropriate, are also suitable for regulating the cell structure of the foams.
- examples include siloxane-oxyalkylene copolymers and other organopolysiloxanes, ethoxylated alkylphenols, ethoxylated fatty alcohols, paraffin oils, castor oil or castor oil esters and Turkish red oil, which are used in amounts of 0.1 to 5 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of the mixture of polyisocyanate and polyols will.
- the organic polyisocyanates are reacted with the polyols, preferably polyester and / or polyether polyols, in such amounts that the ratio of reactive hydrogen atoms to NCO groups is 1: 0.8 to 2.5, preferably 1: 0 , 9 to 1.2 and in particular approximately 1: 1.
- the foams containing urethane and / or isocyanurate groups are preferably produced by the one-shot process.
- the polyisocyanates are mixed with the Polyols, the catalysts, blowing agents and, if appropriate, auxiliaries and additives are used intensively in the proportions mentioned at temperatures from 0 to 50 ° C., preferably 15 to 40 ° C., and then the reaction mixture is foamed in open or closed forms.
- hypophosphite / halogen system makes it possible to produce foams containing urethane and / or isocyanate groups, which have increased flame resistance, are low brittleness and have good mechanical properties.
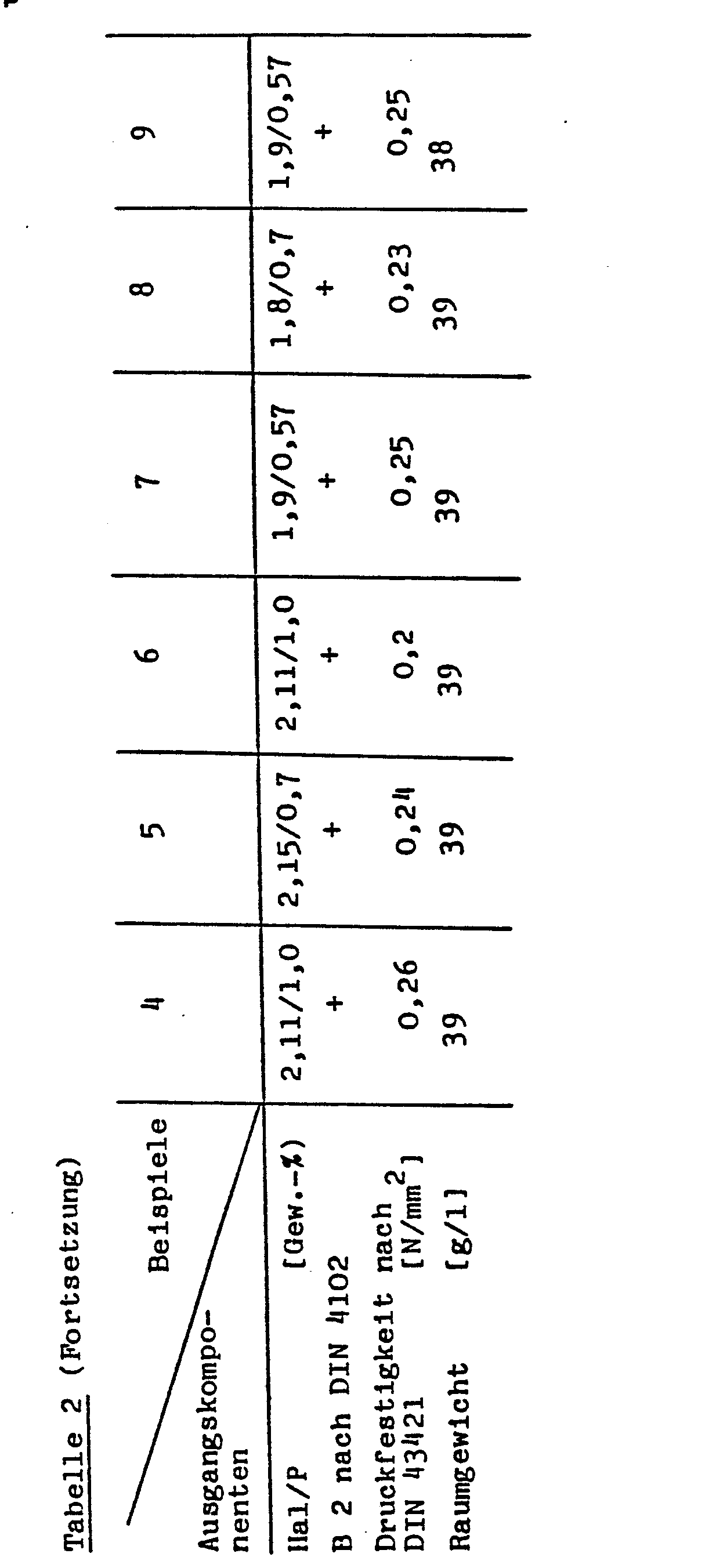
- Component A and component B are mixed intensively at 23 ° C and allowed to foam in a box (size 22 x 22 x 20cm).
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Polyurethanes Or Polyureas (AREA)
- Manufacture Of Porous Articles, And Recovery And Treatment Of Waste Products (AREA)
Abstract
- a) Halogen oder Halogen und Phosphor enthaltenden Verbindungen und
- b) anorganischen und/oder organischen Hypophosphiten als Flammschutzmittel, Katalysatoren und Treibmitteln sowie gegebenenfalls Kettenverlängerungsmitteln, Vernetzern, Hilfsmitteln und Zusatzstoffen.
Description
- Die Herstellung von Polyurethan- und Polyurethangruppen enthaltenden Polyisocyanuratschaumstoffen Ist bekannt. Zur Verbesserung der Flammschutzwirkung können in diese Schaumstoffe halogenhaltige Polyole und/oder Halogen und Phosphor enthaltende Additive incorporiert werden. -
- Zur Verstärkung der Flammschutzwirkung kann man außerdem eine Reihe von Metalloxiden zusetzen, wie z.B. ZnO, B203, Fe203, CaO, Sb203. Diese Verbindungen zeigen selbst keinen Flammschutzeffekt, sie sind aber zusammen mit dem organisch gebundenen Halogen synergistisch wirksam. Als wirksamstes System in Polyurethanschaumstoffen hat sich dabei Antimon--(III)-oxid/Halogen erwiesen (s. W.C. Kuryla u. A.J. Lapa, Flame Retardancy of Polymeric Materials, Bd.3 (Verlag Marcel Dekker, New York, 1975).
- Der Nachteil dabei ist, daß das Antimon-(III)-oxid eine gewisse Versprödung der Schaumstoffe bewirkt. Ebenso sind seine toxikologischen Eigenschaften nicht unbedenklich (vermutlich cancerogen). Schließlich erweist es sich aufgrund seiner großen Härte als schwer einarbeitbar und verursacht Abrasion an den Mischaggregaten der Maschinen.
- Als weitere flammhemmende Zusätze sind in der Literatur eine Reihe von phosphorhaltigen Flammschutzmitteln beschrieben z.B. Phosphate, Phosphonate, Phosphite. Diese Ver- . bindungen, die zum Teil zusätzlich Halogen enthalten, werden entweder allein oder kombiniert mit halogenhaltigen Verbindungen eingesetzt. Einen Synergismus Phosphor/Halogen vergleichbar dem Antimon/Halogen konnte aber bisher nicht nachgewiesen werden (s. E.D. Weil in Flame Retardancy of Polymeric Material Bd. 3; Hindersinn u. Witschard in Flame Retardancy of Polymeric Materials Bd. 4 (Verlag Marcel Dekker, New York, 1978)).
- Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung war es einen Ersatz für Antimon-(III)-oxid zu finden, der einen gleichwertigen Synergismus mit Halogen aufweist, ohne dessen Nachteile zu besitzen.
- Diese Aufgabe konnte überraschenderweise gelöst werden durch die Verwendung von salzartigen anorganischen und/oder organischen Hypophosphiten in Kombination mit den genannten organischen Halogen oder Halogen und Phosphor enthaltenden Verbindungen. Die Hypophosphite haben selbst keine flammhemmende Wirkung.
- Gegenstand der vorliegenden Erfindung ist somit ein Verfahren zur Herstellung von urethan- und/oder isocyanuratgruppenhaltigen, flammwidrigen Schaumstoffen durch Umsetzung von organischen Polyisocyanaten mit Polyolen in Gegenwart von Flammschutzmitteln, Katalysatoren und Treibmitteln sowie gegebenenfalls Kettenverlängerungsmitteln, Vernetzern, Hilfsmitteln und Zusatzstoffen, das dadurch gekennzeichnet ist, daß man als Flammschutzmittel synergistisch wirkende Systeme aus
- a) organischen Halogen oder Halogen und Phosphor enthaltenden Verbindungen und
- b) anorganischen und/oder organischen Eypophosphiten verwendet.
- Setzt man die Hypophosphite in urethan- und/oder isocyanuratgruppenhaltigen Schaumstoffen zusammen mit reaktiven oder additiven organischen, halogenhaltigen oder halogen-und phosphorhaltigen Flammschutzmitteln ein, so zeigen diese Verbindungen eine dem Antimon-(III)-oxid vergleichbare synergistische Wirkung.
- Vorteilhaft ist ferner die leichte Herstellbarkeit der Hypophosphite sowie soweit bekannt, deren relative Ungiftigkeit.
- Die so hergestellten Schaumstoffe weisen eine wesentlich geringere Sprödigkeit auf als entsprechende Antimon-(III)--oxid haltige Schaumstoffe. Sie zeigen gute mechanische Eigenschaften und eine erhöhte Flammbeständigkeit.
- Verglichen mit herkömmlichen phosphor/halogenhaltigen Flammschutzsystemen bringt die erfindungsgemäße Verwendung des Systems Hypophosphit/Halogen eine erhebliche Einsparung an Halogenverbindungen. Diese Einsparung an Flammschutzmitteln wirkt sich auf die mechanischen Eigenschaften der Schäume positiv aus. Bei den bisher im Polyurethan als Flammschutzmittel eingesetzten additiven Phosphorverbindungen ist bekannt, daß sie in größerer Menge eine gewisse Weichmacherwirkung haben. Dies ist bei den Hypophosphiten nicht der Fall, da nur geringe Mengen notwendig sind, um die Wirkung des Halogens zu verstärken.
- Für das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren verwendbar sind organische, organisch salzartige und vorzugsweise anorganisch salzartige Hypophosphite.
- Als organische Hypophosphite kommen z.B. in Betracht: Hypophosphite von ein- und mehrwertigen Alkoholen, wie z.B. solche der Formel R-0-PH20, in der R einen linearen oder verzweigten Alkylrest mit 1 bis 20, vorzugsweise 4 bis 14 C-Atomen, einen Arylrest oder einen Sauerstoff, Stickstoff oder Schwefel enthaltenden heterocyclischen Rest, bedeutet. Im einzelnen seien beispielhaft genannt n-Butyl, n-Hexyl-, n-Octyl- und 2-Ethyl-octylhypophosphit, 1,6-Hexandiol-, 1.10-Decandiolhypophosphit und 1.10-Decandiol-dihypophosphit. Weiterhin kommen in Betracht Hypophos- phite von Cellulose- und Vinylalkohol-Polymerisaten. Besonders bewährt haben sich auch organisch salzartige Hypophcsphite, wie z.B. die Salze von 1 Mol Melamin mit 1 bis 3, vorzugsweise einem Mol unterphosphoriger Säure. Vorzugsweise Anwendung finden anorganische salzartige Hypophosphite, z.B. Hypophosphite der Formel
Doppelhypophosphite der Formel
komplexe Hypophosphite der Formeln - Besonders bewährt haben sich und daher vcrzugsweise verwendet werden NaH2PO2, Mg(H2PO2)2, Ca(H2PO2), Sn(H2PO2)2 und insbesondere Al(H2PO23).
- Soweit die genannten Hypophosphite keine Handelsprodukte sind, können sie nach bekannten Verfahren hergestellt werden.
- Wie bereits dargelegt wurde, bewirken die erfindungsgemäß verwendbaren Hypophosphite jedoch nur in Kombination mit Halogen oder Halogen und Phosphor enthaltenden Verbindungen, beispielsweise üblichen Flammschutzmittel der genannten Art, eine Verbesserung der Flammwidrigkeit. Vorzugsweise verwendet werden solche Halogen oder Halogen und Phosphor enthaltende Verbindungen, die zusätzlich noch Substituenten mit reaktiven Wasserstoffatomen, wie z.B. Amino-, Carboxyl- und/oder Hydroxylgruppen oder Epoxidreste gebunden enthalten. Im einzelnen seien beispielhaft genannt:
- a) Nicht reaktive halogenhaltige oder halogen- und phosphorhaltige Verbindungen wie z.B. Perchlordiphenyl, Perchlortriphenyl usw. Hexabrombenzol, Octabromdiphenyl, Dekabromdiphenyl, Pentabromdiphenyl, Dekabromdiphenyl-, Pentabromdiphenylether, Halogenparaffine, Hexachlorcyclopentadien, Pentabromchlorcyclohexan, Hexabromcyclododecan, Tris-(2,3-dichlor)propylphos- phat, Tetrakis(2-chlorethyl)ethylendiphosphat, Tris-2--chlorethylphosphat.
- b) Mit NCO-Gruppen reaktive halogenhaltige Verbindungen, wie z.B. Mono-, Di- oder Tribromphenol, Tetrachlor-, Tetrabromphthalsäure, Tetrachlor-, Tetrabromphthalsäuremonoester oder -diester mit Diolen und/oder Triolen, Tetrabrom-bis-phenolidl-β-hydroxy-ethylamino-octachlorbiphenyl, Dibrombutendiol, 2,3-Dibrombernsteinsäure, 2,3-Dibrompropionsäure oder deren Monoester mit Diolen und/oder Triolen. Epichlorhydrin, Epibromhydrin, Hexachlor-endomethylen-cyclohexandicarbonsäure, deren Monoester oder Diester mit Diolen und/oder Triolen, -cyclohexandiol, Pentabromphenol, Tetrabrombrenzcatechin, Tetrabromhydrochinon, Trichlorbutylenoxid-Polymer und Butindiol-Epichlorhydrin-Umsetzungsprodukte. Die beispielhaft genannten Verbindungen können gegebenenfalls durch Addition von Alkylenoxiden, wie z.B. Ethylen-und/oder Propylenoxid, modifiziert werden. In Betracht kommen insbesondere halogenhaltige Polyether--polyole, wie sie in der DE-AS 2445 571 (US-PSen 4 020 024 und 4 067 911) beschrieben werden.
- c) mit NCO-Gruppen reaktive halogen- und phosphorhaltige Verbindungen, wie z.B. Halogen-Phosphor-Polyole der Formel
- Im allgemeinen hat es sich als vorteilhaft erwiesen, 5 bis 50 Gew.-Teile, vorzugsweise 5 bis 25 Gew.-Teile der Halogen- oder Halogen und Phosphor enthaltenden Verbindungen für jeweils 100 Gew.-Teile an organischem Polyisocyanat zu verwenden. Die erforderliche Menge an Hypophosphit ist abhängig von der Wirksamkeit der Halogen oder Halogen und Phosphor enthaltenden Verbindung. Zweckmäßigerweise verwendet man ungefähr 0,1 bis 5 Gew.-%, vorzugsweise 1 bis 2.5 Gew.-% Hypophosphit, bezogen auf das Gesamtgewicht von Polyisocyanat und Polyolen.
- Zu den für das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren verwendbaren Ausgangskomponenten ist folgendes auszuführen:
- Als Polyisocyanate kommen aliphatische, cycloaliphatische, araliphatische und vorzugsweise aromatische mehrwertige Isocyanate in Frage. Im einzelnen seien beispielhaft genannt: Alkylehdiisocyanate mit 4 bis 12 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkylenrest, wie 1,12-Dodecamethylen-diisocyanat, Tetramethylen-diisocyanat-1,4 und vorzugsweise Hexamethylen-diisocyanat-1,6; cycloaliphatische Diisocyanate, wie Cyclohexan-1,3- und -1,4-diisocyanat sowie beliebige Gemische dieser Isomeren, 1-Isocyanato-3,3,5-trimethyl-5-isocyanatomethyl-cyclohexan (Isophoron-diisocyanat) 2,4- und 2,6-Hexahydrotoluylen-diisocyanat sowie entsprechende Isomerengemische, 4,4'-, 2,2'- und 2,4'-bicyclohexylmethan-diisocyanat sowie die entsprechenden Isomerengemische und vorzugsweise aromatische Di- und Polyisocyanate wie 4,4'-, 2,4'- und 2,2'-Diisocyanato-diphenylmethan und die entsprechenden Isomerengemische, 2,4- und 2,6-Diisocyanato-toluol und die entsprechenden Isomerengemische, 1,5-Diisocyanato-naphthalin, Polyphenyl-polymethylen-polyisocyanate, 2,4,6-Triisocyanato-toluol und vorzugsweise Gemische aus Diphenylmethan-diisocyanaten und Polyphenyl-polymethylen-polyisocyanaten. Die genannten Di- und Polyisocyanate können einzeln oder in Form von Mischungen eingesetzt werden.
- Häufig werden auch sogenannte modifizierte mehrwertige Iso- cyanate, d.h. Produkte, die durch chemische Umsetzung obiger Di- und/oder Polyisocyanate erhalten werden, verwendet. Als modifizierte organische Di- und Polyisocyanate kommen beispielsweise in Betracht: Carbodiimidgruppen aufweisende Polyisocyanate gemäß DE-PS 10 92 007, Allophanatgruppen aufweisende Polyisocyanate, wie sie z.B. in der GB-PS 994 890, den ausgelegten Unterlagen des belgischen Patents 761 626 und der NL-OS 71 02 524 beschrieben werden, Isocyanuratgruppen aufweisende Polyisocyanate wie sie z.B. in den DE-PSen 10 22 789, 12 22 067 und 10 27 394 sowie den DE-OSen 19 29 034 und 20 04 048 beschrieben werden, Urethangruppen aufweisende Polyisocyanate, wie sie z.B. in den ausgelegten Unterlagen des belgischen Patents 752 261 oder der US-PS 3 394 164 beschrieben werden, acylierte Harnstoffgruppen aufweisende Polyisocyanate z.B. gemäß DE-PS 12 30 778, Biuretgruppen aufweisende Polyisocyanate z.B. gemäß DE-PS 11 01 394 und GB-PS 889 050; durch Telomerisationsreaktionen hergestellte Polyisocyanate z.B. entsprechend den ausgelegten Unterlagen des belgischen Patents 723 640, Estergruppen aufweisende Polyisocyanate, wie sie z.B. in der GB-PS 965 474 und 10 72 956, der US-PS 3 567 765 und der DE-PS 12 31 688 genannt werden.
- Vorzugsweise kommen jedoch zur Anwendung: urethangruppenhaltige Polyisocyanate, beispielsweise mit niedermolekularen Diolen, Triolen oder Polypropylenglykolen, modifiziertes 4,4'-Diphenylmethan-diisocyanat oder Toluylen-diisocyanat, Carbodiimidgruppen und/oder Isocyanuratringe enthaltende Polyisocyanate, z.B. auf Diphenylmethan-diisocyanat und/ oder Toluylendiisocyanat-Basis und insbesondere Toluylendiisocyanate, Diphenylmethan-diisocyanate, Mischungen aus
- Diphenylmethan-diisocyanaten und Polyphenyl-polymethylen- ' -polyisocyanaten (Roh-MDI) und Gemische aus Toluylendiisocyanaten und Roh-MDI.
- Als Polyole kommen beispielsweise in Betracht:
- Polyester-polyole mit Funktionalitäten von 2 bis 6, vorzugsweise 2 bis 4 und Hydroxylzahlen von 200 bis 700, vorzugsweise von 280 bis 490 auf Basis von organischen Dicarbonsäuren, vorzugsweise aliphatischen Dicarbonsäuren mit 2 bis 12, vorzugsweise 4 bis 8 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkylenrest und mehrwertigen Alkoholen, vorzugsweise Diolen. Genannt seien beispielhaft aliphatische Dicarbonsäuren, wie Bernsteinsäure, Glutarsäure, Pimelinsäure, Undecandisäure, Dodecandisäure und vorzugsweise Adipinsäure und aromatische Dicarbonsäuren, wie Phthalsäure und Terephthalsäure. Beispiele für zwei- und mehrwertige, insbesondere zweiwertige Alkohole sind: 1,2- bzw. 1,3-Propylenglykol, Dipropylenglykol, 1,5-Pentamethylenglykol, 1,8-Octamethylenglykol, Decamethylenglykol-1,10, Glycerin, Trimethylol- propan, Pentaerythrit sowie Zuckeralkohole, z.B. Sorbit und vorzugsweise Ethylenglykol, Diethylenglykol, 1,4-Butylenglykol und 1,6-Hexamethylenglykol. Als mehrwertige Alkohole können ferner Alkanolamine, Dialkanolamine und Trialkanolamine, z.B. Ethanolamin, Diethanolamin, Triethanolamin und Triisopropanolamin verwendet werden. Die genannten Dicarbonsäuren und mehrwertigen Alkohole können auch in Form von Mischungen eingesetzt werden. Besonders bewährt haben sich und daher vorzugsweise verwendet werden Polyester-polyole aus Adipinsäure oder Mischungen aus Bernstein-, Glutar- und Adipinsäure und Diethylenglykol und Alkoholmischungen aus Ethylenglykol/l,4-Butylenglykol, Ethylenglykol/Diethylenglykol, Ethylenglykol/Trimethylolpropan, Diethylenglykol/Trimethylolpropan, Ethylenglykol/ Pentaerythrit, Ethylenglykol/Triisopropanolamln und Diethylenglykol/Triisopropanolamin.
- Anstelle der genannten Polyester-polyole, die einzeln oder als Gemische eingesetzt werden können, können auch hanogene, bei 10 bis 300C flüssige Mischungen aus den oben genannten Polyester-polyolen und löslichen harten organischen Komponenten, z.B. hydroxylgrupperhaltigen Polyestern aus aromatischen Dicarbonsäuren und vorzugsweise unsubstituierten, linearen Diolen, Anwendung finden.
- Vorzugsweise als Polyole verwendet man jedoch Polyether--polyole mit Funktionalitäten von 2 bis 8, vorzugsweise 2 bis 4 und Hydroxylzahlen von 150 bis 800, vorzugsweise von 200 bis 600, die nach bekannten Verfahren, beispielsweise durch anionische Polymerisation mit Alkalihydroxiden, wie Natrium- oder Kaliumhydroxid oder Alkalialkoholaten, wie Natrium- oder Kaliummethylat, -ethylat oder Kaliumisopropylat als Katalysatoren oder durch kationische Polymerisation mit Lewissäuren, wie Antimonpentachlorid, Borfluorid--Etherat u.a. als Katalysatoren aus einem oder mehreren Alkylenoxiden mit 2 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkylenrest und einem Startermolekül, das 2 bis 8, vorzugsweise 2 bis 4 aktive Wasserstoffatome enthält, hergestellt werden.
- Geeignete Alkylenoxide sind beispielsweise Tetrahydrofuran, 1,3-Propylenoxid, 1,2- bzw. 2,3-Butylenoxid, Styroloxid, Epichlorhydrin und vorzugsweise Ethylenoxid und 1,2-Propylenoxid. Die Alkylenoxide können einzeln, alternierend nacheinander oder als Mischungen verwendet werden.
- Als Startermoleküle kommen beispielsweise in Betracht:
- Wasser, organische Dicarbonsäuren, wie Bernsteinsäure, Adipinsäure, Phthalsäure und Terephthalsäure, aliphatische und aromatische, gegebenenfalls N-mono-, N,N- und N,N'-di- alkylsubstituierte Diamine mit 1 bis 4 Kohlenstoffatomen im Alkylrest, wie gegebenenfalls mono- und dialkylsubstituiertes Ethylendiamin, Diethylentriamin, Triethylentetramin, 1,3-Propylendiamin, 1,3- bzw. 1,4-Butylendiamin, 1,2-, 1,3-, 1,4-, 1,5- und 1,6-Hexamethylendiamin, Phenylendiamine, 2,4- und 2,6-Toluylendiamin und 4,4'-, 2,4'- und 2,2'-Diamino-diphenylmethan. Als Polyether-polyole, hergestellt aus Verbindungen der erwähnten Gruppe sind besonders interessant N,N,N',N'-Tetrakis-(2-hydroxyethyl)-ethylendiamin, N,N,N',N'-Tetrakis-(2-hydroxypropyl)-ethylendiamin, N,N,N',N",N"-Pentakis-(2-hydroxypropyl)-diethylentriamin, Phenyldiisopropanolamin und höhere Alkylenoxidaddukte von Anilin.
- Als Startermoleküle kommen ferner in Betracht Alkanolamine, wie Ethanolamin, Diethanolamin, N-Methyl- und N-Ethylethanolamin, N-Methyl- und N-Ethyl-diethanolamin und Triethanolamin, Ammoniak, Hydrazin und Hydrazide. Vorzugsweise verwendet werden mehrwertige, insbesondere zwei- und/oder dreiwertige Alkohole, wie Ethylenglykol, Propylenglykol-1,2 und -1,3, Diethylenglykol, Dipropylenglykol, Butylenglykol-1,4, Hexamethylenglykol-1,6, Glycerin, Trimethylol-propan, Pentaerythrit, Sorbit und Saccharose.
- Die Polyether-polyole können ebenso wie die Polyester--polyole einzeln oder in Form von Mischungen verwendet werden.
- Als Polyole kommen ferner Kristallitsuspensionen in Betracht, wie sie in der EP-OS 32980 beschrieben sind. Sie können entweder einzeln oder in Form von Mischungen eingesetzt werden.
- Zu-Treibmitteln, welche im erfindungsgemäßen Verfahren zur Herstellung der Schaumstoffe verwendet werden können, gehört Wasser, das mit Isocyanatgruppen unter Bildung von Kohlendioxid reagiert. Die Wassermengen, die zweckmäßigerweise verwendet werden, betragen 0,1 bis 3 Gew.-%, bezogen auf das Gewicht an Polyisocyanat, bzw. 0,1 bis 2 Gew.-%, bezogen auf das Gesamtgewicht von Polyisocyanat und Polyol. Gegebenenfalls können auch größere Wassermengen verwendet werden.
- Andere verwendbare Treibmittel sind niedrig siedende Flüssigkeiten, die unter dem Einfluß der exothermen Polymerisation- bzw. Polyadditionsreaktion verdampfen. Geeignet sind Flüssigkeiten, welche gegenüber dem organischen Polyisocyanat inert sind und Siedepunkte unter 50°C aufweisen. Beispiele derartiger, vorzugsweise verwendeter Flüssigkeiten sind halogenierte Kohlenwasserstoffe, wie Methylenchlorid, Trichlorfluormethan, Dichlordifluormethan, Dichlormonofluormethan, Dichlortetrafluorethan und 1,1,2-Trichlor-1,2,2-trifluorethan. Auch Gemische dieser niedrigsiedenden Flüssigkeiten untereinander und/oder mit anderen substituierten oder unsubstituierten Kohlenwasserstoffen können verwendet werden.
- Die zweckmäßigste Menge an niedrigsiedender Flüssigkeit zur Herstellung der Schaumstoffe hängt ab von der Schaumdichte, die man erreichen will, sowie gegebenenfalls von der Mitverwendung von Wasser. Im allgemeinen liefern Mengen von 5 bis 40 Gew.-%, bezogen auf organisches Polyisocyanat, bzw. 2 bis 30 Gew.-%, bezogen auf das Gesamtgewicht von Polyisocyanat und Polyol zufriedenstellende Ergebnisse.
- Geeignete Katalysatoren zur Beschleunigung der Reaktion zwischen den Polyolen, gegebenenfalls Wasser und den Polyisocyanaten sind beispielsweise tertiäre Amine, wie Dimethylbenzylamin, N,N,N',N'--Tetramethyldiamino-ethylether, Bis-(dimethylaminopropyl)--harnstoff, N-Methyl- bzw. N-Ethylmorpholin, Dimethylpeperazin, 1,2-Dimethylimidazol, 1-Aza-bicyclo-(3,3,0)--octan und vorzugsweise Triethylendiamin, Metallsalze, wie Zinndioctoat, Bleioctoat, Zinn-diethylhexoat und vorzugsweise Zinn-(II)-salze und Dibutylzinndilaurat sowie insbesondere Mischungen aus tert. Aminen und organischen Zinnsalzen. Vorzugsweise verwendet werden 0,1 bis 5,0 Gew.-% Katalysator auf Basis tertiärer Amine und/oder 0,01 bis 1,0 Gew.-% Metallsalze, bezogen auf das Gewicht der Polyole.
- Zur Herstellung von isocyanuratgruppenhaltigen Schaumstoffen haben sich die üblichen Cyclisierungs- und Polymerisationskatalysatoren für Polyisocyanate bewährt. Als Beispiele seien genannt: starke Basen, wie quarternäre Ammoniumhydroxide, beispielsweise Benzyltrimethylammoniumhydroxid; Alkalimetallhydroxide, beispielsweise Natrium- oder Kaliumhydroxid; Alkalimetallalkoxide, beispielsweise Natriummethylat und Kaliumisopropylat; Trialkylphosphine, beispielsweise Triethylphosphin; Alkylaminoalkylphenole, beispielsweise 2,4,6-Tris-(dimethylaminomethyl)-phenol; 3- und/oder 4-substituierte Pyridine, beispielsweise 3-oder 4-Methylpyridin; metall-organische Salze, beispielsweise Tetrakis-(hydroxyethyl)-natriumborat; Friedel-Crafts--Katalysatoren, beispielsweise Aluminiumchlorid, Eisen-(III)--chlorid, Borfluorid und Zinkchlorid und Alkalimetallsalze von schwachen organischen Säuren und Nitrophenolaten, beispielsweise Kaliumoctoat, Kalium-2-ethyl-hexoat, Kaliumbenzoat, Natriumpikrat und Phthalimid-kalium. Vorzugsweise verwendet werden die stark basischen N,N',N"-Tris--(dialkylaminoalkyl)-s-hexahydrotriazine, beispielsweise das N,N',N"-Tris-(dimethylaminopropyl)-s-hexahydrotriazin, gegebenenfalls in Kombination mit aliphatischen niedermolekularen Mono- und/oder Dicarbonsäuren, beispielsweise Essigsäure und/oder Adipinsäure oder aromatischen Carbonsäuren, wie Benzoesäure.
- Die geeignete Menge an Isocyanuratgruppen bildenden Katalysatoren ist abhängig von der Wirksamkeit des in Frage kommenden Katalysators. Im allgemeinen hat es sich als zweckmäßig erwiesen, 1 bis 15 Gewichtsteile, vorzugsweise 3,5 bis 10 Gewichtsteile Katalysator für jeweils 100 Gewichtsteile an organischem Polyisocyanat zu verwenden.
- Zur Herstellung von Urethan- und Isocyanuratgruppen-enthaltenden Schaumstoffen können die die Urethan- und Isocyanuratgruppenbildung fördernde Katalysatoren auch gemischt werden.
- Nach dem erfindungsgemäßen Verfahren werden die Hartschaumstoffe, vorzugsweise ohne zusätzliche Mitverwendung von üblichen Kettenverlängerungsmitteln oder Vernetzern hergestellt. Dennoch hat es sich in manchen Fällen, beispielsweise aus verarbeitungstechnischen Gründen, als zweckmäßig erwiesen, Kettenverlängerungsmittel oder Vernetzer einzusetzen. Geeignete Kettenverlängerungsmittel oder Vernetzer besitzen Molekulargewichte von 30 bis 600, vorzugsweise 60 bis 300 und weisen vorzugsweise zwei aktive Wasserstoffatome auf. In Betracht kommen beispielsweise aliphatische und/oder aromatische Diole mit 2 bis l4, vorzugsweise 2 bis 6 Kohlenstoffatomen, wie Propandiol, Pentandiol, Hexandiol-1,6 und vorzugsweise Ethandiol, Butandiol-1,4 und Bis-(2-hydroxyethyl)-hydrochinon, Diamine, wie Ethylendiamin und gegebenenfalls 3,3'- bzw. 3,3',5,5'-di- bzw. tetrasubstituierte 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane, Ethanolamine, wie Triethanolamin und Polyhydroxylverbindungen, wie Glycerin, Trimethylolpropan und niedermolekulare hydroxylgruppenhaltige Polyalkylenoxide aus den vorgenannten Ausgangsstoffen.
- Der Reaktionsmischung können auch noch Hilfsmittel und Zusatzstoffe einverleibt werden. Genannt seien beispiels- weise Stabilisatoren, Hydrolyseschutzmittel, Porenregler, fungistatisch und bakteriostatisch wirkende Substanzen, Farbstoffe, Pigmente, Füllstoffe, oberflächenaktive Stoffe und Weichmacher.
- .Als organische Füllstoffe seien beispielhaft genannt: Sprödharze, wie sie bekannt sind als Bindemittel für die Druckindustrie, z.B. solche auf Basis Phenol, Kolophonium oder Melamin und Formaldehyd, Polyester mit Schmelzpunkten größer 190°C, vorzugsweise vernetzte Polyester auf Basis von di- oder höherfunktionellen Carbonsäuren mit Di- oder mit Monomeren wie (Meth)- acrylsäurederivaten, Homo- und Copolymerisate des Cyclopentadiens, Ketonharze, z.B. auf Basis von Cyclohexanon und spröde Polyurethanmaterialien, mit Schmelzpunkten größer als 190°C, beispielsweise vernetzte Polyurethane und Isocyanuratgruppen enthaltende Polyurethane, Polyvinylchlorid, Polyamid-6 und -6,6, Acrylatpfropfkautschuke, Butadienpfropfkautschuke sowie Polyvinylacetat.
- Besonders bewährt haben sich und daher vorzugsweise verwendet werden jedoch anorganische Füllstoffe, wie die an sich bekannten üblichen Füllstoffe, Verstärkungsmittel, Beschwerungsmittel, Mittel zur Verbesserung des Abriebverhaltens in Anstrichfarben, Beschichtungsmittel usw. Verwendet werden können jedoch auch anorganische Pigmente. Im einzelnen seien beispielhaft genannt: silikatische Mineralien, beispielsweise Schichtsilikate, wie Antigorit, Serpentin, Hornblenden, Amphibole, Chrisotil, Talkum, Metalloxide, wie Kaolin, Aluminiumoxidhydrat, Titanoxide, Eisenoxide, Metallsalze, wie Kreide, Schwerspat, Bariumsulfat, anorganische Pigmente, wie Cadmiumsulfid, Zinksulfid sowie Glas.
- Als Hilfsmittel genannt seien ferner beispielsweise oberflächenaktive Substanzen, welche zur Unterstützung der Homogenisierung der Ausgangsstoffe dienen und gegebenenfalls auch geeignet sind, die Zellstruktur der Schaumstoffe zu regulieren. Genannt seien beispielhaft Siloxan--Oxyalkylen-Mischpolymerisate und andere Organopolysiloxane, oxethylierte Alkylphenole, oxethylierte Fettalkohole, Paraffinöle, Rizinusöl- bzw. Rizinolsäureester und Türkischrotöl, die in Mengen von 0,1-bis 5 Gewichtsteilen pro 100 Gewichtsteile der Mischung aus Polyisocyanat und Polyolen angewandt werden.
- Nähere Angaben über die obengenannten anderen üblichen Zusatzstoffe sind der Fachliteratur, beispielsweise der Monographie von J.H. Saunders und K.C. Frisch "High Polymers" Band XIV, Polyurethanes, Teil 1 und 2, Verlag Interscience Publishers 1962 bzw. 1964, zu entnehmen.
- Zur Herstellung von urethangruppenhaltigen Schaumstoffen werden die organischen Polyisocyanate mit den Polyolen, vorzugsweise Polyester- und/oder Polyetherpolyolen in solchen Mengen zur Umsetzung gebracht, daß das Verhältnis von reaktiven Wasserstoffatomen zu NCO-Gruppen 1:0,8 bis 2,5 vorzugsweise 1:0,9 bis 1,2 und insbesondere ungefähr 1:1 beträgt.
- Zur Herstellung von Urethan- und Isocyanuratgruppen enthaltenden Schaumstoffen haben sich Mengenverhältnisse von NCO-Gruppen der Polyisocyanate zu reaktiven Wasserstoffatomen der Polyole von 6 bis 60:1, vorzugsweise von 2 bis 10:1 bewährt.
- Die urethan- und/oder isocyanuratgruppenhaltigen Schaumstoffe werden vorzugsweise nach dem one shot Verfahren hergestellt. Hierzu mischt man die Polyisocyanate mit den Polyolen, den Katalysatoren, Treibmittel und gegebenenfalls Hilfs- und Zusatzstoffen intensiv in den genannten Mengenverhältnissen bei Temperaturen von 0 bis 50°C, vorzugsweise 15 bis 40°C und läßt danach die Reaktionsmischung in offenen oder geschlossenen Formen aufschäumen.
- Das System Hypophosphit/Halogen erlaubt es urethan- und/ oder isocyanatgruppenhaltige Schaumstoffe herzustellen, die eine erhöhte Flammbeständigkeit aufweisen, von geringer Sprödigkeit sind und gute mechanische Eigenschaften besitzen.
- A-Komponente: Mischung aus
- Polyol
- Flammschutzmittel
- Hypophosphit
- Trichlorfluormethan
- Schaumstabilisator und
- Katalysator
- B-Komponente: Mischung aus
- Diphenylmethan-diisocyanaten und
- Polyphenyl-polymethylen-polyisocyanaten (Roh-MDI; NCO-Gehalt: 31 Gew.-%)
- Die Komponente A und die Komponente B werden bei 23°C intensiv gemischt und in einem Karton (Größe 22 x 22 x 20cm) aufschäumen lassen.
- Die Art und Mengen der verwendeten Ausgangskomponenten sowie das Raumgewicht und Brandverhalten der erhaltenen Schaumstoffe sind in den folgenden Tabellen zusammengefaßt.
- Für die in den Tabellen genannten Ausgangskomponenten wurden folgende Abkürzungen gewählt:
- Roh-MDI:
- Mischung aus Diphenylmethan-diisocyanaten und Polyphenyl--polymethylen-polyisocyanaten. NCO-Gehalt 31 %
- Kristallitsusp.:
- Kristallitsuspension mit einer OH-Zahl 265, bestehend aus 48 Teilen eines Sucrosepolyols, 28 Teilen Diethylenglykoladipat und 24 Teilen Neopentylglykolisophthalat.
- (R)Thermolin RF 230:
- Halogenhaltiges Flammschutzmittel auf Basis eines Trichlorbutylenoxid-Polymeren. Handelsprodukt der Firma Olin
- G 70-600:
- Polyol wird als Zusatz zu Thermolin RP 230 empfohlen, Handelsprodukt der Firma Olin
- (R)Ixol B 251:
- Halogen und Phosphor enthaltendes Flammschutzpolyol. Handelsprodukt der Firma Solvay
- (R) Bromkal 70:
- Gemisch bromierter Diphenylether, Handelsprodukt der Chemische Fabrik Kalk
- DC 193:
- Schaumstabilisator auf Silikonbasis. Handelsprodukt der Firma Dow Corning
- PCF:
- Trischlorpropylphosphat
- TEA:
- Triethylamin
- Kat:
- Kaliumformiat; 35 %ige Lösung in Ethylenglykol
- R 11:
- Trichlorfluormethan
- Hal/P:
- Halogenphosphorgehalt in Gew.-%, bezogen auf die Gesamtmenge Polyisocyanat und Polyol
- (R)Dabco TMR 2:
- Katalysator auf Basis Trimethyl-2-hydroxypropylammonium- formiat, Handelsprodukt der Firma Air Products
- Polyol A:
- auf Basis Saccharose/Propylenoxid OH-Zahl: 400
- Polyol B:
- Polypropylenglykol mit der OH-Zahl 250.
und
Claims (6)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT82106046T ATE12782T1 (de) | 1981-07-15 | 1982-07-07 | Verfahren zur herstellung von flammwidrigen polyurethan- und/oder polyisocyanuratgruppen enthaltenden schaumstoffen. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19813127914 DE3127914A1 (de) | 1981-07-15 | 1981-07-15 | Verfahren zur herstellung von flammwidrigen polyutheran- und/oder polyisocyanuratgruppen enthaltenden schaumstoffen |
| DE3127914 | 1981-07-15 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0069975A1 true EP0069975A1 (de) | 1983-01-19 |
| EP0069975B1 EP0069975B1 (de) | 1985-04-17 |
Family
ID=6136958
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP82106046A Expired EP0069975B1 (de) | 1981-07-15 | 1982-07-07 | Verfahren zur Herstellung von flammwidrigen Polyurethan- und/oder Polyisocyanuratgruppen enthaltenden Schaumstoffen |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0069975B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE12782T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE3127914A1 (de) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1988000199A1 (en) * | 1986-07-09 | 1988-01-14 | Richard John Maerschel | New thiophosphate ester; also polyurethane foam or prepolymer, containing tris- and bis- (2,4,6-tribromophenoxy) (thio) phosphate |
| CN101570518B (zh) * | 2009-06-12 | 2010-11-17 | 东华大学 | 一种膨胀型三聚氰胺次磷酸盐阻燃剂的制备方法 |
| WO2020030549A1 (de) | 2018-08-08 | 2020-02-13 | Covestro Deutschland Ag | Phosphinat als flammschutzadditiv für pur-/pir-hartschaumstoffe |
| JP2020143194A (ja) * | 2019-03-05 | 2020-09-10 | 大和化学工業株式会社 | 難燃性ポリウレタン樹脂組成物 |
| WO2020204113A1 (ja) * | 2019-04-01 | 2020-10-08 | 大和化学工業株式会社 | ポリウレタンフォーム用難燃剤組成物及びこれを配合した難燃性ポリウレタンフォーム |
| CN113015757A (zh) * | 2018-11-26 | 2021-06-22 | 旭有机材株式会社 | 不燃性聚氨酯泡沫用发泡性组合物 |
| JP2021130801A (ja) * | 2019-04-01 | 2021-09-09 | 大和化学工業株式会社 | ポリウレタンフォーム用難燃剤組成物及びこれを配合した難燃性ポリウレタンフォーム |
| CN114989105A (zh) * | 2022-07-15 | 2022-09-02 | 什邡市太丰新型阻燃剂有限责任公司 | 无污染合成超细三聚氰胺次磷酸盐的方法及其阻燃方法 |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3631146A (en) * | 1966-06-22 | 1971-12-28 | Ici Ltd | Polymeric materials |
-
1981
- 1981-07-15 DE DE19813127914 patent/DE3127914A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1982
- 1982-07-07 AT AT82106046T patent/ATE12782T1/de active
- 1982-07-07 DE DE8282106046T patent/DE3263120D1/de not_active Expired
- 1982-07-07 EP EP82106046A patent/EP0069975B1/de not_active Expired
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3631146A (en) * | 1966-06-22 | 1971-12-28 | Ici Ltd | Polymeric materials |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| W.C. KURYLA et al.: "Flame retardancy of polymeric materials", Band 3, 1975, Seiten 32-60, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, USA * |
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1988000199A1 (en) * | 1986-07-09 | 1988-01-14 | Richard John Maerschel | New thiophosphate ester; also polyurethane foam or prepolymer, containing tris- and bis- (2,4,6-tribromophenoxy) (thio) phosphate |
| CN101570518B (zh) * | 2009-06-12 | 2010-11-17 | 东华大学 | 一种膨胀型三聚氰胺次磷酸盐阻燃剂的制备方法 |
| WO2020030549A1 (de) | 2018-08-08 | 2020-02-13 | Covestro Deutschland Ag | Phosphinat als flammschutzadditiv für pur-/pir-hartschaumstoffe |
| US11279809B2 (en) | 2018-08-08 | 2022-03-22 | Covestro Intellectual Property Gmbh & Co. Kg | Phosphinate as flame-proofing additive for PUR/PIR hard foam material |
| JP2021533234A (ja) * | 2018-08-08 | 2021-12-02 | コベストロ・インテレクチュアル・プロパティ・ゲゼルシャフト・ミット・ベシュレンクテル・ハフツング・アンド・コー・カーゲー | Pur/pir硬質フォーム材料用の防炎性添加剤としてのホスフィン酸塩 |
| CN112638976A (zh) * | 2018-08-08 | 2021-04-09 | 科思创知识产权两合公司 | 作为pur/pir硬质泡沫材料的阻燃添加剂的次膦酸盐 |
| CN113015757A (zh) * | 2018-11-26 | 2021-06-22 | 旭有机材株式会社 | 不燃性聚氨酯泡沫用发泡性组合物 |
| CN113015757B (zh) * | 2018-11-26 | 2023-07-18 | 旭有机材株式会社 | 不燃性聚氨酯泡沫用发泡性组合物 |
| JP2020143194A (ja) * | 2019-03-05 | 2020-09-10 | 大和化学工業株式会社 | 難燃性ポリウレタン樹脂組成物 |
| JP2021130801A (ja) * | 2019-04-01 | 2021-09-09 | 大和化学工業株式会社 | ポリウレタンフォーム用難燃剤組成物及びこれを配合した難燃性ポリウレタンフォーム |
| WO2020204113A1 (ja) * | 2019-04-01 | 2020-10-08 | 大和化学工業株式会社 | ポリウレタンフォーム用難燃剤組成物及びこれを配合した難燃性ポリウレタンフォーム |
| JP7718009B2 (ja) | 2019-04-01 | 2025-08-05 | 大和化学工業株式会社 | ポリウレタンフォーム用難燃剤組成物及びこれを配合した難燃性ポリウレタンフォーム |
| CN114989105A (zh) * | 2022-07-15 | 2022-09-02 | 什邡市太丰新型阻燃剂有限责任公司 | 无污染合成超细三聚氰胺次磷酸盐的方法及其阻燃方法 |
| CN114989105B (zh) * | 2022-07-15 | 2024-01-12 | 什邡市太丰新型阻燃剂有限责任公司 | 无污染合成超细三聚氰胺次磷酸盐的方法及其阻燃方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3263120D1 (en) | 1985-05-23 |
| DE3127914A1 (de) | 1983-02-03 |
| EP0069975B1 (de) | 1985-04-17 |
| ATE12782T1 (de) | 1985-05-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0111121B1 (de) | Flüssige Urethangruppen enthaltende Polyisocyanatmischungen auf Diphenylmethan-diisocyanat-basis, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und deren Verwendung zur Herstellung von Polyurethan-Weichschaum-stoffen | |
| EP0482507B2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von flammwidrigen Polyurethan-Weichschaumstoffen mit verminderter Rauchgasdichte und Melamin-Blähgraphit-Polyether-polyol-dispersionen hierfür | |
| EP0032380B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von urethan- und/oder isocyanuratgruppenhaltigen Schaumstoffen | |
| EP0433889B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Polyurethan-Weichschaumstoffen mit geringer Stauchhärte und hierfür verwendbare Blockpolyoxypropylen-polyoxyethylen-polyolgemische | |
| EP0056121B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von flexiblen Polyurethan-Weichschaumstoffen sowie hierzu verwendbare Polyester-polyol-Polyether-polyol-Mischungen | |
| DE3636604A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von polyurethanformkoerpern | |
| EP0004879B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Polyurethan-Weichschaumstoffen unter Verwendung einer urethanmodifizierten Mischung aus Diphenylmethan-diisocyanaten und Polyphenyl-polymethylen-polyisocyanaten mit einem Diphenylmethan-diisocyanat-Isomerengehalt von 55 bis 85 Gewichtsprozent als Polyisocyanat | |
| EP0004617A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Polyurethan-Weichschaumstoffen mit hoher Trag- und Stossabsorptionsfähigkeit auf Basis von Roh-MDI mit einem Diphenylmethan-diisocyanatgehalt von 55 bis 85 Gew.% und Polyesterolen | |
| EP0069975B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von flammwidrigen Polyurethan- und/oder Polyisocyanuratgruppen enthaltenden Schaumstoffen | |
| EP0115072B1 (de) | Neue Additionsprodukte aus olefinisch ungesättigten Polyester-polyolen und Alkylenpolyaminen, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung analog der Michael-Reaktion und deren Verwendung als Zusatzmittel für Kunststoffe auf Polyisocyanatbasis und zur Herstellung von Polyurethangruppen enthaltenden Polyisocyanuratschaumstoffen | |
| EP0099531B1 (de) | Stabile Wasserglaslösungen, Verfahren zu deren Herstellung und Verwendung für Organosilikatschaumstoffe sowie ein Herstellungs-verfahren hierfür | |
| EP0017947B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung urethangruppenhaltiger Polyisocyanuratschaumstoffe | |
| EP0124071B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von elastischen, kompakten oder zelligen Polyurethanen | |
| DE3844049A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von flammwidrigen, elastischen polyurethan-weichschaumstoffen und niedrigviskose melamin-polyether-polyoldispersionen hierfuer | |
| EP0761736A2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von flammwidrigen Polyurethan-Weichschaumstoffen | |
| DE3801456A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von flammwidrig ausgeruesteten polyurethan-massen | |
| DE3304889A1 (de) | Fluessige, isocyanuratgruppen enthaltende polyisocyanatmischungen aus 4,4'- und 2,4'-diphenylmethan-diisocyanaten, verfahren zu deren herstellung und deren verwendung fuer polyurethan- oder polyisocyanurat-kunststoffe | |
| EP0377868A2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von flammwidrigen, elastischen Polyurethan-Weichschaumstoffen unter Mitverwendung mindestens eines Polyoxyalkylenpolyamins und Melamin | |
| EP0041618A2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von elastischen Polyurethanschaumstoffen | |
| DE3621264A1 (de) | Geschlossenzellige, flammwidrige urethan- und isocyanuratgruppen enthaltende hartschaumstoffe, verfahren zu deren herstellung und deren verwendung | |
| EP0017948B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Polyurethanschaumstoffen | |
| DE2724609A1 (de) | Chlor- und estergruppenhaltige polyole | |
| EP0045393A1 (de) | Polyether-polyol-Mischungen und deren Verwendung | |
| DE2640011A1 (de) | Phosphor-haltige urethane | |
| DE3006634A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von gegebenenfalls geschaeumten, isocyanuratgruppenhaltigen polyurethanen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19830713 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 12782 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19850515 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3263120 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19850523 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19920619 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19920622 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19920622 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19920625 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19920701 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19920716 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19920731 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19920807 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19930707 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19930707 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19930708 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19930717 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19930731 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19930731 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19930731 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: BASF A.G. Effective date: 19930731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19940201 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19930707 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19940331 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 82106046.4 Effective date: 19940210 |