EP0056550B1 - Dispositif d'orientation selon deux axes orthogonaux, en particulier pour une antenne hyperfréquence - Google Patents
Dispositif d'orientation selon deux axes orthogonaux, en particulier pour une antenne hyperfréquence Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0056550B1 EP0056550B1 EP81402051A EP81402051A EP0056550B1 EP 0056550 B1 EP0056550 B1 EP 0056550B1 EP 81402051 A EP81402051 A EP 81402051A EP 81402051 A EP81402051 A EP 81402051A EP 0056550 B1 EP0056550 B1 EP 0056550B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- axis
- transmission means
- pinion
- fixed
- orientation device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 29
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01Q—ANTENNAS, i.e. RADIO AERIALS
- H01Q3/00—Arrangements for changing or varying the orientation or the shape of the directional pattern of the waves radiated from an antenna or antenna system
- H01Q3/02—Arrangements for changing or varying the orientation or the shape of the directional pattern of the waves radiated from an antenna or antenna system using mechanical movement of antenna or antenna system as a whole
- H01Q3/08—Arrangements for changing or varying the orientation or the shape of the directional pattern of the waves radiated from an antenna or antenna system using mechanical movement of antenna or antenna system as a whole for varying two co-ordinates of the orientation
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T74/00—Machine element or mechanism
- Y10T74/19—Gearing
- Y10T74/19014—Plural prime movers selectively coupled to common output
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T74/00—Machine element or mechanism
- Y10T74/19—Gearing
- Y10T74/19023—Plural power paths to and/or from gearing
- Y10T74/19051—Single driven plural drives
- Y10T74/1906—Nonparallel
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T74/00—Machine element or mechanism
- Y10T74/20—Control lever and linkage systems
- Y10T74/20207—Multiple controlling elements for single controlled element
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a steering device of a driven member along two orthogonal axes of rotation and more particularly to a steering device p Ol, r sings hyperfré- .quence.
- each orientation axis has a motor mechanism which actuates a platform carrying the following orientation axis and its motor.
- the present invention aims to remedy the above drawbacks by proposing an orientation device along two orthogonal axes with which the positioning in azimuth and in elevation can be carried out simultaneously with a single motor.
- the claimed device also has the advantage of releasing a large useful volume thanks to the offset of the motor mechanisms in the fixed part.
- the present invention relates to a device for orienting an element driven along two orthogonal axes
- a device for orienting an element driven along two orthogonal axes comprising a fixed support, a mobile support that can rotate around one of the axes known as the first axis and supporting the driven element by coaxial arms with the other axis called the second axis and decoupled from the mobile support, two motor mechanisms positioned in the fixed part capable of giving movements along each of the axes, characterized in that one of the motor mechanisms controls a transmission means giving simultaneous movement of rotation around each axis and the other motor mechanism controls a set of transmission means giving only a rotational movement around the second axis.
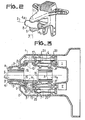
- FIG. 1 represents a perspective view of a device of the prior art used to orient a radar antenna.
- the motor 31 drives a pinion (not visible in the figure) which meshes with the toothed part 33 of a part 34 supporting the motor 32 and a toothed wheel 35.
- the motor 32 drives a pinion 36 which meshes the toothed wheel 35.
- On the outside diameter of the latter is fixed at its top a piece 37 in the form of a V at the two ends of which is articulated a rod 40 and 41 respectively, the other end of which is articulated on a point of the surface. of the antenna 42 to be oriented.
- the latter is also held in its center by a part 38 which can pivot relative to the part 34 around the articulation 39.
- the two motors 31 and 32 therefore make it possible to orient the antenna 42 by making it pivot relative to two axes, respectively the axis 43 by pivoting of the part 34 around the articulation 39 and the axis 44 by pivoting of the part 37 therefore of the wheel 35. But the circular movement of the antenna around the axis 43 is slowed down by the inertia of the weight of the motor 32.
- the present invention overcomes this drawback.
- FIG. 3 represents a side view in section of FIG. 2, after having made the structure 8 rotate by 90 ° around the axis 3.
- the arm 1 of the fixed part houses the motor mechanism 1 controlling the so-called circular movement of the system to be oriented.
- This mechanism is connected to a transmission shaft 6 placed inside the arm 1 and decoupled therefrom using means 20.
- the opposite end of the transmission shaft 6 acts on a conical torque formed by a pinion 17, disposed at the end of the shaft 6, and a toothed wheel 18 of axis 3 orthogonal to that of the pinion 17 and the shaft 6.
- This wheel 18 is placed inside the arm 1 and is connected through the wall of the arm 1 to the structure 8 via the cylindrical part 21 forming one of the points of articulation of the structure 8 with the fixed part.
- This cylindrical part 21 is decoupled by means 10 from the wall of the arm 1 which it passes through.
- a cylindrical part formed by two distinct hollow parts 4a and 4b of cylindrical shape, situated on either side of the axis 3. These two parts 4a and 4b have a common axis 5 with the external structure 8 from which they are decoupled by means 9.
- the arm 2 of the C-shaped fixed part houses the motor mechanism II controlling the so-called elevation movement of the system to be oriented.
- This mechanism is connected to a transmission shaft 7 placed inside the arm 2 and decoupled therefrom by means 20.
- the opposite end of the shaft 7 acts on a conical couple housed by the arm 2 and formed by a pinion 13 disposed at the end of the shaft 7 and a toothed wheel 14 of axis 3.
- the first bevel couple drives, by means of a cylindrical part 19 of axis 3, a second bevel couple arranged inside the structure 8 and comprising a toothed wheel 15 of axis 3 coming to mesh with a toothed wheel 16 of axis 5 placed at the periphery of the cylindrical part 4a.
- the cylindrical transition piece 19 passes through the wall of the arm 2 and of the structure 8, with respect to which it is decoupled by means 11 and 12.
- the system to be oriented is fixed at A, B and A ', B' on the cylindrical parts 4a and 4b respectively, outside the structure 8. It constitutes the second branch of the gimbal.
- the motor It rotates, by means of the shaft 7 provided with the pinion 13, the toothed wheel 14 therefore the wheel 15 coupled by the cylindrical part 19.
- the wheel 15 comes to mesh the wheel 16 and rotates the piece 4a around the axis 5.
- the system fixed to this piece 4a also pivots around this axis and in its movement drives the piece 4b in synchronism. But the parts 4a and 4b being decoupled from the structure 8, the latter remains stationary.
- the motor rotates, via the shaft 6 provided with the pinion 17, the toothed wheel 18 around the axis 3 and therefore the structure 8 to which it is fixed, as well as the parts 4a and 4b arranged inside the structure, and therefore the system to be oriented. It is the circular movement around the axis 3.
- the structure 8 is decoupled, by means 11, from the cylindrical part 19, and the latter and therefore the wheel 15 which is fixed to it, are stationary since the motor mechanism It is not powered.
- the wheel 16 As the part 4a and therefore the wheel 16 rotate around the axis 3, given the circular movement of the structure 8, the wheel 16 must move along the toothed wheel 15 of axis 3 with which it is in contact, which causes the rotation of the part 4a around the axis 5 and consequently that of the system to be oriented and that of the part 4b. It is the movement in elevation around axis 5.
- Means such as gyrometers or annular digital encoders arranged between fixed parts and mobile parts make it possible to know and measure the movements in circular and elevation which makes it possible to control the motor mechanisms accordingly. It is possible to cancel the elevation movement when the motor mechanism of the circular movement 1 is supplied. Indeed, it suffices to simultaneously control, via the motor mechanism II, the toothed wheel 15 of the same angular quantity as the toothed wheel 18 in order to neutralize the relative movement of the two wheels 16 and 15.
- the motor mechanisms can be geared motors.
- the decoupling means 9, 10, 11, 12, 20 are for example ball bearings.
- the device according to the invention can be used in particular for orienting a microwave antenna. Indeed, such an antenna must be able to be oriented quickly along two axes;
- the motor mechanisms occupy in the mobile parts a certain volume which could be used more advantageously for accommodating microwave rotary joints therein.
- the microwave receiver is placed in this case as close as possible to the antenna. It is therefore generally attached to the back of the antenna and is subjected to very strong vibrations. De-plus it gives additional inertia during antenna movements and the motors, on moving parts, limit the strikes of antenna travel.
- the motor mechanisms being installed on fixed parts, allow significant antenna deflections.
- they release the volume located in the center of the gimbal in favor of rotating joints, thus allowing the microwave receiver to be moved to a fixed part where the vibration environment is less severe.
Landscapes
- Variable-Direction Aerials And Aerial Arrays (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR8100946 | 1981-01-20 | ||
| FR8100946A FR2498379A1 (fr) | 1981-01-20 | 1981-01-20 | Dispositif d'orientation selon deux axes orthogonaux, utilisation dans une antenne hyperfrequence et antenne hyperfrequence comportant un tel dispositif |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0056550A2 EP0056550A2 (fr) | 1982-07-28 |
| EP0056550A3 EP0056550A3 (en) | 1982-08-11 |
| EP0056550B1 true EP0056550B1 (fr) | 1985-04-17 |
Family
ID=9254312
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP81402051A Expired EP0056550B1 (fr) | 1981-01-20 | 1981-12-22 | Dispositif d'orientation selon deux axes orthogonaux, en particulier pour une antenne hyperfréquence |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4491847A (ko) |
| EP (1) | EP0056550B1 (ko) |
| DE (1) | DE3170061D1 (ko) |
| FR (1) | FR2498379A1 (ko) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4716416A (en) * | 1985-03-28 | 1987-12-29 | Satellite Technology Services, Inc. | Antenna dish reflector with integral declination adjustment |
| US4692771A (en) * | 1985-03-28 | 1987-09-08 | Satellite Technology Services, Inc. | Antenna dish reflector with integral azimuth track |
| US5077560A (en) * | 1986-02-19 | 1991-12-31 | Sts Enterprises, Inc. | Automatic drive for a TVRO antenna |
| FR2685081B1 (fr) * | 1991-12-11 | 1994-02-04 | Thomson Csf | Structure a controle d'endommagement intrinseque, procede de fabrication et methode d'utilisation. |
| KR101478890B1 (ko) * | 1996-06-27 | 2015-01-05 | 인터디지탈 테크날러지 코포레이션 | 쇼트 코드를 사용하여 cdma 시스템에서 초기 전력 램프-업을 제어하는 방법 |
| US5769748A (en) * | 1997-01-16 | 1998-06-23 | Hughes Electronics Corporation | Gimbal employing differential combination of offset drives |
| US6478434B1 (en) | 1999-11-09 | 2002-11-12 | Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. | Cryo micropositioner |
| GB2505066A (en) * | 2012-06-27 | 2014-02-19 | Sub10 Systems Ltd | Positioning gear, bracket and system having gear segments |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2410827A (en) * | 1943-06-28 | 1946-11-12 | Sperry Gyroscope Co Inc | Scanning device |
| US2651721A (en) * | 1946-03-22 | 1953-09-08 | Sperry Corp | Antenna apparatus |
| NL173647B (nl) * | 1951-11-08 | Naphtachimie Sa | Werkwijze voor de bereiding van katalysatoren voor de polymerisatie van alkenen, werkwijze voor de bereiding van polymeren of copolymeren en gevormde voortbrengselen, vervaardigd onder toepassing van de aldus bereide polymeren of copolymeren. | |
| US2980255A (en) * | 1958-03-04 | 1961-04-18 | Bernhard M Aagaard | Method and apparatus for the grading of coffee beans |
| US2930255A (en) * | 1958-11-28 | 1960-03-29 | Thompson Ramo Wooldridge Inc | Dual drive transmissions |
| GB1186424A (en) * | 1967-03-28 | 1970-04-02 | Marconi Co Ltd | Improvements in or relating to Aerial Drive Mechanisms |
| CH622129A5 (ko) * | 1977-09-30 | 1981-03-13 | Bbc Brown Boveri & Cie | |
| US4238802A (en) * | 1978-12-18 | 1980-12-09 | General Dynamics Corporation, Pomona Division | Differential drive rolling arc gimbal |
-
1981
- 1981-01-20 FR FR8100946A patent/FR2498379A1/fr active Granted
- 1981-12-22 EP EP81402051A patent/EP0056550B1/fr not_active Expired
- 1981-12-22 DE DE8181402051T patent/DE3170061D1/de not_active Expired
-
1982
- 1982-01-20 US US06/341,119 patent/US4491847A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| FR2498379A1 (fr) | 1982-07-23 |
| DE3170061D1 (en) | 1985-05-23 |
| EP0056550A3 (en) | 1982-08-11 |
| FR2498379B1 (ko) | 1984-10-19 |
| US4491847A (en) | 1985-01-01 |
| EP0056550A2 (fr) | 1982-07-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0056550B1 (fr) | Dispositif d'orientation selon deux axes orthogonaux, en particulier pour une antenne hyperfréquence | |
| EP0205376B1 (fr) | Tête articulée pour robot industriel et robot équipé d'une telle tête | |
| FR2562459A1 (fr) | Bras de manipulation modulaire | |
| FR2593106A1 (fr) | Dispositif de deplacement d'un outil ou analogue en porte-a-faux, notamment autour d'un objet. | |
| FR2761286A1 (fr) | Positionneur multiaxe | |
| EP3956219B1 (fr) | Dispositif de propulsion pour aérodyne à voilure tournante et à décollage et atterrissage verticaux, et aérodyne comprenant au moins un tel dispositif de propulsion | |
| FR2563141A1 (fr) | Mecanisme articule formant un poignet pour robot | |
| FR2774056A1 (fr) | Systeme de direction pour vehicule automobile | |
| EP0188164A1 (fr) | Bloc de direction de véhicule automobile, comportant un coussin central fixe | |
| FR2504051A1 (fr) | Tete articulee pour robot industriel | |
| FR2704050A1 (fr) | Système de support orientable d'un équipement de mission monté sur un porteur fixe ou mobile. | |
| FR2653219A1 (fr) | Detecteur et procede de detection de verticalite, et base de maintien d'attitude d'un appareil. | |
| EP1582326A1 (fr) | Mécanisme pour bras de support de convoyeur et ensemble de bras de support équipé d'un tel mécanisme | |
| EP0007861B1 (fr) | Dispositif de réglage d'un rétroviseur notamment pour véhicule | |
| EP0081024A1 (fr) | Mécanisme d'entraînement sélectif de machines ou dispositifs à partir de l'arbre de prise de force d'un tracteur agricole | |
| FR2490335A1 (fr) | Horizon artificiel pour aeronef | |
| CA2060773C (fr) | Dispositif de support et d'entrainement en rotation d'une charge utile par rapport a une structure, notamment pour un mecanisme de pointage d'antenne de satellite | |
| EP0084482B1 (fr) | Télémanipulateur téléscopique du type maître-esclave et ses moyens d'équilibrage | |
| EP3839604B1 (fr) | Dispositif de scan à excentrique amélioré | |
| FR2610562A1 (fr) | Pince d'intervention articulee a cinq degres de liberte | |
| EP0455543B1 (fr) | Dispositif de pointage d'un réflecteur d'antenne | |
| EP0465582A1 (fr) | Dispositif d'entrainement de la roue avant d'une motocyclette a deux roues motrices et la motocyclette associee | |
| FR2503461A1 (fr) | Dispositif telecommande d'orientation d'antenne | |
| WO2022238421A1 (fr) | Dispositif de transmission et de transformation de mouvement et vehicule equipe d'un tel dispositif | |
| CA2487063C (fr) | Actionneur a limiteur de couple |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): DE GB IT |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): DE GB IT |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19820827 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): DE GB IT |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3170061 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19850523 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19911122 Year of fee payment: 11 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19911122 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19921222 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19921222 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19930901 |