DE102011121853A1 - Integrated predictive powertrain control device for controlling longitudinal dynamics of i.e. commercial vehicle, according to preceding guide vehicle, has powertrain control unit for prioritizing consumption-optimized position requests - Google Patents
Integrated predictive powertrain control device for controlling longitudinal dynamics of i.e. commercial vehicle, according to preceding guide vehicle, has powertrain control unit for prioritizing consumption-optimized position requests Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- DE102011121853A1 DE102011121853A1 DE102011121853A DE102011121853A DE102011121853A1 DE 102011121853 A1 DE102011121853 A1 DE 102011121853A1 DE 102011121853 A DE102011121853 A DE 102011121853A DE 102011121853 A DE102011121853 A DE 102011121853A DE 102011121853 A1 DE102011121853 A1 DE 102011121853A1
- Authority
- DE
- Germany
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- distance
- control
- driving strategy
- speed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W30/00—Purposes of road vehicle drive control systems not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. of systems using conjoint control of vehicle sub-units, or advanced driver assistance systems for ensuring comfort, stability and safety or drive control systems for propelling or retarding the vehicle
- B60W30/14—Adaptive cruise control
- B60W30/16—Control of distance between vehicles, e.g. keeping a distance to preceding vehicle
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W50/00—Details of control systems for road vehicle drive control not related to the control of a particular sub-unit, e.g. process diagnostic or vehicle driver interfaces
- B60W50/0097—Predicting future conditions
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2552/00—Input parameters relating to infrastructure
- B60W2552/20—Road profile
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60W—CONJOINT CONTROL OF VEHICLE SUB-UNITS OF DIFFERENT TYPE OR DIFFERENT FUNCTION; CONTROL SYSTEMS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR HYBRID VEHICLES; ROAD VEHICLE DRIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR PURPOSES NOT RELATED TO THE CONTROL OF A PARTICULAR SUB-UNIT
- B60W2554/00—Input parameters relating to objects
- B60W2554/80—Spatial relation or speed relative to objects
- B60W2554/801—Lateral distance
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Vorrichtung zur Regelung der Längsdynamik eines Fahrzeugs gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Patentanspruchs 1. Die Erfindung betrifft weiterhin ein Verfahren zur Regelung der Längsdynamik eines Fahrzeugs gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Patentanspruchs 3.The invention relates to a device for controlling the longitudinal dynamics of a vehicle according to the preamble of
Auf dem Markt sind bereits Vorrichtungen zur Regelung der Längsdynamik von Fahrzeugen verfügbar, die die Fahrgeschwindigkeit eines Fahrzeugs auf eine vom Fahrer als Wunschgeschwindigkeit vorgebbare Setzgeschwindigkeit regeln, sofern hierdurch ein vorgebbarer Sollabstand zu einem vorausfahrenden Fahrzeug, nachfolgend Frontfahrzeug genannt, nicht unterschritten wird. Wenn die Geschwindigkeitsregelung ohne Unterschreitung des Sollabstands nicht möglich ist, wird eine Abstandsregelung durchgeführt, um den Abstand zwischen dem Fahrzeug und Frontfahrzeug auf den Sollabstand zu regeln. Der Sollabstand wird üblicherweise als Zeitabstand, auch Zeitlücke genannt, vorgegeben. Eine derartige Vorrichtung wird üblicherweise auch als Abstandsregeltempomat oder ACC-System (ACC = adaptive cruise control) bezeichnet.Devices for regulating the longitudinal dynamics of vehicles are already available on the market, which regulate the driving speed of a vehicle to a set speed by the driver as desired speed, provided that a predefinable setpoint distance to a preceding vehicle, referred to below as the front vehicle, is not undershot. If the speed control is not possible without falling below the target distance, a distance control is performed to regulate the distance between the vehicle and front vehicle to the target distance. The nominal distance is usually specified as a time interval, also called the time gap. Such a device is commonly referred to as Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC).
Aus der
Aus der
Aus der
Aus der
Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde eine Vorrichtung zur Regelung der Längsdynamik eines Fahrzeugs, insbesondere eines Nutzfahrzeugs, und ein Verfahren zum Betreiben einer solchen Vorrichtung anzugeben, die bzw. das einen verbrauchsgünstigen Regelbetrieb beim Folgen eines vorausfahrenden Fahrzeugs ermöglicht.The invention has for its object a device for controlling the longitudinal dynamics of a vehicle, in particular a commercial vehicle, and to provide a method for operating such a device, which allows a low-consumption control operation when following a preceding vehicle.
Die Aufgabe wird durch die Merkmale der unabhängigen Ansprüche gelöst. Vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen und Weiterbildungen ergeben sich aus den Unteransprüchen.The object is solved by the features of the independent claims. Advantageous embodiments and further developments emerge from the subclaims.
Erfindungsgemäß umfasst eine Vorrichtung zur Regelung der Längsdynamik eines Fahrzeugs eine Abstandsregeleinheit, eine Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit und eine Antriebsstrangsteuerungseinheit. Die Abstandsregeleinheit ist zur Detektion eines vorausfahrenden Frontfahrzeugs und zur Erzeugung von Stellanforderungen für die Regelung des Abstands zwischen dem Fahrzeug und dem Frontfahrzeug vorgesehen. die Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit ist zur Erzeugung von verbrauchsoptimierten Stellanforderungen für eine verbrauchsoptimierte Regelung der Längsdynamik des Fahrzeugs vorgesehen, wobei die verbrauchsoptimierten Stellanforderung nach einer situationsabhängig ausgewählten anzuwendenden Fahrstrategie erzeugt werden. Die Antriebsstrangsteuerungseinheit ist zur Regelung und Koordination von Stelleingriffen an einem Antriebsstrang des Fahrzeugs in Abhängigkeit der Stellanforderungen der Abstandsregeleinheit und der Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit vorgesehen. Die Antriebsstrangsteuerungseinheit ist dabei eingerichtet, die Stellanforderungen der Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit gegenüber den Stellanforderungen der Abstandsregeleinheit bei der Regelung und Koordination der Stelleingriffe zu priorisieren, sofern vorgegebene Sicherheitsanforderungen, insbesondere bezüglich der Einhaltung von Sicherheitsabständen, nicht verletzt werden.According to the invention, an apparatus for controlling the longitudinal dynamics of a vehicle comprises a distance control unit, a driving strategy determination unit and a drive train control unit. The distance control unit is provided for detecting a preceding vehicle in front and for generating parking requests for the regulation of the distance between the vehicle and the front vehicle. the driving strategy determining unit is for generating consumption-optimized setting requests for a consumption-optimized control of the longitudinal dynamics of the vehicle provided, wherein the consumption-optimized parking request to be generated according to a situationally selected driving strategy to be used. The powertrain control unit is provided for controlling and coordinating control actions on a drive train of the vehicle in dependence on the setting requests of the distance control unit and the driving strategy determination unit. The drive train control unit is set up to prioritize the setting requests of the driving strategy determination unit with respect to the setting requests of the distance control unit in the regulation and coordination of the setting interventions, provided that predetermined safety requirements, in particular with regard to the observance of safety distances, are not violated.
In einer vorteilhaften Ausgestaltung der Vorrichtung umfasst die Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit ein Vorausschaumodul zur Ermittlung eines Vorausschauhorizonts in Abhängigkeit der aktuellen Position des Fahrzeugs, ein Prädiktionsmodul zur Prädiktion von Fahrzuständen des Fahrzeugs und des Frontfahrzeugs sowie ein Fahrstrategiemodul zur Auswahl der anzuwendenden Fahrstrategie in Abhängigkeit von einem aus einer Menge von vorgegebenen Anwendungsfällen auswählbarem Anwendungsfall und zur Erzeugung der weiteren Stellanforderungen in Abhängigkeit der ausgewählten Fahrstrategie.In an advantageous embodiment of the device, the driving strategy determination unit comprises a look-ahead module for determining a look-ahead horizon as a function of the current position of the vehicle, a prediction module for predicting driving conditions of the vehicle and the front vehicle, and a driving strategy module for selecting the driving strategy to be used as a function of one of a set of predetermined application cases selectable application case and for generating the other adjustment requirements depending on the selected driving strategy.
Bei einem erfindungsgemäßen Verfahren zur Regelung der Längsdynamik eines Fahrzeugs unter Berücksichtigung eines vorausfahrenden Führungsfahrzeugs werden in einem Abstandsregelschritt Stellanforderungen für abstandsregelnde Stelleingriffe an einem Antriebsstrang des Fahrzeugs erzeugt, in einem Prädiktionsregelschritt prädiktive Stellanforderungen für verbrauchsoptimierte Stelleingriffe an dem Antriebsstrang des Fahrzeugs erzeugt, falls eine Prädiktion ergibt, dass einer von mehreren vorgegebenen Anwendungsfällen vorliegt, und in einem Koordinationsschritt werden die prädiktiven Stellanforderungen gegenüber den im Abstandsregelschritt erzeugten Stellanforderungen priorisiert, sofern vorgegebene Sicherheitsanforderungen nicht verletzt werden.In a method according to the invention for controlling the longitudinal dynamics of a vehicle taking into account a preceding leading vehicle, in a distance control step, setting requests for distance-regulating actuating interventions on a drive train of the vehicle are generated, predictive setting requests for consumption-optimized actuating interventions on the drive train of the vehicle are generated in a prediction control step, if a prediction results, that one of a plurality of predetermined application cases exists, and in a coordination step, the predictive adjustment requirements are prioritized over the adjustment requests generated in the distance control step, provided that given security requirements are not violated.
Die vorgegebenen Sicherheitsanforderungen beinhalten vorzugsweise zumindest Anforderungen bezügliche der Einhaltung eines vorgebbaren Sicherheitsabstandes zum Frontfahrzeug.The predetermined safety requirements preferably include at least requirements relating to compliance with a predefinable safety distance to the front vehicle.
In einer vorteilhaften Ausgestaltung des Verfahrens wird im Prädiktionsregelschritt geprüft wird, ob einer der vorgegebenen Anwendungsfälle vorliegt. Wenn erkannt wird, dass einer der vorgegebenen Anwendungsfälle vorliegt wird aus einer Menge von vorgegebenen Steuerungsvarianten eine dem vorliegenden Anwendungsfall zugeordnete Steuerungsvariante als anzuwendende Fahrstrategie ausgewählt und die prädiktiven Stellanforderungen werden dann gemäß der anzuwendenden Fahrstrategie erzeugt.In an advantageous embodiment of the method, it is checked in the prediction control step whether one of the predefined application cases exists. If it is detected that one of the predetermined applications exists, a control variant assigned to the present application is selected from a set of predetermined control variants as the driving strategy to be used, and the predictive setting requests are then generated according to the driving strategy to be used.
Vorteilhafterweises beziehen sich die vorgegebenen Anwendungsfälle sich auf Fahrten in einem Gelände mit Steigungen und/oder Gefällen und zumindest eine der Steuerungsvarianten sieht vor, dass der Abstand zum Frontfahrzeug in Abhängigkeit des Geländeprofils vorausschauend durch eine Absenkung der Geschwindigkeit des Fahrzeugs vergrößert wird, um anschließend ausreichend Platz für eine Geschwindigkeitsanhebung durch Ausnutzung eines im Gelände entstandenen oder entstehenden Schwungs zu haben.Advantageously, the given applications relate to driving in a terrain with gradients and / or gradients, and at least one of the control variants provides that the distance to the front vehicle depending on the terrain profile is anticipated increased by lowering the speed of the vehicle to then sufficient space to increase the speed by taking advantage of an off-road or swinging momentum.
Die Absenkung der Geschwindigkeit des Fahrzeugs erfolgt vorzugsweise um eine Geschwindigkeitsdifferenz, die in Abhängigkeit der Verkehrsdichte vorgegeben wird.The lowering of the speed of the vehicle is preferably carried out by a speed difference which is predetermined as a function of the traffic density.
Die Erfindung wird nachfolgend anhand von Figuren näher beschrieben. Dabei zeigen:The invention will be described in more detail with reference to figures. Showing:
Gemäß
Die Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit
Die Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit
Die Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit
Die Abstandsregeleinheit
Der Abstandsregler
Die Antriebsstrangsteuerungseinheit
Der Kanstantgeschwindigkeitsregler
Der Antriebsstrangmomentenkoordinator
Die Abstandsreglereinheit
Die erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung arbeitet wie folgt: Wenn vor dem eigenen Fahrzeug ein langsameres vorausfahrendes Fahrzeug, nachfolgend Frontfahrzeug genannt, von der Sensorauswerteeinheit
Die verschiedenen Steuerungsvarianten sind jeweils einer von mehreren vorgegebenen Fahrsituationen zugeordnet. Diese vorgegebenen Fahrsituationen, nachfolgend auch Anwendungsfälle (englisch: use cases) genannt, werden weiter unten im Detail beschrieben. The various control variants are each assigned to one of several predefined driving situations. These predefined driving situations, also referred to below as use cases, will be described in detail below.
Wenn nun im abstandsgeregelten Fahrbetrieb erkannt wird, dass eine der vorgegebenen Fahrsituationen vorliegt, wird die der Fahrsituation zugeordnete Steuerungsvariante als die in der aktuellen Fahrsituation anzuwendende prädiktive Fahrstrategie ausgewählt und es wird der Zeitpunkt oder Ort bestimmt, ab dem der Wechsel zur ausgewählten Fahrstrategie erfolgen soll. Danach werden die Signale
Wenn festgestellt wird, dass vorgegebene Sicherheitsanforderungen, insbesondere Anforderungen bezüglich der Einhaltung von vorgegebenen Sicherheitsabständen zu vorausfahrenden Fahrzeugen, nicht verletzt werden, wird den von der Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit
Bei einem Verlust des Zielfahrzeugs oder wenn dieses soweit beschleunigt, dass die Abstandsregelung eine Überschreitung der Setzgeschwindigkeit zur Folge hätte, wird den Stellanforderungen des Konstantgeschwindigkeitsreglers
Die vom Fahrstrategiemodul
In allen Figuren ist das eigene Fahrzeug mit dem Bezugszeichen F1 bezeichnet, das vorausfahrende Frontfahrzeug mit dem Bezugszeichen F2 bezeichnet, die Geschwindigkeit des eigenen Fahrzeugs mit dem Bezugszeichen v1 bezeichnet und die Geschwindigkeit des Frontfahrzeugs mit dem Bezugszeichen v2 bezeichnet. Die Figuren zeigen die Fahrzeuge F1 und F2 beim Durchfahren von Strecken mit bestimmtem Höhenprofil sowie die zugehörigen Geschwindigkeitstrajektorien v(s) der Geschwindigkeiten v1, v2 über der Strecke s.In all figures, the own vehicle is designated by the reference character F1, the preceding vehicle in front by the reference character F2, the speed of the own vehicle by the reference symbol v1, and the speed of the vehicle ahead by the reference symbol v2. The figures show the vehicles F1 and F2 when driving through routes with a certain height profile and the associated speed trajectories v (s) of the speeds v1, v2 over the distance s.
Folgende Fahrsituationen, in denen durch eine situationsabhängige prädiktive Fahrstrategie Kraftstoff eingespart werden kann, werden vom Fahrstrategiemodul
A1: Abstandsregelung beim Passieren einer Kuppe,
A2: Abstandsregelung beim Passieren einer Senke,
A3: Abstandsregelung beim Bergauffahren mit Volllast,
A4: Abstandsregelung beim Ausfahren aus steilem Berg,
A5: Abstandsregelung durch Segeln.The following driving situations, in which fuel can be saved by a situation-dependent predictive driving strategy, are used by the driving strategy module
A1: distance control when passing a dome,
A2: distance control when passing a sink,
A3: distance control when driving uphill at full load,
A4: distance control when driving out of steep mountain,
A5: Distance control by sailing.
Jedem dieser Anwendungsfälle A1 bis A6 ist eine eigene Steuerungsvariante S1 bis S6 zugeordnet, die entsprechen dem jeweils vorliegenden Anwendungsfall als anzuwendende prädiktive Fahrstrategie, nach der die Längsdynamik des Fahrzeugs F1 geregelt werden soll, ausgewählt wird.Each of these applications A1 to A6 is assigned its own control variant S1 to S6, which are selected in accordance with the application in each case as the applicable predictive driving strategy according to which the longitudinal dynamics of the vehicle F1 is to be controlled.
Anwendungsfall A1: Abstandsregelung beim Passieren einer KuppeApplication A1: Distance control when passing a dome
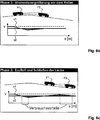
Der Anwendungsfall A1 ist in den
In Phase 1 (
Während der Phase 1 oder während des abstandsgeregelten Fahrbetriebs erkennt die Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit
Um diese Steuerungsvariante S1 im abstandsgeregelten Fahrbetrieb umsetzen zu können, müssen die von der Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit
Um den Abstand nicht zu groß werden zu lassen, sollte die vorgegebene Geschwindigkeitsdifferenz Δv an die momentanen Verkehrsverhältnisse angepasst werden. Registriert beispielsweise der Abstandssensor
Nach dem Passieren des Scheitels der Kuppe wird Phase 3 eingeleitet. Gemäß
Anwendungsfall A2: Abstandsregelung beim Passieren einer SenkeApplication A2: Distance control when passing a sink
Der Anwendungsfall A2 ist in den
Die in
Während der Phase 1 oder während des abstandsgeregelten Fahrbetriebs registriert die Fahrstrategiebestimmungseinheit 1 eine Geländesenke oder ein eine Ebene auslaufendes Gefälle und wählt die dem Anwendungsfall A2 zugeordneter Steuerungsvariante S2 als anzuwendende prädiktive Fahrstrategie aus. Das Prädiktionsmodul
Gemäß
Die Phase 3 wird nach dem Verlassen des Gefälles in der anschließenden Steigung bzw. Ebene beendet. Vorteilhafterweise wird die Phase 3 nach dem Abbau des Geschwindigkeitsüberschusses, d. h. nach dem Angleichen der Geschwindigkeit v1 des Fahrzeugs F1 an die Geschwindigkeit v2 des Frontfahrzeugs F2. Nach Beendigung der Phase 3 übernimmt die Abstandsregeleinheit
Anwendungsfall A3: Abstandsregelung beim Bergauffahren mit VolllastApplication A3: Distance control when driving uphill at full load
Der Anwendungsfall A3 ist in den
In Phase 1 (
In Phase 2 (
Nachdem ein ausreichend großer Abstand zum Frontfahrzeug F2 aufgebaut worden ist, wird das Fahrzeug F1 in Phase
Wie in den vorherigen Anwendungsfällen A1, A2 übernimmt die Abstandsregeleinheit
Anwendungsfall A4: Abstandsregelung beim Ausfahren aus steilem BergApplication A4: Distance control when driving out of a steep mountain
Der Anwendungsfall A4 ist in den
In Phase 1 (
Das Vorausschaumodul
Die herkömmliche Abstands- und Geschwindigkeitsregelung versucht unter Beibehaltung der Volllast die Sollgeschwindigkeit vsoll bzw. die Geschwindigkeit v2 des Frontfahrzeugs F2 so schnell wie möglich wieder zu erreichen, wenn das Frontfahrzeug F2 im flacher werdenden Gelände beschleunigt. Dies ist in aller Regel nicht die energieoptimale Lösung, Gemäß der ausgewählten Fahrstrategie wird daher in Phase 2 (
Die Phase 3 ist beendet, wenn das Fahrzeug F1 sich dem Frontfahrzeug F2 soweit genähert hat, dass der Abstand zum Frontfahrzeug F2 wieder dem von der Abstandsregeleinheit 2 einzuregelndem Sollabstand entspricht.
Wie in den vorherigen Anwendungsfällen A1, A2 übernimmt die Abstandsregeleinheit
Anwendungsfall A5: Abstandsregelung durch SegelnApplication A5: Distance control by sailing
Der Anwendungsfall A5 ist in den
In Phase 1 (
Das Vorausschaumodul
Das Prädiktionsmodul
In Phase 3 (
BezugszeichenlisteLIST OF REFERENCE NUMBERS
- 11
- FahrstrategiebestimmungseinheitDriving strategy determination unit
- 22
- AbstandsregeleinheitDistance control unit
- 33
- AntriebsstrangsteuerungseinheitPowertrain control unit
- 44
- Positionsbestimmungseinrichtung (GPS-Empangseinrichtung)Position determining device (GPS receiving device)
- 55
- Abstandssensordistance sensor
- 66
- VorausschaumodulPredictive module
- 77
- Prädiktionsmodulprediction
- 88th
- FahrstrategiemodulDriving strategy module
- 99
- Sensorauswerteeinheitsensor evaluation
- 1010
- AbstandsreglerAdaptive Cruise Control
- 1111
- Konstantgeschwindigkeitsregler (Tempomatregler)Constant speed controller (cruise control)
- 1212
- GangschaltesteuereinheitGang Switch control unit
- 1313
- AntriebsstrangmomentenkoordinatorPowertrain torque coordinator
- 1414
- Motorbremseengine brake
- 1515
- Betriebsbremseservice brake
- 1616
- DauerbremseMountain brake
- 1717
- Elektromotorelectric motor
- 1818
- Verbrennungsmotorinternal combustion engine
- 2020
- Information über vorausfahrende FahrzeugeInformation about vehicles in front
- 2121
- Eingriffsinformationintervention information
- 2222
- Stellanforderungen für SollgeschwindigkeitsvorgabeSetting requirements for setpoint velocity
- 2323
- Stellanforderungen für GangwahlSetting requirements for gear selection
- 24 24
- Zustandssignalestate signals
- 2525
- Zustandssignalestate signals
- 2626
- Stellanforderungen für AbstandsregelungSetting requirements for distance control
- F1F1
- eigenes FahrzeugOwn vehicle
- F2F2
- vorausfahrendes Fahrzeug (Frontfahrzeug)preceding vehicle (front vehicle)
- vv
- Geschwindigkeitspeed
- vsollvsoll
- Sollgeschwindigkeittarget speed
- ss
- Entfernungdistance
- v1v1
- Geschwindigkeit des eigenen Fahrzeugs F1Speed of own vehicle F1
- v2v2
- Geschwindigkeit des vorausfahrenden Fahrzeugs F2Speed of the preceding vehicle F2
- Δv.DELTA.v
- Geschwindigkeitsdifferenzspeed difference
ZITATE ENTHALTEN IN DER BESCHREIBUNG QUOTES INCLUDE IN THE DESCRIPTION
Diese Liste der vom Anmelder aufgeführten Dokumente wurde automatisiert erzeugt und ist ausschließlich zur besseren Information des Lesers aufgenommen. Die Liste ist nicht Bestandteil der deutschen Patent- bzw. Gebrauchsmusteranmeldung. Das DPMA übernimmt keinerlei Haftung für etwaige Fehler oder Auslassungen.This list of the documents listed by the applicant has been generated automatically and is included solely for the better information of the reader. The list is not part of the German patent or utility model application. The DPMA assumes no liability for any errors or omissions.
Zitierte PatentliteraturCited patent literature
- DE 4209147 C1 [0003] DE 4209147 C1 [0003]
- DE 10345319 A1 [0004] DE 10345319 A1 [0004]
- DE 102008019174 A1 [0005] DE 102008019174 A1 [0005]
- DE 102009040682 A1 [0006, 0044] DE 102009040682 A1 [0006, 0044]
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011121853A DE102011121853A1 (en) | 2011-12-21 | 2011-12-21 | Integrated predictive powertrain control device for controlling longitudinal dynamics of i.e. commercial vehicle, according to preceding guide vehicle, has powertrain control unit for prioritizing consumption-optimized position requests |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011121853A DE102011121853A1 (en) | 2011-12-21 | 2011-12-21 | Integrated predictive powertrain control device for controlling longitudinal dynamics of i.e. commercial vehicle, according to preceding guide vehicle, has powertrain control unit for prioritizing consumption-optimized position requests |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| DE102011121853A1 true DE102011121853A1 (en) | 2012-06-28 |
Family
ID=46508918
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011121853A Withdrawn DE102011121853A1 (en) | 2011-12-21 | 2011-12-21 | Integrated predictive powertrain control device for controlling longitudinal dynamics of i.e. commercial vehicle, according to preceding guide vehicle, has powertrain control unit for prioritizing consumption-optimized position requests |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| DE (1) | DE102011121853A1 (en) |
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102012013689A1 (en) * | 2012-07-07 | 2014-01-09 | Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft | Method for a driver assistance system of a vehicle |
| DE102012216875A1 (en) * | 2012-09-20 | 2014-03-20 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Method for determining driving strategy for motor vehicle from information about driving route ahead, involves generating control signal depending on reference speed, and adjusting band limits of speed band depending on traffic density |
| DE102012014468A1 (en) * | 2012-07-21 | 2014-05-15 | Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft | Method for changing a driving strategy for a vehicle and vehicle control device for a vehicle |
| DE102014214140A1 (en) * | 2014-07-21 | 2016-01-21 | Zf Friedrichshafen Ag | Method for the predictive control of a cruise control system of a motor vehicle |
| EP2826686A3 (en) * | 2013-07-11 | 2016-06-01 | MAN Truck & Bus AG | Method for controlling the distance between a vehicle and a preceding vehicle |
| WO2016122383A1 (en) * | 2015-01-28 | 2016-08-04 | Scania Cv Ab | Method and control unit for adjusting a time gap |
| EP2952402A3 (en) * | 2014-06-05 | 2016-11-23 | Scania CV AB | Method and system for adaptation of the propulsion of a vehicle relative a preceding vehicle |
| DE102017200612A1 (en) | 2017-01-17 | 2018-07-19 | Audi Ag | Method for generating a control signal for a longitudinal guidance of a motor vehicle and motor vehicle |
| WO2018203790A1 (en) * | 2017-05-03 | 2018-11-08 | Scania Cv Ab | A method and a control arrangement for determining a control profile for a vehicle |
| WO2019013694A1 (en) * | 2017-07-13 | 2019-01-17 | Scania Cv Ab | A method and a system for adjusting vehicle speed |
| EP3492329A1 (en) * | 2017-12-03 | 2019-06-05 | Audi Ag | Motor vehicle and method for operating a corresponding motor vehicle |
| DE102019003963A1 (en) | 2019-06-05 | 2020-01-02 | Daimler Ag | Method for determining a driving strategy of a vehicle, in particular a commercial vehicle |
| DE102015209955B4 (en) * | 2014-05-30 | 2020-03-26 | Denso Corporation | Device and program for driver assistance in a vehicle |
| SE2050625A1 (en) * | 2020-06-01 | 2021-12-02 | Scania Cv Ab | Method and control arrangement in a vehicle approaching an uphill slope |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10345319A1 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2004-06-03 | Daimlerchrysler Ag | Predictive speed control for a motor vehicle |
| DE102008019174A1 (en) | 2008-04-17 | 2009-10-22 | Daimler Ag | Vehicle e.g. passenger car, operating method, involves adjusting and controlling preset vehicle speed and braking torque in dependent of parameters of preceding path and/or in dependent of parameter of ahead-driving vehicle |
| DE102009040682A1 (en) | 2009-09-08 | 2011-03-10 | Daimler Ag | Method for controlling speed control system of e.g. lorry, involves examining influence of selected variants and suitability of variants based on simulation of speed process, activating suitable variants, and rejecting unsuitable variants |
-
2011
- 2011-12-21 DE DE102011121853A patent/DE102011121853A1/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10345319A1 (en) | 2002-10-04 | 2004-06-03 | Daimlerchrysler Ag | Predictive speed control for a motor vehicle |
| DE102008019174A1 (en) | 2008-04-17 | 2009-10-22 | Daimler Ag | Vehicle e.g. passenger car, operating method, involves adjusting and controlling preset vehicle speed and braking torque in dependent of parameters of preceding path and/or in dependent of parameter of ahead-driving vehicle |
| DE102009040682A1 (en) | 2009-09-08 | 2011-03-10 | Daimler Ag | Method for controlling speed control system of e.g. lorry, involves examining influence of selected variants and suitability of variants based on simulation of speed process, activating suitable variants, and rejecting unsuitable variants |
Cited By (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9421971B2 (en) | 2012-07-07 | 2016-08-23 | Volkswagen Ag | Method for a driver assistance system of a vehicle |
| DE102012013689A1 (en) * | 2012-07-07 | 2014-01-09 | Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft | Method for a driver assistance system of a vehicle |
| DE102012014468A1 (en) * | 2012-07-21 | 2014-05-15 | Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft | Method for changing a driving strategy for a vehicle and vehicle control device for a vehicle |
| DE102012216875A1 (en) * | 2012-09-20 | 2014-03-20 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Method for determining driving strategy for motor vehicle from information about driving route ahead, involves generating control signal depending on reference speed, and adjusting band limits of speed band depending on traffic density |
| EP2826686A3 (en) * | 2013-07-11 | 2016-06-01 | MAN Truck & Bus AG | Method for controlling the distance between a vehicle and a preceding vehicle |
| DE102015209955B4 (en) * | 2014-05-30 | 2020-03-26 | Denso Corporation | Device and program for driver assistance in a vehicle |
| US10843695B2 (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2020-11-24 | Denso Corporation | Apparatus and program for assisting drive of vehicle |
| EP2952402A3 (en) * | 2014-06-05 | 2016-11-23 | Scania CV AB | Method and system for adaptation of the propulsion of a vehicle relative a preceding vehicle |
| DE102014214140A1 (en) * | 2014-07-21 | 2016-01-21 | Zf Friedrichshafen Ag | Method for the predictive control of a cruise control system of a motor vehicle |
| US9707962B2 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2017-07-18 | Zf Friedrichshafen Ag | Method for anticipatory controlling a cruise control of a motor vehicle |
| US10293821B2 (en) | 2015-01-28 | 2019-05-21 | Scania Cv Ab | Method and control unit for adjusting a time gap |
| WO2016122383A1 (en) * | 2015-01-28 | 2016-08-04 | Scania Cv Ab | Method and control unit for adjusting a time gap |
| KR20170107008A (en) * | 2015-01-28 | 2017-09-22 | 스카니아 씨브이 악티에볼라그 | Method and control unit for adjusting time intervals |
| KR102084702B1 (en) | 2015-01-28 | 2020-03-04 | 스카니아 씨브이 악티에볼라그 | Method and control unit for adjusting the time interval |
| DE102017200612A1 (en) | 2017-01-17 | 2018-07-19 | Audi Ag | Method for generating a control signal for a longitudinal guidance of a motor vehicle and motor vehicle |
| DE102017200612B4 (en) | 2017-01-17 | 2019-03-21 | Audi Ag | Method for generating a control signal for a longitudinal guidance of a motor vehicle and motor vehicle |
| WO2018203790A1 (en) * | 2017-05-03 | 2018-11-08 | Scania Cv Ab | A method and a control arrangement for determining a control profile for a vehicle |
| US11685388B2 (en) | 2017-05-03 | 2023-06-27 | Scania Cv Ab | Method and a control arrangement for determining a control profile for a vehicle |
| WO2019013694A1 (en) * | 2017-07-13 | 2019-01-17 | Scania Cv Ab | A method and a system for adjusting vehicle speed |
| CN109866769A (en) * | 2017-12-03 | 2019-06-11 | 奥迪股份公司 | For run motor vehicle method and corresponding motor vehicle |
| DE102017221740A1 (en) * | 2017-12-03 | 2019-06-06 | Audi Ag | Method for operating a motor vehicle and corresponding motor vehicle |
| US11345345B2 (en) | 2017-12-03 | 2022-05-31 | Audi Ag | Method for operating a motor vehicle, and corresponding motor vehicle |
| EP3492329A1 (en) * | 2017-12-03 | 2019-06-05 | Audi Ag | Motor vehicle and method for operating a corresponding motor vehicle |
| CN109866769B (en) * | 2017-12-03 | 2023-10-10 | 奥迪股份公司 | Method for operating a motor vehicle and corresponding motor vehicle |
| DE102019003963A1 (en) | 2019-06-05 | 2020-01-02 | Daimler Ag | Method for determining a driving strategy of a vehicle, in particular a commercial vehicle |
| SE2050625A1 (en) * | 2020-06-01 | 2021-12-02 | Scania Cv Ab | Method and control arrangement in a vehicle approaching an uphill slope |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE102011121853A1 (en) | Integrated predictive powertrain control device for controlling longitudinal dynamics of i.e. commercial vehicle, according to preceding guide vehicle, has powertrain control unit for prioritizing consumption-optimized position requests | |
| EP2010423B1 (en) | Speed control apparatus and motor vehicle with a speed control apparatus of this type | |
| EP1713658B1 (en) | Distance control system for motor vehicles | |
| DE102008019174A1 (en) | Vehicle e.g. passenger car, operating method, involves adjusting and controlling preset vehicle speed and braking torque in dependent of parameters of preceding path and/or in dependent of parameter of ahead-driving vehicle | |
| EP2870041B1 (en) | Method for a driver assistance system of a vehicle | |
| EP2198186B1 (en) | Method for controlling an automatic multi-step shift transmission | |
| EP2526003B1 (en) | Starting assistant for motor vehicles | |
| DE112017004027T5 (en) | AUTONOMOUS DRIVING WITH DYNAMIC SKIP FIRE | |
| EP2540589B1 (en) | Control device and method for controlling and/or regulating vehicle systems | |
| DE102014215673A1 (en) | Driver assistance system in a motor vehicle | |
| DE102006003625B4 (en) | Method for regulating the distance of a vehicle to a leading vehicle ahead | |
| WO2012146268A1 (en) | Hybrid drive control device | |
| WO2010121861A1 (en) | Method for operating a vehicle having a freewheel mode or a rolling mode | |
| DE102010018097A1 (en) | Method for controlling a driving speed of a vehicle | |
| DE102009028242A1 (en) | Method for controlling a rolling or sailing mode of a vehicle | |
| WO2013020760A1 (en) | Method for influencing a gearshift strategy of a motor vehicle | |
| DE102015223588A1 (en) | Control system with at least one electronic control unit for controlling an internal combustion engine in a hybrid vehicle | |
| DE102016011411A1 (en) | Method for operating a drive train of a motor vehicle | |
| DE102012213933A1 (en) | Method for controlling cruise control system of e.g. motor car, involves terminating vehicle turning mode when variable corresponding to lateral acceleration of vehicle reaches or exceeds maximum value | |
| EP3018028A2 (en) | Method for limiting a speed of a commercial vehicle and speed limiting device | |
| DE102014204763A1 (en) | Cruise control system for controlling the speed of a vehicle | |
| DE102015213189A1 (en) | Longitudinal driver assistance system in a motor vehicle | |
| WO2022268705A1 (en) | Method and device for prioritizing route incidents | |
| DE102019134966A1 (en) | Method and motor vehicle control system for controlling longitudinal dynamics of a motor vehicle by specifying a tolerance interval for acceleration or deceleration; as well as motor vehicle | |
| EP2918468A2 (en) | Method for adapting at least one target speed in a motor vehicle speed control and driver assistance system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| R230 | Request for early publication | ||
| R119 | Application deemed withdrawn, or ip right lapsed, due to non-payment of renewal fee |