CN1136815C - Medical laser apparatus and diagnosing/curing apparatus using the medical laser apparatus - Google Patents
Medical laser apparatus and diagnosing/curing apparatus using the medical laser apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1136815C CN1136815C CNB941069079A CN94106907A CN1136815C CN 1136815 C CN1136815 C CN 1136815C CN B941069079 A CNB941069079 A CN B941069079A CN 94106907 A CN94106907 A CN 94106907A CN 1136815 C CN1136815 C CN 1136815C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- laser
- wavelength
- machine
- photosensitizer
- lesion
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Radiation-Therapy Devices (AREA)
Abstract
一种可以实现在治疗期间同时进行诊断的诊断/治疗机具有用半导体激光器作光源的医用激光机(21),该激光光源产生的激光其半峰全宽度窄,而且其振荡波长可调,该诊断/治疗机还具有将医用激光机(21)发射的照射激光3a传输到病灶(5)附近的光传输线22)、用于观测病灶(5)及其四周的像传输线(23)、用于只分离受照射激光(3a)激发而从光敏剂发射的荧光的荧光分离装置(27)、采集和分析由荧光分离装置得到的荧光像的像采集/分析装置(25)和显示分析结果的像显示装置(26)。
A diagnostic/therapeutic machine that can realize simultaneous diagnosis during treatment has a medical laser machine (21) that uses a semiconductor laser as a light source. The laser light produced by the laser light source has a narrow half-maximum full width and an adjustable oscillation wavelength. The diagnosis/treatment machine also has an optical transmission line 22) for transmitting the irradiation laser 3a emitted by the medical laser machine (21) to the vicinity of the lesion (5), an image transmission line (23) for observing the lesion (5) and its surroundings, A fluorescence separation device (27) for separating only the fluorescence emitted from the photosensitizer excited by the irradiated laser light (3a), an image collection/analysis device (25) for collecting and analyzing the fluorescence image obtained by the fluorescence separation device, and an image for displaying the analysis result Display device (26).
Description
本发明涉及被用作诊断/治疗机光源的医用激光机,诊断/治疗机使光照射在病灶上医治例如癌症等肿瘤的病灶。与病灶具有亲和作用的光敏剂事先被积存在病灶中,当波长与光敏剂吸收波长一致的光照射在病灶上时,光敏剂受激,因而可诊断和医治病灶。本发明同时涉及使用医用激光机的诊断/治疗机。The present invention relates to a medical laser machine used as a light source of a diagnosis/treatment machine which irradiates light on a lesion to treat a lesion of a tumor such as cancer. The photosensitizer that has an affinity with the lesion is accumulated in the lesion in advance, and when the light with the same wavelength as the absorption wavelength of the photosensitizer is irradiated on the lesion, the photosensitizer is stimulated, so the lesion can be diagnosed and treated. The invention also relates to diagnostic/therapeutic machines using medical laser machines.
近来随着电子医疗技术的发展,利用激光的两种方法光动力诊断法(以下称作PDD法)和光动力治疗法(以下称作PDT法)得到了很快的发展。PDD法和PDT法具体讲就是,事先使与肿瘤具有亲和力并显示光化学反应例如发射荧光或杀灭细胞作用的光敏剂聚集在肿瘤的病灶中,然后用光照射病灶,这种照射引起光敏剂激发,测量发射的荧光,据此可以诊断病灶(PDD),或利用杀灭细胞的作用治疗病灶(PDT)。为有效激发光敏剂,照射病灶的光的波长最好与光敏剂的吸收波长一致,因此一般采用激光源作照射病灶的光源。在这种情况下,激光光源应适合所用光敏剂的吸收波长。Recently, with the development of electronic medical technology, two methods using laser light, photodynamic diagnosis (hereinafter referred to as PDD method) and photodynamic therapy (hereinafter referred to as PDT method), have been rapidly developed. Specifically, the PDD method and the PDT method are to gather in the lesion of the tumor a photosensitizer that has an affinity with the tumor and exhibits a photochemical reaction, such as emitting fluorescence or killing cells, and then irradiates the lesion with light, which causes the photosensitizer to be excited. , to measure the emitted fluorescence, according to which the lesion can be diagnosed (PDD), or the lesion can be treated by killing cells (PDT). In order to effectively excite the photosensitizer, the wavelength of the light irradiating the lesion should preferably be consistent with the absorption wavelength of the photosensitizer, so a laser source is generally used as the light source for irradiating the lesion. In this case, the laser light source should be suitable for the absorption wavelength of the photosensitizer used.
在上述类型的医治癌症的诊断/治疗机中常常使用用血卟啉作光敏剂和用准分子激光器作激光光源的染料激光(下面称作准分子染料激光),如在日本专利出版物NO.63-2633(2633-1988)和63-9464(9464/1988)中所述。下面参照附图4说明应用出版物NO.63-2633和63-9464公开的激光器的常规诊断/治疗机。A dye laser (hereinafter referred to as an excimer dye laser) using hematoporphyrin as a photosensitizer and an excimer laser as a laser light source is often used in the above-mentioned type of diagnostic/therapeutic machine for treating cancer, as described in Japanese Patent Publication No. 63-2633 (2633-1988) and 63-9464 (9464/1988). A conventional diagnosis/treatment machine using the laser disclosed in Publication Nos. 63-2633 and 63-9464 will be described below with reference to FIG. 4 .
图4示意示出用常规激光机的癌症诊断/治疗机的构成。图4中A是癌症的病灶,B表示病灶A的周围区域,在该区域事先已吸收作为光敏剂的血卟啉。诊断用的第一脉冲源31和治疗用的第二脉冲源32都由准分子染料激光器组成。激发第一和第二染料激光31、32的准分子染料激光重复振荡,振荡波长308nm,脉冲宽度30ns,而能量在几毫焦至100毫焦的范围内变化。第一脉冲源31的振荡波长是405nm,第二脉冲源32的振荡波长是630nm。第一和第二脉冲源31和32用开关部件33开关。其它的编号,34代表光传输线;35代表电视摄像机;36代表电视监视器;37代表半反射镜;38代表分光镜;39代表光谱分析仪;40代表显示器。Fig. 4 schematically shows the constitution of a cancer diagnosis/treatment machine using a conventional laser machine. In Fig. 4, A is the focus of cancer, and B is the area around the focus A, where hematoporphyrin as a photosensitizer has been absorbed in advance. Both the first pulse source 31 for diagnosis and the
上述构成的诊断/治疗机以下述方式操作。The diagnosis/treatment machine constructed as described above operates in the following manner.
在诊断癌时,第一脉冲光源31产生的波长为405nm的激光通过开关部件33和光传输线34照射在病灶A和周围区域B上。由波长为405nm的激光激发的波长为630nm、690nm的荧光的像由电视摄像机35摄像,并显示在电视监视器36的屏幕上以便观测。同时,由半反射镜37反射的荧光像由分光镜38分光。光谱在光谱仪39中被分解,光谱的波长由显示器40显示。随后,为医治癌症,由第二脉冲光源32产生的波长为630nm的激光通过开关部件33和光传输线34照射在病灶A上。工作模式随后再切换到诊断模式以确定治疗的结果。用上述方式反复切换上述工作模式便可以诊断和治疗癌症。When diagnosing cancer, laser light with a wavelength of 405 nm generated by the first pulse light source 31 is irradiated on the lesion A and the surrounding area B through the
因为波长为405nm的光可以有效地激发血卟啉特有的荧光,而且由于波长为630nm和波长为690nm的荧光的波长差别大,可以限制散射光的有害影响,所以诊断用的第一脉冲光源31用405nm波长的光。治疗用的第二脉冲光源32被设置在波长630nm的原因是,波长为630nm的激光能很好地透过组织并由血卟啉有效吸收。Because the light with a wavelength of 405nm can effectively excite the unique fluorescence of hematoporphyrin, and because the wavelength difference between the fluorescence with a wavelength of 630nm and that with a wavelength of 690nm is large, the harmful effects of scattered light can be limited, so the first pulse light source for diagnosis 31 Use light with a wavelength of 405nm. The reason why the second
除上述例子而外,下面表1中列出了已提出用在PDD和PDT法中的光敏剂,表中还示出了正设法用作PDT法激光光源的激光。In addition to the above examples, photosensitizers that have been proposed for use in PDD and PDT methods are listed in Table 1 below, which also shows lasers that are being tried to be used as laser light sources for PDT methods.
表1
常规的癌症诊断/治疗机的缺点是发射的激光的波长很难控制。A disadvantage of conventional cancer diagnosis/treatment machines is that it is difficult to control the wavelength of emitted laser light.
换言之,需要使激光的波长与光敏剂的吸收带的波长一致,从而有效地激发光敏剂。通常,气体激光(表1)不可能满足许多光敏剂的吸收带。更坏的是,气体激光很难具有与甚至一种光敏剂的最大吸收波长相一致的波长。如根据上述常规例子所述,虽然染料激光已被用来解决这一问题,但是为了改变染料激光的振荡波长,需要改变有色物质溶液。因此,应当预备对应于许多不同种类有色物质溶液的许多激光,如果需要改变激光的波长,例如当改变使用的光敏剂,或当激光的波长从诊断时的波长改变到治疗时的波长时,则转换激光到每个波长。In other words, it is necessary to match the wavelength of laser light with the wavelength of the absorption band of the photosensitizer to efficiently excite the photosensitizer. In general, it is not possible for gas lasers (Table 1) to satisfy the absorption bands of many photosensitizers. Worse, it is difficult for a gas laser to have a wavelength that coincides with the maximum absorption wavelength of even a photosensitizer. As described in accordance with the above-mentioned conventional examples, although dye laser light has been used to solve this problem, in order to change the oscillation wavelength of the dye laser light, it is necessary to change the colored substance solution. Therefore, many lasers corresponding to many different kinds of colored substance solutions should be prepared, and if the wavelength of the laser needs to be changed, for example, when the photosensitizer used is changed, or when the wavelength of the laser is changed from a diagnostic wavelength to a therapeutic wavelength, then Convert laser light to each wavelength.
在使用染料激光的情况下,为了容纳许多种有色物质的溶液和溶液的切换部件,诊断/治疗机在尺寸上变得过大而成为缺点。In the case of using a dye laser, in order to accommodate solutions of many kinds of colored substances and switching parts for the solutions, the diagnostic/therapeutic machine becomes excessively large in size to be disadvantageous.
使用染料激光的诊断/治疗机的第二个缺点是染料激光的有色物质溶液容易变质,引起产生的激光波长的改变或输出的降低。为了保证PDD法,特别是PDT法的效果,激光的安全性是最重要和必不可少的条件,因此染料激光的一个大问题是有色物质的溶液必须经常更换,有色物质的循环系统必须经常清洗。另外,如果在染料激光中用的溶液容易降解,则在照射期间激光波长发生不希望的改变,或激光输出降低,即应当按照上述的考虑根据波长和输出这种变化来设定激光的照射,并安排检测激光的改变。A second disadvantage of a diagnostic/therapeutic machine using a dye laser is that the colored substance solution of the dye laser is easily deteriorated, causing a change in the wavelength of the generated laser light or a decrease in output. In order to ensure the effect of the PDD method, especially the PDT method, the safety of the laser is the most important and indispensable condition, so a big problem with the dye laser is that the solution of the colored substance must be replaced frequently, and the circulation system of the colored substance must be cleaned frequently . In addition, if the solution used in the dye laser is easily degraded, the wavelength of the laser light changes undesirably during irradiation, or the output of the laser light decreases, that is, the irradiation of the laser light should be set according to such changes in wavelength and output in consideration of the above, And arrange to detect the change of the laser light.
第三,当染料激光器变换波长时,所得激光波长的半峰全宽度稍为加宽,至少约10nm,如果半峰全宽度加宽了,则激光对光敏剂的吸收带偏移加大,因此恶化了光敏剂的激发效率。虽然可以利用带通滤光器或衍射光栅减少染料激光的半峰全宽度,但是仅能切去多余的部分,激发效率仍然得不到改善。Third, when the wavelength of the dye laser is converted, the full width at half maximum of the obtained laser wavelength is slightly widened, at least about 10nm. If the full width at half maximum is widened, the absorption band shift of the laser to the photosensitizer will increase, so the deterioration The excitation efficiency of the photosensitizer. Although band-pass filters or diffraction gratings can be used to reduce the full width at half maximum of the dye laser, the excess part can only be cut off, and the excitation efficiency still cannot be improved.
第四个缺点是波长转换时,染料激光的能量转换效率差。因此,为了从转换的激光得到足够的能量,要求用作光源激发染料激光的准分子激光器等的输出高。换言之,常规的医用激光机和使用常规医用激光机的癌症诊断/治疗机容易变得体积大,价格贵。The fourth disadvantage is the poor energy conversion efficiency of dye lasers during wavelength conversion. Therefore, in order to obtain sufficient energy from the converted laser light, the output of an excimer laser or the like used as a light source to excite dye laser light is required to be high. In other words, conventional medical laser machines and cancer diagnosis/treatment machines using the conventional medical laser machines tend to become bulky and expensive.
先有技术固有的第五个缺点是必需用诊断和治疗两个光源,以及切换光源用的切换部件。因此机器庞大,价格昂贵,另外,切换光源不方便,还担心误操作。A fifth disadvantage inherent in the prior art is the necessity of both diagnostic and therapeutic light sources, as well as switching components for switching the light sources. Therefore, the machine is huge and expensive. In addition, it is inconvenient to switch the light source, and there is also concern about misoperation.
为了消除上述常规机器的缺点,本发明的目的是提供一种紧凑的价格低的医用激光机,该机可以获得振荡波长可与许多种光敏剂配合,也与其许多激发条件配合的激光,而且维修容易、半峰全宽度窄、激发效率高。In order to eliminate the disadvantages of the above-mentioned conventional machines, the object of the present invention is to provide a compact and low-cost medical laser machine, which can obtain lasers with oscillation wavelengths that can be matched with many photosensitizers and many excitation conditions, and can be easily maintained. Easy, narrow full width at half maximum, high excitation efficiency.
本发明的另一个目的是提供一种使用这种医用激光机的诊断/治疗机,该机用一个单一的光源实现了诊断和治疗,因此在治疗期间可以同时进行诊断。Another object of the present invention is to provide a diagnosis/treatment machine using such a medical laser machine, which realizes diagnosis and treatment with a single light source, so that diagnosis can be performed simultaneously during treatment.
为了实现这些和其它目的,按照本发明的第一方面,提供了一种医用激光机,该机利用光源发出的光照射在病灶上诊断或治疗病灶,在病灶区域预先积存和病灶有亲和力的光敏剂,由此使光敏剂激发,该机器包括用作光源的激光器和用于控制激光的波长控制装置,该激光器能够控制振荡波长,激光的半峰全宽度比一个谱带的宽度窄,在该谱带区域,光敏剂的能量吸收等于或大于靠近振荡波长的最大值的90%。In order to achieve these and other objects, according to the first aspect of the present invention, a medical laser machine is provided, which uses the light emitted by the light source to irradiate the lesion on the lesion to diagnose or treat the lesion, and pre-stores in the lesion area a photosensitive laser that has an affinity for the lesion. agent, whereby the photosensitizer is excited, the machine includes a laser used as a light source and a wavelength control device for controlling the laser, the laser can control the oscillation wavelength, the full width at half maximum of the laser is narrower than the width of a spectral band, in which The band region where the energy absorption of the photosensitizer is equal to or greater than 90% of the maximum near the oscillation wavelength.
按照本发明的第二方面,提供了一种诊断/治疗机,该机利用光源发出的光照射在病灶上诊断或治疗病灶,在病灶区域预先积存和病灶有亲和力的光敏剂,由此使光敏剂激发,该诊断/治疗机包括医用激光机、光传输线、像传输线、荧光分离装置和像采集/分析装置,医用激光机又包括用作光源的激光器和用于控制激光的波长控制装置,该激光器能够控制振荡波长,激光的半峰全宽度比一个谱带的宽度窄,在该谱带区域,光敏剂的能量吸收等于或大于靠近该振荡波长的最大值的90%;光传输线将医用激光机发出的激光引导到病灶的附近;像传输系统用于传输用激光激发的由光敏剂发射的荧光,以便观测病灶及其四周;荧光分离装置仅用于分离荧光;像采集/分析装置用于采集和分析由荧光分离装置得到的荧光的像。According to the second aspect of the present invention, a diagnosis/treatment machine is provided, which uses the light emitted by the light source to irradiate the lesion on the lesion for diagnosis or treatment, and pre-stores a photosensitizer that has an affinity with the lesion in the lesion area, thereby making the photosensitizer Agent excitation, the diagnosis/treatment machine includes a medical laser machine, optical transmission line, image transmission line, fluorescence separation device and image acquisition/analysis device, and the medical laser machine includes a laser used as a light source and a wavelength control device for controlling the laser. The laser can control the oscillation wavelength. The half-maximum full width of the laser is narrower than the width of a band. In this band region, the energy absorption of the photosensitizer is equal to or greater than 90% of the maximum value close to the oscillation wavelength; the optical transmission line will be medical laser The laser emitted by the machine is guided to the vicinity of the lesion; the image transmission system is used to transmit the fluorescence emitted by the photosensitizer excited by the laser, so as to observe the lesion and its surroundings; the fluorescence separation device is only used to separate the fluorescence; the image acquisition/analysis device is used for The fluorescence image obtained by the fluorescence separation device is collected and analyzed.
一种医用激光机,该机利用将光源发射的激光照射病灶上使病灶中的光敏剂(6)激发的方法来诊断或治疗病灶,与病灶具有亲和力的光敏剂事先积存在病灶中,该机包括作为光源的激光器和控制激光的波长控制装置(8),该激光器可以控制振荡波长,而且激光的半峰全宽度比一个吸收带的宽度窄,在该吸收带区域,光敏剂的能量吸收等于或大于振荡波长附近的最大值的90%。A medical laser machine, which diagnoses or treats the lesion by irradiating the laser light emitted by the light source on the lesion to excite the photosensitizer (6) in the lesion. Comprising a laser as a light source and a wavelength control device (8) for controlling the laser, the laser can control the oscillation wavelength, and the half-maximum full width of the laser is narrower than the width of an absorption band, and in the absorption band region, the energy absorption of the photosensitizer is equal to Or more than 90% of the maximum value near the oscillation wavelength.
一种诊断/治疗机,该机利用将光源发射激光照射在病灶上使病灶中的光敏剂(6)激发的方法来诊断或治疗病灶,该光敏剂与病灶具有亲和力,预先积存在病灶中,该诊断/治疗机包括:A diagnosis/treatment machine, which diagnoses or treats a lesion by irradiating a light source with laser light on the lesion to excite a photosensitizer (6) in the lesion. The photosensitizer has an affinity with the lesion and is pre-accumulated in the lesion, This diagnostic/therapeutic unit includes:
医用激光机(21),该激光机包括作光源用的半导体激光器和用于控制该半导体激光器的波长控制装置,其中,该波长控制装置是用于控制该半导体激光器温度的温度控制设备,而该半导体激光器可以控制振荡波长,而且激光的半峰全宽度比一个吸收带的宽度窄,在该吸收带区域,光敏剂的能量吸收等于或大于振荡波长附近的最大值的90%;A medical laser machine (21), which includes a semiconductor laser used as a light source and a wavelength control device for controlling the semiconductor laser, wherein the wavelength control device is a temperature control device for controlling the temperature of the semiconductor laser, and the The semiconductor laser can control the oscillation wavelength, and the half-maximum full width of the laser is narrower than the width of an absorption band. In the absorption band region, the energy absorption of the photosensitizer is equal to or greater than 90% of the maximum value near the oscillation wavelength;
光传输线(22),用于将医用激光机发射的激光传输到病灶附近;Optical transmission line (22), used for transmitting the laser light emitted by the medical laser machine to the vicinity of the lesion;
像传输线(23),用于传送激光激发的光敏剂发射的荧光,以便观测病灶和病灶的四周;Like a transmission line (23), it is used to transmit the fluorescence emitted by the photosensitizer excited by the laser, so as to observe the lesion and its surroundings;
荧光分离装置(27),用于只将荧光分出;Fluorescence separation device (27), used to separate only fluorescence;
像采集/分析装置(25),用于采集和分析用荧光分离装置分出的荧光像。An image collection/analysis device (25), used for collecting and analyzing the fluorescent images separated by the fluorescence separation device.
下面参照附图结合最佳实施例进行说明,由此可以明了本发明的这些以及其它的目的和特征。These and other objects and features of the present invention will be apparent from the following description of preferred embodiments with reference to the accompanying drawings.
图1是方块图,示出本发明第一实施例的医用激光机的组成;Fig. 1 is a block diagram showing the composition of the medical laser machine of the first embodiment of the present invention;
图2是方块图,示出本发明第二实施例的诊断/治疗机的组成;Fig. 2 is a block diagram showing the composition of a diagnosis/treatment machine of a second embodiment of the present invention;
图3是本发明第二实施例中所用的带通滤光器特性图;Fig. 3 is a characteristic diagram of the bandpass filter used in the second embodiment of the present invention;
图4是方块图,示出用常规激光机的癌症诊断/治疗机的组成。Fig. 4 is a block diagram showing the composition of a cancer diagnosis/treatment machine using a conventional laser machine.
在说明本发明之前应注意到,在所有附图中,相同的部件用相同的编号表示。Before describing the present invention, it should be noted that throughout the drawings, like parts are represented by like numerals.
下面参照附图讨论本发明第一实施例的医用激光机。A medical laser machine according to a first embodiment of the present invention will be discussed below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
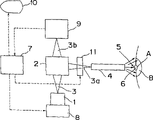
本发明的第一实施例的医用激光机的组成示于图1。参照图1,ALGaInP半导体激光器1保证振荡波长为664nm,半峰全宽度为±1nm,振荡波长的温度特征为0.2nm/℃,在0℃激励期间,可操作的温度范围从-100℃到+80℃。光学系统2将半导体激光器1发射的激光3分成照射激光3a和波长检测激光3b。光敏剂6预先供给包括病灶A和病灶A四周区域B的待治疗的靶部分5。其它的编号,4表示光导纤维,7表示控制装置,8表示温度控制装置,9表示检测激光3b波长的波长检测装置,10表示波长显示装置,11表示快门,与控制装置7结合构成自动照射中断装置。The composition of the medical laser machine of the first embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 1 . Referring to Figure 1, the ALGaInP semiconductor laser 1 guarantees an oscillation wavelength of 664nm, a full width at half maximum of ±1nm, and a temperature characteristic of the oscillation wavelength of 0.2nm/°C. During excitation at 0°C, the operable temperature range is from -100°C to + 80°
下面说明如上构成的医用激光机的操作。The operation of the medical laser machine constructed as above will be described below.
由半导体激光器1发射的激光3的波长可以根据半导体激光器1的温度来测定。即,当半导体激光器1的温度利用温度控制装置8在-100℃至+80℃的范围内改变时,激光3的波长在644nm至680nm范围内变化。因而可以得到适合于所用光敏剂6吸收波长的和适合于治疗目的的激光3的波长。The wavelength of laser light 3 emitted from semiconductor laser 1 can be measured from the temperature of semiconductor laser 1 . That is, when the temperature of the semiconductor laser 1 is changed within the range of -100°C to +80°C using the
在本实施例中,应用表1中的叶绿三酸族的NPe6(日本石油化学有限公司的商品名称)作光敏剂6。当要求波长为光敏剂6的从660nm至680nm吸收带的中心波长664nm的激光3时,半导体激光器1的温度被设置在0℃。另一方面,基于下述目的为了得到吸收带中较短波长660nm的激光,半导体激光器1的温度被控制在-15℃。当应用表1中的脱镁叶绿酸族的PH-1126(Hamari化学品有限公司的商品名称),要求得到从647nm到653nm吸收带的中心波长650nm的和较短波长644nm的激光3时,半导体激光器应分别控制在-70℃和-100℃。半峰全宽度比吸收带的宽度窄,在吸收带区域,光敏剂的能量吸收等于或大于靠近振荡波长的最大值的90%。In this embodiment, NPe6 (trade name of Nippon Petrochemical Co., Ltd.) of the chlorophyllin family in Table 1 was used as the
因为半峰全宽度是±1nm,所以控制在温度0℃、-15℃、-70℃和-100℃的半导体激光器1发射的激光3的波长是663~665nm、659~661nm、649~651nm和643~645nm,即激光3的能量保持在所用光敏剂6的吸收带内。Because the full width at half maximum is ±1nm, the wavelengths of the laser light 3 emitted by the semiconductor laser 1 controlled at temperatures of 0°C, -15°C, -70°C and -100°C are 663-665nm, 659-661nm, 649-651nm and 643-645nm, that is, the energy of the laser light 3 is kept within the absorption band of the
受控半导体激光器1发射的一部分激光3由光学系统2分出,作为波长检测激光3b引到波长检测装置9。检测装置9检测激光3b的波长。检测结果被送到控制装置7。控制装置7决定激光3b是否与控制其波长的预定条件一致。检测结果和波长值由波长显示装置10显示。控制装置7在激光3b不与预定的控制条件一致的情况下使自动照射快门11开始工作,从而关闭照射激光3a。Part of the laser light 3 emitted by the controlled semiconductor laser 1 is separated by the
当激光3与预定的控制条件一致时,快门11打开,照射激先3a被聚光进入光导纤维4,然后从光导纤维4的端部射出照射在靶部5上。When the laser light 3 is consistent with the predetermined control condition, the shutter 11 is opened, and the irradiation laser 3a is focused into the optical fiber 4, and then emitted from the end of the optical fiber 4 to irradiate the
如上所述,可以控制激光的振荡波长来得到半峰全宽度窄的其波长适合许多光敏剂的吸收波长并可用于治疗的激光,因而光敏剂可以被有效激发。另外,激光机几乎可以不维修,尺寸紧凑,价格低。As described above, the oscillation wavelength of the laser light can be controlled to obtain a laser light having a narrow full width at half maximum whose wavelength is suitable for the absorption wavelength of many photosensitizers and which can be used for treatment, so that the photosensitizers can be efficiently excited. In addition, the laser machine is almost maintenance-free, compact in size, and low in price.
以下参照图2和3说明本发明第二实施例的癌症诊断/治疗机。A cancer diagnosis/treatment machine according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to FIGS. 2 and 3. FIG.
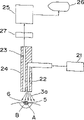
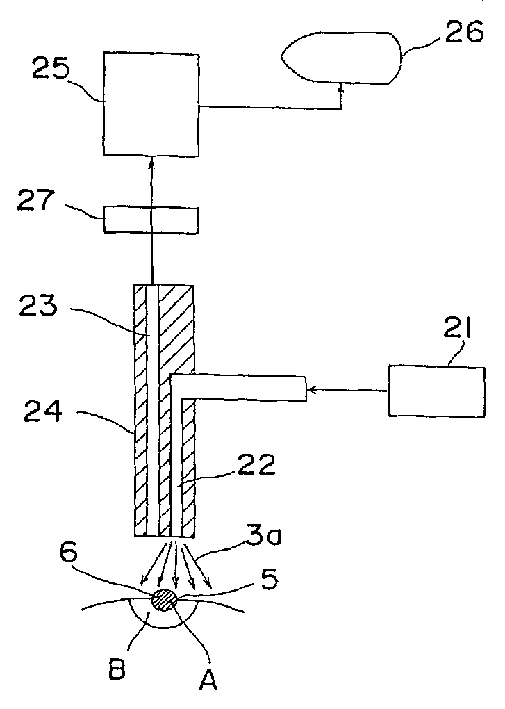
图2是方块图,示出本发明第二实施例的癌症诊断/治疗机的构成。图2中,参考编号21表示激光光源,该光源是采用上述第一实施例中半导体激光器的医用激光机,22表示光传输线,由激光光源21射出的照射激光3a通过该传输线引到病灶的附近,23表示像传输线,荧光像通过该像传输线传送,从而可观测病灶和病灶的四周。包含光传输线22和像传输线23的光导向装置24将两个传输线22和23导向病灶的附近。像采集/分析装置25通过像传输线23采集病灶附近的像并分析像。分析结果显示在像显示装置26上。带宽相当窄即从约±3nm到指定波长的带通滤光器27由介电多层膜组成(例如,日本真空光学公司的完全的介电干涉滤光器DIF具有图3所示的特性)。带通滤光器27只允许所用光敏剂荧光波长邻近的波长的光通过,而与照射激光3a分开。当应用叶绿三酸族光敏剂时,通过波长约为670nm,当应用脱镁叶绿酸族光敏剂时,通过波长约为654nm。带通滤光器27置于使像传输线23和像采集/分析装置25相连接的光轴上。应注意到带通滤光器27可以分别装上许多对应于许多光敏剂的带通滤光片,也可以装上切换带通滤光片的切换装置(未示出)。其余的参考编号例如5等代表与图1中相同的部件。Fig. 2 is a block diagram showing the constitution of a cancer diagnosis/treatment machine of a second embodiment of the present invention. In Fig. 2,
下面说明按上述配置构成的癌症诊断/治疗机的操作。The operation of the cancer diagnosis/treatment machine configured as above will be explained below.
首先,使激光光源21发射的照射激光3a通过光传输线22照射在靶部分5上,在靶部分5中预先积存了光敏剂。此时,激光3a受到温度装置的控制而具有光敏剂吸收带的中心波长,因而治疗产生最佳效果。换言之,当使用NPe6和PH-1126作光敏剂时,激光3a的波长被分别控制为664nm和650nm。控制操作在前面的第一实施例中已被说明。First, the irradiation laser light 3a emitted from the
当激光3a照射在靶部分5上时,由于预先积存在其中的光敏剂的作用,病灶A得到有选择地治疗。同时,在病灶A中的光敏剂受到激光3a的激发,随后如前所述发射特定波长的荧光。因此分析荧光的像可以诊断靶部分5。荧光的波长相当接近于照射激光3a的波长,而且荧光强度弱,因此荧光强烈受到激光3a的散射光的影响。因而采集和分析荧光像用常规方法一般是很困难的。When the laser light 3a is irradiated on the
因此在本实施例中,使通过像传输线23的荧光穿过带通滤光器27。具体地讲,使荧光通过具有图3例示特性的带通滤光器27,该滤光器仅允许所用光敏剂发射的荧光通过,而滤去照射激光3a,因而可以消除激光3a的散射光的影响。结果只有荧光的像输入到像采集/分析装置25。像采集/分析装置25采集和分析荧光的像数据,其结果显示在像显示装置26例如电视上并由记录装置例如VTR(磁带录像机)记录。观察显示图象,便可以实时诊断病灶A,即使在治疗过程中。Therefore, in this embodiment, the fluorescent light passing through the
为了改善荧光(S)与照射激光3a的散射光(N)的分离程度(S/N比),还可以相对于荧光的波长控制和移动照射激光3a的波长。即可以控制照射激光3a,使其波长从所用光敏剂吸收带的中心波长(例如当采用NPe6或PH-1126时,中心波长为664nm或650nm)移动离开吸收带内的荧光波长(例如采用NPe6或PH~1126时,660nm或644nm)。如果按上述方式控制照射激光的波长,则可以改善信噪比S/N。同时,因为照射激光3a的能量仍如先前在第一实施例中所述那样保持在光敏剂的吸收带内,所以治疗效果几乎不受影响。In order to improve the degree of separation (S/N ratio) of the fluorescence (S) from the scattered light (N) of the irradiation laser light 3a, it is also possible to control and shift the wavelength of the irradiation laser light 3a relative to the wavelength of the fluorescence. That is, the irradiation laser 3a can be controlled so that its wavelength moves from the central wavelength of the absorption band of the photosensitizer used (for example, when using NPe6 or PH-1126, the central wavelength is 664nm or 650nm) to move away from the fluorescence wavelength in the absorption band (such as using NPe6 or PH-1126). PH~1126, 660nm or 644nm). If the wavelength of the irradiating laser light is controlled as described above, the signal-to-noise ratio S/N can be improved. Meanwhile, since the energy of the irradiating laser light 3a remains within the absorption band of the photosensitizer as previously described in the first embodiment, the therapeutic effect is hardly affected.
在仅采用特定光敏剂(例如NPe6或PH-1126)的诊断/治疗机中也可以使激光3的振荡波长在光敏剂的有效吸收带范围内(例如在NPe6或PH-1126的情况下为664±5nm或650±10nm)变化。In diagnostic/therapeutic machines that only use a specific photosensitizer (such as NPe6 or PH-1126), the oscillation wavelength of the laser 3 can also be made within the effective absorption band range of the photosensitizer (such as 664 in the case of NPe6 or PH-1126). ±5nm or 650±10nm) change.
因为在本发明实施例的医用激光机中可以容易地控制照射激光3a的波长,所以即使不需要同时进行诊断和治疗,也可以将照射激光3a的波长转回到光敏剂吸收带的中心波长,即转到最佳的治疗波长。另外,上述实施例的医用激光机的一个优点是可以显示激光3的波长是否符合控制条件。如果激光3的波长与控制条件不一致,则如前所述激光被切断。Because the wavelength of the irradiation laser 3a can be easily controlled in the medical laser machine of the embodiment of the present invention, even if it is not necessary to perform diagnosis and treatment at the same time, the wavelength of the irradiation laser 3a can be turned back to the central wavelength of the absorption band of the photosensitizer, That is to switch to the optimal therapeutic wavelength. In addition, one advantage of the medical laser machine in the above embodiment is that it can display whether the wavelength of the laser light 3 meets the control conditions. If the wavelength of the laser light 3 does not match the control conditions, the laser light is cut off as described above.
因此,由于在上述实施例的诊断/治疗机中配置了带通滤光器,因此可以用一个激光光源同时进行诊断和治疗。激光的波长可以由波长控制装置控制而移离光敏剂吸收带内光敏剂发射的荧光波长,因而在同时进行诊断和治疗期间可以达到保证图像稳定的信噪比S/N。Therefore, since the band-pass filter is provided in the diagnosis/treatment machine of the above-mentioned embodiment, it is possible to simultaneously perform diagnosis and treatment with one laser light source. The wavelength of the laser can be controlled by the wavelength control device to move away from the fluorescence wavelength emitted by the photosensitizer in the absorption band of the photosensitizer, so that the signal-to-noise ratio S/N that ensures image stability can be achieved during simultaneous diagnosis and treatment.
虽然在第一实施例中的激光器是半导体激光器,但只要半峰全宽度窄,激光的振荡波长可以改变,也可以采用其它类型的激光器。当然,半导体激光器1不限于具有在第一实施例中所述特性的激光器。例如,可以装配外共振型半导体激光器,该激光波长可从其外部改变共振而进行控制。Although the laser in the first embodiment is a semiconductor laser, as long as the full width at half maximum is narrow, the oscillation wavelength of the laser can be changed, and other types of lasers can also be used. Of course, the semiconductor laser 1 is not limited to the laser having the characteristics described in the first embodiment. For example, it is possible to assemble an external resonance type semiconductor laser whose laser wavelength can be controlled by changing the resonance from the outside.
另外,虽然在第一实施例中采用波长检测装置9以反馈控制方式控制温度,但是如果利用存储了所用半导体激光器的振荡波长和温度之间关系的存储器装置并根据这种关系来控制半导体激光器的温度,则也可以正确地控制波长。In addition, although in the first embodiment, the temperature is controlled by the feedback control method using the wavelength detecting device 9, if the memory device which stores the relationship between the oscillation wavelength and the temperature of the semiconductor laser used is used and the semiconductor laser is controlled based on this relationship temperature, the wavelength can also be correctly controlled.
如本文前面所作的详细说明,医用激光机装有用作激光光源的激光器和激光的波长控制装置。该激光器发射半峰全宽度窄的激光,而且该激光的振荡波长可调。因此该医用激光机可以达到使振荡波长适合于所用类型的光敏剂以及光敏剂的激发条件,因而可以有效激发光敏剂。另外,医用激光机的优点还在于几乎不维修、紧凑和价格低。As described in detail earlier herein, a medical laser machine is equipped with a laser used as a laser light source and a wavelength control device for the laser. The laser emits laser light with a narrow half-maximum full width, and the oscillation wavelength of the laser light is adjustable. Therefore, the medical laser machine can achieve an oscillation wavelength suitable for the type of photosensitizer used and the excitation conditions of the photosensitizer, thereby effectively exciting the photosensitizer. In addition, the advantages of medical laser machines are that they are almost maintenance-free, compact and inexpensive.
按照本发明的诊断/治疗机,因为荧光像在治疗病灶期间也显示在像显示装置上,所以可以用一个单一的光源对病灶进行诊断和治疗,并在治疗期间以简单而紧凑的装置诊断病灶。诊断/治疗机操作容易。According to the diagnosis/treatment machine of the present invention, since the fluorescent image is also displayed on the image display device during the treatment of the lesion, it is possible to diagnose and treat the lesion with a single light source, and to diagnose the lesion during the treatment with a simple and compact device . The diagnosis/treatment machine is easy to operate.
虽然已经参照附图结合最佳实施例充分说明了本发明,但是应当注意到,对于本技术专业人员,显然可以进行各种变化和修改。这种变化和修改应当被理解为包括在所附权利要求书所叙述的本发明的范围内,除非这些变化和修改超越了这个范围。Although the present invention has been fully described with reference to the preferred embodiments thereof with reference to the accompanying drawings, it should be noted that various changes and modifications will be apparent to those skilled in the art. Such changes and modifications should be understood to be included within the scope of the present invention described in the appended claims, unless these changes and modifications go beyond this scope.
Claims (13)
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP209325/1993 | 1993-08-24 | ||
| JP5209325A JP2596221B2 (en) | 1992-12-28 | 1993-08-24 | Medical laser device and diagnostic / therapy device |
| JP209325/93 | 1993-08-24 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1100619A CN1100619A (en) | 1995-03-29 |
| CN1136815C true CN1136815C (en) | 2004-02-04 |
Family
ID=16571080
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB941069079A Expired - Lifetime CN1136815C (en) | 1993-08-24 | 1994-06-02 | Medical laser apparatus and diagnosing/curing apparatus using the medical laser apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN1136815C (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103536355A (en) * | 2013-08-21 | 2014-01-29 | 熊力 | Tumor targeted non-destructive low-power laser multi-functional scalpel system |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6821289B2 (en) * | 2003-03-25 | 2004-11-23 | Ceramoptec Industries, Inc. | Efficacy and safety of photodynamic therapy by multiple application protocols with photosensitizers that show extended tumor retention |
| JP4972707B2 (en) * | 2008-07-08 | 2012-07-11 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Optical measuring device |
| CN101502702B (en) * | 2009-01-19 | 2012-12-19 | 深圳市微创医学科技有限公司 | Photodynamic installation with optical transmission structure |
| US9504608B2 (en) * | 2009-07-29 | 2016-11-29 | Alcon Lensx, Inc. | Optical system with movable lens for ophthalmic surgical laser |
| CN103815964A (en) * | 2014-03-20 | 2014-05-28 | 熊力 | Multi-functional operating knife |
| DE102014016990B3 (en) * | 2014-11-18 | 2016-02-11 | Wavelight Gmbh | Nozzle unit for cross-linking of eye tissue |
| CN108371756B (en) * | 2018-02-10 | 2024-01-30 | 中国医学科学院生物医学工程研究所 | Diagnosis and treatment integrated cervical lesion photodynamic therapy system |
-
1994
- 1994-06-02 CN CNB941069079A patent/CN1136815C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103536355A (en) * | 2013-08-21 | 2014-01-29 | 熊力 | Tumor targeted non-destructive low-power laser multi-functional scalpel system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1100619A (en) | 1995-03-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100853655B1 (en) | Device, light source system and method of use for optical diagnosis and treatment of skin diseases | |
| US6510338B1 (en) | Method of and devices for fluorescence diagnosis of tissue, particularly by endoscopy | |
| EP0604931B1 (en) | Medical laser apparatus and diagnosing/curing apparatus using the medical laser apparatus | |
| JP4954858B2 (en) | Fluorescence observation apparatus and endoscope apparatus | |
| US20030229270A1 (en) | Endoscope apparatus and diagnosing method using it | |
| WO2011007461A1 (en) | Aperture stop | |
| KR100798486B1 (en) | Light source device for fluorescence diagnosis and photodynamic therapy | |
| JP5285967B2 (en) | LIGHT SOURCE DEVICE AND ENDOSCOPE DEVICE USING THE SAME | |
| KR19980019193A (en) | Spectrum Monitor Device (MONITORING DEVICE) | |
| JPH10113327A (en) | Endoscope device | |
| CN1136815C (en) | Medical laser apparatus and diagnosing/curing apparatus using the medical laser apparatus | |
| JP3525235B2 (en) | Optical diagnostic equipment | |
| JP2000189527A (en) | Laser diagnosis / treatment method and apparatus | |
| JP3718024B2 (en) | Fluorescence diagnostic equipment | |
| JP5418707B2 (en) | Aperture stop | |
| JP3221169B2 (en) | Cancer lesion diagnostic device | |
| JPH01151436A (en) | Apparatus for diagnosis and treatment of cancer | |
| JP2738390B2 (en) | Diagnosis and treatment equipment | |
| EP1030719A1 (en) | System and method for endoscopically applying and monitoring photodynamic therapy and photodynamic diagnosis | |
| JP4087397B2 (en) | Fluorescence diagnostic treatment device | |
| JPH0414973B2 (en) | ||
| JP5224078B2 (en) | Aperture stop | |
| JP4424279B2 (en) | Photochemical medical equipment | |
| JP4137618B2 (en) | Endoscope light source device | |
| JP2005152367A (en) | Special light observation system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right |
Owner name: PANASONIC HEALTHCARE + MEDICAL EQUIPMENT CO., LTD. Free format text: FORMER OWNER: MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC INDUSTRIAL CO, LTD. Effective date: 20140428 |
|
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |
Effective date of registration: 20140428 Address after: Ehime Prefecture, Japan Patentee after: Panasonic Healthcare Co., Ltd Address before: Japan Osaka kamato City Patentee before: Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. |
|
| C17 | Cessation of patent right | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term |
Expiration termination date: 20140602 Granted publication date: 20040204 |