JP4449973B2 - Imaging apparatus and program thereof - Google Patents
Imaging apparatus and program thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4449973B2 JP4449973B2 JP2006332488A JP2006332488A JP4449973B2 JP 4449973 B2 JP4449973 B2 JP 4449973B2 JP 2006332488 A JP2006332488 A JP 2006332488A JP 2006332488 A JP2006332488 A JP 2006332488A JP 4449973 B2 JP4449973 B2 JP 4449973B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- display
- image data
- control means
- continuous shooting
- displayed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、撮像装置及びそのプログラムに係り、詳しくは、被写体を撮像して記録する撮像装置及びそのプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus and a program thereof, and more particularly, to an imaging apparatus that captures and records a subject and a program thereof.
従来、シャッタチャンスを逃すのを防止するための機能を備えた撮像装置が知られている。例えば、シャッタボタンが操作されると、シャッタボタンが操作されたときの画像、及びその前後の画像を記録媒体に記録する。これにより、シャッタボタンの操作タイミングがシャッタチャンスとズレた場合であっても、シャッタチャンスの画像を得ることができる(特許文献1)。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, an imaging apparatus having a function for preventing missing a photo opportunity is known. For example, when the shutter button is operated, an image when the shutter button is operated and images before and after the image are recorded on a recording medium. Thereby, even if the operation timing of the shutter button deviates from the photo opportunity, an image of the photo opportunity can be obtained (Patent Document 1).
しかしながら、このようにシャッタボタンが操作されたときの画像及びその前後の画像を記録すると、必要でない画像までも記録されてしまう。この場合、該記録した画像を再生表示させながら、シャッタチャンス以外の画像を削除しなければならないといった煩雑な作業を強いられることになる。 However, if the image when the shutter button is operated and the images before and after the shutter button are recorded in this way, even unnecessary images are recorded. In this case, a complicated operation is required in which the recorded image is reproduced and displayed, and an image other than the photo opportunity must be deleted.
そこで本発明は、かかる従来の問題点に鑑みてなされたものであり、撮影記録後において煩雑な作業を強いられることなく、シャッタチャンスの画像を記録することができる撮像装置及びそのプログラムを提供することを目的とする。 Therefore, the present invention has been made in view of such conventional problems, and provides an imaging apparatus capable of recording an image of a photo opportunity and a program thereof without being forced to perform complicated operations after shooting and recording. For the purpose.
上記目的達成のため、請求項1記載の発明は、被写体を撮像する撮像手段と、
前記撮像手段を用いて被写体を所定の撮像フレームレートで連続して撮影する連続撮影制御手段と、
前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを前記所定の撮像フレームレートと同じ表示フレームレートで表示手段にリアルタイム表示させる第1の表示制御手段と、
前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを一時的に記憶させるための記憶媒体に順次記憶させていく記憶制御手段と、
前記記憶制御手段により順次記憶される画像データを、前記所定の撮像フレームレートより低い表示フレームレートで表示手段にスロー表示させていく第2の表示制御手段と、
前記第1の表示制御手段による前記連続撮影画像の表示中に、スロー表示開始を指示する指示手段と、
前記指示手段によりスロー表示開始が指示された場合に、前記第2の表示制御手段による撮影画像の表示に切替える切替手段と、
前記第2の表示制御手段による撮影画像の表示中に、ユーザの操作に応じて画像データの記録を指示する記録指示手段と、
前記記録指示手段により画像データの記録が指示された場合は、該記録が指示された際に前記第2の表示制御手段により表示されている画像データをファイル化して記録媒体に記録する記録制御手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする。
In order to achieve the above object, the invention according to
Continuous shooting control means for continuously shooting a subject at a predetermined imaging frame rate using the imaging means;
First display control means for causing the display means to display in real time the image data continuously shot by the continuous shooting control means at the same display frame rate as the predetermined imaging frame rate;
Storage control means for sequentially storing image data continuously photographed by the continuous photographing control means in a storage medium for temporarily storing the data;
Second display control means for causing the display means to slowly display the image data sequentially stored by the storage control means at a display frame rate lower than the predetermined imaging frame rate;
Instructing means for instructing start of slow display during display of the continuously shot image by the first display control means;
Switching means for switching to display of a photographed image by the second display control means when an instruction to start slow display is given by the instruction means;
Recording instruction means for instructing recording of image data in accordance with a user operation during display of a captured image by the second display control means;
When recording of image data is instructed by the recording instruction means, recording control means for recording the image data displayed by the second display control means in a file and recording it on a recording medium when the recording is instructed When,
It is provided with.
また、請求項2記載の発明は、上記請求項1記載の発明において、前記記憶制御手段により前記記憶媒体に記憶され、前記第2の表示制御手段によりスロー表示される画像データを、前記連続撮影制御手段による連続撮影の時間経過とともに、古い画像データから間引いていく間引き手段と、
を更に備え、
前記第2の表示制御手段は、
前記記憶制御手段により前記記憶媒体に記憶された画像データを順次読み出してスロー表示させていくことを特徴とする。
The invention of
Further comprising
The second display control means includes
The image data stored in the storage medium is sequentially read out by the storage control means and displayed slowly.
また、請求項3記載の発明は、上記請求項1又は2記載の発明において、前記第2の表示制御手段は、
所定時間の間に前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを、スロー表示させることを特徴とする。
According to a third aspect of the present invention, in the first or second aspect of the invention, the second display control means includes:
The image data continuous shooting by the continuous photographing control unit during a predetermined time period, characterized in that to the slow display.
また、請求項4記載の発明は、上記請求項3記載の発明において、前記第2の表示制御手段は、
前記指示手段によりスロー表示の開始が指示されたタイミングに基づく所定時間の間に、前記連続撮影制御手段より連続撮影された画像データのスロー表示を開始させることを特徴とする。
The invention according to claim 4 is the invention according to claim 3, wherein the second display control means includes:
Wherein the instruction means during a predetermined time based on the timing of the start is instructed of slow display, characterized in that to start the slow display of image data continuous shooting from the continuous photographing control unit.
また、請求項5記載の発明は、上記請求項4記載の発明において、前記第2の表示制御手段は、
前記指示手段によりスロー表示の開始が指示されたタイミング時の一定時間前から前記連続撮影制御手段により撮影された画像データを、スロー表示させることを特徴とする。
The invention according to claim 5 is the invention according to claim 4, wherein the second display control means includes:
The image data captured by the continuous photographing control unit before a predetermined time at the timing of the start of the slow display is instructed by the instruction means, and characterized in that the slow display.
また、請求項6記載の発明は、上記請求項1乃至5の何れかに記載の発明において、前記表示手段は第1の表示領域と第2の表示領域とを有し、
前記第2の表示制御手段によるスロー表示を前記第1の表示領域にて行うと同時に、前記連続撮影制御手段により撮影された画像データのリアルタイムの表示を前記第2の表示領域にて行うリアルタイム表示制御手段を更に備えたことを特徴とする。
The invention according to
Wherein at the same time the slow display by the second display control means performs at the first display region, earthenware pots row by the second display area display of real-time image data captured by the continuous photographing control unit realtime A display control means is further provided.
また、請求項7記載の発明は、上記請求項1乃至6の何れかに記載の発明において、前記第2の表示制御手段は、
前記連続撮影された画像データが全てスロー表示された場合は、再び最初からスロー表示させた画像データをスローでリピート表示させることを特徴とする。
The invention according to claim 7 is the invention according to any one of
When all the continuously photographed image data is displayed in a slow manner, the image data that has been slow-displayed from the beginning is again displayed in a slow and repeat manner.
また、上記目的達成のため、請求項8記載の発明は、撮像部、表示部、及び、記録媒体を備える撮像装置が有するコンピュータを、
前記撮像部を用いて被写体を所定の撮像フレームレートで連続して撮影する連続撮影制御手段、
前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを前記所定の撮像フレームレートと同じ表示フレームレートで表示手段にリアルタイム表示させる第1の表示制御手段、
前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを一時的に記憶させるための記憶媒体に順次記憶させていく記憶制御手段、
前記記憶制御手段により順次記憶される画像データを、前記所定の撮像フレームレートより低い表示フレームレートで表示手段にスロー表示させていく第2の表示制御手段、
前記第1の表示制御手段による前記連続撮影画像の表示中に、スロー表示開始を指示する指示手段、
前記指示手段によりスロー表示開始が指示された場合に、前記第2の表示制御手段による撮影画像の表示に切替える切替手段、
前記第2の表示制御手段による撮影画像の表示中に、ユーザの操作に応じて画像データの記録を指示する記録指示手段、
前記記録指示手段により画像データの記録が指示された場合は、該記録が指示された際に前記第2の表示制御手段により表示されている画像データをファイル化して記録媒体に記録する記録制御手段
として機能させることを特徴とする。
In order to achieve the above object, the invention described in
Continuous shooting control means for continuously shooting a subject at a predetermined imaging frame rate using the imaging unit;
First display control means for causing the display means to display in real time the image data continuously shot by the continuous shooting control means at the same display frame rate as the predetermined imaging frame rate;
Storage control means for sequentially storing the image data continuously photographed by the continuous photographing control means in a storage medium for temporarily storing the image data;
Second display control means for causing the display means to slowly display the image data sequentially stored by the storage control means at a display frame rate lower than the predetermined imaging frame rate;
Instruction means for instructing to start slow display during display of the continuously shot image by the first display control means;
Switching means for switching to display of a photographed image by the second display control means when an instruction to start slow display is given by the instruction means;
A recording instruction means for instructing recording of image data in accordance with a user operation during display of a photographed image by the second display control means;
When recording of image data is instructed by the recording instruction means, recording control means for recording the image data displayed by the second display control means in a file and recording it on a recording medium when the recording is instructed It functions as <br/>.
本願発明によれば、撮影時においてユーザが意図するシャッタチャンスに対応する画像を確実に記録することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to reliably record an image corresponding to a shutter chance intended by the user at the time of shooting.
以下、本実施の形態について、本発明の撮像装置をデジタルカメラに適用した一例として図面を参照して詳細に説明する。
[第1の実施の形態]
A.デジタルカメラの構成
図1は、本発明の撮像装置を実現するデジタルカメラ1の電気的な概略構成を示すブロック図である。
デジタルカメラ1は、撮影レンズ2、レンズ駆動ブロック3、絞り4、CCD5、ドライバ6、TG(timing generator)7、ユニット回路8、画像生成部9、CPU10、キー入力部11、メモリ12、DRAM13、フラッシュメモリ14、画像表示部15、バス16を備えている。
Hereinafter, the present embodiment will be described in detail with reference to the drawings as an example in which the imaging apparatus of the present invention is applied to a digital camera.
[First embodiment]
A. Configuration of Digital Camera FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a schematic electrical configuration of a
The
撮影レンズ2は、図示しない複数のレンズ群から構成されるフォーカスレンズ、ズームレンズ等を含む。そして、撮影レンズ2にはレンズ駆動ブロック3が接続されている。レンズ駆動ブロック3は、フォーカスレンズ、ズームレンズをそれぞれ光軸方向に沿って駆動させるフォーカスモータ、ズームモータと、CPU10から送られてくる制御信号にしたがって、フォーカスモータ、ズームモータを駆動させるフォーカスモータドライバ、ズームモータドライバから構成されている(図示略)。
The photographing
絞り4は、図示しない駆動回路を含み、駆動回路はCPU10から送られてくる制御信号にしたがって絞り4を動作させる。
絞り4とは、撮影レンズ2から入ってくる光の量を制御する機構のことをいう。
The diaphragm 4 includes a drive circuit (not shown), and the drive circuit operates the diaphragm 4 in accordance with a control signal sent from the
The diaphragm 4 is a mechanism that controls the amount of light that enters from the photographing
CCD5(撮像素子)は、ドライバ6によって駆動され、一定周期毎に被写体像のRGB値の各色の光の強さを光電変換して撮像信号としてユニット回路8に出力する。このドライバ6、ユニット回路8の動作タイミングはTG7を介してCPU10により制御される。なお、CCD5はベイヤー配列の色フィルターを有しており、電子シャッタとしての機能も有する。この電子シャッタのシャッタ速度は、ドライバ6、TG7を介してCPU10によって制御される。
The CCD 5 (imaging device) is driven by a
ユニット回路8には、TG7が接続されており、CCD5から出力される撮像信号を相関二重サンプリングして保持するCDS(Correlated Double Sampling)回路、そのサンプリング後の撮像信号の自動利得調整を行なうAGC(Automatic Gain Control)回路、その自動利得調整後のアナログの撮像信号をデジタル信号に変換するA/D変換器から構成されており、CCD5から出力された撮像信号はユニット回路8を経てデジタル信号として画像生成部9に送られる。
A TG 7 is connected to the
画像生成部9は、ユニット回路8から送られてきた画像データに対してγ補正処理、ホワイトバランス処理などの処理を施すとともに、輝度色差信号(YUVデータ)を生成し、該生成された輝度色差信号の画像データはCPU10に送られる。つまり、画像生成部9は、CCD5から出力された画像データに対して画像処理を施す。
The
CPU10は、デジタルカメラ1の各部を制御するワンチップマイコンである。また、CPU10は、クロック回路を含み時刻を計時する機能も有する。
主に、CPU10は、CCD5及びドライバ6、TG7を介して被写体を所定時間連写撮像(連続撮影)する機能(連続撮影制御手段)、該連写撮像により得られた画像データを、連写撮像の連写スピードより遅いスピードでスロー表示させる機能(スロー表示制御手段)、ユーザによって指定された撮影タイミングでスロー表示されている画像データを記録する機能(記録制御手段)を有する。
The
Mainly, the
キー入力部11は、半押し全押しの2段階操作可能なシャッタボタン、撮影指示ボタン、モード切替キー、メニューキー、十字キー、SETキー等の複数の操作キーを含み、ユーザのキー操作に応じた操作信号をCPU10に出力する。
メモリ12には、CPU10が各部を制御するのに必要な制御プログラム、及び必要なデータが記録されており、CPU10は、該プログラムに従い動作する。
The
The
DRAM13は、CCD5によって撮像された後、CPU10に送られてきた画像データを一時記憶するバッファメモリとして使用されるとともに、CPU10のワーキングメモリとして使用される。
フラッシュメモリ14は、圧縮された画像データを保存する記録媒体である。
The
The
画像表示部15は、カラーLCDとその駆動回路を含み、撮影待機状態にあるときには、CCD5によって撮像された被写体をスルー画像として表示し、記録画像の再生時には、フラッシュメモリ14から読み出され、伸張された記録画像を表示させる。
The
B.デジタルカメラ1の動作
実施の形態におけるデジタルカメラ1の動作を図2及び図3のフローチャートに従って説明する。
ユーザのキー入力部11のモード切替キーの操作により静止画撮影モードが設定されると、ステップS1で、CPU10は、TG7、ドライバ6を介してCCD5に所定のフレームレート(ここでは、60fps)で被写体の動画を撮像する動画撮像処理を開始する(連続撮影制御手段)。
次いで、ステップS2で、該動画撮像処理により順次得られたフレーム画像データをリアルタイムで画像表示部15に表示させていくスルー画像表示(通常のスルー画像表示)を開始する(スルー表示制御手段)。この通常のスルー画像表示とは、CCD5により撮像された画像データを1画面で表示させることをいう。
B. Operation of
When the still image shooting mode is set by the user operating the mode switching key of the
Next, in step S2, through image display (normal through image display) in which the frame image data sequentially obtained by the moving image imaging processing is displayed on the
ここで、CCD5により順次撮像され、画像生成部9により順次生成された輝度色差信号はバッファメモリ(DRAM13)に記憶されていき、該記憶されたフレーム画像データが画像表示部15に表示されていくが、バッファメモリには1フレーム分のフレーム画像データのみが記憶されるものとし、前述のフレームレートで撮像されたフレーム画像データはバッファメモリに更新記憶(上書き記憶)されていき、このバッファメモリに更新記憶されたフレーム画像データが直ちにスルー画像として順次表示されていく。
Here, the luminance color difference signals sequentially picked up by the CCD 5 and sequentially generated by the
スルー画像表示を開始すると、ステップS3に進み、CPU10は、シャッタボタンが半押し操作されたか否かを判断する。この判断は、シャッタボタンの半押し操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてきたか否かにより判断する。
ステップS3で、シャッタボタンが半押しされていないと判断すると、ステップS4に進み、CPU10は、連写スピードの設定変更を行なうか否かを判断する。
When the through image display is started, the process proceeds to step S3, and the
If it is determined in step S3 that the shutter button is not half-pressed, the process proceeds to step S4, and the
この連写スピードとは、後述する連写撮像処理により連続して撮像するスピード(撮像間隔)のことをいい、スピードが速い程、1秒間に撮影する回数は大きくなる(撮像間隔は短くなる)。ここでは、連写スピードとして、毎秒60枚(1秒間に60枚連写できる連写スピード)以下のスピードで設定することができるものとする。
このとき、ユーザは、連写スピードの設定変更を行なう場合は、メニューキーの操作を行なうことにより連写スピードの設定変更を行なうことができ、CPU10は、該連写スピードの設定変更を行なう操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてきた場合には連写スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断する。
The continuous shooting speed refers to the speed (imaging interval) at which images are continuously captured by continuous imaging processing described later (the imaging interval increases as the speed increases). . Here, it is assumed that the continuous shooting speed can be set at a speed equal to or less than 60 frames per second (a continuous shooting speed at which 60 frames can be continuously captured per second).
At this time, when changing the setting of the continuous shooting speed, the user can change the setting of the continuous shooting speed by operating the menu key, and the
ステップS4で連写スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断すると、CPU10は、ステップS5に進み、ユーザの操作に応じた連写スピードに設定を変更してステップS6に進み、ステップS4で連写スピードの設定変更を行なわないと判断するとそのままステップS6に進む。この設定変更された連写スピードは、メモリ12の連写スピード記憶領域に上書きして記憶される。
If it is determined in step S4 that the setting of the continuous shooting speed is to be changed, the
ステップS6に進むと、CPU10は、連写時間の設定変更を行なうか否かを判断する。
この連写時間とは、後述する連写撮像処理により連続して撮像する時間のことをいう。
このとき、ユーザは、連写時間の設定変更を行なう場合は、メニューキーの操作を行なうことにより連写時間の設定変更を行なうことができ、CPU10は、該連写時間の設定変更を行なう操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてきた場合には連写時間の設定変更を行なうと判断する。
In step S6, the
The continuous shooting time refers to a time for continuous imaging by continuous shooting processing described later.
At this time, when changing the setting of the continuous shooting time, the user can change the setting of the continuous shooting time by operating the menu key, and the
ステップS6で連写時間の設定変更を行なうと判断すると、CPU10は、ステップS7に進み、ユーザの操作に応じた連写時間に設定を変更してステップS8に進み、ステップS6で連写時間の設定変更を行なわないと判断するとそのままステップS8に進む。この設定変更された連写時間は、メモリ12の連写時間記憶領域に上書きして記憶される。
If it is determined in step S6 that the continuous shooting time setting is to be changed, the
ステップS8に進むと、CPU10は、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうか否かを判断する。
このスロー表示スピードとは、後述するスロー表示により表示される表示間隔のことをいい、スピードが速い程表示間隔が短くなり(表示レートが上がり)、スピードが遅い程表示間隔が長くなる(表示レートが下がる)。ここでは、スロー表示スピードとして、表示スピードが1倍未満の表示スピードで設定することができるものとする。この1倍とは、リアルタイム表示、通常のスルー画像表示により表示されるスピードのことを言い、例えば、毎秒60枚で撮像された場合は、毎秒60枚表示させることを表示スピードが1倍といい、毎秒30枚で撮像された場合は、毎秒30で表示させることを表示スピードが1倍という。つまり、表示スピードは、撮像された画像データの撮像間隔によって異なることになる。
なお、毎秒何枚(1秒間に何枚画像を書き換え表示するか)というように、スロー表示スピードを設定することができるようにしてもよい。このときは、連写スピードより速くすることはできない(連写スピードにより毎秒撮像される回数以上の回数にはすることはできない)。
このとき、ユーザは、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なう場合は、メニューキーの操作を行なうことによりスロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうことができ、CPU10は、該スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なう操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてきた場合にはスロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断する。
In step S8, the
The slow display speed refers to a display interval displayed by a slow display described later. The faster the speed, the shorter the display interval (the display rate increases), and the slower the speed, the longer the display interval (display rate). ). Here, as the slow display speed, it is assumed that the display speed can be set at a display speed less than one time. This 1 × means the speed displayed by real-time display or normal through image display. For example, when 60 images are captured per second, displaying 60 images per second is called 1 × display speed. When 30 images are captured per second, displaying at 30 per second is referred to as a display speed of 1 ×. That is, the display speed varies depending on the imaging interval of the captured image data.
Note that the slow display speed may be set such as how many per second (how many images are rewritten and displayed per second). At this time, it cannot be faster than the continuous shooting speed (it cannot be more than the number of times of image capturing per second due to the continuous shooting speed).
At this time, when changing the setting of the slow display speed, the user can change the setting of the slow display speed by operating the menu key, and the
ステップS8でスロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断すると、CPU10は、ステップS9に進み、ユーザの操作に応じたスロー表示スピードに設定を変更してステップS3に戻り、ステップS6でスロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なわないと判断するとそのままステップS3に戻る。この設定変更されたスロー表示スピードは、メモリ12のスロー表示スピード記憶領域に上書きして記憶される。
If it is determined in step S8 that the setting of the slow display speed is to be changed, the
一方、ステップS3で、シャッタボタンが半押しされたと判断すると、図3のステップS10に進み、CPU10は、連写スピード記憶領域に記憶されている連写スピードで(ステップS5で設定変更された連写スピードで)、連続して被写体を撮像する連写撮像処理を開始する(連続撮影制御手段)。このとき、CPU10は、タイマーをスタートさせる。
次いで、ステップS11で、CPU10は、CCD5により撮影された画像データ(連写撮像処理により得られた画像データ、及び、動画撮像処理により得られたフレーム画像データを含む)をバッファメモリに記憶させる処理を開始する(記憶制御手段)。ここでは、撮像された画像データはバッファメモリに更新記憶(上書き記憶)されることなく記憶させる。つまり、バッファメモリには複数の画像データが記憶されることになる。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S3 that the shutter button has been half-pressed, the process proceeds to step S10 in FIG. 3, and the
Next, in step S11, the
次いで、ステップS12で、CPU10は、スロー表示スピード記憶領域に記憶されているスロー表示スピード、つまり、ステップS9で設定したスロー表示スピードで、バッファメモリに記憶された画像データを読み出して、画像表示部15の表示領域Aに表示させる処理を開始する(スロー表示制御手段)。
これにより、表示される画像はスロー表示されるので、シャッタチャンスを見つけやすくなり、特に、動きが速い被写体に対して有効である。
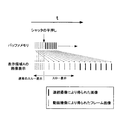
図4は、スロー表示中にシャッタボタンの半押しが解除又は全押し操作等されないとき(シャッタボタンの半押し操作がスロー表示終了まで継続されているとき)に表示領域Aに表示される画像及び表示領域Bに表示される画像のタイムチャートを示す図であり、図5は、スロー表示中にシャッタボタンの半押しが解除、全押し操作、撮影指示ボタンの操作がされたとき(シャッタボタンの半押し操作がスロー表示終了前に解除等されたとき)に表示領域Aに表示される画像及び表示領域Bに表示される画像のタイムチャートを示す図である。なお、図中のtは時間軸を表すものであり、ともに動画撮像処理のフレームレートは60fps、連写撮像処理の連写撮像間隔は、毎秒60枚とする。
Next, in step S12, the
As a result, the displayed image is displayed in a slow manner, making it easy to find a photo opportunity, and is particularly effective for a fast-moving subject.
FIG. 4 illustrates an image displayed in the display area A when the half-press of the shutter button is not released or is not fully pressed during the slow display (when the half-press operation of the shutter button is continued until the end of the slow display). FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a time chart of an image displayed in the display area B. FIG. 5 illustrates a case where the half-press of the shutter button is released, the full-press operation, and the shooting instruction button are operated during the slow display (the shutter button It is a figure which shows the time chart of the image displayed on the display area A, and the image displayed on the display area B when a half-press operation is cancelled | released before the end of slow display. Note that t in the figure represents a time axis, and in both cases, the frame rate of the moving image capturing process is 60 fps, and the continuous shooting interval of the continuous shooting process is 60 frames per second.
図4、図5に示すように、シャッタボタンが半押しされると、連写撮像処理が開始され、該連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データが順次バッファメモリに記憶されていく。このとき、表示領域Aに表示されるスロー表示スピードは、連写撮像処理により撮像される連写スピードより遅いので、現在撮像された画像データと、表示される画像データとの撮像タイミングの時間が徐々にズレていくのが分かる。図中の1(なお、図では丸1の記号で記す、つまり、1を丸で囲った記号で記す)は、連写撮像処理により撮像されている期間を示すものであり、図中のAは連写撮像処理が終了するタイミングを示すものである。この期間は、ステップS7で設定変更した連写時間と必ずしも同一ではなく、連写撮像処理により撮像している最中にシャッタボタンが半押し解除、全押し、撮影指示ボタンの操作が行なわれた場合は、連写撮像処理開始からシャッタボタンの半押し解除又は全押し操作等が行なわれるまでの期間となる。 As shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, when the shutter button is half-pressed, continuous shooting processing is started, and image data picked up by the continuous shooting processing is sequentially stored in the buffer memory. At this time, since the slow display speed displayed in the display area A is slower than the continuous shooting speed captured by the continuous shooting imaging process, the time of the imaging timing between the currently captured image data and the displayed image data is You can see that it gradually shifts. 1 in the figure (indicated by a circle symbol in the figure, that is, 1 by a circled symbol) indicates a period during which images are taken by continuous shooting imaging processing. Indicates the timing when the continuous shooting processing ends. This period is not necessarily the same as the continuous shooting time set and changed in step S7, and the shutter button was released halfway, fully pressed, and the shooting instruction button was operated during the shooting by the continuous shooting process. In this case, it is a period from the start of continuous shooting processing until the half-press release or full-press operation of the shutter button is performed.
次いで、ステップS13で、CPU10は、バッファメモリに記憶されている画像データ(フレーム画像データを含む)を、該画像データが撮像されたスピードと同じスピードで読み出して(リアルタイムで読み出して)、画像表示部15の表示領域Bに表示させる処理を開始させる(リアルタイム表示制御手段)。例えば、60fpsで動画撮像若しくは毎秒60枚のスピードで連写撮像された画像データを表示させる場合には、該撮像スピードと同じスピード、つまり、1秒間に60枚の画像データを書換えて表示させ、例えば、30fps若しくは毎秒30枚のスピードで撮像された画像データを表示させる場合には、該撮像スピードと同じスピード、つまり、1秒間に30枚の画像データを書換えて表示させる。つまり、表示領域Bには撮像された画像がリアルタイムで表示されていく。
Next, in step S13, the
上記ステップS12では、現在撮像された画像データと、表示される画像データとの撮像タイミングの時間が徐々にズレていくが、表示領域Bにはリアルタイムで画像が表示されるのでズレがなく、現在撮像されている画像を表示させることができ、現在どのような被写体が撮像されているかを認識することができる。 In step S12, the time of the imaging timing of the currently captured image data and the displayed image data gradually shifts. However, since the image is displayed in real time in the display area B, there is no shift. The captured image can be displayed, and what kind of subject is currently captured can be recognized.
次いで、CPU10は、連写スピードの設定変更を行なうか否かを判断する。
このとき、ユーザは、十字キーの「↑」キー、又は「↓」キーを操作することにより、連写スピードの設定変更を行なうことができ、CPU10は該操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてき場合は連写スピードを設定変更すると判断する。
ここで、ユーザは連写スピードを上げたい場合は、十字キーの「↑」キーの操作を行ない、連写スピードを下げたい場合は、十字キーの「↓」キーの操作を行なう。これにより、ユーザは、実際に連写撮像が行なわれているときに、その撮影状況に適切な連写スピードを設定することができる。
Next, the
At this time, the user can change the setting of the continuous shooting speed by operating the “↑” key or “↓” key of the cross key, and the
Here, the user operates the “↑” key of the cross key to increase the continuous shooting speed, and operates the “↓” key of the cross key to decrease the continuous shooting speed. Thus, the user can set a continuous shooting speed suitable for the shooting situation when continuous shooting is actually performed.
ステップS14で、連写スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断すると、ステップS15で、CPU10は、該操作に従って連写スピードの一時的な設定変更を行ってステップS16に進み、ステップS14で、連写スピードの設定変更を行なわないと判断するとそのままステップS16に進む。この一時的な設定変更とは、今回の連写撮像に限り連写スピードを変更させるものであり、このステップS15で連写スピードが設定変更されても、該設定変更された連写スピードはメモリ12の連写スピード記憶領域に記憶されない。したがって、次回の連写撮像においては、図2のステップS5によって連写スピード記憶領域に記憶された連写スピードで連写撮像処理を行うことになる。
また、この連写スピードの一時的な設定変更が行なわれた場合は、連写撮像処理により撮像される連写スピードが連写撮像の最中に変わることになる。つまり、該設定変更された連写スピードで連写撮像処理を行う。
If it is determined in step S14 that the setting of the continuous shooting speed is to be changed, in step S15, the
When the continuous shooting speed setting is temporarily changed, the continuous shooting speed captured by the continuous shooting processing is changed during the continuous shooting. That is, continuous shooting processing is performed at the continuous shooting speed with the setting changed.
ステップS16に進むと、CPU10は、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうか否かを判断する。
このとき、ユーザは、十字キーの「→」キー、「←」キーを操作することにより、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうことができ、CPU10は該操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてきた場合はスロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断する。
ここで、ユーザはスロー表示スピードを上げたい場合は、十字キーの「→」キーの操作を行ないスロー表示スピードを下げたい場合は、十字キーの「←」キーの操作を行なう。これにより、ユーザは、実際に連写撮像が行なわれているときに、その撮影状況に適切なスロー表示スピードを設定することができる。
In step S16, the
At this time, the user can change the setting of the slow display speed by operating the “→” key and the “←” key of the cross key, and the
If the user wants to increase the slow display speed, the user operates the “→” key of the cross key, and operates the “←” key of the cross key to decrease the slow display speed. Thereby, the user can set a slow display speed suitable for the shooting situation when continuous shooting is actually performed.
ステップS16で、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断すると、ステップS17に進み、CPU10は、該操作に従ってスロー表示スピードの一時的な設定変更を行なってステップS18に進み、ステップS16で、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なわないと判断するとそのままステップS18に進む。この一時的な設定変更とは、今回の連写撮像に伴うスロー表示に限りスロー表示スピードを変更させるものであり、このステップS17でスロー表示スピードが設定変更されても、該設定変更されたスロー表示スピードはメモリ12のスロー表示スピード記憶領域に記憶されない。したがって、次回の連写撮像に伴うスロー表示においては、図2のステップS9によってスロー表示スピード記憶領域に記憶されたスロー表示スピードで連写撮像処理を行うことになる。
また、このスロー表示スピードの一時的な設定変更が行なわれた場合は、表示領域Aに表示されるスロー表示のスピードがスロー表示の最中に変わることになる。つまり、該設定変更されたスロー表示スピードでバッファメモリから画像データを読出し、該読み出した画像データを表示領域Aに表示させることになる。
If it is determined in step S16 that the setting of the slow display speed is to be changed, the process proceeds to step S17, and the
When the setting of the slow display speed is temporarily changed, the speed of the slow display displayed in the display area A is changed during the slow display. That is, the image data is read from the buffer memory at the slow display speed whose setting has been changed, and the read image data is displayed in the display area A.
ステップS18に進むと、連写撮像処理により得られた全ての画像データのスロー表示が行われたか否かを判断する。
つまり、図4に示すように、連写撮像処理により撮像された全ての画像データがスロー表示されたか否かを判断する。図4のBは、連写撮像処理により撮像された全ての画像データをスロー表示した時のタイミングを示すものである。
In step S18, it is determined whether or not all the image data obtained by the continuous shooting processing has been displayed in a slow manner.
That is, as shown in FIG. 4, it is determined whether or not all image data captured by the continuous shooting processing has been displayed in a slow manner. FIG. 4B shows the timing when all the image data picked up by the continuous shooting pick-up processing is displayed in slow motion.
ステップS18で、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データのスロー表示が終了していないと判断すると、ステップS19に進み、CPU10は、シャッタボタンの半押し解除が行なわれたか否かの判断を行う。
つまり、図5に示すように、連写撮像処理により得られた全ての画像データがスロー表示される前に、シャッタボタンの半押しが解除されたか否かを判断する。
この判断は、シャッタボタンの半押しに対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてこなくなり、且つ、シャッタボタンの全押し操作に対応する操作信号も送られてきていない場合には、シャッタボタンの半押しが解除されたと判断する。
If it is determined in step S18 that the slow display of the image data obtained by the continuous shooting processing has not ended, the process proceeds to step S19, and the
That is, as shown in FIG. 5, it is determined whether or not the half-press of the shutter button has been released before all the image data obtained by the continuous shooting processing is displayed in slow motion.
This determination is made when an operation signal corresponding to half-pressing of the shutter button is not sent from the
ステップS19で、シャッタ半押しの解除が行なわれていないと判断すると、ステップS20に進み、CPU10は、撮影指示ボタン(第2の記録指示手段)が操作されたか否かを判断する。この判断は、撮影指示ボタンの操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてきたか否かにより判断する。
ステップS20で、撮影指示ボタンが操作されていないと判断すると、ステップS21に進み、CPU10は、シャッタボタン全押し(第1の記録指示手段)操作が行なわれたか否かを判断する。この判断は、シャッタボタンの全押し操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてきた場合にはシャッタボタンの全押し操作が行なわれたと判断する。
If it is determined in step S19 that the shutter half-press has not been released, the process proceeds to step S20, and the
If it is determined in step S20 that the shooting instruction button has not been operated, the process proceeds to step S21, and the
ステップS21で、シャッタボタンの全押しが行なわれていないと判断すると、ステップS22に進み、現在連写撮像処理によって被写体の撮像を行なっているか否かを判断する。
ステップS22で、現時点において連写撮像処理によって被写体を撮像していると判断すると、ステップS23に進み、CPU10は、連写撮像処理を行ってから連写時間記憶領域に記憶されている連写時間が経過したか否か判断する。つまり、タイマーが連写時間を経過したか否かを判断する。
If it is determined in step S21 that the shutter button has not been fully pressed, the process proceeds to step S22, and it is determined whether or not the subject is currently being imaged by continuous shooting imaging processing.
If it is determined in step S22 that the subject is being captured by the continuous shooting process at the present time, the process proceeds to step S23, and the
ステップS23で、連写時間が経過したと判断すると、ステップS24に進み、CPU10は、連写撮像処理から動画撮像処理に切替えて、ステップS16に戻る。
一方、ステップS22で、現在連写撮像処理によって撮像していないと判断した場合、つまり、動画撮像処理を行っていると判断した場合はそのままステップS16に戻り、ステップS23で、連写時間が経過していないと判断した場合は、そのままステップS14に戻る。
If it is determined in step S23 that the continuous shooting time has elapsed, the process proceeds to step S24, where the
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S22 that no image is currently being captured by the continuous shooting process, that is, if it is determined that a moving image capturing process is being performed, the process returns to step S16 and the continuous shooting time has elapsed in step S23. If it is determined that it has not, the process returns to step S14.
図4、図5のAは、連写時間が経過するタイミングを示しており、図4、図5を見ると、Aのタイミングが経過するまでは連写撮像処理により被写体を撮像しており、Aのタイミングが経過すると、連写撮像処理から動画撮像処理に切り替わって被写体を撮像しているのが分かる。図4、図5中の2(なお、図では丸2の記号で記す、つまり、2を丸で囲った記号で記す)は、スロー表示中に動画撮像処理により撮像されている期間を示すものである。
4 and FIG. 5A shows the timing at which the continuous shooting time elapses. Looking at FIG. 4 and FIG. 5, the subject is imaged by continuous shooting imaging processing until the timing of A passes, When the timing A has elapsed, it can be seen that the continuous shooting imaging process is switched to the moving image imaging process and the subject is being imaged. 2 in FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 (indicated by a
一方、ステップS21でシャッタボタンの全押し操作が行なわれたと判断すると、ステップS25に進み、CPU10は、現在(シャッタボタンの全押し操作時点において)画像表示部15の表示領域Aにスロー表示している画像データ(バッファメモリに記憶されている画像データ)を圧縮処理した上でフラッシュメモリ14に記録させて(記録制御手段)、ステップS27に進む。
図5に示すように、シャッタボタン全押しがされたときにスロー表示された画像データがフラッシュメモリ14に記録される。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S21 that the shutter button has been fully pressed, the process proceeds to step S25, where the
As shown in FIG. 5, image data that is displayed in a slow manner when the shutter button is fully pressed is recorded in the
一方、ステップS20で撮影指示ボタンが操作されたと判断すると、ステップS26に進み、CPU10は、現在画像表示部15の表示領域Bに表示させている画像データ(フレーム画像データも含む)を圧縮処理した上でフラッシュメモリ14に記録させて(記録制御手段)、ステップS27に進む。つまり、撮影指示ボタンが操作されると、リアルタイムで現在表示させている画像データを記録することになる。
一方、ステップS18で連写撮像により得られた画像データのスロー表示が終了したと判断した場合、ステップ19でシャッタボタンの半押しが解除されたと判断した場合はそのままステップS27に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S20 that the shooting instruction button has been operated, the process proceeds to step S26, and the
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S18 that the slow display of the image data obtained by continuous shooting has been completed, or if it is determined in step 19 that the half-press of the shutter button has been released, the process proceeds directly to step S27.
ステップS27に進むと、現在バッファメモリに記憶されている画像データに基づいて間欠(フレーム間引き)表示を行う。この間欠表示が行われている間も、動画撮像処理若しくは連写撮像処理は継続して行なわれる。
図4の3(なお、図では丸3の記号で記す、つまり、3を丸で囲った記号で記す)は、連写撮像処理により撮像された全ての画像データをスロー表示させたと判断された場合に、間欠表示される画像の様子を示すものであり、図5の3(なお、図では丸3の記号で記す)は、連写撮像処理により撮像された全ての画像データをスロー表示させる前に、シャッタボタンが半押し解除又は全押し又は撮影指示操作がされたと判断した場合に、間欠表示される画像の様子を示すものである。
In step S27, intermittent (frame thinning) display is performed based on the image data currently stored in the buffer memory. Even during the intermittent display, the moving image capturing process or the continuous capturing process is continuously performed.
4 in FIG. 4 (indicated by a circle 3 symbol in the figure, that is, 3 is circled) is determined to be a slow display of all image data captured by the continuous shooting process. In this case, the state of the intermittently displayed image is shown, and 3 in FIG. 5 (indicated by the symbol of circle 3 in the figure) displays all the image data picked up by the continuous shooting processing in a slow manner. When the shutter button is released halfway, fully pressed, or a shooting instruction operation is determined before, the state of an image displayed intermittently is shown.
図4の間欠表示の場合は、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データは全てスロー表示されているので、連写時間経過後に、動画撮像処理により得られたフレーム画像データが間欠表示され、図5の間欠表示の場合は、シャッタボタン半押し解除又は全押し時又は撮影指示ボタン操作時に未だスロー表示されていない画像データ、及び連写時間経過後に動画撮像処理により得られたフレーム画像データが間欠表示される。なお、連写時間経過前に、シャッタボタン半押し解除又は全押し時又は撮影指示ボタン操作がなされた場合には、シャッタボタン半押し解除又は全押し時に未だスロー表示されていない、連写撮像処理により得られる画像データのみが間欠表示されることになる。 In the case of the intermittent display of FIG. 4, all the image data obtained by the continuous shooting process is displayed in a slow manner. Therefore, after the continuous shooting time has elapsed, the frame image data obtained by the moving picture imaging process is displayed intermittently. In the case of the intermittent display of 5, the image data that has not yet been displayed slowly when the shutter button is half-pressed or fully pressed or when the shooting instruction button is operated, and the frame image data obtained by the moving image capturing process after the continuous shooting time has elapsed. Is displayed. If the shutter button is half-pressed or fully pressed or the shooting instruction button is operated before the continuous shooting time elapses, the continuous shooting processing is not yet displayed when the shutter button is half-pressed or fully pressed. Only the image data obtained by the above is intermittently displayed.
この間欠表示中に撮像された画像データ(フレーム画像データも含む)も間欠表示の対象画像となる。つまり、スロー表示終了時以後に撮像された画像データやシャッタボタン半押し解除又は全押し時又は撮影指示ボタン操作時以後に撮像された画像データも間欠表示の対象となり、要は現在撮像されている画像データと表示領域Aに表示される画像とをスムーズに繋げるためであり、表示される画像を見るユーザの違和感を無くすためである。この現在撮像される画像と表示領域Aにスロー表示された画像をスムーズに繋げる機能は、本発明の(調整表示手段)に相当する。
また、図4、図5の間欠表示は、未だ表示されていない画像データ(フレーム画像データも含む)を間引くとともに、スルー画像表示のスピードより高速で表示させるようにしたが、単に間引いて表示させるようにしてもよい。また、間引かずに、未だ表示されていない画像データを高速表示させていくようにしてもよい。
Image data (including frame image data) captured during this intermittent display is also a target image for intermittent display. That is, image data captured after the end of slow display, image data captured after half-press release or full-press of the shutter button, or operation of the shooting instruction button is also subject to intermittent display, and is currently being captured. This is to smoothly connect the image data and the image displayed in the display area A, and to eliminate the user's uncomfortable feeling when viewing the displayed image. The function of smoothly connecting the currently captured image and the image slowly displayed in the display area A corresponds to (adjustment display means) of the present invention.
The intermittent display in FIGS. 4 and 5 thins out image data (including frame image data) that has not yet been displayed, and displays it at a speed higher than the through image display speed. You may do it. Further, image data that has not yet been displayed may be displayed at high speed without being thinned out.
なお、連写時間経過後のスロー画像表示中に行われる動画撮像処理の撮像フレームレートを、間欠表示されるフレーム画像のみを撮像するようなフレームレート(連写撮像時よりも低いフレームレート)とすることにより、撮像処理の負荷を軽減させたり、画像データの間引き処理を省略できるようにしてもよい。この場合は、既に間欠表示に必要な画像データのみが撮像されバッファメモリに記憶されているので、バッファメモリに記憶された画像データを全て表示させるようにする。
また、連写時間経過後に動画撮像処理により撮像された全てのフレーム画像データをバッファメモリに記憶し、該記憶したフレーム画像データを用いて間欠表示させるようにしたが、動画撮像処理により撮像されたフレーム画像データをバッファメモリに記憶する段階で間引いて記憶させるようにしてもよい。
この場合は、既に間引かれた画像データがバッファメモリに記憶されているので、バッファメモリに記憶された画像データを全て表示させるようにする。
In addition, the imaging frame rate of the moving image imaging process performed during the slow image display after the continuous shooting time has elapsed is set to a frame rate (a frame rate lower than that during continuous shooting) that captures only the intermittently displayed frame images. By doing so, the load of the imaging process may be reduced, or the thinning-out process of the image data may be omitted. In this case, since only the image data necessary for the intermittent display has already been captured and stored in the buffer memory, all the image data stored in the buffer memory is displayed.
In addition, all frame image data captured by the moving image capturing process after the continuous shooting time has elapsed is stored in the buffer memory and intermittently displayed using the stored frame image data. The frame image data may be stored by being thinned out at the stage of storing it in the buffer memory.
In this case, since the already thinned image data is stored in the buffer memory, all the image data stored in the buffer memory is displayed.
この間欠表示を行う理由は、上述したように、表示領域Aに表示される画像はスロー表示されているので、現在撮像された画像データと、表示される画像データとの撮像タイミングの時間が徐々にズレていくので、シャッタボタン半押し解除後又は全押し後に通常のスルー画像表示に復帰すると、スロー表示させていた画像と通常のスルー表示により表示される画像との連続性が無く不自然となってしまい、違和感があるので、未だスロー表示されていない画像データ(フレーム画像データも含む)を表示させることにより、現在撮像されている画像データとの連続性を持たせることができ、自然な動画を表示させることができる。 The reason for this intermittent display is that, as described above, the image displayed in the display area A is displayed slowly, so that the time of the imaging timing of the currently captured image data and the displayed image data gradually increases. When the shutter button is half-pressed or fully pressed and then returns to normal through image display, there is no continuity between the slow-displayed image and the image displayed by normal through display. Since there is a sense of incongruity, by displaying image data (including frame image data) that has not yet been displayed slowly, it is possible to have continuity with the currently captured image data, which is natural. A video can be displayed.
次いで、ステップS28に進み、CPU10は、現在連写撮像処理により被写体を撮像しているか否かを判断し、連写撮像処理により撮像している場合はステップS1に戻り、動画撮像処理により撮像している場合はステップS2に戻り、通常のスルー画像表示に復帰する。
これにより、次のシャッタチャンスが到来するまでリアルタイムで画像を表示させることができ、シャッタチャンスが間もなく到来するか否かの判断を適切に行うことができる。つまり、シャッタボタンが全押しされた場合や半押しが解除、又は撮影指示ボタンが押下された場合には、シャッタチャンスは間近に迫っておらず、シャッタチャンスが間近に迫ってないのにスロー表示させると、スロー表示されている画像を見てシャッタチャンスが間もなく到来すると判断した時はもう既にシャッタチャンスは到来してしまっているからである。
また、ユーザが間もなくシャッタチャンスが来るだろうと判断してシャッタボタンを半押ししても、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データを全てスロー表示させた場合は、スロー表示された画像データの中にはシャッタチャンスの画像はないので、一度通常のスルー画像表示に復帰させることにより、ユーザに再度シャッタチャンスが間もなく到来するか否かの判断を適切に行なわせることができる。
Next, the process proceeds to step S28, in which the
Thereby, an image can be displayed in real time until the next photo opportunity comes, and it can be appropriately determined whether or not the photo opportunity will come soon. In other words, when the shutter button is fully pressed, when the half-press is released, or when the shooting instruction button is pressed, the shutter chance is not approaching immediately, and the shutter chance is not approaching soon, but the slow display is displayed. This is because when it is determined that a photo opportunity is coming soon by looking at the slow-displayed image, the photo opportunity has already come.
Even if the user determines that a photo opportunity will be coming soon and the shutter button is half-pressed, if all of the image data obtained by the continuous shooting process is displayed slowly, Since there is no image of the photo opportunity, once the display is restored to the normal through image display, the user can appropriately determine whether or not the photo opportunity will come soon again.
C.以上のように、第1の実施の形態においては、連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データを、該画像データが撮像された撮像スピードより遅いスピード(スロー表示スピード)で表示させるので、撮影時においてユーザが意図するシャッタチャンスに対応する画像のみを確実に記録することができる。したがって、撮影終了後に、シャッタチャンスに対応する画像以外の画像を削除する煩雑な作業が不要になり、シャッタチャンスに対応する画像のみを記録することができる。 C. As described above, in the first embodiment, the image data captured by the continuous imaging process is displayed at a speed (slow display speed) slower than the imaging speed at which the image data was captured. Thus, it is possible to reliably record only an image corresponding to the shutter chance intended by the user. Accordingly, it is not necessary to perform a complicated operation of deleting an image other than the image corresponding to the photo opportunity after the photographing is completed, and it is possible to record only the image corresponding to the photo opportunity.
また、連写撮像により得られた画像データのスロー表示から、通常のスルー画像表示に復帰する場合は、スロー表示されている画像と現在撮像されている画像との流れをよくするために間欠表示を行うようにしたので、単にスロー表示を終了して、通常のスロー画像表示に復帰する場合よりも違和感がなくなる。
また、シャッタボタンが半押しされた場合は、スロー画像とリアルタイム画像とを同時に表示させるので、現在撮像されている被写体を認識することができるとともに、スロー表示を見ながらシャッタチャンスの画像を見つけやすくなる。
In addition, when returning to the normal through image display from the slow display of the image data obtained by continuous shooting, intermittent display is performed to improve the flow between the slow displayed image and the currently captured image. Therefore, the user feels less uncomfortable than when the user simply ends the slow display and returns to the normal slow image display.
When the shutter button is pressed halfway, a slow image and a real-time image are displayed at the same time, so that the currently captured subject can be recognized and it is easy to find a shutter chance image while watching the slow display. Become.
また、撮影指示ボタンが操作された場合は、リアルタイムで表示されている画像を記録するので、連写撮像された画像データにシャッタチャンスがない場合等に、特に有効である。つまり、スロー表示されている画像は連写撮像により撮像された画像データであるが、リアルタイムで表示されている画像は連写撮像により撮像された画像データと、動画撮像により撮像されたフレーム画像データであるので、必ずしも現在リアルタイムで表示されている画像データがスロー表示されるとは限らないからである。
また、シャッタボタンを半押し状態からシャッタボタンを全押しすると、表示領域Aにスロー表示されていた画像データを記録するとともに、通常のスルー画像表示に復帰するので、スロー表示の解除ボタンをわざわざ設けることなく、シャッタボタン全押し操作がスロー表示の解除としての機能も有し、操作が楽になる。また、シャッタボタンを全押しすることなく、シャッタボタンの半押しを解除した場合も同様に、シャッタボタンの半押し解除がスロー表示の解除としての機能も有し、操作が楽になる。
In addition, when the shooting instruction button is operated, an image displayed in real time is recorded, which is particularly effective when there is no photo opportunity in continuously shot image data. In other words, the slow-displayed image is image data captured by continuous shooting, while the image displayed in real time is image data captured by continuous shooting and frame image data captured by moving-image capturing. This is because the image data currently displayed in real time is not always displayed in a slow manner.
Further, when the shutter button is fully pressed from the half-pressed state, the image data that has been slowly displayed in the display area A is recorded, and the normal through image display is restored. Therefore, a slow display cancel button is provided. In addition, the operation of fully pressing the shutter button also has a function of canceling the slow display, which makes the operation easier. Similarly, when the half-press of the shutter button is released without fully pressing the shutter button, the release of the half-press of the shutter button also has a function of releasing the slow display, and the operation becomes easy.
[第2の実施の形態]
次に、第2の実施の形態について説明する。
第1の実施の形態においては、所定時間連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データのスロー表示中に、シャッタボタンが全押し又は半押し解除又は撮影指示ボタンが操作されない(シャッタボタンの半押し操作がスロー表示終了まで継続されている)場合は、通常のスルー画像表示に復帰するようにしたが、第2の実施の形態においては、所定時間連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データのスロー表示中に、シャッタボタンが全押し又は半押し解除又は撮影指示ボタンが操作されない場合は、スロー表示させた画像をスローでリピート再生するというものである。
これにより、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データの中にシャッタチャンスの画像があるのだけれども、シャッタボタン全押し操作するタイミングを逃した場合や、シャッタチャンスと思われる画像が複数有り、どの画像が一番最適か迷った場合等に特に効果がある。
[Second Embodiment]
Next, a second embodiment will be described.
In the first embodiment, the shutter button is fully pressed or half-pressed or the shooting instruction button is not operated during the slow display of the image data captured by the continuous shooting processing for a predetermined time (half-press operation of the shutter button). Is continued until the end of the slow display), the normal through image display is restored. However, in the second embodiment, the slow display of the image data captured by the continuous shooting imaging process for a predetermined time is performed. When the shutter button is fully pressed or half-pressed or the shooting instruction button is not operated, the slow-displayed image is played back repeatedly in slow motion.
As a result, although there is a photo opportunity image in the image data obtained by the continuous shooting process, if there is a missed timing when the shutter button is fully pressed, or there are multiple images that appear to be photo opportunities, This is particularly effective when the image is most optimal.
D.デジタルカメラ1の動作
第2の実施の形態も、図2に示したものと同様の構成を有するデジタルカメラ1を用いることにより本発明の撮像装置を実現する。
以下、第2の実施の形態のデジタルカメラ1の動作を図6及び図7のフローチャートにしたがって説明する。
D. Operation of
Hereinafter, the operation of the
図2のステップS3で、シャッタボタンが半押しされたと判断すると、図6のステップS51に進み、CPU10は、連写スピード記憶領域に記憶されている連写スピードで(ステップS5で設定変更された連写スピードで)、連続して被写体を撮像する連写撮像処理を開始する(連続撮影制御手段)。このとき、CPU10は、タイマーをスタートさせる。
If it is determined in step S3 in FIG. 2 that the shutter button has been half-pressed, the process proceeds to step S51 in FIG. 6, and the
次いで、ステップS52で、CPU10は、CCD5により連写撮像された画像データをバッファメモリに記憶させる処理を開始する(記憶制制御手段)。ここでは、撮像された画像データはバッファメモリに更新記憶(上書き記憶)されることなく記憶させる。つまり、バッファメモリには複数の画像データが記憶されることになる。
Next, in step S52, the
次いで、ステップS53で、連写撮像により得られバッファメモリに記憶された画像データを、スロー表示スピード記憶領域に記憶されているスロー表示スピード、つまり、図2のステップS9で設定したスロー表示スピードで読み出して、画像表示部15の表示領域Aに表示させる処理を開始する(スロー表示制御手段)。
これにより、表示される画像はスロー表示されるので、シャッタチャンスを見つけやすくなり、特に、動きが速い被写体に対して有効である。
Next, in step S53, the image data obtained by continuous shooting and stored in the buffer memory is displayed at the slow display speed stored in the slow display speed storage area, that is, the slow display speed set in step S9 in FIG. A process of reading and displaying the image in the display area A of the
As a result, the displayed image is displayed in a slow manner, making it easy to find a photo opportunity, and is particularly effective for a fast-moving subject.
次いで、ステップS54で、CPU10は、CCD5により撮像されバッファメモリに記憶された画像データ(連写撮像により得られた画像データ、及び、後述するステップS73で動画撮像により撮像されバッファメモリに記憶されたフレーム画像データを含む)を、該画像データが撮像されたスピードと同じスピードで読み出して(リアルタイムで読み出して)、画像表示部15の表示領域Bに表示させる処理を開始させる(リアルタイム表示制御手段)。つまり、表示領域Bには撮像された画像がリアルタイムで表示されていく。
Next, in step S54, the
次いで、ステップS55に進み、CPU10は、連写撮像処理を開始してから時間T1が経過したか否かを判断する。つまり、タイマーが時間T1を経過したか否かを判断する。
ステップS55で、連写撮像処理を開始してから時間T1が経過したと判断すると、ステップS56に進み、CPU10は、時間T1までに連写撮像された画像データの枚数を既に間引いたか否かを判断する。つまり、後述するステップS57の処理を既に行ったか否かを判断する。
Next, the process proceeds to step S55, and the
If it is determined in step S55 that the time T1 has elapsed since the start of the continuous shooting process, the process proceeds to step S56, and the
ステップS56で、時間T1までに連写撮像された画像データの枚数を未だ間引いていないと判断すると、ステップS57に進み、CPU10は、時間T1までに連写撮像されバッファメモリに記憶されている複数の画像データの枚数を間引く処理を行ってステップS58に進む。ここで、間引き処理とは、間引き対象となる画像データを消去する処理であってもよいし、画像管理データのみを変更して間引き対象となる画像データが記憶されていた領域に新たな画像データを上書き可能な状態とする処理であってもよい。
ここでは、2枚に1枚の画像データを間引くので、例えば、毎秒60枚で連写撮像処理を行ってバッファメモリに記憶した場合は、この間引き処理により残る画像データの枚数は、毎秒30枚で連写撮像されたときと同様の枚数となる。つまり、動画撮像で言うならば撮像されたフレーム画像のフレームレートを60fpsから30fpsに下げるのと同様の結果となる。
If it is determined in step S56 that the number of image data continuously captured by time T1 has not yet been thinned, the process proceeds to step S57, and the
Here, since one image data is thinned out every two images, for example, when continuous shooting processing is performed at 60 images per second and stored in the buffer memory, the number of image data remaining by this thinning processing is 30 images per second. The number of images is the same as when continuous shooting was performed with. That is, in moving image capturing, the result is the same as when the frame rate of the captured frame image is reduced from 60 fps to 30 fps.
これにより、スロー画像表示されている画像と現在撮像されている画像の撮像タイミングとはズレていき、徐々にバッファメモリに表示されていない画像データが増えていくが、この間引き処理により記憶される画像データの枚数を減らすことができ、バッファメモリの空き容量を増やすことができる。
一方、ステップS55で連写撮像処理開始から時間T1を経過していないと判断した場合、ステップS56で時間T1までに撮像された画像の枚数を間引いたと判断した場合は、そのままステップS58に進む。
As a result, the image capturing timing of the image displayed as a slow image and the image capturing timing of the currently captured image are shifted, and the image data not displayed in the buffer memory gradually increases, but is stored by this thinning process. The number of image data can be reduced, and the free space of the buffer memory can be increased.
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S55 that the time T1 has not elapsed since the start of the continuous shooting process, or if it is determined in step S56 that the number of images taken up to time T1 has been thinned, the process proceeds directly to step S58.
ステップS58に進むと、CPU10は、連写撮像処理を開始してから時間T2が経過したか否かを判断する。つまり、タイマーが時間T2を経過したか否かを判断する。なお、時間T1<時間T2とする。なお、ここでは、連写時間は時間T2より長いものとする。
ステップS58で、連写撮像処理を開始してから時間T2が経過したと判断すると、ステップS59に進み、CPU10は、時間T2までに連写撮像された画像データの枚数を既に間引いたか否かを判断する。つまり、後述するステップS60の処理を既に行ったか否かを判断する。
In step S58, the
If it is determined in step S58 that the time T2 has elapsed since the start of the continuous shooting process, the process proceeds to step S59, and the
ステップS59で、時間T2までに連写撮像された画像データの枚数を未だ間引いていないと判断すると、ステップS60に進み、CPU10は、時間T2までに連写撮像されバッファメモリに記憶されている複数の画像データの枚数を間引く処理を行って、ステップS61に進む。
ここでも、2枚に1枚の画像データを間引くので、例えば、毎秒60枚で連写撮像処理を行ってバッファッメモリに記憶した場合は、時間T1から時間T2までに撮像された画像データの枚数は、60枚から30枚に減り、時間T1までに撮像された画像データの枚数は30枚から更に15枚に減る。
If it is determined in step S59 that the number of image data continuously captured by time T2 has not yet been thinned out, the process proceeds to step S60, and the
Again, since one image data is thinned out every two images, for example, when continuous shooting processing is performed at 60 images per second and stored in the buffer memory, the image data captured from time T1 to time T2 is stored. The number of images is reduced from 60 to 30, and the number of image data captured by time T1 is further reduced from 30 to 15.
なお、ステップS57、ステップS60での間引き処理は2枚に1枚の画像を間引くようにしたが、これに限定されるものではなく、また、ステップS57の間引き処理と、ステップS60の間引き処理を異ならせるようにしてもよい。例えば、ステップS57の間引き処理を3枚に1枚間引き、ステップS60の間引き処理を4枚に1枚間引くというようにしてもよい。 Note that the thinning process in step S57 and step S60 is such that one image is thinned out in two sheets, but the present invention is not limited to this, and the thinning process in step S57 and the thinning process in step S60 are performed. You may make it differ. For example, the thinning process in step S57 may be thinned out by 1 sheet, and the thinning process in step S60 may be thinned by 1 sheet in 4 sheets.
図8は、時間の経過とともにバッファメモリに記憶される画像データの様子を示すものである。t軸は連写撮像開始時からの時間の経過を示すものである。
図8を見ると、時間T1が経過するまでは、毎秒60枚で連写撮像された画像データが記憶されており、時間T1が経過すると、時間T1までに撮像された画像データが2枚に1枚間引かれた画像データが記憶されているのがわかる。この図中の太線は連写撮像により撮像されバッファメモリに記憶されている画像データを示し、破線はステップS57で間引かれて消去された画像データを示している。このように、ステップS57の間引き処理により時間T1までに記憶された画像データの枚数は、毎秒60枚で連写撮像されて記憶された場合であっても、毎秒30枚で連写撮像された枚数と同じになる。
FIG. 8 shows the state of image data stored in the buffer memory over time. The t-axis indicates the passage of time from the start of continuous shooting.
Referring to FIG. 8, the image data continuously captured at 60 frames per second is stored until the time T1 elapses, and when the time T1 elapses, the image data captured by the time T1 becomes two images. It can be seen that the image data thinned out by one sheet is stored. The thick line in this figure indicates the image data captured by the continuous shooting and stored in the buffer memory, and the broken line indicates the image data that has been thinned out and deleted in step S57. As described above, the number of image data stored up to time T1 by the thinning-out process in step S57 is 30 images per second, even when 60 images are captured and stored continuously per second. It becomes the same as the number of sheets.
また、時間T1が経過し、更に時間T2が経過すると、時間T2までに撮像された画像データが2枚に1枚間引かれた画像データが記憶されているのがわかる。この図中の点線はステップS60で間引かれて消去された画像データを示している。このように、ステップS60の間引き処理により時間T1から時間T2までに記憶された画像データの枚数は、毎秒60枚で連写撮像されて記憶された場合であっても、毎秒30枚で連写撮像されたときの枚数と同じになり、時間T1までの画像データの枚数は、既にステップS57で間引かれているので、毎秒60枚で連写撮像されて記憶された場合であっても、毎秒15枚で連写撮像されたときとの枚数と同じになっているのが分かる。
このステップS55〜ステップS60までの処理は、本発明の間引き手段に相当する。
Further, it can be seen that when the time T1 elapses and the time T2 elapses, the image data obtained by thinning out two pieces of image data captured by the time T2 is stored. The dotted lines in this figure indicate the image data that has been thinned out and deleted in step S60. As described above, the number of image data stored from the time T1 to the time T2 by the thinning-out process in step S60 is continuously shot at 30 frames per second even when the images are continuously captured and stored at 60 frames per second. Since the number of image data up to time T1 has already been thinned out in step S57, the number of image data up to time T1 is already thinned out. It can be seen that the number of images is the same as when 15 images were taken continuously per second.
The processing from step S55 to step S60 corresponds to the thinning means of the present invention.
このように、時間の経過とともに、バッファメモリに記憶されている画像データのうち、古い画像データほど間引かれていくことになる。
なお、2段階で画像データを間引くようにしたが、時間の経過とともに3段階以上の段階で画像データを間引いていくようにしてもよい。
Thus, as time elapses, older image data is thinned out of image data stored in the buffer memory.
Although the image data is thinned out in two stages, the image data may be thinned out in three or more stages as time passes.
ステップS61に進むと、CPU10は、連写スピードの設定変更を行なうか否かを判断する。このとき、ユーザは、十字キーの「↑」キー、又は「↓」キーを操作することにより、連写スピードの設定変更を行なうことができ、CPU10は該操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてき場合は連写スピードを設定変更すると判断する。
ここで、ユーザは連写スピードを上げたい場合は、十字キーの「↑」キーの操作を行ない、連写スピードを下げたい場合は、十字キーの「↓」キーの操作を行なう。これにより、ユーザは、実際に連写撮像が行なわれているときに、その撮影状況に適切な連写スピードを設定することができる。
In step S61, the
Here, the user operates the “↑” key of the cross key to increase the continuous shooting speed, and operates the “↓” key of the cross key to decrease the continuous shooting speed. Thus, the user can set a continuous shooting speed suitable for the shooting situation when continuous shooting is actually performed.
ステップS61で、連写スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断すると、ステップS62で、CPU10は、該操作に従って連写スピードの一時的な設定変更を行ってステップS63に進み、ステップS61で、連写スピードの設定変更を行なわないと判断するとそのままステップS63に進む。この一時的な設定変更とは、今回の連写撮像に限り連写スピードを変更させるものであり、このステップS62で連写スピードが設定変更されても、該設定変更された連写スピードはメモリ12の連写スピード記憶領域に記憶されない。したがって、次回の連写撮像においては、図2のステップS5によって連写スピード記憶領域に記憶された連写スピードで連写撮像処理を行うことになる。
また、この連写スピードの一時的な設定変更が行なわれると、CPU10は、連写撮像処理により連写撮像される連写スピードを変更させる。つまり、連写スピードの設定が変更されると、該設定変更された連写スピードで連写撮像処理を行う。
If it is determined in step S61 that the setting of the continuous shooting speed is to be changed, in step S62, the
In addition, when the setting of the continuous shooting speed is temporarily changed, the
ステップS63に進むと、CPU10は、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうか否かを判断する。
このとき、ユーザは、十字キーの「→」キー、「←」キーを操作することにより、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうことができ、CPU10は該操作に対応する操作信号がキー入力部11から送られてきた場合はスロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断する。
ここで、ユーザはスロー表示スピードを上げたい場合は、十字キーの「→」キーの操作を行ないスロー表示スピードを下げたい場合は、十字キーの「←」キーの操作を行なう。これにより、ユーザは、実際に連写撮像が行なわれているときに、その撮影状況に適切なスロー表示スピードを設定することができる。
In step S63, the
At this time, the user can change the setting of the slow display speed by operating the “→” key and the “←” key of the cross key, and the
If the user wants to increase the slow display speed, the user operates the “→” key of the cross key, and operates the “←” key of the cross key to decrease the slow display speed. Thereby, the user can set a slow display speed suitable for the shooting situation when continuous shooting is actually performed.
ステップS63で、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なうと判断すると、ステップS64に進み、CPU10は、該操作に従ってスロー表示スピードの一時的な設定変更を行なって、ステップS65に進み、ステップS63で、スロー表示スピードの設定変更を行なわないと判断するとそのままステップS65に進む。この一時的な設定変更とは、今回の連写撮像に伴うスロー表示に限りスロー表示スピードを変更させるものであり、このステップS64でスロー表示スピードが設定変更されても、該設定変更されたスロー表示スピードはメモリ12のスロー表示スピード記憶領域に記憶されない。したがって、次回の連写撮像に伴うスロー表示においては、図2のステップS9によってスロー表示スピード記憶領域に記憶されたスロー表示スピードで連写撮像処理を行うことになる。
また、このスロー表示スピードの一時的な設定変更が行なわれると、CPU10は、スロー表示されるスロー表示スピードを変更させる。つまり、スロー表示スピードの設定が変更されると、該設定変更されたスロー表示スピードで画像を読出し、該読み出した画像を表示領域Aに表示させる。
If it is determined in step S63 that the setting of the slow display speed is to be changed, the process proceeds to step S64, and the
When the setting of the slow display speed is temporarily changed, the
ステップS65に進むと、連写撮像処理により得られた全ての画像データがスロー表示されたか否かを判断する。
ステップS65で連写撮像処理により得られた全ての画像データのスロー表示が終了したと判断すると、ステップS66に進み、CPU10は、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データを、スロー表示スピード記憶領域に記憶されているスロー表示スピード又はステップS64で直近に一時的に設定変更されたスロー表示スピードでバッファメモリから再び読出し、表示領域Aに表示させるというリピート表示を開始して(スロー表示制御手段)、ステップS67に進む。これにより、スロー表示中にシャッタチャンスの画像がある場合に、シャッタチャンスを見逃してしまった場合等でも再びリピート表示を行うことができるので、シャッタチャンスの画像を得ることができる。
In step S65, it is determined whether all the image data obtained by the continuous shooting process has been displayed in a slow manner.
If it is determined in step S65 that the slow display of all the image data obtained by the continuous shooting process has been completed, the process proceeds to step S66, and the
このとき、連写撮像処理により得られた全ての画像データのスロー表示が終了したと判断する場合は、連写撮像処理開始時から連写時間経過しており、バッファメモリには、図6のステップ57、ステップS60で間引かれた画像データが記憶されている。したがって、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データの1回目のスロー表示は、スロー表示させている最中に徐々に画像データを間引くのに対して、2回目以降のスロー表示は、既に間引かれた後の画像データを単にスロー表示させるので、1回目のスロー表示と2回目のスロー表示とでは、表示される態様が異なる。
At this time, when it is determined that the slow display of all the image data obtained by the continuous shooting processing has been completed, the continuous shooting time has elapsed since the start of the continuous shooting processing, and the buffer memory stores The image data thinned out in
つまり、1回目のスロー表示は、最初は毎秒60枚で連写撮像された画像データが表示されていき、時間の経過とともに毎秒30枚、毎秒15枚というように間引かれた画像データがスロー表示されていくのに対し、2回目以降のスロー表示は、最初は毎秒15枚の画像データがスロー表示され、次に毎秒30枚、毎秒60枚の画像データがスロー表示されるということになる。 In other words, in the first slow display, image data captured continuously at 60 images per second is displayed first, and image data that has been thinned out such as 30 images per second and 15 images per second as time passes. On the other hand, in the slow display after the second time, the image data of 15 images per second is first displayed slowly, and then the image data of 30 images per second and 60 images per second are displayed slowly. .
一方、ステップS65で、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データのスロー表示が終了していないと判断するとそのままステップS67に進む。
ステップS67に進むと、CPU10は、シャッタボタンの半押しが解除されたか否かを判断する。
ステップS67で、シャッタボタンの半押しが解除されていないと判断すると、ステップS68に進み、CPU10は、撮影指示ボタンが操作されたか否かを判断する。
ステップS68で、撮影指示ボタン(第2の記録指示手段)が操作されていないと判断すると、ステップS69に進み、CPU10は、シャッタボタンが全押しされたか否かを判断する。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S65 that the slow display of the image data obtained by the continuous shooting process has not ended, the process proceeds to step S67 as it is.
In step S67, the
If it is determined in step S67 that the half-press of the shutter button has not been released, the process proceeds to step S68, and the
If it is determined in step S68 that the shooting instruction button (second recording instruction means) has not been operated, the process proceeds to step S69, and the
ステップS69で、シャッタボタン全押(第1の記録指示手段)が操作されていないと判断すると、ステップS70に進み、現在連写撮像処理により被写体を撮像しているか否かを判断する。
ステップS70で、連写撮像処理により被写体を撮像していると判断すると、ステップS71に進み、連写撮像処理を開始してから連写時間が経過したか否かを判断する。つまり、タイマーが連写時間を経過したか否かを判断する。
なお、実際に連写撮像される連写時間と、連写撮像により得られた全ての画像データのスロー表示時間とでは、連写時間の方が短いので、ステップS65で連写撮像により得られた全ての画像データのスロー表示を行ったと判断するまえに、ステップS71で連写時間が経過したと判断することになる。
If it is determined in step S69 that the shutter button full press (first recording instruction means) has not been operated, the process proceeds to step S70, and it is determined whether or not the subject is currently being imaged by the continuous shooting imaging process.
If it is determined in step S70 that the subject is imaged by the continuous shooting process, the process proceeds to step S71, and it is determined whether or not the continuous shooting time has elapsed since the start of the continuous shooting process. That is, it is determined whether the timer has passed the continuous shooting time.
It should be noted that the continuous shooting time actually obtained by continuous shooting and the slow display time of all image data obtained by continuous shooting are shorter than the continuous shooting time, and thus are obtained by continuous shooting in step S65. Before it is determined that all image data has been displayed slowly, it is determined in step S71 that the continuous shooting time has elapsed.
ステップS71で連写時間が経過していないと判断すると、図6のステップS55に戻り、ステップS71で連写時間が経過したと判断すると、ステップS72に進み、CPU10は、連写撮像処理を終了し、動画撮像処理を開始する。
次いで、ステップS73で、CPU10は、該動画撮像処理により得られた画像データをバッファッメモリに更新記憶させていく処理を開始する。このとき、バッファメモリは動画撮像処理により得られたフレーム画像データを1フレームのみ記憶し、新たにフレーム画像データが撮像されると、該撮像されたフレーム画像データを更新記憶(上書き記憶)させて、図6のステップS63に戻る。なお、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データはそのままバッファッメモリに保持され、ステップS66のリピート再生に用いられる。
一方、ステップS70で、連写撮像処理により被写体を撮像していないと判断するとステップS63に戻る。
If it is determined in step S71 that the continuous shooting time has not elapsed, the process returns to step S55 in FIG. 6, and if it is determined in step S71 that the continuous shooting time has elapsed, the process proceeds to step S72, and the
Next, in step S73, the
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S70 that the subject is not imaged by the continuous shooting process, the process returns to step S63.
一方、ステップS67で、シャッタボタンの半押しが解除されたと判断するとそのままステップS76に進む。
また、ステップS69で、シャッタボタンが全押しされたと判断すると、ステップS74に進み、CPU10は、現在表示領域Aにスロー表示させている画像データをフラッシュメモリ14に記録して(記録制御手段)、ステップS76に進む。
また、ステップS68で、撮影指示ボタンが操作されたと判断すると、ステップS75に進み、CPU10は、現在表示領域Bにリアルタイム表示させている画像データ(フレーム画像データも含む)をフラッシュメモリ14に記録して(記録制御手段)、ステップS76に進む。
ステップS76に進むと、CPU10は、現在連写撮像処理により被写体を撮像しているか否かを判断し、連写撮像処理により撮像している場合はステップS1に戻り、動画撮像処理により撮像している場合はステップS2に戻り、通常のスルー画像表示に復帰する。
これにより、次のシャッタチャンスが到来するまでリアルタイムで画像を表示させることができ、シャッタチャンスが間もなく到来するか否かの判断を適切に行うことができる。つまり、シャッタボタンが全押しされた場合や半押しが解除、又は撮影指示ボタンが押下された場合には、シャッタチャンスは間近に迫っておらず、シャッタチャンスが間近に迫ってないのにスロー表示させると、スロー表示されている画像を見てシャッタチャンスが間もなく到来すると判断した時はもう既にシャッタチャンスは到来してしまっているからである。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S67 that the half-press of the shutter button has been released, the process proceeds directly to step S76.
If it is determined in step S69 that the shutter button has been fully pressed, the process proceeds to step S74, where the
If it is determined in step S68 that the photographing instruction button has been operated, the process proceeds to step S75, and the
In step S76, the
Thereby, an image can be displayed in real time until the next photo opportunity comes, and it can be appropriately determined whether or not the photo opportunity will come soon. In other words, when the shutter button is fully pressed, when the half-press is released, or when the shooting instruction button is pressed, the shutter chance is not approaching immediately, and the shutter chance is not approaching soon, but the slow display is displayed. This is because when it is determined that a photo opportunity is coming soon by looking at the slow-displayed image, the photo opportunity has already come.
なお、ステップS67でシャッタボタンの半押しが解除されたと判断した場合、ステップS69でシャッタボタンが全押しされたと判断し、ステップS74で該シャッタボタン全押し時にスロー表示されている画像データを記録した場合、ステップS68で撮影指示ボタンが操作されたと判断し、ステップS75で該撮影指示ボタン操作時にリアルタイム表示されている画像データを記録した場合は、そのままステップS76に進むようにしたが、上記第1の実施の形態の図3のステップS27と同様に間欠表示させてからステップS76に進むようにしてもよい。この場合は、ステップS73では動画撮像処理により得られた画像を更新記憶させずに、記憶させていく必要がある。更新記憶では過去の画像データが消えてしまうので間欠表示させることはできないからである。また、間欠表示に必要な画像のみを撮像して記憶させて表示させたり、動画撮像処理により撮像された画像データをバッファメモリに記憶させる段階で、間欠表示させない画像データを間引いて記憶させ、該記憶された画像データを表示させるようにしてもよい。 If it is determined in step S67 that the half-press of the shutter button has been released, it is determined in step S69 that the shutter button has been fully pressed, and in step S74, the image data displayed in a slow display when the shutter button is fully pressed is recorded. If it is determined in step S68 that the shooting instruction button has been operated, and image data displayed in real time when the shooting instruction button is operated is recorded in step S75, the process proceeds directly to step S76. Similarly to step S27 in FIG. 3 of the embodiment, the display may be intermittently performed and then the process may proceed to step S76. In this case, in step S73, it is necessary to store the image obtained by the moving image capturing process without updating and storing the image. This is because the past image data disappears in the update storage and cannot be displayed intermittently. Further, only the images necessary for intermittent display are captured and stored and displayed, or the image data captured by the moving image capturing process is stored in the buffer memory, and the image data that is not intermittently displayed is thinned and stored. The stored image data may be displayed.
E.以上のように、第2の実施の形態においては、連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データを、該画像データが撮像された撮像スピードより遅いスピード(スロー表示スピード)で表示させるので、撮影時においてユーザが意図するシャッタチャンスに対応する画像のみを確実に記録することができる。したがって、撮影終了後に、シャッタチャンスに対応する画像以外の画像を削除する煩雑な作業が不要になり、シャッタチャンスに対応する画像のみを記録することができる。 E. As described above, in the second embodiment, the image data captured by the continuous imaging process is displayed at a speed (slow display speed) slower than the imaging speed at which the image data was captured. Thus, it is possible to reliably record only an image corresponding to the shutter chance intended by the user. Accordingly, it is not necessary to perform a complicated operation of deleting an image other than the image corresponding to the photo opportunity after the photographing is completed, and it is possible to record only the image corresponding to the photo opportunity.
また、連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データが最後までスロー表示された場合は、該連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データをリピート再生するので、例えば、ユーザがシャッタチャンスを見逃してしまった場合や、どれが一番よいかユーザが迷った場合でも、シャッタチャンスの画像を記録することができる。
また、連写撮像により撮像されバッファメモリに記憶された画像データを時間の経過とともに、古い画像データから間引く処理を(ステップS55〜ステップS60の処理を)行なうようにしたので、バッファメモリに空き容量を増やすことができ、1回目にスロー表示される画像の様子と、2回目以降にリピートスロー再生される画像の様子を異ならせることができる。
また、シャッタボタンが半押しされた場合は、スロー画像とリアルタイム画像とを同時に表示させるので、現在撮像されている被写体を認識することができるとともに、スロー表示を見ながらシャッタチャンスの画像を見つけやすくなる。
In addition, when the image data captured by the continuous shooting processing is slow-displayed to the end, the image data captured by the continuous shooting processing is repeatedly reproduced, so that, for example, the user misses the shutter chance. Even when the user is at a loss as to which is best, an image of a photo opportunity can be recorded.
In addition, since the image data picked up by continuous shooting and stored in the buffer memory is thinned out from the old image data with the passage of time (steps S55 to S60), the buffer memory has a free space. Thus, it is possible to make the state of the image that is slow-displayed for the first time different from the state of the image that is repeatedly slow-played after the second time.
When the shutter button is pressed halfway, a slow image and a real-time image are displayed at the same time, so that the currently captured subject can be recognized and it is easy to find a shutter chance image while watching the slow display. Become.
また、撮影指示ボタンが操作された場合は、リアルタイムで表示されている画像を記録するので、連写撮像された画像データにシャッタチャンスがなく、動画撮像により得られたフレーム画像データにシャッタチャンスがある場合等に、特に有効である。
また、シャッタボタンを半押し状態から全押し状態にすると、表示領域Aにスロー表示されていた画像データを記録するとともに、通常のスルー画像表示に復帰するので、スロー表示の解除ボタンをわざわざ設けることなく、シャッタボタン全押し操作がスロー表示の解除としての機能も有し、操作が楽である。また、シャッタボタンを全押しすることなく、シャッタボタンの半押しを解除した場合も同様に、シャッタボタンの半押し解除がスロー表示の解除としての機能も有し、操作が楽になる。
In addition, when the shooting instruction button is operated, an image displayed in real time is recorded. Therefore, there is no shutter chance in continuously shot image data, and there is no shutter chance in frame image data obtained by moving image shooting. This is particularly effective in some cases.
In addition, when the shutter button is pressed from the half-pressed state to the fully-pressed state, the image data that has been slowly displayed in the display area A is recorded and the normal through image display is restored. In addition, the shutter button full press operation also has a function of canceling the slow display, and the operation is easy. Similarly, when the half-press of the shutter button is released without fully pressing the shutter button, the release of the half-press of the shutter button also has a function of releasing the slow display, and the operation becomes easy.
[変形例]
F.上記各実施の形態は以下のような態様でもよい。
(1)上記各実施の形態においては、スロー画像とリアルタイム画像との両方を同時に表示させるようにしたが、スロー画像のみを表示させるようにしてもよい。
[Modification]
F. Each of the above embodiments may be as follows.
(1) In each of the above embodiments, both the slow image and the real-time image are displayed simultaneously, but only the slow image may be displayed.
(2)また、上記各実施の形態において、連写撮像処理が所定時間経過すると、動画撮像処理を行うようにしたが、間欠表示に必要なタイミングの画像だけ撮像するようにしてもよい。つまり、動画撮像処理に代えて、所定の周期(例えば、間欠表示に必要なタイミング)で被写体を撮像する撮像処理を用いるようにしてもよい。
つまり、上記各実施の形態の間欠表示に代えて、この撮像処理により撮像された画像データを表示させる(調整表示手段)。
これにより、間欠表示において、フレーム画像を間引いて表示する場合には、間引かれるフレーム画像データは必要ないので、間欠表示させないタイミングのフレーム画像データを撮像する必要がなくなり、CPU10の処理負担、消費電力を抑えることができる。
なお、動画撮像処理に代えて所定の周期で撮像する撮像処理を用いる場合は、間欠表示が終了すると、通常のスルー画像表示に復帰するために動画撮像処理を開始するようにする。
(2) In each of the above-described embodiments, the moving image imaging process is performed when the continuous shooting imaging process has elapsed for a predetermined time. However, only an image at a timing necessary for intermittent display may be captured. That is, instead of the moving image imaging process, an imaging process for imaging a subject at a predetermined cycle (for example, a timing necessary for intermittent display) may be used.
That is, instead of the intermittent display in each of the above embodiments, the image data captured by this imaging process is displayed (adjustment display means).
Thereby, in the intermittent display, when the frame image is thinned and displayed, the frame image data to be thinned is not necessary, so that it is not necessary to capture the frame image data at a timing at which the intermittent display is not performed. Power can be reduced.
In addition, when using the imaging process which images instead of a moving image imaging process at a predetermined period, when an intermittent display is complete | finished, in order to return to a normal through image display, a moving image imaging process is started.
(3)また、上記各実施の形態においては、間欠表示において画像データを単純に間引いて表示させるようにしたが、所定枚数の画像データを合成した画像データを表示させるようにしてもよい。例えば、10枚分の画像データに基づいて1枚の画像データを合成して表示させるようにしてもよい。 (3) In the above-described embodiments, the image data is simply thinned and displayed in intermittent display. However, image data obtained by combining a predetermined number of image data may be displayed. For example, one piece of image data may be synthesized and displayed based on 10 pieces of image data.
(4)また、上記各実施の形態においては、シャッタボタンが半押しされると連写撮像処理を開始し(図2のステップS10、図6のステップS51)、該連写撮像処理により得られた画像データからスロー表示させるようにしたが(ステップS12、ステップS53)、シャッタ半押し前に撮像された一定枚数(一定時間)のフレーム画像データからスロー表示を行うようにしてもよい。
シャッタ半押し前に撮像されたフレーム画像データは既に通常のスルー画像表示(図2のステップS2)で表示されているので、シャッタ半押し前に撮像された一定枚数のフレーム画像データは、重複して表示されることになる。
(4) In each of the above-described embodiments, when the shutter button is half-pressed, continuous shooting processing is started (step S10 in FIG. 2, step S51 in FIG. 6), and obtained by the continuous shooting processing. Although slow display is performed from the image data (steps S12 and S53), slow display may be performed from a predetermined number of frame image data (predetermined time) captured before half-pressing the shutter.
Since the frame image data captured before the shutter half-press is already displayed in the normal through image display (step S2 in FIG. 2), a certain number of frame image data captured before the shutter half-press overlaps. Will be displayed.
図9は、そのときの様子を示すものであり、図9を見ると、シャッタ半押しされると、一定枚数前のフレームがスロー表示されてから、連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データがスロー表示されているのがわかる。これにより、シャッタ半押し前の画像データからスロー表示されるので、シャッタチャンスより遅れたタイミングでシャッタボタンを半押しした場合でもシャッタチャンスの画像をリピート再生することができ、シャッタチャンスの画像を得ることができる。
なお、この場合は、通常のスルー表示においても、動画撮像処理により得られたフレーム画像データを更新記憶させることなく、一定枚数前までのフレーム画像データを常時バッファメモリに保持しておくといった記憶処理を行う必要がある。
なお、この一定枚数や一定時間をユーザが任意に設定することができるようにしてもよい。
FIG. 9 shows the situation at that time. Referring to FIG. 9, when the shutter is half-pressed, a predetermined number of frames are displayed slowly, and the image data captured by the continuous shooting processing is displayed. You can see that it is slow. As a result, since the image data before the shutter half-press is displayed in a slow manner, even when the shutter button is half-pressed at a timing later than the shutter chance, the image of the shutter chance can be repeatedly reproduced, and an image of the shutter chance is obtained. be able to.
Note that in this case, even in normal through display, the storage processing is such that frame image data up to a certain number of frames is always held in the buffer memory without updating and storing the frame image data obtained by the moving image imaging processing. Need to do.
Note that the user may arbitrarily set the fixed number of sheets and the fixed time.
(5)また、上記変形例(4)を第2の実施の形態に適用する場合は、図7のステップS66でリピート表示を行う場合は、スロー表示として表示された画像データをそのままリピート表示させるようにしてもよい。つまり、シャッタ半押し前に(連写撮像処理の前に)動画撮像された所定枚数のフレーム画像データからスローでリピート表示させるようにしてもよい。 (5) When the modification (4) is applied to the second embodiment, when the repeat display is performed in step S66 of FIG. 7, the image data displayed as the slow display is displayed as it is. You may do it. In other words, a predetermined number of frame image data obtained by moving image capturing may be displayed in slow repetition before the shutter is half-pressed (before continuous shooting processing).
(6)また、上記各実施の形態においては、スロー表示中に、連写時間の設定変更を行なうことができなかったが、連写時間の設定を変更できるようにしてもよい。これにより、設定した連写時間内にシャッタチャンスが来ないと判断した場合は、連写時間を延長することによりシャッタチャンスの画像を連写撮像により撮像することができる。
なお、連写時間を短くする場合には、連写撮像処理を開始してから既に経過した時間より短くすることはできないことは言うまでもない。短くしても既に連写撮像により撮像されてしまっているからである。
(6) In each of the above embodiments, the continuous shooting time setting cannot be changed during slow display. However, the continuous shooting time setting may be changed. Thereby, when it is determined that the photo opportunity does not come within the set continuous shooting time, an image of the photo opportunity can be taken by continuous shooting by extending the continuous shooting time.
Needless to say, when the continuous shooting time is shortened, the continuous shooting time cannot be shorter than the time already elapsed after the continuous shooting processing is started. This is because even if it is shortened, it has already been picked up by continuous shooting.
(7)また、上記各実施の形態において、シャッタボタンが半押しされることなく、いきなり全押しされた場合は、シャッタボタンの全押し時に、通常のスルー画像表示によってリアルタイムで表示されている画像データを記録するようにしてもよい。
また、シャッタボタンが半押しされることなく、撮影指示ボタンが操作された場合は、撮影指示ボタンの操作時に、通常のスルー画像表示によってリアルタイムで表示されている画像データを記録するようにしてもよい。
(7) In each of the above embodiments, when the shutter button is suddenly fully pressed without being half pressed, an image displayed in real time by a normal through image display when the shutter button is fully pressed Data may be recorded.
Further, when the shooting instruction button is operated without the shutter button being pressed halfway, the image data displayed in real time by the normal through image display may be recorded when the shooting instruction button is operated. Good.
(8)また、上記各実施の形態においては、シャッタボタン半押しでスロー画像表示を指示し、シャッタボタン全押しで表示領域Aにスロー表示されている画像の記録を指示し、撮影指示ボタンの操作で表示領域Bにリアルタイムで表示されている画像の記録を指示するようにしたが、他のボタンで上記各指示を行うような態様であってもよい。
例えば、スロー表示ボタンを設け、スロー表示ボタンが操作された場合は、スロー表示を開始する。
(8) Further, in each of the above-described embodiments, the slow image display is instructed by half-pressing the shutter button, the recording of the image displayed in the display area A is instructed by fully pressing the shutter button, and the shooting instruction button Although the recording of the image displayed in real time in the display area B is instructed by the operation, the above-described instructions may be performed by using other buttons.
For example, a slow display button is provided, and when the slow display button is operated, the slow display is started.
(9)また、上記各実施の形態において、シャッタボタンが半押しされると、連写撮像処理を行うようにしたが、連写撮像処理に代えて動画撮像処理を行うようにしてもよい。この場合は、シャッタボタン半押し前における動画撮像処理と、シャッタ半押し後の動画撮像処理の撮像制御(例えば、フレームレート等)を異ならせるようにしてもよい。
また、動画撮像処理に代えて、全て連写撮像処理を行うようにしてもよい。
この場合の連写時間は、連写撮像処理又は動画撮像処理により撮像される画像のうち、スロー表示される画像を撮像する時間のことをいう。
(9) In each of the above embodiments, the continuous shooting imaging process is performed when the shutter button is half-pressed. However, the moving image imaging process may be performed instead of the continuous shooting imaging process. In this case, the imaging control (for example, the frame rate) of the moving image imaging process before the shutter button is half-pressed and the moving image imaging process after the shutter button is half-pressed may be made different.
Further, instead of moving image capturing processing, continuous shooting processing may be performed.
The continuous shooting time in this case refers to a time for capturing a slow-displayed image among images captured by the continuous shooting imaging process or the moving image imaging process.
(10)また、上記各実施の形態において、連写撮像処理から動画撮像処理に切り替わった場合は(図3のステップS24、図7のステップS27)、切り替わった旨をユーザに対して報知するようにしてもよい。この報知の例としては、画像表示部15に切り替わった旨を表示させたり、音により放音するようにしてもよい。
これにより、これから撮像される画像はスロー表示されない画像であることをユーザは認識することができる。
(10) In each of the above embodiments, when switching from continuous shooting processing to moving image shooting processing (step S24 in FIG. 3 and step S27 in FIG. 7), the user is notified of the switching. It may be. As an example of this notification, it may be displayed on the
As a result, the user can recognize that the image to be captured from now on is an image that is not displayed slowly.
(11)また、第1の実施の形態において、連写時間の間、連写撮像処理を行うようにしたが、予め連写時間を設けずにシャッタボタンが半押しされている最中は、連写撮像処理を行うようにしてもよい。 (11) In the first embodiment, the continuous shooting process is performed during the continuous shooting time. While the shutter button is half-pressed without providing the continuous shooting time in advance, Continuous shooting imaging processing may be performed.
(12)また、第1の実施の形態において、表示領域Aをスロー表示、表示領域Bをリアルタイム表示としたが、半押し全押し可能な第1のシャッタボタン及び第2のシャッタボタンを備え、第1のシャッタボタンと表示領域Aとを対応させ、第2のシャッタボタンと表示領域Bとを対応させるようにしてもよい。
例えば、第1のシャッタボタンが半押しされると、第1のシャッタボタンの半押し時から連写撮像された画像データを表示領域Aにスロー表示させ、第2のシャッタボタンが半押しされると、第2のシャッタボタンの半押し時から連写撮像された画像データを表示領域Bにスロー表示させるようにする。
(12) In the first embodiment, the display area A is displayed slowly and the display area B is displayed in real time. However, the display area A includes a first shutter button and a second shutter button that can be fully pressed halfway. The first shutter button and display area A may be associated with each other, and the second shutter button and display area B may be associated with each other.
For example, when the first shutter button is half-pressed, image data captured continuously from the time when the first shutter button is half-pressed is slowly displayed in the display area A, and the second shutter button is half-pressed. Then, the image data continuously shot from when the second shutter button is half-pressed is slowly displayed on the display area B.
また、両方のシャッタボタンが半押しされた状態となった場合は、先にシャッタボタンの半押しに伴ってスロー表示させていた方の表示領域をリアルタイム表示に復帰させるようにしてもよい。つまり、同時に2つの表示領域でスロー表示させることを回避させるために、シャッタボタンが新たに半押しされた方をスロー表示させ、先にシャッタボタンが半押しされていた方をリアルタイムで表示させるようにしてもよい。例えば、第1のシャッタボタンが半押しされた後に、第2のシャッタボタンが半押しされた場合は、スロー表示されていた表示領域Aをリアルタイム表示に切り替えるとともに、表示領域Bをスロー表示に切替えるようにする。 In addition, when both shutter buttons are half-pressed, the display area that was previously slow-displayed when the shutter button was half-pressed may be returned to real-time display. In other words, in order to avoid the slow display in the two display areas at the same time, the one where the shutter button is newly pressed halfway is displayed in a slow manner, and the one where the shutter button was previously pressed halfway is displayed in real time. It may be. For example, when the second shutter button is pressed halfway after the first shutter button is pressed halfway, the display area A that has been displayed slowly is switched to real-time display, and the display area B is switched to slow display. Like that.
(13)また、第2の実施の形態で説明した、連写撮像により撮像されバッファメモリに記憶された画像データを時間の経過とともに、古い画像データから間引く処理を(ステップS55〜ステップS60の処理を)、第1の実施の形態においても適用するようにしてもよい。これにより、バッファメモリの空き容量を確保することができる。
また、第2の実施の形態では、連写撮像により撮像されバッファメモリに記憶された画像データを時間の経過とともに、古い画像データから間引く処理(ステップS55〜ステップS60の処理)を行なうようにしたが、行なわないようにしてもよい。
また、連写撮像により撮像されバッファメモリに記憶された画像データを時間の経過とともに、古い画像データから間引く方法として、連写撮像処理開始時を基準とし、連写撮像処理開始時から所定の時間経過したときに、該所定の時間(T1やT2)までに連写撮像された画像データを間引くようにしたが、現時点から所定時間(所定枚数)前より以前の画像データを間引く処理を周期的に行うようにしてもよい。
例えば、5秒前より前に撮像された画像データを間引くという処理を周期的に行うようにすれば、時間の経過とともに、古い画像データ程間引かれる回数が多くなり、新しい画像データ程間引かれる回数は少なくなるので、バッファメモリに記憶されている画像データのうち、古い画像データほど間引くことができる。
(13) Also, the process of thinning out the image data picked up by continuous shooting and stored in the buffer memory from the old image data with the passage of time described in the second embodiment (the process of steps S55 to S60) And may also be applied to the first embodiment. As a result, a free space in the buffer memory can be secured.
In the second embodiment, the processing (step S55 to step S60) of thinning out the image data picked up by the continuous shooting and stored in the buffer memory from the old image data with the passage of time is performed. However, it may not be performed.
In addition, as a method of thinning out the image data captured by the continuous shooting and stored in the buffer memory from the old image data with the passage of time, a predetermined time from the start of the continuous shooting processing is set on the basis of the start of the continuous shooting processing. When the time has elapsed, the image data captured continuously by the predetermined time (T1 or T2) is thinned out, but the process of thinning out the image data before the predetermined time (predetermined number) before the present time is periodically performed. You may make it carry out.
For example, if the process of thinning out image data captured before 5 seconds is periodically performed, the older image data is thinned over time, and new image data is thinned out. Since the number of times is reduced, older image data can be thinned out of the image data stored in the buffer memory.
(14)また、上記第2の実施の形態においては、シャッタボタンが全押しされたと判断すると(ステップS69でY)、ステップS74で画像データを記録した後通常のスルー画像表示に復帰してしまうが、シャッタボタンが全押しされた場合は、ステップS74で画像データを記録した後、ステップS70に進むようにしてもよい。つまり、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データのスロー表示乃至スローリピート表示がシャッタボタンの全押しで解除されることがない。
これにより、シャッタボタンが全押しされても、スロー表示は解除されないので、シャッタボタンが全押しされても通常のスルー画像表示に復帰せず、連写撮像処理により得られた画像データの中でシャッタチャンスだと思う画像を何枚でも記録することができる。
(14) In the second embodiment, if it is determined that the shutter button is fully pressed (Y in step S69), the image data is recorded in step S74 and then the normal through image display is restored. However, if the shutter button is fully pressed, the image data may be recorded in step S74 and then the process may proceed to step S70. That is, the slow display or slow repeat display of the image data obtained by the continuous shooting process is not canceled by fully pressing the shutter button.
As a result, even if the shutter button is fully pressed, the slow display is not canceled, so even if the shutter button is fully pressed, the normal through image display is not restored, and the image data obtained by the continuous shooting processing is not included. You can record any number of images that you think is a photo opportunity.
(15)また、上記各実施の形態においては、連写撮像処理の連写スピードのみを設定変更することができるようにしたが、動画撮影処理により撮影される撮影間隔(フレームレート)も一緒に変更することができるようにしてもよい。 (15) In each of the above embodiments, only the continuous shooting speed of the continuous shooting processing can be changed. However, the shooting interval (frame rate) shot by the moving image shooting processing is also set together. It may be possible to change it.
(16)また、上記各実施の形態は、シャッタボタンが半押しされると、単にスロー表示とリアルタイム表示を行うようにしたが、スロー表示により表示されている画像がどのタイミングで撮像された画像であるかを示す情報も表示させるようにしてもよい。
以下、変形例(16)における表示例を図10を用いて説明する。
図10は、画像表示部に表示される画面の表示タイムチャートを示すものである。
(16) In each of the above embodiments, when the shutter button is half-pressed, the slow display and the real-time display are simply performed. However, at what timing the image displayed by the slow display is captured. The information indicating whether or not may be displayed.
Hereinafter, a display example in the modification (16) will be described with reference to FIG.
FIG. 10 shows a display time chart of the screen displayed on the image display unit.
図2のステップS3で、シャッタボタンが半押しと判断されるまでは、図10(a)に示すように、画像表示部15には通常のスルー画像が表示される。
そして、図2のステップS3で、シャッタボタンが半押しされたと判断されると、図10(b)に示すように、図3のステップS10又は図6のステップS51で連写撮像処理が開始され、該連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データがバッファメモリに記憶されていくとともに、画像表示部15の表示領域Aにはスロー表示され(ステップS12又はステップS53)、表示領域Bにはリアルタイム表示がされる(ステップS13又はステップS54)。なお、図中の左上にある「×0.5」という文字は、現在のスロー表示スピードを示すものであり、原則として図2のステップS9で設定されたスロー表示スピードが表示されることになるが、スロー表示中にスロー表示スピードが変更された場合は(図3のステップS17又は図6のステップS64)、該変更されたスロー表示スピードが表示される。これにより、現在設定されているスロー表示スピードをユーザは認識することができる。
Until step S3 in FIG. 2 determines that the shutter button is half-pressed, a normal through image is displayed on the
If it is determined in step S3 in FIG. 2 that the shutter button has been half-pressed, as shown in FIG. 10B, continuous shooting processing is started in step S10 in FIG. 3 or step S51 in FIG. The image data picked up by the continuous shooting processing is stored in the buffer memory, and is slowly displayed in the display area A of the image display unit 15 (step S12 or step S53), and is displayed in real time in the display area B. (Step S13 or Step S54). The character “× 0.5” in the upper left in the figure indicates the current slow display speed, and in principle, the slow display speed set in step S9 in FIG. 2 is displayed. However, when the slow display speed is changed during the slow display (step S17 in FIG. 3 or step S64 in FIG. 6), the changed slow display speed is displayed. Thereby, the user can recognize the currently set slow display speed.
このとき、図10(b)に示すように、スロー表示バーも一緒に表示させる。つまり、スロー表示中はスロー表示バーも表示させる。このスロー表示バーは、簡単に説明すると、現在、どのタイミングで撮像された画像データがスロー表示されているかを示すものである。なお、図10(b)は、シャッタボタンの半押し直後の様子を示している。 At this time, as shown in FIG. 10B, a slow display bar is also displayed. That is, a slow display bar is also displayed during slow display. In brief, the slow display bar indicates at which timing image data captured at present is being displayed in a slow manner. FIG. 10B shows a state immediately after the shutter button is half-pressed.
以下、図11(a)を用いてスロー表示バーについて説明する。なお、図11は、スロー表示バーを説明するための図である。
図11(a)に示すように、スロー表示バーは、大まかに表示バー21とキャッシュバー23を備える。この表示バー21及びキャッシュバー23の右に表示されている4s(4秒)は、スロー表示される画像データの撮像時間を示し、ここでは、連写時間ということになる。つまり、ユーザによって設定された連写時間が表示されることになる。なお、連写時間の変わりに撮影枚数を表示させるようにしてもよい。これにより、スロー表示される画像が撮像される撮像時間(連写時間)をユーザは認識することができる。
この表示バー21とキャッシュバー23の左端がシャッタボタンの半押しタイミングを示すものであり、表示バー21とキャッシュバー23の右端がシャッタボタンの半押しタイミングから連写時間(ここでは4秒)経過したタイミングを示している。
Hereinafter, the slow display bar will be described with reference to FIG. In addition, FIG. 11 is a figure for demonstrating a slow display bar.
As shown in FIG. 11A, the slow display bar roughly includes a
The left end of the
表示バー21の中に表示タイミング部22があり、この表示タイミング部22は、表示バー21の範囲内で移動可能であり、この表示タイミング部22は、スロー表示により現在表示されている画像がどのタイミングで撮像(記憶)された画像であるかを示すものである。
また、キャッシュバー23の中にある縦線部24は、シャッタボタンの半押しタイミングから撮像された画像データ(連写撮像により撮像された画像データ)のバッファメモリの記憶状況を示すものであり、この縦線部24を見ることによりシャッタボタンの半押しタイミングからどのタイミングまでに撮像された画像データが実際に記憶されているのかがわかる。なお、縦線部24は、シャッタボタンの半押しタイミングから現在までに撮像(記憶)された画像データを示すようにしたが、表示タイミング部22のように現在撮像(記憶)されているタイミングのみを表示させるようにしてもよい。
There is a
A
図10(b)に戻り、このときは、未だシャッタボタンの半押し直後なので、キャッシュバー23を見ると分かるように、バッファメモリに記憶されている画像データの量が少ないことがわかる。また、半押し直後なので、直近に記憶された画像データが撮像されたタイミング(縦線部24の右端の位置)と、現在表示させている画像が撮像されたタイミング(表示タイミング部22の位置)とは、余りズレていないことも分かる。
Returning to FIG. 10B, at this time, since the shutter button is still just half-pressed, it can be seen that the amount of image data stored in the buffer memory is small, as can be seen from the
そして、図10(c)、(d)に示すように、時間が経過するとともに、記憶される画像データの量が増えるとともに(キャッシュバー23の縦線部24が長くなるとともに)、直近に記憶された画像データが撮像されたタイミング(縦線部24の右端の位置)と、現在表示させている画像が撮像されたタイミング(表示タイミング部22の位置)とはズレていくことがわかる。
しかし、図10(d)に示すように、スロー表示により表示される画像データがすべて撮像されると(連写撮像が終了すると)、スロー表示される画像データは記憶されていかないので、連写撮像処理により直近に撮像された画像データが撮像されたタイミング(縦線部24の右端の位置)と、現在表示されている画像が撮像されたタイミング(表示タイミング部22の位置)との差は徐々に縮まっていく。
Then, as shown in FIGS. 10C and 10D, as time passes, the amount of image data to be stored increases (as the
However, as shown in FIG. 10D, when all the image data displayed in the slow display is captured (when the continuous shooting is completed), the image data displayed in the slow display is not stored, so the continuous shooting is not performed. The difference between the timing at which the most recently captured image data is captured by the imaging process (the right end position of the vertical line portion 24) and the timing at which the currently displayed image is captured (the position of the display timing portion 22) is It gradually shrinks.
これにより、スロー表示させるために撮像された画像データの中で、現在どのタイミングで撮像された画像データがスロー表示されているのかが分かり、後どのくらいスロー表示されるのかも分かる。
また、スロー表示させる画像データの記憶(撮影)状況も表示させるので、現在撮像されている画像データのタイミングがわかるとともに、後どのくらい撮像するのかも分かる。
なお、間欠表示が行われる時は、スロー表示バーを表示させても、表示させなくてもよい。このとき、スロー表示バーを表示させる場合であって、連写撮像により撮像された画像データがスロー表示されずに間欠表示させる場合には、その間欠表示に合わせて間欠表示される画像データの位置に表示タイミング部22を表示させるようにしてもよい。また、その際にも表示スピードを合わせて表示させるようにしてもよい。この場合は、間欠表示により高速再生されることになるので「×2.0」、「×3.0」といった文字が表示されることになる。
As a result, it is possible to know at which timing the image data currently captured in the image data captured for the slow display is being displayed in a slow manner, and also how long the image data is to be displayed later.
In addition, since the storage (shooting) status of image data to be slowly displayed is also displayed, it is possible to know the timing of the image data that is currently captured and how long the image is captured later.
When intermittent display is performed, the slow display bar may or may not be displayed. At this time, when the slow display bar is displayed and the image data captured by the continuous shooting is intermittently displayed without being displayed slowly, the position of the image data intermittently displayed in accordance with the intermittent display is displayed. Alternatively, the
(17)また、上記変形例(4)を上記変形例(16)に適用する場合には、つまり、変形例(4)で、シャッタボタンの半押しがされると、半押し前に撮像された一定枚数(一定時間)の画像データからスロー表示させる場合に、変形例(16)を適用する場合は、以下のようにしてもよい。
図11(b)は、変形例(17)において表示させるスロー表示バーを示すものであり、図11(a)と同様の部分は同じ符号を付しており説明を省略する。
(17) When the modification (4) is applied to the modification (16), that is, when the shutter button is half-pressed in the modification (4), the image is captured before the half-press. In the case where the modification (16) is applied in the case where the image data is slowly displayed from a certain number (a certain time) of image data, the following may be performed.
FIG.11 (b) shows the slow display bar displayed in a modification (17), and the part similar to FIG.11 (a) attaches | subjects the same code | symbol, and abbreviate | omits description.
図11(b)の三角部25は、シャッタボタンの半押しタイミングを示すものであり、細い縦線部26は、シャッタボタンの半押しタイミング時までにバッファメモリに記憶されているフレーム画像データを示している。変形例4ではシャッタボタンが半押しされなくても、現在から一定時間前までのフレーム画像データは保持しているので、細い縦線部26はその保持されているフレーム画像データを表している。なお、縦線部24をここでは太い縦線部24ということにする。
11B indicates the half-press timing of the shutter button, and the thin
以下、変形例(17)における表示例を図12を用いて説明する。
図12は、変形例(17)における画像表示部に表示される画面の表示タイムチャートを示すものである。
図12(a)は、静止画撮影モードに設定されスルー画像表示の開始直後に表示される画像の様子を示すものである。
図12(a)を見るとわかるように、まだ、一定時間分のフレーム画像データがまだ撮像されていないので、細い縦線部26は、三角部25の位置からキャッシュバー23の左端まで延びていないのが分かる。なお、シャッタボタンが半押しされるまでは表示タイミング部22は表示バー21には表示されない。
Hereinafter, a display example in the modified example (17) will be described with reference to FIG.
FIG. 12 shows a display time chart of the screen displayed on the image display unit in the modified example (17).
FIG. 12A shows a state of an image displayed immediately after the through image display is set in the still image shooting mode.
As can be seen from FIG. 12A, since the frame image data for a predetermined time has not yet been captured, the thin
そして、図12(b)に示すように時間の経過とともにバッファメモリにフレーム画像データが記憶されていき、一定時間が経過すると(一定時間分のフレーム画像データが記憶されると)、図12(C)の示すように三角部25の位置からキャッシュバー23の左端まで細い縦線部26が表示される。
なお、一定時間が経過すると、バッファメモリに記憶されている一定時間分のフレーム画像データは新しいフレーム画像データに更新されていく。
Then, as shown in FIG. 12B, the frame image data is stored in the buffer memory as time elapses, and when a certain time elapses (when frame image data for a certain time is stored), FIG. As shown in (C), a thin
When a certain time has elapsed, the frame image data for a certain time stored in the buffer memory is updated to new frame image data.
そして、シャッタボタンが半押しされると、シャッタボタンの半押しタイミングの一定時間前の画像からスロー表示させるので、図12(d)に示すように表示タイミング部22は、表示バー21の左端に位置しているのが分かり、時間の経過とともに表示タイミング22は右に動いていく。また、シャッタボタンの半押しが行なわれ連写撮像処理により撮像された画像データもバッファメモリに記憶されていき、その記憶状況は、上記変形例(16)と同様に太い縦線部24で表示させていく。
When the shutter button is half-pressed, the display is slow-displayed from an image a predetermined time before the half-press timing of the shutter button, so that the
なお、通常のスルー画像表示においても、スロー表示バーを表示させるようにしたが、シャッタボタンが半押しされてから図12(d)に示すようなスロー表示バーを表示させるようにしてもよい。
また、上記変形例(16)、(17)においては、キャッシュバー23を表示させるようにしたが表示させずに表示バー21のみを表示させるようにしてもよい。
また、スルー表示バー以外の方法で表示させるようにしてもよい。例えば、スロー表示により表示されている画像がどのタイミングで撮像(記憶)された画像であるかを表示バー21ではなく、1/5というように、連写撮像処理により撮像される全画像データの枚数(時間)とスロー表示させた画像データの枚数(時間)との比を表示させるようにしてもよい。また、キャッシュバー23も同様に、連写撮像により撮像される全画像データの枚数(時間)と、現在までに撮像(記憶)された画像データの枚数(時間)との比で表示させるようにしてもよい。要は、現在スロー表示させている画像がどのタイミングで撮像(記憶)された画像であるか、現在どのタイミングの画像データを撮像(記憶)させているのかが分かる方法で表示させるものであればよい。
Although the slow display bar is displayed also in the normal through image display, the slow display bar as shown in FIG. 12D may be displayed after the shutter button is pressed halfway.
In the modified examples (16) and (17), the
Moreover, you may make it display by methods other than a through display bar. For example, the timing at which the image displayed by the slow display is captured (stored) is not the
また、表示バー21及びキャッシュバー23の右側に連写時間(ここでは4s)を表示させるようにしたが、表示バー21に右側にはスロー表示時間(連写撮像された画像データがスロー表示される時間)を、キャッシュバー23の右側には連写時間をそれぞれ別個に表示させるようにしてもよい。これにより、スロー表示されるスロー表示時間と、スロー表示される画像が撮像される撮像時間(連写時間)をユーザは認識することができる。
このスロー表示時間は、現在のスロー表示スピードと、連写時間によって異なる。図10、図12の場合は、スロー表示スピードが1/2倍、連写時間が4sなので、スロー表示時間は8s(8秒)ということになる。
また、図12の場合のおいては、表示バー21及びキャッシュバー23の左側に表示される一定時間も同様に、表示バー21の左側にはスロー表示時間(ここでは1s)、キャッシュバー23の左側には一定時間(ここでは0.5s)を表示させる。
Further, the continuous shooting time (4s in this case) is displayed on the right side of the
This slow display time varies depending on the current slow display speed and the continuous shooting time. In the case of FIGS. 10 and 12, since the slow display speed is ½ times and the continuous shooting time is 4 seconds, the slow display time is 8 seconds (8 seconds).
In the case of FIG. 12, the fixed time displayed on the left side of the
(18)また、上記変形例(1)乃至(17)を任意に組み合わせた態様であってもよい。 (18) Moreover, the aspect which combined the said modification (1) thru | or (17) arbitrarily may be sufficient.
(19)最後に、上記実施の形態においては、本発明の撮像装置をデジタルカメラ1に適用した場合について説明したが、カメラ付き携帯電話、カメラ付きPDA、カメラ付きパソコン、カメラ付きICレコーダ、又はデジタルビデオカメラ等に適用してもよく、被写体を撮像することができる機器であればよい。
(19) Finally, in the above embodiment, the case where the imaging device of the present invention is applied to the
1 デジタルカメラ
2 撮影レンズ
3 レンズ駆動ブロック
4 絞り
5 CCD
6 ドライバ
7 TG
8 ユニット回路
9 画像生成部
10 CPU
11 キー入力部
12 メモリ
13 DRAM
14 フラッシュメモリ
15 画像表示部
16 バス
1
6 Driver 7 TG
8
11
14
Claims (8)
前記撮像手段を用いて被写体を所定の撮像フレームレートで連続して撮影する連続撮影制御手段と、
前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを前記所定の撮像フレームレートと同じ表示フレームレートで表示手段にリアルタイム表示させる第1の表示制御手段と、
前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを一時的に記憶させるための記憶媒体に順次記憶させていく記憶制御手段と、
前記記憶制御手段により順次記憶される画像データを、前記所定の撮像フレームレートより低い表示フレームレートで表示手段にスロー表示させていく第2の表示制御手段と、
前記第1の表示制御手段による前記連続撮影画像の表示中に、スロー表示開始を指示する指示手段と、
前記指示手段によりスロー表示開始が指示された場合に、前記第2の表示制御手段による撮影画像の表示に切替える切替手段と、
前記第2の表示制御手段による撮影画像の表示中に、ユーザの操作に応じて画像データの記録を指示する記録指示手段と、
前記記録指示手段により画像データの記録が指示された場合は、該記録が指示された際に前記第2の表示制御手段により表示されている画像データをファイル化して記録媒体に記録する記録制御手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする撮像装置。 Imaging means for imaging a subject;
Continuous shooting control means for continuously shooting a subject at a predetermined imaging frame rate using the imaging means;
First display control means for causing the display means to display in real time the image data continuously shot by the continuous shooting control means at the same display frame rate as the predetermined imaging frame rate;
Storage control means for sequentially storing image data continuously photographed by the continuous photographing control means in a storage medium for temporarily storing the data;
Second display control means for causing the display means to slowly display the image data sequentially stored by the storage control means at a display frame rate lower than the predetermined imaging frame rate;
Instructing means for instructing start of slow display during display of the continuously shot image by the first display control means;
Switching means for switching to display of a photographed image by the second display control means when an instruction to start slow display is given by the instruction means;
Recording instruction means for instructing recording of image data in accordance with a user operation during display of a captured image by the second display control means;
When recording of image data is instructed by the recording instruction means, recording control means for recording the image data displayed by the second display control means in a file and recording it on a recording medium when the recording is instructed When,
An imaging apparatus comprising:
を更に備え、
前記第2の表示制御手段は、
前記記憶制御手段により前記記憶媒体に記憶された画像データを順次読み出してスロー表示させていくことを特徴とする請求項1記載の撮像装置。 Wherein stored in the storage medium by the storage control means, the image data that is slow display by the second display control means, with time of continuous shooting by the continuous photographing control unit, thinning means going thinned from the old image data When,
Further comprising
The second display control means includes
Imaging device according to claim 1, wherein the gradually slows displayed sequentially reads the image data stored in the storage medium by the storage control unit.
所定時間の間に前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを、スロー表示させることを特徴とする請求項1又は2記載の撮像装置。 The second display control means includes
The image data continuous shooting by the continuous photographing control unit for a predetermined time, the imaging apparatus according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the slowing displayed.
前記指示手段によりスロー表示の開始が指示されたタイミングに基づく所定時間の間に、前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データのスロー表示を開始させることを特徴とする請求項3記載の撮像装置。 The second display control means includes
4. The imaging according to claim 3 , wherein slow display of image data continuously photographed by the continuous photographing control means is started during a predetermined time based on a timing at which start of slow display is instructed by the instruction means. apparatus.
前記指示手段によりスロー表示の開始が指示されたタイミング時の一定時間前から前記連続撮影制御手段により撮影された画像データを、スロー表示させることを特徴とする請求項4記載の撮像装置。 The second display control means includes
The continuous shooting image data captured by the control unit, the imaging apparatus according to claim 4, wherein the slowing displayed before a certain time at the timing of the start is instructed for the slow display by the indicating means.
前記第2の表示制御手段によるスロー表示を前記第1の表示領域にて行うと同時に、前記連続撮影制御手段により撮影された画像データのリアルタイムの表示を前記第2の表示領域にて行うリアルタイム表示制御手段を更に備えたことを特徴とする請求項1乃至5の何れかに記載の撮像装置。 The display means has a first display area and a second display area,
Wherein at the same time the slow display by the second display control means performs at the first display region, earthenware pots row by the second display area display of real-time image data captured by the continuous photographing control unit realtime 6. The imaging apparatus according to claim 1, further comprising display control means.
前記連続撮影された画像データが全てスロー表示された場合は、再び最初からスロー表示させた画像データをスローでリピート表示させることを特徴とする請求項1乃至6の何れかに記載の撮像装置。 The second display control means includes
The image pickup apparatus according to claim 1, wherein when all the continuously photographed image data is slowly displayed, the image data slowly displayed from the beginning is displayed again with a slow repeat.
前記撮像部を用いて被写体を所定の撮像フレームレートで連続して撮影する連続撮影制御手段、
前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを前記所定の撮像フレームレートと同じ表示フレームレートで表示手段にリアルタイム表示させる第1の表示制御手段、
前記連続撮影制御手段により連続撮影された画像データを一時的に記憶させるための記憶媒体に順次記憶させていく記憶制御手段、
前記記憶制御手段により順次記憶される画像データを、前記所定の撮像フレームレートより低い表示フレームレートで表示手段にスロー表示させていく第2の表示制御手段、
前記第1の表示制御手段による前記連続撮影画像の表示中に、スロー表示開始を指示する指示手段、
前記指示手段によりスロー表示開始が指示された場合に、前記第2の表示制御手段による撮影画像の表示に切替える切替手段、
前記第2の表示制御手段による撮影画像の表示中に、ユーザの操作に応じて画像データの記録を指示する記録指示手段、
前記記録指示手段により画像データの記録が指示された場合は、該記録が指示された際に前記第2の表示制御手段により表示されている画像データをファイル化して記録媒体に記録する記録制御手段
として機能させることを特徴とするプログラム。
A computer included in an imaging device including an imaging unit, a display unit, and a recording medium,
Continuous shooting control means for continuously shooting a subject at a predetermined imaging frame rate using the imaging unit;
First display control means for causing the display means to display in real time the image data continuously shot by the continuous shooting control means at the same display frame rate as the predetermined imaging frame rate;
Storage control means for sequentially storing the image data continuously photographed by the continuous photographing control means in a storage medium for temporarily storing the image data;
Second display control means for causing the display means to slowly display the image data sequentially stored by the storage control means at a display frame rate lower than the predetermined imaging frame rate;
Instruction means for instructing to start slow display during display of the continuously shot image by the first display control means;
Switching means for switching to display of a photographed image by the second display control means when an instruction to start slow display is given by the instruction means;
A recording instruction means for instructing recording of image data in accordance with a user operation during display of a photographed image by the second display control means;
When recording of image data is instructed by the recording instruction means, recording control means for recording the image data displayed by the second display control means in a file and recording it on a recording medium when the recording is instructed A program characterized by functioning as a <br/>.
Priority Applications (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006332488A JP4449973B2 (en) | 2006-12-08 | 2006-12-08 | Imaging apparatus and program thereof |
| TW096135696A TWI394437B (en) | 2006-09-28 | 2007-09-26 | Imaging apparatus, recording medium for recording a computer program, and imaging control method |
| PCT/JP2007/069407 WO2008038831A1 (en) | 2006-09-28 | 2007-09-27 | Imaging apparatus and control method for capturing and recording a still image from a video |
| KR1020087012681A KR100960081B1 (en) | 2006-09-28 | 2007-09-27 | Imaging apparatus and control method for capturing and recording a still image from a video |
| EP20070829146 EP2067350A1 (en) | 2006-09-28 | 2007-09-27 | Imaging apparatus and control method for capturing and recording a still image from a video |
| CN200780001433.7A CN101356797B (en) | 2006-09-28 | 2007-09-27 | Imaging apparatus and imaging control method |
| US11/906,075 US8488043B2 (en) | 2006-09-28 | 2007-09-28 | Imaging apparatus, recording medium for recording a computer program, and imaging control method |
| HK09104648.9A HK1126064A1 (en) | 2006-09-28 | 2009-05-21 | Imaging apparatus and imaging control method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006332488A JP4449973B2 (en) | 2006-12-08 | 2006-12-08 | Imaging apparatus and program thereof |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008147966A JP2008147966A (en) | 2008-06-26 |
| JP2008147966A5 JP2008147966A5 (en) | 2009-10-22 |
| JP4449973B2 true JP4449973B2 (en) | 2010-04-14 |
Family
ID=39607652
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006332488A Active JP4449973B2 (en) | 2006-09-28 | 2006-12-08 | Imaging apparatus and program thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4449973B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100045821A1 (en) * | 2008-08-21 | 2010-02-25 | Nxp B.V. | Digital camera including a triggering device and method for triggering storage of images in a digital camera |
| JP5434038B2 (en) | 2008-10-08 | 2014-03-05 | 株式会社ニコン | Imaging device |
| JP5350850B2 (en) * | 2009-03-24 | 2013-11-27 | オリンパスイメージング株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program |
| JP5332797B2 (en) * | 2009-03-25 | 2013-11-06 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program |
| JP2011114801A (en) * | 2009-11-30 | 2011-06-09 | Olympus Imaging Corp | Display device, photographing apparatus, and, display method |
| JP2012109686A (en) * | 2010-11-15 | 2012-06-07 | Olympus Imaging Corp | Imaging device and imaging method |
| US9282306B2 (en) * | 2011-03-15 | 2016-03-08 | Nec Corporation | Imaging device, information processing device, and non-transitory computer readable medium storing program |
| JP5882677B2 (en) * | 2011-10-28 | 2016-03-09 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, control method thereof, and program |
| JP5917222B2 (en) * | 2012-03-23 | 2016-05-11 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, control method thereof, and program |
| JP6456121B2 (en) * | 2014-11-25 | 2019-01-23 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and imaging method |
| JP6498051B2 (en) * | 2015-06-19 | 2019-04-10 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof |
-
2006
- 2006-12-08 JP JP2006332488A patent/JP4449973B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2008147966A (en) | 2008-06-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4449973B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| JP4761146B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| TWI394437B (en) | Imaging apparatus, recording medium for recording a computer program, and imaging control method | |
| JP4548156B2 (en) | Camera device and automatic focus control method of camera device | |
| JP4777180B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP4697078B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| US8018497B2 (en) | Image pick-up apparatus having still image advancing/retreating manipulation function, and method and non-transitory computer readable medium therefor | |
| US20120200757A1 (en) | Imaging device and control method thereof | |
| JP4556195B2 (en) | Imaging device, moving image playback device, and program | |
| JP4501927B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| JP5909997B2 (en) | IMAGING DEVICE AND IMAGING DEVICE CONTROL METHOD | |
| JP2007325152A (en) | Imaging device, and program thereof | |
| JP2005117369A (en) | Moving image recorder, moving image reproducer and digital camera | |
| JP2009077265A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JP2003262786A (en) | Imaging device and its automatic focusing method | |
| JP2005086219A (en) | Digital camera and photographing control method | |
| JP2007067660A (en) | Imaging apparatus, and reproduction control method | |
| JP5105298B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| JP2006339728A (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| JP4243844B2 (en) | Image capturing apparatus and image capturing method | |
| JP2008054128A (en) | Image pickup device, image display apparatus, and its program | |
| JP4803375B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| JP2014086869A (en) | Digital camera | |
| JP2006094200A (en) | Imaging apparatus, focusing display method, and program | |
| JP5207930B2 (en) | IMAGING DEVICE, IMAGING DEVICE CONTROL METHOD, PROGRAM, AND RECORDING MEDIUM |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090904 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090904 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20090908 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20091006 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20091015 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091207 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100105 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100118 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4449973 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130205 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130205 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140205 Year of fee payment: 4 |