WO2022014500A1 - ニューラルネットワーク処理装置、情報処理装置、情報処理システム、電子機器、ニューラルネットワーク処理方法およびプログラム - Google Patents
ニューラルネットワーク処理装置、情報処理装置、情報処理システム、電子機器、ニューラルネットワーク処理方法およびプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022014500A1 WO2022014500A1 PCT/JP2021/025989 JP2021025989W WO2022014500A1 WO 2022014500 A1 WO2022014500 A1 WO 2022014500A1 JP 2021025989 W JP2021025989 W JP 2021025989W WO 2022014500 A1 WO2022014500 A1 WO 2022014500A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- coefficient
- zero
- variable
- value
- matrix
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/045—Combinations of networks
- G06N3/0455—Auto-encoder networks; Encoder-decoder networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F17/00—Digital computing or data processing equipment or methods, specially adapted for specific functions
- G06F17/10—Complex mathematical operations
- G06F17/16—Matrix or vector computation, e.g. matrix-matrix or matrix-vector multiplication, matrix factorization
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F17/00—Digital computing or data processing equipment or methods, specially adapted for specific functions
- G06F17/10—Complex mathematical operations
- G06F17/15—Correlation function computation including computation of convolution operations
- G06F17/153—Multidimensional correlation or convolution
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/0464—Convolutional networks [CNN, ConvNet]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/0495—Quantised networks; Sparse networks; Compressed networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/06—Physical realisation, i.e. hardware implementation of neural networks, neurons or parts of neurons
- G06N3/063—Physical realisation, i.e. hardware implementation of neural networks, neurons or parts of neurons using electronic means
Definitions
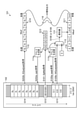
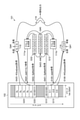
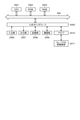
- the input data DT11 is audio data for one channel in the time interval for 7910 samples.
- the input data DT11 is audio data for one channel consisting of sample values of 7910 samples (time samples).
- the intermediate data DT15 is converted into the identification result data DT16 of one dimension ⁇ 1 sample which is the output of the classifier, and the identification result data DT16 thus obtained is the result (identification) of the identification process for the input data DT11. Result) is output.
- the processing boundary for the current frame is the sample position of the input data DT11 where the next arithmetic processing should be started after the arithmetic processing of the current frame is completed. Calculations must be made if this sample position does not match the sample position of the input data DT11 where the calculation processing for the immediately preceding frame adjacent to the current frame is started, that is, the sample position at the end (last) of the immediately preceding frame, which is the processing boundary of the immediately preceding frame. The amount and amount of memory cannot be reduced.
- the number of sample advances was 10 in the convolution layer 1, whereas the number of sample advances was 10.
- the number of sample advances is set to 8.
- one frame is 1024 samples, and this 1025th sample is the last (last) sample of the immediately preceding frame, so the 1025th sample is the processing boundary in the immediately preceding frame. Therefore, in the example of FIG. 4, the processing boundary in the current frame adjacent to each other and the processing boundary in the immediately preceding frame coincide with each other. In particular, in this example, the position of the processing boundary of the frame is the boundary position of the frame. As a result, the convolution for the data (interval) other than the processing target in the current frame is performed in the past frame.
- the number of taps and the number of sample advances in the convolution layer 3' are determined for the data shape and frame length of the input data DT11' and the configuration (structure) of each layer before the convolution layer 3'. Therefore, in the convolution layer 3', the processing boundaries of adjacent frames in the intermediate data DT 24 can be matched.
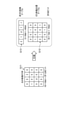
- the quadrangle in the coefficient matrix shown by the arrow Q11 represents the filter coefficient
- the numerical value in the quadrangle represents the value of the filter coefficient
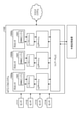
- the convolution processing unit 21 to the convolution processing unit 25 configure a classifier having a neural network structure described with reference to FIG.
- the convolution processing unit 21 to the convolution processing unit 25 constitute a neural network.
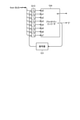
- the convolution processing unit 21 has a decoding unit 41, a memory 42, and a coefficient holding unit 43.
- the convolution processing unit 25 has a decoding unit 81, a memory 82, and a coefficient holding unit 83.
- step S105 of 9 A part of step S105 of 9 and corresponding to step S105b of FIG. 10).
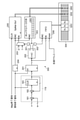
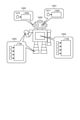
- the coefficient matrix Q11 is restored in the coefficient buffer 114, and the variable matrix Q14 to be processed is read out in the variable buffer 115.
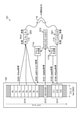
- the selector 203 inputs a value of “0” or “1” to the sparse matrix buffer 205 according to the control signal input from the determination circuit 202. For example, the selector 203 outputs “0” to the sparse matrix buffer 205 when a control signal indicating that the variable X is zero is input, and “1” when this control signal is not input. May be output.
- the determination circuit 202 is configured to output a control signal indicating that the variable X is non-zero to the selector 203, and the selector 203 receives this control signal and outputs "1" to the sparse matrix buffer 205. You may.
- the AND circuit 302 has a control signal “1” indicating that the variable X output from the determination circuit 202 is a non-zero variable, and the coefficient W output from the register 303 is a zero coefficient or a non-zero coefficient.
- the logical product with the value (“0” or “1”) indicating the above is taken, and the result is input to the write buffer 206.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- Computational Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Algebra (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Compression, Expansion, Code Conversion, And Decoders (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP21842420.8A EP4184392A4 (en) | 2020-07-17 | 2021-07-09 | NEURONAL NETWORK PROCESSING APPARATUS, INFORMATION PROCESSING APPARATUS, INFORMATION PROCESSING SYSTEM, ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENT, NEURONAL NETWORK PROCESSING METHOD AND PROGRAM |
| JP2022536329A JPWO2022014500A1 (enExample) | 2020-07-17 | 2021-07-09 | |
| US18/010,377 US20230267310A1 (en) | 2020-07-17 | 2021-07-09 | Neural network processing apparatus, information processing apparatus, information processing system, electronic device, neural network processing method, and program |
| KR1020237004217A KR20230038509A (ko) | 2020-07-17 | 2021-07-09 | 뉴럴 네트워크 처리 장치, 정보 처리 장치, 정보 처리 시스템, 전자 기기, 뉴럴 네트워크 처리 방법 및 프로그램 |
| CN202180049508.9A CN115843365A (zh) | 2020-07-17 | 2021-07-09 | 神经网络处理装置、信息处理装置、信息处理系统、电子设备、神经网络处理方法和程序 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020123312 | 2020-07-17 | ||
| JP2020-123312 | 2020-07-17 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022014500A1 true WO2022014500A1 (ja) | 2022-01-20 |
Family
ID=79555419
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2021/025989 Ceased WO2022014500A1 (ja) | 2020-07-17 | 2021-07-09 | ニューラルネットワーク処理装置、情報処理装置、情報処理システム、電子機器、ニューラルネットワーク処理方法およびプログラム |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20230267310A1 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP4184392A4 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JPWO2022014500A1 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR20230038509A (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN115843365A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2022014500A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023167153A1 (ja) * | 2022-03-03 | 2023-09-07 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | 情報処理装置及び情報処理方法 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015079946A1 (ja) | 2013-11-29 | 2015-06-04 | ソニー株式会社 | 周波数帯域拡大装置および方法、並びにプログラム |
| WO2019146398A1 (ja) * | 2018-01-23 | 2019-08-01 | ソニー株式会社 | ニューラルネットワーク処理装置および方法、並びにプログラム |
| JP2020500365A (ja) * | 2016-10-27 | 2020-01-09 | グーグル エルエルシー | ニューラルネットワーク計算ユニットにおける入力データのスパース性の活用 |
| JP2020517014A (ja) * | 2017-04-17 | 2020-06-11 | マイクロソフト テクノロジー ライセンシング,エルエルシー | メモリ帯域幅利用を低減するために活性化データの圧縮及び復元を使用するニューラルネットワークプロセッサ |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10891538B2 (en) * | 2016-08-11 | 2021-01-12 | Nvidia Corporation | Sparse convolutional neural network accelerator |
| CN107239823A (zh) * | 2016-08-12 | 2017-10-10 | 北京深鉴科技有限公司 | 一种用于实现稀疏神经网络的装置和方法 |
| US10175980B2 (en) * | 2016-10-27 | 2019-01-08 | Google Llc | Neural network compute tile |
| US20180330235A1 (en) * | 2017-05-15 | 2018-11-15 | National Taiwan University | Apparatus and Method of Using Dual Indexing in Input Neurons and Corresponding Weights of Sparse Neural Network |
| US11481218B2 (en) * | 2017-08-02 | 2022-10-25 | Intel Corporation | System and method enabling one-hot neural networks on a machine learning compute platform |
| WO2019053835A1 (ja) * | 2017-09-14 | 2019-03-21 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 演算回路、演算方法、およびプログラム |
| US11966835B2 (en) * | 2018-06-05 | 2024-04-23 | Nvidia Corp. | Deep neural network accelerator with fine-grained parallelism discovery |
| US10644721B2 (en) * | 2018-06-11 | 2020-05-05 | Tenstorrent Inc. | Processing core data compression and storage system |
| JP7340926B2 (ja) * | 2018-12-14 | 2023-09-08 | 日本光電工業株式会社 | 生体情報処理装置、生体情報センサ及び生体情報システム |
| US11625584B2 (en) * | 2019-06-17 | 2023-04-11 | Intel Corporation | Reconfigurable memory compression techniques for deep neural networks |
-
2021
- 2021-07-09 JP JP2022536329A patent/JPWO2022014500A1/ja not_active Abandoned
- 2021-07-09 EP EP21842420.8A patent/EP4184392A4/en active Pending
- 2021-07-09 US US18/010,377 patent/US20230267310A1/en active Pending
- 2021-07-09 KR KR1020237004217A patent/KR20230038509A/ko not_active Abandoned
- 2021-07-09 WO PCT/JP2021/025989 patent/WO2022014500A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2021-07-09 CN CN202180049508.9A patent/CN115843365A/zh not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015079946A1 (ja) | 2013-11-29 | 2015-06-04 | ソニー株式会社 | 周波数帯域拡大装置および方法、並びにプログラム |
| JP2020500365A (ja) * | 2016-10-27 | 2020-01-09 | グーグル エルエルシー | ニューラルネットワーク計算ユニットにおける入力データのスパース性の活用 |
| JP2020517014A (ja) * | 2017-04-17 | 2020-06-11 | マイクロソフト テクノロジー ライセンシング,エルエルシー | メモリ帯域幅利用を低減するために活性化データの圧縮及び復元を使用するニューラルネットワークプロセッサ |
| WO2019146398A1 (ja) * | 2018-01-23 | 2019-08-01 | ソニー株式会社 | ニューラルネットワーク処理装置および方法、並びにプログラム |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| I AN GOODFELLOWYOSHUA BENG IOAARON COURVILLE: "Deep Learning", 2016, THE MIT PRESS |
| KEVIN P. MURPHY: "Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective", 2012, THE MIT PRESS |
| See also references of EP4184392A4 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023167153A1 (ja) * | 2022-03-03 | 2023-09-07 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | 情報処理装置及び情報処理方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP4184392A1 (en) | 2023-05-24 |
| US20230267310A1 (en) | 2023-08-24 |
| CN115843365A (zh) | 2023-03-24 |
| JPWO2022014500A1 (enExample) | 2022-01-20 |
| KR20230038509A (ko) | 2023-03-20 |
| EP4184392A4 (en) | 2024-01-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7379524B2 (ja) | ニューラルネットワークモデルの圧縮/解凍のための方法および装置 | |
| KR102822770B1 (ko) | 웨이블릿 변환 기반 이미지 인코딩/디코딩 방법 및 장치 | |
| US10599935B2 (en) | Processing artificial neural network weights | |
| US8666179B2 (en) | Image encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus | |
| KR20210023006A (ko) | 딥러닝 기반 이미지 압축 효율 향상을 위한 방법 및 시스템 | |
| JP7200950B2 (ja) | ニューラルネットワーク処理装置および方法、並びにプログラム | |
| WO2022014500A1 (ja) | ニューラルネットワーク処理装置、情報処理装置、情報処理システム、電子機器、ニューラルネットワーク処理方法およびプログラム | |
| CN103634598A (zh) | 视频处理的转置缓冲 | |
| US8787686B2 (en) | Image processing device and image processing method | |
| US20050084169A1 (en) | Image processing apparatus that can generate coded data applicable to progressive reproduction | |
| EP2901411B1 (fr) | Dispositif de decomposition d'images par transformee en ondelettes | |
| US8861880B2 (en) | Image processing device and image processing method | |
| US9532044B2 (en) | Arithmetic decoding device, image decoding apparatus and arithmetic decoding method | |
| KR20240124304A (ko) | 포인트 클라우드 압축을 위한 하이브리드 프레임워크 | |
| CN118575194A (zh) | 用于点云压缩的可缩放框架 | |
| CN119364003B (zh) | 图像编码方法、模块、设备、存储介质及程序产品 | |
| US20250150640A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for image encoding and decoding | |
| CN112188216B (zh) | 视频数据的编码方法、装置、计算机设备及存储介质 | |
| KR20230096525A (ko) | 1d 컨볼루션을 이용한 오디오 신호 분석 방법 및 오디오 신호 분석 장치 | |
| WO2025096198A1 (en) | Learning-based mesh compression using latent mesh | |
| JP2025530715A (ja) | ストリーミングデータの処理 | |
| CN120409568A (zh) | 数据处理方法、电子设备和可读介质 | |
| CN119946266A (zh) | 用于图像编码和解码的装置和方法 | |
| JPWO2018230465A1 (ja) | ノイズ除去処理システム、ノイズ除去処理回路およびノイズ除去処理方法 | |
| JPWO2016047472A1 (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、及び、プログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 21842420 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2022536329 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20237004217 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021842420 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20230217 |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: 1020237004217 Country of ref document: KR |