WO2017097579A1 - Propylene based polymer composition - Google Patents
Propylene based polymer composition Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017097579A1 WO2017097579A1 PCT/EP2016/078417 EP2016078417W WO2017097579A1 WO 2017097579 A1 WO2017097579 A1 WO 2017097579A1 EP 2016078417 W EP2016078417 W EP 2016078417W WO 2017097579 A1 WO2017097579 A1 WO 2017097579A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- polymer composition
- propylene
- propylene polymer
- component
- composition according
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L23/00—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L23/02—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after-treatment
- C08L23/10—Homopolymers or copolymers of propene
- C08L23/14—Copolymers of propene
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
- B32B27/06—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin as the main or only constituent of a layer, which is next to another layer of the same or of a different material
- B32B27/08—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin as the main or only constituent of a layer, which is next to another layer of the same or of a different material of synthetic resin
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
- B32B27/32—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin comprising polyolefins
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F2/00—Processes of polymerisation
- C08F2/001—Multistage polymerisation processes characterised by a change in reactor conditions without deactivating the intermediate polymer
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F210/00—Copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond
- C08F210/04—Monomers containing three or four carbon atoms
- C08F210/06—Propene
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F210/00—Copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond
- C08F210/14—Monomers containing five or more carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J5/00—Manufacture of articles or shaped materials containing macromolecular substances
- C08J5/18—Manufacture of films or sheets
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L23/00—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L23/02—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after-treatment
- C08L23/10—Homopolymers or copolymers of propene
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L23/00—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L23/02—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after-treatment
- C08L23/10—Homopolymers or copolymers of propene
- C08L23/12—Polypropene
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L23/00—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L23/02—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after-treatment
- C08L23/16—Elastomeric ethene-propene or ethene-propene-diene copolymers, e.g. EPR and EPDM rubbers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B2250/00—Layers arrangement
- B32B2250/24—All layers being polymeric
- B32B2250/242—All polymers belonging to those covered by group B32B27/32
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B2270/00—Resin or rubber layer containing a blend of at least two different polymers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F2500/00—Characteristics or properties of obtained polyolefins; Use thereof
- C08F2500/12—Melt flow index or melt flow ratio
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2323/00—Characterised by the use of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Derivatives of such polymers
- C08J2323/02—Characterised by the use of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after treatment
- C08J2323/10—Homopolymers or copolymers of propene
- C08J2323/14—Copolymers of propene
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2423/00—Characterised by the use of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Derivatives of such polymers
- C08J2423/02—Characterised by the use of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after treatment
- C08J2423/10—Homopolymers or copolymers of propene
- C08J2423/14—Copolymers of propene
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2203/00—Applications
- C08L2203/16—Applications used for films
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2203/00—Applications
- C08L2203/16—Applications used for films
- C08L2203/162—Applications used for films sealable films
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2205/00—Polymer mixtures characterised by other features
- C08L2205/02—Polymer mixtures characterised by other features containing two or more polymers of the same C08L -group
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2205/00—Polymer mixtures characterised by other features
- C08L2205/02—Polymer mixtures characterised by other features containing two or more polymers of the same C08L -group
- C08L2205/025—Polymer mixtures characterised by other features containing two or more polymers of the same C08L -group containing two or more polymers of the same hierarchy C08L, and differing only in parameters such as density, comonomer content, molecular weight, structure
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2207/00—Properties characterising the ingredient of the composition
- C08L2207/02—Heterophasic composition
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a composition
- a composition comprising a copolymers of propylene with 1-hexene and a copolymer of propylene and ethylene particularly suited for preparing films, in particular biaxially oriented polypropylene films (BOPP) and cast films having a low seal initiation temperature (SIT), high transparency and printability.
- BOPP biaxially oriented polypropylene films
- SIT seal initiation temperature
- Copolymer of propylene and 1-hexene are already known in the art, for example WO 2006/002778 relates to a copolymer of propylene and 1-hexene having from 0.2 to 5 wt of 1- hexene derived units. This copolymer have a molecular weight distribution of monomodal type and are used for pipes systems.
- WO 2009/077287 relates to a a copolymer of propylene with hexene-1 containing from 5 to 9% by weight of recurring units derived from hexene-1, said copolymer having a melting temperature from 125°C to 140°C and Melt Flow Rate (ASTM D1238, 230°C/2.16 kg) from 0.1 to 3 g/10 min.
- WO 2015/062787 relates to a multimodal copolymers of propylene and 1-hexene having a content of 1-hexene derived units ranging from 0.6 wt to 3.0 wt especially suitable for the production of industrial sheets.
- a propylene polymer composition comprising:
- MFR Melt Flow Rate
- MFR Melt Flow Rate
- the present disclosure provides a propylene polymer composition comprising:
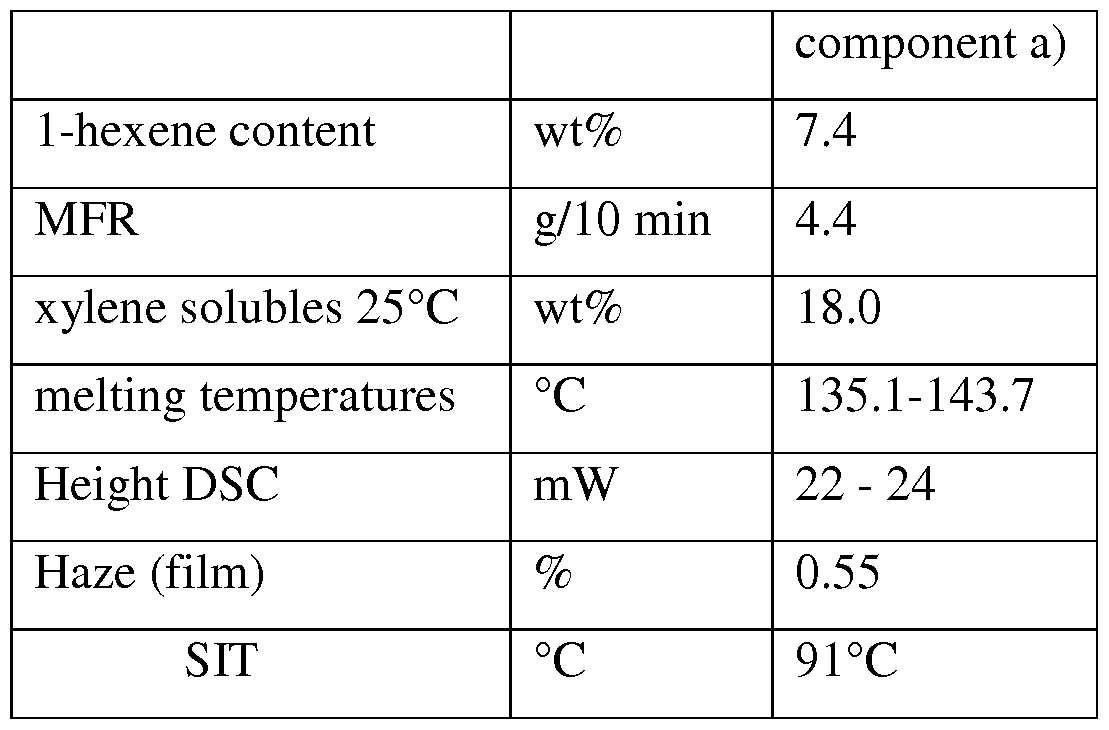
- propylene 1-hexene copolymers component a) is endowed with one or more of the following features:
- the DSC plot shows at least two peaks having a difference in height ranging from 0 to 5 mW ; preferably from 0 to 3 mW;
- the higher melting temperature measured by DSC, ranging from 141.0 °C to 151.0 °C; preferably from 142.0°C to 149.0°C; more preferably from 142.5°C to 145.0°C.
- the difference of the melting temperature of the two peaks ranges from 5°C to 20°C; more preferably from 7°C to 15°C; even more preferably from 8°C to 12°C.
- the propylene 1-hexene copolymer of the present disclosure contains only propylene and 1-hexene derived units the copolymer can further contain up to 1.0 wt% by weight of ethylene derived units .
- the propylene ethylene copolymer of the present disclosure contains only propylene and ethylene derived units.
- the copolymer can further contain up to 1.0 wt by weight of 1-hexene derived units.
- a peak in the DSC curve (temperature/heat of fusion(mW)) is defined as a point on the DSC curve (temperature/heat of fusion) having the highest value of heat of fusion at a temperature A with respect to the values of heat of fusion (mW) in the range + 5 °C with respect to temperature A.
- the melting temperature values are determined by differential scanning calorimetry, according to ISO 11357-3, with a heating rate of 20 °C/minute.
- composition of the present disclosure is endowed with a very low HAZE and a low seal initiating temperature (SIT) so that this material can be advantageously used for the production of film in particular cast or BOPP films.
- SIT seal initiating temperature
- Components a) and b) of the propylene polymer composition can be obtained with polymerization processes carried out in the presence of stereo specific Ziegler-Natta catalysts supported on magnesium dihalides. By properly dosing the molecular weight regulator
- the polymerization process which can be continuous or batch, is carried out following known techniques and operating in gas phase, or in liquid phase in the presence or not of inert diluent, or by mixed liquid-gas techniques. It is preferable to carry out the
- Polymerization reaction time, pressure and temperature are not critical, however it is best if the temperature is from 20 to 100°C.
- the pressure can be atmospheric or higher.
- the said stereospecific polymerization catalysts comprise the product of the reaction between:
- Said catalysts are preferably capable of producing homopolymers of propylene having an isotactic index higher than 90% (measured as weight amount of the fraction insoluble in xylene at room temperature).
- the solid catalyst component (1) contains as electron-donor a compound generally selected among the ethers, ketones, lactones, compounds containing N, P and/or S atoms, and mono- and dicarboxylic acid esters.
- Catalysts having the above mentioned characteristics are well known in the patent literature; particularly advantageous are the catalysts described in US patent 4,399,054 and European patent 45977.
- Particularly suited among the said electron-donor compounds are phthalic acid esters and succinic acid esters.
- Suitable succinic acid esters are represented by the formula (I):
- radicals R and R 2 are a C1-C20 linear or branched alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl or alkylaryl group, optionally containing heteroatoms;
- the radicals R 3 to R 6 equal to or different from each other, are hydrogen or a C1-C20 linear or branched alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl or alkylaryl group, optionally containing heteroatoms, and the radicals R 3 to R 6 which are joined to the same carbon atom can be linked together to form a cycle.
- Ri and R 2 are preferably C1-C8 alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl and alkylaryl groups. Particularly preferred are the compounds in which Ri and R 2 are selected from primary alkyls and in particular branched primary alkyls. Examples of suitable Ri and R 2 groups are methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, neopentyl, 2-ethylhexyl. Particularly preferred are ethyl, isobutyl, and neopentyl.
- R 3 to R5 are hydrogen and R 6 is a branched alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl and alkylaryl radical having from 3 to 10 carbon atoms.
- Another preferred group of compounds within those of formula (I) is that in which at least two radicals from R 3 to R 6 are different from hydrogen and are selected from C1-C20 linear or branched alkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, arylalkyl or alkylaryl group, optionally containing heteroatoms.
- Particularly preferred are the compounds in which the two radicals different from hydrogen are linked to the same carbon atom.
- the compounds in which at least two radicals different from hydrogen are linked to different carbon atoms that is R 3 and R5 or R 4 and R 6 are particularly preferred.
- the electron-donor compounds (3) that can be used as external electron-donors (added to the Al-alkyl compound) comprise the aromatic acid esters (such as alkylic benzoates), heterocyclic compounds (such as the 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine and the 2,6- diisopropylpiperidine), and in particular silicon compounds containing at least one Si-OR bond (where R is a hydrocarbon radical).
- aromatic acid esters such as alkylic benzoates
- heterocyclic compounds such as the 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine and the 2,6- diisopropylpiperidine
- silicon compounds containing at least one Si-OR bond where R is a hydrocarbon radical
- Examples of the said silicon compounds are those of formula where a and b are integer numbers from 0 to 2, c is an integer from 1 to 3 and the sum (a+b+c) is 4; R 1 , R2 , and R 3 are alkyl, cycloalkyl or aryl radicals with 1-18 carbon atoms optionally containing heteroatoms.
- Thexyltrimethoxysilane (2,3-dimethyl-2-trimethoxysilyl-butane) is particularly preferred.
- the previously said 1,3- diethers are also suitable to be used as external donors.
- the internal donor is one of the said 1,3-diethers, the external donor can be omitted.
- the catalysts may be precontacted with small quantities of olefin
- prepolymerization maintaining the catalyst in supension in a hydrocarbon solvent, and polymerizing at temperatures from room to 60 °C, thus producing a quantity of polymer from 0.5 to 3 times the weight of the catalyst.
- composition according to the present disclosure can also be prepared by subsequential polymerization in two or more reactors wherein in the first reactor component a) is prepared and then component b) is prepared in a subsequent reactor in the presence of component a) or vice versa.
- the polymerization processes that can be used are that one above described.
- composition of the present disclosure can also contain additives commonly used for olefin polymers like, for example, nucleating and clarifying agents and processing aids.
- the propylene polymer composition of the present disclosure can be advantageously used for the production of films.
- the film obtained with the propylene polymer composition of the present disclosure is characterized by a good dyne retention, this renders the film suitable to being printed even after long time that for example plasma or corona treatment have been applied.
- the multilayer films obtained with the propylene polymer composition of the present disclosure are characterized by having at least a skin layer comprising the propylene polymer composition of the present disclosure, the remaining layers can be formed of any material known in the art for use in multilayer films or in film-coated products.
- each layer can be formed of a polypropylene homopolymer or copolymer or polyethylene homopolymer or copolymer or other kind of polymers such as EVA, EVOH
- the combination and number of the layers of the multilayer structure is not particularly limited.
- the number is usually from 3 to 11 layers, preferably 3 to 9 layers, and more preferably 3 to 7 layers, and more preferably 3 to 5 layers and combinations including A/B/A, A/B/C, A/B/C/B/A, A/B/C/D/C/B/A are possible, provided that at least a skin layer A comprises the propylene polymer composition of the present disclosure.
- Preferred layers of the multilayer film of the present disclosure are 3 or 5 wherein at least one skin layer comprises the propylene/ethylene copolymer of the present disclosure.
- the preferred structure is A/B/A or A/B/C wherein A is the propylene polymer composition of the present disclosure.
- the skin layer is the top layer and/or the bottom layer of a multilayer film.
- the top and the bottom layer of the film comprised the propylene/ethylene copolymer of the present disclosure.
- 13 C NMR spectra are acquired on an AV-600 spectrometer operating at 150.91 MHz in the Fourier transform mode at 120 °C.
- the peak of the propylene CH was used as internal reference at 28.83.
- the 13 C NMR spectrum is acquired using the following parameters:
- P% mol is the molar percentage of propylene content
- MWE and MWp are the molecular weights of ethylene and propylene, respectively.
- the tacticity of Propylene sequences was calculated as mm content from the ratio of the PPP mmTpp (28.90-29.65 ppm) and the whole Tpp (29.80-28.37 ppm)
- the resulting laminates are stretched longitudinally and transversally, i.e. biaxially, by a factor 6 with a TOM Long film stretcher at 150°C, thus obtaining a 20 ⁇ thick film (18 ⁇ homopolymer+2 ⁇ test). 2x5 cm specimens are cut from the films.
- the SIT. is the minimum sealing temperature at which the seal does not break when a load of at least 2 Newtons is applied in the said test conditions.
- the copolymer is prepared as follows.
- the solid catalyst component used in polymerization is a highly stereo specific Ziegler-Natta catalyst component supported on magnesium chloride, containing about 2.2% by weight of titanium and diisobutylphthalate as internal donor, prepared by analogy with the method described in WO03/054035 for the preparation of catalyst component A .
- CATALYST SYSTEM AND PREPOLYMERIZATION TREATMENT is a highly stereo specific Ziegler-Natta catalyst component supported on magnesium chloride, containing about 2.2% by weight of titanium and diisobutylphthalate as internal donor, prepared by analogy with the method described in WO03/054035 for the preparation of catalyst component A .
- the solid catalyst component described above is contacted at 15 °C for about 6 minutes with aluminum triethyl (TEAL) and thexyltrimethoxysilane (2,3-dimethyl-2-trimethoxysilyl-butane), in a TEAL/ thexyltrimethoxysilane weight ratio equal to about 7 and in such quantity that the TEAL/solid catalyst component weight ratio be equal to about 6.
- TEAL aluminum triethyl
- thexyltrimethoxysilane 2,3-dimethyl-2-trimethoxysilyl-butane
- the catalyst system is then subjected to prepolymerization by maintaining it in suspension in liquid propylene at 20 °C for about 20 minutes before introducing it into the polymerization reactor.
- the polymerization is carried out in a two gas phase polymerization reactors by feeding in a continuous and constant flow the prepolymerized catalyst system, hydrogen (used as molecular weight regulator), propylene and 1-hexene in the gas state.
- the polymer particles exiting the reactor are subjected to a steam treatment to remove the reactive monomers and volatile substances, and then dried.
- the polymers of examples 1, 3 and 4 have been used to produce a A/B/A multilayer film wherein the A layer are the polymers of the examples and the B layer is a propylene homopolymer MOPLEN HP515M sold by Lyondellbasell.
- the film is 50 micron thick wherein layer A is 20 % of the overall thickness and layer B is 60 % of the overall thickness the processing parameters are reported in table 5.
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201680068710.5A CN108431122B (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2016-11-22 | Propylene-based polymer composition |
| JP2018545686A JP6578069B2 (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2016-11-22 | Propylene polymer composition |
| KR1020187017996A KR102024496B1 (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2016-11-22 | Propylene-based Polymer Composition |
| US16/061,258 US10611901B2 (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2016-11-22 | Propylene based polymer composition |
| BR112018010717-4A BR112018010717B1 (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2016-11-22 | Polymer composition based on propylene |
| RU2018121812A RU2729781C2 (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2016-11-22 | Propylene-based polymer composition |
| EP16805337.9A EP3387066B1 (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2016-11-22 | Propylene based polymer composition |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP15199651.9 | 2015-12-11 | ||
| EP15199651 | 2015-12-11 | ||
| EP16193190.2 | 2016-10-11 | ||
| EP16193190 | 2016-10-11 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017097579A1 true WO2017097579A1 (en) | 2017-06-15 |
Family
ID=57471815
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP2016/078417 WO2017097579A1 (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2016-11-22 | Propylene based polymer composition |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10611901B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3387066B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6578069B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102024496B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN108431122B (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112018010717B1 (en) |
| RU (1) | RU2729781C2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2017097579A1 (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107877966A (en) * | 2017-11-28 | 2018-04-06 | 安徽松泰包装材料有限公司 | A kind of boiling level is cast compound CPP films |
| EP3666804A1 (en) * | 2018-12-14 | 2020-06-17 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene composition with favourable combination of optics, softness and low sealing |
| EP3670547A1 (en) * | 2018-12-21 | 2020-06-24 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene composition for film sealing layer |
| RU2734641C1 (en) * | 2017-07-14 | 2020-10-21 | Бореалис Аг | Polypropylene composition |
| WO2020249388A1 (en) | 2019-06-13 | 2020-12-17 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Propylene based polymer composition |
| EP3912810A1 (en) * | 2020-05-18 | 2021-11-24 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene composition |
| EP3967716A1 (en) | 2020-09-11 | 2022-03-16 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene-based article having an increased surface tension retention |
| WO2022189270A1 (en) | 2021-03-09 | 2022-09-15 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Propylene based polymer composition |
| WO2023110386A1 (en) | 2021-12-14 | 2023-06-22 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Propylene based polymer composition |
| WO2024028042A1 (en) | 2022-08-03 | 2024-02-08 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Polypropylene composition for heat sealable films |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR112019004611B1 (en) * | 2016-10-06 | 2022-10-25 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L | COMPOSITION BASED ON PROPYLENE FOR PIPES |
| RU2724050C1 (en) * | 2016-12-29 | 2020-06-19 | Бореалис Аг | Polypropylene-based composition having low welding start temperature and high melting point |
| RU2735731C1 (en) * | 2017-05-04 | 2020-11-06 | Базелл Полиолефин Италия С.Р.Л. | Propylene-based polymer composition |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0045977A2 (en) | 1980-08-13 | 1982-02-17 | Montedison S.p.A. | Components and catalysts for the polymerization of olefins |
| US4399054A (en) | 1978-08-22 | 1983-08-16 | Montedison S.P.A. | Catalyst components and catalysts for the polymerization of alpha-olefins |
| EP0361493A1 (en) | 1988-09-30 | 1990-04-04 | Himont Incorporated | Diethers usable in the preparation of Ziegler-Natta catalysts and their preparation |
| EP0728769A1 (en) | 1995-02-21 | 1996-08-28 | Montell North America Inc. | Components and catalysts for the polymerization of olefins |
| WO2003054035A1 (en) | 2001-12-12 | 2003-07-03 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.P.A. | Process for the polymerization of olefins |
| US6818703B2 (en) * | 2002-03-29 | 2004-11-16 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Propylene-based resin composition and film made of the same |
| WO2006002778A1 (en) | 2004-06-25 | 2006-01-12 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | PIPE SYSTEMS MADE FROM RANDOM COPOLYMERS OF PROPYLENE AND α-OLEFINS |
| WO2009077287A1 (en) | 2007-12-18 | 2009-06-25 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Copolymers of propylene with hexene-1 and blown films obtained from them |
| WO2009080485A1 (en) * | 2007-12-19 | 2009-07-02 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Soft and flexible polyolefin compositions |
| WO2015062787A1 (en) | 2013-10-30 | 2015-05-07 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Multimodal copolymers of propylene and 1-hexene |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT1269914B (en) * | 1994-03-24 | 1997-04-16 | Himonty Inc | PAINTABLE COMPOSITIONS OF PROPYLENE CRYSTALLINE COPOLYMERS HAVING LOW WELDABILITY TEMPERATURE |
| JPH10152530A (en) | 1996-11-25 | 1998-06-09 | Nippon Poriorefuin Kk | Polypropylene-based resin composition for stretch blow molding, molding product therefrom and its production |
| EP1041114B1 (en) * | 1999-03-30 | 2006-07-19 | Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. | Polyolefin resin modifier, polyolefin resin composition and oriented polyolefin film |
| JP4655344B2 (en) * | 2000-08-30 | 2011-03-23 | 住友化学株式会社 | PROPYLENE COPOLYMER, PROCESS FOR PRODUCING THE SAME, AND FILM COMPRISING THE PROPYLENE COPOLYMER |
| JP4250993B2 (en) * | 2002-03-29 | 2009-04-08 | 住友化学株式会社 | Polypropylene resin composition and film |
| JP4830756B2 (en) * | 2005-09-27 | 2011-12-07 | 住友化学株式会社 | Polypropylene resin composition, and sheet and container comprising the same |
| JP5611529B2 (en) * | 2009-02-16 | 2014-10-22 | 三井化学株式会社 | Surface modified film |
| BR112012026909B1 (en) | 2010-04-21 | 2020-03-10 | Borealis Ag | COMPOSITION OF PROPYLENE / 1-HEXEN COPOLYMER WITH LOW SEALING TEMPERATURE, ITS PREPARATION PROCESS, FILM, AND EXTRUSION COATED SUBSTRATE |
| JP2012020471A (en) * | 2010-07-14 | 2012-02-02 | Mitsui Chemicals Inc | Laminated film and method for manufacturing the same |
| WO2012058789A1 (en) * | 2010-11-05 | 2012-05-10 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Polymeric films and methods to manufacture the same |
| ES2605038T3 (en) * | 2011-10-31 | 2017-03-10 | Borealis Ag | Polypropylene mixture with better balance between SIT and melting point |
| JP2015193831A (en) * | 2014-03-26 | 2015-11-05 | 日本ポリプロ株式会社 | Polypropylene resin composition and molded body thereof |
-
2016
- 2016-11-22 JP JP2018545686A patent/JP6578069B2/en active Active
- 2016-11-22 KR KR1020187017996A patent/KR102024496B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2016-11-22 EP EP16805337.9A patent/EP3387066B1/en active Active
- 2016-11-22 RU RU2018121812A patent/RU2729781C2/en active
- 2016-11-22 BR BR112018010717-4A patent/BR112018010717B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2016-11-22 US US16/061,258 patent/US10611901B2/en active Active
- 2016-11-22 WO PCT/EP2016/078417 patent/WO2017097579A1/en active Application Filing
- 2016-11-22 CN CN201680068710.5A patent/CN108431122B/en active Active
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4399054A (en) | 1978-08-22 | 1983-08-16 | Montedison S.P.A. | Catalyst components and catalysts for the polymerization of alpha-olefins |
| EP0045977A2 (en) | 1980-08-13 | 1982-02-17 | Montedison S.p.A. | Components and catalysts for the polymerization of olefins |
| EP0361493A1 (en) | 1988-09-30 | 1990-04-04 | Himont Incorporated | Diethers usable in the preparation of Ziegler-Natta catalysts and their preparation |
| EP0728769A1 (en) | 1995-02-21 | 1996-08-28 | Montell North America Inc. | Components and catalysts for the polymerization of olefins |
| WO2003054035A1 (en) | 2001-12-12 | 2003-07-03 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.P.A. | Process for the polymerization of olefins |
| US6818703B2 (en) * | 2002-03-29 | 2004-11-16 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Propylene-based resin composition and film made of the same |
| WO2006002778A1 (en) | 2004-06-25 | 2006-01-12 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | PIPE SYSTEMS MADE FROM RANDOM COPOLYMERS OF PROPYLENE AND α-OLEFINS |
| WO2009077287A1 (en) | 2007-12-18 | 2009-06-25 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Copolymers of propylene with hexene-1 and blown films obtained from them |
| WO2009080485A1 (en) * | 2007-12-19 | 2009-07-02 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Soft and flexible polyolefin compositions |
| WO2015062787A1 (en) | 2013-10-30 | 2015-05-07 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Multimodal copolymers of propylene and 1-hexene |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| C. J. CARMAN; R. A. HARRINGTON; C. E. WILKES: "Monomer Sequence Distribution in Ethylene-Propylene Rubber Measured by 13C NMR. 3. Use of Reaction Probability Mode", MACROMOLECULES, vol. 10, 1977, pages 536 |
| C.J. CARMAN; R.A. HARRINGTON; C.E. WILKES, MACROMOLECULES, vol. 10, 1977, pages 536 |
| M. KAKUGO; Y. NAITO; K. MIZUNUMA; T. MIYATAKE: "Carbon-13 NMR determination of monomer sequence distribution in ethylene-propylene copolymers prepared with ?-titanium trichloride-diethylaluminum chloride", MACROMOLECULES, vol. 15, 1982, pages 1150 |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2734641C1 (en) * | 2017-07-14 | 2020-10-21 | Бореалис Аг | Polypropylene composition |
| EP3652247B1 (en) | 2017-07-14 | 2021-09-01 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene composition |
| CN107877966A (en) * | 2017-11-28 | 2018-04-06 | 安徽松泰包装材料有限公司 | A kind of boiling level is cast compound CPP films |
| EP3666804A1 (en) * | 2018-12-14 | 2020-06-17 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene composition with favourable combination of optics, softness and low sealing |
| EP3670547A1 (en) * | 2018-12-21 | 2020-06-24 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene composition for film sealing layer |
| WO2020126516A1 (en) * | 2018-12-21 | 2020-06-25 | Borealis Ag | Polypropylene composition for film sealing layer |
| CN113811572A (en) * | 2019-06-13 | 2021-12-17 | 巴塞尔聚烯烃意大利有限公司 | Propylene-based polymer composition |
| WO2020249388A1 (en) | 2019-06-13 | 2020-12-17 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Propylene based polymer composition |
| CN113811572B (en) * | 2019-06-13 | 2023-06-23 | 巴塞尔聚烯烃意大利有限公司 | Propylene-based polymer composition |
| WO2021233771A1 (en) * | 2020-05-18 | 2021-11-25 | Borealis Ag | Polypropylene composition |
| EP3912810A1 (en) * | 2020-05-18 | 2021-11-24 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene composition |
| EP3967716A1 (en) | 2020-09-11 | 2022-03-16 | Borealis AG | Polypropylene-based article having an increased surface tension retention |
| WO2022053475A1 (en) | 2020-09-11 | 2022-03-17 | Borealis Ag | Polypropylene-based article having an increased surface tension retention |
| WO2022189270A1 (en) | 2021-03-09 | 2022-09-15 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Propylene based polymer composition |
| WO2023110386A1 (en) | 2021-12-14 | 2023-06-22 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Propylene based polymer composition |
| WO2024028042A1 (en) | 2022-08-03 | 2024-02-08 | Basell Poliolefine Italia S.R.L. | Polypropylene composition for heat sealable films |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3387066A1 (en) | 2018-10-17 |
| EP3387066B1 (en) | 2019-11-06 |
| CN108431122A (en) | 2018-08-21 |
| BR112018010717B1 (en) | 2022-01-25 |
| BR112018010717A8 (en) | 2019-02-26 |
| US20180362748A1 (en) | 2018-12-20 |
| US10611901B2 (en) | 2020-04-07 |
| KR102024496B1 (en) | 2019-09-23 |
| RU2729781C2 (en) | 2020-08-12 |
| JP2018536084A (en) | 2018-12-06 |
| JP6578069B2 (en) | 2019-09-18 |
| BR112018010717A2 (en) | 2018-11-21 |
| RU2018121812A3 (en) | 2020-03-10 |
| RU2018121812A (en) | 2019-12-16 |
| CN108431122B (en) | 2020-11-24 |
| KR20180094930A (en) | 2018-08-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3387066B1 (en) | Propylene based polymer composition | |
| EP3619266B1 (en) | Propylene based polymer composition | |
| EP3387027B1 (en) | Propylene hexene copolymers | |
| US11174379B2 (en) | Compositions obtained from recycled polyolefins | |
| EP2750860B1 (en) | Propylene-based terpolymers for films | |
| WO2012031952A1 (en) | Polypropylene-based terpolymers for films | |
| EP3655445B1 (en) | Propylene copolymers | |
| WO2019091841A1 (en) | Heat-shrinkable label | |
| WO2024083610A1 (en) | Polypropylene composition with good sealing properties |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16805337 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2018545686 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112018010717 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2018121812 Country of ref document: RU |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20187017996 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1020187017996 Country of ref document: KR |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2016805337 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112018010717 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20180525 |