WO2016088347A1 - 管理装置及び画像処理システム - Google Patents
管理装置及び画像処理システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016088347A1 WO2016088347A1 PCT/JP2015/005939 JP2015005939W WO2016088347A1 WO 2016088347 A1 WO2016088347 A1 WO 2016088347A1 JP 2015005939 W JP2015005939 W JP 2015005939W WO 2016088347 A1 WO2016088347 A1 WO 2016088347A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- data
- resolution
- image data
- unit
- image
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/23—Processing of content or additional data; Elementary server operations; Server middleware
- H04N21/234—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs
- H04N21/2343—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs involving reformatting operations of video signals for distribution or compliance with end-user requests or end-user device requirements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/085—Secret sharing or secret splitting, e.g. threshold schemes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0894—Escrow, recovery or storing of secret information, e.g. secret key escrow or cryptographic key storage
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/85—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using pre-processing or post-processing specially adapted for video compression
- H04N19/88—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using pre-processing or post-processing specially adapted for video compression involving rearrangement of data among different coding units, e.g. shuffling, interleaving, scrambling or permutation of pixel data or permutation of transform coefficient data among different blocks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/23—Processing of content or additional data; Elementary server operations; Server middleware
- H04N21/231—Content storage operation, e.g. caching movies for short term storage, replicating data over plural servers, prioritizing data for deletion
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/23—Processing of content or additional data; Elementary server operations; Server middleware
- H04N21/234—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs
- H04N21/2343—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs involving reformatting operations of video signals for distribution or compliance with end-user requests or end-user device requirements
- H04N21/234327—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs involving reformatting operations of video signals for distribution or compliance with end-user requests or end-user device requirements by decomposing into layers, e.g. base layer and one or more enhancement layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/23—Processing of content or additional data; Elementary server operations; Server middleware
- H04N21/234—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs
- H04N21/2343—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs involving reformatting operations of video signals for distribution or compliance with end-user requests or end-user device requirements
- H04N21/23439—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs involving reformatting operations of video signals for distribution or compliance with end-user requests or end-user device requirements for generating different versions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/23—Processing of content or additional data; Elementary server operations; Server middleware
- H04N21/234—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs
- H04N21/2347—Processing of video elementary streams, e.g. splicing of video streams, manipulating MPEG-4 scene graphs involving video stream encryption
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/23—Processing of content or additional data; Elementary server operations; Server middleware
- H04N21/235—Processing of additional data, e.g. scrambling of additional data or processing content descriptors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/60—Network structure or processes for video distribution between server and client or between remote clients; Control signalling between clients, server and network components; Transmission of management data between server and client, e.g. sending from server to client commands for recording incoming content stream; Communication details between server and client
- H04N21/61—Network physical structure; Signal processing
- H04N21/6106—Network physical structure; Signal processing specially adapted to the downstream path of the transmission network
- H04N21/6125—Network physical structure; Signal processing specially adapted to the downstream path of the transmission network involving transmission via Internet
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/60—Network structure or processes for video distribution between server and client or between remote clients; Control signalling between clients, server and network components; Transmission of management data between server and client, e.g. sending from server to client commands for recording incoming content stream; Communication details between server and client
- H04N21/61—Network physical structure; Signal processing
- H04N21/6156—Network physical structure; Signal processing specially adapted to the upstream path of the transmission network
- H04N21/6175—Network physical structure; Signal processing specially adapted to the upstream path of the transmission network involving transmission via Internet
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N5/00—Details of television systems
- H04N5/76—Television signal recording
- H04N5/91—Television signal processing therefor
- H04N5/913—Television signal processing therefor for scrambling ; for copy protection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N7/00—Television systems
- H04N7/01—Conversion of standards, e.g. involving analogue television standards or digital television standards processed at pixel level
- H04N7/0117—Conversion of standards, e.g. involving analogue television standards or digital television standards processed at pixel level involving conversion of the spatial resolution of the incoming video signal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N9/00—Details of colour television systems
- H04N9/79—Processing of colour television signals in connection with recording
- H04N9/80—Transformation of the television signal for recording, e.g. modulation, frequency changing; Inverse transformation for playback
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N5/00—Details of television systems
- H04N5/76—Television signal recording
- H04N5/91—Television signal processing therefor
- H04N5/913—Television signal processing therefor for scrambling ; for copy protection
- H04N2005/91357—Television signal processing therefor for scrambling ; for copy protection by modifying the video signal
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a management device for distributing and secretly managing video data and an image processing system using the management device.
- Patent Document 1 main video data is received through a first route (broadcast wave), and when necessary, difference data for high image quality is received through a second route (network) and the difference from the main video data.
- a technique for synthesizing data is disclosed. With the technique disclosed in Patent Document 1, the video data is reproduced only by acquiring the main video data.
- content video, surveillance camera video, etc. are transmitted / stored in a network environment, The purpose is to ensure security against privacy.
- the management apparatus includes a resolution conversion unit that converts input image data into N types (N is a plurality) of image data having different resolutions, and each of the plurality of image data (n is N + 1 or more). Dividing into distributed data of integers that are the same value in all image data, and using k pieces (k is an integer of 2 to n and different from each other for each image data)
- the secret sharing processing unit that performs secret sharing processing so that it can be restored to the original image data and the distributed data selected one by one so as not to overlap each other are generated to generate n combined data,
- a data combining unit that stores data in different storages.
- an image processing system includes the management device described above and a storage that stores combined data.
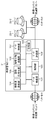
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an image processing system according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure.
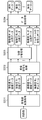
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating an internal configuration of the video management server according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure.
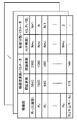
- FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating an example of information stored in the video management server according to Embodiment 1 of the present disclosure.
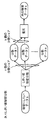
- FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining the secret sharing process.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a processing procedure performed by the video management server according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a specific example of processing performed by the video management server according to Embodiment 1 of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing an internal configuration of the receiving apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an image processing system according to the first embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating an internal configuration of the video management server according to the
- FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating a procedure of processing performed by the reception apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 9 is a block diagram illustrating an internal configuration of the video management server according to the second embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating a procedure of processes performed by the video management server according to the second embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating a specific example of processing performed by the video management server according to the second embodiment of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing an internal configuration of the receiving apparatus according to Embodiment 2 of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 13 is a diagram illustrating a procedure of processing performed by the reception apparatus according to Embodiment 2 of the present disclosure.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an image processing system according to the present embodiment.
- the image processing system mainly includes a video / content creation unit 10, a video / content storage unit 20, and a video / content browsing unit 30.
- the video / content creation unit 10 sends video data created by the cameras 11, 12, video data saved in the personal computer 13, etc. via a communication device 14 such as a router / modem connected to the Internet. Transmit to the content storage unit 20.
- the video / content storage unit 20 processes the video data received from the video / content creation unit 10 by the video management server 21 to create distributed data, and a plurality of storages 22 (22-1, 22-2,... 22-n), the distributed data is distributed and stored.
- the internal configuration of the video management server 21 and the manner in which the distributed data is stored in the storage 22 will be described later.
- the video / content browsing unit 30 receives the distributed data stored in the plurality of storages 22 by the receiving device 33 via the communication device 31 such as the router / modem, and the receiving device 33 combines the received distributed data.
- the video data is restored, and the restored video data is output to the display 34.
- the processing performed by the receiving device 33 may be performed inside the mobile terminal 32 or the personal computers 35 and 36. The internal configuration of the receiving device 33 will be described later.
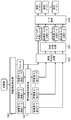
- the video management server 21 includes a data receiving unit 101, a storage unit 102, a control unit 103, a resolution conversion unit 104, an image encoding unit 105, a secret sharing processing unit 106, data It is mainly composed of a coupling unit 107 and a data transmission unit 108.
- the data reception unit 101 receives the video data transmitted from the video / content creation unit 10 via the Internet, and outputs the video data to the control unit 103 and the resolution conversion unit 104.
- the storage unit 102 stores N types (N is an integer of 2 or more) of converted resolutions and resolution conversion parameters (horizontal pixels) for each post-conversion resolution for each resolution of original image data that is image data before conversion. (Number, number of vertical pixels) and secret sharing parameters (n (number of shares), k (threshold)) are stored in association with each other in a table format (see FIG. 3). Note that n is N + ⁇ ( ⁇ is an integer of 1 or more). K is an integer of 2 to n. In this embodiment, k takes a different value for each resolution after conversion, and takes a larger value as the resolution is higher.
- the control unit 103 selects N types of converted resolutions based on the resolution (number of pixels) of the image data of the video data input from the data receiving unit 101, and instructs the resolution conversion unit 104 of the converted resolutions. .
- the resolution conversion unit 104 receives the video input from the data reception unit 101 based on information (resolution conversion parameters corresponding to each resolution) stored in the storage unit 102 so that each resolution instructed by the control unit 103 is obtained.
- the resolution of the data original image data
- video data of N types of resolutions is generated and output to the image encoding unit 105.
- the resolution conversion unit 104 converts the resolution of the original image data to the resolution RS for thumbnails, generates thumbnails, and generates image codes. To the conversion unit 105.
- the image encoding unit 105 performs compression encoding processing on the image data of each resolution output from the resolution conversion unit 104 and outputs the result to the secret sharing processing unit 106.
- the image encoding unit 105 performs compression encoding processing on the thumbnail and outputs the result to the data combining unit 107.
- the secret sharing processing unit 106 applies each compression-encoded image data output from the image encoding unit 105 based on information stored in the storage unit 102 (secret sharing parameters corresponding to each resolution). Secret sharing processing is performed, n pieces of shared data are generated for each resolution, and output to the data combining unit 107.
- secret sharing processing one data s to be kept secret can be divided into a plurality of n pieces of distributed data, and k (k ⁇ n) of them can be used to restore the original data s. This is processing that prevents the original data s from being restored from less than the number of pieces of distributed data (see FIG. 4).
- the data combining unit 107 adds a head marker, a secret sharing parameter, and a terminal marker to each distributed data, and generates combined data by combining the distributed data selected one by one so as not to overlap each resolution. Therefore, a total of n pieces of combined data are generated.
- the data combining unit 107 adds the thumbnail after compression encoding to all the combined data.
- the data transmission unit 108 transmits the generated n pieces of combined data to different storages 22-i (i is an integer of 1 to n) and stores them.
- the storage 22-i may be connected via an intranet, or may be connected via the Internet.
- the data transmission unit 108 has a function of selecting j pieces of combined data (j is an integer not less than 2 and not more than n) from the storage 22-i in response to a request from the reception device 33 and transmitting the selected combination data to the reception device 33. There may be.
- the resolution conversion unit 104 converts the resolution of the original image data, and generates image data of N types of resolutions. In addition, when attaching a thumbnail, the resolution conversion part 104 also produces
- the image encoding unit 105 performs compression encoding processing on N types of image data of each resolution.
- the image encoding unit 105 also performs compression encoding processing on the thumbnail image data (S202).
- the secret sharing processing unit 106 performs secret sharing processing on the compression-encoded image data of N types of resolutions excluding thumbnails, and generates n pieces of shared data for each resolution (S203). .
- the data combination unit 107 combines the distributed data selected one by one so as not to overlap from each resolution, and generates n pieces of combined data.
- the thumbnail is added to all the combined data (S204).
- image data and thumbnails of three types of resolution R1 (3840 ⁇ 2160 dots), resolution R2 (1920 ⁇ 1080 dots), and resolution R3 (640 ⁇ 480 dots) are generated. Then, the image data of each resolution is divided into four pieces of distributed data by secret sharing processing.
- the image data with the resolution R1 can be restored to the original image data by using four pieces of distributed data.
- the image data with the resolution R2 can be restored to the original image data by using three pieces of distributed data.
- the image data with the resolution R3 can be restored to the original image data by using two pieces of distributed data.
- the thumbnail is a reduced version of the original image data.
- the thumbnail has deteriorated to the extent that copyright cannot be claimed in the content video, or has deteriorated to the extent that privacy information is not included in the surveillance camera video. Is in a low state. Even if thumbnails are played, security for copyright and privacy is ensured. Also, the original image data cannot be restored from the thumbnail.
- thumbnails are combined with the shared data 1-1, 2-1, 3-1 selected so as not to overlap from the resolutions R1, R2, and R3, and stored in the storage 22-1 Is done.
- the thumbnails are combined with the distributed data 1-2, 2-2, and 3-2 selected one by one so as not to overlap from the resolutions R1, R2, and R3, and are stored in the storage 22-2.
- the distributed data 1-3, 2-3, 3-3 selected one by one so as not to overlap from the resolutions R1, R2, R3 and the thumbnail are combined and stored in the storage 22-3, and each resolution R1, R2 , R3 and the shared data 1-4, 2-4, 3-4 selected one by one so as not to overlap, and the thumbnail are combined and stored in the storage 22-4.
- the reception device 33 includes a data reception unit 301, a control unit 302, a data separation unit 303, a secret sharing / restoration unit 304, an image decryption unit 305, and a data transmission unit 306. Configured.
- the data receiving unit 301 receives j pieces of combined data (j is an integer from 2 to n) from the storage 22-i (i is an integer from 1 to n) via the Internet.
- the data is output to the separation unit 303.
- the number of combined data that can be received by the data receiving unit 301 is determined based on the authority of the user. For example, the data receiving unit 301 is more connected to a user with higher authority (such as paying a higher fee for the system or having higher access authority as a data administrator). Data can be accessed and received. As a result, a user with higher authority can view high-quality image data.
- the data received by the data receiving unit 301 may be configured such that the video management server 21 selects and sends j pieces of combined data from the storage 22-i in response to a request from the receiving device 33.
- the control unit 302 selects the resolution of the image data to be restored (hereinafter referred to as “restored image data”) based on the number j of combined data input from the data receiving unit 301, and the data separation unit 303 Specify the distributed data of the selected resolution.
- the resolution R2 can be restored, so the resolution of the restored image data is R2.
- the data separator 303 is instructed with three pieces of distributed data (for example, distributed data 2-1, 2-2, 2-3) having a resolution R2.
- the data separation unit 303 separates the distributed data instructed by the control unit 302 from the combined data and outputs the separated data to the secret sharing restoration unit 304.
- the secret sharing restoration unit 304 performs secret sharing restoration processing on the shared data output from the data separation unit 303 and outputs the restored image data to the image decoding unit 305. Note that the image data restored by the secret sharing restoration unit 304 is in an encoded state.
- the image decoding unit 305 performs a decoding process corresponding to the compression coding of the image coding unit 105 on the restored image data output from the secret sharing restoration unit 304, and generates restored image data that can be viewed by the user. To the data transmission unit 306.
- the data transmission unit 306 outputs the restored image data output from the image decoding unit 305 to the display 34, and the restored image data is displayed on the display 34.
- the secret sharing restoration unit 304 performs secret sharing restoration processing on k pieces of shared data
- the image decoding unit 305 performs decoding processing to generate restored image data that can be viewed by the user (S402). , S403).
- the restored image data generated by the image decoding unit 305 is displayed on the display 34. Further, the processing performed by the receiving device 33 may be performed inside the mobile terminal 32 or the personal computers 35 and 36.
- each of a plurality of pieces of image data having different resolutions is converted into n pieces (n is an integer of 3 or more and the same value in all image data).
- n is an integer of 3 or more and the same value in all image data.
- secret sharing processing is performed so that the original image data can be restored.
- the distributed data selected one by one so as not to overlap is combined to generate n pieces of combined data, and each piece of combined data is stored in different storages.
- the video management server 21a shown in FIG. 9 adopts a configuration in which a difference image generation unit 501 is added to the video management server 21 shown in FIG.
- the resolution conversion unit 104 generates image data and thumbnails of N types of resolutions and outputs them to the difference image generation unit 501.
- the difference image generation unit 501 generates N pieces of difference data from N kinds of resolution image data and thumbnails. Specifically, the difference image generation unit 501 takes a difference between image data having a resolution Rm (m is an integer of 1 to N ⁇ 1, and the smaller m is, the higher the resolution is) and image data having a resolution Rm + 1. Thus, difference data of resolution Rm is generated. Also, the difference image generation unit 501 generates difference data of resolution RN by taking the difference between the image data of resolution RN and the thumbnail. The difference image generation unit 501 outputs N pieces of difference data to the image encoding unit 105.
- the image encoding unit 105 performs compression encoding processing on each difference data output from the difference image generation unit 501 and outputs the result to the secret sharing processing unit 106. Also, the image encoding unit 105 performs compression encoding processing on the thumbnail resolution image data and outputs the result to the data combining unit 107.
- the secret sharing processing unit 106 performs secret sharing processing on each differential data after the compression encoding process output from the image encoding unit 105, generates n shared data for each differential data, and generates a data combining unit It outputs to 107.
- the resolution conversion unit 104 converts the resolution of the original image data, and generates N types of resolution image data and thumbnail resolution image data (S601).
- the difference image generation unit 501 generates N pieces of difference data from the image data and thumbnails of N types of resolutions (S602).
- the image encoding unit 105 performs compression encoding processing on each difference data and thumbnail (S603).
- the secret sharing processing unit 106 performs secret sharing processing on the N pieces of differential data after compression encoding, and generates n pieces of shared data for each difference data (S604).
- the data combining unit 107 combines the distributed data selected one by one so as not to overlap each difference data, and generates n pieces of combined data.
- the thumbnail is added to all the combined data (S605).
- image data and thumbnails of three types of resolution R1 (3840 ⁇ 2160 dots), resolution R2 (1920 ⁇ 1080 dots), and resolution R3 (640 ⁇ 480 dots) are generated.
- difference data of resolution R1 which is a difference between image data of resolution R1 and image data of resolution R2
- difference data of resolution R2 which is a difference between image data of resolution R2 and image data of resolution R3
- difference data of resolution R3 that is a difference between image data of resolution R3 and a thumbnail is generated. Then, the difference data of each resolution is divided into four pieces of distributed data by the secret sharing process.
- difference data of resolution R1 can be restored to the original difference data by using four pieces of distributed data.
- the difference data of resolution R2 can be restored to the original difference data by using three pieces of distributed data.
- the difference data of resolution R3 can be restored to the original difference data by using two pieces of distributed data.
- the difference data between the thumbnail and the resolution R3 can be used to restore the image data with the resolution R3. Also, it is possible to restore the image data with the resolution R2 using the image data with the resolution R3 and the difference data with the resolution R2. Further, it is possible to restore the image data of the resolution R1 using the image data of the resolution R2 and the difference data of the resolution R1.
- thumbnails are combined with the shared data 1-1, 2-1, 3-1 selected so as not to overlap from the resolutions R1, R2, and R3, and stored in the storage 22-1 Is done.
- the thumbnails are combined with the distributed data 1-2, 2-2, and 3-2 selected one by one so as not to overlap from the resolutions R1, R2, and R3, and are stored in the storage 22-2.
- the distributed data 1-3, 2-3, 3-3 selected one by one so as not to overlap from the resolutions R1, R2, R3 and the thumbnail are combined and stored in the storage 22-3, and each resolution R1, R2 , R3 and the shared data 1-4, 2-4, 3-4 selected one by one so as not to overlap, and the thumbnail are combined and stored in the storage 22-4.
- receiving apparatus 33a Next, the internal configuration of receiving apparatus 33a according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. In the receiving apparatus 33a shown in FIG. 12, parts common to the receiving apparatus 33 shown in FIG.
- the data separation unit 303 separates the distributed data and thumbnails instructed by the control unit 302 from the combined data, outputs the distributed data to the secret sharing restoration unit 304, and outputs the thumbnails to the image decoding unit 305.
- the secret sharing restoration unit 304 performs secret sharing restoration processing on the shared data output from the data separation unit 303, and outputs the restored difference data (hereinafter referred to as “restored difference data”) to the image decoding unit 305. . Note that the difference data restored by the secret sharing restoration unit 304 is in an encoded state.
- the image decoding unit 305 performs a decoding process corresponding to the compression encoding of the image encoding unit 105 on the thumbnail output from the data separation unit 303 and the restored difference data output from the secret sharing restoration unit 304, and performs the difference
- the image is output to the image composition unit 701.
- the difference image composition unit 701 performs composition processing on the thumbnail and the restoration difference data output from the image decoding unit 305, and generates restored image data that can be viewed by the user.
- the secret sharing restoration unit 304 performs a secret sharing restoration process on the distributed data of each resolution.
- the number k of the distributed data necessary for the secret sharing restoration process varies depending on each resolution, and the lower the resolution, the smaller the number of necessary distributed data.
- the image decoding unit 305 performs a decoding process, and generates thumbnails and restoration difference data (S802, S803).
- the difference image composition unit 701 performs composition processing on the thumbnail and the restored difference data to generate restored image data that can be viewed by the user (S804).
- the restored image data generated by the difference image composition unit 701 is displayed on the display 34.
- the processing performed by the receiving device 33a may be performed in the mobile terminal 32 or the personal computers 35 and 36.
- a plurality of difference data is generated from a plurality of image data having different resolutions, and n pieces of difference data (n is an integer of 3 or more, It is possible to restore the original difference data by dividing into the distributed data having the same value in the difference data and using k pieces (k is an integer of 2 to n and different from each other for each difference data).
- k is an integer of 2 to n and different from each other for each difference data.
- the secret sharing process is performed, and the pieces of distributed data selected one by one so as not to overlap from each resolution are combined to generate n pieces of combined data, and each piece of combined data is stored in different storages.
- the more distributed data is collected, the higher the resolution of the image data can be reproduced, and the security for copyright, privacy, etc. can be ensured in each distributed data.
- the processing performed by the video management server 21 may be performed by the personal computer 13 or the like. Further, the processing performed by the receiving device 33 may be performed by the mobile terminal 32 or the personal computers 35 and 36.
- the storage 22-i may be a cloud storage, or a part of on-premises server storage or storage of a personal computer, a camera, or a mobile terminal may be used.
- the video management server 21 may select the distributed data necessary for the restoration and transmit it to the receiving devices 33 and 33a.
- the receiving device 33 or 33a may select the necessary shared data and download it from the storage 22-i.
- a configuration is shown in which distributed data selected one by one so as not to overlap from each resolution is combined as a file, but as a group without combining these distributed data as files,
- a configuration may be adopted in which distributed data of each group is stored in different storages. In this configuration, if the storage that can be accessed is managed based on the user's authority or the like, the same effect as when files are combined can be obtained.
- This disclosure is suitable for use in an image processing system for distributing and managing video data in a secret manner.
- Video / Content Creation Unit 20 Video / Content Storage Unit 21, 21a Video Management Server 22 Storage 30 Video / Content Browsing Unit 33, 33a Reception Device 101, 301 Data Reception Unit 102 Storage Unit 103, 302 Control Unit 104 Resolution Conversion Unit 105 Image encoding unit 106 Secret sharing processing unit 107 Data combining unit 108, 306 Data transmission unit 303 Data separation unit 304 Secret sharing restoration unit 305 Image decoding unit 501 Difference image generation unit 701 Difference image synthesis unit
Abstract
解像度変換部は、入力画像データを、互いに解像度が異なるN種類(Nは複数)の画像データに変換する。秘密分散処理部は、複数の画像データのそれぞれをn個(nはN+1以上の整数であって、全ての画像データにおいて同一の値)の分散データに分割し、その中のk個(kは2以上n以下の整数であって、画像データ毎に互いに異なる値)を用いると元の画像データに復元できるように秘密分散処理を行う。データ結合部は、各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合してn個の結合データを生成し、各結合データを互いに異なるストレージに保存させる。分散データを多く集める程、より解像度の高い画像データを再生することができると共に、各々の分散データにおいて著作権やプライバシー等に対するセキュリティを確保できる。
Description
本開示は、映像データを分散して秘密に管理するための管理装置及びこれを用いた画像処理システムに関する。
特許文献1には、第1の経路(放送波)で主映像データを受信して、必要な場合には第2の経路(ネットワーク)で高画質化の差分データを受信し主映像データと差分データを合成する技術が開示されている。特許文献1に示された技術は、主映像データを取得されるだけで、当該映像データが再生される。
本開示は、分散データを多く集める程、より解像度の高い画像データを再生することができると共に、コンテンツ映像や監視カメラ映像等をネットワーク環境で伝送・蓄積する場合、各々の分散データにおいて著作権やプライバシー等に対するセキュリティを確保することを目的とする。
本開示の管理装置は、入力画像データを、互いに解像度が異なるN種類(Nは複数)の画像データに変換する解像度変換部と、前記複数の画像データのそれぞれをn個(nはN+1以上の整数であって、全ての画像データにおいて同一の値)の分散データに分割し、その中のk個(kは2以上n以下の整数であって、画像データ毎に互いに異なる値)を用いると元の画像データに復元できるように秘密分散処理を行う秘密分散処理部と、各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合してn個の結合データを生成し、各結合データを互いに異なるストレージに保存させるデータ結合部と、を具備する。
また、本開示の画像処理システムは、上記の管理装置と、結合データを保存するストレージと、を具備する。
以下、本開示の実施の形態に係る画像処理システムについて、図面を参照しながら説明する。
(実施の形態1)
実施の形態1では、可逆方式の秘密分散処理を用いる場合について説明する。
実施の形態1では、可逆方式の秘密分散処理を用いる場合について説明する。
図1は、本実施の形態の画像処理システムの構成を示す図である。画像処理システムは、映像・コンテンツ作成部10と、映像・コンテンツ蓄積部20と、映像・コンテンツ閲覧部30と、から主に構成される。
映像・コンテンツ作成部10は、カメラ11、12等で作成された映像データやパーソナルコンピュータ13に保存されている映像データ等を、インターネットと接続するルータ/モデム等の通信装置14を介して、映像・コンテンツ蓄積部20に送信する。
映像・コンテンツ蓄積部20は、映像・コンテンツ作成部10から受信した映像データを映像管理サーバ21で加工して分散データを作成し、複数のストレージ22(22-1、22-2、・・・、22-n)に分散データを分散して保存する。なお、映像管理サーバ21の内部構成、及び、ストレージ22の分散データの保存の様子については後述する。
映像・コンテンツ閲覧部30は、複数のストレージ22に保存された分散データを、ルータ/モデム等の通信装置31を介して受信装置33で受信し、受信装置33は受信した分散データを合成して映像データを復元し、復元された映像データをディスプレイ34に出力する。なお、受信装置33で実施される処理は、モバイル端末32や、パーソナルコンピュータ35、36の内部で実施されても構わない。また、受信装置33の内部構成については後述する。
次に、映像管理サーバ21の内部構成について、図2のブロック図を用いて説明する。図2に示すように、映像管理サーバ21は、データ受信部101と、記憶部102と、制御部103と、解像度変換部104と、画像符号化部105と、秘密分散処理部106と、データ結合部107と、データ送信部108と、から主に構成される。
データ受信部101は、映像・コンテンツ作成部10から送信された映像データを、インターネットを介して受信し、制御部103及び解像度変換部104に出力する。
記憶部102には、変換前の画像データである元画像データの解像度毎に、N種類(Nは2以上の整数)の変換後の解像度と、変換後の解像度毎の解像度変換パラメータ(横画素数、縦画素数)と、秘密分散パラメータ(n(分散数)、k(閾値))とが、関連付けてテーブル形式で保存される(図3参照)。なお、nは、N+α(αは1以上の整数)である。また、kは、2以上n以下の整数である。また、本実施の形態では、kは、変換後の解像度毎に互いに異なる値を採り、解像度が高い程、大きな値を採る。
制御部103は、データ受信部101から入力した映像データの画像データの解像度(画素数)に基づいて、N種類の変換後の解像度を選択し、解像度変換部104に変換後の解像度を指示する。
解像度変換部104は、制御部103に指示された各解像度となるように、記憶部102に保存された情報(各解像度に対応する解像度変換パラメータ)に基づいて、データ受信部101から入力した映像データ(元画像データ)の解像度を変換し、N種類の解像度の映像データを生成して画像符号化部105に出力する。なお、N種類の解像度の映像データに加え、サムネール(縮小画像)を付ける場合、解像度変換部104は、元画像データの解像度をサムネール用の解像度RSに変換して、サムネールを生成し、画像符号化部105に出力する。
画像符号化部105は、解像度変換部104から出力された各解像度の画像データに対して圧縮符号化処理を行い、秘密分散処理部106に出力する。なお、サムネールを付ける場合、画像符号化部105は、サムネールに対して圧縮符号化処理を行い、データ結合部107に出力する。
秘密分散処理部106は、記憶部102に保存された情報(各解像度に対応する秘密分散パラメータ)に基づいて、画像符号化部105から出力された圧縮符号化処理後の各画像データに対して秘密分散処理を行い、解像度毎にn個の分散データを生成してデータ結合部107に出力する。なお、秘密分散処理とは、秘密にしたい一つのデータsを複数のn個の分散データに分割し、その中のk個(k≦n)を用いると元のデータsに復元できるが、k個未満の分散データからでは元のデータsに復元できないようにする処理である(図4参照)。秘密分散処理を行うことにより、分散データを盗まれたとしても、その数がk個未満であれば元のデータsを復元できないことから個々の分散データに対して高いセキュリティを実現できる。また、解像度毎に復元に必要な分散データの数kを、解像度が低い画像データ程、kが小さくなるように設定することにより、少ない分散データでも解像度の低い画像を復元することができると共に、分散データを多く集めるほど高解像度の映像を再生できるようになる。
データ結合部107は、各分散データに先頭マーカ、秘密分散パラメータ、終端マーカを付加し、各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合して結合データを生成する。従って、結合データは合計n個生成される。なお、サムネールを付ける場合、データ結合部107は、圧縮符号化後のサムネールを全ての結合データに付加する。
データ送信部108は、生成されたn個の結合データを互いに異なるストレージ22-i(iは1以上n以下の整数)に送信し、保存する。なお、ストレージ22-iはイントラネットを介して接続されていてもよいし、インターネットを介して接続されていてもよい。
さらに、データ送信部108は、受信装置33の要求に応じて、ストレージ22-iからj個(jは2以上n以下の整数)の結合データを選択して、受信装置33に送信する機能を備えている場合もある。
次に、映像管理サーバ21が行う処理の手順について、図5を用いて説明する。
まず、解像度変換部104が、元画像データの解像度を変換し、N種類の解像度の画像データを生成する。なお、サムネールを付ける場合には、解像度変換部104が、サムネール用の解像度の画像データも生成する(S201)。
次に、画像符号化部105が、N種類の各解像度の画像データに対して圧縮符号化処理を行う。なお、サムネールを付ける場合には、画像符号化部105が、サムネール用の画像データに対しても圧縮符号化処理を行う(S202)。
次に、秘密分散処理部106が、サムネールを除く、N種類の各解像度の圧縮符号化後の画像データに対して秘密分散処理を行い、解像度毎にn個の分散データを生成する(S203)。
次に、データ結合部107が、各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合してn個の結合データを生成する。なお、サムネールを付ける場合には、サムネールはすべての結合データに付加される(S204)。
次に、映像管理サーバ21が行う処理の具体例について、図6を用いて説明する。図6の例では、元画像データが解像度R1(3840×2160ドット)であり、N=3、n=4、サムネール付の場合の例を示している。
この場合、解像度R1(3840×2160ドット)、解像度R2(1920×1080ドット)、解像度R3(640×480ドット)の3種類の解像度の画像データとサムネールが生成される。そして、各解像度の画像データは、秘密分散処理により、それぞれ、4個の分散データに分割される。
ここで、解像度R1の画像データについては、4個の分散データを用いると元の画像データに復元することができる。また、解像度R2の画像データについては、3個の分散データを用いると元の画像データに復元することができる。また、解像度R3の画像データについては、2個の分散データを用いると元の画像データに復元することができる。なお、サムネールは、元画像データを縮小したものであって、例えばコンテンツ映像において著作権を主張できない程度に劣化した、あるいは監視カメラ映像においてプライバシー情報が含まれない程度に劣化した、映像としての価値が低い状態のものである。サムネールを再生しても、著作権やプライバシーに対するセキュリティは確保される。また、サムネールから元画像データを復元することはできない。
秘密分散処理の後、各解像度R1、R2、R3から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データ1-1、2-1、3-1とサムネールが結合されて、ストレージ22-1に保存される。同様に、各解像度R1、R2、R3から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データ1-2、2-2、3-2とサムネールが結合されて、ストレージ22-2に保存され、各解像度R1、R2、R3から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データ1-3、2-3、3-3とサムネールが結合されて、ストレージ22-3に保存され、各解像度R1、R2、R3から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データ1-4、2-4、3-4とサムネールが結合されて、ストレージ22-4に保存される。
次に、受信装置33の内部構成について、図7のブロック図を用いて説明する。図7に示すように、受信装置33は、データ受信部301と、制御部302と、データ分離部303と、秘密分散復元部304と、画像復号部305と、データ送信部306と、から主に構成される。
データ受信部301は、ストレージ22-i(iは1からnまでの整数)からj個(jは2以上n以下の整数)の結合データを、インターネットを介して受信し、制御部302及びデータ分離部303に出力する。
ここで、データ受信部301が受信できる結合データの数は、ユーザの権限等に基づいて決定される。例えば、データ受信部301は、(システムに対してより高額の料金を納めている、あるいは、データ管理者でより高いアクセス権限を有している等の)権限の高いユーザ程、より多くの結合データにアクセスすることができ、受信することができる。これにより、権限の高いユーザ程、高画質の画像データを閲覧することができる。
なお、データ受信部301が受信するデータは、受信装置33の要求に応じて、映像管理サーバ21がj個の結合データをストレージ22-iから選択して送信する構成であってもよい。
制御部302は、データ受信部301から入力した結合データの数j=kに基づいて、復元される画像データ(以下、「復元画像データ」という)の解像度を選択し、データ分離部303に、選択した解像度の分散データを指示する。
例えば、図6で例示したようにN=3、n=4で分散データが作成される場合、j=k=3であれば、解像度R2が復元できるので、復元画像データの解像度はR2となり、データ分離部303には解像度R2の3個の分散データ(例えば、分散データ2-1、2-2、2-3)が指示される。
データ分離部303は、制御部302に指示された分散データを各結合データから分離し、秘密分散復元部304に出力する。
秘密分散復元部304は、データ分離部303から出力された分散データに対して秘密分散復元処理を行い、復元画像データを画像復号部305に出力する。なお、秘密分散復元部304で復元される画像データは、符号化された状態のものである。
画像復号部305は、秘密分散復元部304から出力された復元画像データに対して、画像符号化部105の圧縮符号化に対応する復号処理を行い、ユーザが視聴可能な復元画像データを生成し、データ送信部306に出力する。
データ送信部306は、画像復号部305から出力された復元画像データをディスプレイ34に出力し、復元画像データはディスプレイ34で表示される。
次に、受信装置33が行う処理の手順について、図8を用いて説明する。
まず、データ分離部303が、j個の結合データから、j=kに対応する解像度のk個の分散データを分離する(S401)。
次に、秘密分散復元部304が、k個の分散データに対して秘密分散復元処理を行い、さらに、画像復号部305が復号処理を行い、ユーザが視聴可能な復元画像データを生成する(S402、S403)。
なお、画像復号部305で生成された復元画像データは、ディスプレイ34で表示される。また、受信装置33が行う処理はモバイル端末32や、パーソナルコンピュータ35、36の内部で実施されても構わない。
以上のように、本実施の形態によれば、互いに解像度が異なる複数の画像データのそれぞれをn個(nは3以上の整数であって、全ての画像データにおいて同一の値)の分散データに分割し、その中のk個(kは2以上n以下の整数であって、画像データ毎に互いに異なる値)を用いると元の画像データに復元できるように秘密分散処理を行い、各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合してn個の結合データを生成し、各結合データを互いに異なるストレージに保存させる。これにより、分散データを多く集める程、より解像度の高い画像データを再生することができると共に、各々の分散データにおいて著作権やプライバシー等に対するセキュリティを確保することができる。
(実施の形態2)
実施の形態2では、非可逆方式の秘密分散処理を用いる場合について説明する。なお、本実施の形態の画像処理システムの構成は、実施の形態1で用いた図1のものと同一である。
実施の形態2では、非可逆方式の秘密分散処理を用いる場合について説明する。なお、本実施の形態の画像処理システムの構成は、実施の形態1で用いた図1のものと同一である。
まず、本実施の形態に係る映像管理サーバ21aの内部構成について、図9を用いて説明する。なお、図9に示す映像管理サーバ21aにおいて、図2に示した映像管理サーバ21と共通する部分に、図2と同一符号を付してその詳しい説明を省略する。
図9に示す映像管理サーバ21aは、図2に示した映像管理サーバ21に対して差分画像生成部501を追加した構成を採る。
解像度変換部104は、N種類の解像度の画像データ及びサムネールを生成して差分画像生成部501に出力する。
差分画像生成部501は、N種類の解像度の画像データとサムネールからN個の差分データを生成する。具体的には、差分画像生成部501は、解像度Rm(mは1以上N-1以下の整数、mが少ない程、解像度が高い)の画像データと解像度Rm+1の画像データとの差分を採ることにより、解像度Rmの差分データを生成する。また、差分画像生成部501は、解像度RNの画像データとサムネールとの差分を採ることにより、解像度RNの差分データを生成する。差分画像生成部501は、N個の差分データを画像符号化部105に出力する。
画像符号化部105は、差分画像生成部501から出力された各差分データに対して圧縮符号化処理を行い、秘密分散処理部106に出力する。また、画像符号化部105は、サムネール用の解像度の画像データに対して圧縮符号化処理を行い、データ結合部107に出力する。
秘密分散処理部106は、画像符号化部105から出力された圧縮符号化処理後の各差分データに対して秘密分散処理を行い、差分データ毎にn個の分散データを生成してデータ結合部107に出力する。
次に、映像管理サーバ21aが行う処理の手順について、図10を用いて説明する。
まず、解像度変換部104が、元画像データの解像度を変換し、N種類の解像度の画像データ及びサムネール用の解像度の画像データを生成する(S601)。
次に、差分画像生成部501が、N種類の各解像度の画像データ及びサムネールからN個の差分データを生成する(S602)。
次に、画像符号化部105が、各差分データとサムネールに対して圧縮符号化処理を行う(S603)。
次に、秘密分散処理部106が、N個の圧縮符号化後の差分データに対して秘密分散処理を行い、差分データ毎にn個の分散データを生成する(S604)。
次に、データ結合部107が、各差分データから重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合してn個の結合データを生成する。なお、サムネールは、全ての結合データに付加される(S605)。
次に、映像管理サーバ21aが行う処理の具体例について、図11を用いて説明する。図11の例では、元画像データが解像度R1(3840×2160ドット)であり、N=3、n=4、サムネール付の場合の例を示している。
この場合、解像度R1(3840×2160ドット)、解像度R2(1920×1080ドット)、解像度R3(640×480ドット)の3種類の解像度の画像データとサムネールが生成される。
そして、解像度R1の画像データと解像度R2の画像データとの差分である解像度R1の差分データが生成される。同様に、解像度R2の画像データと解像度R3の画像データとの差分である解像度R2の差分データが生成される。同様に、解像度R3の画像データとサムネールとの差分である解像度R3の差分データが生成される。そして、各解像度の差分データは、秘密分散処理により、それぞれ、4個の分散データに分割される。
なお、解像度R1の差分データについては、4個の分散データを用いると元の差分データに復元することができる。解像度R2の差分データについては、3個の分散データを用いると元の差分データに復元することができる。また、解像度R3の差分データについては、2個の分散データを用いると元の差分データに復元することができる。
また、サムネールと解像度R3の差分データを用いて解像度R3の画像データに復元することができる。また、解像度R3の画像データと解像度R2の差分データを用いて解像度R2の画像データに復元することができる。また、解像度R2の画像データと解像度R1の差分データを用いて解像度R1の画像データに復元することができる。
秘密分散処理の後、各解像度R1、R2、R3から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データ1-1、2-1、3-1とサムネールが結合されて、ストレージ22-1に保存される。同様に、各解像度R1、R2、R3から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データ1-2、2-2、3-2とサムネールが結合されて、ストレージ22-2に保存され、各解像度R1、R2、R3から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データ1-3、2-3、3-3とサムネールが結合されて、ストレージ22-3に保存され、各解像度R1、R2、R3から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データ1-4、2-4、3-4とサムネールが結合されて、ストレージ22-4に保存される。
次に、本実施の形態に係る受信装置33aの内部構成について、図12を用いて説明する。なお、図12に示す受信装置33aにおいて、図7に示した受信装置33と共通する部分に、図7と同一符号を付してその詳しい説明を省略する。
図12に示す受信装置33aは、図7に示した受信装置33に対して差分画像合成部701を追加した構成を採る。
制御部302は、データ受信部301から入力した結合データの数j=kに基づいて、復元画像データの解像度を選択し、データ分離部303に、選択した解像度の復元画像データを生成するために必要な分散データを指示する。例えば、解像度Rmの復元画像データを生成するためには、解像度Rm及び解像度Rmより低い解像度の差分データ、及び、サムネールが必要となり、各差分データを復元するために、各解像度に対応する分散データが必要となる。必要な分散データの数は各解像度によって異なり、解像度が低いほど必要な分散データの数は少ない。
データ分離部303は、制御部302に指示された分散データ及びサムネールを各結合データから分離し、分散データを秘密分散復元部304に出力し、サムネールを画像復合部305に出力する。
秘密分散復元部304は、データ分離部303から出力された分散データに対して秘密分散復元処理を行い、復元された差分データ(以下、「復元差分データ」という)を画像復号部305に出力する。なお、秘密分散復元部304で復元される差分データは、符号化された状態のものである。
画像復号部305は、データ分離部303から出力されたサムネール及び秘密分散復元部304から出力された復元差分データに対して、画像符号化部105の圧縮符号化に対応する復号処理を行い、差分画像合成部701に出力する。
差分画像合成部701は、画像復号部305から出力されたサムネール及び復元差分データに対して合成処理を行い、ユーザが視聴可能な復元画像データを生成する。
次に、受信装置33aが行う処理の手順について、図13を用いて説明する。
まず、データ分離部303が、j個の結合データから、j=kに対応する解像度R(N-j+2)の分散データ及び当該解像度より低い解像度(R(N-j+3)からRN)の分散データを分離する(S801)。
次に、秘密分散復元部304が、各解像度の分散データに対して秘密分散復元処理を行う。ここで、秘密分散復元処理に必要な分散データの数kは各解像度によって異なり、解像度が低いほど必要な分散データの数は少ない。さらに、画像復号部305が復号処理を行い、サムネール及び復元差分データを生成する(S802、S803)。
次に、差分画像合成部701が、サムネール及び復元差分データに対して合成処理を行い、ユーザが視聴可能な復元画像データを生成する(S804)。
なお、差分画像合成部701で生成された復元画像データは、ディスプレイ34で表示される。また、受信装置33aが行う処理はモバイル端末32や、パーソナルコンピュータ35、36の内部で実施されても構わない。
以上のように、本実施の形態によれば、互いに解像度が異なる複数の画像データから複数の差分データを生成し、差分データのそれぞれをn個(nは3以上の整数であって、全ての差分データにおいて同一の値)の分散データに分割し、その中のk個(kは2以上n以下の整数であって、差分データ毎に互いに異なる値)を用いると元の差分データに復元できるように秘密分散処理を行い、各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合してn個の結合データを生成し、各結合データを互いに異なるストレージに保存させる。これにより、分散データを多く集める程、より解像度の高い画像データを再生することができると共に、各々の分散データにおいて著作権やプライバシー等に対するセキュリティを確保することができる。
上記実施例1、2において、映像管理サーバ21で実施される処理は、パーソナルコンピュータ13等で実施されても構わない。また、受信装置33で実施される処理はモバイル端末32や、パーソナルコンピュータ35、36で実施されても構わない。
また、ストレージ22-iはクラウドストレージであっても構わないし、オンプレミスのサーバストレージや、パソコン、カメラ、モバイル端末のストレージの一部を利用しても構わない。
また、ストレージ22-iに保存された分散データを復元する際は、復元に必要な分散データを映像管理サーバ21が選択して、受信装置33や33aに送信する構成であっても構わないし、必要な分散データを受信装置33や33aが選択して、ストレージ22-iからダウンロードする構成であっても構わない。
また、データ結合部において、各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データをファイルとして結合する構成を示したが、これらの分散データをファイルとして結合することなく、1つのグループとして、それぞれのグループの分散データが互いに異なるストレージに保存される構成でも構わない。この構成において、ユーザの権限等に基づいてアクセスできるストレージを管理すれば、ファイル結合した場合と同様の効果が得られる。
また、本実施例において、映像データを対象に説明を行ったが、本開示は映像データだけでなく、静止画像データにも適用することができる。
本開示は、映像データを分散して秘密に管理するための画像処理システムに用いるに好適である。
10 映像・コンテンツ作成部
20 映像・コンテンツ蓄積部
21,21a 映像管理サーバ
22 ストレージ
30 映像・コンテンツ閲覧部
33,33a 受信装置
101,301 データ受信部
102 記憶部
103,302 制御部
104 解像度変換部
105 画像符号化部
106 秘密分散処理部
107 データ結合部
108,306 データ送信部
303 データ分離部
304 秘密分散復元部
305 画像復号部
501 差分画像生成部
701 差分画像合成部
20 映像・コンテンツ蓄積部
21,21a 映像管理サーバ
22 ストレージ
30 映像・コンテンツ閲覧部
33,33a 受信装置
101,301 データ受信部
102 記憶部
103,302 制御部
104 解像度変換部
105 画像符号化部
106 秘密分散処理部
107 データ結合部
108,306 データ送信部
303 データ分離部
304 秘密分散復元部
305 画像復号部
501 差分画像生成部
701 差分画像合成部
Claims (10)
- 入力画像データを、互いに解像度が異なるN種類(Nは複数)の画像データに変換する解像度変換部と、
前記複数の画像データのそれぞれをn個(nはN+1以上の整数であって、全ての画像データにおいて同一の値)の分散データに分割し、その中のk個(kは2以上n以下の整数であって、画像データ毎に互いに異なる値)を用いると元の画像データに復元できるように秘密分散処理を行う秘密分散処理部と、
各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合してn個の結合データを生成し、各結合データを互いに異なるストレージに保存させるデータ結合部と、
を具備する管理装置。 - 前記入力画像データの解像度に基づいて、変換後の解像度を選択し、前記解像度変換部に変換後の解像度を指示する制御部を更に具備する、
請求項1に記載の管理装置。 - 前記解像度変換部から出力された各解像度の画像データに対して圧縮符号化処理を行う画像符号化部を更に具備し、
前記秘密分散処理部は、圧縮符号化処理された画像データに対して秘密分散処理を行う、
請求項1に記載の管理装置。 - 前記解像度変換部は、前記複数の画像データの中の一つとして前記入力画像データをそのまま出力する、
請求項1に記載の管理装置。 - 前記秘密分散処理部は、解像度が低い画像データ程、kが小さくなるように秘密分散処理を行う、
請求項1に記載の管理装置。 - 前記解像度変換部は、前記入力画像データのサムネールを生成し、
前記データ結合部は、前記各結合データに前記サムネールを含める、
請求項1に記載の管理装置。 - ユーザからの要求に応じて、j個(jは2以上n以下の整数)の結合データを前記ユーザ宛に送信するデータ送信部を更に具備する、
請求項1に記載の管理装置。 - 前記データ送信部は、前記要求を出したユーザの権限に応じて、送信する結合データの数jを決定する、
請求項7に記載の管理装置。 - 入力画像データを、互いに解像度が異なるN種類(Nは複数)の画像データに変換する解像度変換部と、
解像度がm番目(mは1以上N-1以下の整数)の画像データと解像度がm+1番目の画像データとの差分である複数の差分データを生成する差分画像生成部と、
前記複数の差分データのそれぞれをn個(nはN+1以上の整数であって、全ての差分データにおいて同一の値)の分散データに分割し、その中のk個(kは2以上n以下の整数であって、差分データ毎に互いに異なる値)を用いると元の差分データに復元できるように秘密分散処理を行う秘密分散処理部と、
各解像度から重複しないように1つずつ選択された分散データを結合してn個の結合データを生成し、各結合データを互いに異なるストレージに保存させるデータ結合部と、
を具備する管理装置。 - 請求項1又は請求項9のいずれか一項に記載の管理装置と、
前記結合データを保存するストレージと、
を具備する画像処理システム。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/524,108 US10230997B2 (en) | 2014-12-05 | 2015-11-30 | Management device and image processing system |
| EP15864842.8A EP3229465B1 (en) | 2014-12-05 | 2015-11-30 | Management device and image processing system |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014-246924 | 2014-12-05 | ||
| JP2014246924A JP6489413B2 (ja) | 2014-12-05 | 2014-12-05 | 管理装置及び画像処理システム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016088347A1 true WO2016088347A1 (ja) | 2016-06-09 |
Family
ID=56091310
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/005939 WO2016088347A1 (ja) | 2014-12-05 | 2015-11-30 | 管理装置及び画像処理システム |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10230997B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3229465B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6489413B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2016088347A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20190356744A1 (en) * | 2018-05-17 | 2019-11-21 | International Business Machines Corporation | Transforming a shortened link based upon social event for tracking sharing analytics |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004274320A (ja) * | 2003-03-07 | 2004-09-30 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 秘密分散装置、秘密再構成装置、秘密分散再構成システム、秘密分散方法、及び秘密再構成方法 |
| JP2007010862A (ja) * | 2005-06-29 | 2007-01-18 | Kddi Corp | 画像分散情報生成装置およびその合成装置 |
| JP2012175626A (ja) * | 2011-02-24 | 2012-09-10 | Kddi Corp | 配信映像の超解像化装置および超解像映像再生装置 |
| JP2014138314A (ja) * | 2013-01-17 | 2014-07-28 | Toshiba Corp | 電子機器、電子機器の制御方法及び制御プログラム |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4629555B2 (ja) * | 2005-11-07 | 2011-02-09 | インターナショナル・ビジネス・マシーンズ・コーポレーション | 復元装置、プログラム、情報システム、復元方法、保管装置、保管システム及び保管方法 |
| US9268750B2 (en) * | 2012-04-04 | 2016-02-23 | Offerpop Corporation | Shared link tracking in online social networking systems |
| JP6273566B2 (ja) * | 2013-04-12 | 2018-02-07 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 通信システム、画像生成方法、及び通信装置 |
| CA2931058C (en) * | 2013-12-03 | 2021-04-06 | Sony Corporation | Reception device |
| US9794604B2 (en) * | 2014-11-14 | 2017-10-17 | Panopto, Inc. | Systems and methods for transmitting segment-quality units of a streaming video session |
-
2014
- 2014-12-05 JP JP2014246924A patent/JP6489413B2/ja active Active
-
2015
- 2015-11-30 WO PCT/JP2015/005939 patent/WO2016088347A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2015-11-30 US US15/524,108 patent/US10230997B2/en active Active
- 2015-11-30 EP EP15864842.8A patent/EP3229465B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004274320A (ja) * | 2003-03-07 | 2004-09-30 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 秘密分散装置、秘密再構成装置、秘密分散再構成システム、秘密分散方法、及び秘密再構成方法 |
| JP2007010862A (ja) * | 2005-06-29 | 2007-01-18 | Kddi Corp | 画像分散情報生成装置およびその合成装置 |
| JP2012175626A (ja) * | 2011-02-24 | 2012-09-10 | Kddi Corp | 配信映像の超解像化装置および超解像映像再生装置 |
| JP2014138314A (ja) * | 2013-01-17 | 2014-07-28 | Toshiba Corp | 電子機器、電子機器の制御方法及び制御プログラム |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP3229465A4 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US10230997B2 (en) | 2019-03-12 |
| JP2016111511A (ja) | 2016-06-20 |
| EP3229465B1 (en) | 2022-01-05 |
| US20170318316A1 (en) | 2017-11-02 |
| JP6489413B2 (ja) | 2019-03-27 |
| EP3229465A4 (en) | 2017-12-06 |
| EP3229465A1 (en) | 2017-10-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11683540B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for spatial enhanced adaptive bitrate live streaming for 360 degree video playback | |
| US9003558B1 (en) | Allowing degraded play of protected content using scalable codecs when key/license is not obtained | |
| KR102027410B1 (ko) | 계층화된 신호 품질 계층에서의 재구성 데이터의 송신 | |
| US9276997B2 (en) | Web browser proxy—client video system and method | |
| CN1867055A (zh) | 用于保护数字输出的信息接口 | |
| WO2012096794A1 (en) | Web browser proxy and client video system and method | |
| EP3301937B1 (en) | Communication system | |
| AU2013316468B2 (en) | Communication server, communication system, program, and communication method | |
| EP3691257B1 (en) | Internet protocol camera security system allowing secure encryption information to be transmitted | |
| US20150199498A1 (en) | Flexible and efficient signaling and carriage of authorization acquisition information for dynamic adaptive streaming | |
| JP5941000B2 (ja) | 映像配信装置及び映像配信方法 | |
| Agham et al. | A novel approach towards separable reversible data hiding technique | |
| WO2016088347A1 (ja) | 管理装置及び画像処理システム | |
| US8989432B2 (en) | System and method of adding a watermark to a JPEG image file | |
| Papadopoulos et al. | Sequential multiple LSB methods and real-time data hiding: variations for visual cryptography ciphers | |
| US20110280398A1 (en) | Secured content distribution system | |
| WO2021100524A1 (ja) | データ処理装置およびその制御方法、プログラム | |
| JP2003264816A (ja) | データ配信方法、配信装置、及びプログラム | |
| CN108449601B (zh) | 电影数据的传输方法及装置 | |
| US11039181B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for secure video manifest/playlist generation and playback | |
| JP6669402B2 (ja) | 通信装置、システム、情報処理方法及びプログラム | |
| JP5084389B2 (ja) | 送信機、受信機、付加情報の埋め込み方法、付加情報の復元方法およびプログラム | |
| KR101415691B1 (ko) | 스트리밍 영상 컨버터 | |
| CN109743592B (zh) | 基于二维密码本的实时码流加密方法 | |
| CN115225934B (zh) | 视频播放方法、系统、电子设备以及存储介质 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15864842 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15524108 Country of ref document: US |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2015864842 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |