WO2016008765A1 - Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture - Google Patents
Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016008765A1 WO2016008765A1 PCT/EP2015/065428 EP2015065428W WO2016008765A1 WO 2016008765 A1 WO2016008765 A1 WO 2016008765A1 EP 2015065428 W EP2015065428 W EP 2015065428W WO 2016008765 A1 WO2016008765 A1 WO 2016008765A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- liquid detergent
- detergent composition
- range
- composition according
- laundry
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 90
- 239000003599 detergent Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 84
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 78
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title description 3
- -1 alkali metal salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 28
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 24
- 239000002738 chelating agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 18
- PDIZYYQQWUOPPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid;2-(methylamino)acetic acid Chemical class CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O.CNCC(O)=O PDIZYYQQWUOPPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 17
- 239000003945 anionic surfactant Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glutamic acid Chemical class OC(=O)C(N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 235000013922 glutamic acid Nutrition 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 239000004220 glutamic acid Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 150000001340 alkali metals Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 239000002736 nonionic surfactant Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene oxide Chemical compound C1CO1 IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- GOOHAUXETOMSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene oxide Chemical compound CC1CO1 GOOHAUXETOMSMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamic acid Chemical class OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 claims description 8
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 8
- 235000015203 fruit juice Nutrition 0.000 claims description 8
- 235000020095 red wine Nutrition 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000007844 bleaching agent Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 235000016213 coffee Nutrition 0.000 claims description 7
- 235000013353 coffee beverage Nutrition 0.000 claims description 7
- 235000013616 tea Nutrition 0.000 claims description 7
- 235000013311 vegetables Nutrition 0.000 claims description 7
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- HRXKRNGNAMMEHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-K trisodium citrate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O HRXKRNGNAMMEHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 4
- XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium benzoate Chemical compound [K+].[O-]C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- HFQQZARZPUDIFP-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;2-dodecylbenzenesulfonate Chemical compound [Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC=C1S([O-])(=O)=O HFQQZARZPUDIFP-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- 241001122767 Theaceae Species 0.000 claims 2
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 15
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 13
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 159000000000 sodium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 9
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 8
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCO LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 235000011389 fruit/vegetable juice Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 244000269722 Thea sinensis Species 0.000 description 5
- 244000078534 Vaccinium myrtillus Species 0.000 description 5
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920000742 Cotton Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 229920002125 Sokalan® Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000003139 biocide Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229940088598 enzyme Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 239000003752 hydrotrope Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000004584 polyacrylic acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229960004063 propylene glycol Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 239000000344 soap Substances 0.000 description 4
- KEQGZUUPPQEDPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dichloro-5,5-dimethylimidazolidine-2,4-dione Chemical compound CC1(C)N(Cl)C(=O)N(Cl)C1=O KEQGZUUPPQEDPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- CIEZZGWIJBXOTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]propanoic acid Chemical class OC(=O)C(C)N(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O CIEZZGWIJBXOTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 244000060011 Cocos nucifera Species 0.000 description 3
- 235000013162 Cocos nucifera Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000003095 Vaccinium corymbosum Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 235000017537 Vaccinium myrtillus Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- WDJHALXBUFZDSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetoacetic acid Chemical compound CC(=O)CC(O)=O WDJHALXBUFZDSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 235000021014 blueberries Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229960004592 isopropanol Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 159000000001 potassium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002689 soil Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004034 viscosity adjusting agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- SMZOUWXMTYCWNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)ethanamine Chemical compound COC1=CC=C(C)C=C1CCN SMZOUWXMTYCWNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Propenoic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=C NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SVTBMSDMJJWYQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpentane-2,4-diol Chemical compound CC(O)CC(C)(C)O SVTBMSDMJJWYQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WYVVKGNFXHOCQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-iodoprop-2-yn-1-yl butylcarbamate Chemical compound CCCCNC(=O)OCC#CI WYVVKGNFXHOCQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000013142 Amylases Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010065511 Amylases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- ZCTQGTTXIYCGGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzyl salicylate Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 ZCTQGTTXIYCGGC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000005575 Cellulases Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010084185 Cellulases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen peroxide Chemical compound OO MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108090001060 Lipase Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000004882 Lipase Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 239000004367 Lipase Substances 0.000 description 2
- CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methacrylic acid Chemical compound CC(=C)C(O)=O CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108091005804 Peptidases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000035195 Peptidases Human genes 0.000 description 2
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 239000004365 Protease Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019418 amylase Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229940025131 amylases Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 235000015197 apple juice Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- DMSMPAJRVJJAGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzo[d]isothiazol-3-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)NSC2=C1 DMSMPAJRVJJAGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QRUDEWIWKLJBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzotriazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N[N][N]C2=C1 QRUDEWIWKLJBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000021028 berry Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 230000003115 biocidal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000001768 cations Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000004927 clay Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- VRLDVERQJMEPIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N dbdmh Chemical compound CC1(C)N(Br)C(=O)N(Br)C1=O VRLDVERQJMEPIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UKMSUNONTOPOIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N docosanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O UKMSUNONTOPOIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BRDYCNFHFWUBCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecaneperoxoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OO BRDYCNFHFWUBCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecanoic acid Chemical class CCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229960004756 ethanol Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229940093476 ethylene glycol Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000003205 fragrance Substances 0.000 description 2
- IPCSVZSSVZVIGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O IPCSVZSSVZVIGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 2
- ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N isobutanol Chemical compound CC(C)CO ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000019421 lipase Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229910003002 lithium salt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 159000000002 lithium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 125000000896 monocarboxylic acid group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 150000004682 monohydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000002978 peroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCO BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000010457 zeolite Substances 0.000 description 2
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-VKHMYHEASA-N (+)-propylene glycol Chemical compound C[C@H](O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- JIRHAGAOHOYLNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N (3-cyclopentyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)methanol Chemical compound COC1=CC=C(CO)C=C1OC1CCCC1 JIRHAGAOHOYLNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-propanediol Substances OCCCO YPFDHNVEDLHUCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940035437 1,3-propanediol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- SYRBOMODLUADBZ-RNIAWFEPSA-N 1-[(E)-[(E)-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methylidenehydrazinylidene]methyl]naphthalen-2-ol Chemical compound N(\N=C\C1=C(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)O)=C/C1=C(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)O SYRBOMODLUADBZ-RNIAWFEPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PIEXCQIOSMOEOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylimidazolidine-2,4-dione Chemical compound CC1(C)N(Br)C(=O)N(Cl)C1=O PIEXCQIOSMOEOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAYXUHPQHDHDDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-butoxyethoxy)ethanol Chemical compound CCCCOCCOCCO OAYXUHPQHDHDDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Aminoethan-1-ol Chemical compound NCCO HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-METHOXYETHANOL Chemical compound COCCO XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LBLYYCQCTBFVLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Methylbenzenesulfonic acid Chemical class CC1=CC=CC=C1S(O)(=O)=O LBLYYCQCTBFVLH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZNQVEEAIQZEUHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethoxyethanol Chemical compound CCOCCO ZNQVEEAIQZEUHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QCDWFXQBSFUVSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenoxyethanol Chemical compound OCCOC1=CC=CC=C1 QCDWFXQBSFUVSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YEYKMVJDLWJFOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-propoxyethanol Chemical compound CCCOCCO YEYKMVJDLWJFOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YNJSNEKCXVFDKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(5-amino-1h-indol-3-yl)-2-azaniumylpropanoate Chemical compound C1=C(N)C=C2C(CC(N)C(O)=O)=CNC2=C1 YNJSNEKCXVFDKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HRPQWSOMACYCRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC(S(O)(=O)=O)=C1 HRPQWSOMACYCRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940099451 3-iodo-2-propynylbutylcarbamate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- CVLHGLWXLDOELD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(Propan-2-yl)benzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound CC(C)C1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 CVLHGLWXLDOELD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KWXICGTUELOLSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 KWXICGTUELOLSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000215068 Acacia senegal Species 0.000 description 1
- HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acrylamide Chemical compound NC(=O)C=C HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920001817 Agar Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 241000416162 Astragalus gummifer Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000021357 Behenic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000005711 Benzoic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- DPUOLQHDNGRHBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Brassidinsaeure Natural products CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O DPUOLQHDNGRHBS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZKQDCIXGCQPQNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium hypochlorite Chemical compound [Ca+2].Cl[O-].Cl[O-] ZKQDCIXGCQPQNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QDHHCQZDFGDHMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloramine Chemical compound ClN QDHHCQZDFGDHMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000858 Cyclodextrin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- VVNCNSJFMMFHPL-VKHMYHEASA-N D-penicillamine Chemical compound CC(C)(S)[C@@H](N)C(O)=O VVNCNSJFMMFHPL-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004375 Dextrin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001353 Dextrin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- HMEKVHWROSNWPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Erioglaucine A Chemical compound [NH4+].[NH4+].C=1C=C(C(=C2C=CC(C=C2)=[N+](CC)CC=2C=C(C=CC=2)S([O-])(=O)=O)C=2C(=CC=CC=2)S([O-])(=O)=O)C=CC=1N(CC)CC1=CC=CC(S([O-])(=O)=O)=C1 HMEKVHWROSNWPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- URXZXNYJPAJJOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Erucic acid Natural products CCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O URXZXNYJPAJJOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108090000371 Esterases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 235000016623 Fragaria vesca Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 240000009088 Fragaria x ananassa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000011363 Fragaria x ananassa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000206672 Gelidium Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920000544 Gore-Tex Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000084 Gum arabic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000004157 Hydrolases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000604 Hydrolases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000004354 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000663 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002153 Hydroxypropyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- SHBUUTHKGIVMJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydroxystearate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OO SHBUUTHKGIVMJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005639 Lauric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000234269 Liliales Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920000161 Locust bean gum Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000021314 Palmitic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 108700020962 Peroxidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000003992 Peroxidases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010064785 Phospholipases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000015439 Phospholipases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 108010059820 Polygalacturonase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 1
- OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propanedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)CC(O)=O OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005708 Sodium hypochlorite Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001615 Tragacanth Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910021536 Zeolite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000010489 acacia gum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000205 acacia gum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000010419 agar Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GUUHFMWKWLOQMM-NTCAYCPXSA-N alpha-hexylcinnamaldehyde Chemical compound CCCCCC\C(C=O)=C/C1=CC=CC=C1 GUUHFMWKWLOQMM-NTCAYCPXSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GUUHFMWKWLOQMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-n-hexylcinnamic aldehyde Natural products CCCCCCC(C=O)=CC1=CC=CC=C1 GUUHFMWKWLOQMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003863 ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003125 aqueous solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 1
- PQRDTUFVDILINV-UHFFFAOYSA-N bcdmh Chemical compound CC1(C)N(Cl)C(=O)N(Br)C1=O PQRDTUFVDILINV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940116226 behenic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000010233 benzoic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960004365 benzoic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- CADWTSSKOVRVJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl(dimethyl)azanium;chloride Chemical class [Cl-].C[NH+](C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 CADWTSSKOVRVJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010005774 beta-Galactosidase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000005936 beta-Galactosidase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 235000012745 brilliant blue FCF Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004161 brilliant blue FCF Substances 0.000 description 1
- BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N butan-2-ol Chemical compound CCC(C)O BTANRVKWQNVYAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CDQSJQSWAWPGKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N butane-1,1-diol Chemical compound CCCC(O)O CDQSJQSWAWPGKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005018 casein Substances 0.000 description 1
- BECPQYXYKAMYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N casein, tech. Chemical compound NCCCCC(C(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CC(C)C)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(C(C)O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=O)N=C(O)C(COP(O)(O)=O)N=C(O)C(CCC(O)=N)N=C(O)C(N)CC1=CC=CC=C1 BECPQYXYKAMYBN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000021240 caseins Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- VDQQXEISLMTGAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloramine T Chemical compound [Na+].CC1=CC=C(S(=O)(=O)[N-]Cl)C=C1 VDQQXEISLMTGAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DHNRXBZYEKSXIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloromethylisothiazolinone Chemical compound CN1SC(Cl)=CC1=O DHNRXBZYEKSXIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003240 coconut oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019864 coconut oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008139 complexing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940097362 cyclodextrins Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000019425 dextrin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCOCCO MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004683 dihydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N dioxosilane;oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Si]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=O HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FPAYXBWMYIMERV-UHFFFAOYSA-L disodium;5-methyl-2-[[4-(4-methyl-2-sulfonatoanilino)-9,10-dioxoanthracen-1-yl]amino]benzenesulfonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)C1=CC(C)=CC=C1NC(C=1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C=11)=CC=C1NC1=CC=C(C)C=C1S([O-])(=O)=O FPAYXBWMYIMERV-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- VTIIJXUACCWYHX-UHFFFAOYSA-L disodium;carboxylatooxy carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)OOC([O-])=O VTIIJXUACCWYHX-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- YRIUSKIDOIARQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecyl benzenesulfonate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCOS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 YRIUSKIDOIARQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DPUOLQHDNGRHBS-KTKRTIGZSA-N erucic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O DPUOLQHDNGRHBS-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BEFDCLMNVWHSGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethenylcyclopentane Chemical compound C=CC1CCCC1 BEFDCLMNVWHSGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010093305 exopolygalacturonase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- GNBHRKFJIUUOQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluorescein Chemical compound O1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C21C1=CC=C(O)C=C1OC1=CC(O)=CC=C21 GNBHRKFJIUUOQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001530 fumaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 108010002430 hemicellulase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229940051250 hexylene glycol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019447 hydroxyethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001863 hydroxypropyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010977 hydroxypropyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004900 laundering Methods 0.000 description 1
- SDQFDHOLCGWZPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N lilial Chemical compound O=CC(C)CC1=CC=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C1 SDQFDHOLCGWZPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010420 locust bean gum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000711 locust bean gum Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- YZQBYALVHAANGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium;dihypochlorite Chemical compound [Mg+2].Cl[O-].Cl[O-] YZQBYALVHAANGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011976 maleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000325 methylidene group Chemical group [H]C([H])=* 0.000 description 1
- BEGLCMHJXHIJLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methylisothiazolinone Chemical compound CN1SC=CC1=O BEGLCMHJXHIJLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000005700 microbiome Species 0.000 description 1
- WQEPLUUGTLDZJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Pentadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O WQEPLUUGTLDZJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JMXROTHPANUTOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-H naphthol green b Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Fe+3].C1=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=CC2=C(N=O)C([O-])=CC=C21.C1=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=CC2=C(N=O)C([O-])=CC=C21.C1=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=CC2=C(N=O)C([O-])=CC=C21 JMXROTHPANUTOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019198 oils Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004006 olive oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000008390 olive oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001451 organic peroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000004967 organic peroxy acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003346 palm kernel oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019865 palm kernel oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000010987 pectin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001814 pectin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001277 pectin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960001639 penicillamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- JRKICGRDRMAZLK-UHFFFAOYSA-L persulfate group Chemical group S(=O)(=O)([O-])OOS(=O)(=O)[O-] JRKICGRDRMAZLK-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229960005323 phenoxyethanol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000711 polarimetry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000010287 polarization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920005646 polycarboxylate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000193 polymethacrylate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000166 polytrimethylene carbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960003975 potassium Drugs 0.000 description 1
- SATVIFGJTRRDQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N potassium hypochlorite Chemical compound [K+].Cl[O-] SATVIFGJTRRDQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940096992 potassium oleate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940114930 potassium stearate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- MLICVSDCCDDWMD-KVVVOXFISA-M potassium;(z)-octadec-9-enoate Chemical compound [K+].CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC([O-])=O MLICVSDCCDDWMD-KVVVOXFISA-M 0.000 description 1
- IFIDXBCRSWOUSB-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium;1,5-dichloro-4,6-dioxo-1,3,5-triazin-2-olate Chemical compound [K+].ClN1C(=O)[N-]C(=O)N(Cl)C1=O IFIDXBCRSWOUSB-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- ANBFRLKBEIFNQU-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium;octadecanoate Chemical compound [K+].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O ANBFRLKBEIFNQU-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- KXXXUIKPSVVSAW-UHFFFAOYSA-K pyranine Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].C1=C2C(O)=CC(S([O-])(=O)=O)=C(C=C3)C2=C2C3=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C2=C1 KXXXUIKPSVVSAW-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 235000012752 quinoline yellow Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- FZUOVNMHEAPVBW-UHFFFAOYSA-L quinoline yellow ws Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].O=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C1C1=NC2=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C(S(=O)(=O)[O-])C=C2C=C1 FZUOVNMHEAPVBW-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000011369 resultant mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011435 rock Substances 0.000 description 1
- RMAQACBXLXPBSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicic acid Chemical compound O[Si](O)(O)O RMAQACBXLXPBSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- MSFGZHUJTJBYFA-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium dichloroisocyanurate Chemical compound [Na+].ClN1C(=O)[N-]C(=O)N(Cl)C1=O MSFGZHUJTJBYFA-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- SUKJFIGYRHOWBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium hypochlorite Chemical compound [Na+].Cl[O-] SUKJFIGYRHOWBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001922 sodium perborate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940045872 sodium percarbonate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- YKLJGMBLPUQQOI-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;oxidooxy(oxo)borane Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]OB=O YKLJGMBLPUQQOI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004334 sorbic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010199 sorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940075582 sorbic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003760 tallow Substances 0.000 description 1
- UJMBCXLDXJUMFB-GLCFPVLVSA-K tartrazine Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)C1=NN(C=2C=CC(=CC=2)S([O-])(=O)=O)C(=O)C1\N=N\C1=CC=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C1 UJMBCXLDXJUMFB-GLCFPVLVSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 235000012756 tartrazine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004149 tartrazine Substances 0.000 description 1
- TUNFSRHWOTWDNC-HKGQFRNVSA-N tetradecanoic acid Chemical class CCCCCCCCCCCCC[14C](O)=O TUNFSRHWOTWDNC-HKGQFRNVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004685 tetrahydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000010487 tragacanth Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000196 tragacanth Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940116362 tragacanth Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920003169 water-soluble polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/83—Mixtures of non-ionic with anionic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
- C11D1/12—Sulfonic acids or sulfuric acid esters; Salts thereof
- C11D1/22—Sulfonic acids or sulfuric acid esters; Salts thereof derived from aromatic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/16—Organic compounds
- C11D3/20—Organic compounds containing oxygen
- C11D3/2075—Carboxylic acids-salts thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D3/00—Other compounding ingredients of detergent compositions covered in group C11D1/00
- C11D3/16—Organic compounds
- C11D3/26—Organic compounds containing nitrogen
- C11D3/33—Amino carboxylic acids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/02—Anionic compounds
- C11D1/12—Sulfonic acids or sulfuric acid esters; Salts thereof
- C11D1/29—Sulfates of polyoxyalkylene ethers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D1/00—Detergent compositions based essentially on surface-active compounds; Use of these compounds as a detergent
- C11D1/66—Non-ionic compounds
- C11D1/72—Ethers of polyoxyalkylene glycols
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C11—ANIMAL OR VEGETABLE OILS, FATS, FATTY SUBSTANCES OR WAXES; FATTY ACIDS THEREFROM; DETERGENTS; CANDLES
- C11D—DETERGENT COMPOSITIONS; USE OF SINGLE SUBSTANCES AS DETERGENTS; SOAP OR SOAP-MAKING; RESIN SOAPS; RECOVERY OF GLYCEROL
- C11D2111/00—Cleaning compositions characterised by the objects to be cleaned; Cleaning compositions characterised by non-standard cleaning or washing processes
- C11D2111/10—Objects to be cleaned
- C11D2111/12—Soft surfaces, e.g. textile
Definitions
- the present invention is directed towards a liquid detergent composition
- a liquid detergent composition comprising (A) at least one chelating agent selected from alkali metal salts of methyl glycine diacetate and glutamic acid diacetate,
- (C) at least one non-ionic surfactant according to the general formula (II), the weight ratio of all chelating agent (A) to all anionic surfactant (B) being in the range of from 1 :1 to 1 :8, with the integers being defined as follows: n being a number in the range of from 10 to 18,
- n being a number in the range of from 10 to 18,
- M being selected from alkali metals
- AO being different or identical and selected from ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, and butyl- ene oxide, x being a number in the range of from 1 to 5,
- the present invention is directed towards a method for making liquid detergent compositions, and to the use of such liquid detergent compositions as or for making a liquid laundry care composition.
- Liquid laundry detergents have numerous benefits. The most common advantage over powder detergents is that they leave no residues on the clothes that may affect the appearance, in particular in the case of dark clothes. Such residues may also adversely affect membranes of clothes such as Gore-Tex®. Most of such residues found when using powder detergents mainly consist of bleaching agents and zeolites. For that reason, liquid laundry detergents are advantageously used for laundering colored clothes. Further advantages of liquid laundry detergents are that they are dispensed easily, and they readily dissolve in the washing liquor. With detergent powders, a common disadvantage is that they tend to caking when exposed to humidity. That disadvantage can be avoided when using liquid laundry detergents. The removal of stains from soiled laundry is often referred to as primary detergency.
- liquid laundry detergents show a reduced ability to remove stains from colored soilings such as, but not limited to red wine, tea, coffee, vegetables, and various fruit juices like berry juices.
- Adding a bleaching agent would improve the ability of liquid laundry detergents to remove bleachable stains but deteriorate the detergent in aspects other than the ones discussed before.
- many bleaching agents are incompatible with certain surfactants, and they may lead to deterioration or degradation of enzymes.
- liquid laundry detergent that has a good primary deter- gency.
- a liquid laundry detergent that has a good ability to remove bleachable stains such as red wine, tea, coffee, vegetables, and fruit juices.
- a process for manufacturing such liquid laundry detergents Accordingly, the liquid detergent compositions defined at the outset were found, hereinafter also referred to as inventive detergent compositions or inventive liquid detergent compositions or liquid detergent compositions according to the present invention.
- Inventive detergent compositions are liquid. This property refers to normal conditions (25°C, one atmosphere). They appear clear or lightly opaque to the naked eye, and they can be poured like water.
- gel-type liquid laundry detergents are a special embodiment of liquid laundry detergents. Gel-type liquid laundry detergents usually contain at least one viscosity modifier, and they contain little or no non-aqueous solvents. Gel-type liquid laundry detergents can be directly applied to stains in soiled laundry.
- liquid detergent compositions according to the present invention have a dynamic viscosity in the range of from 500 to 20,000 mPa-s, determined at 25°C according to Brookfield, for example spindle 3 at 20 rpm with a Brookfield viscosimeter LVT-II.
- liquid detergent compositions according to the present invention may have a water content in the range of from 50 to 98% by weight, preferably up to 95%. In one embodiment of the present invention, liquid detergent compositions according to the present invention may have a total solids content in the range of from 2 to 50% by weight, preferably 10 to 35% by weight.
- liquid detergent compositions according to the pre- sent invention may comprise solvents other than water, for example ethanol, n-propanol, iso- propanol, n-butanol, iso-butanol, sec.-butanol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, 1 ,3-propane diol, butane diol, glycerol, diglycol, propyl diglycol, butyl diglycol, hexylene glycol, ethylene gly- col methyl ether, ethylene glycol ethyl ether, ethylene glycol propyl ether, and phenoxyethanol, preferred are ethanol, isopropanol or propylene glycol.
- solvents other than water for example ethanol, n-propanol, iso- propanol, n-butanol, iso-butanol, sec.-butanol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, 1 ,3-propan
- liquid detergent compositions according to the pre- sent invention comprise 0.5 to 12 % by weight of organic solvent, referring to the total respective liquid detergent composition.
- the content of organic solvent may be in the range of from 8 to 25% by weight, referring to the total respective liquid detergent composition.
- Inventive liquid detergent compositions contain
- (A) at least one chelating agent selected from alkali metal salts of methyl glycine diacetate (MGDA) and glutamic acid diacetate (GLDA), hereinafter generally also being referred to as complexing agent (A).
- MGDA methyl glycine diacetate
- GLDA glutamic acid diacetate
- alkali metal salts of methylglycine diacetic acid are selected from lithium salts, potassium salts and preferably sodium salts of methylglycine diacetic acid.
- Methylglycine diacetic acid can be partially or preferably fully neutralized with the respective alkali.
- an average of from 2.7 to 3 COOH groups of MGDA is neutralized with alkali metal, preferably with sodium.
- chelating agent (A) is the trisodium salt of MGDA.
- alkali metal salts of glutamic acid diacetic acid are selected from lithium salts, potassium salts and preferably sodium salts of glutamic acid diacetic acid.
- Glutamic acid diacetic acid can be partially or preferably fully neutralized with the respective alkali.
- an average of from 3.5 to 4 COOH groups of MGDA is neutralized with alkali metal, preferably with sodium.
- chelating agent (A) is the tetrasodi- um salt of GLDA.
- alkali metal salts of MGDA are selected from those of general formula (III)
- alkali metal salts of GLDA are selected from those of general formula (IV)
- MGDA and its respective alkali metal salts can be selected from the racemic mixtures, the D- isomers and the L-isomers, and from mixtures of the D- and L-isomers other than the racemic mixtures.
- MGDA and its respective alkali metal salts are selected from the racemic mixture and from mixtures containing in the range of from 55 to 85 mole-% of the L-isomer, the balance being D-isomer.
- Particularly preferred are mixtures containing in the range of from 60 to 80 mole-% of the L-isomer, the balance being D-isomer.
- the distribution of L- and D-enantiomer can be determined by measuring the polarization (polar- imetry) or preferably by chromatography, for example by HPLC with a chiral column, for example with one or more cyclodextrins as immobilized phase. Preferred is determination of the ee by HPLC with an immobilized optically active ammonium salt such as D-penicillamine.
- GLDA and its respective alkali metal salts can be selected from the racemic mixtures, the D- isomers and the L-isomers, and from mixtures of the D- and L-isomers other than the racemic mixtures.
- GLDA and its respective alkali metal salts are selected from mixtures con- taining in the range of from 75 to 99 mole-% of the L-isomer, the balance being D-isomer.
- Particularly preferred are mixtures containing in the range of from 80 to 97.5 mole-% of the L- isomer, the balance being D-isomer.
- minor amounts of chelating agent (A) may bear a cation other than alkali metal. It is thus possible that minor amounts, such as 0.01 to 5 mol-% of total chelating agent (A) bear alkali earth metal cations such as Mg 2+ or Ca 2+ , or an Fe 2+ or Fe 3+ cation.
- chelating agent (A) is selected from the trisodium salt of methyl glycine diacetate and the tetrasodium salt of glutamic acid diacetate.
- inventive liquid detergent compositions may contain a mixture from the sodium salts of MGDA and GLDA.
- Inventive liquid detergent compositions contain at least one anionic surfactant according to the general formula (I)
- M being selected from alkali metals, preferably potassium and even more preferably sodium.
- n and x may be average numbers and therefore they are not necessarily whole numbers, while in individual molecules according to formula (I), both n and x denote whole numbers.
- Inventive liquid detergent compositions further contain
- (C) at least one non-ionic surfactant according to the general formula (II), hereinafter also being referred to as surfactant (C) or non-ionic surfactant (C), with the integers being defined as follows: m being a number in the range of from 10 to 18, preferably 16 to 18,
- M being selected from alkali metals, preferably potassium and even more preferably sodium,
- AO being different or identical and selected from ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, and butyl- ene oxide, especially ethylene oxide, CH2CH2O,
- y being different or identical and selected from numbers in the range of from 1 to 12, prefer- ably 5 to 10.
- m and y may be average numbers and therefore they are not necessarily whole numbers, while in individual molecules according to formula (II), both m and y denote whole numbers.
- the weight ratio of all chelating agent (A) to all anionic surfactant (B) is in the range of from 1 :1 to 1 :8, preferably from 1 :1.5 to 1 :4.
- inventive liquid detergent compositions have a pH value in the range of from 7 to 9.5, preferably 8 to 9.
- inventive liquid detergent compositions comprise (A) in the range of from 5 to 15 % by weight of chelating agent, preferably 6 to 12 % by
- inventive liquid detergent compositions are free from bleaching agents.
- Bleaching agents in the context of the present invention are organic peroxides, inorganic peroxides and chlorine bleaches.
- organic and inorganic peroxides are sodium perborate, anhydrous or for example as monohydrate or as tetrahydrate or so-called dihydrate, sodium percarbonate, anhydrous or, for example, as monohydrate, hydrogen peroxide, persulfates, organic peracids such as peroxylauric acid, peroxystearic acid, peroxy-a-naphthoic acid, 1 ,12-diperoxydodecanedioic acid, per- benzoic acid, peroxylauric acid, 1 ,9-diperoxyazelaic acid, diperoxyisophthalic acid, in each case as free acid or as alkali metal salt, in particular as sodium salt, also sulfonylperoxy acids and cationic peroxy acids, chlorine-containing bleaches are, for example, 1 ,3-dichloro-5,5-dimethyl- hydantoin, N-N-chlorosulfamide, chloramine T, chloramine B, sodium hypo
- Free from in the context of bleaching agents means less than 0.5% by weight, referring to the total solids content.
- inventive liquid detergent compositions contain at least one alkali metal salt, preferably at least one potassium salt of a fatty acid.
- alkali metal salt preferably at least one potassium salt of a fatty acid.
- examples are the sodium salts and especially the potassium salts of lauric acid, myristic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, (hydrogenated) erucic acid and behenic acid, and especially soap mixtures derived from natural fatty acids such as coconut oil fatty acid, palm kernel oil fatty acid, olive oil fatty acid or tallow fatty acid.
- Preferred examples are potassium coconut soap, potassium stearate, potassium oleate, potassium coconut soap with an average formula of n-C ⁇ HbsCOOK being even more preferred.
- the amount of potassium salt of fatty acid may be in the range of from 10 to 25 % by weight referring to the total solids content of said liquid detergent composition.
- inventive liquid detergent compositions comprise linear sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate, for example a mixture from the sodium salts of linear 4-dodecylbenzenesulphonate and linear 5-dodecylbenzenesulphonate.
- the amount of linear sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate may be in the range of from 10 to 40 % by weight referring to the total solids content of said liquid detergent composition.
- Inventive liquid detergent compositions are liquid laundry detergent compositions. They may comprise ingredients other than the aforementioned. Examples are fragrances, dyestuffs, bio- cides, preservatives, enzymes, hydrotropes, builders, viscosity modifiers, polymers, buffers, defoamers, and anti-corrosion additives. Examples of fragrances are benzyl salicylate, 2-(4-tert.-butylphenyl) 2-methylpropional, commercially available as Lilial®, and hexyl cinnamaldehyde.
- dyestuffs are Acid Blue 9, Acid Yellow 3, Acid Yellow 23, Acid Yellow 73, Pigment Yellow 101 , Acid Green 1 , Solvent Green 7, and Acid Green 25.
- Inventive liquid detergent compositions may contain one or more preservatives or biocides.
- Bio- cides and preservatives prevent alterations of inventive liquid detergent compositions due to attacks from microorganisms.
- biocides and preservatives are BTA (1 ,2,3- benzotriazole), benzalkonium chlorides, 1 ,2-benzisothiazolin-3-one ("BIT”), 2-methyl-2H- isothiazol-3-one (,, ⁇ ') and 5-chloro-2-methyl-2H-isothiazol-3-one diligentCIT"), benzoic acid, sorbic acid, iodopropynyl butylcarbamate (“IPBC”), dichlorodimethylhydantoine (“DCDMH”), bromo- chlorodimethylhydantoine (“BCDMH”), and dibromodimethylhydantoine (“DBDMH”).
- BTA 1,2,3- benzotriazole
- BIT ,2-benziso
- viscosity modifiers examples include agar-agar, carragene, tragacanth, gum arabic, alginates, pectins, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, starch, gelatin, locust bean gum, cross- linked poly(meth)acrylates, for example polyacrylic acid cross-linked with methylene bis- (meth)acrylamide, furthermore silicic acid, clay such as - but not limited to - montmorrilionite, zeolite, dextrin, and casein.
- cross- linked poly(meth)acrylates for example polyacrylic acid cross-linked with methylene bis- (meth)acrylamide, furthermore silicic acid, clay such as - but not limited to - montmorrilionite, zeolite, dextrin, and casein.
- Hydrotropes in the context with the present invention are compounds that facilitate the dissolution of compounds that exhibit limited solubility in water.
- examples of hydrotropes are organic solvents such as ethanol, isopropanol, ethylene glycol, 1 ,2-propylene glycol, and further organic solvents that are water-miscible under normal conditions without limitation.
- suitable hydrotropes are the sodium salts of toluene sulfonic acid, of xylene sulfonic acid, and of cumene sulfonic acid.
- useful enzymes are lipases, hydrolases, amylases, proteases, cellulases, hemi- cellulases, lipases, phospholipases, esterases, pectinases, lactases and peroxidases, and combinations of at least two of the foregoing types of the foregoing.
- Particularly useful enzymes are selected from are proteases, amylases, and cellulases.
- polymers are especially polyacrylic acid and its respective alkali metal salts, especially its sodium salt.
- a suitable polymer is in particular polyacrylic acid, preferably with an aver- age molecular weight M w in the range from 2,000 to 40,000 g/mol. preferably 2,000 to 10,000 g/mol, in particular 3,000 to 8,000 g/mol, each partially or fully neutralized with alkali, especially with sodium.
- copolymeric polycarboxylates in particular those of acrylic acid with methacrylic acid and of acrylic acid or methacrylic acid with maleic acid and/or fumaric acid.
- Polyacrylic acid and its respective alkali metal salts may serve as soil anti-redeposition agents.
- Further examples of polymers are polyvinylpyrrolidones (PVP). Polyvinylpyrrolidones may serve as dye transfer inhibitors.
- polymers are polyethylene terephthalates, polyoxyethylene terphthalates, and polyethylene terephthalates that are end-capped with one or two hydrophilic groups per molecule, hydrophilic groups being selected from ChbChbCI-b-SOsNa, CH 2 CH(CH2-S03Na)2, and CH 2 CH(CH 2 S02Na)CH2-S03Na.
- buffers are monoethanolamine and ⁇ , ⁇ , ⁇ -triethanolamine.
- defoamers are silicones.
- Inventive liquid detergent compositions are not only good in cleaning soiled laundry with respect to inorganic soil such as clay, or organic fatty soil such as oil.
- Inventive liquid detergent compo- sitions are very useful for removing non-bleachable stains such as, but not limited to stains from red wine, tea, coffee, vegetables, and various fruit juices like berry juices from laundry. They still do not leave residues on the clothes.
- liquid laundry detergent inventive liquid detergent compositions may be in bulk form or as unit doses, for example in the form of sachets or pouches.
- Suitable materials for pouches are water-soluble polymers such as polyvinyl alcohol.
- an inventive liquid detergent composition for cleaning laundry is the use of an inventive liquid detergent composition for cleaning laundry.
- an aspect of the present invention is the use of inventive liquid detergent compositions for cleaning laundry stained with at least one of red wine, tea, coffee, vegetables, or fruit juice.
- fruit juices are apple juice, blueberry juice and blackberry juice.
- Another aspect of the present invention is a process to clean laundry, hereinafter also referred to as inventive process.
- the inventive process is directed towards cleaning laundry stained with bleachable stains such as at least one of red wine, tea, coffee, vegetables, or fruit juice such as, but not limited to apple juice, blueberry juice or blackberry juice by applying at least one inventive liquid detergent composition.
- the inventive process can be performed in an automatic laundry cleaner or manually.
- Said inventive detergent composition is preferably diluted with water before applying it to the soiled laundry.
- the inventive process is characterized in that the respective inventive liquid detergent composition is being applied to soiled laundry at a temperature in the range of from 20 to 65°C.
- a further aspect of the present invention is a process for making inventive liquid detergent compositions, hereinafter also referred to as inventive method.
- inventive method comprises mixing chelating agent (A), surfactant (B) and surfactant (C), and, optionally, further ingredients as outlined above, with water in one or more steps.
- the present invention is further illustrated by working examples.
- the present invention is further illustrated by working examples.
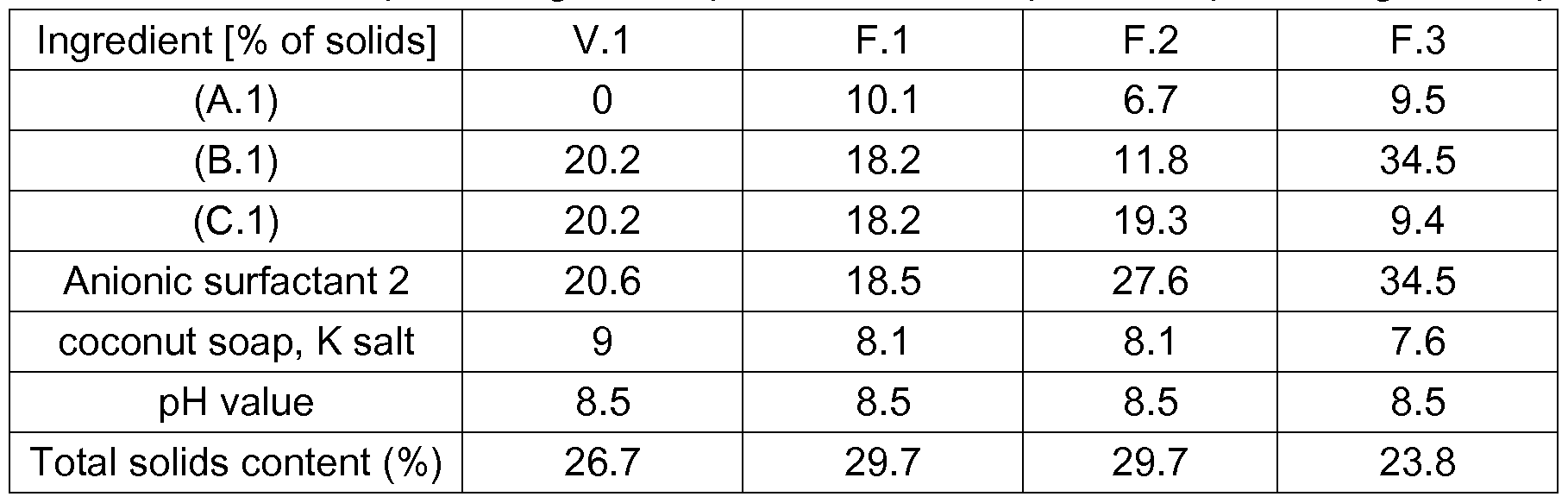
- the wash performance of for- mulations F.1 , F.2 and F.3 was determined and compared to the formulation without MGDA
- a vessel was charged with 120 ml of water.
- Anionic surfactant 2 according to Table 1 and 1 ,2- propylene glycol - amount: 6 % by weight referring to the total solids content - were added and the resultant mixture was heated to 50-55°C under stirring.
- the pH value was adjusted to 3 to 4 with aqueous potassium hydroxide solution (50%) and potassium coconut soap was added.
- Chelating agent (A.1 ) was added to the mixture so obtained, and the pH value was adjusted to
- Anionic surfactant 2 sodium salt of linear dodecylbenzenesulphonate
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Detergent Compositions (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Cleaning By Liquid Or Steam (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| MX2017000777A MX2017000777A (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture. |
| KR1020177001276A KR20170032310A (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture |
| CN201580036723.XA CN106536698A (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture |
| JP2017502839A JP2017528552A (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent composition and method for producing the same |
| BR112017000752A BR112017000752A2 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | liquid detergent composition, processes for cleaning stained clothing and making a liquid detergent composition, and use of a liquid detergent composition. |
| US15/323,889 US20170145354A1 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture |
| RU2017105100A RU2695059C2 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent compositions and production thereof |
| EP15734385.6A EP3169759A1 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture |
| CA2953045A CA2953045A1 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14177481 | 2014-07-17 | ||
| EP14177481.0 | 2014-07-17 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016008765A1 true WO2016008765A1 (en) | 2016-01-21 |
Family
ID=51178802
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP2015/065428 WO2016008765A1 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-07 | Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20170145354A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3169759A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2017528552A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20170032310A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN106536698A (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112017000752A2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2953045A1 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX2017000777A (en) |
| RU (1) | RU2695059C2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2016008765A1 (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017189703A1 (en) | 2016-04-27 | 2017-11-02 | Dow Corning Corporation | Detergent composition comprising a carbinol functional trisiloxane |
| WO2020234597A1 (en) | 2019-05-22 | 2020-11-26 | Reckitt Benckiser Llc | Detergent formulations having enhanced germ removal efficacy |
| WO2020260038A1 (en) * | 2019-06-28 | 2020-12-30 | Unilever Plc | Detergent composition |
| WO2022063708A1 (en) | 2020-09-24 | 2022-03-31 | Unilever Ip Holdings B.V. | Composition |
| WO2023051978A1 (en) | 2021-09-29 | 2023-04-06 | Unilever Ip Holdings B.V. | Composition |
| US11713435B2 (en) | 2018-01-30 | 2023-08-01 | Eastman Chemical Company | Aminocarboxylate chelating agents and detergent compositions containing them |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES2855023T3 (en) * | 2014-11-26 | 2021-09-23 | Procter & Gamble | Cleaning bag |
| JP7064743B2 (en) * | 2017-12-27 | 2022-05-11 | 株式会社ニイタカ | Effervescent detergent composition |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1998013467A1 (en) * | 1996-09-27 | 1998-04-02 | Unilever N.V. | Aqueous structured liquid detergent composition comprising aminocarboxylate sequestrant |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000008099A (en) * | 1998-06-23 | 2000-01-11 | Kao Corp | Liquid detergent composition |
| JP2000026890A (en) * | 1998-07-06 | 2000-01-25 | Kao Corp | Detergent composition |
| JP4017940B2 (en) * | 2002-08-14 | 2007-12-05 | 花王株式会社 | Foam-coated laundry pretreatment agent |
| ES2264111T3 (en) * | 2003-02-22 | 2006-12-16 | Reckitt, Benckiser, Inc. | COMPOSITIONS FOR CLEANING HARD SURFACES. |
| DE102004007860A1 (en) * | 2004-02-17 | 2005-09-15 | Henkel Kgaa | Dispenser bottle for liquid detergents consisting of at least two partial compositions |
| WO2007084729A2 (en) * | 2006-01-23 | 2007-07-26 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Laundry care compositions with thiazolium dye |
| ES2412707T5 (en) * | 2009-06-19 | 2023-06-12 | Procter & Gamble | Liquid detergent composition for hand dishwashing |
| EP2431452B1 (en) * | 2010-09-21 | 2015-07-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Liquid cleaning composition |
| US20120205581A1 (en) * | 2011-02-16 | 2012-08-16 | Robert Richard Dykstra | Compositions and methods of bleaching |
| JP5832813B2 (en) * | 2011-08-11 | 2015-12-16 | 花王株式会社 | Liquid detergent composition |
-
2015
- 2015-07-07 US US15/323,889 patent/US20170145354A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2015-07-07 BR BR112017000752A patent/BR112017000752A2/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2015-07-07 CA CA2953045A patent/CA2953045A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2015-07-07 RU RU2017105100A patent/RU2695059C2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2015-07-07 MX MX2017000777A patent/MX2017000777A/en unknown
- 2015-07-07 EP EP15734385.6A patent/EP3169759A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2015-07-07 JP JP2017502839A patent/JP2017528552A/en active Pending
- 2015-07-07 KR KR1020177001276A patent/KR20170032310A/en unknown
- 2015-07-07 CN CN201580036723.XA patent/CN106536698A/en active Pending
- 2015-07-07 WO PCT/EP2015/065428 patent/WO2016008765A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1998013467A1 (en) * | 1996-09-27 | 1998-04-02 | Unilever N.V. | Aqueous structured liquid detergent composition comprising aminocarboxylate sequestrant |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017189703A1 (en) | 2016-04-27 | 2017-11-02 | Dow Corning Corporation | Detergent composition comprising a carbinol functional trisiloxane |
| US10829718B2 (en) | 2016-04-27 | 2020-11-10 | Dow Silicones Corporation | Detergent composition comprising a carbinol functional trisiloxane |
| US11713435B2 (en) | 2018-01-30 | 2023-08-01 | Eastman Chemical Company | Aminocarboxylate chelating agents and detergent compositions containing them |
| WO2020234597A1 (en) | 2019-05-22 | 2020-11-26 | Reckitt Benckiser Llc | Detergent formulations having enhanced germ removal efficacy |
| WO2020260038A1 (en) * | 2019-06-28 | 2020-12-30 | Unilever Plc | Detergent composition |
| CN114008183A (en) * | 2019-06-28 | 2022-02-01 | 联合利华知识产权控股有限公司 | Detergent composition |
| WO2022063708A1 (en) | 2020-09-24 | 2022-03-31 | Unilever Ip Holdings B.V. | Composition |
| WO2023051978A1 (en) | 2021-09-29 | 2023-04-06 | Unilever Ip Holdings B.V. | Composition |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| MX2017000777A (en) | 2017-04-27 |
| BR112017000752A2 (en) | 2017-11-14 |
| RU2017105100A (en) | 2018-08-17 |
| CN106536698A (en) | 2017-03-22 |
| CA2953045A1 (en) | 2016-01-21 |
| RU2017105100A3 (en) | 2019-01-24 |
| KR20170032310A (en) | 2017-03-22 |
| US20170145354A1 (en) | 2017-05-25 |
| JP2017528552A (en) | 2017-09-28 |
| RU2695059C2 (en) | 2019-07-19 |
| EP3169759A1 (en) | 2017-05-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3169759A1 (en) | Liquid detergent compositions and their manufacture | |
| US11339357B2 (en) | Sustainable laundry sour compositions with iron control | |
| CA2748533C (en) | Development of an aluminum hydroxycarboxylate builder | |
| WO2012145688A1 (en) | Calcium sequestering composition | |
| US20120295986A1 (en) | Calcium sequestering composition | |
| EP1120459A1 (en) | Detergent package | |
| JP6968198B2 (en) | A container containing a detergent composition containing salts of MGDA and GLDA | |
| US10273438B2 (en) | Container comprising a detergent composition containing GLDA | |
| EP3207114B1 (en) | Container comprising a detergent composition containing mgda | |
| WO2014190130A1 (en) | Concentrated surfactant composition | |
| US10316277B2 (en) | High performance laundry powder unit dose and methods of making the same | |
| WO2017174358A1 (en) | Liquid detergent composition containing dye transfer inhibitors and optical brighteners | |
| WO2021016633A1 (en) | Automatic dishwashing detergent composition | |
| CN108713056B (en) | Detergent composition in the form of a suspension | |
| US20190048290A1 (en) | Automatic dishwashing composition | |
| AU2015353890B2 (en) | Cleaning pouch | |
| EP3894536B1 (en) | Method for treating fabrics with a varying ph profile during wash and rinse cycles | |
| WO2017216215A1 (en) | Concentrated liquid detergents containing polymers | |
| JP2018504502A5 (en) | ||
| JP2018504502A (en) | Aqueous formulations, their manufacture and use | |
| EP4370637A1 (en) | Liquid phosphate-free detergent composition for the reduction of microfiber release | |
| JP2023540122A (en) | Automatic dishwashing detergent composition | |
| KR20220117884A (en) | Redeposition inhibiting polymer and detergent composition containing same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPE2 | Request for preliminary examination filed before expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15734385 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2015734385 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2015734385 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2953045 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15323889 Country of ref document: US |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20177001276 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2017502839 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: MX/A/2017/000777 Country of ref document: MX |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112017000752 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2017105100 Country of ref document: RU Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112017000752 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20170113 |