WO2015098384A1 - 携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 - Google Patents
携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015098384A1 WO2015098384A1 PCT/JP2014/080843 JP2014080843W WO2015098384A1 WO 2015098384 A1 WO2015098384 A1 WO 2015098384A1 JP 2014080843 W JP2014080843 W JP 2014080843W WO 2015098384 A1 WO2015098384 A1 WO 2015098384A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- biometric authentication
- biometric
- context
- key device
- unit
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/31—User authentication
- G06F21/34—User authentication involving the use of external additional devices, e.g. dongles or smart cards
- G06F21/35—User authentication involving the use of external additional devices, e.g. dongles or smart cards communicating wirelessly
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/31—User authentication
- G06F21/32—User authentication using biometric data, e.g. fingerprints, iris scans or voiceprints
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F21/00—Security arrangements for protecting computers, components thereof, programs or data against unauthorised activity
- G06F21/30—Authentication, i.e. establishing the identity or authorisation of security principals
- G06F21/31—User authentication
- G06F21/34—User authentication involving the use of external additional devices, e.g. dongles or smart cards
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07C—TIME OR ATTENDANCE REGISTERS; REGISTERING OR INDICATING THE WORKING OF MACHINES; GENERATING RANDOM NUMBERS; VOTING OR LOTTERY APPARATUS; ARRANGEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS FOR CHECKING NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- G07C9/00—Individual registration on entry or exit
- G07C9/30—Individual registration on entry or exit not involving the use of a pass
- G07C9/32—Individual registration on entry or exit not involving the use of a pass in combination with an identity check
- G07C9/37—Individual registration on entry or exit not involving the use of a pass in combination with an identity check using biometric data, e.g. fingerprints, iris scans or voice recognition
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/06—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network
- H04L63/061—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network for key exchange, e.g. in peer-to-peer networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/08—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities
- H04L63/0853—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities using an additional device, e.g. smartcard, SIM or a different communication terminal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/08—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities
- H04L63/0861—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities using biometrical features, e.g. fingerprint, retina-scan
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/06—Authentication
- H04W12/065—Continuous authentication
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an apparatus control technique using a portable key device using a biometric authentication technique.
- the mobile device is locked, for example, with a password or pattern lock.
- the personal identification number or pattern may be analyzed and the portable device may be used illegally.
- biometric authentication there are cases where authentication fails due to changes in biometric input methods, biometric information, etc., regardless of the identity of the individual, as defined as the rejection rate of the individual. Also, in order to prevent impersonation, every time the mobile device is unlocked, a biometric input is required. For this reason, it may be less convenient than a password or pattern lock.
- the device can be miniaturized and can be built in a portable device, but the finger vein authentication device using the vein pattern inside the finger, the palm vein authentication device using the palm, Compared with fingerprint authentication, iris authentication devices that use the iris of the eye use internal information of the living body, so it is difficult to duplicate, less affected by the state of the living body such as hand shake, and the amount of information is larger than fingerprint authentication
- it is difficult to reduce the size of the apparatus it is difficult to incorporate it into a portable device.
- the present invention incorporates a wireless communication function, and device control technology using a portable key device using a biometric authentication technology that can reduce the number of authentications while taking advantage of biometric authentication. I will provide a.
- the portable device When wireless communication between the two portable key devices is established, the portable device enters the unlock signal transmission state, and when wireless communication is disconnected, the biometric authentication success context is discarded and the unlock signal transmission is performed. Transition to the stop state and requesting biometric authentication is required to send the unlock signal again.
- the biometric authentication success context is retained to reduce the number of times the user performs biometric authentication, and when the key device is misplaced or the like, the authentication success context is discarded to restrict use by others, thereby improving usability and safety. Can be improved.
- 1 is a device control system using wireless communication according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 1 is a device control system using a server-use type biometric authentication device according to an embodiment of the present invention. It is an apparatus control system using the wearable biometric authentication apparatus concerning the Example of this invention. It is an apparatus control system using the wearable device concerning the Example of this invention.
- 1 is a wearable biometric authentication device according to an embodiment of the present invention. 1 is an example of a wearable device according to an example of the present invention. 1 is a circuit example of a wearable device according to an embodiment of the present invention. It is an operation
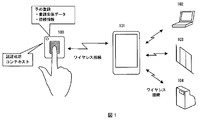
- Fig. 1 shows an overall conceptual diagram of this embodiment.
- the biometric authentication device 100 the portable device 101, and the control target devices 102 to 104 are used.
- the biometric authentication device 100 includes a communication unit and a biometric information input unit, and registers registered biometric data used for collation and connection information of the connection destination portable device 101 in advance. Registered biometric data and connection information are registered by connecting to a biometric authentication device alone or a host device such as a PC (Personal Computer).
- a biometric authentication device alone or a host device such as a PC (Personal Computer).
- the biometrics to be authenticated will be described using finger veins, but other biometrics such as fingerprints, palm prints, palm veins, irises and faces may be used.
- connection information with the mobile device 101 corresponds to pairing information between devices in a wireless standard such as Bluetooth (registered trademark), for example, and only a specific biometric authentication device and a specific mobile device are secured one-to-one. Connection information for enabling a wireless connection to be established.
- the biometric authentication device 100 is a device that incorporates a battery or the like and can be used on a mobile.
- the portable device 101 includes a communication unit, an input / output unit (for example, a display with a touch panel), and a calculation unit (processor).
- a communication unit for example, a communication unit, an input / output unit (for example, a display with a touch panel), and a calculation unit (processor).
- the control target devices 102 to 104 are devices controlled by the biometric authentication device.
- control targets for example, login control of the PC 102, door locking / opening / closing of the entrance / exit management device 103, and the settlement terminal 104 Payment processing is applicable.
- FIG. 8 shows an operation flow diagram of the biometric authentication device 100.
- the biometric authentication device 100 After the user turns the biometric authentication device 100 from OFF to ON (S701 to 702), the biometric authentication device 100 starts connection with the portable device 101 by wireless communication (S703). If the wireless communication is not established for a certain period, the biometric authentication device shifts to a power OFF state (S701). When the wireless communication is established, the biometric authentication device 100 prompts the user to input biometric information and performs biometric authentication (S704). If the biometric authentication is successful, the biometric authentication device 100 stores the authentication success context in the device, and the portable device 101 that has received the authentication success information shifts to the unlocked state (S705, 706). If the authentication fails, the biometric authentication device 100 shifts to the power OFF state (S701).
- the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 continue to monitor the wireless communication state (S708). While the wireless communication between the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 is established, the portable device 101 continues to maintain the unlocked state (S709).
- the user can use the portable device without performing unlocking operation such as password entry by always carrying the biometric authentication device and the portable device at a distance that allows wireless communication.
- step S710 the biometric authentication apparatus 101 discards the authentication success context (S711), and shifts to the power OFF state.
- FIG. 9 shows a flowchart regarding the operation of the mobile device 101.
- the biometric authentication device 100 When the power of the mobile device 101 is turned on (S801) and it is brought close to the biometric authentication device 100 registered in the connection information in advance, the mobile device 101 and the biometric authentication device 100 automatically establish a connection by wireless communication, The biometric authentication device 100 enters a biometric input waiting state (S802, S803).
- the wireless connection is assumed to be a one-to-one connection between the specific biometric authentication device 100 and the specific portable device 101 securely by encryption key exchange or the like.
- the biometric authentication device 100 measures the biometric information of the input biometric and creates authentication biometric data, which is registered in advance with the authentication biometric data.
- Biometric authentication is performed by checking the registered biometric data. As a result of the verification, if it is determined that the authentication biometric data and the registered biometric data are the same, the authentication is successful, the authentication success context is generated and stored in the apparatus, and the wireless device authentication is successful. Send with. If the authentication fails, the biometric authentication device shifts to a power-off state in order to reduce battery consumption.
- the portable device waits for reception of authentication success while monitoring wireless communication (S804, S805). At this time, if the wireless communication is interrupted, the wireless communication device 100 returns to the wireless communication monitoring state and the biometric authentication device 100 stops the biometric authentication (S806, S802). When the biometric authentication is successful, the portable device 101 that has received the authentication success starts to send an unlock signal for changing the control target measure from the locked state to the unlocked state (S807).
- the portable device 101 keeps the unlock signal transmission state, and the biometric authentication device 101 keeps the context of the authentication success.
- the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 monitor the state of wireless communication (S809), and if the wireless communication between the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 is disconnected even once, the biometric authentication device 100 is in the context of successful authentication. And the portable device 101 shifts to the stop state.
- FIG. 10 shows a flowchart regarding the operation of the control target devices 102 to 104.
- control target device is turned on from power OFF (S901, S902).
- the device to be controlled is in a locked state, that is, no operation is accepted. Then, it waits for an unlock signal from the mobile device 101.
- the unlock signal When the unlock signal is received, authentication of the portable device is started. If it is determined that the unlock signal is for the control target device, the authentication is successful, and the authentication context is stored (S904 to S906). At this time, it may further communicate with the portable device 101 to request information. Here, even if the context of biometric authentication information is further requested from the portable device 101, the user is not requested to input biometric information anew. If the authentication fails, the lock state is continued (S902).
- the device to be controlled is unlocked and becomes operable (S907).
- the user can use the control target device.
- the device to be controlled continues to monitor the unlock signal from the portable device 101, and continues to be operable and unlocked while receiving the unlock signal (S909).
- the lock release signal is not received, the lock state is entered, the operation becomes impossible, the authentication context is discarded, and the process returns to the lock release signal wait (S910, S911, S902).
- the operations of the biometric authentication device 100, the portable device 101, and the control target devices 102 to 104 have the following effects.
- biometric information is required in order to unlock the control target devices 102 to 104 and make them operable. As a result, only the user himself / herself can unlock the control target device, so that safety can be increased.
- the device to be controlled is unlocked depending on the presence or absence of a lock release signal, and does not require new biometric information to be read from the user's body when the lock is released.
- the user holds the biometric authentication success context by establishing wireless communication by carrying the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 in the pockets of clothes or the like. Since wireless communication remains established, the mobile device continues to transmit the unlock signal, and the user can release the lock when approaching the device to be controlled, and it is necessary to read biometric information each time the lock is released. No.
- the biometric authentication device 100 or the portable device 101 is separated due to theft or misplacement, the distance between the portable device 101 and the biometric authentication device 100 exceeds the communication distance, and wireless communication is disconnected, and the biometric authentication device 100 discards the context of successful authentication and shifts to the power-off state, and the portable device 101 stops issuing the unlock signal.
- the biometric authentication device 100 In order to recover from this state, the biometric authentication device 100 must be turned on to communicate with the mobile device to perform biometric authentication. That is, only the user can be in a state of transmitting the unlock signal again. Even if only one or both are separately acquired by a third party, there is no biometric information, so it cannot be used.
- an authentication application is installed on a smartphone as the portable device 101.
- the mobile device 101 can be used as a smartphone having functions other than the mobile key.
- a notebook PC or tablet PC may be used as long as the user can carry it.
- the portable device 101 is put in a place where it can be easily taken out such as a breast pocket or a bag. Since the biometric authentication device 100 does not need to be used by the user after successful authentication and only needs to maintain the establishment of wireless communication with the portable device 101, the biometric authentication device 100 is not easily dropped with the user such as a pants pocket. It is desirable to keep it. If the biometric authentication terminal used exclusively for the portable key is combined with the portable device 101 used for other purposes, the user can easily remove the portable device 101 and the biometric authentication device 100 is not easily disturbed or dropped. Carrying in difficult places and in different places, the possibility of losing them together can be reduced.
- the radio wave output of the biometric authentication device 100 or the portable device 101 may be an output that can establish a connection only at a short distance of about 1 to 3 m.
- the device to be controlled to be unlocked can be used in combination with the PC 102 equipped with the wireless function, the door entrance / exit management device 103, the settlement terminal 104, or the like.
- the portable device 101 in the lock release signal transmission state approaches the PC 102 in the logout state, and the PC 102 and the portable device 101 are connected by wireless communication, and when mutual authentication is completed, the PC 102 is set in the logon state.
- the user can log on to the PC 102 without performing biometric authentication for each logon, as in the case of performing identity verification for each logon with a single biometric authentication.
- the portable device 101 in the lock release signal transmission state approaches the door entry / exit management device, connects with wireless communication, and when the mutual authentication is completed, the door is unlocked.
- PC it is possible to enter and leave the room in the same way as when confirming the identity of each room with a single biometric authentication, without performing a biometric for each room (entrance or exit). Become.
- the mobile device that is in the lock release signal transmission state at the time of payment is brought close to the payment terminal 104, so that the mobile device 101 and the payment terminal 104 are connected by wireless communication, and mutual authentication is completed and payment is completed. I do.
- a simple operation on the payment terminal 104 may be requested to confirm the payment.
- the user can make a payment in the same manner as in the case of performing identity verification for each payment with a single biometric authentication without performing the biometric authentication for each payment.
- the user may be able to set the valid time of the authentication success context for the biometric authentication device 100. Counts the time since biometric authentication succeeds and generates a context. When the time set by the user has elapsed, the authentication success context stored in biometric authentication device 100 is discarded and the power is turned off. Migrate to Alternatively, a clock is built in the biometric authentication device 100, and when the time set by the user comes, the authentication success context in the authentication device is discarded, and the power-off state is entered.
- the user If the user sets the context destruction time to night, the user authenticates in the morning and uses the mobile device 101 until the night. After leaving work, the biometric authentication device 100 and the mobile device can be left together. At this time, the context of successful authentication can be discarded and the portable device 101 can be shifted to the locked state.
- the lost location can be estimated when the biometric authentication device or the portable device is lost.
- the time at which the wireless connection between the biometric authentication device and the portable device is interrupted is recorded on the biometric authentication device or the portable device, or the portable device 101 is recorded on a server on the network and lost due to misplacement of the biometric authentication device 100 or the portable device 101.
- the time at which the wireless connection is interrupted can be confirmed, and the location where the other device is lost can be estimated from the user's behavior at that time (for example, location information based on GPS or entry / exit records).
- two portable key devices biometric authentication device 100 and portable device 101 that perform wireless communication with each other are provided, and at least one of them has a function of holding a biometric authentication success context. If so, the function of inputting biometric information, the registered biometric data, and the biometric authentication function may be provided so as to communicate with a device different from the two portable key devices.
- Example 2 will be described.
- the second embodiment is mostly the same as the first embodiment and will not be described in detail, but the differences are as follows.
- the registered biometric data is registered in the biometric authentication device 100.
- the biometric authentication device 100 is lost, the registered biometric data in the biometric authentication device 100 is also lost.
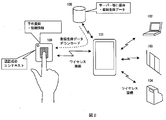
- the registered biometric data is stored in a place other than the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 such as the server 105, and wireless communication between the biometric authentication device 100 and the portable device 101 is established.
- the portable device 101 communicates with the server 105 to download the registered biometric data from the server 105.
- the portable device 101 transmits the downloaded registered biometric data to the biometric authentication device 100.
- the biometric authentication device 100 uses the received registered biometric data to collate with the input biometric information and perform biometric authentication.
- the biometric authentication device 100 When the authentication is successful, the biometric authentication device 100 creates a biometric authentication success context, stores it in the biometric authentication device 100, and then discards the received registered biometric data. The subsequent processing is the same as in the first embodiment.
- the biometric authentication device 100 discards the received registered biometric data and shifts to the power OFF state.
- the registered biometric data can be protected by the above method even if the biometric authentication device 100 is lost.
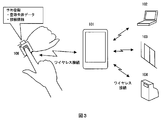
- the biometric authentication device 106 may be a wearable biometric authentication device 106 that is worn by the user, such as a wristwatch or a bracelet. In the first and second embodiments, it is detected that the key device is separated from the user because wireless communication is interrupted. However, in this embodiment, the wearable device worn on the body is separated from the user's body. Is detected.
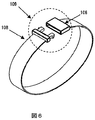
- FIG. 3 shows a conceptual diagram of the wearable biometric authentication device 106.
- the wearable biometric authentication device 106 includes a biometric detection function 107 such as a pulse meter, and can detect that it has been removed from the human body.
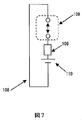
- the circuit configuration shown in FIG. 7 having the shape shown in FIG. 6 and the opening / closing mechanism 109 need to be opened in order to remove it from the human body, such as detecting the removal from the living body by the opening / closing mechanism 109.
- the removal from the human body may be detected by detecting the change in shape.
- the wearable biometric authentication device 106 performs biometric authentication only in a state worn by the user as in the first and second embodiments. If the authentication is successful, a context for successful authentication is generated and stored in the device.
- the wearable biometric authentication device 106 since the wearable biometric authentication device 106 is completely integrated with the user, even if the wireless connection between the wearable biometric authentication device 106 and the portable device 101 is disconnected, the wearable biometric authentication device 106 is not lost. Therefore, there is no need to discard the context of successful authentication in the biometric authentication device 100.
- the context of successful authentication in the wearable biometric authentication device 106 can be discarded only by the user removing the wearable biometric authentication device 106 or instructing it with a switch or the like provided in the wearable biometric authentication device 106.
- the wireless communication between the wearable biometric authentication device and the portable device is again performed after the wireless communication between the wearable biometric authentication device and the portable device is disconnected. Is established, the wearable biometric authentication device retains the context of successful authentication, and the portable device can be unlocked again without performing biometric authentication.
- the wearable biometric authentication device 106 may transmit a lock release signal while holding the biometric authentication success context without using the portable device 101. Even in this case, when the wearable biometric authentication device 106 is removed from the user's human body, this is detected, the biometric authentication success context is discarded, and the transmission of the unlock signal is stopped, which is effective.
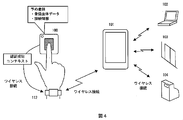
- the embodiment shown in FIG. 4 is an embodiment in the case where the authentication success context generated by the biometric authentication apparatus is transferred to another device and used.
- another wearable device 111 such as a wristwatch or a bracelet having a wireless communication function is used.
- the wearable device 111 is assumed to have a function of detecting what the user wears through a living body detection function, a shape change detection, or the like, as in the third embodiment.
- the biometric authentication device 100 generates a context of successful authentication upon successful authentication, and transmits it to the wearable device 111.
- the wearable device 111 receives and holds the context, and further returns a successful reception to the biometric authentication device 100.
- the biometric authentication device 100 discards the context of the authentication success when it is received.
- the wearable device 111 monitors what the user wears using the biometric detection function, and discards the context of authentication success when the wearable device 111 is removed from the user.
- the wearable device 111 When the wearable device 111 that holds the context of the authentication success approaches the mobile device 101 such as a mobile phone or smartphone that is locked with a wireless function, it establishes a wireless connection between the wearable device and the mobile device, and Perform device authentication. If the device authentication is successful, the portable device 101 shifts to an unlock signal transmission state, and thereafter, the wireless device 101 continues to maintain the lock release signal transmission state while the wireless connection with the wearable device is established.
- the mobile device 101 such as a mobile phone or smartphone that is locked with a wireless function
- the mobile device 101 When the mobile device 101 is in the lock release signal transmission state, the mobile device 101 can be used for the PC 102, the door entrance / exit management 103, and the settlement terminal 104 as in the first embodiment.
- the mobile device 101 If the mobile device 101 is lost due to theft or misplacement, if the wireless connection is disconnected due to the distance between the wearable device 111 and the mobile device 101 exceeding the wireless communication distance, the mobile device 101 A third party becomes unusable after shifting to the outgoing call suspension state.
- the wearable device 111 since the wearable device 111 has a function of detecting what the user wears, the wearable device 111 can be worn even after the wireless connection with the mobile device 101 is disconnected. As long as you continue to detect it, you do n’t need to discard the authentication success context stored inside the wearable device, and wireless connectivity with the mobile device is re-established. When established, the portable device shifts to a lock release signal transmission state.
- the biometric authentication success context may be discarded, or the wireless connection disconnection and the wearable device removal may be used as the context discarding condition.
- the wearable device worn by the user does not include a biometric authentication device, it is possible to use a biometric authentication device that has a large casing size but high authentication accuracy, such as a vein authentication device or an iris authentication device. it can.
- the wearable device since the wearable device only needs to incorporate a wireless communication function, it is possible to reduce the size and power consumption.
- Biometric Authentication Device 101 Mobile Device 102 PC 103 Door entry / exit management 104 Payment terminal 105 Server 106 Wearable biometric authentication 107 Biometric detection function 108 Wristband 109 Open / close detection mechanism 110 Battery 111 Wearable device
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Telephone Function (AREA)
- Lock And Its Accessories (AREA)
Abstract
生体認証を用いた装置制御においては、装置を使用するたびに生体情報を要求される。それを解消させるために携帯キーデバイスに生体認証成功コンテキストを保持させると、これを入手した他者に使用される恐れがある。 互いに通信するワイヤレス通信機能を搭載する携帯型キーデバイスを二つ用意し、生体認証に成功した場合は認証成功のコンテキストを保存しロック解除信号を発信して、制御対象装置にロック解除し操作可能にする。二つの携帯型キーデバイス間のワイヤレス通信が切断された場合は、生体認証成功のコンテキストを破棄してロック解除信号の発信を止め、再度のロック解除信号発信には、生体認証を要求する。 これにより、ユーザが生体認証する回数を低減し、キーデバイスを置き忘れ等した場合に認証成功コンテキストを破棄することで他人による使用を制限し、使い勝手と安全性の両立を向上できる。
Description
本発明は、生体認証技術を用いた携帯型キーデバイスによる装置制御技術に関するものである。
携帯電話やスマートフォン、タブレットPCなどの携帯デバイスの高機能化が進み、決済や会社業務に使用する機会が増加するに従い、なりすましを防止するセキュリティ技術の重要性が高まっている。
携帯デバイスは、例えば暗証番号やパターンロックなどでロックされている。しかしながら、携帯端末が盗難や紛失等で第三者の手に渡った時に暗証番号やパターンを解析され、携帯デバイスを不正に使用されてしまう可能性がある。
このようななりすましを防止し、確実に本人であることを認証するには、暗証番号やパターンロックの代わりに、個人ごとに異なる生体の特徴を利用した生体認証により本人確認を行うことが有効である。
現在、生体認証の一つである小型の指紋認証装置を内蔵した携帯デバイスが開発されており、生体認証による本人確認を用いて第三者のなりすましによる不正使用を防止している(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
しかしながら、生体認証においては本人拒否率として規定されるように、本人であるにも関わらず生体入力の仕方や生体情報の変化等によって認証に失敗する場合がある。また、なりすましを防止するために、携帯デバイスのロックを解除する都度に生体の入力を要求される。そのため、暗証番号やパターンロックと比較して使い勝手が悪くなることがある。
また、指紋認証では指先だけを使用するので装置の小型化が可能であり、携帯デバイスに内蔵できているが、指内部の静脈パターンを用いる指静脈認証装置、手のひらを使用する手のひら静脈認証装置や目の虹彩を使用する虹彩認証装置等は、指紋認証と比較して生体の内部情報を使用するので複製しにくい、手あれなどの生体の状態による影響を受けにくい、情報量が多いので指紋認証よりも精度が高い、といったメリットがあるものの、装置の小型化が難しいために携帯デバイスに内蔵することが難しい。
これらの問題点を解決するため、本発明ではワイヤレス通信機能を内蔵し、生体認証による本人確認の利点を生かしつつ認証回数を減らすことができる生体認証技術を用いた携帯型キーデバイスによる装置制御技術を提供する。
本発明の解決手段の一例としては、以下の通りである。
互いに通信するワイヤレス通信機能を搭載する携帯型キーデバイス(ワイヤレスキーデバイス、アプリケーションをインストールした携帯電話やスマートフォン等の携帯デバイス、ワイヤレス通信機能付き生体認証装置など)を二つ用意し、ワイヤレス通信を確立した状態において生体認証動作を行い、生体認証に成功した場合は、いずれかの携帯型キーデバイス内で認証成功のコンテキストを保存し、ロック解除信号発信状態に移行させる。制御対象装置は、ロック解除信号を受信すると、さらなる生体認証は要求せずにロック解除し操作可能になり、該信号を受信しなくなるとロック状態になる。
二つの携帯型キーデバイスのワイヤレス通信が確立されている状態では、携帯デバイスはロック解除信号発信状態とし、ワイヤレス通信が切断された場合は、生体認証成功のコンテキストを破棄し、ロック解除信号発信の停止状態に移行し、再度のロック解除信号発信には、生体認証を要求する。
本発明によると、生体認証成功コンテキストを保持してユーザが生体認証する回数を低減し、キーデバイスを置き忘れ等した場合に認証成功コンテキストを破棄することで他人による使用を制限し、使い勝手と安全性の両立を向上できる。
以下、本発明の実施形態について説明する。
図1に本実施例の全体の概念図を示す。本実施例では、生体認証装置100と、携帯デバイス101と、制御対象装置102~104を使用する。
生体認証装置100は、通信部と生体情報入力部とを備え、予め照合に使用する登録生体データと、接続先の携帯デバイス101の接続情報を登録しておく。登録生体データ、接続情報の登録は、生体認証装置単独、もしくはPC(Personal Computer)等の上位デバイスと接続して登録するものとする。認証する生体としては指静脈を用いて説明するが、指紋、掌紋、掌静脈、虹彩、顔など他の生体認証を用いてもよい。
携帯デバイス101との接続情報は、例えばBluetooth(登録商標)等の無線規格における各装置間のペアリング情報に相当するもので、特定の生体認証装置と特定の携帯デバイスのみが1対1でセキュアにワイヤレス接続を確立できるようにするための接続情報となる。また、生体認証装置100は電池などを内蔵し、モバイルで使用できる装置とする。
携帯デバイス101は、通信部と、入出力部(例えばタッチパネル付ディスプレイ)と、演算部(プロセッサ)とを備える。
制御対象装置102~104は、本生体認証装置により制御される装置であり、制御対象としては、一例として、PC102のログイン制御や、入退室管理装置103のドア施錠・開閉や、決済端末104の決済処理が該当する。
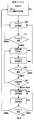
図8に生体認証装置100の動作フロー図を示す。
ユーザが生体認証装置100の電源をOFFからONにした後(S701~702)、生体認証装置100はワイヤレス通信で携帯デバイス101との接続を開始する(S703)。ワイヤレス通信が一定期間の間に確立されなかった場合は、生体認証装置は電源OFF状態に移行する(S701)。ワイヤレス通信が確立された場合、生体認証装置100はユーザに生体情報の入力を促し、生体認証を行う(S704)。生体認証に成功した場合、生体認証装置100は認証成功のコンテキストを装置内に保存し、認証成功の情報を受取った携帯デバイス101はロック解除状態に移行する(S705,706)。認証に失敗した場合は、生体認証装置100は電源OFF状態に移行する(S701)。コンテキストを保存し、携帯デバイス101がロック解除状態に移行した後、生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101はワイヤレス通信の状態を監視し続ける(S708)。生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101間のワイヤレス通信が確立されている間は、携帯デバイス101はロック解除状態を維持し続ける(S709)。ユーザは生体認証装置と携帯デバイスを常時携帯してワイヤレス通信可能な距離にしておくことにより、パスワード入力等のロック解除動作をすることなく携帯デバイスを使用することができる。
生体認証装置100または携帯デバイス101を落したり置き忘れたことにより、通信可能距離以上に生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101間の距離が離れてワイヤレス通信が途切れた場合は、携帯デバイス101はロック状態に移行し(S710)、生体認証装置101は認証成功のコンテキストを破棄し(S711)、電源OFF状態に移行する。
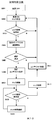
図9に携帯デバイス101の動作に関するフローチャートを示す。
携帯デバイス101の電源をONにし(S801)、あらかじめ接続情報で登録しておいた生体認証装置100に近づけると、携帯デバイス101と生体認証装置100とは自動でとワイヤレス通信による接続を確立し、生体認証装置100は生体の入力待ち状態となる(S802,S803)。ワイヤレス接続は、暗号鍵交換等によってセキュアに特定の生体認証装置100と特定の携帯デバイス101間で1対1で接続されるものとする。
この状態において、ユーザが生体認証装置100に生体を入力すると、生体認証装置100は入力された生体の生体情報を計測して認証生体データを作成し、その認証生体データと予め登録しておいた登録生体データを照合することにより、生体認証を行う。照合の結果、認証生体データと登録生体データが同一であると判定した場合は認証成功となり、認証成功のコンテキストを生成として装置内に保存するとともに、携帯デバイスに対して認証が成功したことをワイヤレスで送信する。認証に失敗した場合は、生体認証装置は電池の消費量を抑えるために電源OFF状態に移行する。
携帯デバイスは、ワイヤレス通信を監視しながら、認証成功の受信待ちをする(S804,S805)。このときに、ワイヤレス通信が途絶えた場合には、ワイヤレス通信監視状態に戻り、生体認証装置100は生体認証を中止する(S806,S802)。生体認証に成功した場合、認証成功を受信した携帯デバイス101は、制御対象措置をロック状態からロック解除状態にするためのロック解除信号の発信を始める(S807)。
以降、生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101間のワイヤレス通信が維持されている間、携帯デバイス101はロック解除信号発信状態を保持し、生体認証装置101は認証成功のコンテキストを保持し続ける。
生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101は、ワイヤレス通信の状態を監視し(S809)、一度でも生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101間のワイヤレス通信が切断された場合、生体認証装置100は認証成功のコンテキストを破棄して電源OFF状態に移行し、携帯デバイス101はロック信号発信を停止状態に移行する。
図10に制御対象装置102~104の動作に関するフローチャートを示す。
まずは、制御対象装置を電源OFFから電源ONにする(S901,S902)。この状態で、制御対象装置はロックされている状態であり、すなわち操作を受け付けない。そして、携帯デバイス101からのロック解除信号を待つ。
ロック解除信号を受信すると、携帯デバイスの認証を始め、そのロック解除信号が制御対象装置のためのものであると判定されると認証成功になり、その認証コンテキスを保存する(S904~S906)。このときに、さらに携帯デバイス101と通信して、情報を要求してもよい。ここで、生体認証情報のコンテキストをさらに携帯デバイス101に求めることはあっても、ユーザに生体情報を新たに入力要求することは行わない。認証に失敗すると、ロック状態を継続する(S902)。
認証コンテキストを保存すると、制御対象装置はロックを解除し、操作可能な状態になる(S907)。そして、ユーザは制御対象装置を使用することができる。
ロック解除の状態で、制御対象装置は携帯デバイス101からのロック解除信号の監視を続け、ロック解除信号を受信しているうちは、操作可能なロック解除状態を継続する(S909)。ロック解除信号を受信しなくなったら、ロック状態になり操作不能になり、認証コンテキストを廃棄し、ロック解除信号待ちに戻る(S910,S911,S902)。
これら生体認証装置100、携帯デバイス101、制御対象装置102~104の動作により、以下の作用効果を有する。
制御対象装置102~104をロック解除して操作可能にするには、生体認証装置100、携帯デバイス101に加え、生体情報が要求される。これによって、ユーザ本人以外は制御対象装置のロックを解除することができないので、安全性を高くすることができる。
また、制御対象装置としては、ロック解除信号の有無によりロック解除を行っており、ロック解除に際してユーザの身体から新たに生体情報を読み込ませることを要求しない。ユーザーは、生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101をそれぞれ衣服のポケット等に入れて携行することにより、ワイヤレス通信を確立して生体認証成功コンテキストを保持する。ワイヤレス通信は確立されたままなので携帯デバイスはロック解除信号発信を維持し続けており、ユーザは制御対象装置に近づけばロックを解除することができ、ロック解除する都度に生体情報を読み込ませる必要が無い。
一方で、生体認証装置100または携帯デバイス101を盗難や置き忘れなどで離した場合、携帯デバイス101と生体認証装置100間の距離が通信距離を越えることになり、ワイヤレス通信が切断され、生体認証装置100は認証成功のコンテキストを破棄して電源OFF状態に移行し、携帯デバイス101はロック解除信号発信を停止する。この状態から復旧するには、生体認証装置100の電源を入れて携帯デバイスと通信し、生体認証を行わなければならない。すなわち、ユーザのみが再びロック解除信号を発信する状態にできる。一方のみ、または両方を別々に第三者が取得しても、生体情報が無いため、使用できない。
ユーザが携行する生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101は、両方を一緒に落としたり置き忘れることが無いよう、ユーザは別々の衣類ポケットや荷物等で保持することが望ましい。本実施例では、スマートフォンに認証用アプリケーションをインストールして携帯デバイス101としている。これにより、携帯デバイス101を、携帯鍵以外の機能も有するスマートフォンとしても利用することができる。これ以外でも、ユーザが携行できるものであれば、ノートPCやタブレットPCを用いてもよい。
また、携帯デバイス101は、認証の他にもユーザが継続して使用するので、胸ポケットやバッグの中など取り出しやすい場所に入れておくことになる。生体認証装置100は、認証成功後にユーザが使用する必要が無く、携帯デバイス101との間でワイヤレス通信の確立を保持すれば良いだけなので、ズボンのポケットなどのユーザ本人と一体で落しにくい場所に入れておくことが望ましい。もっぱら携帯鍵専用に用いる生体認証端末と、他の用途にも用いる携帯デバイス101との組み合わせであれば、ユーザは、携帯デバイス101は取り出しやすい箇所に、生体認証装置100は邪魔になりにくいまたは落としにくい箇所にと、異なる箇所で携行すると考えられ、一緒に紛失する可能性を低くすることができる。
セキュリティ性を高めるために、生体認証装置100、若しくは携帯デバイス101のワイヤレス通信の電波出力は、1~3m程度の近距離でしか接続を確立できないような出力としても良い。
ロック解除される制御対象装置としては、ワイヤレス機能を搭載したPC102やドア入退管理装置103、決済端末104等と組合わされて使用することができる。
PC102の場合、ログアウト状態にあるPC102にロック解除信号発信状態の携帯デバイス101が近づき、PC102と携帯デバイス101の間でワイヤレス通信で接続し、相互認証が完了した時点でPC102をログオン状態にする。これにより、ユーザはログオンごとに生体認証を行うことなく、一回の生体認証でログオンごとに本人確認を行うのと同じようにPC102にログオンが可能となる。
ドア入退管理103の場合は、ロック解除信号発信状態にある携帯デバイス101がドア入退管理装置に近づき、ワイヤレス通信で接続して相互認証が完了した時点でドアをロック解除状態にする。これにより、PCの場合と同じく、入退室(入室または退室)ごとに生体証を行うことなく、一回の生体認証で入室ごとに本人確認を行う場合と同じように入退室することが可能となる。
決済端末104の場合は、決済時にロック解除信号発信状態にある携帯デバイスを決済端末104に近づけることで、携帯デバイス101と決済端末104の間でワイヤレス通信で接続し、相互認証が完了して決済を行う。このとき、決済の確認のために、決済端末104に対する簡単な操作を要求してもよい。これにより、ユーザは決済ごとに生体認証を行うことなく、一回の生体認証で決済ごとに本人確認を行う場合と同じように決済することが可能となる。
また、ユーザは生体認証装置100に対して認証成功のコンテキストの有効時間を設定できるようにしても良い。生体認証に成功し、コンテキストを生成してからの時間をカウントし、ユーザが設定した時間が経過した場合に、生体認証装置100内に保存されている認証成功のコンテキストを破棄し、電源OFF状態に移行する。若しくは、生体認証装置100内に時計を内蔵しておき、ユーザが設定した時刻になった時に、認証装置内の認証成功のコンテキストを破棄し、電源OFF状態に移行する。
ユーザはコンテキスト破棄の時刻を夜に設定しておくと、朝に認証を行って夜まで携帯デバイス101を使用し、退勤後に生体認証装置100と携帯デバイスを一緒に放置しておいても、指定した時間に認証成功のコンテキストを破棄して携帯デバイス101をロック状態に移行させることができる。
また、生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101のワイヤレス通信の記録を利用すると、生体認証装置、もしくは携帯デバイスを紛失した場合に、紛失した場所を推定することが可能である。生体認証装置と携帯デバイスのワイヤレス接続が途切れた時刻を生体認証装置か携帯デバイスに記録、あるいは携帯デバイス101がネットワーク上のサーバーへ記録し、生体認証装置100や携帯デバイス101を置き忘れ等で紛失した場合にはワイヤレス接続が途切れた時刻を確認し、その時刻のユーザの行動(例えばGPSや入退室記録などによる位置情報)から別デバイスを紛失した場所を推定できる。
上記のように、生体認証装置100、携帯デバイス101の2つの装置とワイヤレス通信を利用することにより、1度の生体認証で、都度の生体認証を行わなくても、制御対象装置の利用ごとの生体認証を行う場合と同じように本人確認を可能とし、本人確認の結果をPCログオンや入退管理、決済などに利用することができる。
なお、後述の実施例で説明するが、互いにワイヤレス通信を行う二つの携帯鍵装置(生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101)を備え、こられの少なくとも一方に生体認証成功コンテキストを保持する機能を備えていれば、生体情報を入力する機能、登録生体データや生体認証機能を、二つの携帯鍵装置とは別のデバイスに通信可能に設けてもよい。
実施例2について説明する。実施例2は、実施例1と大部分は同様であり詳細な説明を省略するが、異なる点は次のとおりである。実施例1において登録生体データは生体認証装置100内に登録されているが、生体認証装置100を紛失した場合に、中にある登録生体データも一緒に紛失することになる。
そこで、図2に示すように登録生体データをサーバー105等の生体認証装置100や携帯デバイス101以外の別の場所に保管しておき、生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101のワイヤレス通信が確立された段階で、携帯デバイス101はサーバー105と通信を行い、登録生体データをサーバー105からダウンロードする形態とする。登録生体データのダウンロードが完了したら、携帯デバイス101はダウンロードした登録生体データを生体認証装置100に送信する。生体認証装置100は、受信した登録生体データを使用して、入力された生体情報との照合を行い、生体認証を行う。
認証が成功した場合、生体認証装置100は生体認証成功のコンテキストを作成し、生体認証装置100内部に保存し、その後、受信した登録生体データを破棄する。その後の処理は、実施例1と同様である。
認証が失敗した場合、生体認証装置100は受信した登録生体データを破棄し、電源OFF状態に移行する。
上記のような方法により、生体認証装置100を紛失しても、登録生体データを守ることが可能となる。
実施例3について説明する。生体認証装置を腕時計やブレスレット等、ユーザが身に付ける形態にしたウェアラブル生体認証装置106としても良い。実施例1、2では、ワイヤレス通信が途切れたことにより、キーデバイスがユーザから離れたことを検知したが、本実施例では身体に装着するウェアラブルデバイスとすることで、ユーザの身体から離れたことを検知する。
図3にウェアラブル生体認証装置106の概念図を示す。この場合、図5に示すようにウェアラブル生体認証装置106は脈拍計等の生体検知機能107を備え、人体から取り外されたことを検知することができるものとする。もしくは、図6に示すような形状で図7のような回路構成とし、取り外すために開閉機構109を開ける必要がある構造として、開閉機構109で生体からの取り外しを検出する等、人体から取り外すために形状の変化が必要な構造として、その形状変化を検出することによって人体からの取り外しを検出しても良い。
ウェアラブル生体認証装置106は、実施例1、実施例2と同様にユーザが身に付けた状態においてのみ生体認証を行い、認証に成功した場合は認証成功のコンテキストを生成し装置内に保存する。
本実施例ではウェアラブル生体認証装置106が完全にユーザと一体となっているため、ウェアラブル生体認証装置106と携帯デバイス101の間のワイヤレス接続が切断されたとしても、ウェアラブル生体認証装置106を紛失ではないため、生体認証装置100内の認証成功のコンテキストを破棄する必要は無い。
ウェアラブル生体認証装置106内の認証成功のコンテキスト破棄は、ユーザがウェアラブル生体認証装置106を取り外すか、ウェアラブル生体認証装置106に設けられたスイッチ等で指示することでのみとする。
ユーザがウェアラブル生体認証装置106を体に取り付けた状態を維持していた場合、ウェアラブル生体認証装置と携帯デバイスのワイヤレス通信が切断された後に、再び生体認証装置と携帯デバイスが近づくことで再度ワイヤレス通信が確立された時、ウェアラブル生体認証装置は認証成功のコンテキストを保持したままであり、生体認証を行うことなく再び携帯デバイスをロック解除状態とすることができる。
また、本実施例では、携帯デバイス101を用いず、ウェアラブル生体認証装置106が、生体認証成功コンテキストを保持してロック解除信号を発信してもよい。この場合でも、ウェアラブル生体認証装置106がユーザの人体から取り外された場合には、それを検知して生体認証成功コンテキストが破棄されてロック解除信号の発信が停止され、効果を奏する。
図4に示す実施例は、生体認証装置で生成した認証成功のコンテキストを、さらに別のデバイスに転送して使用する場合の実施例となる。生体認証装置100と携帯デバイス101の他に、ワイヤレス通信機能を持った腕時計やブレスレット等の別のウェアラブルデバイス111を使用する。ウェアラブルデバイス111は、実施例3と同様に生体検知機能や形状変化検知等により、ユーザが身に付けていることを検出する機能を持つものとする。
生体認証装置100は、認証に成功すると認証成功のコンテキストを生成し、それをウェアラブルデバイス111に送信する。ウェアラブルデバイス111がコンテキストを受信して保持し、さらに受信成功を生体認証装置100に返信し、生体認証装置100はこれを受信した時点で認証成功のコンテキストを破棄する。
ウェアラブルデバイス111は、生体検知機能を使用してユーザが身に付けていることを監視し、ウェアラブルデバイス111がユーザから外された時点で認証成功のコンテキストを破棄する。
認証成功のコンテキストを保持したウェアラブルデバイス111が、ワイヤレス機能を持ったロック状態にある携帯電話やスマートフォン等の携帯デバイス101に近づくと、ウェアラブルデバイスと携帯デバイスの間でワイヤレス接続を確立し、相互で機器認証を行う。機器認証に成功したら、携帯デバイス101はロック解除信号発信状態に移行し、その後はウェアラブルデバイスとのワイヤレス接続が確立している間、ロック解除信号発信状態を維持し続ける。
携帯デバイス101がロック解除信号発信状態にある時は、実施例1と同様に、携帯デバイス101をPC102、ドア入退管理103や決済端末104に使用することができる。
携帯デバイス101を盗難や置忘れなどで紛失した場合、ウェアラブルデバイス111と携帯デバイス101の距離がワイヤレス通信可能な距離以上に離れることによってワイヤレス接続が切断されると、携帯デバイス101はロック解除信号の発信停止状態に移行して第三者が使用不可状態になる。
実施例3と同様に、ウェアラブルデバイス111にはユーザが身に付けていることを検出する機能が備えられているため、携帯デバイス101とのワイヤレス接続が切断された後も、ユーザが身に付けていることを検知し続けている間はユーザと一体であることが保証されるため、ウェアラブルデバイス内部に保存されている認証成功のコンテキストを破棄する必要はなく、再び携帯デバイスとのワイヤレス接続が確立された時は、携帯デバイスはロック解除信号発信状態に移行する。
なお、携帯デバイス101とウェアラブルデバイス111との間のワイヤレス接続が途切れた場合に生体認証成功コンテキストを破棄するようにしてもよいし、ワイヤレス接続切断且つウェアラブルデバイスの取り外しをコンテキスト破棄の条件としてもよい。
本実施例では、ユーザが身に付けるウェアラブルデバイスに生体認証装置を備えないため、静脈認証装置や虹彩認証装置等の筐体寸法は大きめだが認証精度が高精度な生体認証装置を使用することができる。また、ウェアラブルデバイスはワイヤレス通信機能を内蔵するだけで良いので、小型化と省電力化が可能である。
100 生体認証装置
101 携帯デバイス
102 PC
103 ドア入退管理
104 決済端末
105 サーバー
106 ウェアラブル生体認証
107 生体検知機能
108 リストバンド
109 開閉検知機構
110 電池
111 ウェアラブルデバイス
101 携帯デバイス
102 PC
103 ドア入退管理
104 決済端末
105 サーバー
106 ウェアラブル生体認証
107 生体検知機能
108 リストバンド
109 開閉検知機構
110 電池
111 ウェアラブルデバイス
Claims (10)
- 制御対象装置と無線通信を行って使用制限の解除を行う携帯鍵装置において、
互いに無線通信を行う第一の鍵装置と第二の鍵装置と、
他の装置と無線通信を行う通信部と、
生体認証成功のコンテキストを保持する生体認証コンテキスト保持部と、
を備え、
前記通信部が、前記第一の鍵装置と前記第二の鍵装置との間で通信を行っているときに、前記生体コンテキスト保持部は、生体認証成功のコンテキストを受け付けて保持し、
前記生体認証コンテキスト保持部が前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを保持しているときに、前記通信部は、前記制御対象装置の使用制限を解除させる解除信号を発信し、
前記通信部が、前記第一の鍵装置と前記第二の鍵装置との間に通信が無いことを検知したときに、前記生体コンテキスト保持部は、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを破棄し、前記通信部は、前記解除信号の発信を停止させることを特徴とする携帯鍵装置。 - 請求項1において、
前記制御対象装置が受信していた前記解除信号を受信しなくなった場合、前記使用制限を有効にし、前記生体コンテキスト保持部は、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを破棄せず保持し続けることを特徴とする携帯鍵装置。 - 請求項1において、
前記通信部が、前記第一の鍵装置と前記第二の鍵装置との間で通信を行っているときに、生体認証を行うための生体情報の入力を受け付ける生体情報入力部と、
前記入力された生体情報と、記憶部に記憶された登録生体データとの生体認証処理を行う生体認証部と、
を備え、
当該生体認証処理の成功のコンテキストを、前記生体認証コンテキスト保持部に保持することを特徴とする携帯鍵装置。 - 制御対象装置と無線通信を行って使用制限の解除を行う携帯鍵装置において、
他の装置と無線通信を行う通信部と、
生体認証成功のコンテキストを保持する生体認証コンテキスト保持部と、
人体への装着を検知する検知部と、
を備え、
前記検知部が、人体への装着を検知している場合に、前記生体コンテキスト保持部は、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを受け付けて保持し、
前記生体認証コンテキスト保持部が生体認証成功のコンテキストを保持している場合に、前記通信部は、前記制御対象装置の使用制限を解除させる解除信号を発信し、
前記検知部が、人体から外されたことを検知したときに、前記生体コンテキスト保持部は、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを破棄し、前記通信部は、前記解除信号の発信を停止させることを特徴とする携帯鍵装置。 - 請求項4において、
前記検知部は、人体との接触を検知する、または、人体への装着による形状変化を検知することを特徴とする携帯鍵装置。 - 携帯鍵装置が制御対象装置と無線通信を行って使用制限の解除を行う装置制御方法において、
前記携帯鍵装置は、互いに無線通信を行う第一の鍵装置と第二の鍵装置と、を備え、
通信部が、前記第一の鍵装置と前記第二の鍵装置との間で通信を行っているときに、生体コンテキスト保持部は、生体認証成功のコンテキストを受け付けて保持し、
前記生体認証コンテキスト保持部が、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを保持しているときに、前記通信部は、前記制御対象装置の使用制限を解除させる解除信号を発信し、
前記通信部が、前記第一の鍵装置と前記第二の鍵装置との間に通信が無いことを検知したときに、前記生体コンテキスト保持部は、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを破棄し、前記通信部は、前記解除信号の発信を停止させることを特徴とする装置制御方法。 - 請求項6において、
前記制御対象装置が、受信していた前記解除信号を受信しなくなった場合、使用制限を有効にし、前記生体コンテキスト保持部は、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを破棄せず保持し続けることを特徴とする装置制御方法。 - 請求項6において、
前記通信部が、前記第一の鍵装置と前記第二の鍵装置との間で通信を行っている場合に、生体情報入力部は、生体認証を行うための生体情報の入力を受け付け、
前記入力された生体情報と、記憶部に記憶された登録生体データとの生体認証処理を行う生体認証部と、
を備え、
当該生体認証処理の成功のコンテキストを、前記生体認証コンテキスト保持部に保持することを特徴とする装置制御方法。 - 携帯鍵装置が制御対象装置と無線通信を行って使用制限の解除を行う装置制御方法において、
前記鍵装置の検知部が、人体への装着を検知している場合に、前記鍵装置の生体コンテキスト保持部は、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを受け付けて保持し、
前記生体認証コンテキスト保持部が生体認証成功のコンテキストを保持している場合に、前記鍵装置の通信部は、前記制御対象装置の使用制限を解除させる解除信号を発信し、 前記検知部が、人体から外されたことを検知した場合に、前記生体コンテキスト保持部は、前記生体認証成功のコンテキストを破棄し、前記通信部は、前記解除信号の発信を停止させることを特徴とする装置制御方法。 - 請求項9において、
前記検知部は、人体との接触を検知する、または、人体への着脱による形状変化を検知することを特徴とする装置制御方法。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/021,014 US20160224779A1 (en) | 2013-12-24 | 2014-11-21 | Portable key device and device control method |
| EP14874447.7A EP3089062B1 (en) | 2013-12-24 | 2014-11-21 | Portable key device and device control method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013264833A JP6063859B2 (ja) | 2013-12-24 | 2013-12-24 | 携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 |
| JP2013-264833 | 2013-12-24 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015098384A1 true WO2015098384A1 (ja) | 2015-07-02 |
Family
ID=53478256
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/080843 WO2015098384A1 (ja) | 2013-12-24 | 2014-11-21 | 携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20160224779A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3089062B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6063859B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015098384A1 (ja) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3118764A1 (en) * | 2015-07-15 | 2017-01-18 | Biowatch SA | A biometric sensor apparatus for authenticating a user, and a user authenticating method |
| JP2017111730A (ja) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-22 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 情報処理システム、処理装置、端末装置、認証結果提供方法、およびコンピュータプログラム |
| US11297479B2 (en) | 2018-01-10 | 2022-04-05 | Sony Corporation | Portable wireless device, communication method, and server |
| US11323450B2 (en) | 2017-09-11 | 2022-05-03 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, client system, and control method of client system |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20160342784A1 (en) * | 2011-07-15 | 2016-11-24 | Vmware, Inc. | Mobile device authentication |
| EP3128453B1 (en) * | 2015-08-06 | 2021-11-03 | Nokia Technologies Oy | An apparatus comprising a biometric sensor |
| JP6077077B1 (ja) * | 2015-09-14 | 2017-02-08 | ヤフー株式会社 | 認証装置、認証方法及び認証プログラム |
| JP6380360B2 (ja) * | 2015-12-10 | 2018-08-29 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 画像処理システム、画像出力装置、端末装置、画像出力方法、およびコンピュータプログラム |
| US20170300678A1 (en) * | 2016-04-13 | 2017-10-19 | Motorola Solutions, Inc | Method and apparatus for using a biometric template to control access to a user credential for a shared wireless communication device |
| US10127926B2 (en) | 2016-06-10 | 2018-11-13 | Google Llc | Securely executing voice actions with speaker identification and authentication input types |
| JP6801251B2 (ja) * | 2016-06-16 | 2020-12-16 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 情報機器管理システム、個人識別装置およびプログラム |
| JP6798169B2 (ja) * | 2016-07-13 | 2020-12-09 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 認証システム、制御方法およびプログラム |
| CN106878344A (zh) * | 2017-04-25 | 2017-06-20 | 北京洋浦伟业科技发展有限公司 | 一种生物特征认证、注册方法及装置 |
| JP6902225B2 (ja) * | 2017-09-13 | 2021-07-14 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 認証システム |
| WO2020018940A1 (en) * | 2018-07-20 | 2020-01-23 | The Trustees Of Dartmouth College | Token-based authentication for digital devices |
| US11093659B2 (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2021-08-17 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Controlling content visibility on a computing device based on wearable device proximity |
| US11455411B2 (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2022-09-27 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Controlling content visibility on a computing device based on computing device location |
| US11562051B2 (en) | 2019-04-25 | 2023-01-24 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Varying computing device behavior for different authenticators |
| US11082402B2 (en) * | 2019-04-25 | 2021-08-03 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Controlling computing device virtual private network usage with a wearable device |
| US11431514B1 (en) * | 2019-05-06 | 2022-08-30 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Systems for determining authenticated transmissions of encrypted payloads |
| JP2020201805A (ja) * | 2019-06-12 | 2020-12-17 | 国立大学法人福井大学 | 認証プログラム、認証装置及び認証システム |
| JP7535706B2 (ja) | 2022-02-15 | 2024-08-19 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | ゲート開閉制御用の顔認証機および顔認証方法 |
| JP7173648B1 (ja) | 2022-05-02 | 2022-11-16 | 久米機電工業株式会社 | ログイン管理システム |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003058509A (ja) * | 2001-08-15 | 2003-02-28 | Sony Corp | 認証処理システム、認証処理方法、および認証デバイス、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
| JP2003085150A (ja) * | 2001-09-12 | 2003-03-20 | Sony Corp | 個人認証システム及び個人認証方法、携帯情報端末、携帯認証媒体、認証装置、並びに記憶媒体 |
| JP2005071225A (ja) * | 2003-08-27 | 2005-03-17 | Sony Corp | 電子機器および認証方法 |
| JP2008073462A (ja) * | 2006-09-25 | 2008-04-03 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 認証装置、及び認証方法 |
| US20090094681A1 (en) * | 2007-10-03 | 2009-04-09 | Sadler Daniel J | Method and system for providing extended authentication |
| JP2009286343A (ja) | 2008-05-30 | 2009-12-10 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 遠隔車両制御システム、乗員認証装置および遠隔車両制御方法 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001195145A (ja) * | 2000-01-07 | 2001-07-19 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 情報処理装置、個人認証方法およびその方法をコンピュータに実行させるプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
| US8674804B2 (en) * | 2007-03-01 | 2014-03-18 | Deadman Technologies, Llc | Control of equipment using remote display |
| US9443071B2 (en) * | 2010-06-18 | 2016-09-13 | At&T Intellectual Property I, L.P. | Proximity based device security |
| JP2013078175A (ja) * | 2011-09-29 | 2013-04-25 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 電子機器 |
-
2013
- 2013-12-24 JP JP2013264833A patent/JP6063859B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-11-21 US US15/021,014 patent/US20160224779A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2014-11-21 EP EP14874447.7A patent/EP3089062B1/en active Active
- 2014-11-21 WO PCT/JP2014/080843 patent/WO2015098384A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003058509A (ja) * | 2001-08-15 | 2003-02-28 | Sony Corp | 認証処理システム、認証処理方法、および認証デバイス、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム |
| JP2003085150A (ja) * | 2001-09-12 | 2003-03-20 | Sony Corp | 個人認証システム及び個人認証方法、携帯情報端末、携帯認証媒体、認証装置、並びに記憶媒体 |
| JP2005071225A (ja) * | 2003-08-27 | 2005-03-17 | Sony Corp | 電子機器および認証方法 |
| JP2008073462A (ja) * | 2006-09-25 | 2008-04-03 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 認証装置、及び認証方法 |
| US20090094681A1 (en) * | 2007-10-03 | 2009-04-09 | Sadler Daniel J | Method and system for providing extended authentication |
| JP2009286343A (ja) | 2008-05-30 | 2009-12-10 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | 遠隔車両制御システム、乗員認証装置および遠隔車両制御方法 |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3118764A1 (en) * | 2015-07-15 | 2017-01-18 | Biowatch SA | A biometric sensor apparatus for authenticating a user, and a user authenticating method |
| US10659456B2 (en) | 2015-07-15 | 2020-05-19 | Biowatch SA | Method, device and computer program for authenticating a user |
| JP2017111730A (ja) * | 2015-12-18 | 2017-06-22 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 情報処理システム、処理装置、端末装置、認証結果提供方法、およびコンピュータプログラム |
| US11323450B2 (en) | 2017-09-11 | 2022-05-03 | Sony Corporation | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, client system, and control method of client system |
| US11297479B2 (en) | 2018-01-10 | 2022-04-05 | Sony Corporation | Portable wireless device, communication method, and server |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3089062A1 (en) | 2016-11-02 |
| EP3089062A4 (en) | 2017-06-21 |
| JP6063859B2 (ja) | 2017-01-18 |
| US20160224779A1 (en) | 2016-08-04 |
| EP3089062B1 (en) | 2019-08-28 |
| JP2015121910A (ja) | 2015-07-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6063859B2 (ja) | 携帯鍵装置及び装置制御方法 | |
| US11720656B2 (en) | Live user authentication device, system and method | |
| US9472033B2 (en) | Preauthorized wearable biometric device, system and method for use thereof | |
| EP3078157B1 (en) | A wearable device and a method for storing credentials associated with an electronic device in said wearable device | |
| US11451536B2 (en) | User state monitoring system and method using motion, and a user access authorization system and method employing same | |
| US11678186B2 (en) | Cryptographic process for portable devices, and user presence and/or access authorization system and method employing same | |
| US11605255B2 (en) | User activity-related monitoring system and method, and a user access authorization system and method employing same | |
| KR101219957B1 (ko) | 바이오메트릭스를 이용한 사용자 인증 방법, 장치 및 시스템, 이를 위한 기록 매체 | |
| KR102291715B1 (ko) | 웨어러블 단말기와의 상호 작용에 의한 도어락 제어 시스템 | |
| US20170286655A1 (en) | Wearable device, system including the same, and operation methods thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14874447 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014874447 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014874447 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15021014 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |