WO2015065103A1 - 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 방법 및 장치 - Google Patents
통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 방법 및 장치 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015065103A1 WO2015065103A1 PCT/KR2014/010362 KR2014010362W WO2015065103A1 WO 2015065103 A1 WO2015065103 A1 WO 2015065103A1 KR 2014010362 W KR2014010362 W KR 2014010362W WO 2015065103 A1 WO2015065103 A1 WO 2015065103A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- packet
- fec
- source
- repair
- flow
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/004—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using forward error control
- H04L1/0041—Arrangements at the transmitter end
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/03—Error detection or forward error correction by redundancy in data representation, i.e. code words containing more digits than the source words
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/03—Error detection or forward error correction by redundancy in data representation, i.e. code words containing more digits than the source words
- H03M13/05—Error detection or forward error correction by redundancy in data representation, i.e. code words containing more digits than the source words using block codes, i.e. a predetermined number of check bits joined to a predetermined number of information bits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/03—Error detection or forward error correction by redundancy in data representation, i.e. code words containing more digits than the source words
- H03M13/05—Error detection or forward error correction by redundancy in data representation, i.e. code words containing more digits than the source words using block codes, i.e. a predetermined number of check bits joined to a predetermined number of information bits
- H03M13/13—Linear codes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/27—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes using interleaving techniques
- H03M13/2703—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes using interleaving techniques the interleaver involving at least two directions
- H03M13/2707—Simple row-column interleaver, i.e. pure block interleaving
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/37—Decoding methods or techniques, not specific to the particular type of coding provided for in groups H03M13/03 - H03M13/35
- H03M13/373—Decoding methods or techniques, not specific to the particular type of coding provided for in groups H03M13/03 - H03M13/35 with erasure correction and erasure determination, e.g. for packet loss recovery or setting of erasures for the decoding of Reed-Solomon codes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/63—Joint error correction and other techniques
- H03M13/635—Error control coding in combination with rate matching
- H03M13/6356—Error control coding in combination with rate matching by repetition or insertion of dummy data, i.e. rate reduction
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03M—CODING; DECODING; CODE CONVERSION IN GENERAL
- H03M13/00—Coding, decoding or code conversion, for error detection or error correction; Coding theory basic assumptions; Coding bounds; Error probability evaluation methods; Channel models; Simulation or testing of codes
- H03M13/65—Purpose and implementation aspects
- H03M13/6522—Intended application, e.g. transmission or communication standard
- H03M13/6547—TCP, UDP, IP and associated protocols, e.g. RTP
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/004—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using forward error control
- H04L1/0056—Systems characterized by the type of code used
- H04L1/0057—Block codes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/004—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using forward error control
- H04L1/0075—Transmission of coding parameters to receiver
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/02—Details
- H04L12/16—Arrangements for providing special services to substations
- H04L12/18—Arrangements for providing special services to substations for broadcast or conference, e.g. multicast
- H04L12/1863—Arrangements for providing special services to substations for broadcast or conference, e.g. multicast comprising mechanisms for improved reliability, e.g. status reports
- H04L12/1868—Measures taken after transmission, e.g. acknowledgments
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/02—Details
- H04L12/16—Arrangements for providing special services to substations
- H04L12/18—Arrangements for providing special services to substations for broadcast or conference, e.g. multicast
- H04L12/189—Arrangements for providing special services to substations for broadcast or conference, e.g. multicast in combination with wireless systems
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving packets in a communication system.
- Data congestion is intensifying due to the diversification of various contents and the increase of high capacity contents such as high definition (HD) content and ultra high definition (UHD) content in a communication system. Due to such a situation, contents sent from a sender (for example, Host A) are not normally delivered to a receiver (for example, Host B), and a part of the contents is lost on a route.
- a sender for example, Host A
- a receiver for example, Host B
- the packet is composed of one block (payload) of data to be transmitted, address information (for example, source address and destination address), and management information (for example, header). Therefore, when packet loss occurs in the network, the receiver cannot receive the lost packet, so that data and management information in the lost packet cannot be known. This causes user inconvenience in various forms such as deterioration of audio quality, deterioration of video quality of the video, broken screen, missing subtitles, and loss of files.
- A-FEC application layer forward error correction
- a packet for AL-FEC operation that improves network reliability by transmitting a recovery packet generated by using one or more error correction codes together with a data packet is improved. It provides a method and apparatus for configuring and transmitting and receiving.
- a packet protection method and apparatus and a payload protection method and apparatus are provided without modification of a data packet (source packet) after the FEC encoding.
- SS_ID Source Symbol ID
- each data stream is divided into a data payload having a predetermined size
- a source packet flow for the N data streams is configured by adding a header including ID information for distinguishing the N respective data streams to each data payload divided from the respective data streams.
- Generating a source packet Determining an FEC Source Packet Flow consisting of source packets generated from N-M data streams, wherein M is an integer greater than or equal to 1 and less than 1 of N data streams in the source packet flow; Classifying at least one source packet block composed of a predetermined number of source packets in the determined FEC source packet flow; Generating a source symbol block from the divided at least one source packet block; Generating a repair symbol block composed of at least one repair symbol by applying a FEC code to the generated source symbol block; Determining a repair flow ID for identifying a repair flow composed of repair symbols generated by applying an FEC code from the FEC source packet flow; Generating a FEC repair packet by adding a header including the repair flow ID and the FEC repair payload ID to each repair symbol of the repair flow; And transmitting the source packet and the FEC repair packet.
- the header for the source packet includes a packet sequence number based on ID information for each data stream
- the header of the FEC repair packet is a packet serial number based on the repair flow ID. It has a (Packet Sequence Number).
- the FEC repair payload ID includes information on the number of data streams included in the source packet block protected by the FEC repair packet having the repair flow ID (O is less than or equal to NM), and the respective data in the source packet block.
- All or part of the packet ID list, the applied FEC coding structure, the applied FEC code point, and the applied SSBG_modes are AL- in the FEC repair packet, the ID information of the data streams included in the source packet block. It is included in the FEC message and transmitted in a separate packet.
- the packet ID list which is ID information of the data streams included in the FEC source packet flow
- the AL-FEC provides mapping information about repair flow ID protecting the data streams corresponding to the packet ID list. to provide.
- the transmitting apparatus divides each data stream into data payloads having a predetermined size, A source packet flow for the N data streams is configured by adding a header including ID information for distinguishing the N respective data streams to each data payload divided from the respective data streams.
- a source packet is generated, and an FEC source packet flow consisting of source packets generated from NM (where M is an integer greater than or equal to 1) of N data streams in the source packet flow (FEC Source) Packet Flow) and at least a predetermined number of source packets in the determined FEC source packet flow.
- Distinguish my source packet block generate a source symbol block from the separated at least one source packet block, apply an FEC code to the generated source symbol block, and apply at least one repair symbol Determine a repair flow ID for identifying a repair flow consisting of repair symbols generated by applying a FEC code from the FEC source packet flow.
- a controller configured to add a header including the repair flow ID and the FEC repair payload ID to each repair symbol of the repair flow to generate a FEC repair packet.
- a transmitter for transmitting the source packet and the FEC repair packet.
- the header for the source packet includes a packet sequence number based on ID information for each data stream
- the header of the FEC repair packet is a packet serial number based on the repair flow ID. It has a (Packet Sequence Number).
- the FEC repair payload ID includes information on the number of data streams included in the source packet block protected by the FEC repair packet having the repair flow ID (O is less than or equal to NM), and the respective data in the source packet block.
- All or part of the packet ID list, the applied FEC coding structure, the applied FEC code point, and the applied SSBG_modes are AL- in the FEC repair packet, the ID information of the data streams included in the source packet block. It is included in the FEC message and transmitted in a separate packet.
- the packet ID list which is ID information of the data streams included in the FEC source packet flow
- the AL-FEC provides mapping information about repair flow ID protecting the data streams corresponding to the packet ID list. to provide.
- a receiving method includes a method of receiving a packet in a communication system, the method comprising: distinguishing a source packet or an FEC recovery packet from a packet received from a transmitter; Obtaining a recovery symbol from the FEC repair packet; Distinguishing source packets included in a source packet block protected by the FEC repair packet from an FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet; Constructing an encoded symbol block or an FEC block from the separated source packets and the recovered symbols; Restoring a source symbol lost through FEC decoding to the configured encoding symbol block to obtain a source packet lost during transmission from the source symbol.
- the receiving apparatus distinguishes whether a packet is a source packet or an FEC recovery packet from a packet received from a transmitter, and obtains a recovery symbol from the FEC recovery packet. And dividing source packets included in a source packet block protected by the FEC repair packet from an FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet, and encoding symbols including the separated source packets and the repair symbols. And a control unit for constructing a block (Encoding Symbol Block or FEC Block), restoring a source symbol lost through FEC decoding to the configured encoding symbol block to obtain a source packet lost during transmission from the source symbol.
- a method of receiving a packet in a communication system comprising: obtaining an AL-FEC message by receiving a packet including an AL-FEC message from a transmitter; Obtaining, from the AL-FEC message, packet ID list, which is ID information for data streams included in an FEC source packet flow, and mapping information on repair flow ID protecting the same; Discriminating whether a packet is a source packet or an FEC recovery packet from a packet received from a transmitter; Acquiring a repair symbol from the FEC repair packet; distinguishing source packets included in a source packet block protected by the FEC repair packet from an FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet; Constructing an encoding symbol block from the recovery symbols; Restoring a source symbol by performing FEC decoding on the configured encoding symbol block; Obtaining a source packet of a source packet block lost during transmission from the recovered source symbol.
- Another receiving device in a device for receiving a packet in a communication system, receives a packet including an AL-FEC message from a transmitter to obtain an AL-FEC message, and the AL-FEC Obtains the packet ID list which is ID information for the data streams included in the FEC source packet flow and the mapping information about the repair flow ID which protects it from the message, and distinguishes the source packet or FEC repair packet from the packet received from the transmitter. And acquiring a repair symbol from the FEC repair packet, distinguishing source packets included in a source packet block protected by the FEC repair packet from an FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet, and identifying the separated source. Construct an encoding symbol block from packets and the repair symbols, and apply the encoded symbol block And a control unit for recovering a source symbol by performing FEC decoding and obtaining a source packet of a source packet block lost during transmission from the recovered source symbol.
- Another transmission method is a method for transmitting a packet for at least N (one or more integer) data streams in a communication system, wherein each data stream is converted into a data payload having a predetermined size.
- the header for the source packet includes a packet sequence number based on ID information for each data stream
- the header of the FEC repair packet is a packet serial number based on the repair flow ID. It has a (Packet Sequence Number).
- the FEC repair payload ID is information on the number of data streams included in the source payload block protected by the FEC repair packet having the repair flow ID (O is less than or equal to NM), and each of the respective in the source payload block.
- the whole or part of the packet ID list, the applied FEC coding structure, the applied FEC code point, and the applied SSBG_mode are the FEC repair packet, which is ID information of the data streams included in the source payload block. It is sent as a separate packet as an AL-FEC message.
- the AL-FEC maps the repair flow ID for protecting the data streams corresponding to the packet ID list.
- Another transmission device is a device for transmitting a packet for N (or more than one) data streams in a communication system, each of the data streams in a data payload of a predetermined size
- a source payload flow consisting of the data payloads, and consisting of data payloads generated from NM (where M is an integer of 1 or less than N) of the N data streams.
- a FEC source payload flow distinguish at least one source payload block consisting of a predetermined number of source payloads in the determined FEC source payload flow, and distinguish A source symbol block from the at least one source payload block, and generating the source symbol block Apply a FEC code to the symbol symbol block to generate a repair symbol block composed of at least one repair symbol, and apply the FEC code from the FEC source payload flow to the repair symbol generated.
- a controller for generating a FEC repair packet by adding a header including the repair flow ID and the FEC repair payload ID to each repair symbol of the repair flow, and transmitting the source packet and the FEC repair packet. It includes a transmission unit.
- the header for the source packet includes a packet sequence number based on ID information for each data stream
- the header of the FEC repair packet is a packet serial number based on the repair flow ID. It has a (Packet Sequence Number).
- the FEC repair payload ID is information on the number of data streams included in the source payload block protected by the FEC repair packet having the repair flow ID (O is less than or equal to NM), and each of the respective in the source payload block.
- the whole or part of the packet ID list, the applied FEC coding structure, the applied FEC code point, and the applied SSBG_mode are the FEC repair packet, which is ID information of the data streams included in the source payload block. It is sent as a separate packet as an AL-FEC message.
- the AL-FEC maps the repair flow ID for protecting the data streams corresponding to the packet ID list.
- a method of receiving a packet in a communication system comprising: distinguishing a source packet or an FEC recovery packet from a packet received from a transmitter; Acquiring a data payload from the source packet and obtaining a repair symbol from the FEC repair packet, and included in a source payload block protected by the FEC repair packet from an FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet. Constructing an Encoding Symbol Block from data payloads and the recovery symbols; Recovering a source symbol by applying FEC decoding to the encoded symbol block; Obtaining a source payload of a source packet lost during transmission from the recovered source symbol.
- Another receiving device in a device for receiving a packet in a communication system, distinguishes whether the source packet or FEC recovery packet from the packet received from the transmitter, and the data payload from the source packet Acquiring and obtaining a repair symbol from the FEC repair packet; and data payloads and the repair symbol included in a source payload block protected by the FEC repair packet from an FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet.
- Configure an encoding symbol block from the data stream apply FEC decoding to the encoded symbol block, recover a source symbol, and source payload of a source packet lost during transmission from the recovered source symbol. It includes a control unit for obtaining.
- a method of receiving a packet in a communication system comprising: obtaining an AL-FEC message by receiving a packet including an AL-FEC message from a transmitter; Obtaining, from the AL-FEC message, packet ID list, which is ID information for data streams included in an FEC source packet flow, and mapping information on repair flow ID protecting the same; Discriminating whether a packet is a source packet or an FEC recovery packet from a packet received from a transmitter; Acquiring a data payload from the source packet and obtaining a repair symbol from the FEC repair packet, and included in a source payload block protected by the FEC repair packet from an FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet. Constructing an encoding symbol block from source payloads and the repair symbols; Restoring a source symbol by applying FEC decoding to the configured encoding symbol block; Obtaining a source payload of a source packet lost during transmission from the recovered source symbol.
- Another receiving device in a device for receiving a packet in a communication system, receives a packet including an AL-FEC message from a transmitter to obtain an AL-FEC message, and the AL-FEC Obtains the packet ID list which is ID information for the data streams included in the FEC source packet flow and the mapping information about the repair flow ID which protects it from the message, and distinguishes the source packet or FEC repair packet from the packet received from the transmitter. Acquiring a data payload from the source packet and obtaining a repair symbol from the FEC repair packet, and including the data payload in a source payload block protected by the FEC repair packet from an FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet.
- An encoding symbol block is derived from the source payloads and the recovery symbols. Sex and includes restoring the source symbols by applying an FEC decoding is configured to encode the symbol block, and obtains the source payload of the source packet loss during transmission from the reconstructed source symbols controller.
- the header of the source packet or the FEC repair packet has information for identifying whether the source packet or the FEC repair packet.
- the packet transmission method of adding a separate Source Symbol ID (SS_ID) to the source packet to inform the order of the source symbols in the Source Symbol Block and the packet transmission method of the present invention are used together, the embodiment of the present invention According to the header of the source packet or FEC repair packet according to whether the packet is a Source Packet + SS_ID, the Source Packet itself, whether the FEC Repair Packet different from the embodiment of the present invention, FEC Repair Packet according to an embodiment of the present invention Has information
- Table 1 below shows an embodiment of the FEC type of the MMT Packet Header.
- the packet classification information is transmitted to the receiver by payload ID_Mode Flag indicating whether the packet is transmitted by applying a different FEC or an FEC according to the embodiment of the present invention through an AL-FEC message. .
- Paylaod ID_Mode Flag 1 indicates a packet transmission method using FEC according to an embodiment of the present invention. That is, the information in the source packet replaces the SS_ID without using a separate SS_ID for the source packet, and follows the FEC repair packet format (especially FEC Repair Payload ID) according to the embodiment of the present invention.
- Payload ID_Mode Flag 0
- FIG. 1A and 1B illustrate a network topology and a data flow
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram of an MMT system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating a structure of an MMT package according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of configuration information included in an MMT package according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 5A is a configuration diagram of a source packet, a source symbol, and an FEC repair packet according to an embodiment of the present invention
- 5b and 5c are diagrams illustrating a format of a source payload, a source symbol, and an FEC repair packet according to an embodiment of the present invention
- 6A illustrates an MMT Packet Header and a Repair FEC Payload ID format according to an embodiment of the present invention
- 6B illustrates an MMT Packet Header for Source Packet, an MMT Packet Header for FEC Repair Packet, and a Repair FEC Payload ID format according to an embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 6C illustrates a Repair FEC payload ID format having FEC Configuration Info according to an embodiment of the present invention
- 6D is a diagram illustrating an AL-FEC message format having an MMT Packet for AL-FEC Message and an FEC Configuration Info according to an embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 7A illustrates a method of configuring a source packet flow according to an embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 7B illustrates a method for generating two repair flows for each FEC source packet flow by configuring two FEC source packet flows from the source packet flow according to an embodiment of the present invention, and an example of an MMT packet header and an FEC repair payload ID.
- 8A is a block diagram illustrating a transmission device for packet protection according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 8B is a block diagram illustrating a transmission device for payload protection according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 9A is a block diagram illustrating a receiving device for packet protection according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- 9B is a block diagram illustrating a receiving device for payload protection according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating an operation of configuring a source symbol block according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- Explanation access unit smallest media data entity to which timing information can be attributed asset any multimedia data entity that is associated with a unique identifier and that is used for building a multimedia presentation code rate ratio between the number of source symbols and the number of encoding symbols encoding symbol unit of data generated by the encoding process encoding symbol block set of encoding symbols
- FEC code algorithm for encoding data such that the encoded data flow is resilient to data loss
- FEC encoded flow logical set of flows that consists of an FEC source flow and one or more associated FEC repair flows
- FEC payload ID identifier that identifies the contents of a MMT packet with respect to the MMT FEC scheme
- FEC repair flow data flow carrying repair symbols to protect an FEC source flow
- FEC payload identifier media fragment unit fragment of a
- FIGS. 1A and 1B are diagrams illustrating a network topology and a data flow.
- a network topology includes Host A 102 acting as a transmitter and Host B 108 acting as a receiver, where Host A 102 and Host B 108 are one or more routers 104 and 106. Is connected through. Host A 102 and Host B 108 are connected to routers 104 and 106 via Ethernet 118 and 122, which routers 104 and 106 are fiber, satellite communication or other means 120 possible. ) Can be connected to each other. Data flow between host A 102 and host B 108 is through link layer 116, internet layer 114, transport layer 112, and application layer 110.
- the application layer 130 generates data 130 to be transmitted through the AL-FEC.
- the data 130 may be RTP packet data obtained by splitting data compressed by an audio / video (AV) codec stage using RTP (Real Time Protocol) or MMT packet data according to MMT. have.
- the data 130 is converted by the transport layer 112 into a UDP packet 132 into which, for example, a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) header is inserted.
- UDP User Datagram Protocol
- the Internet layer 114 attaches an IP header to the UDP packet 132 to generate an IP packet 134, and the link layer 116 adds a frame header 136 to the IP packet 134 and a frame footer if necessary.
- a frame 116 to be transmitted is attached with a footer).
- MMT MPEG Media Transport
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the configuration of the MMT system, the right is a diagram showing the detailed structure of the delivery function (Delivery Function).
- the media coding layer 205 compresses audio and / or video data and transmits it to an encapsulation function layer 210 (E. Layer).
- the encapsulation function layer 210 packages compressed audio / video data in a form similar to a file format and delivers the compressed audio / video data to a delivery function layer 220.
- the transport function layer 220 (or “D. Layer”) formats the output of the encapsulation function layer 210 in an MMT payload, and then adds an MMT transport packet header to the transport protocol layer 230 in the form of an MMT transport packet. To pass on.
- the transport function layer 220 delivers the output of the encapsulation function layer 210 to the transport protocol layer 230 in the form of an RTP packet using an existing RTP protocol.
- the transport protocol layer 230 converts the transport protocol into any one of a user datagram protocol (UDP) and a transmission control protocol (TCP) and then transmits it to the IP layer 240.
- IP layer 240 converts the output of transport protocol layer 230 into IP packets and transmits them using IP protocol.
- the control function layer 200 (C. Layer) manages a presentation session and a delivery session.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating the structure of an MMT package. As shown in FIG. 3, the MMT package 310 is transmitted and received with the client 350 through the D. Layers 330-1 and 330-2 of the network, and the MMT assets 303 are provided. -1 to 303-3, composition information 301, and transport characteristics 305-1 and 305-2.
- the MMT package 310 has functionality and operations for utilizing configuration information.
- the configuration information includes a list of MMT assets 303-1 to 303-3, configuration information 301, and transmission characteristics 305-1 and 305-2.
- Description information describes the MMT package 310 and the MMT assets 303-1 through 303-3.
- the configuration information 301 assists in the consumption of the MMT assets 303-1 through 303-3.
- Transmission characteristics 305-1 and 305-2 provide hints for the delivery of MMT assets 303-1 through 303-3.
- the MMT package 310 describes transmission characteristics for each MMT asset.
- the transport characteristics 305-1 and 305-2 include error resiliency information, and simple transport characteristic information for one MMT asset may or may not be lost.
- the transmission characteristics 305-1 and 305-2 may include a quality of service (QoS) of each MMT asset (loss tolerant, delay tolerant).
- QoS quality of service
- the configuration information includes additional information together with identification information 312 of the package, asset list information 314 which is a component of the package, composition information 316, transport characteristics 318, and contents, as shown in FIG. It provides structural information such as how these components are contained in the package and where they are contained.
- 5A illustrates a source packet, a source symbol, and an FEC repair packet according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the source symbol is generated by adding Possibly Padding to the source packet.
- Padding data (all 00h) is added as a difference from a predetermined size of repair symbol or given as an AL-FEC message.
- the FEC Repair Packet consists of a MMT Packet Header, a FEC Repair Payload ID, and a Repair Symbol generated from a Source Symbol Block by FEC encoding.
- 5B illustrates a source payload, a source symbol, and an FEC repair packet according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- Source symbol is generated by adding Possibly Padding to Source Payload.
- Padding data (all 00h) is added as difference with predetermined size of repair symbol or given as AL-FEC message.
- the FEC Repair Packet consists of a MMT Packet Header, a FEC Repair Payload ID, and a Repair Symbol generated from a Source Symbol Block by FEC encoding.
- 5c illustrates a source payload, a source symbol, and an FEC repair packet according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- Source symbol is generated by adding Possibly Padding to Source Payload.
- Padding data (all 00h) is added as difference with predetermined size of repair symbol or given as AL-FEC message.
- the FEC Repair Packet consists of a MMT Packet Header, a FEC Repair Payload ID, and a Repair Symbol generated from a Source Symbol Block by FEC encoding.
- 6A is an MMT Packet Header and FEC Repair Payload ID format according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the MMT Packet Header for the Source Packet and FEC Repair Packet has a Packet_ID field and a Packet Sequence Number field.
- Packet_ID is set to identify the data stream including the payload transmitted by the MMTP packet. If the MMTP Packet transmits data of a certain Asset, Packet_ID mapped with the Asset ID is set in this field through MPT (Message Package Table) of Signaling Message and if the MMTP Packet transmits repair symbol of Repair Flow In this case, Repair Flow ID and Packet_ID mapped through AL-FEC Message are set in this field.
- MPT Message Package Table
- the Packet Sequence Number indicates a sequence number of packets having the same Packet_ID value. In case of transmitting asset, it shows sequence number starting from any number and increasing by 1 based on the transmission order of packets transmitting data of the asset.
- FEC Repair Payload ID includes SS_Start_Seq_Nr [1] to SS_Start_Seq_Nr [n], L [1] / SSB_Length [1] to L [n] / SSB_Length [n], RS_ID and Block Code based FEC Code (eg LDPC, RS) RSB_Length may be additionally included in this case (when a rateless FEC code such as Raptor or RaptorQ uses RSB_Length, the number of repair symbols lost from RSB_Length to the repair symbol block may be measured).
- RS_ID and Block Code based FEC Code eg LDPC, RS
- the order of the data streams is the same as the order in which the Packet_IDs for the Source Packet Flow, which are mapped to the Packet_ID set in the FEC Repair Packet, are provided in the AL-FEC Message.
- L [i] is a value that is allocated 2 bits to adjust the size of SSB_Length Field.
- RS_ID indicates the position of the repair symbol of this FEC repair packet in the repair symbol block, starting from 0 and incrementing by one.
- RSB_Length represents the number of repair symbols in a repair packet block including this FEC repair packet.
- the order of the data streams is the same as the order in which the Packet_IDs for the Source Packet Flow, which are mapped to the Packet_ID set in the FEC Repair Packet, are provided in the AL-FEC Message.
- FIG. 6B illustrates an MMT Packet Header for Source Packet, an MMT Packet Header for FEC Repair Packet, and an FEC Repair Payload ID format according to an embodiment of the present invention, wherein a packet sequence number of an MMT Packet Header for an FEC Repair Packet is an FEC Repair Payload ID.
- the description is the same as that in FIG. 6-1 except that RS_ID is changed to.
- FEC Configuration Info includes # of Packet_IDs, List of Packet_IDs, SSBG_MODE, FEC Code Point, FEC Coding Structure, Size of Repair Symbol, although not shown, the duration of the FEC Source or Repair Packet Block (eg first Source Packet and last Source Packet). Time information on the transmitted time difference or the number of packets) is further included.
- # of Packet_IDs Number of data streams included in Source Packet Block protected by this FEC Repair Packet
- List of Packet_IDs List of Packet_IDs identifying the data streams contained in the Source Packet Block protected by this FEC Repair Packet.
- SSBG_MODE Indicates Source Symbol Generation Mode, SSBG_MODE0 or SSBG_MODE1
- FEC Coding Structure Represents a coding structure applied to a source packet block protected by this FEC repair packet. Distinguishes one stage, two stage and LA-FEC.
- FEC Code Point Represents the FEC code used to generate this FEC Repair Packet.
- Size of Repair Symbol This indicates the size of a repair symbol of a repair symbol block including this FEC repair packet.
- FIG. 6D illustrates an AL-FEC message including FEC Configuration Info according to an embodiment of the present invention, in which FEC Configuration Info is the same as FIG. 6-3.
- AL-FEC Message includes Message ID and Length fields, # of FEC Flows, and FEC Configuration Info for each FEC Flow.
- 7A relates to a method of generating a source packet flow according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- each asset is divided into data of a predetermined size and then MMT Payload Header, MMT Packet A header is added to configure an MMT Packet Flow (Source Packet Flow).
- MMT Packet Flow Source Packet Flow
- Each of Assets A, B, and C is divided into five data payloads, and a header including Packet_ID and Packet Sequence Number is added to each data payload.
- An example of the header may be an MMT Packet Header.
- 7B relates to a method for generating a FEC source packet flow and a repair flow according thereto according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FEC Source Packet Flow 1 is composed of Source Packets generated from Assets A and B to generate FEC Source Packet Block 1 (or Source Symbol Block), and FEC Source Packet Flow 2 is an Asset. Composed of source packets generated from B and Asset C, FEC Source Packet Block 2 (or Source Symbol Block) is generated as shown in the figure, and FEC encoding is performed. From this, the FEC Source Packet Block is converted to the Source Symbol Block by one of the methods of SSBG_MODE described in FIG. 10, and FEC Repair packets are generated by performing FEC Encoding.
- the MMT Payload Header and the FEC Repair Payload ID information of the FEC Repair Packet indicate an embodiment based on FIGS. 6A and 6B. Although not shown, assuming that the position of the source packets in the source packet block is determined by the transmission order when generating the source symbol block from the source packet block, the position of the source symbol corresponding to each source packet is in the source symbol block. May differ from each other. The source symbols should be placed in the source symbol block based on the order of Packet_IDs specified in the FEC repair payload ID of the repair packet.
- the source packet block is composed of Assets A and B
- the source symbols for Asset A are placed first in the source symbol block, and then Asset After arranging source symbols for B or vice versa, mapping the FEC repair payload ID of the FEC repair packet to the number of Packet IDs included in the source packet block (or source symbol block) and assets matching the arrangement order. Lists Packet_IDs.
- packets for Asset A may be included in the Source Packet Block (or Source Symbol Block).
- the packets are arranged for the next Asset B, and the Packet_IDs are listed according to the number and order of Packet_IDs.
- the source packet flow is a stream of source packets based on transmission order, so that source packets corresponding to Packet_ID of the first source packet transmitted first among the source packets for each source packet block are first source packet block (or source). It is preferable to arrange the source packets corresponding to the Packet_ID and then arrange the packet within a Symbol Block).
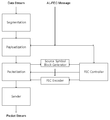
- the data stream is transmitted as a packet stream by the transmitter through segmentation, payloadization, and packetization.
- Payloadization adds a header to the data, and information for reconstructing the data from the packet received at the receiving end is stored in the header. For example, MMT payload corresponds to this.
- Packetization adds MMT Packet Header to MMT Payload.
- the MMT Packet Header has a Packet_ID and a Packet Sequence Number and is used for FEC.
- MMT packets for FEC protection are input to the Source Symbol Block Generator under the control of the FEC Controller.
- the source symbol block generator generates a source symbol block from MMT packets (source packets) (refer to the example of FIG. 10), and the FEC encoder generates a repair symbol by receiving a source symbol block, and each repair symbol generates an MMT packet header. It is sent to FEC Repair Packet by adding FEC Repair Payload ID.
- the MMT Packet Header and the FEC Repair Payload ID are composed of the fields shown in FIGS. 6A, 6B, and 6C of the present invention according to the method.
- Payload protection is the same except that MMT Payload or Payload data is input to the Source Symbol Block.
- the AL-FEC message is sent through a payload, that is, an MMT Payload Header is added, and then an MMT Packet Header is transmitted as a separate packet from the data.
- 9A and 9B show a receiver operation in a packet protection and payload protection entry.
- a packet is received, it is identified whether it is a source packet or an FEC recovery packet. If several types of source packets (for example, MMT Packet (existing invention) having a separate SS_ID and MMT Packet (existing invention) that do not coexist) and several kinds of FEC recovery packets (for example, When the FEC recovery packet and the FEC recovery packet according to the present invention coexist, information for identifying the FEC recovery packet is present in the MMT Packet Header and the receiver distinguishes each packet based on the information. De-packetization (e.g., MMT Packet (existing invention) having a separate SS_ID and MMT Packet (existing invention) that do not coexist) and several kinds of FEC recovery packets (for example, When the FEC recovery packet and the FEC recovery packet according to the present invention coexist, information for identifying the FEC recovery packet is present in the MMT
- MMT De-packetization or Parse De-payloadization
- MMT Payload Depayloadization or Parse De-segmentation restore the data stream.
- Packet Protection When Packet Protection is applied, receiver operation grasps basic information about FEC Configuration necessary for FEC Decoding from AL-FEC Message. If the received packet is a repair packet, other information from # of Packet_IDs, List of Packet_IDs, List of SS_Start_Seq_Nrs, List of SSB_Length [], and the recovery symbol of the repair packet and the Packet_ID in the MMT Packet Header and the FEC Repair Payload ID.
- the encoding symbol generator converts a source symbol according to a given SSBG mode from a source packet and forms an encoding symbol block together with a recovery symbol.
- the FEC decoder uses the recovery symbol to recover the lost source symbol, obtains the source packet, and transmits it to the De-packetiztion block.
- payload protection When payload protection is applied, it is the same as packet protection in terms of utilization of MMT packet header information or utilization of FEC repair payload ID information of FEC repair packet, except for restoring payload rather than packet.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating a first embodiment SSBG_MODE1 of a source symbol block configuration in the encoding symbol block generation unit 520 according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 10 illustrates an example of generating a source packet block (or source symbol block) according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- padding is required if the lengths of the source packets are different (SSBG_MODE1). If all lengths are the same, no padding is needed (SSBG_MODE0).
- the receiving apparatus distinguishes each data stream from stream classification information in the FEC packet or control information different from the source packet, and identifies a recovery stream generated for FEC protection of each data stream.
- the FEC decoding may be smoothly performed, and a repair flow may be generated without affecting the source packet for a predetermined number of data streams included in the generated source packet flow.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Probability & Statistics with Applications (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Detection And Prevention Of Errors In Transmission (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/032,002 US10313055B2 (en) | 2013-10-31 | 2014-10-31 | Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving packet in communication system |
| EP14858134.1A EP3065326A4 (en) | 2013-10-31 | 2014-10-31 | Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving packet in communication system |
| CN201480059692.5A CN105684334B (zh) | 2013-10-31 | 2014-10-31 | 用于在通信系统中发送和接收分组的方法和装置 |
| CN201910659890.XA CN110224795B (zh) | 2013-10-31 | 2014-10-31 | 用于在通信系统中发送和接收分组的方法和装置 |
| JP2016527353A JP2016535507A (ja) | 2013-10-31 | 2014-10-31 | 通信システムにおけるパケット送受信方法及び装置 |
| US16/428,025 US10958376B2 (en) | 2013-10-31 | 2019-05-31 | Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving packet in communication system |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR10-2013-0131587 | 2013-10-31 | ||
| KR1020130131587A KR20150050133A (ko) | 2013-10-31 | 2013-10-31 | 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 방법 및 장치 |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/032,002 A-371-Of-International US10313055B2 (en) | 2013-10-31 | 2014-10-31 | Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving packet in communication system |
| US16/428,025 Continuation US10958376B2 (en) | 2013-10-31 | 2019-05-31 | Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving packet in communication system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015065103A1 true WO2015065103A1 (ko) | 2015-05-07 |
Family
ID=53004608
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/KR2014/010362 Ceased WO2015065103A1 (ko) | 2013-10-31 | 2014-10-31 | 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 방법 및 장치 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US10313055B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP3065326A4 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP2016535507A (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR20150050133A (enExample) |
| CN (3) | CN105684334B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015065103A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20150084632A (ko) * | 2014-01-13 | 2015-07-22 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 방법 및 장치 |
| KR102464803B1 (ko) * | 2017-10-13 | 2022-11-09 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 응용 계층 순방향 오류 정정 방식을 사용하는 멀티미디어 서비스 제공 방법 및 장치 |
| KR102506507B1 (ko) | 2018-01-19 | 2023-03-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 통신 시스템에서 신호를 송/수신하는 장치 및 방법 |
| WO2019143208A1 (ko) * | 2018-01-19 | 2019-07-25 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | 방송 시스템에서의 통신 장치 및 방법 |
| US10833799B2 (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2020-11-10 | Itron Global Sarl | Message correction and dynamic correction adjustment for communication systems |
| CN112954255B (zh) * | 2021-01-29 | 2024-04-16 | 深圳市捷视飞通科技股份有限公司 | 视频会议码流的传输方法、装置、计算机设备和存储介质 |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20120317461A1 (en) * | 2011-06-11 | 2012-12-13 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving packet in broadcasting and communication system |
| WO2013077662A1 (ko) * | 2011-11-24 | 2013-05-30 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 장치 및 방법 |
| US20130136193A1 (en) * | 2011-11-30 | 2013-05-30 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | Apparatus and method of transmitting/receiving broadcast data |
| US20130227376A1 (en) * | 2012-02-27 | 2013-08-29 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | Packet transmission/reception apparatus and method using forward error correction scheme |
| US20130283132A1 (en) * | 2012-04-23 | 2013-10-24 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving packet in communication system |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US304490A (en) * | 1884-09-02 | Corn-planter check-rower | ||
| EP1126708A1 (en) * | 1999-08-27 | 2001-08-22 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | System for interconnecting devices through analog line |
| WO2001067702A1 (en) * | 2000-03-07 | 2001-09-13 | Vyyo, Ltd. | Adaptive downstream modulation scheme for broadband wireless access systems |
| DE60118609T2 (de) * | 2000-10-11 | 2007-05-03 | Broadcom Corp., Irvine | Kabelmodemsystem und Verfahren zur Unterstützung erweiterter Protokolle |
| US20030023915A1 (en) * | 2001-07-30 | 2003-01-30 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Forward error correction system and method for packet based communication systems |
| ES2379082T3 (es) * | 2003-11-12 | 2012-04-20 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Transmisión de paquete de datos |
| US7660245B1 (en) * | 2004-09-16 | 2010-02-09 | Qualcomm Incorporated | FEC architecture for streaming services including symbol-based operations and packet tagging |
| US7752532B2 (en) * | 2005-03-10 | 2010-07-06 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Methods and apparatus for providing linear erasure codes |
| CN101405942A (zh) * | 2006-02-13 | 2009-04-08 | 数字方敦股份有限公司 | 使用可变fec开销和保护周期的流送和缓冲 |
| US9136983B2 (en) * | 2006-02-13 | 2015-09-15 | Digital Fountain, Inc. | Streaming and buffering using variable FEC overhead and protection periods |
| WO2008013528A1 (en) * | 2006-07-25 | 2008-01-31 | Thomson Licensing | Recovery from burst packet loss in internet protocol based wireless networks using staggercasting and cross-packet forward error correction |
| US8171370B2 (en) * | 2006-11-14 | 2012-05-01 | Futurewei Technologies, Inc. | Method and apparatus for applying forward error correction in 66b systems |
| US20090010259A1 (en) * | 2007-07-08 | 2009-01-08 | Alexander Sirotkin | Device, system, and method of classification of communication traffic |
| KR101518507B1 (ko) * | 2007-07-19 | 2015-05-11 | 한국전자통신연구원 | 영상신호 송수신 장치 및 방법 |
| EP2200229B1 (en) * | 2008-12-18 | 2012-03-07 | Alcatel Lucent | Method and apparatus for delivering error-critical traffic through a packet-switched network |
| US8543893B2 (en) * | 2009-09-02 | 2013-09-24 | Agere Systems Llc | Receiver for error-protected packet-based frame |
| US8539319B2 (en) * | 2011-01-28 | 2013-09-17 | Cisco Technology, Inc. | Providing capacity optimized streaming data with forward error correction |
| KR101829923B1 (ko) * | 2011-10-13 | 2018-02-22 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 데이터 통신 시스템에서 부호화 장치 및 방법 |
| BR112014015647A8 (pt) * | 2011-12-21 | 2017-07-04 | Intel Corp | mecanismo para facilitar o gerenciamento e o controle remotos de dispositivos computadores e não-computadores com base em interface de usuário intermediária |
-
2013
- 2013-10-31 KR KR1020130131587A patent/KR20150050133A/ko not_active Ceased
-
2014
- 2014-10-31 CN CN201480059692.5A patent/CN105684334B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-10-31 CN CN201910659890.XA patent/CN110224795B/zh active Active
- 2014-10-31 WO PCT/KR2014/010362 patent/WO2015065103A1/ko not_active Ceased
- 2014-10-31 CN CN201910659763.XA patent/CN110417513B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2014-10-31 EP EP14858134.1A patent/EP3065326A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2014-10-31 US US15/032,002 patent/US10313055B2/en active Active
- 2014-10-31 JP JP2016527353A patent/JP2016535507A/ja active Pending
-
2019
- 2019-05-31 US US16/428,025 patent/US10958376B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20120317461A1 (en) * | 2011-06-11 | 2012-12-13 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving packet in broadcasting and communication system |
| WO2013077662A1 (ko) * | 2011-11-24 | 2013-05-30 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 장치 및 방법 |
| US20130136193A1 (en) * | 2011-11-30 | 2013-05-30 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | Apparatus and method of transmitting/receiving broadcast data |
| US20130227376A1 (en) * | 2012-02-27 | 2013-08-29 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | Packet transmission/reception apparatus and method using forward error correction scheme |
| US20130283132A1 (en) * | 2012-04-23 | 2013-10-24 | Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd. | Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving packet in communication system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3065326A4 (en) | 2017-06-28 |
| JP2016535507A (ja) | 2016-11-10 |
| CN110417513A (zh) | 2019-11-05 |
| CN110417513B (zh) | 2021-10-22 |
| US10313055B2 (en) | 2019-06-04 |
| US20190288791A1 (en) | 2019-09-19 |
| CN110224795B (zh) | 2022-04-08 |
| US10958376B2 (en) | 2021-03-23 |
| KR20150050133A (ko) | 2015-05-08 |
| CN105684334A (zh) | 2016-06-15 |
| CN110224795A (zh) | 2019-09-10 |
| CN105684334B (zh) | 2019-08-16 |
| EP3065326A1 (en) | 2016-09-07 |
| US20160277146A1 (en) | 2016-09-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10985870B2 (en) | Method and device for transmitting and receiving packet in communication system | |
| KR102048452B1 (ko) | 멀티미디어 시스템에서 순방향 오류 정정 패킷을 생성하는 방법과 그 오류 정정 패킷을 송수신하는 방법 및 장치 | |
| WO2015065103A1 (ko) | 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 방법 및 장치 | |
| JP6606240B2 (ja) | 放送システムにおけるマルチメディアデータの転送装置及び方法 | |
| WO2013165155A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving packet in a communication system | |
| US8438450B2 (en) | Method and system for performing data integrity verification of a transport stream | |
| JPH11331310A (ja) | データ伝送制御方法及びデータ伝送システム | |
| WO2014171763A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving forward error correction packet | |
| WO2015147613A1 (ko) | 방송 및/또는 통신 시스템에서 패킷 생성 및 복원 방법 및 장치 | |
| WO2015194919A1 (ko) | 방송 및 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 방법 및 장치 | |
| KR20140047556A (ko) | 방송 및 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 장치 및 방법 | |
| WO2013162250A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving packet in communication system | |
| WO2015147610A2 (ko) | 통신 시스템에서 패킷 송수신 방법 및 장치 | |
| EP2395727A1 (en) | Data transport container, source device, destination device and method for transferring different types of data | |
| WO2015194903A1 (ko) | 응용 계층 순방향 오류 정정 방식을 사용하여 제공되는 방송 서비스의 수신을 제어하는 방법 및 장치 | |
| CN1407758A (zh) | 数字视频系统的远程集中式管理方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14858134 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15032002 Country of ref document: US |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2016527353 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014858134 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014858134 Country of ref document: EP |