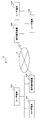WO2014007347A1 - 共有秘密鍵生成装置、暗号化装置、復号化装置、共有秘密鍵生成方法、暗号化方法、復号化方法、及びプログラム - Google Patents
共有秘密鍵生成装置、暗号化装置、復号化装置、共有秘密鍵生成方法、暗号化方法、復号化方法、及びプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014007347A1 WO2014007347A1 PCT/JP2013/068419 JP2013068419W WO2014007347A1 WO 2014007347 A1 WO2014007347 A1 WO 2014007347A1 JP 2013068419 W JP2013068419 W JP 2013068419W WO 2014007347 A1 WO2014007347 A1 WO 2014007347A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- bit string
- matrix
- secret key
- mod
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/0838—Key agreement, i.e. key establishment technique in which a shared key is derived by parties as a function of information contributed by, or associated with, each of these
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0861—Generation of secret information including derivation or calculation of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0869—Generation of secret information including derivation or calculation of cryptographic keys or passwords involving random numbers or seeds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/06—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols the encryption apparatus using shift registers or memories for block-wise or stream coding, e.g. DES systems or RC4; Hash functions; Pseudorandom sequence generators
- H04L9/065—Encryption by serially and continuously modifying data stream elements, e.g. stream cipher systems, RC4, SEAL or A5/3
- H04L9/0656—Pseudorandom key sequence combined element-for-element with data sequence, e.g. one-time-pad [OTP] or Vernam's cipher
- H04L9/0662—Pseudorandom key sequence combined element-for-element with data sequence, e.g. one-time-pad [OTP] or Vernam's cipher with particular pseudorandom sequence generator
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/0838—Key agreement, i.e. key establishment technique in which a shared key is derived by parties as a function of information contributed by, or associated with, each of these
- H04L9/0841—Key agreement, i.e. key establishment technique in which a shared key is derived by parties as a function of information contributed by, or associated with, each of these involving Diffie-Hellman or related key agreement protocols
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a shared secret key generation device, an encryption device, a decryption device, a shared secret key generation method, an encryption method, a decryption method, and a program.
- the present invention provides a shared secret key generation device, an encryption device, a decryption device, a shared secret key generation method, an encryption method, a decryption method, and a program capable of generating a secure shared secret key at high speed
- the purpose is to do.
- the shared secret key generation apparatus includes a prime number p, a natural number d, a matrix Q (mod p) of d ⁇ d whose determinant value is not 1, and an inverse matrix A public data setting unit that sets public data including an existing d ⁇ d matrix S (mod p), and a secret key generation unit that generates a secret key including natural numbers n A (mod p) and k A (mod p)
- a matrix calculation unit that calculates a d ⁇ d matrix M A (mod p) according to the following equation (I) using the secret key, and includes the matrix calculation unit that transmits the matrix M A (mod p) to the communication partner:
- M A S ⁇ kA Q nA S kA (I)
- M B S ⁇ kB Q nB S kB (II)
- M AB S -kA M B nA S kA (III)
- the program according to the second aspect includes a computer that includes a prime number p, a natural number d, a d ⁇ d matrix Q (mod p) whose determinant is not 1, and a d ⁇ d matrix S () having an inverse matrix.
- a public data setting unit that sets public data including mod p
- a secret key generating unit that generates a secret key including natural numbers n A (mod p) and k A (mod p), and using the secret key
- a d ⁇ d matrix M A (mod p) is calculated and transmitted to a communication partner
- a natural number n B (mod p), k B ( mod p) using is calculated according to the following formula (V)
- matrix acquisition unit for acquiring the matrix M B (mod p) of d ⁇ d
- a d ⁇ d matrix M AB (mod p) according to the following equation (VI): It is a program for functioning as a shared secret key calculation unit for calculating as a shared secret key.
- M A S -kA Q nA S kA (IV)
- M B S -kB Q nB S kB (V)
- M AB S -kA M B nA S kA (VI)
- the matrix calculated using the public data and the secret key is exchanged with the communication partner, and the shared secret key is calculated using the matrix obtained from the communication partner.
- a key can be generated.
- the secret key generation unit may generate and update a secret key including natural numbers n A (mod p) and k A (mod p) for each communication with the communication partner. it can. As a result, a more secure shared secret key can be generated.
- the encryption device is configured in common with the decryption device, the shared secret key M AB generated by the shared secret key generation device according to claim 1 or 2, and two prime numbers p1, Based on p2, a matrix generator for generating two non-commutative matrices A1 and A2, a d-dimensional initial vector v 0 set in common with the decoding device, or a d-dimensional vector v i previously obtained -1 1 is applied to the non-commutative matrix A1 to obtain the vector v i 1, and the initial vector v 0 or the d-dimensional vector v i-1 2 previously obtained is applied to the non-commutative matrix A2 Is a matrix operation unit for obtaining a vector v i 2 , and at least one of a sum operation and a product operation when operating the non-commutative matrices A 1 and A 2 is a plurality of types of predetermined operations.
- a matrix acts portion exerting A2, the matrix is converted into a bit string by performing a nonlinear transformation to the vector v i 1 determined by the action part, by joining bit string obtained by the conversion into a bit string W1 previously obtained
- a bit string conversion unit that obtains the bit string W1 and performs a non-linear transformation on the vector v i 2 to convert it into a bit string, and combines the converted bit string with the previously obtained bit string W2 to obtain the bit string W2.
- At least one of the sum operation and the product operation when operating the non-commutative matrices A1, A2 is replaced with an operation method combining a plurality of types of operators, and the vector is replaced with the non-commutative matrix A1, A2 is repeatedly applied and nonlinear transformation is performed, and the exclusive OR of the obtained bit strings W1 and W2 is calculated to obtain a pseudo random number bit string.
- the matrix operation unit operates the non-commutative matrix A1 on the initial vector v 0 or the previously obtained vector v i-1 1 to obtain the vector v i 1 in calculating, for each element of the vector v i 1, already computed vector v i the initial vector v 0 or the vector v i-1 1 was replaced by elements 1, by the action of non-commutative matrix A1 calculates the elements of the vector v i 1, the initial vector v 0, or vectors v i-1 2 previously obtained, by applying the non-commutative matrix A2, in determining said vectors v i 2 for each element of the vector v i 2, the initial vector v 0 or the vector v i-1 2 was replaced by previously computed vector v i 2 element, by applying a non-commutative matrix A2, the vector v The element of i 2 can be calculated. As a result, the decryption strength can be further increased.
- the bit string conversion unit converts the vector v i 1 obtained by the matrix operation unit into a bit string as the nonlinear conversion, and a predetermined value is determined for the converted bit string
- a cut-off process is performed to cut a leading bit string that satisfies a condition, and the bit string from which the leading bit string is cut is coupled to the previously obtained bit string W1, and the vector v i 2 is converted into a bit string
- the cut-off process may be performed so that the bit string from which the leading bit string is cut is coupled to the previously obtained bit string W2.
- the decryption strength can be further increased.
- bit string conversion unit of the encryption device is configured such that, as the cut-off process, for the converted bit string, as a leading bit string that satisfies the predetermined condition, The first bit sequence consisting of 1 that appears first from the beginning can be cut, and the first bit sequence having a predetermined number of bits can be cut from the bit sequence from which the first bit sequence has been cut. .
- the decryption strength can be further increased.
- the decryption device is configured to share the shared secret key M AB generated by the shared secret key generation device according to claim 1 or 2 and the two prime numbers p1 and p2 set in common with the encryption device.
- the matrix generation unit that generates the two non-commutative matrices A1 and A2
- the vector v i 1 is obtained by operating the non-commutative matrix A1 on 1
- the non-commutative matrix A2 is applied to the initial vector v 0 or the d-dimensional vector v i-1 2 obtained previously.
- a matrix operation unit for obtaining a vector v i 2 , wherein at least one of a sum operation and a product operation when operating the non-commutative matrices A1 and A2 is performed using a plurality of predetermined operators.
- a A matrix acts portion exerting said matrix is converted into a bit string by performing a nonlinear transformation to the vector v i 1 determined by the working portion, the bit string a bit string obtained by the conversion is coupled to a bit string W1 previously obtained
- a bit string conversion unit that obtains W1 and performs nonlinear conversion on the vector v i 2 to convert it into a bit string, and combines the converted bit string with the bit string W2 obtained last time to obtain the bit string W2, and the bit string conversion Until the number of bits of each of the bit string W1 and the bit string W2 obtained by the unit becomes the number of bits of the bit string representing the data to be decoded, the action by the matrix action part and the conversion and
- a matrix calculated using public data and a secret key is exchanged with a communication partner, and a matrix obtained from the communication partner is used.
- a secure shared secret key can be generated at high speed.
- the encryption device the encryption method, the decryption device, and the decryption method that are one aspect of the present invention
- a plurality of at least one of a sum operation and a product operation when operating the non-commutative matrices A1 and A2 are performed.
- an encryption processing system 10 includes encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B, a plurality of user terminals 14A, a plurality of user terminals 14B, and an Internet access network 16. I have.
- the encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B are examples of an encryption device and a decryption device.
- the plurality of user terminals 14A are connected to the encryption / decryption device 12A, and the encryption / decryption device 12A is connected to the Internet access network 16.
- the plurality of user terminals 14B are connected to the encryption / decryption device 12B, and the encryption / decryption device 12B is connected to the Internet access network 16.
- the encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B are connected to each other via the Internet access network 16.
- the transmission data is output to the Internet access network 16 via the encryption / decryption device 12A.
- the received data is input from the Internet access network 16 via the encryption / decryption device 12A.
- the transmission data is output to the Internet access network 16 via the encryption / decryption device 12B.
- the received data is input from the Internet access network 16 via the encryption / decryption device 12B.
- the encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B include a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a RAM (Random Access Memory), and a ROM (program that executes a shared secret key generation processing routine and a pseudo-random number sequence generation processing routine described later). It is configured with a computer equipped with “Read Only Memory” and functionally configured as shown below. As shown in FIG. 2, the encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B include a communication unit 20, a public data acquisition unit 22, a secret key generation unit 24, a non-commutative matrix generation unit 26, a shared secret key calculation unit 28, and a data input / output unit.
- the non-commutative matrix generation unit 26 is an example of a matrix calculation unit
- the shared secret key calculation unit 28 is an example of a matrix acquisition unit and a shared secret key calculation unit.
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 is an example of a matrix generation unit, a matrix operation unit, a bit string conversion unit, a bit number determination unit, and a pseudo random number generation sequence unit.
- the communication unit 20 transmits and receives data via the Internet access network 16.
- the data input / output unit 32 receives data output from the user terminals 14A and 14B and outputs data to the user terminals 14A and 14B.
- the public data acquisition unit 22 of the encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B is a prime number p, a natural number d, a matrix Q (mod p) of d ⁇ d, and Obtain a d ⁇ d matrix S (mod p) in which an inverse matrix exists.
- det Q ⁇ 1, and (mod p) indicates that the value of the variable or the element of the matrix is a prime p.
- the secret key generation unit 24 of the encryption / decryption device 12A generates a secret key composed of natural numbers n A (mod p) and k A (mod p).
- the secret key generation unit 24 of the encryption / decryption device 12B generates a secret key composed of natural numbers n B (mod p) and k B (mod p).
- the secret key generation unit 24 generates a new secret key and updates the secret key every time communication is performed.
- the non-commutative matrix generation unit 26 of the encryption / decryption device 12A calculates the d ⁇ d matrix M A (mod p) according to the following equation (1) using the secret keys n A and k A , and the communication unit through 20, the decryption device 12B as a communication partner, and transmits the matrix M a.
- the non-commutative matrix generation unit 26 of the encryption / decryption device 12B calculates the d ⁇ d matrix M B (mod p) according to the following equation (2) using the secret keys n B and k B , and the communication unit Through 20, the matrix MB is transmitted to the encryption / decryption device 12 ⁇ / b> A which is the communication partner.
- Shared secret key calculation unit 28 of the decryption apparatus 12A obtains the matrices M B received by the communication unit 20, using the obtained matrices M B, the matrix M AB of d ⁇ d in accordance with the following equation (3) Calculate (mod p).
- Shared secret key calculation unit 28 of the decryption apparatus 12B obtains the matrix M A received by the communication unit 20, using the obtained matrix M A, the matrix M BA of d ⁇ d in accordance with the following equation (4) Calculate (mod p).
- M AB S ⁇ (KA + KB)
- Q nAnB S (KA + KB) S ⁇ (KB + KA)
- Q nAnB S (KB + KA) M BA ... (7)
- the shared secret key calculation unit 28 of the encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B outputs the calculated matrices M AB and M BA to the common data setting unit 34 as a shared secret key.
- the common data setting unit 34 sets common data in the encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B. Specifically, a matrix M AB (M BA ) that is a shared secret key, prime numbers p1 and p2 that are private data, and an initial vector v 0 are set as common data.
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 generates a pseudo random number bit sequence using a matrix M AB (M BA ) that is a shared secret key, primes p1 and p2 that are private data, and an initial vector v 0 by a method that will be described later. .
- M BA matrix AB
- the encryption unit 38 uses the pseudo random number bit sequence generated by the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 as a key for the one-time pad encryption, so that the data to be encrypted input by the data input / output unit 32 is stream encrypted. To do. For example, as shown in FIG. 4A, the encryption unit 38 calculates the XOR between the plain text represented by the bit string and the pseudo random number bit string as the encryption key, so that each bit from the front is calculated. Encrypt (or every byte). The data encrypted by the encryption unit 38 is transmitted by the communication unit 20.
- the decryption unit 40 decrypts the data to be decrypted received by the communication unit 20 by using the pseudo random number bit sequence generated by the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 as a key for the one-time pad encryption. .
- the decryption unit 40 calculates XOR between an encrypted text (cypher text) represented by a bit string and a pseudo random number bit string as an encryption key, thereby generating one bit from the front. Decrypt every (or every byte).
- the data decoded by the decoding unit 40 is output to the data terminals 14A and 14B by the data input / output unit 32.
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 uses the d ⁇ d matrix M AB (or M BA ) generated as the common secret key and the prime numbers p1 and p2 set as the common private data as follows. Two non-commutative matrices A1 and A2 are generated.
- M AB is a 2 ⁇ 2 matrix
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 calculates the matrix A1 ′ using the matrix M AB and the prime number p1, as shown in the following equation (8).
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 calculates the matrix A2 ′ using the matrix M AB and the prime number p2, and similarly to the above, the non-commutative matrix A2 is calculated. Generate.
- the period length O (A) of the pseudo-random number sequence generated using the non-commutative matrices A1 and A2 is an arbitrary prime number p used for generating the non-commutative matrices A1 and A2. It can be written as the following equation (11).
- the period of A becomes longer than that.
- v i A 1 i v 0 .
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 obtains the bit sequence W1 from the obtained vector sequence V by non-linear conversion.
- a cut-off process is performed to remove the leading bit string including the bit string composed of 0 and the next 1 appearing from the leading bit.
- the cut-off it is known that the remaining bit string has high randomness.
- Random cut as described above, the leading bit string consisting of the consecutive 0 that appears first and the 1 that appears next is cut.
- Fixed cut the number of bits set in advance is cut. For example, when the number of bits to be cut by Fixed cut is 3, the first 3 bits of the bit string obtained as a result of Random cut are cut.
- This cut-off process is performed on all the elements of v i , and W is a bit string in which all the elements after the cut-off process are arranged.
- the vector v i by the action of non-commutative matrix A1, A2, in obtaining the new vector v i + 1, a sum operation and product operation number between, as follows Replace with an operation that combines multiple operators.
- a and b are 32-bit numbers, and the symbol a ⁇ k is a symbol for shifting a by k bits, (sum operation) a + b is replaced with a + b mod 2 32 . Also, (product operation) a ⁇ b is replaced with a ⁇ (b / 2 27 ) xorb.
- a ⁇ (b / 2 27 ) represents that a is shifted by a quotient obtained by dividing b by 2 27 , and xor represents a bitwise exclusive OR.
- v i (v i 1 , v i 2 ,..., V i d ) be obtained by applying the matrix A to the initial vector v 0 i times (d is the dimension of A).
- a method for obtaining i + 1 (v i + 1 1 , v i + 1 2 ,..., v i + 1 d ) is as follows.
- v i + 1 2 (A (v i + 1 1 , v i 2 ,..., V i d )) 2 .
- This a non-commutative matrix A the first element of v i is applied to replaced with a v i + 1 1, in which removal of the second element. Note that the calculation required here is only the calculation of the second element.
- v i + 1 3 (A (v i + 1 1 , v i + 1 2 ,..., V i d )) 2 .
- the first and second elements of v i are replaced, the non-commutative matrix A is applied, and the third element is extracted.
- the processing for the bit string W1 is interrupted at the moment when the bit number of the bit string W1 reaches n, and the remaining part of the bit string W1 is discarded.
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 repeats the vector operation and the cut-off process for the non-commutative matrix A 2 to generate the bit sequence W2. Also, at the moment when the number of bits of the bit string W2 reaches n, the processing for the bit string W2 is interrupted and the remaining part of the bit string W2 is discarded.
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 calculates the XOR of the finally obtained bit sequence W1 and the bit sequence W2, and sets the obtained bit sequence as the pseudo random number bit sequence.
- a non-linear transformation may be further performed on the bit string obtained by XOR of the bit string W1 and the bit string W2, and the result may be a pseudo-random bit string.
- the pseudo random number sequence generation unit 36 generates a pseudo random number bit sequence having the same number of bits as the number of bits of the encryption target data or the number of bits of the decryption target data.
- the user terminal 14A when data is transmitted from the user terminal 14A to the user terminal 14B, the user terminal 14A outputs the transmission data to the encryption / decryption device 12A.
- the encryption / decryption device 12A transmits a communication start request to the communication partner's encryption / decryption device 12B and receives a response signal from the encryption / decryption device 12B
- the encryption / decryption device 12A receives the shared secret shown in FIG.
- a key calculation processing routine is executed.
- the shared secret key calculation processing routine shown in FIG. 5 is executed.
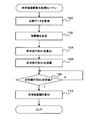
- the shared secret key calculation processing routine is executed in the encryption / decryption device 12A will be described.
- the encryption / decryption device 12A obtains public data (p, d, Q, S) used in communication between the encryption / decryption devices 12A and 12B. For example, it obtains by accessing public data published on the Web.
- step 102 the encryption / decryption device 12A generates secret keys n A and k A.
- the decryption unit 12A includes calculating a public data obtained at Step 100, based on the secret key generated in step 102, according to the above (1), a non-commutative matrix M A To do.
- the decryption unit 12A includes a non-commutative matrix M A calculated in step 104, and transmits to the decryption device 12B of the communication partner.
- the decryption unit 12A from the decryption unit 12B determines whether it has received a non-commutative matrix M B.
- Decryption device 12A receives the non-commutative matrix M B which is calculated similarly by decryption unit 12B, the process proceeds to step 110.
- the decryption unit 12A includes a public data obtained at Step 100, and the secret key generated in step 102, based on the non-commutative matrix M B received in step 108, the (3 ) To calculate the matrix M AB and set it as a shared secret key in communication with the encryption / decryption device 12B, and the shared secret key calculation processing routine is terminated.
- the shared secret key calculation processing routine is executed every time communication is started, and each time a new secret key is generated, a new shared secret key is set.
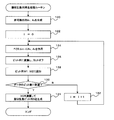
- the pseudo-random number sequence generation processing routine shown in FIG. 6 is executed in the encryption / decryption device 12A.
- the encryption / decryption device 12A generates non-commutative matrices A1 and A2 using the shared secret key M AB and the prime numbers p1 and p2 set in common with the encryption / decryption device 12B.
- the encryption / decryption device 12A sets a variable i for identifying the vector to 0, which is an initial value. Also, the encryption / decryption device 12A sets an initial vector v0.
- the decryption unit 12A is in the vector v i, respectively by the action of non-commutative matrix A1, A2, to calculate the vector v i + 1 1, v i + 1 2.
- the encryption / decryption device 12A converts each of the vectors v i + 1 1 and v i + 1 2 calculated in step 124 into a bit string and performs a cutoff process on each bit string. And cut off the first bit string.
- the encryption / decryption device 12A adds each of the bit strings obtained in step 126 so as to be further aligned with the bit strings W1 and W2.
- step 130 the encryption / decryption device 12A determines whether or not the number of bits of each of the bit strings W1 and W2 has reached the bit number of the bit string of the transmission data (encryption target data).
- the encryption / decryption device 12A The variable i is incremented by 1, and the process returns to step 124 to repeat the processes after step 124.
- the process using the non-commutative matrix A1 is not performed in the processes after step 124.
- the process using the non-commutative matrix A2 is not performed in the processes after step 124.
- step 130 If it is determined in step 130 that the number of bits of both the bit strings W1 and W2 has reached the bit number of the bit string of the transmission data, the process proceeds to step 134.
- step 134 the encryption / decryption device 12A calculates the XOR of the bit strings W1 and W2, generates a pseudo random number bit string S, and ends the pseudo random number string generation processing routine.
- the encryption / decryption device 12A is encrypted by calculating the XOR between the pseudo random number bit sequence S generated by the pseudo random number sequence generation processing routine and the bit sequence of the transmission data input from the user terminal 14. Generate transmission data. Also, the encryption / decryption device 12A transmits the encrypted transmission data to the user terminal 14B via the Internet access network 16.
- the encrypted transmission data is received by the encryption / decryption device 12B, and the pseudo-random number sequence generation processing routine of FIG. 6 is executed in the encryption / decryption device 12B in the same manner, and the pseudo-random number having the same number of bits as the encrypted transmission data is executed.
- a random bit string S is generated.
- the encryption / decryption device 12B generates a plaintext of the encrypted transmission data by calculating an XOR between the generated pseudo random number bit string S and the bit string of the encrypted transmission data. Also, the encryption / decryption device 12B outputs the plaintext of the transmission data to the user terminal B designated as the transmission destination.
- This terminal is Nokia (R) N70 platform.
- the comparison targets are Diffie-Hellman encryption (see DH in FIG. 8) and Elliptic Curve (elliptical) encryption (see ECC in FIG. 8).
- the RSA public key encryption is omitted because it takes a very long time to execute.
- the horizontal axis is the method name and key length, and the vertical axis is the execution time. From the graph shown in FIG. 8, the method proposed in the present embodiment (see QP in FIG. 8) is overwhelmingly faster in execution time than other methods even in a small device, and the execution time does not increase even if the key length is increased. I understood that.
- the encryption / decryption device exchanges a non-commutative matrix calculated using public data and a secret key with a communication partner, and obtains a non-commutation obtained from the communication partner.
- a secure shared secret key can be generated at high speed.
- the encryption / decryption device can share a long key with high-speed processing.
- the attacker solves the following problem from the public information (p, d, Q, S) and the public keys M A and M B , and the secret key n It is necessary to obtain A 1 , k A , (or n B , k B ).
- the encryption / decryption device replaces the sum operation and product operation when operating the non-commutative matrices A1 and A2 with an operation method combining a plurality of types of operators, and converts the non-commutative matrix A1 into an initial vector.
- A2 is repeatedly applied and nonlinear transformation is performed, and XOR of the obtained bit strings W1 and W2 is calculated to obtain a pseudo-random bit string.
- the encryption / decryption device performs encryption or decryption using a pseudo random number bit string, thereby speeding up the encryption process or the decryption process when the number of bits of the data to be encrypted or the data to be decrypted is variable, In addition, the decryption strength can be increased. Further, the encryption / decryption device can start the stream cipher at high speed and safely by combining the method for generating the shared secret key and the encryption / decryption method using random numbers.
- pseudo random number sequence generation algorithm statistical randomness and long period of the pseudo random number sequence can be guaranteed by using some non-linear transformation, and by using the generated pseudo random number sequence, a safe A disposable encryption key (One-Time-Pad key) can be generated.
- streaming encryption can be realized, multimedia files such as audio and video can be transferred safely and at high speed.
- communication between the server and the mobile may be performed.
- the method for generating the shared secret key described above is suitable for communication between the server and the mobile because it operates at high speed even in a mobile environment and can bias the amount of calculation between two parties performing key exchange.
- the present invention may be applied, and may be applied to keyless entry of automobiles. Further, the present invention may be applied to HDD (hard disk disk drive) encryption. For example, all data stored in the HDD may be encrypted by the encryption method described in the present embodiment so that only authorized users can read it. Further, the present invention may be applied to the security of the Cloud service.
- HDD hard disk disk drive
- the program has been described as an embodiment in which the program is installed in advance.
- the program can be provided by being stored in a computer-readable recording medium.
- the computer-readable medium of one embodiment of the present invention is a computer-readable medium including a prime number p, a natural number d, a d ⁇ d matrix Q (mod p) whose determinant is not 1, and a d ⁇ d matrix having an inverse matrix.
- a public data setting unit for setting public data including S (mod p), a secret key generating unit for generating a secret key including natural numbers n A (mod p) and k A (mod p), and using the secret key, in accordance with the following formula (IV), to calculate the d ⁇ d matrix M a (mod p), matrix calculation unit for transmitting to the communication partner, a natural number n B contained in the secret key of the communication counterpart (mod p), k with B a (mod p) is calculated according to the following formula (V), matrix acquisition unit for acquiring the matrix M B (mod p) of d ⁇ d, and the matrices M B acquired by the matrix acquisition unit using the matrix M AB (m of d ⁇ d in accordance with the following (VI) formula
- a computer-readable medium storing a program for functioning as a shared secret key calculation unit that calculates a d p) as a shared secret key.
- M A S -kA Q nA S k
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Storage Device Security (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201380034391.2A CN104488218B (zh) | 2012-07-05 | 2013-07-04 | 加密装置、解密装置、加密方法、解密方法 |
| EP13813271.7A EP2882132B1 (en) | 2012-07-05 | 2013-07-04 | Encryption device, decryption device, encryption method, decryption method, and program |
| US14/412,028 US9608812B2 (en) | 2012-07-05 | 2013-07-04 | Common secret key generation device, encryption device, decryption device, common secret key generation method, encryption method, decryption method, and program |
| KR1020157002300A KR102136904B1 (ko) | 2012-07-05 | 2013-07-04 | 공유 비밀키 생성 장치, 암호화 장치, 복호화 장치, 공유 비밀키 생성 방법, 암호화 방법, 복호화 방법, 및 프로그램 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-151835 | 2012-07-05 | ||
| JP2012151835A JP6019453B2 (ja) | 2012-07-05 | 2012-07-05 | 暗号化装置、復号化装置、及びプログラム |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014007347A1 true WO2014007347A1 (ja) | 2014-01-09 |
Family
ID=49882098
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/068419 Ceased WO2014007347A1 (ja) | 2012-07-05 | 2013-07-04 | 共有秘密鍵生成装置、暗号化装置、復号化装置、共有秘密鍵生成方法、暗号化方法、復号化方法、及びプログラム |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9608812B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2882132B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6019453B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR102136904B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN104488218B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2014007347A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104640110A (zh) * | 2015-01-15 | 2015-05-20 | 南京邮电大学 | 一种终端直通通信中基于信道特性的对称密钥生成方法 |
| CN104993927A (zh) * | 2015-07-07 | 2015-10-21 | 安徽师范大学 | 一种对称密钥生成方法及其应用 |
| CN112887079A (zh) * | 2021-03-11 | 2021-06-01 | 中国石油大学(华东) | 基于一段随机比特序列生成的变换加密算法 |
Families Citing this family (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102520502B1 (ko) * | 2016-08-02 | 2023-04-12 | 엑스-로고스, 엘엘씨 | 기하 대수학을 이용한 강화된 데이터-중심 암호화 시스템을 위한 방법 및 시스템 |
| CN106788980B (zh) * | 2017-01-16 | 2019-07-30 | 中国人民解放军国防科学技术大学 | 一种面向云计算的矩阵乘法外包过程中安全加密方法 |
| CN107104796B (zh) * | 2017-05-02 | 2018-06-29 | 北京邮电大学 | 一种基于非交换群上的对称乘法同态加密方法及装置 |
| CN107578363B (zh) * | 2017-07-25 | 2020-10-30 | 湖北民族学院 | 基于多混沌链式算法和位平面的数字图像加解密方法 |
| GB201713499D0 (en) | 2017-08-23 | 2017-10-04 | Nchain Holdings Ltd | Computer-implemented system and method |
| TWI760546B (zh) | 2017-08-23 | 2022-04-11 | 安地卡及巴布達商區塊鏈控股有限公司 | 用於高安全性高速資料加密及傳輸的電腦實施系統與方法 |
| CN107979590B (zh) * | 2017-11-02 | 2020-01-17 | 财付通支付科技有限公司 | 数据共享方法、客户端、服务器、计算设备及存储介质 |
| US10586057B2 (en) * | 2017-11-16 | 2020-03-10 | Intuit Inc. | Processing data queries in a logically sharded data store |
| US11218291B2 (en) * | 2018-02-26 | 2022-01-04 | Stmicroelectronics (Rousset) Sas | Method and circuit for performing a substitution operation |
| CN108667598B (zh) * | 2018-04-28 | 2021-10-15 | 克洛斯比尔有限公司 | 用于实现安全密钥交换的设备和方法及安全密钥交换方法 |
| CN108833423B (zh) * | 2018-06-25 | 2020-07-31 | 厦门大学 | 一种基于强化学习的多途径保密信息通信方法 |
| TWI672932B (zh) * | 2018-09-27 | 2019-09-21 | 國立交通大學 | 基於質數陣列的後量子非對稱密鑰產生方法及系統、加密方法、解密方法及加密通訊系統 |
| CN109787754B (zh) * | 2018-12-14 | 2023-04-18 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | 一种数据加解密方法、计算机可读存储介质及服务器 |
| CN111107062B (zh) * | 2019-11-29 | 2022-04-05 | 珠海金山网络游戏科技有限公司 | 一种基于贪婪算法的游戏资源打包方法及系统 |
| US11943348B1 (en) * | 2019-12-11 | 2024-03-26 | Q-Net Security, Inc. | Method and system for secure cryptographic exchanges using a five-pass protocol |
| WO2021130935A1 (ja) * | 2019-12-25 | 2021-07-01 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 電子透かし埋め込み装置、電子透かし抽出装置、電子透かし埋め込み方法、電子透かし抽出方法及びプログラム |
| CN111431698B (zh) * | 2020-04-23 | 2023-08-15 | 兰州交通大学 | 运用Haar变换和高斯分布的矢量空间数据加密方法 |
| US11632246B2 (en) * | 2020-12-30 | 2023-04-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | Hybrid key derivation to secure data |
| WO2022185336A1 (en) * | 2021-03-01 | 2022-09-09 | International Institute Of Information Technology, Hyderabad | System and method for proven secret key agreement between initiating unit and responding unit |
| CN114186246A (zh) * | 2021-10-26 | 2022-03-15 | 广州辰创科技发展有限公司 | 一种数据库存储加密方法、解密方法、系统及设备 |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05216409A (ja) | 1991-09-27 | 1993-08-27 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | 制御ベクトルに基づく公開鍵暗号システムの鍵管理 |
| JPH07212356A (ja) * | 1993-12-30 | 1995-08-11 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | 通信パートナの認証方法及びシステム |
| JP2000516733A (ja) | 1996-08-19 | 2000-12-12 | エヌティーアールユー クリプトシステムズ,インコーポレーテッド | 公開鍵暗号システム方法および装置 |
| JP2001202010A (ja) | 1999-12-21 | 2001-07-27 | Contentguard Holdings Inc | メッセージの公開型且つ非可換性の符号化方法及び暗号化方法 |
| JP2004534971A (ja) | 2001-07-12 | 2004-11-18 | エレクトロニクス アンド テレコミュニケーションズ リサーチ インスチチュート | 有限非可換群を用いた公開鍵暗号システム |
| JP2006262425A (ja) | 2005-03-16 | 2006-09-28 | Shin Sato | 公開鍵暗号方式によるネットワーク上での相互認証および公開鍵の相互交換システム |
| JP2007288254A (ja) * | 2006-04-12 | 2007-11-01 | Sony Corp | 通信システム、通信装置および方法、並びにプログラム |
| JP2012151835A (ja) | 2010-12-28 | 2012-08-09 | Panasonic Corp | 映像変換装置 |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3773226B2 (ja) * | 1997-10-06 | 2006-05-10 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | 暗号化装置 |
| JP2001016196A (ja) * | 1999-04-28 | 2001-01-19 | Fuji Soft Abc Inc | 多重アファイン鍵を用いる暗号化・復号化方法、認証方法、及びこれを用いる各装置 |
| US6782101B1 (en) * | 2000-04-20 | 2004-08-24 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Encryption using fractal key |
| US6898288B2 (en) * | 2001-10-22 | 2005-05-24 | Telesecura Corporation | Method and system for secure key exchange |
| US7184551B2 (en) * | 2002-09-30 | 2007-02-27 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Public key cryptography using matrices |
| US8666065B2 (en) * | 2003-02-07 | 2014-03-04 | Britesmart Llc | Real-time data encryption |
| JP2007264147A (ja) * | 2006-03-27 | 2007-10-11 | Fukuoka Institute Of Technology | 疑似乱数列生成装置、暗号化復号化装置、疑似乱数列生成方法、暗号化復号化方法、疑似乱数列生成プログラムおよび暗号化復号化プログラム |
| US8781117B2 (en) * | 2007-08-29 | 2014-07-15 | Red Hat, Inc. | Generating pseudo random bits from polynomials |
-
2012
- 2012-07-05 JP JP2012151835A patent/JP6019453B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2013
- 2013-07-04 EP EP13813271.7A patent/EP2882132B1/en active Active
- 2013-07-04 KR KR1020157002300A patent/KR102136904B1/ko not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-07-04 CN CN201380034391.2A patent/CN104488218B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-07-04 US US14/412,028 patent/US9608812B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-07-04 WO PCT/JP2013/068419 patent/WO2014007347A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05216409A (ja) | 1991-09-27 | 1993-08-27 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | 制御ベクトルに基づく公開鍵暗号システムの鍵管理 |
| JPH07212356A (ja) * | 1993-12-30 | 1995-08-11 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | 通信パートナの認証方法及びシステム |
| JP2000516733A (ja) | 1996-08-19 | 2000-12-12 | エヌティーアールユー クリプトシステムズ,インコーポレーテッド | 公開鍵暗号システム方法および装置 |
| JP2001202010A (ja) | 1999-12-21 | 2001-07-27 | Contentguard Holdings Inc | メッセージの公開型且つ非可換性の符号化方法及び暗号化方法 |
| JP2004534971A (ja) | 2001-07-12 | 2004-11-18 | エレクトロニクス アンド テレコミュニケーションズ リサーチ インスチチュート | 有限非可換群を用いた公開鍵暗号システム |
| JP2006262425A (ja) | 2005-03-16 | 2006-09-28 | Shin Sato | 公開鍵暗号方式によるネットワーク上での相互認証および公開鍵の相互交換システム |
| JP2007288254A (ja) * | 2006-04-12 | 2007-11-01 | Sony Corp | 通信システム、通信装置および方法、並びにプログラム |
| JP2012151835A (ja) | 2010-12-28 | 2012-08-09 | Panasonic Corp | 映像変換装置 |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| ACCARDI, L ET AL.: "The QP-DYN algorithms", 2011, XP007919884, Retrieved from the Internet <URL:http://www.cryptalarm.it/ca/documenti/upload2set/8125_chap01.pdf> [retrieved on 20130408] * |
| OTTAVIANI, V. ET AL.: "Conjugation as public key agreement protocol in mobile cryptography, Security and Cryptography (SECRYPT)", PROCEEDINGS OF THE 2010 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE, July 2010 (2010-07-01), pages 1 - 6, XP031936422 * |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104640110A (zh) * | 2015-01-15 | 2015-05-20 | 南京邮电大学 | 一种终端直通通信中基于信道特性的对称密钥生成方法 |
| CN104640110B (zh) * | 2015-01-15 | 2018-05-29 | 南京邮电大学 | 一种终端直通通信中基于信道特性的对称密钥生成方法 |
| CN104993927A (zh) * | 2015-07-07 | 2015-10-21 | 安徽师范大学 | 一种对称密钥生成方法及其应用 |
| CN104993927B (zh) * | 2015-07-07 | 2018-03-20 | 安徽师范大学 | 一种对称密钥生成方法 |
| CN112887079A (zh) * | 2021-03-11 | 2021-06-01 | 中国石油大学(华东) | 基于一段随机比特序列生成的变换加密算法 |
| CN112887079B (zh) * | 2021-03-11 | 2022-10-04 | 中国石油大学(华东) | 基于一段随机比特序列生成的变换加密算法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20150037913A (ko) | 2015-04-08 |
| EP2882132A1 (en) | 2015-06-10 |
| CN104488218B (zh) | 2017-07-04 |
| CN104488218A (zh) | 2015-04-01 |
| JP6019453B2 (ja) | 2016-11-02 |
| US9608812B2 (en) | 2017-03-28 |
| JP2014017556A (ja) | 2014-01-30 |
| KR102136904B1 (ko) | 2020-07-23 |
| EP2882132B1 (en) | 2019-12-18 |
| US20150156018A1 (en) | 2015-06-04 |
| EP2882132A4 (en) | 2016-03-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6019453B2 (ja) | 暗号化装置、復号化装置、及びプログラム | |
| JP6035459B2 (ja) | 暗号化装置、復号化装置、及びプログラム | |
| CN104320393B (zh) | 重加密可控的高效属性基代理重加密方法 | |
| CN114095170B (zh) | 数据处理方法、装置、系统及计算机可读存储介质 | |
| JP2014017556A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP2020532177A (ja) | データの高度なセキュリティ、高速暗号化および、伝送のためのコンピュータ実装システムおよび方法 | |
| CN107911209A (zh) | 建立抗量子计算攻击的安全性公钥密码的方法 | |
| JP6556955B2 (ja) | 通信端末、サーバ装置、プログラム | |
| Mitra et al. | Prevention of the man-in-the-middle attack on Diffie–Hellman key exchange algorithm: A review | |
| Hodowu et al. | An enhancement of data security in cloud computing with an implementation of a two-level cryptographic technique, using AES and ECC algorithm | |
| Djordjevic | Conventional cryptography fundamentals | |
| CN116915407A (zh) | 基于区块链的电子公证书校验方法及系统 | |
| CN119382960B (zh) | 混合加解密方法、电子设备和存储介质 | |
| Kumar et al. | A novel framework for secure file transmission using modified AES and MD5 algorithms | |
| US12174971B1 (en) | System and method for secure electronic transmission | |
| CN107483206B (zh) | 一种快速的量子安全的非对称加密方法 | |
| JP5489115B2 (ja) | 原本性保証装置、原本性保証プログラム、及びこのプログラムを記録する記録媒体 | |
| KR100388059B1 (ko) | 비대칭키 암호 알고리즘을 이용한 데이터 암호화 시스템및 그 방법 | |
| Siva et al. | Hybrid cryptography security in public cloud using TwoFish and ECC algorithm | |
| CN113141249B (zh) | 一种门限解密方法、系统及可读存储介质 | |
| Kumar et al. | Analysis of Hybrid Cryptography for Secure Exchange of Information | |
| CN118018204B (zh) | 一种基于椭圆曲线的消息处理系统以及消息处理方法 | |
| Mohamed | Cryptography concepts: Confidentiality | |
| Paterson et al. | Statistical attacks on cookie masking for RC4 | |
| Sujatha et al. | Renowned information security algorithms: a comparative study |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13813271 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14412028 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20157002300 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2013813271 Country of ref document: EP |