WO2013161871A1 - Thiophene derivative having tlr-inhibiting activity - Google Patents
Thiophene derivative having tlr-inhibiting activity Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013161871A1 WO2013161871A1 PCT/JP2013/062049 JP2013062049W WO2013161871A1 WO 2013161871 A1 WO2013161871 A1 WO 2013161871A1 JP 2013062049 W JP2013062049 W JP 2013062049W WO 2013161871 A1 WO2013161871 A1 WO 2013161871A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- group
- alkyl group
- ring
- phenyl
- thiophen
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 *NC=C1C=CC(***C(C=CC=CC=C)=C)=CC=C1 Chemical compound *NC=C1C=CC(***C(C=CC=CC=C)=C)=CC=C1 0.000 description 12
- FDRGGAPHXGEHPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Brc(cc1)ccc1C1=CCNCC1 Chemical compound Brc(cc1)ccc1C1=CCNCC1 FDRGGAPHXGEHPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GXRPGGFZFLZGFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(CCCCC/C(/Nc1ccc(-c(cc2)ccc2C2=CCNCC2)[s]1)=[O]\C)C(CCC1)CCC1[N]1(C)CCCCC1 Chemical compound CC(CCCCC/C(/Nc1ccc(-c(cc2)ccc2C2=CCNCC2)[s]1)=[O]\C)C(CCC1)CCC1[N]1(C)CCCCC1 GXRPGGFZFLZGFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IUXBVVCYZZVQMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCC(CC1)=CCCC1(C)c(ccc(-c1ccc(C)[s]1)c1)c1C(N)=O Chemical compound CCC(CC1)=CCCC1(C)c(ccc(-c1ccc(C)[s]1)c1)c1C(N)=O IUXBVVCYZZVQMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZZADMGBSNVRYAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N C[BrH]c1ccc(C(NCCCN(CC2)CCC2N2CCCCC2)=O)[s]1 Chemical compound C[BrH]c1ccc(C(NCCCN(CC2)CCC2N2CCCCC2)=O)[s]1 ZZADMGBSNVRYAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D333/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D333/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings
- C07D333/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings not substituted on the ring sulphur atom
- C07D333/26—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having one sulfur atom as the only ring hetero atom not condensed with other rings not substituted on the ring sulphur atom with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, e.g. ester or nitrile radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D333/30—Hetero atoms other than halogen
- C07D333/36—Nitrogen atoms
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P1/00—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system
- A61P1/04—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system for ulcers, gastritis or reflux esophagitis, e.g. antacids, inhibitors of acid secretion, mucosal protectants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
- A61P11/06—Antiasthmatics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P17/00—Drugs for dermatological disorders
- A61P17/06—Antipsoriatics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/02—Drugs for skeletal disorders for joint disorders, e.g. arthritis, arthrosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P27/00—Drugs for disorders of the senses
- A61P27/02—Ophthalmic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/04—Antibacterial agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
- A61P37/06—Immunosuppressants, e.g. drugs for graft rejection
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/08—Antiallergic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D409/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing aromatic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D409/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
Definitions
- the present invention has a Toll-like receptor (TLR) inhibitory action, and diseases caused by inhibition of signals downstream of TLR, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS) ), Multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis and other autoimmune diseases, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) Or a novel compound useful as an agent for preventing and / or treating cardiomyopathy caused by sepsis.
- TLR Toll-like receptor
- Non-patent Document 1 a myriad of receptors having different antigen specificities are expressed on the surface of T cells and B cells by a method called gene rearrangement, and deal with any unknown foreign antigen.
- Non-patent Document 2 nucleic acid recognition receptors that transmit signals into cells typified by TLR not only play a role in catching infection at the front line, but also transmit signals to cells and turn on the activation of the innate immune system. There is an important role to do.
- Non-patent Document 2 In that sense, induction of gene expression of cytokines and chemokines such as type I interferon and the group of molecules involved in antigen presentation induced by activation of the innate immune system known so far, and subsequent activity of the adaptive immune system It has become clear that the pathway leads to activation of specific immune responses by coordinating with the development (Non-patent Document 2).
- TLR3 recognizes virus-derived double-stranded RNA
- TLR7 similarly recognizes virus-derived single-stranded RNA
- TLR9 recognizes bacterial CpG (cytosine guanine) DNA and is activated. CpG DNA repeats at a certain frequency with a characteristic sequence of bacterial genomic DNA that is not methylated. In mammalian genomic DNA, the frequency of CpG sequences is low and methylated frequently, so there is no immunostimulatory effect (Non-patent Document 3).
- TLRs 7 and 9 function as receptors that recognize extracellular RNA and DNA in endosomes and lysosomes, and induce gene expression of type I interferons and inflammatory cytokines. Both are mediated by a MyD88-dependent signal transduction pathway, whereas the former involves IRAK1 / IKK ⁇ -IRF-7, while the latter involves NF- ⁇ B, IRF-5 and MAP kinase pathways.
- MyD88 is known to associate with IRF-1 and IRF-4 in addition to IRF-7 and IRF-5 (Non-Patent Documents 4, 5, and 6), but IRF transcription factors involved downstream of TLR9 The type and role vary depending on the cell type.
- TLR recognizes RNA or DNA as a ligand, but under normal conditions, self-nucleic acid is not recognized as a ligand and does not activate innate immunity. This is because the self-nucleic acid released by cell death is degraded before being recognized by the TLR by a nuclease in the serum.
- the intracellular localization of TLR3, 7 and 9 not in the cell surface but in the endosome is also considered as a mechanism that does not recognize self-nucleic acids.
- autoimmune reaction or inflammation it is considered that such a defense mechanism breaks down, forms a complex with an endogenous protein, and activates a TLR signal (Non-patent Document 7). .
- RA rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE systemic lupus erythematosus
- SS Sjogren's syndrome
- MS multiple sclerosis
- IBD inflammatory bowel disease
- psoriatic arthritis It is considered possible to improve cardiomyopathy due to Behcet's syndrome, autoimmune diseases such as vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis. As shown below, these several diseases have a specific relationship with TLR.
- Non-patent Document 8 rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Non-Patent Document 10 Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Non-patent Document 11 results have been reported.
- CPG 52364 Patent Document 1
- TLR7 knockout mice MRL / lpr mice that spontaneously develop SLE-like symptoms
- SLE-like symptoms such as a decrease in protein in urine and a decrease in blood IgG
- Non-patent Document 11 suppression of SLE-like symptoms has also been reported by administering an inhibitory nucleic acid. From these reports, it is inferred that TLR7 is also very useful as a target of SLE.
- EAE model which is a model of MS in mice
- TLR2 and TLR9 knockout mice have a weak pathological condition, and the involvement of TLR has been shown (Non-Patent Document 14).
- Non-patent Document 15 salivary gland epithelial cells of patients with Sjogren's syndrome (SS) are highly sensitive to apoptosis due to activation of TLR3, and TLR is considered to be involved.
- TLR inhibition acts on a diseased body
- TLR activation Have been reported to act in a suppressive manner on the pathology, and it is generally not thought that only the inhibitory action functions to recover the pathological condition, but involvement with TLR has been shown (Non-patent Document 16).
- Non-patent Document 17 There has been a report that the contractility of cardiomyocytes has been lost by inflammatory cytokines produced by the ligand CpG-B DNA, and its action was attenuated in TLR9 knockout mice. It is thought that it is concerned with the cardiomyopathy resulting from sepsis from such a thing.
- Hydroxychloroquine is known to have a TLR9 inhibitory action and is already used in clinical practice, but it is not so strong as a TLR9 inhibitory action, and a drug having a stronger TLR9 inhibitory action has a stronger drug effect. I can expect. Hydroxychloroquine has concerns about side effects such as chloroquine retinopathy, but it is also possible that compounds with different skeletons can eliminate such side effects.
- low-molecular-weight drugs that exhibit strong TLR inhibitory action and can be administered orally are future rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS), multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammation
- RA rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE systemic lupus erythematosus
- SS Sjogren's syndrome
- MS multiple sclerosis
- inflammation In the treatment of cardiomyopathy caused by inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), autoimmune diseases such as psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis It is considered useful.
- IBD inflammatory bowel disease
- Behcet's syndrome vasculitis
- inflammation allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis It is considered useful.
- Patent Document 2 effects as a therapeutic agent for central nervous system diseases
- Patent Documents 3, 4, and 5 effects as a therapeutic agent for cancer therapeutic agent
- Patent Documents 3, 4, and 5 effects as a therapeutic agent for central nervous system diseases
- Patent Documents 3, 4, and 5 effects as a therapeutic agent for central nervous system diseases
- Patent Documents 3, 4, and 5 effects as a therapeutic agent for central nervous system diseases
- Patent Documents 3, 4, and 5 effects as a therapeutic agent for central nervous system diseases
- Patent Document 7 prostaglandin E synthase inhibitor
- Patent Document 8 calcium channel modulator
- Non-Patent Document 18 Non-Patent Document 18
- immunity An effect as a therapeutic agent for immune allergic diseases such as an inhibitor of cell activation (Patent Document 9) is also known.
- any of these documents there is no description or suggestion related to the TLR inhibitory action.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a novel compound having a low molecular TLR inhibitory action. More specifically, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS), multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, etc. It is to provide a medicament useful for the prevention and / or treatment of cardiomyopathy caused by autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis.
- RA rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE systemic lupus erythematosus
- SS Sjogren's syndrome
- MS multiple sclerosis
- IBD inflammatory bowel disease
- Behcet's syndrome vasculitis
- the present inventors have found that the thiophene derivative represented by the following general formula (1) expresses human TLR3 internally.
- Test using ECV304 derived from human vascular endothelial cells test using HEK293 cells derived from human fetal kidney cells expressing human TLR7, HEK293 cells derived from human fetal kidney cells expressing human TLR9 And found that it has a TLR inhibitory action, and has completed the present invention.
- Ring A represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring
- Ring B represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring
- ring A and ring B are each a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1.
- Q 2 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group 1 to 2 substituents selected from a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group, R 4 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the
- Ring C represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring C is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, or a C 1-6 alkyl Oxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group A substituent selected from a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, You may have 1 to 3 Q 3 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the
- Benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1- A 6 alkylamino group, a di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a group of formula (4):
- R 5 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, may have a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups
- Ring D represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic
- X represents the formula (3) and the ring C represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring
- the ring Y represents a saturated or unsaturated fat having a substituent represented by the formula (4).
- An aromatic carbocyclic ring an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring
- ring Y has a substituent represented by formula (4) and ring D represents an aromatic carbocycle
- ring Y is a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing An aliphatic heterocycle or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle
- X represents the formula (3) and Q 3 represents an alkylene group having an oxo group
- the ring Y is a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, or a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring.
- the ring Y is a halogen atom, C 1-6 alkyl group, hydroxyl group, C 1-6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1- 5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di May have 1 to 3 substituents selected from a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a group of formula (4);
- Q 1 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group,
- X represents formula (2),
- ring B represents an aromatic carbocycle, a saturated aliphatic carbocycle, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring B is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1- 6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 Substitution selected from alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have 1 to 3 groups, The compound according to the above [1], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
- X represents formula (2),
- ring A represents a pyrrolidine ring, a piperidine ring, a piperazine ring or a tetrahydropyridine ring
- Ring B is a benzene ring, cyclohexane ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadiazole ring or Showing the thiadiazole ring
- ring A and ring B are each a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C
- X represents formula (3),
- ring C represents a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring C is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy Group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, A substituent selected from a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group; You may have up to 3 Q 3 represents a single bond or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 2-6 alkenylene group
- Q 1 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups may have 1 to 2,
- Ring Y represents an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring, wherein said ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1- 6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 An alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a formula ( 1 to 3 substituents selected from the group 4) may be included.
- Ring Y is a benzene ring, piperidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperazine ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring Represents an oxadiazole ring or a thiadiazole ring, wherein the ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group Cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group,
- Ring Y has a substituent represented by formula (4),
- ring D represents a saturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, aromatic carbocyclic ring or saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, wherein the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1-6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1 -5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have 1 to 3 substituents
- Q 4 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene
- the ring D represents a cyclohexane ring, a benzene ring, a pyrrolidine ring, a piperidine ring or a piperazine ring, wherein the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1- 1 to 3 substituents selected from 3- alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have, The compound according to [8] above, or a salt thereof,
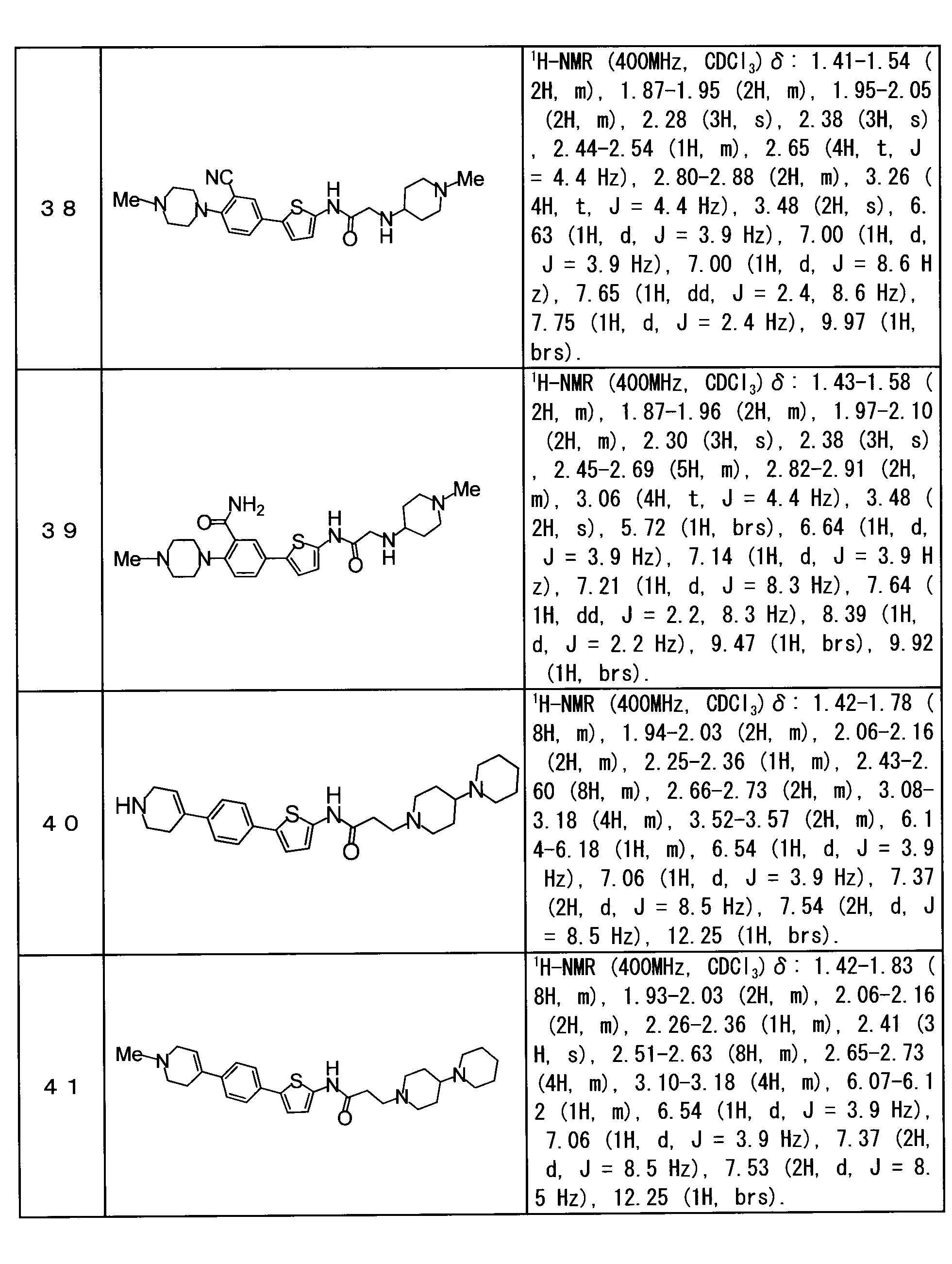
- the compound represented by the general formula (1) is N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 1) , 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide (Example 2), N- ⁇ 3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl ⁇ -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 3), 5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- ⁇ 3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] prop
- autoimmune disease is rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome or vasculitis .
- the present invention is selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9 containing the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof as an active ingredient.
- the present invention relates to a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for diseases caused by activation of at least one signal. More specifically, the present invention relates to rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic, comprising the compound according to any one of the above [1] to [11], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof as an active ingredient.
- RA rheumatoid arthritis
- the present invention relates to a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy due to rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis.
- the present invention also relates to a disease caused by activation of at least one signal selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS) , Multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, autoimmune diseases such as vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) Or the use of the compound according to any one of the above [1] to [11], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof for the manufacture of an agent for preventing and / or treating cardiomyopathy due to sepsis, etc. .
- RA rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE systemic lupus erythematosus
- SS Sjogren's syndrome
- MS Multiple sclerosis
- the present invention provides a TLR3 characterized by administering an effective amount of the compound according to any one of the above [1] to [11], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof, Diseases resulting from activation of at least one signal selected from the group consisting of TLR7 and TLR9, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS), multiple sclerosis (MS) Prevention of autoimmune diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis cardiomyopathy And / or a therapeutic method.
- RA rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE systemic lupus erythematosus
- SS Sjogren's syndrome
- MS multiple sclerosis
- IBD inflammatory bowel disease
- the present invention also relates to the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof for use as a medicament.
- the present invention also relates to a disease caused by activation of at least one signal selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS) , Multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, autoimmune diseases such as vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD)
- the present invention relates to the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof for use in prevention and / or treatment of cardiomyopathy due to sepsis.
- the compound represented by the general formula (1) or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof, which is an active ingredient of at least one inhibitor selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9 of the present invention is RA, Useful for the prevention and / or treatment of autoimmune diseases such as SLE, SS, MS, IBD, psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, GvHD or sepsis cardiomyopathy .
- autoimmune diseases such as SLE, SS, MS, IBD, psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, GvHD or sepsis cardiomyopathy .
- saturated aliphatic carbocycle refers to a 4- to 7-membered aliphatic carbocycle having no multiple bond between adjacent ring carbon atoms.
- saturated aliphatic carbocycle examples include cyclobutane ring, cyclopentane ring, cyclohexane ring, cycloheptane and the like.
- “unsaturated aliphatic carbocycle” refers to a 4- to 7-membered aliphatic carbocycle having one or more multiple bonds between adjacent ring member atoms.
- Examples of the “unsaturated aliphatic carbocycle” include, for example, cyclobutene ring, cyclopentene ring, cyclohexene ring, 1,3-cyclohexadiene ring, 1,4-cyclohexadiene ring, 1,3-cycloheptadiene ring, 1, Examples include 4-cycloheptadiene ring.
- saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle means that there are no multiple bonds between adjacent ring member atoms, one or more nitrogen atoms as ring member atoms, and the rest Represents a 4- to 7-membered aliphatic heterocyclic ring in which the ring member atom is a carbon atom, nitrogen atom, oxygen atom, or sulfur atom.
- saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle include azetidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperidine ring, azepane ring, piperazine ring and the like.
- an “unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle” has one or more multiple bonds between adjacent ring member atoms, and contains one or more nitrogen atoms as ring member atoms. And a 4- to 7-membered aliphatic heterocyclic ring in which the remaining ring member atoms are carbon atoms, nitrogen atoms, oxygen atoms, or sulfur atoms.
- Examples of the “unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle” include azetine ring, pyrroline ring, tetrahydropyridine ring, dihydropyridine ring, tetrahydropyrazine ring, dihydropyrazine ring, tetrahydroazepine ring, oxazine ring and thiazine ring. .
- aromatic carbocycle means a 6 to 10 membered aromatic carbocycle in which all ring member atoms are carbon atoms.
- aromatic carbocycle examples include a benzene ring, an azulene ring, a naphthalene ring and the like.
- nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle means one or more nitrogen atoms as ring member atoms, and the remaining ring members are hetero atoms other than nitrogen atoms (oxygen or sulfur atoms). Or a 5- to 9-membered aromatic heterocycle which is a carbon atom.
- nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle examples include pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadi An azole ring, a thiadiazole ring, an indole ring, etc. are mentioned.
- halogen atom examples include a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, and an iodine atom.
- C 1-6 alkyl group means a straight or branched saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
- Examples of the “C 1-6 alkyl group” include, for example, methyl group, ethyl group, n-propyl group, isopropyl group, n-butyl group, isobutyl group, tert-butyl group, n-pentyl group, 2-methylbutyl group, Examples include 2,2-dimethylpropyl group and n-hexyl group.
- C 1-6 alkyloxy group means a group in which a linear or branched saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms is bonded to an oxygen atom.
- Examples of the “C 1-6 alkyloxy group” include methoxy group, ethoxy group, n-propoxy group, isopropoxy group, n-butoxy group, isobutoxy group, tert-butoxy group, n-pentyloxy group, 2- Examples include methylbutoxy group, 2,2-dimethylpropoxy group, n-hexyloxy group and the like.
- “carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group” means a straight-chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms substituted with a carboxy group at the end.
- Examples of the “carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group” include carboxymethyl group, carboxyethyl group, carboxypropyl group, carboxybutyl group, carboxypentyl group and the like.
- benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group means a straight-chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms substituted with a benzyloxycarbonyl group.
- examples of the “benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group” include benzyloxycarbonylmethyl group, benzyloxycarbonylethyl group, benzyloxycarbonylpropyl group, benzyloxycarbonylbutyl group, benzyloxycarbonylpentyl group and the like.
- “carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group” means a straight-chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms substituted with a carbamoyl group at the terminal.
- Examples of the “carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group” include carbamoylmethyl group, carbamoylethyl group, carbamoylpropyl group, carbamoylbutyl group, carbamoylpentyl group and the like.
- the “C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group” means the carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group substituted at the end with a C 1-3 alkyl group.
- Examples of the “C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group” include, for example, a 1-methylamino-1-oxoethane-2-yl group, a 1-methylamino-1-oxopropan-3-yl group, Methylamino-1-oxobutan-4-yl group, 1-methylamino-1-oxopentan-5-yl group, 1-methylamino-1-oxohexane-6-yl group, 1-ethylamino-1-oxoethane -2-yl group, 1-ethylamino-1-oxopropan-3-yl group, 1-ethylamino-1-oxobutan-4-yl group, 1-ethylamino
- C 1-6 alkylamino group means an amino group in which a linear or branched saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms is substituted.
- Examples of the “C 1-6 alkylamino group” include, for example, methylamino group, ethylamino group, n-propylamino group, isopropylamino group, n-butylamino group, isobutylamino group, tert-butylamino group, n- Examples include pentylamino group, 2-methylbutylamino group, 2,2-dimethylpropylamino group, n-hexylamino group and the like.
- the “di-C 1-6 alkylamino group” is an amino group in which a linear or branched saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms is the same or different and is disubstituted. means.
- Examples of the “di-C 1-6 alkylamino group” include (ethyl) (methyl) amino group, (isopropyl) (n-propyl) amino group, (n-butyl) (isobutyl) amino group, (tert-butyl) ) (N-pentyl) amino group, (2,2-dimethylpropyl) (2-methylbutyl) amino group, dimethylamino group, diethylamino group, di-n-propylamino group, di-isopropylamino group, di-n- Examples thereof include a butylamino group, a di-tert-butylamino group, a di-n-pentylamino group, and a di-n-he
- di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group C 1-6 group that the di-C 1-6 alkylamino group at the end of the alkyl group is substituted Means.
- examples of the “di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group” include (ethyl) (methyl) aminomethyl group, (isopropyl) (n-propyl) aminomethyl group, (n-butyl) (isobutyl) Aminomethyl group, (tert-butyl) (n-pentyl) aminomethyl group, (2,2-dimethylpropyl) (2-methylbutyl) aminomethyl group, dimethylaminomethyl group, diethylaminomethyl group, di-n-propylamino Methyl group, di-isopropylaminomethyl group, di-n-butylaminomethyl group, di-t-butylaminomethyl group, di-n-pentylaminomethyl group
- C 1-6 alkylene group means a saturated divalent straight chain or branched chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
- Examples of the “C 1-6 alkylene group” include methylene group, ethylene group, n-propylene group, isopropylene group, n-butylene group, isobutylene group, tert-butylene group, n-pentylene group, 2-methylbutylene. Group, 2,2-dimethylpropylene group, n-hexylene group and the like.
- C 2-6 alkenylene group means a divalent linear or branched unsaturated hydrocarbon group having 2 to 6 carbon atoms containing one double bond.
- Examples of the “C 2-6 alkenylene group” include vinylene group, propenylene group, 1-butenylene group, 2-butenylene group, 1-pentenylene group, 2-pentenylene group, 1-hexenylene group, 2-hexenylene group, 3 -A hexenylene group and the like.
- hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group means a linear or branched C 1-6 alkyl group having a terminal substituted with a hydroxyl group.
- Examples of the “hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group” include, for example, hydroxymethyl group, hydroxyethyl group, hydroxy-n-propyl group, hydroxyisopropyl group, hydroxy-n-butyl group, hydroxyisobutyl group, hydroxy-tert-butyl group Hydroxy-n-pentyl group, hydroxy-2-methylbutyl group, hydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropyl group, hydroxy-n-hexyl group and the like.
- C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group means a hydroxy group of a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group substituted with a linear or branched C 1-3 alkyl group. Means the group.
- Examples of the “C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group” include methoxymethyl group, methoxyethyl group, methoxy-n-propyl group, methoxyisopropyl group, methoxy-n-butyl group, methoxyisobutyl group, methoxy -Tert-butyl group, methoxy-n-pentyl group, methoxy-2-methylbutyl group, methoxy-2,2-dimethylpropyl group, methoxy-n-hexyl group, ethoxymethyl group, ethoxyethyl group, ethoxy-n-propyl Group, ethoxyisopropyl group, ethoxy-n-butyl group,
- C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group means a sulfonyl group substituted with a linear or branched C 1-3 alkyl group.
- Examples of the “C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group” include methylsulfonyl group, ethylsulfonyl group, n-propylsulfonyl group, isopropylsulfonyl group and the like.
- C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group means a straight or branched C 1-3 alkyl group substituted with a 6-10 membered aromatic carbocycle. To do.
- Examples of the “C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group” include benzyl group, phenethyl group, 1-phenyl-n-propan-1-yl group, 2-phenyl-n-propan-1-yl group, 3-phenyl-n-propan-1-yl group, 1-phenyl-isopropan-2-yl group, 2-phenyl-isopropan-2-yl group, azulenemethyl group, 1-azulenethan-1-yl group 2-azulenethan-1-yl group, 1-azulene-n-propan-1-yl group, 2-azulene-n-propan-1-yl group, 3-azulene-n-propan-1-yl group, 1-azulene-isopropan-2-yl group, 2-azulene-is
- the saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring is preferably a piperidine ring, a piperazine ring, or a pyrrolidine ring.
- the unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring is preferably a 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine ring.
- the aromatic carbocycle is preferably a benzene ring.
- the nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle is preferably a pyridine ring, an indole ring or a pyrazole ring.
- the halogen atom is preferably a bromine atom.
- the C 1-6 alkyl group is preferably a methyl group, an isopropyl group or an isobutyl group.
- the C 1-6 alkyloxy group is preferably a methoxy group.
- the carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group is preferably a carboxybutyl group.
- the benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group is preferably a benzyloxycarbonylmethyl group or a benzyloxycarbonylpentyl group.
- the carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group is preferably a carbamoylpentyl group.
- the C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group is preferably a 1-methylamino-1-oxohexane-6-yl group.
- the C 1-6 alkylamino group is preferably a methylamino group.
- the diC 1-6 alkylamino group is preferably a dimethylamino group.
- the C 1-6 alkylene group is preferably a methylene group, an ethylene group, a propylene group, a butylene group or a pentylene group.
- the hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group is preferably a hydroxy-n-propyl group or a hydroxy-n-pentyl group.
- the C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group is preferably a methoxyethyl group.
- the C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group is preferably a methylsulfonyl group.
- the C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group is preferably a benzyl group.
- ring A is preferably a pyrrolidine ring, piperidine ring, piperazine ring or tetrahydropyridine ring, more preferably a piperidine ring, piperazine ring or tetrahydropyridine ring.
- examples of the substituent that the ring A may have include a C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, and a benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group.
- a methyl group, an isopropyl group, a 1-methylamino-1-oxopentan-5-yl group, a benzyloxycarbonylmethyl group, and a benzyloxycarbonylpentyl group are more preferable.
- ring B is preferably an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring.
- Triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadiazole ring, thiadiazole ring are more preferable, benzene ring, cyclohexane ring, pyridine ring, pyrazole ring are more preferable. .
- the substituent that ring B may have is preferably a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a cyano group, or a carbamoyl group.
- the C 1-6 alkyloxy group is more preferably a methoxy group.
- Q 2 is preferably a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, more preferably a single bond, a methylene group, an ethylene group, an n-propylene group, an n-butylene group or an n-pentylene group. .
- the substituent that Q 2 may have is preferably an oxo group.
- the substitution position of R 4 to the ring B is not particularly limited as long as substitution is possible.
- the ring B is a 6-membered ring
- the ring B of the thiophene ring as the mother nucleus
- it is the 3rd or 4th position counted from the bonding position of, for example, when the ring B is a 5-membered ring, it is preferably the 3rd position counted from the bonding position to the ring B of the thiophene ring which is the mother nucleus. preferable.
- ring C is preferably a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, and a piperidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperazine ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring , A triazine ring, a pyrrole ring, a pyrazole ring, an isoxazole ring, an oxazole ring, an isothiazole ring, a thiazole ring, an oxadiazole ring, a thiadiazole ring, and an indole ring, more preferably a piperazine ring and an indole ring.
- the substituent that the ring C may have is preferably a C 1-6 alkyl group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, a methyl group, a dimethylaminopropyl group Is more preferable.
- Q 3 is preferably a single bond or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, and the C 2-6 alkenylene group is more preferably a propenylene group.
- the substituent that Q 3 may have is preferably an oxo group.
- ring Y is preferably an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring.
- examples of the substituent that the ring Y may have include a C 1-6 alkyl group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, And groups of formula (4) are preferred, methyl groups, dimethylamino groups, dimethylaminomethyl groups and groups of formula (4) are more preferred.
- the substitution position is not particularly limited as long as substitution is possible.
- R 1 is bonded to ring Y.
- at least one is substituted at the 4-position counting from 1, for example, when the ring Y is a 5-membered ring, at least one is substituted at the 2-position counting from the bonding position of R 1 to the ring Y. preferable.
- ring D is preferably an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, or a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, and a benzene ring, a cyclohexane ring, a pyrrolidine ring, a piperazine ring, or a piperidine ring. More preferred are benzene, cyclohexane, piperazine and piperidine rings.
- examples of the substituent that the ring D may have include a C 1-6 alkyl group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group.
- a methyl group, a dimethylamino group, and a dimethylaminomethyl group are more preferable.
- Q 4 is preferably a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, more preferably a single bond or a methylene group.
- R 5 is preferably a single bond or an NH group.
- Q 1 is preferably a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, more preferably a single bond, a methylene group, an ethylene group, an n-propylene group, an n-butylene group or an n-pentylene group.
- the substituent of Q 1 is preferably a C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, or a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group, An isobutyl group, a methoxyethyl group, and a benzyl group are more preferable.
- R 1 when R 1 is an NH group and is substituted, the substituent is preferably a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group or a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and a hydroxy-n-propyl group More preferred are a hydroxy-n-pentyl group and a methylsulfonyl group.
- N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 1) , 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide (Example 2), N- ⁇ 3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl ⁇ -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 3), 5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- ⁇ 3-[(1-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carbox
- the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof includes not only the thiophene derivative of the present invention, but also a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, various hydrations thereof. Substances, solvates, substances having crystalline polymorphs, and substances that become prodrugs of these substances.
- salts acceptable as the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention include inorganic acids (for example, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid). And acid addition salts with organic acids (for example, methanesulfonic acid, ethanesulfonic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, etc.).
- solvate of the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof examples include hydrates and various solvates (for example, solvates with alcohols such as ethanol). Etc.).
- the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention can be produced by a known method. Although the manufacturing method of a thiophene derivative is shown in the following reaction process drawing, a manufacturing method is not limited to this.
- the compound (I) of the present invention can be produced from the 2-nitrothiophene derivative (II).
- R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above, A 1 represents a leaving group, R 6 and R 7 represent a hydrogen atom or C 1-6 alkyl Group, R 6 and R 7 may be combined to form a ring, and R 8 represents a halogen atom.
- Step 1 The coupling reaction between the thiophene derivative (II) having a leaving group and the borane compound (III) can produce the thiophene derivative (IV) using the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction.
- the metal catalyst, base and reaction conditions used are not particularly limited as long as they are reagents and conditions used for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Miyaura, A .; Suzuki, Chem. Rev. The methods described in 1995, 95, 2457-2483, (1995) and the like can be used.
- the metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited.
- the base is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, tert-butoxy sodium, and tert-butoxy potassium.
- the solvent is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-dioxane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene; amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone. Dimethyl sulfoxide, water and the like can be used alone or in combination.
- the reaction temperature is 0 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 60 ° C. to 150 ° C.
- the reaction time is 30 minutes to 48 hours, preferably 1 hour to 20 hours.
- the borane compound (III) used in the above reaction a commercially available one can be used as it is, or it can be suitably produced by a known method, but is not limited thereto.
- the thiophene derivative (IV) can be produced by a coupling reaction between the thiophene derivative (II) having a leaving group and the halogen compound (III ′).
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination.
- the metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited.
- a ligand such as o-tritoluylphosphine, triphenylphosphine, 1,1'-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene, tri-tert-butylphosphine, and the like may be added.
- an organic base such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, and trimethylamine may be added.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 20 ° C. to 150 ° C., preferably 20 ° C. to 120 ° C.
- the reaction time is 5 minutes to 2 days, preferably 1 hour to 20 hours.
- the aminothiophene derivative (V) can be produced by reacting the nitro group of the thiophene derivative (IV) in a solvent in the presence of a reducing agent.
- This reduction method is (a) catalytic hydrogenation in which a nitro group is reduced using a catalytic hydrogen reduction catalyst in a hydrogen atmosphere in a suitable inert solvent, or (b) a metal in a suitable inert solvent.
- the reduction is carried out by metal reduction using a metal salt and acid or a mixture of metal or metal salt and alkali metal hydroxide, sulfide or ammonium salt as a reducing agent to reduce the nitro group.
- examples of the solvent include water; organic acid solvents such as acetic acid; alcohol solvents such as methanol, ethanol and isopropanol; hydrocarbon solvents such as n-hexane and cyclohexane; -Ether solvents such as dioxane, tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, diethylene glycol dimethyl ether; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and methyl acetate; aprotic polar solvents such as N, N-dimethylformamide, etc., or mixed solvents thereof can be used. .
- organic acid solvents such as acetic acid
- alcohol solvents such as methanol, ethanol and isopropanol
- hydrocarbon solvents such as n-hexane and cyclohexane
- -Ether solvents such as dioxane, tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, diethylene glycol dimethyl ether
- the catalytic hydrogen reduction catalyst for example, palladium, palladium-black, palladium-carbon, platinum-carbon, platinum, platinum oxide, copper chromite, Raney nickel and the like can be used alone or in combination.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 20 ° C. to 150 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 100 ° C.
- the reaction time is 30 minutes to 48 hours, preferably 1 hour to 24 hours.
- the solvent examples include water; organic acid solvents such as acetic acid; alcohol solvents such as methanol or ethanol; ether solvents such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane.
- the reaction temperature is, for example, 0 ° C. to 150 ° C., preferably 50 ° C. to 120 ° C. when zinc and acetic acid are used as the reducing agent.
- the reaction time is 1 minute to 12 hours, preferably 1 minute to 6 hours.
- Step 3 The dehydration condensation reaction between the aminothiophene derivative (V) and the carboxylic acid derivative (VI) uses a condensing agent in the presence or absence of a base in the solvent and in the presence or absence of a condensation accelerator. Or after the carboxylic acid is made the active intermediate.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. .
- the base is not particularly limited.
- organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Alkali metal hydrides such as potassium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C.
- the reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
- the reaction between the aminothiophene derivative (V) and the acid halide derivative (VI ′) can be performed in a solvent in the presence or absence of a base.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane
- ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate
- aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene
- Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane
- Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile
- Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination.
- the base is not particularly limited.
- organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Alkali metal hydrides such as potassium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C.
- the reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
- the compound (I) of the present invention can be produced from the thiophenecarbonyl derivative represented by the general formula (VII).
- R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above, A 1 represents a leaving group, A 2 represents OH or a leaving group, R 6 and R 7 represents a hydrogen atom or a C 1-6 alkyl group, and R 6 and R 7 may be combined to form a ring. ]
- the thiophene derivative (I) can be produced by a combination of Step 4 and Step 5.
- the coupling reaction between the thiophene derivative (VII) having a leaving group or a condensed derivative of the thiophene derivative (VII) and the amine derivative (VIII) and the borane compound (III) is a Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction.
- the metal catalyst, base and reaction conditions to be used are not particularly limited as long as they are reagents and conditions generally used for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Miyaura, A.A. Suzuki, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457-2483, (1995) can be used.
- the metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited.
- the base is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, tert-butoxy sodium, and tert-butoxy potassium. Sodium carbonate and cesium carbonate.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-dioxane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether
- aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene and toluene
- N, N-dimethylformamide, N-methylpyrrolidone and the like Amides of dimethyl sulfoxide, water and the like can be used alone or in combination.
- the reaction temperature is 0 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 60 ° C. to 150 ° C.
- the reaction time is 30 minutes to 48 hours, preferably 1 hour to 20 hours.
- the borane compound (III) used in the above reaction a commercially available one can be used as it is, or it can be appropriately produced by a known method, but is not limited thereto.
- Step 5 The reaction of thiophene derivative (VII) or a coupling derivative of thiophene derivative (VII) with borane compound (III) and amine derivative (VIII) is carried out in the presence or absence of a base in a solvent.
- the condensation can be carried out using a condensing agent in the presence or absence of an accelerator, or using carboxylic acid as an active intermediate.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; esters such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; tetrahydrofuran Ethers such as 1,4-dioxane; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; water and the like can be used alone or in combination.
- the base is not particularly limited.
- organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Mosquito Alkali metal hydrides such as lithium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used.
- the reaction temperature is generally ⁇ 20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C. (depending on the starting materials and reagents used).
- the reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
- the compound (I) of the present invention can be produced from the 2-amino-thiophene derivative (V).
- the thiophene derivative (I) can be produced by a urea formation reaction between the amine-containing thiophene derivative (V) and the amine derivative (VIII).
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; esters such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination.
- a base may be added as necessary, and the base is not particularly limited.
- organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, and trimethylamine Can be used.
- the reaction reagent for forming urea is not particularly limited, and phenyl chloroformate, 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate, carbonyldiimidazole, triphosgene and the like can be used.
- the reaction temperature is generally ⁇ 20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 60 ° C. (depending on the starting materials and reagents used).
- the reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
- the compound (I) of the present invention can be produced from the 2-amino-thiophene derivative (V).
- R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above, A 1 represents a leaving group, and R 8 represents a halogen atom.
- a thiophene derivative (X) having a leaving group can be produced by a dehydration condensation reaction between the aminothiophene derivative (V) and the carboxylic acid derivative (IX).
- the dehydration condensation reaction can be carried out using a condensing agent in the presence or absence of a base in a solvent, in the presence or absence of a condensation accelerator, or after using a carboxylic acid as an active intermediate.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. .
- the base is not particularly limited.
- organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Alkali metal hydrides such as potassium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C.
- the reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
- the thiophene derivative (X) having a leaving group can be produced by the reaction of the aminothiophene derivative (V) and the acid halide derivative (IX ′).
- the reaction can be performed in a solvent in the presence or absence of a base.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. .
- the base is not particularly limited.
- organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Alkali metal hydrides such as potassium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C.
- the reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
- the thiophene derivative (I) can be produced by the reaction of the thiophene derivative (X) amine derivative (VIII) having a leaving group.
- the reaction can be performed in a solvent in the presence of a base.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; dimethyl sulfoxide; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile Can be used alone or in combination, and the base is not particularly limited.
- alkali metal hydrides such as lithium hydride, sodium hydride, potassium hydride, metal lithium, metal sodium
- metal Alkali metals such as potassium
- alkali hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide
- alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, lithium diisopropylamide, sodium diisopropyl Amides, potassium Isopropylamide, lithium hexamethyldisilazide, sodium hexamethyldisilazide, potassium hexamethyldisilazide, tert-butoxy sodium, tert-butoxy potassium, n-butyl lithium, s-butyl lithium, tert-butyl lithium, etc.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 10 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 120 ° C.
- the reaction time is 1 hour to 72 hours, preferably
- the borane compound (III) used in the above production method can be used as it is, or can be produced appropriately by a known method.
- it can be produced by the following method. It is not limited.
- a 3 represents a leaving group
- R 6 and R 7 represent a hydrogen atom or a C 1-6 alkyl group
- R 6 and R 7 represent Together, they may form a ring.
- borane compound (III) is produced from compound (XI) using a metal catalyst.
- the metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited.
- a ligand such as o-tritoluylphosphine, triphenylphosphine, 1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene, tri-tert-butylphosphine, and the like may be added.
- the base to be used include lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, potassium acetate, sodium acetate and the like, preferably potassium acetate.
- the solvent to be used is not particularly limited.
- ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane
- aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene
- amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone Dimethyl sulfoxide, water and the like
- a mixed solvent of 1,4-dioxane and water is preferred.
- the reaction temperature is 0 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 80 ° C. to 150 ° C.
- the reaction time is 1 hour to 48 hours, preferably 2 hours to 24 hours.
- the carboxylic acid derivative (VI) used in the above production method can be used as it is, or can be appropriately produced by a known method, for example, it can be produced by the following method. It is not limited.
- R 1 , Ring D, Q 1 , Q 4 , R 5 and Ring Y are the same as defined above, P is a protecting group, W 1 , W 2 , W 4 and W 6 are leaving groups, An aldehyde group, an amino group or a hydroxyl group is shown, and W 3 , W 5 and W 7 are C ⁇ O or NH.
- W 1 and W 4 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group
- W 2 and W 6 represent an amino group or a hydroxyl group
- W 2 and W 6 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group
- W 1 and W 4 Represents an amino group or a hydroxyl group (note that the compounds (XV) and (XV ′) represent a case where the ring Y has a substituent formed by Q 4 , R 5 and the ring D in the carboxylic acid derivative (VI)). Is shown.)]
- Step 10 compound (XIII) or compound (XV) is produced from compound (XII), compound (XIV) or (XIV ') by a) reductive amination or b) alkylation.
- a) Reductive amination can be carried out using a reducing reagent in a solvent in the presence or absence of an acid.
- the dehydration operation may be performed using a Dean-Stark apparatus or the like.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, isopropyl acetate, toluene, benzene, tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-dioxane, acetonitrile, propionitrile, methanol, ethanol, isopropanol , Acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid and the like can be used alone or in combination.
- Lewis acids such as proton acids, such as propionic acid and benzoic acid, titanium tetrachloride, boron trifluoride, and stannic chloride, can be used.
- a reducing reagent for example, sodium triacetoxyborohydride, tetramethylammonium borohydride tetramethylammonium, sodium cyanoborohydride, sodium borohydride, lithium borohydride, sodium trimethoxyborohydride,
- borohydride reagents such as lithium triethylborohydride, lithium hydride lithium, diisopropylaluminum hydride, aluminum hydride reagents such as sodium bis (2-methoxyethoxy) aluminum hydride, metal catalyst and hydrogen source Reduction can be used.
- a hydrogen source for catalytic reduction for example, hydrogen, cyclohexadiene, formic acid, ammonium formate and the like can be used, and as a metal catalyst, for example, palladium carbon, palladium black, palladium hydroxide, Raney nickel, platinum dioxide, platinum Black etc. can be used.
- a metal catalyst for example, palladium carbon, palladium black, palladium hydroxide, Raney nickel, platinum dioxide, platinum Black etc. can be used.
- Alkylation can be carried out in a solvent in the presence of a base.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone
- dimethyl sulfoxide ethers such as 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran
- nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile Can be used alone or in combination, and the base is not particularly limited.
- alkali metal hydrides such as lithium hydride, sodium hydride, potassium hydride, metal lithium, metal sodium
- metal Alkali metals such as potassium
- alkali hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide
- alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate
- lithium diisopropylamide sodium diisopropyl Amides
- potassium Isopropylamide lithium hexamethyldisilazide, sodium hexamethyldisilazide, potassium hexamethyldisilazide, tert-butoxy sodium, tert-butoxy potassium, n-butyl lithium, s-butyl lithium, tert-butyl lithium, etc.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 10 ° C. to 200 ° C., and varies depending on the reaction conditions, but is preferably 0 ° C. to 120 ° C.
- the reaction time varies from 1 hour to 72 hours depending on the reaction conditions, but is preferably 1 hour to 36 hours.
- Step 11 There is no particular limitation on the deprotection of the protecting group, but a method that can be introduced by a generally used method (Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) or the like can be used as appropriate. However, the present invention is not limited to this.
- the amine derivative (VIII) used in the above production method can be used as it is, or can be produced appropriately by a known method, for example, it can be produced by the following method, but is not limited thereto. Is not to be done.
- R 1 , Ring D, Q 1 , Q 4 , R 5 and Ring Y are the same as defined above, P is a protecting group, W 1 , W 2 , W 4 and W 6 are leaving groups or An aldehyde group, an amino group, or a hydroxyl group is represented, and W 3 , W 5, and W 7 represent C ⁇ O or NH.
- W 1 and W 4 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group
- W 2 and W 6 represent an amino group or a hydroxyl group
- W 2 and W 6 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group
- W 1 and W 4 Represents an amino group or a hydroxyl group (note that compounds (XIX) and (XX) represent the case where ring Y has a substituent formed by Q 4 , R 5 and ring D in amine derivative (VIII)).
- Step 12 compound (XVII) or compound (XIX) is produced from compound (XVI), compound (XVIII) or (XVIII ′) by a) reductive amination or b) alkylation.
- a) Reductive amination can be carried out using a reducing reagent in a solvent in the presence or absence of an acid.
- the dehydration operation may be performed using a Dean-Stark apparatus or the like.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; esters such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; tetrahydrofuran Ethers such as 1,4-dioxane; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; alcohols such as methanol, ethanol and isopropanol; organic acids such as acetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid can be used alone or in combination. .
- esters such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate
- aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene
- tetrahydrofuran Ethers such as 1,4-dioxane
- nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile
- alcohols such as methanol, ethanol and iso
- Lewis acids such as proton acids, such as propionic acid and benzoic acid, titanium tetrachloride, boron trifluoride, and stannic chloride, can be used.
- a reducing reagent for example, sodium triacetoxyborohydride, tetramethylammonium borohydride tetramethylammonium, sodium cyanoborohydride, sodium borohydride, lithium borohydride, sodium trimethoxyborohydride,
- borohydride reagents such as lithium triethylborohydride, lithium hydride lithium, diisopropylaluminum hydride, aluminum hydride reagents such as sodium bis (2-methoxyethoxy) aluminum hydride, metal catalyst and hydrogen source Reduction can be used.
- a hydrogen source for catalytic reduction for example, hydrogen, cyclohexadiene, formic acid, ammonium formate, etc.
- Alkylation can be carried out in a solvent in the presence of a base.
- the solvent is not particularly limited.
- amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; dimethyl sulfoxide; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile Can be used alone or in combination, and the base is not particularly limited.
- alkali metal hydrides such as lithium hydride, sodium hydride, potassium hydride, metal lithium, metal sodium
- metal Alkali metals such as potassium
- alkali hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide
- alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, lithium diisopropylamide, sodium diisopropyl Amides, potassium Isopropylamide, lithium hexamethyldisilazide, sodium hexamethyldisilazide, potassium hexamethyldisilazide, tert-butoxy sodium, tert-butoxy potassium, n-butyl lithium, s-butyl lithium, tert-butyl lithium, etc.
- the reaction temperature is ⁇ 10 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 120 ° C.
- the reaction time is 1 hour to 72 hours, preferably
- Step 13 Although there is no particular limitation on the deprotection of the protecting group, a method that can be introduced by a generally used method (Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) or the like can be used as appropriate. However, the present invention is not limited to this.
- Substituents on the X and Y rings in the above general formula, R 2 , R 3 and the like are oxidized, reduced with reference to methods generally used as necessary (Comprehensive Organic Transformation Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.),
- the desired product can be obtained by appropriate conversion by alkylation, amidation, esterification, hydrolysis, reductive amination or the like.
- the protecting group is not particularly limited, and those that can be introduced by a generally used method (Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) can be used as appropriate.
- the present invention is not limited to this.
- various isomers can be isolated by applying a conventional method using the difference in physicochemical properties between isomers.
- a racemic mixture is obtained by a general racemic resolution method such as a method of optically resolving a diastereomeric salt with a general optically active acid such as tartaric acid or a method using optically active column chromatography.
- a general racemic resolution method such as a method of optically resolving a diastereomeric salt with a general optically active acid such as tartaric acid or a method using optically active column chromatography.
- the diastereomeric mixture can be divided by, for example, fractional crystallization or various chromatography.
- An optically active compound can also be produced by using an appropriate optically active raw material.
- the TLR3, 7 and / or 9 inhibitor of the present invention, or an agent for preventing and / or treating autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection and GvHD is a thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1):
- the salt or a solvate thereof is contained as an active ingredient and can be used as a pharmaceutical composition.
- the compound of the present invention may be used alone, but it is usually used in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and / or diluent.
- the administration route is not particularly limited, but can be appropriately selected depending on the purpose of treatment.
- any of oral preparations, injections, suppositories, inhalants and the like may be used.
- Pharmaceutical compositions suitable for these dosage forms can be produced by utilizing known preparation methods.
- the compound represented by the general formula (1) is a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and further, if necessary, a binder, a disintegrant, a lubricant, a coloring agent, and a corrigent.
- a flavoring agent After adding a flavoring agent, tablets, coated tablets, granules, powders, capsules and the like can be produced using conventional methods.
- the additive may be one commonly used in the art.
- excipients include lactose, sucrose, sodium chloride, glucose, starch, calcium carbonate, kaolin, microcrystalline cellulose, silicic acid and the like.
- binder examples include water, ethanol, propanol, simple syrup, glucose solution, starch solution, gelatin solution, carboxymethylcellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose, hydroxypropyl starch, methylcellulose, ethylcellulose, shellac, calcium phosphate, polyvinylpyrrolidone and the like.
- disintegrant examples include dry starch, sodium alginate, agar powder, sodium hydrogen carbonate, calcium carbonate, sodium lauryl sulfate, stearic acid monoglyceride, and lactose.
- lubricant examples include purified talc, stearate, borax, and polyethylene glycol.
- corrigent examples include sucrose, orange peel, citric acid, tartaric acid and the like.
- an oral solution, syrup, etc. are added to the compound represented by the general formula (1) by adding a corrigent, a buffer, a stabilizer, a corrigent and the like using a conventional method.
- An elixir or the like can be produced.
- the flavoring agent include those listed above.
- the buffering agent include sodium citrate
- examples of the stabilizing agent include tragacanth, gum arabic, and gelatin.
- a pH regulator, a buffer, a stabilizer, a tonicity agent, a local anesthetic, etc. are added to the compound represented by the general formula (1), and subcutaneously using a conventional method.
- Intramuscular and intravenous injections can be manufactured.
- the pH adjusting agent and buffer include sodium citrate, sodium acetate, sodium phosphate and the like.
- the stabilizer include sodium pyrosulfite, EDTA (sodium edetate), thioglycolic acid, and thiolactic acid.
- the local anesthetic include procaine hydrochloride and lidocaine hydrochloride.
- the isotonic agent include sodium chloride and glucose.
- a known suppository carrier such as polyethylene glycol, lanolin, cacao butter, fatty acid triglyceride, etc., and a surfactant (for example, , Tween (registered trademark)) and the like can be added and then manufactured using a conventional method.
- a surfactant for example, , Tween (registered trademark)
- the dose of the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention varies depending on age, body weight, symptom, dosage form, number of administrations, etc.
- 0.1 mg to 1000 mg preferably 1 mg to 100 mg, more preferably 1 mg to 10 mg per day is orally or parenterally administered in one or several divided doses.
- Step 1 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide
- Step 2 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine
- Step 3 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [ 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide (70 mg, 0.17 mmol), tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0) (10 mg, 0.009 mmol), 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine (66 mg, 0.22 mmol), 2M carbonic acid Aqueous sodium (0.22 mL) was mixed with 1,4-dioxane (2 mL) and refluxed overnight.
- Step 2 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine
- Step 4 Preparation of methyl 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetate
- Step 5 Preparation of 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetic acid
- Step 6 Preparation of 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetyl chloride
- Step 7 2- [N- (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il ⁇ acetamide production
- Step 8 Preparation of 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide
- 2- [N- (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide (75.3 mg, 0.11 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (1.1 mL), and potassium carbonate (45 mg, 0.33 mmol) and thiophenol (24.7 mg, 0.22 mmol) were added.
- Step 2 Preparation of N- ⁇ 3- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl ⁇ -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide
- Step 3 N- ⁇ 3- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl ⁇ -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2- Production of carboxamide
- Step 4 Preparation of N- ⁇ 3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl ⁇ -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- ⁇ 3- With [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl ⁇ -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (30%) was obtained as a pale brown solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of 5-bromo-N- ⁇ 3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl ⁇ thiophene-2-carboxamide
- Step 2 5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- ⁇ 3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl ⁇ thiophene-2- Carboxamide production
- Step 3 Preparation of 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- ⁇ 3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl ⁇ thiophene-2-carboxamide 5- [4- With (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- ⁇ 3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl ⁇ thiophene-2-carboxamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (40%) was obtained as an orange solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of methyl 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate
- Step 2 Preparation of methyl 2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide] acetate
- Step 3 Preparation of 2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetic acid
- Step 4 N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide] Production of acetamide
- Step 5 Preparation of N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N- ⁇ 5- With [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (2 step yield: 6%) was obtained as a black-brown oil.
- Step 2 Preparation of N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide
- 1-methyl-4 -[4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine (47 mg, 0.17 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (3 mL), and triethylamine (100 ⁇ L, 0.68 mmol) was added to make a solution.
- 2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetyl chloride was added in an ice bath. It returned to room temperature and stirred for 2 hours.
- Step 2 Preparation of 4- (4-bromophenyl) -1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- Step 3 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- Step 4 N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl]
- thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4 , 4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1, The title compound (72%) was obtained as a yellow solid.
- Example 8 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Thiophene-2-carboxamide (10 mg, 0.02 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (1 mL), concentrated hydrochloric acid (10 ⁇ L) and 10% palladium carbon (10 mg) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 hours under a hydrogen atmosphere.
- Step 3 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) cyclohexyl] piperazine
- Step 4 Preparation of benzyl 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate
- Step 5 Preparation of benzyl 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide] acetate
- Step 6 Preparation of 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetic acid
- Step 7 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -N- ( Preparation of 1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 1 Preparation of (E) -tert-butyl 3- (5- ⁇ [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) acrylate
- N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide (80 mg, 0.2 mmol) is dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (2 mL) O-tritoluylphosphine (18 mg, 0.06 mmol), tert-butyl acrylate (150 ⁇ L, 1 mmol), diisopropylamine (100 ⁇ L, 0.6 mmol), tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0) (18 mg, 0.02 mmol) was added and the mixture was stirred at 100 ° C. for 19 hours.
- Step 2 (E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop-1-ene
- E -tert-butyl 3-
- 5- ⁇ [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl ⁇ thiophene-2 -Yl) acrylate 55 mg, 0.12 mmol
- Step 1 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-4-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide
- Step 2 N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide
- Step 1 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide
- Step 2 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,4 The title compound (51%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1 using 5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine.
- Step 1 Preparation of tert-butyl 4-[(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl) amino] piperidine-1-carboxylate
- Step 2 Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [N- (2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] piperidine-1-carboxylate
- Step 3 Preparation of 2- ⁇ N- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido ⁇ acetic acid
- Step 4 tert-Butyl 4- ⁇ N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide ⁇ Production of piperidine-1-carboxylate
- Step 5 Preparation of N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2- [2-nitro-N- (piperidin-4-yl) phenylsulfonamido] acetamide
- Step 6 Preparation of N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N- ⁇ 5- [4- Step 4 of Example 2 using (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2- [2-nitro-N- (piperidin-4-yl) phenylsulfonamido] acetamide In the same manner as the above, the title compound (61%) was obtained as a light brown solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methoxythiophene-2-carboxamide
- Step 2 N- ⁇ 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl ⁇ -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide
- Step 1 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- Step 2 Preparation of 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine
- Step 3 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino ) -2-Oxoethyl] -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 4 N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Preparation of amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9, the title compound (3 step yield 55%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate
- Step 4 tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- ⁇ 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine- 1-carboxylate production
- Step 5 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- [2-oxo-2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (piperidin-4-yloxy) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il ⁇ amino) ethyl] acetamide production
- Step 6 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophene -2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ acetamide
- Step 7 Preparation of 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- ⁇ 4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) acetamide 2, 2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophene-2 -Il) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (73%) as a pale yellow solid.
- Example 18 Production of 2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide 1 Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 with methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine and 2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] acetic acid Similarly, the title compound (48%) was obtained as a brown solid.
- Step 1 Production of (R) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- Step 2 Preparation of (R) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Performed with (R) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid and 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine Analogously to steps 6 and 7 of example 2, the title compound (40%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
- Step 1 Production of (S) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- Step 2 Preparation of (S) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Performed with (S) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid and 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine In the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 19, the title compound (49%) was obtained as a slightly yellow solid.
- Example 21 2-[(5-hydroxypentyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇
- the title compound (89%) was obtained as a pale yellow oil in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using hydroxypentanal.
- Step 1 Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- ⁇ [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
- Step 2 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide tert-Butyl 4- [ 4- (5- ⁇ [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate was used to In the same manner as in Step 5, the title compound (87%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
- Example 24 Benzyl 6- ⁇ 4- [4- (5- ⁇ [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1- Yl ⁇ hexanoate N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide and benzyl 6 Using bromohexanoate, the title compound (69%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Example 23.
- Step 2 Preparation of 1′-methyl-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide 1′-methyl —N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide
- the title compound (2 step yield: 31%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
- Step 2 Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
- Step 3 tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- ⁇ 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine- 1-carboxylate production
- Step 4 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- [2-oxo-2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il ⁇ amino) ethyl] acetamide production
- Step 5 N-methyl-6- ⁇ 4- [4- (5- ⁇ 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) Of phenyl] piperazin-1-yl ⁇ hexanamide
- Step 6 Of N-methyl-6- ⁇ 4- [4- (5- ⁇ 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl ⁇ hexanamide
- Phenyl] piperazin-1-yl ⁇ hexanamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 40%) as a brown solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of 2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] -4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenol
- Step 2 Preparation of 2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] -4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol
- Step 4 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2
- Step 5 N- (5- ⁇ 4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] Using -2-oxoethyl ⁇ -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9, the title compound (4 step yield: 2%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid. Got as.
- Step 1 2-[ ⁇ 3-[(tert-Butyldimethylsilyl) oxy] propyl ⁇ (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl ] Preparation of thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide
- Step 2 2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide
- Step 1 Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide
- Step 2 Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide
- Step 3 Preparation of N- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamide
- Step 4 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamido] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 5 Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- ⁇ 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamido] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (66%) as a yellow solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of 3- (5-bromo-1H-indol-1-yl) -N, N-dimethylpropan-1-amine
- Step 2 Of N, N-dimethyl-3- [5- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) -1H-indol-1-yl] propan-1-amine Manufacturing
- Step 3 Preparation of N, N-dimethyl-3- [5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) -1H-indol-1-yl] propan-1-amine
- Step 4 Preparation of 5- ⁇ 1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl ⁇ thiophen-2-amine
- Step 5 N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ -2,2,2- Preparation of trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 6 N- (5- ⁇ 1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide
- -trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide the title compound (3 step yield: 39%) was obtained as a gray solid in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
- Step 1 Preparation of tert-butyl [1-( ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl] carbamate
- Example 1 Step 1 of Example 1 with 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine and 2-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl) amino] -3-phenylpropanoic acid. In the same manner as above, the title compound (crude) was obtained.
- Step 2 Preparation of 2-amino-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -3-phenylpropanamide
- Step 3 Preparation of N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropanamide Examples using 2-amino-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -3-phenylpropanamide and 1-methyl-4-piperidone In the same manner as in Step 1 of 5, the title compound (52%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous.
- Example 32 N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -1- (1-methylpiperidine-4- Yl) Preparation of pyrrolidine-3-carboxamide 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 1- (1-methylpiperidine- The title compound (4%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using 4-yl) pyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acid.
- Example 34 4-methyl-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1- Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] pentanamide
- Step 1 tert-butyl [4-methyl-1-( ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -1- Of Oxopentan-2-yl] carbamate
- Step 2 Preparation of 2-amino-4-methyl-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ pentanamide
- Step 3 4-methyl-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- Preparation of 4-yl) amino] pentanamide 2-amino-4-methyl-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Using 2-yl ⁇ pentanamide and 4-methyl-1-piperidone, the title compound (3%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5.
- Step 1 tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5- ⁇ 3- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] ureido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
- Step 2 Preparation of 1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- ⁇ 5- [4- [1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ urea tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- ⁇ 3- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] ureido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (58 mg, 0.1 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (2 mL), and TFA (2 mL) was added under ice cooling, followed by stirring for 1 hour.
- Example 36 4-methoxy-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1- Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] butanamide
- Step 1 (9H-Fluoren-9-yl) methyl [4-methoxy-1-( ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2- Yil ⁇ amino) -1-oxobutan-2-yl] carbamate
- Step 2 Preparation of 2-amino-4-methoxy-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ butanamide
- Step 3 4-methoxy-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- Preparation of 4-yl) amino] butanamide 2-amino-4-methoxy-N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 The title compound (10%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using -yl ⁇ butanamide.
- Step 1 Preparation of 1- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -4-methylpiperazine
- Step 3 Preparation of 5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine
- Step 4 N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2- Preparation of trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 5 Of N- ⁇ 5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Production N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2 Using -trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide, the title compound (75%) was obtained as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
- Step 2 Preparation of 5- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile
- Step 3 N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [3-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro Preparation of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 4 Preparation of N- ⁇ 5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N -[2-( ⁇ 5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro- The title compound (86%) was obtained as a pale-yellow crystalline powder in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 using N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide.
- Step 1 Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzamide
- Step 2 Preparation of 5- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide
- Step 3 2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- ⁇ 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido ⁇ thiophene-2 -Il) Production of benzamide
- Step 4 Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- ⁇ 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) benzamide
- 2- (4- Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- ⁇ 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) benzamide
- Step 1 tert-Butyl 4- ⁇ 4- [5- (3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl ⁇ -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
- Step 2 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇
- the title compound (93%) was obtained as a pale gray solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using -1 (2H) -carboxylate.
- Example 41 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl
- thiophen-2-yl ⁇ propanamide 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4] -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ propanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (58%) as a yellow solid.
- Example 42 Benzyl 2- [4- (4- ⁇ 5- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine
- -1 (2H) -yl] acetate 3-([1,4'-bipiperidin] -1'-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4 -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ propanamide and benzyl chloroacetate were used in the same manner as in Example 23 to obtain the title compound (77%) as a pale yellow solid.
- Example 43 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-isopropyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl
- Preparation of thiophen-2-yl ⁇ propanamide 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4] -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ propanamide and acetone were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (5%) as a pale yellow solid.
- Step 1 tert-Butyl 4- ⁇ 4- [5- (2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl ⁇ -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
- Step 2 2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ Production of acetamide
- Step 3 2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-
- the title compound (2 step yield: 85%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide and formaldehyde.
- Step 1 tert-Butyl 4- ⁇ 4- [5- (4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) butanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl ⁇ -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
- Step 2 4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ Production of butanamide
- Step 3 4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-
- 2-yl ⁇ butanamide 4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl
- the title compound (2 step yield: 54%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using thiophen-2-yl ⁇ butanamide and formaldehyde.
- Step 1 tert-Butyl 4- ⁇ 4- [5- (5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) pentanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl ⁇ -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
- Step 2 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ Production of pentanamide
- Step 3 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-
- 2-yl ⁇ pentanamide 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ pentanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 52%) as a yellow solid.
- Step 1 tert-Butyl 4- ⁇ 4- [5- (6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) hexanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl ⁇ -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
- Step 2 6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ Hexanamide production
- Step 3 6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-
- 2-yl ⁇ hexaneamide 6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ hexanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 79%) as a yellow solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of 5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -2- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzonitrile
- Step 3 N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [2-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro Preparation of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 4 Preparation of N- ⁇ 5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N -[2-( ⁇ 5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro- Using N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide, the title compound (81%) was obtained as a yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
- Step 1 Production of 4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol
- Step 2 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- ⁇ 2- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] ethyl ⁇ piperazine
- Step 3 Preparation of 5- ⁇ 4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-amine
- Step 4 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 5 Preparation of N- (5- ⁇ 4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (3 steps, yield 16%) as a yellow amorphous substance.
- Step 1 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- ⁇ 4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] butyl ⁇ piperazine
- Step 2 Preparation of 5- ⁇ 4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-amine
- Step 3 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 4 Preparation of N- (5- ⁇ 4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (3 step yield: 13%) as a yellow amorphous.
- Step 1 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- ⁇ 5- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] pentyl ⁇ piperazine
- Step 2 Preparation of 5- (4- ⁇ [5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy ⁇ phenyl) thiophen-2-amine
- Step 4 N- [5- (4- ⁇ [5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy ⁇ phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino]
- Amino ⁇ -2-oxoethyl) -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to give the title compound (3 step yield 14%) as a yellow amorphous substance. Obtained.
- Step 1 tert-butyl 4- (4- ⁇ 5- [2-( ⁇ [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] methyl ⁇ amino) acetamido] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ phenyl) -5,6- Preparation of dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate
- Step 2 tert-butyl 4- (4- ⁇ 5- [2- (N- ⁇ [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] methyl ⁇ -2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido) acetamido] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl ⁇ phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate
- Step 3 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-oxo-2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino ) Ethyl] -N- (piperidin-4-ylmethyl) acetamide
- Step 4 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino ) -2-Oxoethyl] -N-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methyl] acetamide
- Step 5 N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2- ⁇ [(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Preparation of methyl] amino ⁇ acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] ] Thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl] -N-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methyl] acetamide in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9, the title compound (84 %) As a pale yellow solid.
- Step 2 Preparation of 5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-amine
- Step 3 Preparation of N- (5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide 5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and pyrrolidine were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40 to obtain the title compound (15 %) As a tan solid.
- Example 54 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- (5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophene-2- Yl) Preparation of pentanamide Using 5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and 1,4′-bipiperidine The title compound (12%) was obtained as a brown amorphous product in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40.
- Example 55 Preparation of N- (5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -5- (piperidin-1-yl) pentanamide 5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and piperidine were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40 to obtain the title. The compound (15%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
- Step 1 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
- Step 2 Preparation of N- (5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- ⁇ 2-[(5- ⁇ 4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl ⁇ -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 4%).
- Step 1 tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5- ⁇ [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -1H-pyrazol-1-yl] piperidine 1-carboxylate production
- Step 2 N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] thiophene-2
- carboxamide tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- ⁇ [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl ⁇ thiophen-2-yl) -1H-pyrazole-1 -Il] piperidine-1-carboxylate (98 mg, 0.17 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (2 mL), TFA (0.5 mL) was added and stirred for 0.5 h, the reaction mixture was concentrated, and the residue was Obtained.
- Example 58 6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ nicotine Preparation of Amides Using 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] nicotinic acid In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1, the title compound (46%) was obtained as a yellow solid.
- Example 59 N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -4- (4-methylpiperazine-1- Yl) Preparation of benzamide 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) The title compound (4%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1 using benzoic acid.
- Step 1 Preparation of methyl 4- ⁇ [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl ⁇ benzoate
- Step 2 Preparation of 4- ⁇ [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl ⁇ benzoic acid
- Step 3 N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -4- ⁇ [N- (1-methylpiperidine-4 -Il) -2-Nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl ⁇ benzamide
- Step 4 N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -4- ⁇ [(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Preparation of amino] methyl ⁇ benzamide N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -4- ⁇ [N -(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl ⁇ benzamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2 to give the title compound (2 step yield: 11%) as an orange solid. Got as.
- Step 1 Preparation of methyl 2- ⁇ 6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl ⁇ acetate
- Step 2 Production of 2- ⁇ 6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl ⁇ acetic acid
- Step 3 tert-butyl 4- ⁇ 4- [5- (2- ⁇ 6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl ⁇ acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl ⁇ -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
- Step 4 2- ⁇ 6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl ⁇ -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ Production of Acetamide tert-Butyl 4- ⁇ 4- [5- (2- ⁇ 6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl ⁇ acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl ⁇ -5,6-dihydropyridine The title compound (2 step yield: 24%) was obtained as an orange solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using -1 (2H) -carboxylate.
- Example 62 2- ⁇ 6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl ⁇ -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Preparation of phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide 2- ⁇ 6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl ⁇ -N- ⁇ 5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine- 4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ acetamide and formaldehyde were used as in Step 1 of Example 5 to give the title compound (71%) as an orange solid.
- Step 1 Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) pyridin-2-yl] piperazine
- Step 2 Preparation of 5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-amine
- Step 4 Production of N- ⁇ 5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2 , 2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-( ⁇ 5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl ⁇ amino) -2-oxoethyl]- The title compound (quantitative) was obtained as a pale brown solid in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 using N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide.
- TLR9 activation inhibition test using TLR9-expressing reporter cells 1) Establishment of TLR9-expressing reporter cells Human TLR9-expressing cells are cells obtained by expressing human TLR9 in human fetal kidney cell line, Invivogen. (HTLR9 / 293xL). hTLR9 / 293xL was subcultured using Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM (sigma)) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin. PGL4.28 (Promega) in which a firefly luciferase gene was linked to the NF ⁇ B recognition sequence four times was introduced by lipofection using Fugene6 (Roche).
- DMEM Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium
- Hygromycin and blasticidin resistant cell clones were selected and used as TLR9 expression reporter cells (hTLR9 NF ⁇ B-luc / 293xL). 2) TLR9 plated at activation inhibition test hTLR9 NF ⁇ B-luc / 96 well-white 293xL microtiter plate 1.0 ⁇ 10 4 / 80 ⁇ L, 37 °C in CO 2 incubator, and cultured overnight. A test compound (10 ⁇ L) diluted with DMEM was added to a final concentration of 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1 ⁇ M. One hour later, CpG-B DNA (ODN2006) (Invivogen) as a TLR9 ligand was added to a final concentration of 1 ⁇ M (10 ⁇ L).
- Luciferase activity was measured as TLR9 activity after incubation in a CO 2 incubator for a total of 100 ⁇ L for 4 hours. Luciferase activity was measured by adding 60 ⁇ L of Bright Glo (Promega) and measuring the amount of luminescence with a multi-microplate reader ARVO (Perkin Elmer). The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC 50 value) of each test compound was calculated with the luciferase activity when no test compound was added as 100%.
- TLR7 activation inhibition test using TLR7-expressing reporter cells 1) Establishment of TLR7-expressing reporter cells Human TLR7-expressing cells were obtained by expressing cells expressing human TLR7 in human fetal kidney cell line, Invivogen. (HTLR7 / 293xL). hTLR7 / 293xL was subcultured using Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM (sigma)) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin. PGL4.28 (Promega) in which a firefly luciferase gene was linked to the NF ⁇ B recognition sequence four times was introduced by lipofection using Fugene6 (Roche).
- DMEM Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium
- Hygromycin and blasticidin resistant cell clones were selected and used as TLR7 expression reporter cells (hTLR7 NF ⁇ B-luc / 293 ⁇ L). 2) The TLR7 activation Inhibition Test hTLR7 NF ⁇ B-luc / 293xL plated at 1.0 ⁇ 10 4 / 80 ⁇ L in a 96 well white microtiter plate, 37 ° C. in a CO 2 incubator, and cultured overnight. A test compound (10 ⁇ L) diluted with DMEM was added to a final concentration of 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 ⁇ M. One hour later, Imiquimod (Invivogen), a TLR7 ligand, was added to a final concentration of 10 ⁇ M (10 ⁇ L).
- Luciferase activity was measured as TLR7 activity after incubation in a CO 2 incubator for a total of 100 ⁇ L for 4 hours. Luciferase activity was measured by adding 60 ⁇ L of Bright Glo (Promega) and measuring the amount of luminescence with a multi-microplate reader ARVO (Perkin Elmer). The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC 50 value) of each test compound was calculated with the luciferase activity when no test compound was added as 100%. 3) Results Table 2 shows the activity values (IC 50 values) of the compounds obtained in the above examples.
- the compound of the present invention has a strong TLR7 and 9 inhibitory action. Therefore, the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention is used as a TLR7 and 9 inhibitor as a disease associated with activation of TLR7 and 9 signals such as RA, SLE, SS, MS, IBD, psoriasis. It has been found to be useful as an active ingredient for preventive and therapeutic agents for autoimmune diseases such as osteoarthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection and GvHD.
- autoimmune diseases such as osteoarthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection and GvHD.
- mice Male DBA / 1J mice (Nippon Charles River Co., Ltd.) were used. The body weight of 7-week-old DBA / 1J mice was measured, and grouping was performed using a single-block blocking assignment using this as an index.
- the group composition was the control group (administration medium (0.5% hydroxymethylpropylcellulose aqueous solution) administration group), the compound of Example 5 administered with 25 mg / kg, and the compound of Example 5 administered with 50 mg / kg.
- test method A 0.2% type 2 collagen solution is prepared by mixing 0.3% type 2 collagen solution (collagen technical workshop) and physiological saline (Otsuka Pharmaceutical) in a ratio of 2: 1. did. Next, an equal amount of 0.2% type 2 collagen solution and Adjuvant Complete Freund (DIFCO) were mixed, and a first-sensitized emulsion was prepared with a handy microhomogenizer NS-310E (Microtech Nithion) under ice cooling. After shaving the ridges of the animals with clippers, 0.05 mL each of the first sensitizing emulsion was intradermally administered to the left and right sides of the ridges. After the first sensitization, the drug solution was orally administered once a day until 34 days after the first sensitization (14 days after the additional sensitization).
- DIFCO Adjuvant Complete Freund
- Additional sensitization was performed by the following procedure 20 days after the first sensitization.
- a 0.2% type 2 collagen solution was prepared by mixing 0.3% type 2 collagen solution and physiological saline at a ratio of 2: 1. Then, an equal amount of 0.2% type 2 collagen solution and Adjuvant Incomplete Freund (DIFCO) were mixed, and an additional sensitive emulsion was prepared with a handy microhomogenizer NS-310E under ice cooling. Additional sensitization was performed by administering 0.1 mL of the prepared additional sensitizing emulsion into the ridge skin to induce arthritis.
- DIFCO Adjuvant Incomplete Freund
- the primary endpoint, limb swelling, was determined by arthritis score by three judges in a blinded trial, 3 times in total: initial assessment 7 days after additional sensitization, intermediate assessment 10 days later, and final assessment 14 days later.
- the arthritis score was determined.
- As the evaluation criteria for swelling the following four criteria were applied to each limb, and the total of the limbs was used as the individual arthritis score.
- plasma anti-type 2 collagen IgG antibody titer was measured by ELISA using an orbital blood sample 15 days after additional sensitization.
- FIG. 6 is a graph showing changes over time in arthritis scores of a mouse collagen-induced arthritis model in a control group (drug non-administration group) and the compound of Example 5 in a 25 mg / kg administration group and a 50 mg / kg administration group.
- the control group an increase in the arthritis score was observed after 7 days from the additional sensitization.
- the administration group of the compound of Example 5 showed a significant inhibitory effect suggesting dose dependency at a dose of 50 mg / kg.
- ** indicates that the risk rate is less than 1% (p ⁇ 0.01) in Steel's multiple comparison test using the control group as a comparison control.
- FIG. 2 shows the average value of anti-type 2 collagen IgG antibody titer 15 days after the additional sensitization.
- FIG. 2 In contrast to the control group, the 25 and 50 mg / kg administration groups of the compound of Example 5 showed a significant inhibitory effect suggesting dose dependency.
- * and ** indicate a risk rate of less than 5% (p ⁇ 0.05) and less than 1% (p ⁇ 0.01), respectively, in Steel's multiple comparison test using the control group as a comparison control. Indicates that
- the compound of Example 5 is effective as a therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis.
- the present invention for the first time finds that the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof has an excellent TLR3, 7 and / or 9 inhibitory action, and autoimmunity.
- the present invention provides a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy due to disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis.
- the present invention provides a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy caused by autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis, and is useful in the pharmaceutical industry. Has industrial applicability.
Abstract
Provided is a novel compound that inhibits at least one selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7, and TLR9 and has excellent preventive and therapeutic activity against autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, and the like. The present invention is a compound represented by the following general formula (1):
[where X is an optionally substituted carbocycle or heterocycle optionally formed via alkylene or alkenylene groups; ring Y is an optionally substituted carbocycle or heterocycle; R2 and R3 are the same or different and are a hydrogen atom, C1-6 alkyl group or C1-6 alkyloxy group; Q1 is a bond or an optionally substituted C1-6 alkylene group or C2-6 alkenylene group; R1 is a bond, oxygen atom, or optionally substituted NH group; and the combination of q, m, and n is (q, m, n) = (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 1), (1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1) or (1, 1, 1)]; or a salt thereof or solvate of the same.
Description
本発明はToll様受容体(Toll-like receptor;TLR)阻害作用を有し、TLR下流のシグナルの阻害に起因する疾患、例えば関節リウマチ(RA)、全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)、シェーグレン症候群(SS)、多発性硬化症(MS)、炎症性腸疾患(IBD)、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎等の自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症に起因する心筋症の予防及び/又は治療剤として有用な新規化合物に関する。
The present invention has a Toll-like receptor (TLR) inhibitory action, and diseases caused by inhibition of signals downstream of TLR, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS) ), Multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis and other autoimmune diseases, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) Or a novel compound useful as an agent for preventing and / or treating cardiomyopathy caused by sepsis.
病原体が生体に侵入すると、免疫系はそれらの病原体をすみやかに識別し排除する。哺乳類では免疫系は大きく自然免疫と獲得免疫に分けることができる。獲得免疫では、遺伝子再構成という方法で無数の個々に異なる抗原特異性を有する受容体がT細胞やB細胞表面に発現され、あらゆる未知の外来抗原に対処する(非特許文献1)。
When pathogens enter the body, the immune system immediately identifies and eliminates them. In mammals, the immune system can be broadly divided into innate immunity and acquired immunity. In acquired immunity, a myriad of receptors having different antigen specificities are expressed on the surface of T cells and B cells by a method called gene rearrangement, and deal with any unknown foreign antigen (Non-patent Document 1).
一方で、マクロファージや樹状細胞等によって担われる自然免疫系は非特異的な免疫応答で微生物の排除が行われると考えられていたが、TLRの発見や樹状細胞を中心とした諸研究の急速な進展により、適応免疫系における抗原認識ほどの親和性や特異性は高くない、特徴的な微生物認識機構が存在していることが明らかになってきた(非特許文献2)。とくにTLRに代表される細胞内にシグナルを伝達する核酸認識受容体は、感染をいち早く前線においてキャッチするという役割のみならず、その後、細胞内にシグナルを伝え、自然免疫系活性化のスイッチをオンにする重要な役割がある。その意味において、これまで知られていた自然免疫系の活性化によって誘導されるI型インターフェロン等のサイトカインやケモカイン、そして抗原提示に関与する分子群の遺伝子発現誘導と、その後の適応免疫系の活性化へと連携させて特異的な免疫応答発動へと導くという経路が明らかとなった(非特許文献2)。
On the other hand, the innate immune system carried by macrophages, dendritic cells, etc. was thought to eliminate microorganisms by nonspecific immune responses. With rapid progress, it has become clear that there is a characteristic microbial recognition mechanism that does not have as high affinity and specificity as antigen recognition in the adaptive immune system (Non-patent Document 2). In particular, nucleic acid recognition receptors that transmit signals into cells typified by TLR not only play a role in catching infection at the front line, but also transmit signals to cells and turn on the activation of the innate immune system. There is an important role to do. In that sense, induction of gene expression of cytokines and chemokines such as type I interferon and the group of molecules involved in antigen presentation induced by activation of the innate immune system known so far, and subsequent activity of the adaptive immune system It has become clear that the pathway leads to activation of specific immune responses by coordinating with the development (Non-patent Document 2).
TLRのうちTLR3はウイルス由来の二本鎖RNAを認識し、TLR7は同様にウイルス由来の一本鎖RNAを認識することが明らかとなっている。TLR9は細菌のCpG(シトシン・グアニン)DNAを認識して活性化される。CpG DNAは細菌のゲノムDNAの特徴的な配列でメチル化されてないCpG配列がある頻度で繰り返されている。哺乳類のゲノムDNAではCpG配列の頻度が少なく高頻度にメチル化されているため、免疫賦活作用はない(非特許文献3)。
Among the TLRs, TLR3 recognizes virus-derived double-stranded RNA, and TLR7 similarly recognizes virus-derived single-stranded RNA. TLR9 recognizes bacterial CpG (cytosine guanine) DNA and is activated. CpG DNA repeats at a certain frequency with a characteristic sequence of bacterial genomic DNA that is not methylated. In mammalian genomic DNA, the frequency of CpG sequences is low and methylated frequently, so there is no immunostimulatory effect (Non-patent Document 3).
これまでRNAやDNAセンサーとして報告されてきたTLR7、9に関しては多くの研究がなされ、その詳細がかなり明らかになってきている。TLR7、9はエンドソームやライソソームにおいて細胞外に存在するRNAやDNAを認識する受容体として機能し、I型インターフェロンや炎症性サイトカインの遺伝子発現を誘導する。この両者ともMyD88依存性のシグナル伝達経路を介するが、前者がIRAK1/IKKα-IRF-7が関与するのに対し、後者では、NF-κBやIRF-5やMAPキナーゼの経路が関与する。MyD88にはIRF-7やIRF-5の他に、IRF-1やIRF-4が会合することが知られているが(非特許文献4、5、6)、TLR9下流で関与するIRF転写因子の種類や役割は細胞の種類によって異なっている。
Much research has been done on TLRs 7 and 9 that have been reported as RNA and DNA sensors so far, and the details have become quite clear. TLRs 7 and 9 function as receptors that recognize extracellular RNA and DNA in endosomes and lysosomes, and induce gene expression of type I interferons and inflammatory cytokines. Both are mediated by a MyD88-dependent signal transduction pathway, whereas the former involves IRAK1 / IKKα-IRF-7, while the latter involves NF-κB, IRF-5 and MAP kinase pathways. MyD88 is known to associate with IRF-1 and IRF-4 in addition to IRF-7 and IRF-5 (Non-Patent Documents 4, 5, and 6), but IRF transcription factors involved downstream of TLR9 The type and role vary depending on the cell type.
上記に示したようにTLRはRNAやDNAをリガンドとして認識するが、正常な状態では自己核酸はリガンドとして認識されず、自然免疫を活性化しない。これは細胞死により放出された自己核酸は血清中のヌクレアーゼによりTLRにより認識される前に分解されるからである。またTLR3、7及び9の、細胞表面ではなく、エンドソームでの細胞内局在も、自己核酸を認識しない機構として考えられている。しかしながら、自己免疫反応や炎症が起こっている状況下ではこのような防御機構が破綻し、内在性のタンパク質と複合体を形成し、TLRシグナルを活性化することが考えられる(非特許文献7)。
As shown above, TLR recognizes RNA or DNA as a ligand, but under normal conditions, self-nucleic acid is not recognized as a ligand and does not activate innate immunity. This is because the self-nucleic acid released by cell death is degraded before being recognized by the TLR by a nuclease in the serum. The intracellular localization of TLR3, 7 and 9 not in the cell surface but in the endosome is also considered as a mechanism that does not recognize self-nucleic acids. However, under the circumstances where autoimmune reaction or inflammation occurs, it is considered that such a defense mechanism breaks down, forms a complex with an endogenous protein, and activates a TLR signal (Non-patent Document 7). .
これらのことからTLRを阻害することにより、関節リウマチ(RA)、全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)、シェーグレン症候群(SS)、多発性硬化症(MS)、炎症性腸疾患(IBD)、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎等の自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症に起因する心筋症を改善することが可能であると考えられる。以下に示すようにこれらのいくつかの疾患についてはTLRと具体的な関係が示されている。
By inhibiting TLR from these, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS), multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, It is considered possible to improve cardiomyopathy due to Behcet's syndrome, autoimmune diseases such as vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis. As shown below, these several diseases have a specific relationship with TLR.
関節リウマチ(RA)についてはTLR9阻害作用を有する核酸配列を用いて、TLR9を阻害することによりプリスタン誘導性ラット関節炎モデルにおいて発症と病態が抑制されたことが報告されている(非特許文献8)。また抗マラリア薬であるヒドロキシクロロキンはエンドソームの酸性化抑制によりTLR7及び9の阻害作用を有していることが知られ、日本を除くほとんどの国でRA及びSLEの治療薬として承認されている(非特許文献9)。
Regarding rheumatoid arthritis (RA), it has been reported that the onset and pathology of pristane-induced rat arthritis were suppressed by inhibiting TLR9 using a nucleic acid sequence having TLR9 inhibitory activity (Non-patent Document 8). . In addition, hydroxychloroquine, an antimalarial drug, is known to have an inhibitory action on TLR7 and 9 by suppressing acidification of endosomes, and is approved as a therapeutic drug for RA and SLE in most countries except Japan ( Non-patent document 9).
全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)についてはTLR9ノックアウトマウスにおいてSLE様の病体において見られる抗核抗体の減弱が報告されており(非特許文献10)、TLR9阻害作用を有する核酸を用いた実験においても同様の結果が報告されている(非特許文献11)。さらに同様の作用を有する低分子化合物についても報告されている(CPG52364:特許文献1)。
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has been reported to attenuate antinuclear antibodies observed in SLE-like disease in TLR9 knockout mice (Non-Patent Document 10). The same applies to experiments using nucleic acids having TLR9 inhibitory activity. Results have been reported (Non-patent Document 11). Furthermore, a low molecular weight compound having a similar action has also been reported (CPG 52364: Patent Document 1).
TLR7ノックアウトマウス(SLE様の症状を自然発症するMRL/lprマウス)においても尿中タンパク質の減少、血中IgGの減少等SLE様の症状の発症が抑制されることが知られている(非特許文献12、13)。さらに抑制性の核酸を投与することによりSLE様の症状の抑制も報告されている(非特許文献11)。これらの報告からはTLR7もSLEのターゲットとして非常に有用であることが推察される。マウスにおけるMSのモデルであるEAEモデルにおいては、TLR2及びTLR9ノックアウトマウスで病態の発症が弱いという報告があり、TLRの関与が示されている(非特許文献14)。
In TLR7 knockout mice (MRL / lpr mice that spontaneously develop SLE-like symptoms), it is known that the onset of SLE-like symptoms such as a decrease in protein in urine and a decrease in blood IgG is suppressed (non-patented) Reference 12, 13). Furthermore, suppression of SLE-like symptoms has also been reported by administering an inhibitory nucleic acid (Non-patent Document 11). From these reports, it is inferred that TLR7 is also very useful as a target of SLE. In the EAE model, which is a model of MS in mice, there is a report that TLR2 and TLR9 knockout mice have a weak pathological condition, and the involvement of TLR has been shown (Non-Patent Document 14).
シェーグレン症候群(SS)患者の唾液腺上皮細胞では、TLR3の活性化によるアポトーシスに感受性が高いという報告がなされており、TLRの関与が考えられる(非特許文献15)。
It has been reported that salivary gland epithelial cells of patients with Sjogren's syndrome (SS) are highly sensitive to apoptosis due to activation of TLR3, and TLR is considered to be involved (Non-patent Document 15).
炎症性腸疾患(IBD)等の腸炎では様々なTLRが炎症に関与していることがマウスの腸炎モデルを用いて示されており、TLR阻害により病体に抑制的に働く場合、TLRの活性化が病体に抑制的に働く場合が報告されており、一概に阻害作用のみが病態回復に機能するとは考えられないが、TLRとの関与は示されている(非特許文献16)。
In enteritis such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), it has been shown that various TLRs are involved in inflammation using a mouse enteritis model. When TLR inhibition acts on a diseased body, TLR activation Have been reported to act in a suppressive manner on the pathology, and it is generally not thought that only the inhibitory action functions to recover the pathological condition, but involvement with TLR has been shown (Non-patent Document 16).
リガンドであるCpG-B DNAにより産生される炎症性サイトカインにより、心筋細胞の収縮性が失われたとされる報告があり、TLR9ノックアウトマウスではその作用が減弱された(非特許文献17)。このようなことから敗血症に起因する心筋症に関与していると考えられる。
There has been a report that the contractility of cardiomyocytes has been lost by inflammatory cytokines produced by the ligand CpG-B DNA, and its action was attenuated in TLR9 knockout mice (Non-patent Document 17). It is thought that it is concerned with the cardiomyopathy resulting from sepsis from such a thing.
ヒドロキシクロロキンはTLR9阻害作用を有することが公知であり、すでに臨床でも使用されている薬剤であるが、TLR9阻害作用としてはそれほど強くなく、さらに強いTLR9阻害作用を有する薬剤により、より強力な薬効が期待できる。またヒドロキシクロロキンはクロロキン網膜症等の副作用の懸念があるが、異なる骨格の化合物により、このような副作用の懸念は払拭できる可能性も考えられる。
Hydroxychloroquine is known to have a TLR9 inhibitory action and is already used in clinical practice, but it is not so strong as a TLR9 inhibitory action, and a drug having a stronger TLR9 inhibitory action has a stronger drug effect. I can expect. Hydroxychloroquine has concerns about side effects such as chloroquine retinopathy, but it is also possible that compounds with different skeletons can eliminate such side effects.
したがって、強いTLR阻害作用を示し、経口投与可能な低分子性の薬剤が、今後の関節リウマチ(RA)、全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)、シェーグレン症候群(SS)、多発性硬化症(MS)、炎症性腸疾患(IBD)、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎等の自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症に起因する心筋症の治療において有用であると考えられる。
Therefore, low-molecular-weight drugs that exhibit strong TLR inhibitory action and can be administered orally are future rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS), multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammation In the treatment of cardiomyopathy caused by inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), autoimmune diseases such as psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis It is considered useful.
一方、チオフェン誘導体としては、中枢神経系疾患の治療薬(特許文献2)、癌治療薬(特許文献3、4、5)としての効果が知られている。また、p38MAPキナーゼ阻害剤(特許文献6)やプロスタグランジンE合成酵素阻害剤(特許文献7)、カルシウムチャネルモジュレータ(特許文献8)、マトリックスメタロプロテイナーゼ-12阻害剤(非特許文献18)、免疫細胞活性化の阻害剤(特許文献9)等、免疫アレルギー疾患治療薬としての効果も知られている。しかし、これらいずれの文献においても、TLR阻害作用に関連する記載や示唆はない。
On the other hand, as thiophene derivatives, effects as a therapeutic agent for central nervous system diseases (Patent Document 2) and a cancer therapeutic agent (Patent Documents 3, 4, and 5) are known. In addition, p38 MAP kinase inhibitor (Patent Document 6), prostaglandin E synthase inhibitor (Patent Document 7), calcium channel modulator (Patent Document 8), matrix metalloproteinase-12 inhibitor (Non-Patent Document 18), immunity An effect as a therapeutic agent for immune allergic diseases such as an inhibitor of cell activation (Patent Document 9) is also known. However, in any of these documents, there is no description or suggestion related to the TLR inhibitory action.
本発明の目的は、低分子性のTLR阻害作用を有する新規化合物を提供することにある。さらに詳細には、関節リウマチ(RA)、全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)、シェーグレン症候群(SS)、多発性硬化症(MS)、炎症性腸疾患(IBD)、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎等の自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症に起因する心筋症の予防及び/又は治療に有用な医薬を提供することにある。
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel compound having a low molecular TLR inhibitory action. More specifically, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS), multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, etc. It is to provide a medicament useful for the prevention and / or treatment of cardiomyopathy caused by autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis.
上記実情に鑑み、本発明者らは、鋭意TLR3、7及び/又は9阻害作用を持つ化合物を探索した結果、下記一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体が、内在的にヒトTLR3を発現しているヒト血管内皮細胞由来のECV304を用いた試験、ヒトTLR7を発現させたヒト胎児腎臓細胞由来のHEK293細胞を用いた試験、ヒトTLR9を発現させたヒト胎児腎臓細胞由来のHEK293細胞を用いた試験においてTLR阻害作用を有することを見出し、本発明を完成するに至った。
In view of the above situation, as a result of searching for compounds having an inhibitory action on TLR3, 7, and / or 9, the present inventors have found that the thiophene derivative represented by the following general formula (1) expresses human TLR3 internally. Test using ECV304 derived from human vascular endothelial cells, test using HEK293 cells derived from human fetal kidney cells expressing human TLR7, HEK293 cells derived from human fetal kidney cells expressing human TLR9 And found that it has a TLR inhibitory action, and has completed the present invention.
即ち、本発明は、以下に示す発明に関する。
[1]
式(1): That is, this invention relates to the invention shown below.
[1]
Formula (1):
[1]
式(1): That is, this invention relates to the invention shown below.
[1]
Formula (1):
[式中、
Xは、次の式(2): [Where:
X is the following formula (2):
Xは、次の式(2): [Where:
X is the following formula (2):
{式中、
環Aは、飽和又は不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、
環Bは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環A及び環Bはそれぞれ、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q2は、単結合、又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R4は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよい}
又は式(3): {Where,
Ring A represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring,
Ring B represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, ring A and ring B are each a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1. -5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, It may have 1 to 3 substituents selected from a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group,
Q 2 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group 1 to 2 substituents selected from a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
R 4 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 may have an alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups}
Or formula (3):
環Aは、飽和又は不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、
環Bは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環A及び環Bはそれぞれ、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q2は、単結合、又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R4は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよい}
又は式(3): {Where,
Ring A represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring,
Ring B represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, ring A and ring B are each a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1. -5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, It may have 1 to 3 substituents selected from a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group,
Q 2 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group 1 to 2 substituents selected from a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
R 4 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 may have an alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups}
Or formula (3):
{式中、
環Cは、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Cは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q3は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい}
を示し、
環Yは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基: {Where,
Ring C represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring C is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, or a C 1-6 alkyl Oxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group A substituent selected from a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, You may have 1 to 3
Q 3 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, oxo group, hydroxyl group,C 2 1 to 2 substituents selected from a 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group May}
Indicate
Ring Y represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, the ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, a carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group. Benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1- A 6 alkylamino group, a di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a group of formula (4):
環Cは、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Cは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q3は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい}
を示し、
環Yは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基: {Where,
Ring C represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring C is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, or a C 1-6 alkyl Oxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group A substituent selected from a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, You may have 1 to 3
Q 3 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, oxo group, hydroxyl group,
Indicate
Ring Y represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, the ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, a carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group. Benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1- A 6 alkylamino group, a di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a group of formula (4):
{式中、
Q4は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R5は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよく、
環Dは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい}
から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつ環Cが飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示す時、環Yは式(4)で示される置換基を有する飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
但し、環Yが式(4)で示される置換基を有し、かつ環Dが芳香族炭素環を示す時、環Yは飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつQ3がオキソ基を有するアルキレン基を示す時、環Yは飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、又は飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q1は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつQ3がオキソ基を有するC1-6アルキレン基を示す時、Q1はC1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記Q1におけるC1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R1は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよく、
R2及びR3は、互いに同一又は異なってもよく、水素原子、C1-6アルキル基又はC1-6アルキルオキシ基を示し、そして
q、m及びnの組み合わせが(q,m,n)=(0,1,0)、(0,0,1)、(0,1,1)、(1,1,0)、(1,0,1)又は(1,1,1)である]
で示される化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 {Where,
Q 4 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, C 1 to 2 substituents selected from a 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group You can,
R 5 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, may have a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups,
Ring D represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group. Benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1- 1 to 3 substituents selected from a 6 alkylamino group and a di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group}
1 to 3 substituents selected from:
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and the ring C represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, the ring Y represents a saturated or unsaturated fat having a substituent represented by the formula (4). An aromatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Provided that when ring Y has a substituent represented by formula (4) and ring D represents an aromatic carbocycle, ring Y is a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing An aliphatic heterocycle or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle;
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and Q 3 represents an alkylene group having an oxo group, the ring Y is a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, or a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring. Wherein the ring Y is a halogen atom, C 1-6 alkyl group, hydroxyl group, C 1-6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1- 5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di May have 1 to 3 substituents selected from a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a group of formula (4);
Q 1 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, C 1 1 to 2 substituents selected from a 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group You can,
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and Q 3 represents a C 1-6 alkylene group having an oxo group, Q 1 represents a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, where The C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group in Q 1 is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1 It may have 1 or 2 substituents selected from a -6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
R 1 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, may have a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups,
R 2 and R 3 may be the same or different from each other, each represents a hydrogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group or a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, and the combination of q, m and n is (q, m, n ) = (0,1,0), (0,0,1), (0,1,1), (1,1,0), (1,0,1) or (1,1,1) is there]
Or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
Q4は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R5は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよく、
環Dは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい}
から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつ環Cが飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示す時、環Yは式(4)で示される置換基を有する飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
但し、環Yが式(4)で示される置換基を有し、かつ環Dが芳香族炭素環を示す時、環Yは飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつQ3がオキソ基を有するアルキレン基を示す時、環Yは飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、又は飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q1は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつQ3がオキソ基を有するC1-6アルキレン基を示す時、Q1はC1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記Q1におけるC1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R1は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよく、
R2及びR3は、互いに同一又は異なってもよく、水素原子、C1-6アルキル基又はC1-6アルキルオキシ基を示し、そして
q、m及びnの組み合わせが(q,m,n)=(0,1,0)、(0,0,1)、(0,1,1)、(1,1,0)、(1,0,1)又は(1,1,1)である]
で示される化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 {Where,
Q 4 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, C 1 to 2 substituents selected from a 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group You can,
R 5 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, may have a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups,
Ring D represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group. Benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1- 1 to 3 substituents selected from a 6 alkylamino group and a di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group}
1 to 3 substituents selected from:
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and the ring C represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, the ring Y represents a saturated or unsaturated fat having a substituent represented by the formula (4). An aromatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Provided that when ring Y has a substituent represented by formula (4) and ring D represents an aromatic carbocycle, ring Y is a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing An aliphatic heterocycle or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle;
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and Q 3 represents an alkylene group having an oxo group, the ring Y is a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, or a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring. Wherein the ring Y is a halogen atom, C 1-6 alkyl group, hydroxyl group, C 1-6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1- 5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di May have 1 to 3 substituents selected from a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a group of formula (4);
Q 1 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, C 1 1 to 2 substituents selected from a 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group You can,
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and Q 3 represents a C 1-6 alkylene group having an oxo group, Q 1 represents a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, where The C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group in Q 1 is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1 It may have 1 or 2 substituents selected from a -6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
R 1 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, may have a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups,
R 2 and R 3 may be the same or different from each other, each represents a hydrogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group or a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, and the combination of q, m and n is (q, m, n ) = (0,1,0), (0,0,1), (0,1,1), (1,1,0), (1,0,1) or (1,1,1) is there]
Or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[2]
Xが式(2)を示し、
ここで環Bは、芳香族炭素環、飽和の脂肪族炭素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Bは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[1]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [2]
X represents formula (2),
Here, ring B represents an aromatic carbocycle, a saturated aliphatic carbocycle, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring B is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1- 6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 Substitution selected from alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have 1 to 3 groups,
The compound according to the above [1], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
Xが式(2)を示し、
ここで環Bは、芳香族炭素環、飽和の脂肪族炭素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Bは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[1]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [2]
X represents formula (2),
Here, ring B represents an aromatic carbocycle, a saturated aliphatic carbocycle, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring B is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1- 6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 Substitution selected from alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have 1 to 3 groups,
The compound according to the above [1], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[3]
Xが式(2)を示し、
ここで環Aは、ピロリジン環、ピペリジン環、ピペラジン環又はテトラヒドロピリジン環を示し、
環Bは、ベンゼン環、シクロヘキサン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環又はチアジアゾール環を示し、
ここで前記環A及び環Bはそれぞれ、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[2]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [3]
X represents formula (2),
Here, ring A represents a pyrrolidine ring, a piperidine ring, a piperazine ring or a tetrahydropyridine ring,
Ring B is a benzene ring, cyclohexane ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadiazole ring or Showing the thiadiazole ring,
Here, ring A and ring B are each a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1. -5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, 1 to 3 substituents selected from a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group may be present,
The compound according to [2] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
Xが式(2)を示し、
ここで環Aは、ピロリジン環、ピペリジン環、ピペラジン環又はテトラヒドロピリジン環を示し、
環Bは、ベンゼン環、シクロヘキサン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環又はチアジアゾール環を示し、
ここで前記環A及び環Bはそれぞれ、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[2]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [3]
X represents formula (2),
Here, ring A represents a pyrrolidine ring, a piperidine ring, a piperazine ring or a tetrahydropyridine ring,
Ring B is a benzene ring, cyclohexane ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadiazole ring or Showing the thiadiazole ring,
Here, ring A and ring B are each a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1. -5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, 1 to 3 substituents selected from a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group may be present,
The compound according to [2] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[4]
Xが式(3)を示し、
ここで環Cは、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Cは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q3は、単結合又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい、
上記[1]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [4]
X represents formula (3),
Here, ring C represents a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring C is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy Group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, A substituent selected from a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group; You may have up to 3
Q 3 represents a single bond or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups may have 1 to 2,
The compound according to the above [1], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
Xが式(3)を示し、
ここで環Cは、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Cは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q3は、単結合又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい、
上記[1]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [4]
X represents formula (3),
Here, ring C represents a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring C is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy Group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, A substituent selected from a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group; You may have up to 3
Q 3 represents a single bond or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups may have 1 to 2,
The compound according to the above [1], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[5]
Q1が、単結合又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい、
上記[1]~[4]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [5]
Q 1 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups may have 1 to 2,
The compound according to any one of [1] to [4] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
Q1が、単結合又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい、
上記[1]~[4]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [5]
Q 1 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups may have 1 to 2,
The compound according to any one of [1] to [4] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[6]
環Yが、芳香族炭素環、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[1]~[5]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [6]
Ring Y represents an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring, wherein said ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1- 6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 An alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a formula ( 1 to 3 substituents selected from the group 4) may be included.
The compound according to any one of [1] to [5] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
環Yが、芳香族炭素環、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[1]~[5]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [6]
Ring Y represents an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring, wherein said ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1- 6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 An alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a formula ( 1 to 3 substituents selected from the group 4) may be included.
The compound according to any one of [1] to [5] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[7]
環Yが、ベンゼン環、ピペリジン環、ピロリジン環、ピペラジン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環又はチアジアゾール環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[6]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [7]
Ring Y is a benzene ring, piperidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperazine ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring Represents an oxadiazole ring or a thiadiazole ring, wherein the ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group Cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkyl Mino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a substituent selected from the group may have 1 to 3 of formula (4),
The compound according to [6] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
環Yが、ベンゼン環、ピペリジン環、ピロリジン環、ピペラジン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環又はチアジアゾール環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[6]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [7]
Ring Y is a benzene ring, piperidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperazine ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring Represents an oxadiazole ring or a thiadiazole ring, wherein the ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group Cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkyl Mino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a substituent selected from the group may have 1 to 3 of formula (4),
The compound according to [6] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[8]
環Yが式(4)で示される置換基を有し、
ここで環Dは、飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、又は飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q4は、単結合又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R5は、単結合又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよい、
上記[1]~[7]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [8]
Ring Y has a substituent represented by formula (4),
Here, ring D represents a saturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, aromatic carbocyclic ring or saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, wherein the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1-6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1 -5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have 1 to 3 substituents,
Q 4 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 can have one or two substituents selected from alkyl groups,
R 5 represents a single bond or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1- May have a substituent selected from a 3 alkylsulfonyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
The compound according to any one of [1] to [7] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
環Yが式(4)で示される置換基を有し、
ここで環Dは、飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、又は飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q4は、単結合又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R5は、単結合又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよい、
上記[1]~[7]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [8]
Ring Y has a substituent represented by formula (4),
Here, ring D represents a saturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, aromatic carbocyclic ring or saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, wherein the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1-6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1 -5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have 1 to 3 substituents,
Q 4 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 can have one or two substituents selected from alkyl groups,
R 5 represents a single bond or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1- May have a substituent selected from a 3 alkylsulfonyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
The compound according to any one of [1] to [7] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[9]
前記環Dが、シクロヘキサン環、ベンゼン環、ピロリジン環、ピペリジン環又はピペラジン環を示し、ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[8]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [9]
The ring D represents a cyclohexane ring, a benzene ring, a pyrrolidine ring, a piperidine ring or a piperazine ring, wherein the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1- 1 to 3 substituents selected from 3- alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have,
The compound according to [8] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
前記環Dが、シクロヘキサン環、ベンゼン環、ピロリジン環、ピペリジン環又はピペラジン環を示し、ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
上記[8]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [9]
The ring D represents a cyclohexane ring, a benzene ring, a pyrrolidine ring, a piperidine ring or a piperazine ring, wherein the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1- 1 to 3 substituents selected from 3- alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have,
The compound according to [8] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[10]
q、m及びnの組み合わせが(q,m,n)=(0,1,0)、(0,0,1)、又は(1,1,1)である、上記[1]~[9]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [10]
[1] to [9], wherein the combination of q, m, and n is (q, m, n) = (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1), or (1, 1, 1). Or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
q、m及びnの組み合わせが(q,m,n)=(0,1,0)、(0,0,1)、又は(1,1,1)である、上記[1]~[9]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [10]
[1] to [9], wherein the combination of q, m, and n is (q, m, n) = (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1), or (1, 1, 1). Or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
[11]
一般式(1)で示される化合物が、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例1)、
2-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例2)、
N-{3-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例3)、
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例4)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例5)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセトアミド(実施例6)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例7)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例8)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例9)、
(E)-N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-3-オキソプロパ-1-エン-1-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例10)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-4-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例11)、
N-[3-([1,4’ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-3-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例12)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(ピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例13)、
N-{3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル}-3-メトキシ-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例14)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例15)、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例16)、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アセトアミド(実施例17)、
2-[4-(ジメチルアミノ)ピペリジン-1-イル]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例18)、
(R)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例19)、
(S)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例20)、
2-[(5-ヒドロキシペンチル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例21)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例22)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-(4-{4-[6-(メチルアミノ)-6-オキソヘキシル]ピペラジン-1-イル}フェニル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例23)、
ベンジル 6-{4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサノエート(実施例24)、
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミド(実施例25)、
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミド(実施例26)、
N-(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例27)、
2-[(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例28)、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミド(実施例29)、
N-(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例30)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパンアミド(実施例31)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-3-カルボキサミド(実施例32)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチルスルホンアミド]アセトアミド(実施例33)、
4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ペンタンアミド(実施例34)、
1-(ピペリジン-4-イル)-3-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ウレア(実施例35)、
4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ブタンアミド(実施例36)、
N-{5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例37)、
N-{5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例38)、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミド(実施例39)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例40)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例41)、
ベンジル 2-[4-(4-{5-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-イル]アセテート(実施例42)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-イソプロピル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例43)、
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例44)、
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミド(実施例45)、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミド(実施例46)、
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミド(実施例47)、
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例48)、
N-(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例49)、
N-(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例50)、
N-[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例51)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アミノ}アセトアミド(実施例52)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピロリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例53)、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例54)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピペリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例55)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例56)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-4-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例57)、
6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ニコチンアミド(実施例58)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミド (実施例59)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンズアミド(実施例60)、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例61)、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例62)及び、
N-{5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例63)
からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1つの化合物である、上記[1]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [11]
The compound represented by the general formula (1) is
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 1) ,
2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 2),
N- {3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 3),
5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 4),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 5),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide (Example 6),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 7),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 8) ,
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 9),
(E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop-1-ene -1-yl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 10),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide ( Example 11),
N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide Example 12),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 13),
N- {3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl} -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide ( Example 14),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Amino] acetamide (Example 15),
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 16),
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) acetamide (Example 17 ),
2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 18),
(R) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Example 19),
(S) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Example 20),
2-[(5-hydroxypentyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide ( Example 21),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 22),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- (4- {4- [6- (methylamino) -6-oxohexyl] piperazin-1-yl} Phenyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 23),
Benzyl 6- {4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanoate (Example 24),
1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide (Example 25),
N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide ( Example 26),
N- (5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 27),
2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide ( Example 28),
2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide Example 29),
N- (5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ( Example 30),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropanamide Example 31),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine -3-carboxamide (Example 32),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methylsulfonamido] acetamide (Examples) 33),
4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] pentanamide (Example 34),
1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} urea (Example 35),
4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] butanamide (Example 36),
N- {5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ( Example 37),
N- {5- [3-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 38),
2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide (Example 39),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Propanamide (Example 40),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide (Example 41),
Benzyl 2- [4- (4- {5- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 ( 2H) -yl] acetate (Example 42),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-isopropyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide (Example 43),
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} acetamide (Example 44),
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} butanamide (Example 45),
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} pentanamide (Example 46),
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} hexanamide (Example 47),
N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 48),
N- (5- {4- [2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 49),
N- (5- {4- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 50),
N- [5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Acetamide (Example 51),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Methyl] amino} acetamide (Example 52),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide (Example 53),
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) pentane An amide (Example 54),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (piperidin-1-yl) pentanamide (Example 55),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 56),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] thiophene-2 Carboxamide (Example 57),
6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} nicotinamide Example 58),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide (Example 59),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Amino] methyl} benzamide (Example 60),
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Acetamide (Example 61),
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene -2-yl} acetamide (Example 62) and
N- {5- [6- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 63)
The compound according to the above [1], a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof, which is at least one compound selected from the group consisting of:
一般式(1)で示される化合物が、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例1)、
2-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例2)、
N-{3-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例3)、
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例4)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例5)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセトアミド(実施例6)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例7)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例8)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例9)、
(E)-N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-3-オキソプロパ-1-エン-1-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例10)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-4-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例11)、
N-[3-([1,4’ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-3-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例12)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(ピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例13)、
N-{3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル}-3-メトキシ-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例14)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例15)、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例16)、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アセトアミド(実施例17)、
2-[4-(ジメチルアミノ)ピペリジン-1-イル]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例18)、
(R)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例19)、
(S)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例20)、
2-[(5-ヒドロキシペンチル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例21)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例22)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-(4-{4-[6-(メチルアミノ)-6-オキソヘキシル]ピペラジン-1-イル}フェニル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例23)、
ベンジル 6-{4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサノエート(実施例24)、
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミド(実施例25)、
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミド(実施例26)、
N-(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例27)、
2-[(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例28)、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミド(実施例29)、
N-(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例30)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパンアミド(実施例31)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-3-カルボキサミド(実施例32)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチルスルホンアミド]アセトアミド(実施例33)、
4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ペンタンアミド(実施例34)、
1-(ピペリジン-4-イル)-3-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ウレア(実施例35)、
4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ブタンアミド(実施例36)、
N-{5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例37)、
N-{5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例38)、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミド(実施例39)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例40)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例41)、
ベンジル 2-[4-(4-{5-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-イル]アセテート(実施例42)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-イソプロピル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例43)、
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例44)、
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミド(実施例45)、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミド(実施例46)、
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミド(実施例47)、
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例48)、
N-(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例49)、
N-(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例50)、
N-[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例51)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アミノ}アセトアミド(実施例52)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピロリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例53)、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例54)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピペリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例55)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例56)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-4-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例57)、
6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ニコチンアミド(実施例58)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミド (実施例59)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンズアミド(実施例60)、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例61)、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例62)及び、
N-{5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例63)
からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1つの化合物である、上記[1]に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 [11]
The compound represented by the general formula (1) is
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 1) ,
2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 2),
N- {3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 3),
5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 4),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 5),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide (Example 6),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 7),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 8) ,
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 9),
(E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop-1-ene -1-yl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 10),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide ( Example 11),
N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide Example 12),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 13),
N- {3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl} -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide ( Example 14),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Amino] acetamide (Example 15),
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 16),
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) acetamide (Example 17 ),
2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 18),
(R) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Example 19),
(S) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Example 20),
2-[(5-hydroxypentyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide ( Example 21),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 22),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- (4- {4- [6- (methylamino) -6-oxohexyl] piperazin-1-yl} Phenyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 23),
Benzyl 6- {4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanoate (Example 24),
1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide (Example 25),
N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide ( Example 26),
N- (5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 27),
2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide ( Example 28),
2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide Example 29),
N- (5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ( Example 30),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropanamide Example 31),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine -3-carboxamide (Example 32),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methylsulfonamido] acetamide (Examples) 33),
4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] pentanamide (Example 34),
1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} urea (Example 35),
4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] butanamide (Example 36),
N- {5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ( Example 37),
N- {5- [3-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 38),
2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide (Example 39),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Propanamide (Example 40),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide (Example 41),
Benzyl 2- [4- (4- {5- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 ( 2H) -yl] acetate (Example 42),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-isopropyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide (Example 43),
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} acetamide (Example 44),
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} butanamide (Example 45),
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} pentanamide (Example 46),
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} hexanamide (Example 47),
N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 48),
N- (5- {4- [2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 49),
N- (5- {4- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 50),
N- [5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Acetamide (Example 51),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Methyl] amino} acetamide (Example 52),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide (Example 53),
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) pentane An amide (Example 54),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (piperidin-1-yl) pentanamide (Example 55),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 56),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] thiophene-2 Carboxamide (Example 57),
6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} nicotinamide Example 58),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide (Example 59),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Amino] methyl} benzamide (Example 60),
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Acetamide (Example 61),
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene -2-yl} acetamide (Example 62) and
N- {5- [6- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 63)
The compound according to the above [1], a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof, which is at least one compound selected from the group consisting of:
[12]
上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分とする、TLR3、TLR7及びTLR9からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の阻害剤。 [12]
At least one inhibitor selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9, comprising as an active ingredient the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. .
上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分とする、TLR3、TLR7及びTLR9からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の阻害剤。 [12]
At least one inhibitor selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9, comprising as an active ingredient the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. .
[13]
上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分とする、自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病又は敗血症に起因する心筋症の予防及び/又は治療剤。 [13]
Autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft pair, comprising as an active ingredient the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof A prophylactic and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy caused by host disease or sepsis.
上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分とする、自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病又は敗血症に起因する心筋症の予防及び/又は治療剤。 [13]
Autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft pair, comprising as an active ingredient the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof A prophylactic and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy caused by host disease or sepsis.
[14]
自己免疫疾患が、関節リウマチ、全身性エリテマトーデス、シェーグレン症候群、多発性硬化症、炎症性腸疾患、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群又は血管炎である、上記[13]に記載の予防及び/又は治療剤。 [14]
The preventive and / or therapeutic agent according to [13] above, wherein the autoimmune disease is rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome or vasculitis .
自己免疫疾患が、関節リウマチ、全身性エリテマトーデス、シェーグレン症候群、多発性硬化症、炎症性腸疾患、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群又は血管炎である、上記[13]に記載の予防及び/又は治療剤。 [14]
The preventive and / or therapeutic agent according to [13] above, wherein the autoimmune disease is rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome or vasculitis .
また、本発明は、上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分とするTLR3、TLR7及びTLR9からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種のシグナルの活性化に起因する疾患の予防及び/又は治療剤に関する。より詳細には、本発明は、上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分とする関節リウマチ(RA)、全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)、シェーグレン症候群(SS)、多発性硬化症(MS)、炎症性腸疾患(IBD)、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎などの自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症による心筋症等の予防及び/又は治療剤に関する。
Further, the present invention is selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9 containing the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof as an active ingredient. The present invention relates to a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for diseases caused by activation of at least one signal. More specifically, the present invention relates to rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic, comprising the compound according to any one of the above [1] to [11], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof as an active ingredient. Lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS), multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis and other autoimmune diseases, inflammation, allergies, asthma, grafts The present invention relates to a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy due to rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis.
また、本発明は、TLR3、TLR7及びTLR9からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種のシグナルの活性化に起因する疾患、例えば、関節リウマチ(RA)、全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)、シェーグレン症候群(SS)、多発性硬化症(MS)、炎症性腸疾患(IBD)、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎などの自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症による心筋症等の予防及び/又は治療剤の製造のための、上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物の使用に関する。
The present invention also relates to a disease caused by activation of at least one signal selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS) , Multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, autoimmune diseases such as vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) Or the use of the compound according to any one of the above [1] to [11], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof for the manufacture of an agent for preventing and / or treating cardiomyopathy due to sepsis, etc. .
また、本発明は、上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物の有効量を患者に投与することを特徴とする、TLR3、TLR7及びTLR9からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種のシグナルの活性化に起因する疾患、例えば、関節リウマチ(RA)、全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)、シェーグレン症候群(SS)、多発性硬化症(MS)、炎症性腸疾患(IBD)、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎などの自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症による心筋症等の予防及び/又は治療方法に関する。
Further, the present invention provides a TLR3 characterized by administering an effective amount of the compound according to any one of the above [1] to [11], or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof, Diseases resulting from activation of at least one signal selected from the group consisting of TLR7 and TLR9, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS), multiple sclerosis (MS) Prevention of autoimmune diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis cardiomyopathy And / or a therapeutic method.
また、本発明は、医薬としての使用のための上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物に関する。
The present invention also relates to the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof for use as a medicament.
また、本発明は、TLR3、TLR7及びTLR9からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種のシグナルの活性化に起因する疾患、例えば、関節リウマチ(RA)、全身性エリテマトーデス(SLE)、シェーグレン症候群(SS)、多発性硬化症(MS)、炎症性腸疾患(IBD)、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎などの自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症による心筋症等の予防及び/又は治療における使用のための、上記[1]~[11]のいずれか1つに記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物に関する。
The present invention also relates to a disease caused by activation of at least one signal selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjogren's syndrome (SS) , Multiple sclerosis (MS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, autoimmune diseases such as vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) Alternatively, the present invention relates to the compound according to any one of [1] to [11] above, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof for use in prevention and / or treatment of cardiomyopathy due to sepsis.
本発明のTLR3、TLR7及びTLR9からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の阻害剤の有効成分である、一般式(1)で表される化合物若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物は、RA、SLE、SS、MS、IBD、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎などの自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、GvHD又は敗血症による心筋症等の予防及び/又は治療に有用である。
The compound represented by the general formula (1) or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof, which is an active ingredient of at least one inhibitor selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9 of the present invention is RA, Useful for the prevention and / or treatment of autoimmune diseases such as SLE, SS, MS, IBD, psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, GvHD or sepsis cardiomyopathy .
以下、本発明について詳細に説明する。本発明における用語の定義は以下のとおりである。
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail. The definitions of terms in the present invention are as follows.
本明細書で使用するとき、「飽和の脂肪族炭素環」とは、隣接する環員炭素原子間で多重結合を有さない、4~7員の脂肪族炭素環を示す。「飽和の脂肪族炭素環」としては、例えば、シクロブタン環、シクロペンタン環、シクロヘキサン環、シクロヘプタン等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “saturated aliphatic carbocycle” refers to a 4- to 7-membered aliphatic carbocycle having no multiple bond between adjacent ring carbon atoms. Examples of the “saturated aliphatic carbocycle” include cyclobutane ring, cyclopentane ring, cyclohexane ring, cycloheptane and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「不飽和の脂肪族炭素環」とは、隣接する環員原子間で1以上の多重結合を有する、4~7員の脂肪族炭素環を示す。「不飽和の脂肪族炭素環」としては、例えば、シクロブテン環、シクロペンテン環、シクロヘキセン環、1,3-シクロヘキサジエン環、1,4-シクロヘキサジエン環、1,3-シクロヘプタジエン環、1,4-シクロヘプタジエン環等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “unsaturated aliphatic carbocycle” refers to a 4- to 7-membered aliphatic carbocycle having one or more multiple bonds between adjacent ring member atoms. Examples of the “unsaturated aliphatic carbocycle” include, for example, cyclobutene ring, cyclopentene ring, cyclohexene ring, 1,3-cyclohexadiene ring, 1,4-cyclohexadiene ring, 1,3-cycloheptadiene ring, 1, Examples include 4-cycloheptadiene ring.
本明細書で使用するとき、「飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環」とは、隣接する環員原子間で多重結合を有さず、環員原子として1個以上の窒素原子を含有し、残りの環員原子が炭素原子、窒素原子、酸素原子、又は硫黄原子である、4~7員の脂肪族複素環を示す。「飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環」としては、例えば、アゼチジン環、ピロリジン環、ピペリジン環、アゼパン環、ピペラジン環等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle” means that there are no multiple bonds between adjacent ring member atoms, one or more nitrogen atoms as ring member atoms, and the rest Represents a 4- to 7-membered aliphatic heterocyclic ring in which the ring member atom is a carbon atom, nitrogen atom, oxygen atom, or sulfur atom. Examples of the “saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle” include azetidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperidine ring, azepane ring, piperazine ring and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環」とは、隣接する環員原子間で1以上の多重結合を有し、環員原子として1個以上の窒素原子を含有し、残りの環員原子が炭素原子、窒素原子、酸素原子、又は硫黄原子である、4~7員の脂肪族複素環を示す。「不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環」としては、例えば、アゼチン環、ピロリン環、テトラヒドロピリジン環、ジヒドロピリジン環、テトラヒドロピラジン環、ジヒドロピラジン環、テトラヒドロアゼピン環、オキサジン環、チアジン環等が挙げられる。
As used herein, an “unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle” has one or more multiple bonds between adjacent ring member atoms, and contains one or more nitrogen atoms as ring member atoms. And a 4- to 7-membered aliphatic heterocyclic ring in which the remaining ring member atoms are carbon atoms, nitrogen atoms, oxygen atoms, or sulfur atoms. Examples of the “unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle” include azetine ring, pyrroline ring, tetrahydropyridine ring, dihydropyridine ring, tetrahydropyrazine ring, dihydropyrazine ring, tetrahydroazepine ring, oxazine ring and thiazine ring. .
本明細書で使用するとき、「芳香族炭素環」とは、環員原子がすべて炭素原子である、6~10員の芳香族炭素環を意味する。「芳香族炭素環」としては、例えば、ベンゼン環、アズレン環、ナフタレン環等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “aromatic carbocycle” means a 6 to 10 membered aromatic carbocycle in which all ring member atoms are carbon atoms. Examples of the “aromatic carbocycle” include a benzene ring, an azulene ring, a naphthalene ring and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「含窒素芳香族複素環」とは、環員原子として1個以上の窒素原子を含有し、残りの環員が窒素原子以外のヘテロ原子(酸素若しくは硫黄原子)又は炭素原子である、5~9員の芳香族複素環を示す。「含窒素芳香族複素環」としては、例えば、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環、チアジアゾール環、インドール環等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle” means one or more nitrogen atoms as ring member atoms, and the remaining ring members are hetero atoms other than nitrogen atoms (oxygen or sulfur atoms). Or a 5- to 9-membered aromatic heterocycle which is a carbon atom. Examples of the “nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle” include pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadi An azole ring, a thiadiazole ring, an indole ring, etc. are mentioned.
本明細書で使用するとき、「ハロゲン原子」としては、例えば、フッ素原子、塩素原子、臭素原子、ヨウ素原子が挙げられる。
As used herein, examples of the “halogen atom” include a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, and an iodine atom.
本明細書で使用するとき、「C1-6アルキル基」とは、直鎖又は分岐鎖の炭素数1~6の飽和炭化水素基を意味する。「C1-6アルキル基」としては、例えば、メチル基、エチル基、n-プロピル基、イソプロピル基、n-ブチル基、イソブチル基、tert-ブチル基、n-ペンチル基、2-メチルブチル基、2,2-ジメチルプロピル基、n-ヘキシル基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “C 1-6 alkyl group” means a straight or branched saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms. Examples of the “C 1-6 alkyl group” include, for example, methyl group, ethyl group, n-propyl group, isopropyl group, n-butyl group, isobutyl group, tert-butyl group, n-pentyl group, 2-methylbutyl group, Examples include 2,2-dimethylpropyl group and n-hexyl group.
本明細書で使用するとき、「C1-6アルキルオキシ基」とは、直鎖又は分岐鎖の炭素数1~6の飽和炭化水素基が酸素原子と結合した基を意味する。「C1-6アルキルオキシ基」としては、例えば、メトキシ基、エトキシ基、n-プロポキシ基、イソプロポキシ基、n-ブトキシ基、イソブトキシ基、tert-ブトキシ基、n-ペンチルオキシ基、2-メチルブトキシ基、2,2-ジメチルプロポキシ基、n-ヘキシルオキシ基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “C 1-6 alkyloxy group” means a group in which a linear or branched saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms is bonded to an oxygen atom. Examples of the “C 1-6 alkyloxy group” include methoxy group, ethoxy group, n-propoxy group, isopropoxy group, n-butoxy group, isobutoxy group, tert-butoxy group, n-pentyloxy group, 2- Examples include methylbutoxy group, 2,2-dimethylpropoxy group, n-hexyloxy group and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「カルボキシC1-5アルキル基」とは、末端にカルボキシ基が置換した直鎖の炭素数1~5の飽和炭化水素基を意味する。「カルボキシC1-5アルキル基」としては、例えば、カルボキシメチル基、カルボキシエチル基、カルボキシプロピル基、カルボキシブチル基、カルボキシペンチル基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group” means a straight-chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms substituted with a carboxy group at the end. Examples of the “carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group” include carboxymethyl group, carboxyethyl group, carboxypropyl group, carboxybutyl group, carboxypentyl group and the like.
本発明で使用するとき、「ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基」とは、ベンジルオキシカルボニル基が置換した直鎖の炭素数1~5の飽和炭化水素基を意味する。「ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基」としては、例えば、ベンジルオキシカルボニルメチル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルエチル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルプロピル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルブチル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルペンチル基等が挙げられる。
As used in the present invention, “benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group” means a straight-chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms substituted with a benzyloxycarbonyl group. Examples of the “benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group” include benzyloxycarbonylmethyl group, benzyloxycarbonylethyl group, benzyloxycarbonylpropyl group, benzyloxycarbonylbutyl group, benzyloxycarbonylpentyl group and the like.
本発明で使用するとき、「カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基」とは、末端にカルバモイル基が置換した直鎖の炭素数1~5の飽和炭化水素基を意味する。「カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基」としては、例えば、カルバモイルメチル基、カルバモイルエチル基、カルバモイルプロピル基、カルバモイルブチル基、カルバモイルペンチル基等が挙げられる。
As used in the present invention, “carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group” means a straight-chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 5 carbon atoms substituted with a carbamoyl group at the terminal. Examples of the “carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group” include carbamoylmethyl group, carbamoylethyl group, carbamoylpropyl group, carbamoylbutyl group, carbamoylpentyl group and the like.
本発明で使用するとき、「C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基」とは、末端にC1-3アルキル基が置換した前記カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基を意味する。「C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基」としては、例えば、1-メチルアミノ-1-オキソエタン-2-イル基、1-メチルアミノ-1-オキソプロパン-3-イル基、1-メチルアミノ-1-オキソブタン-4-イル基、1-メチルアミノ-1-オキソペンタン-5-イル基、1-メチルアミノ-1-オキソヘキサン-6-イル基、1-エチルアミノ-1-オキソエタン-2-イル基、1-エチルアミノ-1-オキソプロパン-3-イル基、1-エチルアミノ-1-オキソブタン-4-イル基、1-エチルアミノ-1-オキソペンタン-5-イル基、1-エチルアミノ-1-オキソヘキサン-6-イル基、1-オキソ-1-n-プロピルアミノエタン-2-イル基、1-オキソ-1-n-プロピルアミノプロパン-3-イル基、1-オキソ-1-n-プロピルアミノブタン-4-イル基、1-オキソ-1-n-プロピルアミノペンタン-5-イル基、1-オキソ-1-n-プロピルアミノヘキサン-6-イル基等が挙げられる。
As used in the present invention, the “C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group” means the carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group substituted at the end with a C 1-3 alkyl group. Examples of the “C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group” include, for example, a 1-methylamino-1-oxoethane-2-yl group, a 1-methylamino-1-oxopropan-3-yl group, Methylamino-1-oxobutan-4-yl group, 1-methylamino-1-oxopentan-5-yl group, 1-methylamino-1-oxohexane-6-yl group, 1-ethylamino-1-oxoethane -2-yl group, 1-ethylamino-1-oxopropan-3-yl group, 1-ethylamino-1-oxobutan-4-yl group, 1-ethylamino-1-oxopentan-5-yl group, 1-ethylamino-1-oxohexane-6-yl group, 1-oxo-1-n-propylaminoethane-2-yl group, 1-oxo-1-n-propylaminopropane-3-yl 1-oxo-1-n-propylaminobutan-4-yl group, 1-oxo-1-n-propylaminopentan-5-yl group, 1-oxo-1-n-propylaminohexane-6- Yl group and the like.
本発明で使用するとき、「C1-6アルキルアミノ基」とは、直鎖又は分岐鎖の炭素数1~6の飽和炭化水素基が1置換したアミノ基を意味する。「C1-6アルキルアミノ基」としては、例えば、メチルアミノ基、エチルアミノ基、n-プロピルアミノ基、イソプロピルアミノ基、n-ブチルアミノ基、イソブチルアミノ基、tert-ブチルアミノ基、n-ペンチルアミノ基、2-メチルブチルアミノ基、2,2-ジメチルプロピルアミノ基、n-ヘキシルアミノ基等が挙げられる。
As used in the present invention, “C 1-6 alkylamino group” means an amino group in which a linear or branched saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms is substituted. Examples of the “C 1-6 alkylamino group” include, for example, methylamino group, ethylamino group, n-propylamino group, isopropylamino group, n-butylamino group, isobutylamino group, tert-butylamino group, n- Examples include pentylamino group, 2-methylbutylamino group, 2,2-dimethylpropylamino group, n-hexylamino group and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基」とは、直鎖又は分岐鎖の炭素数1~6の飽和炭化水素基が、同一又は異なって、2置換したアミノ基を意味する。「ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基」としては、例えば、(エチル)(メチル)アミノ基、(イソプロピル)(n-プロピル)アミノ基、(n-ブチル)(イソブチル)アミノ基、(tert-ブチル)(n-ペンチル)アミノ基、(2,2-ジメチルプロピル)(2-メチルブチル)アミノ基、ジメチルアミノ基、ジエチルアミノ基、ジ-n-プロピルアミノ基、ジ-イソプロピルアミノ基、ジ-n-ブチルアミノ基、ジ-tert-ブチルアミノ基、ジ-n-ペンチルアミノ基、ジ-n-ヘキシルアミノ基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, the “di-C 1-6 alkylamino group” is an amino group in which a linear or branched saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms is the same or different and is disubstituted. means. Examples of the “di-C 1-6 alkylamino group” include (ethyl) (methyl) amino group, (isopropyl) (n-propyl) amino group, (n-butyl) (isobutyl) amino group, (tert-butyl) ) (N-pentyl) amino group, (2,2-dimethylpropyl) (2-methylbutyl) amino group, dimethylamino group, diethylamino group, di-n-propylamino group, di-isopropylamino group, di-n- Examples thereof include a butylamino group, a di-tert-butylamino group, a di-n-pentylamino group, and a di-n-hexylamino group.
本明細書で使用するとき、「ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基」とは、C1-6アルキル基の末端に前記ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基が置換している基を意味する。「ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基」としては、例えば、(エチル)(メチル)アミノメチル基、(イソプロピル)(n-プロピル)アミノメチル基、(n-ブチル)(イソブチル)アミノメチル基、(tert-ブチル)(n-ペンチル)アミノメチル基、(2,2-ジメチルプロピル)(2-メチルブチル)アミノメチル基、ジメチルアミノメチル基、ジエチルアミノメチル基、ジ-n-プロピルアミノメチル基、ジ-イソプロピルアミノメチル基、ジ-n-ブチルアミノメチル基、ジ-t-ブチルアミノメチル基、ジ-n-ペンチルアミノメチル基、ジ-n-ヘキシルアミノメチル基、(エチル)(メチル)アミノエチル基、(イソプロピル)(n-プロピル)アミノエチル基、(n-ブチル)(イソブチル)アミノエチル基、(tert-ブチル)(n-ペンチル)アミノエチル基、(2,2-ジメチルプロピル)(2-メチルブチル)アミノエチル基、ジメチルアミノエチル基、ジエチルアミノエチル基、ジ-n-プロピルアミノエチル基、ジ-イソプロピルアミノエチル基、ジ-n-ブチルアミノエチル基、ジ-tert-ブチルアミノエチル基、ジ-n-ペンチルアミノエチル基、ジ-n-ヘキシルアミノエチル基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, the term "di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group", C 1-6 group that the di-C 1-6 alkylamino group at the end of the alkyl group is substituted Means. Examples of the “di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group” include (ethyl) (methyl) aminomethyl group, (isopropyl) (n-propyl) aminomethyl group, (n-butyl) (isobutyl) Aminomethyl group, (tert-butyl) (n-pentyl) aminomethyl group, (2,2-dimethylpropyl) (2-methylbutyl) aminomethyl group, dimethylaminomethyl group, diethylaminomethyl group, di-n-propylamino Methyl group, di-isopropylaminomethyl group, di-n-butylaminomethyl group, di-t-butylaminomethyl group, di-n-pentylaminomethyl group, di-n-hexylaminomethyl group, (ethyl) ( Methyl) aminoethyl group, (isopropyl) (n-propyl) aminoethyl group, (n-butyl) (isobutyl) amino group Group, (tert-butyl) (n-pentyl) aminoethyl group, (2,2-dimethylpropyl) (2-methylbutyl) aminoethyl group, dimethylaminoethyl group, diethylaminoethyl group, di-n-propylaminoethyl group Group, di-isopropylaminoethyl group, di-n-butylaminoethyl group, di-tert-butylaminoethyl group, di-n-pentylaminoethyl group, di-n-hexylaminoethyl group and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「C1-6アルキレン基」とは、飽和の2価の直鎖又は分岐鎖の炭素数1~6の飽和炭化水素基を意味する。「C1-6アルキレン基」としては、例えば、メチレン基、エチレン基、n-プロピレン基、イソプロピレン基、n-ブチレン基、イソブチレン基、tert-ブチレン基、n-ペンチレン基、2-メチルブチレン基、2,2-ジメチルプロピレン基、n-ヘキシレン基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “C 1-6 alkylene group” means a saturated divalent straight chain or branched chain saturated hydrocarbon group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms. Examples of the “C 1-6 alkylene group” include methylene group, ethylene group, n-propylene group, isopropylene group, n-butylene group, isobutylene group, tert-butylene group, n-pentylene group, 2-methylbutylene. Group, 2,2-dimethylpropylene group, n-hexylene group and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「C2-6アルケニレン基」とは、二重結合を1つ含む、2価の直鎖又は分岐鎖の炭素数2~6の不飽和炭化水素基を意味する。「C2-6アルケニレン基」としては、例えば、ビニレン基、プロペニレン基、1-ブテニレン基、2-ブテニレン基、1-ペンテニレン基、2-ペンテニレン基、1-ヘキセニレン基、2-ヘキセニレン基、3-ヘキセニレン基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “C 2-6 alkenylene group” means a divalent linear or branched unsaturated hydrocarbon group having 2 to 6 carbon atoms containing one double bond. . Examples of the “C 2-6 alkenylene group” include vinylene group, propenylene group, 1-butenylene group, 2-butenylene group, 1-pentenylene group, 2-pentenylene group, 1-hexenylene group, 2-hexenylene group, 3 -A hexenylene group and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基」とは、末端に水酸基が置換した直鎖又は分岐鎖のC1-6アルキル基を意味する。「ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基」としては、例えば、ヒドロキシメチル基、ヒドロキシエチル基、ヒドロキシ-n-プロピル基、ヒドロキシイソプロピル基、ヒドロキシ-n-ブチル基、ヒドロキシイソブチル基、ヒドロキシ-tert-ブチル基、ヒドロキシ-n-ペンチル基、ヒドロキシ-2-メチルブチル基、ヒドロキシ-2,2-ジメチルプロピル基、ヒドロキシ-n-ヘキシル基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group” means a linear or branched C 1-6 alkyl group having a terminal substituted with a hydroxyl group. Examples of the “hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group” include, for example, hydroxymethyl group, hydroxyethyl group, hydroxy-n-propyl group, hydroxyisopropyl group, hydroxy-n-butyl group, hydroxyisobutyl group, hydroxy-tert-butyl group Hydroxy-n-pentyl group, hydroxy-2-methylbutyl group, hydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropyl group, hydroxy-n-hexyl group and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基」とは、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基のヒドロキシ基に直鎖又は分岐鎖のC1-3アルキル基が置換した基を意味する。「C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基」としては、例えば、メトキシメチル基、メトキシエチル基、メトキシ-n-プロピル基、メトキシイソプロピル基、メトキシ-n-ブチル基、メトキシイソブチル基、メトキシ-tert-ブチル基、メトキシ-n-ペンチル基、メトキシ-2-メチルブチル基、メトキシ-2,2-ジメチルプロピル基、メトキシ-n-ヘキシル基、エトキシメチル基、エトキシエチル基、エトキシ-n-プロピル基、エトキシイソプロピル基、エトキシ-n-ブチル基、エトキシイソブチル基、エトキシ-tert-ブチル基、エトキシ-n-ペンチル基、エトキシ-2-メチルブチル基、エトキシ-2,2-ジメチルプロピル基、エトキシ-n-ヘキシル基、n-プロポキシメチル基、n-プロポキシエチル基、n-プロポキシ-n-プロピル基、n-プロポキシイソプロピル基、n-プロポキシ-n-ブチル基、n-プロポキシイソブチル基、n-プロポキシ-tert-ブチル基、n-プロポキシ-n-ペンチル基、n-プロポキシ-2-メチルブチル基、n-プロポキシ-2,2-ジメチルプロピル基、n-プロポキシ-n-ヘキシル基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group” means a hydroxy group of a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group substituted with a linear or branched C 1-3 alkyl group. Means the group. Examples of the “C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group” include methoxymethyl group, methoxyethyl group, methoxy-n-propyl group, methoxyisopropyl group, methoxy-n-butyl group, methoxyisobutyl group, methoxy -Tert-butyl group, methoxy-n-pentyl group, methoxy-2-methylbutyl group, methoxy-2,2-dimethylpropyl group, methoxy-n-hexyl group, ethoxymethyl group, ethoxyethyl group, ethoxy-n-propyl Group, ethoxyisopropyl group, ethoxy-n-butyl group, ethoxyisobutyl group, ethoxy-tert-butyl group, ethoxy-n-pentyl group, ethoxy-2-methylbutyl group, ethoxy-2,2-dimethylpropyl group, ethoxy- n-hexyl group, n-propoxymethyl group, n-propoxy group Til, n-propoxy-n-propyl, n-propoxyisopropyl, n-propoxy-n-butyl, n-propoxyisobutyl, n-propoxy-tert-butyl, n-propoxy-n-pentyl N-propoxy-2-methylbutyl group, n-propoxy-2,2-dimethylpropyl group, n-propoxy-n-hexyl group and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「C1-3アルキルスルホニル基」とは、直鎖又は分岐鎖のC1-3アルキル基が置換したスルホニル基を意味する。「C1-3アルキルスルホニル基」としては、例えば、メチルスルホニル基、エチルスルホニル基、n-プロピルスルホニル基、イソプロピルスルホニル基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group” means a sulfonyl group substituted with a linear or branched C 1-3 alkyl group. Examples of the “C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group” include methylsulfonyl group, ethylsulfonyl group, n-propylsulfonyl group, isopropylsulfonyl group and the like.
本明細書で使用するとき、「C6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基」とは、6~10員の芳香環炭素環が置換した直鎖又は分岐鎖のC1-3アルキル基を意味する。「C6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基」としては、例えば、ベンジル基、フェネチル基、1-フェニル-n-プロパン-1-イル基、2-フェニル-n-プロパン-1-イル基、3-フェニル-n-プロパン-1-イル基、1-フェニル-イソプロパン-2-イル基、2-フェニル-イソプロパン-2-イル基、アズレンメチル基、1-アズレンエタン-1-イル基、2-アズレンエタン-1-イル基、1-アズレン-n-プロパン-1-イル基、2-アズレン-n-プロパン-1-イル基、3-アズレン-n-プロパン-1-イル基、1-アズレン-イソプロパン-2-イル基、2-アズレン-イソプロパン-2-イル基、ナフタレン-1-イル-メチル基、1-ナフタレン-1-イル-エタン-1-イル基、2-ナフタレン-1-イル-エタン-1-イル基、1-ナフタレン-1-イル-n-プロパン-1-イル基、2-ナフタレン-1-イル-n-プロパン-1-イル基、3-ナフタレン-1-イル-n-プロパン-1-イル基、1-ナフタレン-1-イル-イソプロパン-2-イル基、2-ナフタレン-1-イル-イソプロパン-2-イル基等が挙げられる。
As used herein, “C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group” means a straight or branched C 1-3 alkyl group substituted with a 6-10 membered aromatic carbocycle. To do. Examples of the “C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group” include benzyl group, phenethyl group, 1-phenyl-n-propan-1-yl group, 2-phenyl-n-propan-1-yl group, 3-phenyl-n-propan-1-yl group, 1-phenyl-isopropan-2-yl group, 2-phenyl-isopropan-2-yl group, azulenemethyl group, 1-azulenethan-1-yl group 2-azulenethan-1-yl group, 1-azulene-n-propan-1-yl group, 2-azulene-n-propan-1-yl group, 3-azulene-n-propan-1-yl group, 1-azulene-isopropan-2-yl group, 2-azulene-isopropan-2-yl group, naphthalen-1-yl-methyl group, 1-naphthalen-1-yl-ethane-1-yl group, 2- Naphthalene-1- Ru-ethane-1-yl group, 1-naphthalen-1-yl-n-propan-1-yl group, 2-naphthalen-1-yl-n-propan-1-yl group, 3-naphthalen-1-yl -N-propan-1-yl group, 1-naphthalen-1-yl-isopropan-2-yl group, 2-naphthalen-1-yl-isopropan-2-yl group and the like.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環としては、ピペリジン環、ピペラジン環、ピロリジン環が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3), and (4), the saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring is preferably a piperidine ring, a piperazine ring, or a pyrrolidine ring.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環としては、1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン環が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring is preferably a 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine ring.
一般式(1)、(2)、(4)中、芳香族炭素環としては、ベンゼン環が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), and (4), the aromatic carbocycle is preferably a benzene ring.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、含窒素芳香族複素環としては、ピリジン環、インドール環、ピラゾール環が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle is preferably a pyridine ring, an indole ring or a pyrazole ring.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、ハロゲン原子としては、臭素原子が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3), and (4), the halogen atom is preferably a bromine atom.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、C1-6アルキル基としては、メチル基、イソプロピル基、イソブチル基が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the C 1-6 alkyl group is preferably a methyl group, an isopropyl group or an isobutyl group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、C1-6アルキルオキシ基としては、メトキシ基が好ましい。
In the general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the C 1-6 alkyloxy group is preferably a methoxy group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基としては、カルボキシブチル基が好ましい。
In the general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group is preferably a carboxybutyl group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基としては、ベンジルオキシカルボニルメチル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルペンチル基が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group is preferably a benzyloxycarbonylmethyl group or a benzyloxycarbonylpentyl group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基としては、カルバモイルペンチル基が好ましい。
In the general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group is preferably a carbamoylpentyl group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基としては、1-メチルアミノ-1-オキソヘキサン-6-イル基が好ましい。
In the general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group is preferably a 1-methylamino-1-oxohexane-6-yl group. .
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、C1-6アルキルアミノ基としては、メチルアミノ基が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the C 1-6 alkylamino group is preferably a methylamino group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基としては、ジメチルアミノ基が好ましい。
In the general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the diC 1-6 alkylamino group is preferably a dimethylamino group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、C1-6アルキレン基としては、メチレン基、エチレン基、プロピレン基、ブチレン基、ペンチレン基が好ましい。
In the general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the C 1-6 alkylene group is preferably a methylene group, an ethylene group, a propylene group, a butylene group or a pentylene group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基としては、ヒドロキシ-n-プロピル基、ヒドロキシ-n-ペンチル基が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3), and (4), the hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group is preferably a hydroxy-n-propyl group or a hydroxy-n-pentyl group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基としては、メトキシエチル基が好ましい。
In the general formulas (1), (2), (3) and (4), the C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group is preferably a methoxyethyl group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(4)中、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基としては、メチルスルホニル基が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), and (4), the C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group is preferably a methylsulfonyl group.
一般式(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)中、C6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基としては、ベンジル基が好ましい。
In general formulas (1), (2), (3), and (4), the C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group is preferably a benzyl group.
一般式(2)中、環Aとしては、ピロリジン環、ピペリジン環、ピペラジン環、テトラヒドロピリジン環が好ましく、ピペリジン環、ピペラジン環、テトラヒドロピリジン環がより好ましい。
In general formula (2), ring A is preferably a pyrrolidine ring, piperidine ring, piperazine ring or tetrahydropyridine ring, more preferably a piperidine ring, piperazine ring or tetrahydropyridine ring.
一般式(2)中、環Aが有しても良い置換基としては、C1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基が好ましく、メチル基、イソプロピル基、1-メチルアミノ-1-オキソペンタン-5-イル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルメチル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルペンチル基がより好ましい。
In the general formula (2), examples of the substituent that the ring A may have include a C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, and a benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group. A methyl group, an isopropyl group, a 1-methylamino-1-oxopentan-5-yl group, a benzyloxycarbonylmethyl group, and a benzyloxycarbonylpentyl group are more preferable.
一般式(2)中、環Bとしては、芳香族炭素環、飽和の脂肪族炭素環、含窒素芳香族複素環が好ましく、ベンゼン環、シクロヘキサン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環、チアジアゾール環がより好ましく、ベンゼン環、シクロヘキサン環、ピリジン環、ピラゾール環がさらにより好ましい。
In general formula (2), ring B is preferably an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring. A benzene ring, a cyclohexane ring, a pyridine ring, a pyridazine ring, a pyrimidine ring, or a pyrazine ring. , Triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadiazole ring, thiadiazole ring are more preferable, benzene ring, cyclohexane ring, pyridine ring, pyrazole ring are more preferable. .
一般式(2)中、環Bが有しても良い置換基としては、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、シアノ基及びカルバモイル基が好ましい。ここでC1-6アルキルオキシ基としては、メトキシ基がより好ましい。
In general formula (2), the substituent that ring B may have is preferably a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a cyano group, or a carbamoyl group. Here, the C 1-6 alkyloxy group is more preferably a methoxy group.
一般式(2)中、Q2としては、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基が好ましく、単結合、メチレン基、エチレン基、n-プロピレン基、n-ブチレン基、n-ペンチレン基がより好ましい。
In general formula (2), Q 2 is preferably a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, more preferably a single bond, a methylene group, an ethylene group, an n-propylene group, an n-butylene group or an n-pentylene group. .
一般式(2)中、Q2が有してもよい置換基としては、オキソ基が好ましい。
In general formula (2), the substituent that Q 2 may have is preferably an oxo group.
一般式(2)において、R4の環Bへの置換位置は、置換が可能である限り特に限定されないが、例えば環Bが6員環であるとき、母核であるチオフェン環の環Bへの結合位置から数えて3位又は4位であることが好ましく、例えば環Bが5員環であるとき、母核であるチオフェン環の環Bへの結合位置から数えて3位であることが好ましい。
In the general formula (2), the substitution position of R 4 to the ring B is not particularly limited as long as substitution is possible. For example, when the ring B is a 6-membered ring, to the ring B of the thiophene ring as the mother nucleus Preferably, it is the 3rd or 4th position counted from the bonding position of, for example, when the ring B is a 5-membered ring, it is preferably the 3rd position counted from the bonding position to the ring B of the thiophene ring which is the mother nucleus. preferable.
一般式(3)中、環Cとしては、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、含窒素芳香族複素環が好ましく、ピペリジン環、ピロリジン環、ピペラジン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環、チアジアゾール環、インドール環がより好ましく、ピペラジン環、インドール環がさらにより好ましい。
In general formula (3), ring C is preferably a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, and a piperidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperazine ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring , A triazine ring, a pyrrole ring, a pyrazole ring, an isoxazole ring, an oxazole ring, an isothiazole ring, a thiazole ring, an oxadiazole ring, a thiadiazole ring, and an indole ring, more preferably a piperazine ring and an indole ring.
一般式(3)中、環Cが有しても良い置換基としては、C1-6アルキル基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基が好ましく、メチル基、ジメチルアミノプロピル基がより好ましい。
In the general formula (3), the substituent that the ring C may have is preferably a C 1-6 alkyl group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, a methyl group, a dimethylaminopropyl group Is more preferable.
一般式(3)中、Q3としては、単結合又はC2-6アルケニレン基が好ましく、ここでC2-6アルケニレン基としてはプロペニレン基がより好ましい。
In the general formula (3), Q 3 is preferably a single bond or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, and the C 2-6 alkenylene group is more preferably a propenylene group.
一般式(3)中、Q3が有してもよい置換基としては、オキソ基が好ましい。
In general formula (3), the substituent that Q 3 may have is preferably an oxo group.
一般式(1)中、環Yとしては、芳香族炭素環、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、含窒素芳香族複素環が好ましく、ベンゼン環、ピペリジン環、ピロリジン環、ピペラジン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環又はチアジアゾール環が好ましく、ベンゼン環、ピペリジン環、ピロリジン環、ピペラジン環、ピリジン環がさらにより好ましい。
In general formula (1), ring Y is preferably an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring. A benzene ring, piperidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperazine ring, pyridine ring, Pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadiazole ring or thiadiazole ring are preferable, benzene ring, piperidine ring, pyrrolidine ring Further preferred are a piperazine ring and a pyridine ring.
一般式(1)中、環Yが有しても良い置換基としては、C1-6アルキル基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基が好ましく、メチル基、ジメチルアミノ基、ジメチルアミノメチル基及び式(4)の基がより好ましい。
In the general formula (1), examples of the substituent that the ring Y may have include a C 1-6 alkyl group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, And groups of formula (4) are preferred, methyl groups, dimethylamino groups, dimethylaminomethyl groups and groups of formula (4) are more preferred.
一般式(1)において環Yが置換基を有するとき、その置換位置は置換が可能である限り特に限定されないが、例えば環Yが6員環であるとき、環YへのR1の結合位置から数えて4位に少なくとも1つ置換されることが好ましく、例えば環Yが5員環であるとき、環YへのR1の結合位置から数えて2位に少なくとも1つ置換されることが好ましい。
When ring Y has a substituent in general formula (1), the substitution position is not particularly limited as long as substitution is possible. For example, when ring Y is a 6-membered ring, R 1 is bonded to ring Y. It is preferable that at least one is substituted at the 4-position counting from 1, for example, when the ring Y is a 5-membered ring, at least one is substituted at the 2-position counting from the bonding position of R 1 to the ring Y. preferable.
一般式(4)中、環Dとしては、芳香族炭素環、飽和の脂肪族炭素環、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環が好ましく、ベンゼン環、シクロヘキサン環、ピロリジン環、ピペラジン環、ピペリジン環がより好ましく、ベンゼン環、シクロヘキサン環、ピペラジン環、ピペリジン環がさらにより好ましい。
In general formula (4), ring D is preferably an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, or a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, and a benzene ring, a cyclohexane ring, a pyrrolidine ring, a piperazine ring, or a piperidine ring. More preferred are benzene, cyclohexane, piperazine and piperidine rings.
一般式(4)中、環Dが有しても良い置換基としては、C1-6アルキル基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基が好ましく、メチル基、ジメチルアミノ基、ジメチルアミノメチル基がより好ましい。
In the general formula (4), examples of the substituent that the ring D may have include a C 1-6 alkyl group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group. A methyl group, a dimethylamino group, and a dimethylaminomethyl group are more preferable.
一般式(4)中、Q4としては、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基が好ましく、単結合、メチレン基がより好ましい。
In formula (4), Q 4 is preferably a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, more preferably a single bond or a methylene group.
一般式(4)中、R5としては、単結合、NH基が好ましい。
In general formula (4), R 5 is preferably a single bond or an NH group.
一般式(1)中、Q1としては、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基が好ましく、単結合、メチレン基、エチレン基、n-プロピレン基、n-ブチレン基、n-ペンチレン基がより好ましい。
In general formula (1), Q 1 is preferably a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, more preferably a single bond, a methylene group, an ethylene group, an n-propylene group, an n-butylene group or an n-pentylene group. .
一般式(1)中、Q1の有する置換基としては、C1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基が好ましく、イソブチル基、メトキシエチル基、ベンジル基がより好ましい。
In general formula (1), the substituent of Q 1 is preferably a C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, or a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group, An isobutyl group, a methoxyethyl group, and a benzyl group are more preferable.
一般式(1)中、R1がNH基であって且つ置換される場合、置換基としては、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基が好ましく、ヒドロキシ-n-プロピル基、ヒドロキシ-n-ペンチル基、メチルスルホニル基がより好ましい。
In the general formula (1), when R 1 is an NH group and is substituted, the substituent is preferably a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group or a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and a hydroxy-n-propyl group More preferred are a hydroxy-n-pentyl group and a methylsulfonyl group.
一般式(1)中、q、m及びnの組み合わせとしては、(q,m,n)=(0,1,0)、(0,0,1)又は(1,1,1)が好ましい。
In general formula (1), the combination of q, m and n is preferably (q, m, n) = (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1) or (1, 1, 1). .
一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体のより好ましい化合物としては、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例1)、
2-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例2)、
N-{3-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例3)、
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例4)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例5)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセトアミド(実施例6)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例7)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例8)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例9)、
(E)-N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-3-オキソプロパ-1-エン-1-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例10)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-4-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例11)、
N-[3-([1,4’ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-3-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例12)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(ピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例13)、
N-{3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル}-3-メトキシ-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例14)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例15)、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例16)、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アセトアミド(実施例17)、
2-[4-(ジメチルアミノ)ピペリジン-1-イル]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例18)、
(R)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例19)、
(S)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例20)、
2-[(5-ヒドロキシペンチル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例21)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例22)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-(4-{4-[6-(メチルアミノ)-6-オキソヘキシル]ピペラジン-1-イル}フェニル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例23)、
ベンジル 6-{4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサノエート(実施例24)、
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミド(実施例25)、
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミド(実施例26)、
N-(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例27)、
2-[(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例28)、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミド(実施例29)、
N-(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例30)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパンアミド(実施例31)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-3-カルボキサミド(実施例32)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチルスルホンアミド]アセトアミド(実施例33)、
4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ペンタンアミド(実施例34)、
1-(ピペリジン-4-イル)-3-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ウレア(実施例35)、
4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ブタンアミド(実施例36)、
N-{5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例37)、
N-{5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例38)、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミド(実施例39)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例40)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例41)、
ベンジル 2-[4-(4-{5-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-イル]アセテート(実施例42)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-イソプロピル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例43)、
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例44)、
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミド(実施例45)、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミド(実施例46)、
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミド(実施例47)、
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例48)、
N-(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例49)、
N-(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例50)、
N-[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例51)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アミノ}アセトアミド(実施例52)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピロリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例53)、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例54)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピペリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例55)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例56)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-4-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例57)、
6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ニコチンアミド(実施例58)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミド (実施例59)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンズアミド(実施例60)、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例61)、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例62)及び、
N-{5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例63)、
からなる群から選ばれる化合物を挙げることができる。 As a more preferable compound of the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 1) ,
2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 2),
N- {3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 3),
5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 4),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 5),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide (Example 6),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 7),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 8) ,
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 9),
(E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop-1-ene -1-yl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 10),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide ( Example 11),
N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide Example 12),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 13),
N- {3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl} -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide ( Example 14),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Amino] acetamide (Example 15),
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 16),
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) acetamide (Example 17 ),
2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 18),
(R) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Example 19),
(S) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Example 20),
2-[(5-hydroxypentyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide ( Example 21),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 22),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- (4- {4- [6- (methylamino) -6-oxohexyl] piperazin-1-yl} Phenyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 23),
Benzyl 6- {4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanoate (Example 24),
1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide (Example 25),
N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide ( Example 26),
N- (5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 27),
2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide ( Example 28),
2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide Example 29),
N- (5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ( Example 30),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropanamide Example 31),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine -3-carboxamide (Example 32),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methylsulfonamido] acetamide (Examples) 33),
4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] pentanamide (Example 34),
1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} urea (Example 35),
4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] butanamide (Example 36),
N- {5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ( Example 37),
N- {5- [3-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 38),
2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide (Example 39),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Propanamide (Example 40),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide (Example 41),
Benzyl 2- [4- (4- {5- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 ( 2H) -yl] acetate (Example 42),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-isopropyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide (Example 43),
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} acetamide (Example 44),
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} butanamide (Example 45),
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} pentanamide (Example 46),
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} hexanamide (Example 47),
N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 48),
N- (5- {4- [2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 49),
N- (5- {4- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 50),
N- [5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Acetamide (Example 51),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Methyl] amino} acetamide (Example 52),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide (Example 53),
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) pentane An amide (Example 54),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (piperidin-1-yl) pentanamide (Example 55),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 56),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] thiophene-2 Carboxamide (Example 57),
6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} nicotinamide Example 58),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide (Example 59),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Amino] methyl} benzamide (Example 60),
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Acetamide (Example 61),
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene -2-yl} acetamide (Example 62) and
N- {5- [6- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 63),
A compound selected from the group consisting of:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例1)、
2-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例2)、
N-{3-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例3)、
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例4)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例5)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセトアミド(実施例6)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例7)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例8)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例9)、
(E)-N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-3-オキソプロパ-1-エン-1-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例10)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-4-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例11)、
N-[3-([1,4’ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-3-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例12)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(ピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例13)、
N-{3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル}-3-メトキシ-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例14)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例15)、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例16)、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アセトアミド(実施例17)、
2-[4-(ジメチルアミノ)ピペリジン-1-イル]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例18)、
(R)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例19)、
(S)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例20)、
2-[(5-ヒドロキシペンチル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例21)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例22)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-(4-{4-[6-(メチルアミノ)-6-オキソヘキシル]ピペラジン-1-イル}フェニル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例23)、
ベンジル 6-{4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサノエート(実施例24)、
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミド(実施例25)、
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミド(実施例26)、
N-(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例27)、
2-[(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例28)、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミド(実施例29)、
N-(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例30)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパンアミド(実施例31)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-3-カルボキサミド(実施例32)、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチルスルホンアミド]アセトアミド(実施例33)、
4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ペンタンアミド(実施例34)、
1-(ピペリジン-4-イル)-3-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ウレア(実施例35)、
4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ブタンアミド(実施例36)、
N-{5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例37)、
N-{5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例38)、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミド(実施例39)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例40)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例41)、
ベンジル 2-[4-(4-{5-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-イル]アセテート(実施例42)、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-イソプロピル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド(実施例43)、
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例44)、
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミド(実施例45)、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミド(実施例46)、
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミド(実施例47)、
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例48)、
N-(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例49)、
N-(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例50)、
N-[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例51)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アミノ}アセトアミド(実施例52)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピロリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例53)、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例54)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピペリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド(実施例55)、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例56)、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-4-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(実施例57)、
6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ニコチンアミド(実施例58)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミド (実施例59)、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンズアミド(実施例60)、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例61)、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(実施例62)及び、
N-{5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド(実施例63)、
からなる群から選ばれる化合物を挙げることができる。 As a more preferable compound of the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 1) ,
2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 2),
N- {3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 3),
5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 4),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 5),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide (Example 6),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 7),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 8) ,
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 9),
(E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop-1-ene -1-yl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 10),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide ( Example 11),
N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide Example 12),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 13),
N- {3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl} -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide ( Example 14),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Amino] acetamide (Example 15),
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 16),
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) acetamide (Example 17 ),
2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (Example 18),
(R) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Example 19),
(S) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Example 20),
2-[(5-hydroxypentyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide ( Example 21),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 22),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- (4- {4- [6- (methylamino) -6-oxohexyl] piperazin-1-yl} Phenyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide (Example 23),
Benzyl 6- {4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanoate (Example 24),
1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide (Example 25),
N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide ( Example 26),
N- (5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Example 27),
2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide ( Example 28),
2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide Example 29),
N- (5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ( Example 30),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropanamide Example 31),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine -3-carboxamide (Example 32),
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methylsulfonamido] acetamide (Examples) 33),
4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] pentanamide (Example 34),
1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} urea (Example 35),
4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] butanamide (Example 36),
N- {5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ( Example 37),
N- {5- [3-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 38),
2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide (Example 39),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Propanamide (Example 40),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide (Example 41),
Benzyl 2- [4- (4- {5- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 ( 2H) -yl] acetate (Example 42),
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-isopropyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide (Example 43),
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} acetamide (Example 44),
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} butanamide (Example 45),
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} pentanamide (Example 46),
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} hexanamide (Example 47),
N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 48),
N- (5- {4- [2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 49),
N- (5- {4- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 50),
N- [5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Acetamide (Example 51),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Methyl] amino} acetamide (Example 52),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide (Example 53),
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) pentane An amide (Example 54),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (piperidin-1-yl) pentanamide (Example 55),
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Example 56),
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] thiophene-2 Carboxamide (Example 57),
6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} nicotinamide Example 58),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide (Example 59),
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Amino] methyl} benzamide (Example 60),
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Acetamide (Example 61),
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene -2-yl} acetamide (Example 62) and
N- {5- [6- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (Examples) 63),
A compound selected from the group consisting of:
本発明の一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物は、本発明のチオフェン誘導体のみならず、その医薬として許容される塩、それらの各種の水和物や溶媒和物、及び結晶多形を有する物質、及びこれらの物質のプロドラッグとなる物質を包含している。
The thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof includes not only the thiophene derivative of the present invention, but also a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, various hydrations thereof. Substances, solvates, substances having crystalline polymorphs, and substances that become prodrugs of these substances.
本発明の一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体として許容される塩としては、具体的には、無機酸(例えば、塩酸、臭化水素酸、ヨウ化水素酸、硫酸、硝酸、リン酸等)や有機酸(例えば、メタンスルホン酸、エタンスルホン酸、p-トルエンスルホン酸等)との酸付加塩等が挙げられる。
Specific examples of salts acceptable as the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention include inorganic acids (for example, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid). And acid addition salts with organic acids (for example, methanesulfonic acid, ethanesulfonic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, etc.).
本発明の一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体やその医薬として許容される塩の溶媒和物としては、水和物や各種の溶媒和物(例えば、エタノール等のアルコールとの溶媒和物等)が挙げられる。
Examples of the solvate of the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof include hydrates and various solvates (for example, solvates with alcohols such as ethanol). Etc.).
本発明の一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体は、公知の方法により製造することができる。チオフェン誘導体の製造方法を下記反応工程図に示すが、製造法はこれに限定されるものではない。
The thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention can be produced by a known method. Although the manufacturing method of a thiophene derivative is shown in the following reaction process drawing, a manufacturing method is not limited to this.
一般式(1)中、m=1、n=0、q=0を示す時、本発明化合物(I)は2-ニトロチオフェン誘導体(II)から製造することができる。
In the general formula (1), when m = 1, n = 0, and q = 0, the compound (I) of the present invention can be produced from the 2-nitrothiophene derivative (II).
[式中、
R1、R2、R3、X、Q1、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、A1は脱離基を示し、R6及びR7は、水素原子又はC1-6アルキル基を意味し、R6とR7が一緒になって環を形成してもよく、R8はハロゲン原子を示す] [Where:
R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above, A 1 represents a leaving group, R 6 and R 7 represent a hydrogen atom or C 1-6 alkyl Group, R 6 and R 7 may be combined to form a ring, and R 8 represents a halogen atom.]
R1、R2、R3、X、Q1、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、A1は脱離基を示し、R6及びR7は、水素原子又はC1-6アルキル基を意味し、R6とR7が一緒になって環を形成してもよく、R8はハロゲン原子を示す] [Where:
R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above, A 1 represents a leaving group, R 6 and R 7 represent a hydrogen atom or C 1-6 alkyl Group, R 6 and R 7 may be combined to form a ring, and R 8 represents a halogen atom.]
[工程1]脱離基を有するチオフェン誘導体(II)とボラン化合物(III)とのカップリング反応は、鈴木-宮浦カップリング反応を用いてチオフェン誘導体(IV)を製造することができる。使用される金属触媒、塩基ならびに反応条件は、通常、鈴木-宮浦カップリング反応に使用される試薬及び条件であれば特に限定されないが、例えばN.Miyaura,A.Suzuki,Chem.Rev.1995,95,2457-2483,(1995)等に記載されている方法を用いることができる。使用される金属触媒としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、酢酸パラジウム(II)、パラジウム(0)ジベンジリデンアセトン、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)ジパラジウム(0)、ビス(トリ-tert-ブチルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)(クロロホルム)ジパラジウム(0)、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、ビス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(II)ジクロリド、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)等のパラジウム錯体であり、好ましくは、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)である。塩基としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム、tert-ブトキシナトリウム、tert-ブトキシカリウム等であり、好ましくは炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸セシウムである。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン、エチレングリコールジメチルエーテル等のエーテル類;トルエン等の芳香族炭化水素類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;ジメチルスルホキシド、水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。好ましくはテトラヒドロフラン、エチレングリコールジメチルエーテル、N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、水、及びそれらの混合溶媒である。反応温度は、0℃~200℃、好ましくは60℃~150℃である。反応時間は、30分間~48時間、好ましくは1時間~20時間である。上記反応で用いるボラン化合物(III)は、市販の入手可能なものをそのまま使用するか、或いは、公知の方法により適宜製造できるが、これに限定されるものではない。
[Step 1] The coupling reaction between the thiophene derivative (II) having a leaving group and the borane compound (III) can produce the thiophene derivative (IV) using the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. The metal catalyst, base and reaction conditions used are not particularly limited as long as they are reagents and conditions used for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Miyaura, A .; Suzuki, Chem. Rev. The methods described in 1995, 95, 2457-2483, (1995) and the like can be used. The metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited. For example, palladium (II) acetate, palladium (0) dibenzylideneacetone, tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0), bis (tri-tert-butylphosphine) Palladium (0), tris (dibenzylideneacetone) (chloroform) dipalladium (0), [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), bis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) Palladium complexes such as dichloride and tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0), preferably [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium ( 0). The base is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, tert-butoxy sodium, and tert-butoxy potassium. Sodium carbonate and cesium carbonate. The solvent is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-dioxane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene; amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone. Dimethyl sulfoxide, water and the like can be used alone or in combination. Preferred are tetrahydrofuran, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, N, N-dimethylformamide, water, and mixed solvents thereof. The reaction temperature is 0 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 60 ° C. to 150 ° C. The reaction time is 30 minutes to 48 hours, preferably 1 hour to 20 hours. As the borane compound (III) used in the above reaction, a commercially available one can be used as it is, or it can be suitably produced by a known method, but is not limited thereto.
また、脱離基を有するチオフェン誘導体(II)とハロゲン化合物(III’)とのカップリング反応によって、チオフェン誘導体(IV)を製造することができる。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン等のハロゲン化炭化水素類;酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル等のエステル系溶媒;トルエン、ベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。使用される金属触媒としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、酢酸パラジウム(II)、パラジウム(0)ジベンジリデンアセトン、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)ジパラジウム(0)、ビス(トリ-tert-ブチルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)(クロロホルム)ジパラジウム(0)、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、ビス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(II)ジクロリド、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)等のパラジウム錯体であり、好ましくは、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)である。必要に応じて、o-トリトルイルホスフィン、トリフェニルホスフィン、1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン、トリ-tert-ブチルホスフィン、などのリガンドを添加してもよい。必要に応じて、ピリジン、DMAP、コリジン、ルチジン、DBU、DBN、DABCO、トリエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルペンチルアミン、トリメチルアミン等の有機塩基を添加してもよい。反応温度は、-20℃~150℃、好ましくは20℃~120℃である。反応時間は、5分間~2日間、好ましくは1時間~20時間である。
Further, the thiophene derivative (IV) can be produced by a coupling reaction between the thiophene derivative (II) having a leaving group and the halogen compound (III ′). The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. . The metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited. For example, palladium (II) acetate, palladium (0) dibenzylideneacetone, tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0), bis (tri-tert-butylphosphine) Palladium (0), tris (dibenzylideneacetone) (chloroform) dipalladium (0), [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), bis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) Palladium complexes such as dichloride and tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0), preferably [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium ( 0). If necessary, a ligand such as o-tritoluylphosphine, triphenylphosphine, 1,1'-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene, tri-tert-butylphosphine, and the like may be added. If necessary, an organic base such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, and trimethylamine may be added. The reaction temperature is −20 ° C. to 150 ° C., preferably 20 ° C. to 120 ° C. The reaction time is 5 minutes to 2 days, preferably 1 hour to 20 hours.
[工程2]チオフェン誘導体(IV)のニトロ基を、還元剤の存在下、溶媒中で反応させ、アミノチオフェン誘導体(V)を製造することができる。この還元方法は、(a)適当な不活性溶媒中、水素雰囲気下、接触水素還元触媒を用いてニトロ基を還元する接触水素付加であるか、又は(b)適当な不活性溶媒中、金属若しくは金属塩と酸又は金属若しくは金属塩とアルカリ金属水酸化物、硫化物若しくはアンモニウム塩等との混合物等を還元剤として用いてニトロ基を還元する金属還元により行われる。(a)接触水素付加の場合、溶媒としては、例えば、水;酢酸等の有機酸溶媒;メタノール、エタノール、イソプロパノール等のアルコール系溶媒;n-ヘキサン、シクロヘキサン等の炭化水素系溶媒;1,4-ジオキサン、テトラヒドロフラン、ジエチルエーテル、ジエチレングリコールジメチルエーテル等のエーテル系溶媒;酢酸エチル、酢酸メチル等のエステル系溶媒;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド等の非プロトン性極性溶媒等又はこれらの混合溶媒等を使用できる。接触水素還元触媒としては、例えば、パラジウム、パラジウム-黒、パラジウム-炭素、白金-炭素、白金、酸化白金、亜クロム酸銅、ラネーニッケル等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。反応温度は、-20℃~150℃、好ましくは0℃~100℃である。反応時間は、30分間~48時間、好ましくは1時間~24時間である。(b)金属還元の場合、鉄、硫酸鉄、鉛、スズ、塩化スズと塩酸、硫酸等の無機酸類との混合物、鉄若しくは亜鉛と酢酸等の有機酸類との混合物、又は鉄、硫酸鉄、亜鉛若しくはスズと水酸化ナトリウム等のアルカリ金属水酸化物、硫化アンモニウム等の硫化物、アンモニア水若しくは塩化アンモニウム等のアンモニウム塩との混合物が還元剤として用いられる。溶媒としては、例えば、水;酢酸等の有機酸溶媒;メタノール又はエタノール等のアルコール系溶媒;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル系溶媒等が挙げられる。反応温度は、例えば、亜鉛と酢酸とを還元剤として用いる場合、0℃~150℃、好ましくは50℃~120℃である。反応時間は、1分間~12時間、好ましくは1分間~6時間である。
[Step 2] The aminothiophene derivative (V) can be produced by reacting the nitro group of the thiophene derivative (IV) in a solvent in the presence of a reducing agent. This reduction method is (a) catalytic hydrogenation in which a nitro group is reduced using a catalytic hydrogen reduction catalyst in a hydrogen atmosphere in a suitable inert solvent, or (b) a metal in a suitable inert solvent. Alternatively, the reduction is carried out by metal reduction using a metal salt and acid or a mixture of metal or metal salt and alkali metal hydroxide, sulfide or ammonium salt as a reducing agent to reduce the nitro group. (A) In the case of catalytic hydrogenation, examples of the solvent include water; organic acid solvents such as acetic acid; alcohol solvents such as methanol, ethanol and isopropanol; hydrocarbon solvents such as n-hexane and cyclohexane; -Ether solvents such as dioxane, tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, diethylene glycol dimethyl ether; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and methyl acetate; aprotic polar solvents such as N, N-dimethylformamide, etc., or mixed solvents thereof can be used. . As the catalytic hydrogen reduction catalyst, for example, palladium, palladium-black, palladium-carbon, platinum-carbon, platinum, platinum oxide, copper chromite, Raney nickel and the like can be used alone or in combination. The reaction temperature is −20 ° C. to 150 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 100 ° C. The reaction time is 30 minutes to 48 hours, preferably 1 hour to 24 hours. (B) In the case of metal reduction, a mixture of iron, iron sulfate, lead, tin, tin chloride and inorganic acids such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid, a mixture of iron or zinc and organic acids such as acetic acid, or iron, iron sulfate, A mixture of zinc or tin and an alkali metal hydroxide such as sodium hydroxide, a sulfide such as ammonium sulfide, or an ammonium salt such as aqueous ammonia or ammonium chloride is used as the reducing agent. Examples of the solvent include water; organic acid solvents such as acetic acid; alcohol solvents such as methanol or ethanol; ether solvents such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane. The reaction temperature is, for example, 0 ° C. to 150 ° C., preferably 50 ° C. to 120 ° C. when zinc and acetic acid are used as the reducing agent. The reaction time is 1 minute to 12 hours, preferably 1 minute to 6 hours.
[工程3]アミノチオフェン誘導体(V)とカルボン酸誘導体(VI)との脱水縮合反応は、溶媒中塩基の存在下又は非存在下、縮合促進剤の存在下又は非存在下において縮合剤を用いて行うか、又はカルボン酸を活性中間体としたのちに縮合を行うことができる。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン等のハロゲン化炭化水素類;酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル等のエステル系溶媒;トルエン、ベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。塩基としては特に制限はないが、例えば、ピリジン、DMAP、コリジン、ルチジン、DBU、DBN、DABCO、トリエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルペンチルアミン、トリメチルアミン等の有機塩基、水素化リチウム、水素化ナトリウム、水素化カリウム等の水素化アルカリ金属類、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム等の水酸化アルカリ金属類、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム等の炭酸アルカリ金属類、炭酸水素ナトリウム、炭酸水素カリウム等の重炭酸アルカリ金属等を使用することができる。縮合促進剤としては特に制限はないが、DMAP、HOAt、HOBt、HODhbt、HONB、HOPfp、HOPht、HOSu等を使用することができる。縮合剤としては特に制限はないが、DCC、DIPCI、WSCI、WSC・HCl、DEPC、BOP、PyBOP、TBTU等を使用することができる。活性中間体としては特に制限はないが、酸ハロゲン化物、ピバル酸等との混合酸無水物、若しくはp-ニトロフェニルエステル等を使用することができる。反応温度は、-20℃~100℃、好ましくは0℃~40℃である。反応時間は、5分間~1日間、好ましくは10分間~12時間である。
[Step 3] The dehydration condensation reaction between the aminothiophene derivative (V) and the carboxylic acid derivative (VI) uses a condensing agent in the presence or absence of a base in the solvent and in the presence or absence of a condensation accelerator. Or after the carboxylic acid is made the active intermediate. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. . The base is not particularly limited. For example, organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Alkali metal hydrides such as potassium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used. Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as a condensation promoter, DMAP, HOAt, HOBt, HODhbt, HONB, HOPfp, HOPht, HOSu etc. can be used. Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as a condensing agent, DCC, DIPCI, WSCI, WSC * HCl, DEPC, BOP, PyBOP, TBTU etc. can be used. The active intermediate is not particularly limited, and an acid halide, a mixed acid anhydride with pivalic acid, or the like, or p-nitrophenyl ester can be used. The reaction temperature is −20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C. The reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
また、アミノチオフェン誘導体(V)と酸ハロゲン化物誘導体(VI’)との反応は、溶媒中塩基の存在下又は非存在下、行うことができる。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン等のハロゲン化炭化水素類;酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル等のエステル系溶媒;トルエン、ベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。塩基としては特に制限はないが、例えば、ピリジン、DMAP、コリジン、ルチジン、DBU、DBN、DABCO、トリエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルペンチルアミン、トリメチルアミン等の有機塩基、水素化リチウム、水素化ナトリウム、水素化カリウム等の水素化アルカリ金属類、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム等の水酸化アルカリ金属類、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム等の炭酸アルカリ金属類、炭酸水素ナトリウム、炭酸水素カリウム等の重炭酸アルカリ金属等を使用することができる。反応温度は、-20℃~100℃、好ましくは0℃~40℃である。反応時間は、5分間~1日間、好ましくは10分間~12時間である。
In addition, the reaction between the aminothiophene derivative (V) and the acid halide derivative (VI ′) can be performed in a solvent in the presence or absence of a base. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. . The base is not particularly limited. For example, organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Alkali metal hydrides such as potassium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used. The reaction temperature is −20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C. The reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
一般式(1)中、m=0、n=1、q=0を示す時、本発明化合物(I)は一般式(VII)で示されるチオフェンカルボニル誘導体から製造することができる。
In the general formula (1), when m = 0, n = 1, and q = 0, the compound (I) of the present invention can be produced from the thiophenecarbonyl derivative represented by the general formula (VII).
[式中、
R1、R2、R3、X、Q1、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、A1は脱離基を示し、A2はOH又は脱離基を示し、R6及びR7は、水素原子又はC1-6アルキル基を意味し、R6とR7が一緒になって環を形成してもよい。] [Where:
R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above, A 1 represents a leaving group, A 2 represents OH or a leaving group, R 6 and R 7 represents a hydrogen atom or a C 1-6 alkyl group, and R 6 and R 7 may be combined to form a ring. ]
R1、R2、R3、X、Q1、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、A1は脱離基を示し、A2はOH又は脱離基を示し、R6及びR7は、水素原子又はC1-6アルキル基を意味し、R6とR7が一緒になって環を形成してもよい。] [Where:
R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above, A 1 represents a leaving group, A 2 represents OH or a leaving group, R 6 and R 7 represents a hydrogen atom or a C 1-6 alkyl group, and R 6 and R 7 may be combined to form a ring. ]
チオフェン誘導体(I)は、工程4と工程5の組み合わせにより製造することができる。
[工程4]脱離基を有するチオフェン誘導体(VII)或いはチオフェン誘導体(VII)とアミン誘導体(VIII)との縮合誘導体と、ボラン化合物(III)とのカップリング反応は、鈴木-宮浦カップリング反応を用いて行うことができる。使用される金属触媒、塩基ならびに反応条件は、通常、鈴木-宮浦カップリング反応に使用される試薬及び条件であれば特に限定されないが、例えばN. Miyaura, A. Suzuki, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457-2483, (1995) 等に記載されている方法を用いることができる。使用される金属触媒としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、酢酸パラジウム(II)、パラジウム(0)ジベンジリデンアセトン、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)ジパラジウム(0)、ビス(トリ-tert-ブチルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)(クロロホルム)ジパラジウム(0)、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、ビス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(II)ジクロリド、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)等のパラジウム錯体であり、好ましくは、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)である。塩基としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム、tert-ブトキシナトリウム、tert-ブトキシカリウム等であり、好ましくは炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸セシウムである。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン、エチレングリコールジメチルエーテル等のエーテル類;ベンゼン、トルエン等の芳香族炭化水素類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;ジメチルスルホキシド、水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。好ましくはテトラヒドロフラン、エチレングリコールジメチルエーテル、N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、水、及びそれらの混合溶媒である。反応温度は、0℃~200℃、好ましくは60℃~150℃である。反応時間は、30分間~48時間、好ましくは1時間~20時間である。上記反応で用いるボラン化合物(III)は、市販の入手可能なものをそのまま使用するか、或いは、公知の方法により適宜製造できるが、これに限定されるものではない。 The thiophene derivative (I) can be produced by a combination of Step 4 and Step 5.
[Step 4] The coupling reaction between the thiophene derivative (VII) having a leaving group or a condensed derivative of the thiophene derivative (VII) and the amine derivative (VIII) and the borane compound (III) is a Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Can be used. The metal catalyst, base and reaction conditions to be used are not particularly limited as long as they are reagents and conditions generally used for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Miyaura, A.A. Suzuki, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457-2483, (1995) can be used. The metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited. For example, palladium (II) acetate, palladium (0) dibenzylideneacetone, tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0), bis (tri-tert-butylphosphine) Palladium (0), tris (dibenzylideneacetone) (chloroform) dipalladium (0), [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), bis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) Palladium complexes such as dichloride and tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0), preferably [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium ( 0). The base is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, tert-butoxy sodium, and tert-butoxy potassium. Sodium carbonate and cesium carbonate. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-dioxane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether; aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene and toluene; N, N-dimethylformamide, N-methylpyrrolidone and the like Amides of dimethyl sulfoxide, water and the like can be used alone or in combination. Preferred are tetrahydrofuran, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, N, N-dimethylformamide, water, and mixed solvents thereof. The reaction temperature is 0 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 60 ° C. to 150 ° C. The reaction time is 30 minutes to 48 hours, preferably 1 hour to 20 hours. As the borane compound (III) used in the above reaction, a commercially available one can be used as it is, or it can be appropriately produced by a known method, but is not limited thereto.
[工程4]脱離基を有するチオフェン誘導体(VII)或いはチオフェン誘導体(VII)とアミン誘導体(VIII)との縮合誘導体と、ボラン化合物(III)とのカップリング反応は、鈴木-宮浦カップリング反応を用いて行うことができる。使用される金属触媒、塩基ならびに反応条件は、通常、鈴木-宮浦カップリング反応に使用される試薬及び条件であれば特に限定されないが、例えばN. Miyaura, A. Suzuki, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457-2483, (1995) 等に記載されている方法を用いることができる。使用される金属触媒としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、酢酸パラジウム(II)、パラジウム(0)ジベンジリデンアセトン、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)ジパラジウム(0)、ビス(トリ-tert-ブチルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)(クロロホルム)ジパラジウム(0)、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、ビス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(II)ジクロリド、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)等のパラジウム錯体であり、好ましくは、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)である。塩基としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム、tert-ブトキシナトリウム、tert-ブトキシカリウム等であり、好ましくは炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸セシウムである。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン、エチレングリコールジメチルエーテル等のエーテル類;ベンゼン、トルエン等の芳香族炭化水素類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;ジメチルスルホキシド、水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。好ましくはテトラヒドロフラン、エチレングリコールジメチルエーテル、N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、水、及びそれらの混合溶媒である。反応温度は、0℃~200℃、好ましくは60℃~150℃である。反応時間は、30分間~48時間、好ましくは1時間~20時間である。上記反応で用いるボラン化合物(III)は、市販の入手可能なものをそのまま使用するか、或いは、公知の方法により適宜製造できるが、これに限定されるものではない。 The thiophene derivative (I) can be produced by a combination of Step 4 and Step 5.
[Step 4] The coupling reaction between the thiophene derivative (VII) having a leaving group or a condensed derivative of the thiophene derivative (VII) and the amine derivative (VIII) and the borane compound (III) is a Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Can be used. The metal catalyst, base and reaction conditions to be used are not particularly limited as long as they are reagents and conditions generally used for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction. Miyaura, A.A. Suzuki, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457-2483, (1995) can be used. The metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited. For example, palladium (II) acetate, palladium (0) dibenzylideneacetone, tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0), bis (tri-tert-butylphosphine) Palladium (0), tris (dibenzylideneacetone) (chloroform) dipalladium (0), [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), bis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) Palladium complexes such as dichloride and tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0), preferably [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium ( 0). The base is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, tert-butoxy sodium, and tert-butoxy potassium. Sodium carbonate and cesium carbonate. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-dioxane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether; aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene and toluene; N, N-dimethylformamide, N-methylpyrrolidone and the like Amides of dimethyl sulfoxide, water and the like can be used alone or in combination. Preferred are tetrahydrofuran, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, N, N-dimethylformamide, water, and mixed solvents thereof. The reaction temperature is 0 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 60 ° C. to 150 ° C. The reaction time is 30 minutes to 48 hours, preferably 1 hour to 20 hours. As the borane compound (III) used in the above reaction, a commercially available one can be used as it is, or it can be appropriately produced by a known method, but is not limited thereto.
[工程5]チオフェン誘導体(VII)或いはチオフェン誘導体(VII)とボラン化合物(III)とのカップリング誘導体と、アミン誘導体(VIII)との反応は、溶媒中塩基の存在下又は非存在下、縮合促進剤の存在下又は非存在下において縮合剤を用いて行うか、カルボン酸を活性中間体としたのち縮合を行うことができる。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン等のハロゲン化炭化水素類;酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル等のエステル類;トルエン、ベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができ、塩基としては特に制限はないが、例えば、ピリジン、DMAP、コリジン、ルチジン、DBU、DBN、DABCO、トリエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルペンチルアミン、トリメチルアミン等の有機塩基、水素化リチウム、水素化ナトリウム、水素化カリウム等の水素化アルカリ金属類、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム等の水酸化アルカリ金属類、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム等の炭酸アルカリ金属類、炭酸水素ナトリウム、炭酸水素カリウム等の重炭酸アルカリ金属等を使用することができる。縮合促進剤としては特に制限はないが、DMAP、HOAt、HOBt、HODhbt、HONB、HOPfp、HOPht、HOSu等を使用することができる。縮合剤としては特に制限はないが、DCC、DIPCI、WSCI、WSC・HCl、DEPC、BOP、PyBOP、TBTU等を使用することができる。活性中間体としては特に制限はないが、酸ハロゲン化物、ピバル酸等との混合酸無水物、若しくはp-ニトロフェニルエステル等を使用することができる。反応温度は、(使用する原料、試薬によって異なるが、)一般に-20℃~100℃、好ましくは0℃~40℃である。反応時間は、5分間~1日間、好ましくは10分間~12時間である。
[Step 5] The reaction of thiophene derivative (VII) or a coupling derivative of thiophene derivative (VII) with borane compound (III) and amine derivative (VIII) is carried out in the presence or absence of a base in a solvent. The condensation can be carried out using a condensing agent in the presence or absence of an accelerator, or using carboxylic acid as an active intermediate. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; esters such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; tetrahydrofuran Ethers such as 1,4-dioxane; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; water and the like can be used alone or in combination. The base is not particularly limited. For example, organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Mosquito Alkali metal hydrides such as lithium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used. Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as a condensation promoter, DMAP, HOAt, HOBt, HODhbt, HONB, HOPfp, HOPht, HOSu etc. can be used. Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as a condensing agent, DCC, DIPCI, WSCI, WSC * HCl, DEPC, BOP, PyBOP, TBTU etc. can be used. The active intermediate is not particularly limited, and an acid halide, a mixed acid anhydride with pivalic acid, or the like, or p-nitrophenyl ester can be used. The reaction temperature is generally −20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C. (depending on the starting materials and reagents used). The reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
一般式(1)中、m=1、n=1、q=0を示す時、本発明化合物(I)は2-アミノ-チオフェン誘導体(V)から製造することができる。
In the general formula (1), when m = 1, n = 1, and q = 0, the compound (I) of the present invention can be produced from the 2-amino-thiophene derivative (V).
[式中、R1、R2、R3、X、Q1、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示す。]
[Wherein R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above. ]
[工程6]アミンを有するチオフェン誘導体(V)とアミン誘導体(VIII)とのウレア形成反応によって、チオフェン誘導体(I)を製造することができる。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン等のハロゲン化炭化水素類;、酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル等のエステル類;トルエン、ベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。必要に応じて塩基を加えてもよく、塩基としては特に制限はないが、例えば、ピリジン、DMAP、コリジン、ルチジン、DBU、DBN、DABCO、トリエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルペンチルアミン、トリメチルアミン等の有機塩基を使用することができる。ウレアを形成する反応試薬としては特に制限はないが、クロロギ酸フェニル、クロロギ酸4-ニトロフェニル、カルボニルジイミダゾール、トリホスゲン等を使用することができる。反応温度は、(使用する原料、試薬によって異なるが、)一般に-20℃~100℃、好ましくは0℃~60℃である。反応時間は、5分間~1日間、好ましくは10分間~12時間である。
[Step 6] The thiophene derivative (I) can be produced by a urea formation reaction between the amine-containing thiophene derivative (V) and the amine derivative (VIII). The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; esters such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. . A base may be added as necessary, and the base is not particularly limited. For example, organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, and trimethylamine Can be used. The reaction reagent for forming urea is not particularly limited, and phenyl chloroformate, 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate, carbonyldiimidazole, triphosgene and the like can be used. The reaction temperature is generally −20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 60 ° C. (depending on the starting materials and reagents used). The reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
一般式(1)中、m=1、n=1、q=1を示す時、本発明化合物(I)は2-アミノ-チオフェン誘導体(V)から製造することができる。
In the general formula (1), when m = 1, n = 1, and q = 1, the compound (I) of the present invention can be produced from the 2-amino-thiophene derivative (V).
[式中、R1、R2、R3、X、Q1、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、A1は脱離基を示し、R8はハロゲン原子を示す。]
[Wherein R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , X, Q 1 and ring Y are the same as defined above, A 1 represents a leaving group, and R 8 represents a halogen atom. ]
[工程7]アミノチオフェン誘導体(V)とカルボン酸誘導体(IX)との脱水縮合反応によって、脱離基を有するチオフェン誘導体(X)を製造することができる。脱水縮合反応は、溶媒中塩基の存在下又は非存在下、縮合促進剤の存在下又は非存在下において縮合剤を用いて行うか、カルボン酸を活性中間体としたのち縮合を行うことができる。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン等のハロゲン化炭化水素類;酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル等のエステル系溶媒;トルエン、ベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。塩基としては特に制限はないが、例えば、ピリジン、DMAP、コリジン、ルチジン、DBU、DBN、DABCO、トリエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルペンチルアミン、トリメチルアミン等の有機塩基、水素化リチウム、水素化ナトリウム、水素化カリウム等の水素化アルカリ金属類、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム等の水酸化アルカリ金属類、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム等の炭酸アルカリ金属類、炭酸水素ナトリウム、炭酸水素カリウム等の重炭酸アルカリ金属等を使用することができる。縮合促進剤としては特に制限はないが、DMAP、HOAt、HOBt、HODhbt、HONB、HOPfp、HOPht、HOSu等を使用することができる。縮合剤としては特に制限はないが、DCC、DIPCI、WSCI、WSC・HCl、DEPC、BOP、PyBOP、TBTU等を使用することができる。活性中間体としては特に制限はないが、酸ハロゲン化物、ピバル酸等との混合酸無水物、若しくはp-ニトロフェニルエステル等を使用することができる。反応温度は、-20℃~100℃、好ましくは0℃~40℃である。反応時間は、5分間~1日間、好ましくは10分間~12時間である。
[Step 7] A thiophene derivative (X) having a leaving group can be produced by a dehydration condensation reaction between the aminothiophene derivative (V) and the carboxylic acid derivative (IX). The dehydration condensation reaction can be carried out using a condensing agent in the presence or absence of a base in a solvent, in the presence or absence of a condensation accelerator, or after using a carboxylic acid as an active intermediate. . The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. . The base is not particularly limited. For example, organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Alkali metal hydrides such as potassium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used. Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as a condensation promoter, DMAP, HOAt, HOBt, HODhbt, HONB, HOPfp, HOPht, HOSu etc. can be used. Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as a condensing agent, DCC, DIPCI, WSCI, WSC * HCl, DEPC, BOP, PyBOP, TBTU etc. can be used. The active intermediate is not particularly limited, and an acid halide, a mixed acid anhydride with pivalic acid, or the like, or p-nitrophenyl ester can be used. The reaction temperature is −20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C. The reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
また、アミノチオフェン誘導体(V)と酸ハロゲン化物誘導体(IX’)の反応によって、脱離基を有するチオフェン誘導体(X)を製造することができる。反応は、溶媒中塩基の存在下又は非存在下、行うことができる。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン等のハロゲン化炭化水素類;酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル等のエステル系溶媒;トルエン、ベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。塩基としては特に制限はないが、例えば、ピリジン、DMAP、コリジン、ルチジン、DBU、DBN、DABCO、トリエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルエチルアミン、ジイソプロピルペンチルアミン、トリメチルアミン等の有機塩基、水素化リチウム、水素化ナトリウム、水素化カリウム等の水素化アルカリ金属類、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム等の水酸化アルカリ金属類、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム等の炭酸アルカリ金属類、炭酸水素ナトリウム、炭酸水素カリウム等の重炭酸アルカリ金属等を使用することができる。反応温度は、-20℃~100℃、好ましくは0℃~40℃である。反応時間は、5分間~1日間、好ましくは10分間~12時間である。
Moreover, the thiophene derivative (X) having a leaving group can be produced by the reaction of the aminothiophene derivative (V) and the acid halide derivative (IX ′). The reaction can be performed in a solvent in the presence or absence of a base. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; Ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; Nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; Amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; Water and the like can be used alone or in combination. . The base is not particularly limited. For example, organic bases such as pyridine, DMAP, collidine, lutidine, DBU, DBN, DABCO, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, diisopropylpentylamine, trimethylamine, lithium hydride, sodium hydride, hydrogenated Alkali metal hydrides such as potassium, alkali metal hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and cesium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, An alkali metal bicarbonate such as potassium bicarbonate can be used. The reaction temperature is −20 ° C. to 100 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 40 ° C. The reaction time is 5 minutes to 1 day, preferably 10 minutes to 12 hours.
[工程8]脱離基を有するチオフェン誘導体(X)アミン誘導体(VIII)の反応によって、チオフェン誘導体(I)を製造することができる。反応は、溶媒中、塩基の存在下により行うことができる。溶媒としては、特に制限は無いが、例えばN,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;ジメチルスルホキシド;1,4-ジオキサン、テトラヒドロフラン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができ、塩基としては、特に制限は無いが、例えば、水素化リチウム、水素化ナトリウム、水素化カリウム等の水素化アルカリ金属類、金属リチウム、金属ナトリウム、金属カリウム等のアルカリ金属類、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム等の水酸化アルカリ金属類、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム等の炭酸アルカリ金属類、リチウムジイソプロピルアミド、ナトリウムジイソプロピルアミド、カリウムジイソプロピルアミド、リチウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、ナトリウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、カリウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、tert-ブトキシナトリウム、tert-ブトキシカリウム、n-ブチルリチウム、s-ブチルリチウム、tert-ブチルリチウム等を使用することができる。反応条件によって異なるが、反応温度は-10℃~200℃、好ましくは0℃~120℃である。反応時間は1時間~72時間、好ましくは1時間~36時間である。
[Step 8] The thiophene derivative (I) can be produced by the reaction of the thiophene derivative (X) amine derivative (VIII) having a leaving group. The reaction can be performed in a solvent in the presence of a base. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; dimethyl sulfoxide; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile Can be used alone or in combination, and the base is not particularly limited. For example, alkali metal hydrides such as lithium hydride, sodium hydride, potassium hydride, metal lithium, metal sodium, metal Alkali metals such as potassium, alkali hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, lithium diisopropylamide, sodium diisopropyl Amides, potassium Isopropylamide, lithium hexamethyldisilazide, sodium hexamethyldisilazide, potassium hexamethyldisilazide, tert-butoxy sodium, tert-butoxy potassium, n-butyl lithium, s-butyl lithium, tert-butyl lithium, etc. Can be used. Although depending on the reaction conditions, the reaction temperature is −10 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 120 ° C. The reaction time is 1 hour to 72 hours, preferably 1 hour to 36 hours.
なお、上記製造方法で用いるボラン化合物(III)は、入手可能なものをそのまま使用するか、或いは、公知の方法により適宜製造でき、例えば以下の方法により製造することが可能であるが、これに限定されるものではない。
The borane compound (III) used in the above production method can be used as it is, or can be produced appropriately by a known method. For example, it can be produced by the following method. It is not limited.
[式中、Xは、前記定義と同じものを示し、A3は脱離基を示し、R6及びR7は、水素原子又はC1-6アルキル基を意味し、R6とR7が一緒になって環を形成してもよい。]
[Wherein X represents the same as defined above, A 3 represents a leaving group, R 6 and R 7 represent a hydrogen atom or a C 1-6 alkyl group, and R 6 and R 7 represent Together, they may form a ring. ]
[工程9]化合物(XI)から金属触媒を用いてボラン化合物(III)を製造する工程である。使用される金属触媒としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、酢酸パラジウム(II)、パラジウム(0)ジベンジリデンアセトン、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)ジパラジウム(0)、ビス(トリ-tert-ブチルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)(クロロホルム)ジパラジウム(0)、[1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン]ジクロロパラジウム(II)、ビス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(II)ジクロリド、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)等のパラジウム錯体等であり、好ましくはビス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(II)ジクロリドである。必要に応じて、o-トリトルイルホスフィン、トリフェニルホスフィン、1,1’-ビス(ジフェニルホスフィノ)フェロセン、トリ-tert-ブチルホスフィン、などのリガンドを添加してもよい。使用される塩基としては、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム、酢酸カリウム、酢酸ナトリウム等であり、好ましくは酢酸カリウムである。使用される溶媒としては特に制限は無いが、例えば、テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;トルエン等の芳香族炭化水素類;N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;ジメチルスルホキシド、水等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。好ましくは1,4-ジオキサンと水の混合溶媒である。反応温度は、0℃~200℃、好ましくは80℃~150℃である。反応時間は、1時間~48時間、好ましくは2時間~24時間である。
なお、上記製造方法で用いるカルボン酸誘導体(VI)は入手可能なものをそのまま使用するか、或いは、公知の方法により適宜製造でき、例えば以下の方法により製造することが可能であるが、これに限定されるものではない。 [Step 9] In this step, borane compound (III) is produced from compound (XI) using a metal catalyst. The metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited. For example, palladium (II) acetate, palladium (0) dibenzylideneacetone, tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0), bis (tri-tert-butylphosphine) Palladium (0), tris (dibenzylideneacetone) (chloroform) dipalladium (0), [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), bis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) Palladium complexes such as dichloride and tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0) are preferred, and bis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) dichloride is preferred. If necessary, a ligand such as o-tritoluylphosphine, triphenylphosphine, 1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene, tri-tert-butylphosphine, and the like may be added. Examples of the base to be used include lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, potassium acetate, sodium acetate and the like, preferably potassium acetate. The solvent to be used is not particularly limited. For example, ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene; amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone Dimethyl sulfoxide, water and the like can be used alone or in combination. A mixed solvent of 1,4-dioxane and water is preferred. The reaction temperature is 0 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 80 ° C. to 150 ° C. The reaction time is 1 hour to 48 hours, preferably 2 hours to 24 hours.
In addition, the carboxylic acid derivative (VI) used in the above production method can be used as it is, or can be appropriately produced by a known method, for example, it can be produced by the following method. It is not limited.
なお、上記製造方法で用いるカルボン酸誘導体(VI)は入手可能なものをそのまま使用するか、或いは、公知の方法により適宜製造でき、例えば以下の方法により製造することが可能であるが、これに限定されるものではない。 [Step 9] In this step, borane compound (III) is produced from compound (XI) using a metal catalyst. The metal catalyst to be used is not particularly limited. For example, palladium (II) acetate, palladium (0) dibenzylideneacetone, tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0), bis (tri-tert-butylphosphine) Palladium (0), tris (dibenzylideneacetone) (chloroform) dipalladium (0), [1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (II), bis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) Palladium complexes such as dichloride and tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0) are preferred, and bis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (II) dichloride is preferred. If necessary, a ligand such as o-tritoluylphosphine, triphenylphosphine, 1,1′-bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene, tri-tert-butylphosphine, and the like may be added. Examples of the base to be used include lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, potassium acetate, sodium acetate and the like, preferably potassium acetate. The solvent to be used is not particularly limited. For example, ethers such as tetrahydrofuran and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene; amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone Dimethyl sulfoxide, water and the like can be used alone or in combination. A mixed solvent of 1,4-dioxane and water is preferred. The reaction temperature is 0 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 80 ° C. to 150 ° C. The reaction time is 1 hour to 48 hours, preferably 2 hours to 24 hours.
In addition, the carboxylic acid derivative (VI) used in the above production method can be used as it is, or can be appropriately produced by a known method, for example, it can be produced by the following method. It is not limited.
[式中、
R1、環D、Q1、Q4、R5、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、Pは保護基を示し、W1、W2、W4、W6は脱離基、アルデヒド基、アミノ基或いは水酸基を示し、W3、W5及びW7はC=O又はNHを示す。但し、W1、W4が脱離基或いはアルデヒド基の時、W2、W6はアミノ基或いは水酸基を示し、W2、W6が脱離基或いはアルデヒド基の時、W1、W4はアミノ基或いは水酸基を示す(なお、化合物(XV)及び(XV’)は、カルボン酸誘導体(VI)において、環YがQ4、R5及び環Dにより形成される置換基を有する場合を示している。)] [Where:
R 1 , Ring D, Q 1 , Q 4 , R 5 and Ring Y are the same as defined above, P is a protecting group, W 1 , W 2 , W 4 and W 6 are leaving groups, An aldehyde group, an amino group or a hydroxyl group is shown, and W 3 , W 5 and W 7 are C═O or NH. However, when W 1 and W 4 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group, W 2 and W 6 represent an amino group or a hydroxyl group, and when W 2 and W 6 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group, W 1 and W 4 Represents an amino group or a hydroxyl group (note that the compounds (XV) and (XV ′) represent a case where the ring Y has a substituent formed by Q 4 , R 5 and the ring D in the carboxylic acid derivative (VI)). Is shown.)]
R1、環D、Q1、Q4、R5、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、Pは保護基を示し、W1、W2、W4、W6は脱離基、アルデヒド基、アミノ基或いは水酸基を示し、W3、W5及びW7はC=O又はNHを示す。但し、W1、W4が脱離基或いはアルデヒド基の時、W2、W6はアミノ基或いは水酸基を示し、W2、W6が脱離基或いはアルデヒド基の時、W1、W4はアミノ基或いは水酸基を示す(なお、化合物(XV)及び(XV’)は、カルボン酸誘導体(VI)において、環YがQ4、R5及び環Dにより形成される置換基を有する場合を示している。)] [Where:
R 1 , Ring D, Q 1 , Q 4 , R 5 and Ring Y are the same as defined above, P is a protecting group, W 1 , W 2 , W 4 and W 6 are leaving groups, An aldehyde group, an amino group or a hydroxyl group is shown, and W 3 , W 5 and W 7 are C═O or NH. However, when W 1 and W 4 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group, W 2 and W 6 represent an amino group or a hydroxyl group, and when W 2 and W 6 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group, W 1 and W 4 Represents an amino group or a hydroxyl group (note that the compounds (XV) and (XV ′) represent a case where the ring Y has a substituent formed by Q 4 , R 5 and the ring D in the carboxylic acid derivative (VI)). Is shown.)]
[工程10]化合物(XII)、化合物(XIV)、或いは(XIV’)からa)還元的アミノ化或いは、b)アルキル化によって化合物(XIII)或いは化合物(XV)を製造する工程である。a)還元的アミノ化は、溶媒中、酸の存在下又は非存在下にて還元試薬を用いて行うことができる。その際、Dean-Stark装置等を用いて脱水操作を行っても良い。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン、酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル、トルエン、ベンゼン、テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン、アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル、メタノール、エタノール、イソプロパノール、酢酸、トリフルオロ酢酸等を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。酸としては特に制限はないが、例えば、プロピオン酸、安息香酸等のプロトン酸、四塩化チタン、三フッ化ホウ素、塩化第二スズ等のルイス酸を使用することができる。還元試薬としては特に制限はないが、例えば、トリアセトキシ水素化ホウ素ナトリウム、トリアセトキシ水素化ホウ素テトラメチルアンモニウム、シアノ水素化ホウ素ナトリウム、水素化ホウ素ナトリウム、水素化ホウ素リチウム、トリメトキシ水素化ホウ素ナトリウム、トリエチル水素化ホウ素リチウム等の水素化ホウ素系試薬、水素化アルミニウムリチウム、ジイソプロピル水素化アルミニウム、ビス(2-メトキシエトキシ)水素化アルミニウムナトリウム等の水素化アルミニウム試薬、金属触媒及び水素源を用いた接触還元を使用することができる。接触還元の水素源としては、例えば、水素、シクロヘキサジエン、ギ酸、ギ酸アンモニウム等を使用することができ、金属触媒としては、例えば、パラジウム炭素、パラジウム黒、水酸化パラジウム、ラネーニッケル、二酸化白金、白金黒等を使用することができる。b)アルキル化は、溶媒中、塩基の存在下により行うことができる。溶媒としては、特に制限は無いが、例えばN,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;ジメチルスルホキシド;1,4-ジオキサン、テトラヒドロフラン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができ、塩基としては、特に制限は無いが、例えば、水素化リチウム、水素化ナトリウム、水素化カリウム等の水素化アルカリ金属類、金属リチウム、金属ナトリウム、金属カリウム等のアルカリ金属類、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム等の水酸化アルカリ金属類、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム等の炭酸アルカリ金属類、リチウムジイソプロピルアミド、ナトリウムジイソプロピルアミド、カリウムジイソプロピルアミド、リチウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、ナトリウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、カリウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、tert-ブトキシナトリウム、tert-ブトキシカリウム、n-ブチルリチウム、s-ブチルリチウム、tert-ブチルリチウム等を使用することができる。反応温度は、-10℃~200℃、反応条件によって異なるが好ましくは0℃~120℃である。反応時間は、1時間~72時間、反応条件によって異なるが好ましくは1時間~36時間である。
[Step 10] In this step, compound (XIII) or compound (XV) is produced from compound (XII), compound (XIV) or (XIV ') by a) reductive amination or b) alkylation. a) Reductive amination can be carried out using a reducing reagent in a solvent in the presence or absence of an acid. At that time, the dehydration operation may be performed using a Dean-Stark apparatus or the like. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, isopropyl acetate, toluene, benzene, tetrahydrofuran, 1,4-dioxane, acetonitrile, propionitrile, methanol, ethanol, isopropanol , Acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid and the like can be used alone or in combination. Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as an acid, For example, Lewis acids, such as proton acids, such as propionic acid and benzoic acid, titanium tetrachloride, boron trifluoride, and stannic chloride, can be used. There is no particular limitation as a reducing reagent, for example, sodium triacetoxyborohydride, tetramethylammonium borohydride tetramethylammonium, sodium cyanoborohydride, sodium borohydride, lithium borohydride, sodium trimethoxyborohydride, Contact using borohydride reagents such as lithium triethylborohydride, lithium hydride lithium, diisopropylaluminum hydride, aluminum hydride reagents such as sodium bis (2-methoxyethoxy) aluminum hydride, metal catalyst and hydrogen source Reduction can be used. As a hydrogen source for catalytic reduction, for example, hydrogen, cyclohexadiene, formic acid, ammonium formate and the like can be used, and as a metal catalyst, for example, palladium carbon, palladium black, palladium hydroxide, Raney nickel, platinum dioxide, platinum Black etc. can be used. b) Alkylation can be carried out in a solvent in the presence of a base. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; dimethyl sulfoxide; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile Can be used alone or in combination, and the base is not particularly limited. For example, alkali metal hydrides such as lithium hydride, sodium hydride, potassium hydride, metal lithium, metal sodium, metal Alkali metals such as potassium, alkali hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, lithium diisopropylamide, sodium diisopropyl Amides, potassium Isopropylamide, lithium hexamethyldisilazide, sodium hexamethyldisilazide, potassium hexamethyldisilazide, tert-butoxy sodium, tert-butoxy potassium, n-butyl lithium, s-butyl lithium, tert-butyl lithium, etc. Can be used. The reaction temperature is −10 ° C. to 200 ° C., and varies depending on the reaction conditions, but is preferably 0 ° C. to 120 ° C. The reaction time varies from 1 hour to 72 hours depending on the reaction conditions, but is preferably 1 hour to 36 hours.
[工程11]保護基の脱保護としては特に制限はないが、一般に用いられる方法(Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.)等により導入できるものを適宜使用し、脱保護をおこなうことができるが、これに限定されるものではない。
[Step 11] There is no particular limitation on the deprotection of the protecting group, but a method that can be introduced by a generally used method (Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) or the like can be used as appropriate. However, the present invention is not limited to this.
なお、上記製造方法で用いるアミン誘導体(VIII)は入手可能なものをそのまま使用するか、或いは、公知の方法により適宜製造でき、例えば以下の方法により製造することが可能であるが、これに限定されるものではない。
The amine derivative (VIII) used in the above production method can be used as it is, or can be produced appropriately by a known method, for example, it can be produced by the following method, but is not limited thereto. Is not to be done.
[式中、
R1、環D、Q1、Q4、R5、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、Pは保護基を示し、W1、W2、W4、W6は脱離基或いはアルデヒド基或いはアミノ基或いは水酸基を示し、W3、W5及びW7はC=O又はNHを示す。但し、W1、W4が脱離基或いはアルデヒド基の時、W2、W6はアミノ基或いは水酸基を示し、W2、W6が脱離基或いはアルデヒド基の時、W1、W4はアミノ基或いは水酸基を示す(なお、化合物(XIX)及び(XX)は、アミン誘導体(VIII)において、環YがQ4、R5及び環Dにより形成される置換基を有する場合を示している。)] [Where:
R 1 , Ring D, Q 1 , Q 4 , R 5 and Ring Y are the same as defined above, P is a protecting group, W 1 , W 2 , W 4 and W 6 are leaving groups or An aldehyde group, an amino group, or a hydroxyl group is represented, and W 3 , W 5, and W 7 represent C═O or NH. However, when W 1 and W 4 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group, W 2 and W 6 represent an amino group or a hydroxyl group, and when W 2 and W 6 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group, W 1 and W 4 Represents an amino group or a hydroxyl group (note that compounds (XIX) and (XX) represent the case where ring Y has a substituent formed by Q 4 , R 5 and ring D in amine derivative (VIII)). )]
R1、環D、Q1、Q4、R5、環Yは、前記定義と同じものを示し、Pは保護基を示し、W1、W2、W4、W6は脱離基或いはアルデヒド基或いはアミノ基或いは水酸基を示し、W3、W5及びW7はC=O又はNHを示す。但し、W1、W4が脱離基或いはアルデヒド基の時、W2、W6はアミノ基或いは水酸基を示し、W2、W6が脱離基或いはアルデヒド基の時、W1、W4はアミノ基或いは水酸基を示す(なお、化合物(XIX)及び(XX)は、アミン誘導体(VIII)において、環YがQ4、R5及び環Dにより形成される置換基を有する場合を示している。)] [Where:
R 1 , Ring D, Q 1 , Q 4 , R 5 and Ring Y are the same as defined above, P is a protecting group, W 1 , W 2 , W 4 and W 6 are leaving groups or An aldehyde group, an amino group, or a hydroxyl group is represented, and W 3 , W 5, and W 7 represent C═O or NH. However, when W 1 and W 4 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group, W 2 and W 6 represent an amino group or a hydroxyl group, and when W 2 and W 6 are a leaving group or an aldehyde group, W 1 and W 4 Represents an amino group or a hydroxyl group (note that compounds (XIX) and (XX) represent the case where ring Y has a substituent formed by Q 4 , R 5 and ring D in amine derivative (VIII)). )]
[工程12]化合物(XVI)、化合物(XVIII)或いは(XVIII’)からa)還元的アミノ化或いは、b)アルキル化によって化合物(XVII)或いは化合物(XIX)を製造する工程である。a)還元的アミノ化は、溶媒中、酸の存在下又は非存在下にて還元試薬を用いて行うことができる。その際、Dean-Stark装置等を用いて脱水操作を行っても良い。溶媒としては特に制限はないが、例えば、1,2-ジクロロエタン、クロロホルム、ジクロロメタン等のハロゲン化炭化水素類;酢酸エチル、酢酸イソプロピル等のエステル類;トルエン、ベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、1,4-ジオキサン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類;メタノール、エタノール、イソプロパノール等のアルコール類;酢酸、トリフルオロ酢酸等の有機酸類を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができる。酸としては特に制限はないが、例えば、プロピオン酸、安息香酸等のプロトン酸、四塩化チタン、三フッ化ホウ素、塩化第二スズ等のルイス酸を使用することができる。還元試薬としては特に制限はないが、例えば、トリアセトキシ水素化ホウ素ナトリウム、トリアセトキシ水素化ホウ素テトラメチルアンモニウム、シアノ水素化ホウ素ナトリウム、水素化ホウ素ナトリウム、水素化ホウ素リチウム、トリメトキシ水素化ホウ素ナトリウム、トリエチル水素化ホウ素リチウム等の水素化ホウ素系試薬、水素化アルミニウムリチウム、ジイソプロピル水素化アルミニウム、ビス(2-メトキシエトキシ)水素化アルミニウムナトリウム等の水素化アルミニウム試薬、金属触媒及び水素源を用いた接触還元を使用することができる。接触還元の水素源としては、例えば、水素、シクロヘキサジエン、ギ酸、ギ酸アンモニウム等を使用することができ、金属触媒としては例えば、パラジウム炭素、パラジウム黒、水酸化パラジウム、ラネーニッケル、二酸化白金、白金黒等を使用することができる。b)アルキル化は、溶媒中、塩基の存在下により行うことができる。溶媒としては、特に制限は無いが、例えばN,N-ジメチルホルムアミド、N-メチルピロリドン等のアミド類;ジメチルスルホキシド;1,4-ジオキサン、テトラヒドロフラン等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル等のニトリル類を単独又は組み合わせて使用することができ、塩基としては、特に制限は無いが、例えば、水素化リチウム、水素化ナトリウム、水素化カリウム等の水素化アルカリ金属類、金属リチウム、金属ナトリウム、金属カリウム等のアルカリ金属類、水酸化リチウム、水酸化ナトリウム、水酸化カリウム等の水酸化アルカリ金属類、炭酸リチウム、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸セシウム等の炭酸アルカリ金属類、リチウムジイソプロピルアミド、ナトリウムジイソプロピルアミド、カリウムジイソプロピルアミド、リチウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、ナトリウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、カリウムヘキサメチルジシラジド、tert-ブトキシナトリウム、tert-ブトキシカリウム、n-ブチルリチウム、s-ブチルリチウム、tert-ブチルリチウム等を使用することができる。反応条件によって異なるが、反応温度は-10℃~200℃、好ましくは0℃~120℃である。反応時間は1時間~72時間、好ましくは1時間~36時間である。
[Step 12] In this step, compound (XVII) or compound (XIX) is produced from compound (XVI), compound (XVIII) or (XVIII ′) by a) reductive amination or b) alkylation. a) Reductive amination can be carried out using a reducing reagent in a solvent in the presence or absence of an acid. At that time, the dehydration operation may be performed using a Dean-Stark apparatus or the like. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, halogenated hydrocarbons such as 1,2-dichloroethane, chloroform and dichloromethane; esters such as ethyl acetate and isopropyl acetate; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and benzene; tetrahydrofuran Ethers such as 1,4-dioxane; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile; alcohols such as methanol, ethanol and isopropanol; organic acids such as acetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid can be used alone or in combination. . Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular as an acid, For example, Lewis acids, such as proton acids, such as propionic acid and benzoic acid, titanium tetrachloride, boron trifluoride, and stannic chloride, can be used. There is no particular limitation as a reducing reagent, for example, sodium triacetoxyborohydride, tetramethylammonium borohydride tetramethylammonium, sodium cyanoborohydride, sodium borohydride, lithium borohydride, sodium trimethoxyborohydride, Contact using borohydride reagents such as lithium triethylborohydride, lithium hydride lithium, diisopropylaluminum hydride, aluminum hydride reagents such as sodium bis (2-methoxyethoxy) aluminum hydride, metal catalyst and hydrogen source Reduction can be used. As a hydrogen source for catalytic reduction, for example, hydrogen, cyclohexadiene, formic acid, ammonium formate, etc. can be used, and as a metal catalyst, for example, palladium carbon, palladium black, palladium hydroxide, Raney nickel, platinum dioxide, platinum black, etc. Etc. can be used. b) Alkylation can be carried out in a solvent in the presence of a base. The solvent is not particularly limited. For example, amides such as N, N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone; dimethyl sulfoxide; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran; nitriles such as acetonitrile and propionitrile Can be used alone or in combination, and the base is not particularly limited. For example, alkali metal hydrides such as lithium hydride, sodium hydride, potassium hydride, metal lithium, metal sodium, metal Alkali metals such as potassium, alkali hydroxides such as lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, alkali carbonates such as lithium carbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, lithium diisopropylamide, sodium diisopropyl Amides, potassium Isopropylamide, lithium hexamethyldisilazide, sodium hexamethyldisilazide, potassium hexamethyldisilazide, tert-butoxy sodium, tert-butoxy potassium, n-butyl lithium, s-butyl lithium, tert-butyl lithium, etc. Can be used. Although depending on the reaction conditions, the reaction temperature is −10 ° C. to 200 ° C., preferably 0 ° C. to 120 ° C. The reaction time is 1 hour to 72 hours, preferably 1 hour to 36 hours.
[工程13]保護基の脱保護としては特に制限はないが、一般に用いられる方法(Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.)等により導入できるものを適宜使用し、脱保護をおこなうことができるが、これに限定されるものではない。
[Step 13] Although there is no particular limitation on the deprotection of the protecting group, a method that can be introduced by a generally used method (Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) or the like can be used as appropriate. However, the present invention is not limited to this.
上記一般式におけるX、Y環上の置換基やR2、R3等は必要に応じ一般に用いられる方法(Comprehensive Organic Transformations Second Edition,John Wiley & Sons,Inc.)を参考に、酸化、還元、アルキル化、アミド化、エステル化、加水分解、還元的アミノ化等により適宜変換させることにより、目的物が得られる。また、保護基を用いる場合には、保護基としては特に制限はないが、一般に用いられる方法(Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition,John Wiley & Sons,Inc.)等により導入できるものを適宜使用できるが、これに限定されるものではない。
Substituents on the X and Y rings in the above general formula, R 2 , R 3 and the like are oxidized, reduced with reference to methods generally used as necessary (Comprehensive Organic Transformation Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.), The desired product can be obtained by appropriate conversion by alkylation, amidation, esterification, hydrolysis, reductive amination or the like. In addition, when a protecting group is used, the protecting group is not particularly limited, and those that can be introduced by a generally used method (Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) can be used as appropriate. However, the present invention is not limited to this.
前記の各反応で得られた中間体及び目的物は、有機合成化学で常用されている精製法、例えば、ろ過、抽出、洗浄、乾燥、濃縮、再結晶、各種クロマトグラフィー等に付して必要に応じて単離、精製することができる。また、中間体においては、特に精製することなく次反応に供することもできる。
Intermediates and target products obtained in the above reactions are necessary for purification methods commonly used in organic synthetic chemistry, such as filtration, extraction, washing, drying, concentration, recrystallization, various chromatography, etc. Can be isolated and purified. In addition, the intermediate can be subjected to the next reaction without any particular purification.
さらに、各種の異性体は異性体間の物理化学的性質の差を利用した常法を適用して単離できる。例えば、ラセミ混合物は、例えば、酒石酸等の一般的な光学活性酸とのジアステレオマー塩に導き光学分割する方法、又は、光学活性カラムクロマトグラフィーを用いた方法等の一般的ラセミ分割法により、光学的に純粋な異性体に導くことができる。また、ジアステレオマー混合物は、例えば、分別結晶化又は各種クロマトグラフィー等により分割できる。また、光学活性な化合物は適当な光学活性な原料を用いることにより製造することもできる。
Furthermore, various isomers can be isolated by applying a conventional method using the difference in physicochemical properties between isomers. For example, a racemic mixture is obtained by a general racemic resolution method such as a method of optically resolving a diastereomeric salt with a general optically active acid such as tartaric acid or a method using optically active column chromatography. Can lead to optically pure isomers. Further, the diastereomeric mixture can be divided by, for example, fractional crystallization or various chromatography. An optically active compound can also be produced by using an appropriate optically active raw material.
本発明のTLR3、7及び/又は9阻害剤、又は自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶およびGvHDの予防及び/又は治療剤は、一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体、その塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分として含有するものであって、医薬組成物として使用することができる。その場合、本発明の化合物を単独で用いてもよいが、通常は医薬として許容される担体、及び/又は希釈剤を配合して使用される。
The TLR3, 7 and / or 9 inhibitor of the present invention, or an agent for preventing and / or treating autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection and GvHD is a thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1): The salt or a solvate thereof is contained as an active ingredient and can be used as a pharmaceutical composition. In that case, the compound of the present invention may be used alone, but it is usually used in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and / or diluent.
投与経路は、特に限定されないが、治療目的に応じて適宜選択することができる。例えば、経口剤、注射剤、坐剤、吸入剤等のいずれでもよい。これらの投与形態に適した医薬組成物は、公知の製剤方法を利用することによって製造できる。
The administration route is not particularly limited, but can be appropriately selected depending on the purpose of treatment. For example, any of oral preparations, injections, suppositories, inhalants and the like may be used. Pharmaceutical compositions suitable for these dosage forms can be produced by utilizing known preparation methods.
経口用固形製剤を調製する場合は、一般式(1)で表される化合物に医薬として許容される賦形剤、更に必要に応じて結合剤、崩壊剤、滑沢剤、着色剤、矯味剤、矯臭剤等を加えた後、常法を利用して、錠剤、被覆錠剤、顆粒剤、散剤、カプセル剤等を製造することができる。添加剤は、当該分野で一般的に使用されているものでよい。例えば、賦形剤としては、乳糖、白糖、塩化ナトリウム、ブドウ糖、デンプン、炭酸カルシウム、カオリン、微結晶セルロース、珪酸等が挙げられる。結合剤としては、例えば、水、エタノール、プロパノール、単シロップ、ブドウ糖液、デンプン液、ゼラチン液、カルボキシメチルセルロース、ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース、ヒドロキシプロピルスターチ、メチルセルロース、エチルセルロース、シェラック、リン酸カルシウム、ポリビニルピロリドン等が挙げられる。崩壊剤としては、例えば、乾燥デンプン、アルギン酸ナトリウム、カンテン末、炭酸水素ナトリウム、炭酸カルシウム、ラウリル硫酸ナトリウム、ステアリン酸モノグリセリド、乳糖等が挙げられる。滑沢剤としては、例えば、精製タルク、ステアリン酸塩、ホウ砂、ポリエチレングリコール等が挙げられる。矯味剤としては、例えば、白糖、橙皮、クエン酸、酒石酸等が挙げられる。
When preparing an oral solid preparation, the compound represented by the general formula (1) is a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and further, if necessary, a binder, a disintegrant, a lubricant, a coloring agent, and a corrigent. After adding a flavoring agent, tablets, coated tablets, granules, powders, capsules and the like can be produced using conventional methods. The additive may be one commonly used in the art. Examples of excipients include lactose, sucrose, sodium chloride, glucose, starch, calcium carbonate, kaolin, microcrystalline cellulose, silicic acid and the like. Examples of the binder include water, ethanol, propanol, simple syrup, glucose solution, starch solution, gelatin solution, carboxymethylcellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose, hydroxypropyl starch, methylcellulose, ethylcellulose, shellac, calcium phosphate, polyvinylpyrrolidone and the like. . Examples of the disintegrant include dry starch, sodium alginate, agar powder, sodium hydrogen carbonate, calcium carbonate, sodium lauryl sulfate, stearic acid monoglyceride, and lactose. Examples of the lubricant include purified talc, stearate, borax, and polyethylene glycol. Examples of the corrigent include sucrose, orange peel, citric acid, tartaric acid and the like.
経口用液体製剤を調製する場合は、一般式(1)で表される化合物に、矯味剤、緩衝剤、安定化剤、矯臭剤等を加えて常法を利用して内服液剤、シロップ剤、エリキシル剤等を製造することができる。矯味剤としては上記に挙げられたものでよく、緩衝剤としては、例えば、クエン酸ナトリウム等が、安定化剤としては、例えば、トラガント、アラビアゴム、ゼラチン等が挙げられる。
When preparing an oral liquid preparation, an oral solution, syrup, etc. are added to the compound represented by the general formula (1) by adding a corrigent, a buffer, a stabilizer, a corrigent and the like using a conventional method. An elixir or the like can be produced. Examples of the flavoring agent include those listed above. Examples of the buffering agent include sodium citrate, and examples of the stabilizing agent include tragacanth, gum arabic, and gelatin.
注射剤を調製する場合は、一般式(1)で表される化合物にpH調節剤、緩衝剤、安定化剤、等張化剤、局所麻酔剤等を添加し、常法を利用して皮下、筋肉及び静脈内注射剤を製造することができる。pH調製剤及び緩衝剤としては、例えば、クエン酸ナトリウム、酢酸ナトリウム、リン酸ナトリウム等が挙げられる。安定化剤としては、例えば、ピロ亜硫酸ナトリウム、EDTA(エデト酸ナトリウム)、チオグリコール酸、チオ乳酸等が挙げられる。局所麻酔剤としては、例えば、塩酸プロカイン、塩酸リドカイン等が挙げられる。等張化剤としては、例えば、塩化ナトリウム、ブドウ糖等が挙げられる。
When preparing an injection, a pH regulator, a buffer, a stabilizer, a tonicity agent, a local anesthetic, etc. are added to the compound represented by the general formula (1), and subcutaneously using a conventional method. Intramuscular and intravenous injections can be manufactured. Examples of the pH adjusting agent and buffer include sodium citrate, sodium acetate, sodium phosphate and the like. Examples of the stabilizer include sodium pyrosulfite, EDTA (sodium edetate), thioglycolic acid, and thiolactic acid. Examples of the local anesthetic include procaine hydrochloride and lidocaine hydrochloride. Examples of the isotonic agent include sodium chloride and glucose.
坐剤を調製する場合は、一般式(1)で表される化合物に公知の坐剤用担体、例えば、ポリエチレングリコール、ラノリン、カカオ脂、脂肪酸トリグリセライド等、更に必要に応じて界面活性剤(例えば、ツイーン(登録商標))等を加えた後、常法を利用して製造することができる。
When preparing a suppository, a known suppository carrier such as polyethylene glycol, lanolin, cacao butter, fatty acid triglyceride, etc., and a surfactant (for example, , Tween (registered trademark)) and the like can be added and then manufactured using a conventional method.
上記以外に、常法を利用して適宜好ましい製剤とすることもできる。
In addition to the above, it is possible to appropriately prepare a preferable preparation using a conventional method.
本発明の一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体の投与量は年齢、体重、症状、投与形態及び投与回数等によって異なるが、通常は成人に対して一般式(1)で表わされる化合物として1日あたり0.1mg~1000mg、好ましくは1mg~100mg、より好ましくは1mg~10mgを、1回又は数回に分けて経口投与又は非経口投与するのが好ましい。
The dose of the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention varies depending on age, body weight, symptom, dosage form, number of administrations, etc. Preferably, 0.1 mg to 1000 mg, preferably 1 mg to 100 mg, more preferably 1 mg to 10 mg per day is orally or parenterally administered in one or several divided doses.
次に、実施例を挙げて本発明をさらに説明するが、本発明はこれら実施例に限定されるものではない。なお、下記実施例中で用いられている略号は下記の意味を示す。
s:シングレット(singlet)
d:ダブレット(doublet)
t:トリプレット(triplet)
q:クアルテット(quartet)
m:マルチプレット(multiplet)
brs:ブロードシングレット(broad singlet)
J:カップリング定数(coupling constant)
Hz:ヘルツ(Hertz)
CDCl3:重クロロホルム
1H-NMR:プロトン核磁気共鳴
DIPEA:ジイソプロピルエチルアミン
TEA:トリエチルアミン
WSC・HCl:1-エチル-3-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]カルボジイミド塩酸塩
HOBt・HCl:1-ヒドロキシベンゾトリアゾール塩酸塩
Ms:メタンスルホニル
THF:テトラヒドロフラン
DMF:N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド
PLC:分取用薄層クロマトグラフィー
DEAD:ジエチル アゾジカルボキシレート
TBAF:テトラブチルアンモニウムフロリド
TFA:トリフルオロ酢酸
Boc:tert-ブトキシカルボニル
crude:粗生成物
Pd-C:パラジウム炭素
TBS:tert-ブチルジメチルシリル EXAMPLES Next, although an Example is given and this invention is further demonstrated, this invention is not limited to these Examples. In addition, the symbol used in the following Example shows the following meaning.
s: singlet
d: doublet
t: triplet
q: quartet
m: multiplet
brs: broad singlet
J: Coupling constant
Hz: Hertz
CDCl 3 : deuterated chloroform
1 H-NMR: proton nuclear magnetic resonance
DIPEA: Diisopropylethylamine
TEA: Triethylamine
WSC · HCl: 1-ethyl-3- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] carbodiimide hydrochloride
HOBt · HCl: 1-hydroxybenzotriazole hydrochloride
Ms: Methanesulfonyl
THF: tetrahydrofuran
DMF: N, N-dimethylformamide
PLC: preparative thin layer chromatography
DEAD: Diethyl azodicarboxylate
TBAF: Tetrabutylammonium fluoride
TFA: trifluoroacetic acid
Boc: tert-butoxycarbonyl
crude: Crude product
Pd-C: Palladium carbon
TBS: tert-butyldimethylsilyl
s:シングレット(singlet)
d:ダブレット(doublet)
t:トリプレット(triplet)
q:クアルテット(quartet)
m:マルチプレット(multiplet)
brs:ブロードシングレット(broad singlet)
J:カップリング定数(coupling constant)
Hz:ヘルツ(Hertz)
CDCl3:重クロロホルム
1H-NMR:プロトン核磁気共鳴
DIPEA:ジイソプロピルエチルアミン
TEA:トリエチルアミン
WSC・HCl:1-エチル-3-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]カルボジイミド塩酸塩
HOBt・HCl:1-ヒドロキシベンゾトリアゾール塩酸塩
Ms:メタンスルホニル
THF:テトラヒドロフラン
DMF:N,N-ジメチルホルムアミド
PLC:分取用薄層クロマトグラフィー
DEAD:ジエチル アゾジカルボキシレート
TBAF:テトラブチルアンモニウムフロリド
TFA:トリフルオロ酢酸
Boc:tert-ブトキシカルボニル
crude:粗生成物
Pd-C:パラジウム炭素
TBS:tert-ブチルジメチルシリル EXAMPLES Next, although an Example is given and this invention is further demonstrated, this invention is not limited to these Examples. In addition, the symbol used in the following Example shows the following meaning.
s: singlet
d: doublet
t: triplet
q: quartet
m: multiplet
brs: broad singlet
J: Coupling constant
Hz: Hertz
CDCl 3 : deuterated chloroform
1 H-NMR: proton nuclear magnetic resonance
DIPEA: Diisopropylethylamine
TEA: Triethylamine
WSC · HCl: 1-ethyl-3- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] carbodiimide hydrochloride
HOBt · HCl: 1-hydroxybenzotriazole hydrochloride
Ms: Methanesulfonyl
THF: tetrahydrofuran
DMF: N, N-dimethylformamide
PLC: preparative thin layer chromatography
DEAD: Diethyl azodicarboxylate
TBAF: Tetrabutylammonium fluoride
TFA: trifluoroacetic acid
Boc: tert-butoxycarbonyl
crude: Crude product
Pd-C: Palladium carbon
TBS: tert-butyldimethylsilyl
実施例1 N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 1 Production of N- [3-([1,4'-bipiperidin] -1'-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide
工程1:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボン酸(200 mg, 0.97 mmol)、[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-プロパンアミン塩酸塩(0.42 g, 1.26 mmol)、WSC・HCl(278 mg, 1.45mmol)、HOBT・H2O(196 mg, 1.45 mmol)およびトリエチルアミン(390 mg, 3.86 mmol)を塩化メチレン(5 mL)に溶解し、室温で一晩攪拌した。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(433 mg, 定量的)を微黄色固体として得た。
5-Bromothiophene-2-carboxylic acid (200 mg, 0.97 mmol), [1,4′-bipiperidine] -1′-propanamine hydrochloride (0.42 g, 1.26 mmol), WSC · HCl (278 mg, 1.45 mmol) ), HOBT · H 2 O (196 mg, 1.45 mmol) and triethylamine (390 mg, 3.86 mmol) were dissolved in methylene chloride (5 mL) and stirred at room temperature overnight. Saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified using silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 10: 1) to give the title compound (433 mg, quantitative) as a pale yellow solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.42-1.49 (2H, m), 1.56-1.83 (10H, m), 1.88-1.96 (2H, m), 2.31-2.43 (1H, m), 2.48-2.57 (6H, m), 3.05-3.12 (2H, m), 3.48-3.55 (2H, m), 7.00 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.32 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.42-1.49 (2H, m), 1.56-1.83 (10H, m), 1.88-1.96 (2H, m), 2.31-2.43 (1H, m), 2.48- 2.57 (6H, m), 3.05-3.12 (2H, m), 3.48-3.55 (2H, m), 7.00 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.32 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz).
工程2:
1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-(ブロモフェニル)ピペラジン(12.6 g, 49.4 mmol)の1,4-ジオキサン(150 mL)溶液に、ビス(ピナコラート)ジボロン(15.1 g, 59.3 mmol)、ビス(ジフェニルフォスフィノフェロセン)パラジウムジクロライド(II)(2.02 g, 2.47 mmol)、ジフェニルフォスフィノフェロセン(1.37 g, 2.47 mmol)、酢酸カリウム(14.5 g, 148 mmol)を加え、80℃で、16時間攪拌した。室温に戻し、飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=97:3→90:10、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(9.53 g, 64%)を赤褐色固体として得た。
To a solution of 1-methyl-4- (bromophenyl) piperazine (12.6 g, 49.4 mmol) in 1,4-dioxane (150 mL), bis (pinacolato) diboron (15.1 g, 59.3 mmol), bis (diphenylphosphinoferrocene ) Palladium dichloride (II) (2.02 g, 2.47 mmol), diphenylphosphinoferrocene (1.37 g, 2.47 mmol) and potassium acetate (14.5 g, 148 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at 80 ° C for 16 hours. It returned to room temperature, saturated sodium hydrogencarbonate aqueous solution was added, and chloroform extracted. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 97: 3 → 90: 10, gradient) to obtain the title compound (9.53 g, 64%) as a reddish brown solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.32 (12H, s), 2.35 (3H, s), 2.52-2.58 (4H, m), 3.25-3.32 (4H, m), 6.89 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.70 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.32 (12H, s), 2.35 (3H, s), 2.52-2.58 (4H, m), 3.25-3.32 (4H, m), 6.89 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.70 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
工程3:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(70 mg, 0.17 mmol)、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)(10 mg, 0.009 mmol)、1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン(66 mg, 0.22 mmol)、2M炭酸ナトリウム水溶液(0.22 mL)を1,4-ジオキサン(2 mL)に混合し、一晩リフラックスした。室温に戻し、飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:アンモニウム飽和メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(70 mg, 82%)を淡黄色固体して得た。 Step 3:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [ 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide (70 mg, 0.17 mmol), tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0) (10 mg, 0.009 mmol), 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine (66 mg, 0.22 mmol), 2M carbonic acid Aqueous sodium (0.22 mL) was mixed with 1,4-dioxane (2 mL) and refluxed overnight. It returned to room temperature, saturated sodium hydrogencarbonate aqueous solution was added, and chloroform extracted. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: ammonium saturated methanol = 10: 1) to obtain the title compound (70 mg, 82%) as a pale yellow solid.
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(70 mg, 0.17 mmol)、テトラキス(トリフェニルホスフィン)パラジウム(0)(10 mg, 0.009 mmol)、1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン(66 mg, 0.22 mmol)、2M炭酸ナトリウム水溶液(0.22 mL)を1,4-ジオキサン(2 mL)に混合し、一晩リフラックスした。室温に戻し、飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:アンモニウム飽和メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(70 mg, 82%)を淡黄色固体して得た。 Step 3:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [ 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide (70 mg, 0.17 mmol), tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (0) (10 mg, 0.009 mmol), 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine (66 mg, 0.22 mmol), 2M carbonic acid Aqueous sodium (0.22 mL) was mixed with 1,4-dioxane (2 mL) and refluxed overnight. It returned to room temperature, saturated sodium hydrogencarbonate aqueous solution was added, and chloroform extracted. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: ammonium saturated methanol = 10: 1) to obtain the title compound (70 mg, 82%) as a pale yellow solid.
実施例2 2-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
Example 2 Production of 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide
工程1:
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine
5-ブロモ-2-ニトロチオフェンと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にし、表題化合物(51%)を赤色固体として得た。
Performed with 5-bromo-2-nitrothiophene and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1, the title compound (51%) was obtained as a red solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.37 (3H, s), 2.55-2.62 (4H, m), 3.31-3.36 (4H, m), 6.92 (2H, d, J = 9.2 Hz), 7.10 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.53 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.37 (3H, s), 2.55-2.62 (4H, m), 3.31-3.36 (4H, m), 6.92 (2H, d, J = 9.2 Hz), 7.10 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.53 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
工程2:
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン(324 mg)をメタノール(5 mL)に溶解し、10%Pd-C(160 mg)を加えた。系中を水素で置換し、室温で6時間攪拌した。反応液をセライトろ過し、ろ液を減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(173 mg, 59%)を緑色固体として得た。
1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine (324 mg) was dissolved in methanol (5 mL), and 10% Pd-C (160 mg) was added. The system was replaced with hydrogen and stirred at room temperature for 6 hours. The reaction solution was filtered through celite, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to obtain the title compound (173 mg, 59%) as a green solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.36 (3H, s), 2.55-2.60 (4H, m), 3.18-3.24 (4H, m), 3.74 (2H, brs), 6.15 (1H, d, J = 3.7 Hz), 6.78 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.36 (3H, s), 2.55-2.60 (4H, m), 3.18-3.24 (4H, m), 3.74 (2H, brs), 6.15 (1H, d, J = 3.7 Hz), 6.78 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
工程3:
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]酢酸メチルの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of methyl 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]酢酸メチルの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of methyl 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate
4-アミノ-N-ベンジルピペリジン(50 g, 263 mmol)のアセトニトリル(500 mL)/DMF(200 mL)溶液に、炭酸カリウム(27.2 g, 197 mmol)を加えた。ブロモ酢酸メチル(20.1 g, 131 mmol)を加え、60℃で5時間攪拌した。室温に戻し、飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:アンモニア飽和メタノール=97:3→90:10、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(34.7 g, crude, 理論量34.4 g)を淡黄色油状物として得た。
To a solution of 4-amino-N-benzylpiperidine (50 g, 263 mmol) in acetonitrile (500 mL) / DMF (200 mL) was added potassium carbonate (27.2 g, 197 mmol). Methyl bromoacetate (20.1 g, 131 mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at 60 ° C for 5 hours. It returned to room temperature, saturated sodium hydrogencarbonate aqueous solution was added, and chloroform extracted. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified using silica gel chromatography (chloroform: ammonia saturated methanol = 97: 3 → 90: 10, gradient) to give the title compound (34.7 g, crude, theoretical amount 34.4) g) as a pale yellow oil. Obtained.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.36-1.50 (2H, m), 1.76-1.84 (2H, m), 1.96-2.06 (2H, m), 2.40-2.50 (1H, m), 2.80-2.87 (2H, m), 3.44 (2H, s), 3.49 (2H, s), 3.72 (3H, s), 7.21-7.32 (5H, m).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.36-1.50 (2H, m), 1.76-1.84 (2H, m), 1.96-2.06 (2H, m), 2.40-2.50 (1H, m), 2.80- 2.87 (2H, m), 3.44 (2H, s), 3.49 (2H, s), 3.72 (3H, s), 7.21-7.32 (5H, m).
工程4:
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸メチルの製造 Step 4:
Preparation of methyl 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetate
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸メチルの製造 Step 4:
Preparation of methyl 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetate
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]酢酸メチル(34.7 g、crude、理論量34.4 g、131 mmol)の塩化メチレン(200 mL)溶液に、トリエチルアミン(26.5 g, 262 mmol)を加えた。氷冷下で、2-ニトロベンゼンスルホニルクロライド(40.6 g, 183 mmol)の塩化メチレン(200 mL)溶液を加え、室温で一晩攪拌した。水を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(ヘキサン:酢酸エチル=4:1→1:9、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(54.2 g, 2工程収率92.5%)を青緑色油状物として得た。
To a solution of methyl 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate (34.7 g, crude, theoretical amount 34.4 g, 131 mmol) in methylene chloride (200 mL), triethylamine (26.5 g, 262 mmol) ) Was added. Under ice-cooling, a solution of 2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride (40.6 g, 183 mmol) in methylene chloride (200 mL) was added and stirred overnight at room temperature. Water was added and extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was purified using silica gel chromatography (hexane: ethyl acetate = 4: 1 → 1: 9, gradient) to give the title compound (54.2 g, 2 step yield 92.5%) as a blue-green oil. It was.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.54-1.74 (4H, m), 1.98-2.10 (2H, m), 2.84-2.92 (2H, m), 3.45 (2H, s), 3.67 (3H, s), 3.74-3.86 (1H, m), 4.13 (2H, s), 7.20-7.32 (5H, m), 7.60-7.72 (3H, m), 8.14-8.20 (1H, m).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.54-1.74 (4H, m), 1.98-2.10 (2H, m), 2.84-2.92 (2H, m), 3.45 (2H, s), 3.67 (3H, s), 3.74-3.86 (1H, m), 4.13 (2H, s), 7.20-7.32 (5H, m), 7.60-7.72 (3H, m), 8.14-8.20 (1H, m).
工程5:
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸の製造 Step 5:
Preparation of 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetic acid
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸の製造 Step 5:
Preparation of 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetic acid
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸メチル(54.2 g, 121 mmol)のメタノール(700 mL)溶液に、4M水酸化ナトリウム水溶液(60.5 mL, 242 mmol)を加えた。室温で4時間攪拌した。氷冷下で、4N塩酸-酢酸エチル溶液を用いて、中性にし、減圧濃縮をした。クロロホルムで抽出を行い、有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。表題化合物(48.2 g, crude)を黄褐色アモルファスとして得た。
2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl acetate (54.2 g, 121 mmol) in methanol (700 mL) was added to a 4M aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (60.5 242 mmol) was added. Stir at room temperature for 4 hours. Under ice-cooling, the solution was neutralized with 4N hydrochloric acid-ethyl acetate solution and concentrated under reduced pressure. Extraction was performed with chloroform, and the organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The title compound (48.2 g, crude) was obtained as a tan amorphous.
工程6:
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセチルクロライドの製造 Step 6:
Preparation of 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetyl chloride
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセチルクロライドの製造 Step 6:
Preparation of 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetyl chloride
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸(162 mg, 375μmol)の塩化メチレン(5 mL)溶液に、氷冷下、DMF(10μL)、二塩化オキザリル(95.2 mg, 750μmol)を加えた。室温に戻し、2時間攪拌した。反応液を減圧濃縮し、トルエン共沸を行い、黄褐色アモルファス(225 mg, crude)を得た。
To a solution of 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetic acid (162 mg, 375 μmol) in methylene chloride (5 mL), DMF (10 μL), Oxalyl chloride (95.2 mg, 750 μmol) was added. It returned to room temperature and stirred for 2 hours. The reaction solution was concentrated under reduced pressure and azeotroped with toluene to obtain a tan amorphous (225 mg, crude).
工程7:2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
Step 7: 2- [N- (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il} acetamide production
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン(51.4 mg, 0.19 mmol)を塩化メチレン(1.4 mL)に溶かし、ジイソプロピルエチルアミン(48.2 mg, 0.38 mmol)、を加えた。氷浴にて、2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセチルクロライドを加えた。室温に戻して2時間攪拌した。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(75.3 mg, crude)を褐色固体として得た。
1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine (51.4 mg, 0.19 mmol) is dissolved in methylene chloride (1.4 mL), and diisopropylethylamine (48.2 mg, 0.38 mmol) is added. added. In an ice bath, 2- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetyl chloride was added. It returned to room temperature and stirred for 2 hours. Saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to obtain the title compound (75.3 mg, crude) as a brown solid.
工程8:
2-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(75.3 mg, 0.11 mmol)をアセトニトリル(1.1 mL)に溶解し、炭酸カリウム(45 mg, 0.33 mmol)、チオフェノール(24.7 mg,0.22 mmol)を加えた。室温で一晩攪拌した。反応液をセライトろ過し、ろ液を減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をPLC(クロロホルム:アンモニウム飽和メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製した。得られた化合物をクロロホルム-ヘキサンより再結晶を行い、表題化合物(32.2 mg, 2工程収率34%)を微褐色固体として得た。 Step 8:
Preparation of 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide 2- [N- (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (75.3 mg, 0.11 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (1.1 mL), and potassium carbonate (45 mg, 0.33 mmol) and thiophenol (24.7 mg, 0.22 mmol) were added. Stir at room temperature overnight. The reaction solution was filtered through celite, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified using PLC (chloroform: ammonium saturated methanol = 10: 1). The obtained compound was recrystallized from chloroform-hexane to give the title compound (32.2 mg, 2 step yield 34%) as a pale brown solid.
2-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
2-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(75.3 mg, 0.11 mmol)をアセトニトリル(1.1 mL)に溶解し、炭酸カリウム(45 mg, 0.33 mmol)、チオフェノール(24.7 mg,0.22 mmol)を加えた。室温で一晩攪拌した。反応液をセライトろ過し、ろ液を減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をPLC(クロロホルム:アンモニウム飽和メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製した。得られた化合物をクロロホルム-ヘキサンより再結晶を行い、表題化合物(32.2 mg, 2工程収率34%)を微褐色固体として得た。 Step 8:
Preparation of 2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide 2- [N- (1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (75.3 mg, 0.11 mmol) was dissolved in acetonitrile (1.1 mL), and potassium carbonate (45 mg, 0.33 mmol) and thiophenol (24.7 mg, 0.22 mmol) were added. Stir at room temperature overnight. The reaction solution was filtered through celite, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified using PLC (chloroform: ammonium saturated methanol = 10: 1). The obtained compound was recrystallized from chloroform-hexane to give the title compound (32.2 mg, 2 step yield 34%) as a pale brown solid.
実施例3 N-{3-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 3 Production of N- {3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide
工程1:
5-ブロモ-N-(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 5-bromo-N- (3-hydroxypropyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモ-N-(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 5-bromo-N- (3-hydroxypropyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボン酸と3-アミノプロパノールを用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(91%)を微褐色固体として得た。
Using 5-bromothiophene-2-carboxylic acid and 3-aminopropanol, the title compound (91%) was obtained as a slightly brown solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.74-1.84 (2H, m), 2.69 (1H, t, J = 7.7 Hz), 3.56-3.62 (2H, m), 3.71-3.78 (2H, m), 6.48 (1H, brs), 7.03 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.22 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.74-1.84 (2H, m), 2.69 (1H, t, J = 7.7 Hz), 3.56-3.62 (2H, m), 3.71-3.78 (2H, m) , 6.48 (1H, brs), 7.03 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.22 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz).
工程2:
N-{3-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of N- {3- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide
N-{3-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of N- {3- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモ-N-(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(145 mg, 0.55 mmol)のTHF(2.8 mL)溶液に、N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロベンゼンスルホンアミド(242 mg, 0.66 mmol)、DEAD(2.2 Mトルエン溶液, 0.3 mL, 0.66 mmol)、トリフェニルホスフィン(173 mg, 0.66 mmol)を加え、室温で3時間攪拌した。反応液を減圧濃縮し、得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(272 mg, crude)を淡緑色アモルファスとして得た。
To a solution of 5-bromo-N- (3-hydroxypropyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide (145 mg, 0.55 mmol) in THF (2.8 mL) was added N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrobenzenesulfone. Amide (242 mg, 0.66 mmol), DEAD (2.2 M toluene solution, 0.3 mL, 0.66 mmol) and triphenylphosphine (173 mg, 0.66 mmol) were added and stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the resulting residue was purified using silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18) to give the title compound (272 mg, crude) as a pale green amorphous substance.
工程3:
N-{3-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 3:
N- {3- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2- Production of carboxamide
N-{3-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 3:
N- {3- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2- Production of carboxamide
N-{3-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)をオレンジ色アモルファスとして得た。
N- {3- [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4 Using 4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine, the title compound (crude) is obtained as an orange amorphous in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1. It was.
工程4:
N-{3-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-{3-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(30%)を微褐色固体として得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of N- {3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- {3- With [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (30%) was obtained as a pale brown solid.
N-{3-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-{3-[N-(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(30%)を微褐色固体として得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of N- {3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- {3- With [N- (1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (30%) was obtained as a pale brown solid.
実施例4 5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 4 Production of 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide
工程1:
5-ブロモ-N-{3-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 5-bromo-N- {3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモ-N-{3-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 5-bromo-N- {3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモ-N-(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドとN-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロベンゼンスルホンアミドを用いて、実施例3の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(29%)を黄色油状物として得た。
As in Step 2 of Example 3, using 5-bromo-N- (3-hydroxypropyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide and N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrobenzenesulfonamide. The title compound (29%) was obtained as a yellow oil.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.64-2.06 (8H, m), 2.25 (3H, s), 2.84-2.90 (2H, m), 3.43 (2H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 3.49-3.55 (2H, m), 3.65-3.74 (1H, m), 6.82 (1H, brs), 7.04 (1H, dd, J = 4.0, 1.2 Hz), 7.27 (1H, d, J = 5.2 Hz), 7.60-7.76 (3H, m), 7.98 (1H, d, J = 6.0 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.64-2.06 (8H, m), 2.25 (3H, s), 2.84-2.90 (2H, m), 3.43 (2H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 3.49 -3.55 (2H, m), 3.65-3.74 (1H, m), 6.82 (1H, brs), 7.04 (1H, dd, J = 4.0, 1.2 Hz), 7.27 (1H, d, J = 5.2 Hz), 7.60-7.76 (3H, m), 7.98 (1H, d, J = 6.0 Hz).
工程2:
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 2:
5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} thiophene-2- Carboxamide production
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 2:
5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} thiophene-2- Carboxamide production
5-ブロモ-N-{3-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を淡オレンジ色アモルファスとして得た。
5-Bromo-N- {3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4 Using 4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine, the title compound (crude) was converted to a pale orange amorphous in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1. Obtained.
工程3:
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(40%)を橙色固体として得た。 Step 3:
Preparation of 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide 5- [4- With (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (40%) was obtained as an orange solid.
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(40%)を橙色固体として得た。 Step 3:
Preparation of 5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide 5- [4- With (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (40%) was obtained as an orange solid.
実施例5 N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 5 Production of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide
工程1:
メチル2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセテートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of methyl 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate
メチル2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセテートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of methyl 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate
1-メチル-4-ピペリドン(27.2 g, 240 mmol)とグリシンメチルエステル(25.0 g, 200 mmol)の塩化メチレン(250 mL)溶液にトリアセトキシ水素化ホウ素ナトリウム(63.6 g, 300 mmol)を、氷冷下で加えた。室温で2時間攪拌した。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、混合溶媒(クロロホルム/メタノール=8/1)で10回抽出を行った。有機層を無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。表題化合物(32.6 g, crude)を黄褐色油状物として得た。
To a solution of 1-methyl-4-piperidone (27.2 g, 240 mmol) and glycine methyl ester (25.0 g, 200 mmol) in methylene chloride (250 mL), add sodium triacetoxyborohydride (63.6 g, 300 mmol) to ice Added under cold. Stir at room temperature for 2 hours. A saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and extraction was performed 10 times with a mixed solvent (chloroform / methanol = 8/1). The organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. The title compound (32.6 g, crude) was obtained as a tan oil.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.45-1.57 (2H, m), 1.84-1.94 (2H, m), 2.08-2.20 (2H, m), 2.32 (3H, s), 2.48-2.58 (1H, m), 2.80-2.93 (2H, m), 3.44 (2H, s), 3.74 (3H, s).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.45-1.57 (2H, m), 1.84-1.94 (2H, m), 2.08-2.20 (2H, m), 2.32 (3H, s), 2.48-2.58 ( 1H, m), 2.80-2.93 (2H, m), 3.44 (2H, s), 3.74 (3H, s).
工程2:
メチル2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセテートの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of methyl 2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide] acetate
メチル2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセテートの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of methyl 2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide] acetate
メチル2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセテートと2-ニトロベンゼンスルホニルクロライドを用いて、実施例2の工程4と同様にして、表題化合物(55.5%)を褐色油状物として得た。
The title compound (55.5%) is obtained as a brown oil in the same manner as in Step 4 of Example 2 using methyl 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate and 2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride. It was.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.58-1.78 (4H, m), 1.98-2.08 (2H, m), 2.25 (3H, s), 2.82-2.90 (2H, m), 3.68 (3H, s), 3.74-3.86 (1H, m), 4.13 (2H, s), 7.64-7.73 (3H, m), 8.16-8.22 (1H, m).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.58-1.78 (4H, m), 1.98-2.08 (2H, m), 2.25 (3H, s), 2.82-2.90 (2H, m), 3.68 (3H, s), 3.74-3.86 (1H, m), 4.13 (2H, s), 7.64-7.73 (3H, m), 8.16-8.22 (1H, m).
工程3:
2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸の製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetic acid
2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸の製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetic acid
メチル2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセテートを用いて、実施例2の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
Using methyl 2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetate in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 2, the title compound (crude) was obtained as a brown amorphous substance. It was.
工程4:
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide] Production of acetamide
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide] Production of acetamide
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンと2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黒褐色油状物として得た。
Using 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine and 2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetic acid In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1, the title compound (crude) was obtained as a black-brown oil.
工程5:
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率6%)を黒褐色油状物として得た。 Step 5:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N- {5- With [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (2 step yield: 6%) was obtained as a black-brown oil.
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率6%)を黒褐色油状物として得た。 Step 5:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N- {5- With [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] acetamide, In the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2, the title compound (2 step yield: 6%) was obtained as a black-brown oil.
実施例6 N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 6 Production of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide
工程1:
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセチルクロライドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetyl chloride
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセチルクロライドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetyl chloride
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]酢酸(100 mg, 0.34 mmol)を塩化メチレン(2 mL)に加え、氷冷下、DMF(10μL)、二塩化オキザリル(50μL, 0.51 mmol)を加えた。室温に戻し、2時間攪拌後、減圧濃縮し、表題化合物(crude)を黄褐色アモルファスとして得た。
2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetic acid (100 mg, 0.34 mmol) is added to methylene chloride (2 mL), and with ice cooling, DMF (10 μL), oxalyl dichloride (50 μL, 0.51 mmol) ) Was added. The mixture was returned to room temperature, stirred for 2 hours, and concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain the title compound (crude) as a tan amorphous.
工程2:
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセトアミドの製造
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン(47 mg, 0.17mmol)を塩化メチレン(3 mL)に溶かし、トリエチルアミン(100 μL, 0.68 mmol)、を加え溶液とした後、氷浴にて2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセチルクロライドを加えた。室温に戻して2時間攪拌した。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(56 mg, 77%)を褐色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide 1-methyl-4 -[4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine (47 mg, 0.17 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (3 mL), and triethylamine (100 μL, 0.68 mmol) was added to make a solution. 2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetyl chloride was added in an ice bath. It returned to room temperature and stirred for 2 hours. Saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to obtain the title compound (56 mg, 77%) as a brown solid.
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセトアミドの製造
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン(47 mg, 0.17mmol)を塩化メチレン(3 mL)に溶かし、トリエチルアミン(100 μL, 0.68 mmol)、を加え溶液とした後、氷浴にて2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセチルクロライドを加えた。室温に戻して2時間攪拌した。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(56 mg, 77%)を褐色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide 1-methyl-4 -[4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine (47 mg, 0.17 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (3 mL), and triethylamine (100 μL, 0.68 mmol) was added to make a solution. 2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetyl chloride was added in an ice bath. It returned to room temperature and stirred for 2 hours. Saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to obtain the title compound (56 mg, 77%) as a brown solid.
実施例7 N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 7 N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) ) Phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide
工程1:
4-(4-ブロモフェニル)-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 4- (4-bromophenyl) -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
4-(4-ブロモフェニル)-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 4- (4-bromophenyl) -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
4-(4-ブロモフェニル)-4-ヒドロキシピペリジン(1.2 g, 4.68 mmol)に濃塩酸(5 mL)を加え、100℃で8時間攪拌した。室温に戻し、水酸化ナトリウム水溶液を加え、塩基性にし、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。表題化合物(1.08 g, 97%)を褐色固体として得た。
Concentrated hydrochloric acid (5 mL) was added to 4- (4-bromophenyl) -4-hydroxypiperidine (1.2 g, 4.68 mmol), and the mixture was stirred at 100 ° C for 8 hours. It returned to room temperature, the sodium hydroxide aqueous solution was added, it was made basic, and chloroform extracted. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The title compound (1.08 g, 97%) was obtained as a brown solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.39-2.47 (2H, m), 3.10 (2H, t, J = 5.8 Hz), 3.52 (2H, dd, J = 6.1, 3.0 Hz), 6.13-6.17 (1H, m), 7.25 (2H, d, J = 9.0 Hz), 7.44 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.39-2.47 (2H, m), 3.10 (2H, t, J = 5.8 Hz), 3.52 (2H, dd, J = 6.1, 3.0 Hz), 6.13-6.17 (1H, m), 7.25 (2H, d, J = 9.0 Hz), 7.44 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
工程2:
4-(4-ブロモフェニル)-1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 4- (4-bromophenyl) -1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
4-(4-ブロモフェニル)-1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 4- (4-bromophenyl) -1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
4-(4-ブロモフェニル)-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を微桃色固体として得た。
Using 4- (4-bromophenyl) -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine and formaldehyde, the title compound (crude) was obtained as a slightly pink solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5.
工程3:
1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
4-(4-ブロモフェニル)-1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンとビス(ピナコラート)ジボロンを用いて、実施例1の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率82%)を黒褐色として得た。
Using 4- (4-bromophenyl) -1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine and bis (pinacolato) diboron in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 1, the title compound (3-step yield) was obtained. 82%) was obtained as a blackish brown color.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.34 (12H, s), 2.49 (3H, s), 2.63-2.69 (2H, m), 2.85 (2H, t, J = 5.8 Hz), 3.26-3.30 (2H, m), 6.11 (1H, brs), 7.39 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.76 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.34 (12H, s), 2.49 (3H, s), 2.63-2.69 (2H, m), 2.85 (2H, t, J = 5.8 Hz), 3.26-3.30 (2H, m), 6.11 (1H, brs), 7.39 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.76 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz).
工程4:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(72%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 4:
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Preparation of thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4 , 4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in the same manner as inStep 3 of Example 1, The title compound (72%) was obtained as a yellow solid.
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(72%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 4:
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Preparation of thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4 , 4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in the same manner as in
実施例8 N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(10 mg, 0.02mmol)をエタノール(1 mL)に溶解し、濃塩酸(10μL)と10%パラジウム炭素(10 mg)を加え、水素雰囲気下、室温にて18時間撹拌した。反応液をろ過し、濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(6 mg, 62%)を白色固体として得た。 Example 8 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Thiophene-2-carboxamide (10 mg, 0.02 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (1 mL), concentrated hydrochloric acid (10 μL) and 10% palladium carbon (10 mg) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 hours under a hydrogen atmosphere. . The reaction mixture was filtered and concentrated, and the resulting residue was purified using silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to give the title compound (6 mg, 62%) as a white solid Got as.
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(10 mg, 0.02mmol)をエタノール(1 mL)に溶解し、濃塩酸(10μL)と10%パラジウム炭素(10 mg)を加え、水素雰囲気下、室温にて18時間撹拌した。反応液をろ過し、濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(6 mg, 62%)を白色固体として得た。 Example 8 Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Thiophene-2-carboxamide (10 mg, 0.02 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (1 mL), concentrated hydrochloric acid (10 μL) and 10% palladium carbon (10 mg) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 hours under a hydrogen atmosphere. . The reaction mixture was filtered and concentrated, and the resulting residue was purified using silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to give the title compound (6 mg, 62%) as a white solid Got as.
実施例9 N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 9 Production of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide
工程1:
4-(5-ニトロ-2-チエニル)シクロヘキサノンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 4- (5-nitro-2-thienyl) cyclohexanone
4-(5-ニトロ-2-チエニル)シクロヘキサノンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 4- (5-nitro-2-thienyl) cyclohexanone
無水酢酸(1.5 mL)に濃硝酸(210μL)を加え、-10℃に冷却し、無水酢酸(1.5 mL)に溶解した4-(2-チエニル)シクロヘキサノン(562 mg, 3.11 mmol)をゆっくりと加え、-10℃にて1.5時間撹拌した。反応液に水を加えクロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液で洗浄後、硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(ヘキサン:酢酸エチル=100:0→75:25、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(298 mg, 43%)を褐色固体として得た。
Concentrated nitric acid (210 μL) was added to acetic anhydride (1.5 mL), cooled to −10 ° C., and 4- (2-thienyl) cyclohexanone (562 mg, 3.11 mmol) dissolved in acetic anhydride (1.5 mL) was slowly added. The mixture was stirred at −10 ° C. for 1.5 hours. Water was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue obtained was purified by silica gel chromatography (hexane: ethyl acetate = 100 : 0 → 75: 25, gradient) to give the title compound (298 mg, 43%) as a brown solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.95-2.01 (2H, m), 2.39-2.42 (2H, m), 2.51-2.54 (4H, m), 3.31-3.36 (1H, m), 6.87 (1H, d, J = 4.9 Hz), 7.81 (1H, d, J = 4.9 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.95-2.01 (2H, m), 2.39-2.42 (2H, m), 2.51-2.54 (4H, m), 3.31-3.36 (1H, m), 6.87 ( 1H, d, J = 4.9 Hz), 7.81 (1H, d, J = 4.9 Hz).
工程2:
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)シクロヘキシル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) cyclohexyl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)シクロヘキシル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) cyclohexyl] piperazine
4-(5-ニトロ-2-チエニル)シクロヘキサノン(332 mg, 1.47 mmol)を塩化メチレンに溶解し、1-メチルピペラジン(191 mg, 1.91 mmol)、酢酸(150μL)、水素化トリアセトキシホウ素ナトリウム(488 mg, 2.2 mmol)を加えて、室温にて1.5時間撹拌後、反応液に水を加えクロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液で洗浄後、硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(223 mg, 49%)を褐色油状物として得た。
4- (5-Nitro-2-thienyl) cyclohexanone (332 mg, 1.47 mmol) is dissolved in methylene chloride, and 1-methylpiperazine (191 mg, 1.91 mmol), acetic acid (150 μL), sodium triacetoxyborohydride ( 488 mg, 2.2 mmol) and stirred at room temperature for 1.5 hours, water was added to the reaction solution and extracted with chloroform, and the organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution, dried over sodium sulfate, and filtered. The residue obtained by concentration was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to give the title compound (223 mg, 49%) as a brown oil.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.61-1.64 (2H, m), 1.75-1.79 (4H, m), 1.98-2.01 (2H, m), 2.25-2.28 (4H, br m), 2.44-2.46 (8H, m), 3.01-3.07 (1H, m), 6.80 (1H, dd, J = 3.9, 1.0 Hz), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.61-1.64 (2H, m), 1.75-1.79 (4H, m), 1.98-2.01 (2H, m), 2.25-2.28 (4H, br m), 2.44 -2.46 (8H, m), 3.01-3.07 (1H, m), 6.80 (1H, dd, J = 3.9, 1.0 Hz), 7.77 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz).
工程3:
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)シクロヘキシル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) cyclohexyl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)シクロヘキシル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) cyclohexyl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)シクロヘキシル]ピペラジン(80 mg、0.26 mmol)をメタノール(3 mL)に溶解し、10%パラジウム炭素を加えて、水素雰囲気下室温にて14時間撹拌後、ろ過して濃縮し表題化合物(22 mg, crude)を褐色油状物として得た。
1-Methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) cyclohexyl] piperazine (80 mg, 0.26 mmol) was dissolved in methanol (3 mL), 10% palladium carbon was added, and hydrogen atmosphere was added. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 14 hours, filtered and concentrated to give the title compound (22 mg, crude) as a brown oil.
工程4:
ベンジル 2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセテートの製造 Step 4:
Preparation of benzyl 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate
ベンジル 2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセテートの製造 Step 4:
Preparation of benzyl 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate
1-メチル-4-ピペリドン(27.2 g, 240 mmol)とグリシンベンジルエステルを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黄褐色油状物として得た。
Using 1-methyl-4-piperidone (27.2 g, 240 mmol) and glycine benzyl ester in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5, the title compound (crude) was obtained as a tan oil.
工程5:
ベンジル 2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセテートの製造 Step 5:
Preparation of benzyl 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide] acetate
ベンジル 2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセテートの製造 Step 5:
Preparation of benzyl 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide] acetate
ベンジル 2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセテート(6.98 g, crude、理論量6.51 g, 24.8 mmol)の塩化メチレン(100 mL)溶液に、氷冷下で、トリエチルアミン(5.02 g, 49.6 mmol)、トリフルオロ酢酸無水物(7.81 g, 37.2 mmol)を加えた。室温に戻し、2時間攪拌した。反応液に、飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→90:10、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(6.90 g, 2工程収率77.6%)を淡褐色アモルファスとして得た。
To a solution of benzyl 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetate (6.98 g, crude, theoretical amount 6.51 g, 24.8 mmol) in methylene chloride (100 mL) under ice-cooling, triethylamine (5.02 g) , 49.6 mmol), trifluoroacetic anhydride (7.81 g, 37.2 mmol) was added. It returned to room temperature and stirred for 2 hours. A saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction solution, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 90: 10, gradient) to obtain the title compound (6.90 g, 2 step yield 77.6%) as a light brown amorphous.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.56-1.83 (4H, m), 1.98-2.07 (2H, m), 2.27 (3H, s), 2.86-2.94 (2H, m), 3.78-3.88 (1H, m), 4.09 (2H, s), 5.17 (2H, s), 7.30-7.39 (5H,m)
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.56-1.83 (4H, m), 1.98-2.07 (2H, m), 2.27 (3H, s), 2.86-2.94 (2H, m), 3.78-3.88 ( 1H, m), 4.09 (2H, s), 5.17 (2H, s), 7.30-7.39 (5H, m)
工程6:
2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸の製造 Step 6:
Preparation of 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetic acid
2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸の製造 Step 6:
Preparation of 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetic acid
ベンジル 2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセテート(6.90 g, 19.3 mmol)のメタノール(60 mL) 溶液に、10%Pd-C(690 mg)を加えた。系中を水素で置換し、室温で一晩攪拌した。反応液をセライトろ過し、ろ液を減圧濃縮した。表題化合物(5.00 g, crude)を白色アモルファスとして得た。
Benzyl 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide] acetate (6.90 g, 19.3 mmol) in a methanol (60 mL) solution in 10% Pd-C ( 690 mg) was added. The system was replaced with hydrogen and stirred overnight at room temperature. The reaction solution was filtered through celite, and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The title compound (5.00 g, crude) was obtained as a white amorphous.
工程7:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 7:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -N- ( Preparation of 1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 7:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -N- ( Preparation of 1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)シクロヘキシル]ピペラジンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および工程7と同様に、表題化合物(crude)を褐色油状物として得た。
1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) cyclohexyl] piperazine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetic acid Was used to obtain the title compound (crude) as a brown oil in the same manner as in Step 6 and Step 7 of Example 2.
工程8:
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド(66 mg)を8Mアンモニア-メタノールに溶解し、室温にて5.5時間撹拌後濃縮し残渣を得た。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(30 mg, 3工程収率26%)を黄色個体として得た。 Step 8:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2 -Trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -N- (1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) acetamide (66 mg) was dissolved in 8M ammonia-methanol, stirred at room temperature for 5.5 hours and concentrated to give a residue. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to obtain the title compound (30 mg, yield of 3 steps, 26%) as a yellow solid.
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド(66 mg)を8Mアンモニア-メタノールに溶解し、室温にて5.5時間撹拌後濃縮し残渣を得た。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(30 mg, 3工程収率26%)を黄色個体として得た。 Step 8:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino]
実施例10 (E)-N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-3-オキソプロパ-1-エン-1-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 10 (E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop Preparation of 1-en-1-yl] thiophene-2-carboxamide
工程1:
(E)-tert-ブチル 3-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)アクリレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of (E) -tert-butyl 3- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) acrylate
(E)-tert-ブチル 3-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)アクリレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of (E) -tert-butyl 3- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) acrylate
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミド(80 mg、0.2 mmol)を1,4-ジオキサン(2 mL)に溶解し、o-トリトルイルホスフィン(18 mg、0.06 mmol)、tert-ブチルアクリレート(150μL、1 mmol)、ジイソプロピルアミン(100μL、0.6 mmol)、トリス(ジベンジリデンアセトン)ジパラジウム(0)(18 mg、0.02 mmol)を加え、100℃にて19時間撹拌した。反応液に水を加えクロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(55 mg, 60%)を褐色油状物として得た。
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide (80 mg, 0.2 mmol) is dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (2 mL) O-tritoluylphosphine (18 mg, 0.06 mmol), tert-butyl acrylate (150 μL, 1 mmol), diisopropylamine (100 μL, 0.6 mmol), tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0) (18 mg, 0.02 mmol) was added and the mixture was stirred at 100 ° C. for 19 hours. Water was added to the reaction solution and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue obtained was subjected to silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient). To give the title compound (55 mg, 60%) as a brown oil.
1H-NMR(400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.42-1.44 (2H, m), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.57-1.63 (8H, m), 1.72-1.80 (4H, m), 1.89-1.92 (2H, m), 2.32-2.35 (1H, m), 2.49-2.50 (4H, m), 3.05-3.08 (2H, m), 3.51 (2H, q, J = 5.5 Hz), 6.19 (1H, d, J = 15.6 Hz), 7.11 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.45 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.58 (1H, d, J = 15.6 Hz), 8.43 (1H, s).
1 H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.42-1.44 (2H, m), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.57-1.63 (8H, m), 1.72-1.80 (4H, m), 1.89-1.92 ( 2H, m), 2.32-2.35 (1H, m), 2.49-2.50 (4H, m), 3.05-3.08 (2H, m), 3.51 (2H, q, J = 5.5 Hz), 6.19 (1H, d, J = 15.6 Hz), 7.11 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.45 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.58 (1H, d, J = 15.6 Hz), 8.43 (1H, s).
工程2:
(E)-N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-3-オキソプロパ-1-エン-1-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
(E)-tert-ブチル 3-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)アクリレート(55 mg、0.12 mmol)を4M塩酸-酢酸エチル(1 mL)に加え、室温にて4時間撹拌後濃縮し、(E)-3-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)アクリル酸を白色固体として得た。得られた(E)-3-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)アクリル酸を塩化メチレンに加え、N-メチルピペラジン(15 mg, 0.15 mmol)、トリエチルアミン(50μL, 0.36 mmol)、WSC・HCl(28 mg, 0.15 mmol)、HOBt(20 mg、0.15 mmol)を加えて、室温にて15時間撹拌後、反応液に水を加えクロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液で洗浄後、硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(48 mg, 82%)を無色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 2:
(E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop-1-ene Preparation of -1-yl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (E) -tert-butyl 3- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophene-2 -Yl) acrylate (55 mg, 0.12 mmol) was added to 4M hydrochloric acid-ethyl acetate (1 mL), and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours and concentrated. , 4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) acrylic acid was obtained as a white solid. The resulting (E) -3- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) acrylic acid is added to methylene chloride and N -Methylpiperazine (15 mg, 0.15 mmol), triethylamine (50 μL, 0.36 mmol), WSC · HCl (28 mg, 0.15 mmol), HOBt (20 mg, 0.15 mmol) were added, and after stirring at room temperature for 15 hours, Water was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with a saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue obtained was chromatographed on silica gel (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to give the title compound (48 mg, 82%) as a colorless amorphous.
(E)-N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-3-オキソプロパ-1-エン-1-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
(E)-tert-ブチル 3-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)アクリレート(55 mg、0.12 mmol)を4M塩酸-酢酸エチル(1 mL)に加え、室温にて4時間撹拌後濃縮し、(E)-3-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)アクリル酸を白色固体として得た。得られた(E)-3-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)アクリル酸を塩化メチレンに加え、N-メチルピペラジン(15 mg, 0.15 mmol)、トリエチルアミン(50μL, 0.36 mmol)、WSC・HCl(28 mg, 0.15 mmol)、HOBt(20 mg、0.15 mmol)を加えて、室温にて15時間撹拌後、反応液に水を加えクロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液で洗浄後、硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(48 mg, 82%)を無色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 2:
(E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop-1-ene Preparation of -1-yl] thiophene-2-carboxamide (E) -tert-butyl 3- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophene-2 -Yl) acrylate (55 mg, 0.12 mmol) was added to 4M hydrochloric acid-ethyl acetate (1 mL), and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours and concentrated. , 4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) acrylic acid was obtained as a white solid. The resulting (E) -3- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) acrylic acid is added to methylene chloride and N -Methylpiperazine (15 mg, 0.15 mmol), triethylamine (50 μL, 0.36 mmol), WSC · HCl (28 mg, 0.15 mmol), HOBt (20 mg, 0.15 mmol) were added, and after stirring at room temperature for 15 hours, Water was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with a saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue obtained was chromatographed on silica gel (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18, gradient) to give the title compound (48 mg, 82%) as a colorless amorphous.
実施例11 N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-4-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 11 N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Manufacture of carboxamide
工程1:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-4-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-4-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-4-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-4-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモ-4-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボン酸と[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-プロパンアミン塩酸塩を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様に、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
Using 5-bromo-4-methylthiophene-2-carboxylic acid and [1,4′-bipiperidine] -1′-propanamine hydrochloride in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1, the title compound (crude) was prepared. Obtained.
工程2:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-4-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-4-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様に、表題化合物(10%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide Preparation N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-4-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4 , 5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine was used to obtain the title compound (10%) as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as inStep 3 of Example 1. .
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-4-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-4-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様に、表題化合物(10%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide Preparation N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-4-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4 , 5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine was used to obtain the title compound (10%) as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in
実施例12 N-[3-([1,4’ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-3-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 12 N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2- Carboxamide production
工程1:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-3-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-3-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモ-3-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボン酸と[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-プロパンアミン塩酸塩を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様に、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
Using 5-bromo-3-methylthiophene-2-carboxylic acid and [1,4′-bipiperidine] -1′-propanamine hydrochloride, the title compound (crude) was prepared in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1. Obtained.
工程2:
N-[3-([1,4’ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-3-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-3-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様に、表題化合物(51%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,4 The title compound (51%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as inStep 3 of Example 1 using 5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine.
N-[3-([1,4’ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-3-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-3-メチルチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様に、表題化合物(51%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methylthiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,4 The title compound (51%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in
実施例13 N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(ピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 13 Production of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-[(2-メトキシ-2-オキソエチル)アミノ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4-[(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl) amino] piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[(2-メトキシ-2-オキソエチル)アミノ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4-[(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl) amino] piperidine-1-carboxylate
1-Boc-4-ピペリドンとグリシンメチルエステルを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を白色油状物として得た。
The title compound (crude) was obtained as a white oil in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using 1-Boc-4-piperidone and glycine methyl ester.
工程2:
tert-ブチル 4-[N-(2-メトキシ-2-オキソエチル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [N- (2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[N-(2-メトキシ-2-オキソエチル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [N- (2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[(2-メトキシ-2-オキソエチル)アミノ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートと2-ニトロベンゼンスルホニルクロライドを用いて、実施例2の工程4と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を白色粉末として得た。
tert-Butyl 4-[(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl) amino] piperidine-1-carboxylate and 2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride were used in the same manner as in Step 4 of Example 2 to obtain the title compound (crude). Obtained as a white powder.
工程3:
2-{N-[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド}酢酸の製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 2- {N- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido} acetic acid
2-{N-[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド}酢酸の製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 2- {N- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido} acetic acid
tert-ブチル 4-[N-(2-メトキシ-2-オキソエチル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例2の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黄色粉末として得た。
tert-Butyl 4- [N- (2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] piperidine-1-carboxylate was used in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 2 to obtain the title compound (crude ) Was obtained as a yellow powder.
工程4:
tert-ブチル 4-{N-[2-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド}ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 4:
tert-Butyl 4- {N- [2-({5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide } Production of piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-{N-[2-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド}ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 4:
tert-Butyl 4- {N- [2-({5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide } Production of piperidine-1-carboxylate
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンと2-{N-[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド}酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および実施例2の工程7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色粉末として得た。
1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine and 2- {N- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide } Using acetic acid, the title compound (crude) was obtained as a brown powder in the same manner as in Step 6 of Example 2 and Step 7 of Example 2.
工程5:
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[2-ニトロ-N-(ピペリジン-4-イル)フェニルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドの製造 Step 5:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [2-nitro-N- (piperidin-4-yl) phenylsulfonamido] acetamide
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[2-ニトロ-N-(ピペリジン-4-イル)フェニルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドの製造 Step 5:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [2-nitro-N- (piperidin-4-yl) phenylsulfonamido] acetamide
tert-ブチル 4-{N-[2-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド}ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレート(0.63 g, 0.9 mmol)のメタノール(10 mL)溶液に、4N HCl/EtOAc(5 mL)を加え、室温にて4時間攪拌した。減圧濃縮をし、残渣を得た。残渣に、水を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。水層を飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液で中和した。混合溶媒(クロロホルム/メタノール=10/1)にて抽出し、有機層を硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥した。減圧濃縮して得られた残渣を、シリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:アンモニア飽和メタノール=90:10)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(0.45 g, 2工程収率36%)を褐色固体として得た。
tert-Butyl 4- {N- [2-({5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2-nitrophenylsulfonamide } To a solution of piperidine-1-carboxylate (0.63 g, 0.9 mmol) in methanol (10 mL) was added 4N HCl / EtOAc (5 mL), and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. Concentration under reduced pressure gave a residue. Water was added to the residue and extracted with chloroform. The aqueous layer was neutralized with a saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution. Extraction was performed with a mixed solvent (chloroform / methanol = 10/1), and the organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate. The residue obtained by concentration under reduced pressure was purified using silica gel chromatography (chloroform: ammonia saturated methanol = 90: 10) to obtain the title compound (0.45 g, 2 step yield 36%) as a brown solid.
工程6
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(ピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[2-ニトロ-N-(ピペリジン-4-イル)フェニルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(61%)を淡褐色固体として得た。 Step 6
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N- {5- [4- Step 4 of Example 2 using (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [2-nitro-N- (piperidin-4-yl) phenylsulfonamido] acetamide In the same manner as the above, the title compound (61%) was obtained as a light brown solid.
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(ピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[2-ニトロ-N-(ピペリジン-4-イル)フェニルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(61%)を淡褐色固体として得た。 Step 6
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N- {5- [4- Step 4 of Example 2 using (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [2-nitro-N- (piperidin-4-yl) phenylsulfonamido] acetamide In the same manner as the above, the title compound (61%) was obtained as a light brown solid.
実施例14 N-{3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル}-3-メトキシ-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 14 N- {3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl} -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Manufacture of carboxamide
工程1:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-3-メトキシチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methoxythiophene-2-carboxamide
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-3-メトキシチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methoxythiophene-2-carboxamide
5-ブロモ-3-メトキシチオフェン-2-カルボン酸と[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-プロパンアミン塩酸塩を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様に、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
Using 5-bromo-3-methoxythiophene-2-carboxylic acid and [1,4′-bipiperidine] -1′-propanamine hydrochloride in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1, the title compound (crude) was prepared. Obtained.
工程2:
N-{3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル}-3-メトキシ-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-3-メトキシチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様に、表題化合物(2工程収率1%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
N- {3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl} -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide Preparation N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methoxythiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4 , 5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine, the title compound (2 step yield 1%) was pale yellow as inStep 3 of Example 1. Obtained as a solid.
N-{3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル}-3-メトキシ-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモ-3-メトキシチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様に、表題化合物(2工程収率1%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
N- {3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl} -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide Preparation N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromo-3-methoxythiophene-2-carboxamide and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4 , 5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine, the title compound (2 step yield 1%) was pale yellow as in
実施例15 N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 15 N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine-4 -Il) amino] acetamide production
工程1:
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンと1-メチル-4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(79%)を黄色固体として得た。
2-Bromo-5-nitrothiophene and 1-methyl-4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3 , 6-Tetrahydropyridine was used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1 to obtain the title compound (79%) as a yellow solid.
1H-NMR(400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.43 (3H, s), 2.61 (2H, t, J = 2.4 Hz), 2.70 (2H, t, J = 5.6 Hz), 3.15 (2H, q, J = 3.1 Hz), 6.18-6.20 (1H, m), 7.23 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.47 (2H, dd, J = 6.8, 2.0 Hz), 7.59 (2H, dd, J = 6.8, 2.0 Hz), 7.90 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.43 (3H, s), 2.61 (2H, t, J = 2.4 Hz), 2.70 (2H, t, J = 5.6 Hz), 3.15 (2H, q, J = 3.1 Hz), 6.18-6.20 (1H, m), 7.23 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.47 (2H, dd, J = 6.8, 2.0 Hz), 7.59 (2H, dd, J = 6.8, 2.0 Hz), 7.90 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
工程2:
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジンを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色固体として得た。
In the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2, using 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine, the title compound ( crude) as a brown solid.
工程3:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino ) -2-Oxoethyl] -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino ) -2-Oxoethyl] -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色固体として得た。
5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1- Methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetic acid was used in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 to obtain the title compound (crude) as a brown solid.
工程4:
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率55%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 4:
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Preparation of amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9, the title compound (3 step yield 55%) Was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率55%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 4:
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Preparation of amino]
実施例16 2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例8と同様にして、表題化合物(82%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 16 Preparation of 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] The title compound (82%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Example 8 using acetamide.
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例8と同様にして、表題化合物(82%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 16 Preparation of 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] The title compound (82%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Example 8 using acetamide.
実施例17 2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アセトアミドの製造
Example 17 2-[(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) acetamide Manufacturing
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-(4-ヨードフェノキシ)ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートとビス(ピナコラート)ジボロンを用いて、実施例1の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を淡黄色固体として得た。
The title compound (crude) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 1 using tert-butyl 4- (4-iodophenoxy) piperidine-1-carboxylate and bis (pinacolato) diboron. .
工程2
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造Process 2
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンとtert-ブチル 4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(62%)を黄色固体として得た。
2-Bromo-5-nitrothiophene and tert-butyl 4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate Was used to give the title compound (62%) as a yellow solid in a manner similar to Step 3 of Example 1.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.52 (9H, s), 1.72-1.81 (2H, m), 1.90-1.99 (2H, m), 3.32-3.41 (2H, m), 3.67-3.74 (2H, m), 4.11-4.18 (1H, m), 6.97 (2H, d, J = 8.2 Hz), 7.13 (1H, d, J = 4.8 Hz), 7.57 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.89 (1H, d, J = 4.7 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.52 (9H, s), 1.72-1.81 (2H, m), 1.90-1.99 (2H, m), 3.32-3.41 (2H, m), 3.67-3.74 ( 2H, m), 4.11-4.18 (1H, m), 6.97 (2H, d, J = 8.2 Hz), 7.13 (1H, d, J = 4.8 Hz), 7.57 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.89 (1H, d, J = 4.7 Hz).
工程3
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造Process 3
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(定量的)を褐色固体として得た。
Using tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate, the title compound (quantitative) was converted to a brown solid in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2. Got as.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.47 (9H, s), 1.70-1.80 (2H, m), 1.84-1.97 (2H, m), 3.30-3.37 (2H, m), 3.67-3.80 (4H, m), 4.42-4.50 (1H, m), 6.15 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 6.79 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 6.87 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.47 (9H, s), 1.70-1.80 (2H, m), 1.84-1.97 (2H, m), 3.30-3.37 (2H, m), 3.67-3.80 ( 4H, m), 4.42-4.50 (1H, m), 6.15 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 6.79 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 6.87 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz).
工程4:
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 4:
tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine- 1-carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 4:
tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine- 1-carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率39%)を得た。
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine-1-carboxylate and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) ) Acetamide] The title compound (2 step yield: 39%) was obtained in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.47 (9H, s), 1.72-2.10 (10H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.90-3.02 (2H, m), 3.31-3.38 (2H, m), 3.65-3.74 (2H, m), 3.82-3.89 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 4.45-4.50 (1H, m), 6.61 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 3.8 Hz), 7.46 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.47 (9H, s), 1.72-2.10 (10H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.90-3.02 (2H, m), 3.31-3.38 (2H, m), 3.65-3.74 (2H, m), 3.82-3.89 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 4.45-4.50 (1H, m), 6.61 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 3.8 Hz), 7.46 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
工程5:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(ピペリジン-4-イルオキシ)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]アセトアミドの製造 Step 5:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (piperidin-4-yloxy) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il} amino) ethyl] acetamide production
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(ピペリジン-4-イルオキシ)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]アセトアミドの製造 Step 5:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (piperidin-4-yloxy) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il} amino) ethyl] acetamide production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] piperidine- The title compound (crude) was obtained using 1-carboxylate in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13.
工程6:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-{2-[(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}アセトアミドの製造 Step 6:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- {2-[(5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophene -2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl} acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-{2-[(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}アセトアミドの製造 Step 6:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- {2-[(5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophene -2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl} acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(ピペリジン-4-イルオキシ)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]アセトアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率55%)を得た。
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (piperidin-4-yloxy) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il} amino) ethyl] acetamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield 55%).
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.78-2.07 (10H, m), 2.28-2.31 (8H, m), 2.65-2.73 (2H, m), 2.94-2.97 (2H, m), 3.80-3.90 (1H, m), 4.16 (2H, s), 4.28-4.36 (1H, m), 6.60 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.45 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 8.85 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.78-2.07 (10H, m), 2.28-2.31 (8H, m), 2.65-2.73 (2H, m), 2.94-2.97 (2H, m), 3.80- 3.90 (1H, m), 4.16 (2H, s), 4.28-4.36 (1H, m), 6.60 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.92 (1H , d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.45 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 8.85 (1H, brs).
工程7:
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-{2-[(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(73%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 7:
Preparation of 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) acetamide 2, 2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- {2-[(5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophene-2 -Il) amino] -2-oxoethyl} acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (73%) as a pale yellow solid.
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-{2-[(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(73%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 7:
Preparation of 2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl)
実施例18 2-[4-(ジメチルアミノ)ピペリジン-1-イル]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンと2-[4-(ジメチルアミノ)ピペリジン-1-イル]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(48%)を褐色固体として得た。 Example 18 Production of 2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide 1Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 with methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine and 2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] acetic acid Similarly, the title compound (48%) was obtained as a brown solid.
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンと2-[4-(ジメチルアミノ)ピペリジン-1-イル]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(48%)を褐色固体として得た。 Example 18 Production of 2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide 1
実施例19 (R)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 19 (R) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidin-2- Carboxamide production
工程1:
(R)-1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボン酸の製造 Step 1:
Production of (R) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
(R)-1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボン酸の製造 Step 1:
Production of (R) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
(R)-tert-ブチル ピロリジン-2-カルボキシレート塩酸塩(1 g, 5 mmol)を酢酸(3 mL)に溶解し、1-メチル-4-ピペリドン(622 mg, 5.5 mmol)、水素化トリアセトキシホウ素ナトリウム(488 mg, 2.2 mmol)を加えて、室温にて15時間撹拌後、反応液に飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=100:0→80:20、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、(R)tert-ブチル 1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキシレート(1.07 g, crude)を黄色油状物として得た。得られた、(R)tert-ブチル 1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキシレート(1.07 g, 4 mmol)を酢酸に溶解し、氷冷下4M塩酸-酢酸エチルを加えて室温にて7時間撹拌後濃縮して表題化合物(1.1 g, crude)を白色固体として得た。
(R) -tert-butyl pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate hydrochloride (1 g, 5 mmol) was dissolved in acetic acid (3 mL), 1-methyl-4-piperidone (622 mg, 5.5 mmol), trihydrogenated Sodium acetoxyboron (488 mg, 2.2 mg mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15 hours. A saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction mixture, extracted with chloroform, and the organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate and filtered. The residue obtained by concentration was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 100: 0 → 80: 20, gradient), and (R) tert-butyl 1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) Pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (1.07 g, crude) was obtained as a yellow oil. The obtained (R) tert-butyl 1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate (1.07 g, 4 mmol) was dissolved in acetic acid, and 4M hydrochloric acid-ethyl acetate was added under ice cooling. In addition, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 7 hours and then concentrated to obtain the title compound (1.1 g, crude) as a white solid.
工程2:
(R)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
(R)-1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボン酸と1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(40%)を微黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of (R) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Performed with (R) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid and 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine Analogously tosteps 6 and 7 of example 2, the title compound (40%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
(R)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
(R)-1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボン酸と1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(40%)を微黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of (R) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Performed with (R) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid and 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine Analogously to
実施例20 (S)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 20 (S) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidin-2- Carboxamide production
工程1:
(S)-1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボン酸の製造 Step 1:
Production of (S) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
(S)-1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボン酸の製造 Step 1:
Production of (S) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
(S)-tert-ブチル ピロリジン-2-カルボキシレート塩酸塩と1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例19の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を微黄色固体として得た。
(S) -tert-Butyl pyrrolidine-2-carboxylate hydrochloride and 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine as in Step 1 of Example 19 The title compound (crude) was obtained as a slightly yellow solid.
工程2:
(S)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
(S)-1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボン酸と1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例19の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(49%)を微黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of (S) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Performed with (S) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid and 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine In the same manner as inStep 2 of Example 19, the title compound (49%) was obtained as a slightly yellow solid.
(S)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
(S)-1-(1-メチルピペラジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボン酸と1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例19の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(49%)を微黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of (S) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide Performed with (S) -1- (1-methylpiperazin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid and 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine In the same manner as in
実施例21 2-[(5-ヒドロキシペンチル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドと5-ヒドロキシペンタナールを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(89%)を淡黄色油状物として得た。 Example 21 2-[(5-hydroxypentyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Preparation of Acetamide N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide and 5- The title compound (89%) was obtained as a pale yellow oil in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using hydroxypentanal.
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドと5-ヒドロキシペンタナールを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(89%)を淡黄色油状物として得た。 Example 21 2-[(5-hydroxypentyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Preparation of Acetamide N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide and 5- The title compound (89%) was obtained as a pale yellow oil in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using hydroxypentanal.
実施例22 N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 22 Production of N- [3-([1,4'-bipiperidin] -1'-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドとtert-ブチル 4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(91.7%)を淡黄色アモルファスとして得た。
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide and tert-butyl 4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetra Methyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate was used in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1 to obtain the title compound (91.7%) as a pale yellow amorphous product. .
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.37-1.44 (2H, m), 1.49 (9H, s), 1.48-1.56 (2H, m), 1.59-1.83 (8H, m), 1.88-1.96 (2H, m), 2.30-2.40 (1H, m), 2.46-2.55 (6H, m), 3.07-3.14 (2H, m), 3.18-3.22 (4H, m), 3.52-3.62 (6H, m), 6.92 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.10 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz),7.48-7.54 (3H, m)
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.37-1.44 (2H, m), 1.49 (9H, s), 1.48-1.56 (2H, m), 1.59-1.83 (8H, m), 1.88-1.96 ( 2H, m), 2.30-2.40 (1H, m), 2.46-2.55 (6H, m), 3.07-3.14 (2H, m), 3.18-3.22 (4H, m), 3.52-3.62 (6H, m), 6.92 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.10 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.48-7.54 (3H, m)
工程2:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(87%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide tert-Butyl 4- [ 4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate was used to In the same manner as in Step 5, the title compound (87%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(87%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide tert-Butyl 4- [ 4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate was used to In the same manner as in Step 5, the title compound (87%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
実施例23 N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-(4-{4-[6-(メチルアミノ)-6-オキソヘキシル]ピペラジン-1-イル}フェニル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド (50 mg, 0.10 mmol)のアセトニトリル溶液(1 mL)に、炭酸カリウム(16.8 mg, 0.12 mmol)、ヨウ化カリウム(20.1 mg, 0.12 mmol)、6-ブロモ-N-メチルヘキサンアミド (23.1 mg, 0.11 mmol)を加えた。80℃で4時間攪拌した。室温に戻し、反応液に、飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をPLC(クロロホルム:アンモニア飽和メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(47.3 mg, 75%)を淡褐色固体として得た。 Example 23 N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- (4- {4- [6- (methylamino) -6-oxohexyl] piperazine-1 Preparation of -yl} phenyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene -2-Carboxamide (50 mg, 0.10 mmol) in acetonitrile (1 mL) was added potassium carbonate (16.8 mg, 0.12 mmol), potassium iodide (20.1 mg, 0.12 mmol), 6-bromo-N-methylhexanamide. (23.1 mg, 0.11 mmol) was added. Stir at 80 ° C. for 4 hours. After returning to room temperature, a saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified using PLC (chloroform: ammonia saturated methanol = 10: 1) to obtain the title compound (47.3 mg, 75%) as a light brown solid.
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド (50 mg, 0.10 mmol)のアセトニトリル溶液(1 mL)に、炭酸カリウム(16.8 mg, 0.12 mmol)、ヨウ化カリウム(20.1 mg, 0.12 mmol)、6-ブロモ-N-メチルヘキサンアミド (23.1 mg, 0.11 mmol)を加えた。80℃で4時間攪拌した。室温に戻し、反応液に、飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をPLC(クロロホルム:アンモニア飽和メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(47.3 mg, 75%)を淡褐色固体として得た。 Example 23 N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- (4- {4- [6- (methylamino) -6-oxohexyl] piperazine-1 Preparation of -yl} phenyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene -2-Carboxamide (50 mg, 0.10 mmol) in acetonitrile (1 mL) was added potassium carbonate (16.8 mg, 0.12 mmol), potassium iodide (20.1 mg, 0.12 mmol), 6-bromo-N-methylhexanamide. (23.1 mg, 0.11 mmol) was added. Stir at 80 ° C. for 4 hours. After returning to room temperature, a saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified using PLC (chloroform: ammonia saturated methanol = 10: 1) to obtain the title compound (47.3 mg, 75%) as a light brown solid.
実施例24 ベンジル 6-{4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサノエートの製造
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドとベンジル 6-ブロモヘキサノエートを用いて、実施例23と同様にして、表題化合物(69%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Example 24 Benzyl 6- {4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1- Yl} hexanoate N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide and benzyl 6 Using bromohexanoate, the title compound (69%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Example 23.
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドとベンジル 6-ブロモヘキサノエートを用いて、実施例23と同様にして、表題化合物(69%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Example 24 Benzyl 6- {4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1- Yl} hexanoate N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide and benzyl 6 Using bromohexanoate, the title compound (69%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Example 23.
実施例25 1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミドの製造
工程1:
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミドの製造 Example 25 Production of 1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide 1:
1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-Production of carboxamide
工程1:
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミドの製造 Example 25 Production of 1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide 1:
1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-Production of carboxamide
1’-メチル-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボン酸と5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンを用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を微黄色固体として得た。
1'-methyl- [1,4'-bipiperidine] -4-carboxylic acid and 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2- The title compound (crude) was obtained as a slightly yellow solid in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using amine.
工程2:
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミドの製造
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミドを用いて、実施例8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率31%)を微黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of 1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide 1′-methyl —N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide In the same manner as in Example 8, the title compound (2 step yield: 31%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミドの製造
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミドを用いて、実施例8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率31%)を微黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of 1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide 1′-methyl —N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide In the same manner as in Example 8, the title compound (2 step yield: 31%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
実施例26 N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造
Example 26 N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} Hexanamide production
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンとtert-ブチル 4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(44%)を淡赤色固体として得た。
2-bromo-5-nitrothiophene and tert-butyl 4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate Was used to give the title compound (44%) as a pale red solid in a manner similar to Step 3 of Example 1.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.49 (9H, s), 3.22-3.30 (4H, m), 3.56-3.62 (4H, m), 6.93 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.12 (1H, d, J = 4.2 Hz), 7.54 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.49 (9H, s), 3.22-3.30 (4H, m), 3.56-3.62 (4H, m), 6.93 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.12 (1H, d, J = 4.2 Hz), 7.54 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
工程2:
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(96%)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate was used to treat the title compound (96%) as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2. Got as.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.49 (9H, s), 3.10-3.16 (4H, m), 3.55-3.61 (4H, m), 3.75 (2H, brs), 6.15 (1H, d, J = 3.7 Hz), 6.79 (1H, d, J = 3.7 Hz), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.49 (9H, s), 3.10-3.16 (4H, m), 3.55-3.61 (4H, m), 3.75 (2H, brs), 6.15 (1H, d, J = 3.7 Hz), 6.79 (1H, d, J = 3.7 Hz), 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
工程3:
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 3:
tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine- 1-carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 3:
tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine- 1-carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(66%)を黒褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine-1-carboxylate and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) ) Acetamide] The title compound (66%) was obtained as a black-brown amorphous in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.34-1.50 (11H, m), 1.78-1.85 (2H, m), 1.98-2.10 (2H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.92-3.06 (6H, m), 3.14-3.20 (4H, m), 3.85 (1H, brs), 4.17 (2H, s), 6.61 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz), 6.89 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz), 7.45 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
工程4:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]アセトアミドの製造 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.34-1.50 (11H, m), 1.78-1.85 (2H, m), 1.98-2.10 (2H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.92-3.06 ( 6H, m), 3.14-3.20 (4H, m), 3.85 (1H, brs), 4.17 (2H, s), 6.61 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz), 6.89 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz ), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz), 7.45 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il} amino) ethyl] acetamide production
工程4:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]アセトアミドの製造 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.34-1.50 (11H, m), 1.78-1.85 (2H, m), 1.98-2.10 (2H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.92-3.06 ( 6H, m), 3.14-3.20 (4H, m), 3.85 (1H, brs), 4.17 (2H, s), 6.61 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz), 6.89 (2H, d, J = 8.5 Hz ), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz), 7.45 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz).
Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il} amino) ethyl] acetamide production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5の工程と同様にして、表題化合物(57%)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine- The title compound (57%) was obtained as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using 1-carboxylate.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.32-1.56 (2H, m), 1.76-1.86 (2H, m), 1.96-2.10 (2H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.92-2.98 (2H, m), 3.01-3.06 (4H, m), 3.14-3.20 (4H, m), 3.80-3.89 (1H, m), 4.17 (2H, s), 6.61 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.89 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.45 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 8.85 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.32-1.56 (2H, m), 1.76-1.86 (2H, m), 1.96-2.10 (2H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.92-2.98 ( 2H, m), 3.01-3.06 (4H, m), 3.14-3.20 (4H, m), 3.80-3.89 (1H, m), 4.17 (2H, s), 6.61 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz) , 6.89 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.92 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.45 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 8.85 (1H, brs).
工程5:
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造 Step 5:
N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) Of phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造 Step 5:
N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) Of phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]アセトアミドと6-ブロモ-N-メチルヘキサンアミドを用いて、実施例23と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黄色油状物として得た。
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 The title compound (crude) was obtained as a yellow oil in the same manner as in Example 23 using -yl} amino) ethyl] acetamide and 6-bromo-N-methylhexaneamide.
工程6:
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率40%)を褐色固体として得た。 Step 6:
Of N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide Preparation N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl ) Phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 40%) as a brown solid.
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率40%)を褐色固体として得た。 Step 6:
Of N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide Preparation N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl ) Phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 40%) as a brown solid.
実施例27 N-(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 27 N- (5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Amino] acetamide production
工程1:
2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]-4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェノールの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] -4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenol
2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]-4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェノールの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] -4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenol
4-ブロモ-2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェノールとビス(ピナコラート)ジボロンを用いて、実施例1の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黒褐色油状物として得た。
Using 4-bromo-2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenol and bis (pinacolato) diboron in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 1, the title compound (crude) was converted into a blackish brown oil Got as.
工程2:
2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]-4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノールの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] -4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol
2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]-4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノールの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] -4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンと2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]-4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェノールを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黒褐色油状物として得た。
2-Bromo-5-nitrothiophene and 2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] -4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl ) Using phenol, the title compound (crude) was obtained as a blackish brown oil in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.33 (3H, s), 2.40-2.82 (8H, m), 3.78 (2H, S), 6.88 (1H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.09 (1H, d, J = 4.2 Hz), 7.24-7.29 (1H, m), 7.46 (1H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
工程3:
4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェノールの製造 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.33 (3H, s), 2.40-2.82 (8H, m), 3.78 (2H, S), 6.88 (1H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.09 (1H , d, J = 4.2 Hz), 7.24-7.29 (1H, m), 7.46 (1H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
Step 3:
Preparation of 4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenol
工程3:
4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェノールの製造 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.33 (3H, s), 2.40-2.82 (8H, m), 3.78 (2H, S), 6.88 (1H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.09 (1H , d, J = 4.2 Hz), 7.24-7.29 (1H, m), 7.46 (1H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.88 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
Step 3:
Preparation of 4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenol
2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]-4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノールを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黒褐色油状物として得た。
Using 2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] -4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2, the title compound (crude) was obtained. Obtained as a black-brown oil.
工程4:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2 Preparation of -oxoethyl} -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2 Preparation of -oxoethyl} -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェノールと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を茶色アモルファスとして得た。
4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenol and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) acetamide] The title compound (crude) was obtained as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
工程5:
N-(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8の工程と同様にして、表題化合物(4工程収率2%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 5:
N- (5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] Using -2-oxoethyl} -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9, the title compound (4 step yield: 2%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid. Got as.
N-(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8の工程と同様にして、表題化合物(4工程収率2%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 5:
N- (5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino]
実施例28 2-[(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
Example 28 2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Production of acetamide
工程1:
2-[{3-[(tert-ブチルジメチルシリル)オキシ]プロピル}(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造 Step 1:
2-[{3-[(tert-Butyldimethylsilyl) oxy] propyl} (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl ] Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} acetamide
2-[{3-[(tert-ブチルジメチルシリル)オキシ]プロピル}(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造 Step 1:
2-[{3-[(tert-Butyldimethylsilyl) oxy] propyl} (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl ] Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} acetamide
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドと3-[(tert-ブチルジメチルシリル)オキシ]プロパナールを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様に、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide and 3-[(tert- (Butyldimethylsilyl) oxy] propanal was used to obtain the title compound (crude) as in Step 1 of Example 5.
工程2:
2-[(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
2-[{3-[(tert-ブチルジメチルシリル)オキシ]プロピル}(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの(12 mg, 0.016 mmol)のTHF(1 mL)溶液に、TBAF(33μL, 0.033 mmol)を加え、1時間攪拌した。別のフラスコで、2-[{3-[(tert-ブチルジメチルシリル)オキシ]プロピル}(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(150 mg, 0.21 mmol)のTHF(2 mL)溶液に、TBAF(0.42mL, 0.42 mmol)を加え、4時間攪拌した。二つの反応液を併せた。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、混合溶媒(クロロホルム/メタノール=10/1)で抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をPLC(クロロホルム:アンモニウム飽和メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(8 mg, 9%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide Preparation 2-[{3-[(tert-Butyldimethylsilyl) oxy] propyl} (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) To a solution of (phenyl) thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (12 mg, 0.016 mmol) in THF (1 mL) was added TBAF (33 μL, 0.033 mmol) and stirred for 1 hour. In another flask, 2-[{3-[(tert-butyldimethylsilyl) oxy] propyl} (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazine- To a solution of 1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (150 mg, 0.21 mmol) in THF (2 mL) was added TBAF (0.42 mL, 0.42 mmol) and stirred for 4 hours. The two reaction solutions were combined. A saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was extracted with a mixed solvent (chloroform / methanol = 10/1). The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified using PLC (chloroform: ammonium saturated methanol = 10: 1) to obtain the title compound (8 mg, 9%) as a pale yellow solid.
2-[(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
2-[{3-[(tert-ブチルジメチルシリル)オキシ]プロピル}(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの(12 mg, 0.016 mmol)のTHF(1 mL)溶液に、TBAF(33μL, 0.033 mmol)を加え、1時間攪拌した。別のフラスコで、2-[{3-[(tert-ブチルジメチルシリル)オキシ]プロピル}(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド(150 mg, 0.21 mmol)のTHF(2 mL)溶液に、TBAF(0.42mL, 0.42 mmol)を加え、4時間攪拌した。二つの反応液を併せた。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、混合溶媒(クロロホルム/メタノール=10/1)で抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をPLC(クロロホルム:アンモニウム飽和メタノール=10:1)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(8 mg, 9%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide Preparation 2-[{3-[(tert-Butyldimethylsilyl) oxy] propyl} (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) To a solution of (phenyl) thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (12 mg, 0.016 mmol) in THF (1 mL) was added TBAF (33 μL, 0.033 mmol) and stirred for 1 hour. In another flask, 2-[{3-[(tert-butyldimethylsilyl) oxy] propyl} (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazine- To a solution of 1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide (150 mg, 0.21 mmol) in THF (2 mL) was added TBAF (0.42 mL, 0.42 mmol) and stirred for 4 hours. The two reaction solutions were combined. A saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was extracted with a mixed solvent (chloroform / methanol = 10/1). The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified using PLC (chloroform: ammonium saturated methanol = 10: 1) to obtain the title compound (8 mg, 9%) as a pale yellow solid.
実施例29 2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドの製造
Example 29 2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] Production of acetamide
工程1:
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide
N-(4-ブロモフェニル)-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)アセトアミドとビス(ピナコラート)ジボロンを用いて、実施例1の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(82%)を深緑色固体として得た。
In the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 1, using N- (4-bromophenyl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamide and bis (pinacolato) diboron, the title compound (82%) was obtained. Obtained as a dark green solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.34 (12H, s),2.34 (3H, s), 2.45-2.70 (8H, m), 3.14 (2H, s), 7.57 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.78 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.34 (12H, s), 2.34 (3H, s), 2.45-2.70 (8H, m), 3.14 (2H, s), 7.57 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz), 7.78 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz).
工程2:
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンと2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(82%)を深緑色固体として得た。
2-Bromo-5-nitrothiophene and 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl ) Phenyl] acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1 to obtain the title compound (82%) as a dark green solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.34 (3H, s), 2.48-2.72 (8H, m), 3.17 (2H, s), 7.20 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.61 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.68 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.90 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 9.31 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.34 (3H, s), 2.48-2.72 (8H, m), 3.17 (2H, s), 7.20 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.61 (2H , d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.68 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.90 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 9.31 (1H, brs).
工程3:
N-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of N- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamide
N-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of N- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamide
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を紫色固体として得た。
In the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2, using 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide, the title compound (crude ) Was obtained as a purple solid.
工程4:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)アセトアミド]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamido] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)アセトアミド]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamido] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
N-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)アセトアミドと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率74%)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
N- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamide and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methyl) Piperidin-4-yl) acetamide] acetic acid was used in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 to obtain the title compound (2-step yield: 74%) as a brown amorphous substance.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.70-1.84 (2H, m), 1.96-2.10 (4H, m), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.34 (3H, s), 2.44-2.58 (4H, m), 2.62-2.72 (4H, m), 2.92-3.00 (2H, m), 3.15 (2H, s), 3.80-3.92 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 3.8 Hz), 7.00 (1H, d, J = 3.7 Hz), 7.51 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.55 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 8.98 (1H, brs), 9.15 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.70-1.84 (2H, m), 1.96-2.10 (4H, m), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.34 (3H, s), 2.44-2.58 (4H, m), 2.62-2.72 (4H, m), 2.92-3.00 (2H, m), 3.15 (2H, s), 3.80-3.92 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 3.8 Hz), 7.00 (1H, d, J = 3.7 Hz), 7.51 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.55 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 8.98 (1H, brs), 9.15 (1H, brs).
工程5:
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)アセトアミド]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8の工程と同様にして、表題化合物(66%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 5:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) acetamido] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (66%) as a yellow solid.
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)アセトアミド]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8の工程と同様にして、表題化合物(66%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 5:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl]
実施例30 N-(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 30 N- (5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino Acetamide production
工程1:
3-(5-ブロモ-1H-インドール-1-イル)-N,N-ジメチルプロパン-1-アミンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 3- (5-bromo-1H-indol-1-yl) -N, N-dimethylpropan-1-amine
3-(5-ブロモ-1H-インドール-1-イル)-N,N-ジメチルプロパン-1-アミンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 3- (5-bromo-1H-indol-1-yl) -N, N-dimethylpropan-1-amine
5-ブロモ-1H-インドール(2.4 g、12.2 mmol)をDMF(50 mL)に溶解し、ヨウ化カリウム(2.0 g、12.2 mmol)、炭酸カリウム(3.1 g、36.8 mmol)、3-クロロ-N,N-ジメチルプロパン-1-アミン塩酸塩(2.2 g、13.5 mmol)を加えて、60℃にて16時間撹拌した。反応液に水を加え、酢酸エチルにて抽出し、有機層を硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=100:0→90:10、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(820 mg, 24%)を黄色油状物として得た。
5-Bromo-1H-indole (2.4 g, 12.2 mmol) is dissolved in DMF (50 mL), potassium iodide (2.0 g, 12.2 mmol), potassium carbonate (3.1 g, 36.8 mmol), 3-chloro-N , N-dimethylpropan-1-amine hydrochloride (2.2 g, 13.5 mmol) was added and stirred at 60 ° C for 16 hours. Water was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue obtained was chromatographed on silica gel (chloroform: methanol = 100: 0 → 90: 10, gradient). ) To give the title compound (820 mg, 24%) as a yellow oil.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.93-2.00 (2H, m), 2.20-2.22 (8H, m), 4.19 (2H, t, J = 6.8 Hz), 6.43 (1H, d, J = 3.4 Hz), 7.12 (1H, d, J = 3.4 Hz), 7.25-7.28 (2H, m), 7.75 (1H, s).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.93-2.00 (2H, m), 2.20-2.22 (8H, m), 4.19 (2H, t, J = 6.8 Hz), 6.43 (1H, d, J = 3.4 Hz), 7.12 (1H, d, J = 3.4 Hz), 7.25-7.28 (2H, m), 7.75 (1H, s).
工程2:
N,N-ジメチル-3-[5-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)-1H-インドール-1-イル]プロパン-1-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Of N, N-dimethyl-3- [5- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) -1H-indol-1-yl] propan-1-amine Manufacturing
N,N-ジメチル-3-[5-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)-1H-インドール-1-イル]プロパン-1-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Of N, N-dimethyl-3- [5- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) -1H-indol-1-yl] propan-1-amine Manufacturing
3-(5-ブロモ-1H-インドール-1-イル)-N,N-ジメチルプロパン-1-アミンとビス(ピナコラート)ジボロンを用いて、実施例1の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黄色固体として得た。
In the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 1, using 3- (5-bromo-1H-indol-1-yl) -N, N-dimethylpropan-1-amine and bis (pinacolato) diboron, the title compound ( crude) as a yellow solid.
工程3:
N,N-ジメチル-3-[5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)-1H-インドール-1-イル]プロパン-1-アミンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of N, N-dimethyl-3- [5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) -1H-indol-1-yl] propan-1-amine
N,N-ジメチル-3-[5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)-1H-インドール-1-イル]プロパン-1-アミンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of N, N-dimethyl-3- [5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) -1H-indol-1-yl] propan-1-amine
N,N-ジメチル-3-[5-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)-1H-インドール-1-イル]プロパン-1-アミンと2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(36%)を黄色固体として得た。
N, N-dimethyl-3- [5- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) -1H-indol-1-yl] propan-1-amine and The title compound (36%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1 using 2-bromo-5-nitrothiophene.
1H-NMR(400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.95-2.02 (2H, m), 2.22-2.24 (8H, m), 4.23 (2H, t, J = 6.8 Hz), 6.56 (1H, d, J = 2.9 Hz), 7.19-7.21 (2H, m), 7.44-7.46 (2H, m), 7.91-7.92 (2H, m).
1 H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.95-2.02 (2H, m), 2.22-2.24 (8H, m), 4.23 (2H, t, J = 6.8 Hz), 6.56 (1H, d, J = 2.9 Hz), 7.19-7.21 (2H, m), 7.44-7.46 (2H, m), 7.91-7.92 (2H, m).
工程4:
5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 4:
Preparation of 5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-amine
5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 4:
Preparation of 5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-amine
N,N-ジメチル-3-[5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)-1H-インドール-1-イル]プロパン-1-アミンを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色固体として得た。
Similar to Step 2 of Example 2 using N, N-dimethyl-3- [5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) -1H-indol-1-yl] propan-1-amine The title compound (crude) was obtained as a brown solid.
工程5:
N-{2-[(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 5:
N- {2-[(5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl} -2,2,2- Preparation of trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
N-{2-[(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 5:
N- {2-[(5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl} -2,2,2- Preparation of trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-アミンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を灰色固体として得た。
5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-amine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidine-4) -Yl) acetamido] The title compound (crude) was obtained as a gray solid using acetic acid in the same manner as steps 6 and 7 of Example 2.
工程6:
N-(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-{2-[(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率39%)を灰色固体として得た。 Step 6:
N- (5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Production N- {2-[(5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl} -2,2,2 Using -trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide, the title compound (3 step yield: 39%) was obtained as a gray solid in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
N-(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-{2-[(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率39%)を灰色固体として得た。 Step 6:
N- (5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Production N- {2-[(5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl} -2,2,2 Using -trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide, the title compound (3 step yield: 39%) was obtained as a gray solid in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
実施例31 N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパンアミドの製造
Example 31 N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropane Amide production
工程1:
tert-ブチル [1-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-1-オキソ-3-フェニルプロパン-2-イル]カルバメートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl [1-({5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl] carbamate
tert-ブチル [1-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-1-オキソ-3-フェニルプロパン-2-イル]カルバメートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of tert-butyl [1-({5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl] carbamate
1-メチル-4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジンと2-[(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパン酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
Example 1 Step 1 of Example 1 with 1-methyl-4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazine and 2-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl) amino] -3-phenylpropanoic acid. In the same manner as above, the title compound (crude) was obtained.
工程2:
2-アミノ-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-3-フェニルプロパンアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2-amino-N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -3-phenylpropanamide
2-アミノ-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-3-フェニルプロパンアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2-amino-N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -3-phenylpropanamide
tert-ブチル [1-({5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-1-オキソ-3-フェニルプロパン-2-イル]カルバメートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率75%)を得た。
tert-Butyl [1-({5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl] carbamate In the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13, the title compound (2 step yield: 75%) was obtained.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.35 (3H, s), 2.54-2.62 (4H, m), 2.81 (1H, dd, J = 14.0, 9.2 Hz), 3.20-3.26 (4H, m), 3.36 (1H, dd, J = 13.6, 4.0 Hz), 3.79 (1H, dd, J = 9.2, 4.4 Hz), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.90 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.93 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.23-7.34 (5H, m), 7.48 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 10.25 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.35 (3H, s), 2.54-2.62 (4H, m), 2.81 (1H, dd, J = 14.0, 9.2 Hz), 3.20-3.26 (4H, m) , 3.36 (1H, dd, J = 13.6, 4.0 Hz), 3.79 (1H, dd, J = 9.2, 4.4 Hz), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.90 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.93 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.23-7.34 (5H, m), 7.48 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 10.25 (1H, brs).
工程3:
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパンアミドの製造
2-アミノ-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-3-フェニルプロパンアミドと1-メチル-4-ピペリドンを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(52%)を淡黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 3:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropanamide Examples using 2-amino-N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -3-phenylpropanamide and 1-methyl-4-piperidone In the same manner as in Step 1 of 5, the title compound (52%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous.
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパンアミドの製造
2-アミノ-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-3-フェニルプロパンアミドと1-メチル-4-ピペリドンを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(52%)を淡黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 3:
Preparation of N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropanamide Examples using 2-amino-N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -3-phenylpropanamide and 1-methyl-4-piperidone In the same manner as in Step 1 of 5, the title compound (52%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous.
実施例32 N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-3-カルボキサミドの製造
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-3-カルボン酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(4%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 32 N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidine-4- Yl) Preparation of pyrrolidine-3-carboxamide 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 1- (1-methylpiperidine- The title compound (4%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as inSteps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using 4-yl) pyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acid.
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-3-カルボン酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(4%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 32 N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidine-4- Yl) Preparation of pyrrolidine-3-carboxamide 5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 1- (1-methylpiperidine- The title compound (4%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in
実施例33 N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチルスルホンアミド]アセトアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(64 mg, 0.15 mmol)をTHF(1 mL)に溶解し、トリエチルアミン(30μL, 0.21 mmol)、メタンスルホニルクロリド(14μL, 0.18 mmol)を加えて室温で2時間撹拌後、反応液に水とクロロホルムを加え析出した結晶を濾取した。得られた結晶をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:飽和アンモニアメタノール=90:10)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(32 mg, 42%)を褐色油状物として得た。 Example 33 N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methylsulfonamide] acetamide N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (64 mg, 0.15 mmol) was dissolved in THF (1 mL), triethylamine (30 μL, 0.21 mmol) and methanesulfonyl chloride (14 μL, 0.18 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. Was collected by filtration. The obtained crystals were purified using silica gel chromatography (chloroform: saturated ammonia methanol = 90: 10) to give the title compound (32 mg, 42%) as a brown oil.
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド(64 mg, 0.15 mmol)をTHF(1 mL)に溶解し、トリエチルアミン(30μL, 0.21 mmol)、メタンスルホニルクロリド(14μL, 0.18 mmol)を加えて室温で2時間撹拌後、反応液に水とクロロホルムを加え析出した結晶を濾取した。得られた結晶をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:飽和アンモニアメタノール=90:10)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(32 mg, 42%)を褐色油状物として得た。 Example 33 N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methylsulfonamide] acetamide N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide (64 mg, 0.15 mmol) was dissolved in THF (1 mL), triethylamine (30 μL, 0.21 mmol) and methanesulfonyl chloride (14 μL, 0.18 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. Was collected by filtration. The obtained crystals were purified using silica gel chromatography (chloroform: saturated ammonia methanol = 90: 10) to give the title compound (32 mg, 42%) as a brown oil.
実施例34 4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ペンタンアミドの製造
Example 34 4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1- Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] pentanamide
工程1:
tert-ブチル [4-メチル-1-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-1-オキソペンタン-2-イル]カルバメートの製造 Step 1:
tert-butyl [4-methyl-1-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -1- Of Oxopentan-2-yl] carbamate
tert-ブチル [4-メチル-1-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-1-オキソペンタン-2-イル]カルバメートの製造 Step 1:
tert-butyl [4-methyl-1-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -1- Of Oxopentan-2-yl] carbamate
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンとN-Boc-ロイシンを用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
Similar to Step 1 of Example 1 using 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and N-Boc-leucine The title compound (crude) was obtained.
工程2:
2-アミノ-4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2-amino-4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} pentanamide
2-アミノ-4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2-amino-4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} pentanamide
tert-ブチル [4-メチル-1-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-1-オキソペンタン-2-イル]カルバメートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率44%)を得た。
tert-butyl [4-methyl-1-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -1- The title compound (2 step yield 44%) was obtained in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using oxopentan-2-yl] carbamate.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 0.97 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz), 1.00 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz), 1.43 (1H, heptet, J = 6.0 Hz), 1.72-1.92 (2H, m), 2.41 (3H, s), 2.56-2.63 (2H, m), 2.68 (2H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 3.13 (2H, d, J = 3.2 Hz), 3.59 (1H, dd, J = 9.2, 3.6 Hz), 6.09 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.07 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.38 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.53 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 10.10 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 0.97 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz), 1.00 (3H, d, J = 6.4 Hz), 1.43 (1H, heptet, J = 6.0 Hz), 1.72- 1.92 (2H, m), 2.41 (3H, s), 2.56-2.63 (2H, m), 2.68 (2H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 3.13 (2H, d, J = 3.2 Hz), 3.59 (1H , dd, J = 9.2, 3.6 Hz), 6.09 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.07 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.38 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.53 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 10.10 (1H, brs).
工程3:
4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ペンタンアミドの製造
2-アミノ-4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドと4-メチル-1-ピペリドンを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(3%)を淡黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 3:
4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- Preparation of 4-yl) amino] pentanamide 2-amino-4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Using 2-yl} pentanamide and 4-methyl-1-piperidone, the title compound (3%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5.
4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ペンタンアミドの製造
2-アミノ-4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドと4-メチル-1-ピペリドンを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(3%)を淡黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 3:
4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- Preparation of 4-yl) amino] pentanamide 2-amino-4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Using 2-yl} pentanamide and 4-methyl-1-piperidone, the title compound (3%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5.
実施例35 1-(ピペリジン-4-イル)-3-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ウレアの製造
Example 35 Production of 1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} urea
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{3-[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]ウレイド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5- {3- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] ureido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{3-[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]ウレイド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5- {3- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] ureido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレート(356 mg, 1 mmol)をジクロロメタンに溶解し、ピリジン(81μL, 1 mmol)、クロロギ酸4-ニトロフェニル(201 mg, 1 mmol)を加え、室温で2時間撹拌後、析出した結晶を濾取した。得られた結晶にDMF(6 mL)を加え、tert-ブチル 4-アミノピペリジン-1-カルボキシレート(182 mg, 0.91 mmol)、トリエチルアミン(160μL, 1.15 mmol)を加え、室温にて0.5時間撹拌後、反応液に水と酢酸エチルを加え析出した結晶を濾取した。得られた結晶を、酢酸エチルを用いて再結晶し、表題化合物(335 mg, crude)を微黄色固体として得た。
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (356 mg, 1 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane and pyridine (81μL , 1 mmol), 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (201 mg, 1 mmol), and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, and the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. DMF (6 mL) was added to the obtained crystals, tert-butyl 4-aminopiperidine-1-carboxylate (182 mg, 0.91 mmol), triethylamine (160 μL, 1.15 mmol) were added, and 0.5 hours at room temperature. After stirring, water and ethyl acetate were added to the reaction solution, and the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. The obtained crystals were recrystallized from ethyl acetate to give the title compound (335 mg, crude) as a pale yellow solid.
工程2:
1-(ピペリジン-4-イル)-3-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ウレアの製造
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{3-[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]ウレイド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレート(58 mg, 0.1 mmol)を塩化メチレン(2 mL)に溶解し、氷冷下、TFA(2 mL)を加え、1時間撹拌した。反応液に飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、析出した結晶を濾取した。結晶をクロロホルム-ヘキサンにて再結晶し、表題化合物(24 mg, 60%)を微黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of 1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- {5- [4- [1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} urea tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- {3- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] ureido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (58 mg, 0.1 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (2 mL), and TFA (2 mL) was added under ice cooling, followed by stirring for 1 hour. A saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction solution, and the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. The crystals were recrystallized from chloroform-hexane to give the title compound (24 mg, 60%) as a pale yellow solid.
1-(ピペリジン-4-イル)-3-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ウレアの製造
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{3-[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]ウレイド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレート(58 mg, 0.1 mmol)を塩化メチレン(2 mL)に溶解し、氷冷下、TFA(2 mL)を加え、1時間撹拌した。反応液に飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、析出した結晶を濾取した。結晶をクロロホルム-ヘキサンにて再結晶し、表題化合物(24 mg, 60%)を微黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of 1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- {5- [4- [1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} urea tert-butyl 4- [4- (5- {3- [1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] ureido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (58 mg, 0.1 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (2 mL), and TFA (2 mL) was added under ice cooling, followed by stirring for 1 hour. A saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction solution, and the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. The crystals were recrystallized from chloroform-hexane to give the title compound (24 mg, 60%) as a pale yellow solid.
実施例36 4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ブタンアミドの製造
Example 36 4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1- Methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] butanamide
工程1:
(9H-フルオレン-9-イル)メチル [4-メトキシ-1-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-1-オキソブタン-2-イル]カルバメートの製造 Step 1:
(9H-Fluoren-9-yl) methyl [4-methoxy-1-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2- Yil} amino) -1-oxobutan-2-yl] carbamate
(9H-フルオレン-9-イル)メチル [4-メトキシ-1-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-1-オキソブタン-2-イル]カルバメートの製造 Step 1:
(9H-Fluoren-9-yl) methyl [4-methoxy-1-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2- Yil} amino) -1-oxobutan-2-yl] carbamate
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと2-({[(9H-フルオレン-9-イル)メトキシ]カルボニル}アミノ)-4-メトキシブタン酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 2-({[(9H-fluoren-9-yl) methoxy] carbonyl } The title compound (crude) was obtained in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1 using amino) -4-methoxybutanoic acid.
工程2:
2-アミノ-4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4- (1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2-amino-4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} butanamide
2-アミノ-4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4- (1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2-amino-4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} butanamide
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.84-1.94 (1H, m), 2.16-2.28 (1H, m), 2.41 (3H, s), 2.54-2.62 (2H, m), 2.68 (2H, t, J = 6.0 Hz), 3.10-3.18 (2H, m), 3.49 (3H, s), 3.56-3.65 (2H, m), 3.66-3.73 (1H, m), 6.10 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 7.06 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.53 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.84-1.94 (1H, m), 2.16-2.28 (1H, m), 2.41 (3H, s), 2.54-2.62 (2H, m), 2.68 (2H, t, J = 6.0 Hz), 3.10-3.18 (2H, m), 3.49 (3H, s), 3.56-3.65 (2H, m), 3.66-3.73 (1H, m), 6.10 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 7.06 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.53 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz).
工程3:
4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ブタンアミドの製造
2-アミノ-4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(10%)を淡黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 3:
4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- Preparation of 4-yl) amino] butanamide 2-amino-4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 The title compound (10%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using -yl} butanamide.
4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ブタンアミドの製造
2-アミノ-4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(10%)を淡黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 3:
4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- Preparation of 4-yl) amino] butanamide 2-amino-4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 The title compound (10%) was obtained as a pale yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using -yl} butanamide.
実施例37 N-{5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 37 N- {5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino Acetamide production
工程1:
1-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]-4-メチルピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -4-methylpiperazine
1-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]-4-メチルピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -4-methylpiperazine
1-(4-ブロモ-2,5-ジメトキシフェニル)-4-メチルピペラジンとビス(ピナコラート)ジボロンを用いて、実施例1の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色油状物として得た。
Using 1- (4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl) -4-methylpiperazine and bis (pinacolato) diboron as in Step 2 of Example 1, the title compound (crude) was treated as a brown oil. Obtained.
工程2:
1-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-4-メチルピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -4-methylpiperazine
1-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-4-メチルピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -4-methylpiperazine
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンと1-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェニル]-4-メチルピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率25%)を赤茶色固体として得た。
2-Bromo-5-nitrothiophene and 1- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenyl] -4-methyl The title compound (2 step yield: 25%) was obtained as a red-brown solid in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1 using piperazine.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.38 (3H, s), 2.60-2.67 (4H, m), 3.17-3.26 (4H, m), 3.90 (3H, s), 3.98 (3H, s), 6.57 (1H, s), 7.15 (1H, s), 7.31 (1H, d, J = 4.6 Hz), 7.90 (1H, d, J = 4.6 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.38 (3H, s), 2.60-2.67 (4H, m), 3.17-3.26 (4H, m), 3.90 (3H, s), 3.98 (3H, s) , 6.57 (1H, s), 7.15 (1H, s), 7.31 (1H, d, J = 4.6 Hz), 7.90 (1H, d, J = 4.6 Hz).
工程3:
5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine
5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine
1-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-4-メチルピペラジンを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を赤色アモルファスとして得た。
Using 1- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -4-methylpiperazine in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2, the title compound (crude) Obtained as amorphous.
工程4:
N-[2-({5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
N- [2-({5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2- Preparation of trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
N-[2-({5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
N- [2-({5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2- Preparation of trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率68%)を赤褐色油状物として得た。
5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidine-4) -Yl) acetamido] The title compound (2 step yield 68%) was obtained as a reddish brown oil in the same manner as in steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.78-1.83 (2H, m), 1.92-2.10 (4H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.40 (3H, s), 2.64-2.72 (4H, m), 2.90-3.00 (2H, m), 3.10-3.20 (4H, m), 3.84 (3H, s), 3.85 (3H, s), 4.18 (2H, s), 6.56 (1H, s), 6.67 (1H, d, J = 3.8 Hz), 7.03 (1H, s), 7.16 (1H, d, J = 4.2 Hz), 9.07 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.78-1.83 (2H, m), 1.92-2.10 (4H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.40 (3H, s), 2.64-2.72 (4H, m), 2.90-3.00 (2H, m), 3.10-3.20 (4H, m), 3.84 (3H, s), 3.85 (3H, s), 4.18 (2H, s), 6.56 (1H, s), 6.67 (1H, d, J = 3.8 Hz), 7.03 (1H, s), 7.16 (1H, d, J = 4.2 Hz), 9.07 (1H, brs).
工程5:
N-{5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-[2-({5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(75%)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 5:
Of N- {5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Production N- [2-({5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2 Using -trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide, the title compound (75%) was obtained as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
N-{5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-[2-({5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(75%)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 5:
Of N- {5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Production N- [2-({5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2 Using -trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide, the title compound (75%) was obtained as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
実施例38 N-{5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
工程1:
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリルの製造 Example 38 N- {5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Step 1:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzonitrile
工程1:
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリルの製造 Example 38 N- {5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Step 1:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzonitrile
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンと2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリルを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
2-Bromo-5-nitrothiophene and 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) benzonitrile In the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1, the title compound (crude) was obtained.
工程2:
5-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンゾニトリルの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile
5-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンゾニトリルの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリルを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
The title compound (crude) was obtained in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2 using 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzonitrile. .
工程3:
N-[2-({5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
N- [2-({5- [3-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro Preparation of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
N-[2-({5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
N- [2-({5- [3-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro Preparation of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンゾニトリルと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率69%)を淡褐色固体として得た。
5- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4- Yl) acetamide] The title compound (3 step yield: 69%) was obtained as a light brown solid in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.76-1.84 (2H, m), 1.96-2.11 (4H, m), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.39 (3H, s), 2.63-2.68 (4H, m), 2.93-3.00 (2H, m), 3.24-3.29 (4H, m), 3.80-3.92 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.95-5.99 (2H, m), 7.61 (1H, dd, J = 9.0, 2.2 Hz), 7.72 (1H, d, J = 2.2 Hz), 8.98 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.76-1.84 (2H, m), 1.96-2.11 (4H, m), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.39 (3H, s), 2.63-2.68 (4H, m), 2.93-3.00 (2H, m), 3.24-3.29 (4H, m), 3.80-3.92 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 6.95 -5.99 (2H, m), 7.61 (1H, dd, J = 9.0, 2.2 Hz), 7.72 (1H, d, J = 2.2 Hz), 8.98 (1H, brs).
工程4:
N-{5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-[2-({5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(86%)を淡黄色結晶性粉末として得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of N- {5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N -[2-({5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro- The title compound (86%) was obtained as a pale-yellow crystalline powder in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 using N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide.
N-{5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-[2-({5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(86%)を淡黄色結晶性粉末として得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of N- {5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N -[2-({5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro- The title compound (86%) was obtained as a pale-yellow crystalline powder in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 using N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide.
実施例39 2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドの製造
Example 39 Production of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide
工程1:
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzamide
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzamide
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリル(300 mg, 0.91 mmol)のトルエン(10 mL)溶液に、アセトアルデヒドオキシム(270 mg, 4.57 mmol)、トリス(トリフェニルホスフィン)ロジウムクロライド(93 mg, 0.091 mmol)を加えた。100℃で、10時間攪拌した。室温に戻し、減圧濃縮をした。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=100:0→18:1)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
To a solution of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzonitrile (300 mg, 0.91 mmol) in toluene (10 mL) was added acetaldehyde oxime (270 mg, 4.57). mmol) and tris (triphenylphosphine) rhodium chloride (93 mg, 0.091 mmol). The mixture was stirred at 100 ° C. for 10 hours. It returned to room temperature and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 100: 0 → 18: 1) to obtain the title compound (crude).
工程2:
5-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide
5-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミドの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
The title compound (crude) was obtained in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2 using 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzamide.
工程3:
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドの製造 Step 3:
2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophene-2 -Il) Production of benzamide
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドの製造 Step 3:
2- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophene-2 -Il) Production of benzamide
5-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミドと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率35%)を淡黄色固体として得た。
5- (5-Aminothiophen-2-yl) -2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) ) Acetamide] The title compound (35% yield over 3 steps) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.76-1.84 (2H, m), 1.96-2.10 (4H, m), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.37 (3H, s), 2.50-2.68 (4H, m), 2.94-3.00 (2H, m), 3.04-3.08 (4H, m), 3.80-3.90 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 5.74 (1H, brs), 6.94 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.10 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.19 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.61 (1H, dd, J = 8.4, 2.4 Hz), 8.36 (1H, d, J = 2.8 Hz), 8.95 (1H, brs), 9.44 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.76-1.84 (2H, m), 1.96-2.10 (4H, m), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.37 (3H, s), 2.50-2.68 (4H, m), 2.94-3.00 (2H, m), 3.04-3.08 (4H, m), 3.80-3.90 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 5.74 (1H, brs), 6.94 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.10 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.19 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.61 (1H, dd, J = 8.4, 2.4 Hz), 8.36 (1H, d, J = 2.8 Hz), 8.95 (1H, brs), 9.44 (1H, brs).
工程4:
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドの製造
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(89%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide 2- (4- Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide Was used to give the title compound (89%) as a pale yellow solid in a manner similar to Step 8 of Example 9.
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドの製造
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(89%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of 2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide 2- (4- Methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamido] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide Was used to give the title compound (89%) as a pale yellow solid in a manner similar to Step 8 of Example 9.
実施例40 3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドの製造
Example 40 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2 -Il} propanamide production
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレート(100 mg, 0.28 mmol)の塩化メチレン(1 mL)溶液に、氷冷下、DIPEA(54.2 mg, 0.42 mmol)と3-ブロモプロパノイルクロライド(58 mg, 0.34 mmol)を加え、1時間攪拌した。TEA(152 mg, 0.70 mmol)、および1,4'-ビピペリジン(118 mg, 0.70 mmol)を加え、さらに1時間攪拌した。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=100:0→82:18)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(71%)を淡黄色固体として得た。
Tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (100 mg, 0.28 mmol) in methylene chloride (1 mL) Under ice cooling, DIPEA (54.2 mg, 0.42 mmol) and 3-bromopropanoyl chloride (58 mg, 0.34 mmol) were added and stirred for 1 hour. TEA (152 mg, 0.70 mmol) and 1,4′-bipiperidine (118 mg, 0.70 mmol) were added, and the mixture was further stirred for 1 hour. Saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 100: 0 → 82: 18) to obtain the title compound (71%) as a pale yellow solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.50 (9H, s), 1.52-1.70 (8H, m), 1.96-2.04 (2H, m), 2.07-2.15 (2H, m), 2.27-2.40 (1H, m), 2.50-2.62 (8H, m), 2.68-2.72 (2H, m), 3.12-3.18 (2H, m), 3.64 (2H, t, J = 5.6 Hz), 4.05-4.11 (2H, m), 6.06 (1H, brs), 6.55 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.07 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.55 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 12.24 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.50 (9H, s), 1.52-1.70 (8H, m), 1.96-2.04 (2H, m), 2.07-2.15 (2H, m), 2.27-2.40 ( 1H, m), 2.50-2.62 (8H, m), 2.68-2.72 (2H, m), 3.12-3.18 (2H, m), 3.64 (2H, t, J = 5.6 Hz), 4.05-4.11 (2H, m), 6.06 (1H, brs), 6.55 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.07 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.55 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 12.24 (1H, brs).
工程2:
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドの製造
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(93%)を微灰色固体として得た。 Step 2:
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Preparation of propanamide tert-butyl 4- {4- [5- (3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine The title compound (93%) was obtained as a pale gray solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using -1 (2H) -carboxylate.
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドの製造
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(93%)を微灰色固体として得た。 Step 2:
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Preparation of propanamide tert-butyl 4- {4- [5- (3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine The title compound (93%) was obtained as a pale gray solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using -1 (2H) -carboxylate.
実施例41 3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドの製造
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(58%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 41 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} propanamide 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4] -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} propanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (58%) as a yellow solid.
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(58%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 41 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} propanamide 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4] -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} propanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (58%) as a yellow solid.
実施例42 ベンジル 2-[4-(4-{5-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-イル]アセテートの製造
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドとベンジル クロロアセテートを用いて、実施例23と同様にして、表題化合物(77%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Example 42 Benzyl 2- [4- (4- {5- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine Preparation of -1 (2H) -yl] acetate 3-([1,4'-bipiperidin] -1'-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4 -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} propanamide and benzyl chloroacetate were used in the same manner as in Example 23 to obtain the title compound (77%) as a pale yellow solid.
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドとベンジル クロロアセテートを用いて、実施例23と同様にして、表題化合物(77%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Example 42 Benzyl 2- [4- (4- {5- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine Preparation of -1 (2H) -yl] acetate 3-([1,4'-bipiperidin] -1'-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4 -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} propanamide and benzyl chloroacetate were used in the same manner as in Example 23 to obtain the title compound (77%) as a pale yellow solid.
実施例43 3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-イソプロピル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドの製造
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドとアセトンを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(5%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Example 43 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-isopropyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} propanamide 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4] -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} propanamide and acetone were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (5%) as a pale yellow solid.
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミドとアセトンを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(5%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Example 43 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-isopropyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} propanamide 3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-4] -Iyl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} propanamide and acetone were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (5%) as a pale yellow solid.
実施例44 2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
Example 44 2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl ] Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} acetamide
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)アセトアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)アセトアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートとクロロアセチルクロライドと1,4’-ビピペリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(84%)を淡褐色アモルファスとして得た。
Tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate, chloroacetyl chloride, and 1,4′-bipiperidine In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40, the title compound (84%) was obtained as a light brown amorphous.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.49 (9H, s), 1.50-1.82 (10H, m), 1.92-2.03 (2H, m), 2.26-2.35 (2H, m), 2.50-2.69 (5H, m), 2.95-3.02 (2H, m), 3.18 (2H, s), 3.62-3.67 (2H, m), 4.05-4.11 (2H, m), 6.07 (1H, m), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.09 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.55 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz), 9.66 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.49 (9H, s), 1.50-1.82 (10H, m), 1.92-2.03 (2H, m), 2.26-2.35 (2H, m), 2.50-2.69 ( 5H, m), 2.95-3.02 (2H, m), 3.18 (2H, s), 3.62-3.67 (2H, m), 4.05-4.11 (2H, m), 6.07 (1H, m), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.09 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.55 (2H, d, J = 8.3 Hz), 9.66 (1H, brs) .
工程2:
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造 Step 2:
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Production of acetamide
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造 Step 2:
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Production of acetamide
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)アセトアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を淡褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) Using the carboxylate, the title compound (crude) was obtained as a light brown amorphous in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13.
工程3:
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率85%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 3:
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} acetamide 2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl The title compound (2 step yield: 85%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using thiophen-2-yl} acetamide and formaldehyde.
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率85%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 3:
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} acetamide 2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl The title compound (2 step yield: 85%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using thiophen-2-yl} acetamide and formaldehyde.
実施例45 4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドの製造
Example 45 4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl ] Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} butanamide
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ブタンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) butanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ブタンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) butanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -Production of carboxylates
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートと4-ブロモブタノイルクロライドと1,4’-ビピペリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(18%)を淡褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate, 4-bromobutanoyl chloride and 1,4′-bipiperidine In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40, the title compound (18%) was obtained as a light brown amorphous.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.38-1.52 (2H, m), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.57-1.78 (6H, m), 1.82-2.09 (6H, m), 2.45-2.66 (11H, m), 3.03-3.13 (2H, m), 3.60-3.66 (2H, m), 4.05-4.12 (2H, m), 6.06 (1H, brs), 6.69 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.05 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.35 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.52 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 10.80 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.38-1.52 (2H, m), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.57-1.78 (6H, m), 1.82-2.09 (6H, m), 2.45-2.66 ( 11H, m), 3.03-3.13 (2H, m), 3.60-3.66 (2H, m), 4.05-4.12 (2H, m), 6.06 (1H, brs), 6.69 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz) , 7.05 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.35 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.52 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 10.80 (1H, brs).
工程2:
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドの製造 Step 2:
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Production of butanamide
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドの製造 Step 2:
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Production of butanamide
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ブタンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を淡黄色固体として得た。
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) butanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) The title compound (crude) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using carboxylate.
工程3:
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドの製造
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率54%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 3:
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} butanamide 4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl The title compound (2 step yield: 54%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using thiophen-2-yl} butanamide and formaldehyde.
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドの製造
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率54%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 3:
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} butanamide 4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl The title compound (2 step yield: 54%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 using thiophen-2-yl} butanamide and formaldehyde.
実施例46 5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドの製造
Example 46 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl ] Preparation of thiophen-2-yl} pentanamide
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ペンタンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) pentanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ペンタンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) pentanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートと5-ブロモペンタノイルクロライドと1,4’-ビピペリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(75%)を淡褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and 1,4′-bipiperidine In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40, the title compound (75%) was obtained as a light brown amorphous.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.43-1.52 (2H, m), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.56-1.90 (12H, m), 1.96-2.04 (2H, m), 2.38-2.62 (11H, m), 3.00-3.05 (2H, m), 3.60-3.66 (2H, m), 4.01-4.10 (2H, m), 6.06 (1H, brs), 6.67 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.06 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.54 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 8.74 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.43-1.52 (2H, m), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.56-1.90 (12H, m), 1.96-2.04 (2H, m), 2.38-2.62 ( 11H, m), 3.00-3.05 (2H, m), 3.60-3.66 (2H, m), 4.01-4.10 (2H, m), 6.06 (1H, brs), 6.67 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz) , 7.06 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.54 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 8.74 (1H, brs).
工程2:
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドの製造 Step 2:
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Production of pentanamide
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドの製造 Step 2:
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Production of pentanamide
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ペンタンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を淡黄色固体として得た。
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) pentanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate was used to obtain the title compound (crude) as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13.
工程3:
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドの製造
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率52%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 3:
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} pentanamide 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} pentanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 52%) as a yellow solid.
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドの製造
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率52%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 3:
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} pentanamide 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} pentanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 52%) as a yellow solid.
実施例47
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造 Example 47
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-Il} hexanamide production
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造 Example 47
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-Il} hexanamide production
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ヘキサンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) hexanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ヘキサンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) hexanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートと6-ブロモヘキサノイルクロライドと1,4’-ビピペリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(66%)を淡褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate, 6-bromohexanoyl chloride and 1,4′-bipiperidine In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40, the title compound (66%) was obtained as a light brown amorphous.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.38-1.52 (4H, m), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.54-1.90 (12H, m), 1.96-2.10 (2H, m), 2.35-2.46 (5H, m), 2.50-2.60 (6H, m), 3.02-3.08 (2H, m), 3.62-3.66 (2H, m), 4.05-4.10 (2H, m), 6.06 (1H, brs), 6.66 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.06 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.54 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 8.48 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.38-1.52 (4H, m), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.54-1.90 (12H, m), 1.96-2.10 (2H, m), 2.35-2.46 ( 5H, m), 2.50-2.60 (6H, m), 3.02-3.08 (2H, m), 3.62-3.66 (2H, m), 4.05-4.10 (2H, m), 6.06 (1H, brs), 6.66 ( 1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.06 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.54 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 8.48 (1H, brs).
工程2:
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造 Step 2:
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Hexanamide production
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造 Step 2:
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Hexanamide production
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)ヘキサンアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を淡褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) hexanamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate was used in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 to obtain the title compound (crude) as a light brown amorphous.
工程3:
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率79%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 3:
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} hexaneamide 6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} hexanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 79%) as a yellow solid.
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミドの製造
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率79%)を黄色固体として得た。 Step 3:
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} hexaneamide 6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} hexanamide and formaldehyde were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 79%) as a yellow solid.
実施例48
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造 Example 48
Preparation of N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造 Example 48
Preparation of N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide
工程1:
5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-2-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリルの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -2- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzonitrile
5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-2-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリルの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -2- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzonitrile
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンと5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-2-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリルを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
2-Bromo-5-nitrothiophene and 5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -2- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) benzonitrile In the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1, the title compound (crude) was obtained.
工程2:
2-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンゾニトリルの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile
2-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンゾニトリルの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 2- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) -5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile
5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-2-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ベンゾニトリルを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
The title compound (crude) was obtained in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2 using 5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -2- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) benzonitrile. .
工程3:
N-[2-({5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
N- [2-({5- [2-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro Preparation of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
N-[2-({5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
N- [2-({5- [2-Cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro Preparation of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)-5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンゾニトリルと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率57%)を淡褐色固体として得た。
2- (5-Aminothiophen-2-yl) -5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzonitrile and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4- Yl) acetamide] The title compound (3 step yield 57%) was obtained as a light brown solid in the same manner as in steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.73-1.80 (2H, m), 1.97-2.09 (4H, m), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.36 (3H, s), 2.50-2.60 (4H, m), 2.90-3.03 (2H, m), 3.20-3.29 (4H, m), 3.79-3.89 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 6.66 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.07 (1H, d, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz), 7.14 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz), 7.32 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.44 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 8.92 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.73-1.80 (2H, m), 1.97-2.09 (4H, m), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.36 (3H, s), 2.50-2.60 (4H, m), 2.90-3.03 (2H, m), 3.20-3.29 (4H, m), 3.79-3.89 (1H, m), 4.18 (2H, s), 6.66 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.07 (1H, d, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz), 7.14 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz), 7.32 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.44 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 8.92 (1H, brs).
工程4:
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-[2-({5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(81%)を黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N -[2-({5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro- Using N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide, the title compound (81%) was obtained as a yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
N-[2-({5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(81%)を黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide N -[2-({5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -2,2,2-trifluoro- Using N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide, the title compound (81%) was obtained as a yellow amorphous in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9.
実施例49 N-(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 49 N- (5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Production of acetamide
工程1:
4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノールの製造 Step 1:
Production of 4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol
4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノールの製造 Step 1:
Production of 4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンと4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)フェノールを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
As in Step 3 of Example 1, using 2-bromo-5-nitrothiophene and 4- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) phenol. The title compound (crude) was obtained.
工程2:
1-メチル-4-{2-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]エチル}ピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- {2- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] ethyl} piperazine
1-メチル-4-{2-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]エチル}ピペラジンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- {2- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] ethyl} piperazine
4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノール(500 mg, 2.26 mmol)をDMF(10 mL)に溶解し、炭酸カリウム(624 mg, 3.4 mmol)、1,2-ジブロモエタン(300μL, 3.4 mmol)を加え、60℃で2時間撹拌し、水を加え析出した結晶を濾取した。濾取した結晶にアセトニトリルを加え、1-メチルピペラジン(500μL, 4.52 mmol)、炭酸カリウム(625 mg, 4.5 mmol)を加え、60℃で13時間撹拌した。反応液に飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=100:0→80:20、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(151 mg, 2工程収率14%)を黄色固体として得た。
4- (5-Nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol (500 mg, 2.26 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (10 mL), potassium carbonate (624 mg, 3.4 mg), 1,2-dibromoethane (300 μL, 3.4 mg). mmol) was added, and the mixture was stirred at 60 ° C. for 2 hours. Water was added and the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. Acetonitrile was added to the crystals collected by filtration, 1-methylpiperazine (500 μL, 4.52 mmol) and potassium carbonate (625 mg, 4.5 mmol) were added, and the mixture was stirred at 60 ° C. for 13 hours. Saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue obtained was chromatographed on silica gel (chloroform: methanol = 100: 0 → 80: 20, gradient) to give the title compound (151 mg, 14% yield over 2 steps) as a yellow solid.
1H-NMR(400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.31 (3H, s), 2.48-2.51 (4H, m), 2.62-2.65 (4H, m), 2.85 (2H, t, J = 5.9 Hz), 4.16 (2H, t, J = 5.9 Hz), 6.97 (2H, dd, J = 6.8, 2.4 Hz), 7.13 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.56 (2H, dd, J = 6.8, 2.4 Hz), 7.89 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400 MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.31 (3H, s), 2.48-2.51 (4H, m), 2.62-2.65 (4H, m), 2.85 (2H, t, J = 5.9 Hz), 4.16 (2H, t, J = 5.9 Hz), 6.97 (2H, dd, J = 6.8, 2.4 Hz), 7.13 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.56 (2H, dd, J = 6.8, 2.4 Hz) , 7.89 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz).
工程3:
5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine
5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 3:
Preparation of 5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine
1-メチル-4-{2-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]エチル}ピペラジンを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
Using 1-methyl-4- {2- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] ethyl} piperazine in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2, the title compound (crude) was converted into a brown amorphous Got as.
工程4:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidine-4-] Yl) acetamide] The title compound (crude) was obtained as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
工程5:
N-(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率16%)を黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 5:
Preparation of N- (5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (3 steps, yield 16%) as a yellow amorphous substance.
N-(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率16%)を黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 5:
Preparation of N- (5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino]
実施例50 N-(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 50 N- (5- {4- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Production of acetamide
工程1:
1-メチル-4-{4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ブチル}ピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- {4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] butyl} piperazine
1-メチル-4-{4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ブチル}ピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- {4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] butyl} piperazine
4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノールと1,4-ジブロモブタンと1-メチルピペラジンを用いて、実施例49の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(14%)を黄色固体として得た。
Use 4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol, 1,4-dibromobutane and 1-methylpiperazine in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 49 to give the title compound (14%) as a yellow solid. Obtained.
工程2:
5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine
5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine
1-メチル-4-{4-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ブチル}ピペラジンを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
Using 1-methyl-4- {4- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] butyl} piperazine in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2, the title compound (crude) was converted into a brown amorphous Got as.
工程3:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidine-4-] Yl) acetamide] The title compound (crude) was obtained as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
工程4:
N-(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率13%)を黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of N- (5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (3 step yield: 13%) as a yellow amorphous.
N-(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率13%)を黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 4:
Preparation of N- (5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino]
実施例51 N-[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 51 N- [5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Production of amino] acetamide
工程1:
1-メチル-4-{5-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ペンチル}ピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- {5- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] pentyl} piperazine
1-メチル-4-{5-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ペンチル}ピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- {5- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] pentyl} piperazine
4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノールと1,5-ジブロモペンタンと1-メチルピペラジンを用いて、実施例49の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(14%)を黄色固体として得た。
Use 4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol, 1,5-dibromopentane, and 1-methylpiperazine in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 49 to give the title compound (14%) as a yellow solid. Obtained.
工程2:
5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-amine
5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-amine
1-メチル-4-{5-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]ペンチル}ピペラジンを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
Using 1-methyl-4- {5- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] pentyl} piperazine in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2, the title compound (crude) was converted into a brown amorphous Got as.
工程3:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(2-{[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]アミノ}-2-オキソエチル)-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (2-{[5- (4-{[5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] amino}- Preparation of 2-oxoethyl) -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(2-{[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]アミノ}-2-オキソエチル)-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (2-{[5- (4-{[5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] amino}- Preparation of 2-oxoethyl) -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-アミンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。
5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-amine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidine -4-yl) acetamide] The title compound (crude) was obtained as a brown amorphous in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
工程4:
N-[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(2-{[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]アミノ}-2-オキソエチル)-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率14%)を黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 4:
N- [5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Preparation of acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (2-{[5- (4-{[5- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] Amino} -2-oxoethyl) -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to give the title compound (3 step yield 14%) as a yellow amorphous substance. Obtained.
N-[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(2-{[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]アミノ}-2-オキソエチル)-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(3工程収率14%)を黄色アモルファスとして得た。 Step 4:
N- [5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Preparation of
実施例52 N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アミノ}アセトアミドの製造
Example 52 N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-{[(1-methylpiperidine- Preparation of 4-yl) methyl] amino} acetamide
工程1:
tert-ブチル4-(4-{5-[2-({[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]メチル}アミノ)アセトアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-butyl 4- (4- {5- [2-({[1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] methyl} amino) acetamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6- Preparation of dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate
tert-ブチル4-(4-{5-[2-({[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]メチル}アミノ)アセトアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-butyl 4- (4- {5- [2-({[1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] methyl} amino) acetamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6- Preparation of dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレート (100 mg, 0.28 mmol)の塩化メチレン(1 mL)溶液に、氷冷下でDIPEA(73μL,0.42 mmol)、クロロアセチルクロライドを加え、30分攪拌した。1-Boc-4-アミノメチルピペリジン(150 mg)、炭酸カリウム(100 mg)、アセトニトリル(1 mL)を加えた。60℃に昇温し、2時間攪拌した。氷冷下、飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=100:0→81:19、グラジエント)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(156 mg, 91%)を淡黄色固体として得た。
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate (100 mg, 0.28 mmol) in methylene chloride (1 mL) Under ice cooling, DIPEA (73 μL, 0.42 mmol) and chloroacetyl chloride were added and stirred for 30 minutes. 1-Boc-4-aminomethylpiperidine (150 mg), potassium carbonate (100 mg), and acetonitrile (1 ml) were added. The temperature was raised to 60 ° C. and stirred for 2 hours. A saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added under ice cooling, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 100: 0 → 81: 19, gradient) to obtain the title compound (156 mg, 91%) as a pale yellow solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.12-1.25 (2H, m), 1.46 (9H, s), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.55-1.68 (1H, m), 1.72-1.79 (2H, m), 2.51-2.57 (2H, m), 2.59 (2H, d, J = 6.8 Hz), 2.65-2.78 (2H, m), 3.45 (2H, s), 3.61-3.67 (2H, m), 4.05-4.21 (4H, m), 6.07 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 7.09 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.55 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 9.79 (1H, brs)
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.12-1.25 (2H, m), 1.46 (9H, s), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.55-1.68 (1H, m), 1.72-1.79 (2H, m), 2.51-2.57 (2H, m), 2.59 (2H, d, J = 6.8 Hz), 2.65-2.78 (2H, m), 3.45 (2H, s), 3.61-3.67 (2H, m), 4.05 -4.21 (4H, m), 6.07 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 7.09 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz) , 7.55 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 9.79 (1H, brs)
工程2:
tert-ブチル 4-(4-{5-[2-(N-{[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]メチル}-2,2,2-トリフルオロアセトアミド)アセトアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 2:
tert-butyl 4- (4- {5- [2- (N-{[1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] methyl} -2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido) acetamido] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-(4-{5-[2-(N-{[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]メチル}-2,2,2-トリフルオロアセトアミド)アセトアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 2:
tert-butyl 4- (4- {5- [2- (N-{[1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] methyl} -2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido) acetamido] thiophene- Preparation of 2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate
tert-ブチル 4-(4-{5-[2-({[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]メチル}アミノ)アセトアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートとトリフルオロ酢酸無水物を用いて、実施例9の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(86%)を黄色固体として得た。
tert-butyl 4- (4- {5- [2-({[1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] methyl} amino) acetamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6- The title compound (86%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 9 using dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate and trifluoroacetic anhydride.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.07-1.23 (2H, m), 1.44 (9H, s), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.54-1.60 (2H, m), 1.98-2.10 (1H, m), 2.48-2.56 (2H, m), 2.63-2.74 (2H, m), 3.62-3.67(2H, m), 3.48 (2H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 4.04-4.32 (6H, m), 6.07 (1H, brs),6.65 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.07 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.52 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 9.01 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.07-1.23 (2H, m), 1.44 (9H, s), 1.50 (9H, s), 1.54-1.60 (2H, m), 1.98-2.10 (1H, m), 2.48-2.56 (2H, m), 2.63-2.74 (2H, m), 3.62-3.67 (2H, m), 3.48 (2H, d, J = 7.2 Hz), 4.04-4.32 (6H, m) , 6.07 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.07 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.36 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.52 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 9.01 (1H, brs).
工程3:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]-N-(ピペリジン-4-イルメチル)アセトアミド
の製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino ) Ethyl] -N- (piperidin-4-ylmethyl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]-N-(ピペリジン-4-イルメチル)アセトアミド
の製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino ) Ethyl] -N- (piperidin-4-ylmethyl) acetamide
tert-ブチル 4-(4-{5-[2-(N-{[1-(tert-ブトキシカルボニル)ピペリジン-4-イル]メチル}-2,2,2-トリフルオロアセトアミド)アセトアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を褐色油状物として得た。
tert-butyl 4- (4- {5- [2- (N-{[1- (tert-butoxycarbonyl) piperidin-4-yl] methyl} -2,2,2-trifluoroacetamido) acetamido] thiophene The title compound (crude) was obtained as a brown oil in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using 2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate.
工程4:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino ) -2-Oxoethyl] -N-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methyl] acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アセトアミドの製造 Step 4:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino ) -2-Oxoethyl] -N-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methyl] acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-オキソ-2-({5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)エチル]-N-(ピペリジン-4-イルメチル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(16%)を淡黄色固体として得た。
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-oxo-2-({5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} amino ) Ethyl] -N- (piperidin-4-ylmethyl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 5 to obtain the title compound (16%) as a pale yellow solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.20-1.38 (2H, m), 1.50-1.73 (2H, m), 1.89-1.97 (2H, m), 2.26 (3H,s), 2.27-2.30 (1H, m), 2.42(3H, s), 2.56-2.62 (2H, m), 2.66-2.71 (2H, m), 2.83-2.90 (2H, m), 3.12-3.15 (2H, m), 3.48(2H, d, J = 7.2), 4.21 (2H, s), 6.10 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.05 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.37 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.51 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz.)
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.20-1.38 (2H, m), 1.50-1.73 (2H, m), 1.89-1.97 (2H, m), 2.26 (3H, s), 2.27-2.30 ( 1H, m), 2.42 (3H, s), 2.56-2.62 (2H, m), 2.66-2.71 (2H, m), 2.83-2.90 (2H, m), 3.12-3.15 (2H, m), 3.48 ( 2H, d, J = 7.2), 4.21 (2H, s), 6.10 (1H, brs), 6.65 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.05 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.37 (2H , d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.51 (2H, d, J = 8.4 Hz.)
工程5:
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アミノ}アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(84%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 5:
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Preparation of methyl] amino} acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] ] Thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] -N-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methyl] acetamide in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9, the title compound (84 %) As a pale yellow solid.
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アミノ}アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(84%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 5:
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Preparation of methyl] amino}
実施例53 N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピロリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミドの製造
工程1:
1-メチル-4-{3-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]プロピル}ピペラジンの製造 Example 53 Production of N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide Step 1 :
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- {3- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] propyl} piperazine
工程1:
1-メチル-4-{3-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]プロピル}ピペラジンの製造 Example 53 Production of N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide Step 1 :
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- {3- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] propyl} piperazine
4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノールと1,3-ジブロモプロパンと1-メチルピペラジンを用いて、実施例49の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(25%)を得た。
The title compound (25%) was obtained in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 49 using 4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenol, 1,3-dibromopropane, and 1-methylpiperazine.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.00 (2H, tt, J = 6.8, 6.8 Hz), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.35-2.60 (10H, m), 4.07 (2H, t, J = 6.0 Hz), 6.96 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.13 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.56 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.89 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.00 (2H, tt, J = 6.8, 6.8 Hz), 2.30 (3H, s), 2.35-2.60 (10H, m), 4.07 (2H, t, J = 6.0 Hz), 6.96 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.13 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz), 7.56 (2H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 7.89 (1H, d, J = 4.0 Hz) ).
工程2:
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine
1-メチル-4-{3-[4-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)フェノキシ]プロピル}ピペラジンを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
The title compound (crude) was obtained in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2 using 1-methyl-4- {3- [4- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) phenoxy] propyl} piperazine. .
工程3:
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピロリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミドの製造
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと5-ブロモペンタノイルクロライドとピロリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(15%)を黄褐色固体として得た。 Step 3:
Preparation of N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide 5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and pyrrolidine were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40 to obtain the title compound (15 %) As a tan solid.
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピロリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミドの製造
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと5-ブロモペンタノイルクロライドとピロリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(15%)を黄褐色固体として得た。 Step 3:
Preparation of N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide 5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and pyrrolidine were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40 to obtain the title compound (15 %) As a tan solid.
実施例54 5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)ペンタンアミドの製造
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと5-ブロモペンタノイルクロライドと1,4’-ビピペリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(12%)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。 Example 54 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophene-2- Yl) Preparation of pentanamide Using 5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and 1,4′-bipiperidine The title compound (12%) was obtained as a brown amorphous product in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40.
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと5-ブロモペンタノイルクロライドと1,4’-ビピペリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(12%)を褐色アモルファスとして得た。 Example 54 5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophene-2- Yl) Preparation of pentanamide Using 5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and 1,4′-bipiperidine The title compound (12%) was obtained as a brown amorphous product in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40.
実施例55 N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピペリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミドの製造
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと5-ブロモペンタノイルクロライドとピペリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(15%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Example 55 Preparation of N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (piperidin-1-yl) pentanamide 5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and piperidine were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40 to obtain the title. The compound (15%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと5-ブロモペンタノイルクロライドとピペリジンを用いて、実施例40の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(15%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Example 55 Preparation of N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (piperidin-1-yl) pentanamide 5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine, 5-bromopentanoyl chloride and piperidine were used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 40 to obtain the title. The compound (15%) was obtained as a pale yellow solid.
実施例56 N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 56 N- (5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Production of acetamide
工程1:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 1:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 1:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } Production of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-アミンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を得た。
5- {4- [3- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-amine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidine-4-] Yl) acetamide] The title compound (crude) was obtained in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
工程2:
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率4%)を得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2,2,2-trifluoro-N- {2-[(5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) amino] -2-oxoethyl } -N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 to obtain the title compound (2 step yield: 4%).
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-{2-[(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アミノ]-2-オキソエチル}-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率4%)を得た。 Step 2:
Preparation of N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino]
実施例57 N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-4-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
Example 57 N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] Preparation of thiophene-2-carboxamide
工程1:
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-1-イル]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) -1H-pyrazol-1-yl] piperidine 1-carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-1-イル]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 1:
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) -1H-pyrazol-1-yl] piperidine 1-carboxylate production
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-ブロモチオフェン-2-カルボキサミドとtert-ブチル 4-[4-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-1-イル]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を黄色固体として得た。
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5-bromothiophene-2-carboxamide and tert-butyl 4- [4- (4,4,5,5-tetra Methyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) -1H-pyrazol-1-yl] piperidine-1-carboxylate was used in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1 to obtain the title compound (crude). Obtained as a yellow solid.
工程2:
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-4-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-1-イル]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレート(98 mg、0.17 mmol)を塩化メチレン(2 mL)に溶解し、TFA(0.5 mL)を加えて0.5時間撹拌し、反応液を濃縮し、残渣を得た。得られた残渣に塩化メチレン(0.5 mL)、酢酸(2 mL)、ホルムアルデヒド水溶液(36%水溶液、15μL、0.18 mmol)、水素化トリアセトキシホウ素ナトリウム(21 mg、0.1 mmol)を加えて、室温で2時間撹拌し、反応液に飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:飽和アンモニアメタノール=90:10)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(23 mg, 2工程収率21%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] thiophene-2 Preparation of carboxamide tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) -1H-pyrazole-1 -Il] piperidine-1-carboxylate (98 mg, 0.17 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (2 mL), TFA (0.5 mL) was added and stirred for 0.5 h, the reaction mixture was concentrated, and the residue was Obtained. Methylene chloride (0.5 mL), acetic acid (2 mL), aqueous formaldehyde solution (36% aqueous solution, 15 μL, 0.18 mmol), sodium triacetoxyborohydride (21 mg, 0.1 mmol) were added to the resulting residue, and at room temperature. The mixture was stirred for 2 hours, a saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue was chromatographed on silica gel (chloroform: saturated ammonia methanol). = 90: 10) to give the title compound (23 mg, 21% yield over 2 steps) as a pale yellow solid.
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-4-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミドの製造
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-1-イル]ピペリジン-1-カルボキシレート(98 mg、0.17 mmol)を塩化メチレン(2 mL)に溶解し、TFA(0.5 mL)を加えて0.5時間撹拌し、反応液を濃縮し、残渣を得た。得られた残渣に塩化メチレン(0.5 mL)、酢酸(2 mL)、ホルムアルデヒド水溶液(36%水溶液、15μL、0.18 mmol)、水素化トリアセトキシホウ素ナトリウム(21 mg、0.1 mmol)を加えて、室温で2時間撹拌し、反応液に飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムにて抽出し、有機層を硫酸ナトリウムで乾燥し、濾過後濃縮して得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:飽和アンモニアメタノール=90:10)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(23 mg, 2工程収率21%)を淡黄色固体として得た。 Step 2:
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] thiophene-2 Preparation of carboxamide tert-butyl 4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) -1H-pyrazole-1 -Il] piperidine-1-carboxylate (98 mg, 0.17 mmol) was dissolved in methylene chloride (2 mL), TFA (0.5 mL) was added and stirred for 0.5 h, the reaction mixture was concentrated, and the residue was Obtained. Methylene chloride (0.5 mL), acetic acid (2 mL), aqueous formaldehyde solution (36% aqueous solution, 15 μL, 0.18 mmol), sodium triacetoxyborohydride (21 mg, 0.1 mmol) were added to the resulting residue, and at room temperature. The mixture was stirred for 2 hours, a saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added to the reaction mixture, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, filtered and concentrated. The residue was chromatographed on silica gel (chloroform: saturated ammonia methanol). = 90: 10) to give the title compound (23 mg, 21% yield over 2 steps) as a pale yellow solid.
実施例58 6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ニコチンアミドの製造
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ニコチン酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(46%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 58 6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} nicotine Preparation of Amides Using 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] nicotinic acid In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1, the title compound (46%) was obtained as a yellow solid.
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ニコチン酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(46%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 58 6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} nicotine Preparation of Amides Using 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] nicotinic acid In the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1, the title compound (46%) was obtained as a yellow solid.
実施例59 N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミドの製造
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)安息香酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(4%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 59 N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4- (4-methylpiperazine-1- Yl) Preparation of benzamide 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) The title compound (4%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1 using benzoic acid.
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)安息香酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(4%)を黄色固体として得た。 Example 59 N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4- (4-methylpiperazine-1- Yl) Preparation of benzamide 5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) The title compound (4%) was obtained as a yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1 using benzoic acid.
実施例60 N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンズアミドの製造
Example 60 N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[(1-methylpiperidine- Preparation of 4-yl) amino] methyl} benzamide
工程1:
メチル 4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}ベンゾエートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of methyl 4-{[N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzoate
メチル 4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}ベンゾエートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of methyl 4-{[N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzoate
メチル 4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンゾエートと2-ニトロベンゼンスルホニルクロライドを用いて、実施例2の工程4と同様にして、表題化合物(62%)を淡緑色アモルファスとして得た。
Methyl 4-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] methyl} benzoate and 2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride were used in the same manner as in Step 4 of Example 2 to obtain the title compound (62%) as light green Obtained as amorphous.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.58-1.70 (4H, m), 1.94-2.02 (2H, m), 2.20 (3H, s), 2.75-2.82 (2H, m), 3.82-3.94 (1H, m), 3.90 (3H, s), 4.60 (2H, s), 7.38 (2H, J = d Hz), 7.51-7.57 (1H, m), 7.62-7.68 (2H, m), 7.86-7.93 (3H, m).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.58-1.70 (4H, m), 1.94-2.02 (2H, m), 2.20 (3H, s), 2.75-2.82 (2H, m), 3.82-3.94 ( 1H, m), 3.90 (3H, s), 4.60 (2H, s), 7.38 (2H, J = d Hz), 7.51-7.57 (1H, m), 7.62-7.68 (2H, m), 7.86-7.93 (3H, m).
工程2:
4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}安息香酸の製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 4-{[N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzoic acid
4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}安息香酸の製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 4-{[N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzoic acid
メチル 4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}ベンゾエートを用いて、実施例2の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を微黄色固体として得た。
Methyl 4-{[N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzoate is used to obtain the title compound (crude) in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 2. Obtained as a yellow solid.
工程3:
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}ベンズアミドの製造 Step 3:
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[N- (1-methylpiperidine-4 -Il) -2-Nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzamide
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}ベンズアミドの製造 Step 3:
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[N- (1-methylpiperidine-4 -Il) -2-Nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzamide
5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-アミンと4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}安息香酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を茶褐色固体として得た。
5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-amine and 4-{[N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)- 2-Nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzoic acid was used in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1 to obtain the title compound (crude) as a brown solid.
工程4:
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンズアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}ベンズアミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率11%)を橙色固体として得た。 Step 4:
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Preparation of amino] methyl} benzamide N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[N -(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2 to give the title compound (2 step yield: 11%) as an orange solid. Got as.
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンズアミドの製造
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-2-ニトロフェニルスルホンアミド]メチル}ベンズアミドを用いて、実施例2の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率11%)を橙色固体として得た。 Step 4:
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Preparation of amino] methyl} benzamide N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[N -(1-Methylpiperidin-4-yl) -2-nitrophenylsulfonamido] methyl} benzamide was used in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 2 to give the title compound (2 step yield: 11%) as an orange solid. Got as.
実施例61 2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
Example 61 2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- Production of 2-yl} acetamide
工程1:
メチル 2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}アセテートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of methyl 2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetate
メチル 2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}アセテートの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of methyl 2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetate
メチル 2-[6-(ヒドロキシメチル)ピリジン-3-イル]アセテート(190 mg, 1.05 mmol)の塩化メチレン(3.5 mL)溶液に、氷冷下で、塩化チオニル(179 mg, 1.58 mmol)を加え、4時間攪拌した。減圧濃縮し、氷冷下で、塩化メチレン(3.5 ml)、TEA(214 mg, 2.1 mmol)、ジメチルアミン水溶液(9.5M, 0.16 mL, 1.52 mmol)を加えた。室温で一晩攪拌した。飽和炭酸水素ナトリウム水溶液を加え、クロロホルムで抽出した。有機層を飽和食塩水にて洗浄し、無水硫酸ナトリウムにて乾燥後、減圧濃縮した。得られた残渣をシリカゲルクロマトグラフィー(クロロホルム:メタノール=98:2→82:18)を用いて精製し、表題化合物(78.8 mg, 36%)を褐色油状物として得た。
To a solution of methyl 2- [6- (hydroxymethyl) pyridin-3-yl] acetate (190 mg, 1.05 mmol) in methylene chloride (3.5 mL) was added thionyl chloride (179 mg, 1.58 mmol) under ice cooling. Stir for 4 hours. After concentration under reduced pressure, methylene chloride (3.5 塩 化 ml), TEA (214 mg, 2.1 mmol), and aqueous dimethylamine (9.5M, 0.16 mL, 1.52 mmol) were added under ice cooling. Stir overnight at room temperature. Saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and the mixture was extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (chloroform: methanol = 98: 2 → 82: 18) to obtain the title compound (78.8 mg, 36%) as a brown oily substance.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.29 (6H, s), 3.58 (2H, s), 3.62 (2H, s), 3.71 (3H, s), 7,37 (1H, d, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.62 (1H, dd, J = 8.1, 2.4 Hz), 8.45 (1H, d, J = 2.2 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.29 (6H, s), 3.58 (2H, s), 3.62 (2H, s), 3.71 (3H, s), 7,37 (1H, d, J = 8.1 Hz), 7.62 (1H, dd, J = 8.1, 2.4 Hz), 8.45 (1H, d, J = 2.2 Hz).
工程2:
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}酢酸の製造 Step 2:
Production of 2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetic acid
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}酢酸の製造 Step 2:
Production of 2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetic acid
メチル 2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}アセテートを用いて、実施例2の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を淡黄色固体として得た。
The title compound (crude) was obtained as a pale yellow solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 2 using methyl 2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetate.
工程3:
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}アセトアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 3:
tert-butyl 4- {4- [5- (2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}アセトアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートの製造 Step 3:
tert-butyl 4- {4- [5- (2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H ) -Carboxylate production
tert-ブチル 4-[4-(5-アミノチオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートと2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}酢酸を用いて、実施例1の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)を淡褐色アモルファスとして得た。
tert-Butyl 4- [4- (5-aminothiophen-2-yl) phenyl] -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 (2H) -carboxylate and 2- {6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] pyridine-3 The title compound (crude) was obtained as a light brown amorphous in the same manner as in Step 1 of Example 1 using -yl} acetic acid.
工程4:
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}アセトアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率24%)を橙色固体として得た。 Step 4:
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Production of Acetamide tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine The title compound (2 step yield: 24%) was obtained as an orange solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using -1 (2H) -carboxylate.
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
tert-ブチル 4-{4-[5-(2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}アセトアミド)チオフェン-2-イル]フェニル}-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-カルボキシレートを用いて、実施例13の工程5と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率24%)を橙色固体として得た。 Step 4:
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Production of Acetamide tert-Butyl 4- {4- [5- (2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} acetamido) thiophen-2-yl] phenyl} -5,6-dihydropyridine The title compound (2 step yield: 24%) was obtained as an orange solid in the same manner as in Step 5 of Example 13 using -1 (2H) -carboxylate.
実施例62 2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドの製造
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(71%)を橙色固体として得た。 Example 62 2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Preparation of phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide 2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine- 4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide and formaldehyde were used as in Step 1 of Example 5 to give the title compound (71%) as an orange solid.
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミドとホルムアルデヒドを用いて、実施例5の工程1と同様にして、表題化合物(71%)を橙色固体として得た。 Example 62 2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) Preparation of phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide 2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine- 4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide and formaldehyde were used as in Step 1 of Example 5 to give the title compound (71%) as an orange solid.
実施例63 N-{5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
Example 63 N- {5- [6- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide Manufacturing of
工程1:
1-メチル-4-[5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ピリジン-2-イル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) pyridin-2-yl] piperazine
1-メチル-4-[5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ピリジン-2-イル]ピペラジンの製造 Step 1:
Preparation of 1-methyl-4- [5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) pyridin-2-yl] piperazine
2-ブロモ-5-ニトロチオフェンと1-メチル-4-[5-(4,4,5,5-テトラメチル-1,3,2-ジオキサボロラン-2-イル)ピペリジン-2-イル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例1の工程3と同様にして、表題化合物(crude)をオレンジ色固体として得た。
2-bromo-5-nitrothiophene and 1-methyl-4- [5- (4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl) piperidin-2-yl] piperazine The title compound (crude) was obtained as an orange solid in the same manner as in Step 3 of Example 1.
工程2:
5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-amine
5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-アミンの製造 Step 2:
Preparation of 5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-amine
1-メチル-4-[5-(5-ニトロチオフェン-2-イル)ピリジン-2-イル]ピペラジンを用いて、実施例2の工程2と同様にして、表題化合物(2工程収率63%)を黒緑色固体として得た。
Using 1-methyl-4- [5- (5-nitrothiophen-2-yl) pyridin-2-yl] piperazine in the same manner as in Step 2 of Example 2, the title compound (2 step yield: 63%) ) Was obtained as a black-green solid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 2.31 (3H, s), 2.47-2.57 (4H, m), 3.46-3.59 (4H, m), 3.75 (2H, brs), 6.14 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.74 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 7.54 (1H, dd, J = 8.4, 2.0 Hz), 8.31 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 2.31 (3H, s), 2.47-2.57 (4H, m), 3.46-3.59 (4H, m), 3.75 (2H, brs), 6.14 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 6.62 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.74 (1H, d, J = 3.6 Hz), 7.54 (1H, dd, J = 8.4, 2.0 Hz), 8.31 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz).
工程3:
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] Preparation of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドの製造 Step 3:
2,2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl] Preparation of —N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide
5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-アミンと2-[2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミド]酢酸を用いて、実施例2の工程6および7と同様にして、表題化合物(61%)を淡褐色固体として得た。
5- [6- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-amine and 2- [2,2,2-trifluoro-N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) ) Acetamide] The title compound (61%) was obtained as a light brown solid in the same manner as in Steps 6 and 7 of Example 2 using acetic acid.
1H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl3)δ: 1.75-1.84 (2H, m), 1.92-2.08 (4H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.35 (3H, s), 2.50-2.55 (4H, m), 2.90-2.98 (2H, m), 3.55-3.62 (4H, m), 3.80-3.89 (1H, m), 4.16 (2H, s), 6.60 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz), 6.63 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.89 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.61 (1H, dd, J = 8.8, 2.7 Hz), 8.39 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz), 8.92 (1H, brs).
1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ: 1.75-1.84 (2H, m), 1.92-2.08 (4H, m), 2.29 (3H, s), 2.35 (3H, s), 2.50-2.55 (4H, m), 2.90-2.98 (2H, m), 3.55-3.62 (4H, m), 3.80-3.89 (1H, m), 4.16 (2H, s), 6.60 (1H, d, J = 4.1 Hz), 6.63 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), 6.89 (1H, d, J = 3.9 Hz), 7.61 (1H, dd, J = 8.8, 2.7 Hz), 8.39 (1H, d, J = 2.4 Hz), 8.92 (1H, brs).
工程4:
N-{5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(定量的)を淡褐色固体として得た。 Step 4:
Production of N- {5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide 2 , 2,2-trifluoro-N- [2-({5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} amino) -2-oxoethyl]- The title compound (quantitative) was obtained as a pale brown solid in the same manner as in Step 8 of Example 9 using N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) acetamide.
N-{5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミドの製造
2,2,2-トリフルオロ-N-[2-({5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}アミノ)-2-オキソエチル]-N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アセトアミドを用いて、実施例9の工程8と同様にして、表題化合物(定量的)を淡褐色固体として得た。 Step 4:
Production of N- {5- [6- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino]
上記実施例によって得られた化合物の物性値を以下に示す。
The physical property values of the compounds obtained by the above examples are shown below.
[試験例1]TLR9発現レポーター細胞を用いたTLR9活性化阻害試験
1)TLR9発現レポーター細胞の樹立
ヒトTLR9発現細胞は、ヒト胎児腎臓細胞株であるHEK293にヒトTLR9を発現させた細胞をInvivogen社より購入した(hTLR9/293xL)。hTLR9/293xLは10%ウシ胎仔血清、ペニシリン、ストレプトマイシンを含むダルベッコ改変イーグル培地(DMEM(sigma))を用いて継代培養した。NFκB認識配列の4回繰り返しにホタルルシフェラーゼ遺伝子を連結したpGL4.28(Promega)を、Fugene6(Roche)を用いてリポフェクションにより遺伝子導入した。ハイグロマイシン、ブラストサイジン耐性細胞クローンを選択し、TLR9発現レポーター細胞とした(hTLR9 NFκB-luc/293xL)。
2)TLR9活性化阻害試験
hTLR9 NFκB-luc/293xLを96ウェルホワイトマイクロタイタープレートに1.0×104/80μLで播き、CO2インキュベータ中で37℃、1晩培養した。DMEMにより希釈した被検化合物(10μL)を添加し、終濃度0.01,0.03,0.1,0.3,1μMとした。1時間後にTLR9リガンドであるCpG-B DNA(ODN2006)(Invivogen)を終濃度1μMとなるように添加した(10μL)。合計100μLとして4時間CO2インキュベータ中でインキュベート後にルシフェラーゼ活性をTLR9活性として測定した。ルシフェラーゼ活性はBright Glo(Promega)を60μL添加し、マルチマイクロプレートリーダーARVO(Perkin Elmer)により発光量を測定した。被検化合物を添加していない場合のルシフェラーゼ活性を100%として、各被検化合物の50%阻害濃度(IC50値)を計算した。 [Test Example 1] TLR9 activation inhibition test using TLR9-expressing reporter cells 1) Establishment of TLR9-expressing reporter cells Human TLR9-expressing cells are cells obtained by expressing human TLR9 in human fetal kidney cell line, Invivogen. (HTLR9 / 293xL). hTLR9 / 293xL was subcultured using Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM (sigma)) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin. PGL4.28 (Promega) in which a firefly luciferase gene was linked to the NFκB recognition sequence four times was introduced by lipofection using Fugene6 (Roche). Hygromycin and blasticidin resistant cell clones were selected and used as TLR9 expression reporter cells (hTLR9 NFκB-luc / 293xL).
2) TLR9 plated at activation inhibition test hTLR9 NFκB-luc / 96 well-white 293xL microtiter plate 1.0 × 10 4 / 80μL, 37 ℃ in CO 2 incubator, and cultured overnight. A test compound (10 μL) diluted with DMEM was added to a final concentration of 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1 μM. One hour later, CpG-B DNA (ODN2006) (Invivogen) as a TLR9 ligand was added to a final concentration of 1 μM (10 μL). Luciferase activity was measured as TLR9 activity after incubation in a CO 2 incubator for a total of 100 μL for 4 hours. Luciferase activity was measured by adding 60 μL of Bright Glo (Promega) and measuring the amount of luminescence with a multi-microplate reader ARVO (Perkin Elmer). The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC 50 value) of each test compound was calculated with the luciferase activity when no test compound was added as 100%.
1)TLR9発現レポーター細胞の樹立
ヒトTLR9発現細胞は、ヒト胎児腎臓細胞株であるHEK293にヒトTLR9を発現させた細胞をInvivogen社より購入した(hTLR9/293xL)。hTLR9/293xLは10%ウシ胎仔血清、ペニシリン、ストレプトマイシンを含むダルベッコ改変イーグル培地(DMEM(sigma))を用いて継代培養した。NFκB認識配列の4回繰り返しにホタルルシフェラーゼ遺伝子を連結したpGL4.28(Promega)を、Fugene6(Roche)を用いてリポフェクションにより遺伝子導入した。ハイグロマイシン、ブラストサイジン耐性細胞クローンを選択し、TLR9発現レポーター細胞とした(hTLR9 NFκB-luc/293xL)。
2)TLR9活性化阻害試験
hTLR9 NFκB-luc/293xLを96ウェルホワイトマイクロタイタープレートに1.0×104/80μLで播き、CO2インキュベータ中で37℃、1晩培養した。DMEMにより希釈した被検化合物(10μL)を添加し、終濃度0.01,0.03,0.1,0.3,1μMとした。1時間後にTLR9リガンドであるCpG-B DNA(ODN2006)(Invivogen)を終濃度1μMとなるように添加した(10μL)。合計100μLとして4時間CO2インキュベータ中でインキュベート後にルシフェラーゼ活性をTLR9活性として測定した。ルシフェラーゼ活性はBright Glo(Promega)を60μL添加し、マルチマイクロプレートリーダーARVO(Perkin Elmer)により発光量を測定した。被検化合物を添加していない場合のルシフェラーゼ活性を100%として、各被検化合物の50%阻害濃度(IC50値)を計算した。 [Test Example 1] TLR9 activation inhibition test using TLR9-expressing reporter cells 1) Establishment of TLR9-expressing reporter cells Human TLR9-expressing cells are cells obtained by expressing human TLR9 in human fetal kidney cell line, Invivogen. (HTLR9 / 293xL). hTLR9 / 293xL was subcultured using Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM (sigma)) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin. PGL4.28 (Promega) in which a firefly luciferase gene was linked to the NFκB recognition sequence four times was introduced by lipofection using Fugene6 (Roche). Hygromycin and blasticidin resistant cell clones were selected and used as TLR9 expression reporter cells (hTLR9 NFκB-luc / 293xL).
2) TLR9 plated at activation inhibition test hTLR9 NFκB-luc / 96 well-white 293xL microtiter plate 1.0 × 10 4 / 80μL, 37 ℃ in CO 2 incubator, and cultured overnight. A test compound (10 μL) diluted with DMEM was added to a final concentration of 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1 μM. One hour later, CpG-B DNA (ODN2006) (Invivogen) as a TLR9 ligand was added to a final concentration of 1 μM (10 μL). Luciferase activity was measured as TLR9 activity after incubation in a CO 2 incubator for a total of 100 μL for 4 hours. Luciferase activity was measured by adding 60 μL of Bright Glo (Promega) and measuring the amount of luminescence with a multi-microplate reader ARVO (Perkin Elmer). The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC 50 value) of each test compound was calculated with the luciferase activity when no test compound was added as 100%.
3)結果
上記実施例によって得られた化合物の活性値(IC50値)を表1に示す。 3) Results Table 1 shows the activity values (IC 50 values) of the compounds obtained in the above examples.
上記実施例によって得られた化合物の活性値(IC50値)を表1に示す。 3) Results Table 1 shows the activity values (IC 50 values) of the compounds obtained in the above examples.
[試験例2] TLR7発現レポーター細胞を用いたTLR7活性化阻害試験
1)TLR7発現レポーター細胞の樹立
ヒトTLR7発現細胞は、ヒト胎児腎臓細胞株であるHEK293にヒトTLR7を発現させた細胞をInvivogen社より購入した(hTLR7/293xL)。hTLR7/293xLは10%ウシ胎仔血清、ペニシリン、ストレプトマイシンを含むダルベッコ改変イーグル培地(DMEM(sigma))を用いて継代培養した。NFκB認識配列の4回繰り返しにホタルルシフェラーゼ遺伝子を連結したpGL4.28(Promega)を、Fugene6(Roche)を用いてリポフェクションにより遺伝子導入した。ハイグロマイシン、ブラストサイジン耐性細胞クローンを選択し、TLR7発現レポーター細胞とした(hTLR7 NFκB-luc/293xL)。
2)TLR7活性化阻害試験
hTLR7 NFκB-luc/293xLを96ウェルホワイトマイクロタイタープレートに1.0×104/80μLで播き、CO2インキュベータ中で37℃、1晩培養した。DMEMにより希釈した被検化合物(10μL)を添加し、終濃度0.03,0.1,0.3,1,3,10μMとした。1時間後にTLR7リガンドであるImiquimod(Invivogen)を終濃度10μMとなるように添加した(10μL)。合計100μLとして4時間CO2インキュベータ中でインキュベート後にルシフェラーゼ活性をTLR7活性として測定した。ルシフェラーゼ活性はBright Glo(Promega)を60μL添加し、マルチマイクロプレートリーダーARVO(Perkin Elmer)により発光量を測定した。被検化合物を添加していない場合のルシフェラーゼ活性を100%として、各被検化合物の50%阻害濃度(IC50値)を計算した。
3)結果
上記実施例によって得られた化合物の活性値(IC50値)を表2に示す。 [Test Example 2] TLR7 activation inhibition test using TLR7-expressing reporter cells 1) Establishment of TLR7-expressing reporter cells Human TLR7-expressing cells were obtained by expressing cells expressing human TLR7 in human fetal kidney cell line, Invivogen. (HTLR7 / 293xL). hTLR7 / 293xL was subcultured using Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM (sigma)) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin. PGL4.28 (Promega) in which a firefly luciferase gene was linked to the NFκB recognition sequence four times was introduced by lipofection using Fugene6 (Roche). Hygromycin and blasticidin resistant cell clones were selected and used as TLR7 expression reporter cells (hTLR7 NFκB-luc / 293 × L).
2) The TLR7 activation Inhibition Test hTLR7 NFκB-luc / 293xL plated at 1.0 × 10 4 / 80μL in a 96 well white microtiter plate, 37 ° C. in a CO 2 incubator, and cultured overnight. A test compound (10 μL) diluted with DMEM was added to a final concentration of 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 μM. One hour later, Imiquimod (Invivogen), a TLR7 ligand, was added to a final concentration of 10 μM (10 μL). Luciferase activity was measured as TLR7 activity after incubation in a CO 2 incubator for a total of 100 μL for 4 hours. Luciferase activity was measured by adding 60 μL of Bright Glo (Promega) and measuring the amount of luminescence with a multi-microplate reader ARVO (Perkin Elmer). The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC 50 value) of each test compound was calculated with the luciferase activity when no test compound was added as 100%.
3) Results Table 2 shows the activity values (IC 50 values) of the compounds obtained in the above examples.
1)TLR7発現レポーター細胞の樹立
ヒトTLR7発現細胞は、ヒト胎児腎臓細胞株であるHEK293にヒトTLR7を発現させた細胞をInvivogen社より購入した(hTLR7/293xL)。hTLR7/293xLは10%ウシ胎仔血清、ペニシリン、ストレプトマイシンを含むダルベッコ改変イーグル培地(DMEM(sigma))を用いて継代培養した。NFκB認識配列の4回繰り返しにホタルルシフェラーゼ遺伝子を連結したpGL4.28(Promega)を、Fugene6(Roche)を用いてリポフェクションにより遺伝子導入した。ハイグロマイシン、ブラストサイジン耐性細胞クローンを選択し、TLR7発現レポーター細胞とした(hTLR7 NFκB-luc/293xL)。
2)TLR7活性化阻害試験
hTLR7 NFκB-luc/293xLを96ウェルホワイトマイクロタイタープレートに1.0×104/80μLで播き、CO2インキュベータ中で37℃、1晩培養した。DMEMにより希釈した被検化合物(10μL)を添加し、終濃度0.03,0.1,0.3,1,3,10μMとした。1時間後にTLR7リガンドであるImiquimod(Invivogen)を終濃度10μMとなるように添加した(10μL)。合計100μLとして4時間CO2インキュベータ中でインキュベート後にルシフェラーゼ活性をTLR7活性として測定した。ルシフェラーゼ活性はBright Glo(Promega)を60μL添加し、マルチマイクロプレートリーダーARVO(Perkin Elmer)により発光量を測定した。被検化合物を添加していない場合のルシフェラーゼ活性を100%として、各被検化合物の50%阻害濃度(IC50値)を計算した。
3)結果
上記実施例によって得られた化合物の活性値(IC50値)を表2に示す。 [Test Example 2] TLR7 activation inhibition test using TLR7-expressing reporter cells 1) Establishment of TLR7-expressing reporter cells Human TLR7-expressing cells were obtained by expressing cells expressing human TLR7 in human fetal kidney cell line, Invivogen. (HTLR7 / 293xL). hTLR7 / 293xL was subcultured using Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM (sigma)) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin. PGL4.28 (Promega) in which a firefly luciferase gene was linked to the NFκB recognition sequence four times was introduced by lipofection using Fugene6 (Roche). Hygromycin and blasticidin resistant cell clones were selected and used as TLR7 expression reporter cells (hTLR7 NFκB-luc / 293 × L).
2) The TLR7 activation Inhibition Test hTLR7 NFκB-luc / 293xL plated at 1.0 × 10 4 / 80μL in a 96 well white microtiter plate, 37 ° C. in a CO 2 incubator, and cultured overnight. A test compound (10 μL) diluted with DMEM was added to a final concentration of 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 μM. One hour later, Imiquimod (Invivogen), a TLR7 ligand, was added to a final concentration of 10 μM (10 μL). Luciferase activity was measured as TLR7 activity after incubation in a CO 2 incubator for a total of 100 μL for 4 hours. Luciferase activity was measured by adding 60 μL of Bright Glo (Promega) and measuring the amount of luminescence with a multi-microplate reader ARVO (Perkin Elmer). The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC 50 value) of each test compound was calculated with the luciferase activity when no test compound was added as 100%.
3) Results Table 2 shows the activity values (IC 50 values) of the compounds obtained in the above examples.
試験例1及び2の結果より、本発明の化合物は強いTLR7及び9阻害作用を有していることが確認された。したがって、本発明の一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体は、TLR7及び9阻害剤として、TLR7及び9シグナルの活性化に関連する疾患、例えば、RA、SLE、SS、MS、IBD、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群、血管炎などの自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶およびGvHDの病態の予防剤や治療剤の有効成分として有用であることがわかった。
From the results of Test Examples 1 and 2, it was confirmed that the compound of the present invention has a strong TLR7 and 9 inhibitory action. Therefore, the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) of the present invention is used as a TLR7 and 9 inhibitor as a disease associated with activation of TLR7 and 9 signals such as RA, SLE, SS, MS, IBD, psoriasis. It has been found to be useful as an active ingredient for preventive and therapeutic agents for autoimmune diseases such as osteoarthritis, Behcet's syndrome, vasculitis, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection and GvHD.
[試験例3]関節リウマチモデルを用いたTLR9活性化阻害化合物の病態抑制効果
実施例5の化合物の関節リウマチ(RA)治療効果を、RAの動物モデルであるマウスコラーゲン誘発関節炎モデル(マウスCIAモデル)で評価した。(FDA,CBER,CDER,CDRH:Guidance for industry -Clinical development programs for drugs,devices,and biological products for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis(RA)-.(1999))。 [Test Example 3] Disease state-suppressing effect of TLR9 activation-inhibiting compound using rheumatoid arthritis model The therapeutic effect of the compound of Example 5 on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was compared with a mouse collagen-induced arthritis model (mouse CIA model) which is an animal model of RA. ). (FDA, CBER, CDER, CDRH: Guidance for industry-Clinical development programs for devices, devices, and biological products for the treatment of RA. 19).
実施例5の化合物の関節リウマチ(RA)治療効果を、RAの動物モデルであるマウスコラーゲン誘発関節炎モデル(マウスCIAモデル)で評価した。(FDA,CBER,CDER,CDRH:Guidance for industry -Clinical development programs for drugs,devices,and biological products for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis(RA)-.(1999))。 [Test Example 3] Disease state-suppressing effect of TLR9 activation-inhibiting compound using rheumatoid arthritis model The therapeutic effect of the compound of Example 5 on rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was compared with a mouse collagen-induced arthritis model (mouse CIA model) which is an animal model of RA. ). (FDA, CBER, CDER, CDRH: Guidance for industry-Clinical development programs for devices, devices, and biological products for the treatment of RA. 19).
(1)使用動物および群設定
動物は、雄性DBA/1Jマウス(日本チャールスリバー(株))を使用した。
7週齢のDBA/1Jマウスの体重を測定し、これを指標にした単変数によるブロック化割付を用いて群分けを行った。群構成は、コントロ-ル群(投与媒体(0.5%ヒドロキシメチルプロピルセルロース水溶液)投与群)、実施例5の化合物 25mg/kg投与群、実施例5の化合物 50mg/kg投与群とした。 (1) Use animals and group setting As animals, male DBA / 1J mice (Nippon Charles River Co., Ltd.) were used.
The body weight of 7-week-old DBA / 1J mice was measured, and grouping was performed using a single-block blocking assignment using this as an index. The group composition was the control group (administration medium (0.5% hydroxymethylpropylcellulose aqueous solution) administration group), the compound of Example 5 administered with 25 mg / kg, and the compound of Example 5 administered with 50 mg / kg.
動物は、雄性DBA/1Jマウス(日本チャールスリバー(株))を使用した。
7週齢のDBA/1Jマウスの体重を測定し、これを指標にした単変数によるブロック化割付を用いて群分けを行った。群構成は、コントロ-ル群(投与媒体(0.5%ヒドロキシメチルプロピルセルロース水溶液)投与群)、実施例5の化合物 25mg/kg投与群、実施例5の化合物 50mg/kg投与群とした。 (1) Use animals and group setting As animals, male DBA / 1J mice (Nippon Charles River Co., Ltd.) were used.
The body weight of 7-week-old DBA / 1J mice was measured, and grouping was performed using a single-block blocking assignment using this as an index. The group composition was the control group (administration medium (0.5% hydroxymethylpropylcellulose aqueous solution) administration group), the compound of Example 5 administered with 25 mg / kg, and the compound of Example 5 administered with 50 mg / kg.
(2)試験方法
0.3%の2型コラーゲン溶液(コラーゲン技術研修会)と生理食塩液(大塚製薬工業)を2:1の割合に混合し、0.2%の2型コラーゲン溶液を調製した。次いで、0.2%の2型コラーゲン溶液とAdjuvant Complete Freund(DIFCO)を等量混和して、氷冷下でハンディマイクロホモジナイザーNS-310E(マイクロテックニチオン)により初回感作用エマルジョンを調製した。動物の尾根部をバリカンで刈毛した後、尾根部の左右2箇所に、初回感作用エマルジョンを各0.05mL皮内投与した。初回感作終了後、初回感作34日後(追加感作14日後)まで、1日1回の薬液の経口投与を行った。 (2) Test method A 0.2% type 2 collagen solution is prepared by mixing 0.3% type 2 collagen solution (collagen technical workshop) and physiological saline (Otsuka Pharmaceutical) in a ratio of 2: 1. did. Next, an equal amount of 0.2% type 2 collagen solution and Adjuvant Complete Freund (DIFCO) were mixed, and a first-sensitized emulsion was prepared with a handy microhomogenizer NS-310E (Microtech Nithion) under ice cooling. After shaving the ridges of the animals with clippers, 0.05 mL each of the first sensitizing emulsion was intradermally administered to the left and right sides of the ridges. After the first sensitization, the drug solution was orally administered once a day until 34 days after the first sensitization (14 days after the additional sensitization).
0.3%の2型コラーゲン溶液(コラーゲン技術研修会)と生理食塩液(大塚製薬工業)を2:1の割合に混合し、0.2%の2型コラーゲン溶液を調製した。次いで、0.2%の2型コラーゲン溶液とAdjuvant Complete Freund(DIFCO)を等量混和して、氷冷下でハンディマイクロホモジナイザーNS-310E(マイクロテックニチオン)により初回感作用エマルジョンを調製した。動物の尾根部をバリカンで刈毛した後、尾根部の左右2箇所に、初回感作用エマルジョンを各0.05mL皮内投与した。初回感作終了後、初回感作34日後(追加感作14日後)まで、1日1回の薬液の経口投与を行った。 (2) Test method A 0.2
初回感作20日後に以下の手順で追加感作を行った。0.3%の2型コラーゲン溶液と生理食塩液を2:1の割合に混合し、0.2%の2型コラーゲン溶液を調製した。次いで、0.2%の2型コラーゲン溶液とAdjuvant Incomplete Freund(DIFCO)を等量混和して、氷冷下でハンディマイクロホモジナイザーNS-310Eにより追加感作用エマルジョンを調製した。調製した追加感作用エマルジョン0.1mLを、尾根部皮内に投与することで追加感作を行い、関節炎を誘発させた。
主要評価項目である四肢腫脹の判定は、追加感作の7日後の初回判定、10日後の中間判定、14日後の最終判定の計3回、盲験下で3名の判定者によるarthritis score(関節炎スコア)判定で行った。腫脹の評価基準は、下記に示した4段階の基準を四肢毎に適用し、四肢の合計を個体の関節炎スコアとした。 Additional sensitization was performed by the following procedure 20 days after the first sensitization. A 0.2% type 2 collagen solution was prepared by mixing 0.3% type 2 collagen solution and physiological saline at a ratio of 2: 1. Then, an equal amount of 0.2% type 2 collagen solution and Adjuvant Incomplete Freund (DIFCO) were mixed, and an additional sensitive emulsion was prepared with a handy microhomogenizer NS-310E under ice cooling. Additional sensitization was performed by administering 0.1 mL of the prepared additional sensitizing emulsion into the ridge skin to induce arthritis.
The primary endpoint, limb swelling, was determined by arthritis score by three judges in a blinded trial, 3 times in total:initial assessment 7 days after additional sensitization, intermediate assessment 10 days later, and final assessment 14 days later. The arthritis score was determined. As the evaluation criteria for swelling, the following four criteria were applied to each limb, and the total of the limbs was used as the individual arthritis score.
主要評価項目である四肢腫脹の判定は、追加感作の7日後の初回判定、10日後の中間判定、14日後の最終判定の計3回、盲験下で3名の判定者によるarthritis score(関節炎スコア)判定で行った。腫脹の評価基準は、下記に示した4段階の基準を四肢毎に適用し、四肢の合計を個体の関節炎スコアとした。 Additional sensitization was performed by the following procedure 20 days after the first sensitization. A 0.2
The primary endpoint, limb swelling, was determined by arthritis score by three judges in a blinded trial, 3 times in total:
0点:腫脹なし
1点:1指に腫脹が認められる、或いは肢全体に僅かな腫脹が認められる場合
2点:2~4指に腫脹が認められる、或いは肢全体に明らかな腫脹が認められる場合
3点:全指に腫脹が認められる、または肢全体に強い腫脹が認められる、或いは肢全体に明らかな腫脹が認められ、かつ2指以上に腫脹が認められる場合 0 point: no swelling 1 point: swelling in one finger or slight swelling in theentire limb 2 points: swelling in 2 to 4 fingers, or obvious swelling in the entire limb Case 3 points: When all fingers are swollen, or the whole limb is swollen, or the whole limb is clearly swollen, and swollen by more than 2 fingers
1点:1指に腫脹が認められる、或いは肢全体に僅かな腫脹が認められる場合
2点:2~4指に腫脹が認められる、或いは肢全体に明らかな腫脹が認められる場合
3点:全指に腫脹が認められる、または肢全体に強い腫脹が認められる、或いは肢全体に明らかな腫脹が認められ、かつ2指以上に腫脹が認められる場合 0 point: no swelling 1 point: swelling in one finger or slight swelling in the
副次的評価項目として、追加感作15日後の眼窩採血サンプルを用いた、ELISA法による血漿中抗2型コラーゲンIgG抗体価の測定を行った。
As a secondary evaluation item, plasma anti-type 2 collagen IgG antibody titer was measured by ELISA using an orbital blood sample 15 days after additional sensitization.
(3)試験結果
図1に、関節炎スコアの経時変化を平均値で示した。コントロ-ル群(薬剤非投与群)、実施例5の化合物 25mg/kg投与群および50mg/kg投与群における、マウスコラ-ゲン誘発関節炎モデルの関節炎スコアの経時変化を示す図である。コントロール群は、追加感作7日後以降、関節炎スコアの上昇が認められた。これに対し、実施例5の化合物の投与群は、用量依存性が示唆される有意な抑制作用を50mg/kgの用量で示した。なお、図中の**は、コントロール群を比較対照としたSteelの多重比較検定において、危険率が1%未満(p<0.01)であることを示す。 (3) Test result In FIG. 1, the time-dependent change of the arthritis score was shown by the average value. FIG. 6 is a graph showing changes over time in arthritis scores of a mouse collagen-induced arthritis model in a control group (drug non-administration group) and the compound of Example 5 in a 25 mg / kg administration group and a 50 mg / kg administration group. In the control group, an increase in the arthritis score was observed after 7 days from the additional sensitization. On the other hand, the administration group of the compound of Example 5 showed a significant inhibitory effect suggesting dose dependency at a dose of 50 mg / kg. In the figure, ** indicates that the risk rate is less than 1% (p <0.01) in Steel's multiple comparison test using the control group as a comparison control.
図1に、関節炎スコアの経時変化を平均値で示した。コントロ-ル群(薬剤非投与群)、実施例5の化合物 25mg/kg投与群および50mg/kg投与群における、マウスコラ-ゲン誘発関節炎モデルの関節炎スコアの経時変化を示す図である。コントロール群は、追加感作7日後以降、関節炎スコアの上昇が認められた。これに対し、実施例5の化合物の投与群は、用量依存性が示唆される有意な抑制作用を50mg/kgの用量で示した。なお、図中の**は、コントロール群を比較対照としたSteelの多重比較検定において、危険率が1%未満(p<0.01)であることを示す。 (3) Test result In FIG. 1, the time-dependent change of the arthritis score was shown by the average value. FIG. 6 is a graph showing changes over time in arthritis scores of a mouse collagen-induced arthritis model in a control group (drug non-administration group) and the compound of Example 5 in a 25 mg / kg administration group and a 50 mg / kg administration group. In the control group, an increase in the arthritis score was observed after 7 days from the additional sensitization. On the other hand, the administration group of the compound of Example 5 showed a significant inhibitory effect suggesting dose dependency at a dose of 50 mg / kg. In the figure, ** indicates that the risk rate is less than 1% (p <0.01) in Steel's multiple comparison test using the control group as a comparison control.
図2に、追加感作15日後における抗2型コラーゲンIgG抗体価を平均値で示した。コントロ-ル群(薬剤非投与群)、実施例5の化合物 25mg/kg投与群および50mg/kg投与群における、マウスコラ-ゲン誘発関節炎モデルの追加感作15日後の抗2型コラーゲンIgG抗体価を示す図である。コントロ-ル群に対して、実施例5の化合物の25および50mg/kg投与群は、用量依存性が示唆される有意な抑制作用を示した。なお、図中の*と**は、コントロール群を比較対照としたSteelの多重比較検定において、危険率がそれぞれ5%未満(p<0.05)および1%未満(p<0.01)であることを示す。
FIG. 2 shows the average value of anti-type 2 collagen IgG antibody titer 15 days after the additional sensitization. The anti-type 2 collagen IgG antibody titer 15 days after the additional sensitization of the mouse collagen-induced arthritis model in the control group (drug non-administration group), the compound of Example 5 in the 25 mg / kg administration group and the 50 mg / kg administration group FIG. In contrast to the control group, the 25 and 50 mg / kg administration groups of the compound of Example 5 showed a significant inhibitory effect suggesting dose dependency. In the figure, * and ** indicate a risk rate of less than 5% (p <0.05) and less than 1% (p <0.01), respectively, in Steel's multiple comparison test using the control group as a comparison control. Indicates that
関節炎スコアおよび抗2型コラーゲンIgG抗体価の結果より、実施例5の化合物は関節リウマチの治療剤として有効である。
From the results of arthritis score and anti-type 2 collagen IgG antibody titer, the compound of Example 5 is effective as a therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis.
本発明は、一般式(1)で表されるチオフェン誘導体若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物が、優れたTLR3、7及び/又は9阻害作用を有していることを初めて見出し、自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症に起因する心筋症の予防及び/又は治療剤を提供するものである。本発明は、自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病(GvHD)又は敗血症に起因する心筋症の予防及び/又は治療剤を提供し、製薬工業において有用であり、産業上の利用可能性を有している。
The present invention for the first time finds that the thiophene derivative represented by the general formula (1) or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof has an excellent TLR3, 7 and / or 9 inhibitory action, and autoimmunity. The present invention provides a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy due to disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis. The present invention provides a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy caused by autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or sepsis, and is useful in the pharmaceutical industry. Has industrial applicability.
Claims (14)
- 次の一般式(1):
Xは、次の式(2):
環Aは、飽和又は不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、
環Bは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環A及び環Bはそれぞれ、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q2は、単結合、又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R4は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよい}
又は式(3):
環Cは、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Cは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q3は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい}
を示し、
環Yは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基:
Q4は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R5は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよく、
環Dは、飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい}
から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつ環Cが飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示す時、環Yは式(4)で示される置換基を有する飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
但し、環Yが式(4)で示される置換基を有し、かつ環Dが芳香族炭素環を示す時、環Yは飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつQ3がオキソ基を有するC1-6アルキレン基を示す時、環Yは飽和若しくは不飽和の脂肪族炭素環、又は飽和若しくは不飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q1は、単結合、C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
但し、Xが式(3)を示し、かつQ3がオキソ基を有するC1-6アルキレン基を示す時、Q1はC1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記Q1におけるC1-6アルキレン基又はC2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R1は、単結合、酸素原子又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよく、
R2及びR3は、互いに同一又は異なってもよく、水素原子、C1-6アルキル基又はC1-6アルキルオキシ基を示し、そして
q、m及びnの組み合わせが、(q,m,n)=(0,1,0)、(0,0,1)、(0,1,1)、(1,1,0)、(1,0,1)又は(1,1,1)である]
で示される化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 The following general formula (1):
X is the following formula (2):
Ring A represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring,
Ring B represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, ring A and ring B are each a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1. -5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, It may have 1 to 3 substituents selected from a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group,
Q 2 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group 1 to 2 substituents selected from a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
R 4 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 may have an alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups}
Or formula (3):
Ring C represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring C is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, or a C 1-6 alkyl Oxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group A substituent selected from a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, You may have 1 to 3
Q 3 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, oxo group, hydroxyl group, C 2 1 to 2 substituents selected from a 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group May}
Indicate
Ring Y represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, the ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, a carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group. Benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1- A 6 alkylamino group, a di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a group of formula (4):
Q 4 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, C 1 to 2 substituents selected from a 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group You can,
R 5 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, may have a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups,
Ring D represents a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Here, the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group. Benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1- 1 to 3 substituents selected from a 6 alkylamino group and a di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group}
1 to 3 substituents selected from:
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and the ring C represents a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, the ring Y represents a saturated or unsaturated fat having a substituent represented by the formula (4). An aromatic carbocyclic ring, an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring,
Provided that when ring Y has a substituent represented by formula (4) and ring D represents an aromatic carbocycle, ring Y is a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing An aliphatic heterocycle or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle;
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and Q 3 represents a C 1-6 alkylene group having an oxo group, the ring Y is a saturated or unsaturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, or a saturated or unsaturated nitrogen-containing group. An aliphatic heterocycle, wherein the ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, Carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkyl It may have 1 to 3 substituents selected from an amino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a group of the formula (4).
Q 1 represents a single bond, a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, C 1 1 to 2 substituents selected from a 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group You can,
Provided that when X represents the formula (3) and Q 3 represents a C 1-6 alkylene group having an oxo group, Q 1 represents a C 1-6 alkylene group or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, where The C 1-6 alkylene group or C 2-6 alkenylene group in Q 1 is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1 It may have 1 or 2 substituents selected from a -6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
R 1 represents a single bond, an oxygen atom or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, may have a C 1-3 alkylsulfonyl group, and C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups,
R 2 and R 3 may be the same or different from each other, each represents a hydrogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group or a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, and the combination of q, m and n is (q, m, n) = (0,1,0), (0,0,1), (0,1,1), (1,1,0), (1,0,1) or (1,1,1) Is]
Or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. - Xが式(2)を示し、
ここで環Bは、芳香族炭素環、飽和の脂肪族炭素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Bは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
請求項1に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 X represents formula (2),
Here, ring B represents an aromatic carbocycle, a saturated aliphatic carbocycle, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring B is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1- 6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 Substitution selected from alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have 1 to 3 groups,
The compound according to claim 1, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. - Xが式(2)を示し、
ここで環Aは、ピロリジン環、ピペリジン環、ピペラジン環又はテトラヒドロピリジン環を示し、
環Bは、ベンゼン環、シクロヘキサン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環又はチアジアゾール環を示し、
ここで前記環A及び環Bはそれぞれ、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
請求項2に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 X represents formula (2),
Here, ring A represents a pyrrolidine ring, a piperidine ring, a piperazine ring or a tetrahydropyridine ring,
Ring B is a benzene ring, cyclohexane ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring, oxadiazole ring or Showing the thiadiazole ring,
Here, ring A and ring B are each a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a cyano group, or a carboxy C 1. -5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, 1 to 3 substituents selected from a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group may be present,
The compound of Claim 2, or its salt, or those solvates. - Xが式(3)を示し、
ここで環Cは、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Cは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q3は、単結合又はC2-6アルケニレン基を示し、ここで前記C2-6アルケニレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい、
請求項1に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 X represents formula (3),
Here, ring C represents a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocycle or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocycle, wherein the ring C is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy Group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, A substituent selected from a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group and a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group; You may have up to 3
Q 3 represents a single bond or a C 2-6 alkenylene group, wherein the C 2-6 alkenylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups may have 1 to 2,
The compound according to claim 1, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. - Q1が、単結合又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよい、
請求項1~4のいずれか1項に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 Q 1 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 substituent selected from alkyl groups may have 1 to 2,
The compound according to any one of claims 1 to 4, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. - 環Yが、芳香族炭素環、飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環、又は含窒素芳香族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
請求項1~5のいずれか1項に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 Ring Y represents an aromatic carbocyclic ring, a saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, or a nitrogen-containing aromatic heterocyclic ring, wherein said ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1- 6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 An alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, a C 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino group, a diC 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a formula ( 1 to 3 substituents selected from the group 4) may be included.
The compound according to any one of claims 1 to 5, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. - 環Yが、ベンゼン環、ピペリジン環、ピロリジン環、ピペラジン環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、トリアジン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、イソオキサゾール環、オキサゾール環、イソチアゾール環、チアゾール環、オキサジアゾール環又はチアジアゾール環を示し、ここで前記環Yは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基、及び式(4)の基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
請求項6に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 Ring Y is a benzene ring, piperidine ring, pyrrolidine ring, piperazine ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, triazine ring, pyrrole ring, pyrazole ring, isoxazole ring, oxazole ring, isothiazole ring, thiazole ring Represents an oxadiazole ring or a thiadiazole ring, wherein the ring Y is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group Cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkyl Mino C 1-6 alkyl group, and a substituent selected from the group may have 1 to 3 of formula (4),
The compound according to claim 6, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. - 環Yが式(4)で示される置換基を有し、
ここで環Dは、飽和の脂肪族炭素環、芳香族炭素環、又は飽和の含窒素脂肪族複素環を示し、ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよく、
Q4は、単結合又はC1-6アルキレン基を示し、ここで前記C1-6アルキレン基は、ハロゲン原子、オキソ基、水酸基、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~2個有してもよく、
R5は、単結合又はNH基を示し、ここで前記NH基は、C1-6アルキル基、ヒドロキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、C1-3アルキルスルホニル基及びC6-10アリールC1-3アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を有してもよい、
請求項1~7のいずれか1項に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 Ring Y has a substituent represented by formula (4),
Here, ring D represents a saturated aliphatic carbocyclic ring, aromatic carbocyclic ring or saturated nitrogen-containing aliphatic heterocyclic ring, wherein the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, C 1-6 alkyloxy group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1 -5 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have 1 to 3 substituents,
Q 4 represents a single bond or a C 1-6 alkylene group, wherein the C 1-6 alkylene group is a halogen atom, an oxo group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 can have one or two substituents selected from alkyl groups,
R 5 represents a single bond or an NH group, wherein the NH group is a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, a C 1- May have a substituent selected from a 3 alkylsulfonyl group and a C 6-10 aryl C 1-3 alkyl group,
The compound according to any one of claims 1 to 7, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. - 前記環Dが、シクロヘキサン環、ベンゼン環、ピロリジン環、ピペリジン環又はピペラジン環を示し、ここで前記環Dは、ハロゲン原子、C1-6アルキル基、水酸基、C1-6アルキルオキシ基、C1-3アルキルオキシC1-6アルキル基、シアノ基、カルボキシC1-5アルキル基、ベンジルオキシカルボニルC1-5アルキル基、カルバモイル基、アミド基、カルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-3アルキルカルバモイルC1-5アルキル基、C1-6アルキルアミノ基、ジC1-6アルキルアミノ基及びジC1-6アルキルアミノC1-6アルキル基から選ばれる置換基を1~3個有してもよい、
請求項8に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 The ring D represents a cyclohexane ring, a benzene ring, a pyrrolidine ring, a piperidine ring or a piperazine ring, wherein the ring D is a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a C 1-6 alkyloxy group, a C 1 1-3 alkyloxy C 1-6 alkyl group, cyano group, carboxy C 1-5 alkyl group, benzyloxycarbonyl C 1-5 alkyl group, carbamoyl group, amide group, carbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1- 1 to 3 substituents selected from 3- alkylcarbamoyl C 1-5 alkyl group, C 1-6 alkylamino group, di-C 1-6 alkylamino group and di-C 1-6 alkylamino C 1-6 alkyl group May have,
The compound according to claim 8, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof. - q、m及びnの組み合わせが(q,m,n)=(0,1,0)、(0,0,1)、又は(1,1,1)である、請求項1~9のいずれか1項に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 The combination of q, m, and n is (q, m, n) = (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1), or (1, 1, 1). Or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof.
- 一般式(1)で示される化合物が、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
2-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド、
N-{3-[(1-ベンジルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]-N-{3-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]プロピル}チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]アセトアミド、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)シクロヘキシル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
(E)-N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-3-オキソプロパ-1-エン-1-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-4-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
N-[3-([1,4’ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-3-メチル-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(ピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
N-{3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル}-3-メトキシ-5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド、
2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-(5-{4-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)オキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)アセトアミド、
2-[4-(ジメチルアミノ)ピペリジン-1-イル]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド、
(R)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド、
(S)-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-2-カルボキサミド、
2-[(5-ヒドロキシペンチル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[4-(ピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-(4-{4-[6-(メチルアミノ)-6-オキソヘキシル]ピペラジン-1-イル}フェニル)チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
ベンジル 6-{4-[4-(5-{[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]カルバモイル}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサノエート、
1’-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-[1,4’-ビピペリジン]-4-カルボキサミド、
N-メチル-6-{4-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]ピペラジン-1-イル}ヘキサンアミド、
N-(5-{4-ヒドロキシ-3-[(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)メチル]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
2-[(3-ヒドロキシプロピル)(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-N-[4-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)フェニル]アセトアミド、
N-(5-{1-[3-(ジメチルアミノ)プロピル]-1H-インドール-5-イル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]-3-フェニルプロパンアミド、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)ピロリジン-3-カルボキサミド、
N-{5-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[N-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチルスルホンアミド]アセトアミド、
4-メチル-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ペンタンアミド、
1-(ピペリジン-4-イル)-3-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ウレア、
4-メトキシ-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]ブタンアミド、
N-{5-[2,5-ジメトキシ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
N-{5-[3-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)-5-(5-{2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド}チオフェン-2-イル)ベンズアミド、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド、
ベンジル 2-[4-(4-{5-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロパンアミド]チオフェン-2-イル}フェニル)-5,6-ジヒドロピリジン-1(2H)-イル]アセテート、
3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-イソプロピル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}プロパンアミド、
2-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド、
4-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ブタンアミド、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ペンタンアミド、
6-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ヘキサンアミド、
N-{5-[2-シアノ-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
N-(5-{4-[2-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)エトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
N-(5-{4-[4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ブトキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
N-[5-(4-{[5-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ペンチル]オキシ}フェニル)チオフェン-2-イル]-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)メチル]アミノ}アセトアミド、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピロリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド、
5-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)-N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)ペンタンアミド、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-5-(ピペリジン-1-イル)ペンタンアミド、
N-(5-{4-[3-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)プロポキシ]フェニル}チオフェン-2-イル)-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]アセトアミド、
N-[3-([1,4’-ビピペリジン]-1’-イル)プロピル]-5-[1-(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)-1H-ピラゾール-4-イル]チオフェン-2-カルボキサミド、
6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}ニコチンアミド、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ベンズアミド 、
N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}-4-{[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル)アミノ]メチル}ベンズアミド、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド、
2-{6-[(ジメチルアミノ)メチル]ピリジン-3-イル}-N-{5-[4-(1-メチル-1,2,3,6-テトラヒドロピリジン-4-イル)フェニル]チオフェン-2-イル}アセトアミド、及び、
N-{5-[6-(4-メチルピペラジン-1-イル)ピリジン-3-イル]チオフェン-2-イル}-2-[(1-メチルピペリジン-4-イル) アミノ]アセトアミド、
からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1つの化合物である、請求項1に記載の化合物、若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物。 The compound represented by the general formula (1) is
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide;
2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide,
N- {3-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} -5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide;
5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] -N- {3-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] propyl} thiophene-2-carboxamide;
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide
N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] acetamide,
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] Thiophene-2-carboxamide,
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide;
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) cyclohexyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
(E) -N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -3-oxoprop-1-ene -1-yl] thiophene-2-carboxamide,
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -4-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide;
N- [3-([1,4′bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -3-methyl-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide;
N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(piperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
N- {3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl} -3-methoxy-5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide;
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) Amino] acetamide,
2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide,
2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- (5- {4-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) oxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) acetamide,
2- [4- (dimethylamino) piperidin-1-yl] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide,
(R) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide;
(S) -N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide;
2-[(5-hydroxypentyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide;
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [4- (piperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophene-2-carboxamide;
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- (4- {4- [6- (methylamino) -6-oxohexyl] piperazin-1-yl} Phenyl) thiophene-2-carboxamide,
Benzyl 6- {4- [4- (5-{[3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] carbamoyl} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanoate ,
1′-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl}-[1,4′-bipiperidine] -4-carboxamide;
N-methyl-6- {4- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] piperazin-1-yl} hexanamide,
N- (5- {4-hydroxy-3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) methyl] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide ,
2-[(3-hydroxypropyl) (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} acetamide;
2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -N- [4- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) phenyl] acetamide,
N- (5- {1- [3- (dimethylamino) propyl] -1H-indol-5-yl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
N- {5- [4- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] -3-phenylpropanamide,
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) pyrrolidine -3-carboxamide,
N- {5- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2- [N- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) methylsulfonamido] acetamide,
4-methyl-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] pentanamide,
1- (piperidin-4-yl) -3- {5- [4- [1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} urea,
4-methoxy-N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidine- 4-yl) amino] butanamide,
N- {5- [2,5-dimethoxy-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
N- {5- [3-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) -5- (5- {2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamido} thiophen-2-yl) benzamide;
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} Propanamide,
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide,
Benzyl 2- [4- (4- {5- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propanamido] thiophen-2-yl} phenyl) -5,6-dihydropyridine-1 ( 2H) -yl] acetate,
3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-isopropyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} propanamide,
2-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} acetamide,
4-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} butanamide,
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} pentanamide,
6-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene- 2-yl} hexanamide,
N- {5- [2-cyano-4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
N- (5- {4- [2- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) ethoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
N- (5- {4- [4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) butoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
N- [5- (4-{[5- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pentyl] oxy} phenyl) thiophen-2-yl] -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] Acetamide,
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Methyl] amino} acetamide,
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (pyrrolidin-1-yl) pentanamide,
5-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) -N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) pentane Amide,
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -5- (piperidin-1-yl) pentanamide,
N- (5- {4- [3- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) propoxy] phenyl} thiophen-2-yl) -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
N- [3-([1,4′-bipiperidin] -1′-yl) propyl] -5- [1- (1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) -1H-pyrazol-4-yl] thiophene-2 -Carboxamide,
6-[(dimethylamino) methyl] -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} nicotinamide,
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4- (4-methylpiperazin-1-yl) benzamide ,
N- {5- [4- (1-Methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl} -4-{[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl ) Amino] methyl} benzamide,
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophen-2-yl } Acetamide,
2- {6-[(Dimethylamino) methyl] pyridin-3-yl} -N- {5- [4- (1-methyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridin-4-yl) phenyl] thiophene -2-yl} acetamide, and
N- {5- [6- (4-Methylpiperazin-1-yl) pyridin-3-yl] thiophen-2-yl} -2-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl) amino] acetamide,
The compound according to claim 1, or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof, which is at least one compound selected from the group consisting of: - 請求項1~11のいずれか1項に記載の化合物若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分とする、TLR3、TLR7及びTLR9からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の阻害剤。 12. At least one inhibitor selected from the group consisting of TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9, comprising the compound according to any one of claims 1 to 11 or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof as an active ingredient.
- 請求項1~11のいずれか1項に記載の化合物若しくはその塩、又はそれらの溶媒和物を有効成分とする、自己免疫疾患、炎症、アレルギー、喘息、移植片拒絶、移植片対宿主病又は敗血症に起因する心筋症の予防及び/又は治療剤。 An autoimmune disease, inflammation, allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease, comprising the compound according to any one of claims 1 to 11 or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof as an active ingredient A preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cardiomyopathy caused by sepsis.
- 自己免疫疾患が、関節リウマチ、全身性エリテマトーデス、シェーグレン症候群、多発性硬化症、炎症性腸疾患、乾癬性関節炎、ベーチェット症候群又は血管炎である、請求項13に記載の予防及び/又は治療剤。 The preventive and / or therapeutic agent according to claim 13, wherein the autoimmune disease is rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriatic arthritis, Behcet's syndrome or vasculitis.
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012099748 | 2012-04-25 | ||
| JP2012-099748 | 2012-04-25 | ||
| JP2012178787 | 2012-08-10 | ||
| JP2012-178787 | 2012-08-10 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013161871A1 true WO2013161871A1 (en) | 2013-10-31 |
Family
ID=49483179
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/062049 WO2013161871A1 (en) | 2012-04-25 | 2013-04-24 | Thiophene derivative having tlr-inhibiting activity |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JPWO2013161871A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2013161871A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10836769B2 (en) | 2018-02-26 | 2020-11-17 | Gilead Sciences, Inc. | Substituted pyrrolizine compounds and uses thereof |
| US10874640B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2020-12-29 | Gilead Sciences, Inc. | Substituted pyrrolizine compounds and uses thereof |
Citations (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5939332A (en) * | 1998-02-27 | 1999-08-17 | Roche Diagnostics Corp. | Phencyclidine analogs for immunoassay |
| JPH11322711A (en) * | 1998-04-15 | 1999-11-24 | Pfizer Prod Inc | Heterocyclic carboxamide |
| WO2001074791A1 (en) * | 2000-03-31 | 2001-10-11 | Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Diazepane derivatives or salts thereof |
| JP2002121153A (en) * | 2000-09-06 | 2002-04-23 | Pfizer Prod Inc | Combined therapy for depression and anxiety |
| JP2004506734A (en) * | 2000-08-21 | 2004-03-04 | ファルマシア・アンド・アップジョン・カンパニー | Quinuclide-substituted heteroaryl moieties for disease treatment |
| JP2005504058A (en) * | 2001-08-24 | 2005-02-10 | ファルマシア アンド アップジョン カンパニー リミティド ライアビリティー カンパニー | Substituted heteroaryl-7-aza [2.2.1] bicycloheptane for the treatment of disease |
| JP2006505530A (en) * | 2002-09-02 | 2006-02-16 | アストラゼネカ・アクチエボラーグ | Combination of alpha-7 nicotinic receptor agonist and statin |
| JP2007529490A (en) * | 2004-03-19 | 2007-10-25 | アロー セラピューティクス リミテッド | Benzodiazepines for the treatment or prevention of RSV infection |
| JP2007531757A (en) * | 2004-03-30 | 2007-11-08 | カイロン コーポレイション | Substituted thiophene derivatives as anticancer agents |
| JP2008531723A (en) * | 2005-03-03 | 2008-08-14 | アムジエン・インコーポレーテツド | Phthalazine, aza and diazaphthalazine compounds and methods of use |
| JP2010508288A (en) * | 2006-10-27 | 2010-03-18 | ブリストル−マイヤーズ スクイブ カンパニー | Heterocyclic amide compounds useful as kinase inhibitors |
| JP2010513444A (en) * | 2006-12-21 | 2010-04-30 | アストラゼネカ アクチボラグ | New compounds |
| JP2011506361A (en) * | 2007-12-10 | 2011-03-03 | バイエル・シエーリング・ファーマ アクチエンゲゼルシャフト | Novel 2-hetarylthiazole-4-carboxamide derivatives, their preparation and use as pharmaceuticals |
| JP2011506362A (en) * | 2007-12-10 | 2011-03-03 | バイエル・シエーリング・ファーマ アクチエンゲゼルシャフト | 2-Arylthiazole-4-carboxamide derivatives, their preparation and use as medicaments |
| JP2011506358A (en) * | 2007-12-10 | 2011-03-03 | バイエル・シエーリング・ファーマ アクチエンゲゼルシャフト | Novel 2-substituted thiazole-4-carboxamide derivatives, their preparation and use as pharmaceuticals |
-
2013
- 2013-04-24 WO PCT/JP2013/062049 patent/WO2013161871A1/en active Application Filing
- 2013-04-24 JP JP2014512646A patent/JPWO2013161871A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5939332A (en) * | 1998-02-27 | 1999-08-17 | Roche Diagnostics Corp. | Phencyclidine analogs for immunoassay |
| JPH11322711A (en) * | 1998-04-15 | 1999-11-24 | Pfizer Prod Inc | Heterocyclic carboxamide |
| WO2001074791A1 (en) * | 2000-03-31 | 2001-10-11 | Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Diazepane derivatives or salts thereof |
| JP2004506734A (en) * | 2000-08-21 | 2004-03-04 | ファルマシア・アンド・アップジョン・カンパニー | Quinuclide-substituted heteroaryl moieties for disease treatment |
| JP2002121153A (en) * | 2000-09-06 | 2002-04-23 | Pfizer Prod Inc | Combined therapy for depression and anxiety |
| JP2005504058A (en) * | 2001-08-24 | 2005-02-10 | ファルマシア アンド アップジョン カンパニー リミティド ライアビリティー カンパニー | Substituted heteroaryl-7-aza [2.2.1] bicycloheptane for the treatment of disease |
| JP2006505530A (en) * | 2002-09-02 | 2006-02-16 | アストラゼネカ・アクチエボラーグ | Combination of alpha-7 nicotinic receptor agonist and statin |
| JP2007529490A (en) * | 2004-03-19 | 2007-10-25 | アロー セラピューティクス リミテッド | Benzodiazepines for the treatment or prevention of RSV infection |
| JP2007531757A (en) * | 2004-03-30 | 2007-11-08 | カイロン コーポレイション | Substituted thiophene derivatives as anticancer agents |
| JP2008531723A (en) * | 2005-03-03 | 2008-08-14 | アムジエン・インコーポレーテツド | Phthalazine, aza and diazaphthalazine compounds and methods of use |
| JP2010508288A (en) * | 2006-10-27 | 2010-03-18 | ブリストル−マイヤーズ スクイブ カンパニー | Heterocyclic amide compounds useful as kinase inhibitors |
| JP2010513444A (en) * | 2006-12-21 | 2010-04-30 | アストラゼネカ アクチボラグ | New compounds |
| JP2011506361A (en) * | 2007-12-10 | 2011-03-03 | バイエル・シエーリング・ファーマ アクチエンゲゼルシャフト | Novel 2-hetarylthiazole-4-carboxamide derivatives, their preparation and use as pharmaceuticals |
| JP2011506362A (en) * | 2007-12-10 | 2011-03-03 | バイエル・シエーリング・ファーマ アクチエンゲゼルシャフト | 2-Arylthiazole-4-carboxamide derivatives, their preparation and use as medicaments |
| JP2011506358A (en) * | 2007-12-10 | 2011-03-03 | バイエル・シエーリング・ファーマ アクチエンゲゼルシャフト | Novel 2-substituted thiazole-4-carboxamide derivatives, their preparation and use as pharmaceuticals |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| FRANCISCO-JAVIER GAMO, ET AL.: "Thousands of chemical starting points for antimalarial lead identification", NATURE, vol. 465, no. 7296, 20 May 2010 (2010-05-20), LONDON, UNITED KINGDOM, pages 305 - 310+2PP * |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10874640B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2020-12-29 | Gilead Sciences, Inc. | Substituted pyrrolizine compounds and uses thereof |
| US10836769B2 (en) | 2018-02-26 | 2020-11-17 | Gilead Sciences, Inc. | Substituted pyrrolizine compounds and uses thereof |
| US11420974B2 (en) | 2018-02-26 | 2022-08-23 | Gilead Sciences, Inc. | Substituted pyrrolizine compounds and uses thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2013161871A1 (en) | 2015-12-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8067457B2 (en) | Compounds useful as antagonists of CCR2 | |
| JP5736507B2 (en) | Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound or salt thereof | |
| KR102057366B1 (en) | Substituted benzene compounds | |
| US10287255B2 (en) | Compounds as histone deacetylase 6 inhibitors and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same | |
| DE602004006994T2 (en) | 3-ARYLOXY AND 2-HETEROARYLOXY-SUBSTITUTED BENZO [B] THIOPHEN AS A THERAPEUTIC AGENT WITH PI3K ACTIVITY | |
| AU2012221927B2 (en) | Diaminopyrimidine derivatives and processes for the preparation thereof | |
| US20090149460A1 (en) | New Compounds | |
| RU2454412C2 (en) | New piperazine amide derivatives | |
| KR20030026979A (en) | Medicine Comprising Dicyanopyridine Derivative | |
| TWI647227B (en) | 2-guanamine thiazole derivative or a salt thereof | |
| US20120208818A1 (en) | Compounds useful as antagonists of ccr2 | |
| WO2013161871A1 (en) | Thiophene derivative having tlr-inhibiting activity | |
| WO2013108837A1 (en) | Pyrazole derivative with tlr inhibiting properties | |
| JP7386576B2 (en) | N-(1H-imidazol-2-yl)benzamide compounds and pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds as active ingredients | |
| WO2014034719A1 (en) | Quinoline derivative having tlr inhibitory activity | |
| JP2013091624A (en) | Quinazoline derivative having tlr inhibitory action | |
| WO2021170658A1 (en) | Heterocyclic compounds for modulating nr2f6 | |
| WO2013180066A1 (en) | Pyridine derivative having inhibitory effect on tlr | |
| CN108137505B (en) | Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound | |
| JP2014148491A (en) | Thiazole derivatives with tlr inhibitory action | |
| RU2806754C1 (en) | N-(1h-imidazol-2-yl)benzamide and pharmaceutical composition containing it as active ingredient | |
| JP2014118401A (en) | Furan derivative having tlr inhibition effect | |
| JP5665537B2 (en) | Pyrazole 3,5 carboxylate derivatives, their preparation and therapeutic application | |
| JP2014101314A (en) | Pyrrole derivative having tlr inhibitory action | |
| JP2014144928A (en) | Thiazole derivatives having tlr inhibitory action |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13782406 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2014512646 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13782406 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |