WO2013136545A1 - 構造化文書管理装置、構造化文書検索方法 - Google Patents
構造化文書管理装置、構造化文書検索方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013136545A1 WO2013136545A1 PCT/JP2012/068505 JP2012068505W WO2013136545A1 WO 2013136545 A1 WO2013136545 A1 WO 2013136545A1 JP 2012068505 W JP2012068505 W JP 2012068505W WO 2013136545 A1 WO2013136545 A1 WO 2013136545A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- document
- headline
- heading
- relevance
- structured document
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/24—Querying
- G06F16/245—Query processing
- G06F16/2455—Query execution
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/80—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of semi-structured data, e.g. markup language structured data such as SGML, XML or HTML
- G06F16/83—Querying
- G06F16/835—Query processing
- G06F16/8373—Query execution
Definitions
- Embodiments described herein relate generally to a structured document management apparatus and a structured document search method.
- HTML Hyper Text Markup Language
- XML Extensible Markup Language
- KWIC KYWORD IN CONTEXT
- KWIC extracts and displays a predetermined number of characters before and after text including a search keyword from a search target document.
- a method of displaying the result of searching the structured document a method of displaying a headline corresponding to a document including a vocabulary that matches the keyword used for the search as a search result is known.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above, and it is an object of the present invention to provide a structured document management apparatus capable of improving the convenience of retrieval.
- the structured document management apparatus includes a document storage unit, a headline extraction unit, a relevance calculation unit, a document search unit, a headline selection unit, A headline display unit.
- the document storage unit stores a plurality of structured documents.
- the headline extraction unit extracts a headline of the structured document and creates a headline list including the extracted headline.
- the relevance calculation unit calculates the relevance of the concept between the vocabulary in the structured document and the heading corresponding to the structured document.
- the document search unit searches for a structured document including a vocabulary that matches the search keyword.
- the headline selection unit selects a headline having a high degree of association with a vocabulary that matches the search keyword in preference to a headline having a low degree of association.
- the display control unit causes the display unit to display the headline selected by the headline selection unit as a display headline.
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a system construction example of a structured document management system.
- FIG. 2 is a module configuration diagram of the server and the client terminal.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of the server and the client terminal according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of a structured document according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an example of a structured document according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example of a heading list according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example of the concept dictionary according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 8 is a data diagram illustrating the degree of association between vocabularies according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 8 is a data diagram illustrating the degree of association between vocabularies according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating the degree of association with the vocabulary in the text with respect to the headline of the first embodiment.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a search result display method according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating a modified example of a method of displaying search results according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing the flow of processing when registering the structured document according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing the flow of processing for calculating the degree of association between the headline and the vocabulary in the text in the first embodiment.
- FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing a flow of processing for determining a headline to be displayed as a search result at the time of search according to the first embodiment.
- FIG. 15 is a flowchart showing a flow of processing for determining a headline to be displayed as a search result at the time of search according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram illustrating a system construction example of the structured document management system according to the first embodiment.
- a network 2 such as a LAN (Local Area Network) is connected to a server computer (hereinafter referred to as a server) 1 which is a structured document management apparatus.
- a server A server client system to which a plurality of client computers (hereinafter referred to as client terminals) 3 are connected is assumed.
- FIG. 2 is a module configuration diagram of the server 1 and the client terminal 3.
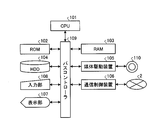
- the server 1 and the client terminal 3 have a hardware configuration using, for example, a normal computer. That is, the server 1 and the client terminal 3 include a CPU (Central Processing Unit) 101 that performs information processing, a ROM (Read Only Memory) 102 that is a read-only memory that stores a BIOS, and a RAM (RAM that stores various data in a rewritable manner).
- a CPU Central Processing Unit
- ROM Read Only Memory
- Random Access Memory (103), HDD (Hard Disc Drive) 104 that functions as various databases and stores various programs, and storage medium 110 to store information, distribute information outside, and obtain information from outside
- a medium drive device 105 such as a CD-ROM drive
- a communication control device 106 for communicating information with other external computers via the network 2, processing progress and results, etc.
- a display unit 107 such as CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) or LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) to be displayed to the operator
- an input unit 108 such as a keyboard or mouse for the operator to input commands and information to the CPU 101
- the bus controller 109 operates by arbitrating data transmitted and received between these units.
- the CPU 101 activates a program called a loader in the ROM 102, and a program for managing the hardware and software of an OS (Operating System) from the HDD 104 is stored in the RAM 103.
- an OS activates a program, reads information, and stores information in accordance with a user operation.
- OSes Windows (registered trademark), UNIX (registered trademark), and the like are known.
- Programs that run on these OSs are called application programs.
- the application program is not limited to one that runs on a predetermined OS, and may be one that causes the OS to execute some of the various processes described below, or constitutes predetermined application software, an OS, or the like. It may be included as part of a group of program files.
- the server 1 stores a structured document management program in the HDD 104 as an application program.
- the HDD 104 functions as a storage medium that stores the structured document management program.
- application programs installed in the HDD 104 of the server 1 include various types of optical disks such as CD-ROM and DVD, various magnetic disks such as various magneto-optical disks and flexible disks, and various types of semiconductor memories. It is recorded on a storage medium 110 such as a medium and provided. Therefore, the portable storage medium 110 such as an optical information recording medium such as a CD-ROM or a magnetic medium such as an FD can also be a storage medium for storing the structured document management program.
- the structured document management program may be imported from the outside via the communication control device 106 and installed in the HDD 104, for example.
- the CPU 101 executes various arithmetic processes according to the structured document management program and centrally controls each unit.
- the CPU 101 executes various arithmetic processes according to the application program, and controls each unit intensively.
- processing characteristic in the structured document management system of the embodiment will be described below.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of the server 1 and the client terminal 3 in the first embodiment.
- the client terminal 3 includes a structured document registration unit 11 and a search unit 12 as a functional configuration realized by an application program.
- the structured document registration unit 11 stores the structured document data input from the input unit 108 and the structured document data stored in advance in the HDD 104 of the client terminal 3 into a structured document database (structured document DB) of the server 1 described later. ) 21 for registration.
- the structured document registration unit 11 transmits a storage request to the server 1 together with the structured document data to be registered.
- the search unit 12 creates query data describing a search keyword for searching for desired data from the structured document DB 21 according to an instruction input from the input unit 108 by the user, and includes the query data. A request is transmitted to the server 1. In addition, the search unit 12 receives result data corresponding to the search request transmitted from the server 1 and displays the result data on the display unit 107.
- the server 1 includes a registration unit 22 and a search unit 23 as functional configurations realized by the structured document management program.
- the server 1 also includes a structured document DB 21 that uses a storage device such as the HDD 104.
- the registration unit 22 performs a process of storing the structured document data transmitted from the client terminal 3 in the structured document DB 21.
- the registration unit 22 includes a storage interface unit 24, a headline extraction unit 25, and an association degree calculation unit 26.
- the storage interface unit 24 receives input of structured document data and parses the structured document data transmitted from the client terminal 3 in order to store the structured document data in the structured document DB 21. Then, the storage interface unit 24 assigns an identifier (hereinafter referred to as an element ID) whose appearance order can be compared between elements to the element appearing in the data, and then the structured document data to which the element ID is assigned. Is stored in the structured document DB 21 (structured document data storage means). The element ID may be manually assigned to the structured document in advance on the client terminal 3 side.
- FIG. 4 shows an example of structured document data to which this element ID is assigned.
- a typical language for describing structured document data is XML (Extensible Markup Language).
- the structured document data shown in FIG. 4 is described in XML.
- individual parts constituting a document structure are called “elements” (elements), and elements are described using tags.
- one element is expressed by sandwiching data between two tags, a tag indicating the start of an element (start tag) and a tag indicating the end (end tag).
- start tag a tag indicating the start of an element
- end tag end tag
- the text data sandwiched between the start tag and the end tag is a text element included in one element represented by the start tag and the end tag.
- the ⁇ doc> element has a ⁇ title> element, and the ⁇ title> element indicates the heading of the structured document.
- the ⁇ doc> element has five ⁇ sec> elements.
- the ⁇ sec> element is a structured document having a parent-child relationship with the structured document defined by the ⁇ doc> element, and is referred to as a partial document in this embodiment.
- a ⁇ sec> element and a ⁇ para> element are included in the ⁇ sec> tag.
- ⁇ Sector> is a tag indicating the heading of the partial document.
- ⁇ Para> is a tag indicating an explanatory text of the partial document.
- the text defined by the ⁇ section> and ⁇ para> corresponds to the “body”.
- Each tag is assigned an element ID in the form of @eid.
- the headline extracting unit 25 extracts headlines from the structured document received from the storage interface unit 24, and lists the extracted headlines.
- the text enclosed by the ⁇ title> element in the structured document is recognized as the headline.
- FIG. 6 shows an example of data in which headings are listed in two structured documents of document ID 1 and document ID 2.
- @ eid 110, 103, 107, 113, and 116 for the partial documents indicated by the element IDs 109, 102, 106, 112, and 115.
- a subordinate document is a partial document defined by a ⁇ sec> element in a child hierarchy within a ⁇ sec> element that defines a partial document of a parent hierarchy.
- the headline extraction unit 25 stores the generated headline list in the structured document DB 21 and delivers the headline list to the relevance calculation unit 26.
- the degree-of-association calculation unit 26 calculates the degree of association between the headline extracted by the headline extraction unit 25 and the vocabulary included in the corresponding partial document.
- the concept dictionary shown in FIG. 7 is used.
- the concept dictionary shows how close each concept is based on the hierarchical structure of the concept. For example, “router” and “access point” in FIG. 7 are located in the same hierarchy branched from the same node, and the conceptual distance length is indicated as “1”. The conceptual distance length between the parent node and the child node is also indicated as “1”.
- the relevance calculation unit 26 extracts vocabulary from each headline, and calculates relevance with the vocabulary in the text.
- the relevance of “LAN, wireless LAN, router, access point” to the vocabulary “LAN” is “1.0, 0.333, 0.333, 0.333” in order, and “LAN, wireless to the vocabulary“ wireless LAN ”.
- the degree of association of “LAN, router, access point” is “0.333, 1.0, 0.25, 0.25” in this order.
- the relevance calculation unit 26 performs this calculation for each combination of headline and partial document, and stores the calculation result in the structured document DB 21 as a headline vocabulary relevance table shown in FIG.
- the search unit 23 includes a search interface unit 29, a matching unit 30, and a headline selection unit 31.
- the search interface unit 29 receives an input of a search keyword and calls the collation unit 30 to obtain data including a vocabulary that matches the search keyword specified by the query data including the received search keyword.
- the collation unit 30 accesses the structured document DB 21, searches the structured document data 27 for a structured document that includes the search keyword specified by the query data, and searches for a partial document that includes a vocabulary that matches the search keyword.
- the headline selection unit 31 selects a headline having a high degree of association with a vocabulary that matches the search keyword in preference to a headline having a low degree of relevance, and delivers the selection result to the search interface unit 29.
- a method of giving priority to a headline having a high degree of association a method in which a headline having a low degree of association is not selected or only a headline having a high degree of association is selected can be considered.
- the headline selection unit 31 first checks the degree of relevance to the vocabulary that matches the search keyword of the headline of each of the hit partial documents from the headline vocabulary relevance degree table.
- the headline selection unit 31 selects the top N, for example, two of the acquired degrees of association, and selects a headline to be displayed as a display headline in the search result.
- the headline selection unit 31 sends this selection result to the search interface unit 29.
- the search interface unit 29 outputs the headline received from the headline selection unit 31 to be displayed on the display unit 107.
- FIG. 10 shows an example of the search result screen displayed on the display unit.
- the search interface unit 29 displays “Network connection” and “Wireless LAN troubleshooting” which are the display headlines under the “PC instruction manual” which is the title of the document ID 1. Processing is performed to display two display headings.
- the search interface unit 29 displays “network setting” and “access point setting” which are display headlines under the “mobile terminal instruction manual” which is the title of the document ID 2. The user can browse the text associated with the display heading by selecting the displayed display heading.
- this display screen it can be set to a mode shown in FIG.
- the search interface unit 29 displays the sentences before and after the vocabulary that matches the search keyword for headings other than the headline sent from the headline selection unit 31.
- the search interface unit 29 corresponds to a headline display control unit and a text display control unit.
- FIG. 12 shows the flow of processing when registering a structured document.
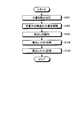
- the processing in FIG. 12 starts when, for example, an instruction to register a structured document is issued from the structured document registration unit 11 of the client terminal 3.
- the storage interface unit 24 reads the structured document sent from the client terminal 3 (step S101).
- the headline extraction unit 25 extracts a headline from the read structured document (step S102).
- the headline extraction unit 25 creates a headline list from the extracted headlines (step S103) and stores it in the structured document DB 21 (step S104). Then, the process ends.
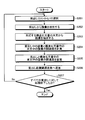
- the relevance calculation unit 26 selects a heading for one line of data from the heading list stored in the structured document DB 21 (step S201).
- the relevance calculation unit 26 extracts vocabulary from the selected headline (step S202).
- the relevance calculation unit 26 extracts a vocabulary from the body text corresponding to the headline, here, the text defined by ⁇ section> and ⁇ para> (step S203).
- the relevance calculation unit 26 calculates the relevance between the vocabulary in the headline and the vocabulary in the partial document. (Step S204).
- the relevance level calculation unit 26 sets the higher value of the relevance levels of each vocabulary as the relevance level of the headline (step S205). Then, the relevance calculation unit 26 adds relevance data to the item “headline vocabulary relevance” of the combination data of the corresponding partial document and the headline in the headline vocabulary relevance table (step S206). Finally, it is determined whether or not the processing for calculating the relevance for all the headings has been completed (step S207). When the processing is completed (step S207: Yes), the series of processing ends and the processing is completed. If not (step S207: No), the same processing is repeated for the next line heading.
- the headline selection unit 31 acquires a structured document including a vocabulary that matches the search keyword (step S301).
- the headline selection unit 31 acquires, from the headline vocabulary relevance degree table, the degree of relevance for the keyword with respect to the headline of the partial document including the vocabulary that matches the search keyword in the acquired structured document (step S302).
- the headline selection unit 31 determines whether or not the degree of association has been acquired for the partial document including all the matching vocabularies (step S303), and if all have been acquired (step S303: Yes), the matching vocabulary Are sorted in descending order based on the degree of relevance (step S304).
- step S302 determines whether or not the headline selection has been completed for all structured documents (in this embodiment, two documents with document ID 1 and document ID 2) (step S306). If completed (step S306: Yes), the heading sorted and selected in step S305 is sent as a display heading to the search interface unit 29 (step S307), and the process is terminated. If selection of headings in all structured documents has not been completed (step S306: No). The processing from step S301 is repeated to acquire another structured document.
- the structured document management apparatus of the present embodiment described above when there is a partial document including a vocabulary that matches the keyword used for the search, priority is given to a headline having a high degree of association with the search keyword. Since the display is made, the user can easily determine whether or not the information requested by the user is included in the document from the display headline. When using display headlines, users do not have to bother with reading text to determine if the text is close to what they are looking for, and quickly know where the desired information exists in the structured document. It becomes possible.
- the headline selection unit 31 may select a headline with a relevance level equal to or higher than a predetermined value, instead of selecting the top N headlines with the relevance level.
- the headline selection unit 31 may select headlines having the top N relevance levels and a predetermined value or more.
- tags defining headings and texts are not limited to those of this embodiment, and can be freely defined.
- the degree of association between the heading of the partial document and the vocabulary in the text is not calculated and registered in advance when the structured document is registered, but matches the keyword when the user searches. The only difference is that the degree of relevance is calculated only for the partial documents containing the vocabulary.
- FIG. 15 is a flowchart showing the flow of processing for selecting a headline during a search.
- the headline selection unit 31 obtains a structured document including a vocabulary that matches the search keyword (step S401).
- the relevance calculation unit 26 selects one partial document including a vocabulary that matches the search keyword from the obtained structured documents, and calculates the relevance between the corresponding headline and the search keyword (Ste S402).
- the calculation method at this time is the same as the method of calculating the degree of association between the headline shown in the first embodiment and the vocabulary in the text.
- the headline selection unit 31 determines whether or not the calculation of the degree of association has been completed for the headlines of all the partial documents including the vocabulary that matches the search keyword (step S403), and when all have been calculated (step S403). Step S403: Yes), the headings of the partial documents including the vocabulary with the matching search keyword are sorted in descending order based on the degree of association (step S404). On the other hand, when it is determined that the relevance level for all partial documents including the vocabulary that matches the search keyword cannot be calculated (step S403: No), the process of step 402 is repeated.
- the headline selection unit 31 selects the top N headlines with the relevance and sorts them in the order of appearance of the headlines in the structured document (step S405).
- the headline selection unit 31 determines whether or not the headline selection has been completed for all structured documents (two documents of document ID 1 and document ID 2 in this embodiment) (step S406). If completed (step S406: Yes), the heading sorted and selected in step S305 is sent to the search interface unit 29 as a display heading (step S407), and the process is terminated. If selection of headings in all structured documents has not been completed (step S406: No). The processing from step S401 is repeated.
- the present invention since it is not necessary to calculate the degree of association between the headline and the vocabulary in the text in advance, the present invention is used even when the storage capacity for storing the calculation result cannot be secured. Will be able to. Further, since the degree of relevance can be calculated only by the degree of relevance between the search keyword and the heading in the partial document including the vocabulary that matches the search keyword, the calculation time can be suppressed. .
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2012800029691A CN103415850A (zh) | 2012-03-14 | 2012-07-20 | 结构化文档管理装置、结构化文档检索方法 |
| US13/845,878 US20130268554A1 (en) | 2012-03-14 | 2013-03-18 | Structured document management apparatus and structured document search method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-057240 | 2012-03-14 | ||
| JP2012057240A JP5417471B2 (ja) | 2012-03-14 | 2012-03-14 | 構造化文書管理装置、構造化文書検索方法 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/845,878 Continuation US20130268554A1 (en) | 2012-03-14 | 2013-03-18 | Structured document management apparatus and structured document search method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013136545A1 true WO2013136545A1 (ja) | 2013-09-19 |
Family
ID=49160504
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2012/068505 Ceased WO2013136545A1 (ja) | 2012-03-14 | 2012-07-20 | 構造化文書管理装置、構造化文書検索方法 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20130268554A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5417471B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN103415850A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2013136545A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10157175B2 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2018-12-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | Business intelligence data models with concept identification using language-specific clues |
| US10698924B2 (en) | 2014-05-22 | 2020-06-30 | International Business Machines Corporation | Generating partitioned hierarchical groups based on data sets for business intelligence data models |
| US10002179B2 (en) | 2015-01-30 | 2018-06-19 | International Business Machines Corporation | Detection and creation of appropriate row concept during automated model generation |
| US9984116B2 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2018-05-29 | International Business Machines Corporation | Automated management of natural language queries in enterprise business intelligence analytics |
| CN105912585A (zh) * | 2016-04-01 | 2016-08-31 | 乐视控股(北京)有限公司 | 一种邮件搜索方法及装置 |
| CN106407330A (zh) * | 2016-09-04 | 2017-02-15 | 乐视控股(北京)有限公司 | 一种电子邮件的显示方法及装置 |
| US10657158B2 (en) * | 2016-11-23 | 2020-05-19 | Google Llc | Template-based structured document classification and extraction |
| CN107391535B (zh) * | 2017-04-20 | 2021-01-12 | 创新先进技术有限公司 | 在文档应用中搜索文档的方法及装置 |
| JP6710007B1 (ja) * | 2019-04-26 | 2020-06-17 | Arithmer株式会社 | 対話管理サーバ、対話管理方法、及びプログラム |
| CN110175322A (zh) * | 2019-05-22 | 2019-08-27 | 北京神州泰岳软件股份有限公司 | 一种文档的结构化方法及装置 |
| CN110688842B (zh) * | 2019-10-14 | 2023-06-09 | 鼎富智能科技有限公司 | 一种文档标题层级的分析方法、装置及服务器 |
| US11663215B2 (en) | 2020-08-12 | 2023-05-30 | International Business Machines Corporation | Selectively targeting content section for cognitive analytics and search |
| CN113204579B (zh) * | 2021-04-29 | 2024-06-07 | 北京金山数字娱乐科技有限公司 | 内容关联方法、系统、装置、电子设备及存储介质 |
| CN113408660B (zh) * | 2021-07-15 | 2024-05-24 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | 图书聚类方法、装置、设备和存储介质 |
| CN116894176A (zh) * | 2023-07-27 | 2023-10-17 | 国网江苏省电力有限公司经济技术研究院 | 一种面向输变电工程设计文档的指标提取优化方法和系统 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003242175A (ja) * | 2002-02-15 | 2003-08-29 | Ricoh Co Ltd | 文書検索システム、文書検索方法、その方法によったプログラムおよびそのプログラムを記憶した記憶媒体 |
| JP2004126770A (ja) * | 2002-09-30 | 2004-04-22 | Toshiba Corp | 構造化文書検索方法、構造化文書検索システム及び構造化文書データベース管理装置 |
| JP2006195667A (ja) * | 2005-01-12 | 2006-07-27 | Toshiba Corp | 構造化文書検索装置、構造化文書検索方法、及び構造化文書検索プログラム |
| JP2008146209A (ja) * | 2006-12-07 | 2008-06-26 | Just Syst Corp | 文書検索装置、文書検索方法および文書検索プログラム |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6385602B1 (en) * | 1998-11-03 | 2002-05-07 | E-Centives, Inc. | Presentation of search results using dynamic categorization |
| US7587381B1 (en) * | 2002-01-25 | 2009-09-08 | Sphere Source, Inc. | Method for extracting a compact representation of the topical content of an electronic text |
| US20060150076A1 (en) * | 2004-12-30 | 2006-07-06 | Microsoft Corporation | Methods and apparatus for the evaluation of aspects of a web page |
| US7546294B2 (en) * | 2005-03-31 | 2009-06-09 | Microsoft Corporation | Automated relevance tuning |
| US20070150473A1 (en) * | 2005-12-22 | 2007-06-28 | Microsoft Corporation | Search By Document Type And Relevance |
| JP2007206822A (ja) * | 2006-01-31 | 2007-08-16 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | 文書管理システム、文書廃棄管理システム、文書管理方法および文書廃棄管理方法 |
| US7779370B2 (en) * | 2006-06-30 | 2010-08-17 | Google Inc. | User interface for mobile devices |
| US9218414B2 (en) * | 2007-02-06 | 2015-12-22 | Dmitri Soubbotin | System, method, and user interface for a search engine based on multi-document summarization |
| US20090055386A1 (en) * | 2007-08-24 | 2009-02-26 | Boss Gregory J | System and Method for Enhanced In-Document Searching for Text Applications in a Data Processing System |
| US8538989B1 (en) * | 2008-02-08 | 2013-09-17 | Google Inc. | Assigning weights to parts of a document |
| JP5355949B2 (ja) * | 2008-07-16 | 2013-11-27 | 株式会社東芝 | 次検索キーワード提示装置、次検索キーワード提示方法、及び次検索キーワード提示プログラム |
| GB2472250A (en) * | 2009-07-31 | 2011-02-02 | Stephen Timothy Morris | Method for determining document relevance |
| US8209361B2 (en) * | 2010-01-19 | 2012-06-26 | Oracle International Corporation | Techniques for efficient and scalable processing of complex sets of XML schemas |
| US8140512B2 (en) * | 2010-04-12 | 2012-03-20 | Ancestry.Com Operations Inc. | Consolidated information retrieval results |
| US8504567B2 (en) * | 2010-08-23 | 2013-08-06 | Yahoo! Inc. | Automatically constructing titles |
-
2012
- 2012-03-14 JP JP2012057240A patent/JP5417471B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2012-07-20 WO PCT/JP2012/068505 patent/WO2013136545A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2012-07-20 CN CN2012800029691A patent/CN103415850A/zh active Pending
-
2013
- 2013-03-18 US US13/845,878 patent/US20130268554A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003242175A (ja) * | 2002-02-15 | 2003-08-29 | Ricoh Co Ltd | 文書検索システム、文書検索方法、その方法によったプログラムおよびそのプログラムを記憶した記憶媒体 |
| JP2004126770A (ja) * | 2002-09-30 | 2004-04-22 | Toshiba Corp | 構造化文書検索方法、構造化文書検索システム及び構造化文書データベース管理装置 |
| JP2006195667A (ja) * | 2005-01-12 | 2006-07-27 | Toshiba Corp | 構造化文書検索装置、構造化文書検索方法、及び構造化文書検索プログラム |
| JP2008146209A (ja) * | 2006-12-07 | 2008-06-26 | Just Syst Corp | 文書検索装置、文書検索方法および文書検索プログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013191046A (ja) | 2013-09-26 |
| CN103415850A (zh) | 2013-11-27 |
| JP5417471B2 (ja) | 2014-02-12 |
| US20130268554A1 (en) | 2013-10-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5417471B2 (ja) | 構造化文書管理装置、構造化文書検索方法 | |
| US9910932B2 (en) | System and method for completing a user query and for providing a query response | |
| US10073913B2 (en) | System and method for displaying of most relevant vertical search results | |
| CN110362727B (zh) | 用于搜索系统的第三方搜索应用 | |
| US9940387B2 (en) | Search query generation using query segments and semantic suggestions | |
| US9965569B2 (en) | Truncated autosuggest on a touchscreen computing device | |
| US8527507B2 (en) | Custom ranking model schema | |
| US20160179816A1 (en) | Near Real Time Auto-Suggest Search Results | |
| US9519703B2 (en) | Refining search results for a compound search query | |
| US20120290561A1 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, program, and information processing system | |
| US11347815B2 (en) | Method and system for generating an offline search engine result page | |
| CN104838414A (zh) | 用于电子书的自定义字典 | |
| US10089412B2 (en) | Method of and system for processing a search query | |
| US10078686B2 (en) | Combination filter for search query suggestions | |
| US20150339387A1 (en) | Method of and system for furnishing a user of a client device with a network resource | |
| US20170193119A1 (en) | Add-On Module Search System | |
| WO2013015811A1 (en) | Search query generation using query segments and semantic suggestions | |
| US10496711B2 (en) | Method of and system for processing a prefix associated with a search query | |
| JP5285491B2 (ja) | 情報検索システム、方法及びプログラム、索引作成システム、方法及びプログラム、 | |
| JP5104329B2 (ja) | ドキュメント検索システム | |
| RU2767965C2 (ru) | Способ и система для перевода исходной фразы на первом языке целевой фразой на втором языке | |
| JP2019028927A (ja) | 検索ワードサジェスト装置、検索ワードサジェスト方法、および、検索ワードサジェストプログラム | |
| CN119720157A (zh) | 一种数据访问控制方法、装置、设备、介质及程序产品 | |
| JP2010272082A (ja) | 情報共有システム、情報共有方法、および情報共有プログラム | |
| JP2006072881A (ja) | 文書管理システム、及び、文書管理方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 12871382 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 12871382 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |