WO2013126947A1 - Emulsifiable concentrate formulation - Google Patents
Emulsifiable concentrate formulation Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013126947A1 WO2013126947A1 PCT/AU2013/000164 AU2013000164W WO2013126947A1 WO 2013126947 A1 WO2013126947 A1 WO 2013126947A1 AU 2013000164 W AU2013000164 W AU 2013000164W WO 2013126947 A1 WO2013126947 A1 WO 2013126947A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- solvent
- active ingredient
- miscible
- benzyl acetate
- substantially water
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 127
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 97
- 239000004495 emulsifiable concentrate Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 44
- QUKGYYKBILRGFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl acetate Chemical compound CC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 QUKGYYKBILRGFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 124
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 72
- 229940007550 benzyl acetate Drugs 0.000 claims abstract description 62
- 239000006184 cosolvent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 45
- 239000012868 active agrochemical ingredient Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 27
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 claims description 45
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 claims description 34
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 claims description 29
- -1 ethylene, propylene Chemical group 0.000 claims description 25
- 239000004009 herbicide Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000005507 Diflufenican Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- WYEHFWKAOXOVJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N diflufenican Chemical compound FC1=CC(F)=CC=C1NC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1OC1=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1 WYEHFWKAOXOVJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 15
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 12
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCO LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- TVFWYUWNQVRQRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4-tris(2-phenylethenyl)phenol Chemical class C=1C=CC=CC=1C=CC1=C(C=CC=2C=CC=CC=2)C(O)=CC=C1C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 TVFWYUWNQVRQRG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000002917 insecticide Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- HJOVHMDZYOCNQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N isophorone Chemical compound CC1=CC(=O)CC(C)(C)C1 HJOVHMDZYOCNQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- MEJYDZQQVZJMPP-ULAWRXDQSA-N (3s,3ar,6r,6ar)-3,6-dimethoxy-2,3,3a,5,6,6a-hexahydrofuro[3,2-b]furan Chemical compound CO[C@H]1CO[C@@H]2[C@H](OC)CO[C@@H]21 MEJYDZQQVZJMPP-ULAWRXDQSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000005590 Oxyfluorfen Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- OQMBBFQZGJFLBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxyfluorfen Chemical compound C1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C(OCC)=CC(OC=2C(=CC(=CC=2)C(F)(F)F)Cl)=C1 OQMBBFQZGJFLBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 8
- JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanone Chemical compound O=C1CCCCC1 JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000005906 Imidacloprid Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- YWTYJOPNNQFBPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidacloprid Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)\N=C1/NCCN1CC1=CC=C(Cl)N=C1 YWTYJOPNNQFBPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 229940056881 imidacloprid Drugs 0.000 claims description 7
- LFULEKSKNZEWOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N propanil Chemical compound CCC(=O)NC1=CC=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1 LFULEKSKNZEWOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- KWOLFJPFCHCOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetophenone Chemical compound CC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 KWOLFJPFCHCOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical group C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000003905 agrochemical Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl ether Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1OC1=CC=CC=C1 USIUVYZYUHIAEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000002170 ethers Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCO BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- VKSWWACDZPRJAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dioxepan-2-one Chemical class O=C1OCCCCO1 VKSWWACDZPRJAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 claims description 5
- QMEQBOSUJUOXMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2h-oxadiazine Chemical compound N1OC=CC=N1 QMEQBOSUJUOXMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000005874 Bifenthrin Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004322 Butylated hydroxytoluene Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butylhydroxytoluene Chemical group CC1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000005500 Clopyralid Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000005907 Indoxacarb Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000005587 Oryzalin Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- ISRUGXGCCGIOQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Rhoden Chemical compound CNC(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1OC(C)C ISRUGXGCCGIOQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000005846 Triadimenol Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000003931 anilides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- OMFRMAHOUUJSGP-IRHGGOMRSA-N bifenthrin Chemical compound C1=CC=C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C(C)=C1COC(=O)[C@@H]1[C@H](\C=C(/Cl)C(F)(F)F)C1(C)C OMFRMAHOUUJSGP-IRHGGOMRSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229940095259 butylated hydroxytoluene Drugs 0.000 claims description 4
- 235000010354 butylated hydroxytoluene Nutrition 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000073 carbamate insecticide Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- HUBANNPOLNYSAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N clopyralid Chemical group OC(=O)C1=NC(Cl)=CC=C1Cl HUBANNPOLNYSAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000417 fungicide Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000002363 herbicidal effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- VBCVPMMZEGZULK-NRFANRHFSA-N indoxacarb Chemical compound C([C@@]1(OC2)C(=O)OC)C3=CC(Cl)=CC=C3C1=NN2C(=O)N(C(=O)OC)C1=CC=C(OC(F)(F)F)C=C1 VBCVPMMZEGZULK-NRFANRHFSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- LZGUHMNOBNWABZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-nitro-n-phenylnitramide Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)N([N+]([O-])=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 LZGUHMNOBNWABZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- UNAHYJYOSSSJHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N oryzalin Chemical compound CCCN(CCC)C1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C(S(N)(=O)=O)C=C1[N+]([O-])=O UNAHYJYOSSSJHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- BAZVSMNPJJMILC-UHFFFAOYSA-N triadimenol Chemical compound C1=NC=NN1C(C(O)C(C)(C)C)OC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 BAZVSMNPJJMILC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000003852 triazoles Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- HOKKPVIRMVDYPB-UVTDQMKNSA-N (Z)-thiacloprid Chemical compound C1=NC(Cl)=CC=C1CN1C(=N/C#N)/SCC1 HOKKPVIRMVDYPB-UVTDQMKNSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N D-Glucitol Natural products OC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000005940 Thiacloprid Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000004996 alkyl benzenes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000118 dimethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000002334 glycols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000600 sorbitol Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000015112 vegetable and seed oil Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000008158 vegetable oil Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000005682 diethyl carbonates Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003893 lactate salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000002728 pyrethroid Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000012424 soybean oil Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000003549 soybean oil Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 238000010899 nucleation Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 45
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 24
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 22
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 21
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 21
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 229960001760 dimethyl sulfoxide Drugs 0.000 description 11
- 238000010257 thawing Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 9
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 5
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 231100000419 toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 4
- 230000001988 toxicity Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 3
- QYMFNZIUDRQRSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethyl butanedioate;dimethyl hexanedioate;dimethyl pentanedioate Chemical compound COC(=O)CCC(=O)OC.COC(=O)CCCC(=O)OC.COC(=O)CCCCC(=O)OC QYMFNZIUDRQRSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003759 ester based solvent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000011068 loading method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000575 pesticide Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000021317 phosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 150000003014 phosphoric acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 description 3
- QZSFJRIWRPJUOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethylhexyl 2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetate Chemical compound CCCCC(CC)COC(=O)COC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1Cl QZSFJRIWRPJUOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IDGRPSMONFWWEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethylhexyl 2-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)acetate Chemical compound CCCCC(CC)COC(=O)COC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1C IDGRPSMONFWWEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 description 2
- 241000238631 Hexapoda Species 0.000 description 2
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000004945 aromatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 159000000007 calcium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000004359 castor oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019438 castor oil Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 125000000753 cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N glycerol triricinoleate Natural products CCCCCC[C@@H](O)CC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](COC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@@H](O)CCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@H](O)CCCCCC ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 231100000053 low toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 239000004530 micro-emulsion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007764 o/w emulsion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008520 organization Effects 0.000 description 2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002798 polar solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012430 stability testing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910021653 sulphate ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 231100000440 toxicity profile Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 241000238876 Acari Species 0.000 description 1
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- REIYHFWZISXFKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyl acetoacetate Chemical compound CCCCOC(=O)CC(C)=O REIYHFWZISXFKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical group [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000233866 Fungi Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000237852 Mollusca Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000244206 Nematoda Species 0.000 description 1
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000283973 Oryctolagus cuniculus Species 0.000 description 1
- ULUAUXLGCMPNKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfobutanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(C(O)=O)S(O)(=O)=O ULUAUXLGCMPNKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 231100000230 acceptable toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 229940022663 acetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 231100000460 acute oral toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 231100000293 acute skin toxicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 239000003945 anionic surfactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003466 anti-cipated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- JXLHNMVSKXFWAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N azane;7-fluoro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound N.OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(F)C2=NON=C12 JXLHNMVSKXFWAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001797 benzyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- RRMOCUKULIQWDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanone;1-phenylethanone Chemical compound O=C1CCCCC1.CC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 RRMOCUKULIQWDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QKIUAMUSENSFQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylazanide Chemical compound C[N-]C QKIUAMUSENSFQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YRIUSKIDOIARQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecyl benzenesulfonate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCOS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 YRIUSKIDOIARQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KWKXNDCHNDYVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecylbenzene Chemical class CCCCCCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC=C1 KWKXNDCHNDYVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QYDYPVFESGNLHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N elaidic acid methyl ester Natural products CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC QYDYPVFESGNLHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002193 fatty amides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 244000000013 helminth Species 0.000 description 1
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxyacetaldehyde Natural products OCC=O WGCNASOHLSPBMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000004702 methyl esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QYDYPVFESGNLHU-KHPPLWFESA-N methyl oleate Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OC QYDYPVFESGNLHU-KHPPLWFESA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940073769 methyl oleate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000003094 microcapsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002736 nonionic surfactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019198 oils Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005180 public health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013049 sediment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004062 sedimentation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002689 soil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000013112 stability test Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010998 test method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N25/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators, characterised by their forms, or by their non-active ingredients or by their methods of application, e.g. seed treatment or sequential application; Substances for reducing the noxious effect of the active ingredients to organisms other than pests
- A01N25/02—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators, characterised by their forms, or by their non-active ingredients or by their methods of application, e.g. seed treatment or sequential application; Substances for reducing the noxious effect of the active ingredients to organisms other than pests containing liquids as carriers, diluents or solvents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N25/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators, characterised by their forms, or by their non-active ingredients or by their methods of application, e.g. seed treatment or sequential application; Substances for reducing the noxious effect of the active ingredients to organisms other than pests
- A01N25/02—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators, characterised by their forms, or by their non-active ingredients or by their methods of application, e.g. seed treatment or sequential application; Substances for reducing the noxious effect of the active ingredients to organisms other than pests containing liquids as carriers, diluents or solvents
- A01N25/04—Dispersions, emulsions, suspoemulsions, suspension concentrates or gels
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N25/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators, characterised by their forms, or by their non-active ingredients or by their methods of application, e.g. seed treatment or sequential application; Substances for reducing the noxious effect of the active ingredients to organisms other than pests
- A01N25/30—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators, characterised by their forms, or by their non-active ingredients or by their methods of application, e.g. seed treatment or sequential application; Substances for reducing the noxious effect of the active ingredients to organisms other than pests characterised by the surfactants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N33/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic nitrogen compounds
- A01N33/16—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic nitrogen compounds containing nitrogen-to-oxygen bonds
- A01N33/18—Nitro compounds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N33/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic nitrogen compounds
- A01N33/16—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic nitrogen compounds containing nitrogen-to-oxygen bonds
- A01N33/18—Nitro compounds
- A01N33/20—Nitro compounds containing oxygen or sulfur attached to the carbon skeleton containing the nitro group
- A01N33/22—Nitro compounds containing oxygen or sulfur attached to the carbon skeleton containing the nitro group having at least one oxygen or sulfur atom and at least one nitro group directly attached to the same aromatic ring system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N37/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids
- A01N37/18—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing the group —CO—N<, e.g. carboxylic acid amides or imides; Thio analogues thereof
- A01N37/22—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing the group —CO—N<, e.g. carboxylic acid amides or imides; Thio analogues thereof the nitrogen atom being directly attached to an aromatic ring system, e.g. anilides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N39/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing aryloxy- or arylthio-aliphatic or cycloaliphatic compounds, containing the group or, e.g. phenoxyethylamine, phenylthio-acetonitrile, phenoxyacetone
- A01N39/02—Aryloxy-carboxylic acids; Derivatives thereof
- A01N39/04—Aryloxy-acetic acids; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N41/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a sulfur atom bound to a hetero atom
- A01N41/02—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a sulfur atom bound to a hetero atom containing a sulfur-to-oxygen double bond
- A01N41/04—Sulfonic acids; Derivatives thereof
- A01N41/06—Sulfonic acid amides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/34—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- A01N43/40—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom six-membered rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/48—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with two nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- A01N43/50—1,3-Diazoles; Hydrogenated 1,3-diazoles
- A01N43/52—1,3-Diazoles; Hydrogenated 1,3-diazoles condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. benzimidazoles
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/64—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with three nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- A01N43/647—Triazoles; Hydrogenated triazoles
- A01N43/653—1,2,4-Triazoles; Hydrogenated 1,2,4-triazoles
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N47/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom not being member of a ring and having no bond to a carbon or hydrogen atom, e.g. derivatives of carbonic acid
- A01N47/08—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom not being member of a ring and having no bond to a carbon or hydrogen atom, e.g. derivatives of carbonic acid the carbon atom having one or more single bonds to nitrogen atoms
- A01N47/10—Carbamic acid derivatives, i.e. containing the group —O—CO—N<; Thio analogues thereof
- A01N47/22—O-Aryl or S-Aryl esters thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N47/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom not being member of a ring and having no bond to a carbon or hydrogen atom, e.g. derivatives of carbonic acid
- A01N47/08—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom not being member of a ring and having no bond to a carbon or hydrogen atom, e.g. derivatives of carbonic acid the carbon atom having one or more single bonds to nitrogen atoms
- A01N47/28—Ureas or thioureas containing the groups >N—CO—N< or >N—CS—N<
- A01N47/38—Ureas or thioureas containing the groups >N—CO—N< or >N—CS—N< containing the group >N—CO—N< where at least one nitrogen atom is part of a heterocyclic ring; Thio analogues thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N47/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom not being member of a ring and having no bond to a carbon or hydrogen atom, e.g. derivatives of carbonic acid
- A01N47/40—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom not being member of a ring and having no bond to a carbon or hydrogen atom, e.g. derivatives of carbonic acid the carbon atom having a double or triple bond to nitrogen, e.g. cyanates, cyanamides
- A01N47/42—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom not being member of a ring and having no bond to a carbon or hydrogen atom, e.g. derivatives of carbonic acid the carbon atom having a double or triple bond to nitrogen, e.g. cyanates, cyanamides containing —N=CX2 groups, e.g. isothiourea
- A01N47/44—Guanidine; Derivatives thereof
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N51/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds having the sequences of atoms O—N—S, X—O—S, N—N—S, O—N—N or O-halogen, regardless of the number of bonds each atom has and with no atom of these sequences forming part of a heterocyclic ring
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N53/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing cyclopropane carboxylic acids or derivatives thereof
Definitions
- the invention relates to an emulsifiable concentrate (EC) formulation of agrochemical active ingredients utilising an improved solvent system comprising benzyl acetate as a primary solvent in combination with other co-solvents. More preferably, the improved solvent system provides a substantially storage-stable and dilution-stable emulsifiable concentrate (EC) formulation.
- agrochemical active ingredient in the art of formulating agrochemicals, it is often necessary to dissolve the agrochemical active ingredient in a solvent and then dilute it in a larger volume of water in order for it to be broadcast in the form of a fine spray. In still other cases, it is necessary to dilute the active ingredient in a solution and apply it to a seed or other solid carrier. While some active ingredients, which arc usually in the form of a salt, can be simply dissolved and then diluted in water, the majority of agrochemical active ingredients are hydrophobic and are therefore not water-soluble.
- EW Emulsion- in- Water
- ME Microemulsion
- Water-immiscible solvents commonly used for EC and EW formulations include, but are not limited to, aromatic hydrocarbons such as the SOLVESSO® series, paraffinic hydrocarbons such as the EXXSOL ® range, ester solvents such as the EXXATE® range, all of which arc manufactured by EXXONMOBIL, and ester solvents such as methyloleate.
- aromatic hydrocarbons such as the SOLVESSO® series
- paraffinic hydrocarbons such as the EXXSOL ® range
- ester solvents such as the EXXATE® range, all of which arc manufactured by EXXONMOBIL
- ester solvents such as methyloleate.
- solvents which are water-immiscible at high concentration include cyclic hydrocarbons, such as cyclohexanone and isophorone. In more recent times, solvents which exhibit improved toxicity and reduced flammability profiles have been used.
- dibasic ester solvents of long chain di-acids having from 8-16 carbon units which are usually methyl ester derivatives
- fatty acid amide solvents examples of which are the dimethylamide and morpholineamidc derivatives of Ce-Cjfi fatty acids.
- Mono-alkylene carbonates such as ethylene, propylene and butylene carbonates, also find use as co-solvents.
- Such active ingredients include, but are not limited to, pyridine- based herbicides such as clopyralid and diflufenican; diphenylether herbicides such as oxyfluorfen; anilide herbicides such as propanil; triazole fungicides such as triadimenol; dinitroaniline herbicides such as oryzalin; carbamate insecticides such as propoxur; oxadiazine insecticides such as indoxacarb; synthetic pyrethroid insecticides such as bifenthrin; and neonicotinoid insecticides such as imidacloprid and thiocloprid.
- pyridine- based herbicides such as clopyralid and diflufenican
- diphenylether herbicides such as oxyfluorfen
- anilide herbicides such as propanil
- triazole fungicides such as triadimenol
- dinitroaniline herbicides
- benzyl acetate as a solvent for agrochemical active ingredients is known.
- Japanese Patent Application No. JP 2009J 73569A teaches the use of benzyl acetate and butylacetoacetate in combination with a water-miscible co-solvent, l ,3-dimethyl-2- imidazolidinone and an aromatic hydrocarbon to prepare emulsion compositions of various hydrophobic agrochemical active ingredients up to 50 weight/volume %.
- International Patent Publication No. WO 20 U/017480 teaches the use of benzyl acetate as a suitable solvent for dissolving certain active ingredients in preparation for forming microcapsule compositions.
- the present invention seeks to provide an improved solvent system for high concentration emulsifiable concentrate formulations that at least ameliorates certain disadvantages associated with previously known solvent systems.
- an emulsifiable concentrate (EC) formulation comprising a least one agrochemical active ingredient; at least one surfactant emulsifier; optionally, a stabiliser; and a primary solvent system, wherein the solvent system comprises a combination of benzyl acetate and a sufficient amount of at least one polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent.
- EC emulsifiable concentrate
- the solvent system comprises a combination of benzyl acetate and a sufficient amount of at least one polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent.
- benzyl acetate when used with polar, substantially water-miscible co- solvents, for example, _V-methyl pryrrolidinone and dimethylsulphoxide, benzyl acetate is able to afford formulations, which are both stable in concentrate form and stable to crystallisation upon dilution in water. That is, benzyl acetate is able to substantially overcome the problem of crystallization on dilution which is often associated with using polar, substantially water-miscible solvents as co-solvents to achieve the desired solubility in the concentrate.
- polar, substantially water-miscible co- solvents for example, _V-methyl pryrrolidinone and dimethylsulphoxide
- the ratio of benzyl acetate to the water-miscible co-solvent is preferably in the mixing range of from 99.9:0.1 to 40:60 and more preferably, in the range of from 90:10 to 60:40.
- the at least one substantially water-miscible co-solvent is preferably selected from the group of -V-methylpyrrolidinone (NMP); dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO); dimethylformamide (DMF); dimethylisosorbide (DMI); isophorone; acetophenone; cyclohcxanone; l,3-dimethyl-2-imida-iolidonone; ethylene, propylene and butylene carbonates; lactate esters; dimethyl and diethyicarbonates; alkylglycol ethers; glycols including propylene glycol, ethylene glycol and polyethylene glycols; alcohols including methanol; ethanol; wo-propanol; n-propanol; n-butanol; ijo-butanol; and terf-butanol; or mixtures thereof.
- NMP -V-methylpyrrolidinone
- DMSO dimethylsulphoxide
- DMF dimethylformamide
- the active ingredient is preferably selected from a pesticide or an herbicide, such as from pyridine-based herbicides; diphenylether herbicides; anilide herbicides; dinitroaniline herbicides; triazole fungicides; carbamate insecticides; oxadiazine insecticides; and neonicotinoid insecticides; or mixtures thereof.
- a pesticide or an herbicide such as from pyridine-based herbicides; diphenylether herbicides; anilide herbicides; dinitroaniline herbicides; triazole fungicides; carbamate insecticides; oxadiazine insecticides; and neonicotinoid insecticides; or mixtures thereof.
- the active ingredient is selected from clopyralid, diflufenican, oxyfluorfen, propanil, triadimenol, oryzalin, propoxur, bifenthrin, indoxacarb, imidacloprid and thiacloprid, or mixtures thereof.
- the active ingredient is diflufenican present at greater than 2% weight/volume.
- the formulation of the present invention further comprises a phenoxyacid ester herbicide.
- the at least one surfactant emulsifier used in the EC formulation is selected from the group comprising alkoxylated alcohols; alkoxylated alkylphenols; ethoxylatcd fatty acids; ethoxylated vegetable oils; ethoxylated tristyrylphenol; fatty acid esters of sorbitol and ethoxylated derivatives thereof; ethoxylated amines and condensates of glycerol; sulfonated alkylbenzenes in the range Cn-Cie and salts thereof; alkylether sulphates; alkyletherphosphatcs; alkylphenoletherphosphates; or combinations thereof; salts of phosphate esters of ethoxylated tristyrylphenol; salts of sulphated ethers of ethoxylated tristyrylphenol; or a catanionic system, wherein a cationic amine is present in combination with an alky
- the EC formulation of the present invention preferably further comprises a stabiliser, selected from butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) and epoxidized soybean oil (ESBO).
- BHT butylated hydroxytoluene
- ESBO epoxidized soybean oil
- the stabiliser is preferably present in a concentration of up to 3% weight/volume and is more preferably added to the formulation once the active ingredient is dissolved in the solvent system.
- Combinations of benzyl acetate with polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvents have been found to have good utility with certain crystalline active ingredients including, but not limited to, pyridine-based herbicides such as clopyralid and diflufenican; diphcnylether herbicides such as oxyfluorfen; anilide herbicides such as propanil; triazole fungicides such as triadimenol; dinitroaniline herbicides such as oryzalin; carbamate insecticides such as propoxur; oxadiazine insecticides such as indoxacarb; and neonicotinoid insecticides such as imidacloprid and thiacloprid.
- pyridine-based herbicides such as clopyralid and diflufenican
- diphcnylether herbicides such as oxyfluorfen
- anilide herbicides such as propanil
- triazole fungicides
- the present invention is directed to a method of making an emulsifiable concentrate (EC) formulation of at least one agrochemical active ingredient comprising the following steps of either firstly forming a mixture of the agrochemical active ingredient in a polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent and then adding benzyl acetate; or alternatively forming a mixture of the agrochemical active ingredient in benzyl acetate and then adding a polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent; or alternatively forming a mixture of the agrochemical active ingredient in a combination of benzyl acetate and a polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent; or alternatively combining the agrochemical active ingredient, benzyl acetate and a polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent; followed by adding at least one suitable emulsifier/s and/or at least one stabilizer/s to make an EC formulation, whereby the active ingredient is
- the present invention is also directed to a method of making an emulsion-in-water (EW) formulation comprising at least one agrochemical active ingredient, the method comprising the following steps of either firstly, forming a mixture of the agrochemical active ingredient in a polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent and then adding benzyl acetate; or alternatively forming a mixture of the agrochemical active ingredient in benzyl acetate and then adding a polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent; or alternatively forming a mixture of the agrochemical active ingredient in a combination of benzyl acetate and a polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvent; or alternatively, combining the agrochemical active ingredient, benzyl acetate and a polar, substantially water-miscible co- solvent; followed by adding at least one suitable surfactant emulsifier/s and/or at least one stabilizer/s to make an emulsif
- a further advantage in using benzyl acetate solvent is that it is relatively cheap compared to many of the specialty solvents, which may be able to achieve high loading formulations of similar strength.
- An additional advantage is that benzyl acetate has a low odour.
- benzyl acetate together with other co-solvents can usefully be emulsified together with one or more desired active ingredients using conventional surfactants known to be useful as emulsifiers for agrochemical formulations, such as EC formulations.
- the benzyl acetate solvent does not require any specialized cmulsificr systems to achieve a stable emulsion upon dilution.
- TLV as TWA ppm 10 Benzyi acetate shows relatively low toxicity.
- DMSO dimethylsulphoxide
- DMF dimethylformamide
- DI dimethylisosorbide
- isophovone acetophenone and cyclohexanone and various lactate ester derivatives.
- An EC formulation is preferably diluted in water at rates ranging from 0.1 to 20% w/v and more preferably, in the range of 0.5 to 5% w/v.
- Typical time standards 10 for dilution stability of active ingredients are set out by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and may be found in the various technical monographs prepared by them.
- FEO Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
- a sufficient amount of benzyl actctatc is used in combination with a sufficient amount of at least one polar, substantially watcr- miscible co-solvent such as, for example, NMP, DMI or DMSO, as the primary solvent system, sufficient solubility to certain crystalline active ingredients is afforded to maintain JO stability of the emulsifiable concentrate (EC) formulation, whilst also affording stability on dilution in water regarding crystallisation.
- the term "primary solvent” as used herein is a solvent or combination of solvents which must be present to dissolve the active ingredient.
- non-primary solvent is a solvent which may optionally also be present in the solvent system, but which is not required for the purposes of dissolving the active ingredient.
- a non-primary solvent may incidentally be present in emulsifier blends, or as an agent, which adds additional features or characteristics, such as colour, stability or viscosity to the overall formulation. In general, if less than about 1 % of a non-primary solvent is present, such a solvent will not function as part of the primary solvent system.
- the polar, substantially water-miscible co-solvents useful in the present invention preferably include, but are not limited to: N-methylpyrroIidinone (NMP) dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO); dimethylformamide (DMF); dimethylisosorbide ( MI); isophorone; acetophenone cyclohexanone; l,3-dimemyl-2-i broadlydazol-donone; ethylene, propylene and butylene carbonates; dimethyl and diethylcarbonates; alkylglycol ethers; glycols such as propylene glycol, ethylene glycol and polyethylene glycols; alcohols such as methanol, cthanol, wo-propanol, n-propanol, n-butanol, /sobutanol and 1 ⁇ 2rf-butanol.
- NMP N-methylpyrroIidinone
- DMSO dimethylsulphoxide
- DMF dimethylform
- agrochemical active or "agrochemically active” as used herein arc intended to also cover all the related uses of the EC formulations, such as in animal health, public health, water treatment, wood treatment, home garden and domestic vector control.
- the agrochemical active ingredients useful in the present invention preferably include those as listed in The Pesticide Manual of the British Crop Protection Council (14 ⁇ Edition), which are soluble in polar, substantially water-mimiscible solvents.
- the active ingredient s and EC formulation s wherein there is advantageous dilution performance in regard to a lack of crystallisation than would otherwise be observed in the absence of benzyl acetate, preferably include/s, but is/are not limited to, diflufenican alone or diflufenican in the presence of phenoxyacid ester herbicide, oxyfluorfen, propanil and/or imidacloprid.
- Benzyl acetate is preferably used with the substantially water-miscible co-solvent in a ratio range of from 99-9:0.1 to 40:60, more preferably, in the range of from 90:10 to 60:40, as the primary solvent system.
- the present invention may further comprise one or more substantially water-immiscible or partially water-irnrniscible co-solvent/s as a non-primary solvent, so long as such a solvent is not present in sufficient quantity to re-induce crystallisation of the active ingredient upon dilution in water or storage.
- the water-immiscible co-solvent is present at no more than 10% w/v in the total formulation used.
- the agrochemical formulations of the present invention are preferably applied to plant leaves as foliar sprays, or to plant shoots and the surrounding soil. Such formulations may also be applied to animals, either topically, orally or as injectables. They may also be applied directly to insects, acarina, fungi, molluscs, nematodes and helminths, to wood and wood products and as a component of mixtures applied as coatings for buildings, insect protection nets and so on.
- composition of the active ingredient/s made using the primary solvent combination is preferably formulated as an emulsifiable concentrate (EC), or also as an oil-in-water emulsion (EW) made from such a concentrate.
- EC emulsifiable concentrate
- EW oil-in-water emulsion
- additives such as emulsifiers and stabilisers are preferably used.
- Such additives may add or subtract from the total solubility level of the active ingredient/s depending upon what is used.
- surfactant emulsifiers containing a salt of dodecylbenzene sulphonate, such as the calcium salt or one or more amine salts preferably contain additional solvents, like short chain alcohols, which enhance overall solubility.
- the addition of emulsifiers may dilute the total level of the active ingredient in the formulation.
- the active ingredient/s is/are dissolved in the benzyl acetate/substantially water-miscible co-solvent combination and surfactant emulsifiers are added in the range 3 - 20% w/v and the formulation made up to the required volume.
- further co- solvents which may be substantially water-miscible or partially water-miscible may be added.
- Such optional co-solvents preferably include, but are not limited to, a cyclic hydrocarbon/s such as cyclohexanone and isopherone; mono-alkylene carbonates, such as ethylene, propylene and butylene carbonates; or dibasic esters.
- Emulsifiers for the EC formulations preferably include, but arc not limited to, non-ionic surfactants, such as alkoxylated alcohols and alkoxylated alkylphenols; ethoxylated fatty acids; ethoxylated vegetable oils such as ethoxylated castor oil; ethoxylated tristyrylphenol: fatty acid esters of sorbitol and ethoxylated derivatives thereof; ethoxylated amines, and condensates of glycerol.
- non-ionic surfactants such as alkoxylated alcohols and alkoxylated alkylphenols
- ethoxylated fatty acids such as ethoxylated vegetable oils such as ethoxylated castor oil
- ethoxylated tristyrylphenol fatty acid esters of sorbitol and ethoxylated derivatives thereof
- ethoxylated amines and condensates of gly
- Anionic surfactants such as salts of sulphonated dodecylbenzene and other alkylbenzenes in the range Cn-Ci6 and salts thereof; alkylether sulphates; and ether phosphates including alkyletherphosphates; alkylphenoletherphosphates; or combinations thereof; salts of phosphate esters of ethoxylated tristyrylphenol and salts of sulphated ethers of ethoxylated tristyrylphenol, can be used as emulsifiers.
- Catanionic systems where a cationic amine is present in combination with an alkylsulphonate, an alkylethersulphonate, an ether sulphate or an ether phosphate such as alkyletherphosphate, can also be useful.
- the emulsifiers for EC formulations can be selected from the group of castor oil ethoxylates, in particular TERMUL ® 1284 emulsifier; alkoxylated alcohols, in particular TERMUL® 5459 emulsifier; alkoxylated alkylphenols, in particular TERMUL® 200 emulsifier; ethoxylated amines, in particular TERWET® 3784 and TERIC® 16M15 emulsifiers; ethoxylated tristyrylphenol, in particular TERMUL® 3150 emulsifier; alcohol ethoxylates in particular TERIC ® 12A7, 13A9 and 17A2 emulsifiers; fatty acid ethoxylates such as TERIC ® OF6 emulsifier; sorbitan ester ethoxylates, such as ECOTERIC ® T85 emulsifier; a sulphosuccinate, such as TER
- the EC formulation should, upon dilution, give a stable emulsion free of crystallisation for a sufficient time period, preferably at least two hours, to allow convenient use.
- emulsion stability is usually determined visually by measuring the amount of cream or sediment which forms in a diluted solution of the active ingredient after the required time period.
- the tests required to determine the internationally acceptable standards for stability of EC formulations may be found in the Handbooks as provided by the Collaborative International Pesticides Analytical Council (CIPAC).
- CIPAC Collaborative International Pesticides Analytical Council
- a typical test method used would be CIPAC MT36.3.
- the internationally acceptable standard of emulsion stability, as determined by the CIPAC methods, for various active ingredients are provided by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and may be found in the various technical monographs prepared by them.
- FEO Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
- Example formulations were seeded with at least one crystal of the active ingredient being investigated and stored at 0 ° C for 7 days as per the cold storage stability testing methodology outlined in CIPAC MT39.1 (CIPAC Volume F, l28). On completion of the 7 day storage, the fonnulations were assessed for visible signs of crystal growth.
- Example formulations were stored at 54 C for 14 days as per tfie accelerated storage stability testing methodology outlined in CIPAC MT46.1.3 (CIPAC Volume F, pl50). Following 14 days storage, the formulations were assessed for stability, paying particular note to sedimentation or separation.
- Example formulations were evaluated according to CIPAC T36.1.1 (CIPAC volume F, pl08) at ambient temperature. The volume percent of cream and the presence or otherwise of crystals after 0.5, 1, 2, and 24 hours was observed and recorded for a 5 in 100 parts dilution. The emulsion tubes were subsequently inverted 10 times and a final reassessment was made at 24.5 hours. The purpose of the emulsion test in this instance is to look for the development of crystals upon dilution. An effort was not made to fully optimize the emulsion performance with respect to cream and oil separation. 25g L DIFLUFENICAN
- Example 4 Comparative Example
- Example 1 the formulation was made to the required volume with Solvesso ® 150, and then stirred over moderate heat (approx. 60 * C) for 15 minutes until it was homogenous.
- Example 1 containing benzyl acetate in combination with the substantially water-miscible co-solvent, was able to overcome the problem of crystallisation upon dilution caused by reliance on the substantially water-miscible co-solvent, while still being sufficiently polar to maintain the solubility of the active ingredient in the concentrate.
- Example 5 the formulation was made to the required volume with Solvesso ® 150, and stirred over moderate heat (approx. 60 ° C) for 15 minutes until homogenous. Storage Stability Results
- Example 5 although stable after storage at O'C for 7 days, both show trace crystallisation upon dilution in water to form the emulsion after 24 hours. It is evidenced however that Example 5, comprising benzyl acetate in combination with a substantially water misciblc co-solvent, shows a 67.5% decrease in the 5 average level of precipitate when compared to Example 6.
- Example 7 the formulation was made up to the required volume with Solvesso ® ) 1 0, and stirred over moderate heat (approx. 60 ° C) for 15 minutes until homogenous. Storage Stability Results
- Crystal growth Crystals crystal growth. Crystals at 0 ° C for 7 days
- Example 7 Although stable after storage at 0°G for 7 days, both show trace crystallisation upon dilution in water to form the emulsion after 24 hours. It is evidenced however that Example 7, comprising benzyl acetate in combination with a substantially water misciblc co-solvent, shows a 25.7% decrease in the average level of precipitate when compared to Example 8.
- Example 5 the formulation was made to volume with xylene, and stirred over moderate heat (approx. 60 ° C) for 15 minutes until homogenous.
- Example 9 containing benzyl acetate in combination with the substantially water-miscible co-solvent, was able to overcome the problem of crystallisation upon dilution caused by reliance on the substantially water-miscible co-solvent, while still being sufficiently polar to maintain the solubility of the active in the 5 concentrate.
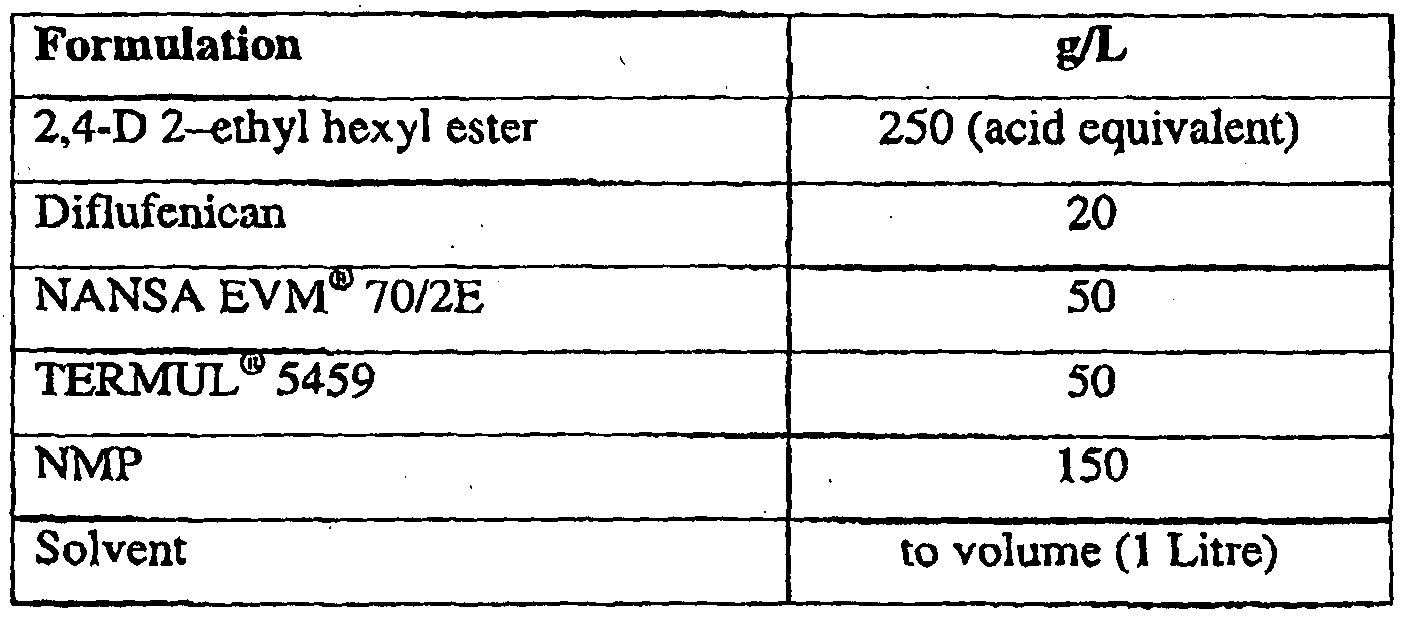
- oxyfluorfen was weighed, followed by the addition of 33g L of TERIC ® 200, 14g L of TERIC ® 16M15 and 58.5g/L NA SA ® EVM 70/2E. The formulation was then made to volume with benzyl acetate, and stirred over .5 moderate heat (approx. 60 ° C) for 15 minutes until homogenous.
- Example 11 150g L NMP was added and made up to volume with Solvesso ® 150, and then stirred over moderate heat (approx. 60 ° C) for 15 minutes until homogenous.
- Example 11 150g L NMP was added and made to volume with benzyl acetate, and then stirred over moderate heat (approx. 60 ° C) for 15 minutes until homogenous. Storage Stability Results
- Crystals growth Crystals 0°C for 7 days Crystals insoluble on
- Example 14 the formulation was made to volume with a 10:90 blend of DMSO/benzyl acetate, and stined over moderate heat (approx. 60 ° C) for 15 minutes until homogenous.
- Example 15 is potentially a useable formulation.
- Example 16 50g/L of DMSO was added and the formulation was made to the
- JEFFSOL ® AG 1710 250g/L JEFFSOL ® AG 1710 was added and the formulation was made to the required volume with benzyl acetate, and stirred over moderate heat (approx. 60 * C) for 15 minutes until homogenous.
- JEFFSOL ® AG 1710 is a dibasic ester solvent which is not substantially water miscible. W
- Example 17 containing benzyl acetate in combination with the substantially water-miscible co-solvent, was able to overcome the problem of crystallisation upon dilution caused by reliance on the substantially water-miscible co-solvent, while still being sufficiently polar to maintain the solubility of the active ingredient in the concentrate.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- Plant Pathology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Pest Control & Pesticides (AREA)
- Agronomy & Crop Science (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Agricultural Chemicals And Associated Chemicals (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA2861558A CA2861558C (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | Agrochemical emulsifiable concentrate formulations using solvent system having benzyl acetate |
| AU2013225608A AU2013225608B2 (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | Emulsifiable concentrate formulation |
| JP2014557945A JP6227566B2 (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | Emulsifying thick preparation |
| MX2014009955A MX367453B (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | Emulsifiable concentrate formulation. |
| CN201380009802.2A CN104125772A (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | EC formulations |
| EP13754349.2A EP2819513B1 (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | Emulsifiable concentrate formulation |
| US14/377,322 US9781921B2 (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | Emulsifiable concentrate formulation |
| ES13754349.2T ES2639188T3 (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | Emulsifiable concentrate formulation |
| BR112014019372-0A BR112014019372B1 (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | FORMULATION, AND, METHOD OF OBTAINING A FORMULATION |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AU2012900731A AU2012900731A0 (en) | 2012-02-27 | Emulsifiable concentrate formulation | |
| AU2012900731 | 2012-02-27 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013126947A1 true WO2013126947A1 (en) | 2013-09-06 |
Family
ID=49081454
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/AU2013/000164 WO2013126947A1 (en) | 2012-02-27 | 2013-02-25 | Emulsifiable concentrate formulation |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9781921B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2819513B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6227566B2 (en) |
| CN (2) | CN104125772A (en) |
| AR (1) | AR090149A1 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2013225608B2 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112014019372B1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2861558C (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2639188T3 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX367453B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2013126947A1 (en) |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104106565A (en) * | 2013-10-21 | 2014-10-22 | 曾立雄 | Novel water-emulsion type solvent capable of replacing xylene |
| WO2016109641A1 (en) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-07 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Fungicidal compositions |
| WO2016176742A1 (en) * | 2015-05-07 | 2016-11-10 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Emulsifiable concentrate comprising a phenoxy-alkanoic acid herbicide |
| WO2017156751A1 (en) | 2016-03-17 | 2017-09-21 | Dow Global Technologies Llc | Emulsifiable concentrates |
| WO2019215613A1 (en) | 2018-05-07 | 2019-11-14 | Adama Agan Ltd. | Stable phytoene desaturase inhibitor herbicide formulation |
| US10772323B2 (en) | 2015-05-07 | 2020-09-15 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Benzoic acid herbicide composition |
| WO2021012173A1 (en) * | 2019-07-23 | 2021-01-28 | Jiangsu Rotam Chemistry Co., Ltd. | Emulsifiable concentrate formulations and their uses |
| WO2021158421A1 (en) * | 2020-02-06 | 2021-08-12 | Dow Global Technologies Llc | Tebuconazole formulations |
| US11116207B2 (en) | 2015-05-07 | 2021-09-14 | Nufarm Autralia Limited | Emulsifiable concentrate comprising picolinic acid herbicide |
| WO2023208447A1 (en) * | 2022-04-25 | 2023-11-02 | Basf Se | An emulsifiable concentrate having a (substituted) benzaldehyde-based solvent system |
| WO2025094190A1 (en) * | 2023-10-19 | 2025-05-08 | Parijat Industries (India) Private Limited | A stable insecticidal composition comprising dinotefuran and bifenthrin |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2978946A1 (en) * | 2015-03-18 | 2016-09-22 | Ag Precision Formulators | Emulsifiable concentrate liquid compositions and methods |
| CN106857550B (en) * | 2015-12-11 | 2019-11-12 | 沈阳中化农药化工研发有限公司 | It is a kind of containing the fungicide for stablizing component |
| WO2019186575A1 (en) * | 2018-03-28 | 2019-10-03 | Parijat Industries (India) Private Limited | A pesticidal emulsifiable concentrate formulation |
| AU2019100546B4 (en) * | 2018-12-20 | 2019-10-03 | Titan Ag Pty Ltd | Agricultural chemical composition |
| CN111066800A (en) * | 2019-12-26 | 2020-04-28 | 安徽久易农业股份有限公司 | Prothioconazole series missible oil and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN116606669B (en) * | 2023-05-31 | 2024-07-02 | 石河子大学 | A solvent for deasphalting cycloalkyl vacuum residue and a solvent deasphalting method |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4452630A (en) * | 1979-07-27 | 1984-06-05 | Montedison S.P.A. | Stable, heat-resistant solutions of pesticidal carbamates |
| EP0839447A1 (en) * | 1996-11-01 | 1998-05-06 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Pesticidal emulsifiable concentrate |
| US5846997A (en) * | 1995-05-05 | 1998-12-08 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Liquid formulations |
| WO2007039215A1 (en) * | 2005-09-29 | 2007-04-12 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Fungicidal composition comprising cyprodinil |
| WO2007068420A1 (en) * | 2005-12-16 | 2007-06-21 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Method for the control of phytopathogenic fungi on soybean |
| WO2007073933A2 (en) * | 2005-12-27 | 2007-07-05 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Herbicidal composition |
| WO2008006456A1 (en) * | 2006-07-13 | 2008-01-17 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Herbicidal composition |
| JP2009173569A (en) | 2008-01-23 | 2009-08-06 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Process for producing bis {2- [2- (4-dibenzo [b, f] [1,4] thiazepin-11-yl-1-piperazinyl) ethoxy] ethanol} monofumarate |
| WO2011017480A2 (en) | 2009-08-07 | 2011-02-10 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Meso-sized capsules useful for the delivery of agricultural chemicals |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB8617741D0 (en) * | 1986-07-21 | 1986-08-28 | May & Baker Ltd | Compositions of matter |
| US5444078A (en) | 1993-10-01 | 1995-08-22 | Rohm And Haas Company | Fully water-dilutable microemulsions |
| AR032844A1 (en) | 2001-02-26 | 2003-11-26 | Syngenta Participations Ag | HERBICIDE COMPOSITION |
| CA2619018A1 (en) | 2005-09-05 | 2007-03-15 | Cheminova A/S | Concentrated liquid triazole-fungicide formulations |
| JP5233293B2 (en) * | 2008-01-25 | 2013-07-10 | 住友化学株式会社 | Emulsion composition |
-
2013
- 2013-02-25 AU AU2013225608A patent/AU2013225608B2/en active Active
- 2013-02-25 CA CA2861558A patent/CA2861558C/en active Active
- 2013-02-25 EP EP13754349.2A patent/EP2819513B1/en active Active
- 2013-02-25 ES ES13754349.2T patent/ES2639188T3/en active Active
- 2013-02-25 BR BR112014019372-0A patent/BR112014019372B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2013-02-25 JP JP2014557945A patent/JP6227566B2/en active Active
- 2013-02-25 MX MX2014009955A patent/MX367453B/en active IP Right Grant
- 2013-02-25 CN CN201380009802.2A patent/CN104125772A/en active Pending
- 2013-02-25 US US14/377,322 patent/US9781921B2/en active Active
- 2013-02-25 CN CN201810543208.6A patent/CN108552171B/en active Active
- 2013-02-25 WO PCT/AU2013/000164 patent/WO2013126947A1/en active Application Filing
- 2013-02-26 AR ARP130100573A patent/AR090149A1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4452630A (en) * | 1979-07-27 | 1984-06-05 | Montedison S.P.A. | Stable, heat-resistant solutions of pesticidal carbamates |
| US5846997A (en) * | 1995-05-05 | 1998-12-08 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Liquid formulations |
| EP0839447A1 (en) * | 1996-11-01 | 1998-05-06 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Pesticidal emulsifiable concentrate |
| WO2007039215A1 (en) * | 2005-09-29 | 2007-04-12 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Fungicidal composition comprising cyprodinil |
| WO2007068420A1 (en) * | 2005-12-16 | 2007-06-21 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Method for the control of phytopathogenic fungi on soybean |
| WO2007073933A2 (en) * | 2005-12-27 | 2007-07-05 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Herbicidal composition |
| WO2008006456A1 (en) * | 2006-07-13 | 2008-01-17 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Herbicidal composition |
| JP2009173569A (en) | 2008-01-23 | 2009-08-06 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Process for producing bis {2- [2- (4-dibenzo [b, f] [1,4] thiazepin-11-yl-1-piperazinyl) ethoxy] ethanol} monofumarate |
| WO2011017480A2 (en) | 2009-08-07 | 2011-02-10 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Meso-sized capsules useful for the delivery of agricultural chemicals |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| "The Pesticide Manual", BRITISH CROP PROTECTION COUNCIL |
| See also references of EP2819513A4 |
Cited By (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104106565A (en) * | 2013-10-21 | 2014-10-22 | 曾立雄 | Novel water-emulsion type solvent capable of replacing xylene |
| AU2015374106B2 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2019-01-03 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Fungicidal compositions |
| WO2016109634A1 (en) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-07 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Fungicidal compositions |
| WO2016109640A1 (en) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-07 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Fungicidal compositions |
| WO2016109641A1 (en) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-07-07 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Fungicidal compositions |
| AU2015374035B2 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2019-04-18 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Fungicidal compositions |
| EP3240416B1 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2022-07-27 | Corteva Agriscience LLC | Fungicidal compositions |
| EP3240414B1 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2022-07-20 | Corteva Agriscience LLC | Fungicidal compositions |
| EP3240415B1 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2022-07-20 | Corteva Agriscience LLC | Fungicidal compositions |
| WO2016176742A1 (en) * | 2015-05-07 | 2016-11-10 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Emulsifiable concentrate comprising a phenoxy-alkanoic acid herbicide |
| US11116207B2 (en) | 2015-05-07 | 2021-09-14 | Nufarm Autralia Limited | Emulsifiable concentrate comprising picolinic acid herbicide |
| US10492488B2 (en) | 2015-05-07 | 2019-12-03 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Emulsifiable concentrate comprising a phenoxy-alkanoic acid herbicide |
| US10772323B2 (en) | 2015-05-07 | 2020-09-15 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Benzoic acid herbicide composition |
| WO2017156751A1 (en) | 2016-03-17 | 2017-09-21 | Dow Global Technologies Llc | Emulsifiable concentrates |
| EP3429348A4 (en) * | 2016-03-17 | 2019-11-06 | Dow Global Technologies, LLC | EMULSIFIABLE CONCENTRATES |
| EP3915370A1 (en) | 2018-05-07 | 2021-12-01 | Adama Agan Ltd. | Stable phytoene desaturase inhibitor herbicide formulation |
| WO2019215613A1 (en) | 2018-05-07 | 2019-11-14 | Adama Agan Ltd. | Stable phytoene desaturase inhibitor herbicide formulation |
| CN114126407A (en) * | 2019-07-23 | 2022-03-01 | 江苏龙灯化学有限公司 | Emulsifiable concentrate preparation and use thereof |
| WO2021012173A1 (en) * | 2019-07-23 | 2021-01-28 | Jiangsu Rotam Chemistry Co., Ltd. | Emulsifiable concentrate formulations and their uses |
| WO2021158421A1 (en) * | 2020-02-06 | 2021-08-12 | Dow Global Technologies Llc | Tebuconazole formulations |
| WO2023208447A1 (en) * | 2022-04-25 | 2023-11-02 | Basf Se | An emulsifiable concentrate having a (substituted) benzaldehyde-based solvent system |
| WO2025094190A1 (en) * | 2023-10-19 | 2025-05-08 | Parijat Industries (India) Private Limited | A stable insecticidal composition comprising dinotefuran and bifenthrin |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2819513A4 (en) | 2015-11-11 |
| CN108552171B (en) | 2020-07-17 |
| AU2013225608B2 (en) | 2016-06-23 |
| EP2819513A1 (en) | 2015-01-07 |
| CN108552171A (en) | 2018-09-21 |
| BR112014019372A8 (en) | 2017-07-11 |
| ES2639188T3 (en) | 2017-10-25 |
| JP6227566B2 (en) | 2017-11-08 |
| MX2014009955A (en) | 2014-11-13 |
| CN104125772A (en) | 2014-10-29 |
| US9781921B2 (en) | 2017-10-10 |
| BR112014019372A2 (en) | 2017-06-20 |
| US20150335011A1 (en) | 2015-11-26 |
| CA2861558A1 (en) | 2013-09-06 |
| MX367453B (en) | 2019-08-22 |
| CA2861558C (en) | 2020-03-24 |
| JP2015508080A (en) | 2015-03-16 |
| BR112014019372B1 (en) | 2022-08-23 |
| AU2013225608A1 (en) | 2014-07-24 |
| AR090149A1 (en) | 2014-10-22 |
| EP2819513B1 (en) | 2017-08-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2013225608B2 (en) | Emulsifiable concentrate formulation | |
| US10130091B2 (en) | Agrochemical emulsifiable concentrate formulation | |
| EP3054774B1 (en) | Aqueous herbicidal concentrates | |
| CA2802647C (en) | Agrochemical formulation composition | |
| CA2925412A1 (en) | Aqueous herbicidal concentrates | |
| WO2004077945A1 (en) | Pesticides formulations | |
| TWI434653B (en) | Use of a c2-c4 dialkylene glycol di-/mono- c1-c4 alkyl ether | |
| JP2020050647A (en) | Liquid composition for foliage and soil treatment for weeding | |
| CN105050395A (en) | A novel aqueous suspoemulsion and a process for preparing the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13754349 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2014557945 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A Ref document number: 2861558 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2013225608 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20130225 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2013754349 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2013754349 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14377322 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: MX/A/2014/009955 Country of ref document: MX |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112014019372 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112014019372 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20140806 |