WO2013019866A2 - Use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol-based solvents - Google Patents
Use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol-based solvents Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2013019866A2 WO2013019866A2 PCT/US2012/049171 US2012049171W WO2013019866A2 WO 2013019866 A2 WO2013019866 A2 WO 2013019866A2 US 2012049171 W US2012049171 W US 2012049171W WO 2013019866 A2 WO2013019866 A2 WO 2013019866A2
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- glycol
- group
- blend
- dialkyl
- optionally
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 *C1(*)OC(CO)CO1 Chemical compound *C1(*)OC(CO)CO1 0.000 description 4
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K8/00—Compositions for drilling of boreholes or wells; Compositions for treating boreholes or wells, e.g. for completion or for remedial operations
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K8/00—Compositions for drilling of boreholes or wells; Compositions for treating boreholes or wells, e.g. for completion or for remedial operations
- C09K8/60—Compositions for stimulating production by acting on the underground formation
- C09K8/84—Compositions based on water or polar solvents
- C09K8/86—Compositions based on water or polar solvents containing organic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K8/00—Compositions for drilling of boreholes or wells; Compositions for treating boreholes or wells, e.g. for completion or for remedial operations
- C09K8/02—Well-drilling compositions
- C09K8/03—Specific additives for general use in well-drilling compositions
- C09K8/035—Organic additives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K8/00—Compositions for drilling of boreholes or wells; Compositions for treating boreholes or wells, e.g. for completion or for remedial operations
- C09K8/60—Compositions for stimulating production by acting on the underground formation
- C09K8/62—Compositions for forming crevices or fractures
- C09K8/66—Compositions based on water or polar solvents
- C09K8/68—Compositions based on water or polar solvents containing organic compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K2208/00—Aspects relating to compositions of drilling or well treatment fluids
Definitions
- This invention relates to compounds, methods and systems of mutual solvents that are more biodegradable, as well as less toxic and/or safer to use than glycol-based mutual solvents, specifically ethyleneglycolmonobutyl ether (EGMBE), utilized in industrial and oil field applications.
- EGMBE ethyleneglycolmonobutyl ether
- Mutual solvents are typically additives used in oil field and well applications that are soluble in oil, water and acid-based treatment fluids.
- a commonly used mutual solvent is ethyleneglycolmonobutyl ether, generally known as EGMBE.
- EGMBE is routinely used in a range of applications, such as removing heavy hydrocarbon deposits, controlling the wettability of contact surfaces before, during or after a treatment, and preventing or breaking emulsions.
- Some solvents have been used in place of EGMBE; however, many such solvents suffer the same drawbacks as EGMBE, such as being environmentally unfriendly or similarly toxic and hazardous.
- These include glycol ethers like DowanolTM pnB (propylene glycol n-butyl ether), or butyl carbitol (diethylene glycol butyl ether), ethylene glycol monoacetate, butyl carbitol, triethylene glycol monoethyl ether, 1 ,1 '- oxybis(2-propanol), triethylene glycol monomethyl ether, triglyme and diglyme, among others. Some of these solvents are reported as "priority pollutants".
- described herein is a method for replacing glycol-based mutual solvents in an oil field application comprising: -obtaining an alternative solvent blend; and -replacing all or a portion a glycol-based mutual solvent, which forms a component of an oil field formulation, with the alternative solvent, wherein the oil field formulation can be utilized in an oil field application.
- the method further comprises the step of utilizing such alternative solvent blend in the oilfield application.
- the glycol- based mutual solvent is selected from glycol ethers, alkyi ethers of ethylene glycol, alkyi ethers of propylene glycol, ethylene glycol, EGMBE (ethylene glycol mono-butyl ether), propylene glycol n-butyl ether, diethylene glycol butyl ether, ethylene glycol monoacetate, butyl carbitol, triethylene glycol monoethyl ether, 1 ,1 '-oxybis(2-propanol), triethylene glycol monomethyl ether, triglyme or diglyme.
- the oil field application in one embodiment, is a well treatment fluid, a fracturing fluid, a stimulation fluid, a workover fluid or a slickwater fluid
- the alternative solvent blend comprises at least one component selected from one or more of the following:
- R 6 and R 7 which may be identical or different, is individually a hydrogen, an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, a phenyl group, wherein n is an integer of from 1 to 10;
- R 3 OOC-A-CONR 4 R 5 [0018] wherein R 3 is a group chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic hydrocarbon-based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36; wherein R 4 and R 5 , which are identical or different, are groups chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic, optionally substituted hydrocarbon- based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36. R 4 and R 5 in some embodiments together form a ring, which in some embodiments are substituted or comprises a heteroatom.
- A is a linear or branched divalent alkyl group comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 2 to 12, typically from 2 to 4;
- an alkyldimethylamine e.g., N,N-Dimethyldodecylamine
- -C 4 alcohol e.g., isopropyl alcohol
- the alkyldimethylamine is N,N- Dimethyldodecylamine.
- -C 4 alcohol is isopropyl alcohol.
- the alternative solvent blend comprises:
- R 6 and R 7 which may be identical or different, is each individually a hydrogen, an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, a phenyl group, wherein n is an integer of from 1 to 10;
- R 3 is a group chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic hydrocarbon-based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36; wherein R 4 and R 5 , which are identical or different, are groups chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic, optionally substituted hydrocarbon- based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36; wherein A is a linear or branched divalent alkyl group comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 2 to 12.
- alternative solvent blend compositions for use in oilfield applications selected from the group consisting of:
- R6 and R7 which may be identical or different, is individually a hydrogen, an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, a phenyl group, wherein n is an integer of from 1 to 10;
- R 3 is a group chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic hydrocarbon-based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36;
- R 4 and R 5 which are identical or different, are groups chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic, optionally substituted hydrocarbon-based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36; and
- A is a linear or branched divalent alkyl group comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 2 to 12;
- the alternative solvent in some embodiments, can be selected from the group consisting of:
- R 6 and R 7 which may be identical or different, is individually a hydrogen, an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, a phenyl group, wherein n is an integer of from 1 to 10;
- R 3 is a group chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic hydrocarbon-based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36;
- R 4 and R 5 which are identical or different, are groups chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic, optionally substituted hydrocarbon-based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36; and wherein A is a linear or branched divalent alkyl group comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 2 to 12; and
- the "replacement mutual solvent blend” described herein has desirable qualities including one or a combination of being: substantially nontoxic, non-flammable, biodegradable, high flash point, low vapor pressure and low odor; meets the consumer products LVP-VOC exemption criteria established by CARB and the EPA (certain sections) relative to mutual solvents currently used in oilfield applications, such as EGMBE or other glycol ethers.
- alkyl means a saturated straight chain, branched chain, or cyclic hydrocarbon radical, including but not limited to, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, iso-propyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, t-butyl, pentyl, n-hexyl, and cyclohexyl.
- aryl means a monovalent unsaturated
- alkylene means a divalent saturated straight or branched chain hydrocarbon radical, such as for example, methylene, dimethylene, trimethylene.
- surfactant means a compound that when dissolved in an aqueous medium lowers the surface tension of the aqueous medium.
- glycol-based mutual solvents means glycol ethers or derivatives thereof, alkyl ethers of ethylene glycol, alkyl ethers of propylene glycol, ethylene glycol.
- examples of glycol-based mutual solvents include EGMBE (ethylene glycol mono-butyl ether), propylene glycol n-butyl ether, diethylene glycol butyl ether, ethylene glycol monoacetate, butyl carbitol, triethylene glycol monoethyl ether, 1 ,1 '-oxybis(2-propanol), triethylene glycol monomethyl ether, triglyme and/or diglyme.
- oilfield application fluid means any fluid utilized in the processing, extraction or treatment of oil, which in one embodiment includes fluids utilized in and around an oil producing well.
- oilfield application fluids include but are not limited to: well treatment fluids, stimulation fluids, slickwater fluids, drilling fluids, acidizing fluids, workover fluids, completion fluids, packer fluids, subterranean formation treating fluids, mud-reversal fluids, deposit removal fluids (e.g., asphaltene, wax, oil), wellbore cleaning fluids, cutting fluids, carrier fluids, carrier fluids (for mutual solvency), degreasing fluids, fracturing fluids, spacer fluids, hole
- Workover fluids generally are those fluids used during remedial work in a drilled well. Such remedial work includes removing tubing, replacing a pump, cleaning out sand or other deposits, logging, etc. Workover also broadly includes steps used in preparing an existing well for secondary or tertiary recovery such as polymer addition, micellar flooding, steam injection, etc. Fracturing fluids are used in oil recovery operations where subterranean is treated to create pathways for the formation fluids to be recovered.
- Described herein are systems and methods for replacing glycol based mutual solvents in industrial applications, namely oil field applications. Also described herein are alternative solvents and solvent blends which is can replace glycol-based mutual solvents such as EGMBE. Also described herein are oil field formulations with improved toxicity profile or otherwise, environmental profile, which can be utilized in oil field applications.
- the method for replacing glycol-based mutual solvents in an oil field application includes obtaining an alternative solvent blend, then
- the glycol-based mutual solvent forms part of a oil field formulation.
- the oil field formulation is typically utilized in an oil field application such as fracturing, acidizing, workover, etc.
- the alternative solvent blend once incorporated as part of the formulation, imparts an improved environmental profile, including ecotox profiles, with respect to the formulation and application.
- the glycol-based mutual solvent forms part of a industrial formulation.
- Industrial formulations can include ⁇ but are not limited to) weatherizing formulations, which prevent freezing of a fluid, or maintain the viscosity of a fluid below a certain level.
- the alternative solvent is chosen from one of the following components (a through h), below.
- the alternative solvent is an alternative solvent blend chosen from at least one component (a through h), below, typically, two or more components.
- R 6 and R 7 which may be identical or different, is individually a hydrogen, an alkyl group, an alkenyl group, a phenyl group, wherein n is an integer of from 1 to 10;
- R 3 is a group chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic hydrocarbon-based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36; wherein R 4 and R 5 , which are identical or different, are groups chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic, optionally substituted hydrocarbon- based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36, it being possible for R 4 and R 5 to optionally together form a ring, that is optionally substituted and/or that optionally comprises a heteroatom; and wherein A is a linear or branched divalent alkyl group comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 2 to 12, typically from 2 to 4; [0078] f) an alkyldimethylamine;
- the a C C 4 alcohol is chosen from t-butyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, iso-propyl alcohol, or propyl alcohol.
- the C-1 -C4 alcohol is iso-propyl alcohol.
- the alternative solvent comprises (i) one or a (ii) blend of dibasic esters.
- the blend comprises adducts of alcohol and linear diacids, the adducts having the formula R-i-OOC-A-COO-R 2 wherein R and/or R 2 comprise, individually, a C 1 -C- 12 alkyl, more typically a C-
- Ri and/or R 2 comprise, individually, a C 4 -C-
- Ri and R 2 can individually comprise a hydrocarbon group originating from fusel oil.
- Ri and R 2 individually can comprise a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 8 carbon atoms.
- Ri and R 2 individually can comprise a
- A comprises a least one, typically at least two, of: -(CH 2 ) 4 -, -CH 2 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )-, -CH 2 CH(C 2 H 5 )-, - (CH 2 ) 4 -, -CH 2 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )-, or -CH 2 CH(C 2 H 5 )-.
- the blend comprises adducts of alcohol and branched or linear diacids, the adducts having the formula R OOC-A-COO-R 2 wherein R and/or R 2 comprise, individually, a C-
- Ri and/or R 2 comprise, individually, a C 4 -C-
- the acid portion may be derived from such dibasic acids such as adipic, succinic, glutaric, oxalic, malonic, pimelic, suberic and azelaic acids, as well as mixtures thereof.
- the dibasic esters of the present invention can be obtained by a process comprising an "esterification" stage by reaction of a diacid of formula HOOC-A-COOH or of a diester of formula MeOOC-A-COOMe with a branched alcohol or a mixture of alcohols.
- the reactions can be appropriately catalyzed. Use is preferably made of at least 2 molar equivalents of alcohols per diacid or diester.
- the reactions can, if appropriate, be promoted by extraction of the reaction by-products and followed by stages of filtration and/or of purification, for example by distillation.
- the diacids in the form of mixtures can in particular be obtained from a mixture of dinitrile compounds in particular produced and recovered in the process for the manufacture of adiponitrile by double hydrocyanation of butadiene.
- This process used on a large scale industrially to produce the greater majority of the adiponitrile consumed worldwide, is described in numerous patents and works.
- the reaction for the hydrocyanation of butadiene results predominantly in the formulation of linear dinitriles but also in formation of branched dinitriles, the two main ones of which are
- Dibasic esters of the present invention may be derived from one or more byproducts in the production of polyamide, for example, polyamide 6,6. In one
- the cleaning composition comprises a blend of linear or branched, cyclic or noncyclic, C-i-C 2 o alkyl, aryl, alkylaryl or arylalkyl esters of adipic diacids, glutaric diacids, and succinic diacids.
- the cleaning composition comprises a blend of linear or branched, cyclic or noncyclic, C-i-C 2 o alkyl, aryl, alkylaryl or arylalkyl esters of adipic diacids, methylglutaric diacids, and ethylsuccinic diacids
- polyamide is a copolymer prepared by a condensation reaction formed by reacting a diamine and a dicarboxylic acid.
- polyamide 6,6 is a copolymer prepared by a condensation reaction formed by reacting a diamine, typically hexamethylenediamine, with a dicarboxylic acid, typically adipic acid.
- the blend of dibasic esters can be derived from one or more by-products in the reaction, synthesis and/or production of adipic acid utilized in the production of polyamide, the cleaning composition comprising a blend of dialkyl esters of adipic diacids, glutaric diacids, and succinic diacids (herein referred to sometimes as "AGS" or the “AGS blend”).
- the blend of esters is derived from by-products in the reaction, synthesis and/or production of hexamethylenediamine utilized in the
- the cleaning composition comprises a blend of dialkyl esters of adipic diacids, methylglutaric diacids, and ethylsuccinic diacids (herein referred to sometimes as "MGA”, “MGN”, “MGN blend” or “MGA blend”).
- the dibasic ester blend comprises:
- Ri and/or R 2 can individually comprise a hydrocarbon having from about 1 to about 8 carbon atoms, typically, methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, isobutyl, n-butyl, isoamyl, hexyl, heptyl or octyl.
- the blend typically comprises (by weight of the blend) (i) about 15% to about 35% of the diester of formula I, (ii) about 55% to about 70% of the diester of formula II, and (iii) about 7% to about 20% of the diester of formula III, and more typically, (i) about 20% to about 28% of the diester of formula I, (ii) about 59% to about 67% of the diester of formula II, and (iii) about 9% to about 17% of the diester of formula III.
- the blend is generally characterized by a flash point of 98 °C, a vapor pressure at 20 °C of less than about 10 Pa, and a distillation temperature range of about 200-300 °C. Mention may also be made of Rhodiasolv® RPDE (Rhodia Inc., Cranbury, NJ), Rhodiasolv® DIB (Rhodia Inc., Cranbury, NJ) and Rhodiasolv® DEE (Rhodia Inc., Cranbury, NJ).
- the dibasic ester blend comprises:
- Ri and/or R 2 can individually comprise a hydrocarbon having from about 1 to about 8 carbon atoms, typically, methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, butyl, isobutyl, n-butyl, isoamyl, hexyl, heptyl, or octyl.
- the blend typically comprises (by weight of the blend) (i) from about 5% to about 30% of the diester of formula IV, (ii) from about 70% to about 95% of the diester of formula V, and (iii) from about 0% to about 10% of the diester of formula VI.
- the blend typically comprises (by weight of the blend): (i) from about 6% to about 12% of the diester of formula IV, (ii) from about 86% to about 92% of the diester of formula V, and (iii) from about 0.5% to about 4% of the diester of formula VI.
- the blend comprises (by weight of the blend): (i) about 9% of the diester of formula IV, (ii) about 89% of the diester of formula V, and (iii) about 1 % of the diester of formula VI.
- the blend is generally characterized by a flash point of of 98 °C, a vapor pressure at 20 °C of less than about 10 Pa, and a distillation temperature range of about 200-275 °C. Mention may be made of Rhodiasolv® IRIS and
- Rhodiasolv® DEE/M manufactured by Rhodia Inc. (manufactured by Rhodia Inc., Cranbury, NJ)
- the alternative solvent or alternative solvent blend can include other solvents, including but not limited to aliphatic or acyclic hydrocarbons solvents, halogenated solvents, aromatic hydrocarbon solvents, cyclic terpenes, unsaturated hydrocarbon solvents, halocarbon solvents, polyols, alcohols including short chain alcohols, ketones or mixtures thereof.
- solvents including but not limited to aliphatic or acyclic hydrocarbons solvents, halogenated solvents, aromatic hydrocarbon solvents, cyclic terpenes, unsaturated hydrocarbon solvents, halocarbon solvents, polyols, alcohols including short chain alcohols, ketones or mixtures thereof.
- the dioxane compound utilized as the alternative solvent or in the alternative solvent blend as described herein includes those of formula (I), below:
- R 6 and R 7 which are identical or different, represent hydrogen or a Ci-C-14 group or radical.
- R 6 and R 7 are individually selected from an alkyl group, alkenyl group or phenyl radical.
- "n" is an integer of 1 , 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 1 1 or 12.
- "n" is an integer from about 1 to 4. More typically, “n” is 1 or 2. Mention may be made of Augeo ® (Rhodia Inc., Cranbury, NJ).
- R 6 and R 7 are radicals individually selected from methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl or isobutyl radical.
- the dioxolane compound is of formula (I) is 2,2-dimethyl- 1 ,3-dioxolane-4-methanol.
- the dioxolane compound of formula (I) is 2,2-diisobutyl-1 ,3-dioxolane-4-methanol (also known by the acronym IIPG, for the synonym 1 -isobutyl-isopropylidene glycerol).
- a compound utilized as the alternative solvent or as a component in the alternative solvent blend is a compound of general formula (II):
- the expression “compound” denotes any compound corresponding to the general formula (II).
- the term “compound” also refers to mixtures of several molecules corresponding to general formula (II). It may therefore be a molecule of formula (II) or a mixture of several molecules of formula (II), wherein both fall under the definition of the term “compound” when referring to formula (II).
- the R 3 , R 4 and R 5 groups can be, in some embodiments, identical or, in other embodiment, different. In one embodiment, may be groups chosen from C-rC 2 o alkyl, aryl, alkaryl or arylalkyl groups or the phenyl group. In another embodiment, may be groups chosen from C -C alkyl, aryl, alkaryl or arylalkyl groups or the phenyl group. Mention is made especially of Rhodiasolv® PolarClean (Manufactured by Rhodia Inc. of Cranbury, NJ). The R 4 and R 5 groups may optionally be substituted. In one particular embodiment, the groups are substituted with hydroxyl groups.
- R 3 group is chosen from methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, n-pentyl, isopentyl, isoamyl, n-hexyl, cyclohexyl, 2-ethylbutyl, n-octyl, isooctyl, 2-ethylhexyl, tridecyl groups.
- R 4 and R 5 groups which are identical or different, in one embodiment, may especially be chosen from methyl, ethyl, propyl (n-propyl), isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, n- pentyl, amyl, isoamyl, hexyl, cyclohexyl or hydroxyethyl groups.
- the R 4 and R 5 groups may also be such that they form, together with the nitrogen atom, a morpholine, piperazine or piperidine group.
- R 4 and R 5 are each methyl, or R 4 and R 5 are each ethyl, or R 4 and R 5 are each hydroxyethyl.
- A comprises a linear group of formula - CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 -- and/or of formula -- CH 2 -- CH 2 -- CH 2 -- CH 2 -- and/or of formula --( CH 2 ) 8 ⁇ then it is a mixture of A groups.
- A is linear, then it is a mixture of A groups, for example a mixture of two or three - CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ (ethylene); - CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ (n-propylene); and -- CH 2 -- CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 -- CH 2 -- (n- butylene) groups (or isomers thereof).
- the A group is a divalent linear alkyl group chosen from the groups of the following formulae: - CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ (ethylene); -- CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ (n-propylene); - CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 -- (n- butylene), and mixtures thereof.
- the compound is a mixture according to the following mixture of molecules:
- the A group is a divalent branched alkyl group chosen from the groups of the following formulae: -- CH(CH 3 )-- CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ ; ⁇ CH(C 2 H 5 ) ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ ; and, optionally, -- CH 2 -- CH 2 -- CH 2 -- CH 2 --; as well as mixtures thereof.
- the compound is a mixture according to the following mixture of molecules:
- R 3 OOC-CH(C 2 H5)CH 2 -CONR 4 R5 ; and, optionally,
- the compound of the invention is chosen from the following compounds:
- MeOOC- CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CON Me 2 as a mixture with MeOOC--CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 -- CH 2 --CON Me 2 and/or with MeOOC- CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CON Me 2 .
- the A group is a divalent branched alkylene group having one of the following formulae (lla), (lib), (lie), (Ilia) and (lllb), or a mixture of at least two groups chosen from the groups of formulae (lla), (lib) and (lie) or from the groups of formulae (Ilia) and (lllb), or a mixture of at least two groups, one chosen from the groups of formulae (lla), (lib) and (lie) and the others chosen from the groups of formulae (Ilia) and (lllb):
- y is an average integer greater than or equal to 0;
- z is an average integer greater than or equal to 0;
- R 8 which is identical or different, is a CrC 6 , preferably C-i-C 4 , alkyl group; and
- R 9 which is identical or different, is a hydrogen atom or a C-
- the A group is preferably a group such that y and z are 0.
- the compound of the invention is chosen from the following compounds, and mixtures thereof:
- AMG represents an MG a group of formula --CH(CH 3 )--CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ , or MG b group of formula ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ CH(CH 3 )-- or a mixture of MG a and MG b groups;
- a ES represents an ES a group of formula --CH(C 2 H 5 ) ⁇ CH 2 ⁇ , or ES b group of formula --CH 2 --CH(C 2 H 5 )-- or a mixture of ES a and ES b groups;
- Pe represents a pentyl group, preferably an isopentyl or isoamyl group
- Cyclo represents a cyclohexyl group
- Eh represents a 2-ethylhexyl group
- Bu represents a butyl group, preferably an n-butyl or tert-butyl group
- EtBu represents an ethylbutyl group
- n-He represents an n-hexyl group.
- the compound of the invention is a compound different from the following compounds:
- the compound of the invention is a novel compound of the invention, different from the following compounds or mixtures, if the latter, individually, are not used as a mixture with other compounds corresponding to formula (II):
- the compound of the invention is a novel compound of the invention, different from the following compounds or mixtures, if the latter, individually, are not used as a mixture with other compounds corresponding to formula (I I):
- the esteramide has a melting point that is less than or equal to 20 °C, preferably 5 °C, preferably 0°C.
- R 3 is a group chosen from saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched, optionally cyclic, optionally aromatic hydrocarbon- based groups comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 36.
- R 4 and R 5 which are identical or different, are groups chosen from saturated or
- A is a linear or branched divalent alkyl group comprising an average number of carbon atoms ranging from 1 to 20, in some embodiments, from 2 to 12, in other embodiments, from 2 to 8, in yet other embodiments, from 2 to 4.
- the alternative solvent comprises amides, alkyl amides, or dialkyl amides.
- one component in the alternative solvent blend comprises an amide, alkyl amide, and/or dialkyl amide.
- the alternative solvent or alternative solvent blend is alkyldimethylamide (ADMA).
- the alkyl group is a Ci -C 5 o alkyl group, more typically a C 2 -C 3 o alkyl group, even more typically, a C 2 -C 2 o alkyl group.
- the alkyl group is a Ci -C 5 o alkyl group, more typically a C 2 -C 3 o alkyl group, even more typically, a C 2 -C 2 o alkyl group.
- the alkyl group is a Ci -C 5 o alkyl group, more typically a C 2 -C 3 o alkyl group, even more typically, a C 2 -C 2 o alkyl group.
- the alkyl group
- alkyldimethylamide is ⁇ , ⁇ -dimethyldecanamide (miscibility 0.034%) or N,N- dimethyloctanamide (miscibility 0.43%), or mixtures therof. Mention is made especially of the compounds sold by Rhodia, Rhodiasolv® ADMA810 and Rhodiasolv® ADMA10.
- the oil field formulation contains suitable components apart from the alternative solvent or alternative solvent blend.
- additional components can include at least one surfactant, proppants, co-solvents, buffering and/or pH control agents, fragrances, opacifying agents, anti-corrosion agents, whiteners, defoamers, dyes, sudsing control agents, foaming agents, stabilizers, chelating agents, biocides, thickeners and the like.
- the surfactant can be any number of cationic, amphoteric, zwitterionic, anionic or nonionic surfactants, derivatives thereof, as well as blends of such
- the nonionic surfactants generally includes one or more of for example amides such as alkanolamides, ethoxylated alkanolamides, ethylene bisamides; esters such as fatty acid esters, glycerol esters, ethoxylated fatty acid esters, sorbitan esters, ethoxylated sorbitan; ethoxylates such as alkylphenol ethoxylates, alcohol ethoxylates, tristyrylphenol ethoxylates, mercaptan ethoxylates; end-capped and EO/PO block copolymers such as ethylene oxide/propylene oxide block copolymers, chlorine capped ethoxylates, tetra-functional block copolymers;
- amides such as alkanolamides, ethoxylated alkanolamides, ethylene bisamides
- esters such as fatty acid esters, glycerol esters, ethoxyl
- amine oxides such lauramine oxide, cocamine oxide, stearamine oxide,
- stearamidopropylamine oxide palmitamidopropylamine oxide, decylamine oxide
- fatty alcohols such as decyl alcohol, lauryl alcohol, tridecyl alcohol, myristyl alcohol, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, oleyl alcohol, linoleyl alcohol and linolenyl alcohol; and alkoxylated alcohols such as ethoxylated lauryl alcohol, trideceth alcohols
- fatty acids such as lauric acid, oleic acid, stearic acid, myristic acid, cetearic acid, isostearic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, ricinoleic acid, elaidic acid, arichidonic acid, myristoleic acid and mixtures thereof.
- the non-ionic surfactant is a glycol such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), alkyl PEG esters, polypropylene glycol (PPG) and
- PEG polyethylene glycol
- PPG polypropylene glycol
- the surfactant is an alcohol ethoxylate, an alkyl phenol ethoxylate or a terpene alkoxylate. In one exemplary embodiment, the surfactant is a C 6 -Ci 3 alcohol ethoxylate and, more typically, a C 8 -C-
- the surfactant is a cationic surfactant.
- the cationic surfactant includes but is not limited to quaternary ammonium compounds, such as cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (also known as CETAB or cetrimonium bromide), cetyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (also known as cetrimonium chloride), myristyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (also known as myrtrimonium bromide or Quaternium-13), stearyl dimethyl distearyldimonium chloride, dicetyl dimonium chloride, stearyl octyldimonium methosulfate, dihydrogenated palmoylethyl hydroxyethylmonium methosulfate, isostearyl benzylimidonium chloride, cocoyl benzyl hydroxyethyl imidazolinium chloride, dicetyl dimonium chloride and distearyldimonium
- the surfactant is an anionic surfactant.
- the anionic surfactant includes but is not limited to linear alkylbenzene sulfonates, alpha olefin sulfonates, paraffin sulfonates, alkyl ester sulfonates, alkyl sulfates, alkyl alkoxy sulfates, alkyl sulfonates, alkyl alkoxy carboxylates, alkyl alkoxylated sulfates, monoalkyl phosphates, dialkyl phosphates, sarcosinates, sulfosuccinates, isethionates, and taurates, as well as mixtures thereof.
- anionic surfactants that are suitable as the anionic surfactant component of the composition of the present invention include, for example, ammonium lauryl sulfate, ammonium laureth sulfate, triethylamine lauryl sulfate, triethylamine laureth sulfate, triethanolamine lauryl sulfate,
- triethanolamine laureth sulfate monoethanolamine lauryl sulfate, monoethanolamine laureth sulfate, diethanolamine lauryl sulfate, diethanolamine laureth sulfate, lauric monoglyceride sodium sulfate, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium laureth sulfate, potassium lauryl sulfate, potassium laureth sulfate, sodium-monoalkyl phosphates, sodium dialkyl phosphates, sodium lauroyl sarcosinate, lauroyl sarcosine, cocoyl sarcosine, ammonium cocyl sulfate, ammonium lauryl sulfate, sodium cocyl sulfate, sodium trideceth sulfate, sodium tridecyl sulfate, ammonium trideceth sulfate, ammonium tridecyl sulfate,
- Branched anionic surfactants are particularly preferred, such as sodium trideceth sulfate, sodium tridecyl sulfate, ammonium trideceth sulfate, ammonium tridecyl sulfate, and sodium trideceth carboxylate.
- amphoteric surfactant that is acceptable for use includes but is not limited to derivatives of aliphatic secondary and tertiary amines in which the aliphatic radical can be straight chain or branched and wherein one of the aliphatic substituents contains from about 8 to about 18 carbon atoms and one contains an anionic water solubilizing group.
- suitable amphoteric surfactants include the alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, ammonium or substituted ammonium salts of alkyl amphocarboxy glycinates and alkyl amphocarboxypropionates, alkyl
- amphodipropionates alkyl amphodiacetates, alkyl amphoglycinates, and alkyl amphopropionates, as well as alkyl iminopropionates, alkyl iminodipropionates, and alkyl amphopropylsulfonates , such as for example, cocoamphoacetate
- cocoamphopropionate cocoamphodiacetate, lauroamphoacetate, lauroamphodiacetate , lauroamphodipropionate, lauroamphodiacetate, cocoamphopropyl sulfonate
- caproamphodiacetate caproamphoacetate
- caproamphodipropionate caproamphodipropionate
- Suitable zwitterionic surfactants include alkyl betaines, such as cocodimethyl carboxymethyl betaine, lauryl dimethyl carboxymethyl betaine, lauryl dimethyl alpha- carboxy-ethyl betaine, cetyl dimethyl carboxymethyl betaine, lauryl bis-(2-hydroxy- ethyl)carboxy methyl betaine, stearyl bis-(2-hydroxy-propyl)carboxymethyl betaine, oleyl dimethyl gamma-carboxypropyl betaine, and lauryl bis-(2-hydroxypropyl)alpha- carboxyethyl betaine, amidopropyl betaines, and alkyl sultaines, such as cocodimethyl sulfopropyl betaine, stearyldi methyl sulfopropyl betaine, lauryl dimethyl sulfoethyl betaine, lauryl bis-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)sulfopropy
- EGMBE and other glycols are compared with an alternative solvent, or alternative solvent blend, as described herein.
- Such solvent or solvent blends could be made to approach the solvency of EGMBE or other targeted glycol, glycol ethers.
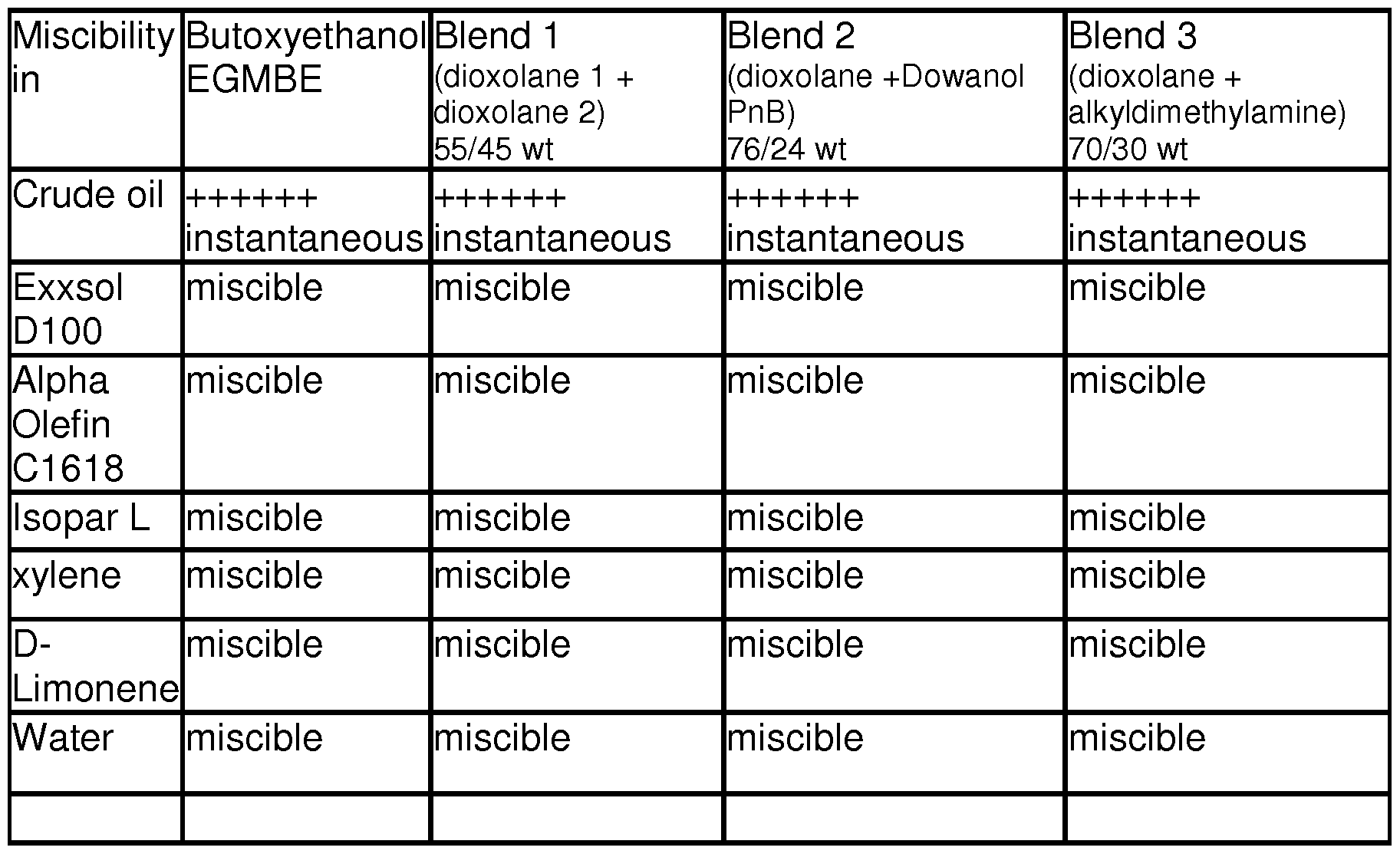
- Miscibility Test Referring generally to Tables 4-6, the test solvent or solvent blend for EGMBE-replacement is mixed with common solvents used in oilfield industries to determine miscibility. For each test solvent, it is blended with a common solvent at 50/50 volume per volume ratio. It is shaken vigorously for about a minute and let stand for about 5 mins. A complete miscibility is recorded if there is no formation of layers. Formation of turbid mixture or multiple layers is recorded as immiscible or separate. [00245] Experiment 1 : Comparing EGMBE's wettability, surface tension and solvency
- Table 6 Blends Miscible in water and in Mud solvents (50/50wt temperature).
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
- Detergent Compositions (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP12820433.6A EP2739699B1 (en) | 2011-08-01 | 2012-08-01 | Use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol-based solvents |
| MX2014001347A MX359074B (en) | 2011-08-01 | 2012-08-01 | Use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol-based solvents. |
| CA2843884A CA2843884C (en) | 2011-08-01 | 2012-08-01 | Use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol-based solvents |
| CN201280047007.8A CN103827253B (en) | 2011-08-01 | 2012-08-01 | The purposes of environmentally friendly solvent substitution glycolic solvents |
| BR112014002607A BR112014002607A2 (en) | 2011-08-01 | 2012-08-01 | use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol solvents |
| EA201490212A EA201490212A1 (en) | 2011-08-01 | 2012-08-01 | USING ENVIRONMENTALLY SAFE SOLVENTS FOR REPLACING SOLVENTS BASED ON GLYCOL |
| AU2012290165A AU2012290165B2 (en) | 2011-08-01 | 2012-08-01 | Use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol-based solvents |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201161574360P | 2011-08-01 | 2011-08-01 | |
| US61/574,360 | 2011-08-01 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2013019866A2 true WO2013019866A2 (en) | 2013-02-07 |
| WO2013019866A3 WO2013019866A3 (en) | 2013-07-11 |
Family
ID=47629898
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2012/049171 WO2013019866A2 (en) | 2011-08-01 | 2012-08-01 | Use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol-based solvents |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10633579B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2739699B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN103827253B (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2012290165B2 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112014002607A2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2843884C (en) |
| EA (1) | EA201490212A1 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX359074B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2013019866A2 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014035762A1 (en) * | 2012-08-30 | 2014-03-06 | Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. | Low toxicity viscosifier and methods of using the same |
| EP2838951A4 (en) * | 2012-04-17 | 2015-12-16 | Rhodia Operations | Polysaccharide slurries with environmentally friendly activator solvents |
| WO2017035445A1 (en) * | 2015-08-26 | 2017-03-02 | Rhodia Operations | High performance eco-friendly non-emulsifier |
| WO2021150430A1 (en) | 2020-01-22 | 2021-07-29 | Eastman Kodak Company | Method for making lithographic printing plates |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104870598A (en) * | 2012-06-28 | 2015-08-26 | 罗地亚经营管理公司 | Environmentally friendly solvent systems/surfactant systems for drilling fluids |
| US10717919B2 (en) * | 2013-03-14 | 2020-07-21 | Flotek Chemistry, Llc | Methods and compositions for use in oil and/or gas wells |
| US9663707B2 (en) * | 2013-10-23 | 2017-05-30 | Baker Hughes Incorporated | Stimulation method using biodegradable zirconium crosslinker |
| US9902894B2 (en) | 2014-10-31 | 2018-02-27 | Chevron U.S.A. Inc. | Polymer compositions |
| WO2017040903A1 (en) | 2015-09-02 | 2017-03-09 | Chevron U.S.A. Inc. | Enhanced oil recovery compositions and methods thereof |
| WO2017082936A1 (en) * | 2015-11-13 | 2017-05-18 | Kyzen Corporation | Cleaning agent for removal of soldering flux |
| WO2017137786A1 (en) * | 2016-02-12 | 2017-08-17 | Rhodia Poliamida E Especialidades Ltda | Paraffin removal formulations |
| CN106883833B (en) * | 2017-02-20 | 2019-10-25 | 西安石油大学 | Oil displacement system for ultrahigh-temperature high rigidity oil reservoir with high salt |
| FR3065732B1 (en) * | 2017-04-27 | 2019-07-19 | Rhodia Operations | INTERFACE AGENTS FOR THE PREPARATION OF COLD ROAD COATINGS |
| US11434414B2 (en) | 2018-07-25 | 2022-09-06 | Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. | Surfactant compositions comprising solid substrates for subterranean well operations |
| US11518926B2 (en) * | 2020-07-17 | 2022-12-06 | Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. | Removal of a mineral phase from a surface associated with a wellbore |
| CN113973815B (en) * | 2021-11-18 | 2022-07-29 | 祺农化工科技(上海)有限公司 | Mixed solvent mainly comprising C6-C18 alkyl dimethyl amide, and preparation method and application thereof |
Family Cites Families (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5198729A (en) * | 1975-02-26 | 1976-08-31 | TORYOYOHAKURIZAISOSEIBUTSU | |
| ATE96328T1 (en) * | 1987-02-13 | 1993-11-15 | Asta Medica Ag | CHAMOMILE OILS WITH HIGH CONTENT OF NATURAL POLYINS AND PROCESS FOR THEIR PRODUCTION. |
| JPH0673318A (en) * | 1992-07-09 | 1994-03-15 | New Japan Chem Co Ltd | Synthetic resin remover |
| US5330788A (en) * | 1992-08-10 | 1994-07-19 | Henkel Corporation | Temporary coating system |
| US5744065A (en) * | 1995-05-12 | 1998-04-28 | Union Carbide Chemicals & Plastics Technology Corporation | Aldehyde-based surfactant and method for treating industrial, commercial, and institutional waste-water |
| MY117988A (en) * | 1995-10-03 | 2004-08-30 | Nor Ind Inc | Cleaning compositions for oil and gas well, lines, casings, formations and equipment and methods of use |
| US7060661B2 (en) * | 1997-12-19 | 2006-06-13 | Akzo Nobel N.V. | Acid thickeners and uses thereof |
| US6176243B1 (en) | 1998-03-30 | 2001-01-23 | Joe A. Blunk | Composition for paraffin removal from oilfield equipment |
| US6908888B2 (en) * | 2001-04-04 | 2005-06-21 | Schlumberger Technology Corporation | Viscosity reduction of viscoelastic surfactant based fluids |
| US6698519B2 (en) | 2002-01-18 | 2004-03-02 | Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. | Methods of forming permeable sand screens in well bores |
| US6699829B2 (en) * | 2002-06-07 | 2004-03-02 | Kyzen Corporation | Cleaning compositions containing dichloroethylene and six carbon alkoxy substituted perfluoro compounds |
| KR20040070114A (en) | 2004-06-17 | 2004-08-06 | 이동재 | Effective and cheap solvents to produce high-quality reclaimed resin from used (expanded) polystyrenes |
| US7615516B2 (en) | 2005-01-21 | 2009-11-10 | Baker Hughes Incorporated | Microemulsion containing oil field chemicals useful for oil and gas field applications |
| US9303203B2 (en) | 2006-06-06 | 2016-04-05 | Schlumberger Technology Corporation | Thermoviscoelastic system fluid and well treatment method |
| US20080139437A1 (en) * | 2006-11-10 | 2008-06-12 | Power John W | Ether-containing paint removing composition |
| FR2912149B1 (en) * | 2007-02-05 | 2012-10-12 | Rhodia Poliamida E Especialidades Ltda | USE OF DIOXOLANE DERIVATIVES IN COATING SYSTEMS AND COATING SYSTEM FORMULATION |
| US7671099B2 (en) * | 2007-08-13 | 2010-03-02 | Rhodia Inc. | Method for spearation crude oil emulsions |
| RU2476254C2 (en) | 2007-08-13 | 2013-02-27 | Родиа Инк. | Method of crude oil emulsion separation |
| EP2252144B1 (en) * | 2008-01-25 | 2023-08-02 | Rhodia Operations | Use of ester amides as solvents, ester amides as such, and method for preparing ester amides |
| US8222194B2 (en) * | 2008-05-09 | 2012-07-17 | Rhodia Operations | Cleaning compositions incorporating green solvents and methods for use |
| JP2011520009A (en) * | 2008-05-09 | 2011-07-14 | ローディア・オペラシオン | Cleaning composition incorporating environmental protection solvent and method of use |
| FR2941462B1 (en) * | 2009-01-23 | 2013-07-05 | Rhodia Operations | STRIPPING COMPOSITION |
| MX2012000413A (en) | 2009-07-09 | 2012-02-08 | 3M Innovative Prosperties Company | Methods for treating carbonate hydrocarbon-bearing formations with fluorinated amphoteric compounds. |
| WO2011086421A1 (en) * | 2010-01-12 | 2011-07-21 | Ecolab Inc. | Floor stripper composition based on renewable raw materials |
| EA201291232A1 (en) * | 2010-06-02 | 2013-07-30 | Родиа Оперейшнс | APPLICATION OF ENVIRONMENTALLY SAFE MICRO-EMULSIONS WHEN CLEANING OIL |
| AU2011289224B2 (en) * | 2010-08-12 | 2015-04-16 | Gfbiochemicals Limited | Carboxy ester ketal removal compositions, methods of manufacture, and uses thereof |
| FR2974113B1 (en) * | 2011-04-18 | 2014-08-29 | Rhodia Poliamida E Especialidades Ltda | PREPARATIONS FOR CLEANING COMPOSITIONS ALL PURPOSES |
-
2012
- 2012-08-01 CA CA2843884A patent/CA2843884C/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2012-08-01 EA EA201490212A patent/EA201490212A1/en unknown
- 2012-08-01 EP EP12820433.6A patent/EP2739699B1/en active Active
- 2012-08-01 AU AU2012290165A patent/AU2012290165B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2012-08-01 CN CN201280047007.8A patent/CN103827253B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2012-08-01 WO PCT/US2012/049171 patent/WO2013019866A2/en active Application Filing
- 2012-08-01 BR BR112014002607A patent/BR112014002607A2/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2012-08-01 MX MX2014001347A patent/MX359074B/en active IP Right Grant
- 2012-08-01 US US13/564,300 patent/US10633579B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| None |
| See also references of EP2739699A4 |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2838951A4 (en) * | 2012-04-17 | 2015-12-16 | Rhodia Operations | Polysaccharide slurries with environmentally friendly activator solvents |
| WO2014035762A1 (en) * | 2012-08-30 | 2014-03-06 | Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. | Low toxicity viscosifier and methods of using the same |
| EA028348B1 (en) * | 2012-08-30 | 2017-11-30 | Хэллибертон Энерджи Сервисиз, Инк. | Low toxicity viscosifier and methods of using the same |
| WO2017035445A1 (en) * | 2015-08-26 | 2017-03-02 | Rhodia Operations | High performance eco-friendly non-emulsifier |
| CN108350348A (en) * | 2015-08-26 | 2018-07-31 | 罗地亚经营管理公司 | High-performance environment-friendly non-emulsifiers |
| WO2021150430A1 (en) | 2020-01-22 | 2021-07-29 | Eastman Kodak Company | Method for making lithographic printing plates |
| US11633948B2 (en) | 2020-01-22 | 2023-04-25 | Eastman Kodak Company | Method for making lithographic printing plates |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2739699B1 (en) | 2021-04-21 |
| EP2739699A4 (en) | 2015-05-06 |
| AU2012290165B2 (en) | 2016-04-28 |
| US20130196885A1 (en) | 2013-08-01 |
| WO2013019866A3 (en) | 2013-07-11 |
| CN103827253B (en) | 2018-12-28 |
| AU2012290165A1 (en) | 2014-02-20 |
| MX2014001347A (en) | 2014-05-13 |
| EA201490212A1 (en) | 2014-05-30 |
| EP2739699A2 (en) | 2014-06-11 |
| MX359074B (en) | 2018-09-13 |
| CA2843884C (en) | 2020-06-16 |
| CN103827253A (en) | 2014-05-28 |
| BR112014002607A2 (en) | 2017-02-21 |
| CA2843884A1 (en) | 2013-02-07 |
| US10633579B2 (en) | 2020-04-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2739699B1 (en) | Use of environmentally friendly solvents to replace glycol-based solvents | |
| AU2011262364B2 (en) | Use of eco-friendly microemulsions in oil cleaning applications | |
| CA2385605C (en) | A method of improving the permeability of an underground petroleum-containing formation | |
| US8628626B2 (en) | Dibasic esters utilized as terpene co-solvents, substitutes and/or carriers in tar sand/bitumen/asphaltene cleaning applications | |
| RU2598959C2 (en) | Thickened viscoelastic fluid media and their application | |
| AU2013284388A1 (en) | Environmentally friendly solvent systems/surfactant systems for drilling fluids | |
| AU773820B2 (en) | A method of improving the permeability of an underground petroleum-containing formation | |
| CA2859162A1 (en) | Solvent systems of n-alkyl thiophosphoric triamides and methods of use in agricultural applications | |
| US8722610B2 (en) | Auto-emulsifying cleaning systems and methods for use | |
| EP2992066A1 (en) | Water-soluble corrosion inhibitor for protection of lifting casings and natural gas pipelines as well as the method of its production. | |
| US20110039749A1 (en) | Methods for cleaning recyclable substrates or containers | |
| AU2010298509B2 (en) | Foamers for downhole injection | |
| US20130157917A1 (en) | Industrial cleaning compositions and methods for using same | |
| EP2992065A1 (en) | Corrosion inhibitor for protection of crude oil extraction equipment, crude oil pipelines, and crude oil tanks as well as the method of its production | |
| AU2013249359A1 (en) | Polysaccharide slurries with environmentally friendly activator solvents |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 12820433 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A2 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2843884 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: MX/A/2014/001347 Country of ref document: MX |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201490212 Country of ref document: EA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2012820433 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2012290165 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20120801 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: A201401982 Country of ref document: UA |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112014002607 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112014002607 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20140203 |