ORAL LIQUID FORMULATION COMPRISING SALBUTAMOL AND GUAIFENESIN
Field of Invention:
The invention is related to pharmaceutical compositions to treat respiratory system disorders. In particular the invention is related to the pharmaceutical compositions to treat coughs. Background Of The Invention:
A respiratory system's function is to allow gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles. A cough in clinical terminology, is a sudden and often repetitively occurring defense reflex which helps to clear the large breathing passages from excess secretions, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. Since cough is a natural protective reflex, suppressing the cough reflex might have deleterious effects, especially if the cough is productive. Nonetheless, coughing might be severe enough (in terms of psychological, physical and social distress) to warrant treatment.
Asthma is a chronic inflammation of the lungs in which the airways (bronchi) are reversibly narrowed. Asthma affects nearly 300 million people worldwide.
Treatment
Coughs can be treated with cough medicines. Dry coughs are treated with cough suppressants (antitussives) that suppress the urge to cough, while productive coughs (coughs that produce phlegm) are treated with expectorants that loosen mucus from the respiratory tract. Asthma is of two major types i.e., a bronchospastic kind when there is a sudden muscular narrowing of air passages, and the inflammatory type which not only narrows the air passages but also creates mucus.
Today, most of the modes of treatment focus on methods of preventing or treating inflammation. Active inflammation is normally treated with the help of corticosteroids whereas broncodialators are used to relax airway muscles.
Suppresants and expectorants: Cough suppressants act to reduce the urge to cough. Centrally acting cough suppressants such as codeine and dextromethorphan work by depolarization or dulling of the vagus nerve, the nerve leading from the brain stem and serving the chest area. Benzonatate, sold under the brand names Tessalon Perles or Tessalon Capsules, works by anesthetizing stretch receptors in the lungs. An expectorant is a medication that helps bring up mucus and other material from the lungs, bronchi, and trachea. An example of an expectorant is guaiphenesin which promotes drainage of mucus from the lungs by thinning the mucus. It also lubricates the irritated respiratory tract. Sometimes the term "expectorant" is incorrectly used to indicate cough medicine of any type. Some of the more commonly used oral anti-asthmatic agents include Salbutamol, and the like. Some of the more commonly used oral expectorants include Guaiphenesin, and the like.
Allergic reactions of degraded components of Salbutamol could compromise safety, particularly of asthmatic patients who are susceptible to degraded products. Children and geriatrics alike suffer from cough and asthma. It is important that severe cases of cough and asthma be treated appropriately. The currently available asthma medications containing Salbutamol (also known as albuterol) and expectorants containing Guaiphenesin have several drawbacks.
Salbutamol, which contains an amino group, is known for its instability in the presence of aldehydes compounds. In particular, it is known that the presence of a
substance such as sucrose, or sorbitol or glycerol in aqueous compositions of salbutamol or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof is associated with an accelerated deterioration in the stability of the salbutamol in the composition. There have been attempts made to improve the stability of salbutamol formulations. US patent 4594359, for example, discloses a salbutamol aqueous formulation which uses a cellulose derivative to enhance the stability the formulation by forming a colloidal dispersion.
Expectorants containing Guaifenesin or guaiphenesin (also known as glyceryl guaiacolate) are widely available as over the counter medication and usually taken by mouth to assist the bringing up or "expectoration" of phlegm from the airways in case of acute respiratory tract infections. Guaiphenesin is sold as pills or syrups under many brand names. It is also available in combination with codeine. Guaiphenesin is also a part of Robitussin DAC which is a prescription cold medicine available in the United States in a solution form. A version without pseudoephedrine is called Robitussin AC whose taste mimics cherries but is said to have an unpleasant after-taste.
Similar medicines derived from the guaiac tree were in use as a generic remedy by native Americans when European explorers reached North America in the 1500's. Guaiphenesin was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1952.
The principal use of guaiphenesin is in the treatment of cough, but the drug has numerous other uses, including medical, veterinary, and personal.
Formulations containing Guaiphenesin (also known as glycerol guaiacolate) are characteristically known for their bitter taste in absence of bitterness-masking agents. US patent RE29359 discloses compositions containing glycerol guaiacolate and theophylline, which use various sweetening and flavoring agents including sugar syrup which was found to be a particularly satisfactory vehicle.
Schering corporation has obtained a patent on Salbutamol Oral Solution claiming pleasant taste and stability (Ref: U.S. patent number 4,499,108). However a drawback of the US patent RE29359 and 4499108 are that these do not cater to asthma and cough simultaneously. As asthma attacks normally go hand in hand with cough there's a need to provide a fixed dose formulation that would be effective against both asthma and related ailments, and cough. Combinations containing salbutamol and Guaiphenesin would serve this purpose. There are medications available which combine salbutamol for its suitability to treat asthma and Guaiphenesin for its expectorant properties. Two such examples are Ventolin expectorant by GlaxoSmithKline and Asthalin Expectorant by CIPLA.
Generally oral liquid preparations are maintained slightly at acidic conditions in order to prevent the microbial growth. However, if such formulations contain any sugar based syrups, any sugars (disaccharide) in the formulation get converted into reducing sugars (monosaccharides) such as glucose and fructose which further decomposes to 5 Hydroxy Methyl Furfural (HMF) which reacts with amino group of Salbutamol. This leads to the degradation of salbutamol. Allergic reactions of degraded components of Salbutamol could compromise safety, particularly of asthmatic patients who are susceptible to exacerbation of asthma resulting from the possible allergic reactions caused by the use of degraded products.
Commercially available leading brands of Salbutamol Sulphate in combination with Guaiphenesin in oral liquid dosage form include Cipla's Asthalin
Expectorant and GlaxoSmitKline' s Ventolin Expectorant. These brands have been commercially available for more than two decades in India as well as in overseas market such as Philippines, and United Kingdom.
Asthalin Expectorant is sugar based formulation with Salbutamol and Guaiphenesin as APIs. Ventolin Expectorant marketed worldwide by GlaxoSmithKline is an oral liquid formulation with Salbutamol and Guaiphenesin as APIs. A key drawback of the GSK Ventolin expectorant is its poor or bitter tase and a foul after-taste. This could lead to rejection of medication by children and geriatrics who represent some of the most vulnerable patient groups. We therefore suggest that Ventolin is a formulation in which salbutamol is found to be stable but which is highly unpalatable. The Cipla product provides a palatable formulation at the cost of stability of salbutamol. It is evident from Figure 1 that the salbutamol of Asthalin undergoes a substantial degradation during its shelf life, as indicated by reduction in the area under the curve for the peak that represents salbutamol.
The formulations that are unpalatable stand the risk that the patient will not consume the medication at a sufficient frequency and in required quantities. The formulations that are unstable stand the risk that inferior quality or substandard product will be consumed by the patient, albeit in recommended quantities. Substandard product also holds out the possibility of causing allergic conditions and anxiety in the consumer. Both scenarios are real especially considering the large number of patients that use such products that fall into children and geriatric categories, both known for their resistance to consume any medication at a required frequency and dosage.
Another aspect of the existing pharmaceutical compositions containing sugar based syrups is that they require a heating step in creation of the syrup. This adds to the cost of the formulations and consumes energy that can be saved if sugar were not to be used in such formulations.
There is a further aspect of stability testing of key APIs of some of the existing pharmaceutical formulations using salbutamol and guaiphenesin. The inventor has found out that the existing methods of testing the quality of the API - salbutamol
in the formulation prevalent in the industry, namely the UV method, is not stability indicating. For example the API - salbutamol degradation observed in the finished formulation prepared by using ingredients which were tested by the UV method suggests that the API - salbutamol is more stable than it actually is. It is also a well known fact that the UV methods of chemical component analysis do not provide accurate way of determining the stability of compositions containing salbutamol in terms of amount of degraded salbutamol present in the product. There is a need to provide a method, preferably based on HPLC technique of accurately determining the stability of formulations containing salbutamol. Therefore there is a need for providing a formulation that will simultaneously address the issues of stability of the key ingredients and palatability of the formulation. There's also a need for formulations that will be useful simultaneously as an expectorant for cough and relief medication for asthma while being stable and palatable over its shelf life and thereby reducing the possibility of allergic reactions to asthmatic patients. There's a further need for such formulation which can be produced in a more environmentally friendly manner than the existing formulations. There is also a need to provide a reliable stability indicating method that indicates true level of degradation of product API.
Object of the present invention: One of the main objects of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical composition suitable as treatment against asthma and cough.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical composition that is useful simultaneously towards cough and asthma and which is stable and palatable over its entire shelf life. Yet another object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical formulation that reduces the chance of allergic reaction particularly for asthma patients.
A further object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical formulation towards cough and asthma that is prepared using a process that is more environment friendly than the currently available formulations. The process of the present invention has very little beneficial impact on the environment when compared to the traditional energy consuming syrup process. However, considering the wide usage of the cough expectorants, the long term and collective beneficial impact of elimination of sugar syrups from expectorant preparation is considerable.
A still further objective of the present invention is to provide an HPLC-based stability indicating method for salbutamol.
List of figures:
Figure 1 : HPLC analysis of 18 months old Asthalin sample chromatograms for salbutamol sulphate
Figure 2: HPLC analysis of 18 months old sample of the product of the present invention chromatograms for salbutamol sulphate
Figure 3: HPLC analysis of standard chromatograms for salbutamol sulphate for Asthalin
Figure 4: HPLC analysis of standard chromatograms for salbutamol sulphate for the present invention Figure 5: Comparison of the invention with existing products (18 month stability tests at room temperature)
Figure 6: Comparison of the invention with existing products (One month stability tests at elevated temperature)
Brief summary of the invention:
Thus, the present invention provides an improved pharmaceutical composition which comprises an aqueous dispersion of one or more cellulose derivatives containing salbutamol and/or one or more of its physiologically acceptable salts and guaiphenesin.
The pH of the formulation has been maintained at around 4.5 with citrate buffer for better stability of salbutamol.
The stability of Salbutamol in the present invention was confirmed on real time and accelerated studies at different conditions in comparison with sugar based Asthalin Expectorant. Stability studies on this present invention indicate that the formulation of the present invention has a guaranteed shelf life which will meet the statutory requirements of regulatory bodies. The studies carried out by the inventors also indicate that Asthalin Expectorant loses its stability and efficacy within 12 months when tested by stability indicating HPLC method. In summary, the present invention is directed to a composition for treating asthma and cough containing a) An active pharmaceutical ingredient, preferably salbutamol or its salt for the treatment of Asthma.
b) An expectorant, preferably guaiphenesin or its salt for the expulsion of mucus from respiratory tract.
c) A liquid base or vehicle containing natural or synthetic polymers, preservatives, sweeteners, buffering agents, and flavours.
d) Water.
The present invention is also directed to an innovative process of formulating an oral liquid dosage form having the above named APIs, namely Salbutamol sulphate & Guaiphenesin, possessing good stability coupled with palatability. The
APIs are incorporated in a liquid base for the treatment of Asthma, and uses as bronchodilator and expectorant in certain respiratory conditions.
Detailed description of the invention:
In a first aspect of the present invention, a novel pharmaceutical composition containing salbutamol and guaiphenesin as APIs is provided The present invention which is a novel pharmaceutical formulation was also stabilised by using Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and Polyvinyl pyrrolidone ( PVP K - 90 ), which are known to be used to stabilize or increase the solubility of APIs (Pharmaceutical Research journal Vol 25, nol Jan 2008). The chemical stabilisation of the API used in the present invention is achieved by eliminating the use of sugar/aldehyde type of compounds, also the step of heating that is commonly used in preparation of existing formulations.
The inventors have succeeded in eliminating the bitter taste contributed by Guaiphenesin while maintaining the stability by carefully designing the formulation. The taste of the formulation of the present invention was improved by using sweetening agents like Neotame and the like for higher palatability along with flavoring agents like Orange flavour® and Taste Masking Agent®, both by Firmenich.
The stability of Salbutamol in the present invention was confirmed on real time and accelerated studies at different conditions in comparison with sugar based Asthalin Expectorant. Stability studies on this present invention indicate that the formulation of the present invention has a guaranteed shelf life which will meet the statutory requirements of regulatory bodies. The studies carried out by the inventors also indicate that Asthalin Expectorant loses its stability and efficacy within 12— months when tested by stability indicating HPLC method.
The presence of reducing sugars in Asthalin Expectorant and absence of reducing sugars in the present invention were confirmed by the inventors using Fehling' s titration method.
The HPLC method designed and modified from the pharmacopoeial method by the inventors to test the stability of the API in the finished formulation allows superior control over quality of API in the end product.
In our present invention Salbutamol Sulphate API in finished product is analyzed by stability indicating, in-house developed HPLC method.
The stability studies were carried out by adapting a method disclosed in the US Pharmacopia (USP) by making appropriate modification. The USP method is designed for salbutamol tablets. Adaptation of the USP method for testing the invention uses a modified mobile phase. The sample preparation for testing purpose was also modified from the USP method, which uses salbutamol tablets. The modified method used in the present invention is summarised in Table 1.
Table 1: USP method of stability analysis of salbutamol tablets and the modified method of stability analysis of salbutamol in the present invention (oral solution)
A Ibuterol table t USP Method Vs Modified metti lod for testing of the liquid formulation of the present in vention
Modified HPLC method to test the formulation of preferred embodiment of the S.No Description Albuterol tablet USP Method invention
1 Chromatographic conditions:
Column 150x4.6mm, LI 150x4.6mm, CI 8
Detection
wavelength 276 nm 276 nm
Injection
volume 25μ1 20 μΐ
Temperature Ambient Ambient
Flow rate 1.5 ml/min 1.0 ml/min
Diluent
preparation 1 % Acetic acid 1 % Acetic acid
Mobile Dissolve 1.13 g of Sodium 1- Dissolve 1.13 g of Sodium 1- phase hexanesulfonate hexanesulfonate
in 1200 ml of water, add 12 ml in 1200 ml of water, add 1.2 of glacial acetic acid, and mix. ml of glacial acetic acid, and
Prepare a filtered and degassed mix. Prepare a filtered and mixture of this solution and degassed mixture of this methanol (6:4). solution and methanol (6:4).
Transfer about 12 mg of USP Transfer about 300 mg of
Standard Albuterol sulphate RS, accurately Salbutamol sulphate WRS, preparation weighed, to a 100 ml volumetric accurately weighed, to a 100 flask. ml volumetric flask.
Add 60ml of 1% Acetic acid, Add 60ml of 1 % Acetic acid, sonicate for 5 minutes, sonicate for 5 minutes, dilute with methanol to volume, dilute with methanol to and mix. volume, and mix.
Pipet 5 ml of this solution into a 50 ml volumetric flask, and
Pipet 25 ml of this solution into a from this dilute 5ml to 50 ml
100 ml volumetric flask, with diluent.
dilute with mixture of water and
methanol (6:4) to volume, and dilute with mixture of diluent mix. and methanol (6:4)
Sample Transfer a number of whole Weigh accurately equivalent to preparation Tablets, equivalent to 5 mg of salbutamol Sulphate about 50mg of albuterol, to a sample into a 200 ml
2000 ml volumetric flask. volumetric flask and
add 120 ml of 1% Glacial
Add 1200 ml of 1 % Acetic acid, acetic acid, Shake by
Shake by mechanical mechanical
means for 45 minutes, sonicate means for 45 minutes, for 10 minutes, sonicate for 15 minutes, allow to cool to room under cool condition and temperature, dilute with methanol make up the volume with to volume, and mix. methanol.
Pass through a suitable filter Filter through 0.45μ membrane having a 0.45 μιη. filter and use.
The inventors have performed the stability tests on the invention as per ICH guidelines against Asthalin Expectorant by the manufacturer Cipla and also on Ventolin expectorant by GSK. The results clearly indicate a surprisingly superior stability of the product of the invention over Asthalin Expectorant. Tests were carried out at room temperature for over a period of 18 months from the date of manufacture and at elevated temperatures of 50 °C and 60 °C at one month from the date of manufacture. The physical appearance of the product during the tests along with their taste and smell was also observed. The taste and smell is of particularly important as poor taste and smell would result in non-consumption by the patients. Results are presented in Tables 2 to 4 and Figures 5 and 6.
Table 2: One-month stability at elevated temperature
Table 3: Eighteen month stability at room temperature (25-30 °C)
Table 4: Physical appearance, taste and smell
From Tables 2 to 4 it is evident that Salbutamol provides superior stability through out its shelf life over the existing products that have been made palatable to children by addition of aldehyde groups. It is also evident that the product of the invention provides superior palatability over the comparable products commercially available and which have been produced without the presence of aldehyde groups but which lend unacceptable palatability for consumption by children.
Figure 2 it is clear that the present invention ensures that salbutamol is stable over its entire shelf life with the stability level remaining within the required range (as per the international norms). It is also observed that one of the existing product, which when tested using the modified USP method of the present invention, appear not to be stable to the required level over their shelf lives, ie within 12 months since their manufacture. The inventors have thus removed several major flaws with the existing pharmaceutical formulations containing salbutamol and guaiphenesin. The present invention thus has provided a single pharmaceutical composition that provides relief both for asthma and cough.
Clinical studies for the present invention was also designed in a way such that the bioavailability of the invention, its efficacy and safety are compared with the reference product Ventolin® Expectorant, containing Salbutamol 2 mg and
Guaiphenesin 100 mg / 10 ml manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline, Philippines. Table 5: Statistical Summary of the Comparative Bioavailability Data for Salbutamol 2 mg
data
Table 6: Statistical Summary of the Comparative Bioavailability Data for Guaifenesin 100 mg
Table 7: Individual Subject plasma Salbutamol Concentrations (ng/mL) for Test Product
BLQ: Below Limit of Quantification (0.1151 ng/mL)
Table 8: Individual Subject plasma Guaifenesin Concentrations (ng/mL) for Test Product
BLQ: Below Limit of Quantification (1.0684 ng/mL) NS: No Sample
Table 9: Individual Subject plasma Salbutamol Concentrations (ng/mL) for Reference Product
BLQ: Below Limit of Quantification (0.1151 ng/mL) M: Missing Sample
Table 10: Individual Subject plasma Guaifenesin Concentrations (ng/mL) for Reference Product t
o
BLQ: Below Limit of Quantification (1.0684 ng/mL) M: Missing Sample
Table 11: Comparative Evaluation of Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Salbutamol 2 mg (Test)
Table 12: Comparative Evaluation of Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Guaifenesin 100 mg (Test)
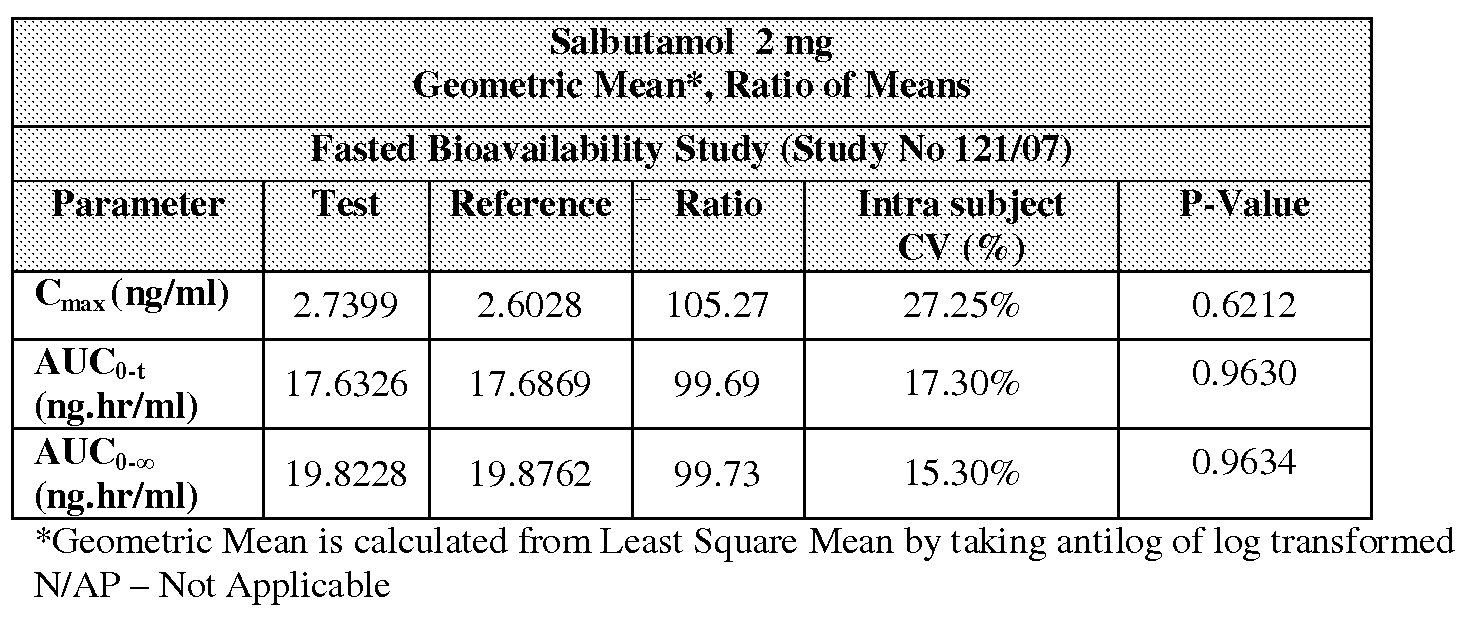
The summary statistics of the comparative bioavailability data and comparative evaluation of pharmacokinetic parameters for Salbutamol and Guaifenesin are presented in the Tables 5, 6 and 11 , 12 respectively. The individual Subject plasma Salbutamol and Guaifenesin concentrations (ng/ml) for test products are presented in Tables 7 and 8 respectively and individual Subject plasma Salbutamol and Guaifenesin concentrations (ng/ml) for reference products are presented in Tables 9 and 10 respectively.
There is no statistical significance found on the Test Vs Reference products at 5 % level of significance for both Salbutamol and Guaifenesin. The P value for Ln transformed PK parameters, Cmax, AUCo-t and AUCo-∞, were 0.6212, 0.9630 and 0.9634 for Salbutamol and 0.2170, 0.5319 and 0.3877 for Guaifenesin respectively. Hence it can be concluded that both Salbutamol and Guaifenesin of Test and Reference products were comparable.
Moreover, based on the point estimate for Salbutamol 2 mg, ratio of Least Square Mean of Test and Reference formulation is comparable. For Cmax, AUCo-t and AUCo-∞o the ratio (%) arel05.27, 99.69, and 99.73 respectively (Refer Table 3A) and the point estimate for Guaifenesin 100 mg, T/R ratio of Least Square Mean of test and reference formulation is comparable. For Cmax, AUCo-t and AUCo-oo the ratio (%) are 89.89, 96.18 and 94.62 respectively (Refer Table 3B).
CONCLUSION
In this study single oral dose of test and reference product did not produce any untoward adverse events and thus it could be concluded that both the test and reference product showed comparable safety profile and were well tolerated in the participating Subjects.
The Statistical Report indicates that the point estimates (T/R ratio) of Test and Reference formulation are within 89.89 to 105.27. Therefore, it can be concluded that the products Salbutamol 2 mg and Guaifenesin 100 mg/10 ml manufactured by apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd., India, and Liquid Ventolin® Expectorant, containing Salbutamol 2 mg and Guaifenesin 100 mg/10 ml manufactured by Glaxo SmithKline, Philippines, are comparable under fasting conditions.
The novel oral liquid dosage form of the present invention, is very stable, efficacious, and highly palatable with a complete lack of bitter taste at ambient conditions and does not need special temperature control during transportation and storage; hence, it will go a long way in achieving the social objectives.
The excipients used in the present invention are selected so that they enhance the taste without affecting the stability of salbutamol. It is well known that the stability of salbutamol is affected by excipients having sugar moieties like sucrose, sorbitol etc. This is because any sugars (disaccharide) in the formulation get converted into reducing sugars (monosaccharides) such as glucose and fructose which further decomposes to 5 Hydroxy Methyl Furfural which reacts with amino group of Salbutamol. This leads to the degradation of salbutamol. This is explained in terms of chemical reactions as below:
The salbutamol sulphate is very labile in sucrose solution. It decomposes to form the corresponding oxidized products. The mode of decomposition of salbutamol in sucrose solution is not very evident. In the presence of dilute acid, sucrose is known to undergo hydrolysis to give a mixture of D-glucose and D-fructose which on further dehydration leads to 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF) as shown below:
OH OH OH O dil acid
Sucrose ► HO" HO"
OH OH O OH OH OH
D-Glucose D-Fructose
5-Hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF)
The resultant HMF undergoes the so called "Molisch Condensation" reaction with two molecules of salbutamol sulphate under acidic conditions to give the
corresponding adduct which on further oxidation leads to coloured compound. The unusual reaction of salbutamol sulphate with HMF is shown above.
The present invention therefore uses those excipients which are devoid of sugar moieties and aldehyde functional groups. In particular, the preferred agents for taste enhancement according to the present invention are any of the group
comprising Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, Povidone ®, Taste Masking Agent and Orange flavour by Firmenich,
On the background of the instability of Salbutamol in the presence of aldehydes, it is of crucial importance that the presence of aldehydes is determined with reliable testing methods. The test method adopted by the inventors is based on Tollen's test (also known as the silver mirror reaction) is now described.
Tollen's Test:
Aldehyde will reduce ammoniacal silver solution to give a precipitate of Silver metal. The aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid. A positive result is the formation of a silver mirror on the surface of the test tube, or a black precipitate of the metal. The reaction often involves an induction period of a few minutes.
RCHO + 2Ag(NH3)2OH ^ 2Ag(s) + RCOO" NH4 + + H2 O + NH3
Test procedure:
Place 30 ml, of silver nitrate solution in a 150ml beaker. Add concentrated (15 M) ammonia drop wise, with stirring, until the brown precipitate just dissolves. Add 15 ml of potassium hydroxide solution. If the brown precipitate reforms, add additional ammonia solution, drop wise, until it dissolves.
Pour 3ml of dextrose solution into the flask. Add the contents of the beaker and stopper the flask. Shake the flask so that the liquid comes in contact with the entire inner surface of the flask. The silver film should begin to form within about 1 minute. Continue to shake until the flask has a silver mirror coating (this may take about 5 minutes).
Dispose of the solution and rinse the flask well with water (at least four complete rinsings). After the flask has dried completely, it may be stoppered with a cork, rubber stopper, or appropriate cap. The flask may be used as a Christmas tree ornament by attaching a wire tree hanger to the cork or stopper (a screw eyelet may be needed in the cork or stopper.) A drop of super glue placed at top of the flask, at the edge of the stopper, will help to hold the stopper in place. The coating in the flask or bottle is permanent. Keep the flask or bottle stoppered to prevent oxidation. Do not add any liquids to the container, as it will remove the silver from the glass.
The Tollen's test is used to detect the presence of aldehyde groups. The reaction that takes place is:
Dextrose (an aldehydic Sugar)
The Tollen's test was carried out on the product of the present invention as well as Asthalin and Ventolin samples.
Table no.13 : Results of aldehydes presence determination tests
The above test indicates that the present invention is free from aldehydic functional group which is achieved by careful design of formulation by screening of excipients.
The preferred embodiments are now disclosed. According to the preferred embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a oral liquid composition for the treatment of Asthma, and use as a bronchodilator and an expectorant in certain respiratory conditions on humans, the composition comprising
from about 0.001% (w/v) to about 5% (w/v ) by weight, preferably from about 0.01 % (w/v) to about 5% (w/v) by weight and most preferably from about 0.01% (w/v) to 2% (w/v) by weight, of Salbutamol sulphate, and,
from about 0.01 % (w/v) to about 10% (w/v) by weight, preferably from about 0.05% (w/v) to about 5% (w/v) by weight and most preferably from about 0.1% (w/v) to 2% (w/v) by weight, of Guaiphenesin, and, a non-syrupy liquid base containing polymers, preservatives, sweeteners, buffering agents, flavouring agents, water, all weights based on the weight of the composition, wherein
- polymers are selected from tragacanth, pectin, carrageen, agar, alginic acid, methylcellulose, hydroxyethylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose, Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP K - 90 ), hydro xypropylcellulose, hydro xypropylmethylcellulose and carbopols and the like from about 0.5% (w/v) to 10% (w/v),
- preservatives are selected from a group comprising Methylparaben sodium, Propylparaben sodium, Sodium benzoate and the like from about 0.005% (w/v) to 5% (w/v),
- Sweeteners are selected from a group comprising Aspartame, Neotame, Saccharin sodium and the like from about 0.005% (w/v) to 1 % (w/v),
- Buffering agents are selected from a group comprising Sodium citrate, citric acid and the like from about 0.05% (w/v) to 1.00% (w/v),
- Flavouring agents are selected from a group comprising Taste Masking agent, Orange flavour and the like from about 0.05% (v/v) to 1.00% (v/v),
According to another embodiment of the present invention a process to manufacture a novel oral liquid formulation for use against asthma and cough is provided comprising the steps of: a. providing individual components comprising:
from about 0.001% (w/v) to about 5% (w/v ) by weight, preferably from about 0.01 % (w/v) to about 5% (w/v) by weight and most preferably from about 0.01% (w/v) to 2% (w/v) by weight, of Salbutamol sulphate, and, from about 0.01 % (w/v) to about 10% (w/v) by weight, preferably from about 0.05% (w/v) to about 5% (w/v) by weight and most preferably from about 0.1 % (w/v) to 2% (w/v) by weight, of Guaiphenesin, and, a non-syrupy liquid base containing polymers, preservatives, sweeteners, buffering agents, flavouring agents, water, all weights based on the weight of the composition, wherein
- Polymers are selected from tragacanth, pectin, carrageen, agar, alginic acid methylcellulose, hydroxyethylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose, Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP K - 90 ), hydro xypropylcellulose, hydro xypropylmethylcellulose and carbopols and the like from about 0.5% (w/v) to 10% (w/v),
Preservatives are selected from a group comprising Methylparaben sodium, Propylparaben sodium, Sodium benzoate and the like from about 0.005% (w/v) to 5% (w/v),
Sweeteners are selected from a group comprising Aspartame, Neotame, Saccharin sodium and the like from about 0.005% (w/v) to 1 % (w/v),
- Buffering agents are selected from a group comprising Sodium citrate, citric acid and the like from about 0.05% (w/v) to 1.00% (w/v),
- Flavouring agents are selected from a group comprising Taste Masking agent, Orange flavour and the like from about 0.05% (v/v) to 1.00% (v/v), b. Dissolving Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose in Purified Water in a manufacturing mixing vessel.
c. Dissolving Methylparaben sodium and Propylparaben sodium in Purified Water and adding to above step b and stirring.
d. Dissolving Polyvinyl pyrrolidone ( PVP K - 90 ) in Purified Water and adding to step c and stirring.
e. Dissolving Neotame in Purified Water and adding to step d and stirring. f. Dissolving Sodium citrate and in Purified Water and adding to step e and stirring.
g. Dissolving Citric acid in Purified Water and adding to step f and stirring. h. Dissolving Salbutamol sulphate in Purified Water and adding to step g and stirring.
i. Dissolving Guaiphenesin in Purified Water and adding to step h and stirring.
j. Adding Flavouring Agent - Orange and Taste Masking Agent to step i and stirring.
k. Filtering the above bulk solution through 200 # mesh and making up the volume and stirring.
1. Checking the pH of the bulk solution and transferring to storage tank.
Mixing thoroughly all the ingredients and making a homogeneous product by using processing equipments such as mixers, homogenizers, stirrers and the like known to the person skilled in the art.
It is evident from the above described process that there is no external heat supply required to manufacture the invention.
Examples:
As an example of the preferred embodiment a formulation was prepared using the following ingredients:
a) 80 to 98 percent Purified Water; preferably 94.7%
b) 0.001 0.05 percent Salbutamol sulphate; preferably 0.025%
c) 0.1 to 2 percent Guaiphenesin; preferably 1%
d) 0.1 to 2 percent Polymer; preferably 0.45 percent Hydro xypropylmethylcellulose
(4000 cps)
e) 0.01 to 0.5 percent Preservative; preferably 0.05 percent Methylparaben sodium
f) 0.001 to 0.5 percent Preservative; preferably 0.005 percent Propylparaben sodium
g) 0.001 to 0.1 percent Sweetening agents; preferably 0.025 percent Neotame h) 0.1 to 1 percent Buffering Agent; preferably 0.3 percent Sodium citrate i) 0.1 to 1 percent Buffering Agent; preferably 0.225 percent Citric acid
j) 1 to 5 percent Polymer; preferably 2.5 percent Polyvinyl pyrrolidone ( PVP K - 90 )
k) 0.01 to 1 percent Flavouring Agent; preferably 0.5 percent Orange flavour®.
1) 0.01 to 1 percent Taste Masking Agent; preferably 0.2 percent Taste Masking Agent®.
The formulation was prepared using the above ingredients and the process described in an embodiment of the present invention.
The composition of the final oral liquid solution formulation as prepared in the above example is given in the Table 14 below.
Table 14: Quantification of the preferred embodiment of the present invention
* IHS - In-house specifications
The therapeutic efficacy of orally administered innovative Salbutamol sulphate - Guaiphenesin oral liquid is due to the pronounced antiasthmatic, bronchodilator, and expectorant activity of the APIs in respiratory conditions and also due to the unique stability & palatability of this formulation.
According to another embodiment of the present invention, there is also provided a process for treating asthma, certain respiratory conditions as a bronchodilator and as an expectorant in humans with the above-disclosed composition.
It is clear from the forgoing discussion that the present invention is made of the following items.
Item 1 : A novel pharmaceutical oral liquid formulation comprising a first active pharmaceutical agent and a second active pharmaceutical agent agent, and a non- syrupy liquid base, wherein said first active is preferably salbutamol sulphate, said second active pharmaceutical agent is guaiphenesin.
Item 2: A novel pharmaceutical oral formulation as described in item 1 , wherein said salbutamol sulphate is provided in the range between 0,001% (w/v) to 5% (w/v), preferably from about 0.01 % (w/v) to about 5% (w/v), and more preferably from about 0.01% (w/v) to 2% (w/v).
Item 3: A novel pharmaceutical oral formulation as described in item 2, wherein said guaphenesin is provided in the range between about 0.01 % (w/v) to about 10% (w/v), preferably from about 0.05% (w/v) to about 5% (w/v), and more preferably from about 0.1 % (w/v) to 2% (w/v).
Item 4: A novel pharmaceutical oral formulation as described in item 3, wherein said non-syrupy liquid base contains at least one of each of a polymer, a preservative, a sweetener, a buffering agent, a flavouring agents, and water. Item 5: A novel pharmaceutical oral formulation as claimed in claim 4, wherein said polymers are selected from a group comprising tragacanth, pectin, carrageen, agar, alginic acid, methylcellulose, hydroxyethylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose, Polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP K - 90 ), hydroxypropylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and carbopols and the
like, preferably in the range between about 0.5% (w/v) to 10% (w/v), and wherein
said preservative is selected from a group comprising Methylparaben sodium, Propylparaben sodium, Sodium benzoate and the like from about 0.005% (w/v) to 5% (w/v), said sweeteners is selected from a group comprising aspartame, neotame, saccharin sodium and the like, preferably in the range between about 0.005% (w/v) to 1% (w/v), said buffering agent is selected from a group comprising Sodium citrate, citric acid and the like, preferably in the range between about 0.05% (w/v) to 1.00% (w/v), and said flavouring agents is selected from a group comprising preferably the
Taste Masking agent®, Orange Flavour®, both supplied by Firmenich, and the like in the range between about 0.05% (v/v) to 1.00% (v/v).
Item 6: A process of making a novel pharmaceutical oral formulation comprising the steps of:
a. providing the ingredients of formulation claimed in claim 1
b. dissolving a first polymer, preferably Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose in purified water in a manufacturing mixing vessel,
c. dissolving a preservative, preferably Methylparaben sodium and Propylparaben sodium in purified water and adding to the mixture obtained in step b and stirring,
d. dissolving a second polymer, preferably Polyvinyl pyrrolidone ( PVP K - 90 ) in purified water adding to the mixture obtained in step c and stirring, e. dissolving a sweetener, preferably Neotame in purified water adding to the mixture obtained in step d and stirring,
f. dissolving a first buffering agent, preferably Sodium citrate in Purified Water and adding to the mixture obtained in step e and stirring, g. optionally dissolving a second buffering agent, preferably citric acid in purified water adding to the mixture obtained in step f and stirring, h. dissolving a first active pharmaceutical agent, preferably Salbutamol sulphate in purified water adding to the mixture obtained in step g and stirring,
i. dissolving a second active pharmaceutical agent, preferably Guaiphenesin in purified water adding to the mixture obtained in step h and stirring, j. adding a flavouring agent, preferably Orange Flavouring® and Taste
Masking Agent or a combination thereof, to the mixture obtained in step i and stirring,
k. filtering the bulk solution obtained at the end of step I through 200 size mesh and making up the volume by adding water, and stirring,
1. checking the pH of the bulk solution obtained at the end of step k and transferring it to a storage tank,
m. making a homogeneous product by using processing equipments such as mixers, homogenizers, stirrers and the like known to the person skilled in the art.