WO2010050503A1 - 移動局及び移動通信方法 - Google Patents
移動局及び移動通信方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2010050503A1 WO2010050503A1 PCT/JP2009/068493 JP2009068493W WO2010050503A1 WO 2010050503 A1 WO2010050503 A1 WO 2010050503A1 JP 2009068493 W JP2009068493 W JP 2009068493W WO 2010050503 A1 WO2010050503 A1 WO 2010050503A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- cell
- mobile station
- communication
- information
- information block
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 18
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 89
- 238000010295 mobile communication Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 101150096310 SIB1 gene Proteins 0.000 abstract 2
- 101150039363 SIB2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 25
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013507 mapping Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/0005—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off
- H04W36/0007—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off for multicast or broadcast services, e.g. MBMS
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/08—Reselecting an access point
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/08—Access restriction or access information delivery, e.g. discovery data delivery
- H04W48/10—Access restriction or access information delivery, e.g. discovery data delivery using broadcasted information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/06—Selective distribution of broadcast services, e.g. multimedia broadcast multicast service [MBMS]; Services to user groups; One-way selective calling services
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/16—Discovering, processing access restriction or access information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W88/00—Devices specially adapted for wireless communication networks, e.g. terminals, base stations or access point devices
- H04W88/02—Terminal devices
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a mobile station and a mobile communication method.
- a radio base station eNB in a subordinate cell has an MIB (Master Information Block, main information block) or SIB1 (System Information Block 1, No. 1). Broadcast information including a system information block) is transmitted, and the mobile station UE in the cell is configured to perform predetermined communication based on the information in the MIB and SIB1 included in the broadcast information.
- MIB Master Information Block, main information block
- SIB1 System Information Block 1, No. 1
- the mobile station UE when the mobile station UE fails to receive SIB1 or the like in the second cell when handing over from the first cell to the second cell, the mobile station UE communicates in the second cell. There was a problem that it was impossible to continue.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a mobile station and a mobile communication method capable of continuing communication in a cell.
- a first feature of the present invention is a mobile station, which receives a main information block included in broadcast information in the second cell when handed over from the first cell to the second cell in response to the received handover command.
- a broadcast information receiving unit configured to receive a first system information block included in the broadcast information based on information included in the main information block; and the broadcast system information receiving unit configured to receive the first system information When the reception of the block is successful, in the second cell, the first communication using the information included in the main information block, the first system information block, and the handover command is started, and the broadcast information When the reception unit fails to receive the first system information block, in the second cell, the main information block and the handover And summarized in that includes a communication unit configured to perform a second communication using information included in the command.
- a second feature of the present invention is a mobile communication method, which is included in broadcast information in the second cell when the mobile station performs handover from the first cell to the second cell in response to the received handover command.
- Receiving a main information block receiving a first system information block included in the broadcast information based on information included in the main information block, and the mobile station successfully receiving the first system information block In the second cell, starting the first communication using the information included in the main information block, the first system information block and the handover command in the second cell, the mobile station, When the reception of the first system information block fails, it is included in the main information block and the handover command in the second cell. And summarized in that a step of performing a second communication using that information.
- a mobile station and a mobile communication method can be provided.
- FIG. 1 is an overall configuration diagram of a mobile communication system according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a functional block diagram of the mobile station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating an example of broadcast information (MIB) transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of broadcast information (SIB1) transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an example of broadcast information (SIB2) transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- MIB broadcast information
- SIB1 broadcast information transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- SIB2 broadcast information transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example of information elements (uE-TimersAndConstants) included in broadcast information (SIB2) transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example of an information element (radioResourceConfigCommon) included in broadcast information (SIB2) transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 8 is a diagram for explaining the contents of an information element (radioResourceConfigCommon) included in broadcast information (SIB2) transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram for explaining the contents of an information element (radioResourceConfigCommon) included in broadcast information (SIB2) transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining the contents of an information element (radioResourceConfigCommon) included in broadcast information (SIB2) transmitted by the radio base station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing an operation of the mobile station according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
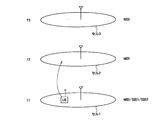
- the mobile communication system is an LTE mobile communication system, in which a cell 1 using a frequency f1, a cell 2 using a frequency f2, and a frequency cell 3 in which f3 is used.
- the broadcast information transmitted in the cell 1 includes MIB, SIB1, and SIB2, whereas the broadcast information transmitted in the cell 2 and the cell 3 Does not include SIB1 and SIB2.
- the mobile station UE performs handover from the cell 1 (first cell) to the cell 2 (second cell) will be described.
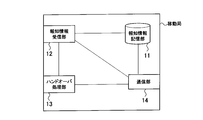
- the mobile station UE includes a broadcast information storage unit 11, a broadcast information reception unit 12, a handover processing unit 13, and a communication unit 14.
- the notification information storage unit 11 is configured to store the notification information received by the notification information storage unit 11.
- the broadcast information storage unit 11 receives broadcast information received by the broadcast information storage unit 11 in the cell 1 which is a cell before handover, and received by the broadcast information storage unit 11 in the cell 2 which is a cell after handover. Both notification information may be stored.
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 is configured to receive broadcast information (for example, MIB, SIB1, SIB2, etc.) transmitted in the cell where the mobile station UE is located and store it in the broadcast information storage unit 11. Has been.
- broadcast information for example, MIB, SIB1, SIB2, etc.
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 receives the MIB included in the broadcast information in the cell 2 when the mobile station UE has handed over from the cell 1 to the cell 2, and broadcasts based on the information included in the MIB. It is configured to receive SIB1 included in the information.
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 is configured to receive “dl-System Bandwidth”, “phich-Configuration”, “system Frame Number”, and the like, which are information included in the MIB. .
- dl-SystemBandwidth is information indicating a frequency band used in the downlink of the mobile communication system
- phich-Configuration is setting information of PHICH (Physical HARQ Indicator Channel)
- systemFrameNumber is information indicating a system frame number in the mobile communication system.
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 is configured to receive “plmn-IdentityList”, “tracking AreaCode”, “schedulingInformation”, and the like, which are information included in the SIB1.
- plmn-IdentityList and “trackingAreaCode” are information not included in the handover command, and the location registration processing (when the mobile station UE is in the “RRC-Connected state (connection state)”) Information used in TAU).
- “SchedulingInformation” is information indicating scheduling information (period information and mapping information) of a plurality of SIs (System Information).
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 is configured to receive “ue-TimersAndConstants”, “radioResourceConfigCommon”, “mbsfn-SubframeConfiguration”, and the like, which are information included in the SIB2. .
- mbsfn-SubframeConfiguration indicates setting information for receiving information for LTE MBMS (Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service) in the cell.
- Such setting information includes, for example, setting information on the position of a subframe allocated for the “MBSFN (MBMS Single Frequency Network) transmission method” for simultaneously transmitting the same information from a plurality of cells using the same frequency resource. included.
- MMSFN MBMS Single Frequency Network
- the mobile station UE applies a channel estimation value different from the channel estimation value in the subframe to which the MBSFN transmission scheme is not applied, for example, in the subframe to which the MBSFN transmission is applied.
- a cell-specific pilot signal is used to identify signals between cells. Therefore, the mobile station UE performs channel estimation for the cell based on the pilot signal for each cell.
- the mobile station UE can be regarded as not performing unicast transmission.
- the mobile station UE can perform an operation different from that in the subframe to which the MBSFN transmission scheme is not applied in the subframe to which the MBSFN transmission scheme is applied.
- “ue-TimersAndConstants” is information indicating setting values of various timers used in the cell.
- “ue-TimersAndConstants” is information indicating a setting value of the timer T300, a setting value of the timer T301, a setting value of the timer T310, a setting value of the timer T311, and the like.
- radioResourceConfigCommon is “RAC-Configuration”, which is RACH (Random Access Channel) setting information
- bcch-Conf which is BCCH (Broadcast Channel) setting information.
- PRACH Physical Random Access Channel
- PDSCH PhysicalDh Setting Information
- PUSCH Physical Uplink Shared Channel
- PUSCH-Configuration which is the setting information of the PUCCH (Physical Uplink Control Channel)" PUCCH-Configuration "and the like.
- “pcch-Configuration” is an information element included in “MobilityControlInformation (see FIG. 9)” that is an information element included in “RRCConnectionReconfiguration (see FIG. 8)” that is an information element transmitted on the dedicated channel.
- Information set in “radioResourceConfigCommon” is set (see FIG. 10).
- “pcch-Configuration” is configured to be set to “defaultPagingCycle” indicating the paging cycle and “nB” indicating the set value of the parameter nB.
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 may be configured not to perform reception processing on the SIB1 when the MIB notifies that the SIB1 is not transmitted in the cell 2.
- the notification may be configured to be performed by 1 bit in the MIB.
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 may be configured not to perform reception processing on the SIB1 when notified by the handover command that the SIB1 is not transmitted in the cell 2. For example, such notification may be configured to be performed by 1 bit in the handover command.
- the handover processing unit 13 is configured to perform processing for the mobile station UE to perform handover from the cell 1 to the cell 2 in response to the handover command received from the radio base station eNB.
- the handover command is the SIB1 and SIB2 necessary for performing the operation of the “RRC-Connected state (connection state)” after the handover in preparation for the case where the broadcast information receiving unit 12 fails to receive the SIB1 and SIB2. It may be configured to include information to be transmitted.
- the communication unit 14 is configured to perform predetermined communication in the cell 2 when the mobile station UE is handed over from the cell 1 to the cell 2.
- the communication unit 14 performs the first communication using information included in the MIB, SIB1, and the handover command in the cell 2. Configured to start.
- the communication unit 14 is configured to perform the second communication using the information included in the MIB and the handover command in the cell 2 when the broadcast information receiving unit 12 fails to receive the SIB1 and SIB2. ing.
- the communication unit 14 when performing the first communication, is configured to perform periodic location registration processing based on the information “plmn-IdentityList” and “tracking AreaCode” included in the SIB1. Also good.
- the communication unit 14 when performing the second communication, the communication unit 14 is configured not to perform the location registration process because the information “plmn-IdentityList” and “trackingAreaCode” included in the SIB1 cannot be acquired. May be. Further, in the case where the setting is such that the location registration process is performed periodically, the location registration process may be configured not to be performed.
- the communication unit 14 when performing the first communication, is configured to use the set value of the timer included in the SIB1 (the set value of the timer included in “ue-TimersAndConstants”). When two communications are performed, the setting value of the timer used in the cell 1 may be used.
- the communication unit 14 when performing the first communication, is configured to receive a paging signal addressed to the mobile station UE based on the information “pcch-Configuration” included in the SIB1.
- the communication unit 14 when 2 communication is performed, since the information “pcch-Configuration” included in the SIB1 cannot be acquired, the paging signal addressed to the mobile station UE may not be received.
- the communication unit 14 when performing the first communication, is configured to receive a paging signal addressed to the mobile station UE based on the information “pcch-Configuration” included in the SIB1.
- the mobile station UE since the information “pcch-Configuration” included in the SIB1 cannot be acquired in the cell 2, the mobile station UE is based on the information “pcch-Configuration” used in the cell 1. It may be configured to receive an addressed paging signal.
- the communication unit 14 regards the predetermined subframe as a subframe to which the MBSFN transmission scheme is applied based on the information “mbsfn-SubframeConfiguration” included in the SIB1.
- the information “mbsfn-SubframeConfiguration” included in the SIB1 cannot be acquired in the cell 2, and thus the predetermined subframe is not applied to the MBSFN scheme. It may be configured to be regarded as a frame.
- the communication unit 14 may regard the predetermined subframe as a subframe to which the MBSFN scheme is applied based on the information “mbsfn-SubframeConfiguration” included in the SIB1.
- the predetermined subframe may be regarded as a subframe to which the MBSFN scheme is applied.
- step S101 the mobile station UE hands over from the cell 1 to the cell 2.
- step S102 the mobile station UE determines whether SIB1 / SIB2 is transmitted in the broadcast information in the cell 2 according to a predetermined flag in the MIB or the handover command.
- step S103 If it is determined that SIB1 / SIB2 is transmitted, the operation proceeds to step S103. If it is determined that SIB1 / SIB2 is not transmitted, the operation proceeds to step S105.
- step S103 the mobile station UE performs reception processing for SIB1 / SIB2.
- the operation proceeds to step S104.
- the reception process fails, the operation proceeds to step S105.
- step S104 in the cell 2, the mobile station UE continues the first communication (ordinary communication) using information included in the MIB, SIB1, SIB2, and the handover command.
- step S105 the mobile station UE continues the second communication using the information included in the MIB and the handover command (communication that can be performed using the information included in the MIB and the handover command) in the cell 2. To do.
- the mobile station UE is included in the MIB and the handover command even when reception of SIB1 / SIB2 fails in the handover destination cell. Since the second communication using the existing information can be continued, the continuity of the communication can be guaranteed.
- each cell does not need to transmit SIB1 and SIB2, so that flexibility can be given to cell design.
- the mobile station UE in the “idle-mode” waits only in the cell 1 to which SIB1 and SIB2 are transmitted, and the mobile station UE in the “RRC-Connected state (connected state, connected-mode)” However, it is possible to operate such that communication is performed in both the cell 1 and the cell 2 to which the SIB1 and SIB2 are not transmitted.
- the mobile station UE can detect that SIB1 / SIB2 is not transmitted in a specific cell, and in such a case, the SIB1 / Since communication can be started without performing reception processing for SIB2, time required for handover processing can be reduced.
- the first feature of the present embodiment is the mobile station UE, which receives the MIB included in the broadcast information in the cell 2 when handed over from the cell 1 to the cell 2 in response to the received handover command, In the cell 2, when the SIB1 is successfully received by the broadcast information receiving unit 12 and the broadcast information receiving unit 12 configured to receive the SIB1 included in the broadcast information based on the included information, the MIB and the SIB1 When the first communication using the information included in the handover command and the broadcast information receiving unit 12 fails to receive the SIB1, the cell 2 stores the information included in the MIB and the handover command.
- the gist of the present invention is to include a communication unit 14 configured to perform the used second communication.
- the communication unit 14 is configured to perform location registration processing based on information included in the SIB1 when performing the first communication, and the second communication.
- the location registration process may not be performed.
- the location registration process may include a periodic location registration process.
- the communication unit 14 is configured to use the set value of the timer included in the SIB1 when performing the first communication, and performs the second communication.
- the setting value of the timer used in the cell 1 may be used.
- the communication unit 14 is configured to receive a paging signal addressed to the mobile station UE based on information included in the SIB1 when performing the first communication. And when performing 2nd communication, you may be comprised so that the paging signal addressed to the mobile station UE may not be received.
- the communication unit 14 is configured to receive a paging signal addressed to the mobile station UE based on information included in the SIB1 when performing the first communication. And when performing 2nd communication, based on the information used in the cell 1, you may be comprised so that the paging signal addressed to the mobile station UE may be received.
- the predetermined subframe may be regarded as a subframe to which the MBSFN transmission scheme is not applied.
- the predetermined subframe may be regarded as a subframe to which the MBSFN transmission scheme is applied based on the information of the cell 1. Good.
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 may be configured not to perform a reception process on the SIB1 when the MIB notifies that the SIB1 is not transmitted in the cell 2. Good.
- the broadcast information receiving unit 12 is configured not to perform reception processing on the SIB1 when notified by the handover command that the SIB1 is not transmitted in the cell 2. Also good.
- the second feature of the present embodiment is a mobile communication method, in which when the mobile station UE performs handover from the cell 1 to the cell 2 in response to the received handover command, the MIB included in the broadcast information in the cell 2 is changed. And receiving the SIB1 included in the broadcast information based on the information included in the MIB, and when the mobile station UE has successfully received the SIB1, the cell 2 includes the MIB, the SIB1, and the handover command. The first communication using the received information, and the second communication using the information included in the MIB and the handover command in the cell 2 when the mobile station UE fails to receive the SIB1. And a step of performing the above.
- the operations of the mobile station UE and the radio base station eNB described above may be implemented by hardware, may be implemented by a software module executed by a processor, or may be implemented by a combination of both. .
- Software modules include RAM (Random Access Memory), flash memory, ROM (Read Only Memory), EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM), EEPROM (Electronically Erasable and Programmable, Removable ROM, and Hard Disk). Alternatively, it may be provided in an arbitrary format storage medium such as a CD-ROM.
- the storage medium is connected to the processor so that the processor can read and write information from and to the storage medium. Further, such a storage medium may be integrated in the processor. Further, such a storage medium and a processor may be provided in the ASIC. Such an ASIC may be provided in the mobile station UE or the radio base station eNB. Further, the storage medium and the processor may be provided as a discrete component in the mobile station UE or the radio base station eNB.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
図1乃至図10を参照して、本発明の第1の実施形態に係る移動通信システムの構成について説明する。
図11を参照して、本発明の第1の実施形態に係る移動通信システムの動作、具体的には、本発明の第1の実施形態に係る移動通信システムで用いられる移動局UEの動作について説明する。
本発明の第1の実施形態に係る移動通信システムによれば、移動局UEは、ハンドオーバ先のセルにおいて、SIB1/SIB2の受信に失敗した場合であっても、MIB及びハンドオーバコマンドに含まれている情報を用いた第2通信を継続することができるため、通信の継続性を保証することができる。
Claims (10)
- 受信したハンドオーバコマンドに応じて第1セルから第2セルにハンドオーバした際に、該第2セルにおける報知情報に含まれる主要情報ブロックを受信し、該主要情報ブロックに含まれる情報に基づいて該報知情報に含まれる第1システム情報ブロックを受信するように構成されている報知情報受信部と、
前記報知情報受信部によって前記第1システム情報ブロックの受信に成功した場合に、前記第2セルにおいて、前記主要情報ブロックと前記第1システム情報ブロックと前記ハンドオーバコマンドとに含まれている情報を用いた第1通信を開始し、該報知情報受信部によって該第1システム情報ブロックの受信に失敗した場合に、該第2セルにおいて、該主要情報ブロック及び該ハンドオーバコマンドに含まれている情報を用いた第2通信を行うように構成されている通信部とを具備することを特徴とする移動局。 - 前記通信部は、前記第1通信を行っている場合、前記第1システム情報ブロックに含まれている情報に基づいて、位置登録処理を行うように構成されており、前記第2通信を行っている場合、位置登録処理を行わないように構成されていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の移動局。
- 前記通信部は、前記第1通信を行っている場合、前記第1システム情報ブロックに含まれているタイマの設定値を用いるように構成されており、前記第2通信を行っている場合、前記第1セルにおいて用いられていたタイマの設定値を用いるように構成されていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の移動局。
- 前記通信部は、前記第1通信を行っている場合、前記第1システム情報ブロックに含まれている情報に基づいて、前記移動局宛てのページング信号を受信するように構成されており、前記第2通信を行っている場合、該移動局宛てのページング信号を受信しないように構成されていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の移動局。
- 前記通信部は、前記第1通信を行っている場合、前記第1システム情報ブロックに含まれている情報に基づいて、前記移動局宛てのページング信号を受信するように構成されており、前記第2通信を行っている場合、前記第1セルにおいて用いられていた情報に基づいて、該移動局宛てのページング信号を受信するように構成されていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の移動局。
- 前記通信部は、前記第1通信を行っている場合、前記第1システム情報ブロックに含まれている情報に基づいて、所定サブフレームを、MBSFN送信方式が適用されているサブフレームと見なすように構成されており、前記第2通信を行っている場合、所定サブフレームを、MBSFN送信方式が適用されていないサブフレームと見なすように構成されていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の移動局。
- 前記通信部は、前記第1通信を行っている場合、前記第1システム情報ブロックに含まれている情報に基づいて、所定サブフレームを、MBSFN送信方式が適用されているサブフレームと見なすように構成されており、前記第2通信を行っている場合、前記第1セルにおいて用いられていた情報に基づいて、所定サブフレームを、MBSFN送信方式が適用されているサブフレームと見なすように構成されていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の移動局。
- 前記報知情報受信部は、前記主要情報ブロックによって、前記第2セルにおいて前記第1システム情報ブロックが送信されていないことが通知された場合、該第1システム情報ブロックに対する受信処理を行わないように構成されていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の移動局。
- 前記報知情報受信部は、前記ハンドオーバコマンドによって、前記第2セルにおいて前記第1システム情報ブロックが送信されていないことが通知された場合、該第1システム情報ブロックに対する受信処理を行わないように構成されていることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の移動局。
- 移動局が、受信したハンドオーバコマンドに応じて第1セルから第2セルにハンドオーバした際に、該第2セルにおける報知情報に含まれる主要情報ブロックを受信し、該主要情報ブロックに含まれる情報に基づいて該報知情報に含まれる第1システム情報ブロックを受信する工程と、
前記移動局が、前記第1システム情報ブロックの受信に成功した場合に、前記第2セルにおいて、前記主要情報ブロックと前記第1システム情報ブロックと前記ハンドオーバコマンドとに含まれている情報を用いた第1通信を開始する工程と、
前記移動局が、前記第1システム情報ブロックの受信に失敗した場合に、前記第2セルにおいて、前記主要情報ブロック及び前記ハンドオーバコマンドに含まれている情報を用いた第2通信を行う工程とを有することを特徴とする移動通信方法。
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/126,882 US8208445B2 (en) | 2008-10-31 | 2009-10-28 | Mobile station and mobile communication method |
| CN200980143472.XA CN102204333B (zh) | 2008-10-31 | 2009-10-28 | 移动台以及移动通信方法 |
| EP09823613.6A EP2352334B1 (en) | 2008-10-31 | 2009-10-28 | Mobile telecommunication station and mobile telecommunication method |
| BRPI0921801A BRPI0921801A2 (pt) | 2008-10-31 | 2009-10-28 | Estação móvel e método de comunicação móvel |
| KR1020117010400A KR101176361B1 (ko) | 2008-10-31 | 2009-10-28 | 이동국 및 이동통신방법 |
| AU2009310907A AU2009310907B2 (en) | 2008-10-31 | 2009-10-28 | Mobile station and mobile communication method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008-282593 | 2008-10-31 | ||
| JP2008282593A JP4740306B2 (ja) | 2008-10-31 | 2008-10-31 | 移動局及び移動通信方法 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2010050503A1 true WO2010050503A1 (ja) | 2010-05-06 |
Family
ID=42128863
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/068493 WO2010050503A1 (ja) | 2008-10-31 | 2009-10-28 | 移動局及び移動通信方法 |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8208445B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2352334B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4740306B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101176361B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102204333B (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU2009310907B2 (ja) |
| BR (1) | BRPI0921801A2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010050503A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8976740B2 (en) * | 2009-11-06 | 2015-03-10 | Qualcomm Incorporated | System information acquisition in connected mode |
| US9001778B2 (en) * | 2010-12-23 | 2015-04-07 | Qualcomm Incorporated | System synchronization in TD-SCDMA and TDD-LTE systems |
| US20140029594A1 (en) * | 2011-04-08 | 2014-01-30 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Method for user equipment setting connection with network in wireless communication system and apparatus for same |
| US20130039257A1 (en) * | 2011-08-11 | 2013-02-14 | Te-Ming Chen | Method of Handling Handover of a Relay Node and Related Communication Device |
| CN102438286A (zh) * | 2011-11-18 | 2012-05-02 | 华为技术有限公司 | 一种小区切换控制方法、相关设备以及通信系统 |
| US9516632B2 (en) * | 2012-01-11 | 2016-12-06 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving downlink data channel signal transmission information in cellular radio communication system using cooperative multi-point scheme |
| GB2504978B (en) * | 2012-08-16 | 2014-11-12 | Ip Access Ltd | Network elements, cellular communication system and methods therefor |
| US10135569B2 (en) | 2015-02-04 | 2018-11-20 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Method and user equipment for receiving SIB1 |
| CN106658611A (zh) * | 2015-10-30 | 2017-05-10 | 展讯通信(上海)有限公司 | 一种移动终端平滑切换通信网络的方法以及移动终端 |
| KR102073619B1 (ko) | 2017-03-22 | 2020-02-05 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 무선 통신 시스템에서 단말과 기지국의 신호 송수신 방법 및 이를 지원하는 장치 |
| CN108391294A (zh) * | 2018-02-09 | 2018-08-10 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | 一种注册网络的方法和移动终端 |
| KR20220047274A (ko) * | 2019-08-14 | 2022-04-15 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 이동 통신 시스템에서 이중 활성화 프로토콜 스택을 지원하는 단말의 핸드오버 방법 및 장치 |
| JP7458793B2 (ja) | 2020-01-14 | 2024-04-01 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 車載通信装置、通信方法、およびプログラム |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008259057A (ja) * | 2007-04-06 | 2008-10-23 | Ntt Docomo Inc | 移動通信端末及び端末制御方法 |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101114869B (zh) * | 2006-07-26 | 2010-10-20 | 大唐移动通信设备有限公司 | 一种umts系统中系统信息块调度的方法及装置 |
-
2008
- 2008-10-31 JP JP2008282593A patent/JP4740306B2/ja active Active
-
2009
- 2009-10-28 AU AU2009310907A patent/AU2009310907B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2009-10-28 BR BRPI0921801A patent/BRPI0921801A2/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2009-10-28 WO PCT/JP2009/068493 patent/WO2010050503A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2009-10-28 EP EP09823613.6A patent/EP2352334B1/en active Active
- 2009-10-28 US US13/126,882 patent/US8208445B2/en active Active
- 2009-10-28 KR KR1020117010400A patent/KR101176361B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2009-10-28 CN CN200980143472.XA patent/CN102204333B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008259057A (ja) * | 2007-04-06 | 2008-10-23 | Ntt Docomo Inc | 移動通信端末及び端末制御方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| "Clarification on connected UE behavior for handling system information", 3GPP TSG RAN WG2#63BIS R2-085096, 29 September 2008 (2008-09-29), pages 1 - 5, XP050320037 * |
| "Summary of the continued discussion on L1 parameter handling in dedicated", TSG-RAN WG2 MEETING #62 TDOC R2-082125, - 5 May 2008 (2008-05-05), pages 1, XP050139908 * |
| See also references of EP2352334A4 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20110255508A1 (en) | 2011-10-20 |
| BRPI0921801A2 (pt) | 2017-08-29 |
| JP2010109953A (ja) | 2010-05-13 |
| CN102204333A (zh) | 2011-09-28 |
| CN102204333B (zh) | 2014-09-03 |
| EP2352334A1 (en) | 2011-08-03 |
| JP4740306B2 (ja) | 2011-08-03 |
| US8208445B2 (en) | 2012-06-26 |
| AU2009310907B2 (en) | 2013-10-10 |
| EP2352334A4 (en) | 2012-05-16 |
| KR20110091661A (ko) | 2011-08-12 |
| EP2352334B1 (en) | 2013-12-04 |
| KR101176361B1 (ko) | 2012-08-22 |
| AU2009310907A1 (en) | 2010-05-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2010050503A1 (ja) | 移動局及び移動通信方法 | |
| US10904786B2 (en) | Method for using radio interface technology, apparatus, and communications system | |
| US10674380B2 (en) | On-demand system information for wireless terminal in connected state | |
| CN108781400B (zh) | 需求式系统信息传递进程 | |
| CN107113116B (zh) | 用于共享频谱中的不连续发送(dtx)的小区切换的方法、装置和计算机可读介质 | |
| EP3120660B1 (en) | Methods and apparatus for device to device synchronization priority | |
| US20160112858A1 (en) | Cellular network assisted device to device (d2d) discovery | |
| US20120008550A1 (en) | Relay-Node, Donor-eNB and method for receiving and sending system information | |
| CN104219740B (zh) | 激活状态处理方法及装置 | |
| US20150280894A1 (en) | Methods, apparatus and computer programs for half-duplex frequency division duplexing | |
| US20130034067A1 (en) | Mobile station and radio base station | |
| US9119104B2 (en) | Mobile communication method and radio base station | |
| US20130122899A1 (en) | Method and system for roaming in a peer to peer network among radio sites having dynamic rest channel base repeater stations | |
| WO2018121449A1 (zh) | 系统消息的传输方法、装置及接收方法、装置、终端 | |
| AU2012240832A1 (en) | Method of providing service to user equipment in wireless communication system and apparatus thereof | |
| CN115243402A (zh) | 用于侧链路不连续接收机制下部分感测的方法和装置 | |
| WO2021028447A1 (en) | Enhanced multi-connection operations | |
| US20170311225A1 (en) | Resource access priority for synchronous transmissions | |
| WO2010053151A1 (ja) | 移動局及び移動通信方法 | |
| JP2021511694A (ja) | ランダムアクセス方法及び装置、コンピュータ記憶媒体 | |
| CN115699650A (zh) | Mbs业务的tci状态管理方法及装置、终端设备 | |
| CN103987127A (zh) | 一种接入方法、装置和系统 | |
| CN105992191B (zh) | 一种上行数据接收控制、接收、发送方法及装置 | |
| JP2011147191A (ja) | 移動局及び移動通信方法 | |
| US9955498B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for faster system information acquisition |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200980143472.X Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09823613 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20117010400 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009310907 Country of ref document: AU |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009823613 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2009310907 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20091028 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13126882 Country of ref document: US |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: PI0921801 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20110429 |