WO1997021435A1 - Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone - Google Patents
Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO1997021435A1 WO1997021435A1 PCT/US1996/020004 US9620004W WO9721435A1 WO 1997021435 A1 WO1997021435 A1 WO 1997021435A1 US 9620004 W US9620004 W US 9620004W WO 9721435 A1 WO9721435 A1 WO 9721435A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- alkyl
- substituted
- compound
- indol
- aryl
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 C*1(C)C(c2cc(*)cc(C)c2)=*(CC*(CCCCc(cc2)ccc2OC)CCCCOC)c2ccccc12 Chemical compound C*1(C)C(c2cc(*)cc(C)c2)=*(CC*(CCCCc(cc2)ccc2OC)CCCCOC)c2ccccc12 0.000 description 5
- MFWLHYDVSXBTIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCCNC(Oc(cc1)cc2c1[nH]c(-c1cc(C)cc(C)c1)c2CCNCCCCc(cc1)ccc1O)=O Chemical compound CCCNC(Oc(cc1)cc2c1[nH]c(-c1cc(C)cc(C)c1)c2CCNCCCCc(cc1)ccc1O)=O MFWLHYDVSXBTIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PSNOFYVWAQTGOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N COc(c(OC)c1)ccc1-c1c(CCNCCCc(cc2)ccc2O)c(cccc2)c2[nH]1 Chemical compound COc(c(OC)c1)ccc1-c1c(CCNCCCc(cc2)ccc2O)c(cccc2)c2[nH]1 PSNOFYVWAQTGOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UMRRQCNOKANYCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oc1ccc(CCCCNCCc2c(C3=CC=[I]C=C3)[nH]c3c2cccc3)cc1 Chemical compound Oc1ccc(CCCCNCCc2c(C3=CC=[I]C=C3)[nH]c3c2cccc3)cc1 UMRRQCNOKANYCU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D209/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D209/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom condensed with one carbocyclic ring
- C07D209/04—Indoles; Hydrogenated indoles
- C07D209/10—Indoles; Hydrogenated indoles with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to carbon atoms of the hetero ring
- C07D209/14—Radicals substituted by nitrogen atoms, not forming part of a nitro radical
- C07D209/16—Tryptamines
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P1/00—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P1/00—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system
- A61P1/06—Anti-spasmodics, e.g. drugs for colics, esophagic dyskinesia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
- A61P11/16—Central respiratory analeptics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P13/00—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system
- A61P13/02—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system of urine or of the urinary tract, e.g. urine acidifiers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P15/00—Drugs for genital or sexual disorders; Contraceptives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P15/00—Drugs for genital or sexual disorders; Contraceptives
- A61P15/16—Masculine contraceptives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P15/00—Drugs for genital or sexual disorders; Contraceptives
- A61P15/18—Feminine contraceptives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P17/00—Drugs for dermatological disorders
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/20—Hypnotics; Sedatives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
- A61P5/02—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the hypothalamic hormones, e.g. TRH, GnRH, CRH, GRH, somatostatin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
- A61P5/24—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the sex hormones
Definitions
- the gonadotropin-releasing hormone also referred to as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH)
- LHRH luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone
- LH released from the pituitary gland is primarily responsible for the regulation of gonadal steroid production in both sexes, whereas FSH regulates spermatogenesis in males and follicular development in females.
- GnRH agonists and antagonists have proven effective in the treatment of certain conditions which require inhibition of LH/FSH release.
- GnJRH-based therapies have proven effective in the treatment of endometriosis, uterine fibroids, polycystic ovarian disease, precocious puberty and several gonadal steroid-dependent neoplasia, most notably cancers of the prostate, breast and ovary.
- GnRH agonists and antagonists have also been utilized in various assisted fertilization techniques and have been investigated as a potential contraceptive in both men and women.
- the compounds of the invention may also be used in combination with bisphosphonates (bisphosphonic acids) and other agents, such as growth hormone secretagogues, e.g.
- MK-0677 for the treatment and the prevention of disturbances of calcium, phosphate and bone metabolism, in particular, for the prevention of bone loss during therapy with the GnRH antagonist, and in combination with estrogens, progesterones, antiestrogens, antiprogestins and/or androgens for the prevention or treatment of bone loss or hypogonadal symptoms such as hot flashes during therapy with the GnRH antagonist.
- a compound of the present invention may be co-administered with a 5 -reductase 2 inhibitor, such as finasteride or epristeride; a 5 -reductase 1 inhibitor such as 4,7 ⁇ -dimethyl-4-aza-5 ⁇ - cholestan-3-one, 3-oxo-4-aza-4,7 ⁇ -dimethyl-16 ⁇ -(4-chlorophenoxy)- 5 ⁇ -androstane, and 3-oxo-4-aza-4,7 ⁇ -dimethyl-16 ⁇ -(phenoxy)-5 ⁇ - androstane as disclosed in WO 93/23420 and WO 95/1 1254; dual inhibitors of 5 ⁇ -reductase 1 and 5 -reductase 2 such as 3-oxo-4-aza- 17 ⁇ -(2,5-trifluoromethylphenyl-carbamoyl)-5oc-androstane as disclosed in WO 95/07927; antiandrogens such as flutamide, casodex
- a compound of the present invention may be used in combination with growth hormone, growth hormone releasing hormone or growth hormone secretagogues, to delay puberty in growth hormone deficient children, which will allow them to continue to gain height before fusion of the epiphyses and cessation of growth at puberty.
- GnRH antagonists are GnRH-like decapeptides which are generally administered intravenously or subcutaneously presumably because of negligible oral activity. These have amino acid substitutions usually at positions one, two, three, six and ten.
- Non-peptide GnRH antagonists offer the possible advantage of oral adminstration.
- Non-peptide GnRH antagonists have been described in European Application 0 219 292 and in De, B. et al., J. Med. Chem., 32, 2036-2038 (1989), in WO 95/28405, WO 95/29900 and EP 0679642 all to Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd.
- Substituted indoles known in the art include those described in the following patents and patent applications.
- US Patent No. 5,030,640 discloses alpha-heterocyclic ethanol aminoalkyl indoles which are potent B-agonists.
- US Patent No. 4,544,663 discloses indolamine derivatives which are allegedly useful as male anti-fertility agents.
- WO 90/05721 discloses alpha-amino-indole-3-acetic acids useful as anti- diabetic, anti-obesity and anti-atherosclerotic agents.
- French patent 2,181 ,559 discloses indole derivatives with sedative, neuroleptic, analgesic, hypotensive, antiserotonin and adrenolytic activity.
- Belgian patent 8793 1 discloses 3-aminoalkyl-l H-indole-5-thioamide and carboxamide derivatives as cardiovascular agents used to treat hypertension, Raynaud's disease and migraine.
- the present invention relates to compounds which are non- peptide antagonists of GnRH which can be used to treat a variety of sex- hormone related conditions in men and women, to methods for their preparation, and to methods and pharmaceutical compositions containing said compounds for use in mammals.
- the compounds of the present invention are useful to treat a variety of sex-hormone related conditions in both men and women. These conditions include endometriosis, uterine fibroids, polycystic ovarian disease, hirsutism, precocious puberty, gonadal steroid- dependent neoplasias such as cancers of the prostate, breast and ovary, gonadotrophe pituitary adenomas, sleep apnea, irritable bowel syndrome, premenstrual syndrome and benign prostatic hypertophy.
- the compounds of the invention are also useful as an adjunct to treatment of growth hormone deficiency and short stature, and for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosis.
- the compounds of the invention may be useful in in vitro fertilization and as contraceptives.
- the compounds may also be useful in combination with androgens, estrogens, progesterones, antiestrogens and antiprogestogens for the treatment of endometriosis, fibroids and in contraception. They may also be useful in combination with testosterone or other androgens or antiprogestogens in men as a contraceptive.
- the compounds may also be used in combination with an angiotensin-con verting enzyme inhibitor such as Enalapril or Captopril, an angiotensin Il-receptor antagonist such as Losartan or a renin inhibitor for the treatment of uterine fibroids.
- an angiotensin-con verting enzyme inhibitor such as Enalapril or Captopril
- an angiotensin Il-receptor antagonist such as Losartan or a renin inhibitor
- the compounds of the invention may also be used in combination with bisphosphonates (bisphosphonic acids) and other agents, for the treatment and the prevention of disturbances of calcium, phosphate and bone metabolism, in particular, for the prevention of bone loss during therapy with the GnRH antagonist , and in combination with estrogens, progesterones and/or androgens for the prevention or treatment of bone loss or hypogonadal symptoms such as hot flashes during therapy with the GnRH antagonist.
- a compound of the present invention may be co-administered with a 5oc-reductase 2 inhibitor, such as finasteride or epristeride; a 5o -reductase 1 inhibitor such as 4,7 ⁇ -dimethyl-4-aza-5oc- cholestan-3-one, 3-oxo-4-aza-4,7 ⁇ -dimethyl- 16 ⁇ -(4-chlorophenoxy)- 5 ⁇ -androstane, and 3-oxo-4-aza-4,7 ⁇ -dimethyl- 16 ⁇ -(phenoxy)-5 ⁇ - androstane as disclosed in WO 93/23420 and WO 95/1 1254; dual inhibitors of 5 -reductase 1 and 5 ⁇ -reductase 2 such as 3-oxo-4-aza- 17 ⁇ -(2,5-trifluoromethylpheny l-carbamoyl)-5 ⁇ -androstane as disclosed in WO 95/07927; antiandrogens such as flutamide
- a compound of the present invention may be used in combination with growth hormone, growth hormone releasing hormone or growth hormone secretagogues, to delay puberty in growth hormone deficient children, which will allow them to continue to gain height before fusion of the epiphyses and cessation of growth at puberty.
- the present invention relates to compounds of the general formula
- A is C 1 -C6 alkyl, substituted C1-C6 alkyl, C3-C7 cycloalkyl, substituted C3-C7 cycloalkyl, C3-C6 alkenyl, substituted C3- C 6 alkenyl, C3-C6 alkynyl, substituted C3-C6 alkynyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, or C0-C5 alkyl-S(0) n -Co-C5 alkyl, C0-C5 alkyl-O- C0-C5 alkyl, C0-C5 alkyl-NR i8-Co-Cs alkyl where R ⁇ and the C0-C5 alkyl can be joined to form a ring,
- Ro is hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, substituted Ci-C ⁇ alkyl, wherein the substituents are as defined below; aryl, substituted aryl, aralkyl or substituted aralkyl, wherein the substituents are as defined for R3, R4 and R5;
- Y is B, C or a bond
- B is O, S(0) n , C(O), NRis or C(RnR ⁇ 2 ) p
- C is B(CH 2 ) P -;
- R2 is hydrogen, Cj-C f i alkyl, substituted Ci-Qs alkyl, aralkyl, substituted aralkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, alkyl -OR ⁇ , Ci-C 6 (NRiiRi2),Ci-C6(CONRiiRi2)orC(NRiiRi 2 )NH;
- R3, R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, substituted
- R3 and R4 taken together form a carbocyclic ring of 3-7 carbon atoms or a heterocyclic ring containing 1-3 heteroatoms selected from N, O and S;
- R is hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, substituted Ci-Cfi alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, C1-C3 perfluoroalkyl, CN, NO2, halogen.
- Rl ⁇ O(CH 2 ) p -, NR ⁇ 2 C(0)R ⁇ 1, NR ⁇ 2 C(0)NR ⁇ 1R12 or SO n R ⁇ 1;
- R7 is hydrogen, Cj-C ⁇ alkyl, or substituted Cj-Cft alkyl, unless X is hydrogen or halogen, then R7 is absent;
- R 8 is hydrogen, C(0)OR 9 , C(0)NR 11 R 12, NR 11 R 12, C(0)R 11 ,
- R7 and Rx taken together form a carbocyclic ring of 3-7 atoms
- R9 and R a are independently hydrogen, Ci-Cf, alkyl, substituted Ci-C f -, alkyl; aryl or substituted aryl, aralkyl or substituted aralkyl when m ⁇ O; or
- R 9 and R a taken together form a carbocyclic ring of 3-7 atoms or when m ⁇ O; R9 and A taken together form a heterocyclic ring containing 3-7 carbon atoms and one or more heteroatoms when m ⁇ O; or RlO and Ri a are independently hydrogen, C1 -C6 alkyl, substituted Ci -
- R 9 and R2 taken together form a heterocyclic ring containing 3-7 carbon atoms and one or more heteroatoms when m ⁇ O; or
- R lO and R2 taken together form a heterocyclic ring containing 3-7 carbon atoms and one or more heteroatoms;
- Rl 1 and R12 are independently hydrogen , Cj -C alkyl, substituted Ci - C alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, aralkyl, substituted aralkyl, a carbocyclic ring of 3-7 atoms or a substituted carbocyclic ring containing 3-7 atoms;
- Rl 1 and R 12 taken together can form an optionally substituted ring of 3- 7 atoms
- R13 is hydrogen, OH, NR 7 R «, NRj ⁇ S02(C ⁇ -C6 alkyl),
- Rl4 and R 15 are independently hydrogen, C 1 -C6 alkyl, substituted C1 -C6 alkyl, C2-C6 alkenyl, substituted C2-C6 alkenyl, CN, nitro, C 1 -C3 perfluoroalkyl, C 1 -C3 perfluoroalkoxy, aryl, substituted aryl, aralkyl, substituted aralkyl, Ri jO(CH 2 )p-, Rl lC(0)0(CH 2 ) p -, R ⁇ ⁇ OC(0)(CH 2 ) p -, -(CH 2 ) p S(0) n Ri7. -(CH2) p C(0)NR ⁇ 1 R 1 2 or halogen; wherein R 1 7 is hydrogen, C1 -C6 alkyl, C1-C3 perfluoroalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl;
- R 1 6 is hydrogen, C1 -C6 alkyl, substituted Cj-Cfi alkyl, or
- R l 8 is hydrogen, C1-C alkyl, substituted Cj-Cfi alkyl, C(0)OR9,
- X is hydrogen, halogen, N, O, S(0) n , C(O), (CRi ⁇ R i2)p.
- m is 0-3; n is 0-2; p is 0-4; and the alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl and alkynyl substituents are selected from C1-C6 alkyl, C3-C7 cycloalkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, aralkyl, substituted aralkyl, hydroxy, oxo, cyano, C1-C6 alkoxy, fluoro, C(0)OR ⁇ , aryl C
- alkyl is intended to include both branched- and straight-chain saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon groups having the specified number of carbon atoms, e.g., methyl (Me), ethyl (Et), propyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, heptyl, octyl, nonanyl, decyl, undecyl, dodecyl, and the isomers thereof such as isopropyl (i-Pr), isobutyl (i-Bu), sec-butyl (s-Bu), tert-butyl (t-Bu), isopentane, isohexane, etc.
- aryl includes phenyl and naphthyl.
- aryl is phenyl.
- halogen or halo is intended to include fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine.
- heterocycle or “heterocyclic ring” is defined by all non-aromatic, heterocyclic rings of 3-7 atoms containing 1 -3 heteroatoms selected from N, O, and S, such as oxirane, oxetane, tetrahydrofuran, tetrahydropyran, pyrrolidine, piperidine, tetrahydropyridine, tetrahydropyrimidine, tetrahydrothiophene, tetrahydrothiopyran, morpholine, hydantoin, valerolactam, pyrrolidinone, and the like.
- composition is intended to encompass a product comprising the specified ingredients in the specified amounts, as well as any product which results, directly or indirectly, from combination of the specified ingredients in the specified amounts
- optical isomeric forms that is mixtures of enantiomers, e.g., racemates, or diastereomers as well as individual enantiomers or diastereomers of the instant compound are included.
- These individual enantiomers are commonly designated according to the optical rotation they effect by the symbols (+) and (-), (L) and (D), (1 ) and (d) or combinations thereof.
- These isomers may also be designated according to their absolute spatial configuration by (S) and (R), which stands for sinister and rectus, respectively.
- the individual optical isomers may be prepared using conventional resolution procedures, e.g., treatment with an appropriate optically active acid, separating the diastereomers and then recovering the desired isomer.
- the individual optical isomers may be prepared by asymmetric synthesis.
- a given chemical formula or name shall encompass pharmaceutically acceptable addition salts thereof and solvates thereof, such as hydrates.
- the compounds of the present invention while effective themselves, may be formulated and administered in the form of their pharmaceutically acceptable addition salts for purposes of stability, convenience of crystallization, increased solubility and other desirable properties.
- the compounds of the present invention may be administered in the form of pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
- pharmaceutically acceptable salt is intended to include all acceptable salts.
- acid salts are hydrochloric, nitric, sulfuric, phosphoric, formic, acetic, trifluoroacetic, propionic, maleic, succinic, malonic, methane sulfonic and the like which can be used as a dosage form for modifying the solubility or hydrolysis characteristics or can be used in sustained release or prodrug formulations.
- salts of the compounds of this invention include those formed from cations such as sodium, potassium, aluminum, calcium, lithium, magnesium, zinc, and from bases such as ammonia, ethylenediamine, N-methyl-glutamine, lysine, arginine, ornithine, choline, N,N'-dibenzylethylenediamine, chloroprocaine, diethanolamine, procaine, N-benzylphenethylamine, diethylamine, piperazine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, and tetramethylammonium hydroxide.
- bases such as ammonia, ethylenediamine, N-methyl-glutamine, lysine, arginine, ornithine, choline, N,N'-dibenzylethylenediamine, chloroprocaine, diethanolamine, procaine, N-benzylphenethylamine, diethylamine, piperazine, tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethan
- esters can be employed, e.g. methyl, ethyl, butyl, acetate, maleate, pivaloyloxymethyl, and the like, and those esters known in the art for modifying solubility or hydrolysis characteristics for use as sustained release or prodrug formulations.
- the compounds of the present invention may have chiral centers other than those centers whose stereochemistry is depicted in formula I, and therefore may occur as racemates, racemic mixtures and as individual enantiomers or diastereomers, with all such isomeric forms being included in the present invention as well as mixtures thereof.
- some of the crystalline forms for compounds of the present invention may exist as polymorphs and as such are intended to be included in the present invention.
- some of the compounds of the instant invention may form solvates with water or common organic solvents. Such solvates are encompassed within the scope of this invention.
- reaction Scheme A As shown in reaction Scheme A, treatment of tryptamine (1 ) with /V-carboxyphthalimide in an inert organic solvent such as tetrahydrofuran at a temperature of 20-65°C, preferably 65°C, for a period of 12-48 hours gives the corresponding /V-phthalimidotryptamine derivative (2).
- an inert organic solvent such as tetrahydrofuran
- the /V-phthalimidotryptamine (2) could be further modified by treatment with a brominating agent such as pyridinium hydrobromide perbromide, pyrrolidone hydrotribromide, or the like in an inert organic solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, methylene chloride, chloroform, or mixtures thereof at 0-25 °C for a period of 30 minutes to 4 hours to provide the 2-bromotryptamine (3).
- Bromide (3) may be reacted with an arylboronic acid (prepared essentially as described in : Gronowitz, S.; Hornfeldt, A.-B.; Yang, Y.-H. Chem. Ser.
- the 2-aryltryptamine may be condensed with a carboxylic acid of type (6) using the coupling reagent 1 -(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), 1 ,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) or the like with or without 1 -hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt) and a tertiary amine base such as N- methylmorpholine (NMM), triethylamine or the like in an inert organic solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, dimethylformamide, or mixtures thereof at or near room temperature for a period of 3-24 hours to provide the corresponding amide derivative (7).
- EDC 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
- DCC 1 ,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
- HOBt 1 -
- 2-aryltryptamine (5) can be treated with an active ester or acid chloride of type (8) in an inert organic solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, or the like and a tertiary amine base such as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, pyridine or the like at a temperature of 0°-25°C for 30 minutes to 4 hours to give (7).
- an inert organic solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, or the like
- a tertiary amine base such as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, pyridine or the like
- reaction Scheme C As shown in reaction Scheme C, the amide carbonyl of (7) can be reduced by treatment with borane, lithium aluminum hydride, or equivalent hydride sources in an inert organic solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, 1 ,4-dioxane or the like at 25°-100°C, preferably 65°C, for a period of 1 -8 hours to give the corresponding amine compound (9).
- an inert organic solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, diethyl ether, 1 ,4-dioxane or the like
- the 2-aryltryptamine (5) can be modified by treatment with an aldehyde or ketone of type (10) in the presence of a weak acid such as trifluorfoacetic acid (TFA), acetic acid or the like, with or without a dessicant such as 3A molecular sieves or magnesium sulfate, and a hydride source such as sodium borohydride or sodium cyanoborohydride, in an inert organic solvent such as methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, tetrahydrofuran, dichloromethane, chloroform, or mixtures thereof at a temperature of 0°-25°C for a period of 1 - 12 hours to give the corresponding secondary or tertiary amine derivative (1 1 ).
- a weak acid such as trifluorfoacetic acid (TFA), acetic acid or the like
- a dessicant such as 3A molecular sieves or magnesium sulfate
- Reaction Scheme E As shown in reaction Scheme E, treatment of an arylhydrazine or arylhydrazine hydrochloride (12) with an arylcyclopropylketone of type (13) in a polar organic solvent such as methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, t-butanol, preferably n-butanol, at a temperature of 70°-120°C for a period of 8- 24 hours gives 2-aryltryptamine (5).
- a polar organic solvent such as methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, t-butanol, preferably n-butanol
- an arylhydrazine or arylhydrazine hydrochloride (12) is treated with an arylbutyl ketone of type (14) containing a leaving group (chloride, bromide, iodide, O-methansulfonate, O-trifluoromethansulfonate, or the like) at the 4-position in a polar solvent such as methanol, ethanol, n- propanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, t-butanol, or mixtures thereof at room temperature for a period of 30 minutes to 2 hours followed by heating to a temperature of 65°- 100°C for 4-24 hours, 2-aryltryptamine (5) is produced.
- Scheme F 2-aryltryptamine
- Reaction Scheme F As shown in reaction Scheme F, iodoanilines of type (15) may be reacted with aryl acetylenes, an appropriate palladium (0) catalyst such as tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium, a copper (I) halide such as cuprous bromide in an inert organic solvent such as triethylamine at a temperature of 50°-88°C for a period of 30 minutes to 5 hours to provide the diarylacetylene (16).
- an appropriate palladium (0) catalyst such as tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium
- a copper (I) halide such as cuprous bromide in an inert organic solvent such as triethylamine at a temperature of 50°-88°C for a period of 30 minutes to 5 hours to provide the diarylacetylene (16).
- Acetylene (16) may be further modified by treatment with a palladium (II) catalyst such as palladium (II) chloride or palladium (II) acetate in an inert organic solvent such as acetonitrile at a temperature of 50°- 82°C for a period of 30 minutes to 6 hours to give 2-arylindole ( 17).
- a palladium (II) catalyst such as palladium (II) chloride or palladium (II) acetate in an inert organic solvent such as acetonitrile at a temperature of 50°- 82°C for a period of 30 minutes to 6 hours to give 2-arylindole ( 17).
- Reaction Scheme G As shown in reaction Scheme G, treatment of 2-arylindole (17) with oxalyl chloride neat or in an inert organic solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, dichloroethane, tetrahydrofuran or the like at a temperature of 25°-65°C for a period of 3-24 hours gives the acylchloride adduct (18).
- the crude product ( 18) may be reacted with an amine of type (19) in an inert organic solvent such as diethylether, tetrahydrofuran, methylene chloride, chloroform or the like and an amine base such as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine or pyridine at a temperature of 0°C-25°C for a period of 30 minutes to 4 hours to provide the amide derivative (20).
- Amide (20) may be further modified by treatment with a reducing agent such as borane or lithium aluminum hydride in an inert organic solvent such as tetrahydrofuran at elevated temperatures, preferably reflux, for a period of 1 -5 hours to give compound (21 ).
- N-benzyl derivatives of type (22a) or N-benzyloxycarbonyl derivatives of type (22b) may be reduced to provide the secondary amine analogs (7) by treatment with hydrogen (1 atm) and an appropriate catalyst such as palladium on carbon, palladium hydroxide on carbon, or the like in an inert organic solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, ethyl acetate, methanol, ethanol, or mixtures thereof to which has been added a weak acid such as 30% aqueous acetic acid for a period of 10 minutes to 3 hours or until the aryl group has been removed to give the secondary amine.
- an appropriate catalyst such as palladium on carbon, palladium hydroxide on carbon, or the like
- an inert organic solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, ethyl acetate, methanol, ethanol, or mixtures thereof to which has been added a weak acid such as 30% aqueous acetic acid for a period of 10 minutes to 3
- reaction Scheme I As shown in reaction Scheme I, treatment of a nitroindole of type (24) with hydrogen (1 atm) and an appropriate catalyst such as Raney® Nickel in an inert organic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, or the like at room temperature for a period of 2-12 hours gives the corresponding aminoindole derivative (25).
- Scheme J As shown in reaction Scheme I, treatment of a nitroindole of type (24) with hydrogen (1 atm) and an appropriate catalyst such as Raney® Nickel in an inert organic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, or the like at room temperature for a period of 2-12 hours gives the corresponding aminoindole derivative (25).
- Scheme J As shown in reaction Scheme I, treatment of a nitroindole of type (24) with hydrogen (1 atm) and an appropriate catalyst such as Raney® Nickel in an inert organic solvent such as ethanol, methanol, or the like at room temperature for a period of 2-12 hours gives the corresponding aminoindole derivative (25).
- amino- or hydroxyindole (25) may be modified by acylation under a variety of conditions.
- treatment of (25) with an acid chloride, acid anhydride or active ester and an amine base such as triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, pyridine, or the like in an inert organic solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, tetrahydrofuran, or mixtures thereof at 0°C to room temperature for a period of 1 to 12 hours gives the corresponding amide or ester derivatives (26).
- (25) may be coupled with a carboxylic acid by one of the many dehydrating agents commonly employed.
- urea or carbamate derivatives of (25) can be prepared by treatment with a carbamoyl chloride of type (27a), or alternatively with an isocyanate reagent of type (27b), and an amine base such as pyridine, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, /V-methylmorpholine or the like in an inert organic solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, dimethylformamide, tetrahydrofuran or mixtures thereof at a temperature of 0°-65°C for a period of 1 -72 hours to give (28).
- an inert organic solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, dimethylformamide, tetrahydrofuran or mixtures thereof at a temperature of 0°-65°C for a period of 1 -72 hours to give (28).
- Compound (25) can also be modified by treatment with a bis(electrophilic) reagent such as phosgene, triphosgene, 1 ,1 '- carbonyldiimidazole, N,N'-disuccinimidyl carbonate, or the like with or without the addition of an amine base such as pyridine, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, /V-methylmo ⁇ holine in an inert solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, or the like at a temperature of -20°- 0°C for a period of 20 minutes to 2 hours. After this time, the reaction mixture is treated with an appropriate mono- or disubstituted amine at -20°-25°C for a period of 1 -5 hours to give the urea or carbamate analog (28).
- a bis(electrophilic) reagent such as phosgene, triphosgene, 1 ,1 '- carbonyld
- amine (25) can be modified by treatment with an appropriate sulfonyl chloride of type (29) or sulfamyl chloride of type (30) with an amine base such as pyridine, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, /V-methylmo ⁇ holine in an inert solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, dichloroethane or the like at a temperature of -20°-25°C for a period of 20 minutes to 2 hours to give the corresponding /V-sulfonamide (31 ) or N- sulfamylamide (32) derivatives, respectively.
- an amine base such as pyridine, triethylamine, diisopropylethylamine, /V-methylmo ⁇ holine in an inert solvent such as methylene chloride, chloroform, dichloroethane or the like
- reaction Scheme M the 2-aryltryptamine (33) can be modified by treatment with an epoxide such as (34) in an inert organic solvent such as methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, butanol, tert- butanol, or mixtures thereof at a temperature of 65°- 1 10°C for a period of 8-20 hours to give the corresponding amino-alcohol derivative (35).
- an epoxide such as (34) in an inert organic solvent such as methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, butanol, tert- butanol, or mixtures thereof at a temperature of 65°- 1 10°C for a period of 8-20 hours to give the corresponding amino-alcohol derivative (35).
- amide derivatives of an acid-containing indole derivative such as (36) can be prepared by treatment with an appropriate amine (R 12R1 1 NH) and a suitable coupling agent such as benzotriazol-1 -yloxy- tris(pyrrolidino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate (PyBOP), benzotriazol- 1 -yloxy-tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate (BOP), l-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3- ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC), 1 ,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) or the like with or without 1 -hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt) and a tertiary amine base such as N-methylmo ⁇ holine (NMM), triethylamine or the like in an inert organic solvent such as
- the compounds of the present invention are useful in the treatment of various sex-hormone related conditions in men and women. This utility is manifested in their ability to act as antagonists of the neuropeptide hormone GnRH as demonstrated by activity in the following in vitro assays.
- the compounds to be assayed were dissolved and diluted in DMSO.
- the final concentration of DMSO in the incubation medium was 0.5%.
- the Wistar male rats (150-200 grams) were obtained from Charles River Laboratories (Wilmington, MA). Rats were maintained at a constant temperature (25°C) on a 12-hr light, 12-hr dark cycle. Rat chow and water were available ad libitum. The animals were sacrificed by decapitation and pituitary glands were aseptically removed and placed in Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS) in a 50-mL polypropylene centrifuge tube. The collection tube was centrifuged for 5 min at 250 x g, and HBSS was removed by aspiration. Pituitary glands were transferred to a disposable petri plate and minced with a scalpel.
- HBSS Hank's Balanced Salt Solution
- the minced tissue was then transferred to a 50-mL disposable centrifuge tube by suspending the tissue fragments in three successive 10-mL aliquots of HBSS containing 0.2% collagenase and 0.2% hyaluronidase.
- the cell dispersion was carried out in a water bath at 37°C with gentle stirring for 30 min.
- the cells were aspirated 20 to 30 times with a pipet and the undigested pituitary fragments were allowed to settle for 3 to 5 min.
- the suspended cells were removed by aspiration, and then subjected to a 1200 x g centrifugation for 5 min. The cells were then resuspended in Culture medium.
- the undigested pituitary fragments were treated with 30 mL aliquots of the digestion enzymes as above for a total of 3 digestions with the collagenase/hyaluronidase mixture.
- the resulting cell suspensions were pooled, counted and diluted to a concentration of 3 x 10 ⁇ cells/ml, and 1.0 ml of this suspension was placed in each well of a 24-well tray (Costar, Cambridge, MA). Cells were maintained in a humidified 5% C ⁇ 2-95% air atmosphere at 37°C for 3 to 4 days.
- the culture medium consisted of DMEM containing 0.37% NaHC03, 10% horse serum, 2.5% fetal bovine serum, 1 % non-essential amino acids, 1 % glutamine, and 0.1 % gentamycin.
- DMEM containing 0.37% NaHC03, 10% horse serum, 2.5% fetal bovine serum, 1 % non- essential amino acids(lOOX), 1 % glutamine(lOOX), 1 % Penicillin/Streptomycin( 10,000 Units of Penicillin and 10,000 micrograms of Streptomycin per ml), and 25 mM HEPES, pH 7.4.
- LH release was initiated by adding 1 ml of fresh medium containing test compounds in the presence of 2 nM GnRH to each well in duplicate. Incubation was carried out at 37°C for 3 hr. After incubation, medium was removed and centrifuged at 2,000 x g for 15 min to remove any cellular material. The supernatant fluid was removed and assayed for LH content with a double antibody RIA procedure using materials obtained from Dr. A. F. Parlow (Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA). The compounds of formula I are useful in a number of areas affected by GnRH.
- Sex-hormone dependent cancers which may benefit from the administration of the compounds of this invention include prostatic cancer, uterine cancer, breast cancer and pituitary gonadotrophe adenomas.
- Other sex-hormone dependent conditions which may benefit from the administration of the compounds of this invention include endometriosis, polycystic ovarian disease, uterine fibroids and precocious puberty.
- the compounds may also be used in combination with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor such as Enalapril or Captopril, an angiotensin Il-receptor antagonist such as Losartan or a renin inhibitor for the treatment of uterine fibroids.
- an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor such as Enalapril or Captopril
- an angiotensin Il-receptor antagonist such as Losartan or a renin inhibitor for the treatment of uterine fibroids.
- the compounds of the invention may also be useful for controlling pregnancy, as a contraceptive in both men and women, for in vitro fertilization, in the treatment of premenstrual syndrome, in the treatment of lupus erythematosis, in the treatment of hirsutism, in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome and for the treatment of sleep disorders such as sleep apnea.
- a further use of the compounds of this invention is as an adjunct to growth hormone therapy in growth hormone deficient children.
- the compounds may be administered with growth hormone or a compound which increases the endogenous production or release of growth hormone.
- Certain compounds have been developed which stimulate the release of endogenous growth hormone.
- Peptides which are known to stimulate the release of endogenous growth hormone include growth hormone releasing hormone, the growth hormone releasing peptides GHRP-6 and GHRP- 1 (described in U.S. Patent No. 4,41 1 ,890, PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 89/071 10, and PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 89/0711 1) and GHRP-2
- Patent No. 5,374,721 U.S. Patent No. 5,430,144; U.S. Patent No. 5,434,261 ; U.S. Patent No. 5,438,136; EPO Patent Pub. No. 0,144,230; EPO Patent Pub. No. 0,513,974; PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 94/07486; PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 94/08583; PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 94/1 1012; PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 94/13696; PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 94/19367; PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 95/03289; PCT Patent Pub. No. WO 95/03290; PCT Patent Pub. No.
- Representative preferred growth hormone secretagoues employed in the present combination include the following:
- the compounds of the invention may also be used in combination with bisphosphonates (bisphosphonic acids) and other agents, such as growth hormone secretagogues, e.g. MK-0677, for the treatment and the prevention of disturbances of calcium, phosphate and bone metabolism, in particular, for the prevention of bone loss during therapy with the GnRH antagonist , and in combination with estrogens, progesterones and or androgens for the prevention or treatment of bone loss or hypogonadal symptoms such as hot flashes during therapy with the GnRH antagonist.
- bisphosphonates bisphosphonic acids
- other agents such as growth hormone secretagogues, e.g. MK-0677
- Bisphosphonates are known to inhibit bone reso ⁇ tion and are useful for the treatment of bone lithiasis as disclosed in U.S. Patent 4,621 ,077 to Rosini, et al.
- the literature discloses a variety of bisphosphonic acids which are useful in the treatment and prevention of diseases involving bone reso ⁇ tion. Representative examples may be found in the following: U.S. Patent No. 3,251,907; U.S. Patent No. 3,422,137; U.S. Patent No. 3,584,125; U.S. Patent No. 3,940,436; U.S. Patent No. 3,944,599; U.S. Patent No. 3,962,432; U.S. Patent No.
- Preferred bisphosphonates are selected from the group of the following compounds: alendronic acid, etidrononic acid, clodronic acid, pamidronic acid, tiludronic acid, risedronic acid, 6-amino- l-hydroxy-hexylidene-bisphosphonic acid, and 1 -hydroxy- 3(methylpentylamino)-propylidene-bisphosphonic acid; or any pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
- a particularly preferred bisphosphonate is alendronic acid (alendronate), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
- An especially preferred bisphosphonate is alendronate sodium, including alendronate sodium trihydrate. Alendronate sodium has received regulatory approval for marketing in the United States under the trademark FOSAMAX®.
- a compound of the present invention may be co-administered with a 5 -reductase 2 inhibitor, such as finasteride or epristeride; a 5oc-reductase 1 inhibitor such as 4,7 ⁇ -dimethyl-4-aza-5 ⁇ - cholestan-3-one, 3-oxo-4-aza-4,7 ⁇ -dimethy 1- 16 ⁇ -(4-chlorophenoxy )- 5cc-androstane, and 3-oxo-4-aza-4,7 ⁇ -dimethyl-16 ⁇ -(phenoxy)-5oc- androstane as disclosed in WO 93/23420 and WO 95/1 1254; dual inhibitors of 5 ⁇ -reductase 1 and 5 -reductase 2 such as 3-oxo-4-aza- 17 ⁇ -(2,5-trifluoromethylphenyl-carbamoyl)-5 -androstane as disclosed in WO 95/07927; antiandrogens such as flutamide
- a compound of the present invention may be used in combination with growth hormone, growth hormone releasing hormone or growth hormone secretagogues, to delay puberty in growth hormone deficient children, which will allow them to continue to gain height before fusion of the epiphyses and cessation of growth at puberty.
- the active agents may be administered separately or in conjunction.
- the administration of one element may be prior to, concurrent to, or subsequent to the administration of the other agent.
- compositions containing the active ingredient may be in a form suitable for oral use, for example, as tablets, troches, lozenges, aqueous or oily suspensions, dispersible powders or granules, emulsions, hard or soft capsules, or syrups or elixirs.
- Compositions intended for oral use may be prepared according to any method known to the art for the manufacture of pharmaceutical compositions and such compositions may contain one or more agents selected from the group consisting of sweetening agents, flavoring agents, coloring agents and preserving agents in order to provide pharmaceutically elegant and palatable preparations. Tablets contain the active ingredient in admixture with non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable excipients which are suitable for the manufacture of tablets.
- excipients may be for example, inert diluents, such as calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate, lactose, calcium phosphate or sodium phosphate; granulating and disintegrating agents, for example, com starch, or alginic acid; binding agents, for example starch, gelatin or acacia, and lubricating agents, for example, magnesium stearate, stearic acid or talc.
- the tablets may be uncoated or they may be coated by known techniques to delay disintegration and abso ⁇ tion in the gastrointestinal tract and thereby provide a sustained action over a longer period.
- a time delay material such as glyceryl monostearate or glyceryl distearate may be employed. They may also be coated by the technique described in the U.S. Patent 4,256,108; 4,166,452; and 4,265,874 to form osmotic therapeutic tablets for control release.
- Formulations for oral use may also be presented as hard gelatin capsules wherein the active ingredient is mixed with an inert solid diluent, for example, calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate or kaolin, or as soft gelatin capsules wherein the active ingredient is mixed with water or an oil medium, for example peanut oil, liquid paraffin, or olive oil.
- an inert solid diluent for example, calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate or kaolin
- water or an oil medium for example peanut oil, liquid paraffin, or olive oil.
- Aqueous suspensions contain the active material in admixture with excipients suitable for the manufacture of aqueous suspensions.
- excipients are suspending agents, for example sodium carboxymethylcellulose, methylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethyl ⁇ cellulose, sodium alginate, polyvinyl-pyrrolidone, gum tragacanth and gum acacia; dispersing or wetting agents may be a naturally-occurring phosphatide, for example lecithin, or condensation products of an alkyiene oxide with fatty acids, for example polyoxyethylene stearate, or condensation products of ethylene oxide with long chain aliphatic alcohols, for example heptadecaethylene-oxycetanol, or condensation products of ethylene oxide with partial esters derived from fatty acids and a hexitol such as polyoxyethylene sorbitol monooleate, or condensation products of ethylene oxide with partial esters derived from fatty acids and hexitol anhydrides, for example polyethylene sorbitan
- the aqueous suspensions may also contain one or more preservatives, for example ethyl, or n-propyl, p-hydroxybenzoate, one or more coloring agents, one or more flavoring agents, and one or more sweetening agents, such as sucrose, saccharin or aspartame.
- preservatives for example ethyl, or n-propyl, p-hydroxybenzoate
- coloring agents for example ethyl, or n-propyl, p-hydroxybenzoate
- coloring agents for example ethyl, or n-propyl, p-hydroxybenzoate
- flavoring agents such as sucrose, saccharin or aspartame.
- sweetening agents such as sucrose, saccharin or aspartame.
- Oily suspensions may be formulated by suspending the active ingredient in a vegetable oil, for example arachis oil, olive oil, sesame oil or coconut oil, or in mineral oil such as liquid paraffin.
- the oily suspensions may contain a thickening agent, for example beeswax, hard paraffin or cetyl alcohol. Sweetening agents such as those set forth above, and flavoring agents may be added to provide a palatable oral preparation. These compositions may be preserved by the addition of an anti-oxidant such as ascorbic acid.
- Dispersible powders and granules suitable for preparation of an aqueous suspension by the addition of water provide the active ingredient in admixture with a dispersing or wetting agent, suspending agent and one or more preservatives.
- a dispersing or wetting agent e.g., glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerin, glycerin, glycerin, glycerin, glycerin, sorbitol, sorbitol, sorbitol, sorbitol, sorbitol, sorbitol, sorbitol, sorbitol, sorbitol, sorbitol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol, glycerol
- the pharmaceutical compositions of the invention may also be in the form of an oil-in- water emulsions.
- the oily phase may be a vegetable oil, for example olive oil or arachis oil, or a mineral oil, for example liquid paraffin or mixtures of these.
- Suitable emulsifying agents may be naturally-occurring phosphatides, for example soy beans, lecithin, and esters or partial esters derived from fatty acids and hexitol anhydrides, for example sorbitan monooleate, and condensation products of the said partial esters with ethylene oxide, for example polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate.
- the emulsions may also contain sweetening and flavouring agents.
- Syrups and elixirs may be formulated with sweetening agents, for example glycerol, propylene glycol, sorbitol or sucrose. Such formulations may also contain a demulcent, a preservative and flavoring and coloring agents.
- sweetening agents for example glycerol, propylene glycol, sorbitol or sucrose.
- Such formulations may also contain a demulcent, a preservative and flavoring and coloring agents.
- the pharmaceutical compositions may be in the form of a sterile injectable aqueous or oleagenous suspension.
- This suspension may be formulated according to the known art using those suitable dispersing or wetting agents and suspending agents which have been mentioned above.
- the sterile injectable preparation may also be a sterile injectable solution or suspension in a non-toxic parenterally- acceptable diluent or solvent, for example as a solution in 1 ,3-butane diol.
- the acceptable vehicles and solvents that may be employed are water, Ringer's solution and isotonic sodium chloride solution.
- sterile, fixed oils are conventionally employed as a solvent or suspending medium. For this pu ⁇ ose any bland fixed oil may be employed including synthetic mono- or diglycerides.
- fatty acids such as oleic acid find use in the preparation of injectables.
- Compounds of Formula I may also be administered in the form of a suppositories for rectal administration of the drug.
- These compositions can be prepared by mixing the drug with a suitable non- irritating excipient which is solid at ordinary temperatures but liquid at the rectal temperature and will therefore melt in the rectum to release the drug.
- suitable non- irritating excipient which is solid at ordinary temperatures but liquid at the rectal temperature and will therefore melt in the rectum to release the drug.
- Such materials are cocoa butter and polyethylene glycols.
- creams, ointments, jellies, solutions or suspensions, etc., containing the compound of Formula I are employed.
- topical application shall include mouth washes and gargles.
- the compounds for the present invention can be administered in intranasal form via topical use of suitable intranasal vehicles, or via transdermal routes, using those forms of transdermal skin patches well known to those of ordinary skill in the art.
- the dosage administration will, of course, be continuous rather than intermittent throughout the dosage regimen.
- Compounds of the present invention may also be delivered as a suppository employing bases such as cocoa butter, glycerinated gelatin, hydrogenated vegetable oils, mixtures of polyethylene glycols of various molecular weights and fatty acid esters of polyethylene glycol.
- the dosage regimen utilizing the compounds of the present invention is selected in accordance with a variety of factors including type, species, age, weight, sex and medical condition of the patient; the severity of the condition to be treated; the route of administration; the renal and hepatic function of the patient; and the particular compound thereof employed.
- a physician or veterinarian of ordinary skill can readily determine and prescribe the effective amount of the drug required to prevent, counter, arrest or reverse the progress of the condition.
- Optimal precision in achieving concentration of drug within the range that yields efficacy without toxicity requires a regimen based on the kinetics of the drug's availability to target sites. This involves a consideration of the distribution, equilibrium, and elimination of a drug.
- doses of the compound of structural formula I useful in the method of the present invention range from 0.01 to 1000 mg per adult human per day. Most preferably, dosages range from 0.1 to 500 mg/day.
- the compositions are preferably provided in the form of tablets containing 0.01 to 1000 milligrams of the active ingredient, particularly 0.01 , 0.05, 0.1 , 0.5, 1.0, 2.5, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 25.0, 50.0, 100 and 500 milligrams of the active ingredient for the symptomatic adjustment of the dosage to the patient to be treated.
- An effective amount of the drug is ordinarily supplied at a dosage level of from about 0.0002 mg kg to about 50 mg/kg of body weight per day. The range is more particularly from about 0.001 mg/kg to 1 mg/kg of body weight per day.
- the active agent of the present invention may be administered in a single daily dose, or the total daily dosage may be administered in dividend doses of two, three or four times daily.
- the amount of active ingredient that may be combined with the carrier materials to produce a single dosage form will vary depending upon the host treated and the particular mode of administration.
- Step 2A 2-12-( l /-indol-3-yl)-ethyl l-isoindole- 1.3-dione
- Step 2B 2-l2-(2-bromo-l//-indol-3-yiyethy ⁇ -isoindole-1.3-dione
- Step 2C 2-(2-r2-(3.5-dimethylphenvn-l/ -indol-3-yll-ethyl l- isoindole-1.3-dione
- Step 2E 3-l3-l2-[2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)- l /-indol-3-yl lethylaminol- 2-hydroxypropoxy .
- phenol benzyl ether
- - ethylamine 25.5 mg in 5 mL dry methanol
- l -f3- (benzyloxy)phenoxy]-2,3-epoxypropane was added 12.1 mg of l -f3- (benzyloxy)phenoxy]-2,3-epoxypropane and the mixture heated to reflux on an oil bath. After 7 hours the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, concentrated in vacuo and the product prified by flash chromatography on silica gel (methylene chloride:methanol, 95:5) to give the title compound ( 13.3 mg).
- Step 2F 3-[3-l2-l2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)- l -indol-3-yl lethylaminol-
- Step 3A 12-l2-(3.4-dimethoxyphenvD- 1 //-indol-3-yl lethyl lcarbamic acid benzyl ester
- Step 3B 2-12-(3.4-dimethoxyphenyl)-l -methyl- l /-indol-3- yllethylamine
- Step 3C S V4-I3-12-12-f 3.5-dimethylphenyn- 1 -methyl- 1 H-indol-3- yllethylaminol-2-hydroxypropoxylphenol
- Step 4.1 B r2-l2-(3.4-dimethoxyphenyl)- lH-indol-3-yllethyll-l2-(4- nitrophenvPethyllamine
- Step 7.1 A 2-l2-(5-benzyloxy- 1 /-indol-3-yl)ethyl
- Step 7 3-(2-aminoethvP-2-f3.5-dimethylphenvP-lrt-indol-5-ol
- 2-[2-l2-(3,5-dimethyI ⁇ henyl)-5-hydroxy- lH-indol-3-yl]ethyl]isoindole- l ,3-dione (418 mg in a mixture of 7 mL ethanol and 7 mL tetrahydrofuran) was added 2.5 mL of 95% aqueous hydrazine and the reaction stirred at room temperature. After 12 hours the mixture was concentrated in vacuo and purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (methylene chloride :methanol:ammonium hydroxide, 89: 1 1 : 1 ) to provide the title compound (228 mg).
- Step 7 IF 4-(4-benzyloxyphenyP-/V-( 2-12-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-5- hydroxy-l /-indol-3-yHethyllbutyramide
- Step 7.1 G 3-l2-[4-(4-benzyloxyphenyPbutylamino1ethvI]-2-(3.5- dimethylphenyP-l /-indol-5-ol
- Step 7.1 H 14-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)-butyH-l2-l 2-(3.5-dimethylphenvP- 5-hydroxy- l /-indol-3-yl lethyllcarbamic acid benzyl ester
- 3-l2-f4-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)butylamino] ethyl]-2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-l /-indol-5-ol (234 mg in 5 mL of dry methylene chloride) at -78° C was added benzyl chloroformate (0.082 mL) and diisopropylethylamine (0.104 mL) and the mixture stirred at room temperature.
- Step A 4-(4-benzyloxyphenyPbutyric acid benzyl ester
- Step B 4-(4-benzyloxyphenyPbutyric acid
- 4-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)butyric acid benzyl ester (277 mg in a mixture of 3 mL methanol and 1 mL methylene chloride) at 0° C was added 1.5 mL of 5M sodium hydroxide and the mixture warmed to room temperature. After 2 hours the mixture was acidified to pH 2 by the addition of aqueous hydrochloric acid, the aqueous portion extracted with ethyl acetate (5x) and the resulting organics concentrated in vacuo. Purification by flash chromatography on silica gel (methylene chloride:methanol, 94:6 then 96:4 + 0.25% TFA) gave the title compound (196 mg).
- Step 7.2A Ethylcarbamic acid 3-(2-rbenzyloxycarbonyl-14-(4- benzyloxyphenyPbutyllaminol-ethyP-2-(3.5- dimethylphenyl)-l -indol-5-yl ester
- Jethyllcarbamic acid benzyl ester 50 mg in 0.5 mL dry tetrahydrofuran
- 0.035 mL of ethyl isocyanate was added 0.035 mL of ethyl isocyanate and the mixture stirred at room temperature.
- Step 7.2B Ethylcarbamic acid 2-(3.5-dimethylphenvP-3-r2-r4-(4- hvdroxyphenvPbutylaminolethyll-lH-indol-5-yl ester
- benzyloxycarbonyl-l4-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)butyl]aminoJ-ethyl)-2-(3,5- dimethylphenyl)-l//-indol-5-yl ester (12 mg in a mixture of 1.5 mL tetrahydrofuran and 0.5 mL methanol) was added 12 mg of 10% palladium hydroxide on carbon catalyst followed by acetic acid (0.010 mL of a 30% solution in water).
- Step 8B 2-(3.5-dimethylphenvP-5-nitro-l /-indole
- Step 8C N-benzyl-2-l2-(3.5-dimethylphenyP-5-nitro- l /-indol-3-yll- V-l4-(4-methanesulfonylaminophenyl)butyH -2-oxo- acetamide
- Step 8D N- ⁇ 4-l4-(benzyl-f 2-[2-(3.5-dimethylphenvP-5-nitro- l /- indol-3-yllethy 1 ) amino)butyllphen yl I -methanesulfonamide
- 4-(4- methanesulfonylaminophenyl)butyl]-2-oxo-acetamide 73 mg in 4 mL dry tetrahydrofuran
- Step 8E N- ( 4-l4-( ( 2-15-amino-2-(3.5-dimethylphenvP- 1 H-indol-3- ylleth yl ) benzylamino butyllphenyl I methanesulfonamide
- 7V- ⁇ 4-[4-(benzyl- ⁇ 2-[2-(3,5- dimethylphenyl)-5-nitro- 1 /-indol-3-yl]ethyl ⁇ amino)butyl]phenyl ⁇ - methanesulfonamide 60 mg in 4 mL absolute ethanol was added ca. 15 mg of Raney® nickel.
- reaction flask was fitted with a hydrogen balloon, evacuated and recharged with hydrogen (3 times) and stirred at room temperature. After 3 hours the reaction was flushed with nitrogen, filtered over diatomaceous earth and concentrated in vacuo. Purification by flash chromatography on silica gel (hexane. "ethyl acetate, 1 :2) gave the title compound (42 mg).
- Step 8F yy- ⁇ 4-[4-(benzyl-( 2-r2-(3.5-dimethylphenvP-5-(3.3- dimethylureido)-l -indol-3-yllethyU- amino)butyl Iphenyl ⁇ methanesulfonamide
- a stirred solution of /V- ⁇ 4-[4-( ⁇ 2-[5-amino-2-(3,5- dimethylphenyl)- 1 H-indol-3-yl]ethyl ⁇ benzylamino)butyl]phenyl ⁇ - methanesulfonamide (15 mg in 1.5 mL of dry methylene chloride) at 0° C was added dimethylcarbamyl chloride (0.03 mL of a 10% v/v solution in methylene chloride) and diisopropylethylamine (0.053 mL of a 10% v/v solution in methylene chloride) and the mixture warmed to room
- Step 8G ⁇ r-r4-(4- ⁇ 2-r2-(3.5-dimethvIphenvP-5-(3.3- dimethylureido)- 1 H-indol-3- yllethylaminolbutvPphenyllmethanesulfonamide
- Iphenyl ⁇ methanesulfonamide 17.
- Step 1 3,5-dimethylphenyl)-(2-methylcyclopropyl)methanone
- Step 1 1 C 2-f2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-lff-indol-3-yl lpropylamine
- Steps 1 ID, 1 IE 4-(4-[2-[2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)- lH-indol-3-yl l- propylamino lbutvDphenol
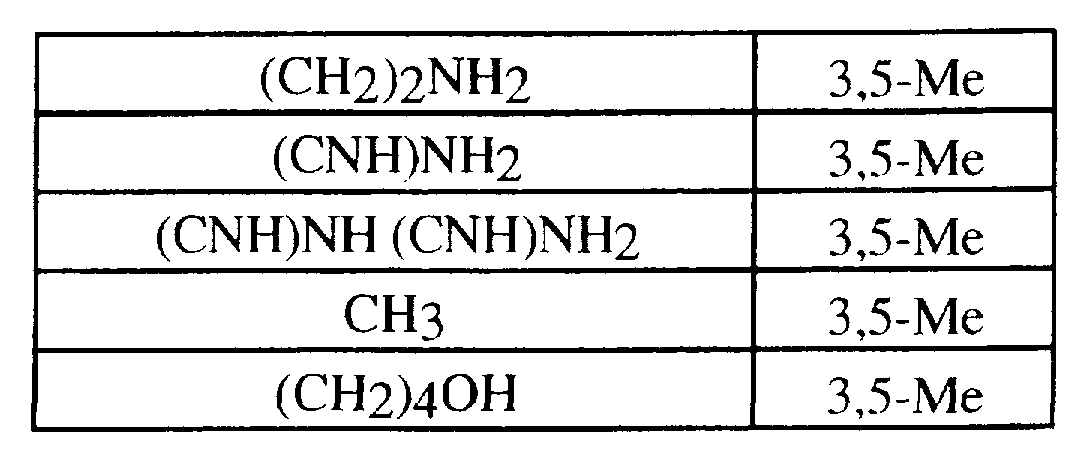
- the title compound was prepared essentially as described in EXAMPLES 1 and 5.2 from 2-[2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)- I /-indol-3- yljpropylamine. Following a procedure similar to that described above, the following compounds were prepared:
- Step 12.2A l -[2-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)ethyll-3- f 2-[2-(3.5- dimethy Iphenyl)- 1 f/-indol-3-yl lethyl 1 urea
- 2-[2-(3, 5-dimethy Iphenyl)- l//-indol-3-yl]- ethylamine EXAMPLE 2 Step D, 39 mg in 1 mL dry methanol) was added 64 mg [2-(4-benzyloxyphenyl)-ethyl]-carbamic acid 4-nitrophenyl ester and the mixture stirred at room temperature.
- Step 12.2B l ( 2-[2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)- lH-indol-3-yllethyl l-3-[2-(4- hvdroxyphenvPethyl lurea
- Step 13.1A r3-(2-aminoethyl)-2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)- l /-indol-5-yl l- acetic acid ethyl ester
- Step 13.1C 13-(2- ⁇ benzyloxycarbonyl- 14-(4-me thanesulfony lamino- pheny Dbutyllamino 1 -ethy l)-2-(3.5-dimethylphenyD- 1 H- indol-5-yl l-acetic acid ethyl ester
- the reaction of (2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-3- ⁇ 2-[4-(4- methanesulfonylaminophenyl)butylamino]ethyl ⁇ - 1 H-indol-5-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester with benzyl chloroformate was carried out according to the procedure of Example 14.1 , Step 14.
- Step 13 ID [3-(2- ⁇ benzyloxycarbonyl-14-(4-methanesulfonylamino- phenyl)butyllamino ⁇ ethyl)-2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-l y- indol-5-yllacetic acid
- Step 13 IE ( 2-r5-diethylcarbamoylmethyl-2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-l//- indol-3-yllethyl ) -r4-(4-methanesulfonylaminophenyl)butyll- carbamic acid benzyl ester
- the reaction of 34.1 mg (0.05 mmol) of [3-(2- ⁇ benzy loxycarbony 1- l4-(4-methanesulfony laminopheny 1 )buty 11 - amino ⁇ ethyl)-2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-l//-indol-5-yljacetic acid with diethylamine in the presence of PyBOP reagent was accomplished according to the procedure of Example 14.1 , Step 14.
- Step 13 I F 2-(2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-3-f 2-r4-(4- methanesulfonylaminophenyD-butylaminol-ethyl l -l /- indol-5-yl)-N./V-diethylacetamide
- Step 13.2 A 2-13-(2-aminoethyl)-2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)- 1 /-indol-5-yll-
- Step 13.2C 2-[3-(2-(benzyloxycarbonyl-l4-(4-methanesulfonylamino- phenyl)butyl lamino ⁇ ethyl -2-(3,5-dimethyl-phenyl)-l - indol-5-yll-2-methylpropionic acid ethyl ester
- the reaction of 2-(2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-3- ⁇ 2-[4-(4- methanesulfonylaminopheny l)buty laminojethy 1 ⁇ - 1 H-indol-5-y l)-2- methylpropionic acid ethyl ester with benzyl chloroformate was carried out according to the procedure of Example 14.1 Step C, to give the titled compound in 72% yield as a stiff foam; homogeneous by TLC in 95:5 CH2Cl2-MeOH. 500 MHz l U NMR was complex, owing to
- Step 13.2D 2-[3-(2- ⁇ benzy loxycarbonyl-l 4-(4-methanesulfony lamino- phenyl)butyl lamino lethyl)-2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-lH- indol-5-yll-2-methylpropionic acid
- the saponification of 2-[3-(2- ⁇ benzyloxycarbonyl-[4-(4- methanesulfonylamino-phenyl)butyl]amino ⁇ ethyl)-2-(3,5-dimethyl- phenyl)-l/ -indol-5-ylJ-2-methylpropionic acid ethyl ester was achieved according to the procedure of Example 14.1 Step D, except that the reaction time was increased to 30 hours, providing a quantitative yield of the titled compound as a powder, mp > 102 °C (gradual; partial decomposition); homogeneous by TLC in 92.5:7.5
- Step I3.2F 2-(2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-3- ( 2-l4-(4- methanesulfonylaminophenyl)-butylaminolethyl l- l/7-indol- 5-yl -/V./V-diethylisobutyramide
- Step AA 4-(4-nitrophenyl)butyric acid, /V-methoxy-N-methylamide
- the solution was diluted with 200 mL of diethyl ether and washed successively with 3 x 100 mL of 2 N .
- hydrochloric acid 1 x 100 mL and 2 x 50 mL of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution, and 1 x 50 mL of saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution.
- the organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo.
- Step BB 4-(4-aminophenyl butyric acid. /V-methoxy-/V-methylamide
- the mixture was filtered through Celite under nitrogen, and the filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to yield 5.29 g of an oil; homogeneous by TLC in 95:5 CH2CI2- MeOH. 400 MHz *H NMR (CDCI3) was consistent with the assigned structure.
- Mass spectrum (PB-NH3/CI): m/e 223 (M + H).
- Step CC 4-[4-(methanesulfonamido)pheny ⁇ butyric acid, /V-methoxy-
- the residue was diluted with 10 mL of methylene chloride and partitioned between a mixture of 100 mL of ethyl acetate + 100 mL of tetrahydrofuran and 100 mL of 2 N hydrochloric acid.
- the organic layer was washed with an additional 4 x 100 mL of 2 N hydrochloric acid, then with 50 mL of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution, and finally with 20 mL of saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution.
- the organic phase was diluted with some tetrahydrofuran, dried over magnesium sulfate, and treated with charcoal. The mixture was filtered through Celite, and the filter cake was washed with additional tetrahydrofuran.
- Step DD 4-[4-(methanesulfonamido)phenyllbutyraldehyde A mixture of 4.20 g (14 mmol) of 4-[4-(methane- sulfonamido)phenyl]butyric acid, /V-methoxy-/V-methylamide and 100 mL of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran was stirred under nitogen with cooling in an ice bath as 17.5 mL (17.5 mmol) of 1 M lithium aluminum hydride in tetrahydrofuran was added gradually by syringe. After 0.75 hours, 70 mL of 5% potassium hydrogen sulfate solution (aqueous) was added cautiously by syringe.
- the mixture was then removed from the ice bath, diluted with 150 mL of water, and shaken with 150 mL of ethyl acetate.
- the milky aqueous phase was extracted with an additional 50 mL of ethyl acetate.
- the combined organic fractions were washed successively with 2 x 100 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid, then 50 mL of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution, and finally 50 mL of saturated aqueous sodium chloride solution.
- the organic phase was dried over magnesium sulfate, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo.
- Step AAA Ethyl 2-(4-hydrazinophenyl)acetate hydrochloride and 2- (4-hydrazinophenyl)acetic acid hydrochloride
- This compound (a mixture of the ethyl ester and the carboxylic acid) was prepared from 1 .4 g (75 mmol) of ethyl 2-(4- aminophenyl)acetate, by diazotization and stannous chloride reduction of the diazonium salt, according to the method of L. J. Street, et al, L Med. Chem.. 36, 1529 (1993).
- the material was obtained in two crops. The first crop consisted of 6.40 g of powder, mp >200 °C.
- 400 MHz 1 H NMR (DMSO-d6) By 400 MHz 1 H NMR (DMSO-d6).
- this material consisted of a mixture of carboxylic acid and ethyl ester in approximately a 4:3 molar ratio.
- the second crop consisted of 4.60 g of powder, mp >180 °C.
- 400 MHz iH NMR (DMSO-d6) this material consisted of a mixture of carboxylic acid and ethyl ester in approximately a 7: 1 molar ratio. After adjustment for the mixture composition of the two crops, the estimated total yield was 69%. Because esterification of any carboxylic acid occurs in the next step, both the ester and the acid react to give the same product.
- Step 14.1A 3-(2-aminoethyl)-2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)- 1 H-indole-5- carboxylic acid ethyl ester
- Step 14 2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-3- ( 2-[4-(4-methanesulfonylamino- phenyDbutylaminolethyl)-l//-indole-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
- the septum was removed, and 100 mg (2.6 mmol) of sodium borohydride was added rapidly.
- the septum was immediately replaced, and the system was again purged with nitrogen.
- the mixture was stirred under nitrogen at about -5 °C as 4 mL of dry methanol was added gradually by syringe. After 20 minutes at this temperature, the reaction was quenched by gradual syringe addition of 1 mL of acetone to destroy excess sodium borohydride. After a few more minutes, the mixture was removed from the cooling bath and partitioned between 25 mL of ethyl acetate and 25 mL of water.
- Step 14.1C 3-(2- ⁇ benzyloxycarbonyl-f 4-(4-methanesuIfonylamino- phenyl)butyllamino )ethyl)-2-(3.5-dimethylphenv ⁇ - l - indole-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
- Step 14 ID 3-(2- ( benzyloxycarbonyl-[4-(4-methanesulfonylamino- phenv ⁇ butyllamino lethyl)-2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl -lH- indole-5-carboxylic acid A solution of 600 mg (0.862 mmol) of 3-(2- ( benzyloxycarbonyl-[4-(4-methanesulfonylamino- phenyl)butyllamino ⁇ ethyl)-2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-lH-indole-5- carboxylic acid ethyl ester in 18 mL (9 mmol) of 0.50 N .
- Step 14 2-[5-diethylcarbamoyl-2-(3,5-dimethylphenvD- 1 / -indol- 3-yl lethyl 1 -[4-(4-methanesulfonylaminophenyD- butyl lcarbamic acid benzyl ester
- 3-(2- ( benzyloxycarbonyl-[4-(4-methanesulfonylamino- phenyl)butylJamino ⁇ ethyl)-2-(3,5-dimethylphenyl)-l/i-indole-5- carboxylic acid in 2.7 mL of dry methylene chloride and 2.7 mL of anhydrous tetrahydrofuran were added 366 mg (0.703 mmol) of PyBOP reagent and 98 mL (71.0 mg; 0.703 mmol) of triethyl
- Step 14 IF 2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-3-( 2-l4-(4-methanesulfonyl- aminopheny Dbuty lamino lethy 1 ) - 1 H-indole-5 -carboxylic acid diethylamide
- Step 19A r2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-l /-indol-3- ylmethylldimethylamine
- Step 19B l2-G.5-dimethylphenyl)-l//-indol-3- ylmethylltrimethylammonium iodide
- a solution of [2-(3,5-dimethylphenyI)-l /-indol-3- ylmethyljdimethylamine 350 mg in 4 mL diethyl ether
- 0.5 L iodomethane 0.5 L iodomethane
- the mixture was filtered and the solids dried in vacuo to provide the crude title compound. (414 mg).
- Step 19C 4-(4-( [2-(3.5-dimethylphenvn- l /-indol-3- ylmethyllamino IbutyDphenol
- Step 20A l-r2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-l H-indol-3-yll-2-(4- phenylpiperazin- 1 -vOethane- 1.2-dione
- Step 20B 2-(3.5-dimethylphenyl)-3-l2-(4-phenylpiperazin- l - yl)ethyll-l//-indole
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Endocrinology (AREA)
- Reproductive Health (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Anesthesiology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Plural Heterocyclic Compounds (AREA)
- Nitrogen Condensed Heterocyclic Rings (AREA)
- Indole Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AU12919/97A AU704937B2 (en) | 1995-12-14 | 1996-12-10 | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| JP09522251A JP3092947B2 (en) | 1995-12-14 | 1996-12-10 | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist |
| EP96943763A EP0868178A4 (en) | 1995-12-14 | 1996-12-10 | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US863295P | 1995-12-14 | 1995-12-14 | |
| US60/008,632 | 1995-12-14 | ||
| GB9603370.9 | 1996-02-16 | ||
| GBGB9603370.9A GB9603370D0 (en) | 1996-02-16 | 1996-02-16 | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO1997021435A1 true WO1997021435A1 (en) | 1997-06-19 |
Family
ID=26308743
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US1996/020004 WO1997021435A1 (en) | 1995-12-14 | 1996-12-10 | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0868178A4 (en) |
| JP (2) | JP3092947B2 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU704937B2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2240115A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO1997021435A1 (en) |
Cited By (35)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0882040A1 (en) * | 1995-12-14 | 1998-12-09 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| WO1999011619A1 (en) * | 1997-09-04 | 1999-03-11 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Limited | Phenylindole derivatives as 5-ht2a receptor ligands |
| WO1999058518A2 (en) * | 1998-05-12 | 1999-11-18 | American Home Products Corporation | Biphenyl oxo-acetic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| EP0986385A1 (en) * | 1997-06-05 | 2000-03-22 | Merck & Co. Inc. | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| US6232322B1 (en) | 1998-05-12 | 2001-05-15 | American Home Products Corporation | Biphenyl oxo-acetic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| US6310081B1 (en) | 1999-05-10 | 2001-10-30 | American Home Products Corporation | Biphenyl sulfonyl aryl carboxylic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| US6346534B1 (en) | 1998-09-23 | 2002-02-12 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| WO2002066459A1 (en) * | 2001-02-20 | 2002-08-29 | Astrazeneca Ab | Indole derivatives and their use as gnrh antagonists |
| WO2002092565A2 (en) * | 2001-05-14 | 2002-11-21 | Astrazeneca Ab | 3-aminoalkyl-2-aryl-indole derivatives and their use as gnrh antagonists |
| US6537998B1 (en) | 1999-10-15 | 2003-03-25 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| FR2833948A1 (en) * | 2001-12-21 | 2003-06-27 | Sod Conseils Rech Applic | New 2,5-disubstituted benzimidazole derivatives, are gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonists useful e.g. for treating endometriosis, breast or prostate cancer or precocious puberty |
| US6608197B2 (en) | 2000-01-25 | 2003-08-19 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6673796B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-01-06 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6677340B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-01-13 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| WO2004018420A1 (en) * | 2002-08-21 | 2004-03-04 | Astrazeneca Ab | Indolylalkylamino-methylidenecarbamate derivatives useful as gnrh antagonists |
| US6740656B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-05-25 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6750350B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-06-15 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6833372B2 (en) | 2002-02-12 | 2004-12-21 | Pfizer, Inc. | Non-peptide GnRH agents, Pharmaceutical compositions, and methods for their use |
| US6903132B2 (en) | 2002-06-13 | 2005-06-07 | Agouron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Non-peptide GnRH agents, pharmaceutical compositions and methods for their use |
| US6939883B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2005-09-06 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7015226B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2006-03-21 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7056927B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2006-06-06 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7071200B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2006-07-04 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7132442B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2006-11-07 | Astrazeneca Ab | 6H-thieno[2, 3-b]pyrrole derivatives as antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) |
| US7253290B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2007-08-07 | Astrazeneca Ab | Pyrazole derivatives as GnRH inhibitors |
| US7306922B2 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2007-12-11 | Astrazeneca Ab | Human and rat PGC-3, PPAR-gamma coactivations and splice variants thereof |
| US7317010B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2008-01-08 | Astrazeneca Ab | Thieno-pyrrole compounds as antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| US7375127B2 (en) | 2004-07-14 | 2008-05-20 | Ae Zentaris Gmbh | Tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives having improved biological action and improved solubility as ligands of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) |
| US7514570B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2009-04-07 | Astrazeneca Ab | Derivatives of 3-hydroxy-4-(cyclyl-alkylaminoalkyl)-5-phenyl-1h-pyrazole as antagonists of the gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) for use in the treatment of sex hormone related conditions, such as prostatic of uterine cancer |
| EP2095818A1 (en) | 2008-02-29 | 2009-09-02 | AEterna Zentaris GmbH | Use of LHRH antagonists at non-castrating doses |
| WO2011076687A1 (en) | 2009-12-22 | 2011-06-30 | Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellschaft | Pyridinone derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions thereof |
| WO2012175514A1 (en) | 2011-06-21 | 2012-12-27 | Bayer Intellectual Property Gmbh | Pyridinone derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions thereof |
| US9198906B2 (en) | 2006-10-02 | 2015-12-01 | Cortendo Ab (Publ) | Ketoconazole enantiomer in humans |
| CN105348168A (en) * | 2015-11-06 | 2016-02-24 | 厦门大学 | 1-(2-(adamantane-1-yl)-1H-indole-5-yl)-3-substituted urea derivative, preparation and use thereof |
| US10821152B2 (en) | 2014-08-26 | 2020-11-03 | Betanien Hospital | Methods, agents and compositions for treatment of inflammatory conditions |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB0031315D0 (en) * | 2000-12-21 | 2001-02-07 | Glaxo Group Ltd | Indole derivatives |
| FR2860514A1 (en) * | 2003-10-03 | 2005-04-08 | Sanofi Synthelabo | ARYLALKYLCARBAMATE DERIVATIVES, THEIR PREPARATION AND THEIR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATION |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4070369A (en) * | 1972-12-13 | 1978-01-24 | Schering Corporation | 2-Aminomethyl-5-chloro-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)indole |
| US4087444A (en) * | 1976-09-08 | 1978-05-02 | Eli Lilly And Company | Amides as ovulation inhibitors |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2181559A1 (en) * | 1972-04-28 | 1973-12-07 | Aec Chimie Organique Bio | N-Phenylalkyl-N-3-indolylalkyl-alkylamines - with sedative, neuroleptic, analgesic, hypotensive, antiserotonin, adrenolytic activity |
| DE3821148A1 (en) * | 1988-06-23 | 1989-12-28 | Erwin Von Dr Angerer | AMINO ALKYLINDOLE, PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION THEREOF AND PHARMACEUTICAL PREPARATIONS CONTAINING THEREOF |
| US5607939A (en) * | 1994-04-28 | 1997-03-04 | Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Condensed heterocyclic compounds, their production and use |
| SK77598A3 (en) * | 1995-12-14 | 1999-01-11 | Merck & Co Inc | Nonpeptide derivatives, pharmaceutical composition containing them and their use |
| HUP9903671A3 (en) * | 1995-12-14 | 2001-11-28 | Merck & Co Inc | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone, pharmaceutical compositions and process for producing them |
| KR19990072123A (en) * | 1995-12-14 | 1999-09-27 | 폴락 돈나 엘. | Antagonists of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same |
-
1996
- 1996-12-10 JP JP09522251A patent/JP3092947B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1996-12-10 WO PCT/US1996/020004 patent/WO1997021435A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1996-12-10 EP EP96943763A patent/EP0868178A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1996-12-10 CA CA002240115A patent/CA2240115A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 1996-12-10 AU AU12919/97A patent/AU704937B2/en not_active Ceased
-
2000
- 2000-05-16 JP JP2000143459A patent/JP2001039871A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4070369A (en) * | 1972-12-13 | 1978-01-24 | Schering Corporation | 2-Aminomethyl-5-chloro-3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)indole |
| US4087444A (en) * | 1976-09-08 | 1978-05-02 | Eli Lilly And Company | Amides as ovulation inhibitors |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP0868178A4 * |
Cited By (63)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0882040A1 (en) * | 1995-12-14 | 1998-12-09 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| EP0882040A4 (en) * | 1995-12-14 | 1999-02-10 | Merck & Co Inc | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| EP0986385A1 (en) * | 1997-06-05 | 2000-03-22 | Merck & Co. Inc. | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| EP0986385A4 (en) * | 1997-06-05 | 2001-05-16 | Merck & Co Inc | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| WO1999011619A1 (en) * | 1997-09-04 | 1999-03-11 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Limited | Phenylindole derivatives as 5-ht2a receptor ligands |
| US6486153B1 (en) | 1997-09-04 | 2002-11-26 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Ltd. | Phenylindole derivatives as 5-HT2A receptor ligands |
| WO1999058518A2 (en) * | 1998-05-12 | 1999-11-18 | American Home Products Corporation | Biphenyl oxo-acetic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| WO1999058518A3 (en) * | 1998-05-12 | 2000-01-20 | American Home Prod | Biphenyl oxo-acetic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| US6232322B1 (en) | 1998-05-12 | 2001-05-15 | American Home Products Corporation | Biphenyl oxo-acetic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| US6369072B2 (en) | 1998-05-12 | 2002-04-09 | American Home Products Corporation | Biphenyl oxo-acetic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| US6391897B2 (en) | 1998-05-12 | 2002-05-21 | American Home Products Corporation | Biphenyl oxo-acetic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| US6346534B1 (en) | 1998-09-23 | 2002-02-12 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6310081B1 (en) | 1999-05-10 | 2001-10-30 | American Home Products Corporation | Biphenyl sulfonyl aryl carboxylic acids useful in the treatment of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia |
| US6537998B1 (en) | 1999-10-15 | 2003-03-25 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6872728B2 (en) | 2000-01-25 | 2005-03-29 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6608197B2 (en) | 2000-01-25 | 2003-08-19 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7179815B2 (en) | 2000-01-25 | 2007-02-20 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7462625B2 (en) | 2000-01-25 | 2008-12-09 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7306922B2 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2007-12-11 | Astrazeneca Ab | Human and rat PGC-3, PPAR-gamma coactivations and splice variants thereof |
| US6809098B2 (en) | 2001-02-20 | 2004-10-26 | Astrazeneca Ab | Compounds |
| WO2002066459A1 (en) * | 2001-02-20 | 2002-08-29 | Astrazeneca Ab | Indole derivatives and their use as gnrh antagonists |
| US7256188B2 (en) | 2001-05-14 | 2007-08-14 | Astrazeneca Ab | 3-aminoalkyl-2-aryl-indole derivatives and their use as GnRH antagonists |
| WO2002092565A3 (en) * | 2001-05-14 | 2002-12-27 | Astrazeneca Ab | 3-aminoalkyl-2-aryl-indole derivatives and their use as gnrh antagonists |
| WO2002092565A2 (en) * | 2001-05-14 | 2002-11-21 | Astrazeneca Ab | 3-aminoalkyl-2-aryl-indole derivatives and their use as gnrh antagonists |
| US6939883B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2005-09-06 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6750350B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-06-15 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6677340B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-01-13 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6740656B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-05-25 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7081459B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2006-07-25 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6921761B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2005-07-26 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6673796B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2004-01-06 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US6951858B2 (en) | 2001-08-02 | 2005-10-04 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7495110B2 (en) | 2001-12-21 | 2009-02-24 | Societe De Conseils De Recherches Et D'applications Scientifiques (S.C.R.A.S.) | Benzimidazole derivatives and their use as GnRH antagonists |
| KR100927500B1 (en) * | 2001-12-21 | 2009-11-17 | 입센 파마 에스.에이.에스 | Benzimidazole Derivatives and Uses thereof as NHNH Antagonists |
| US8236965B2 (en) | 2001-12-21 | 2012-08-07 | Ipsen Pharma S.A.S. | Benzimidazole derivatives and their use as a medicament |
| FR2833948A1 (en) * | 2001-12-21 | 2003-06-27 | Sod Conseils Rech Applic | New 2,5-disubstituted benzimidazole derivatives, are gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonists useful e.g. for treating endometriosis, breast or prostate cancer or precocious puberty |
| WO2003053939A1 (en) * | 2001-12-21 | 2003-07-03 | Societe De Conseils De Recherches Et D'applications Scientifiques (S.C.R.A.S.) | Benzimidazole derivatives and their use as gnrh antagonists |
| US6833372B2 (en) | 2002-02-12 | 2004-12-21 | Pfizer, Inc. | Non-peptide GnRH agents, Pharmaceutical compositions, and methods for their use |
| US6903132B2 (en) | 2002-06-13 | 2005-06-07 | Agouron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Non-peptide GnRH agents, pharmaceutical compositions and methods for their use |
| US7514570B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2009-04-07 | Astrazeneca Ab | Derivatives of 3-hydroxy-4-(cyclyl-alkylaminoalkyl)-5-phenyl-1h-pyrazole as antagonists of the gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) for use in the treatment of sex hormone related conditions, such as prostatic of uterine cancer |
| US7449489B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2008-11-11 | Astrazeneca Ab | Indolylalkylamino-methylidenecarbamate derivatives useful as GnRH antagonists |
| WO2004018420A1 (en) * | 2002-08-21 | 2004-03-04 | Astrazeneca Ab | Indolylalkylamino-methylidenecarbamate derivatives useful as gnrh antagonists |
| US7268158B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2007-09-11 | Astrazeneca Ab | 6H-THIENO [2,3-b]pyrrole derivatives as antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) |
| US7547722B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2009-06-16 | Astrazeneca Ab | Chemical compounds |
| US7317010B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2008-01-08 | Astrazeneca Ab | Thieno-pyrrole compounds as antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
| US7253290B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2007-08-07 | Astrazeneca Ab | Pyrazole derivatives as GnRH inhibitors |
| US7132442B2 (en) | 2002-08-21 | 2006-11-07 | Astrazeneca Ab | 6H-thieno[2, 3-b]pyrrole derivatives as antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) |
| US7329669B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2008-02-12 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7015226B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2006-03-21 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7229995B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2007-06-12 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7419983B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2008-09-02 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods related thereto |
| US7071200B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2006-07-04 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7056927B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2006-06-06 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US7176211B2 (en) | 2003-07-07 | 2007-02-13 | Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc. | Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonists and methods relating thereto |
| US8067456B2 (en) | 2004-07-14 | 2011-11-29 | Aeterna Zentaris Gmbh | Tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives having improved biological action and improved solubility as ligands of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCPs) |
| US7375127B2 (en) | 2004-07-14 | 2008-05-20 | Ae Zentaris Gmbh | Tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives having improved biological action and improved solubility as ligands of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) |
| EP1995238A2 (en) | 2004-07-14 | 2008-11-26 | AEterna Zentaris GmbH | Novel tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives with improved biological action and improved solubility as ligands for g-protein coupled receptors (GPCRS) |
| US9198906B2 (en) | 2006-10-02 | 2015-12-01 | Cortendo Ab (Publ) | Ketoconazole enantiomer in humans |
| EP2095818A1 (en) | 2008-02-29 | 2009-09-02 | AEterna Zentaris GmbH | Use of LHRH antagonists at non-castrating doses |
| WO2011076687A1 (en) | 2009-12-22 | 2011-06-30 | Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellschaft | Pyridinone derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions thereof |
| WO2012175514A1 (en) | 2011-06-21 | 2012-12-27 | Bayer Intellectual Property Gmbh | Pyridinone derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions thereof |
| US10821152B2 (en) | 2014-08-26 | 2020-11-03 | Betanien Hospital | Methods, agents and compositions for treatment of inflammatory conditions |
| CN105348168A (en) * | 2015-11-06 | 2016-02-24 | 厦门大学 | 1-(2-(adamantane-1-yl)-1H-indole-5-yl)-3-substituted urea derivative, preparation and use thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| AU704937B2 (en) | 1999-05-06 |
| JP3092947B2 (en) | 2000-09-25 |
| JPH11504040A (en) | 1999-04-06 |
| CA2240115A1 (en) | 1997-06-19 |
| EP0868178A1 (en) | 1998-10-07 |
| EP0868178A4 (en) | 2000-03-29 |
| AU1291997A (en) | 1997-07-03 |
| JP2001039871A (en) | 2001-02-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6197975B1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| EP0868178A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US5756507A (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| EP0873336B1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| EP0871624A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| WO1998055116A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| CA2291647A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| WO1998055470A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US6156772A (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US5981550A (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| WO1998055119A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| EP1027046A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| EP1049472A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US6159989A (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US6156767A (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US6004984A (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| CA2318957A1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| AU728811B2 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US6211224B1 (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US5985901A (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone | |
| US6159975A (en) | Antagonists of gonadotropin releasing hormone |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AM AU AZ BA BB BG BR BY CA CN CU CZ EE GE HU IL IS JP KG KR KZ LC LK LR LT LV MD MG MK MN MX NO NZ PL RO RU SG SI SK TJ TM TR TT UA US UZ VN AM AZ BY KG KZ MD RU TJ TM |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): KE LS MW SD SZ UG AT BE CH DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LU MC NL PT SE BF BJ CF CG CI CM GA GN ML MR NE SN TD TG |
|
| DFPE | Request for preliminary examination filed prior to expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed before 20040101) | ||
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1996943763 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2240115 Country of ref document: CA Ref country code: CA Ref document number: 2240115 Kind code of ref document: A Format of ref document f/p: F Ref country code: JP Ref document number: 1997 522251 Kind code of ref document: A Format of ref document f/p: F |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 1996943763 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: 1996943763 Country of ref document: EP |