WO1992021313A2 - Novel immunosuppressive compounds - Google Patents
Novel immunosuppressive compounds Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO1992021313A2 WO1992021313A2 PCT/US1992/004391 US9204391W WO9221313A2 WO 1992021313 A2 WO1992021313 A2 WO 1992021313A2 US 9204391 W US9204391 W US 9204391W WO 9221313 A2 WO9221313 A2 WO 9221313A2
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- straight
- alkenyl
- branched alkyl
- alkyl
- branched
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 C[*@@](C(O)=CI)N Chemical compound C[*@@](C(O)=CI)N 0.000 description 3
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D211/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D211/92—Heterocyclic compounds containing hydrogenated pyridine rings, not condensed with other rings with a hetero atom directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D211/96—Sulfur atom
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/02—Immunomodulators
- A61P37/06—Immunosuppressants, e.g. drugs for graft rejection
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D207/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D207/46—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom with hetero atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D207/48—Sulfur atoms
Definitions
- autoimmune diseases A wide variety of diseases can be characterized as "autoimmune diseases". Such diseases are similar to graft rejection, except that the rejection is of self tissue. Immunosuppressive therapy can also be of use in preventing this inappropriate self rejection.
- CsA cyclosporin A
- Gastroenterology/Hepatology Primary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease and other gastrointestinal autoimmune diseases.
- ALS Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- myasthenia gravis myasthenia gravis and multiple sclerosis.
- Nephrotic Syndrome Nephrotic syndrome, membrano- proliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) and related diseases.
- IPDM Insulin-Pependent Piabetes Mellitus
- IPPM Assan, R. et al.. Lancet, 67-71 (1985). IPPM. Bougneres, P.F. et al., New Engl. J. Med.
- IPPM Piabetes 37:1574-1582 (1988). IPPM.
- autoimmune diseases are also characterized as autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases such as those listed above have been observed in mammals. Papa, F.O. et al. , Equine Vet. J. 22:145-146 (1990) infertility of autoimmune origin in the stallion; Gorman, N.T. and L.L.
- CsA causes immunosuppression.
- CsA inhibits the release of ly phokines, such as interleukin 2 (IL-2) [Bunjes, D. et al. , Eur. J. Immuno1. 13.:657-661 (1981)] and prevents clonal expansion of helper and cytotoxic T cells [Larsson, E. J. Immunol. 124:2828-2833 (1980)].
- IL-2 interleukin 2
- CsA has been shown to bind the cytosolic protein, cyclophilin, and inhibit the prolyl-peptidyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) activity of that protein.
- PPIase prolyl-peptidyl cis-trans isomerase
- the PPIases may mediate T cell acti ⁇ vation by catalyzing the rotomerization of peptide bonds of prolyl residues.
- FK-506 a second natural product isolated from Streptomyces, referred to as FK-506, has been demon ⁇ strated to be a potent immunosuppresive agent. Tanaka, H. et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 109:5031-5033 (1987). FK-506 inhibits IL-2 production, inhibits mixed lympho ⁇ cyte culture response and inhibits cytotoxic T-cell generation jLn vitro at 100 times lower concentration than cyclosporin A. Kino, T. et al. , J. Antibiot. 15:1256- 1265 (1987) .
- FK-506 also inhibits PPIase activity, but is structurally different from CsA and binds to a binding protein (FKBP) distinct from cyclophilin.
- FKBP binding protein
- This invention relates to a novel class of immuno ⁇ suppressive compounds having an affinity for the FK-506 binding protein (FKBP) .
- FKBP FK-506 binding protein
- the immunosuppressive compounds inhibit the prolyl peptidyl cis-trans isomerase (rotamase) activity of the FKBP and lead to inhibition of T cell activation.
- the compounds of this invention can be used as immunosuppressive drugs to prevent or significantly reduce graft rejection in bone marrow and organ transplantations and in the treat ⁇ ment of autoimmune disease in humans and other mammals.
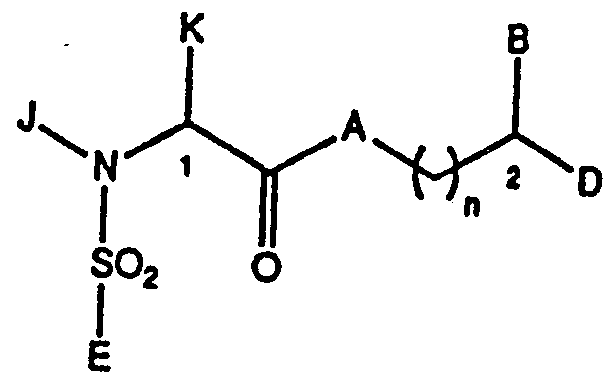
- This invention relates to a novel class of immuno ⁇ suppressive compounds having a sulfonamide substituent and which is represented by the formula I:
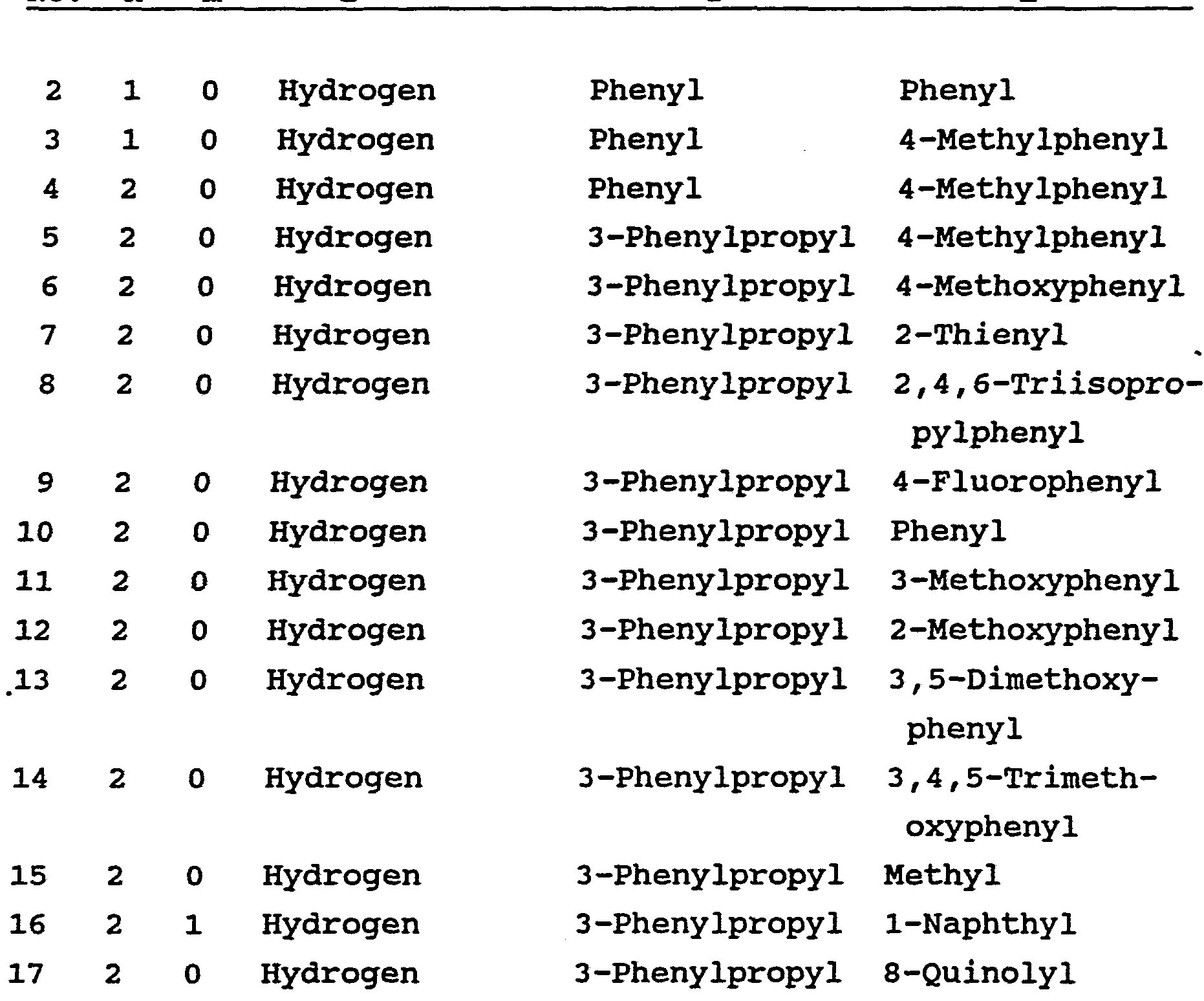
- A is CH,, oxygen, NH or N-(C1-C4 alkyl); wherein B and P are independently Ar, hydrogen, (C1-C6)-straight or branched alkyl, (C1-C6)-straight or branched alkenyl, (C1-C6)-straight or branched alkyl or alkenyl that is substituted with a (C5-C7)-cycloalkyl, (C1-C6)-straight or branched alkyl or alkenyl that is substituted with a (C5-C7)-cycloalkenyl, or Ar substituted (C1-C6)-straight or branched alkyl or alkenyl, wherein, in each case, one or two of the CH_ groups of the alkyl or alkenyl chains may contain 1-2 heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of oxygen, sulfur, SO and S0_ in chemically reasonable substitution patterns, or
- both B and P are not hydrogen; wherein Q is hydrogen, (C1-C6)-straight or branched alkyl or (C1-C6)-straight or branched alkenyl; wherein T is Ar or substituted 5-7 membered cyclo- alkyl with substituents at positions 3 and 4 which are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, hydroxyl, 0-(Cl-C4)-alkyl, 0-(Cl-C4)-alkenyl and carbonyl; wherein Ar is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, 1-naphthyl, 2-naphthyl, 2-furyl, 3-furyl, 2-thienyl, 3-thienyl, 2-pyridyl, 3-pyridyl, 4-pyridyl, monocyclic and bicyclic heterocyclic ring systems with individual ring sizes being 5 or 6 which may contain in either or both rings a total of 1-4 heteroatoms independently selected from 0, N and S; wherein Ar may
- the stereochemistry at position 1 (Formula I) is (R) or (S) , with (S) preferred.
- the stereochemistry at position 2 is (R) or (S) .
- the compounds of the present invention can be used in the form of salts derived from inorganic or organic acids and bases. Included among such acid salts are the following: acetate, adipate, alginate, aspartate, benzoate, benzenesulfonate, bisulf te butyrate, citrate, camphorate, camphorsulfonate, cyclopentanepropionate, digluconate, dodecylsulfate, ethanesulfonate, fumarate, glucoheptanoate, glycerophosphate, hemisulfate, heptanoate, hexanoate, hydro ⁇ hloride, hydrobro ide, hydroiodide, 2-hydroxyethanesulfonate, lactate, maleate, methanesulfonate, 2-naphthalenesulfonate, nicotinate, oxalate, pamoate, pectinate, persulfate,
- Base salts include ammonium salts, alkali metal salts such as sodium and potassium salts, alkaline earth metal salts such as calcium and magnesium salts, salt with organic bases such as dicyclohexylamine salts, N-methyl-P- glucamine, and salts with amino acids such as arginine, lysine, and so forth.
- the basic nitrogen- containing groups can be quaternized with such agents as lower alkyl halides, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, and butyl chloride, bromides and iodides; dialkyl sulfates like dimethyl, diethyl, dibutyl and diamyl sulfates, long chain halides such as decyl, lauryl, myristyl and stearyl chlorides, bromides and iodides, aralkyl halides like benzyl and phenethyl bromides and others. Water or oil-soluble or dispersible products are thereby obtained.
- lower alkyl halides such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, and butyl chloride, bromides and iodides
- dialkyl sulfates like dimethyl, diethyl, dibutyl and diamyl sulfates
- long chain halides such as decy
- the compounds will have a molecular weight below about 750 atomic mass units (a.m.u.) and most preferably below about 500 a.m.u.
- the immunosuppressive compounds of this invention have an affinity for the FK-506 binding protein which is located in the cytosol of lymphocytes, particularly T lymphocytes. When the immunosuppressive compounds are bound to the FKBP, they act to inhibit the prolyl- peptidyl cis-trans isomerase activity of the binding protein and inhibit lymphocyte activation mediated by FKBP.
- FK-506 binding protein has been identified by Harding, M.W. et al. , Nature 341:758-760 (1989) and can be used as the standard by which to evaluate binding affinity of the compounds for FKBP.
- Compounds of this invention may have an affinity for other FK-506 binding proteins. Inhibition of the prolyl peptidyl cis-trans isomerase may further be indicative of binding to an FK-506 binding protein.
- Human FK-506 binding protein can be obtained as described by Harding, M.W. et al. , Nature 341:758-760 (1989) . Values for the apparent K, can be determined from a competitive LH-20 binding assay performed as described by Harding et al. , using 32-[1- 14C]-benzoyl FK-
- FK-506 binding protein was measured.
- the inhibition of the PPIase (rotamase) enzyme activity of the FKBP can also be measured according to the methods described by either Harding, M.W. et al. , Nature 341:758-760 (1989) or Siekierka, J.J. et al. , Nature 341:755-757 (1989).
- the cis-trans isomerization of the proline-alanine peptide bond in a model substrate, N-succinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-p- nitroanilide is monitored spectrophotometrically in a coupled assay with chymotrypsin, which releases 4-nitro- anilide from the trans form of the substrate.
- the compounds of the present invention can be further characterized in cellular biological experiments in vitro where their resemblance in function and use to cyclosporin A and to FK-506 is apparent. (See Table 2) .
- CTLL Prolifera ⁇ »l ⁇ g/ml * 0.01 ⁇ g/ml »l ⁇ g/ral tion + IL-2 1) Assay similar to Yoshimura, N. et al. , Transplantation 47:356-359 (1989). Assay uses fresh human peripheral blood lymphocytes isolated by Ficoll-Hypaque density centrifugation, stimulated by the 0KT3 antibody (anti-CP3) which stimulates via interaction with CP3. Stimulation is measured by incorporation of radioactive thymidine [( H)TdR] into proliferating cells, with an uninhibited control signal of 48,000-75,000 cpm. IC 50 values are estimated from inhibitions of prolifer ⁇ ation observed at various drug concentrations.
- T-cell clone stimulated with antibody to the T-cell receptor (TCR) and antibody to CP2.
- Stimulation is measured by incorpor- ation of radioactive thymidine [( H)TdR] into prolifer ⁇ ating cells, with an uninhibited control signal of 23,000 cpm.
- IC 5f values are estimated from inhibitions of proliferation observed at various drug concentrations.
- the assay uses a T-cell hybridoma similar to that described.
- the assay measures activation-induced (anti-CP3) cell death (evaluated by counting viable cells after staining as described) in a T-cell hybridoma that mimics the effect known to occur in immature thymocytes.
- the ability of cyclosporin A and FK-506 to inhibit this cell death is herein used as a sensitive indication of compounds with cyclosporin-like and/or FK-506-like mechanism of action. Note that the chemically related, but mechanistically distinct, immunosuppressant rapamycin is inactive in this assay.
- IL-2 is provided to overcome this block. Note that the chemically related, but mechanistically distinct immuno- suppressant, rapamycin, is active in this assay.
- the compounds can be used as immunosuppres ⁇ sants for prophylaxis of organ rejection or treatment of chronic graft rejection and for the treatment of auto ⁇ immune diseases.
- the immunosuppressive compounds of this invention can be periodically administered to a patient undergoing bone marrow or organ transplantation or for another reason in which it is desirable to substantially reduce or suppress a patient's immune response, such as in various autoimmune diseases.
- the compounds of this invention can also be administered to mammals other than humans for treatment of various mammalian autoimmune diseases.
- the novel compounds of the present invention possess an excellent degree of activity in suppression of antigen-stimulated growth and clonal expansion of T-cells, especially those T-cells characterized as "helper" T-cells. This activity is useful in the primary prevention of organ transplant rejection, in the rescue of transplanted organs during a rejection episode, and in the treatment of any of several autoimmune diseases known to be associated with inappropriate autoimmune responses.
- autoimmune diseases include: uveitis, Behcet's disease. Graves ophthalmopathy, psoriasis, acute dermato- myositis, atopic skin disease, scleroderma, eczema, pure red cell aplasia, aplastic anemia, primary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, nephrotic syndrome, membrano- proliferative glomerulonephritis, rheumatoid arthritis and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
- Graves ophthalmopathy Graves ophthalmopathy, psoriasis, acute dermato- myositis, atopic skin disease, scleroderma, eczema, pure red cell aplasia, aplastic anemia, primary cirrhosis
- treatment is effective to reduce the symptoms and slow progression of the disease.
- treatment as described below is most effective when instituted before the complete cessation of natural insulin production and transition to complete dependence on external insulin.
- the compounds of the present invention may be administered orally, parenterally, by inhalation spray, topically, rectally, nasally, buccally, vaginally or via an implanted reservoir in dosage formu ⁇ lations containing conventional non-toxic pharma- ceutically-acceptable carriers, adjuvants and vehicles.
- parenteral as used herein includes subcutaneous, intravenous, intramuscular, intrasternal and intracranial injection or infusion techniques.
- the pharmaceutical compositions may be in the form of a sterile injectable preparation, for example as a sterile injectible aqueous or oleagenous suspension. This suspension may be formulated according to techniques known in the art using suitable dispersing or wetting agents and suspending agents.
- the sterile injectable preparation may also be a sterile injectable solution or suspension in a non-toxic parenterally-acceptable diluent or solvent, for example as a solution in 1,3-butanediol.
- a non-toxic parenterally-acceptable diluent or solvent for example as a solution in 1,3-butanediol.
- acceptable vehicles and solvents that may be employed are water. Ringer's solution and isotonic sodium chloride solution.
- sterile, fixed oils are conventionally employed as a solvent or suspending medium.
- any bland fixed oil may be employed including synthetic mono- or di-glycerides.
- Fatty acids such as oleic acid and its glyceride deri ⁇ vatives find use in the preparation of injectables, as do natural pharmaceutically-acceptable oils, such as olive oil or castor oil, especially in their polyoxyethylated versions.
- oils such as olive oil or castor oil, especially in their polyoxyethylated versions.
- These oil solutions or suspensions may also contain a long-chain alcohol diluent or dispersant such as Ph. Helv or similar alcohol.
- the compounds may be administered orally, in the form of capsules or tablets, for example, or as an aqueous suspension or solution.
- carriers which are commonly used include lactose and corn starch.
- Lubricating agents, such as magnesium stearate, are also typically added.
- useful diluents include lactose and dried corn starch.
- aqueous suspensions are required for oral use, the active ingredient is combined with emulsifying and suspending agents. If desired, certain sweetening and/or flavoring and/or coloring agents may be added.
- the compounds of this invention may also be ad ⁇ ministered in the form of suppositories for rectal administration of the drug.
- compositions can be prepared by mixing the drug with a suitable non-irritat ⁇ ing excipient which is solid at room temperature but liquid at the rectal temperature and therefore will melt in the rectum to release the drug.
- suitable non-irritat ⁇ ing excipient include cocoa butter, beeswax and polyethylene glycols.
- the compounds of this invention may also be admin ⁇ istered topically, especially when the conditions addressed for treatment involve areas or organs readily accessible by topical application, including autoimmune diseases of the eye, the skin, or the lower intestinal tract. Suitable topical formulations are readily pre ⁇ pared for each of these areas.
- the compounds can be formulated as micronized suspensions in isotonic, pH adjusted sterile saline, or, preferably, as solutions in isotonic, pH adjusted sterile saline, either with or without a preservative such as benzylalkonium chloride.
- the compounds may be formulated in an ointment such as petrolatum.
- the compounds can be formulated in a suitable ointment containing the compound suspended or dissolved in, for example, a mixture with one or more of the following: mineral oil, liquid petrolatum, white petrolatum, propylene glycol, polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene compound, emulsifying wax and water.
- the compounds can be formulated in a suitable lotion or cream containing the active compound suspended or dissolved in, for example, a ixture of one or more of the following: mineral oil, sorbitan monostearate, polysorbate 60, cetyl esters wax, cetearyl alcohol, 2-octyldodecanol, benzyl alcohol and water.
- Topical application for the lower intestinal tract can be effected in a rectal suppository formulation (see above) or in a suitable enema formulation.
- Posage levels on the order of 0.01 to 100 mg/kg per day of the active ingredient compound are useful in the treatment of the above conditions.
- the amount of active ingredient that may be combined with the carrier materials to produce a single dosage form will vary depending upon the host treated and the particular mode of administration.
- a specific dose level for any particular patient will depend upon a variety of factors, including the activity of the specific compound employed, the age, body weight, general health, sex, diet, time of administration, rate of excretion, drug combination and the severity of the particular disease being treated.
- the compound can also be administered in combination with a steroid, such as methyl prednisalone acetate, for additional immunosuppressive effect.
- a steroid such as methyl prednisalone acetate
- the steroid is administered orally, intravenously, rectally, topically or by inhalation.
- Posages (based upon methyl pre ⁇ dnisalone acetate) of 0.1-5 mg/kg/day may be employed.
- An initial loading dose of 100-500 mg may be employed.
- Steroid doses may be decreased with time from the higher toward the lower doses as the clinical situation indicates.
- the compounds can be administered with other immuno ⁇ suppressant drugs, such as rapamycin, azathioprine, 15-deoxyspergualin, cyclosporin, FK-506 or combinations of these, to increase the immunosuppressive effect.
- OKT3 which is a murine monoclonal antibody to CP3 surface antigen of human T lymphocytes, can also be coadministered intravenously with compounds of the present inventions for rescue and reversal of acute allograft rejections, particularly in renal transplan ⁇ tations.
- H NMR proton nuclear magnetic resonance
- the reaction mixture was concentrated and flash chromatographed (elution with a gradient of 5% ethyl acetate in hexane to 100% ethyl acetate) to give 29 mg of the sulfonamide (5) as an oil.
- the compound is illustrated below.
- Fresh peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) from LeukoPak cells or whole blood from random normal blood donors (tested HIV-negative and hepatitis negative) are isolated and separated by density centrifugation over Histopaque 1077 (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO).
- the murine CTLL cytotoxic T cell line and the human Jurkat T cell line are from ATCC (CTLL-2 ATCC TIB214, JURKAT CLONE E6-1 ATCC TIB152) .
- the human allogeneic B cell lines used for activation of the fresh PBLs are EBV-transformed lymphocytes from normal healthy adult donors with two completely different HLA haplotypes.
- Culture medium consists of RPMI 1640 (Gibco, Grand Island, NY) containing penicillin (50 U/ml) and streptomycin (50 /*g/ml) , L-glutamine 2 mM, 2 mmeerrccaappttooeetthhaa:nol (5 x 10 —5) , 10% heat-inactivated FCS and 10 mM HEPES.
- the MTT assay is a colorimetric technique to determine the toxicity of the compounds on growing lymphoid and non-lymphoid cell lines based on reduction of the tetrazolium salt by intact mitochondria (Mossman, T., J. Immunol. Methods 65:55 (1983)). Cell viability in the presence or absence of different concentrations of test compounds in serum-free medium (HB 104, HANA Biologic, Inc.) was assessed using MTT
- Antigen activated proliferation of PBLs in a primary mixed lymphocyte reaction was assessed in the presence or absence of different concentrations of tested compounds
- EBV-transformed j8-lymphoblastoid cells LB and JVM, in a final volume of 200 ⁇ l per well in 96-well round-bottomed plates (Mishell, B.B. and S.M. Shiigi, Selected Methods in Cellular Immunology W.H. Freeman and Co., San
- CTLL IL-2 Microassay
- 3 x 10 CTLLs were exposed to different concentrations of test compounds and control drugs in the presence of 1 U/ml of human recombinant IL-2 (Genzyme, rIL-2) for 24 h.
- IL-2 human recombinant IL-2
- PMA and OKT3 - mitogens used to stimulate proliferation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBC) Compounds are evaluated on their ability to inhibit proliferation.
- LB and JVM - human viral-transformed B lymphoblastoid cell lines stimulated to proliferate in a mixed lymphocyte reaction
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Transplantation (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP50049793A JP3163104B2 (en) | 1991-05-24 | 1992-05-26 | New immunosuppressive compounds |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US70537191A | 1991-05-24 | 1991-05-24 | |
| US705,371 | 1991-05-24 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO1992021313A2 true WO1992021313A2 (en) | 1992-12-10 |
| WO1992021313A3 WO1992021313A3 (en) | 1993-01-07 |
Family
ID=24833176
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US1992/004391 WO1992021313A2 (en) | 1991-05-24 | 1992-05-26 | Novel immunosuppressive compounds |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0587756A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP3163104B2 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2185092A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2102178A1 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX9202466A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO1992021313A2 (en) |
Cited By (54)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5696135A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1997-12-09 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity effective at stimulating neuronal growth |
| US5707985A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-01-13 | Tanabe Seiyaku Co. Ltd. | Naphthyl-, quinolyl- and isoquinolyl- sulfonamide derivatives as cell adhesion modulators |
| US5721256A (en) * | 1997-02-12 | 1998-02-24 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Method of using neurotrophic sulfonamide compounds |
| US5786378A (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 1998-07-28 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters |
| US5795908A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-08-18 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5798355A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-08-25 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5801187A (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 1998-09-01 | Gpi-Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic esters and amides |
| US5801197A (en) * | 1995-10-31 | 1998-09-01 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Rotamase enzyme activity inhibitors |
| GB2324527A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-10-28 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Non-immunosuppressant rotamase inhibitors |
| US5846981A (en) * | 1993-05-28 | 1998-12-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5846979A (en) * | 1997-02-28 | 1998-12-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-oxides of heterocyclic esters, amides, thioesters, and ketones |
| WO1999010340A1 (en) * | 1997-08-29 | 1999-03-04 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Compounds possessing neuronal activity |
| WO1999015501A1 (en) * | 1997-09-25 | 1999-04-01 | Asta Medica Aktiengesellschaft | Specific immunophilin ligands useful as anti-asthmatic, anti-allergic, anti-rheumatic, immunosuppressive, antipsoriatic and neuroprotective agents |
| US5935989A (en) * | 1996-12-31 | 1999-08-10 | Gpi Nil Holdings Inc. | N-linked ureas and carbamates of heterocyclic thioesters |
| US5958949A (en) * | 1996-12-31 | 1999-09-28 | Gpi Nil Holdings Inc. | N-linked ureas and carbamates of piperidyl thioesters |
| US5968921A (en) * | 1997-10-24 | 1999-10-19 | Orgegon Health Sciences University | Compositions and methods for promoting nerve regeneration |
| WO1999062880A1 (en) * | 1998-06-03 | 1999-12-09 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked sulfonamides of n-heterocyclic carboxylic acids or carboxylic acid isosteres |
| US6004993A (en) * | 1997-06-04 | 1999-12-21 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked sulfonamide of heterocyclic thioester hair growth compounds and uses |
| WO2000009104A2 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-02-24 | Gpi Nhl Holdings, Inc. | Use of sulfonamides for treating vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009109A2 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-02-24 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Pipecolic acid derivatives for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009112A2 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-02-24 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic esters or amides for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009102A2 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-02-24 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Carboxylic acids and isosteres of n-heterocyclic compounds for vision and memory disorders |
| US6096762A (en) * | 1998-06-02 | 2000-08-01 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Neurotrophic difluoroamide agents |
| US6172087B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-01-09 | Gpi Nil Holding, Inc. | N-oxide of heterocyclic ester, amide, thioester, or ketone hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6187784B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-02-13 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Pipecolic acid derivative hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6187796B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-02-13 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Sulfone hair growth compositions and uses |
| WO2001010838A1 (en) * | 1999-08-05 | 2001-02-15 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Multivalent compounds |
| WO2001010837A1 (en) * | 1999-08-05 | 2001-02-15 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Multivalent sulfonamides |
| US6218423B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2001-04-17 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Pyrrolidine derivatives for vision and memory disorders |
| US6218424B1 (en) | 1996-09-25 | 2001-04-17 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic ketone and thioester compounds and uses |
| US6228872B1 (en) | 1998-11-12 | 2001-05-08 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Neurotrophic diamide and carbamate agents |
| US6268384B1 (en) | 1997-08-29 | 2001-07-31 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Compounds possessing neuronal activity |
| US6271244B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-08-07 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked urea or carbamate of heterocyclic thioester hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6274617B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-08-14 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic ester and amide hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6274602B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-08-14 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioester and ketone hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6300341B1 (en) | 1998-09-30 | 2001-10-09 | The Procter & Gamble Co. | 2-substituted heterocyclic sulfonamides |
| US6307049B1 (en) | 1998-09-30 | 2001-10-23 | The Procter & Gamble Co. | Heterocyclic 2-substituted ketoamides |
| US6335348B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-01-01 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Nitrogen-containing linear and azepinyl/ compositions and uses for vision and memory disorders |
| US6337340B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-01-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Carboxylic acids and isosteres of heterocyclic ring compounds having multiple heteroatoms for vision and memory disorders |
| US6339101B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-01-15 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked sulfonamides of N-heterocyclic carboxylic acids or isosteres for vision and memory disorders |
| US6372736B1 (en) | 1998-07-21 | 2002-04-16 | Pfizer Inc | Heterocyclic compounds as inhibitors of rotamase enzymes |
| US6384056B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-05-07 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters or ketones for vision and memory disorders |
| US6395758B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-05-28 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule carbamates or ureas for vision and memory disorders |
| US6399648B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-06-04 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-oxides of heterocyclic ester, amide, thioester, or ketone for vision and memory disorders |
| US6417189B1 (en) | 1999-11-12 | 2002-07-09 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | AZA compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use |
| US6462072B1 (en) | 1998-09-21 | 2002-10-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Cyclic ester or amide derivatives |
| US6506788B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2003-01-14 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked urea or carbamate of heterocyclic thioesters for vision and memory disorders |
| US6610707B1 (en) * | 1998-03-02 | 2003-08-26 | Pfizer Inc. | Heterocyclic compounds as inhibitors of rotomase enzymes |
| US6734211B1 (en) | 1999-07-09 | 2004-05-11 | Oregon Health & Sciences University | Compositions and methods for promoting nerve regeneration |
| US6852496B1 (en) | 1997-08-12 | 2005-02-08 | Oregon Health And Science University | Methods of screening for agents that promote nerve cell growth |
| US6974823B2 (en) | 1999-12-21 | 2005-12-13 | Gpi Nil Holdindgs, Inc. | Hydantoin derivative compounds, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of using same |
| US7253169B2 (en) | 1999-11-12 | 2007-08-07 | Gliamed, Inc. | Aza compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use |
| EP2583678A2 (en) | 2004-06-24 | 2013-04-24 | Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics, Inc. | Small molecule immunopotentiators and assays for their detection |
| CN110054665A (en) * | 2019-04-29 | 2019-07-26 | 湖南新汇制药股份有限公司 | A kind of five titanium compound of ring, preparation method and its preparing the application in immune suppressant drug |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2750087B1 (en) * | 1996-06-19 | 1998-09-04 | Faure Bertrand Equipements Sa | VEHICLE SEAT ELEMENT HAVING A TENSIONED HEADPHONES ON A METAL FRAME |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2431734A1 (en) * | 1974-07-02 | 1976-01-29 | Basf Ag | Beta-keto propane sultones and sultams - useful as immunosuppressants, esp. for inhibiting transplant rejection |
| EP0172458A2 (en) * | 1984-07-31 | 1986-02-26 | Suntory Limited | Novel biologically active compound having anti-prolyl endopeptidase activity |
| EP0384341A2 (en) * | 1989-02-20 | 1990-08-29 | Kabushiki Kaisha Yakult Honsha | New proline derivatives |
| WO1992000278A1 (en) * | 1990-07-02 | 1992-01-09 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Novel immunosuppressive compounds |
-
1992
- 1992-05-25 MX MX9202466A patent/MX9202466A/en unknown
- 1992-05-26 AU AU21850/92A patent/AU2185092A/en not_active Abandoned
- 1992-05-26 WO PCT/US1992/004391 patent/WO1992021313A2/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1992-05-26 EP EP92913385A patent/EP0587756A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1992-05-26 CA CA002102178A patent/CA2102178A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 1992-05-26 JP JP50049793A patent/JP3163104B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2431734A1 (en) * | 1974-07-02 | 1976-01-29 | Basf Ag | Beta-keto propane sultones and sultams - useful as immunosuppressants, esp. for inhibiting transplant rejection |
| EP0172458A2 (en) * | 1984-07-31 | 1986-02-26 | Suntory Limited | Novel biologically active compound having anti-prolyl endopeptidase activity |
| EP0384341A2 (en) * | 1989-02-20 | 1990-08-29 | Kabushiki Kaisha Yakult Honsha | New proline derivatives |
| WO1992000278A1 (en) * | 1990-07-02 | 1992-01-09 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Novel immunosuppressive compounds |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., vol. 57, no. 12, December 1984, T. MIYAZAWA et al.: "Studies of unusual amino acids and their peptides. XV. The chemistry of N-carboxymethyl amino acids. III. The synthesis of N-tosyl-N-carboxymethyl amino acid derivatives by N-alkoxycarbonylmethylation", pages 3605-3606, see whole document * |
| Indian Journal of Chemistry, vol. 9, no. 6, June 1971, T.R. GOVINDACHARI et al.: "Reaction of diazoalkanes with p-toluenesulphonylamino acid", pages 537-538, see whole document * |
| J. Org. Chem., vol. 39, no. 22, 1974, W.R. HERTLER: "Free-radical chain isomerization of N-vinylsulfonamides", pages 3219-3223, see whole document, especially page 3220, table III * |
| Pharmazie, vol. 25, no. 12, 1970, M. GEISERT et al.: "Synthese der optischen Antipoden des N-(N-Methylnorleucyl)-2.6-dimethylanilins mit oberfl{chenan{sthetischer Wirkung", pages 732-734, see whole document, especially page 733 * |
Cited By (103)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5846981A (en) * | 1993-05-28 | 1998-12-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| GB2324527A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-10-28 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Non-immunosuppressant rotamase inhibitors |
| US6500843B2 (en) | 1995-06-07 | 2002-12-31 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US7652060B2 (en) | 1995-06-07 | 2010-01-26 | Glia Med, Inc | Small molecule rotamase enzyme inhibitors |
| US5795908A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-08-18 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5843960A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-12-01 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US7282510B2 (en) | 1995-06-07 | 2007-10-16 | Gliamed, Inc. | Small molecule inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US7960570B2 (en) | 1995-06-07 | 2011-06-14 | Gliamed, Inc. | Small molecule inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US6022878A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 2000-02-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5798355A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-08-25 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5707985A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1998-01-13 | Tanabe Seiyaku Co. Ltd. | Naphthyl-, quinolyl- and isoquinolyl- sulfonamide derivatives as cell adhesion modulators |
| GB2324527B (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1999-12-22 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Small molecule inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5859031A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1999-01-12 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5696135A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1997-12-09 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity effective at stimulating neuronal growth |
| US6140357A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 2000-10-31 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| GB2332673A (en) * | 1995-06-07 | 1999-06-30 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Small molecule inhibitors of rotamase enzyme activity |
| US5801197A (en) * | 1995-10-31 | 1998-09-01 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Rotamase enzyme activity inhibitors |
| US6218544B1 (en) | 1996-09-25 | 2001-04-17 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic esters and amides |
| US5801187A (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 1998-09-01 | Gpi-Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic esters and amides |
| US6218424B1 (en) | 1996-09-25 | 2001-04-17 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic ketone and thioester compounds and uses |
| US6417209B2 (en) | 1996-09-25 | 2002-07-09 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic ketone and thioester compounds and uses |
| US5990131A (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 1999-11-23 | Gpi Nil Holdings Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters and ketones |
| US6200972B1 (en) | 1996-09-25 | 2001-03-13 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic esters and amides |
| US6984639B2 (en) | 1996-09-25 | 2006-01-10 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic ketone and thioester compounds and uses |
| EP0934263A1 (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 1999-08-11 | Guilford Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters and ketones |
| EP1626043A1 (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 2006-02-15 | MGI GP, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters |
| US5786378A (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 1998-07-28 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters |
| EP0934263A4 (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 2002-11-06 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Heterocyclic thioesters and ketones |
| CZ298120B6 (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 2007-06-27 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters or ketones |
| EP1900726A1 (en) * | 1996-09-25 | 2008-03-19 | MGI GP, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters |
| US5935989A (en) * | 1996-12-31 | 1999-08-10 | Gpi Nil Holdings Inc. | N-linked ureas and carbamates of heterocyclic thioesters |
| US6184243B1 (en) | 1996-12-31 | 2001-02-06 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked ureas and carbamates of heterocyclic thioesters |
| US5958949A (en) * | 1996-12-31 | 1999-09-28 | Gpi Nil Holdings Inc. | N-linked ureas and carbamates of piperidyl thioesters |
| US6274607B1 (en) | 1996-12-31 | 2001-08-14 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked ureas and carbamates of heterocyclic thioesters |
| US6245783B1 (en) | 1997-02-12 | 2001-06-12 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Method of using neurotrophic sulfonamide compounds |
| EP1014978A4 (en) * | 1997-02-12 | 2003-05-28 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Method of using neutrophic sulfonamide compounds |
| US5968957A (en) * | 1997-02-12 | 1999-10-19 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Method of using neurotrophic sulfonamide compounds |
| US5721256A (en) * | 1997-02-12 | 1998-02-24 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Method of using neurotrophic sulfonamide compounds |
| EP1014978A1 (en) * | 1997-02-12 | 2000-07-05 | GPI NIL Holdings, Inc. | Method of using neutrophic sulfonamide compounds |
| US5846979A (en) * | 1997-02-28 | 1998-12-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-oxides of heterocyclic esters, amides, thioesters, and ketones |
| US6486151B2 (en) | 1997-02-28 | 2002-11-26 | Gpi Nil Holdings Inc. | N-oxides of heterocyclic esters, amides, thioesters, and ketones |
| US6251892B1 (en) | 1997-02-28 | 2001-06-26 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-oxides of heterocyclic esters, amides, thioesters, and ketones |
| US6004993A (en) * | 1997-06-04 | 1999-12-21 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked sulfonamide of heterocyclic thioester hair growth compounds and uses |
| US6191125B1 (en) | 1997-06-04 | 2001-02-20 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule pipecolic acid derivative hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6194440B1 (en) | 1997-06-04 | 2001-02-27 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule carbamate or urea hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6187806B1 (en) | 1997-06-04 | 2001-02-13 | Gpi Nil Holdings | N-linked sulfone of heterocyclic thioester hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6177455B1 (en) | 1997-06-04 | 2001-01-23 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Pyrrolidine derivative hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6852496B1 (en) | 1997-08-12 | 2005-02-08 | Oregon Health And Science University | Methods of screening for agents that promote nerve cell growth |
| US7282340B2 (en) | 1997-08-12 | 2007-10-16 | Oregon Health Sciences University | Methods for identifying an analog that promotes nerve regeneration |
| KR100859758B1 (en) * | 1997-08-29 | 2008-09-24 | 버텍스 파마슈티칼스 인코포레이티드 | Compounds possessing neuronal activity |
| WO1999010340A1 (en) * | 1997-08-29 | 1999-03-04 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Compounds possessing neuronal activity |
| US7109215B2 (en) * | 1997-08-29 | 2006-09-19 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Compounds possessing neuronal activity |
| SG129998A1 (en) * | 1997-08-29 | 2007-03-20 | Vertex Pharma | Compounds possessing neuronal activity |
| US6268384B1 (en) | 1997-08-29 | 2001-07-31 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Compounds possessing neuronal activity |
| CN100436447C (en) * | 1997-08-29 | 2008-11-26 | 沃泰克斯药物股份有限公司 | Compounds possessing neuronal activity |
| WO1999015501A1 (en) * | 1997-09-25 | 1999-04-01 | Asta Medica Aktiengesellschaft | Specific immunophilin ligands useful as anti-asthmatic, anti-allergic, anti-rheumatic, immunosuppressive, antipsoriatic and neuroprotective agents |
| US6210974B1 (en) | 1997-10-24 | 2001-04-03 | Oregon Health Sciences University | Compositions and methods for promoting nerve regeneration |
| US6881409B2 (en) | 1997-10-24 | 2005-04-19 | Oregon Health And Science University | Compositions and methods for promoting nerve regeneration |
| US5968921A (en) * | 1997-10-24 | 1999-10-19 | Orgegon Health Sciences University | Compositions and methods for promoting nerve regeneration |
| US6610707B1 (en) * | 1998-03-02 | 2003-08-26 | Pfizer Inc. | Heterocyclic compounds as inhibitors of rotomase enzymes |
| US6239146B1 (en) | 1998-06-02 | 2001-05-29 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Neurotrophic difluoroamide agents |
| US6096762A (en) * | 1998-06-02 | 2000-08-01 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Neurotrophic difluoroamide agents |
| US7459473B2 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2008-12-02 | Glia Med, Inc. | N-linked sulfonamides of N-heterocyclic carboxylic acids or carboxylic acid isosteres |
| WO1999062880A1 (en) * | 1998-06-03 | 1999-12-09 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked sulfonamides of n-heterocyclic carboxylic acids or carboxylic acid isosteres |
| US6172087B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-01-09 | Gpi Nil Holding, Inc. | N-oxide of heterocyclic ester, amide, thioester, or ketone hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6187784B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-02-13 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Pipecolic acid derivative hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6187796B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-02-13 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Sulfone hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6271244B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-08-07 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked urea or carbamate of heterocyclic thioester hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6274602B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-08-14 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioester and ketone hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6274617B1 (en) | 1998-06-03 | 2001-08-14 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic ester and amide hair growth compositions and uses |
| US6372736B1 (en) | 1998-07-21 | 2002-04-16 | Pfizer Inc | Heterocyclic compounds as inhibitors of rotamase enzymes |
| US6384056B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-05-07 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic thioesters or ketones for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009104A3 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-12-07 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Use of sulfonamides for treating vision and memory disorders |
| US6395758B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-05-28 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule carbamates or ureas for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009102A2 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-02-24 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Carboxylic acids and isosteres of n-heterocyclic compounds for vision and memory disorders |
| US6218423B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2001-04-17 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Pyrrolidine derivatives for vision and memory disorders |
| US7338976B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2008-03-04 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic esters or amides for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009112A3 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-06-29 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Heterocyclic esters or amides for vision and memory disorders |
| US6337340B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-01-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Carboxylic acids and isosteres of heterocyclic ring compounds having multiple heteroatoms for vision and memory disorders |
| US6333340B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2001-12-25 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Small molecule sulfonamides for vision and memory disorders |
| US6376517B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-04-23 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Pipecolic acid derivatives for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009102A3 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-07-06 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Carboxylic acids and isosteres of n-heterocyclic compounds for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009104A2 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-02-24 | Gpi Nhl Holdings, Inc. | Use of sulfonamides for treating vision and memory disorders |
| US6339101B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-01-15 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked sulfonamides of N-heterocyclic carboxylic acids or isosteres for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009112A2 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-02-24 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Heterocyclic esters or amides for vision and memory disorders |
| US6506788B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2003-01-14 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-linked urea or carbamate of heterocyclic thioesters for vision and memory disorders |
| US6335348B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-01-01 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Nitrogen-containing linear and azepinyl/ compositions and uses for vision and memory disorders |
| US6399648B1 (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2002-06-04 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | N-oxides of heterocyclic ester, amide, thioester, or ketone for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009109A3 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-08-17 | Guilford Pharm Inc | Pipecolic acid derivatives for vision and memory disorders |
| WO2000009109A2 (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 2000-02-24 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Pipecolic acid derivatives for vision and memory disorders |
| US6462072B1 (en) | 1998-09-21 | 2002-10-08 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | Cyclic ester or amide derivatives |
| US6300341B1 (en) | 1998-09-30 | 2001-10-09 | The Procter & Gamble Co. | 2-substituted heterocyclic sulfonamides |
| US6307049B1 (en) | 1998-09-30 | 2001-10-23 | The Procter & Gamble Co. | Heterocyclic 2-substituted ketoamides |
| US6228872B1 (en) | 1998-11-12 | 2001-05-08 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Neurotrophic diamide and carbamate agents |
| US6734211B1 (en) | 1999-07-09 | 2004-05-11 | Oregon Health & Sciences University | Compositions and methods for promoting nerve regeneration |
| WO2001010837A1 (en) * | 1999-08-05 | 2001-02-15 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Multivalent sulfonamides |
| WO2001010838A1 (en) * | 1999-08-05 | 2001-02-15 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Multivalent compounds |
| US7253169B2 (en) | 1999-11-12 | 2007-08-07 | Gliamed, Inc. | Aza compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use |
| US6417189B1 (en) | 1999-11-12 | 2002-07-09 | Gpi Nil Holdings, Inc. | AZA compounds, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use |
| US6974823B2 (en) | 1999-12-21 | 2005-12-13 | Gpi Nil Holdindgs, Inc. | Hydantoin derivative compounds, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of using same |
| EP2583678A2 (en) | 2004-06-24 | 2013-04-24 | Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics, Inc. | Small molecule immunopotentiators and assays for their detection |
| CN110054665A (en) * | 2019-04-29 | 2019-07-26 | 湖南新汇制药股份有限公司 | A kind of five titanium compound of ring, preparation method and its preparing the application in immune suppressant drug |
| CN110054665B (en) * | 2019-04-29 | 2022-08-26 | 湖南新汇制药股份有限公司 | Application of cyclic pentapeptide compound in preparation of immunosuppressant drug |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0587756A1 (en) | 1994-03-23 |
| MX9202466A (en) | 1994-06-30 |
| JP3163104B2 (en) | 2001-05-08 |
| JPH06508141A (en) | 1994-09-14 |
| CA2102178A1 (en) | 1992-11-25 |
| WO1992021313A3 (en) | 1993-01-07 |
| AU2185092A (en) | 1993-01-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO1992021313A2 (en) | Novel immunosuppressive compounds | |
| AU660623B2 (en) | Novel immunosuppressive compounds | |
| CA2102180C (en) | Novel immunosuppressive pyrrolidine/piperidine/azepane-2-carboxylic acid derivatives | |
| US5620971A (en) | Biologically active acylated amino acid derivatives | |
| US6218544B1 (en) | Heterocyclic esters and amides | |
| US5786378A (en) | Heterocyclic thioesters | |
| WO1992004370A1 (en) | Modified di- and tripeptidyl immunosuppressive compounds | |
| FR2602142A1 (en) | THERAPEUTIC USE OF 5HT3 SEROTONINERGIC RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS | |
| CZ154599A3 (en) | N-bonded sulfonamides of heterocyclic thioesters | |
| US5723459A (en) | Biologically active acylated amino acid derivatives | |
| PL152507B1 (en) | Method of obtaining novel derivatives of straight amides | |
| EP0587800B1 (en) | Immunomodulatory azaspiranes | |
| US5591748A (en) | Immunomodulatory azaspiranes | |
| IE83827B1 (en) | Immunomodulatory azaspiranes | |
| AU713302B2 (en) | Rotamase enzyme activity inhibitors |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT AU BB BG BR CA CH CS DE DK ES FI GB HU JP KP KR LK LU MG MN MW NL NO PL RO RU SD SE |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BF BJ CF CG CH CI CM DE DK ES FR GA GB GN GR IT LU MC ML MR NL SE SN TD TG |
|
| DFPE | Request for preliminary examination filed prior to expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed before 20040101) | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2102178 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1992913385 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8642 |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 1992913385 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: 1992913385 Country of ref document: EP |