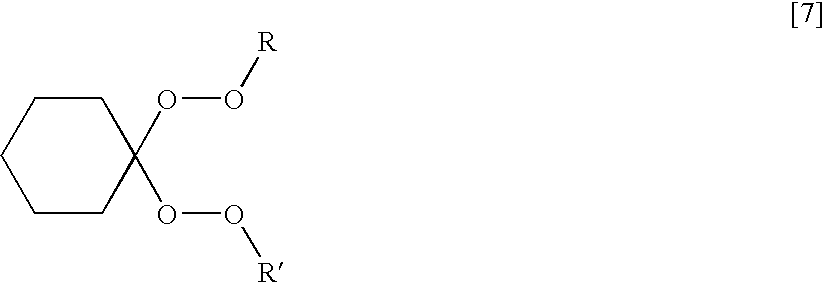US8119830B2 - Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials - Google Patents
Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US8119830B2 US8119830B2 US12/722,185 US72218510A US8119830B2 US 8119830 B2 US8119830 B2 US 8119830B2 US 72218510 A US72218510 A US 72218510A US 8119830 B2 US8119830 B2 US 8119830B2
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- absorber
- absorbers
- ophthalmic lens
- benzotriazole
- benzophenone
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime, expires
Links
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 52
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title claims description 27
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 10
- RWCCWEUUXYIKHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzophenone Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 RWCCWEUUXYIKHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000012965 benzophenone Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- QRUDEWIWKLJBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzotriazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N[N][N]C2=C1 QRUDEWIWKLJBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- 239000012964 benzotriazole Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 7
- IPZJQDSFZGZEOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylmethylene Chemical compound C[C]C IPZJQDSFZGZEOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000002914 sec-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000000524 functional group Chemical group 0.000 abstract description 14
- 238000010526 radical polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 239000003999 initiator Substances 0.000 description 14
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 12
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 0 *C(B)([2H]C(=O)CFC)N=NC(*)(B)[2H]C(=O)CFC Chemical compound *C(B)([2H]C(=O)CFC)N=NC(*)(B)[2H]C(=O)CFC 0.000 description 7
- VFXXTYGQYWRHJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-azobis(4-cyanopentanoic acid) Chemical compound OC(=O)CCC(C)(C#N)N=NC(C)(CCC(O)=O)C#N VFXXTYGQYWRHJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 7
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 7
- OZAIFHULBGXAKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-cyanopropan-2-yldiazenyl)-2-methylpropanenitrile Chemical compound N#CC(C)(C)N=NC(C)(C)C#N OZAIFHULBGXAKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- ILZXXGLGJZQLTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylethyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate Chemical compound CC(=C)C(=O)OCCC1=CC=CC=C1 ILZXXGLGJZQLTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- HPSGLFKWHYAKSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylethyl prop-2-enoate Chemical compound C=CC(=O)OCCC1=CC=CC=C1 HPSGLFKWHYAKSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- -1 3-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4-hydroxyphenethyl Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 5
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 4
- JHWGFJBTMHEZME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-prop-2-enoyloxybutyl prop-2-enoate Chemical compound C=CC(=O)OCCCCOC(=O)C=C JHWGFJBTMHEZME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YCLKWKCHQLIGTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1CCC(C(C)(C)C)CC1 Chemical compound CC1CCC(C(C)(C)C)CC1 YCLKWKCHQLIGTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 3
- AUONHKJOIZSQGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxophosphane Chemical compound P=O AUONHKJOIZSQGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000003505 polymerization initiator Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004810 polytetrafluoroethylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920001343 polytetrafluoroethylene Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002371 ultraviolet--visible spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004580 weight loss Effects 0.000 description 3
- JYEUMXHLPRZUAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2,3-triazine Chemical compound C1=CN=NN=C1 JYEUMXHLPRZUAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FJGQBLRYBUAASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(benzotriazol-2-yl)phenol Chemical group OC1=CC=CC=C1N1N=C2C=CC=CC2=N1 FJGQBLRYBUAASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Dimethylaminopyridine Chemical compound CN(C)C1=CC=NC=C1 VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZCILGMFPJBRCNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-phenyl-2H-benzotriazol-5-ol Chemical compound OC1=CC=C2NN=NC2=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ZCILGMFPJBRCNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OZAIFHULBGXAKX-VAWYXSNFSA-N AIBN Substances N#CC(C)(C)\N=N\C(C)(C)C#N OZAIFHULBGXAKX-VAWYXSNFSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acrylamide Chemical compound NC(=O)C=C HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acrylate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)C=C NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-M Methacrylate Chemical compound CC(=C)C([O-])=O CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012632 extractable Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000004464 hydroxyphenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 238000002386 leaching Methods 0.000 description 2
- FQPSGWSUVKBHSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N methacrylamide Chemical compound CC(=C)C(N)=O FQPSGWSUVKBHSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000001451 organic peroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000007870 radical polymerization initiator Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009257 reactivity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000000391 vinyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- PDLPMGPHYARAFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N (3-hydroxy-2-phenylphenyl)-phenylmethanone Chemical class C=1C=CC=CC=1C=1C(O)=CC=CC=1C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 PDLPMGPHYARAFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GJKGAPPUXSSCFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Hydroxy-4'-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-2-methylpropiophenone Chemical compound CC(C)(O)C(=O)C1=CC=C(OCCO)C=C1 GJKGAPPUXSSCFI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RQLOSVWWQDTFSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N C=CC1=CC(C)=C(C(=O)P(=O)(C2=CC=CC=C2)C2=CC=CC=C2)C(C)=C1 Chemical compound C=CC1=CC(C)=C(C(=O)P(=O)(C2=CC=CC=C2)C2=CC=CC=C2)C(C)=C1 RQLOSVWWQDTFSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ALUFEZANQFXQNS-OSALMABJSA-N CC(C#N)(CCC(=O)O)/N=N/C(C)(C#N)CCC(=O)O.[H]N(C(=O)C(C)(C#N)/N=N/C(C)([N+]#[C-])C(=O)N([H])C(CO)(CO)CO)C(CO)(CO)CO.[H]N(CCO)C(=O)C(C)(C#N)/N=N/C(C)([N+]#[C-])C(=O)N([H])CCO Chemical compound CC(C#N)(CCC(=O)O)/N=N/C(C)(C#N)CCC(=O)O.[H]N(C(=O)C(C)(C#N)/N=N/C(C)([N+]#[C-])C(=O)N([H])C(CO)(CO)CO)C(CO)(CO)CO.[H]N(CCO)C(=O)C(C)(C#N)/N=N/C(C)([N+]#[C-])C(=O)N([H])CCO ALUFEZANQFXQNS-OSALMABJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YUMRPMLHRFZCRO-QJGAVIKSSA-N CC(C#N)(CCC(=O)OCCC1=CC=C(O)C(N2N=C3C=CC=CC3=N2)=C1)/N=N/C(C)(C#N)CCC(=O)OCCC1=CC=C(O)C(N2/N=C3/C=CC=C/C3=N/2)=C1 Chemical compound CC(C#N)(CCC(=O)OCCC1=CC=C(O)C(N2N=C3C=CC=CC3=N2)=C1)/N=N/C(C)(C#N)CCC(=O)OCCC1=CC=C(O)C(N2/N=C3/C=CC=C/C3=N/2)=C1 YUMRPMLHRFZCRO-QJGAVIKSSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CGWGNMXPEVGWGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(O)C(=O)C1=CC=C(CCO)C=C1 Chemical compound CC(C)(O)C(=O)C1=CC=C(CCO)C=C1 CGWGNMXPEVGWGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PEFUDBPKGHPWLI-JHFSVKJWSA-N CC1=CC(C)=C(C(=O)P(=O)(C2=CC=CC=C2)C2=CC=CC=C2)C(C)=C1.C[3H]C.C[3H]C.C[3H]C Chemical compound CC1=CC(C)=C(C(=O)P(=O)(C2=CC=CC=C2)C2=CC=CC=C2)C(C)=C1.C[3H]C.C[3H]C.C[3H]C PEFUDBPKGHPWLI-JHFSVKJWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RHQWLBLNBADUNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N CNOOC(N)=O Chemical compound CNOOC(N)=O RHQWLBLNBADUNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicylcohexylcarbodiimide Chemical compound C1CCCCC1N=C=NC1CCCCC1 QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formaldehyde Chemical compound O=C WSFSSNUMVMOOMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MIGYDYQXLNEJHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N N[IH][IH][IH]C(OOC([IH][IH][IH]N)=O)=O Chemical compound N[IH][IH][IH]C(OOC([IH][IH][IH]N)=O)=O MIGYDYQXLNEJHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JSBGEBJADOAOKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=C(OCCC1=CC=C(O)C(N2N=C3C=CC=CC3=N2)=C1)OOC(=O)OCCC1=CC(N2N=C3C=CC=CC3=N2)=C(O)C=C1 Chemical compound O=C(OCCC1=CC=C(O)C(N2N=C3C=CC=CC3=N2)=C1)OOC(=O)OCCC1=CC(N2N=C3C=CC=CC3=N2)=C(O)C=C1 JSBGEBJADOAOKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910006069 SO3H Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000000751 azo group Chemical group [*]N=N[*] 0.000 description 1
- 150000001718 carbodiimides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002843 carboxylic acid group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000004440 column chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000007334 copolymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000032050 esterification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012374 esterification agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005886 esterification reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007943 implant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010348 incorporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000005634 peroxydicarbonate group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000003011 styrenyl group Chemical group [H]\C(*)=C(/[H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- MDDUHVRJJAFRAU-YZNNVMRBSA-N tert-butyl-[(1r,3s,5z)-3-[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy-5-(2-diphenylphosphorylethylidene)-4-methylidenecyclohexyl]oxy-dimethylsilane Chemical compound C1[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=C)\C1=C/CP(=O)(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 MDDUHVRJJAFRAU-YZNNVMRBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002110 toxicologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000027 toxicology Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 229940124543 ultraviolet light absorber Drugs 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/02—Prostheses implantable into the body
- A61F2/14—Eye parts, e.g. lenses, corneal implants; Implanting instruments specially adapted therefor; Artificial eyes
- A61F2/16—Intraocular lenses
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L27/00—Materials for grafts or prostheses or for coating grafts or prostheses
- A61L27/50—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties, e.g. injectable or lubricating compositions, shape-memory materials, surface modified materials
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F4/00—Polymerisation catalysts
- C08F4/04—Azo-compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/16—Nitrogen-containing compounds
- C08K5/34—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen in the ring
- C08K5/3467—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen in the ring having more than two nitrogen atoms in the ring
- C08K5/3472—Five-membered rings
- C08K5/3475—Five-membered rings condensed with carbocyclic rings
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B1/00—Optical elements characterised by the material of which they are made; Optical coatings for optical elements
- G02B1/04—Optical elements characterised by the material of which they are made; Optical coatings for optical elements made of organic materials, e.g. plastics
- G02B1/041—Lenses
- G02B1/043—Contact lenses
Definitions
- This invention is directed to ophthalmic lens materials.
- this invention relates to ultraviolet light absorbers that also act as polymerization initiators for ophthalmic lens materials.
- UV light absorbers are known as ingredients for polymeric materials used to make ophthalmic lenses. UV absorbers are preferably covalently bound to the polymeric network of the lens material instead of simply physically entrapped in the material to prevent the absorber from migrating, phase separating or leaching out of the lens material. Such stability is particularly important for implantable ophthalmic lenses where the leaching of the UV absorber may present both toxicological issues and lead to the loss of UV blocking activity in the implant.
- UV absorbers Numerous copolymerizable benzatriazole, benzophenone and triazine UV absorbers are known. Many of these UV absorbers contain conventional olefinic polymerizable groups, such as methacrylate, acrylate, methacrylamide, acrylamide or styrene groups. Copolymerization with other ingredients in the lens materials, typically with a radical initiator, incorporates the UV absorbers into the resulting polymer chain. Incorporation of additional functional groups, on a UV absorber may influence one or more of the UV absorber's UV absorbing properties, solubility or reactivity. If the UV absorber does not have sufficient solubility in the remainder of the ophthalmic lens material ingredients or polymeric lens material, the UV absorber may coalesce into domains that could interact with light and result in decreased optical clarity of the lens.
- polymeric ophthalmic lens materials that incorporate UV absorbers can be found in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,290,892; 5,331,073 and 5,693,095.
- the present invention provides dual function UV absorbers. These UV absorbers contain a labile functional group capable of initiating radical to polymerization. These UV absorbers are suitable for use in ophthalmic lenses, including contact lenses, and are particularly useful in implantable lenses, such as intraocular lenses (IOLs).
- IOLs intraocular lenses
- the present invention is based on the finding that UV absorbers can be modified to incorporate a labile functional group capable of initiating polymerization of an olefinic ophthalmic lens material monomers without eliminating the UV absorber's UV absorbing activity, solubility or reactivity with ophthalmic lens material ingredients.
- the dual function UV absorbers (“DFUVAS”) of the present invention contain a functional group that can initiate free radical polymerization. As such, these DFUVAS eliminate the need for two separate monomeric ingredients in the preparation of copolymeric ophthalmic lens materials. Instead of adding a conventional UV absorber to conventional ophthalmic lens-forming materials and separately adding a conventional polymerization initiator, a DFUVAS can be used in place these two conventional ingredients.
- the DFUVAS may be synthesized by reacting a UV absorber that contains a reactive functionality with a radical initiator while preserving the radical generating linkage.
- a UV absorber that contains a reactive functionality
- 3-(2H-benzotriazol-2-yl)-4-hydroxyphenethyl alcohol (1) may be coupled to 4,4′-azobis(4-cyanopentanoic acid) (2) using a carbodiimide esterification agent.
- the product (3) can then initiate radical polymerization of a vinyl monomer (e.g., acrylate, methacrylate, acrylamide, methacrylamide, styrene) by application of heat and/or UV/visible light and the UV absorbing functionality will be to covalently attached to the polymer chain.
- a vinyl monomer e.g., acrylate, methacrylate, acrylamide, methacrylamide, styrene
- This invention provides the synthesis of a single component additive that provides a dual function: UV absorption properties and ability to initiate free radical polymerization.
- the result is a covalently linked UV absorber that will not leach out of the product or phase separate and lead to decreased optical clarity.
- the synthesis permits flexibility in tailoring both UV absorbing strength and initiator half-life. UV-initiation of polymerization of the lens material is still possible with protection of the hydroxy group on the UV absorbing function of the DFUVAS.
- the DFUVAS can be synthesized from azo, organic peroxide, phosphine oxide, and ⁇ -hydroxyketone radical polymerization initiators that contain appropriate functional groups.
- the necessary functionality from each of these initiator classes is the presence of a functional group (carboxylic acid or hydroxyl) through which a UV absorbing benzotriazole, benzophenone or triazine can be covalently linked.
- Preferred DFUVAS are those represented by formulas [1]-[7].
- V-501 (4,4′-azobis(4-cyanopentanoic acid)) from Wako Chemicals.
- This initiator contains a thermally labile azo linkage (—N ⁇ N—) and two terminal carboxylic acid groups.
- VA-086 contains two terminal hydroxyl groups.
- VA-080 contains three hydroxyl groups on each side of the thermally labile azo linkage.
- an azo functional UV absorber can be synthesized from an azo initiator with the following structural characteristics:
- A is —CH 3 or —CH 2 CH 3 .
- B is —CN, —CO 2 H, —COH, —COCH 3 , —CO 2 CH 3 , —SO 3 H, —CF 3 , or —NO 2 when D is (CH 2 ) n , and —CH 3 or —CH 2 CH 3 when D is nothing.
- benzotriazole and benzophenone UV absorbers are known and many are commercially available from a variety of sources, such as Ciba Specialty Chemicals.
- the identity of the benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber is not critical, but should be selected based on its characteristic UV cut-off to give the desired UV absorbing property.
- preferred benzotriazole UV absorbers are hydroxyphenylbenzotriazole and preferred benzophenone UV absorbers are hydroxyphenylbenzophenones that have been modified to contain a functional group that can be covalently bonded to a radical polymerization initiator.
- a preferred hydroxyphenylbenzotriazole UV absorber is 2-N-(2-hydroxyphenyl)benzotriazole, where the UV absorbing group is linked through an ethyl ether linkage at the para position on the hydroxyphenyl group, as shown below linked to an azo functionality.
- ⁇ -hydroxyketones suitable for use as UV polymerization initiators are commercially available.
- 2-hydroxy-1-[4-(2-hydroxy-ethoxy)phenyl]-2-methylpropan-1-one (Irgacure® 2959, Ciba Specialty Chemicals) contains a free primary hydroxyl group covalently attached to a UV light labile ⁇ -hydroxyketone linkage.
- This primary hydroxyl can be used as a covalent linking point.
- Irgacure® 2959 the primary hydroxyl was used to covalently attach hydrophilic functional groups through an ether linkage to create a water-soluble photoinitiator (Gruber, H. F.; Knaus, S. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 1995, 33, 929).
- a generic ⁇ -hydroxyketone photoinitiator that contains the appropriate functional groups for covalently linking a UV chromophore is represented by formula [2]:
- J is CH 3 or CH 2 CH 3 .
- Functionalized phosphine oxide photoinitiators are also known.
- a vinyl functional phosphine oxide was used in the synthesis of polymeric acylphosphine oxide photoinitiators (DeGroot, J. H.; Dillingham, K. A.; Deuring, H.; Haitjema, H. J.; Van Beijma, F. J.; Hodd, K. A.; Norrby, S. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1271).
- a generic phosphine oxide photoinitiator that contains the appropriate functional groups for covalently linking a UV chromophore is represented by formula [3].
- Q is —H, —CH 3 , —CH 2 CH 3 , —CH(CH 3 )CH 3 , or —C(CH 3 ) 3 .
- acylperoxide initiator that contains appropriate functional groups for covalently linking a UV chromophore is represented by formula [4].
- Y nothing or O;
- R a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber;
- R′ a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber;
- —(CH 2 ) n H (n 1-18); —CH(CH 3 )CH 3 ; —C(CH 3 ) 3 ; —C 6 H 5 ; —CH(CH 3 )CH 2 CH 3 ; —C(CH 3 ) 2 CH 2 C(CH 3 ) 3 ; —C(CH 3 ) 2 (CH 2 ) 4 H; —C(CH 2 CH 3 ) 2 (CH 2 ) 4 H; —C(CH 3 ) 2 (CH 2 ) 5 H; —C(CH 2 CH 3 ) 2 (CH 2 ) 5 H; —C(CH 3 ) 2 (CH 2 ) 6 H; —C(CH 2 CH 3 ) 2 (CH 2 ) 6 H; —C(CH 2 CH(CH 2 CH 3 )(CH 2 O;
- R a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber;
- R a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber
- the amount of DFUVAS contained in ophthalmic lens materials will depend upon the desired UV blocking characteristics but will typically range from 1-5 wt %.
- 1,3-Dicyclohexyl carbodiimide (1.5520 g, 7.52 mmol) was added and the reaction mixture was allowed to stir at ambient temperature under a N 2 blanket for 24 hr.
- the reaction mixture was filtered through a fine porosity sintered glass funnel and the solvent was rotovapped.
- the crude product was purified by column chromatography (silica gel, CH 2 Cl 2 ), the solvent was rotovapped and the product was dried under vacuum. Yield 1.3691 g (1.81 mmol, 51%) of a pale yellow powder.
- a scintillation vial was charged with 3.3572 g (19.052 mmol) of 2-phenylethyl acrylate (PEA), 1.5585 g (8.192 mmol) of 2-phenylethyl methacrylate (PEMA), and 0.0611 g (0.308 mmol) of 1,4-butanediol diacrylate (BDDA).
- the monomer mixture was purged with N 2 and 0.2290 g (0.304 mmol) of the UV absorbing initiator prepared in Example 1 was added and allowed to dissolve.
- the initiated formulation was filtered through a 0.2 micron PTFE filter and dispensed into polypropylene molds. The molds were placed in an oven for 1 hr at 70° C.
- a scintillation vial was charged with 3.3502 g (19.012 mmol) of 2-phenylethyl acrylate (PEA), 1.5516 g (8.156 mmol) of 2-phenylethyl methacrylate (PEMA), and 0.0567 g (0.286 mmol) of 1,4-butanediol diacrylate (BDDA).
- the monomer mixture was purged with N 2 and 0.0761 g (0.101 mmol) of the UV absorbing initiator prepared in Example 1 was added and allowed to dissolve.
- the initiated formulation was filtered through a 0.2 micron PTFE filter and dispensed into polypropylene molds. The molds were placed in an oven for 1 hr at 70° C.
- a scintillation vial was charged with 3.3580 g (19.057 mmol) of 2-phenylethyl acrylate (PEA), 1.5629 g (8.215 mmol) of 2-phenylethyl methacrylate (PEMA), and 0.0589 g (0.297 mmol) of 1,4-butanediol diacrylate (BDDA).
- the monomer mixture was purged with N 2 and 0.0502 g (0.306 mmol) of 2,2′-azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) was added and allowed to dissolve.
- the initiated formulation was filtered through a 0.2 micron PTFE filter and dispensed into polypropylene molds.
- the molds were placed in an oven for 1 hr at 70° C. then 2 hrs at 110° C.
- the product polymer was extracted in acetone at room temperature for 16 hrs.
- the polymer was allowed to air dry for 1.5 hr, then placed in a 60° C. vacuum oven for 3 hrs.
- the weight loss following extraction was determined gravimetrically and the UV/Vis spectrum was recorded from 190 to 820 nm on 1 mm thick flat. The data is listed in Table 1.
- Example % extractables 10% T (nm) 1% T (nm) 2 3.86 ⁇ 0.18 381 377 3 4.82 ⁇ 0.25 377 371 4 0.63 ⁇ 0.23 294 279
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Transplantation (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
- Polymerisation Methods In General (AREA)
- Optical Filters (AREA)
- Eyeglasses (AREA)
- Silicon Polymers (AREA)
- Polymerization Catalysts (AREA)
- Prostheses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Therefore, an azo functional UV absorber can be synthesized from an azo initiator with the following structural characteristics:
where:
A is —CH3 or —CH2CH3.
B is —CN, —CO2H, —COH, —COCH3, —CO2CH3, —SO3H, —CF3, or —NO2 when D is (CH2)n, and —CH3 or —CH2CH3 when D is nothing.
D is nothing or (CH2)n, n=1-10
E is O or NH, NCH3, or NCH2CH3
F is nothing, (CH2)x or (CH2CH2O)xCH2CH2 where x=1-10.
G is —R, —OR, —NHR, —NRR′, —CO2R, or —COR, where R=a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber, and R′═—CH3 or —CH2CH3.
A generic α-hydroxyketone photoinitiator that contains the appropriate functional groups for covalently linking a UV chromophore is represented by formula [2]:
where:
J is CH3 or CH2CH3.
L is nothing, (CH2)y or (CH2CH2O)y where y=1-10.
G is —R, —OR, —NHR, —NRR′, —CO2R, or —COR, where R=a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber, and R′=—CH3 or —CH2CH3.
A generic phosphine oxide photoinitiator that contains the appropriate functional groups for covalently linking a UV chromophore is represented by formula [3].
where Q is —H, —CH3, —CH2CH3, —CH(CH3)CH3, or —C(CH3)3.
T is nothing, —(CH2)z, or —(OCH2CH2)z, where z=1-10
G is —R, —OR, —NHR, —NRR′, —CO2R, or —COR, where R=a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber, and R′═—CH3 or —CH2CH3.
where Y=nothing or O; R=a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber; R′=a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber; —(CH2)nH (n=1-18); —CH(CH3)CH3; —C(CH3)3; —C6H5; —CH(CH3)CH2CH3; —C(CH3)2CH2C(CH3)3; —C(CH3)2(CH2)4H; —C(CH2CH3)2(CH2)4H; —C(CH3)2(CH2)5H; —C(CH2CH3)2(CH2)5H; —C(CH3)2(CH2)6H; —C(CH2CH3)2(CH2)6H; —CH2CH(CH2CH3)(CH2O; or
Generic peroxyester, dialkylperoxide and peroxyketal initiators that contain the appropriate functional groups for covalently linking a UV chromophore are represented by formulas [5], [6], and [7], respectively.
where R=a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber; R′=a benzotriazole or benzophenone UV absorber; —(CH2)nH (n=1-18); —CH(CH3)CH3; —C(CH3)3; —C6H5; —CH(CH3)CH2CH3; —C(CH3)2CH2C(CH3)3; —C(CH3)2(CH2)4H; —C(CH2CH3)2(CH2)4H; —C(CH3)2(CH2)5H; —C(CH2CH3)2(CH2)5H; —C(CH3)2(CH2)6H; —C(CH2CH3)2(CH2)6H; —CH2CH(CH2CH3)(CH2)4H; —C(CH3)2C6H5; or
| TABLE 1 |
| Weight % acetone extractables and UV |
| cut-off of ophthalmic lens materials. |
| Example | % extractables | 10% T (nm) | 1% T (nm) | ||
| 2 | 3.86 ± 0.18 | 381 | 377 | ||
| 3 | 4.82 ± 0.25 | 377 | 371 | ||
| 4 | 0.63 ± 0.23 | 294 | 279 | ||
Claims (6)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/722,185 US8119830B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2010-03-11 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US43897803P | 2003-01-09 | 2003-01-09 | |
| US10/753,254 US7119210B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2004-01-08 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US11/539,748 US7396942B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2006-10-09 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US12/125,403 US7709652B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2008-05-22 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US12/722,185 US8119830B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2010-03-11 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/125,403 Division US7709652B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2008-05-22 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20100168438A1 US20100168438A1 (en) | 2010-07-01 |
| US8119830B2 true US8119830B2 (en) | 2012-02-21 |
Family
ID=32713409
Family Applications (4)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/753,254 Active 2024-11-06 US7119210B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2004-01-08 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US11/539,748 Expired - Lifetime US7396942B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2006-10-09 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US12/125,403 Expired - Lifetime US7709652B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2008-05-22 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US12/722,185 Expired - Lifetime US8119830B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2010-03-11 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
Family Applications Before (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/753,254 Active 2024-11-06 US7119210B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2004-01-08 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US11/539,748 Expired - Lifetime US7396942B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2006-10-09 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US12/125,403 Expired - Lifetime US7709652B2 (en) | 2003-01-09 | 2008-05-22 | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
Country Status (12)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (4) | US7119210B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1581272B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2006513291A (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE329629T1 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2003297108B2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2512586A1 (en) |
| CY (1) | CY1106142T1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE60306203T2 (en) |
| DK (1) | DK1581272T3 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2262033T3 (en) |
| PT (1) | PT1581272E (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2004062371A1 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8475691B2 (en) | 2011-08-15 | 2013-07-02 | Novartis Ag | UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US8585938B1 (en) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-11-19 | Novartis Ag | UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US10619065B2 (en) | 2017-01-31 | 2020-04-14 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Photo active agents |
| WO2023052888A1 (en) * | 2021-09-29 | 2023-04-06 | Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. | Ophthalmic lenses and their manufacture by in-mold modification |
| US11912800B2 (en) | 2021-09-29 | 2024-02-27 | Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. | Amide-functionalized polymerization initiators and their use in the manufacture of ophthalmic lenses |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7411053B2 (en) * | 2006-05-25 | 2008-08-12 | Harruna Issifu I | Ligand-functionalized/azo compounds and methods of use thereof |
| BRPI0719199A2 (en) * | 2006-10-13 | 2014-09-09 | Alcon Inc | INTRAOCULAR LENS WITH EXCLUSIVE BLUE-VIOLET CUTTING VALUE AND BLUE LIGHT TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS |
| JP5273748B2 (en) * | 2007-04-30 | 2013-08-28 | アルコン,インコーポレイテッド | UV absorber for ophthalmic lens material |
| US8394906B2 (en) * | 2008-02-12 | 2013-03-12 | Aaren Scientific Inc. | Ophthalmic lens having a yellow dye light blocking component |
| TWI453199B (en) * | 2008-11-04 | 2014-09-21 | Alcon Inc | Uv/visible light absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| NZ592674A (en) * | 2008-12-18 | 2012-08-31 | Novartis Ag | Method for making silicone hydrogel contact lenses |
| AU2009333223B2 (en) | 2008-12-30 | 2012-02-23 | Novartis Ag | Tri-functional UV-absorbing compounds and use thereof |
| NZ598405A (en) * | 2009-09-15 | 2013-05-31 | Novartis Ag | Prepolymers suitable for making ultra-violet absorbing contact lenses |
| TWI583673B (en) | 2010-04-02 | 2017-05-21 | 艾爾康股份有限公司 | Adjustable chromophore compounds and materials incorporating such compounds |
| WO2012082704A1 (en) | 2010-12-13 | 2012-06-21 | Novartis Ag | Ophthalmic lenses modified with functional groups and methods of making thereof |
| US8691925B2 (en) | 2011-09-23 | 2014-04-08 | Az Electronic Materials (Luxembourg) S.A.R.L. | Compositions of neutral layer for directed self assembly block copolymers and processes thereof |
| US8686109B2 (en) | 2012-03-09 | 2014-04-01 | Az Electronic Materials (Luxembourg) S.A.R.L. | Methods and materials for removing metals in block copolymers |
| US8835581B2 (en) * | 2012-06-08 | 2014-09-16 | Az Electronic Materials (Luxembourg) S.A.R.L. | Neutral layer polymer composition for directed self assembly and processes thereof |
| US10457088B2 (en) | 2013-05-13 | 2019-10-29 | Ridgefield Acquisition | Template for self assembly and method of making a self assembled pattern |
| US9093263B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2015-07-28 | Az Electronic Materials (Luxembourg) S.A.R.L. | Underlayer composition for promoting self assembly and method of making and using |
| US9181449B2 (en) | 2013-12-16 | 2015-11-10 | Az Electronic Materials (Luxembourg) S.A.R.L. | Underlayer composition for promoting self assembly and method of making and using |
| TWI755344B (en) | 2016-12-21 | 2022-02-11 | 德商馬克專利公司 | Novel compositions and processes for self-assembly of block copolymers |
Citations (37)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4304895A (en) | 1973-06-20 | 1981-12-08 | Wesley-Jessen, Inc. | Ultraviolet absorbing corneal contact lenses |
| US4528311A (en) | 1983-07-11 | 1985-07-09 | Iolab Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing polymers comprising 2-hydroxy-5-acrylyloxyphenyl-2H-benzotriazoles |
| US4612358A (en) | 1984-10-27 | 1986-09-16 | Rohm Gmbh | UV-absorbing monomer and polymers thereof |
| EP0221630A2 (en) | 1985-08-08 | 1987-05-13 | BAUSCH & LOMB INCORPORATED | Ultraviolet blocking agents for contact lenses |
| US4716234A (en) | 1986-12-01 | 1987-12-29 | Iolab Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing polymers comprising 2-(2'-hydroxy-5'-acryloyloxyalkoxyphenyl)-2H-benzotriazole |
| US4785063A (en) | 1983-07-26 | 1988-11-15 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Copolymerizable 2-(2'-hydroxy-5'-acryloyloxyalkyl)-2H-benzotriazoles |
| EP0343996A2 (en) | 1988-05-26 | 1989-11-29 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | Ultraviolet absorbing hydrogels |
| US4929250A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1990-05-29 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing lenses and method of making the same |
| US4963160A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1990-10-16 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Reactive uv absorbing compositions and method of preparing lenses therefrom |
| US5047556A (en) | 1988-08-09 | 1991-09-10 | Merck Patent Gesellschaft Mit Beschrankter Haftung | Photoinitiators having a combined structure |
| EP0283166B1 (en) | 1987-03-03 | 1992-01-02 | Iolab Corporation | 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl)-5(6) (acryloyloxyalkoxy)-benzotriazole and ultraviolet absorbing polymers therefrom |
| US5133745A (en) | 1988-05-26 | 1992-07-28 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | Ultraviolet absorbing hydrogels |
| US5141990A (en) | 1985-06-07 | 1992-08-25 | California Institute Of Technology | Photocurable acrylic composition, and U.V. curing with development of U.V. absorber |
| US5147902A (en) | 1990-11-26 | 1992-09-15 | Menicon Co., Ltd. | Ultraviolet light absorbing ocular lens |
| US5164462A (en) | 1991-04-25 | 1992-11-17 | Allergan, Inc. | Ultraviolet light absorbing compounds and silicone compositions |
| US5189084A (en) | 1989-12-21 | 1993-02-23 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Process for incorporating o-hydroxyphenyl-s-triazines in organic polymers |
| US5194544A (en) | 1987-10-15 | 1993-03-16 | University Of Florida | UV absorbing vinyl monomers and polymers and ocular implants prepared therefrom |
| US5290892A (en) | 1990-11-07 | 1994-03-01 | Nestle S.A. | Flexible intraocular lenses made from high refractive index polymers |
| US5298033A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1994-03-29 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing lenses and methods of manufacturing thereof |
| US5331073A (en) | 1992-11-09 | 1994-07-19 | Allergan, Inc. | Polymeric compositions and intraocular lenses made from same |
| US5384235A (en) | 1992-07-01 | 1995-01-24 | Eastman Kodak Company | Photographic elements incorporating polymeric ultraviolet absorbers |
| EP0693483A1 (en) | 1994-07-23 | 1996-01-24 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Compounds having ultra-violet absorption properties |
| US5648488A (en) | 1994-07-27 | 1997-07-15 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Compositions stabilized with red-shifted tris-aryl-s-triazines |
| US5693095A (en) | 1995-06-07 | 1997-12-02 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | High refractive index ophthalmic lens materials |
| WO1998050371A1 (en) | 1997-05-08 | 1998-11-12 | Otsuka Chemical Co., Ltd. | 2,2'-bis(6-benzotriazolylphenol) compounds, ultraviolet absorbers comprising the same, copolymers containing the same, and polymer compositions containing the same |
| US5837792A (en) | 1995-06-23 | 1998-11-17 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Polysiloxane light stabilizers |
| US5869588A (en) | 1994-10-04 | 1999-02-09 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Polymeric compounds derived from 2-hydroxy-phenyl-s-triazines substituted with ethylenically unsaturated moieties |
| US5914355A (en) | 1998-05-15 | 1999-06-22 | Bausch & Lomb Incorporated | Method for making contact lenses having UV absorbing properties |
| US5928629A (en) | 1996-07-01 | 1999-07-27 | Societe L'oreal S.A. | Photoprotective/cosmetic compositions comprising dibenzoylmethane/triazine/diphenylacrylate compounds |
| US5928630A (en) | 1996-02-12 | 1999-07-27 | Societe L' Oreal S.A. | Benzalmalonate/phenylcyanoacrylate-substituted s-triazine compounds and photoprotective/cosmetic compositions comprised thereof |
| US5942564A (en) | 1992-09-07 | 1999-08-24 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Hydroxyphenyl-s-triazines |
| US5945465A (en) | 1998-05-15 | 1999-08-31 | Bausch & Lomb Incorporated | Method for polymerizing contact lenses having UV absorbing properties |
| WO1999053348A1 (en) | 1998-04-15 | 1999-10-21 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | High refractive index ophthalmic device materials prepared using a post-polymerization cross-linking method |
| EP0952467A1 (en) | 1998-04-20 | 1999-10-27 | JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION PRODUCTS, INC. | Ocular devices manufactured with free radical-polymerizable latent ultra-violet absorbers |
| WO1999058507A1 (en) | 1998-05-11 | 1999-11-18 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Groningen B.V. | Polymerizable hydrophilic ultraviolet light absorbing monomers |
| WO2000055212A1 (en) | 1999-03-16 | 2000-09-21 | Pharmacia Groningen Bv | Macromolecular compounds |
| WO2002078966A2 (en) | 2001-03-29 | 2002-10-10 | Michael Huber München Gmbh | Prepolymer and screen roller filler for depth-variable laser ablation |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA974981A (en) * | 1970-12-16 | 1975-09-23 | Pennwalt Corporation | Azo or peroxide free radical initiators containing ultraviolet light stabilizing groups |
| US3956269A (en) * | 1970-12-16 | 1976-05-11 | Pennwalt Corporation | Azo free radical initiators containing ultraviolet light stabilizing groups |
| CA1031200A (en) * | 1973-06-20 | 1978-05-16 | Wesley-Jessen | Ultraviolet absorbing lenses |
| NZ208751A (en) * | 1983-07-11 | 1987-04-30 | Iolab Corp | 2-hydroxy-5-acrylyloxyalkylphenyl-2h-benzotriazole derivatives and polymers and copolymers thereof and use as uv absorbing additives in polymer compositions |
| JP3727035B2 (en) * | 1995-03-14 | 2005-12-14 | Hoya株式会社 | Benzotriazole compound, ultraviolet absorber comprising the same, and ophthalmic lens containing the same |
| US6851804B2 (en) * | 2001-12-28 | 2005-02-08 | Jagdish M. Jethmalani | Readjustable optical elements |
-
2003
- 2003-12-15 PT PT03815211T patent/PT1581272E/en unknown
- 2003-12-15 ES ES03815211T patent/ES2262033T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-12-15 AU AU2003297108A patent/AU2003297108B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2003-12-15 DK DK03815211T patent/DK1581272T3/en active
- 2003-12-15 JP JP2004566548A patent/JP2006513291A/en not_active Ceased
- 2003-12-15 WO PCT/US2003/039846 patent/WO2004062371A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2003-12-15 AT AT03815211T patent/ATE329629T1/en active
- 2003-12-15 CA CA002512586A patent/CA2512586A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2003-12-15 EP EP03815211A patent/EP1581272B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2003-12-15 DE DE60306203T patent/DE60306203T2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2004
- 2004-01-08 US US10/753,254 patent/US7119210B2/en active Active
-
2006
- 2006-08-09 CY CY20061101115T patent/CY1106142T1/en unknown
- 2006-10-09 US US11/539,748 patent/US7396942B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2008
- 2008-05-22 US US12/125,403 patent/US7709652B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2010
- 2010-03-11 US US12/722,185 patent/US8119830B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (43)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4304895A (en) | 1973-06-20 | 1981-12-08 | Wesley-Jessen, Inc. | Ultraviolet absorbing corneal contact lenses |
| US4528311A (en) | 1983-07-11 | 1985-07-09 | Iolab Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing polymers comprising 2-hydroxy-5-acrylyloxyphenyl-2H-benzotriazoles |
| US4785063A (en) | 1983-07-26 | 1988-11-15 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Copolymerizable 2-(2'-hydroxy-5'-acryloyloxyalkyl)-2H-benzotriazoles |
| US4612358A (en) | 1984-10-27 | 1986-09-16 | Rohm Gmbh | UV-absorbing monomer and polymers thereof |
| US5141990A (en) | 1985-06-07 | 1992-08-25 | California Institute Of Technology | Photocurable acrylic composition, and U.V. curing with development of U.V. absorber |
| EP0221630A2 (en) | 1985-08-08 | 1987-05-13 | BAUSCH & LOMB INCORPORATED | Ultraviolet blocking agents for contact lenses |
| US4716234A (en) | 1986-12-01 | 1987-12-29 | Iolab Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing polymers comprising 2-(2'-hydroxy-5'-acryloyloxyalkoxyphenyl)-2H-benzotriazole |
| EP0283166B1 (en) | 1987-03-03 | 1992-01-02 | Iolab Corporation | 2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl)-5(6) (acryloyloxyalkoxy)-benzotriazole and ultraviolet absorbing polymers therefrom |
| US5194544A (en) | 1987-10-15 | 1993-03-16 | University Of Florida | UV absorbing vinyl monomers and polymers and ocular implants prepared therefrom |
| US5133745A (en) | 1988-05-26 | 1992-07-28 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | Ultraviolet absorbing hydrogels |
| EP0343996A2 (en) | 1988-05-26 | 1989-11-29 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | Ultraviolet absorbing hydrogels |
| US5047556A (en) | 1988-08-09 | 1991-09-10 | Merck Patent Gesellschaft Mit Beschrankter Haftung | Photoinitiators having a combined structure |
| US5298033A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1994-03-29 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing lenses and methods of manufacturing thereof |
| US4963160A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1990-10-16 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Reactive uv absorbing compositions and method of preparing lenses therefrom |
| US4929250A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1990-05-29 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing lenses and method of making the same |
| US5098445A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1992-03-24 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Ultraviolet radiation absorbing agent for bonding to an ocular lens |
| US5399692A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1995-03-21 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing benzophenone sulfonic acid derivatives |
| US5500024A (en) | 1989-03-14 | 1996-03-19 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Ultraviolet absorbing lenses and methods of manufacture thereof |
| US5189084A (en) | 1989-12-21 | 1993-02-23 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Process for incorporating o-hydroxyphenyl-s-triazines in organic polymers |
| US5290892A (en) | 1990-11-07 | 1994-03-01 | Nestle S.A. | Flexible intraocular lenses made from high refractive index polymers |
| US5147902A (en) | 1990-11-26 | 1992-09-15 | Menicon Co., Ltd. | Ultraviolet light absorbing ocular lens |
| US5164462A (en) | 1991-04-25 | 1992-11-17 | Allergan, Inc. | Ultraviolet light absorbing compounds and silicone compositions |
| EP0582664B1 (en) | 1991-04-25 | 2000-10-25 | Allergan, Inc | Ultraviolet light absorbing compounds and silicone compositions |
| US5384235A (en) | 1992-07-01 | 1995-01-24 | Eastman Kodak Company | Photographic elements incorporating polymeric ultraviolet absorbers |
| US5942564A (en) | 1992-09-07 | 1999-08-24 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Hydroxyphenyl-s-triazines |
| US5331073A (en) | 1992-11-09 | 1994-07-19 | Allergan, Inc. | Polymeric compositions and intraocular lenses made from same |
| EP0693483A1 (en) | 1994-07-23 | 1996-01-24 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Compounds having ultra-violet absorption properties |
| US5648488A (en) | 1994-07-27 | 1997-07-15 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Compositions stabilized with red-shifted tris-aryl-s-triazines |
| US5869588A (en) | 1994-10-04 | 1999-02-09 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Polymeric compounds derived from 2-hydroxy-phenyl-s-triazines substituted with ethylenically unsaturated moieties |
| US5693095A (en) | 1995-06-07 | 1997-12-02 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | High refractive index ophthalmic lens materials |
| US5837792A (en) | 1995-06-23 | 1998-11-17 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Polysiloxane light stabilizers |
| US5928630A (en) | 1996-02-12 | 1999-07-27 | Societe L' Oreal S.A. | Benzalmalonate/phenylcyanoacrylate-substituted s-triazine compounds and photoprotective/cosmetic compositions comprised thereof |
| US5928629A (en) | 1996-07-01 | 1999-07-27 | Societe L'oreal S.A. | Photoprotective/cosmetic compositions comprising dibenzoylmethane/triazine/diphenylacrylate compounds |
| WO1998050371A1 (en) | 1997-05-08 | 1998-11-12 | Otsuka Chemical Co., Ltd. | 2,2'-bis(6-benzotriazolylphenol) compounds, ultraviolet absorbers comprising the same, copolymers containing the same, and polymer compositions containing the same |
| WO1999053348A1 (en) | 1998-04-15 | 1999-10-21 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | High refractive index ophthalmic device materials prepared using a post-polymerization cross-linking method |
| EP0952467A1 (en) | 1998-04-20 | 1999-10-27 | JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION PRODUCTS, INC. | Ocular devices manufactured with free radical-polymerizable latent ultra-violet absorbers |
| WO1999058507A1 (en) | 1998-05-11 | 1999-11-18 | Pharmacia & Upjohn Groningen B.V. | Polymerizable hydrophilic ultraviolet light absorbing monomers |
| US5945465A (en) | 1998-05-15 | 1999-08-31 | Bausch & Lomb Incorporated | Method for polymerizing contact lenses having UV absorbing properties |
| WO1999060428A1 (en) | 1998-05-15 | 1999-11-25 | Bausch & Lomb Incorporated | Method for making contact lenses having uv absorbing properties |
| WO1999063366A1 (en) | 1998-05-15 | 1999-12-09 | Bausch & Lomb Incorporated | Method for polymerizing contact lenses having uv absorbing properties |
| US5914355A (en) | 1998-05-15 | 1999-06-22 | Bausch & Lomb Incorporated | Method for making contact lenses having UV absorbing properties |
| WO2000055212A1 (en) | 1999-03-16 | 2000-09-21 | Pharmacia Groningen Bv | Macromolecular compounds |
| WO2002078966A2 (en) | 2001-03-29 | 2002-10-10 | Michael Huber München Gmbh | Prepolymer and screen roller filler for depth-variable laser ablation |
Non-Patent Citations (8)
| Title |
|---|
| Abu-Abdoun et. al., Journal of Polymer Science, Polymer Chemistry Edition (1983), 21 (11), pp. 3129-3144; abstract only. * |
| Andrea Sustic, et al., "New 2(20hydroxyphenyl)2H-benzotriazole based polymer-bound unltraviolet stabilizers," ACS Polymer Prep., 1987, p. 226, vol. 28(2). |
| J. F. Rabek, Photostabilization of Polymers, Chapter 1.1-1.3 (pp. 1-5) and Chapter 5.1-5.10 (pp. 202-249) and Chapter 7.3 (pp. 368-391), Elsevier Applied Science, London and New York, 1990. |
| Jacqueline H. De Groot, et al., "Hydrophilic Polymeric Acylphospine Oxide Photoinitiators/Crosslinkers for in Vivo Blue-Light Photopolymerization," Biomacromolecules, 2001, pp. 1271-1278, vol. 2. |
| Jiang-Qing Pan, et al., "Synthesis and Characterization of New Monomers Containing UV-Absorber Function," Polymer Degradation and Stability, 1995, pp. 231-237, vol. 49. |
| Jurgen Keck, et al., Deactivation Processes of 2-Hydroxyphenyl-1,3-5Triazines- Polymeric and Monomeric UV Absorbers of the Benzotriazole and Triazine Class, Die Angewandte Makromolekulare Chemie1997, pp. 119-138, vol. 252. |
| S. Knaus, et al., "Photoinitiators With Functional Groups. III. Water-Soluble Photoinitiators Containing Carbohydrate Residues," Journal of Polymer Science, Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 1995, pp. 929-939, vol. 33. |
| William Dickstein, et al., "Functional Polymers. XXVI. Co- and Terpolymers Involving Methacrylates N-Vinylpyrollidone, and Polymerizable Ultraviolet Stabilizers and Antioxidants," J. Macromol. Sci.-Chem., 1985, pp. 387-402, A22(4). |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8475691B2 (en) | 2011-08-15 | 2013-07-02 | Novartis Ag | UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US8585938B1 (en) | 2012-03-30 | 2013-11-19 | Novartis Ag | UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials |
| US10619065B2 (en) | 2017-01-31 | 2020-04-14 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Photo active agents |
| WO2023052888A1 (en) * | 2021-09-29 | 2023-04-06 | Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. | Ophthalmic lenses and their manufacture by in-mold modification |
| US11912800B2 (en) | 2021-09-29 | 2024-02-27 | Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. | Amide-functionalized polymerization initiators and their use in the manufacture of ophthalmic lenses |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20100168438A1 (en) | 2010-07-01 |
| WO2004062371A1 (en) | 2004-07-29 |
| DK1581272T3 (en) | 2006-10-02 |
| US20080221675A1 (en) | 2008-09-11 |
| EP1581272A1 (en) | 2005-10-05 |
| US20040157948A1 (en) | 2004-08-12 |
| JP2006513291A (en) | 2006-04-20 |
| ATE329629T1 (en) | 2006-07-15 |
| CY1106142T1 (en) | 2011-06-08 |
| AU2003297108A1 (en) | 2004-08-10 |
| AU2003297108B2 (en) | 2008-01-10 |
| EP1581272B1 (en) | 2006-06-14 |
| US7119210B2 (en) | 2006-10-10 |
| US7709652B2 (en) | 2010-05-04 |
| US7396942B2 (en) | 2008-07-08 |
| DE60306203T2 (en) | 2006-10-05 |
| PT1581272E (en) | 2006-08-31 |
| DE60306203D1 (en) | 2006-07-27 |
| ES2262033T3 (en) | 2006-11-16 |
| CA2512586A1 (en) | 2004-07-29 |
| US20070078196A1 (en) | 2007-04-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8119830B2 (en) | Dual function UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials | |
| EP2139871B1 (en) | Uv-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials | |
| JP5732456B2 (en) | Visible light absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials | |
| US8262947B2 (en) | UV/visible light absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials | |
| EP2176243B1 (en) | Ophthalmic lens materials containing chromophores that absorb both uv and short wavelength visible light | |
| CA2631595A1 (en) | Polymer composition having a high refractive index | |
| US8585938B1 (en) | UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials | |
| EP0344244A1 (en) | Uv absorbing vinyl monomers and polymers and ocular implants prepared therefrom | |
| US20100207068A1 (en) | Process for producing purified synthesis gas from synthesis gas comprising trace amounts of sulphur contaminants with a metal-organic framework | |
| KR20160085699A (en) | Uv-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials | |
| JPH0622565B2 (en) | Intraocular lens material | |
| JPS6359964A (en) | Material for ultraviolet ray absorbable intraocular lens | |
| TW201518282A (en) | UV-absorbers for ophthalmic lens materials | |
| US20220249737A1 (en) | Micro injectable, low chromatic aberration intraocular lens materials |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: NOVARTIS AG, SWITZERLAND Free format text: MERGER;ASSIGNOR:ALCON, INC.;REEL/FRAME:026376/0076 Effective date: 20110408 |
|
| STCF | Information on status: patent grant |
Free format text: PATENTED CASE |
|
| FPAY | Fee payment |
Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| MAFP | Maintenance fee payment |
Free format text: PAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEE, 8TH YEAR, LARGE ENTITY (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: M1552); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| AS | Assignment |
Owner name: ALCON INC., SWITZERLAND Free format text: CONFIRMATORY DEED OF ASSIGNMENT EFFECTIVE APRIL 8, 2019;ASSIGNOR:NOVARTIS AG;REEL/FRAME:051454/0788 Effective date: 20191111 |
|
| MAFP | Maintenance fee payment |
Free format text: PAYMENT OF MAINTENANCE FEE, 12TH YEAR, LARGE ENTITY (ORIGINAL EVENT CODE: M1553); ENTITY STATUS OF PATENT OWNER: LARGE ENTITY Year of fee payment: 12 |