US556161A - George quarrie - Google Patents
George quarrie Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US556161A US556161A US556161DA US556161A US 556161 A US556161 A US 556161A US 556161D A US556161D A US 556161DA US 556161 A US556161 A US 556161A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- shoe
- heel
- sole
- conductors
- plate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 28
- 239000010985 leather Substances 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910001369 Brass Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000010951 brass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007373 indentation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A43—FOOTWEAR
- A43B—CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES OF FOOTWEAR; PARTS OF FOOTWEAR
- A43B3/00—Footwear characterised by the shape or the use
- A43B3/34—Footwear characterised by the shape or the use with electrical or electronic arrangements
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/02—Details
- A61N1/04—Electrodes
- A61N1/0404—Electrodes for external use
- A61N1/0472—Structure-related aspects
- A61N1/0484—Garment electrodes worn by the patient
Definitions
- My invention is directed particularly to improvements in body-wear as applicable in the art of therapeutics, and its object is to deelectrify the human body. I accomplish this object by the use of the devices hereinafter described, but more particularly pointed out in the claims which follow thisspecification.
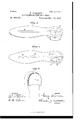
- Figure 1 is a plan view of the unfinished sole of a shoe with a transparent elevational view of the heel of same, showing the application of one form of my improvement.
- Fig. 2 is a plan view of the inside finished sole of a shoe having the same improvement.
- Fig. 3 is a plan view of the ground surface of the heel of Figs. 1 and 2, and
- Fig. 4 is an elevational view of same heel.
- Fig. 5 is a view of the heel tip or plate used in Figs. 1, 3, and 4:.
- Fig. 6 is a plan view of the unfinished sole of a shoe with a transparency of the heel, showing another application of my improvement.
- Fig. 7 is a plan View of Fig. 6 when the sole is finished.
- Fig. 1 is a plan view of the unfinished sole of a shoe with a transparent elevational view of the heel of same, showing the application of one form of my improvement.
- Fig. 2 is a plan view of the inside finished sole of a shoe
- Fig. 8 is a plan view of the outside or ground surface of the heel of Figs. 6 and 7.
- Fig. 9 is a plan view of an unfinished shoe-sole having another application of my improvement.
- Fig/10 is a longitudinal sectional View of Fig. 9.
- Fig. 11 is a plan view of Fig. 9 in the finished state.
- Fig. 12 is a plan View of the outside surface or reverse of the sole shown in Figs. 9 and 11.
- Fig. 13 is a plan view of one half of an insole for a shoe.
- Fig. lat is the same as Fig. 13 with metallic conductors added.
- Fig. 15 is the same halfinsole with the other half or upper finishingleather added.
- Fig. 16 represents a sectional elevation of a shoe and an overshoe thereon, both provided with conductors for de-electrifying the human body.
- Fig. 1 I have disclosed a shoe having built into it in its manufacture an inner heelplate, P, and a strip of conducting material R,
- This tip Q may occupy a part, as shown, of the ground surface of the heel or the whole surface, and it may be made of metal or any other suitable conducting substance, its use being twofold, viz: by acting as an easily-removable protection of the heel from wear, and in affording in its fastening screw or screws, rivets, or nails good electrical contact between the inside conductors P and R and the ground.
- the heel-piece Q, Fig. 5, is preferably of equal thickness throughout at its edges, but may be grooved, as at G, Fig. 5, or otherwise lightened and made less liable to slip by corrugations, indentations, or kindred devices.
- This heel-piece Q is put in place in manufacture of the shoe, and has its space definitely cut in the heel of the shoe, into which space it fits, as shown at Q, Fig. 3, and Q, Fig. L, one object being to enable wearers to replace the worn plate or tip With facility by a new one by having it removable mainly by withdrawing a screw or screws which fasten it from the inside of the shoe to the inner heel-plate.
- Fig. 2 I show the shoe-sole having the conducting heel-plate P and strip R fastened down by the screw S, with or without other fastenings from within, as described and shown in Fig. 1, and now having its finished surface F covering said conductors preferably with perforations through it, as shown at II II, Fig. 2, through which the foot-sole of the wearer will bulge so as to make contact with the conductors R and P, Fig. 2, or the heel-plate P may be left bare, as at I3, Fig. 2, so as to more perfectly contact with the foot.
- FIG. 6 shows the shoe-sole having the heel-plate P and comlucting-strip R fastened by the screw S, which passes down through the heel to its ground surface, as shown at- S, Fig. 8.
- Fig. 7 shows the same sole, now finished with its leather covering F, which either leaves P bare, as at B, or has perforations, as at H H, through which the foot-sole contacts with the condueting-strips R and P, as shown in same figure.
- Fig. 9 I disclose another device for havin g electrical earth connection made at two or more points in both heel and sole of the shoe.
- P is the heel-plate, and S its fastening screw, and
- O is a small conducting sole-plate, preferably of oblong shape, placed under the middle of the sole of the foot, with screws, nails, or rivets N N fastening the plate in place and coming through to the ground surface of the sole, as shown at N N, Fig. 12.
- Fig. 10 shows the same shoe-sole in section with the plates P and 0 let into the finished insole F, as shown, or they may be covered by the insole F, having perforations II II, as shown in Fig. 11, the finished shoesole.
- Fig. 13 represents the lower half of a loose inner sole for a shoe made of any good conducting material, with holes A and B cut into it.
- Fig. 14 is the same half-insole having upon it three pieces of conducting material, as metal-that is to say, a piece 0, Fig. 14, placed upon the hole A, Fig. 13, and a piece E, Fig. 14., on the hole I Fig. 13, and another piece D connecting O and E together; but these pieces may be substituted by one solid piece of approximately this shape cut out of any metal, such as copper, brass, zinc, or wire gauze, or any other suitable good conducting material.
- Fig. 15 shows the canvas sole, Fig. 13, with the conductors C, D, and E, Fig. 14, laid on it, as shown, and a piece of fine leather F as the other half of the insole pasted and sewed over the canvas half, inclosin g the conductors C D E between the two, and having the leather or upper finishing-piece perforated, as at II II II, for contact of the foot-sole with O D E; and any desirable stiffening, such as thin wood, may be used between the two halves to level up the parts surrounding the conductors.
- These loose insoles are for use in ordinary shoes, in combination with the ground-conneetion heel-plate P and screw S, Fig.
- Fig. 16 is illustrated the application of my improvement in connection with a shoe and an overshoe, said figure being a longitudinal sectional view taken through a shoe and an overshoe, in which R represents a conducting insole or strip of the shoe similar to the like part in other figures of the drawings, and S a conductor connected thereto and extending through the heel of the shoe, N and N being corresponding conductors connected to the conducting part R and extending through the sole of the shoe, while N N N are conductors, preferably in the nature of copper rivets, secured in the heel and sole of the overshoe and adapted to contact directly with the conductors S and N N when the overshoe is in position on the shoe, as clearly illustrated, the arrangement being such that when the shoe is upon the foot of the wearer and the overshoe in position the body of the wearer will be in electrical contact with the earth whenever he walks thereon.
- R represents a conducting insole or strip of the shoe similar to the like part in other figures of the drawings
- S a conductor connected thereto and
- a boot or shoe provided with an extended conducting-surface in the nature of a metallic strip or insole having electrical connection through the sole of the shoe with the surface of the earth.
- a boot or shoe having electrical conductors extending through the heel and sole thereof and electrically connected with an insole or surface of comparatively large conductivity.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Footwear And Its Accessory, Manufacturing Method And Apparatuses (AREA)
Description
(No Model.) 4 Sheets-Sheet 1.
GPQUABRIE. E'LEOTROTHERAPE UTIG BODY. WEAR.
N0. 556,161. Patented Mar. 10, 1896.
' WITNESSES:
Arron/1n AN IIRIZW BJSRAHAM. FHOTOMTHuWA SlIINGTDNJ C.
(No Model.) I 4 Sheets-Sheet 2.
' G. QUARRIE.
ELEGTROTHERAPEUTIG BODY WEAR.
Patented Mar. 10, 1896.
- O O Q INVENTOI? 9 ATTORNEY WHEN RGRAHAM PHOTOUHU WASHINGTON. C
(No Model.) 4 Sheets-Sheet 3.
G. QUARRIE. ELECTROTHERAPBUTIG BODY WEAR.
No. 556,161. Patented Mar..10, 1896.
WITNESSES: INVENTOI? @7 6 ATTORNEY AN 0am. EGRAHAM. PHUTO-UTH.WA5HINGTON. D C.
r'No Model.) 4 Sheets-Sheet 4.
G. QUARRIE. ELECTROTHBRAPEUTIG BODY WEAR. N0.-556,161 Patented Mar. 10', 18 96;
. 1&1;
ATTORNEY ANDREW EGRAKAM. PNUTUUTHQWASNNGTOMQC.
UNITED STATES 'ATENT OFFICE.
GEORGE QUARRIE, OF BROOKLYN, ASSIGNOR OF ONE-HALF TO CHARLES J. KINTNER, OF NEW YORK, N. Y.
ELECTROTHERAPEUTIC BODY-WEAR.
SPECIFICATION forming part of Letters Patent No. 556,161, dated March 10, 1896. Application filed May 3, 1894. Serial No. 309,996. (No model.)
To aZZ whom it may concern.-
Be it known that I, GEORGE QUARRIE,,a subject of the Queen of Great Britain, residing at Brooklyn, in the county of Kings and State of New York, have made a new and useful Invention in Therapeutical Apparatus, of which the following is a specification.
My invention is directed particularly to improvements in body-wear as applicable in the art of therapeutics, and its object is to deelectrify the human body. I accomplish this object by the use of the devices hereinafter described, but more particularly pointed out in the claims which follow thisspecification.
Myinvention will be fully understood by referring to the accompanying drawings, which represent various appliances for accomplishing the object named.
Figure 1 is a plan view of the unfinished sole of a shoe with a transparent elevational view of the heel of same, showing the application of one form of my improvement. Fig. 2 is a plan view of the inside finished sole of a shoe having the same improvement. Fig. 3 is a plan view of the ground surface of the heel of Figs. 1 and 2, and Fig. 4 is an elevational view of same heel. Fig. 5 is a view of the heel tip or plate used in Figs. 1, 3, and 4:. Fig. 6 is a plan view of the unfinished sole of a shoe with a transparency of the heel, showing another application of my improvement. Fig. 7 is a plan View of Fig. 6 when the sole is finished. Fig. 8 is a plan view of the outside or ground surface of the heel of Figs. 6 and 7. Fig. 9 is a plan view of an unfinished shoe-sole having another application of my improvement. Fig/10 is a longitudinal sectional View of Fig. 9. Fig. 11 is a plan view of Fig. 9 in the finished state. Fig. 12 is a plan View of the outside surface or reverse of the sole shown in Figs. 9 and 11. Fig. 13 is a plan view of one half of an insole for a shoe. Fig. lat is the same as Fig. 13 with metallic conductors added. Fig. 15 is the same halfinsole with the other half or upper finishingleather added. Fig. 16 represents a sectional elevation of a shoe and an overshoe thereon, both provided with conductors for de-electrifying the human body.
I make electrical connection between the body and the earth by providing the sole or heel Of the boot with metallic or conducting material having actual contact with the earth and the foot of the wearer.
In Fig. 1 I have disclosed a shoe having built into it in its manufacture an inner heelplate, P, and a strip of conducting material R,
running from the heel-plate forward along the middle of the sole, near its finished surface, toward the toe, both being fastened down in place by a metallic screw S, other screws being used if necessary, such as S, these screws going through the upper metallic heel-plate and down through the heel of the shoe and the outer heel plate or tip, Q. This tip Q may occupy a part, as shown, of the ground surface of the heel or the whole surface, and it may be made of metal or any other suitable conducting substance, its use being twofold, viz: by acting as an easily-removable protection of the heel from wear, and in affording in its fastening screw or screws, rivets, or nails good electrical contact between the inside conductors P and R and the ground. It may be necessary to have only one fastener, such as S, going through from the inner plate, P, to the Outer plate or tip, Q, the remaining fastenings being small screws or nails driven from the outside, as at w a: 00, Fig. 3.
The heel-piece Q, Fig. 5, is preferably of equal thickness throughout at its edges, but may be grooved, as at G, Fig. 5, or otherwise lightened and made less liable to slip by corrugations, indentations, or kindred devices. This heel-piece Q, is put in place in manufacture of the shoe, and has its space definitely cut in the heel of the shoe, into which space it fits, as shown at Q, Fig. 3, and Q, Fig. L, one object being to enable wearers to replace the worn plate or tip With facility by a new one by having it removable mainly by withdrawing a screw or screws which fasten it from the inside of the shoe to the inner heel-plate.
In Fig. 2 I show the shoe-sole having the conducting heel-plate P and strip R fastened down by the screw S, with or without other fastenings from within, as described and shown in Fig. 1, and now having its finished surface F covering said conductors preferably with perforations through it, as shown at II II, Fig. 2, through which the foot-sole of the wearer will bulge so as to make contact with the conductors R and P, Fig. 2, or the heel-plate P may be left bare, as at I3, Fig. 2, so as to more perfectly contact with the foot.
I11 Figs. 6, 7 and 8 I disclose another plan of constructing a shoe with electrical earth connection, but without the outer heel plate or tip. (Shown in Figs. 1, 2, 3, at and 5.) Fig. 6 shows the shoe-sole having the heel-plate P and comlucting-strip R fastened by the screw S, which passes down through the heel to its ground surface, as shown at- S, Fig. 8. Fig. 7 shows the same sole, now finished with its leather covering F, which either leaves P bare, as at B, or has perforations, as at H H, through which the foot-sole contacts with the condueting-strips R and P, as shown in same figure.
In Fig. 9 I disclose another device for havin g electrical earth connection made at two or more points in both heel and sole of the shoe. P is the heel-plate, and S its fastening screw, and O is a small conducting sole-plate, preferably of oblong shape, placed under the middle of the sole of the foot, with screws, nails, or rivets N N fastening the plate in place and coming through to the ground surface of the sole, as shown at N N, Fig. 12.
Fig. 10 shows the same shoe-sole in section with the plates P and 0 let into the finished insole F, as shown, or they may be covered by the insole F, having perforations II II, as shown in Fig. 11, the finished shoesole.
Fig. 13 represents the lower half of a loose inner sole for a shoe made of any good conducting material, with holes A and B cut into it. Fig. 14 is the same half-insole having upon it three pieces of conducting material, as metal-that is to say, a piece 0, Fig. 14, placed upon the hole A, Fig. 13, and a piece E, Fig. 14., on the hole I Fig. 13, and another piece D connecting O and E together; but these pieces may be substituted by one solid piece of approximately this shape cut out of any metal, such as copper, brass, zinc, or wire gauze, or any other suitable good conducting material.
Fig. 15 shows the canvas sole, Fig. 13, with the conductors C, D, and E, Fig. 14, laid on it, as shown, and a piece of fine leather F as the other half of the insole pasted and sewed over the canvas half, inclosin g the conductors C D E between the two, and having the leather or upper finishing-piece perforated, as at II II II, for contact of the foot-sole with O D E; and any desirable stiffening, such as thin wood, may be used between the two halves to level up the parts surrounding the conductors. These loose insoles are for use in ordinary shoes, in combination with the ground-conneetion heel-plate P and screw S, Fig. 6, or other equivalent earth connection; or there may be two or more ground connectionsviz., at the heel contacting with E, Fig. 14:, as well as others by screws, rivets, nails, or sewed wire through the sole of the shoe so as to contact with O in the same figure.
I am aware of United States Patent No. 304,050, granted to Charles S. Upton on the 22d of August, 1884c, for improvement in rubber boots or shoes, and I make no claim hereinafter broad enough to include the application of the principle of conveyin g heat from the feet of the wearer of a rubber boot or shoe by a heateonducting agent. My invention is directed to a radical ly-dif ferent application. or use of metallic or equivalent conductors, in that I use such conductors for de-electrifying the body of the wearer and in any and all kinds of foot-wearing material.
In Fig. 16 is illustrated the application of my improvement in connection with a shoe and an overshoe, said figure being a longitudinal sectional view taken through a shoe and an overshoe, in which R represents a conducting insole or strip of the shoe similar to the like part in other figures of the drawings, and S a conductor connected thereto and extending through the heel of the shoe, N and N being corresponding conductors connected to the conducting part R and extending through the sole of the shoe, while N N N are conductors, preferably in the nature of copper rivets, secured in the heel and sole of the overshoe and adapted to contact directly with the conductors S and N N when the overshoe is in position on the shoe, as clearly illustrated, the arrangement being such that when the shoe is upon the foot of the wearer and the overshoe in position the body of the wearer will be in electrical contact with the earth whenever he walks thereon.
I do not limit myself to any specific form of conductor when used in connection. with a boot or shoe and which shall connect the foot of the wearer directly with the surface of the earth or the surface upon which he walks, as I believe I am the first to provide footwear with metallic or other electrical conductors when used in the manner described, and my claims are generic in this particular. I make no claim broadly to the art of de-electrifying the human body and my claims are limited to the extent of the application of conductors to the feet when embedded in or attached to the shoes or boots of the wearer.
IIavin g thus described my invention, what I claim, and desire to secure by Letters Patent of the United States, is-
1. A boot or shoe provided with one ormore electrical conductors extending through the sole thereof, in combination with a plate or insole of conducting material having elec trical contact therewith.
2. A boot or shoe provided with an extended conducting-surface in the nature of a metallic strip or insole having electrical connection through the sole of the shoe with the surface of the earth.
3. A boot or shoe having electrical conductors extending through the heel and sole thereof and electrically connected with an insole or surface of comparatively large conductivity.
4. The described improvement in therapeutical devices consisting of an overshoe, or rubber having conducting material incorporated with or embeddedin the rubber or substance of which the shoe is made, and adapted to make electrical contact with corresponding conductors embedded in the shoe of the wearer.
5. The described improvement in therapentical devices consisting of an overshoe and a shoe having contacting conductors extending through the soles of each, in combination with a conducting-insole.
In testimony whereof I have hereunto subscribed my name this 8th day of December, 1898.
GEORGE QUARRIE.
WVitnesses:
C. J. KINTNER, M. M. ROBINSON.
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US556161A true US556161A (en) | 1896-03-10 |
Family
ID=2624898
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US556161D Expired - Lifetime US556161A (en) | George quarrie |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US556161A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2444098A (en) * | 1944-01-19 | 1948-06-29 | Handfield Arthur | Electrotherapeutic appliance |
| US2904724A (en) * | 1956-07-19 | 1959-09-15 | Mendoza Manuel | Shoe sole |
| WO2000074771A1 (en) * | 1999-02-26 | 2000-12-14 | Joze Pinter | Method and device for promoting energy flow in an organism |
| US20050187601A1 (en) * | 2004-02-19 | 2005-08-25 | Wei-Cheng Wang | Method for moderation of back pain |
-
0
- US US556161D patent/US556161A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2444098A (en) * | 1944-01-19 | 1948-06-29 | Handfield Arthur | Electrotherapeutic appliance |
| US2904724A (en) * | 1956-07-19 | 1959-09-15 | Mendoza Manuel | Shoe sole |
| WO2000074771A1 (en) * | 1999-02-26 | 2000-12-14 | Joze Pinter | Method and device for promoting energy flow in an organism |
| US20050187601A1 (en) * | 2004-02-19 | 2005-08-25 | Wei-Cheng Wang | Method for moderation of back pain |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US500385A (en) | William hall | |
| US892360A (en) | Electric insole. | |
| US360127A (en) | Electric sole | |
| US3410005A (en) | Golf shoe | |
| US1187778A (en) | Antislipping overshoe. | |
| US497822A (en) | Electro-therapeutic | |
| US556161A (en) | George quarrie | |
| US3383559A (en) | Antistatic footwear, such as shoes, boots, sandals and the like | |
| US2074579A (en) | Shoe structure | |
| US1272556A (en) | Sole for boots and shoes. | |
| US2025950A (en) | Foot warming device | |
| US1918276A (en) | Electric body warming device | |
| US520417A (en) | Inside shoe | |
| US444735A (en) | Voltaic insole | |
| US495782A (en) | Electric shoe-sole | |
| JP3217050U (en) | Anti-static shoes | |
| US1208638A (en) | Insole. | |
| GB1423881A (en) | Sports footwear | |
| US166517A (en) | Improvement in wooden-soled boots and shoes | |
| US3032895A (en) | Shoe construction | |
| US398453A (en) | Shank-protector | |
| US1418188A (en) | Boot or shoe | |
| US813053A (en) | Shoe. | |
| US184077A (en) | Improvement in boot and shoe soles | |
| CN210248608U (en) | Grounding conductive health-care shoes |