US2777035A - Air-type circuit interrupter - Google Patents
Air-type circuit interrupter Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US2777035A US2777035A US419753A US41975354A US2777035A US 2777035 A US2777035 A US 2777035A US 419753 A US419753 A US 419753A US 41975354 A US41975354 A US 41975354A US 2777035 A US2777035 A US 2777035A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- arc
- wedge
- plates
- plate portions
- shaped plate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H9/00—Details of switching devices, not covered by groups H01H1/00 - H01H7/00
- H01H9/30—Means for extinguishing or preventing arc between current-carrying parts
- H01H9/34—Stationary parts for restricting or subdividing the arc, e.g. barrier plate
Definitions
- This invention relatesto improvements in circuit interrupters, and more particularly to arc-extinguishing structures for circuit interrupters of the air break type.
- a more specific object is to ⁇ provide an improved spacing arrangement of ⁇ thespaced plates of a circuit interrupter of the foregoing type.
- a more specific object is to improve the interrupting capacity of a circuit interrupter vof the foregoing type Without increasing the .expense ⁇ thereof either in regard to assembling operations or in the cost of constructional materials.
- Another object is to provide an improved plate convfiguration to restrict .the exhaust passages between tbe plates at the exhaust endof the arc-chute.
- Still a further object -of our invention is to provide wedge-shaped, spaced plates in a circuit rinterrupter of the air-break type, utilizing either parallel spacer strips or tapered spacer strips.
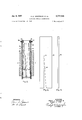
- Figure 1 is a side elevational view, :partially in vertical section, of an air break type of circuit interrupter embodying our invention and .shown in the closed circuit position;
- Fig. 2 is a. vertical sectional view ltaken on the .line l-l--ll of Fig. 1, looking in the direction of vthe arrows;
- Fig. 3 is an enlarged plan view of one Vof the arcextinguishing plates formingl .the arc-extinguishing structure; and' Fig. 4A shows a Vside elevational view of 4the wedgeshaped plate of Fig. 3.
- the reference numeral 1 generally designates suitable contact structure which, when separated to the open circuit position, establishes an arc which is moved upwardly itno an arc chute, generally designated by the reference numeral 2 as a result of the transverse magnetic field set up by the blowout coil 3 and associated magnet 4structure 4.
- a rotatable contact arm 5 carries a conducting bridge 6 which, in the closed circuit position, as shown in Fig. l, interconnects stationary main contacts 7, 8.
- a contact stud 9 carries the current from the stationary main contact 7, through an insulating bushing 10 tothe external circuit.
- the contact stud for the stationary main contact 8 is not shown, but it may be identical to the contact stud 9.
- the electrical circuit comprises the contact stud 9, stationary main contact 7, conducting bridge 6, stationary main contact 8, tothe contact stud therefor, not shown, to the external circuit.
- the contact arm 5 is rotated in a clockwise direction about a pivot pin, not shown, but which isin electrical contact with the stationary main contact 8, to draw an arc between the arcing contacts 11, 12 after the separation of conducting bridge 6 from the main contacts 7, 8.
- blowout coil 3 When this occurs, the blowout coil 3 will be put into series circuit and the transverse magnetic -eld set up thereby between the field pole members 14 (Fig. 2) will move the established ⁇ arc upwardly along the arc terminal members 18, 19 into the arc chute 2.
- the electrical circuit now comprises contact stud 9, conductor 20, blowout coil 3, contact clip 15, arc terminal member 18, the arc itself, arc terminal member 19, llexible shunt 28, contact arm S to the other contact stud, not shown.
- the arc chute 2 comprises an insulating rectangularlyshaped housing member 22 positioned adjacent to an insulating plate 21, the latter serving as a base for the blowout coil 3. Within the housing 22 is placed a plate 24 composed of an insulating material. Two insulating spacer strips 25 space a plate 26, composed of an insulating material, away from the plate 24. The plate 26 may have a plurality of apertures 27 formed therein which facilitate the venting of arc gases therethrough, particularly when high currents are to be interrupted. Two more insulating spacer strips 25 space the plate 26 from a plurality of plates 29, forming a unitary plate assembly.
- the plates 29 are composed preferably of a refractory insulating material, such as a Zircon porcelain, which does not give olf gas when contacting an arc.
- the plates 29 have a construction more clearly shown in Figs. 3 and 4 and are separated by pairs of asbestos rope 35.
- a second insulating plate 26 which is spaced by spacer strips 2S from the right-hand plate 29 of the plate assembly.
- Two additional spacer strips 25 space the right-hand plate 26 from a refractory plate, not shown, which is, in turn, separated from the right-hand end of the housing 22 by a plurality of strips of sh paper.
- Bolts 33a secure the several strips 25, plate 26 and the housing 22 to the plate 21.
- Bolts 34a secure the right-hand plate 26 and its spacer strips 25 and fish paper strips to the housing 22.
- the plates 29 and the spacer strips 35 are cemented together in a preliminary process to form a unitary plate aruosa assembly which may be bodily placed into the rectangular housing 22.
- Insulating holding strips 39 are secured by bolts 38 to the opposed inner sides of the housing 22 to prevent the unitary assembly of plates 29 ⁇ from being forced upwardly out of the housing 22 by the pressure of gas formed during the interrupting operation.
- each plate 29 has an inwardly extending slot or notch llt) which constricts in lateral dimension in a direction toward the top of the plate 29.
- the assembling of the plates 29 is such that the upper closed ends of the slots itl are alternately staggered throughout the arc chute 2 so that when the arc is forced upwardly into the several slots itl it will assume a zig-zag contiguration at the upper closed ends il of the slots dil prior to its being extinguished.
- This magnetically produced gas blast carries ionized gases upwardly to the closed ends il of the slots iti where extinction is caused by the magnetically produced upward gas blast, the exhaust gases passing upwardly between the plates 2l* and out or' the arc chute 2.
- air break circuit interrupters of this type such as set forth in the aforesaid patent, it has been the practice to position the spacers 35 or sections of asbestos rope parallel to each other at the pposed outer-side edges of each plate 29.
- the spacers 35 constitute a side wall means between adjacent plates 29.
- Figs. 3 and 4 show more particularly the wedge-shaped plate 29.
- This plate 29 is wedge-shaped, as shown, and when employed in a stack with parallel spacers 35 will constriet the exhaust passages l2 between each pair of adjacent plates.
- the constricted exhaust passage 4Z may be formed either by wedge-shaped plates alone, with parallel spacers 35, or by wedge-shaped plates 29 with tapered spacers 35, as shown in Fig. 2.
- a circuit interruptor of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced wedgeshaped plates of insulating material, the thickness of each plate increasing in a direction toward the exhaust end of the arc chute, the plates being so disposed that the median plane of each plate is parallel to the median plane of every other plate, means for establishing an arc and moving it against the plates, and the exhaust passages between the plates decreasing in cross-sectional area at the exhaust end of the are chute.
- a circuit interruptor of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced slotted wedge-shaped plates of insulating material, the thickness of each plate increasing in a direction toward the exhaust end of the arc chute, the plates being so disposed that the median plane ot each plate is parallel to the median plane of every other plate, means for establishing an arc and moving it into the slots and against the plates, and the exhaust passages between the plates decreasing in cross-sectional area at the exhaust end of the are chute.
- a circuit interruptor of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a stack of spaced slightly wedgeshaped plate portions, means for establishing an arc, the established arc moving against the slightly wedgeshaped plate portions to effect the extinction thereof, spacing means positioning the slightly wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart which is comparable to the thickness of the plate portions, and the exhaust passages between the slightly wedge-shaped plate portions defined by the slightly wedge-shaped plate portions and by the spacing means becoming smaller toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interruptor of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a stack of spaced Wedge-shaped slotted plate portions, means for establishing an arc, the established arc moving against the wedge-shaped slotted plate portions to effect the extinction thereof, spacing means positioning the wedge-shaped slotted plate portions a relatively short distance apart which is comparable to the thickness of the plate portion, and the exhaust passages between the Wedge-shaped slotted plate portions defined by the wedge-shaped slotted plate portions and by the spacing means becoming smaller toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced wedgeshaped plates of insulating material, each wedge-shaped plate having a closed-end slot extending inwardly from one end thereof, a pair of spacer strips separating adjacent wedge-shaped plates a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it through the slots provided by the several wedge-shaped plates, and the lateral distance between each pair of spacer strips diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced insulating wedge-shaped plate portions, spacing means extending along each side edge of the wedge-shaped plate portions separating adjacent wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially transversely against the insulating wedge-shaped plate portions to etfect the extinction thereof, and the lateral distance between the spacing means along one side edge of the wedge-shaped plate portions and the spacing means along the opposite side edge of the wedge-shaped plate portions progressively diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced slotted insulating wedge-shaped plate portions, spacing means extending along each side edge of the wedge-shaped plate portions separating adjacent wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially transversely against the wedge-shaped plate portions and into the slots thereof to effect the extinction thereof, and the lateral distance between the spacing means along one side edge of the slotted wedge-shaped plate portions and the spacing means along the opposite side edge of the slotted wedge-shaped plate portions progressively diminishing towards the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced insulating wedge-shaped plate portions, side wall means extending along the opposite sides of the arc chute and spacing the wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially transversely against the insulating wedge-shaped plate portions to eiect the extinction thereof, and the lateral distance between the side wall means along one side of the arc chute and the side wall means along the opposite side of the arc chute progressively diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced insulating wedge-shaped plate portions having closed end slots therein, side wall means extending along the opposite sides of the arc chute and spacing the wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially trans versely against the insulating wedge-shaped plate portions and into the slots thereof to effect the extinction of the arc, and the lateral distance between the side wall means along one side of the arc chute and the side wall means along the opposite side of the arc chute progressively diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a stack of spaced insulating Wedge-shaped plate portions, spacing means positioning the wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short disance apart to dene separate exhaust passages therebetween, the median plane of each wedge-shaped plate portion being parallel to the median plane of every other wedge-shaped plate portion so that the end wedge-shaped plate portions of the stack are parallel to each other thereby obtaining adequate ash-over distance at the exhaust end of the arc chute, means for establishing an arc, means for moving the established arc substantially transversely against the wedge-shaped plate portions to eiect the extinction thereof, and the cross-sectional area of the exhaust passages through the wedge-shaped plate portions defined by the spacing means and by the wedgeshaped plate portions becoming progressively smaller toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a stack of spaced insulating wedge-shaped plate portions having closed end slots therein, spacing means positioning the wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart to define separate exhaust passages therebetween, the median plane of each wedge-shaped plate portion being parallel to the median plane of every other wedge-shaped plate portion so that the end wedge-shaped plate portions of the stack are parallel to each other thereby obtaining adequate ash-over distance at the exhaust end of the arc chute, means for establishing an arc, means for moving the established arc into the slots of the wedge-shaped plate portions substantially transversely against the wedge-shaped plate portions to effect the extinction thereof, and the cross-sectional area of the exhaust passages through the wedgeshaped plate portions defined by the spacing means and by the wedge-shaped plate portions becoming progressively smaller toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
- a circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced wedgeshaped plates of insulating material, a pair of spacer strips separating adjacent wedge-shaped plates a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially transversely against the wedge-shaped plates to effect the extinction thereof, and the lateral distance between each pair of spacer strips diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
Landscapes
- Arc-Extinguishing Devices That Are Switches (AREA)
Description
Jan 8, 1957 R. c. DICKlNsoN ETAL 2,777,035
AIRJYPE CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER Original Filed Feb. 25, 1949 2 Sheets-Sheet l Jan- 8, 1957 R. c. DlcKlNsoN ErAL AIMYPE CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER Original Filed Feb. 25, 1949 2 Sheets-Sheet 2 '.SQS LIT;
Fig.3.
WITNESSES:
Fig.
ENTORS C. 'ckinson 8 ell E. Frink.
United States .Patent i AIR-TYPE CIRCUIT lINTERRUPTER Robert C. Dickinson and Russell E. Frink, Pittsburgh, v
Pa., assiguors to `Westinghouse Electric Corporation, East Pittsburgh, Pa., a corporation of Pennsylvania Original application February 23, 1949,-Serial No. 77,794, now Patent No. 2,687,461, dated August 24, 1954.
Divided and this application March .30, 1954, Serial v 12 Claims. (Cl. 20o-144) This invention relatesto improvements in circuit interrupters, and more particularly to arc-extinguishing structures for circuit interrupters of the air break type.
This application'is a division of our application 'filed February 23, 1949, Serial No. 77,794, now United States -Patent 2,687,461, issued lAugust 24, 1954, and assigned series of tapered slots formed in spaced plates vof insulatl ing material. Lateral movement of the arc is obtained by a magnetic eld produced by 'a magnetic blowout coil and magnetic eld poles. This-magnetic eld is also relied upon to produce a blast of unionizedY gas through the arc while the arc is held substantially immovable against the closed ends of the slots in the `plates of insulating material.
It is a general object of the present invention to improve the plateconstruction in an airbreak type of circuit interrupter of the type disclosed fin the aforesaid patent so Vas to .increase .the velocity of the arc ,gases as `they pass upwardly between .the spaced ceramic yplates of the .arc chute structure.
A more specific object is to `provide an improved spacing arrangement of `thespaced plates of a circuit interrupter of the foregoing type.
A more specific object is to improve the interrupting capacity of a circuit interrupter vof the foregoing type Without increasing the .expense `thereof either in regard to assembling operations or in the cost of constructional materials.
Another object is to provide an improved plate convfiguration to restrict .the exhaust passages between tbe plates at the exhaust endof the arc-chute.
Still a further object -of our invention -is to provide wedge-shaped, spaced plates in a circuit rinterrupter of the air-break type, utilizing either parallel spacer strips or tapered spacer strips.
Further objects and advantages will readily lbecome apparent upon a reading of the following specification taken in conjunction with the drawings, in which:
Figure 1 is a side elevational view, :partially in vertical section, of an air break type of circuit interrupter embodying our invention and .shown in the closed circuit position;
Fig. 2 is a. vertical sectional view ltaken on the .line l-l--ll of Fig. 1, looking in the direction of vthe arrows;
Fig. 3 is an enlarged plan view of one Vof the arcextinguishing plates formingl .the arc-extinguishing structure; and' Fig. 4A shows a Vside elevational view of 4the wedgeshaped plate of Fig. 3.
"ice
Referring to the drawings, and more particularly to Fig. l thereof, the reference numeral 1 generally designates suitable contact structure which, when separated to the open circuit position, establishes an arc which is moved upwardly itno an arc chute, generally designated by the reference numeral 2 as a result of the transverse magnetic field set up by the blowout coil 3 and associated magnet 4structure 4. A rotatable contact arm 5 carries a conducting bridge 6 which, in the closed circuit position, as shown in Fig. l, interconnects stationary main contacts 7, 8.
A contact stud 9 carries the current from the stationary main contact 7, through an insulating bushing 10 tothe external circuit. The contact stud for the stationary main contact 8 is not shown, but it may be identical to the contact stud 9.
Consequently, in the closed circuit position of the interrupter, as shown in Fig. l, the electrical circuit comprises the contact stud 9, stationary main contact 7, conducting bridge 6, stationary main contact 8, tothe contact stud therefor, not shown, to the external circuit.
During the opening operation of the interruptor, the contact arm 5 is rotated in a clockwise direction about a pivot pin, not shown, but which isin electrical contact with the stationary main contact 8, to draw an arc between the arcing contacts 11, 12 after the separation of conducting bridge 6 from the main contacts 7, 8.
When the arcing contacts V11, 12 separate, the arc formed therebetween will expand upwardly because of the loop circuit so that one terminal thereof will be transferred to the arc terminal member 1S, and the other arc terminal will be transferred to the other arc terminal member 19.
When this occurs, the blowout coil 3 will be put into series circuit and the transverse magnetic -eld set up thereby between the field pole members 14 (Fig. 2) will move the established `arc upwardly along the arc terminal members 18, 19 into the arc chute 2. The electrical circuit now comprises contact stud 9, conductor 20, blowout coil 3, contact clip 15, arc terminal member 18, the arc itself, arc terminal member 19, llexible shunt 28, contact arm S to the other contact stud, not shown.
The arc chute 2 comprises an insulating rectangularlyshaped housing member 22 positioned adjacent to an insulating plate 21, the latter serving as a base for the blowout coil 3. Within the housing 22 is placed a plate 24 composed of an insulating material. Two insulating spacer strips 25 space a plate 26, composed of an insulating material, away from the plate 24. The plate 26 may have a plurality of apertures 27 formed therein which facilitate the venting of arc gases therethrough, particularly when high currents are to be interrupted. Two more insulating spacer strips 25 space the plate 26 from a plurality of plates 29, forming a unitary plate assembly. The plates 29 are composed preferably of a refractory insulating material, such as a Zircon porcelain, which does not give olf gas when contacting an arc. The plates 29 have a construction more clearly shown in Figs. 3 and 4 and are separated by pairs of asbestos rope 35.
Above the arc terminal member 19 is a second insulating plate 26, which is spaced by spacer strips 2S from the right-hand plate 29 of the plate assembly. Two additional spacer strips 25 space the right-hand plate 26 from a refractory plate, not shown, which is, in turn, separated from the right-hand end of the housing 22 by a plurality of strips of sh paper. Bolts 33a secure the several strips 25, plate 26 and the housing 22 to the plate 21. Bolts 34a secure the right-hand plate 26 and its spacer strips 25 and fish paper strips to the housing 22.
The plates 29 and the spacer strips 35 are cemented together in a preliminary process to form a unitary plate aruosa assembly which may be bodily placed into the rectangular housing 22. Insulating holding strips 39 are secured by bolts 38 to the opposed inner sides of the housing 22 to prevent the unitary assembly of plates 29 `from being forced upwardly out of the housing 22 by the pressure of gas formed during the interrupting operation.
Referring to Fig. 3, which more clearly shows the contiguration of each insulating plate 29, it will be observed that each plate 29 has an inwardly extending slot or notch llt) which constricts in lateral dimension in a direction toward the top of the plate 29. Referring to will be observed that the assembling of the plates 29 is such that the upper closed ends of the slots itl are alternately staggered throughout the arc chute 2 so that when the arc is forced upwardly into the several slots itl it will assume a zig-zag contiguration at the upper closed ends il of the slots dil prior to its being extinguished.
The opening operation of the interrupter will now be explained. Upon the yclockwise rotation of the contact arm 5, an arc is drawn between the arcing contacts ll, l2 which quickly transfers, because of the loop circuit, to the arc terminal members 1S, 19 to thereby connect into series circuit the blowout coil 3. The magnetic lield set up by the blowout coil 3 between the eld pole members M, sets up a transverse magnetic eld through the arc chute 2, to thereby force the established arc upwardly along the arc term' ial members liti, Il@ until it comes into Contact with the closed ends 41 of the slots or notches 4t) provided in the several plates 29. The magnetic held gives an upward component of velocity to the electrons which bernhard gas particles and impart to them an upward velocity. This magnetically produced gas blast carries ionized gases upwardly to the closed ends il of the slots iti where extinction is caused by the magnetically produced upward gas blast, the exhaust gases passing upwardly between the plates 2l* and out or' the arc chute 2. In prior constructions of air break circuit interrupters of this type, such as set forth in the aforesaid patent, it has been the practice to position the spacers 35 or sections of asbestos rope parallel to each other at the pposed outer-side edges of each plate 29. The spacers 35 constitute a side wall means between adjacent plates 29. We have discovered, however, that considerable interrupting improvement is obtained by placing the spacers or sections of asbestos rope 35 so that a tapered constricted exhaust gas passage i2 is provided between each set of adjacent plates 29, as shown more clearly in Fig. 2. in other words, the lateral space A separating the spacers 35 at the upper end of the plate 29 is smaller than the lateral space B separating the spacers 35 at the lower end of the plate 29, as shown more `clearly in Fig. 2.
Thus by drawing the spacers 3S in at the exhaust end ot the interrupting assembly so as to gradually restrict or choke each exhaust passage 42, a considerable increase in interrupting ability has been achieved. The actual reason for this is not known with certainty at present, but the following theory may apply. lt is to be clearly understood, however, that we are not limited or bound by our present theory of the operation, because regardless of any theory proposed, there is a distinct improvement in interrupting ability achieved. We feel, however, that a possible explanation may reside in the fact that when the arc is at the upper closed ends il of the slots liti, it is at a very high temperature, and as the gases are travelling upwardly thro-ugh the arc, they pass upwardly to the exhaust end of the arc chtite, in which passage they are cooled by the surfaces of the plates 29 and contract in volume.
The reduction of the cross-section of the gas path as the gases become progressively cooler maintains the dow at high velocity and increases the turbulence and consequently the back pressure maintaining a higher pressure in the interrupting space, and also giving a more uniform motion of the are in the slot. Even though this proposed theory may be incorrect, nevertheless the fact remains '4 that a substantial improvement is maintained by the construction set forth in our invention without increase in size, and only a slight increase in assembly labor.
Figs. 3 and 4 show more particularly the wedge-shaped plate 29. This plate 29 is wedge-shaped, as shown, and when employed in a stack with parallel spacers 35 will constriet the exhaust passages l2 between each pair of adjacent plates. Thus, the constricted exhaust passage 4Z may be formed either by wedge-shaped plates alone, with parallel spacers 35, or by wedge-shaped plates 29 with tapered spacers 35, as shown in Fig. 2.
The foregoing description of our invention indicates how we have increased the voltage interrupting ability of plate type circuit interrupters of the type set forth in the aforesaid patent by employing wedge-shaped plates 29, as shown in Figs. 3 and 4. Either parallel spacers 35, or tapered spacers 35, as shown in Fig. 2, may be employed with the wedge-shaped plates 29. We have set forth what we believe to be the best theoretical explanation for the phenomena involved but do not limit ourselves as to the correctness of said explanation. By only a small or negligible increase of assembly cost, we have improved the operation of plate type circuit interrupters of the foregoing type without increasing their overall dimensions by merely reducing the cross-section of the space between the plates 29 at the exhaust ends of the plates.
Although we have shown and described speciic structures, it is to be clearly understood that the same were merely for the purpose of illustration, and that changes and modifications may readily be made therein by those skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the appended claims.
We claim as our invention:
l. A circuit interruptor of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced wedgeshaped plates of insulating material, the thickness of each plate increasing in a direction toward the exhaust end of the arc chute, the plates being so disposed that the median plane of each plate is parallel to the median plane of every other plate, means for establishing an arc and moving it against the plates, and the exhaust passages between the plates decreasing in cross-sectional area at the exhaust end of the are chute.
2. A circuit interruptor of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced slotted wedge-shaped plates of insulating material, the thickness of each plate increasing in a direction toward the exhaust end of the arc chute, the plates being so disposed that the median plane ot each plate is parallel to the median plane of every other plate, means for establishing an arc and moving it into the slots and against the plates, and the exhaust passages between the plates decreasing in cross-sectional area at the exhaust end of the are chute.
3. A circuit interruptor of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a stack of spaced slightly wedgeshaped plate portions, means for establishing an arc, the established arc moving against the slightly wedgeshaped plate portions to effect the extinction thereof, spacing means positioning the slightly wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart which is comparable to the thickness of the plate portions, and the exhaust passages between the slightly wedge-shaped plate portions defined by the slightly wedge-shaped plate portions and by the spacing means becoming smaller toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
4. A circuit interruptor of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a stack of spaced Wedge-shaped slotted plate portions, means for establishing an arc, the established arc moving against the wedge-shaped slotted plate portions to effect the extinction thereof, spacing means positioning the wedge-shaped slotted plate portions a relatively short distance apart which is comparable to the thickness of the plate portion, and the exhaust passages between the Wedge-shaped slotted plate portions defined by the wedge-shaped slotted plate portions and by the spacing means becoming smaller toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
5. A circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced wedgeshaped plates of insulating material, each wedge-shaped plate having a closed-end slot extending inwardly from one end thereof, a pair of spacer strips separating adjacent wedge-shaped plates a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it through the slots provided by the several wedge-shaped plates, and the lateral distance between each pair of spacer strips diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
6. A circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced insulating wedge-shaped plate portions, spacing means extending along each side edge of the wedge-shaped plate portions separating adjacent wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially transversely against the insulating wedge-shaped plate portions to etfect the extinction thereof, and the lateral distance between the spacing means along one side edge of the wedge-shaped plate portions and the spacing means along the opposite side edge of the wedge-shaped plate portions progressively diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
7. A circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced slotted insulating wedge-shaped plate portions, spacing means extending along each side edge of the wedge-shaped plate portions separating adjacent wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially transversely against the wedge-shaped plate portions and into the slots thereof to effect the extinction thereof, and the lateral distance between the spacing means along one side edge of the slotted wedge-shaped plate portions and the spacing means along the opposite side edge of the slotted wedge-shaped plate portions progressively diminishing towards the exhaust end of the arc chute.
8. A circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced insulating wedge-shaped plate portions, side wall means extending along the opposite sides of the arc chute and spacing the wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially transversely against the insulating wedge-shaped plate portions to eiect the extinction thereof, and the lateral distance between the side wall means along one side of the arc chute and the side wall means along the opposite side of the arc chute progressively diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
9. A circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced insulating wedge-shaped plate portions having closed end slots therein, side wall means extending along the opposite sides of the arc chute and spacing the wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially trans versely against the insulating wedge-shaped plate portions and into the slots thereof to effect the extinction of the arc, and the lateral distance between the side wall means along one side of the arc chute and the side wall means along the opposite side of the arc chute progressively diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
l0. A circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a stack of spaced insulating Wedge-shaped plate portions, spacing means positioning the wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short disance apart to dene separate exhaust passages therebetween, the median plane of each wedge-shaped plate portion being parallel to the median plane of every other wedge-shaped plate portion so that the end wedge-shaped plate portions of the stack are parallel to each other thereby obtaining adequate ash-over distance at the exhaust end of the arc chute, means for establishing an arc, means for moving the established arc substantially transversely against the wedge-shaped plate portions to eiect the extinction thereof, and the cross-sectional area of the exhaust passages through the wedge-shaped plate portions defined by the spacing means and by the wedgeshaped plate portions becoming progressively smaller toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
l1. A circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a stack of spaced insulating wedge-shaped plate portions having closed end slots therein, spacing means positioning the wedge-shaped plate portions a relatively short distance apart to define separate exhaust passages therebetween, the median plane of each wedge-shaped plate portion being parallel to the median plane of every other wedge-shaped plate portion so that the end wedge-shaped plate portions of the stack are parallel to each other thereby obtaining adequate ash-over distance at the exhaust end of the arc chute, means for establishing an arc, means for moving the established arc into the slots of the wedge-shaped plate portions substantially transversely against the wedge-shaped plate portions to effect the extinction thereof, and the cross-sectional area of the exhaust passages through the wedgeshaped plate portions defined by the spacing means and by the wedge-shaped plate portions becoming progressively smaller toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
12. A circuit interrupter of the airbreak type including an arc chute comprising a plurality of spaced wedgeshaped plates of insulating material, a pair of spacer strips separating adjacent wedge-shaped plates a relatively short distance apart, means for establishing an arc and moving it substantially transversely against the wedge-shaped plates to effect the extinction thereof, and the lateral distance between each pair of spacer strips diminishing toward the exhaust end of the arc chute.
Switzerland Sept. l, 1928 Great Britain Nov. 10, 1932
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB908/50A GB666941A (en) | 1949-02-23 | 1950-01-13 | Improvements in or relating to air break electric circuit interrupters |
| FR1017489D FR1017489A (en) | 1949-02-23 | 1950-02-22 | Air type circuit switch |
| US419753A US2777035A (en) | 1949-02-23 | 1954-03-30 | Air-type circuit interrupter |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US77794A US2687461A (en) | 1949-02-23 | 1949-02-23 | Air-type circuit interrupter |
| US419753A US2777035A (en) | 1949-02-23 | 1954-03-30 | Air-type circuit interrupter |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US2777035A true US2777035A (en) | 1957-01-08 |
Family
ID=26759678
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US419753A Expired - Lifetime US2777035A (en) | 1949-02-23 | 1954-03-30 | Air-type circuit interrupter |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US2777035A (en) |
| FR (1) | FR1017489A (en) |
| GB (1) | GB666941A (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2933574A (en) * | 1954-04-26 | 1960-04-19 | Westinghouse Electric Corp | Circuit interrupters |
| BE546847A (en) * | 1955-04-07 | |||
| DE1089038B (en) * | 1955-04-26 | 1960-09-15 | Carlor Emag Elek Zitaets Ag | Electric switch with arc length inside a jacket with iron disks |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US127629A (en) * | 1872-06-04 | Improvement in wash-boards | ||
| US383127A (en) * | 1888-05-22 | Oven attachment |
-
1950
- 1950-01-13 GB GB908/50A patent/GB666941A/en not_active Expired
- 1950-02-22 FR FR1017489D patent/FR1017489A/en not_active Expired
-
1954
- 1954-03-30 US US419753A patent/US2777035A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US127629A (en) * | 1872-06-04 | Improvement in wash-boards | ||
| US383127A (en) * | 1888-05-22 | Oven attachment |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| GB666941A (en) | 1952-02-20 |
| FR1017489A (en) | 1952-12-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2442199A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US2707739A (en) | Extinguishing device for electrical arcs | |
| US3555224A (en) | Arc chute for an air circuit breaker | |
| US2100753A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US2147419A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US2243040A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US1896779A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US2898427A (en) | Arc extinguishing means | |
| US2584570A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US2616006A (en) | Air break circuit interrupter | |
| US2734970A (en) | Circuit interrupters | |
| US2249499A (en) | Electric circuit interrupter | |
| US2777035A (en) | Air-type circuit interrupter | |
| US2372045A (en) | Switch | |
| US2446027A (en) | Arc chute | |
| US2871318A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US2933574A (en) | Circuit interrupters | |
| US2875303A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US2446859A (en) | Switch | |
| US2626331A (en) | Arc quenching device for electric contactors | |
| US2918552A (en) | Circuit interrupters | |
| US3641294A (en) | Arc chute for air circuit breaker | |
| US3538279A (en) | Blowout magnet structure for air-break circuit interrupter | |
| US2242905A (en) | Circuit interrupter | |
| US2655578A (en) | Arc chute with notched barrier plates |