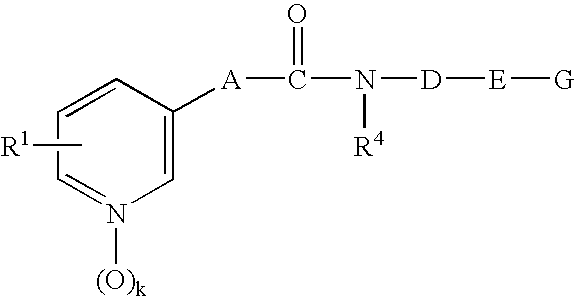
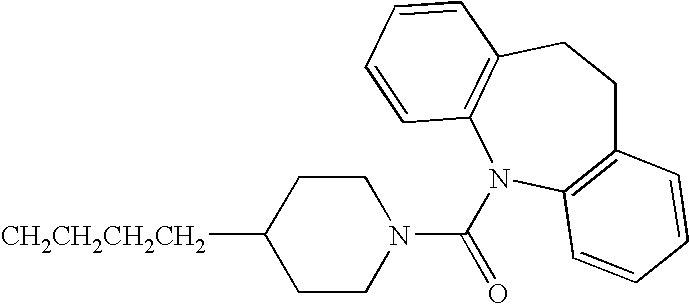
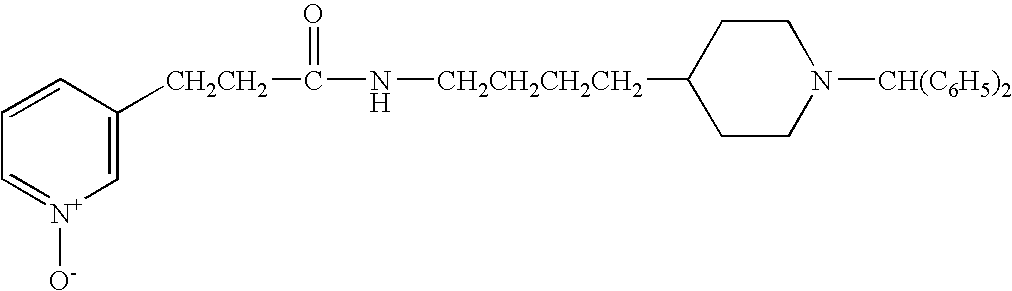US20040029861A1 - Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression - Google Patents
Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US20040029861A1 US20040029861A1 US10/208,253 US20825302A US2004029861A1 US 20040029861 A1 US20040029861 A1 US 20040029861A1 US 20825302 A US20825302 A US 20825302A US 2004029861 A1 US2004029861 A1 US 2004029861A1
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- alkyl
- hydrogen
- hydroxy
- ring
- group
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Abandoned
Links
- -1 pyridyl alkane Chemical class 0.000 title claims abstract description 489
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 title claims abstract description 18
- 230000001506 immunosuppresive effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 10
- 206010062016 Immunosuppression Diseases 0.000 title abstract description 3
- 125000000816 ethylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 claims description 173
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 172
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 172
- NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperidine Chemical compound C1CCNCC1 NQRYJNQNLNOLGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 156
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical class [H]* 0.000 claims description 124
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 123
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 108
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 107
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 claims description 94
- 125000004169 (C1-C6) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 93
- 125000001570 methylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([*:1])[*:2] 0.000 claims description 84
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 69
- 125000004191 (C1-C6) alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 60
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 claims description 59
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 claims description 58
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 58
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 52
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 52
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 claims description 52
- 125000006413 ring segment Chemical group 0.000 claims description 50
- 125000001797 benzyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 48
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 46
- 125000002023 trifluoromethyl group Chemical group FC(F)(F)* 0.000 claims description 46
- 125000006273 (C1-C3) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 45
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 42
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 claims description 42
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 40
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 39
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 claims description 38
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims description 38
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 38
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 36
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 36
- 125000004433 nitrogen atom Chemical group N* 0.000 claims description 36
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 claims description 35
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims description 33
- YNAVUWVOSKDBBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Morpholine Chemical compound C1COCCN1 YNAVUWVOSKDBBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 32
- RWRDLPDLKQPQOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrrolidine Chemical compound C1CCNC1 RWRDLPDLKQPQOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 32
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 31
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 30
- 125000004076 pyridyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 27
- 125000006552 (C3-C8) cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 26
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 claims description 26
- 125000000383 tetramethylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 claims description 26
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 22
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 22
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 claims description 22
- 125000001624 naphthyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 22
- XYOVOXDWRFGKEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N azepine Chemical compound N1C=CC=CC=C1 XYOVOXDWRFGKEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 claims description 20
- SFJGCXYXEFWEBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxazepine Chemical compound O1C=CC=CC=N1 SFJGCXYXEFWEBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- NYERMPLPURRVGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiazepine Chemical compound S1C=CC=CC=N1 NYERMPLPURRVGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- 125000000051 benzyloxy group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])O* 0.000 claims description 19
- 125000006700 (C1-C6) alkylthio group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000000824 cytostatic agent Substances 0.000 claims description 17
- 125000001584 benzyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group C(=O)(OCC1=CC=CC=C1)* 0.000 claims description 16
- 125000003342 alkenyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 15
- 125000006193 alkinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 15
- 125000006828 (C2-C7) alkoxycarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000004070 6 membered heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 14
- GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Piperazine Chemical compound C1CNCCN1 GLUUGHFHXGJENI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000003785 benzimidazolyl group Chemical group N1=C(NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000004618 benzofuryl group Chemical group O1C(=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000001164 benzothiazolyl group Chemical group S1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000004196 benzothienyl group Chemical group S1C(=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000004541 benzoxazolyl group Chemical group O1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000003016 chromanyl group Chemical group O1C(CCC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000002541 furyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000001041 indolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 14
- UYWQUFXKFGHYNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenylmethyl ester of formic acid Natural products O=COCC1=CC=CC=C1 UYWQUFXKFGHYNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000005493 quinolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000001544 thienyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 14
- 125000002947 alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 13
- 125000000753 cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 13
- 125000004454 (C1-C6) alkoxycarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000001715 oxadiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000002971 oxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000004043 oxo group Chemical group O=* 0.000 claims description 12
- RAHZWNYVWXNFOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfur dioxide Inorganic materials O=S=O RAHZWNYVWXNFOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000005931 tert-butyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(OC(*)=O)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000001113 thiadiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000000335 thiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000004450 alkenylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000004453 alkoxycarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- ZSIQJIWKELUFRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N azepane Chemical compound C1CCCNCC1 ZSIQJIWKELUFRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000002883 imidazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen Substances N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000006832 (C1-C10) alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000006274 (C1-C3)alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- YBYIRNPNPLQARY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-indene Natural products C1=CC=C2CC=CC2=C1 YBYIRNPNPLQARY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000003368 amide group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000003917 carbamoyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])C(*)=O 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000003454 indenyl group Chemical group C1(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000003387 indolinyl group Chemical group N1(CCC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000003373 pyrazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000003226 pyrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000000714 pyrimidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000001085 cytostatic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- PXBRQCKWGAHEHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N dichlorodifluoromethane Chemical group FC(F)(Cl)Cl PXBRQCKWGAHEHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000003983 fluorenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3CC12)* 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000001712 tetrahydronaphthyl group Chemical group C1(CCCC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000006823 (C1-C6) acyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- CVEXTAUZJWYDJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3,4,10-Tetrahydro-9(2H)-acridinone Chemical compound N1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C2=C1CCCC2 CVEXTAUZJWYDJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- UKHJNJFJCGBKSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane Chemical compound C1NC2CNC1C2 UKHJNJFJCGBKSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000006577 C1-C6 hydroxyalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- SIKJAQJRHWYJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Indole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC=CC2=C1 SIKJAQJRHWYJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000000641 acridinyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=NC3=CC=CC=C3C=C12)* 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000004419 alkynylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000005428 anthryl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C2C([H])=C3C(*)=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C3=C([H])C2=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000004601 benzofurazanyl group Chemical group N1=C2C(=NO1)C(=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000004619 benzopyranyl group Chemical group O1C(C=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000003354 benzotriazolyl group Chemical group N1N=NC2=C1C=CC=C2* 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000005046 dihydronaphthyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000003392 indanyl group Chemical group C1(CCC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 8
- GWVMLCQWXVFZCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoindoline Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CNCC2=C1 GWVMLCQWXVFZCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000005956 isoquinolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000001786 isothiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000000842 isoxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000001160 methoxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])OC(*)=O 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000002950 monocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000001484 phenothiazinyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2SC3=CC=CC=C3NC12)* 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000002098 pyridazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000000168 pyrrolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000002294 quinazolinyl group Chemical group N1=C(N=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 8
- LBUJPTNKIBCYBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydroquinoline Natural products C1=CC=C2CCCNC2=C1 LBUJPTNKIBCYBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000001425 triazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000003161 (C1-C6) alkylene group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- HONIICLYMWZJFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N azetidine Chemical compound C1CNC1 HONIICLYMWZJFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000002915 carbonyl group Chemical group [*:2]C([*:1])=O 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000005982 diphenylmethyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])(*)C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 7
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000006795 (C2-C7) alkoxycarbonyloxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004761 (C2-C7) alkylaminocarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004763 (C3-C13) dialkylaminocarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- DJWDAKFSDBOQJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane Chemical compound C1NC2CCC1NC2 DJWDAKFSDBOQJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- ASSKVPFEZFQQNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-benzoxazolinone Chemical compound C1=CC=C2OC(O)=NC2=C1 ASSKVPFEZFQQNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- YEDUAINPPJYDJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxybenzothiazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2SC(O)=NC2=C1 YEDUAINPPJYDJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- VSWICNJIUPRZIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-piperideine Chemical compound C1CNC=CC1 VSWICNJIUPRZIK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- GYLMCBOAXJVARF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane Chemical compound C1C2CCC1NC2 GYLMCBOAXJVARF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- SNZSSCZJMVIOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane Chemical compound C1CC2CCC1N2 SNZSSCZJMVIOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N Ascorbic acid Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(O)=C1O CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
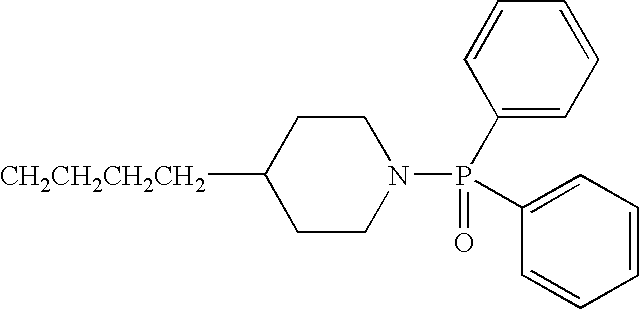
- VWBYXJRDIQCSLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N O=[P](c1ccccc1)c1ccccc1 Chemical group O=[P](c1ccccc1)c1ccccc1 VWBYXJRDIQCSLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000002252 acyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004423 acyloxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000003302 alkenyloxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004414 alkyl thio group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- QXNDZONIWRINJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N azocane Chemical compound C1CCCNCCC1 QXNDZONIWRINJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004603 benzisoxazolyl group Chemical group O1N=C(C2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000005874 benzothiadiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000000609 carbazolyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3NC12)* 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004617 chromonyl group Chemical group O1C(=CC(C2=CC=CC=C12)=O)* 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004598 dihydrobenzofuryl group Chemical group O1C(CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004582 dihydrobenzothienyl group Chemical group S1C(CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000005678 ethenylene group Chemical group [H]C([*:1])=C([H])[*:2] 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000005677 ethinylene group Chemical group [*:2]C#C[*:1] 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000002768 hydroxyalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000005945 imidazopyridyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000002519 immonomodulatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000003018 immunosuppressive agent Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229940125721 immunosuppressive agent Drugs 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004593 naphthyridinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=CC2=CC=CN=C12)* 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- AQNQGBUEVCAVML-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxazepane Chemical compound C1CCNOCC1 AQNQGBUEVCAVML-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004430 oxygen atom Chemical group O* 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000000719 pyrrolidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000001567 quinoxalinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=NC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 claims description 6
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M salicylate Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004306 triazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- CFTOTSJVQRFXOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole Chemical compound N1C2=CC=CC=C2C2=C1CNCC2 CFTOTSJVQRFXOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- DGGKXQQCVPAUEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane Chemical compound C1CCC2CCC1N2 DGGKXQQCVPAUEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- HSUGRBWQSSZJOP-RTWAWAEBSA-N diltiazem Chemical group C1=CC(OC)=CC=C1[C@H]1[C@@H](OC(C)=O)C(=O)N(CCN(C)C)C2=CC=CC=C2S1 HSUGRBWQSSZJOP-RTWAWAEBSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
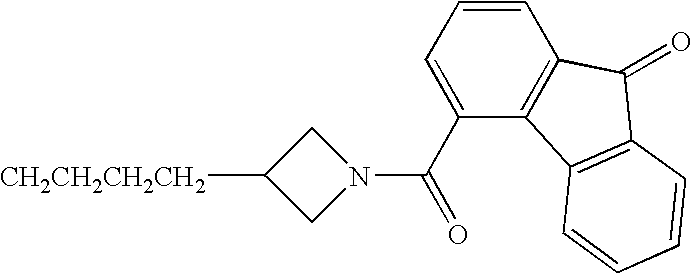
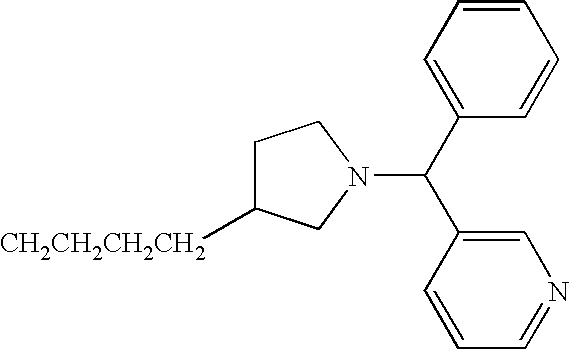
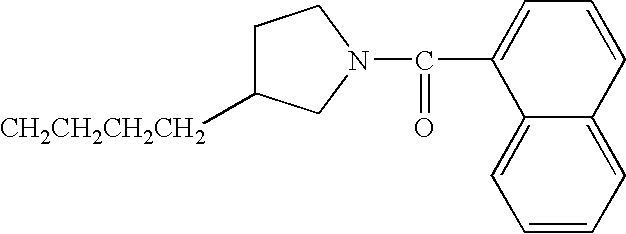
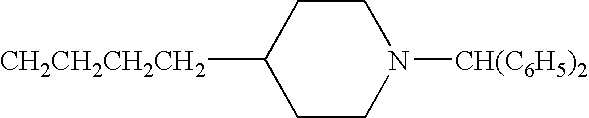
- JBSPSVYVYTWQNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 JBSPSVYVYTWQNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000003386 piperidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000000229 (C1-C4)alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004890 (C1-C6) alkylamino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004739 (C1-C6) alkylsulfonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000005913 (C3-C6) cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- QLDQYRDCPNBPII-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-benzoxazol-3-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(O)=NOC2=C1 QLDQYRDCPNBPII-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- NDOVLWQBFFJETK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-thiazinane 1,1-dioxide Chemical compound O=S1(=O)CCNCC1 NDOVLWQBFFJETK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- WJFKNYWRSNBZNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 10H-phenothiazine Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC3=CC=CC=C3SC2=C1 WJFKNYWRSNBZNX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- TZMSYXZUNZXBOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 10H-phenoxazine Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC3=CC=CC=C3OC2=C1 TZMSYXZUNZXBOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- XHYAKZQOCMEICX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1h-[1,3]oxazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-one Chemical compound C1=CN=C2OC(=O)NC2=C1 XHYAKZQOCMEICX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- KPUSZZFAYGWAHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane Chemical compound C1CC2CCC1NC2 KPUSZZFAYGWAHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- WYVFAIDIZFAWMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-azabicyclo[2.1.1]hexane Chemical compound C1CC2CC1N2 WYVFAIDIZFAWMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- VIQDTRXYTKXIMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5h-benzo[d][1]benzazepine Chemical compound N1C=CC2=CC=CC=C2C2=CC=CC=C12 VIQDTRXYTKXIMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- ATPGYYPVVKZFGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane Chemical compound C1CCC2CCCC1N2 ATPGYYPVVKZFGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen bromide Chemical class Br CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000005108 alkenylthio group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000005194 alkoxycarbonyloxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004457 alkyl amino carbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004390 alkyl sulfonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000002529 biphenylenyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3C12)* 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910002091 carbon monoxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004663 dialkyl amino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004473 dialkylaminocarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- QPMLSUSACCOBDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N diazepane Chemical compound C1CCNNCC1 QPMLSUSACCOBDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000003754 ethoxycarbonyl group Chemical group C(=O)(OCC)* 0.000 claims description 4
- AQYSYJUIMQTRMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N hypofluorous acid Chemical compound FO AQYSYJUIMQTRMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000003453 indazolyl group Chemical group N1N=C(C2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 claims description 4
- JXDYKVIHCLTXOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N isatin Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)C(=O)NC2=C1 JXDYKVIHCLTXOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004170 methylsulfonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 claims description 4
- WTQKSVWKIWLPLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[3-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)propyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 WTQKSVWKIWLPLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000005561 phenanthryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 4
- 235000021317 phosphate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 4
- USPWKWBDZOARPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrazolidine Chemical compound C1CNNC1 USPWKWBDZOARPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- BRNULMACUQOKMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiomorpholine Chemical compound C1CSCCN1 BRNULMACUQOKMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- XRHGYUZYPHTUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 4-chlorobenzoate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 XRHGYUZYPHTUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 4-hydroxybenzoate Chemical compound OC1=CC=C(C([O-])=O)C=C1 FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- ZEYHEAKUIGZSGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methoxybenzoic acid Chemical compound COC1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C1 ZEYHEAKUIGZSGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-M Formate Chemical compound [O-]C=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 229940072107 ascorbate Drugs 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000010323 ascorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011668 ascorbic acid Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000001860 citric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000000 cycloalkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000003937 drug carrier Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- JFCQEDHGNNZCLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N glutaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCC(O)=O JFCQEDHGNNZCLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000003840 hydrochlorides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- HYMGIVPAGRJMPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[2-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 HYMGIVPAGRJMPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- MAWXEKQEHAPAHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[3-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)propyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CN(C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)CCC1CCCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 MAWXEKQEHAPAHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- VZGLEQAAAJNIAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CN(C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 VZGLEQAAAJNIAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
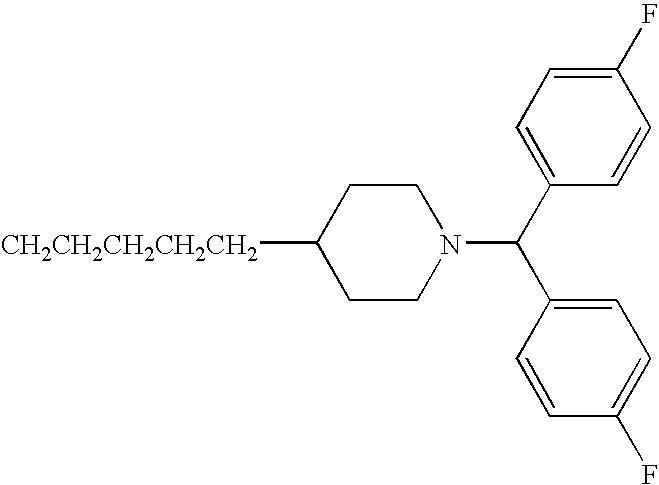
- IYCFQLMGHFHPSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-[bis(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC=C1C(C=1C(=CC=CC=1)Cl)N1CCC(CCCCNC(=O)C=CC=2C=NC=CC=2)CC1 IYCFQLMGHFHPSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- DQZSBXQOCDVKPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C1=CC(F)=CC=C1C(C=1C=CC(F)=CC=1)N1CCC(CCCCNC(=O)C=CC=2C=NC=CC=2)CC1 DQZSBXQOCDVKPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- BBNYHCSTHZADET-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-[cyclohexyl(phenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1CCCCC1 BBNYHCSTHZADET-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 claims description 3
- 229960001860 salicylate Drugs 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000003467 sulfuric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- KQTIIICEAUMSDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N tricarballylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KQTIIICEAUMSDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- KANAPVJGZDNSCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-benzothiazole 1-oxide Chemical compound C1=CC=C2S(=O)N=CC2=C1 KANAPVJGZDNSCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SWEICGMKXPNXNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-dihydroindazol-3-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(O)=NNC2=C1 SWEICGMKXPNXNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XBVTWEMNKKHPEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-dihydropyrazolo[4,3-b]pyridin-3-one Chemical class C1=CN=C2C(=O)NNC2=C1 XBVTWEMNKKHPEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- IRFSXVIRXMYULF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-dihydroquinoline Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C=CCNC2=C1 IRFSXVIRXMYULF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SILNNFMWIMZVEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dihydrobenzimidazol-2-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC(O)=NC2=C1 SILNNFMWIMZVEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PGDIPOWQYRAOSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dihydroimidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-2-one Chemical class C1=CN=C2NC(=O)NC2=C1 PGDIPOWQYRAOSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ZNGWEEUXTBNKFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-oxazepane Chemical group C1CNCCOC1 ZNGWEEUXTBNKFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XHLHPRDBBAGVEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-tetralone Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)CCCC2=C1 XHLHPRDBBAGVEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- NDVAMUMVOJRAJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 10h-phenanthren-9-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3C2=C1 NDVAMUMVOJRAJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HXNDHWLIFLZUKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1h-[1,3]thiazolo[5,4-b]pyridin-2-one Chemical class C1=CN=C2SC(O)=NC2=C1 HXNDHWLIFLZUKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000006067 2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- YQTCQNIPQMJNTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2-dimethylpropan-1-one Chemical group CC(C)(C)[C]=O YQTCQNIPQMJNTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ZBFZXENHYIJZGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4,4a-tetrahydrocarbazol-1-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C3CCCC(=O)C3=NC2=C1 ZBFZXENHYIJZGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000006040 2-hexenyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000006029 2-methyl-2-butenyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000094 2-phenylethyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003903 2-propenyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])=C([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- WYJIOQHUAOQNAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2h-cyclohepta[e][1]benzothiole 3-oxide Chemical class C1=CC=CC=C2C3=CCS(=O)C3=CC=C21 WYJIOQHUAOQNAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- TZOYXRMEFDYWDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,4-dihydro-1h-quinolin-2-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC(=O)CCC2=C1 TZOYXRMEFDYWDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FTAHXMZRJCZXDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-piperideine Chemical group C1CC=CCN1 FTAHXMZRJCZXDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MSTDXOZUKAQDRL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Chromanone Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)CCOC2=C1 MSTDXOZUKAQDRL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003119 4-methyl-3-pentenyl group Chemical group [H]\C(=C(/C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000006043 5-hexenyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(1-cyclopropylpyrazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl]-3-methyl-3,8-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-2-one Chemical class C1(CC1)N1N=CC(=C1)C1=NNC2=C1N=C(N=C2)N1C2C(N(CC1CC2)C)=O HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GDALETGZDYOOGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acridone Natural products C1=C(O)C=C2N(C)C3=CC=CC=C3C(=O)C2=C1O GDALETGZDYOOGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000002853 C1-C4 hydroxyalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- OCUCCJIRFHNWBP-IYEMJOQQSA-L Copper gluconate Chemical class [Cu+2].OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O.OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O OCUCCJIRFHNWBP-IYEMJOQQSA-L 0.000 claims description 2
- 208000007097 Urinary Bladder Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000001242 acetic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000002777 acetyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 claims description 2
- FZEYVTFCMJSGMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N acridone Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=C1 FZEYVTFCMJSGMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000013543 active substance Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- PYKYMHQGRFAEBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N anthraquinone Natural products CCC(=O)c1c(O)c2C(=O)C3C(C=CC=C3O)C(=O)c2cc1CC(=O)OC PYKYMHQGRFAEBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000004056 anthraquinones Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- RJGDLRCDCYRQOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N anthrone Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3CC2=C1 RJGDLRCDCYRQOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MYONAGGJKCJOBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzimidazol-2-one Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=NC(=O)N=C21 MYONAGGJKCJOBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DMSMPAJRVJJAGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzo[d]isothiazol-3-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)NSC2=C1 DMSMPAJRVJJAGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000001558 benzoic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- OTAFHZMPRISVEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N chromone Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)C=COC2=C1 OTAFHZMPRISVEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005366 cycloalkylthio group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001995 cyclobutyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- SJOFOLAJSGAHRL-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohepta[f]quinolin-1-one Chemical class C1=CC=CC2=C3C(=O)C=CN=C3C=CC2=C1 SJOFOLAJSGAHRL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000582 cycloheptyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000113 cyclohexyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000640 cyclooctyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001511 cyclopentyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001559 cyclopropyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004786 difluoromethoxy group Chemical group [H]C(F)(F)O* 0.000 claims description 2
- YLQWCDOCJODRMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluoren-9-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3C2=C1 YLQWCDOCJODRMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-L fumarate(2-) Chemical class [O-]C(=O)\C=C\C([O-])=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-L 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004634 hexahydroazepinyl group Chemical group N1(CCCCCC1)* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004051 hexyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- JXXWJMUPNZDILL-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-2-one Chemical class C1=CC=NC2=NC(=O)N=C21 JXXWJMUPNZDILL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- QNXSIUBBGPHDDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N indan-1-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)CCC2=C1 QNXSIUBBGPHDDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JYGFTBXVXVMTGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N indolin-2-one Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC(=O)CC2=C1 JYGFTBXVXVMTGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodine Chemical compound II PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005929 isobutyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])OC(*)=O 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005928 isopropyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(OC(*)=O)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003893 lactate salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 208000014018 liver neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000002688 maleic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000004701 malic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-M methanesulfonate group Chemical class CS(=O)(=O)[O-] AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000002757 morpholinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- ZUFZDOAYAQWLCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[(4-benzhydrylmorpholin-2-yl)methyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCC(OCC1)CN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 ZUFZDOAYAQWLCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- QEZKOYHOZVNHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[2-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CN(C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)CCC1CCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 QEZKOYHOZVNHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ROFQRYCTOBZTMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CN(CC=2C=CC=CC=2)CCC1CCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 ROFQRYCTOBZTMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JONFDAKGRPQNDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[2-[1-(2-phenylethyl)piperidin-4-yl]ethyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CN(CCC=2C=CC=CC=2)CCC1CCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 JONFDAKGRPQNDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FQTHEQNFMCCPND-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[2-[1-(4-phenylbutyl)piperidin-4-yl]ethyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CN(CCCCC=2C=CC=CC=2)CCC1CCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 FQTHEQNFMCCPND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VZNZAFAWOOBEDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-(2-fluoropyridin-3-yl)prop-2-enamide Chemical compound FC1=NC=CC=C1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC1CCN(C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)CC1 VZNZAFAWOOBEDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DNWDLXKLFYIPTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-(6-fluoropyridin-3-yl)prop-2-enamide Chemical compound C1=NC(F)=CC=C1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC1CCN(C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)CC1 DNWDLXKLFYIPTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YHYLPZLHKRPFNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide;dihydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.Cl.C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 YHYLPZLHKRPFNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ORFWYQXUNZBYFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide;methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O.C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 ORFWYQXUNZBYFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YKRYVWYPIDCPCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(CC1)CCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 YKRYVWYPIDCPCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VQTNGKYWKKGWHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-(2-phenylethyl)piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(CC1)CCN1CCC1=CC=CC=C1 VQTNGKYWKKGWHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YOOZOSOJTWMFFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C1CN(CC=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC=2)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CN=C1 YOOZOSOJTWMFFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HWYZLFOZABWCJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-[(4-phenylphenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(CC1)CCN1CC(C=C1)=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 HWYZLFOZABWCJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- NRRZYDHYTJKIQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[6-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)hexyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 NRRZYDHYTJKIQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001038 naphthoyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12)C(=O)* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005146 naphthylsulfonyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12)S(=O)(=O)* 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003891 oxalate salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000951 phenoxy group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(O*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003170 phenylsulfonyl group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=C1)S(=O)(=O)* 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003013 phosphoric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004193 piperazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001844 prenyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000006412 propinylene group Chemical group [H]C#CC([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004805 propylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 claims description 2
- TUPZMLLDXCWVKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrazolo[4,3-b]pyridin-3-one Chemical class C1=CN=C2C(=O)N=NC2=C1 TUPZMLLDXCWVKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005400 pyridylcarbonyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=CC=C1)C(=O)* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005344 pyridylmethyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(=N1)C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- LISFMEBWQUVKPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N quinolin-2-ol Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC(=O)C=CC2=C1 LISFMEBWQUVKPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229930185107 quinolinone Natural products 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005415 substituted alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003890 succinate salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004434 sulfur atom Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003892 tartrate salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000006318 tert-butyl amino group Chemical group [H]N(*)C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 2
- ZXLDQJLIBNPEFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydro-beta-carboline Natural products C1CNC(C)C2=C1C1=CC=C(OC)C=C1N2 ZXLDQJLIBNPEFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003718 tetrahydrofuranyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001412 tetrahydropyranyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005958 tetrahydrothienyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005301 thienylmethyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(S1)C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003396 thiol group Chemical group [H]S* 0.000 claims description 2
- OBIQBNMWIDNBAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N tricyclo[10.4.0.02,7]hexadeca-1,9,11,13,15-pentaen-3-one Chemical compound C1(CCCC2CC=CC=C3C(=C21)C=CC=C3)=O OBIQBNMWIDNBAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000000876 trifluoromethoxy group Chemical group FC(F)(F)O* 0.000 claims description 2
- AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-N Doxorubicin Chemical compound O([C@H]1C[C@@](O)(CC=2C(O)=C3C(=O)C=4C=CC=C(C=4C(=O)C3=C(O)C=21)OC)C(=O)CO)[C@H]1C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O1 AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- FBOZXECLQNJBKD-ZDUSSCGKSA-N L-methotrexate Chemical compound C=1N=C2N=C(N)N=C(N)C2=NC=1CN(C)C1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1 FBOZXECLQNJBKD-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- NWIBSHFKIJFRCO-WUDYKRTCSA-N Mytomycin Chemical compound C1N2C(C(C(C)=C(N)C3=O)=O)=C3[C@@H](COC(N)=O)[C@@]2(OC)[C@@H]2[C@H]1N2 NWIBSHFKIJFRCO-WUDYKRTCSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- NKANXQFJJICGDU-QPLCGJKRSA-N Tamoxifen Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C(/CC)=C(C=1C=CC(OCCN(C)C)=CC=1)/C1=CC=CC=C1 NKANXQFJJICGDU-QPLCGJKRSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- RJURFGZVJUQBHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N actinomycin D Natural products CC1OC(=O)C(C(C)C)N(C)C(=O)CN(C)C(=O)C2CCCN2C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C1NC(=O)C1=C(N)C(=O)C(C)=C2OC(C(C)=CC=C3C(=O)NC4C(=O)NC(C(N5CCCC5C(=O)N(C)CC(=O)N(C)C(C(C)C)C(=O)OC4C)=O)C(C)C)=C3N=C21 RJURFGZVJUQBHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- 230000000340 anti-metabolite Effects 0.000 claims 2
- 229940100197 antimetabolite Drugs 0.000 claims 2
- 239000002256 antimetabolite Substances 0.000 claims 2
- GLVAUDGFNGKCSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N mercaptopurine Chemical compound S=C1NC=NC2=C1NC=N2 GLVAUDGFNGKCSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- 229960000485 methotrexate Drugs 0.000 claims 2
- DIGQNXIGRZPYDK-WKSCXVIASA-N (2R)-6-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R,3S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[2-[[2-[[2-[(2-amino-1-hydroxyethylidene)amino]-3-carboxy-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxybutylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1,5-dihydroxy-5-iminopentylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxybutylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]hexanoic acid Chemical compound C[C@@H]([C@@H](C(=N[C@@H](CS)C(=N[C@@H](C)C(=N[C@@H](CO)C(=NCC(=N[C@@H](CCC(=N)O)C(=NC(CS)C(=N[C@H]([C@H](C)O)C(=N[C@H](CS)C(=N[C@H](CO)C(=NCC(=N[C@H](CS)C(=NCC(=N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)N=C([C@H](CS)N=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](C)N=C(CN=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](CS)N=C(CN=C(C(CS)N=C(C(CC(=O)O)N=C(CN)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O DIGQNXIGRZPYDK-WKSCXVIASA-N 0.000 claims 1
- FDKXTQMXEQVLRF-ZHACJKMWSA-N (E)-dacarbazine Chemical compound CN(C)\N=N\c1[nH]cnc1C(N)=O FDKXTQMXEQVLRF-ZHACJKMWSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 102100025573 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase Human genes 0.000 claims 1
- BGDOLELXXPTPFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2-benzoxazine Chemical compound C1=CC=C2ONCCC2=C1 BGDOLELXXPTPFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- BMVWCPGVLSILMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5,6-dihydrodibenzo[2,1-b:2',1'-f][7]annulen-11-one Chemical compound C1CC2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C21 BMVWCPGVLSILMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- STQGQHZAVUOBTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-Cyan-hept-2t-en-4,6-diinsaeure Natural products C1=2C(O)=C3C(=O)C=4C(OC)=CC=CC=4C(=O)C3=C(O)C=2CC(O)(C(C)=O)CC1OC1CC(N)C(O)C(C)O1 STQGQHZAVUOBTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 102100033350 ATP-dependent translocase ABCB1 Human genes 0.000 claims 1
- 206010000830 Acute leukaemia Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 108010024976 Asparaginase Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 108010006654 Bleomycin Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 206010006187 Breast cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000026310 Breast neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- COVZYZSDYWQREU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Busulfan Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)OCCCCOS(C)(=O)=O COVZYZSDYWQREU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 208000017897 Carcinoma of esophagus Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- DLGOEMSEDOSKAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carmustine Chemical compound ClCCNC(=O)N(N=O)CCCl DLGOEMSEDOSKAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- CMSMOCZEIVJLDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cyclophosphamide Chemical compound ClCCN(CCCl)P1(=O)NCCCO1 CMSMOCZEIVJLDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229930105110 Cyclosporin A Natural products 0.000 claims 1
- PMATZTZNYRCHOR-CGLBZJNRSA-N Cyclosporin A Chemical compound CC[C@@H]1NC(=O)[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@H](C)C\C=C\C)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)N(C)C(=O)[C@@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)N(C)C(=O)CN(C)C1=O PMATZTZNYRCHOR-CGLBZJNRSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 108010036949 Cyclosporine Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 108010036941 Cyclosporins Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- UHDGCWIWMRVCDJ-CCXZUQQUSA-N Cytarabine Chemical compound O=C1N=C(N)C=CN1[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 UHDGCWIWMRVCDJ-CCXZUQQUSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 108010092160 Dactinomycin Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- GHASVSINZRGABV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorouracil Chemical compound FC1=CNC(=O)NC1=O GHASVSINZRGABV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 102000005720 Glutathione transferase Human genes 0.000 claims 1
- 108010070675 Glutathione transferase Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- BLCLNMBMMGCOAS-URPVMXJPSA-N Goserelin Chemical compound C([C@@H](C(=O)N[C@H](COC(C)(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)N1[C@@H](CCC1)C(=O)NNC(N)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CC=1C2=CC=CC=C2NC=1)NC(=O)[C@H](CC=1NC=NC=1)NC(=O)[C@H]1NC(=O)CC1)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 BLCLNMBMMGCOAS-URPVMXJPSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 108010069236 Goserelin Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 208000017604 Hodgkin disease Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000010747 Hodgkins lymphoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- VSNHCAURESNICA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydroxyurea Chemical compound NC(=O)NO VSNHCAURESNICA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 208000008839 Kidney Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 206010058467 Lung neoplasm malignant Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 206010025323 Lymphomas Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 108010047230 Member 1 Subfamily B ATP Binding Cassette Transporter Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 102000003792 Metallothionein Human genes 0.000 claims 1
- 108090000157 Metallothionein Proteins 0.000 claims 1
- 206010033128 Ovarian cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 229930012538 Paclitaxel Natural products 0.000 claims 1
- 206010060862 Prostate cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 206010038389 Renal cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 206010039491 Sarcoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000000453 Skin Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 231100000632 Spindle poison Toxicity 0.000 claims 1
- 208000005718 Stomach Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- QJJXYPPXXYFBGM-LFZNUXCKSA-N Tacrolimus Chemical compound C1C[C@@H](O)[C@H](OC)C[C@@H]1\C=C(/C)[C@@H]1[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)CC(=O)[C@H](CC=C)/C=C(C)/C[C@H](C)C[C@H](OC)[C@H]([C@H](C[C@H]2C)OC)O[C@@]2(O)C(=O)C(=O)N2CCCC[C@H]2C(=O)O1 QJJXYPPXXYFBGM-LFZNUXCKSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- FOCVUCIESVLUNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Thiotepa Chemical compound C1CN1P(N1CC1)(=S)N1CC1 FOCVUCIESVLUNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 208000024770 Thyroid neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- RJURFGZVJUQBHK-IIXSONLDSA-N actinomycin D Chemical compound C[C@H]1OC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)N(C)C(=O)CN(C)C(=O)[C@@H]2CCCN2C(=O)[C@@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H]1NC(=O)C1=C(N)C(=O)C(C)=C2OC(C(C)=CC=C3C(=O)N[C@@H]4C(=O)N[C@@H](C(N5CCC[C@H]5C(=O)N(C)CC(=O)N(C)[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)O[C@@H]4C)=O)C(C)C)=C3N=C21 RJURFGZVJUQBHK-IIXSONLDSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 208000024447 adrenal gland neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 229940100198 alkylating agent Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 239000002168 alkylating agent Substances 0.000 claims 1
- VSRXQHXAPYXROS-UHFFFAOYSA-N azanide;cyclobutane-1,1-dicarboxylic acid;platinum(2+) Chemical compound [NH2-].[NH2-].[Pt+2].OC(=O)C1(C(O)=O)CCC1 VSRXQHXAPYXROS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960002170 azathioprine Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- LMEKQMALGUDUQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N azathioprine Chemical compound CN1C=NC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1SC1=NC=NC2=C1NC=N2 LMEKQMALGUDUQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 206010061691 benign mesothelioma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 125000003236 benzoyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C(*)=O 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001561 bleomycin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- OYVAGSVQBOHSSS-UAPAGMARSA-O bleomycin A2 Chemical compound N([C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@H](O)C)C(=O)NCCC=1SC=C(N=1)C=1SC=C(N=1)C(=O)NCCC[S+](C)C)[C@@H](O[C@H]1[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](CO)O1)O[C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H](OC(N)=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1)O)C=1N=CNC=1)C(=O)C1=NC([C@H](CC(N)=O)NC[C@H](N)C(N)=O)=NC(N)=C1C OYVAGSVQBOHSSS-UAPAGMARSA-O 0.000 claims 1
- 206010006007 bone sarcoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000003362 bronchogenic carcinoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 229960002092 busulfan Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960004562 carboplatin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960005243 carmustine Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 208000024207 chronic leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001265 ciclosporin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- DQLATGHUWYMOKM-UHFFFAOYSA-L cisplatin Chemical compound N[Pt](N)(Cl)Cl DQLATGHUWYMOKM-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims 1
- 229960004316 cisplatin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960004397 cyclophosphamide Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229930182912 cyclosporin Natural products 0.000 claims 1
- 229960000684 cytarabine Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960003901 dacarbazine Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960000640 dactinomycin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- STQGQHZAVUOBTE-VGBVRHCVSA-N daunorubicin Chemical compound O([C@H]1C[C@@](O)(CC=2C(O)=C3C(=O)C=4C=CC=C(C=4C(=O)C3=C(O)C=21)OC)C(C)=O)[C@H]1C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O1 STQGQHZAVUOBTE-VGBVRHCVSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960000975 daunorubicin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003534 dna topoisomerase inhibitor Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 229960004679 doxorubicin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960005420 etoposide Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- VJJPUSNTGOMMGY-MRVIYFEKSA-N etoposide Chemical compound COC1=C(O)C(OC)=CC([C@@H]2C3=CC=4OCOC=4C=C3[C@@H](O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H]4O[C@H](C)OC[C@H]4O3)O)[C@@H]3[C@@H]2C(OC3)=O)=C1 VJJPUSNTGOMMGY-MRVIYFEKSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 208000021045 exocrine pancreatic carcinoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 229960002949 fluorouracil Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 206010017758 gastric cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003862 glucocorticoid Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 229960002913 goserelin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001330 hydroxycarbamide Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 238000009830 intercalation Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 201000002313 intestinal cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- UWKQSNNFCGGAFS-XIFFEERXSA-N irinotecan Chemical compound C1=C2C(CC)=C3CN(C(C4=C([C@@](C(=O)OC4)(O)CC)C=4)=O)C=4C3=NC2=CC=C1OC(=O)N(CC1)CCC1N1CCCCC1 UWKQSNNFCGGAFS-XIFFEERXSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960004768 irinotecan Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 201000010982 kidney cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000032839 leukemia Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 201000007270 liver cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 201000005296 lung carcinoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000006178 malignant mesothelioma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 201000001441 melanoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001924 melphalan Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- SGDBTWWWUNNDEQ-LBPRGKRZSA-N melphalan Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(N(CCCl)CCCl)C=C1 SGDBTWWWUNNDEQ-LBPRGKRZSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001428 mercaptopurine Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960004857 mitomycin Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- KKZJGLLVHKMTCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N mitoxantrone Chemical compound O=C1C2=C(O)C=CC(O)=C2C(=O)C2=C1C(NCCNCCO)=CC=C2NCCNCCO KKZJGLLVHKMTCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001156 mitoxantrone Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- VSVJUHOKUBMZNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[2-[1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyl)piperidin-4-yl]ethyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C(O)CCCN(CC1)CCC1CCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 VSVJUHOKUBMZNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- HEEAWDWOOFRISF-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[5-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)pentyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 HEEAWDWOOFRISF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001592 paclitaxel Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 208000008443 pancreatic carcinoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000003154 papilloma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000029211 papillomatosis Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 201000001514 prostate carcinoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 206010038038 rectal cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 208000020615 rectal carcinoma Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 201000000849 skin cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 201000011549 stomach cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 229940037128 systemic glucocorticoids Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- QJJXYPPXXYFBGM-SHYZHZOCSA-N tacrolimus Natural products CO[C@H]1C[C@H](CC[C@@H]1O)C=C(C)[C@H]2OC(=O)[C@H]3CCCCN3C(=O)C(=O)[C@@]4(O)O[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@H]4C)OC)[C@@H](C[C@H](C)CC(=C[C@@H](CC=C)C(=O)C[C@H](O)[C@H]2C)C)OC QJJXYPPXXYFBGM-SHYZHZOCSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001967 tacrolimus Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001603 tamoxifen Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-N taxol Chemical compound O([C@@H]1[C@@]2(C[C@@H](C(C)=C(C2(C)C)[C@H](C([C@]2(C)[C@@H](O)C[C@H]3OC[C@]3([C@H]21)OC(C)=O)=O)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(=O)C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC=CC=1)O)C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 210000001550 testis Anatomy 0.000 claims 1
- 229960001196 thiotepa Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- 201000002510 thyroid cancer Diseases 0.000 claims 1
- 229940044693 topoisomerase inhibitor Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- UCFGDBYHRUNTLO-QHCPKHFHSA-N topotecan Chemical compound C1=C(O)C(CN(C)C)=C2C=C(CN3C4=CC5=C(C3=O)COC(=O)[C@]5(O)CC)C4=NC2=C1 UCFGDBYHRUNTLO-QHCPKHFHSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960000303 topotecan Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- OGWKCGZFUXNPDA-XQKSVPLYSA-N vincristine Chemical compound C([N@]1C[C@@H](C[C@]2(C(=O)OC)C=3C(=CC4=C([C@]56[C@H]([C@@]([C@H](OC(C)=O)[C@]7(CC)C=CCN([C@H]67)CC5)(O)C(=O)OC)N4C=O)C=3)OC)C[C@@](C1)(O)CC)CC1=C2NC2=CC=CC=C12 OGWKCGZFUXNPDA-XQKSVPLYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960004528 vincristine Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- OGWKCGZFUXNPDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N vincristine Natural products C1C(CC)(O)CC(CC2(C(=O)OC)C=3C(=CC4=C(C56C(C(C(OC(C)=O)C7(CC)C=CCN(C67)CC5)(O)C(=O)OC)N4C=O)C=3)OC)CN1CCC1=C2NC2=CC=CC=C12 OGWKCGZFUXNPDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- FKBHRUQOROFRGD-IELIFDKJSA-N vinorelbine Chemical compound C1N(CC=2[C]3C=CC=CC3=NC=22)CC(CC)=C[C@H]1C[C@]2(C(=O)OC)C1=CC([C@]23[C@H]([C@@]([C@H](OC(C)=O)[C@]4(CC)C=CCN([C@H]34)CC2)(O)C(=O)OC)N2C)=C2C=C1OC FKBHRUQOROFRGD-IELIFDKJSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 229960002066 vinorelbine Drugs 0.000 claims 1
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 155
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 119
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 110
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 103
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 85
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 83
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 77
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 77
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 75
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 73
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N Trichloro(2H)methane Chemical compound [2H]C(Cl)(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N 0.000 description 60
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 54
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 52
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 50
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 41
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 40
- CTSLXHKWHWQRSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxalyl chloride Chemical compound ClC(=O)C(Cl)=O CTSLXHKWHWQRSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 40
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 40
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 40
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 39
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 34
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 34
- 235000011152 sodium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 34
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 32
- 238000000425 proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum Methods 0.000 description 31
- 238000002329 infrared spectrum Methods 0.000 description 30
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 29
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 28
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 27
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 27
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 25
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 25
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 24
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical group C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 22
- BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium carbonate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C([O-])=O BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 22
- 239000008346 aqueous phase Substances 0.000 description 21
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 21
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 19
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 230000007717 exclusion Effects 0.000 description 18
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 18
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1 UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 15
- 235000019198 oils Nutrition 0.000 description 15
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 13
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 13
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 13
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 13
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propylene glycol Chemical compound CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 125000003258 trimethylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([*:2])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[*:1] 0.000 description 12
- VUVORVXMOLQFMO-ONEGZZNKSA-N (e)-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CN=C1 VUVORVXMOLQFMO-ONEGZZNKSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 239000000443 aerosol Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 11
- 229910000027 potassium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 235000011181 potassium carbonates Nutrition 0.000 description 11
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 10
- 125000006360 carbonyl amino methylene group Chemical group [H]N(C([*:1])=O)C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 description 10
- 150000001735 carboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 10
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 10
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 10
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 10
- RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N triphenylphosphine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- WVDDGKGOMKODPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Benzyl alcohol Chemical compound OCC1=CC=CC=C1 WVDDGKGOMKODPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical class [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 9
- VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Hexane Chemical compound CCCCCC VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 9
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N Lactose Natural products OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@@H]2CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000003925 fat Substances 0.000 description 8
- 235000019197 fats Nutrition 0.000 description 8
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000008101 lactose Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 8
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 238000010626 work up procedure Methods 0.000 description 8
- VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonium hydroxide Chemical compound [NH4+].[OH-] VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical class [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 7
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 7
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 7
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 7
- 150000002170 ethers Chemical class 0.000 description 7
- 239000002674 ointment Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 7
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 7
- 125000002221 trityl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1C([*])(C1=C(C(=C(C(=C1[H])[H])[H])[H])[H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 7
- ZAFNJMIOTHYJRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diisopropyl ether Chemical compound CC(C)OC(C)C ZAFNJMIOTHYJRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- IMNFDUFMRHMDMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Heptane Chemical compound CCCCCCC IMNFDUFMRHMDMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- SJRJJKPEHAURKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylmorpholine Chemical compound CN1CCOCC1 SJRJJKPEHAURKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- OFBQJSOFQDEBGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pentane Chemical compound CCCCC OFBQJSOFQDEBGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 6
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 238000003818 flash chromatography Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000002496 gastric effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000007903 gelatin capsule Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000036571 hydration Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000006703 hydration reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 239000012442 inert solvent Substances 0.000 description 6
- HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium stearate Chemical compound [Mg+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 6
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- NLKNQRATVPKPDG-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium iodide Chemical compound [K+].[I-] NLKNQRATVPKPDG-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 239000003380 propellant Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 6
- FVAUCKIRQBBSSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium iodide Chemical compound [Na+].[I-] FVAUCKIRQBBSSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 239000008347 soybean phospholipid Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 6
- NWZSZGALRFJKBT-KNIFDHDWSA-N (2s)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid;(2s)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O.NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O NWZSZGALRFJKBT-KNIFDHDWSA-N 0.000 description 5
- WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-Dichloroethane Chemical compound ClCCCl WSLDOOZREJYCGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000003776 cleavage reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 5
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 description 5
- IKDUDTNKRLTJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrazine monohydrate Substances O.NN IKDUDTNKRLTJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 5
- 239000013067 intermediate product Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 5
- CZDGUTFVAIPLLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-(4-piperidin-4-ylbutyl)-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CNCCC1CCCCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 CZDGUTFVAIPLLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 230000036961 partial effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- XKJCHHZQLQNZHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N phthalimide Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)NC(=O)C2=C1 XKJCHHZQLQNZHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000007017 scission Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- LVGUZGTVOIAKKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane Chemical compound FCC(F)(F)F LVGUZGTVOIAKKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VFWCMGCRMGJXDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-chlorobutane Chemical compound CCCCCl VFWCMGCRMGJXDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- ZWEHNKRNPOVVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Butanone Chemical compound CCC(C)=O ZWEHNKRNPOVVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- NGNBDVOYPDDBFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[2,4-di(pentan-2-yl)phenoxy]acetyl chloride Chemical compound CCCC(C)C1=CC=C(OCC(Cl)=O)C(C(C)CCC)=C1 NGNBDVOYPDDBFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N D-Mannitol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N 0.000 description 4
- XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethoxyethane Chemical compound COCCOC XTHFKEDIFFGKHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- LCGLNKUTAGEVQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethyl ether Chemical compound COC LCGLNKUTAGEVQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- ZHNUHDYFZUAESO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formamide Chemical compound NC=O ZHNUHDYFZUAESO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920000168 Microcrystalline cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 4
- HSHXDCVZWHOWCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N N'-hexadecylthiophene-2-carbohydrazide Chemical class CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCNNC(=O)c1cccs1 HSHXDCVZWHOWCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920001214 Polysorbate 60 Polymers 0.000 description 4
- ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propane Chemical compound CCC ATUOYWHBWRKTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000007868 Raney catalyst Substances 0.000 description 4
- NPXOKRUENSOPAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Raney nickel Chemical compound [Al].[Ni] NPXOKRUENSOPAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910000564 Raney nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bicarbonate Chemical compound [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium methoxide Chemical compound [Na+].[O-]C WQDUMFSSJAZKTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920002125 Sokalan® Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Chemical compound NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N beta-D-glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000013877 carbamide Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- PFKFTWBEEFSNDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbonyldiimidazole Chemical compound C1=CN=CN1C(=O)N1C=CN=C1 PFKFTWBEEFSNDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 4
- FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl n-ethoxycarbonyliminocarbamate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)N=NC(=O)OCC FAMRKDQNMBBFBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000004677 hydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000001866 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 229920003088 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 235000010979 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 238000001802 infusion Methods 0.000 description 4
- 235000010355 mannitol Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 235000019813 microcrystalline cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000008108 microcrystalline cellulose Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229940016286 microcrystalline cellulose Drugs 0.000 description 4
- OPZQARKHIZZICO-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-(4-piperidin-4-ylbutyl)-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide;dihydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.Cl.C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC1CCNCC1 OPZQARKHIZZICO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 239000003755 preservative agent Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229940080818 propionamide Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000344 soap Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910000104 sodium hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000012453 solvate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000012222 talc Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229940099259 vaseline Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 description 4
- LMDZBCPBFSXMTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide Substances CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C LMDZBCPBFSXMTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WPQJAHKNOGSQFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butan-1-amine Chemical compound C1CC(CCCCN)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPQJAHKNOGSQFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- HIQIXEFWDLTDED-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-hydroxy-1-piperidin-4-ylpyrrolidin-2-one Chemical compound O=C1CC(O)CN1C1CCNCC1 HIQIXEFWDLTDED-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- VZKFZHMCAPEJSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-piperidin-4-ylbutan-1-ol;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.OCCCCC1CCNCC1 VZKFZHMCAPEJSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DKPFZGUDAPQIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyl acetate Natural products CCCCOC(C)=O DKPFZGUDAPQIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- BUDQDWGNQVEFAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dihydropyran Chemical compound C1COC=CC1 BUDQDWGNQVEFAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000001856 Ethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 3
- ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl cellulose Chemical class CCOCC1OC(OC)C(OCC)C(OCC)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC)C(CO)O1 ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229920003134 Eudragit® polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylpyrrolidone Chemical compound CN1CCCC1=O SECXISVLQFMRJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004721 Polyphenylene oxide Substances 0.000 description 3
- XSTXAVWGXDQKEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trichloroethylene Chemical group ClC=C(Cl)Cl XSTXAVWGXDQKEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000029936 alkylation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005804 alkylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000008064 anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000006708 antioxidants Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000004945 aromatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 235000019445 benzyl alcohol Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 229920002988 biodegradable polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004621 biodegradable polymer Substances 0.000 description 3
- OQROAIRCEOBYJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromodiphenylmethane Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C(Br)C1=CC=CC=C1 OQROAIRCEOBYJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000010980 cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000008280 chlorinated hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000012230 colorless oil Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000013270 controlled release Methods 0.000 description 3
- 235000019325 ethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 229920001249 ethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 238000005187 foaming Methods 0.000 description 3
- 235000003599 food sweetener Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000001035 gastrointestinal tract Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 3
- FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-M hexanoate Chemical compound CCCCCC([O-])=O FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 235000019359 magnesium stearate Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000012188 paraffin wax Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 150000003053 piperidines Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000003880 polar aprotic solvent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000570 polyether Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920000193 polymethacrylate Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000001267 polyvinylpyrrolidone Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 3
- ZDYVRSLAEXCVBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridinium p-toluenesulfonate Chemical compound C1=CC=[NH+]C=C1.CC1=CC=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C1 ZDYVRSLAEXCVBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000009257 reactivity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229940100486 rice starch Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007920 subcutaneous administration Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000003459 sulfonic acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003765 sweetening agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000003626 triacylglycerols Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- UBOXGVDOUJQMTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N trichloroethylene Natural products ClCC(Cl)Cl UBOXGVDOUJQMTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000004044 trifluoroacetyl group Chemical group FC(C(=O)*)(F)F 0.000 description 3
- 150000003673 urethanes Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000008215 water for injection Substances 0.000 description 3
- WRIDQFICGBMAFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (E)-8-Octadecenoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCC(O)=O WRIDQFICGBMAFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YFMFNYKEUDLDTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C(F)C(F)(F)F YFMFNYKEUDLDTL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ASOKPJOREAFHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N(O)N=NC2=C1 ASOKPJOREAFHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VOULESRWHPXSSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)acetonitrile Chemical compound C1CC(CC#N)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 VOULESRWHPXSSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IRAIGQPDCDGJNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)ethanamine Chemical compound C1CC(CCN)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 IRAIGQPDCDGJNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-METHOXYETHANOL Chemical compound COCCO XNWFRZJHXBZDAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KSXXAAQEMXCLNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]isoindole-1,3-dione Chemical compound O=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)N1CCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 KSXXAAQEMXCLNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GFIWHEJCUQYQDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[4-[1-(6,11-dihydro-5h-dibenzo[1,2-a:1',2'-e][7]annulen-11-yl)piperidin-4-yl]butyl]isoindole-1,3-dione Chemical compound C12=CC=CC=C2CCC2=CC=CC=C2C1N(CC1)CCC1CCCCN1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C1=O GFIWHEJCUQYQDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CFMZSMGAMPBRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxyisoindole-1,3-dione Chemical class C1=CC=C2C(=O)N(O)C(=O)C2=C1 CFMZSMGAMPBRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LQJBNNIYVWPHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 20:1omega9c fatty acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O LQJBNNIYVWPHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FDGXGCMSMRSYFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)propan-1-amine Chemical compound C1CC(CCCN)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 FDGXGCMSMRSYFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UHRAXOALDKHWQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)propan-1-ol Chemical compound C1CC(CCCO)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 UHRAXOALDKHWQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UXFPMNSYBVPROG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)oxypropan-1-amine Chemical compound C1CC(OCCCN)CCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 UXFPMNSYBVPROG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(dimethylamino)propyliminomethylidene-ethylazanium;chloride Chemical compound Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QMCHNGAUKGVBGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butan-1-ol Chemical compound C1CC(CCCCO)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 QMCHNGAUKGVBGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KCIUHAPGAMLYAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(1-benzylpiperidin-3-ylidene)butanenitrile Chemical compound C1C(=CCCC#N)CCCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 KCIUHAPGAMLYAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BRKBMQMESFTHSC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[1-(6,11-dihydro-5h-dibenzo[1,2-a:1',2'-e][7]annulen-11-yl)piperidin-4-yl]butan-1-amine Chemical compound C1CC(CCCCN)CCN1C1C2=CC=CC=C2CCC2=CC=CC=C21 BRKBMQMESFTHSC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- SVPGRUQBRVZHBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[1-[bis(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]butanenitrile Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC=C1C(C=1C(=CC=CC=1)Cl)N1CCC(CCCC#N)CC1 SVPGRUQBRVZHBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7553-56-2 Chemical compound [I] ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QSBYPNXLFMSGKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-Heptadecensaeure Natural products CCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O QSBYPNXLFMSGKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 208000000044 Amnesia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 235000003911 Arachis Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 244000105624 Arachis hypogaea Species 0.000 description 2
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bisulfite Chemical compound OS([O-])=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 229920002134 Carboxymethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 2
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K Citrate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- GHVNFZFCNZKVNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Decanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCC(O)=O GHVNFZFCNZKVNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920002307 Dextran Polymers 0.000 description 2
- KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N EDTA Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000792859 Enema Species 0.000 description 2
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AEMRFAOFKBGASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycolic acid Chemical compound OCC(O)=O AEMRFAOFKBGASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010020651 Hyperkinesia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 2
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lactic Acid Natural products CC(O)C(O)=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004166 Lanolin Substances 0.000 description 2
- QPJVMBTYPHYUOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl benzoate Natural products COC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 QPJVMBTYPHYUOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butanol Chemical compound CCCCO LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MZRVEZGGRBJDDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Butyllithium Chemical compound [Li]CCCC MZRVEZGGRBJDDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NQTADLQHYWFPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Hydroxysuccinimide Chemical compound ON1C(=O)CCC1=O NQTADLQHYWFPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000009493 Neurokinin receptors Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108050000302 Neurokinin receptors Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 239000005642 Oleic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oleic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium Chemical compound [Na] KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000004147 Sorbitan trioleate Substances 0.000 description 2
- PRXRUNOAOLTIEF-ADSICKODSA-N Sorbitan trioleate Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC)[C@H]1OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC PRXRUNOAOLTIEF-ADSICKODSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229930006000 Sucrose Natural products 0.000 description 2
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N Sucrose Chemical compound O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DOOTYTYQINUNNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethyl citrate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CC(O)(C(=O)OCC)CC(=O)OCC DOOTYTYQINUNNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000209140 Triticum Species 0.000 description 2
- 235000021307 Triticum Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000005557 antagonist Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003266 anti-allergic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000010 aprotic solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000227 bioadhesive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000001273 butane Substances 0.000 description 2
- CJZGTCYPCWQAJB-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium stearate Chemical class [Ca+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O CJZGTCYPCWQAJB-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 230000003327 cancerostatic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004202 carbamide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000001768 carboxy methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010948 carboxy methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000008112 carboxymethyl-cellulose Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004359 castor oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000019438 castor oil Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 125000002091 cationic group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 150000001805 chlorine compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009833 condensation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005494 condensation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000013681 dietary sucrose Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000006196 drop Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007920 enema Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229940095399 enema Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002191 fatty alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000011389 fruit/vegetable juice Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N glycerol triricinoleate Natural products CCCCCC[C@@H](O)CC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@@H](COC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@@H](O)CCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CC[C@H](O)CCCCCC ZEMPKEQAKRGZGQ-XOQCFJPHSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- UKACHOXRXFQJFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N heptafluoropropane Chemical compound FC(F)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)F UKACHOXRXFQJFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NPZTUJOABDZTLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxybenzotriazole Substances O=C1C=CC=C2NNN=C12 NPZTUJOABDZTLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005457 ice water Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007943 implant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000007972 injectable composition Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011630 iodine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000012948 isocyanate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002513 isocyanates Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- FZWBNHMXJMCXLU-BLAUPYHCSA-N isomaltotriose Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1OC[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=O)O1 FZWBNHMXJMCXLU-BLAUPYHCSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QXJSBBXBKPUZAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N isooleic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QXJSBBXBKPUZAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000019388 lanolin Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000787 lecithin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000010445 lecithin Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000002502 liposome Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000004185 liver Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002609 medium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 2
- POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl undecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000010755 mineral Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000003097 mucus Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- IJDNQMDRQITEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-butane Chemical compound CCCC IJDNQMDRQITEOD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LKPFBGKZCCBZDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-hydroxypiperidine Chemical compound ON1CCCCC1 LKPFBGKZCCBZDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000003204 osmotic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 2
- DPBLXKKOBLCELK-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentan-1-amine Chemical compound CCCCCN DPBLXKKOBLCELK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000010412 perfusion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 2
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000003904 phospholipids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229920001308 poly(aminoacid) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920000747 poly(lactic acid) Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000008389 polyethoxylated castor oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004626 polylactic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- LPNYRYFBWFDTMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N potassium tert-butoxide Chemical compound [K+].CC(C)(C)[O-] LPNYRYFBWFDTMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001294 propane Substances 0.000 description 2
- UBQKCCHYAOITMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridin-2-ol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=N1 UBQKCCHYAOITMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003340 retarding agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 210000000813 small intestine Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000012312 sodium hydride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000009518 sodium iodide Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- GEHJYWRUCIMESM-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium sulfite Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])=O GEHJYWRUCIMESM-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 235000019337 sorbitan trioleate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229960000391 sorbitan trioleate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 238000001179 sorption measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000006190 sub-lingual tablet Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229960004793 sucrose Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 125000000472 sulfonyl group Chemical group *S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 2
- 230000002459 sustained effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001308 synthesis method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009885 systemic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- DYHSDKLCOJIUFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butoxycarbonyl anhydride Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)OC(=O)OC(C)(C)C DYHSDKLCOJIUFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HHOFUZXTBHKGTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-(4-aminobutyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)N1CCC(CCCCN)CC1 HHOFUZXTBHKGTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BMHPRMXSKRSFEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-[4-(1,3-dioxoisoindol-2-yl)butyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CCC1CCCCN1C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C1=O BMHPRMXSKRSFEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VGGCSKJNFCVWFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-[4-(3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enoylamino)butyl]piperidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CN=C1 VGGCSKJNFCVWFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IMFACGCPASFAPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N tributylamine Chemical compound CCCCN(CCCC)CCCC IMFACGCPASFAPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001069 triethyl citrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000013769 triethyl citrate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- VMYFZRTXGLUXMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N triethyl citrate Natural products CCOC(=O)C(O)(C(=O)OCC)C(=O)OCC VMYFZRTXGLUXMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UCPYLLCMEDAXFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N triphosgene Chemical compound ClC(Cl)(Cl)OC(=O)OC(Cl)(Cl)Cl UCPYLLCMEDAXFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011782 vitamin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000013343 vitamin Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229940088594 vitamin Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 229930003231 vitamin Natural products 0.000 description 2
- KISVATOISQDZJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N (1-benzhydrylazetidin-3-yl)methanamine Chemical compound C1C(CN)CN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 KISVATOISQDZJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JNYAEWCLZODPBN-JGWLITMVSA-N (2r,3r,4s)-2-[(1r)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]oxolane-3,4-diol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@H]1OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1O JNYAEWCLZODPBN-JGWLITMVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CXPBQHQMQFYHBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-benzhydrylmorpholin-2-yl)methanamine Chemical compound C1COC(CN)CN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 CXPBQHQMQFYHBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RZEKHHBDFHVIKG-HRNDJLQDSA-N (e)-n-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.C=1C=CN=CC=1/C=C/C(=O)NCCC(CC1)CCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 RZEKHHBDFHVIKG-HRNDJLQDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FQUYSHZXSKYCSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-diazepane Chemical group C1CNCCNC1 FQUYSHZXSKYCSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XKQHHIFXAXQKND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-(6,11-dihydro-5h-dibenzo[1,2-a:1',2'-e][7]annulen-11-yl)-4-[4-(oxan-2-yloxy)butyl]piperidine Chemical compound C1CN(C2C3=CC=CC=C3CCC3=CC=CC=C32)CCC1CCCCOC1CCCCO1 XKQHHIFXAXQKND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KZVHEGHIKAJHHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-[4-(oxan-2-yloxy)butyl]piperidine Chemical compound C1=CC(F)=CC=C1C(C=1C=CC(F)=CC=1)N1CCC(CCCCOC2OCCCC2)CC1 KZVHEGHIKAJHHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OTOZCOKGPNCTHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[bromo-(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]-2-chlorobenzene Chemical compound ClC1=CC=CC=C1C(Br)C1=CC=CC=C1Cl OTOZCOKGPNCTHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FHPNLCLHMNPLEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[chloro-(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-4-fluorobenzene Chemical compound C1=CC(F)=CC=C1C(Cl)C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 FHPNLCLHMNPLEW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IXMOEAHDRKNAAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzhydrylazetidine-3-carbonitrile Chemical compound C1C(C#N)CN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 IXMOEAHDRKNAAG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QLWJYOLYCKTBQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-one Chemical compound C1CC(=O)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 QLWJYOLYCKTBQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BBQQULRBTOMLTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzylpiperidin-3-one Chemical compound C1C(=O)CCCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 BBQQULRBTOMLTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CZVVUMKZOQLPLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-bromo-2-cyclohexyl-3-methylbenzene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC(Br)=C1C1CCCCC1 CZVVUMKZOQLPLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AXTGDCSMTYGJND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-dodecylazepan-2-one Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCN1CCCCCC1=O AXTGDCSMTYGJND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BDQNKCYCTYYMAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-isocyanatonaphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(N=C=O)=CC=CC2=C1 BDQNKCYCTYYMAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YXNMXALJJRGLOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 11-chloro-1,6-dihydrobenzo[c][1]benzothiepine Chemical compound S1CC2=CC=CC=C2C(Cl)=C2CC=CC=C21 YXNMXALJJRGLOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QPERNSDCEUTOTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 11-chloro-6,11-dihydro-5h-dibenzo[2,1-b:2',1'-f][7]annulene Chemical compound C1CC2=CC=CC=C2C(Cl)C2=CC=CC=C21 QPERNSDCEUTOTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LZGZDRSZOKQIHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 11-chloro-6,11-dihydrobenzo[c][1]benzoxepine Chemical compound C1OC2=CC=CC=C2C(Cl)C2=CC=CC=C21 LZGZDRSZOKQIHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VFTFKUDGYRBSAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 15-crown-5 Chemical compound C1COCCOCCOCCOCCO1 VFTFKUDGYRBSAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JVSFQJZRHXAUGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2-dimethylpropanoyl chloride Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C(Cl)=O JVSFQJZRHXAUGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SBJTWJOEGIOVIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-2-ylidene)acetonitrile Chemical compound N#CC=C1CCCCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 SBJTWJOEGIOVIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SMZOUWXMTYCWNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)ethanamine Chemical compound COC1=CC=C(C)C=C1CCN SMZOUWXMTYCWNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Propenoic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=C NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JYZKLVMEGXKECK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[3-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)propyl]isoindole-1,3-dione Chemical compound O=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)N1CCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 JYZKLVMEGXKECK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PSUYRMBDNRGWIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[4-[1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]butyl]isoindole-1,3-dione Chemical compound C1=CC(F)=CC=C1C(C=1C=CC(F)=CC=1)N1CCC(CCCCN2C(C3=CC=CC=C3C2=O)=O)CC1 PSUYRMBDNRGWIR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KWMBADTWRIGGGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-diethoxyphosphorylacetonitrile Chemical compound CCOP(=O)(CC#N)OCC KWMBADTWRIGGGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YEYKMVJDLWJFOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-propoxyethanol Chemical compound CCCOCCO YEYKMVJDLWJFOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MBEPWLCDXKKANL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-pyridin-3-yloxyacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)COC1=CC=CN=C1 MBEPWLCDXKKANL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XTUAIKRVIJDPCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)oxypropanenitrile Chemical compound C1CC(OCCC#N)CCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 XTUAIKRVIJDPCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VGUWZCUCNQXGBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-5-nitro-1h-indole Chemical compound C1CN(C)CCN1CC1=CNC2=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C12 VGUWZCUCNQXGBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PAOHMIPLGDOHBB-UHFFFAOYSA-M 3-cyanopropyl(triphenyl)phosphanium;bromide Chemical compound [Br-].C=1C=CC=CC=1[P+](C=1C=CC=CC=1)(CCCC#N)C1=CC=CC=C1 PAOHMIPLGDOHBB-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- BZISNWGGPWSXTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-hydroxypropyl benzoate Chemical compound OCCCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 BZISNWGGPWSXTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OENDTQFJHJVHQK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-piperidin-4-ylpropan-1-ol;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.OCCCC1CCNCC1 OENDTQFJHJVHQK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003349 3-pyridyl group Chemical group N1=C([H])C([*])=C([H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- GENJKOFYLOTVQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butan-1-ol;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.C1CC(CCCCO)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 GENJKOFYLOTVQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RLPWFOVVVNISHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl methanesulfonate Chemical compound C1CC(CCCCOS(=O)(=O)C)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 RLPWFOVVVNISHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IHUYMRIGAVJQHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(1-benzylpiperidin-3-yl)butan-1-amine Chemical compound C1C(CCCCN)CCCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 IHUYMRIGAVJQHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PIWCHIOHXASFFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[1-(6,11-dihydro-5h-dibenzo[1,2-a:1',2'-e][7]annulen-11-yl)piperidin-4-yl]butan-1-ol Chemical compound C1CC(CCCCO)CCN1C1C2=CC=CC=C2CCC2=CC=CC=C21 PIWCHIOHXASFFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YZYAKUNEKACFOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[1-[bis(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]butan-1-amine Chemical compound C1CC(CCCCN)CCN1C(C=1C(=CC=CC=1)Cl)C1=CC=CC=C1Cl YZYAKUNEKACFOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODINVFPWNGBRDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]butan-1-ol Chemical compound C1CC(CCCCO)CCN1C(C=1C=CC(F)=CC=1)C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 ODINVFPWNGBRDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001255 4-fluorophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C([H])C([H])=C1F 0.000 description 1
- 125000004217 4-methoxybenzyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(=C([H])C([H])=C1OC([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- KSPCANKCJUNOOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-piperidin-4-ylbutanenitrile;hydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.N#CCCCC1CCNCC1 KSPCANKCJUNOOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YIURKEJHEYNOBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)pentan-1-amine Chemical compound C1CC(CCCCCN)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 YIURKEJHEYNOBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OCKGFTQIICXDQW-ZEQRLZLVSA-N 5-[(1r)-1-hydroxy-2-[4-[(2r)-2-hydroxy-2-(4-methyl-1-oxo-3h-2-benzofuran-5-yl)ethyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]-4-methyl-3h-2-benzofuran-1-one Chemical compound C1=C2C(=O)OCC2=C(C)C([C@@H](O)CN2CCN(CC2)C[C@H](O)C2=CC=C3C(=O)OCC3=C2C)=C1 OCKGFTQIICXDQW-ZEQRLZLVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CCEWTWCJOWECLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-pyridin-3-ylpenta-2,4-dienoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C=CC=CC1=CC=CN=C1 CCEWTWCJOWECLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AHCDKANCCBEQJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-bromo-9h-fluorene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(Br)C3=CC=CC=C3C2=C1 AHCDKANCCBEQJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GJCOSYZMQJWQCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9H-xanthene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CC3=CC=CC=C3OC2=C1 GJCOSYZMQJWQCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 241000478345 Afer Species 0.000 description 1
- 108010088751 Albumins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000009027 Albumins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 208000024827 Alzheimer disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonium chloride Substances [NH4+].[Cl-] NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000031091 Amnestic disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000001381 Arachidonate 5-Lipoxygenase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010093579 Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- ISYLXLFROBJGFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C(=C12)N1C(CC(CC1)CCCCNC(C=CC=1C=NC=CC1)=O)C Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C(=C12)N1C(CC(CC1)CCCCNC(C=CC=1C=NC=CC1)=O)C ISYLXLFROBJGFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Carbonate Chemical compound [O-]C([O-])=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 201000009030 Carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 244000060011 Cocos nucifera Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000013162 Cocos nucifera Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920002261 Corn starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 244000303965 Cyamopsis psoralioides Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920000858 Cyclodextrin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- XDTMQSROBMDMFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cyclohexane Chemical compound C1CCCCC1 XDTMQSROBMDMFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N D-glucitol Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M D-gluconate Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000019739 Dicalciumphosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicylcohexylcarbodiimide Chemical compound C1CCCCC1N=C=NC1CCCCC1 QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GKQLYSROISKDLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N EEDQ Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N(C(=O)OCC)C(OCC)C=CC2=C1 GKQLYSROISKDLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Elaidinsaeure-aethylester Natural products CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930091371 Fructose Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 239000005715 Fructose Substances 0.000 description 1
- RFSUNEUAIZKAJO-ARQDHWQXSA-N Fructose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@](O)(CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O RFSUNEUAIZKAJO-ARQDHWQXSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010019695 Hepatic neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108091006905 Human Serum Albumin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000008100 Human Serum Albumin Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 229920002153 Hydroxypropyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 208000000269 Hyperkinesis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010020751 Hypersensitivity Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000005909 Kieselgur Substances 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-L L-tartrate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-L 0.000 description 1
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Lactate Chemical compound CC(O)C([O-])=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000005639 Lauric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 206010026749 Mania Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000003820 Medium-pressure liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- BZLVMXJERCGZMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl tert-butyl ether Chemical compound COC(C)(C)C BZLVMXJERCGZMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) Chemical compound CCN(C(C)C)C(C)C JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylacetamide Chemical compound CN(C)C(C)=O FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KPBNHDGDUADAGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-[4-(1-benzoyl-4-piperidinyl)butyl]-3-(3-pyridinyl)-2-propenamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 KPBNHDGDUADAGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005662 Paraffin oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019483 Peanut oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000954 Polyglycolide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M Propionate Chemical compound CCC([O-])=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- GUGOEEXESWIERI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Terfenadine Chemical compound C1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=CC=C1C(O)CCCN1CCC(C(O)(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)CC1 GUGOEEXESWIERI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethanolamine Chemical compound OCCN(CCO)CCO GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007983 Tris buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 240000008042 Zea mays Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000005824 Zea mays ssp. parviglumis Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000002017 Zea mays subsp mays Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- HCBRAEWDLZUPNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N [I+].CCCC[N+](CCCC)(CCCC)CCCC Chemical compound [I+].CCCC[N+](CCCC)(CCCC)CCCC HCBRAEWDLZUPNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KXKVLQRXCPHEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid trimethyl ester Natural products COC(C)=O KXKVLQRXCPHEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001252 acrylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001266 acyl halides Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N adipic acid Chemical class OC(=O)CCCCC(O)=O WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001338 aliphatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000288 alkali metal carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000008041 alkali metal carbonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910001516 alkali metal iodide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000005907 alkyl ester group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000007815 allergy Effects 0.000 description 1
- WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium hydroxide Chemical class [OH-].[OH-].[OH-].[Al+3] WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- CEGOLXSVJUTHNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium tristearate Chemical compound [Al+3].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O CEGOLXSVJUTHNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 229940063655 aluminum stearate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000001014 amino acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N ammonia Natural products N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000011114 ammonium hydroxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000006986 amnesia Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003708 ampul Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000000129 anionic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000008485 antagonism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003288 anthiarrhythmic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001387 anti-histamine Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000739 antihistaminic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003125 aqueous solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007900 aqueous suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008122 artificial sweetener Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003710 aryl alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000006254 arylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012752 auxiliary agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- PCCNIENXBRUYFK-UHFFFAOYSA-O azanium;cerium(4+);pentanitrate Chemical compound [NH4+].[Ce+4].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O PCCNIENXBRUYFK-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000012216 bentonite Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UDEWPOVQBGFNGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid n-propyl ester Natural products CCCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 UDEWPOVQBGFNGE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PASDCCFISLVPSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoyl chloride Chemical compound ClC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 PASDCCFISLVPSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AGEZXYOZHKGVCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl bromide Chemical compound BrCC1=CC=CC=C1 AGEZXYOZHKGVCM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HSDAJNMJOMSNEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl chloroformate Chemical compound ClC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 HSDAJNMJOMSNEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- RTRODVUDEWDGEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate;trichloromethyl hydrogen carbonate Chemical compound OC(=O)OC(Cl)(Cl)Cl.ClC(Cl)(Cl)OC(=O)OC(Cl)(Cl)Cl RTRODVUDEWDGEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 210000001124 body fluid Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000010839 body fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001649 bromium compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000000621 bronchi Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 244000309464 bull Species 0.000 description 1
- 125000000484 butyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001506 calcium phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013539 calcium stearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008116 calcium stearate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004657 carbamic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001718 carbodiimides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000005521 carbonamide group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- KXDHJXZQYSOELW-UHFFFAOYSA-N carbonic acid monoamide Natural products NC(O)=O KXDHJXZQYSOELW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001244 carboxylic acid anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- KXZJHVJKXJLBKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N chembl1408157 Chemical compound N=1C2=CC=CC=C2C(C(=O)O)=CC=1C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 KXZJHVJKXJLBKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007910 chewable tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- AOGYCOYQMAVAFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N chlorocarbonic acid Chemical class OC(Cl)=O AOGYCOYQMAVAFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000544 cholinesterase inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011097 chromatography purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910017052 cobalt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010941 cobalt Substances 0.000 description 1
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt atom Chemical compound [Co] GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003240 coconut oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019864 coconut oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000004440 column chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002648 combination therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000599 controlled substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000005822 corn Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008120 corn starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940097362 cyclodextrins Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000001472 cytotoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003405 delayed action preparation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- SNVTZAIYUGUKNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibenzo[1,2-a:1',2'-e][7]annulen-11-one Chemical compound C1=CC2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C2=CC=CC=C21 SNVTZAIYUGUKNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NEFBYIFKOOEVPA-UHFFFAOYSA-K dicalcium phosphate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[Ca+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NEFBYIFKOOEVPA-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 229940038472 dicalcium phosphate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910000390 dicalcium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000004069 differentiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000004925 dihydropyridyl group Chemical group N1(CC=CC=C1)* 0.000 description 1
- 238000010790 dilution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012895 dilution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003292 diminished effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- MPFLRYZEEAQMLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dinicotinic acid Chemical class OC(=O)C1=CN=CC(C(O)=O)=C1 MPFLRYZEEAQMLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FPAFDBFIGPHWGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N dioxosilane;oxomagnesium;hydrate Chemical compound O.[Mg]=O.[Mg]=O.[Mg]=O.O=[Si]=O.O=[Si]=O.O=[Si]=O.O=[Si]=O FPAFDBFIGPHWGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000007884 disintegrant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000004821 distillation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002552 dosage form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012377 drug delivery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007938 effervescent tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- JROGBPMEKVAPEH-GXGBFOEMSA-N emetine dihydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.Cl.N1CCC2=CC(OC)=C(OC)C=C2[C@H]1C[C@H]1C[C@H]2C3=CC(OC)=C(OC)C=C3CCN2C[C@@H]1CC JROGBPMEKVAPEH-GXGBFOEMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004945 emulsification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000003700 epoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000003628 erosive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002168 ethanoic acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- BEFDCLMNVWHSGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethenylcyclopentane Chemical compound C=CC1CCCC1 BEFDCLMNVWHSGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RIFGWPKJUGCATF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl chloroformate Chemical compound CCOC(Cl)=O RIFGWPKJUGCATF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004494 ethyl ester group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-QXMHVHEDSA-N ethyl oleate Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OCC LVGKNOAMLMIIKO-QXMHVHEDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940093471 ethyl oleate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003885 eye ointment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000010685 fatty oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012065 filter cake Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019634 flavors Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000007667 floating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000037406 food intake Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012458 free base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004392 genitalia Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940050410 gluconate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000004676 glycans Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003979 granulating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005469 granulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003179 granulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- JEGUKCSWCFPDGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N h2o hydrate Chemical compound O.O JEGUKCSWCFPDGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000008282 halocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000010224 hepatic metabolism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000008131 herbal destillate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004475 heteroaralkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004446 heteroarylalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- OHMBHFSEKCCCBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexane-2,5-diol Chemical compound CC(O)CCC(C)O OHMBHFSEKCCCBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000265 homogenisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000887 hydrating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000017 hydrogel Substances 0.000 description 1
- XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen iodide Chemical class I XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008311 hydrophilic ointment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- RIMIDGSPFGJFCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxymethyl benzoate Chemical compound OCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 RIMIDGSPFGJFCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004029 hydroxymethyl group Chemical group [H]OC([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 239000001863 hydroxypropyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010977 hydroxypropyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940031704 hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920003132 hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011065 in-situ storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001764 infiltration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008595 infiltration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003978 infusion fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007918 intramuscular administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001990 intravenous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- HVTICUPFWKNHNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodoethane Chemical compound CCI HVTICUPFWKNHNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003456 ion exchange resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003303 ion-exchange polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000644 isotonic solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940039717 lanolin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 210000002429 large intestine Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000002605 large molecules Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000000867 larynx Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- QDLAGTHXVHQKRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N lichenxanthone Natural products COC1=CC(O)=C2C(=O)C3=C(C)C=C(OC)C=C3OC2=C1 QDLAGTHXVHQKRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002632 lipids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012669 liquid formulation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012280 lithium aluminium hydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007937 lozenge Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004072 lung Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000000873 masking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002483 medication Methods 0.000 description 1
- HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N meso ribitol Natural products OCC(O)C(O)C(O)CO HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CS(Cl)(=O)=O QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FQRRQPZYIYAPAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl 3-pyridin-3-ylpropanoate Chemical compound COC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 FQRRQPZYIYAPAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940050176 methyl chloride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- XMJHPCRAQCTCFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl chloroformate Chemical compound COC(Cl)=O XMJHPCRAQCTCFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004292 methyl p-hydroxybenzoate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010270 methyl p-hydroxybenzoate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- OLXYLDUSSBULGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl pyridine-4-carboxylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=NC=C1 OLXYLDUSSBULGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- LXCFILQKKLGQFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N methylparaben Chemical compound COC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 LXCFILQKKLGQFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004530 micro-emulsion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003094 microcapsule Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004200 microcrystalline wax Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019808 microcrystalline wax Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011859 microparticle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- MOKNUCZPWDTLKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-(4-piperidin-4-ylbutyl)-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide;dihydrochloride Chemical compound Cl.Cl.C1CNCCC1CCCCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 MOKNUCZPWDTLKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YKYONYBAUNKHLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Propyl acetate Natural products CCCOC(C)=O YKYONYBAUNKHLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MVKYZUDWWZWERD-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[(1-benzhydrylazetidin-3-yl)methyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCC(C1)CN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 MVKYZUDWWZWERD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AFHMRNIJNPZNDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C1CN(CC=2C=CC=CC=2)CCC1C(CC)CNC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CN=C1 AFHMRNIJNPZNDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CYWQVWXNGIYVNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[2-[1-[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl]piperidin-4-yl]ethyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1=CC(O)=CC=C1CCCCN1CCC(CCNC(=O)CCC=2C=NC=CC=2)CC1 CYWQVWXNGIYVNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UROYCEAVPSMNLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[3-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)oxypropyl]-3-pyridin-2-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CC=NC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCOC(CC1)CCN1CC1=CC=CC=C1 UROYCEAVPSMNLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZJBZLXGMPYCHSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-2-pyridin-3-yloxyacetamide Chemical compound C1CN(C(C=2C=CC=CC=2)C=2C=CC=CC=2)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)COC1=CC=CN=C1 ZJBZLXGMPYCHSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BNVKAHPPMRDENQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzhydrylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-n-ethyl-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)N(CC)CCCCC(CC1)CCN1C(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 BNVKAHPPMRDENQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BMDQNDLEOMSJTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-benzoylpiperidin-3-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C=1C=CN=CC=1C=CC(=O)NCCCCC(C1)CCCN1C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 BMDQNDLEOMSJTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PKCWQXXZTIHLOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1-naphthalen-2-ylsulfonylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CN(S(=O)(=O)C=2C=C3C=CC=CC3=CC=2)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 PKCWQXXZTIHLOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LPMPMENHCIFVAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-(6,11-dihydro-5h-dibenzo[1,2-a:1',2'-e][7]annulen-11-yl)piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C1CN(C2C3=CC=CC=C3CCC3=CC=CC=C32)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CN=C1 LPMPMENHCIFVAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OSTHEGPTOJALEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-(6,11-dihydrobenzo[c][1]benzothiepin-11-yl)piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C1CN(C2C3=CC=CC=C3SCC3=CC=CC=C32)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CN=C1 OSTHEGPTOJALEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GTDPOIWLQAGLQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-(6,11-dihydrobenzo[c][1]benzoxepin-11-yl)piperidin-2-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CCCN(C2C3=CC=CC=C3OCC3=CC=CC=C32)C1CCCCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CN=C1 GTDPOIWLQAGLQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TTWWGZXVVUWNAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-(9-oxofluorene-4-carbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enamide Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)C=2C=3C4=CC=CC=C4C(=O)C=3C=CC=2)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CN=C1 TTWWGZXVVUWNAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WAISYNLGAFPXTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-[1-(naphthalene-2-carbonyl)piperidin-4-yl]butyl]-2-pyridin-3-ylpropanamide Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)C=2C=C3C=CC=CC3=CC=2)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)C(C)C1=CC=CN=C1 WAISYNLGAFPXTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NVLSOIUQGMKBJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-naphthalen-1-yl-4-[4-(3-pyridin-2-ylpropanoylamino)butyl]piperidine-1-carboxamide Chemical compound C1CN(C(=O)NC=2C3=CC=CC=C3C=CC=2)CCC1CCCCNC(=O)CCC1=CC=CC=N1 NVLSOIUQGMKBJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002105 nanoparticle Substances 0.000 description 1
- XNLBCXGRQWUJLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene-2-carbonyl chloride Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC(C(=O)Cl)=CC=C21 XNLBCXGRQWUJLU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OPECTNGATDYLSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene-2-sulfonyl chloride Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC(S(=O)(=O)Cl)=CC=C21 OPECTNGATDYLSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940100662 nasal drops Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000015097 nutrients Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- NIHNNTQXNPWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N o-biphenylenemethane Natural products C1=CC=C2CC3=CC=CC=C3C2=C1 NIHNNTQXNPWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000021313 oleic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000005022 packaging material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003182 parenteral nutrition solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006072 paste Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000312 peanut oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940100684 pentylamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940021222 peritoneal dialysis isotonic solution Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003800 pharynx Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000005191 phase separation Methods 0.000 description 1
- AHWALFGBDFAJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenyl carbonochloridate Chemical compound ClC(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1 AHWALFGBDFAJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WVDDGKGOMKODPV-ZQBYOMGUSA-N phenyl(114C)methanol Chemical compound O[14CH2]C1=CC=CC=C1 WVDDGKGOMKODPV-ZQBYOMGUSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N phosphinic acid Chemical compound O[PH2]=O ACVYVLVWPXVTIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002798 polar solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001983 poloxamer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004584 polyacrylic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004633 polyglycolic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001282 polysaccharide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005017 polysaccharide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000136 polysorbate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000015497 potassium bicarbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910000028 potassium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011736 potassium bicarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- NTTOTNSKUYCDAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N potassium hydride Chemical compound [KH] NTTOTNSKUYCDAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000105 potassium hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- TYJJADVDDVDEDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium hydrogencarbonate Chemical compound [K+].OC([O-])=O TYJJADVDDVDEDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229940086066 potassium hydrogencarbonate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940090181 propyl acetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000006239 protecting group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000003586 protic polar solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008213 purified water Substances 0.000 description 1
- WHMDPDGBKYUEMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine-2-thiol Chemical compound SC1=CC=CC=N1 WHMDPDGBKYUEMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002285 radioactive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001226 reprecipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000979 retarding effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000033764 rhythmic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- CVHZOJJKTDOEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N saccharin Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C2=C1 CVHZOJJKTDOEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000901 saccharin and its Na,K and Ca salt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003335 secondary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000013049 sediment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003384 small molecules Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- HELHAJAZNSDZJO-OLXYHTOASA-L sodium L-tartrate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O HELHAJAZNSDZJO-OLXYHTOASA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000017557 sodium bicarbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- AJPJDKMHJJGVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium dihydrogen phosphate Chemical compound [Na+].OP(O)([O-])=O AJPJDKMHJJGVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000010265 sodium sulphite Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000001433 sodium tartrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960002167 sodium tartrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000011004 sodium tartrates Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000000935 solvent evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011877 solvent mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004334 sorbic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010199 sorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940075582 sorbic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000003549 soybean oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012424 soybean oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000004611 spectroscopical analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001694 spray drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001954 sterilising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004659 sterilization and disinfection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L succinate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCC([O-])=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940124530 sulfonamide Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000003456 sulfonamides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003460 sulfonic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003461 sulfonyl halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- YBBRCQOCSYXUOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfuryl dichloride Chemical class ClS(Cl)(=O)=O YBBRCQOCSYXUOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000829 suppository Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002511 suppository base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009897 systematic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007910 systemic administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940126703 systemic medication Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940095064 tartrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- GVOGVPFQDCQZNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 4-(4-hydroxybutyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)N1CCC(CCCCO)CC1 GVOGVPFQDCQZNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001302 tertiary amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000005302 thiazolylmethyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])N=C(S1)C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 239000002562 thickening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009974 thixotropic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- KJAMZCVTJDTESW-UHFFFAOYSA-N tiracizine Chemical compound C1CC2=CC=CC=C2N(C(=O)CN(C)C)C2=CC(NC(=O)OCC)=CC=C21 KJAMZCVTJDTESW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N triformin Chemical compound O=COCC(OC=O)COC=O UFTFJSFQGQCHQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tris Chemical compound OCC(N)(CO)CO LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004418 trolamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000004614 tumor growth Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003672 ureas Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- NQPDZGIKBAWPEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N valeric acid Chemical compound CCCCC(O)=O NQPDZGIKBAWPEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000015112 vegetable and seed oil Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008158 vegetable oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001993 wax Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940100445 wheat starch Drugs 0.000 description 1
- HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-SCDXWVJYSA-N xylitol Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-SCDXWVJYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000010447 xylitol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/4427—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/4427—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/4439—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems containing a five-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. omeprazole
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/4427—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/444—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring heteroatom, e.g. amrinone
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/445—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine
- A61K31/4523—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine containing further heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/4545—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine containing further heterocyclic ring systems containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pipamperone, anabasine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/47—Quinolines; Isoquinolines
- A61K31/4709—Non-condensed quinolines and containing further heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/47—Quinolines; Isoquinolines
- A61K31/472—Non-condensed isoquinolines, e.g. papaverine
- A61K31/4725—Non-condensed isoquinolines, e.g. papaverine containing further heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/495—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with two or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring heteroatoms, e.g. piperazine or tetrazines
- A61K31/505—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim
- A61K31/519—Pyrimidines; Hydrogenated pyrimidines, e.g. trimethoprim ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/535—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as the ring hetero atoms, e.g. 1,2-oxazines
- A61K31/5375—1,4-Oxazines, e.g. morpholine
- A61K31/5377—1,4-Oxazines, e.g. morpholine not condensed and containing further heterocyclic rings, e.g. timolol
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/55—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having seven-membered rings, e.g. azelastine, pentylenetetrazole
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/55—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having seven-membered rings, e.g. azelastine, pentylenetetrazole
- A61K31/553—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having seven-membered rings, e.g. azelastine, pentylenetetrazole having at least one nitrogen and one oxygen as ring hetero atoms, e.g. loxapine, staurosporine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/66—Phosphorus compounds
- A61K31/675—Phosphorus compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pyridoxal phosphate
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D413/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D413/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D413/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D451/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 8-azabicyclo [3.2.1] octane, 9-azabicyclo [3.3.1] nonane, or 3-oxa-9-azatricyclo [3.3.1.0<2,4>] nonane ring systems, e.g. tropane or granatane alkaloids, scopolamine; Cyclic acetals thereof
- C07D451/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 8-azabicyclo [3.2.1] octane, 9-azabicyclo [3.3.1] nonane, or 3-oxa-9-azatricyclo [3.3.1.0<2,4>] nonane ring systems, e.g. tropane or granatane alkaloids, scopolamine; Cyclic acetals thereof containing not further condensed 8-azabicyclo [3.2.1] octane or 3-oxa-9-azatricyclo [3.3.1.0<2,4>] nonane ring systems, e.g. tropane; Cyclic acetals thereof
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D491/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00
- C07D491/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed ring system both one or more rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms and one or more rings having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D459/00, C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D489/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D491/04—Ortho-condensed systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F9/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 5 or 15 of the Periodic Table
- C07F9/02—Phosphorus compounds
- C07F9/547—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom
- C07F9/553—Heterocyclic compounds, e.g. containing phosphorus as a ring hetero atom having one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07F9/576—Six-membered rings
- C07F9/59—Hydrogenated pyridine rings
Definitions
- the invention relates to the use of pyridyl aklane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides, especially in the treatment of tumor conditions and/or as cytostatic agents or as immunosuppressive agents as well as medicaments with an amount of these compounds in combination with other cytostatic agents or immunosuppresive agents.
- cytostatic therapy A strong need exists for the enrichment of cytostatic therapy to provide pharmaceuticals and/or medicaments which not only possess a strong activity, but also exert diminished side effects in comparison to many classical cancerostatic agents, whereby treatment of a broad as possible spectrum of tumors should be made accessible. Furthermore, effective cytostatic agents for an efficient therapy should be made available. Active ingredients of this type should also be exceptionally suitable in the mentioned indications for a combination therapy, be it in connection with other cytostatic agents or with radiation (for example X-rays, radioactive elements, such as cobalt, or linear accelerator, etc.), with operative procedures, heat treatment, etc.
- further subject-matter of the invention relates to new medicaments in the form of combinations of the compounds defined below and used according to the invention together with other compounds or immunosuppressive agents customary in the therapy of tumors.
- pyridyl(alkyl)carbonamides pyridyl(alkyl)sulfonamides and analogous ureas, wherein the amide portion is bound over an alkyl chain with a piperidine ring are disclosed in EP-A-0 479 601 as active ingredients with anti-arrhythmic properties.
- EP-A-0 330 026 also discloses substituted piperidine derivatives with possible, generic pyridyl substitutions for which, however, merely a single concrete example is disclosed, namely (E)-3-(3-pyridyl)-N-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-2-propenamide hydrochloride. These compounds are distinguished by an anti-cholinesterase activity, an anti-amnesia activity as well as activities directed against hyperkinesia, senile demensia, mania and Alzheimer's disease.
- subject-matter of the invention relates to the use of one or more compounds of formula (I)
- R 1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, benzyloxy,
- alkyl especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl
- alkenyl especially C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl
- alkinyl especially C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl
- hydroxyalkyl especially C 1 -C 6 -hydroxyalkyl
- alkoxy especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy
- alkenyloxy especially C 3 -C 6 -alkenyloxy
- alkinyloxy especially C 3 -C 6 -alkinyloxy
- alkanoyloxy especially C 1 -C 7 -alkanoyloxy
- alkoxycarbonyloxy especially C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyloxy
- alkylthio especially C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio
- alkenylthio especially C 3 -C 6 -alkenylthio
- alkinylthio especially C 3 -C 6 -alkinylthio
- cycloalkyl especially C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl
- cycloalkytoxy especially C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyloxy
- cycloalkylthio especially C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkylthio
- alkoxycarbonyl especially C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyl
- alkylaminocarbonyl especially C 2 -C 7 -alkylaminocarbonyl
- dialkylaminocarbonyl especially C 3 -C 13 -dialkylaminocarbonyl, or
- R 6 are selected independently of each other from hydrogen
- alkyl especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl
- alkenyl especially C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl
- alkinyl especially C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl
- R 2 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, benzyloxy,
- alkyl especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl
- alkoxy especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy or
- alkanoyloxy especially C 1 -C 7 -alkanoyloxy
- R 1 and R 2 if they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which is selected from —(CH 2 ) 4 —, —(CH ⁇ CH) 2 — and —CH 2 O—CR 7 R 8 —O—, wherein
- R 8 are, independently of each other, hydrogen or alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl,
- R 3 is hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxyalkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -hdroxyalkyl and
- R 4 is hydrogen, hydroxy, benzyloxy,
- alkyl especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl
- alkenyl especially C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl
- alkinyl especially C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl
- cycloalkyl especially C 3 -C 6 -cycloalkyl or
- alkoxy especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy
- k is 0 or 1
- A is alkylene, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by alkyl, especially C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, especially C 1 -C 3 -alkoxy, fluorine or phenyl, or
- alkenylene with at least two C-atoms especially C 2 -C 6 -alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 3 -alkoxy, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
- alkadienylene with at least four C-atoms especially C 4 -C 6 -alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
- 1,3,5-hexatrienylene which is optionally substutited by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, fluorine, cyano, or phenyl,
- alkylene with at least two C-atoms especially C 2 -C 6 -alkylene in which a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR 9 , CO, SO or SO 2 , wherein the isosteric substitution, with the exception of ⁇ CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group and wherein
- R 9 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, alkenyl, especially C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl, alkinyl, especially C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl, acyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -acyl or alkylsulfonyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkylsulfonyl,
- D is selected from alkylene, especially C 1 -C 10 -alkylene, optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, hydroxy, or alkoxy, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy,
- alkenylene with at least two C-atoms especially C 2 -C 10 -alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, hydroxy,
- alkoxy especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
- alkinylene with at least three C-atoms especially C 3 -C 10 -alkinylene, optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, hydroxy or alkoxy, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, and
- alkylene especially C 1 -C 10 -alkylene, alkenylene with at least two C-atoms, especially C 2 -C 10 -alkenylene or alkinylene with at least three C-atoms, especially C 3 -C 10 -alkinylene, whereby one to three methylene units are each isosterically replaced by O, S, NR 10 , CO, SO or SO 2 wherein
- R 10 has the same meaning as
- R 9 but is selected independently thereof
- E is selected from
- heterocyclic ring can also optionally have a double bond
- p can be, independently of one another, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p ⁇ 4 and
- R 11 is hydrogen, alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or alkoxycarbonyl with at least two C-atoms, especially C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyl and
- R 12 is hydrogen, alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl or or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom, wherein
- R 11 and R 12 optionally together, form an alkylene bridge with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 C-atoms, especially a C 1 -C 3 -alkylene bridge under formation of a bicyclic ring system,
- G is selected from hydrogen
- G 1 represents the residue
- r is an integer from 1 to 3 or O and
- s is 0 or 1
- R 13 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, alkenyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl, alkinyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl, cycloalkyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 has the same meaning as R 13 , but is selected independently thereof,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- [0098] can also be a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
- saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O, or
- Ar 1 and Ar 2 are selected independently from one another from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl and
- R 16 is selected from trifluoromethyl, alkoxy, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, alkenyloxy, especially C 3 -C 6 -alkenyloxy, or benzyloxy,
- any aryl residues and/or aromatic ring systems in the substituents R 1 , R 2 , R 4 , R 13 , R 14 , R 15 , R 16 , Ar 1 and Ar 2 and/or in the ring system —NR 13 R 15 can be substituted independently from each other by one to three of the same or different residues which are selected from halogen, cyano, alkyl, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl, cycloalkyl, especially C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, alkoxy, substituted entirely or partially by fluorine, substituted alkoxy, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, alkylthio, especially C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl
- a preferred embodiment according to the invention relates to the use of compounds of formula (I)
- R 1 is a hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl, trifluoromethyl, C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl, C 1 -C 6 -hydroxyalkyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyloxy, C 3 -C 6 -alkinyloxy, benzyloxy, C 1 -C 7 -alkanoyloxy, C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyloxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio, C 3 -C 6 -alkenylthio, C 3 -C 6 -alkinylthio, C 3 -Cg-cycloalkyloxy, C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkylthio, C 2 -C 7 -alkoxy
- R 6 are selected independently from each other from hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl and C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl,
- R 2 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, benzyloxy or C 1 -C 7 -alkanoyloxy,
- R 1 and R 2 in case they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which is selected from the bridge members
- R 8 are, independently from each other, hydrogen or C 1 -C 6 -alkyl
- R 3 is hydrogen, halogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl or C 1 -C 6 -hydroxyalkyl and
- R 4 is hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl, C 3 -C 6 -cycloalkyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy or benzyloxy,
- k is 0 or 1
- A is C 1 -C 6 -alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 3 -alkoxy, fluorine or phenyl, or
- C 2 -C 6 -alkenylene which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 3 -alkoxy, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
- C 4 -C 6 -alkadienylene which is optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl
- 1,3,5-hexatrienylene which is optionally substituted by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl
- C 2 -C 6 -alkylene wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR 9 , CO, SO or SO 2 , wherein the isosteric substitution, with the exception of ⁇ CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group, and
- R 9 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl, C 1 -C 6 -acyl or C 1 -C 6 -alkylsulfonyl,
- D is selected from C 1 -C 10 -alkylene, optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, hydroxy, or C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy,
- C 2 -C 10 -alkenylene which is optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, hydroxy, or C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
- C 3 -C 10 -alkinylene optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, hydroxy, or C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, and
- R 10 has the same meaning as R 9 , but is selected independently therefrom,
- E is selected from
- heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond
- p can be, independently of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p ⁇ 4 and
- R 11 is hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyl and
- R 12 hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom, wherein
- R 11 and R 12 optionally together form a C 1 -C 3 -alkylene bridge under formation of a bi-cyclic ring system
- G is selected from hydrogen
- r is an integer from 1 to 3 or 0 and
- s is 0 or 1
- R 13 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl, C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly, or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic ring or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 has the same meaning as R 13 , but is selected independently thereof,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic ring or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- [0167] can also be a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
- saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O, or
- Ar 1 and Ar 2 are selected independently from one another from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl and
- R 16 is selected from trifluoromethyl, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyloxy, or benzyloxy, and wherein
- aromatic ring systems in the substituents R 1 , R 2 , R 4 , R 13 , R 14 , R 15 , R 16 , Ar 1 and Ar 2 and/or in the ring system —NR 13 R 15 can be substituted independently from each other by one to three of the same or different residues which are selected from halogen, cyano, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C 3 -C 8 -Cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, which can optionally be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio, carboxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C 1 -C 6 -alkylamino or di-(C 1 -C 6 -alkyl
- a further preferred embodiment of the invention constitutes the use of compounds for the indications named above, which are distinguished in that substituents R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , R 8 , R 9 , R 10 , R 13 , R 14 , R 15 and R 16 as well as A and D indicated for formula (I) have the following meaning in connection with the given substitutions according to this formula
- halogen is fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine
- C 1 -C 6 -alkyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably a methyl-, ethyl-, propyl-, isopropyl-, butyl-, isobutyl-, sec-butyl-, tert-butyl-, cyclopropylmethyl-, pentyl-, isopentyl-, tert-pentyl-, neopentyl-, cyclopropylethyl-, cyclobutylmethyl- or a hexyl group
- alkylene is for example methylene, ethylene, propylene, tetramethylene, pentamethylene, hexamethylene, heptamethylene, octamethylene, nonamethylene or decamethylene,
- C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably an allyl-, 2-butenyl-, 3-butenyl-, 2-methyl-2-propenyl-, 2-pentenyl-, 4-pentenyl-, 2-methyl-2-butenyl-, 3-methyl-2-butenyl-, 2-hexenyl-, 5-hexenyl-, 4-methyl-3-pentenyl- or 2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl group,
- alkenylene is for example ethenylene, propenylene, butenylene, pentenylene, hexenylene, hexathenylene, heptenylene, octenylene, nonenylene or decenylene,
- C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably a propargyl-, 2-butinyl-, 3-butinyl-, 4-pentinyt-, 5-hexinyl- or 4-methyl-2-pentinyl group,
- alkinylene is for example propinylene, butinylene, pentinylene, hexinylene, heptinylene, octinylene, noninylene or decinylene,
- C 3 -C 8 -cyloalkyl is preferably cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl or cyclooctyl,
- C 1 -C 6 -hydroxyalkyl contains a hydroxyl group in one of the above-named C 1 -C 6 -alkyl residues, especially in the form of the hydroxymethyl- and hydroxyethyl group, wherein
- C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyloxy, C 3 -C 6 -aklinyloxy each contain, aside from the oxygen atom, one of the C 1 -C 6 -alkyl-, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl- and/or C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl groups named above and the methoxy-, ethoxy-, isopropoxy-, tert-butoxy-, allyloxy- and propargyloxy group are preferred and is to be understood as among C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy entirely or partially substituted with fluorine, for example difluormethoxy, trifluormethoxy or 2,2,2-trifluorethoxy,
- C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio, C 3 -C 6 -alkenylthio, C 3 -C 6 -alkinylthio each contain, aside from the sulfur atom, one of the C 1 -C 6 -alkyl-, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl- or C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl group named above, especially the methylthio-, ethylthio-, isopropylthio- and tert-butylthio groups,
- C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyloxy and C 3 -C 8 -cydoalkylthio are preferred as cyclopentyloxy- and cyclopentylthio- and/or cylohexyloxy- and cyclohexylthio groups,
- C 1 -C 7 -alkanoyloxy groups contain, aside from the oxygen atom, an aliphatic acyl residue with 1 to 7 carbon atoms, especially the acetoxy-, propionyloxy- and pivaloyloxy group,
- C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyl groups contain, aside from the carbonyl group, one of the C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy groups mentioned above, especially the methoxycarbonyl-, ethoxycarbonyl-, isopropoxycarbonyl-, isobutoxycarbonyl-and tert-butoxycarbonyl group,
- C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyloxy groups contain, aside from the oxygen atom, one of the C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyl residues mentioned above, especially the methoxycarbonyloxy-, ethoxycarbonyloxy-, isopropoxycarbonyloxy-, isobutoxycarbonyloxy-and tert-butoxycarbonyl group as well as the allyloxycarbonyloxy group,
- C 2 -C 7 -alkylaminocarbonyl and C 3 -C 13 -dialkylaminocarbonyl groups contain, beside the carbonyl group, an alkylamino- and/or dialkylamino residue, whose C 1 -C 6 -alkyl groups have the above meanings, wherein the dimethylaminocarbonyl-, diethylaminocarbonyl- and the diisopropylatninocarbonyl groups are preferred, and aside from the unsubstituted amino group, one of the following C 1 -C 6 -alkylamino groups and/or di-(C 1 -C 6 -alkyl)amino groups are to be understood under the amino groups of the formula NR 5 R 6 ,
- C 1 -C 6 -alkylamino contains one of the C 1 -C 6 -alkyl groups mentioned above, especially in form of the methylamino-, ethylamino-, propylamino-, isopropylamino-, butylamino- and the tert-butylamino group,
- di-(C 1 -C 6 -alkyl)amino carries two of the same or different of the above named C 1 -C 6 -alkyl groups on the nitrogen atom, especially in form of the dimethylamino-, diethylamino-, dipropylamino-, diisopropylamino-, isopropylmethylamino-, dibutylamino- or tert-butylmethylamino group,
- C 1 -C 6 -acyl is the residue of an aliphatic saturated or unsaturated, straight chain, branched or cyclic carboxylic acid, especially in form of the formyl-, acetyl-, propionyl-, acryloyl-, butyryl-, isobutyryl-, methacryloyl-, cyclopropylcarbonyl-, pentanoyl-, pivaloyl-, cyclobutylcarbonyl-, hexanoyl- and the dimethylacryloyl group,
- C 1 -C 6 -alkansulfonyl is preferably the methanesulfonyl-, ethanesulfonyl-, propanesulfonyl-, butanesulfonyl-, pentanesulfonyl- and the hexanesulfonyl group, saturated five- to seven-membered heterocycles with one or two hetero-atoms are especially tetrahydrofuryl, tetrahydrothienyl, pyrrolidinyl, tetrahydropyranyl, piperidinyl, hexahydroazepinyl, piperazinyl, hexahydrodiazepinyl or morpholinyl,
- monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles with one to three hetero-atoms are especially furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl or triazinyl,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclc ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring are preferably benzocyclobutyl, indanyl, indenyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, biphenylenyl, fluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, phenanthryl, dihydrophenanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocyclooctenyl or tetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenyl, wherein mono- or dioxo-derivates, wherein the residues of indanone, tetralone, anthrone, anthraquinone, fluorenone, phenanthrone, dibenzocycloheptenone, di
- anellated bi- and tricyclische aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring are, for example, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, dihydrobenzofuryl, benzothienyl, dihydrobenzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, benzimidazolyl, indazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzisoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzoisothiazolyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiadiazolyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, isothiazolopyridyl, imidazopyridyl, pyrazolopyridyl, thienopyrimidinyl, chromanyl, benzopyranyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, dihydroquinolyl, te
- saturated and unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles are —NR 13 R 15 as a grouping which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further betero-atoms selected from N and/or S and/or O, for example azetidine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, (1H)tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, (1H)tetrahydroazepine, octahydroazocine, pyrazolidine, piperazine, hexahydrodiazepine, morpholine, hexahydrooxazepine, thiomorpholine or thiomorpholine-1,1-dioxide, saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, represent —NR 3 R 15 as a grouping which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected
- stereoisomers such as, if applicable, cis/trans-isomers, endo/exo-isomers, optic isomers such as enantiomers, diastereomers as pure isomers or mixtures and/or racemic mixtures as well as the pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts with inorganic or organic acids, wherein the hydrochlorides, hydrobromides, hydroiodides, sulfates and phosphates, are preferred as addition salts with suitable inorganic acids and acetates, benzoates, 4-methoxybenzoate, 2- or 4-hydroxybenzoate, 4-chlorobenzoate, ascorbate, salicylate, formiate, glutarate, tricarballylate, citrates, fumarates, gluconates, malates, maleates, methanesulfonates, lactates, oxalates, succinates, tartrates and toluolsulfonates, for example p-toluo
- R 1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C 3 -C 8 -cycloallyl, C 1 -C 4 -hydroxyalkyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 4 -alkoxy, benzyloxy, C 1 -C 4 -alkanoyloxy, C 1 -C 4 -alkylthio, C 2 -C 5 -alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, C 3 -C 9 -dialkylaminocarbonyl, carboxy, phenyl, phenoxy, pyridyloxy or NR 5 R 6 , wherein
- R 6 are selected independently from each other form hydrogen and C 1 -C 6 -alkyl
- R 2 is hydrogen, halogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy, wherein
- R 1 and R 2 in the case they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which are selected from the group of bridge members —(CH 2 ) 4 — and —(CH ⁇ CH) 2 — and —CH 2 O—CR 7 R 8 —O—, wherein
- R 8 can be, independently from each other, hydrogen and C 1 -C 6 -alkyl
- R 3 is selected from hydrogen, halogen and C 1 -C 6 -alkyl and
- R 4 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy and benzyloxy,
- k is 0 or 1
- A is C 1 -C 6 -alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, hydroxy, fluorine or phenyl,
- C 4 -C 6 -alkadienylene which is optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, fluorine, cyano, or phenyl,
- 1,3,5-hexatrienylene which is optionally substituted by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, fluorine, or cyano,
- C 2 -C 6 -alkylene wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR 9 , CO, SO or SO 2 , and wherein the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ⁇ CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group, and wherein
- R 9 is hydrogen, C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, C 1 -C 6 -acyl or methanesulfonyl,
- D is selected from C 1 -C 10 -alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl or hydroxy,
- C 2 -C 10 -alkenylene optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl or hydroxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E or
- C 3 -C 10 -alkinylene which is optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl or hydroxy, and can be selected as well from
- R 10 has the same meaning as R 9 , but is selected independently therefrom,
- heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond
- n and p can be, independent of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p ⁇ 4,
- R 11 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, hydroxcy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or C 2 -C 7 -alkoxycarbonyl and
- R 12 is selected from hydrogen or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom
- G is selected from hydrogen
- r is 0, 1 or 2 and
- s is 0 or 1
- R 13 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyl, C 3 -C 6 -alkinyl, C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, whereby the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from the groups N and/or S and/or O and the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 has the same meaning as R 13 , but is selected independently thereof,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- G2 is selected from the residues
- [0255] can also be a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
- saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from N and/or S and/or O, or
- Ar 2 are selected independently of each other from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl,
- R 16 is trifluoromethyl, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyloxy or benzyloxy and
- aromatic ring systems in which the substituents R 1 , R 2 , R 4 , R 13 , R 14 , R 15 , R 16 , Ar 1 and Ar 2 and/or in the ring system —NR 13 R 15 can carry independently of each other one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, which is optionally entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio, carboxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C 1 -C 6 -alkylamino, di-(C 1 -C 6 -alkyl)-amin
- R 1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, methyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 4 -alkoxy, ethylthio, methoxycarbonyl, tert-butoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, carboxy, and phenoxy,
- R 2 is hydrogen, halogen, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy
- R 3 is hydrogen or halogen
- R 4 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 3 alkyl, hydroxy and C 1 -C 3 -alkoxy,
- k is 0 or 1
- A is C 2 -C 6 -alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, hydroxy or fluorine, as well as
- C 4 -C 6 -alkadienylene which is optionally substituted by is C 1 -C 3 -alkyl or by one or two fluorine atoms,
- C 2 -C 6 -alkylene wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, CO or SO 2 , and the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ⁇ CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group and,
- D is C 1 -Cg-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once twice by methyl or hydroxy,
- heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond
- p can be independent of each other 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p ⁇ 3,
- R 11 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 3 -alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl and
- R 12 is selected from hydrogen or an oxo group which is adjacent to the nitrogen atom
- G is hydrogen or
- r is 0, 1 or 2 and
- s is 0 or 1
- R 13 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl, benzyl orphenyl, benzocyclobutyl, indanyl, indenyl, oxoindanyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, oxotetrahydronaphthyl, biphenylenyl, fluorenyl, oxofluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, oxodihydroanthryl, dioxodihydroanthryl, phenanthryl, dihydrophenanthryl, oxodihydrophenanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodihydrodihydro
- R 14 has the same meaning as R 13 , but is selected independently therefrom,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
- G2 is selected from the residues
- Ar 2 are selected independently of each other from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl,
- R 16 is trifluoromethyl, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, C 3 -C 6 -alkenyloxy or benzyloxy and
- aromatic ring systems in which the substituents can be substituted independently of each other by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C 3 -C 8 -Cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, can carry benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio, carboxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C 1 -C 6 -alkylamino, di-(C 1 -C 6 -alkyl)-amino, wherein two adjacent groups in the ring or ring system can form an additional ring over a methylenedioxy bridge
- a further preferred embodiment of the invention is in the use of compounds which are distinguished in that the labelled substituents in formula (I)
- R 1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, methyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, methoxy or methoxycarbonyl,
- R 2 is hydrogen or halogen
- R 3 is hydrogen
- R 4 is selected from hydrogen, C 1 -C 3 -alkyl or hydroxy
- k is 0 or 1
- A is selected from C 2 -C 6 -alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by hydroxy or fluorine, or
- C 2 -C 6 -alkylene wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S or CO, and the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ⁇ CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group and,
- D is C 2 -C 8 -alkylene, which is optionally substituted by methyl or hydroxy,
- heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond
- n and p can be, independent of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p ⁇ 3 and
- R 11 is hydrogen, methyl or hydroxyl
- R 12 is hydrogen or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom
- G is selected from hydrogen, C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl, methoxycarbonyl, tertbutoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, trifluoroacetyl, diphenylphosphinoyl or the residues
- r is 0, 1 or 2 and
- s is 0 or 1
- R 13 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl
- R 14 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
- the group NR 13 R 15 can be selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, (1H)tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, Octahydroazocine, piperazine, hexahydrodiazepine, morpholine, hexahydrooxazepine, 2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 7-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)-dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoxaline, (4H)-dihydrobenzoxazine, (4H)-dihydrobenzo
- R 1 is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, methyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy
- R 3 are hydrogen
- R 4 is hydrogen or hydroxy
- k is 0 or 1
- A is selected from C 2 -C 6 -alkylene, which is optionally substitued once or twice by hydroxy or fluorine or,
- D is selected from C 2 -C 6 -alkylene, C 2 -C 6 -alkenylene, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E, and C 2 -C 6 -alkylene and C 2 -C 6 -alkenylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, NH, N(CH 3 ) or CO or an ethylene group can be isosterically replaced by NH—CO and/or CO—NH or a propylene group can be isosterically replaced by NH—CO—O and/or O—CO—NH,
- E is selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, 1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, morpholine and hexahydro-1,4-oxazepine, wherein the heterocyclic ring optionally adjacent to the nitrogen atom, can be substituted by an oxo group,
- G is selected from hydrogen, tert-butoxycarbonyl, diphenylphosphinoyl, or one of the residues
- r is 0 or 1
- s is 0 or 1
- R 13 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl
- R 14 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl
- R 15 is hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl
- the group NR 13 R 15 can be selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, hexahydroazepine, morpholine, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]-oxazepine or (11H)-dihydrodibenzo
- aromatic ring systems in the substituents can be substituted, independently of each other, by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C 3 -C 8 -cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, can carry benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio, carboxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C 1 -C 6 -alkylamino or di-(C 1 -C 6 -alkyl)-amino, whereby two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system for an additional ring over a methylenedi
- R 1 is hydrogen, fluorine, methyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy
- R 3 are hydrogen
- R 4 is hydrogen or hydroxy
- A is ethylene, propylene or butylene which can each be optionally substituted by hydroxy or once or twice by fluorine, or
- D is selected from C 2 -C 6 -alkylene or C 2 -C 6 -alkenylene, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
- E is selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, hexahydroazepine or morpholine,
- G is selected from benzyl, phenethyl, fluorenylmethyl, anthrylmethyl, diphenylmethyl, fluorenyl or dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl,
- aromatic ring systems can be substituted independently of each other by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C 1 -C 6 -alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C 3 -Cg-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C 1 -C 6 -alkylthio, carboxy, C 1 -C 6 -alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C 1 -C 6 -alkylamino or di-(C 1 -C 6 -alkyl)-amino, wherein two adjacent groups in the ring or ring system can form an additional ring over a methylendioxy bridge.
- Reactive derivatives of compound (II) can be present, for example, as activated esters, anhydrides, acid halides, especially acid chlorides, or simple low alkyl esters.
- Suitable acitivated esters are, for example, p-nitrophenyl ester, 2,4,6-trichlorphenyl ester, pentachlorophenyl ester, cyanomethyl ester, esters of N-hydroxysuccinimide, of N-hydroxyphthalimides, of 1-hydroxybenzotriazol, of N-hydroxypiperidine, of 2-hydroxypyridine or of 2-mercaptopyridine, etc.
- Anhydrides can be symmetric anhydrides or mixed, as they are obtained, for example, with pivaloyl chloride or with chloroformates.
- Aromatic for example chloroformic phenyl ester
- araliphatic for example chloroformic benzyl ester
- aliphatic chloroformates for example chloroformic methyl ester and/or corresponding -ethyl or -isobutyl ester
- Reaction of compounds (II) with compounds (III) can also be carried out in the presence of condensation agents such as dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, N,N′-carbonyldiimidazol, 1-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline, etc.
- condensation agents such as dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, N,N′-carbonyldiimidazol, 1-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline, etc.
- condensation agent such as dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, N,N′-carbonyld
- Compounds of formula (III) can be used for reaction as free bases as well as in the form of their acid addition salts.
- the salts of inorganic acids are to be preferred, i.e. hydrochlorides, hydrobromides or sulfates.
- Reaction of compounds (II) or their reactive derivatives with compounds (III) are normally carried out in a suitable, preferably inert solvent.
- aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene, toluol, xylene, halogenated hydrocarbons (for example dichloromethane, chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene), ethers (for example diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, glycol dimethyl ether), ethyl acetate, acetonitrile or polar aprotic solvents such as, for example, dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylformamide or N-methylpyrrolidone are to be named. Pure solvents, as well as mixtures of two or more, can be used.
- the reaction is optionally carried out in the presence of an auxiliary base.
- auxiliary base Suitable examples for this are alkali metal carbonates (sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate), alkali metal hydrogen carbonates (sodium hydrogen carbonate, potassium hydrogen carbonate), or organic bases such as, for example, triethylamine, ethyl diisopropylamine, tributylamine, N-methylmorpholine or pyridine.
- a suitable excess of compound (III) can also be used as a base. If compounds (III) are used in form of their acid addition salts, then it is appropriate to consider the amount of auxiliary base used as equivalent.
- the reaction temperatures can—depending on reactivity of the educts—vary in a wide range. Generally, the reaction is carried out at temperatures between ⁇ 40° C. and 180° C., preferably between ⁇ 10° C. and 130° C., especially at the boiling point of the solvent used.
- the starting compounds (II) and (III) are known and/or can be produced according to known methods in an analogous manner. Moreover, the production of representative examples is further described below.
- Compounds of formula (I) can be produced by reaction of compounds of formula (I), wherein G is hydrogen and which themselves possess the above-named pharmacological activities such as a cytostatic and/or immunomodulatory activity, as intermediate products as well as end products, with a compound of formula (V),
- G has the meaning given above, with the exception of hydrogen, and L is a suitable nucleofuge or reactive group.
- L is a suitable nucleofuge or reactive group.
- the type of nucleofuge or reactive group L and the conditions of the reaction are dependent of the nature of group G.
- Compounds of formula (I), in which G, with the exception of hydrogen, has the meaning of (G1) according to the above definition can, aside from method (a), also be produced by reacting compounds of formula (I), wherein G is hydrogen, with a suitable alkylation agent and/or arylation agent of formula (IV), wherein G is an alkyl-, alkenyl-, alkinyl-, cycloalkyl-, aryl-, aralkyl-, heteroaryl- or heteroaralkyl residue according to definition and the leaving group L can be a reactive derivative of an alkohol, for example, a halogen atom such as chlorine, bromine or iodine or a sulfonic acid ester, i.e.
- a suitable alkylation agent and/or arylation agent of formula (IV) wherein G is an alkyl-, alkenyl-, alkinyl-, cycloalkyl-, aryl-, aralkyl-, heteroary
- a reactive group L can be a terminal epoxide group for example.
- solvents can be, for example, aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluol, xylene), ethers (for example tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, glycol dimethyl ether), ethyl acetate, acetonitrile, ketones (acetone, ethyl methyl ketone), polar protic solvents such as alcohols (ethanol, isopropanol, butanol, glycol monomethyl ether) or polar aprotic solvents such as, for example, dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylformamide or N-methylpyrrolidone.
- aromatic hydrocarbons benzene, toluol, xylene
- ethers for example tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, glycol dimethyl ether
- ethyl acetate acetonitrile
- ketones acetone, ethyl methyl ketone
- polar protic solvents such as alcohols (ethanol
- the reactions are carried out in the presence of bases, whereby said bases can be used as in method (a) above.
- bases can be used as in method (a) above.
- chlorides or bromides are used as compound (IV)
- the reaction can be accelerated by the addition of alkali metal iodides (sodium iodide, potassium iodide).
- the reaction temperatures can vary between 0° C. and 180° C. depending on the reactivity of the educts, but preferably lie between 20° C. and 130° C.
- carboxylic acids and/or sulfonic acids (V) which are capable of reaction are symmetric or unsymmetric carboxylic acid anhydrides and/or sulfonic acid anhydrides or acyl- and/or sulfonyl halides, especially acyl- and/or sulfonyl chlorides.
- derivatives of carbamates and/or phosphinic acids which are capable of reaction are the carbamoyl halides and/or phosphinyl halides, especially carbanyl- and/or phosphinyl chlorides.
- [0414] can also be produced, aside from the methods (A) and (B2), by reacting compounds of formula (I), in which C is hydrogen with a carbonyl group transmitter to an intermediate product and subsequently reacting this directly with a primary or secondary amine with the formula (VI)
- R 13 and R 15 and/or the group —NR 13 R 15 have the meanings according to the above definitions without having to purify or isolate the intermediate product.
- Trichloromethylcarbonate (triphosgene) and carbonyldiimidazol have been proven as particularly reactive carbonyl group transmitters.
- the reaction of compounds of formula (I), wherein G is hydrogen, with triphosgene and/or carbonyldiimidazol are typically conducted in an absolute, inert solvent in the presence of a tertiary organic amine as an auxiliary base in such a manner that the solution of compounds (I) and the auxiliary base are slowly poured into a solution of an equivalent amount of carbonyl group transmitter.
- reaction requires molar ratios of 1:1 for the reaction of compound (I) and carbonyldiimidazol, and, in contrast, a ratio of 1:0.35 for the use of triphosgene.
- compound (VI) is added in stochiometric arnounts or in excess as a solution or a solid and the reaction is typically completed at elevated temperature.
- Suitable inert solvents are, for example hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, benzene, toluol, xylene, chlorinated hydrocarbons (for example dichloromethane, chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene), ethers (for example diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane), esters such as ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, acetonitrile or polar aprodic solvents such as formamide or dimethylformamide. Pure solvents as well as mixtures can be used diversely.
- hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, benzene, toluol, xylene
- chlorinated hydrocarbons for example dichloromethane, chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene
- ethers for example diethyl ether, te
- reaction temperatures can lie in between ⁇ 40° C. and 50° C. for the first partial reaction, preferably at 0° C. bis 30° C., and between 0° C. and 150° C. for the second partial reaction, preferably at 20° C. bis 120° C.
- reaction of the compounds of formula (I), in which G is hydrogen, with the isocyanates of formula (VII) are conducted thereby in an absolute, inert solvent which can be a hydrocarbon such as pentane, hexane, heptane, benzene, toluol, or xylene, chlorinated hydrocarbons (such as dichloromethane, chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene), ethers (for example, diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane), esters such as ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, or polar aprotic solvents such as formamide or dimethylformamide. Mixtures of various solvents can also be used.
- the reaction temperatures can vary in the region from ⁇ 20° C. to 150° C., but preferably lie at 20° C. to 100° C.
- compounds of formula (I), in which G is hydrogen are essentially more advantageously produced from other compounds of formula (I), in which G is a selectively cleavable group under mild conditions, i.e. corresponds to a nitrogen protective group.
- G represents a benzyl group, a 4-methoxybenzyl group, a diphenylmethyl group, a triphenylmethyl group, a benzyloxycarbonyl group, a methoxy- and/or ethoxycarbonyl group, a tertbutoxycarbonyl group, an allyloxycarbonyl group or a trifluoroacetyl group.
- compounds according to formula (I) with benzyl, diphenylmethyl, triphenylmethyl or benzyloxycarbonyl groups can already be catalytically transformed into the compounds of formula (I) with hydrogen as G at room temperature under mild conditions with elementary hydrogen or by transfer hydration.
- Compounds of formula (I) with a 4-methoxylbenzyl group are transformed into compounds of formula (I) with hydrogen as G by selective oxidation with ammonium-cer(IV)-nitrate.
- R 4 is an alkyl, alkenyl, alkinyl or cycloalkyl residue according to the above definition and L is a suitable nucleofuge, i.e. for example a halogen atom such as chlorine, bromine or iodine or a sulfonic acid ester of an alcohol.
- Preferred sulfonic acid esters (VIII) contain a methylsulfonyloxy residue, trifluoromethanesulfonyloxy-, p-toluolsulfonyloxy-, p-bromobenzenesulfonyloxy- or m-nitrobenzenesulfonyloxy residue as L.
- auxiliary bases such as potassium-tert-butylate, sodium hydride, potassium hydride or butyl lithium in aprotic, inert solvents.
- solvents can be for example aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbons (pentane, hexane, heptane, benzene, toluol), ethers (for example, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane) or polar solvents such as dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylformamide or N-methylpyrrolidone.
- the reaction temperatures can lie between ⁇ 40° C. and 140° C. preferably between ⁇ 20° C. and 80° C.
- Compounds of formula (I) in which A is a saturated alkylene group can also be produced, aside from methods A, B and C, by hydrating compounds of formula (I) in which A is an unsaturated group according to the above definition, i.e. an alkenylene group or alkadienyl group with elementary hydrogen in the presence of a suitable catalyst.
- This method is also applicable when the compounds of formula (I) with an unsaturated group A in the molecule simultaneously contain a principally hydrogenolytically cleavable group B, i.e.—as already mentioned above—a benzyl group, a diphenylmethyl or triphenylmethyl group.
- the reaction can be controlably driven either to a selective satuation of the C—C multiple bond(s) in the structural element A or to a simultaneous cleavage of the benzyl, diphenylmethyl or triphenylmethyl residue G under formation of the compounds of formula (I) with hydrogen as G.
- the hydration is preferably carried out in barely polar, aprotic solvents for selective hydration of one or more C—C multiple bonds of group A in the compounds of formula (I) according to the invention while attaining a simultaneously present hydrogenolytically cleavable benzyl, diphenylmnethyl or triphenylmethyl residue as the structural element G.
- Esters such as ethyl acetate, propyl acetate, butyl acetate or ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane or ethylene glycol dimethyl ether can be used.
- Compounds of formula (I) to be hydrated can be present as a free base or entirely or partially in the form of a salt by addition of a sub-maximal to a maximal stochiometric amount of a strong acid, preferably a mineral acid.
- a strong acid preferably a mineral acid.
- palladium Is suitable in various proportional amounts from 1, 3, 5 or 10% on solid supports such as activated carbon, activated aluminum oxide or calcium carbonate.
- the hydration is carried out under normal pressure and at a temperature of 10 to maximally 30° C., preferably at 20 to 25° C. and interrupted after consumption of the amount of hydrogen calculated for the saturation of the multiple bonds.
- polar, aprotic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, methoxyethanol or water or mixtures thereof, whereby a considerable excess of a strong acid compared to the stochiometric salt formation, preferably a mineral acid such as concentrated hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid is simultaneously added.
- the molecular ratio of substrate/acid can lie in the range of 1:2 to 1:10 thereby, preferably between 1:3 and 1:5.
- the same catalysts which are mentioned above in connection with the selective hydration are suitable as catalysts.
- the hydration is carried out under normal pressure or slightly increased hydrogen pressure of 2 to 3 bar, preferably under normal pressure, until the termination of the uptake of hydrogen.
- the reaction temperature can vary between 10 and 50, 70 or 80° C. as a function of the boiling point of the solvent and/or solvent mixture and employed pressure. If, for example, the reaction is carried out in ethanol or ethanol/water under normal pressure, the reaction temperature preferably lies between 40 to 60° C.
- the compounds of formula (I) produced according to the method (A), (B1) to (B4), (C) or (D) can be isolated and purified in a known manner, for example by subjecting the residue after distillation of the solvent to partition, extraction, re-precipitation or recrystallization or another purification method. For this, column chromatography on a suitable support or preparative, middle or high pressure liquid chromatography are preferred for this.
- the compounds (I) are first normally obtained in form of their free bases or their hydrates or solvates, depending on the type of isolation and purification. Their addition salts with pharmaceutically suitable acids are obtained in a typical manner by converting the base with the desired acid in a suitable solvent. Depending on the number of basic centers of compound (1), one or more equivalent acids per mole of base can be bound.
- Suitable solvents are, for example, chlorinated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane or chloroform; ethers such as diethyl ether, dioxane or tetrahydrofuran; acetonitrile; ketones such as acetone or ethyl methyl ketone; esters such as methyl acetate or ethyl acetate or low molecular alcohols such as methanol, ethanol or isopropanol; and water. Pure solvents as well as mixtures of two or three solvents can also be used.
- the salts can be isolated by crystallization, precipitation or the evaporation of the solvent. Thereby, they optionally accumulate as hydrates or solvates.
- the bases can be recovered from the salts by alkalization, for example with aqueous ammonia solution, alkali carbonate or diluted sodium hydroxide solution,
- alkalization for example with aqueous ammonia solution, alkali carbonate or diluted sodium hydroxide solution.
- CDI carbonyldlimidazol
- EDC N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethyl-carbodiimide hydrochloride
- TEA triethylamine
- the organic phase is concentrated in vacuum and the residue is chromatographically pre-purified twice over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (95/5 to 90/10 and 98/2 to 95/5), subsequently further purified by flash chromatography with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (100/0 to 98/2) and crystallized three times from 20 ml 1-chlorobutane, 10 ml acetonitrile/diisopropyl ether (1/1) and 8 ml isopropanol/diIsopropyl ether (1/1). Yellow crystals with a MP of 115-117° C.
- the mixture is concentrated under vacuum and subsequently distributed between 100 ml 10% NaOH and 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester.
- the aqueous phase is extracted again with 50 ml acetic acid ethyl ester and the combined organic phases are washed with 50 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum.
- the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (97/3) and crystallized twice from 40 ml and 30 ml acetonitrile after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 125-127° C. were recovered; yield 2.3 g (30%).
- the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (95/5 to 90/10) and crystallized from 15 ml acetonitrile after drawing off the solvent. Beige colored crystals with a MP of 88-90° C.
- the mixture is concentrated under vacuum and subsequently dispersed between 100 ml 10% NaOH and 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester.
- the aqueous phase is extracted again with 50 ml acetic acid ethyl ester and the combined organic phases are washed with 50 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum.
- the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (95/5 to 94/6) and crystallized first from 100 ml ethanol and then from 83 ml ethanol/diisopropyl ether (75/8) after drawing off the solvent. Yellow crystals with a MP of 162-164° C.
- the residue is taken up in 200 ml CHCl 3 and washed twice with 60 ml and 30 ml water. The organic phase is dried over a sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over a silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (96/4 bis 92/8) and crystallized three times, each from 40 ml acetonitrile and once at the conclusion from 50 ml acetonitrile. Colorless crystals with a MP of 143-145° C. were recovered; yield 0,58 g (8%).
- the batch is washed once with 50 ml 1M NaOH and twice each with 70 ml water.
- the organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum.
- the resinous residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (95/5 to 90/10) and crystallized from 30 ml acetic acid ethyl ester after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 103-105° C. were recovered; yield 3.45 g (23%).
- the acid chloride obtained in this manner is suspended in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. in an ice bath under moisture exclusion without further purification.
- 5.0 g (14.8 mmol) 5-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-pentylamine are dissolved in 40 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise to this suspension.
- the ice bath is removed and the reaction mixture is stirred for a further two hours at RT.
- the mixture is subsequently concentrated, taken up in 10% sodium hydroxide solution and extracted three times with acetic acid ethyl ester.
- the organic phase is azeotropically dried on a moisture separator and cooled to ca. 0° C.
- the resulting precipitate is filtered off and crystallized from 190 ml toluol. Colorless crystals with a MP of 139° C. were recovered; yield 46.3 g (93%).
- the organic phase is dried over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (95/5) and crystallized twice at first, each from 10 ml 1-chlorobutane, and subsequently crystallized once from 10 ml acetic acid. Colorless crystals with a MP of 110-112° C. were isolated, yield 0.2 g (3%/O).
- the residue is taken up in 200 ml water and washed three times with a total of 200 ml CHCl 3 .
- the organic phases are discarded and the aqueous phase is made alkaline with 11 g sodium hydroxide and extracted three times, each with 100 ml CHCl 3 .
- the solvent is removed under vacuum.
- the oily residue is filtered over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH/NH 4 OH (80/20/2). Yield of the gradually hardening resin: 53.0 g (83%).
- the organic phases are discarded and the aqueous phase is made alkaline with 400 ml 4M-sodium hydroxide solution and extracted three times each with 200 ml dichloromethane.
- the combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum.
- the wax-like residue is filtered over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH/NH 4 OH (90/9/1). Yield: 58.3 g (91%).
- the acid chloride obtained in this manner is suspended in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. 6.44 g (20.0 mmol) 4.(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-butylamine are dissolved in 40 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise to the suspension. After complete addition, the ice bath is removed and the reaction is stirred for a further two hours at RT. The mixture is subsequently washed with 10% sodium hydroxide solution. The organic phase is washed twice, each with 40 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solution is removed under vacuum.
- the residue is chromatographically purified three times over silica gel with CHCl 3 CH 3 OH (98/2 to 95/5) and crystallized twice from 250 ml acetonitrile after removal of the solvent Beige-colored crystals with a MP of 164-166° C.
- reaction mixture is washed with sodium hydroxide solution.
- the aqueous phase is extracted twice, each with 50 ml dichloromethane.
- the combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum.
- the residue is chromatigraphically pre-purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (98/2 to 95/5) and subsequently purified twice by flash chromatography with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (99/1 to 95/5).
- An amorphous solid with a MP of 72-74° C. remains after the removal of the solvent; yield 0.75 g (7%).
- the mixture is stirred at RT and subsequently extracted by shaking in the heat three timnes with 10 ml water, 2M sodium hydroxide solution and again with water, respectively.
- the organic phase is concentrated under vacuum and the orange colored, oily residue is chromatographically purified twice over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH/NH 4 OH (90/9/1 and 95/50 to 90/10/0) and crystallized twice from 10 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. Colorless crystals with a MP of 100-102° C. were recovered; yield: 1.9 g (35%).
- the reaction time is increased to 6 hours at RT.
- the batch is washed with 50 ml sodium hydroxide solution and the aqueous phase is extracted with 50 ml dichloromethane.
- the combined organic phases are concentrated under vacuum and the residue is chromatigraphically purified twice over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (93/7 and 95/5), subsequently further purified by flash chromatography with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH, 95/5 and 97/3) and crystallized from 5 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. Colorless crystals with a MP of 80-82° C. were recovered; yield 0.9 g (15%).
- reaction solution is filtered and the filter cake is dispersed between 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester and 100 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution.
- the organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum.
- the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH/TEA (95/510 to 94/5/1). Yield: 5.6 g (67%)
- the aqueous phase is extracted with 30 ml THF and thereafter the combined organic phases are washed twice, each with 30 ml saturated NaCl solution, dried over sodium sulfate and the solution is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH/NH 4 OH (90/10/1). Yield: 3.9 g (57%).
- the resulting 4-[3-tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-propyl]-piperidine is dissolved in 90 ml acetonitrile without further purification and added to 35 g (135 mmol) diphenyl bromomethane (95%) and 29 g (210 mmol) potassium carbonate and stirred for four days at RT. The mixture is filtered and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resulting 1-diphenylmethyl-4-[3-tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-propyl]-piperidine is dissolved without further purification in 130 ml methanol and added to 25 ml conc. hydrochloric acid, and the mixture is stirred at RT overnight.
- the solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is taken up with 300 ml water and extracted with 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester.
- the organic phase is discarded and the aqueous phase is made alkaline with 17 g sodium hydroxide and extracted with 300 g acetic acid ethyl ester.
- After washing the organic phase with 40 ml water this is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum.
- the oil is dried under high-vacuum and processed further without purification Yield: 22.4 g (65%).
- the combined organic phases are extracted twice, each with 300 ml 10% hydrochloric acid.
- the combined aqueous phases are adjusted to alkaline with 10% sodium hydroxide solution and extracted twice, each with 400 ml acetic acid ethyl ester.
- the combined organic phases are washed with 100 ml water and dried over sodium sulfate. The solvent is removed under vacuum, the residue is dried under high-vacuum and further processed without additional purification. Yield of gradually solidifying resin: 63 g (99%)
- the aqueous phase is made basic with 200 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution and extracted twice, each with 250 ml toluol.
- the solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 /CH 3 OH (97/3). After drawing off the solvent, a light brown oil remains which is further processed without additional purification. Yield: 47.4 g (90%).
- the active ingredients used according to the invention can be processed to the desired medicaments in the form of their acid addition salts, hydrates or solvates individually or in combination with each other or with others, optionally under addition of other active ingredients, for the indications tumor treatment or immunosuppression.
- these can also optionally be separately present next to each other in the medicine packaging, for example as tablets next to viles, depending on the requirements.
- further subject-matter of the invention is a medicament with an amount of compounds according to the above defined general formula (I) in combination with the further cytostatic agent, cancerostatic agent, immunosuppressing agent and/or immunomodulatory agent.
- a method for the production of medicaments with an amount of one or more compounds according to formula (I), optionally together with another cytostatic agent or immunosuppressive agent and optionally next to further active ingredients and additives customary and suitable for these indications together with respective pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and adjuvents for providing the finished medical form also falls within the scope of protection according to the invention.
- injections are administered for the treatment of tumors.
- These are prepared either in the form of vials or also as so-called ready-to-use injection preparations, for example as ready-to-use syringes or single use syringes in addition to perforation bottles for multiple withdrawals.
- Administration of the injection preparations can occur in the form of subcutaneous (s.c.), intramuscular (i.m.), intravenous (i.v.) or intracutaneous (i.c.) application.
- the respective suitable injection forms can especially be produced as solutions, crystal suspensions, nanoparticular or colloid-disperse systems, such as for example, hydrosols.
- the injectable formulations can also be produced as concentrates which can be adjusted with aqueous isotonic dilution agents to the desired active ingredient dosage. Furthermore, they can also be produced as powders, such as for example lyophilisates, which are then preferably dissolved or dispersed immediately before application with suitable diluents.
- the infusions can also be formulated in the form of isotonic solutions, fat emulsions, liposome formulations, microemulsions and liquids based on mixed micells, for example, based on phospholipids.
- infusion formulations can also be prepared in the form of concentrates to dilute.
- the injectable formulations can also be applied in the form of continuous infusions as in stationary as well as in out-patient therapy, for example in the form of mini-pumps.
- Albumin, plasma expanders, surface active compounds, organic solvents, pH influencing compounds, complex forming compounds or polymeric compounds can be added to the parenteral medicinal forms, especially as substances for influencing the adsorption of the active ingredients to protein or polymers or also with the aim of decreasing the adsorption of the active ingredient to materials such as injection instruments or packaging materials, for example plastic or glass.
- the active ingredients can be bound to nanoparticles in the preparations for parenteral use, for example on finely dispersed particles based on poly(meth)acrylates, polyacetates, polyglycolates, polyamino acids or polyether urethanes.
- the parenteral formulations can also be constructively modified as depot preparations, for example on the multiple unit principle, where the active ingredients are incorporated in a most finely distributed and/or dispersed, suspended form or as crystal suspensions, or on the single unit principle, where the active ingredient is enclosed in a medicinal form, for example, a tablet or a seed which is subsequently implanted.
- these implantations or depot medicaments in single unit and multiple unit medicinal forms consist of so-called biodegradable polymers, such as for example, polyether urethanes of lactic and glycolic acid, polyether urethanes, polyamino acids, poly(meth)acrylates or polysaccharides.
- biodegradable polymers such as for example, polyether urethanes of lactic and glycolic acid, polyether urethanes, polyamino acids, poly(meth)acrylates or polysaccharides.
- Sterilized water pH value influencing substances, such as for example organic and inorganic acids or bases as well as their salts, buffer substances for setting the pH value, agents for isotonicity, such as for example sodium chloride, monosodium carbonate, glucose and fructose, tensides and/or surface active substances and emulsifiers, such as for example, partial fatty acid esters of polyoxyethylene sorbitan (Tween®) or for example fatty acid esters of polyoxethylene (Cremophor®), fatty oils such as for example peanut oil, soybean oil and castor oil, synthetic fatty acid esters, such as for example ethyl oleate, isopropyl myristate and neutral oil (Miglyolq®) as well as polymer adjuvents such as for example gelatin, dextran, polyvinylpyrrolidone, organic solvent additives which increase solubility, such as for example propylene glycol, ethanol, N,N-di
- a further systemic application form of importance is peroral administration as tablets, hard or soft gelatin capsules, coated tablets, powders, pellets, microcapsules, oblong compressives, granules, chewable tablets, lozenges, gums or sachets.
- These solid peroral administration forms can also be prepared as sustained action and/or depot systems.
- film or matrix forming substances such as for example ethylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, poly(meth)acrylate derivatives (for example Eudragit®), hydroxypropylmethylcellulose phthalate are suitable in organic solutions as well as in the form of aqueous dispersions.
- bio-adhesive preparations are also to be named in which the increased retention time in the body is achieved by intensive contact with the mucus membranes of the body.
- An example of a bio-adhesive polymer is the group of Carbomers®.
- compressives such as for example non-disintegrating tablets in oblong form of a suitable size with a slow release of active ingredient
- compressives are especially suitable.
- mixtures of pellets which release at the various places are employable, for example mixtures of gastric fluid soluble and small intestine soluble and/or gastric fluid resistant and large intestine soluble pellets.
- the same goal of releasing at various sections of the gastrointestinal tract can also be conceived by suitably produced laminated tablets with a core, whereby the coating of the agent is quickly released in gastric fluid and the core of the agent is slowly released in the small intestine milieu.
- the goal of controlled release at various sections of the gastrointestinal tract can also be attained by multilayer tablets.
- the pellet mixtures with differentially released agent can be filled into hard gelatin capsules.
- Anti-stick and lubricant and separating agents such as flame dispersed silicone dioxide, disintegrants, such as various starch types, PVC, cellulose esters as granulating or retarding agents, such as for example wax-like and/or polymeric compounds on the basis of Eudragit®, cellulose or Cremophor® are used as a further adjuvents for the production of compressives, such as for example tablets or hard and soft gelatin capsules as well as coated tablets and granulates.
- Anti-oxidants such as for example saccharose, xylite or mannite, masking flavors, aromatics, preservatives, colorants, buffer substances, direct tableting agents, such as for example microcrystalline cellulose, starch and starch hydrolysates (for example Celutab®), lactose, polyethylene glycols, polyvinylpyrrolidone and dicalcium phosphate, lubricants, fillers, such as lactose or starch, binding agents in the form of lactose, starch varieties, such as for example wheat or corn and/or rice starch, cellulose derivatives, for example methylcellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose or silica, talcum powder, stearates, such as for example magnesium stearate, aluminum stearate, calcium stearate, talc, siliconized talc, stearic acid, acetyl alcohol and hydrated fats are used.
- direct tableting agents such as for example microcrystalline cellulose, starch and starch hydrolysates (
- oral therapeutic systems constructed especially on osmotic principles, such as for example GIT (gastrointestinal therapeutic system) or OROS (oral osmotic system), are also to be mentioned.
- GIT gastrointestinal therapeutic system
- OROS oral osmotic system
- Effervescent tablets or tabs both of which represent immediately drinkable instant medicinal forms which are quickly dissolved or suspended in water are among the perorally administratable compressives.
- perorally administratable forms are also solutions, for example drops, juices and suspensions, which can be produced according to the above given method, and can still contain preservatives for increasing stability and optionally aromatics for reasons of easier intake, and colorants for better differentiation as well as antioxidants and/or vitamins and sweeteners such as sugar or artificial sweetening agents. This is also true for inspisated juices which are formulated with water before ingestion.
- Ion exchange resins in combination with one or more active ingredients are also to be mentioned for the production of liquid ingestable forms.
- a special release form consists in the preparation of so-called floating medicinal forms, for example based on tablets or pellets which develop gas after contact with body fluids and therefore float on the surface of the gastric fluid.
- so-called electronically controlled release systems can also be formulated by which active ingredient release can be selectively adjusted to individual needs.
- a further group of systemic administration and also optionally topically effective medicinal forms are represented by rectally applicable medicaments.
- suppositories and enema formulations.
- the enema formulations can be prepared based on tablets with aqueous solvents for producing this administration form.
- Rectal capsules can also be made available based on gelatin or other carriers.
- Hardened fat such as for example Witepsol®, Massa Estarinum®, Novata®, coconut fat, glycerol-gelatin masses, glycerol-soap-gels and polyethylene glycols are suitable as suppository bases.
- pressed implants are suitable which are preferably formulated on the basis of so-called biodegradable polymers.
- transdermal systems are also to be emphasized which distinguish themselves, as with the above-mentioned rectal forms, by circumventing the liver circulation system and/or liver metabolism.
- These plasters can be especially prepared as transdermal systems which are capable of releasing the active ingredient in a controlled manner over longer or shorter time periods based on different layers and/or mixtures of suitable adjuvents and carriers.
- membrane infiltration increasing substances and/or permeation promoters such as for example oleic acid, Azone®, adipinic acid derivatives, ethanol, urea, propylglycol are suitable in the production of transdermal systems of this type for the purpose of improved and/or accelerated penetration.
- vaginally or genitally applicable emulsions creams, foam tablets, depot implants, ovular or transurethral adminstration installation solutions.
- highly sterile eye ointments, solutions and/or drops or creams and emulsions are suitable.
- Sodium algenate as a gel builder for production of a suitable foundation or celluolose derivatives such as for example guar or xanthene gum
- inorganic gel builders such as for example aluminum hydroxides or bentonites (so-called thixotropic gel builder)
- polyacrylic acid derivatives such as for example Carbopol®, polyvinylpyrolidone, microcrystalline cellulose or carboxymethylcellulose are suitable as adjuvents and/or carriers.
- amphiphilic low and high molecular weight compounds as well as phospholipids are suitable.
- the gels can be present either as hydrogels based on water or as hydrophobic organogels, for example based on mixtures of low and high molecular paraffin hydrocarbons and vaseline.
- Anionic, cationic or neutral tensides can be employed as emulsifiers, for example alkalized soaps, methyl soaps, amine soaps, sulfanated compounds, cationic soaps, high fatty alcohols, partial fatty acid esters of sorbitan and polyoxyethylene sorbitan, for example lanette types, wool wax, lanolin, or other synthetic products for the production of oil/water and/or water/oil emulsions.
- Hydrophilic organogels can be formulated, for example, on the basis of high molecular polyethylene glycols. These gel-like forms are washable.
- Osmotically effective acids and bases such as for example hydrochloric acid, citric acid, sodium hydroxide solution, potassium hydroxide solution, monosodium carbonate, further buffer systems, such as for example citrate, phosphate, Tris-buffer or triethanol amine are used for adjusting the pH value.
- Preservatives for example such as methyl- or propyl benzoate (parabenes) or sorbic acid can be added for increasing stability.
- Pastes, powders or solutions are to be mentioned as further topically applicable forms.
- Pastes often contain lipophilic and hydrophilic auxiliary agents with very high amounts of fatty matter as a consistency-giving base.
- Powders or topically applicable powders can contain for example starch varieties such as wheat or rice starch, flame dispersed silicon dioxide or silica, which also serve as diluents, for increasing flowability as well as lubricity as well as for preventing agglomerates.
- starch varieties such as wheat or rice starch
- flame dispersed silicon dioxide or silica which also serve as diluents, for increasing flowability as well as lubricity as well as for preventing agglomerates.
- Nose drops or nose sprays serve as nasal application forms.
- nebulizers or nose creams or ointments can come to use.
- nose spray or dry powder formulations as well as controlled dosage aerosols are also suitable for systemic administeration of the active ingredients.
- these pressure and/or controlled dosage aerosols and dry powder formulations can be inhaled and/or insufflated. Administration forms of this type also certainly have importance for direct, regional application in the lung or bronchi and larynx.
- the dry powder compositions can be formulated for example as active ingredient-soft pellets, as an active ingredient-pellet mixture with suitable carriers, such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- suitable carriers such as for example lactose and/or glucose
- tetrafluoroethane or HFC 134a and/or heptafluoropropane or HFC 227 are suitable, wherein non-fluorinated hydrocarbons or other propellants which are gaseous at normal pressure and room temperature, such as for example propane, butane or dimethyl ether can be preferred.
- propellant-free, manual pump systems can also be used.
- the propellant gas aerosols can also suitably contain surface active adjuvents, such as for example isopropyl myristate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester, sorbitan trioleate, lecithins or soya lecithin.
- surface active adjuvents such as for example isopropyl myristate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester, sorbitan trioleate, lecithins or soya lecithin.
- solutions for installation for example for transurethral administration in bladder tumors or genital tumors, or for profusion in liver tumors or other organ carcinomas are suitable.
- the respective suitable medicinal forms can be produced in accordance with the prescription and procedures based on pharmaceutical-physical fundamentals as they are described for example in the following handbooks and are included in the present inventive subject-matter with respect to the production of the respective suitable medicaments:
- the solution is produced according to the customary method, sterilized and filled into 10 ml vials.
- One vial contains 50 mg of the compound according to the invention.
- Penteral Solution active ingredient used according to the invention 1.000 g hydrochloric acid, dilute 5.000 g sodium chloride 6.000 g water for injection purposes to 1000.000 ml
- the solution is produced according to a customary method by stirring; the medicinal form is adjusted to a suitable pH value by acid addition and subsequently filled into 100 ml vials and sterilized.
- a vial contains 100 mg of the compound according to the invention.
- the active ingredient(s) used according to the invention is dispersed in the saturated triglycerides. Then the soya lecithin is added under stirring, and subsequent to this, the aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide is added with subsequent homogenization. The dispersion is sterilized and filled into 10 ml vials. A vial contains 50 mg of the compound according to the invention.
- Biodegradable Parenteral Depot Medicinal Form active ingredient used according to the invention 10.000 polylactic acid/polygylcolic acid polymer 70.000 polyvinylpyrrolidone 0.200 gelatin 2.000 soya lecithin 2.000 isotonic sodium chloride solution to 1000.000 ml
- the active ingredient is incorporated into the biodegradable polymer comprising polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid by a suitable method (spray drying, solvent-evaporation or phase separation) and subsequently subjected to a sterilization process.
- the particles are introduced into a 2-chamber ready-made syringe in which the adjuvent solution, which is also produced in a sterile manner, is filled.
- the biodegradable microparticles are mixed with the dispersion agent shortly before application and dispersed.
- the content of a ready-made syringe is measured such that this contains 200 mg of the active ingredient according to the invention.
- the active ingredient is dispersed together with soya lecithin and arachis oil.
- the benzyl alcohol is dissolved in Miglyole® and added to the dispersion.
- the entire dispersion is sterilized and subsequently filled into vials with 2 ml content.
- a vial contains 50 mg active ingredient.
- so-called perforation bottles vials
- infusion solutions with an amount of one or more active ingredients according to the invention can also be made available in the customary manner under addition of buffer substances for adjustment of physiological pH value and/or the isotonicity and/or a best possible suitable pH value for the medicinal form (euhydria) and optional further required nutrients, vitamins, amino acids, stablizers and other necessary adjuvents, possibly in combination with further medicinal agents suitable for the mentioned indications.
- the above components are mixed with each other and compacted in a conventional manner, wherein a tablet weight of 180 mg is set. Each tablet contain's 100 mg active ingredient. If desired, the tablets obtained in this manner are coated, provided with a film coat and/or enterically coated.
- a granulate is produced which is pressed to the desired coated tablet cores.
- Each core contains 50 mg of active ingredient.
- the core can be further processed in a customary manner to coated tablets. If desired, a gastric fluid resistant or retarding film coat can be applied in a known manner.
- the active ingredient is compacted together with the adjuvents under high pressure to sublingual tablets, favorably in oblong form.
- the active ingredient is impasted together with the fluid carrier mixture and mixed together with further adjuvents suitable for the incapsulation and filled into elastic soft gelatin capsules which are sealed.
- Hard Gelatin Capsules active ingredient used according to the invention 0.150 g microcrystalline cellulose 0.100 g hydroxypropylmethylcellulose 0.030 g mannite 0.100 g ethylcellulose 0.050 g triethyl citrate 0.010 g
- the active ingredient is mixed together with the adjuvents, microcrystalline cellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and mannite, wet with granulation liquid and formed into pellets. These are subsequently coated with a solution of ethylcellulose and triethyl citrate in organic solvents in a fluidized-bed apparatus.
- a hard gelatin capsule contains 150 mg of active ingredient.
- the active ingredient(s) used according to the invention is dissolved in propylene glycol at ca. 60° C.
- the lipophilic components are melted at 60-70° C. and subsequently combined with the active ingredient solution.
- the ointment is emulsified at first at 60-70° C. and subsequently cooled to 35-40° C. under constant emulsification and then filled in 10 g tubes.
- a tube contains 100 mg of the compound according to the invention.
- Further subject-matter is a pharmaceutical formulation which is characterized in that it contians an active ingredient(s) used according to the invention as a base or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof together with carriers and/or diluents customary for this and suitable for administration by means of inhalation.
- physiologically acceptable salts of the active ingredients are, as already illustrated in the synthesis section, acid addition salts derived from inorganic or organic acids such as for example especially hydrochloride, hydrobromide, sulfate, phosphate, maleate, tartrate, citrate, benzoate, 4-methoxybenzoate, 2- or 4-hydroxybenzoate, 4-chlorobenzoate, p-toluolsulfonate, methanosulfonate, ascorbate, salicylate, acetate, formate, succinate, lactate, glutarate, gluconate or tricarballylate.
- inorganic or organic acids such as for example especially hydrochloride, hydrobromide, sulfate, phosphate, maleate, tartrate, citrate, benzoate, 4-methoxybenzoate, 2- or 4-hydroxybenzoate, 4-chlorobenzoate, p-toluolsulfonate, methanosulfonate, ascorbate, sal
- compositions used of the invention by means of inhalation occurs according to the invention in conventional ways customary for administrations of this form, for example in the form of a commercial controlled dosage aerosol or in combination with a spacer.
- a metering valve is delivered with whose help, a dosed amount of the composition is administered.
- the present compositions can be formulated for example as aqueous solutions or suspensions and be administered by means of an atomizer.
- Aerosol spray formulations in which the active ingredient is either suspended with one or two stabilizers in a propellant as a carrier and/or diluent for example tetrafluoroethane or HFC 134a and/or heptafluoropropane or HFC 227 can equally be used, whereby however, non-fluorinated hydrocarbons or other propellants which are gaseous at normal pressure and room temperature, such as propane, butane or dimethyl ether, can be preferred.
- propellant-free manual pump systems or dry powder systems as desribed below can also be used.
- the propellant aerosols can also contain surface active adjuvents, such as for example isopropyl myristate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester, sorbitan trioleate, lecithins, oleic acid.
- surface active adjuvents such as for example isopropyl myristate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester, sorbitan trioleate, lecithins, oleic acid.
- the medicaments with an amount of compounds according to the invention can also be formulated in the form of dry powder compositions, for example as active ingredient-soft pellets or as an active ingredient-powder mixture with a suitable carrier, such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- a suitable carrier such as for example lactose and/or glucose.
- the powder compositions can be formulated and administered as single doses or as multiple doses.
- the compounds according to the invention are preferably administered by means of a controlled dosage aerosol or in the form of a dry powder dosage formulation, wherein the latter preferably contains glucose and/or lactose as a carrier substance.
- applicators for inhalation of the pharmaceutical formulations containing one or more of the active ingredient(s) used according to the invention all applicators are generally suitable which are suitable for controlled dosage aerosols and/or a dry powder dosage formulation, such as for example usual applicators for the nose, mouth and or pharynx, or also devices standing under propellant gas for the delivery of a spray (as controlled dosage aerosol or dry powder dosage formulation) as they are also used for inhalations in the nose, mouth and/or pharynx.
- a further embodiment can also consist of an aqueous solution of the active ingredient(s) used according to the invention, which also optionally contains further active ingredients and/or additives, which are applied by means of an ultrasound atomizer.
- Intended dose per aerosol per stroke % by weight a) Controlled Dosage Aerosol active ingredient used according 0.500 mg 0.66 to the invention stabilizer 0.075 mg 0.10 HFC 134a 75.500 mg 99.24 b) Controlled Dosage Aerosol active ingredient used according 0.250 mg 0.32 to the invention Stabilizer 0.038 mg 0.05 HFC 227 79.180 mg 99.63
- the micronized active ingredient is, after previous dispersion in a small amount of the stabilizer, placed in a suspension vessel in which the bulk amount of propellant gas solution is found.
- the corresponding suspension is dispersed by means of a suitable stirring system (for example high performance mixer or ultrasound mixer) until an ultra-fine dispersion results.
- the suspension is then continuously held in flux in a filling apparatus suitable for cold propellants or pressure fillings.
- the suspension can also be produced in a suitable cooled stabilizer solution in HFC 134a/227.
- the examples c) to d) describe the composition and production of dosage dry powder formulations.
- mg/dose c) Dosage-Dry Powder Formulation active ingredient used according to the invention 0.500 mg d) Dosage-Dry Powder Formulation active ingredient used according to the invention 0.500 mg lactose Ph.Eur. to 2.5 mg or to 5.0 mg e) Dosage-Dry Powder Formulation active ingredient used according to the invention 0.250 mg lactose Ph.Eur. to 2.5 mg or to 5.0 mg
- the active ingredient is micronized, thereafter, bulk material is mixed with the lactose in the given amounts, and subsequently, filled in a multi-dose powder inhilator.
- the active ingredient or the medicinal agent in the form of the respective suitable pharmaceutical acceptable salt and/or acid addition salts can be present, insofar as the base is not preferred in each case.
- the tumor growth inhibiting activity of the substances was determined on human tumor cells in standardized in vitro test systems. In the screening tests, the substances gave IC 50 -values in a concentration range of 0.1 nM bis 10 ⁇ M.
- the test was ended and the protein amount in the individual wells was determined with the sulforhodamin-B-method (according to P. Skehan et al.: New Colorimetric Cytotoxicity Assay for Anticancer-Drug Screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 82: 1107-1112, 1990).
- the IC 50 -values (defined as that concentration in which the cell growth was inhibited by 50%) was taken from the dose-response curves and given as a comparative measurement for the activity of the test compounds.
- the compounds of formula (I) and their salts permit a therapeutic use in malignant illnesses of humans and animals through their excellent inhibition of the growth of tumor cells.
- the anti-neoplastic activity of the described substances can be used for prophylactic, adjunct, palliative, and curative treatment of solid tumors, leukemic illnesses and lymphomas as well as for decreasing or preventing metastasis formation in humans and animals.
- gynecological tumors such as of the vulva or the uterus, ovarian carcinomas, testicle tumors, prostate carcinomas, skin cancer, kidney cancer, bladder tumors, esophagus carcinomas, stomach cancer, rectal carcinomas, pancreas carcinomas, thyroid cancer, adrenal tumors, various types of leukemia and lymphomas, Hodgkin's disease, tumor illnesses of the CNS, soft-tissue sarcomas, bone sarcomas, benign and malignant mesotheliomas, especially intestine cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, bronchial and lung carcinomas, melanomas, acute and chronic leukemias. Benign papillomatosis tumors can also be inhibited in their growth with the named substances.
- anti-metabolites for example cytarabine, 5-fluorouracil, 6-mercaptopurine, methotrexate
- alkylating agents for example busuffan, carmustine, cisplatin, carboplatin, cyclophosphamide, dacarbazine, melphalane, thiotepa
- DNA-intercalating substances and topoisomerase inhibitors for example actinomycin D, daunorubicin, doxorubicin, mitomycin C, mitoxantrone, etoposide, teniposide, topotecan, irinotecan
- spindle poisons for example vincristine, navelbin, taxol, taxoter
- hormonally active agents for example tamoxifen, flutamide, formestan, goserelin
- other cytostatic agents for example tamoxifen, flutamide, formestan, goserelin
- the spleen of a Swiss mouse served as a lymphocyte source.
- the lymphocyte population was isolated from the spleen cell suspension over a ficoll gradient and taken up in IMEM-ZO culture medium with 0,1% dextran 70,000 and 2% fetal calf serum.
- the cells were plated at a density of ca. 500,000 cells/well/ml in a 12-well plate, 1 ml doubly concentrated test substance solution was pipetted per well and this was subsequently incubated in a tissue culture incubator at 37° C. and 5% CO 2 .
- IC 50 -values were calculated which were also employed in the following Tables for the characterization of the individual substances: Test Substance No. IC 50 [ ⁇ M] 46 0.03 252 0.0002 254 0.00008 306 0.002 315 0.00004
- the special, independent class of the compounds used according to the invention is also suitable for a combination with known immunosuppressive agents from the class of macrolides, for example cyclosporin A, tacrolimus, raparnycin, or anti-metabolites, for example azathioprin or methotrexate and glucocorticoids.
- known immunosuppressive agents from the class of macrolides, for example cyclosporin A, tacrolimus, raparnycin, or anti-metabolites, for example azathioprin or methotrexate and glucocorticoids.
- the invention is in no was limited to the present respective concretely named active ingredients concentrations, dosages, combinations with one or more other cytostatic agents, tumor inhibitors, cancerostatic agents, immunosuppressive agents or further medicinal agents suitable for the respective specific indications or the type of tumor to treated or immunological illness, etc.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- The invention relates to the use of pyridyl aklane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides, especially in the treatment of tumor conditions and/or as cytostatic agents or as immunosuppressive agents as well as medicaments with an amount of these compounds in combination with other cytostatic agents or immunosuppresive agents.
- A strong need exists for the enrichment of cytostatic therapy to provide pharmaceuticals and/or medicaments which not only possess a strong activity, but also exert diminished side effects in comparison to many classical cancerostatic agents, whereby treatment of a broad as possible spectrum of tumors should be made accessible. Furthermore, effective cytostatic agents for an efficient therapy should be made available. Active ingredients of this type should also be exceptionally suitable in the mentioned indications for a combination therapy, be it in connection with other cytostatic agents or with radiation (for example X-rays, radioactive elements, such as cobalt, or linear accelerator, etc.), with operative procedures, heat treatment, etc. As a consequence, further subject-matter of the invention relates to new medicaments in the form of combinations of the compounds defined below and used according to the invention together with other compounds or immunosuppressive agents customary in the therapy of tumors.
- In this connection, a strong need also exists in tumor therapy to open up new possibilities which were not usable up to now in these indications, for example for overcoming or preventing resistances.
- This object was successfully solved in a completely suprising manner by making available the specially structured pyridyl derivatives defined below.
- It was known that various pyridine compounds substituted in a specific manner have pharmacologically useful properties which lie however in completely different indication areas.
- Thus, ω-pyridyl alkane and/or alkene amides with anti-allergic activity are described in EP 0 210 782 which are referred to as having a 5-lipoxygenase-inhibiting and anti-histamine action, wherein the amide components of these compounds contain a piperizine or homopiperizine ring and the pyridine ring can be linked together in the 2-, 3- or 4-position. JP 63,179,869 describes further pyridyl amides, ω-pyridyl alkane and alkene amides as anti-allergic effective substances containing a substituted piperidine ring in the amine component. Such compounds with the same properties are mentioned in Chem. Pharm. Bull 37, 100-105 (1989) and in J. Med. Chem. 1989,583-593.
- Pyridyl ureas, pyridyl thioureas and pyridyl carbonamides, wherein the amide portion is bound over an aryl substituted alkyl chain with a piperidine ring or piprazine ring, are described for example in EP-A-0 428 434 or in EP-A-0 512 902 as antagonists of the neurokinin receptor and subtance P. Furthermore, pyridyl(alkyl)carbonamides, pyridyl(alkyl)sulfonamides and analogous ureas, wherein the amide portion is bound over an alkyl chain with a piperidine ring are disclosed in EP-A-0 479 601 as active ingredients with anti-arrhythmic properties.
- In WO 91/15 485, the production of pyridine-3,5-dicarboxylic acid esters and amides as well as their use for the treatment of tumor conditions is described. These compounds differ from the compounds according to the invention described below in very important structural features, for example by the dicarboxyl grouping on the pyridine ring or the absence of the hydrocarbon chain between the pyridine ring and the amide grouping. The compounds disclosed in WO 89/07 443 in the form of optically pure R(−)-Ni-guldipine and further analogous dihydropyridines with cytotoxic activity have larger structural differences. However, the compounds according to the invention unexpectedly possess a better activity and a wider spectrum of action despite the large structural differences.
- Further structurally closely related compounds are represented by the antagonists of the histimine-H 1-receptor described in EP-A-0 343 307 which discloses a series of substituted piperidine derivatives without naming concrete examples for special 3-pyridyl substitutions.
- EP-A-0 330 026 also discloses substituted piperidine derivatives with possible, generic pyridyl substitutions for which, however, merely a single concrete example is disclosed, namely (E)-3-(3-pyridyl)-N-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl]-2-propenamide hydrochloride. These compounds are distinguished by an anti-cholinesterase activity, an anti-amnesia activity as well as activities directed against hyperkinesia, senile demensia, mania and Alzheimer's disease.
- In view of this art, the finding that the compounds according to the general formula (I) defined below have activities which make them particularly suitable in an excellent manner for the therapy of tumor illnesses was completely unexpected. Equally unexpected was the pharmacological finding that the compounds according to the invention also possess immunosuppressive properties besides cytostatic activity.
- Considering the above-mentioned completely different known medical indications of known piperidine derivatives, such as neurokinin receptor antagonism, hyperkineses, amnesias, allergies, or rhythm disorders, the activity of the compounds used according to the invention with the structural modifications as they are defined below with respect to the present general formula, and the combinations according to the invention in the form of the detected excellent cytostatic or immunomodulatory activity with advantageous therapeutic properties was completely surprising for the person skilled in the art.
- Pharmacological test results from which this conclusion must be drawn, as well as the concrete tumor indications and combination possibilities are detailed and illustrated in the last part of the description.
-
- wherein
- R 1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, benzyloxy,
- aminocarbonyl, carboxy, phenyl, phenoxy, phenylthio, pyridyloxy, pyridylthio,
- alkyl, especially C 1-C6-alkyl,
- alkenyl, especially C 3-C6-alkenyl,
- alkinyl, especially C 3-C6-alkinyl,
- hydroxyalkyl, especially C 1-C6-hydroxyalkyl,
- alkoxy, especially C 1-C6-alkoxy,
- alkenyloxy, especially C 3-C6-alkenyloxy,
- alkinyloxy, especially C 3-C6-alkinyloxy,
- alkanoyloxy, especially C 1-C7-alkanoyloxy,
- alkoxycarbonyloxy, especially C 2-C7-alkoxycarbonyloxy,
- alkylthio, especially C 1-C6-alkylthio,
- alkenylthio, especially C 3-C6-alkenylthio,
- alkinylthio, especially C 3-C6-alkinylthio,
- cycloalkyl, especially C 3-C8-cycloalkyl,
- cycloalkytoxy, especially C 3-C8-cycloalkyloxy,
- cycloalkylthio, especially C 3-C8-cycloalkylthio,
- alkoxycarbonyl, especially C 2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl,
- alkylaminocarbonyl, especially C 2-C7-alkylaminocarbonyl,
- dialkylaminocarbonyl, especially C 3-C13-dialkylaminocarbonyl, or
- NR 5R6, wherein
- R 5 and
- R 6 are selected independently of each other from hydrogen,
- alkyl, especially C 1-C6-alkyl,
- alkenyl, especially C 3-C6-alkenyl and
- alkinyl, especially C 3-C6-alkinyl,
- R 2 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, benzyloxy,
- alkyl, especially C 1-C6-alkyl,
- alkoxy, especially C 1-C6-alkoxy or
- alkanoyloxy, especially C 1-C7-alkanoyloxy,
- wherein R 1 and R2, if they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which is selected from —(CH2)4—, —(CH═CH)2— and —CH2O—CR7R8—O—, wherein
- R 7 and
- R 8 are, independently of each other, hydrogen or alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl,
- R 3 is hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxyalkyl, especially C1-C6-hdroxyalkyl and
- R 4 is hydrogen, hydroxy, benzyloxy,
- alkyl, especially C 1-C6-alkyl,
- alkenyl, especially C 3-C6-alkenyl,
- alkinyl, especially C 3-C6-alkinyl,
- cycloalkyl, especially C 3-C6-cycloalkyl or
- alkoxy, especially C 1-C6-alkoxy,
- k is 0 or 1,
- A is alkylene, especially C 1-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by alkyl, especially C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, especially C1-C3-alkoxy, fluorine or phenyl, or
- 1,2-cyclopropylene or
- alkenylene with at least two C-atoms, especially C 2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, C1-C3-alkoxy, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
- alkadienylene with at least four C-atoms, especially C 4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
- 1,3,5-hexatrienylene, which is optionally substutited by C 1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano, or phenyl,
- ethinylene or
- alkylene with at least two C-atoms, especially C 2-C6-alkylene in which a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR9, CO, SO or SO2, wherein the isosteric substitution, with the exception of ═CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group and wherein
- R 9 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, alkenyl, especially C3-C6-alkenyl, alkinyl, especially C3-C6-alkinyl, acyl, especially C1-C6-acyl or alkylsulfonyl, especially C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl,
- D is selected from alkylene, especially C 1-C10-alkylene, optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy,
- alkenylene with at least two C-atoms, especially C 2-C10-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy,
- or alkoxy, especially C 1-C6-alkoxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
- alkinylene with at least three C-atoms, especially C 3-C10-alkinylene, optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy or alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, and
- alkylene, especially C 1-C10-alkylene, alkenylene with at least two C-atoms, especially C2-C10-alkenylene or alkinylene with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C10-alkinylene, whereby one to three methylene units are each isosterically replaced by O, S, NR10, CO, SO or SO2 wherein
- R 10 has the same meaning as
- R 9 but is selected independently thereof,
-
- wherein the heterocyclic ring can also optionally have a double bond and
- n and
- p can be, independently of one another, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p<4 and
- q is 2 or 3,
- R 11 is hydrogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or alkoxycarbonyl with at least two C-atoms, especially C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl and
- R 12 is hydrogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl or or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom, wherein
- R 11 and R12 optionally together, form an alkylene bridge with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 C-atoms, especially a C1-C3-alkylene bridge under formation of a bicyclic ring system,
- G is selected from hydrogen,
- G1, G2, G3, G4 and G5, wherein
- G 1 represents the residue
- —(CH2)r—(CR14R15)s—R13 (G1)
- wherein
- r is an integer from 1 to 3 or O and
- s is 0 or 1,
- R 13 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, alkenyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C6-alkenyl, alkinyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C6-alkinyl, cycloalkyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C8-cycloalkyl,
- saturated, five to seven membered heterocycles, which can contain one or two hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O, benzyl or phenyl,
- monocyclic aromatic five or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 has the same meaning as R13, but is selected independently thereof,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
- monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
-
- wherein the substituents R 13 and R15 can have the above meaning or the grouping
- NR13R15
- can also be a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
- saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O, or
- saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O,
- G3 is the residue
- SO2—(CH2)rR13 (G3)
- and
-
- wherein
- Ar 1 and Ar2 are selected independently from one another from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl and
- G5 is the residue
- COR16 (G5)
- wherein
- R 16 is selected from trifluoromethyl, alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, alkenyloxy, especially C3-C6-alkenyloxy, or benzyloxy,
- wherein any aryl residues and/or aromatic ring systems in the substituents R 1, R2, R4, R13, R14, R15, R16, Ar1 and Ar2 and/or in the ring system —NR13R15 can be substituted independently from each other by one to three of the same or different residues which are selected from halogen, cyano, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, cycloalkyl, especially C3-C8-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, alkoxy, substituted entirely or partially by fluorine, substituted alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, alkylthio, especially C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, especially C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, monoalkylamino, especially mono-C1-C6-alkylamino, dialkylamino, especially di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino and methylenedioxy for two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system,
- wherein each of the residues alkyl, alkenyl, alkinyl, hydroxyalkyl, alkoxy, alkenyloxy, alkinyloxy, alkanoyloxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkoxycarbonyloxy, alkylthio, alkenylthio, alkinylthio, alkylene, acyl, alkylsulfonyl, alkenylene, alkinylene, cycloalkyl, cycloalkyloxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl or dialkylaminocarbonyl of the substituents R 1 to R14 can have 1 to 2 or 4, 6, 8, 10 or 12 C-atoms and/or 2 or 3 to 5, 7, 9, 11 or 13 and/or 15C-atoms or 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 or 15C-atoms depending on the structure, as well as
- stereoisomers and/or mixtures thereof and pharmacologically acceptable
- acid addition salts thereof
- for the production of medicaments for cytostatic or immunomodulatory and/or immunosuppressive treatment.
-
- for the production of medicaments for the indications named above, wherein in the general formula (I)
- R 1 is a hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, C1-C6-hydroxyalkyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy, C3-C6-alkinyloxy, benzyloxy, C1-C7-alkanoyloxy, C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyloxy, C1-C6-alkylthio, C3-C6-alkenylthio, C3-C6-alkinylthio, C3-Cg-cycloalkyloxy, C3-C8-cycloalkylthio, C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, C2-C7-alkylaminocarbonyl, C3-C13-dialkylaminocarbonyl, carboxy, phenyl, phenoxy, phenylthio, pyridyloxy, pyridylthio, or NR5R6, wherein
- R 5 and
- R 6 are selected independently from each other from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl and C3-C6-alkinyl,
- R 2 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, benzyloxy or C1-C7-alkanoyloxy,
- wherein R 1 and R2, in case they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which is selected from the bridge members
- —(CH 2)4— and —(CH═CH)2— and —CH2O—CR7R8—O—, wherein
- R 7 and
- R 8 are, independently from each other, hydrogen or C1-C6-alkyl,
- R 3 is hydrogen, halogen, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl or C1-C6-hydroxyalkyl and
- R 4 is hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, C3-C6-cycloalkyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy or benzyloxy,
- k is 0 or 1,
- A is C 1-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, C1-C3-alkoxy, fluorine or phenyl, or
- 1,2-cyclopropylene or
- C 2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, C1-C3-alkoxy, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
- C 4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl
- 1,3,5-hexatrienylene, which is optionally substituted by C 1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl
- ethynylene or
- C 2-C6-alkylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR9, CO, SO or SO2, wherein the isosteric substitution, with the exception of ═CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group, and
- R 9 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, C1-C6-acyl or C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl,
- D is selected from C 1-C10-alkylene, optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or C1-C6-alkoxy,
- C 2-C10-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or C1-C6-alkoxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
- C 3-C10-alkinylene, optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or C1-C6-alkoxy, and
- C 1-C10-alkylene, C2-C10-alkenylene or C3-C10-alkinylene, wherein one to three methylene units are each isosterically replaced by O, S, NR10, CO, SO or SO2, wherein
- R 10 has the same meaning as R9, but is selected independently therefrom,
-
- wherein the heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond and
- n and
- p can be, independently of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p≦4 and
- q is 2 or 3,
- R 11 is hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl and
- R 12 hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom, wherein
- R 11 and R12 optionally together form a C1-C3-alkylene bridge under formation of a bi-cyclic ring system,
- G is selected from hydrogen,
- G1, G2, G3, G4 and G5, wherein
- G1 represents the residue
- (CH2)r—(CR14R15)s—R13 (G1)
- wherein
- r is an integer from 1 to 3 or 0 and
- s is 0 or 1,
- R 13 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl,
- saturated, five- to seven-membered heterocycles, which can contain one or two hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O,
- benzyl or phenyl,
- monocyclic aromatic five or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly, or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic ring or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 has the same meaning as R13, but is selected independently thereof,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
- monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic ring or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
-
- wherein the substituents R 13 and R15 can have the above meaning or the grouping
- NR13R15
- can also be a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
- saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O, or
- saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O,
- G3 is the residue
- SO2—(CH2)rR13 (G3)
- and
-
- wherein
- Ar 1 and Ar2 are selected independently from one another from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl and
- G 5 is the residue
- COR16 (G5)
- wherein
- R 16 is selected from trifluoromethyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy, or benzyloxy, and wherein
- aromatic ring systems in the substituents R 1, R2, R4, R13, R14, R15, R16, Ar1 and Ar2 and/or in the ring system —NR13R15 can be substituted independently from each other by one to three of the same or different residues which are selected from halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-Cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which can optionally be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino or di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino and methylenedioxy for two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system,
- stereoisomers thereof and/or mixtures thereof and pharmacologically acceptable
- acid addition salts.
- A further preferred embodiment of the invention constitutes the use of compounds for the indications named above, which are distinguished in that substituents R 1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R13, R14, R15 and R16 as well as A and D indicated for formula (I) have the following meaning in connection with the given substitutions according to this formula
- wherein
- halogen is fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine,
- C 1-C6-alkyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably a methyl-, ethyl-, propyl-, isopropyl-, butyl-, isobutyl-, sec-butyl-, tert-butyl-, cyclopropylmethyl-, pentyl-, isopentyl-, tert-pentyl-, neopentyl-, cyclopropylethyl-, cyclobutylmethyl- or a hexyl group, alkylene is for example methylene, ethylene, propylene, tetramethylene, pentamethylene, hexamethylene, heptamethylene, octamethylene, nonamethylene or decamethylene,
- C 3-C6-alkenyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably an allyl-, 2-butenyl-, 3-butenyl-, 2-methyl-2-propenyl-, 2-pentenyl-, 4-pentenyl-, 2-methyl-2-butenyl-, 3-methyl-2-butenyl-, 2-hexenyl-, 5-hexenyl-, 4-methyl-3-pentenyl- or 2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl group,
- alkenylene is for example ethenylene, propenylene, butenylene, pentenylene, hexenylene, hexathenylene, heptenylene, octenylene, nonenylene or decenylene,
- C 3-C6-alkinyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably a propargyl-, 2-butinyl-, 3-butinyl-, 4-pentinyt-, 5-hexinyl- or 4-methyl-2-pentinyl group,
- alkinylene is for example propinylene, butinylene, pentinylene, hexinylene, heptinylene, octinylene, noninylene or decinylene,
- C 3-C8-cyloalkyl is preferably cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl or cyclooctyl,
- C 1-C6-hydroxyalkyl contains a hydroxyl group in one of the above-named C1-C6-alkyl residues, especially in the form of the hydroxymethyl- and hydroxyethyl group, wherein
- C 1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy, C3-C6-aklinyloxy each contain, aside from the oxygen atom, one of the C1-C6-alkyl-, C3-C6-alkenyl- and/or C3-C6-alkinyl groups named above and the methoxy-, ethoxy-, isopropoxy-, tert-butoxy-, allyloxy- and propargyloxy group are preferred and is to be understood as among C1-C6-alkoxy entirely or partially substituted with fluorine, for example difluormethoxy, trifluormethoxy or 2,2,2-trifluorethoxy,
- C 1-C6-alkylthio, C3-C6-alkenylthio, C3-C6-alkinylthio each contain, aside from the sulfur atom, one of the C1-C6-alkyl-, C3-C6-alkenyl- or C3-C6-alkinyl group named above, especially the methylthio-, ethylthio-, isopropylthio- and tert-butylthio groups,
- C 3-C8-cycloalkyloxy and C3-C8-cydoalkylthio are preferred as cyclopentyloxy- and cyclopentylthio- and/or cylohexyloxy- and cyclohexylthio groups,
- C 1-C7-alkanoyloxy groups contain, aside from the oxygen atom, an aliphatic acyl residue with 1 to 7 carbon atoms, especially the acetoxy-, propionyloxy- and pivaloyloxy group,
- C 2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl groups contain, aside from the carbonyl group, one of the C1-C6-alkoxy groups mentioned above, especially the methoxycarbonyl-, ethoxycarbonyl-, isopropoxycarbonyl-, isobutoxycarbonyl-and tert-butoxycarbonyl group,
- C 2-C7-alkoxycarbonyloxy groups contain, aside from the oxygen atom, one of the C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl residues mentioned above, especially the methoxycarbonyloxy-, ethoxycarbonyloxy-, isopropoxycarbonyloxy-, isobutoxycarbonyloxy-and tert-butoxycarbonyl group as well as the allyloxycarbonyloxy group,
- C 2-C7-alkylaminocarbonyl and C3-C13-dialkylaminocarbonyl groups contain, beside the carbonyl group, an alkylamino- and/or dialkylamino residue, whose C1-C6-alkyl groups have the above meanings, wherein the dimethylaminocarbonyl-, diethylaminocarbonyl- and the diisopropylatninocarbonyl groups are preferred, and aside from the unsubstituted amino group, one of the following C1-C6-alkylamino groups and/or di-(C1-C6-alkyl)amino groups are to be understood under the amino groups of the formula NR5R6,
- C 1-C6-alkylamino contains one of the C1-C6-alkyl groups mentioned above, especially in form of the methylamino-, ethylamino-, propylamino-, isopropylamino-, butylamino- and the tert-butylamino group,
- di-(C 1-C6-alkyl)amino carries two of the same or different of the above named C1-C6-alkyl groups on the nitrogen atom, especially in form of the dimethylamino-, diethylamino-, dipropylamino-, diisopropylamino-, isopropylmethylamino-, dibutylamino- or tert-butylmethylamino group,
- C 1-C6-acyl is the residue of an aliphatic saturated or unsaturated, straight chain, branched or cyclic carboxylic acid, especially in form of the formyl-, acetyl-, propionyl-, acryloyl-, butyryl-, isobutyryl-, methacryloyl-, cyclopropylcarbonyl-, pentanoyl-, pivaloyl-, cyclobutylcarbonyl-, hexanoyl- and the dimethylacryloyl group,
- C 1-C6-alkansulfonyl is preferably the methanesulfonyl-, ethanesulfonyl-, propanesulfonyl-, butanesulfonyl-, pentanesulfonyl- and the hexanesulfonyl group, saturated five- to seven-membered heterocycles with one or two hetero-atoms are especially tetrahydrofuryl, tetrahydrothienyl, pyrrolidinyl, tetrahydropyranyl, piperidinyl, hexahydroazepinyl, piperazinyl, hexahydrodiazepinyl or morpholinyl,
- monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles with one to three hetero-atoms are especially furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl or triazinyl,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclc ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring are preferably benzocyclobutyl, indanyl, indenyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, biphenylenyl, fluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, phenanthryl, dihydrophenanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocyclooctenyl or tetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenyl, wherein mono- or dioxo-derivates, wherein the residues of indanone, tetralone, anthrone, anthraquinone, fluorenone, phenanthrone, dibenzocycloheptenone, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenone or tetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenone are for example also to be understood as partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems,
- anellated bi- and tricyclische aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring are, for example, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, dihydrobenzofuryl, benzothienyl, dihydrobenzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, benzimidazolyl, indazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzisoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzoisothiazolyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiadiazolyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, isothiazolopyridyl, imidazopyridyl, pyrazolopyridyl, thienopyrimidinyl, chromanyl, benzopyranyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, dihydroquinolyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, benzodioxanyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, naphthyridinyl, carbazolyl, tetrahydrocarbazolyl, pyridoindolyl, acridinyl, phenothiazinyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, benzocycloheptathienyl, dihydrothienobenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiepinyl, octahydrodibenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzazepinyl, octahydrodibenzazepinyl, benzocycloheptapyridyl, dihydropyridobenzodiazepinyl, dihydrodibenzoxazepinyl, dihydropyridobenzoxepinyl, dihydropyridobenzoxazepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiazepinyl or dihydropyridobenzothiazepinyl, wherein their mono- or dioxo-derivates and/or optionally their possible tautomeres are also to be understood as partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems, for example, the residues of indolinone, isatin, benzoxazolone and/or its tautomeres hydroxybenzoxazol, of benzisoxazolone, benzothiazolone, benzoisothiazolone and benzimidazolone and/or their tautomeres, hydroxybenzisoxazol, hydroxybenzothiazol, hydroxybenzoisothiazol and hydroxybenzimidazol, of indazolinone, of oxazolopyridinone, thiazolopyridinones, pyrazolopyridinones and imidazopyridinones and/or their tautomeres hydroxyoxazolopyridine, hydroxythiazolopyridines, hydroxypyrazolopyridines and hydroxyimidazopyridines, the residues of chromanone, chromone, quinolinone, dihydroquinolinone, tetrahydrocarbazolone, acridone, of dihydrodibenzoxepinones, benzocycloheptathiophenones, dihydrothienobenzothiepinones, dihydrodibenzothiepinones, dihydrodibenzoazepinones, benzocycloheptapyridinones, dihydropyridobenzoxazepinones, dihydrodibenzothiazepinones and of dihydropyridobenzothiazepinones,
- saturated and unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles are —NR 13R15 as a grouping which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further betero-atoms selected from N and/or S and/or O, for example azetidine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, (1H)tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, (1H)tetrahydroazepine, octahydroazocine, pyrazolidine, piperazine, hexahydrodiazepine, morpholine, hexahydrooxazepine, thiomorpholine or thiomorpholine-1,1-dioxide, saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, represent —NR3R15 as a grouping which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms, selected from N and/or S and/or O, for example 5-aza-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexane, 2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 7-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,5-diaza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 8-aza-bicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 2,5-diaza-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 9-aza-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)-dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoxaline, (4H)-dihydrobenzoxazine, (4H)-dihydrobenothiazine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[c]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (SH)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4-blindol, (10H)-dihydroacridine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (10H)phenoxazin, (10H)phenothiazine, (5H)-dibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-octahydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzodiazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]oxazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]thiazepine or (SH)-tetrahydrodibenzazocine, as well as optionally possible
- tautomeres in the case of substitution of the heterocycle as such or in an anellated ring system by free hydroxy-, mercapto- and/or amino groups, and their
- stereoisomers such as, if applicable, cis/trans-isomers, endo/exo-isomers, optic isomers such as enantiomers, diastereomers as pure isomers or mixtures and/or racemic mixtures as well as the pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts with inorganic or organic acids, wherein the hydrochlorides, hydrobromides, hydroiodides, sulfates and phosphates, are preferred as addition salts with suitable inorganic acids and acetates, benzoates, 4-methoxybenzoate, 2- or 4-hydroxybenzoate, 4-chlorobenzoate, ascorbate, salicylate, formiate, glutarate, tricarballylate, citrates, fumarates, gluconates, malates, maleates, methanesulfonates, lactates, oxalates, succinates, tartrates and toluolsulfonates, for example p-toluolsulfonate are preferred as addition salts of organic acids.
-
- have the following meanings, are especially preferred:
- R 1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-cycloallyl, C1-C4-hydroxyalkyl, hydroxy, C1-C4-alkoxy, benzyloxy, C1-C4-alkanoyloxy, C1-C4-alkylthio, C2-C5-alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, C3-C9-dialkylaminocarbonyl, carboxy, phenyl, phenoxy, pyridyloxy or NR5R6, wherein
- R 5 and
- R 6 are selected independently from each other form hydrogen and C1-C6-alkyl,
- R 2 is hydrogen, halogen, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy, wherein
- R 1 and R2, in the case they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which are selected from the group of bridge members —(CH2)4— and —(CH═CH)2— and —CH2O—CR7R8—O—, wherein
- R 7 and
- R 8 can be, independently from each other, hydrogen and C1-C6-alkyl,
- R 3 is selected from hydrogen, halogen and C1-C6-alkyl and
- R 4 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy and benzyloxy,
- k is 0 or 1,
- A is C 1-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, fluorine or phenyl,
- 1,2-cyclopropylene, C 2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted one to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, fluorine, cyano, or phenyl,
- C 4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano, or phenyl,
- 1,3,5-hexatrienylene, which is optionally substituted by C 1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, or cyano,
- ethinylene or
- C 2-C6-alkylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR9, CO, SO or SO2, and wherein the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ═CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group, and wherein
- R 9 is hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl, C1-C6-acyl or methanesulfonyl,
- D is selected from C 1-C10-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl or hydroxy,
- C 2-C10-alkenylene, optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl or hydroxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E or
- C 3-C10-alkinylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl or hydroxy, and can be selected as well from
- C 1-C10-alkylene, C2-C10-alkenylene or C3-C10-alkinylene, in which one to three methylene units are isosterically replaced by O, S, NR10, CO, SO or SO2, wherein
-
- wherein the heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond and
- n and p can be, independent of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p<4,
- q is 2 or 3,
- R 11 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxcy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl and
- R 12 is selected from hydrogen or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom,
- G is selected from hydrogen,
- G1, G2, G3, G4 and G5, wherein
- G1 represents the residue
- —(CH2)r—(CR14R15)s—R13 (G1)
- wherein
- r is 0, 1 or 2 and
- s is 0 or 1,
- R 13 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl,
- benzyl, phenyl,
- monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles, which contain one to three hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, whereby the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from the groups N and/or S and/or O and the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 has the same meaning as R13, but is selected independently thereof,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
- monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and are bound either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least einem aromatic ring, wherein the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
- anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
-
- wherein the substituents R 13 and R15 the can have the above meaning, or the grouping
- NR13R15
- can also be a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
- saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from N and/or S and/or O, or
- saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from N and/or S and/or O,
- G3 is the residue
- —SO2—(CH2)r R13 (G3),
-
- wherein
- Ar 1 and
- Ar 2 are selected independently of each other from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl,
- G5 is the residue
- —COR16 (G5)
- wherein
- R 16 is trifluoromethyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy or benzyloxy and
- aromatic ring systems in which the substituents R 1, R2, R4, R13, R14, R15, R16, Ar1 and Ar2 and/or in the ring system —NR13R15 can carry independently of each other one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which is optionally entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino, di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino, wherein two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system can form an additional ring over a methylenedioxy bridge.
-
- have the following meanings are particularly preferred:
- R 1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, methyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, C1-C4-alkoxy, ethylthio, methoxycarbonyl, tert-butoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, carboxy, and phenoxy,
- R 2 is hydrogen, halogen, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy,
- R 3 is hydrogen or halogen,
- R 4 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C3alkyl, hydroxy and C1-C3-alkoxy,
- k is 0 or 1,
- A is C 2-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy or fluorine, as well as
- C 2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy or fluorine
- C 4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted by is C1-C3-alkyl or by one or two fluorine atoms,
- 1,3,5-hexatrienylene, which is optionally substituted by fluorine, or
- C 2-C6-alkylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, CO or SO2, and the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ═CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group and,
- D is C 1-Cg-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once twice by methyl or hydroxy,
- C 2-C8-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by methyl or hydroxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
- C 3-C8-alkinylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by methyl or hydroxy, as well as
- C 1-C8-alkylene, C2-C8-alkenylene or C3-C8-alkinylene, in which one to three methylene units can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NH, N(CH3), N(COCH3), N(SO2CH3), CO, SO or SO2,
-
- wherein the heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond and
- n and
- p can be independent of each other 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p<3,
- q is 2 or 3,
- R 11 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl and
- R 12 is selected from hydrogen or an oxo group which is adjacent to the nitrogen atom,
- G is hydrogen or
- G1, G2, G3, G4 and G5, wherein
- G1 represents the residue
- —(CH2)r—(CR14R16)s—R13 (G1)
- wherein
- r is 0, 1 or 2 and
- s is 0 or 1,
- R 13 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, benzyl orphenyl, benzocyclobutyl, indanyl, indenyl, oxoindanyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, oxotetrahydronaphthyl, biphenylenyl, fluorenyl, oxofluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, oxodihydroanthryl, dioxodihydroanthryl, phenanthryl, dihydrophenanthryl, oxodihydrophenanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocyclooctenyl, tetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenyl and oxotetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenyl, bound directly or over a methylene group,
- furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, triazinyl, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, dihydrobenzofuryl, benzothienyl, dihydrobenzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, oxoindolinyl, dioxoindolinyl, benzoxazolyl, oxobenzoxazolinyl, benzisoxazolyl, oxobenzisoxazolinyl, benzothiazolyl, oxobenzthiazolinyl, benzoisothiazolyl, oxobenzoisothiazolinyl, benzimidazolyl, oxobenzimidazolinyl, indazolyl, oxoindazolinyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiadiazolyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, oxodihydrooxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, oxodihydrothiazolopyridyl, isothiazolopyridyl, imidazopyridyl, oxodihydroimidazopyridyl, pyrazolopyridyl, oxodihydropyrazolopyridyl, thienopyrimidinyl, chromanyl, chromanonyl, benzopyranyl, chromonyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, dihydroquinolyl, oxodihydroquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, oxotetrahydroquinolinyl, benzodioxanyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, naphthyridinyl, carbazolyl, tetrahydrocarbazolyl, oxotetrahydrocarbazolyl, pyridoindolyl, acridinyl, oxodihydroacridinyl, phenothiazinyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzoxepinyl, benzocycloheptathienyl, oxobenzocycloheptathienyl, dihydrothienobenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrothienobenzothiepinyl dihydrodibenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiepinyl, octahydrodibenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzazepinyl, octahydrodibenzazepinyl, benzocycloheptapyridyl, oxobenzocycloheptapyridyl, dihydropyridobenzodiazepinyl, dihydrodibenzoxazepinyl, dihydropyridobenzoxepinyl, dihydropyridobenzoxazepinyl, oxodihydropyridobenzoxazepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiazepinyl, dihydropyridobenzothiazepinyl, oxodihydropyridobenzothiazepinyl, bound directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 has the same meaning as R13, but is selected independently therefrom,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
- indanyl, indenyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, pyrazolyl, imidazoyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, triazinyl, benzofuryl, benzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, benzoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzimidazolyl, chromanyl, quinolyl or tetrahydroquinolyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
-
- wherein the substituents R 13 and R15 can have the above meanings, or represents the grouping
- NR13R15
- each over the nitrogen-bound ring atom of azetidine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, (1H)tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, (1H)tetrahydroazepine, octahydroazocine, pyrazolidine, piperazine, hexyhydrodiazepine, morpholine, hexahydrooxazepine, thiomorpholine, thiomorpholine-1,1-dioxide, 5-aza-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexane, 2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 7-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,5-diaza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 8-aza-bicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)-dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoxaline, (4H)-dihydrobenzoxazine, (4H)-dihydrobenzothiazine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[c]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzolb]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole, (10H)-dihydroacridine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (10H)-phenoxazine, (10H)-phenothiazine, (5H)-dibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-Octahydrodibenzazepine, (SH)-dihydrodibenzodiazepine, (1H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxazepine, (11)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]oxazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]thiazepine or (5H)-tetrahydrodibenzazocine,
- G3 is the residue
- —SO2—(CH2)r R13 (G3),
-
- wherein
- Ar 1 and
- Ar 2 are selected independently of each other from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl,
- G5 is the residue
- —COR16 (G5)
- wherein
- R 16 is trifluoromethyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy or benzyloxy and
- aromatic ring systems in which the substituents can be substituted independently of each other by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C 1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-Cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, can carry benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino, di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino, wherein two adjacent groups in the ring or ring system can form an additional ring over a methylenedioxy bridge.
-
- have the following meaning:
- R 1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, methyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, methoxy or methoxycarbonyl,
- R 2 is hydrogen or halogen,
- R 3 is hydrogen,
- R 4 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl or hydroxy,
- k is 0 or 1,
- A is selected from C 2-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by hydroxy or fluorine, or
- C 2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by hydroxy or fluorine,
- C 4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted by one or two fluorine atoms,
- 1,3,5-hexatrienylene or
- C 2-C6-alkylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S or CO, and the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ═CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group and,
- D is C 2-C8-alkylene, which is optionally substituted by methyl or hydroxy,
- C 2-C8-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted by methyl or hydroxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E, or
- C 2-C8-alkylene, C2-Cg-alkenylene, wherein one to three methylene units can be isosterically replaced by O, NH, N(CH3), N(COCH3), N(SO2CH3) or CO,
-
- wherein the heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond and
- n and p can be, independent of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p≦3 and
- q is 2
- R 11 is hydrogen, methyl or hydroxyl and
- R 12 is hydrogen or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom,
-
- wherein
- r is 0, 1 or 2 and
- s is 0 or 1,
- R 13 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
- indanyl, indenyl, oxoindanyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, oxotetrahydronaphthyl, fluorenyl, oxofluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, oxodihydroanthryl, dioxodihydroanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
- furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, dihydrobenzofuryl, benzothienyl, dihydrobenzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, oxoindolinyl, dioxoindolinyl, benzoxazolyl, oxobenzoxazolinyl, benzisoxazolyl, oxobenzisoxazolinyl, benzothiazolyl, oxobenzthiazolinyl, benzolsothiazolyl, oxobenzoisothiazolinyl, benzimidazolyl, oxobenzimidazolinyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiadiazolyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, oxodihydrooxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, oxodihydrothiazolopyridyl, isothiazolopyridyl, imidazopyridyl, oxodihydroimidazopyridyl, pyrazolopyridyl, thienopyrimidinyl, chromanyl, chromanonyl, benzopyranyl, chromonyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, dihydroquinolyl, oxodihydroquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, oxotetrahydroquinolinyl, benzodioxanyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, naphthyridinyl, carbazolyl, tetrahydrocarbazolyl, oxotetrahydrocarbazolyl, pyridoindolyl, acridinyl, oxodihydroacridinyl, phenothiazinyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, benzocycloheptathienyl, oxobenzocycloheptathienyl, dihydrothienobenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrothienobenzothiepinyl dihydrodibenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzazepinyl, octahydrodibenzazepinyl, benzocycloheptapyridyl, oxobenzocycloheptapyridyl, dihydropyridobenzoxepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiazepinyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
- R 15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
- naphthyl, furyl, thienyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, pyridyl, benzofuryl, benzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, benzoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzimidazolyl, chromanyl, quinolyl or tetrahydroquinolyl, bound directly or over a methylene group, wherein in formula (I)
- the group NR 13R15 can be selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, (1H)tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, Octahydroazocine, piperazine, hexahydrodiazepine, morpholine, hexahydrooxazepine, 2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 7-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)-dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoxaline, (4H)-dihydrobenzoxazine, (4H)-dihydrobenzothiazine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol, (10H)-dihydroacridine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzodiazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]oxaze-pine or (5H)-tetrahydrodibenzazocine.
-
- have the following meanings are very particularly preferred:
- R 1 is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, methyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy,
- R 2 and
- R 3 are hydrogen,
- R 4 is hydrogen or hydroxy,
- k is 0 or 1,
- A is selected from C 2-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substitued once or twice by hydroxy or fluorine or,
- C 2-C4-alkylene, which is optionally substituted by fluorine,
- C 4-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted by fluorine,
- D is selected from C 2-C6-alkylene, C2-C6-alkenylene, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E, and C2-C6-alkylene and C2-C6-alkenylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, NH, N(CH3) or CO or an ethylene group can be isosterically replaced by NH—CO and/or CO—NH or a propylene group can be isosterically replaced by NH—CO—O and/or O—CO—NH,
- E is selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, 1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, morpholine and hexahydro-1,4-oxazepine, wherein the heterocyclic ring optionally adjacent to the nitrogen atom, can be substituted by an oxo group,
-
- wherein
- r is 0 or 1 and
- s is 0 or 1,
- R 13 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
- indenyl, oxoindanyl, naphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, fluorenyl, oxofluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, oxodihydroanthryl, dioxodihydroanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
- furyl, thienyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyrimidinyl, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, benzothienyl, indolyl, oxoindolinyl, dioxoindolinyl, benzoxazolyl, oxobenzoxazolinyl, benzothiazolyl, oxobenzthiazolinyl, benzimidazolyl, oxobenzimidazolinyl, benzofurazanyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, oxodihydrooxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, oxodihydrothiazolopyridyl, chromanyl, chromanonyl, benzopyranyl, chromonyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, oxodihydroquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, oxotetrahydroquinolinyl, benzodioxanyl, quinazolinyl, acridinyl, oxodihydroacridinyl, phenothiazinyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, benzocycloheptathienyl, dihydrothienobenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzazepinyl, octahydrodibenzazepinyl, benzocycloheptapyridyl, oxobenzocycloheptapyridyl, dihydrodibenzothiazepinyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
- R 14 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
- R 15 is hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
-
- the group NR 13R15 can be selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, hexahydroazepine, morpholine, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]-oxazepine or (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiazepine and
- wherein aromatic ring systems in the substituents can be substituted, independently of each other, by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C 1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, can carry benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino or di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino, whereby two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system for an additional ring over a methylenedioxy bridge.
-
- have the following meanings:
- R 1 is hydrogen, fluorine, methyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy,
- R 2 and
- R 3 are hydrogen,
- R 4 is hydrogen or hydroxy,
- k is 0,
- A is ethylene, propylene or butylene which can each be optionally substituted by hydroxy or once or twice by fluorine, or
- ethenylene and/or vinylene or
- 1,3-butadienylene
- D is selected from C 2-C6-alkylene or C2-C6-alkenylene, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
- E is selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, hexahydroazepine or morpholine,
- G is selected from benzyl, phenethyl, fluorenylmethyl, anthrylmethyl, diphenylmethyl, fluorenyl or dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl,
- furylmethyl, thienylmethyl, thiazolylmethyl, pyridylmethyl, benzothienylmethyl, quinolylmethyl, phenyl-thienylmethyl, phenyl-pyridylmethyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiepinyl,
- acetyl, pivaloyl, phenylacetyl, diphenylacetyl, diphenylpropionyl, naphthylacetyl, benzbyl, naphthoyl, anthrylcarbonyl, oxofluorenylcarbonyl, oxodihydroanthrylcarbonyl or dioxodihydroanthrylcarbonyl,
- furoyl, pyridylcarbonyl, chromonylcarbonyl, quinolylcarbonyl,
- naphthylaminocarbonyl, dibenzylaminocarbonyl, benzylphenylaminocarbonyl, diphenylaminocarbonyl, indolinyl-1-carbonyl, dihydrodibenzazepin-N-carbonyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl-N-carbonyl, tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepinyl-N-carbonyl,
- methanesulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, p-toluolsulfonyl, naphthylsulfonyl, quinolinsulfonyl and
- diphenylphosphinoyl,
- wherein aromatic ring systems can be substituted independently of each other by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C 1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-Cg-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino or di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino, wherein two adjacent groups in the ring or ring system can form an additional ring over a methylendioxy bridge.
- A series of compounds with the respective substituent definitions are listed as follows in Table 1 for illustration of the use according to the invention without any intended restriction.
TABLE 1 Exemplifying compounds of formula (I) according to the invention Nr R1 k A R4 D—E—G 1 H 0 CH═CH H 2 H 0 CH═CH H 3 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 4 H 0 CH═CH H 5 H 0 CH═CH H 6 H 0 CH2CH2 H 7 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 8 H 0 CH═CH H 9 H 0 CH2CH2 H 10 H 0 CH═CH H 11 H 0 CH2CH2 H 12 H 0 CH═CH H 13 H 0 CH═CH H 14 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 15 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 16 H 0 CH2CH2 H 17 H 0 CH═CH H 18 H 0 CH2CH2 H 19 H 0 CH═CH H 20 H 0 CH2CH2 H 21 H 0 CH2CH2 H 22 H 0 CH═CH H 23 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 24 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 25 H 0 CH2CH2 H 26 H 0 CH2CH2 H 27 6-Cl 0 CH═CH H 28 2-CH3 0 CH2CH2 H 29 H 0 CH═CH H 30 H 0 CH═CH H 31 H 0 CH═CH H 32 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 33 H 0 CH2CH2 H 34 H 0 CH═CH H 35 H 0 CH2 H 36 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 37 H 0 CH2CH2 H 38 H 0 CH2CH2 H 39 H 0 CH2CH2 H 40 H 0 CH2CH2 H 41 H 0 CH2CH2 H 42 H 0 CH═CH H 43 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 44 H 0 CH2CH2 H 45 H 1 CH2CH2 H 46 H 0 CH═CH H 47 H 1 CH═CH H 48 2-Cl 0 CH═CH H 49 2-F 0 CH═CH H 50 5-F 0 CH═CH H 51 6-CH2O 0 CH═CH H 52 H 0 H 53 H 0 CH═CH CH3 54 H 0 CH2CH2 H 55 H 0 CH═CH H 56 H 0 CH═CH H 57 H 0 CH═CH H 58 H 0 CH═CH H 59 H 0 CH2CH2 H 60 H 0 CH═CH H 61 H 0 CH═CH H 62 H 0 CH2CH2 H 63 H 0 CH═CH H 64 H 0 CH═CH H 65 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 66 H 0 CH2CH2 H 67 H 0 H 68 H 0 CH2CH2 H 69 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 70 H 0 CH2CH2 H 71 H 0 CH═CH H 72 H 0 CH2CH2 H 73 H 0 CH═CH H 74 H 0 CH2CH2 H 75 H 0 CH═CH H 76 H 0 CH2CH2 H 77 H 0 CH═CH H 78 H 0 CH═CH H 79 H 0 CH═CH H 80 H 0 CH2CH2 H 81 H 0 CH═CH H 82 H 0 CH2CH2 H 83 H 0 CH2CH2 H 84 H 0 CH═CH H 85 H 0 CH2CH2 H 86 H 0 CH═CH H 87 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 88 H 0 CH2CH2 H 89 H 0 CH═CH H 90 H 0 CH2 H 91 H 0 CH2CH2 H 92 H 1 CH2CH2 H 93 2-F 0 CH2CH2 H 94 6-CH3 0 CH2CH2 H 95 H 0 CH═CH H 96 H 0 CH2CH2 H 97 H 0 CH═CH H 98 H 0 CH2CH2 H 99 H 0 CH═CH H 100 H 0 CH2CH2 H 101 H 1 CH2CH2 H 102 2-OH 0 CH2CH2 H 103 6-CH3O 0 CH2CH2 H 104 0 CH═CH H 105 1 CH═CH H 106 2-OH 0 CH═CH H 107 2-F 0 CH═CH H 108 5-F 0 CH═CH H 109 6-F 0 CH═CH H 110 2-Cl 0 CH═CH H 111 6-C2H5S 0 CH═CH H 112 6-C6H5O 0 C═CH H 113 H 0 H 114 H 0 H 115 H 0 H 116 H 0 H 117 H 0 H 118 H 0 H 119 H 0 H 120 H 0 CH2CF2 H 121 H 0 CH═CH CH3 122 H 0 CH2CH2 C2H5 123 H 0 CH═CH C2H5 124 H 0 CH═CH 125 H 0 CH2CH2 OH 126 H 0 CH═CH OH 127 H 0 H 128 H 0 C≡C H 129 H 0 OCH2 H 130 H 0 SCH2CH2 H 131 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 132 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 133 H 0 CH2NHCH2CH2 H 134 H 0 H 135 H 0 H 136 H 0 CH═CH H 137 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 138 H 0 CH2CH2 H 139 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 140 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 141 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 142 H 0 CH2CH2 H 143 H 0 CH═CH H 144 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 145 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 146 H 0 CH═CH H 147 H 0 CH═CH H 148 H 0 CH═CH H 149 H 0 OCH2 H 150 H 0 CH2CH2 H 151 H 0 CH2 H 152 H 0 CH═CH H 153 H 0 CH2CH2 H 154 H 0 CH═CH H 155 H 0 CH2CH2 H 156 H 0 CH═CH H 157 H 0 CH2CH2 H 158 H 0 CH═CH H 159 H 0 CH═CH H 160 H 0 CH═CH H 161 H 0 CH2CH2 H 162 H 0 CH2CH2 H 163 H 0 CH═CH H 164 H 0 CH2CH2 H 165 H 0 CH═CH H 166 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 167 H 0 CH2CH2 H 168 H 0 CH2CH2 H 169 H 0 CH═CH H 170 H 0 CH2CHF H 171 H 0 CH═CH H 172 H 1 CH═CH H 173 H 0 CH═CH CH3 174 H 0 CH═CH H 175 H 0 CH2CH2 H 176 H 0 CH2CH2 H 177 H 0 CH═CH H 178 H 0 CH═CH H 179 H 0 CH═CH H 180 H 0 H 181 H 0 CH2CH2 H 182 H 0 CH2CH2 H 183 H 0 CH═CH H 184 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 185 H 0 CH2CH2 H 186 H 0 CH═CH H 187 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 188 H 0 CH═CH H 189 H 0 CH2CH2 H 190 H 0 CH═CH H 191 H 0 CH2CH2 H 192 H 0 CH═CH H 193 H 0 CH2CH2 H 194 H 0 CH═CH H 195 H 0 CH2CH2 H 196 H 0 CH2CH2 H 197 H 0 CH═CH H 198 H 0 CH═CH H 199 H 0 SCH2CH2 H 200 H 0 CH═CH H 201 H 0 CH2CH2 H 202 H 0 CH2CH2 H 203 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 204 H 0 CH2CH2 H 205 H 0 CH═CH H 206 H 0 CH2CH2 H 207 H 0 CH═CH H 208 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 209 H 0 CH2CH2 H 210 H 0 CH═CH H 211 H 0 CH2CH2 H 212 H 0 CH═CH H 213 H 0 CH═CH H 214 H 0 CH═CH H 215 H 0 CH2 H 216 H 0 CH═CH H 217 H 0 CH2CH2 H 218 H 0 CH2CH2 H 219 H 0 CH═CH H 220 6-F 0 CH═CH H 221 H 0 CH2CH2 H 222 H 0 CH═CH H 223 H 0 CH2CH2 H 224 H 0 CH═CH H 225 H 0 CH═CH H 226 H 0 CH2CH2 H 227 H 0 CH═CH H 228 H 0 CH═CH H 229 H 0 CH═CH H 230 H 0 CH2CH2 H 231 H 0 CH═CH H 232 H 0 CH2CH2 H 233 H 0 CH═CH H 234 H 0 CH═CH H 235 H 0 CH2CH2 H 236 H 0 CH2CH2 H 237 H 0 CH═CH H 238 H 0 CH2CH2 H 239 H 0 CH═CH H 240 H 0 CH2CH2 H 241 H 0 CH═CH H 242 H 0 CH═CH H 243 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 244 H 0 CH2CH2 H 245 H 0 CH═CH H 248 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 247 H 0 CH2CH2 H 248 H 0 CH═CH H 249 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 250 H 0 CH═CH H 251 H 0 CH2CH2 H 252 H 0 CH═CH H 253 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 254 H 0 CH═CH H 255 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 256 H 0 CH2CH2 H 257 H 0 CH═CH H 258 H 0 CH2CH2 H 259 H 0 CH═CH H 260 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 261 H 0 CH2CH2 H 262 H 0 CH═CH H 263 H 0 CH2CH2 H 264 H 0 CH2CH2 H 265 H 0 CH═CH H 266 H 0 CH2CH2 H 267 H 0 CH2CH2 H 268 H 0 CH═CH H 269 H 0 CH2CH2 H 270 H 0 CH2CH2 H 271 H 0 CH═CH H 272 H 0 CH2CH2 H 273 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 274 H 0 CH2CH2 H 275 H 0 CH2CH2 H 276 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 277 H 0 CH═CH H 278 H 0 CH2CH2 H 279 H 0 CH═CH H 280 H 0 CH2CH2 H 281 H 0 CH2CH2 H 282 H 0 CH═CH H 283 H 0 CH═CH H 284 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 285 H 0 CH2CH2 H 286 H 0 CH═CH H 287 H 0 CH2CH2 H 288 H 0 CH═CH H 289 H 0 CH2CH2 H 290 H 0 CH═CH H 291 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 292 H 0 CH═CH H 293 H 0 CH═CH H 294 H 0 CH2CH2 H 295 H 0 H 295 H 0 CH2CH2 H 297 H 0 CH2CH2 H 298 H 0 CH═CH H 299 H 0 CH═CH H 300 H 0 CH2CH2 H 301 H 0 CH═CH H 302 H 0 CH2CH2 H 303 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 304 H 0 CH2CH2 H 305 H 0 CH2CH2 H 306 H 0 CH═CH H 307 H 0 CH═CH H 308 H 0 CH2CH2 H 309 H 0 CH═CH H 310 H 0 CH═CH H 311 H 0 CH2CH2 H 312 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 313 H 0 CH2CH2 H 314 H 0 CH═CH H 315 H 0 CH═CH H 316 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 317 H 0 CH2CH2 H 318 H 0 C≡C H 319 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 320 H 0 CH2CH2 H 321 H 0 CH═CH H 322 H 0 CH═CH H 323 H 0 CH═CH H 324 H 0 CH2CH2 H 325 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 326 H 0 H 327 H 0 CHphd 2CH2 H 328 H 0 CH2CH2 H 329 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 330 H 0 CH═CH H 331 H 0 CH═CH H 332 H 0 CH2CH2 H 323 H 0 CH2CH2 H 334 H 0 OCH2 H 335 H 0 CH2CH2CH2 H 336 H 0 CH2CH2 H 337 H 0 CH2CH2 H 338 H 0 CH═CH H 339 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 340 H 0 CH2CH2 H 341 H 0 CH2CH2 H 342 H 0 CH═CH H 343 H 0 CH2CH2 H 344 H 0 CH═CH H 345 H 0 CH2CH2 H 346 H 0 H 347 H 0 CH═CH H 348 H 0 CH2CH2 H 349 H 0 CH2CH2CH2CH2 H 350 H 0 CH═CH H 351 H 0 CH═CH H 352 H 0 CH2CH2 H 353 H 0 CH═CH H 354 H 0 CH2CH2 H 355 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 356 H 0 CH2CH2 H 357 H 0 CH═CH H 358 H 0 CH2CH2 H 359 H 0 CH═CH H 360 H 0 CH═CH H 361 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 362 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 363 H 0 CH═CH H 364 H 0 H 365 H 0 C≡C H 366 H 0 (CH2)2CH═CH H 367 H 0 CH═CH H 368 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 359 H 0 CH═CH H 370 H 0 CH═CH H 371 H 0 CH═CH H 372 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 373 H 0 CH2CH2 H 374 H 0 CH2CH2 H 375 H 0 CH═CH H 376 H 0 CH═CH H 377 H 0 CH2CH2 H 378 H 0 CH═CH H 379 H 0 CH═CH H 380 H 0 CH═CH—CH═CH H 381 H 0 CH═CH H 382 H 0 CH═CH H 383 H 0 CH2CH2 H 384 H 0 CH═CH H 385 H 0 CH2CH2 H 386 H 0 CH═CH H 387 H 0 CH2CH2 H 388 H 0 CH2CH2 H 389 H 0 CH═CH H 390 H 0 CH═CH H 391 H 0 CH2CH2 H 392 H 0 CH═CH H 393 H 0 CH2CH2 H 394 H 0 CH2CH2 H 395 H 0 CH═CH H 396 H 0 CH2CH2 H 397 H 0 CH═CH H - Various modes for synthesis of compounds used according to the invention are described in the following for reasons of simplifying reproducability.
- Aside from a few exceptions, the optionally combined compounds presently described and used according to the invention are not previously described in the literature. A smaller portion of these compounds overlaps various previously known generic formulae that are very generally defined with respect to structure and which were named at the beginning as prior art. The synthesis methods for the production of the presently used compounds are entirely known to the person skilled in the art either generally from the relevant literature and/or from the prior art publications named at the beginning; also see the literature information referred to below. Consequently, the presently used compounds of the synthesis encompassed by the defined generic formula are easily accessible by analogous methods, as they are described, for example, in the following.
- Method (A):
-
-
- wherein D, E, G and R 4 have the above meanings.
- Reactive derivatives of compound (II) can be present, for example, as activated esters, anhydrides, acid halides, especially acid chlorides, or simple low alkyl esters. Suitable acitivated esters are, for example, p-nitrophenyl ester, 2,4,6-trichlorphenyl ester, pentachlorophenyl ester, cyanomethyl ester, esters of N-hydroxysuccinimide, of N-hydroxyphthalimides, of 1-hydroxybenzotriazol, of N-hydroxypiperidine, of 2-hydroxypyridine or of 2-mercaptopyridine, etc. Anhydrides can be symmetric anhydrides or mixed, as they are obtained, for example, with pivaloyl chloride or with chloroformates. Aromatic (for example chloroformic phenyl ester), araliphatic (for example chloroformic benzyl ester) or aliphatic chloroformates (for example chloroformic methyl ester and/or corresponding -ethyl or -isobutyl ester) can be used for this.
- Reaction of compounds (II) with compounds (III) can also be carried out in the presence of condensation agents such as dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, N,N′-carbonyldiimidazol, 1-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline, etc. If carbodiimides are used as the condensation agent, reagents such as N-hydroxysuccinimide, N-hydroxyphthalimide, 1-bydroxybenzotriazol, N-hydroxypiperidine, etc. can be advantageously added.
- Compounds of formula (III) can be used for reaction as free bases as well as in the form of their acid addition salts. For this, the salts of inorganic acids are to be preferred, i.e. hydrochlorides, hydrobromides or sulfates.
- Reaction of compounds (II) or their reactive derivatives with compounds (III) are normally carried out in a suitable, preferably inert solvent. As examples, aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene, toluol, xylene, halogenated hydrocarbons (for example dichloromethane, chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene), ethers (for example diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, glycol dimethyl ether), ethyl acetate, acetonitrile or polar aprotic solvents such as, for example, dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylformamide or N-methylpyrrolidone are to be named. Pure solvents, as well as mixtures of two or more, can be used.
- The reaction is optionally carried out in the presence of an auxiliary base. Suitable examples for this are alkali metal carbonates (sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate), alkali metal hydrogen carbonates (sodium hydrogen carbonate, potassium hydrogen carbonate), or organic bases such as, for example, triethylamine, ethyl diisopropylamine, tributylamine, N-methylmorpholine or pyridine. A suitable excess of compound (III) can also be used as a base. If compounds (III) are used in form of their acid addition salts, then it is appropriate to consider the amount of auxiliary base used as equivalent.
- The reaction temperatures can—depending on reactivity of the educts—vary in a wide range. Generally, the reaction is carried out at temperatures between −40° C. and 180° C., preferably between −10° C. and 130° C., especially at the boiling point of the solvent used.
- The starting compounds (II) and (III) are known and/or can be produced according to known methods in an analogous manner. Moreover, the production of representative examples is further described below.
- Method (B)
- Compounds of formula (I) can be produced by reaction of compounds of formula (I), wherein G is hydrogen and which themselves possess the above-named pharmacological activities such as a cytostatic and/or immunomodulatory activity, as intermediate products as well as end products, with a compound of formula (V),
- L-G (IV)
- in which G has the meaning given above, with the exception of hydrogen, and L is a suitable nucleofuge or reactive group. The type of nucleofuge or reactive group L and the conditions of the reaction are dependent of the nature of group G.
- Method (B1)
- Compounds of formula (I), in which G, with the exception of hydrogen, has the meaning of (G1) according to the above definition can, aside from method (a), also be produced by reacting compounds of formula (I), wherein G is hydrogen, with a suitable alkylation agent and/or arylation agent of formula (IV), wherein G is an alkyl-, alkenyl-, alkinyl-, cycloalkyl-, aryl-, aralkyl-, heteroaryl- or heteroaralkyl residue according to definition and the leaving group L can be a reactive derivative of an alkohol, for example, a halogen atom such as chlorine, bromine or iodine or a sulfonic acid ester, i.e. for example a methanesulfonyloxy-, trifluoromethanesulfonyloxy-, ethanesulfonyloxy-, benzenesulfonyloxy-, p-toluolsulfonyloxy-, p-bromobenzenesulfonyloxy- or m-nitrobenzenesulfonyloxy residue, etc. A reactive group L can be a terminal epoxide group for example.
- The reaction of compounds (I), in which G is a hydrogen, and (IV) is usually conducted in a suitably inert solvent. Such solvents can be, for example, aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluol, xylene), ethers (for example tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, glycol dimethyl ether), ethyl acetate, acetonitrile, ketones (acetone, ethyl methyl ketone), polar protic solvents such as alcohols (ethanol, isopropanol, butanol, glycol monomethyl ether) or polar aprotic solvents such as, for example, dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylformamide or N-methylpyrrolidone. Pure solvents as well as mixtures of two or more can also be used. Preferably, the reactions are carried out in the presence of bases, whereby said bases can be used as in method (a) above. If chlorides or bromides are used as compound (IV), the reaction can be accelerated by the addition of alkali metal iodides (sodium iodide, potassium iodide). The reaction temperatures can vary between 0° C. and 180° C. depending on the reactivity of the educts, but preferably lie between 20° C. and 130° C.
- Method (B2)
- Compounds of formula (I), in which G represents an acyl residue, a carbamoyl residue, a sulfonyl residue or a phosphinoyl residue according to the above definition, can also be produced, aside from the above method (a), by reacting compounds of formula (I), in which G is hydrogen, with a carboxylic acid, carbamic acid, sulfonic acid and/or phosphinic acid of formula (V), in which G is an acyl residue, carbamoyl residue, sulfonyl residue or phosphinoyl residue according to definition,
- HO-G (V)
- or their derivatives capable of reaction. Preferred derivatives of carboxylic acids and/or sulfonic acids (V) which are capable of reaction are symmetric or unsymmetric carboxylic acid anhydrides and/or sulfonic acid anhydrides or acyl- and/or sulfonyl halides, especially acyl- and/or sulfonyl chlorides. Preferably, derivatives of carbamates and/or phosphinic acids which are capable of reaction are the carbamoyl halides and/or phosphinyl halides, especially carbanyl- and/or phosphinyl chlorides. The reaction of the acids (V) and/or their reactive derivatives with compounds (I), in which G is hydrogen, preferably occurs in the presence of auxiliary bases in solvents and under conditions as they are described in method (A).
- Method (B3)
-
- can also be produced, aside from the methods (A) and (B2), by reacting compounds of formula (I), in which C is hydrogen with a carbonyl group transmitter to an intermediate product and subsequently reacting this directly with a primary or secondary amine with the formula (VI)
- H—NR13R15 (VI)
- in which R 13 and R15 and/or the group —NR13R15 have the meanings according to the above definitions without having to purify or isolate the intermediate product. Trichloromethylcarbonate (triphosgene) and carbonyldiimidazol have been proven as particularly reactive carbonyl group transmitters. The reaction of compounds of formula (I), wherein G is hydrogen, with triphosgene and/or carbonyldiimidazol are typically conducted in an absolute, inert solvent in the presence of a tertiary organic amine as an auxiliary base in such a manner that the solution of compounds (I) and the auxiliary base are slowly poured into a solution of an equivalent amount of carbonyl group transmitter. Thereby, the reaction requires molar ratios of 1:1 for the reaction of compound (I) and carbonyldiimidazol, and, in contrast, a ratio of 1:0.35 for the use of triphosgene. After complete reaction of the components to the intermediate product, compound (VI) is added in stochiometric arnounts or in excess as a solution or a solid and the reaction is typically completed at elevated temperature. Suitable inert solvents are, for example hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, benzene, toluol, xylene, chlorinated hydrocarbons (for example dichloromethane, chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene), ethers (for example diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane), esters such as ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, acetonitrile or polar aprodic solvents such as formamide or dimethylformamide. Pure solvents as well as mixtures can be used diversely. Sometimes it is of advantage to carry out the first partial reaction at low temperature in a low-viscosity, highly-volatile solvent and to remove the solvent after formation of the intermediate and replace it by a higher boiling solvent. Amines such as for example triethylamine, ethyl diusopropylamine, tributylamine, N-methylmorpholine or pyridine are suitable as auxiliary bases. If compounds (I) or (VI) are used as salts, the amount of the auxiliary base is increased accordingly. The reaction temperatures can lie in between −40° C. and 50° C. for the first partial reaction, preferably at 0° C. bis 30° C., and between 0° C. and 150° C. for the second partial reaction, preferably at 20° C. bis 120° C.
- Method (B4)
-
- can also be produced, aside from methods A, B2 and B3, by reacting the compounds of formula (I) in which G is hydrogen, with an isocyanate of formula (VII) in which R 13 has the meaning according to the above definition
- O═C—N—R13 (VII)
- Reaction of the compounds of formula (I), in which G is hydrogen, with the isocyanates of formula (VII) are conducted thereby in an absolute, inert solvent which can be a hydrocarbon such as pentane, hexane, heptane, benzene, toluol, or xylene, chlorinated hydrocarbons (such as dichloromethane, chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane, trichloroethylene), ethers (for example, diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane), esters such as ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, or polar aprotic solvents such as formamide or dimethylformamide. Mixtures of various solvents can also be used. Thereby, the reaction temperatures can vary in the region from −20° C. to 150° C., but preferably lie at 20° C. to 100° C.
- The above-named intermediate products in the form of compounds according to formula (I), wherein G is hydrogen, which have the above-mentioned activities, such as for example a cytostatic activity in an analogous way to the end products themselves, are suitable for the production of a multitude of end products through the synthesis methods B1-B4.
- They themselves can, in principle, be produced according to method A by reacting a carboxylic acid of formula (II) with amines of formula (III) in which G is hydrogen as described above. However, since the compounds of formula (III) with hydrogen as G represent α,ω-diamines, the formation of product mixtures is always to be expected in their reaction with carboxylic acids (II) or their reactive derivatives making a subsequent separation necessary.
- In contrast, compounds of formula (I), in which G is hydrogen, are essentially more advantageously produced from other compounds of formula (I), in which G is a selectively cleavable group under mild conditions, i.e. corresponds to a nitrogen protective group.
- Among the compounds according to formula (I) with tumor growth inhibiting properties, compounds are particularly suitable for this in which G represents a benzyl group, a 4-methoxybenzyl group, a diphenylmethyl group, a triphenylmethyl group, a benzyloxycarbonyl group, a methoxy- and/or ethoxycarbonyl group, a tertbutoxycarbonyl group, an allyloxycarbonyl group or a trifluoroacetyl group. For example, compounds according to formula (I) with benzyl, diphenylmethyl, triphenylmethyl or benzyloxycarbonyl groups can already be catalytically transformed into the compounds of formula (I) with hydrogen as G at room temperature under mild conditions with elementary hydrogen or by transfer hydration. Compounds of formula (I) with a 4-methoxylbenzyl group are transformed into compounds of formula (I) with hydrogen as G by selective oxidation with ammonium-cer(IV)-nitrate. The cleavage of simple alkoxycarbonyl groups such as the methoxy- or ethoxycarbonyl group as well as the trifluoroacetyl group as G in compounds of formula (I) succeed by alkali hydrolysis under mild conditions without cleaving the A and D linked amide function. This is suitably valid for the cleavage of the triphenylmethyl group and the tert-butoxycarbonyl group as G in compounds of formula (I), which occurs in acidic medium under mild conditions. Finally, compounds of formula (I) with an allyloxycarbonyl group as G can be converted into such with hydrogen as G in neutral medium with palladium catalyst. All these methods are fully familiar to the person skilled in the art, and are furthermore also documented in monographs (see for example Greene, Wuts, Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, New York, 1991).
- Method C
- Compounds of formula (I), in which R 4 is an alkyl, alkenyl, alkinyl or cycloalkyl residue according to the above definition can also be produced, aside from the methods A and B, by reacting compounds of formula (I), in which R4 is hydrogen, with a suitable alkylation agent of formula (VIII)
- L-R4 (VIII)
- in which R 4 is an alkyl, alkenyl, alkinyl or cycloalkyl residue according to the above definition and L is a suitable nucleofuge, i.e. for example a halogen atom such as chlorine, bromine or iodine or a sulfonic acid ester of an alcohol. Preferred sulfonic acid esters (VIII) contain a methylsulfonyloxy residue, trifluoromethanesulfonyloxy-, p-toluolsulfonyloxy-, p-bromobenzenesulfonyloxy- or m-nitrobenzenesulfonyloxy residue as L. As an amide alkylation in the presence of tertiary amino groups, this reaction requires the use of strong auxiliary bases such as potassium-tert-butylate, sodium hydride, potassium hydride or butyl lithium in aprotic, inert solvents. Such solvents can be for example aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbons (pentane, hexane, heptane, benzene, toluol), ethers (for example, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane) or polar solvents such as dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylformamide or N-methylpyrrolidone. Depending on the reactivity of the educts, the reaction temperatures can lie between −40° C. and 140° C. preferably between −20° C. and 80° C.
- Method D
- Compounds of formula (I) in which A is a saturated alkylene group can also be produced, aside from methods A, B and C, by hydrating compounds of formula (I) in which A is an unsaturated group according to the above definition, i.e. an alkenylene group or alkadienyl group with elementary hydrogen in the presence of a suitable catalyst. This method is also applicable when the compounds of formula (I) with an unsaturated group A in the molecule simultaneously contain a principally hydrogenolytically cleavable group B, i.e.—as already mentioned above—a benzyl group, a diphenylmethyl or triphenylmethyl group. In the selection of the conditions, especially the solvent, the temperature and the acid additive in the reaction mixture, the reaction can be controlably driven either to a selective satuation of the C—C multiple bond(s) in the structural element A or to a simultaneous cleavage of the benzyl, diphenylmethyl or triphenylmethyl residue G under formation of the compounds of formula (I) with hydrogen as G.
- The hydration is preferably carried out in barely polar, aprotic solvents for selective hydration of one or more C—C multiple bonds of group A in the compounds of formula (I) according to the invention while attaining a simultaneously present hydrogenolytically cleavable benzyl, diphenylmnethyl or triphenylmethyl residue as the structural element G. Esters such as ethyl acetate, propyl acetate, butyl acetate or ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane or ethylene glycol dimethyl ether can be used. Compounds of formula (I) to be hydrated can be present as a free base or entirely or partially in the form of a salt by addition of a sub-maximal to a maximal stochiometric amount of a strong acid, preferably a mineral acid. As a catalyst, palladium Is suitable in various proportional amounts from 1, 3, 5 or 10% on solid supports such as activated carbon, activated aluminum oxide or calcium carbonate. The hydration is carried out under normal pressure and at a temperature of 10 to maximally 30° C., preferably at 20 to 25° C. and interrupted after consumption of the amount of hydrogen calculated for the saturation of the multiple bonds.
- In contrast, for simultaneous cleavage of the multiple bonds in A and the cleavage of a benzyl, diphenylmethyl or triphenylmethyl group as G in the compound of formula (I), polar, aprotic solvents are used such as methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, methoxyethanol or water or mixtures thereof, whereby a considerable excess of a strong acid compared to the stochiometric salt formation, preferably a mineral acid such as concentrated hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid is simultaneously added. The molecular ratio of substrate/acid can lie in the range of 1:2 to 1:10 thereby, preferably between 1:3 and 1:5. The same catalysts which are mentioned above in connection with the selective hydration are suitable as catalysts. The hydration is carried out under normal pressure or slightly increased hydrogen pressure of 2 to 3 bar, preferably under normal pressure, until the termination of the uptake of hydrogen. Depending on uptake speed, the reaction temperature can vary between 10 and 50, 70 or 80° C. as a function of the boiling point of the solvent and/or solvent mixture and employed pressure. If, for example, the reaction is carried out in ethanol or ethanol/water under normal pressure, the reaction temperature preferably lies between 40 to 60° C.
- The compounds of formula (I) produced according to the method (A), (B1) to (B4), (C) or (D) can be isolated and purified in a known manner, for example by subjecting the residue after distillation of the solvent to partition, extraction, re-precipitation or recrystallization or another purification method. For this, column chromatography on a suitable support or preparative, middle or high pressure liquid chromatography are preferred for this.
- The compounds (I) are first normally obtained in form of their free bases or their hydrates or solvates, depending on the type of isolation and purification. Their addition salts with pharmaceutically suitable acids are obtained in a typical manner by converting the base with the desired acid in a suitable solvent. Depending on the number of basic centers of compound (1), one or more equivalent acids per mole of base can be bound.
- Suitable solvents are, for example, chlorinated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane or chloroform; ethers such as diethyl ether, dioxane or tetrahydrofuran; acetonitrile; ketones such as acetone or ethyl methyl ketone; esters such as methyl acetate or ethyl acetate or low molecular alcohols such as methanol, ethanol or isopropanol; and water. Pure solvents as well as mixtures of two or three solvents can also be used. The salts can be isolated by crystallization, precipitation or the evaporation of the solvent. Thereby, they optionally accumulate as hydrates or solvates.
- The bases can be recovered from the salts by alkalization, for example with aqueous ammonia solution, alkali carbonate or diluted sodium hydroxide solution, The following listed compounds and/or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, if not already concretely labelled as such, are particularly preferred.
- N-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-ethyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
- N-{2-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-ethyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)propionamide
- N-{2-[1-(4-phenylbutyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-ethyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide
- N-{2-[1-(4-hydroxyphenylbutyl)piperidin-4-yl]-ethyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide
- N-[2-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-ethyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
- N-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
- N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
- N-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-{4-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide
- N-{4-[1-(4-biphenylylmethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide
- N-{4-[1-(1-naphthylmethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide
- N-{4-[1-(9-anthrymethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide
- N-{4-[1-(Cyclohexylphenylmethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide
- N-{4-[1-(10,11-dihydro5H-dienzo[ad]cycloheptene-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide
- N-[2-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-ethyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-[5-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-pentyl]-3-pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-[6-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-hexyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-5-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,4-pentadiene acid amide,
- N-(4-{1-[bis-(4-fluorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-(4-{1-[bis-(2-chlorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(2-fluoropyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(6-fluoropyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
- N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide dihydrochloride or,
- N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide methanesulfonate,
- For a better understanding of the use according to the invention and reproducability of the compounds used, a series of synthetic examples is described in the following:
- In the following production examples for the end products, the abbreviations stand for the following terms:
- MP=melting point,
- RT=room temperature,
- THF=tetrahydrofuran,
- DMF=dimethylformamide,
- CDI=carbonyldlimidazol,
- abs.=absolute,
- EDC=N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethyl-carbodiimide hydrochloride,
- HOBT=1-hydroxybenzotriazol,
- TEA=triethylamine.
- 1H-NMR-Spectrum=proton resonance spectrum, taken at 100 MHz. The chemical shifts are given in ppm against TMS as a standard (δ=0.0), whereby
- s=singlet,
- d=doublet,
- t=triplet,
- dt=doublet-triplet,
- m=multiplet,
- ar=aromatic,
- py=pyridine.
- N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-N-ethyl-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 123)
- 10 g (22.0 mmol) N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (substance 104) are dissolved in 100 ml THF and added to 0.73 g (24.3 mmol) 80% NaH (heavy foaming) and stirred 20 minutes at RT. 2.1 ml (26.4 mmol) ethyl iodine are added dropwise and the mixture is stirred five hours at RT. 0.1 g tetrabutyl ammonium iodine are added and the batch is further stirred at RT overnight. Subsequently, 0.1 g (3 mmol) 80% NaH are added and this is heated at 50° C. for one hour under stirring. The batch is carefully hydrolyzed with 50 ml water after cooling to RT. The aqueous phase is extracted with 100 ml dichloromethane and the combined organic phases are washed with 50 ml water. The organic phase is concentrated in vacuum and the residue is chromatographically pre-purified twice over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (95/5 to 90/10 and 98/2 to 95/5), subsequently further purified by flash chromatography with CHCl3/CH3OH (100/0 to 98/2) and crystallized three times from 20 ml 1-chlorobutane, 10 ml acetonitrile/diisopropyl ether (1/1) and 8 ml isopropanol/diIsopropyl ether (1/1). Yellow crystals with a MP of 115-117° C. were recovered; yield: 1.1 g (10%)
C32H39N3O (481.7) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(C═O) 1640 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1600 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-1.95(16H, m, piperidine, piperidine-(CH2)3CH3) 2.70-3.00(2H, m, piperidine) 3.20-3.70(4H, m, CONCH2, J 4.21(1H, s, Ar2CH) 6.89(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.5Hz) 7.00-7.50(11H, m, ar, py) 7.69-7.60(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.5Hz) 7.70-7.95(1H, m, py) 8.50-8.65(1H, m, py) 8.70-8.85(1H, m, py) - N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 104)
- 2.0 g (13.6 mmol) 3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylic acid are suspended in 60 ml abs. dichloromethane and, after addition of three drops of pyridine, cooled to ca. 0° C. in an ice bath under moisture exclusion. 1.8 ml (18.6 mmol) oxalyl chloride are added dropwise and the mixture is stirred at RT overnight. Subsequently, the solvent and excess oxalyl chloride is distilled off in a rotary evaporator. In order to completely remove the oxalyl chloride, the residue is dried further for two hours under high-vacuum. The acid chloride obtained in this manner is suspended in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. in an ice bath under moisture exclusion. 4.0 g (12.4 mmol) 4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butylamine are dissolved in 30 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise to this suspension. After complete addition, the ice bath is removed and the reaction mixture is stirred for a further two hours at RT. The mixture is subsequently washed with 10% sodium hydroxide solution. The aqueous phase is extracted with acetic acid ethyl ether. The combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is crystallized once from 15 ml isopropanol and then twice from acetic acid ethyl ester. Colorless crystals with a MP of 156° C. were recovered, yield: 1.6 g (28%)
C30H35N3O (453.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3310 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1660, 1545 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-2.20(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-(CH2)3) 2.65-3.05(2H, m, piperidine) 3.20-3.60(2H, m, CONCH 2, J 4.21(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.75-6.15(1H, m, NH) 6.45(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6) 6.90-8.00(13H, m, ar, py, CH═CHCO) 8.45-8.70(1H, m, py) 8.70-8.90(1H, m, py) - N-(4-{1-[bis-(4-fluorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (substance 171)
- 3.7 g (24.5 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid are suspended in 100 ml abs. dichloromethane and, after addition of three drops of pyridine, cooled to cA 0° C. in an ice bath under moisture exclusion. 2.8 ml (22.1 mmol) oxalyl chloride are added dropwise and the mixture is stirred at RT overnight Subsequently, the solvent and excess oxalyl chloride is distilled off in a rotary evaporator. In order to completely remove the oxalyl chloride, the residue is dried further for 2 hours under high-vacuum. The acid chloride obtained in this manner is suspended in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. in an ice bath under moisture exclusion. 8.0 g (22.3 mmol) 4-[1-bis-(4-fluorophenyl)-methyl-piperidin-4-yl]-butylamine are dissolved in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise to this suspension. After complete addition, the ice bath is removed and the reaction mixture is stirred for a further two hours at RT. The mixture is subsequently distributed between 10% sodium hydroxide solution and dichlorornethane, and the aqueous phase is extracted a further three times with dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are washed with 100 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (99.5/0.5 to 97/3) and crystallized from 30 ml acetic acid ethyl ester after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 108° C. were recovered; yield 3,5 g (34%).
C30H33F2N3O (489.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3320 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1655, 1540 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.00-2.00(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-(CH2)3) 2.60-2.95(2H, m, piperidine) 3.38(2H, dt, CONHCH 2, J=6.6Hz, J= 12.7Hz) 4.20(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.85-6.10(1H, m, NH) 6.47(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 6.80-7.50(9H, m, ar, py) 7.65-7.90(1H, m, py) 8.45-8.65(1H, m, py) 8.65-8.85(1H, m, py) - N-{4-[1-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (substance 219)
- Production occurred analogously to Example 3.
- Batch size: 2.6 g (17.6 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid, 2.6 g (20.8 mmol) oxalyl chloride and 5.57 g (16.0 mmol) 4-[1-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butylamine.
- In the work up, the mixture is concentrated under vacuum and subsequently distributed between 100 ml 10% NaOH and 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. The aqueous phase is extracted again with 50 ml acetic acid ethyl ester and the combined organic phases are washed with 50 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (97/3) and crystallized twice from 40 ml and 30 ml acetonitrile after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 125-127° C. were recovered; yield 2.3 g (30%).
C32H37F2N3O (479.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3300 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1655, 1540 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-2.00(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-(CH2)3) 2.55-3.00(4H, m, piperidine, ar —CH—CH-ar) 3.36(2H, dt, CONHCH 2, J=6.6Hz, J= 12.7Hz) 3.90(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.60-5.85(1H, m NH) 6.43(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 6.90-7.40(9H, m, ar, py) 7.60(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 7.65-7.90(1H, m, py) 8.50-8.65(1H, m, py) 8.70-8.80(1H, m, py) - N-[4(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 46)
- 6.5 g (18.0 mmol) N-[4-(piperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide dihydrochloride (substance 22) are suspended in 80 ml acetone added to 9.9 g (72.0 mmol) potassium carbonate. A solution of 3.4 g (19.8 mmol) benzyl bromide in 10 ml acetone is added dropwise to this mixture at RT and stirred overnight. Subsequently, the suspension is filtered and the filtrate is concentrated under vacuum. The residue is taken up in 100 ml CHCl 3 and washed with 30 ml water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl3/CH3OH (95/5 to 90/10) and crystallized from 15 ml acetonitrile after drawing off the solvent. Beige colored crystals with a MP of 88-90° C. were recovered; yield: 1.1 g (16%)
C24H31N3O (377.5) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3320 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1655, 1530 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.00-2.10(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-(CH2)3) 2.70-3.00(2H, m, piperidine) 3.20-3.55(4H, m, CONHCH 2, ar, CH2) 5.65-6.00(1H, m, NH) 6.45(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 3.36(2H, dt, CONHCH 2, J=6.6Hz, J= 12.7Hz) 7.10-7.40(6H, m, ar, py) 7.62(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 5.60-5.85(1H, m, NH) 6.43(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 7.65-7.90(1H, m, py) 8.45-8.65(1H, m, py) 8.65-8.85(1H, m, py) - N-[2-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-ethyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 95)
- Production occurred analogously to Example 3.
- Batch size: 2.3 g (15.5 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid, 2.7 g (21.3 mmol) oxalyl chloride and 4.1 g (13.9 mmol) 2-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-ethylamine in 60 ml abs. dichlormethane.
- In the work up, the mixture is concentrated under vacuum and subsequently dispersed between 100 ml 10% NaOH and 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. The aqueous phase is extracted again with 50 ml acetic acid ethyl ester and the combined organic phases are washed with 50 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically pre-purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (95/5) and subsequently purified by flash-chromatography with CHCl3/CH3OH (100/0 to 94/6), After drawing off the solvent, this is crystallized from 19 ml acetic acid ethyl ester/petroleum ether. Colorless crystals with a MP of 141-143° C. were recovered; yield 0.6 g (10%).
C28H31N3O (425.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3820 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1660, 1550 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.05-2.00(9H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2) 2.70-3.00(2H, m, piperidine) 3.41(2H, dt, CONHCH 2, J=6.6Hz, J= 12.7Hz) 4.23(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.55-5.80(1H, m, NH) 6.43(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 7.00-7.55(11H, m, ar, py) 7.61(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 7.60-7.90(1H, m, py) 8.55-8.65(1H, m, py) 8.65-8.80(1H, m, py) - N-{4-[1-(9-anthryl)-methylpiperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 81)
- 5.4 g (15.0 mmol) N-[4-piperidin-4-ylfibutyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide dichloride (substance 22) were suspended in 80 ml dichloromethane and added to 5.1 g (50.0 mmol) TEA. To this mixture, a solution of 3.7 g (16.5 mol) (9-anthyl)-methylchloride in dichloromethane is added at RT and stirred overnight. Subsequently, the mixture is washed twice, each with 100 ml water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (95/5 to 94/6) and crystallized first from 100 ml ethanol and then from 83 ml ethanol/diisopropyl ether (75/8) after drawing off the solvent. Yellow crystals with a MP of 162-164° C. were recovered; yield: 1.8 g (25%)
C32H35N3O (477.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3360 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1680, 1560 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1640 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-1.80(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.05-2.40(2H, m, piperidine) 2.80-3.15(2H, m, piperidine) 3.20-3.55(2H, m, CONHCH 2) 4.45(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.60-5.90(1H, m, NH) 6.42(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 7.20-8.20(10H, m, ar, py, CH═CHCO) 8.40-8.90(4H, m, ar, py) - N-{4-[1-(cyclohexylphenylmethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 84)
- 4.5 g (17.7 mmol) (bromcyclohexylphenyl)-methane, 5.6 g (15.5 mmol) N-[4-(piperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide dihydrochloride (substance 22), 8.5 g (61.8 mmol) potassium carbonate and 2.8 g (16.9 mmol) sodium iodide are stirred in 200 ml DMF 18 hours at ca. 75° C. After cooling, the mixtuure is filtered over a diatomaceous earth layer and the filtrate is concentrated under vacuum. The residue is taken up in 200 ml CHCl 3 and washed twice with 60 ml and 30 ml water. The organic phase is dried over a sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over a silica gel with CHCl3/CH3OH (96/4 bis 92/8) and crystallized three times, each from 40 ml acetonitrile and once at the conclusion from 50 ml acetonitrile. Colorless crystals with a MP of 143-145° C. were recovered; yield 0,58 g (8%).
C30H41N3O (459.7) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3330 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1680, 1570 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1640 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.50-2.20(24H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3, cyclohexane) 2.55-2.90(2H, m, piperidine) 3.08(1H, d, Ar—CH, J=9.2Hz) 3.35(2H, dt, CONHCH 2, J=6.5Hz, J= 12.7Hz) 5.70-6.05(1H, m, NH) 6.45(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 7.00-7.50(6H, m, ar, py) 7.60(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 7.60-7.90(1H, m, py) 8.45-8.65(1H, m, py) 8.65-8.85(1H, m, py) - N-(4-{1-[bis-(2-chlorphenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamid (Substance 186)
- Production occurred analogously to Example 3.
- Batch size: 1.6 g (10.7 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)acrylic acid, 1.9 g (15.0 mmol) oxalyl chloride and 3.9 g (10.0 mmol) 4-{1-[bis-(2-chlorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidine-4-y)}-butylamine. In the purification, chromatographic purification is done twice over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (97/3 and 97/3 to 95/5) and crystallization is from 25 ml acetic acid after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 129-131° C. were recovered; yield 0.6 g (11%).
C30H33Cl2N3O (522.5) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3240 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1655, 1560 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-1.95(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 1.90-2.40(2H, m, piperidine) 2.55-3.00(2H, m, piperidine) 3.38(2H, dt, CONCH 2 J=6.5Hz, J= 12.4Hz) 5.31(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.55-5.90(1H, m, NH) 6.44(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 6.90-8.00(11H, m, ar, py, CH═CHCO) 8.55-8.70(1H, m, py) 8.70-8.95(1H, m, py) - N-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (substance 97)
- Production occurred analogously to Example 3.
- Batch size: 3.9 g (26.1 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid, 4.1 g (47.4 mmol) oxalyl chloride and 7.38 (23.7 mmol) 3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-propylamine.
- In the purification, crystallization is done first from 1-chlorobutane and subsequently once from acetic acid. Colorless crystals with a MP of 110-113° C. were recovered; yield 6.2 g (60%).
C29H33N3O (439.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3240 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1650, 1555 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1605 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-2.25(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.70-3.05(2H, m, piperidine) 3.36(2H, dt, CONCH 2 J=6.5Hz, J= 12.8Hz) 4.21(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.85-6.20(1H, m, NH) 6.46(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 6.90-7.70(11H, m, ar, py) 7.60(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 7.60-7.90(1H, m, py) 8.45-8.65(1H, m, py) 8.65-8.85(1H, m, py) - N-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)propyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 96)
- 3.0 g (6.8 mmol) N-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (substance 97) are suspended in 60 ml THF and added to 5 drops concentrated hydrochloric acid and 0.35 g palladium (5%) on activated carbon. The mixture is stirred at RT under hydrogen atmosphere until consumption of the theoretical amount of hydrogen to be taken up. The suspension is filtered from the catalyst and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over a silica gel with CHCl/CH 3OH/NH4OH (85/15/2) and crystallized twice after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 109-110° C. were recovered; yield 1.7 g (56%).
C29H35N3O2 (441.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3230 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1620, 1555 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.00-2.00(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)2) 2.44(2H, t, CO—CH2, J=7.4Hz) 2.75-3.15(4H, m, piperidine, py-CH2) 3.15(2H, dt, CONCH 2 J=6.7Hz, J= 13.0Hz) 4.21(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.30-5.60(1H, m, NH) 7.00-7.70(12H, m, Ar, pyridine 6.90-7.70(11H, m, ar, py) 8.35-8.55(2H, m, pyridine) - N-[4(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-2-(pyridin-3-yloxy)-acetamide (substance 129)
- 5.0 g (32.6 mmol) 3-pyridyloxyacetic acid and 3.95 g (39.1 mmol) TEA are suspended in 200 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture exclusion. 6.34 g (41.3 mmol) 88% HOBT and 7.49 g (39.1 mmol) EDC are added and the mixture is stirred 30 min under ice cooling. 11.56 g (35.9 mmol) N-4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-butylamine are dissolved in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise under ice cooling. The mixture is stirred without further cooling at RT overnight. Subsequently, the batch is washed once with 50 ml 1M NaOH and twice each with 70 ml water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resinous residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (95/5 to 90/10) and crystallized from 30 ml acetic acid ethyl ester after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 103-105° C. were recovered; yield 3.45 g (23%).
C29H35N3O2 (457.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3360 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1660, 1545 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.95-2.05(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.70-3.00(2H, m, piperidine) 3.34(2H, dt, CONHCH 2, J=6.5Hz, J= 12.9Hz) 4.21(1H, s, Ar2CH) 4.51(2H, s, COCH2O) 6.40-6.70(1H, m, NH) 7.00-7.60(12H, m, Ar, py) 8.20-8.45(2H, m, py) - N-[5(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-pentyl]-3-pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (Substance 142)
- 2.47 g (16.3 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)priopionic acid are suspended in 40 ml abs. dichloromethane and, after addition of three drops of pyridine, cooled to ca. 0° C. in an ice bath under moisture exclusion. 1.90 ml (22.3 mmol) oxalyl chloride are added slowly and the mixture is first stirred under ice cooling for 30 minutes and then at RT overnight. Subsequently, the solvent and excess oxalyl chloride is distilled off in a rotary evaporator. In order to completely remove the oxalyl chloride, the colorless residue is further dried for two hours under high-vacuum. The acid chloride obtained in this manner is suspended in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. in an ice bath under moisture exclusion without further purification. 5.0 g (14.8 mmol) 5-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-pentylamine are dissolved in 40 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise to this suspension. After complete addition, the ice bath is removed and the reaction mixture is stirred for a further two hours at RT. The mixture is subsequently concentrated, taken up in 10% sodium hydroxide solution and extracted three times with acetic acid ethyl ester. The combined organic phases are washed with a saturated NaCl solution, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed in a vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3CH3OH (96/4) and crystallized from 40 ml acetonitrile after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 112-114° C. were recovered; yield: 3.5 g (50%)
C31H39N3O (469.7) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3260 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1635, 1550 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-2.00(15H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)4) 2.40(2H, t, CH—CH2, J=7.5) 2.70-3.10(4H, m, piperidine, py, CH2) 3.19(2H, dt, CONHCH2, J=6.6Hz, J= 12.6Hz) 4.21(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.30-5.60(1H, m, NH) 7.00-7.75(12H, m, Ar, py) 8.35-8.65(2H, m, py) - N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 100)
- 21.6 g (131 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-propionic acid methyl ester, 35.1 g ml (109 mmol) 4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)butylamine and 9.8 g (54.5 mmol) 30% sodium methylate solution in methanol are heated to boiling in 480 ml toluene for five hours. Subsequently, 30 ml of solvent are distilled; thereby, sodium methylate precipitates and the temperature of the suspension increases to 102° C. under heavy foaming. The mixture is cooled to 70-80° C. and extracted twice with 45 ml and 30 ml of water. The organic phase is azeotropically dried on a moisture separator and cooled to ca. 0° C. The resulting precipitate is filtered off and crystallized from 190 ml toluol. Colorless crystals with a MP of 139° C. were recovered; yield 46.3 g (93%).
C30H37N3O (455.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3250 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1630, 1570 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.00-2.10(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.43(2H, t, CO—CH2, J=7.4Hz) 2.70-3.10(4H, m, py-CH2) 3.12(2H, dt, CONHCH 2, J=6.5Hz, J= 12.5Hz) 4.21(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.45-5.75(1H, m, NH) 7.05-7.60(12H, m, Ar, py) 8.30-8.60(2H, m, py) - N-{4-[1-(6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]-oxepin-11-yl)-piperidineyl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 230)
- 3.46 g (15 mmol) 11-chloro-6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxepine are dissolved in 90 ml abs. dichloromethane and 5.43 g (15 mmol) N-(4-piperidin-4-yl-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide dihydrochloride are added. 5.0 g (49.5 mmol) TEA are dissolved in 20 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise under ice cooling. The mixture is stirred without further cooling for two days at RT. Subsequently, the batch is washed twice, each with 50 ml water. The organic phase is dried over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (95/5) and crystallized twice at first, each from 10 ml 1-chlorobutane, and subsequently crystallized once from 10 ml acetic acid. Colorless crystals with a MP of 110-112° C. were isolated, yield 0.2 g (3%/O).
C31H37Cl2N3O2 (483.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3240 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1630, 1570 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.80-2.00(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.43(2H, t, CO—CH2, J=7.5Hz) 2.55-3.30(6H, m, piperidine, py-CH2, CONHCH 2) 3.83(1H, s, Ar2CH) 4.68(1H, d, O—CH, J=11.3Hz) 5.25-5.55(1H, m, NH 6.65-7.65(11H, m, Ar, py, O—CH) 8.35-8.60(2H, m, py) - N-{4-[1-(9H-fluorene)piperidine-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 209)
- 8.0 g (27.7 mmol) N-(4-piperidin-4-yl-butyl)-3-pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide and 5.6 g (55.3 mmol) TEA are present in 100 ml acetonitrile and cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture exclusion. 6.8 g (27.7 mmol) 9-bromofluorene are added in solid form and the mixture is stirred for 2 days at ca. 65° C. and for two days at RT. Subsequently, the solvent is drawn off under vacuum to a large extent and the residue is dispersed between CHCl 3 and 10% NaOH. The organic phase is washed twice with water and dried over sodium sulfate. After the removal of the solvent, the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl3/CH3OH (98/2 to 94/6) and crystallized from 30 ml acetonitrile after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 131-132° C. were recovered; yield 2.5 g (20%).
C30H35N3O (453.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3300 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1630, 1530 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.95-1.80(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.25-2.80(6H, m, piperidine, CO—CH2) 2.97(2H, t, py-CH2, J=7.5Hz) 3.19(2H, dt, CONHCH 2, J=6.5Hz, J= 12.5Hz) 4.82(1H, s, ArCH) 5.25-5.55(1H, m, NH) 7.10-7.80(10H, m, Ar, py,) 8.35-8.55(2H, m, py) - N-{4-[1-(2-naphthylsulfonyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 337)
- 3.5 g (12 mmol) N-(4-piperidin-4-yl-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide and 6.7 g (48.1 mmol) TEA are present in 100 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture exclusion. 3.0 g (13.2 mmol) naphthaline-2-sulfonic acid chloride are dissolved in 40 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise. The mixture is stirred without further cooling at RT overnight. Subsequently, the batch is washed twice, each with 80 ml water The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (97/3) and crystallized from acetic acid ethyl ester after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 103-105° C. were recovered; yield 2.87 g (50%).
C27H33N3O3S (479.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3320 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1645, 1530 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-1.90(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.05-2.40(2H, m, piperidine) 2.42(2H, t, CO—CH2, J=7.4Hz) 2.80-3.30(4H, t, dt, Py-CH2, J=7.4Hz, CONHCH 2) 3.70-4.00(2H, m, piperidine) 5.40-5.70(1H, m, NH) 7.10-8.15(8H, m, Ar, Py,) 8.25-8.55(3H, m, Ar, Py) - N-{4-[1-(naphthylaminocarbonyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3(pyridin-yl)-propionamide (substance 305)
- 2.6 g (17.7 mmol)1-naphthyl isocyanate are dissolved in 15 ml abs. THF and cooled to 0° C. under moisture exclusion. 5.1 g (17.7 mmol) N-(4-piperidine-4-yl-butyl)-3-(pyridine-3-yl)-propionamide are dissolved in 35 ml abs. THF and added dropwise under ice cooling. The mixture is stirred without further cooling at RT overnight. Subsequently, the solution is drawn off under vacuum to a large extent and the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3CH3OH (90/10) and further purified by flash-chromatography with CHCl3/CH3OH (95/5 to 90/10). After drawing off the solvent, crystallization occurs from isopropanol/diisopropanol. Colorless crystals with a MP of 143-144° C. were recovered; yield 0.77 g (9%).
C28H34N4O2 (458.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3240 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1630, 1560 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.95-1.95(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.40(2H, t, CO—CH2, J=7.4Hz) 2.75-3.40(6H, m, piperidine, Py-CH2, CONHCH 2) 4.00-4.30(2H, m, piperidine) 5.55-5.85(1H, m, NH) 6.77(1H, s, NH) 7.10-8.00(9H, m, Ar, Py,) 8.35-8.55(2H, m, Ar, Py) - N-{4-[1-(2-naphthoyl)piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 274)
- 6.0 g (20.7 mmol) N-(4-piperidine-4-yl-butyl)-3-(pyridine-3-yl)-propionamide and 2.1 g (20.7 mmol) TEA are dissolved in 30 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture extraction. 3.95 g (20.7 mmol) 2-naphthoylchloride are dissolved in 40 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise under ice cooling. The mixture is stirred without further cooling at RT overnight. Subsequently, the batch is made basic by the addition of 10% sodium hydroxide solution and washed twice with a small amount of water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resinous residue is chromatographically purified with CHCl 3/CH3OH (96/4). Yield of colorless resin: 5.4 g (59%).
C28H33N3O2 (443.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): n(NH) 3300 cm−1 n(C═O) 1630, 1540 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.00-2.05(11H, m, piperidin, piperidine-(CH2)3) 2.55(2H, t, CH—CH2, J=7.5Hz) 2.70-3.45(6H, m, piperidine, Py-CH2, CONHCH 2) 3.65-4.15(1H, m, piperidin) 4.50-5.05(1H, m, piperidine) 5.60-5.85(1H, m, NH) 7.20-7.35(1H, m, Py) 7.50-7.75(4H, m, Ar, Py) 7.85-8.10(4H, m, Ar) 8.40-8.65(2H, m, Py) - N-(4-piperidin-4-yl-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 21)
- 100 g (219.5 mmol) N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridine-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 100) are dissolved in 500 ml ethanol and mixed with 8.0 g palladium (5%) on activated carbon (moistened with 40 ml water) and 25 ml conc. hydrochloric acid. The mixture is heated to ca. 45° C. and stirred under hydrogen atomosphere until consumption of the theoretical amount of hydrogen to be taken up (ca five hours). After cooling, the catalyst is filtered and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is taken up in 200 ml water and washed three times with a total of 200 ml CHCl 3. The organic phases are discarded and the aqueous phase is made alkaline with 11 g sodium hydroxide and extracted three times, each with 100 ml CHCl3. After washing the organic phase with 30 ml water, the solvent is removed under vacuum. The oily residue is filtered over silica gel with CHCl3/CH3OH/NH4OH (80/20/2). Yield of the gradually hardening resin: 53.0 g (83%).
- For spectroscopic data, see Example 20/2.
- N-(4-piperidin-4-yl-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide (substance 21)
- 100 g (219.5 mmol) N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridine-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 104) are dissolved in 500 ml ethanol and mixed with 8.0 g palladium (5%) on activated carbon (moistened with 40 ml water) and 25 ml conc. hydrochloric acid. The mixture is heated to ca 45° C. and stirred under hydrogen atomosphere until consumption of the theoretical amount of hydrogen to be taken up (ca. 1 day). After cooling, the catalyst is filtered and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is taken up in 400 ml water and washed twice, each with 100 ml toluol. The organic phases are discarded and the aqueous phase is made alkaline with 400 ml 4M-sodium hydroxide solution and extracted three times each with 200 ml dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The wax-like residue is filtered over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH/NH4OH (90/9/1). Yield: 58.3 g (91%). C29H33N3O2 (443.6)
IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3300 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1630, 1540 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-1.80(12H, m, piperidin, NH piperidine-(CH2)3) 2.35-2.75(4H, m, CO—CH2, piperidine) 2.80-3.35(6H, m, piperidine, Py-CH2, CONHCH 2) 6.05-6.40(1H, m, NH) 7.10-7.35(1H, m, Py) 7.40-7.60(1H, m, Py) 7.20-7.35(1H, m, Py) 8.30-8.55(2H, m, Py) - N-{4-[1-(6,11-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiepin-11-yl)-piperidine-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (substance 230)
- 7.02 g (21.5 mmol) N-[4-piperidine-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridine-3-yl)-acrylamide dihydrochloride (substance 22 as dihydrochloride) are suspended in 100 ml abs. dichloromethane and mixed with 7.08 g (70.0 mmol) TEA. The mixture is cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture exclusion and a solution of 5.30 g (21.5 mmol) 11-chloro-6,1-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiepine in 10 ml abs. dichloromethane is added dropwise. The mixture is stirred without further cooling for 24 hours at RT. Subsequently, the batch is washed with 50 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution and 30 ml water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solution is removed under vacuum. The red-brown residue is chromatographically purified three times over silica gel with CHCl 31CH3OH (100/0, 97/3 and 96/4 to 94/6). Subsequently, further purification occurs by means of MPLC with CHCl3/CH3OH (98/2). yield: 0.5 g (5%) of a brittle vitreous solid with a MP of 89-91° C.
C31H35Cl2N3OS (497.7) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3280 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1660, 1550 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.90-2.00(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.55-2.95(2H, m, piperidine) 3.20-3.60(3H, m, CONHCH2 , SCH2) 4.03(1H, s, Ar2CH) 6.10-6.35(1H, m, NH) 5.95-6.30(1H, m, SCH2) 6.44(1H, d, CH═CHO J=15.7Hz) 4.68(1H, d, O—CH, J=11.3Hz) 6.85-7.40(9H, m, Ar, Py) 8.50-8.65(1H, m, Py) 8.65-8.80(1H, m, Py) - N-[4(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-butyl]-5-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,4-pentadienoic Acid Imide (Substance 132)
- 3.85 g (22.0 mmol) 5-(3-pyridyl)-2,4-pentadieneoic acid are suspended in 90 ml abs. dichloromethane and, after addition of three drops of pyridine, cooled to ca. 0° C. in an ice bath under moisture exclusion. 3.8 g (30,0 mmol) oxalyl chloride are added dropwise and the mixture is stirred at RT overnight. Subsequently, the solvent and excess oxalyl chloride are distilled off on a rotary evaporator. In order to completely remove the oxalyl chloride, the residue is dried for a further two hours under high-vacuum. The acid chloride obtained in this manner is suspended in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. 6.44 g (20.0 mmol) 4.(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-butylamine are dissolved in 40 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise to the suspension. After complete addition, the ice bath is removed and the reaction is stirred for a further two hours at RT. The mixture is subsequently washed with 10% sodium hydroxide solution. The organic phase is washed twice, each with 40 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solution is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified three times over silica gel with CHCl 3CH3OH (98/2 to 95/5) and crystallized twice from 250 ml acetonitrile after removal of the solvent Beige-colored crystals with a MP of 164-166° C. are isolated; yield: 4.7 g (49%)
C32H37N3O (479.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3280 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1650, 1550 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1600 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.00-2.00(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.70-3.00(2H, m, piperidine) 3.34(2H, dt, CONHCH2 , J=6.6Hz, J=12.8Hz) 4.21(1H, s, Ar2CH) 5.50-5.75(1H, m, NH) 6.44(1H, d, CH═CH J=14.7Hz) 6.75-6.95(2H, m, CH═CH) 7.05-7.50(12H, m, Ar, Py, CH═CH) 7.65-7.85(1H, m, Py) 8.45-8.55(1H, m, Py) 8.60-8.75(1H, m, Py) - N-[4-(1-benzoylpiperidine-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 259)
- 5.1 g (36.2 mmol) benzoyl chloride are dissolved in 150 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture exclusion. 10.4 g (36.2 mmol) N-[4-piperidine-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 22) are dissolved in 50 ml abs. dichloromethane and added dropwise under ice cooling. The mixture is stirred without further cooling at RT overnight. Subsequently, the suspension is added to 60 ml sodium hydroxide solution and extracted twice, each with 80 ml dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are washed twice, each with 60 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solution is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified three times over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (97/3 to 95/5) and crystallized from 75 ml acetonitrile. Colorless crystals with a MP of 100-102° C. were recovered; yield: 9.8 g(69%).
C24H29N3O2 (391.5) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3280 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1670, 1545 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1630 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.80-2.00(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.55-4.00(5H, m, piperidine, CONHCH2 ) 4.40-4.90(1H, piperidine) 6.00-6.25(1H, m, NH) 6.48(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 8.50-8.65(1H, m, Py) 8.65-8.80(1H, m, Py) - N-(1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-ylmethyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 2)
- Production occurred analogously to Example 22.
- Batch size: 4.3 g (28.7 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid, 6.7 ml (78.4 mmol) oxalyl chloride and 6.6 g (26.1 mmol) 3-(1-diphenylmethylazetidine-3-ylmethyl)-amine.
- In the work up, the reaction mixture is washed with sodium hydroxide solution. The aqueous phase is extracted twice, each with 50 ml dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatigraphically pre-purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (98/2 to 95/5) and subsequently purified twice by flash chromatography with CHCl3/CH3OH (99/1 to 95/5). An amorphous solid with a MP of 72-74° C. remains after the removal of the solvent; yield 0.75 g (7%).
C25H25N3O (383.5) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3280 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1680, 1570 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1640 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 2.40-2.80(1H, m, azetidine) 2.80-3.10(2H, m, azetidine) 3.10-3.40(2H, m, azetidine) 3.60(2H, dd, CONCH2 J=6.5Hz, J=12.8Hz) 4.36(1H, Ar2CH) 6.45-6.75(1H, m, NH) 6.50(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 7.00-7.50(11H, m, Ar, Py) 7.62(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 7.65-7.90(1H, m, Py) 8.50-8.70(1H, m, Py) 8.70-8.85(1H, m, Py) - N-(4-diphenylmethylmorpholin-2-ylmethyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 378)
- Production occurred analogously to Example 22.
- Batch size: 2.3 g (15.6 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid, 5.4 g (42.5 mmol) oxalyl chloride and 3.6 g (14.7 mmol) 2-aminomethyl-4-diphenylmethylmorpholine.
- In the work up, 40 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution are added to the reaction solution. The aqueous phase is extracted with 15 ml dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are washed twice, each with 15 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatigraphically purified three times over silica gel with CHCl/CH 3OH (95/5, 90/10 and 90/10). An amorphous solid with a MP of 71-74° C. remains after the removal of the solvent; yield 0.8 g (13%).
C26H27N3O2 (413.5) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3370 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1655, 1540 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.70-2.30(2H, m, morpholine) 2.55-2.90(2H, m, morpholine) 3.00-3.35(1H, m, morpholine) 3.50-4.00(4H, m, CONHCH2 , morpholine) 4.20(1H, Ar2CH) 6.00-6.25(1H, m, NH) 6.47(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 4.36(1H, Ar2CH) 7.60(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 7.00-7.55(11H, m, Ar, Py) 7.60(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 7.65-7.90(1H, m, Py) 8.50-8.70(1H, m, Py) 8.70-8.80(1H, m, Py) - N-{4-[1-(9-oxo-9H-fluorene-4-carbonyl)-piperidine-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 277)
- 5.0 g (20.0 mmol) 95% 9-fluorene-1-acyl chloride were dissolved in 70 ml abs. dichloromethane and 6.5 g (18.2 mmol) N-[4-(piperidine-4-yl)butyl]-3-(pyridine-3-yl)-acrylamide dihydrochloride (substance 22) are added. The mixture is cooled to ca 0° C. under moisture exclusion and 4.0 g (40.0 mmol) TEA dissolved in 10 ml abs. dichloromethane is added dropwise. The batch is stirred without cooling at RT overnight. In the work up, 150 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution are added to the reaction solution and extracted by shaking. The organic phase is washed with 100 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solution is removed under vacuum. The residue is pre-purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (96/4 to 95/5) and subsequently purified by flash chromatography with CHCl3/CH3OH (95/5). The product remains as a yellow, vitreous solid with MP of 80-82° C. after removal of the solvent; yield: 2.3 g (25%)
C31H31N3O3 (493.6) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3320 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1730, 1640 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1620 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.70-2.05(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.60-3.80(5H, m, piperidine, CONHCH2 ) 4.70-5.05(1H, piperidine) 5.85-6.20(1H, m, NH) 6.47(1H, d, CH═CHO J=15.7Hz) 7.15-7.90(10H, m, Ar, PyCH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 8.50-8.65(1H, m, Py) 8.65-8.85(1H, m, Py) - N-[3-(1-benzylpiperidine-4-yloxy)-propyl]-3-(pyridin-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 55)
- 2.4 g (16.2 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid and 2.3 g (16.2 mmol) TEA were suspended in 50 ml abs. tolueneand a solution of 1.5 ml (15.5 mmol) chloroformic ethyl ester in 20 ml abs. tolueneis added dropwise under moisture exclusion and gentle cooling. This yellow suspension is stirred two hours at RT and then a solution of 3.5 g (14.1 mmol) 3-(1-benzylpiperidine-4-yloxy)propylamine in 20 ml abs. tolueneis added dropwise. The mixture is stirred at RT and subsequently extracted by shaking in the heat three timnes with 10 ml water, 2M sodium hydroxide solution and again with water, respectively. The organic phase is concentrated under vacuum and the orange colored, oily residue is chromatographically purified twice over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH/NH4OH (90/9/1 and 95/50 to 90/10/0) and crystallized twice from 10 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. Colorless crystals with a MP of 100-102° C. were recovered; yield: 1.9 g (35%).
C23H29N3O2 (379.5) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3290 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1650, 1530 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1610 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.50-2.45(8H, m, piperidine, C—CH2—C) 2.70-3.00(2H, m, piperidine) 3.25-3.80(7H, m, piperidine, CONHCH2 , Ar— CH2, O—CH2) 6.54(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 7.25-7.50(6H, m, Ar, Py) 7.69(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.7Hz) 7.80-8.00(1H, m, Py) 8.60-8.75(1H, m, Py) 8.75-8.90(1H, m, Py) - N-[4-(1-benzoylpiperidine-3-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)acrylamide (Substance 56)
- Production occurred analogously to Example 27.
- Batch size: 2.6 g (17.4 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid, 1.6 ml (19.0 mmol) oxalyl chloride and 3.9 g (15.8 mmol) 4-(1-benzlypiperidine-3-yl)-butylamine in 100 ml abs. dichloromethane.
- The reaction time is increased to 6 hours at RT. In the work up, the batch is washed with 50 ml sodium hydroxide solution and the aqueous phase is extracted with 50 ml dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are concentrated under vacuum and the residue is chromatigraphically purified twice over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (93/7 and 95/5), subsequently further purified by flash chromatography with CHCl3/CH3OH, 95/5 and 97/3) and crystallized from 5 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. Colorless crystals with a MP of 80-82° C. were recovered; yield 0.9 g (15%).
C24H31N3O (377.5) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3300 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1650, 1530 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1610 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 1.00-2.10(13H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3) 2.65-2.95(2H, m, piperidine) 3.37(2H, dt, CONHCH2 , J= 6.5Hz, J= 12.7Hz) 3.50(2H, s, Ar—CH2) 5.65-5.95(1H, m NH) 6.46(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 7.10-7.40(6H, m, Ar, Py) 7.62(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 7.65-7.90(1H, m, Py) 8.50-8.65(1H, m, Py) 8.70-8.80(1H, m, Py) - N-[4(1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidine-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (Substance 367)
- Production occurred analogously to Example 22. TEA is also added dropwise with the addition of the amine.
- Batch size: 16.4 g (110 mmol) 3-(3-pyridyl)-acrylic acid, 18.9 g (150 mmol) oxalyl chloride and 25.6 g (100 mmol) 4-(1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidine-4-yl)-butylamine and 10.1 g (100 mmol) TEA in 300 ml abs. dichloromethane.
- In the work up, 100 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution are added to the reaction solution. The aqueous phase is extracted with 30 ml dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are washed twice, each with 25 ml water and the solution is removed under vacuum. The residue is dissolved in CHCl 3/CH3OH (90/10) and filtered through a thin silica gel layer. The crude product remains as a red oil after the revomal of the solvent (44.0 g). For purification this is chromatographed with CHCl3/CH3OH,-(95/5) on a silica gel; yield 26.5 g (68%) as a yellow viscous oil.
C22H33N3O3 (387.50) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3250 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1670, 1540 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1600 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.80-1.90(20H, m, piperidine, piperidine-CH2)3, tert.butyl) 2.30-2.90(2H, m, piperidine) 3.10-3.60(2H, m, piperidine) 3.80-4.30(2H, m, CONHCH2 ) 6.15-6.55(1H, m NH) 6.43(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.6Hz) 3.50(2H, s, Ar—CH2) 8.35-8.55(2H, m, Py) 8.55-8.70(1H, m, Py) - N-[4-(piperidine-4-yl)butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide Dihydrochloride (Substance 22 as Dihydrochloride)
- 44.0 g (<13.5 mmol) crude N-[4-(1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidine-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide (substance 367) are dissolved in 400 ml ethanol and added to 26.0 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid. The mixture is heated to boiling for three hours and the solvent is removed under vacuum after cooling. The yellow residue is crystallized from 500 ml isopropanol. Beige colored crystals with a MP of 178-188° C. were recovered; yield: 32.6 g (90%).
C17H25N3O2 (360.3) IR-Spectrum (KBr): ν(NH) 3260 cm−1 ν(C═O) 1670, 1545 cm−1 ν(C═C) 1630 cm−1 1H-NMR-Spectrum (CDCl3): 0.95-1.95(11H, m, piperidine, piperidine CH2)3) 2.60-3.00(2H, m, piperidine) 3.00-3.40(4H, m, piperidine, CONHCH2 ,) 6.73(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.9Hz) 7.41(1H, d, CH═CHCO, J=15.9Hz) 7.80-8.00(1H, m, Py) 8.50-8.65(2H, m, Py) 8.65-8.90(1H, m, Py) - Further examples of the synthesized compounds are listed in the following Table 2, giving the structural features and melting points, for the further illustration of the compounds used according to the invention with the above characterized pharacological activities.
TABLE 2 Prepared compounds of formula (I) MP [° C.] Nr R1 A D—E—G (solvent)1 2 H CH═CH 72-74 (amorph; CHCl3/MeOH) 5 H CH═CH 164-165 (EE) 21 H CH2CH2 60-62 (CHCl3/MeOH) 22 H CH═CH 140-142 (amorph; CH2Cl2) 22 H CH═CH 178-1884(iPrOH) 23 H CH2CH2CH2CH2 57-59 (CHCl3) 24 H CH═CH—CH═CH 197-2024(iPrOH) 44 H CH2CH2 61-63 (iPr2O) 46 H CH═CH 88-90 (MeCN) 54 H CH2CH2 55-57 (BuCl) 55 H CH═CH 100-102 (EE) 56 H CH═CH 80-82 (EE) 74 H CH2CH2 125 (EE) 75 H CH═CH 147-149 (MeCN) 80 H CH2CH2 133-135 (EtOH) 81 H CH═CH 162-164 (EtOH) 83 H CH2CH2 109-110 (MeCN) 84 H CH═CH 143-145 (MeCN) 89 H CH═CH 135-136 (EE) 95 H CH═CH 141-143 (EE/PE) 96 H CH2CH2 109-110 (BuCl) 97 H CH═CH 110-113 (EE) 98 H CH2CH2 162-1714(iPrOH) 99 H CH═CH 139-140 (EE) 100 H CH2CH2 139 (EE) 101 Harz4 102 2-OH CH2CH2 135-136 (MeCN) 103 6-CH3O CH2CH2 135-137 (BuCl) 104 H CH═CH 156 (EE) 104 H CH═CH 118-1205(Aceton) 104 H CH═CH 1634(iPrOH) 105 ca. 205 (Zers.) (CHCl3) 110 2-Cl CH═CH 136-137 (BuCl) 111 6-C2H5S CH═CH 158-160 (EE) 112 6-C6H5O CH═CH 134-135 (BuCl) 115 H 132 (MeOH) 116 H 58-60 (BuCl) 117 H 139-140 (MeCN) 122 72-74 (BuCl/PE) 123 115-117 (iPrOH/iPr2O) 124 94-96 (EE) 129 H OCH2 103-105 (EE) 131 H CH2CH2CH2CH2 109 (EE) 132 H CH═CH—CH═CH 164-166 (MeCN) 133 H CH2NHCH2CH2 138-1404(iPrOH) 134 H Harz4 142 H CH2CH2 112-114 (MeCN) 143 H CH═CH 150-152 (iPrOH) 147 H CH═CH 178-180 (EE) 150 H CH2CH2 159-161 (MeCN) 153 H CH2CH2 78-78 (MeCN) 154 H CH═CH 129-131 (MeCN) 165 H CH═CH 190-192 (MeCN) 171 H CH═CH 108 (EE) 174 H CH═CH 79-81 (PE) 185 H CH2CH2 125 (iPrOH) 186 H CH═CH 129-131 (EE) 187 H CH2CH2CH2CH2 viskoses Ol4 195 H CH2CH2 82-57 (amorph; CHCl3/MeOH) 198 H CH═CH 150-152 (MeCN) 209 H CH2CH2 131-132 (MeCN) 218 H CH2CH2 113-115 (EE) 219 H CH═CH 125-127 (MeCN) 230 H CH2CH2 110-112 (EE) 231 H CH═CH 139-141 (EE) 233 H CH═CH 89-91 (amorph; CHCl3/MeOH) 239 H CH═CH Harz4 252 H CH═CH 161 (EtOH/Et2O) 253 H CH═CH—CH═CH 77-79 (EE/BuCl) 254 H CH═CH 105-106 (MeCN/MTBE) 259 H CH═CH 100-102 (MeCN) 260 H CH═CH—CH═CH 133-135 (EE/BuCl) 263 H CH2CH2 Harz4 266 H CH2CH2 104-105 (BuCl) 269 H CH2CH2 Harz4 274 H CH2CH2 Harz4 277 H CH═CH 80-82 (amorph; CHCl3/MeOH) 280 H CH2CH2 98-99 (BuCl) 287 H CH2CH2 85-87 (EtOH) 305 H CH2CH2 143-144 (iPrOH) 306 H CH═CH 196-200 (iPrOH) 315 H CH═CH 132-134 (EE) 316 H CH═CH—CH═CH 146-148 (iPrOH) 324 H CH2CH2 Harz4 325 H CH2CH2CH2CH2 Harz4 333 H CH2CH2 Harz4 337 H CH2CH2 103-105 (EE) 338 H CH═CH 85-87 (amorph; CHCl3/MeOH) 339 H CH2CH2CH2CH2 97-98 (EE) 345 H CH2CH2 159-160 (MeCN) 356 H CH2CH2 134-135 (iPr2O) 357 H CH═CH 154-155 (EE) 367 H CH═CH Ol4 368 H CH═CH—CH═CH 135-136 (EE) 378 H CH═CH 71-74 (amorph; CHCl3/MeOH) - In the following, the production of the starting materials necessary for illustration of the reproducibility for providing the compounds used according to the invention is described by means of several examples.
- 4-{1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl)-butane-1-ol
- 20 g (103 mmol) 4-piperidin-4-yl-butan-1-ol hydrochloride are suspended in 70 ml 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrane and added to 1.0 g pyridinium tosylate. The mixture is stirred for two days at RT. After addition of 5 g potassium carbonate, this is concentrated under vacuum to dryness. The resulting 4-[4-tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-butyl]-piperidine is dissolved without further purification in 100 ml acetonitrile and added to 25.18 (105 mmol) bis-(4-fluorophenyl)-chloromethane, 30 g (217 mmol) potassium carbonate and 5.0 g (30 mmol) potassium iodide and stirred for four days at RT. The mixture is filtered and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resulting 1-[bis-(4-fluorophenyl)-methyl]-4-[4-(tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-butyl]-piperidine is dissolved without further purification in 150 ml methanol, added to enough 6 M methanolic hydrochloric acid until the pH of the mixture is acidic and left to stand for two days at RT. Subsequently, the solvent is drawn off under vacuum and the residue is dispersed between sodium hydroxide solution and acetic acid ethyl ester. The aqueous solution is extracted three times with acetic acid. The combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate and the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CH 2Cl2/CH3OH(99/1 to 94/4). Yield: 23.8 g (63%).
- 2-(4-{1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butyl)-isoindol-1,3-dione
- 23.1 g (62.5 mmol) 4-{1-[bis(4-fluoraphenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butan-1-ol, 16.4 g (62.5 mmol) triphenylphosphine and 9.2 g (62.5 mmol) phthalimide are suspended in THF and 10.9 g (62.5 mmol) azodicarboxylic acid diethyl ester is added dropwise under a protective atmosphere and light cooling (ca. 15-25° C.). The mixture is stirred for three hours at RT and subsequently the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CH 2Cl2/CH3OH (99.5/0.5) Yield: 27.6 g (90%).
- 4-[1-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-methylpiperidin-4-yl]-butylamine
- 27.6 g (56.3 mmol) 2-(4-{(1-[bis(4-fluorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butyl)-isoindol-1,3-dione are suspended in 120 ml ethanol and added to 5.6 g (112 mmol) hydrazine hydrate and heated to boiling for four hours. Afer cooling, the mixture is filtered and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is dispersed between 10% sodium hydroxide solution and acetic acid ethyl ester. The aqueous phase is extracted three times with acetic acid ethyl ester. The combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate. The solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH/NHOH (95/5/0 to 90/10/1). Yield: 14.6 g (73%).
- 4-[1-(10,11-dihydro-1H-dibenzo-[a,d]cyclohepten-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butane-1-ol
- 26.3 g (<109 mmol) 4-[4-tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-butyl]-piperidine (crude product) and 23.3 g (229 mmol) TEA are dissolved in 150 ml acetonitrile and added in portions to 25.0 g (109 mmol) 5-chloro-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene under cooling. The mixture is stirred at RT overnight Subsequently, the solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is dispersed betweenacetic acid ethyl ester and water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resulting 1-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene-5-yl)-4-[4 (tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-butyl]-piperidine is dissolved without further purification in 200 ml methanol, added to enough 6 M methanolic hydrochloric acid until the pH of the mixture is acidic and stirred for five hours at RT. Subsequently, the solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is dispersed between 10% sodium hydroxide solution and dichloromethane. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is processed further without additional purification. Yield: 38.2 g.
- 2-{4-[1-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-yl)piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-isoindol-1,3-dione
- Production occurs analogously to Example 2a
- Batch size: 15.0 g (<43 mmol) 4-[1-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butan-1-ol (crude product), 11.3 g (43.1 mmol) triphenylphosphine, 6.4 g (43.5 mmol) phthalimide and 7.5 g (43.0 mmol) azodicarboxylic acid diethyl ester in 200 nml THF. For purification, this is chromatographed over silica gel first with dichloromethane and then with petroleum ether/acetic acid ethyl ester (10/1 to 5/1). Yield: 12.0 g (57%)
- 4-[1-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butylamine
- Production occurs analogously to Example 3a.
- Batch size: 11.5 g (24.0 mmol) 2-(4-[1-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-isoindol-1,3-dione and 2.4 g (48.0 mmol) hydrazine hydrate in 100 ml ethanol.
- For work up, the reaction solution is filtered and the filter cake is dispersed between 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester and 100 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH/TEA (95/510 to 94/5/1). Yield: 5.6 g (67%)
- (1-diphenylmethylpiperidineyliden)acetonitrile
- 2.9 g (97 mmol) 80% sodium hydride are suspended in abs. THF and a solution of 21.5 g (121 mmol) diethyl-(cyanomethyl)-phosphonate in 150 ml abs. THF is added dropwise under light cooling. The mixture is subsequently stirred 30 minutes at RT and then a solution of 26.5 g (100 mmol) N-(diphenylmethyl)-4-piperidone in 80 ml abs. THF is added dropwise. The suspension is left to stand overnight and subsequently added to 200 ml acetic acid ethyl ester and 100 ml water. The organic phase is separated and washed with 100 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with dichloromethane. Yield: 22.7 g (78%).
- (1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-acetonitrile
- 9.8 g (33.5 mmol) (1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-ylidine)-acetonitrile are dissolved in a mixture of 60 ml dioxane and 70 ml ethanol and added dropwise to 1.5 g palladium (5%) on activated carbon. The mixture is stirred at RT under hydrogen atomosphere until consumption of the theoretical amount of hydrogen to be taken up (ca. 14 hours). The mixture is filtered from the catalyst and the solvent is removed under vacuum The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (96/4). Yield of yellow oil: 8.4 g (85%).
- 2-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin 4-yl)ethylamine
- 2.2 g (58.2 mmol) sodium borohydroxide are suspended in 50 ml abs. THF and cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture exclusion. 6.7 g (23.1 mmol) (1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)acetonitrile are added and the mixture is subsequently cooled to −5° C. to −10° C. and added dropwise to 1.5 ml (26.7 mmol) 95% sulfuric acid (vigorous foaming). The suspension is left to stand for two days at RT without further cooling. Under renewed cooling to ca. 0° C., 40 ml 2 M sodium hydroxide solution is added dropwise. The aqueous phase is extracted with 30 ml THF and thereafter the combined organic phases are washed twice, each with 30 ml saturated NaCl solution, dried over sodium sulfate and the solution is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH/NH4OH (90/10/1). Yield: 3.9 g (57%).
- 4-{1-[bis(2-chlorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butyronitrile
- 20 g (106 mmol) 4-(3-cyanoprop-1-yl)-piperidin hydrochloride, 40.2 g (127 mmol) bis(2-chlorophenyl)-bromomethane and 35.2 g (254 mmol) potassium carbonate are heated to boiling in 90 ml acetone for six hours. After cooling, the mixture is freed from solution under vacuum. The residue is dispersed between 90 ml toluene and 90 ml water. The aqueous phase is extracted with 10 ml tolueneand the combined organic phases are washed with 10 ml water. The organic phase is concentrated and the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCL3. Yield: 11.2 g (27%)
- 4-{1-[bis(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butylamine
- 80 g (20.6 mmol) 4-{1-[bis(2-chlorophenyl)-methyl)-piperidin-4-yl}-butyronitrile are dissolved in 240 ml dioxane/ethanol (1/5) and added to 1.5 g Raney-nickel, The mixture is stirred at RT under hydrogen atmosphere until uptake of the theoretical amount of hydrogen. The reaction solution is filtered from the catalyst and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is dispersed between 100 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution and 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. The organic phase is dried with sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resin is processed further without additional purification.
- 3(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propan-1-ol
- 20 g (111 mmol) 3-piperidin-4-yl-propan-1-ol hydrochloride are suspended in 70 ml 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrane and added to 0.5 g pyridinium tosylate. The mixture is stirred for two days at RT. After addition of 1 g potassium carbonate, this is concentrated under vacuum to dryness. The resulting 4-[3-tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-propyl]-piperidine is dissolved in 90 ml acetonitrile without further purification and added to 35 g (135 mmol) diphenyl bromomethane (95%) and 29 g (210 mmol) potassium carbonate and stirred for four days at RT. The mixture is filtered and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resulting 1-diphenylmethyl-4-[3-tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-propyl]-piperidine is dissolved without further purification in 130 ml methanol and added to 25 ml conc. hydrochloric acid, and the mixture is stirred at RT overnight. Subsequently, the solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is taken up with 300 ml water and extracted with 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. The organic phase is discarded and the aqueous phase is made alkaline with 17 g sodium hydroxide and extracted with 300 g acetic acid ethyl ester. After washing the organic phase with 40 ml water, this is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The oil is dried under high-vacuum and processed further without purification Yield: 22.4 g (65%).
- 2-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-propyl]-isoindol-1,3-dione
- 20.3 g (65.6 mmol) 3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propan-1-ol, 17.2 g (65.6 mmol) triphenylphosphine and 9.7 g (65.6 mmol) phthalimide are suspended in 220 nml THF and a solution of 10.4 ml (65.6 mmol) azodicarbonic acid diethyl ester in SO ml THF is added dropwise within one hour under protective atmosphere and light cooling (ca. 15-25° C.). After a further three hours, the solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is crystallized from 60 ml 1-chlorobutane. Yield: 12.9 g (45%).
- 3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propanylamine
- 12.8 g (29.2 mmol) 2-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidine-4-yl)-propyl]-isoindol-],3-dione are suspended in 110 ml ethanol and added to 2.2 ml (58.4 mmol) hydrazine hydrate and heated to boiling for three hours. After cooling, the mixture is concentrated under vacuum. The residue is dispersed between 300 ml dichloromethane and 50 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution. The aqueous phase is extracted twice, each with 200 ml dichloromethane. The combined organic phases are washed twice, each with 20 ml water, and dried over sodium sulfate. The solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is processed fruther without additional purification. Yield 7.3 g (81%)
- 4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butan-1-ol
- 120 g (620 mmol) 4-piperidin-4-yl-butan-1-ol hydrochloride are suspended in 400 ml 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran and added to 1.5 g pyridinium tosylate and 5 ml 8 M methanolic hydrochloric acid. This is stirred for three hours and left to stand at RT overnight. After addition of 5 g potassium carbonate, this is concentrated under vacuum to dryness. The resulting 4-[4-tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-butyl]-piperidine is dissolved in 500 ml acetonitrile without further purification and added to 193 g (742 mmol) diphenylmethylbromide (95%) and 160 g (1157 mmol) potassium carbonate and stirred for three days at RT. The mixture is filtered and the filtrate is stirred for one day at RT with a further 20 g (76.8 mmol) diphenylmethylbromide (95%) and 16 g (115.8 mmol) potassium carbonate. The mixture is filtered and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resulting 1-diphenylmethyl-4-[-(tetrahydropyran-2-yloxy)-butly]-piperidine is dissolved in 700 ml methanol without further purification, added to 120 ml conc. hydrochloric acid, and the mixture is left to stand for two days at RT. Subsequently, the solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is taken up with 1500 ml water and extracted with 1500 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. The organic phase is discarded and the aqueous phase is adjusted to alkaline with sodium hydroxide and extracted with 700 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. After washing the organic phase with 200 ml water, this is dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The brown oil is dried under high-vacuum and processed further without purification. Yield: 145 g (72%).
- 2-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-isoindol-1,3-dione
- 135.0 g (417 mmol) 4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)butan-1-ol, 109.5 g (417 mmol) triphenylphosphine and 61.3 g (417 mmol) phthalimide are suspended in THF and 72.6 g (417 mmol) azodicarboxylic acid diethyl ester are added dropwise within 2½ hours under protective atmosphere and light cooling (ca. 15-25° C.). After a further hour, the solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is crystallized three times from acetic acid ester (1000 ml, 1200 ml and 1100 ml). Colorless crystals with a MP of 150-152 were recovered. Yield: 103 g (54.5%).
- 4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butylamine
- 88.9 g (196 mmol) 2-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-isoindol-1,3-dione are suspended in 1000 ml ethanol and added to 22.0 g (440 mmol) hydrazine hydrate and heated to boiling for four hours. After cooling, the mixture is filtered and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The solid residue is distributed together with the filter residue under heat between 300 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution and 300 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. The aqueous phase is extracted once again with 150 ml warm acetic acid ethyl ester. The combined organic phases are extracted twice, each with 300 ml 10% hydrochloric acid. The combined aqueous phases are adjusted to alkaline with 10% sodium hydroxide solution and extracted twice, each with 400 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. The combined organic phases are washed with 100 ml water and dried over sodium sulfate. The solvent is removed under vacuum, the residue is dried under high-vacuum and further processed without additional purification. Yield of gradually solidifying resin: 63 g (99%)
- 5-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-pentanitrile
- 24.9 g (69.2 mmol) 4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)butan-1-ol hydrochloride are suspended in 160 ml abs. dichloromethane and cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture exclusion. At this temperature, 16.0 g (159 mmol) TEA is first added, and thereafter, a solution of 10.3 g (90.0 mmol) methanesulfonic acid chloride in a little abs. dichloromethane is added dropwise. The mixture is subsequently stirred for three hours at RT and then placed in ice water. The organic phase is washed once with 50 ml water, dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resulting methanesulfonic acid-4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl ester is dissolved in 120 ml DMF without further purification and added to 7.7 g (158 mmol) sodium cyanide and two drops 15-crown-5 and stirred six hours at 65° C. After cooling, the mixture is poured in ice water. The precipitated solid is drawn off and dried under high-vacuum at 40° C. The solid is processed further without additional purification. Yield: 19.9 g (86%).
- 5(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)pentylamine
- 19.0 g (57.1 mmol) 5(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)pentanitrile are dissolved in 240 ml dioxane/ethanol (1/1) and added to 3.2 g Raney-Nickel. The mixture is stirred at RT under hydrogen atmosphere until uptake of the theoretical amount of hydrogen. The mixture is filtered from the catalyst and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is dispersed between 100 ml water and 250 ml acetic acid ethyl ester. The organic phase is dried with sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The resin is processed further without additional purification Yield: 17.0 g (88%).
- 4-(1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-butan-1-ol
- 100 g (458 mmol) 4-piperidin-4-yl-butan-1-ol hydrochloride are dissolved in 120 ml water, added to 216 ml (1550 mmol) TEA and cooled to ca. 5-10° C. 122 g (559 mmol) di-tert-butyl dicarbonate dissolved in 400 ml THF are added dropwise within four hours under further cooling. The mixture is left to stand at RT overnight without further cooling. Subsequently, the THY is largely removed under vacuum and the residue is extracted twice with 300 ml and 200 ml CHCl 3 and the combined organic phases are washed twice, each with 20 ml water. The solvent is removed under vacuum, the residue dried under high-vacuum and processed further without additional purification. Yield: 136 g.
- 2-[4-(1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-isoindol-1,3-dione
- 136.0 g (<528 mmol) 4-(1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidin-4-ylfibutan-1-ol (crude product), 135.3 g (516 mmol) triphenylphosphine and 75.9 g (516 mmol) phthalimide are suspended in THF and 89.9 g (516 mmol) azodicarboxylic acid diethyl ester are added dropwise within 3 hours under protective atmosphere and light cooling (ca. 15° C.). The mixture is left to stand at RT overnight without further cooling. Subsequently, the solvent is removed under vacuum and the oily residue is dissolved in 500 ml acetic acid ethyl ester and held overnight at 0° C. The sedimented precipitate is filtered and discarded. The solution is concentrated under vacuum and the oily residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3 and crystallized from 200 ml isopropanol after drawing off the solvent. Colorless crystals with a MP of 100-102° C. were recovered; yield: 108.5 g (57%).
- 4-(1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-butylamine
- 113.0 g (292 mmol) 2-[4-(1-tert-butoxycarbonylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-isoindol-1,3-dione are dissolved in 600 ml ethanol and added to 29.3 g (585 mmol) hydrazine hydrate are added thereto and heated to boiling for three hours. After cooling the solution, the mixture is filtered and the filtrate is concentrated under vacuum. The residue is distributed under heat between 500 ml toluene and 500 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution. The organic phase is washed once with 50 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution and twice, each with 50 ml water. The solvent is removed under vacuum, the residue is dried under high-vacuum at 70° C. and further processed without additional purification. Yield of colorless oil: 64.0 g (85%),
- (1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-ylmethyl)-amine
- A solution of 10 g (40 mmol) 1-diphenylmethylazetidin-3-carbonitrile in 20 ml abs. THF are added dropwise at RT to a suspension of 3.1 g (80 mmol) lithium aluminum hydride in 80 ml abs. THF and stirred overnight. 2 ml ethanol are carefully added to the batch and the batch is filtered. The filtrate is concentrated under vacuum and dispersed between CHCl 3 and water. The aqueous phase is extracted twice, each with 50 ml CHCl3, and the combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl3/CH3OH/NFLOH (90/10/0 to 90/10/1). Yield: 5.6 g (57%) of slowly solidifying resin.
- 3-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yloxy)-propylamine
- 1.0 g (40.9 mmol) 3-(1-benylpiperidin-4-yloxy)-propionitrile are dissolved in 100 ml ethanol and added to a spatula tip of Raney-Nickel. The mixture is stirred at RT under hydrogen atmosphere until the uptake of the theoretical amount of hydrogen (ca. 2 days). The mixture is filtered from the catalyst and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is distilled in a ball-pipe apparatus. Yield of colorless oil: 7.5 g (73%)
- 4-(1-benzylpiperidin-3-ylidene)-butyronitrile
- 77.3 g (188.3 mmol) 3-cyanopropyl triphenylphosphonium bromide are suspended in 300 ml tolueneand added to 22.0 g (191.9 mmol) potassium-tert-butylate. The mixture is cooled to ca. 0° C. under moisture exclusion and a solution of 34.6 g (182.8 mmol) 1-benzyl-3-piperidone in 50 ml tolueneare added dropwise under cooling. The batch is left to stand overnight at ca. 0° C., subsequently diluted with 200 ml tolueneand washed twice, each with 100 ml water. The organic phase is extracted with 150 ml half-concentrated hydrochloric acid. Subsequently, the aqueous phase is made basic with 200 ml 10% sodium hydroxide solution and extracted twice, each with 250 ml toluol. The solvent is removed under vacuum and the residue is chromatographically purified over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH (97/3). After drawing off the solvent, a light brown oil remains which is further processed without additional purification. Yield: 47.4 g (90%).
- 4-(1-benzylpiperidin-3-yl)butylamine
- 8.0 g (33.3 mmol) 4-(1-benzylpiperidin-3-ylidene)-butyronitrile are dissolved in 80 ml ethanol and added to a spatula tip of Raney-Nickel. The mixture is stirred under hydrogen atmosphere until consumption of the theoretical amount of hydrogen to be taken up (ca. 5 days). The mixture is filtered from the catalyst and the solvent is removed under vacuum. The residue is chromatographically purified twice over silica gel with CHCl 3/CH3OH/NH4OH (90/10/1). After drawing off the solvent, a colorless oil remains which is further processed without additional purification. Yield: 3.9 g (47%).
- The active ingredients used according to the invention can be processed to the desired medicaments in the form of their acid addition salts, hydrates or solvates individually or in combination with each other or with others, optionally under addition of other active ingredients, for the indications tumor treatment or immunosuppression. In the case of the combination of active ingredients according to the invention with other medicinal forms, these can also optionally be separately present next to each other in the medicine packaging, for example as tablets next to viles, depending on the requirements.
- Therefore, further subject-matter of the invention is a medicament with an amount of compounds according to the above defined general formula (I) in combination with the further cytostatic agent, cancerostatic agent, immunosuppressing agent and/or immunomodulatory agent. Therewith, a method for the production of medicaments with an amount of one or more compounds according to formula (I), optionally together with another cytostatic agent or immunosuppressive agent and optionally next to further active ingredients and additives customary and suitable for these indications together with respective pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and adjuvents for providing the finished medical form also falls within the scope of protection according to the invention.
- The invention is more closely illustrated in the following by means of the production of respective medicaments suitable for the use according to the invention and the combinations according to the invention as well-as by means of a series of examples for various medical forms suitable for the respective indications.
- The production of medicaments with an amount of one or more compounds according to the invention and/or their use in the application according to the invention occurs in the customary manner by means of common pharmaceutical technology methods. For this, the active ingredients as such or in the form of their salts are processed together with suitable, pharmaceutically acceptable adjuvents and carriers to medicinal forms suitable for the various indications and types of application. Thereby, the medicaments can be produced in such a manner that the respective desired release rate is obtained, for example a quick flooding and/or a sustained or depot effect.
- Preparations for parenteral use, to which injections and infusions belong, are among the most important systemically employed medicaments for tumor treatment as well as for other indications.
- Preferably, injections are administered for the treatment of tumors. These are prepared either in the form of vials or also as so-called ready-to-use injection preparations, for example as ready-to-use syringes or single use syringes in addition to perforation bottles for multiple withdrawals. Administration of the injection preparations can occur in the form of subcutaneous (s.c.), intramuscular (i.m.), intravenous (i.v.) or intracutaneous (i.c.) application. The respective suitable injection forms can especially be produced as solutions, crystal suspensions, nanoparticular or colloid-disperse systems, such as for example, hydrosols.
- The injectable formulations can also be produced as concentrates which can be adjusted with aqueous isotonic dilution agents to the desired active ingredient dosage. Furthermore, they can also be produced as powders, such as for example lyophilisates, which are then preferably dissolved or dispersed immediately before application with suitable diluents. The infusions can also be formulated in the form of isotonic solutions, fat emulsions, liposome formulations, microemulsions and liquids based on mixed micells, for example, based on phospholipids. As with injection preparations, infusion formulations can also be prepared in the form of concentrates to dilute. The injectable formulations can also be applied in the form of continuous infusions as in stationary as well as in out-patient therapy, for example in the form of mini-pumps.
- Albumin, plasma expanders, surface active compounds, organic solvents, pH influencing compounds, complex forming compounds or polymeric compounds can be added to the parenteral medicinal forms, especially as substances for influencing the adsorption of the active ingredients to protein or polymers or also with the aim of decreasing the adsorption of the active ingredient to materials such as injection instruments or packaging materials, for example plastic or glass.
- The active ingredients can be bound to nanoparticles in the preparations for parenteral use, for example on finely dispersed particles based on poly(meth)acrylates, polyacetates, polyglycolates, polyamino acids or polyether urethanes. The parenteral formulations can also be constructively modified as depot preparations, for example on the multiple unit principle, where the active ingredients are incorporated in a most finely distributed and/or dispersed, suspended form or as crystal suspensions, or on the single unit principle, where the active ingredient is enclosed in a medicinal form, for example, a tablet or a seed which is subsequently implanted. Often, these implantations or depot medicaments in single unit and multiple unit medicinal forms consist of so-called biodegradable polymers, such as for example, polyether urethanes of lactic and glycolic acid, polyether urethanes, polyamino acids, poly(meth)acrylates or polysaccharides.
- Sterilized water, pH value influencing substances, such as for example organic and inorganic acids or bases as well as their salts, buffer substances for setting the pH value, agents for isotonicity, such as for example sodium chloride, monosodium carbonate, glucose and fructose, tensides and/or surface active substances and emulsifiers, such as for example, partial fatty acid esters of polyoxyethylene sorbitan (Tween®) or for example fatty acid esters of polyoxethylene (Cremophor®), fatty oils such as for example peanut oil, soybean oil and castor oil, synthetic fatty acid esters, such as for example ethyl oleate, isopropyl myristate and neutral oil (Miglyolq®) as well as polymer adjuvents such as for example gelatin, dextran, polyvinylpyrrolidone, organic solvent additives which increase solubility, such as for example propylene glycol, ethanol, N,N-dimethylacetamide, propylene glycol or complex forming compounds such as for example citrates and urea, preservatives, such as for example hydroxypropyl benzoate and hydroxymethyl benzoate, benzyl alcohol, anti-oxidants, such as for example sodium sulfite and stabilizers, such as for example EDTA, are suitable as adjuvents and carriers in the production of preparations for parenteral use.
- In suspensions, addition of thickening agents to prevent the settling of the active ingredients from tensides and peptizers, to secure the ability of the sediment to be shaken, or complex formers, such as EDTA, ensues. This can also be achieved with the various polymeric agent complexes, for example with polyethylene glycols, polystyrol, carboxymethylcellulose, Pluronics® or polyethylene glycol sorbitan fatty acid esters. The active ingredient can also be incorporated in liquid formulations in the form of inclusion compounds, for example with cyclodextrins. As further adjuvents, dispersion agents are also suitable. For production of lyophilisates, builders are also used, such as for example mannite, dextran, saccharose, human albumin, lactose, PVP or gelatin varieties.
- As long as the active ingredients are not incorporated in the liquid medicinal formulations in the form of a base, they are used in the form of their acid addition salts, hydrates or solvates in the preparations for parenteral use.
- A further systemic application form of importance is peroral administration as tablets, hard or soft gelatin capsules, coated tablets, powders, pellets, microcapsules, oblong compressives, granules, chewable tablets, lozenges, gums or sachets. These solid peroral administration forms can also be prepared as sustained action and/or depot systems. Among these are medicaments with an amount of one or more micronized active ingredients, diffusions and erosion forms based on matrices, for example by using fats, wax-like and/or polymeric compounds, or so-called reservoir systems. As a retarding agent and/or agent for controlled release, film or matrix forming substances, such as for example ethylcellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, poly(meth)acrylate derivatives (for example Eudragit®), hydroxypropylmethylcellulose phthalate are suitable in organic solutions as well as in the form of aqueous dispersions. In this connection, so-called bio-adhesive preparations are also to be named in which the increased retention time in the body is achieved by intensive contact with the mucus membranes of the body. An example of a bio-adhesive polymer is the group of Carbomers®.
- For sublingual application, compressives, such as for example non-disintegrating tablets in oblong form of a suitable size with a slow release of active ingredient, are especially suitable. For purposes of a targeted release of active ingredients in the various sections of the gastrointestinal tract, mixtures of pellets which release at the various places are employable, for example mixtures of gastric fluid soluble and small intestine soluble and/or gastric fluid resistant and large intestine soluble pellets. The same goal of releasing at various sections of the gastrointestinal tract can also be conceived by suitably produced laminated tablets with a core, whereby the coating of the agent is quickly released in gastric fluid and the core of the agent is slowly released in the small intestine milieu. The goal of controlled release at various sections of the gastrointestinal tract can also be attained by multilayer tablets. The pellet mixtures with differentially released agent can be filled into hard gelatin capsules.
- Anti-stick and lubricant and separating agents, dispersion agents such as flame dispersed silicone dioxide, disintegrants, such as various starch types, PVC, cellulose esters as granulating or retarding agents, such as for example wax-like and/or polymeric compounds on the basis of Eudragit®, cellulose or Cremophor® are used as a further adjuvents for the production of compressives, such as for example tablets or hard and soft gelatin capsules as well as coated tablets and granulates.
- Anti-oxidants, sweetening agents, such as for example saccharose, xylite or mannite, masking flavors, aromatics, preservatives, colorants, buffer substances, direct tableting agents, such as for example microcrystalline cellulose, starch and starch hydrolysates (for example Celutab®), lactose, polyethylene glycols, polyvinylpyrrolidone and dicalcium phosphate, lubricants, fillers, such as lactose or starch, binding agents in the form of lactose, starch varieties, such as for example wheat or corn and/or rice starch, cellulose derivatives, for example methylcellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose or silica, talcum powder, stearates, such as for example magnesium stearate, aluminum stearate, calcium stearate, talc, siliconized talc, stearic acid, acetyl alcohol and hydrated fats are used.
- In this connection, oral therapeutic systems constructed especially on osmotic principles, such as for example GIT (gastrointestinal therapeutic system) or OROS (oral osmotic system), are also to be mentioned.
- Effervescent tablets or tabs, both of which represent immediately drinkable instant medicinal forms which are quickly dissolved or suspended in water are among the perorally administratable compressives. Among the perorally administratable forms are also solutions, for example drops, juices and suspensions, which can be produced according to the above given method, and can still contain preservatives for increasing stability and optionally aromatics for reasons of easier intake, and colorants for better differentiation as well as antioxidants and/or vitamins and sweeteners such as sugar or artificial sweetening agents. This is also true for inspisated juices which are formulated with water before ingestion. Ion exchange resins in combination with one or more active ingredients are also to be mentioned for the production of liquid ingestable forms.
- A special release form consists in the preparation of so-called floating medicinal forms, for example based on tablets or pellets which develop gas after contact with body fluids and therefore float on the surface of the gastric fluid. Furthermore, so-called electronically controlled release systems can also be formulated by which active ingredient release can be selectively adjusted to individual needs.
- A further group of systemic administration and also optionally topically effective medicinal forms are represented by rectally applicable medicaments. Among these are suppositories and enema formulations. The enema formulations can be prepared based on tablets with aqueous solvents for producing this administration form. Rectal capsules can also be made available based on gelatin or other carriers.
- Hardened fat, such as for example Witepsol®, Massa Estarinum®, Novata®, coconut fat, glycerol-gelatin masses, glycerol-soap-gels and polyethylene glycols are suitable as suppository bases.
- For long-term application with a systematic active ingredient release up to several weeks, pressed implants are suitable which are preferably formulated on the basis of so-called biodegradable polymers.
- As a further important group of systemically active medicaments, transdermal systems are also to be emphasized which distinguish themselves, as with the above-mentioned rectal forms, by circumventing the liver circulation system and/or liver metabolism. These plasters can be especially prepared as transdermal systems which are capable of releasing the active ingredient in a controlled manner over longer or shorter time periods based on different layers and/or mixtures of suitable adjuvents and carriers. Aside from suitable adjuvents and carriers such as solvents and polymeric components, for example based on Eudragit®, membrane infiltration increasing substances and/or permeation promoters, such as for example oleic acid, Azone®, adipinic acid derivatives, ethanol, urea, propylglycol are suitable in the production of transdermal systems of this type for the purpose of improved and/or accelerated penetration.
- As topically, locally or regionally administration medicaments, the following are suitable as special formulations: vaginally or genitally applicable emulsions, creams, foam tablets, depot implants, ovular or transurethral adminstration installation solutions. For opthalmological application, highly sterile eye ointments, solutions and/or drops or creams and emulsions are suitable.
- In the same manner, corresponding otological drops, ointments or creams can be designated for application to the ear. For both of the above-mentioned applications, the adminstration of semi-solid formulations, such as for example gels based on Carbopols® or other polymer compounds such as for example polyvinylpyrolidone and cellulose derivatives is also possible.
- For customary application to the skin or also to the mucus membrane, normal emulsions, gels, ointments, creams or mixed phase and/or amphiphilic emulsion systems (oil/water-water/oil mixed phase) as well as liposomes and transfersomes can be named. Sodium algenate as a gel builder for production of a suitable foundation or celluolose derivatives, such as for example guar or xanthene gum, inorganic gel builders, such as for example aluminum hydroxides or bentonites (so-called thixotropic gel builder), polyacrylic acid derivatives, such as for example Carbopol®, polyvinylpyrolidone, microcrystalline cellulose or carboxymethylcellulose are suitable as adjuvents and/or carriers. Furthermore, amphiphilic low and high molecular weight compounds as well as phospholipids are suitable. The gels can be present either as hydrogels based on water or as hydrophobic organogels, for example based on mixtures of low and high molecular paraffin hydrocarbons and vaseline.
- Anionic, cationic or neutral tensides can be employed as emulsifiers, for example alkalized soaps, methyl soaps, amine soaps, sulfanated compounds, cationic soaps, high fatty alcohols, partial fatty acid esters of sorbitan and polyoxyethylene sorbitan, for example lanette types, wool wax, lanolin, or other synthetic products for the production of oil/water and/or water/oil emulsions.
- Hydrophilic organogels can be formulated, for example, on the basis of high molecular polyethylene glycols. These gel-like forms are washable. Vaseline, natural or synthetic waxes, fatty acids, fatty alcohols, fatty acid esters, for example as mono-, di-, or triglycerides, paraffin oil or vegetable oils, hardened castor oil or coconut oil, pig fat, synthetic fats, for example based on acrylic, caprinic, lauric and stearic acid, such as for example Softisan® or triglyceride mixtures such as Miglyol® are employed as lipids in the form of fat and/or oil and/or wax-like components for the production of ointments, creams or emulsions.
- Osmotically effective acids and bases, such as for example hydrochloric acid, citric acid, sodium hydroxide solution, potassium hydroxide solution, monosodium carbonate, further buffer systems, such as for example citrate, phosphate, Tris-buffer or triethanol amine are used for adjusting the pH value.
- Preservatives, for example such as methyl- or propyl benzoate (parabenes) or sorbic acid can be added for increasing stability.
- Pastes, powders or solutions are to be mentioned as further topically applicable forms. Pastes often contain lipophilic and hydrophilic auxiliary agents with very high amounts of fatty matter as a consistency-giving base.
- Powders or topically applicable powders can contain for example starch varieties such as wheat or rice starch, flame dispersed silicon dioxide or silica, which also serve as diluents, for increasing flowability as well as lubricity as well as for preventing agglomerates.
- Nose drops or nose sprays serve as nasal application forms. In this connection, nebulizers or nose creams or ointments can come to use.
- Furthermore, nose spray or dry powder formulations as well as controlled dosage aerosols are also suitable for systemic administeration of the active ingredients.
- These pressure and/or controlled dosage aerosols and dry powder formulations can be inhaled and/or insufflated. Administration forms of this type also certainly have importance for direct, regional application in the lung or bronchi and larynx. Thereby, the dry powder compositions can be formulated for example as active ingredient-soft pellets, as an active ingredient-pellet mixture with suitable carriers, such as for example lactose and/or glucose. For inhalation or insufflation, common applicators are suitable which are suitable for the treatment of the nose, mouth and/or pharynx. The active ingredients can also be applied by means of an ultrasonic nebulizing device. As a propellant gas for aerosol spray formulations and/or controlled dosage aerosols, tetrafluoroethane or HFC 134a and/or heptafluoropropane or HFC 227 are suitable, wherein non-fluorinated hydrocarbons or other propellants which are gaseous at normal pressure and room temperature, such as for example propane, butane or dimethyl ether can be preferred. Instead of controlled dosage aerosols, propellant-free, manual pump systems can also be used.
- The propellant gas aerosols can also suitably contain surface active adjuvents, such as for example isopropyl myristate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester, sorbitan trioleate, lecithins or soya lecithin.
- For regional application in situ, solutions for installation, for example for transurethral administration in bladder tumors or genital tumors, or for profusion in liver tumors or other organ carcinomas are suitable.
- The respective suitable medicinal forms can be produced in accordance with the prescription and procedures based on pharmaceutical-physical fundamentals as they are described for example in the following handbooks and are included in the present inventive subject-matter with respect to the production of the respective suitable medicaments:
- Physical Pharmacy (A. N. Martin, J. Swarbrick, A. Cammarata), 2nd Ed., Philadelphia Pa., (1970), German version: Physikalische Pharmazie, (1987), 3rd edition; Stuttgart;
- R. Voigt, M. Bomschein, Lehrbuch der pharmazeutischen Technologie, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, (1984), 5th edition;
- P. H. List, Arzneimformenlehre, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Stuttgart (1985), 4th edition;
- H. Sucker, P. Fuchs, P. Speiser, Pharmazeutische Technologie, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart—New York, (1991), 2nd edition;
- A. T. Florence, D. Attwood, Physicochemical Principles of Pharmacy, The Maximillan Press Ltd., Hong Kong, (1981);
- L. A. Trissel, Handbook on Injectable Drugs, American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, (1994), 8th edition;
- Y. W. Chien, Transdermal Controlled Systemic Medications, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York—Basel, (1987);
- K. E. Avis, L. Lachmann, H. A Liebermann, Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Parenteral Medications, volume 2, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York—Basel, (1986);
- B. W. Muiller, Controlled Drug Delivery, Paperback APV, volume 17, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Stuttgart, (1987);
- H. Asch, D. Essig, P. C. Schmidt, Technologie von Salben, Suspensionen und Emulsionen, Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Stuttgart, (1984);
- H. A. Liebermann, L. Lachman, J. B. Schwartz, Pharmaceutical Dosage forms: Tablets, Volume 1, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 2nd Edition (1989);
- D. Chulin, M. Deleuil, Y. Pourcelot, Powder Technology and Pharmaceutical Processes, in J. C. Williams, T. Allen, Handbook of Powder Technology, Elsevier Amsterdam—London—New York—Tokyo, (1994);
- J. T. Carstensen, Pharmaceutical Principles of Solid Dosage Forms, Technomic Publishing Co., Inc., Lancaster—Basel, (1993).
- 1. Injection Therapeutics
- a) Parenteral Solution
active ingredient used according to the invention 5.000 g acid sodium phosphate 5.000 g sodium tartrate 12.000 g benzyl alcohol 7.500 g water for injection purposes to 1000.000 ml - The solution is produced according to the customary method, sterilized and filled into 10 ml vials. One vial contains 50 mg of the compound according to the invention.
- b) Penteral Solution
active ingredient used according to the invention 1.000 g hydrochloric acid, dilute 5.000 g sodium chloride 6.000 g water for injection purposes to 1000.000 ml - The solution is produced according to a customary method by stirring; the medicinal form is adjusted to a suitable pH value by acid addition and subsequently filled into 100 ml vials and sterilized. A vial contains 100 mg of the compound according to the invention.
- c) Parenteral Dispersion
active ingredient used according to the invention 10.000 g soya lecithin 20.000 g saturated triglycerides 100.000 g sodium hydroxide 7.650 g water for injection purposes to 1000.000 ml - The active ingredient(s) used according to the invention is dispersed in the saturated triglycerides. Then the soya lecithin is added under stirring, and subsequent to this, the aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide is added with subsequent homogenization. The dispersion is sterilized and filled into 10 ml vials. A vial contains 50 mg of the compound according to the invention.
- d) Biodegradable Parenteral Depot Medicinal Form
active ingredient used according to the invention 10.000 polylactic acid/polygylcolic acid polymer 70.000 polyvinylpyrrolidone 0.200 gelatin 2.000 soya lecithin 2.000 isotonic sodium chloride solution to 1000.000 ml - First, the active ingredient is incorporated into the biodegradable polymer comprising polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid by a suitable method (spray drying, solvent-evaporation or phase separation) and subsequently subjected to a sterilization process. The particles are introduced into a 2-chamber ready-made syringe in which the adjuvent solution, which is also produced in a sterile manner, is filled. The biodegradable microparticles are mixed with the dispersion agent shortly before application and dispersed. The content of a ready-made syringe is measured such that this contains 200 mg of the active ingredient according to the invention.
- e) Parenteral Dispersion for Subcutaneous Installation
active ingredient used according to the invention 25,000 g soya lecithin 25,000 g arachis oil 400,000 g benzyl alcohol 50,000 g Miglyole ® to 1000,000 g - The active ingredient is dispersed together with soya lecithin and arachis oil. The benzyl alcohol is dissolved in Miglyole® and added to the dispersion. The entire dispersion is sterilized and subsequently filled into vials with 2 ml content. A vial contains 50 mg active ingredient.
- f) Parenteral Perfusions Solution
- The solution named under example b) can also be used for perfusion of liver for example.
- According to need, instead of ampules with injection solution, so-called perforation bottles (vials), which can also be optionally preserved, and infusion solutions with an amount of one or more active ingredients according to the invention can also be made available in the customary manner under addition of buffer substances for adjustment of physiological pH value and/or the isotonicity and/or a best possible suitable pH value for the medicinal form (euhydria) and optional further required nutrients, vitamins, amino acids, stablizers and other necessary adjuvents, possibly in combination with further medicinal agents suitable for the mentioned indications.
- 2. Solid, Peroral Administration Medicaments
- a) Tablets
active ingredient used according to the invention 10,000 g lactose 5,200 g starch, soluble 1,800 g hydroxypropylmethylcellulose 900 g magnesium stearate 100 g - The above components are mixed with each other and compacted in a conventional manner, wherein a tablet weight of 180 mg is set. Each tablet contain's 100 mg active ingredient. If desired, the tablets obtained in this manner are coated, provided with a film coat and/or enterically coated.
- b) Coated Tablet Core
active ingredient used according to the invention 10,000 g flame dispersed silicon dioxide 500 g corn starch 2,250 g stearic acid 350 g ethanol 3.0 l gelatin 900 g purified water 10.0 l talcum 300 g magnesium stearate 180 g - From these components, a granulate is produced which is pressed to the desired coated tablet cores. Each core contains 50 mg of active ingredient. The core can be further processed in a customary manner to coated tablets. If desired, a gastric fluid resistant or retarding film coat can be applied in a known manner.
- c) Drink Suspension in Vials
active ingredient used according to the invention 0.050 g glycerin 0.500 g sorbite, 70% solution 0.500 g sodium saccharinate 0.010 g methyl-p-hydroxybenzoate 0.040 g aromatic agent q.s. sterile wasser q.s. to 5 ml - The above-mentioned components are mixed in a customary manner to a suspension and filled in a suitable drink vial having 5 ml content.
- d) Poorly Soluble Sublingual Tablets
active ingredient used according to the invention 0.030 g lactose 0.100 g stearic acid 0.004 g talcum purum 0.015 g sweetener q.s. aromatic agent q.s. rice starch q.s. to 0.500 g - The active ingredient is compacted together with the adjuvents under high pressure to sublingual tablets, favorably in oblong form.
- e) Soft Gel Capsule
active ingredient used according to the invention 0.050 g fatty acid glyceride mixture (Miglyole ®) q.s. to 0.500 g - The active ingredient is impasted together with the fluid carrier mixture and mixed together with further adjuvents suitable for the incapsulation and filled into elastic soft gelatin capsules which are sealed.
f) Hard Gelatin Capsules active ingredient used according to the invention 0.150 g microcrystalline cellulose 0.100 g hydroxypropylmethylcellulose 0.030 g mannite 0.100 g ethylcellulose 0.050 g triethyl citrate 0.010 g - The active ingredient is mixed together with the adjuvents, microcrystalline cellulose, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose and mannite, wet with granulation liquid and formed into pellets. These are subsequently coated with a solution of ethylcellulose and triethyl citrate in organic solvents in a fluidized-bed apparatus. A hard gelatin capsule contains 150 mg of active ingredient.
- 3. Topically Administratable Medicinal Forms
a) Hydrophilic Ointment active ingredient used according to the invention 0.500 g Eucerinum ® anhydricum 60.000 g microcrystalline wax 15.000 g vaseline oil q.s. to 100.000 g - The above-mentioned adjuvents are melted and further processed together with the active ingredient to an ointment in a customary manner.
b) Lipophilic Ointment active ingredient used according to the invention 10.000 g propylene glycol 50.000 g paraffin, liquid 100.000 g paraffin wax 100.000 g vaseline to 1000.000 ml - The active ingredient(s) used according to the invention is dissolved in propylene glycol at ca. 60° C. At the same time, the lipophilic components are melted at 60-70° C. and subsequently combined with the active ingredient solution. The ointment is emulsified at first at 60-70° C. and subsequently cooled to 35-40° C. under constant emulsification and then filled in 10 g tubes. A tube contains 100 mg of the compound according to the invention.
- 4. Inhalation Therapeutic
- Further subject-matter is a pharmaceutical formulation which is characterized in that it contians an active ingredient(s) used according to the invention as a base or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof together with carriers and/or diluents customary for this and suitable for administration by means of inhalation.
- In this connection, particularly suitable physiologically acceptable salts of the active ingredients are, as already illustrated in the synthesis section, acid addition salts derived from inorganic or organic acids such as for example especially hydrochloride, hydrobromide, sulfate, phosphate, maleate, tartrate, citrate, benzoate, 4-methoxybenzoate, 2- or 4-hydroxybenzoate, 4-chlorobenzoate, p-toluolsulfonate, methanosulfonate, ascorbate, salicylate, acetate, formate, succinate, lactate, glutarate, gluconate or tricarballylate.
- The administration of the active ingredient(s) used of the invention by means of inhalation occurs according to the invention in conventional ways customary for administrations of this form, for example in the form of a commercial controlled dosage aerosol or in combination with a spacer. In controlled dosage aerosols, a metering valve is delivered with whose help, a dosed amount of the composition is administered. For spraying, the present compositions can be formulated for example as aqueous solutions or suspensions and be administered by means of an atomizer. Aerosol spray formulations in which the active ingredient is either suspended with one or two stabilizers in a propellant as a carrier and/or diluent, for example tetrafluoroethane or HFC 134a and/or heptafluoropropane or HFC 227 can equally be used, whereby however, non-fluorinated hydrocarbons or other propellants which are gaseous at normal pressure and room temperature, such as propane, butane or dimethyl ether, can be preferred. Thereby, propellant-free manual pump systems or dry powder systems as desribed below can also be used.
- Suitably, the propellant aerosols can also contain surface active adjuvents, such as for example isopropyl myristate, polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester, sorbitan trioleate, lecithins, oleic acid.
- For administration by means of inhalation and/or insufflation, the medicaments with an amount of compounds according to the invention can also be formulated in the form of dry powder compositions, for example as active ingredient-soft pellets or as an active ingredient-powder mixture with a suitable carrier, such as for example lactose and/or glucose. The powder compositions can be formulated and administered as single doses or as multiple doses.
- The compounds according to the invention are preferably administered by means of a controlled dosage aerosol or in the form of a dry powder dosage formulation, wherein the latter preferably contains glucose and/or lactose as a carrier substance.
- As applicators for inhalation of the pharmaceutical formulations containing one or more of the active ingredient(s) used according to the invention, all applicators are generally suitable which are suitable for controlled dosage aerosols and/or a dry powder dosage formulation, such as for example usual applicators for the nose, mouth and or pharynx, or also devices standing under propellant gas for the delivery of a spray (as controlled dosage aerosol or dry powder dosage formulation) as they are also used for inhalations in the nose, mouth and/or pharynx.
- A further embodiment can also consist of an aqueous solution of the active ingredient(s) used according to the invention, which also optionally contains further active ingredients and/or additives, which are applied by means of an ultrasound atomizer.
Intended dose per aerosol per stroke % by weight a) Controlled Dosage Aerosol active ingredient used according 0.500 mg 0.66 to the invention stabilizer 0.075 mg 0.10 HFC 134a 75.500 mg 99.24 b) Controlled Dosage Aerosol active ingredient used according 0.250 mg 0.32 to the invention Stabilizer 0.038 mg 0.05 HFC 227 79.180 mg 99.63 - In the examples a) and b) the micronized active ingredient is, after previous dispersion in a small amount of the stabilizer, placed in a suspension vessel in which the bulk amount of propellant gas solution is found. The corresponding suspension is dispersed by means of a suitable stirring system (for example high performance mixer or ultrasound mixer) until an ultra-fine dispersion results. The suspension is then continuously held in flux in a filling apparatus suitable for cold propellants or pressure fillings. Alternatively, the suspension can also be produced in a suitable cooled stabilizer solution in HFC 134a/227.
- The examples c) to d) describe the composition and production of dosage dry powder formulations.
mg/dose c) Dosage-Dry Powder Formulation active ingredient used according to the invention 0.500 mg d) Dosage-Dry Powder Formulation active ingredient used according to the invention 0.500 mg lactose Ph.Eur. to 2.5 mg or to 5.0 mg e) Dosage-Dry Powder Formulation active ingredient used according to the invention 0.250 mg lactose Ph.Eur. to 2.5 mg or to 5.0 mg - Im example c) the active ingredient is formulated after micronization under addition of steam as pellets with an MMAD between 0,1 and 0,3 mm diameter and brought to use in a multi-dose powder applicator.
- In the examples d) and e) the active ingredient is micronized, thereafter, bulk material is mixed with the lactose in the given amounts, and subsequently, filled in a multi-dose powder inhilator.
- In all of the examples set forth above, the active ingredient or the medicinal agent in the form of the respective suitable pharmaceutical acceptable salt and/or acid addition salts can be present, insofar as the base is not preferred in each case.
- In the following, the pharmaceutical test results obtained in connection with the newly found indications based, in a representative manner, on the specifically structured compounds failling under formula (I) are reproduced and the experimental results are discussed.
- 1. Growth Inhibition of Human Tumor Cells
- The tumor growth inhibiting activity of the substances was determined on human tumor cells in standardized in vitro test systems. In the screening tests, the substances gave IC 50-values in a concentration range of 0.1 nM bis 10 μM.
- HepG2 cells plated at a density of 20,000 cells/ml in 12-well plastic dishes. Cultivation occured in Richters IMEM-ZO nutrient medium with 5% fetal calf serum (FCS) in a tissue culture incubator with a gas mixture of 5% CO 2 and 95% air at a temperature of 37° C. One day after plating, the culture medium was aspirated from the cells and replaced by fresh medium which contained the respective concentrations of the test substances. For the individual concentrations and the controls without test substances, three-fold batches were done for each. Three days after the beginning of treatment, the medium was again renewed with the test compounds. After six days of substance incubation, the test was ended and the protein amount in the individual wells was determined with the sulforhodamin-B-method (according to P. Skehan et al.: New Colorimetric Cytotoxicity Assay for Anticancer-Drug Screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 82: 1107-1112, 1990). The IC50-values (defined as that concentration in which the cell growth was inhibited by 50%) was taken from the dose-response curves and given as a comparative measurement for the activity of the test compounds.
- The following results were obtained:
Test substance No. IC50-value [μM] 46 0.04 75 0.2 81 0.07 84 0.02 95 0.03 97 0.08 104 0.01 143 0.02 171 0.05 174 0.05 186 0.02 198 0.08 219 0.02 - 2. Indications
- The compounds of formula (I) and their salts permit a therapeutic use in malignant illnesses of humans and animals through their excellent inhibition of the growth of tumor cells. The anti-neoplastic activity of the described substances can be used for prophylactic, adjunct, palliative, and curative treatment of solid tumors, leukemic illnesses and lymphomas as well as for decreasing or preventing metastasis formation in humans and animals. The therapeutic use is possible in the following illnesses for example: gynecological tumors, such as of the vulva or the uterus, ovarian carcinomas, testicle tumors, prostate carcinomas, skin cancer, kidney cancer, bladder tumors, esophagus carcinomas, stomach cancer, rectal carcinomas, pancreas carcinomas, thyroid cancer, adrenal tumors, various types of leukemia and lymphomas, Hodgkin's disease, tumor illnesses of the CNS, soft-tissue sarcomas, bone sarcomas, benign and malignant mesotheliomas, especially intestine cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, bronchial and lung carcinomas, melanomas, acute and chronic leukemias. Benign papillomatosis tumors can also be inhibited in their growth with the named substances.
- The broad activity of the new compounds was tested in-vitro according to the method described under point 1. Thereby, the following IC 50-values were obtained for compound number 104:
Cell-Line Source IC50-value [μM] NCI-H69 small cell lung carcinoma 0.02 WERI-Rb-1 retinoblastoma 0.008 THP-1 monocytic leukemia 0.02 - With respect to the compounds used according to the invention, an independent activity profile is suggested by the findings with the observed activity against the various tumor types. Thus, tumors which are resistant to customary cytostatic agents, for example, respond entirely to these substances. In addition, based on the independent characteristics of the compounds used according to the invention, combinations of these compounds together with known chemo-therapeutically used pharmaceuticals, for example cytostatic agents or immunosuppresive agents, etc., are created especially taking a possible complimentation of their properties into consideration.
- The integration of the presently used compounds with their specific structures in a therapy scheme is successful with one or more substances from the following classes for example: anti-metabolites (for example cytarabine, 5-fluorouracil, 6-mercaptopurine, methotrexate), alkylating agents (for example busuffan, carmustine, cisplatin, carboplatin, cyclophosphamide, dacarbazine, melphalane, thiotepa), DNA-intercalating substances and topoisomerase inhibitors (for example actinomycin D, daunorubicin, doxorubicin, mitomycin C, mitoxantrone, etoposide, teniposide, topotecan, irinotecan), spindle poisons (for example vincristine, navelbin, taxol, taxoter), hormonally active agents (for example tamoxifen, flutamide, formestan, goserelin) or other cytostatic agents with complex modes of action (for example L-asparaginase, bleomycin, hydroxyurea). Resistant tumor cells can be made sensitive again by interaction of the new compounds with a mechanism of resistance for common cytostatic agents (for example P-glycoprotein, MRP, glutathione-S-transferase, metallothionein).
- A combination with other therapeutic physical measures or other measures for tumor patients, such as for example radiotherapy, hyperthenmia or immuno therapy is also possible with the compounds used according to the invention. Therefore, further subject-matter under the invention is also combinations of this type in form of new medicaments.
- 3. Immuno Suppressing Activity
- Many anti-tumor agents have not only a cytotoxic effect on tumor cells, but also on the blood cell system. This leads to a weakening of the immune defence, which can, in turn, be specifically employed to suppress the rejection reaction after an organ transplantation for example. Therefore, a use of the main compounds, optionally in combination with other compounds effective for these indications is suitable in diseases such as psoriasis or autoimmune diseases. In order to test the possibility for a therapeutic use in illnesses of this type, the substance activity was tested on freshly isolated lymphocytes as follows:
- The spleen of a Swiss mouse served as a lymphocyte source. The lymphocyte population was isolated from the spleen cell suspension over a ficoll gradient and taken up in IMEM-ZO culture medium with 0,1% dextran 70,000 and 2% fetal calf serum. The cells were plated at a density of ca. 500,000 cells/well/ml in a 12-well plate, 1 ml doubly concentrated test substance solution was pipetted per well and this was subsequently incubated in a tissue culture incubator at 37° C. and 5% CO 2. After 2 days, a 1 ml-aliquot with 5 μl of the fluorescent dye solutions propidium iodide (8 mg/ml) and 3,3′-dihexyloxacarbocyanin iodide (40 μg/ml) each was added per well, and incubated for 3 minutes at room temperature. Subsequently, 10,000 cells per each sample were measured on a flow-through cytometer and the percentage amount of vital cells in the population was determined. By means of the dose-response curves, IC50-values were calculated which were also employed in the following Tables for the characterization of the individual substances:
Test Substance No. IC50 [μM] 46 0.03 252 0.0002 254 0.00008 306 0.002 315 0.00004 - Hence, the special, independent class of the compounds used according to the invention is also suitable for a combination with known immunosuppressive agents from the class of macrolides, for example cyclosporin A, tacrolimus, raparnycin, or anti-metabolites, for example azathioprin or methotrexate and glucocorticoids. Combination of this and/or medicaments with an amount of compounds used according to the invention together with known immunosuppressive agents as well as a method for their production represents further subject-matter of the invention.
- The invention is in no was limited to the present respective concretely named active ingredients concentrations, dosages, combinations with one or more other cytostatic agents, tumor inhibitors, cancerostatic agents, immunosuppressive agents or further medicinal agents suitable for the respective specific indications or the type of tumor to treated or immunological illness, etc.
Claims (19)
1. Use of one or more of the compounds of formula (I)
wherein
R1 hydrogen, halogen, cyano, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, benzyloxy, aminocarbonyl, carboxy, phenyl, phenoxy, phenylthio, pyridyloxy, pyridylthio, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl,
alkenyl, especially C3-C6-alkenyl,
alkinyl, especially C3-C6-alkinyl,
hydroxyalkyl, especially C1-C6-hydroxyalkyl,
alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy,
alkenyloxy, especially C3-C6-alkenyloxy,
alkinyloxy, especially C3-C6-alkinyloxy,
alkanoyloxy, especially C1-C7-alkanoyloxy,
alkoxycarbonyloxy, especially C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyloxy,
alkylthio, especially C1-C6-alkylthio,
alkenylthio, especially C3-C6-alkenylthio,
alkinylthio, especially C3-C6-alkinylthio,
cycloalkyl, especially C3-C8-cycloalkyl,
cycloalkyloxy, especially C3-C8-cycloalkyloxy,
cycloalkylthio, especially C3-C8-cycloalkylthio,
alkoxycarbonyl, especially C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl,
alkylaminocarbonyl, especially C2-C7-alkylaminocarbonyl,
dialkylaminocarbonyl, especially C3-C13-dialkylaminocarbonyl, or
NRSR6, wherein
R5 and
R6 are selected independently of each other from hydrogen,
alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl,
alkenyl, especially C3-C6-alkenyl and
alkinyl, especially C3-C6-alkinyl,
R2 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, hydroxy, trifluoromethyl, benzyloxy,
alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl,
alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy or
alkanoyloxy, especially C1-C7-alkanoyloxy,
wherein R1 and R2, if they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which is selected from
—(CH2)4—, —(CH═C)2— and —CH2O—CR7R8—O—, wherein
R7 and
R8 are, independently of each other, hydrogen or alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl,
R3 is hydrogen, halogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxyalkyl, especially C1-C6-hdroxyalkyl and
R4 is hydrogen, hydroxy, benzyloxy,
alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl,
alkenyl, especially C3-C6-alkenyl,
alkinyl, especially C3-C6-alkinyl,
cycloalkyl, especially C3-C6-cycloalkyl or
alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy,
k is 0 or 1,
A is alkylene, especially C1-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by alkyl, especially C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, especially C1-C3-alkoxy, fluorine or phenyl, or
1,2-cyclopropylene or
alkenylene with at least than two C-atoms, especially C2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, C1-C3-alkoxy, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
alkadienylene with at least four C-atoms, especially C4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
1,3,5-hexatrienylene, which is optionally substutited by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano, or phenyl,
ethinylene or
alkylene with at least two C-atoms, especially C2-C6-alkylene in which a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR9, CO, SO or SO2, wherein the substitution, with the exception of ═CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group and wherein
R9 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, alkenyl, especially C3-C6-alkenyl, alkinyl, especially C3-C6-alkinyl, acyl, especially C1-C6-acyl or alkylsulfonyl, especially C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl,
D is selected from alkylene, especially C1-C I-alkylene, optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy,
alkenylene with at least two C-atoms, especially C2-C10-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
alkinylene with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C10-alkinylene, optionally substituted once or twice by alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy or alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, and
alkylene, especially C1-C10-alkylene, alkenylene with at least two C-atoms, especially C2-C1-alkenylene or alkinylene with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C1-alkinylene, whereby one to three methylene units are each isosterically replaced by O, S, NR10, CO, SO or SO2 wherein
R10 has the same meaning as
R9 but is selected independently thereof,
E is selected from
wherein the heterocyclic ring can also optionally have a double bond and
n and
p can be, independently of one another 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p≦4 and
q is 2 or 3,
R11 is hydrogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or alkoxycarbonyl with at least two C-atoms, especially C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl and
R12 is hydrogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl or or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom, wherein
R11 and R12 optionally together, form an alkylene bridge with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 C-atoms, especially a C1-C3-alkylene bridge under formation of a bicyclic ring system,
G is selected from hydrogen,
G1, G2, G3, G4 and GS, wherein
G1 represents the residue
—(CH2)r—(CR14R16)s—R13 (G1)
wherein
r is an integer from 1 to 3 or 0 and
s is 0 or 1,
R13 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, alkenyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C6-alkenyl, alkinyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C6-alkinyl, cycloalkyl with at least three C-atoms, especially C3-C8-cycloalkyl,
saturated, five to seven membered heterocycles, which can contain one or two hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O,
benzyl or phenyl,
monocyclic aromatic five or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
R14 has the same meaning as R13, but is selected independently thereof,
R15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
G2 is the residue
wherein the substituents R13 and R15 can have the above meaning or the grouping
NR13R15
can also be a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O, or
saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O,
G3 is the residue
—SO2 (CH2)r R13 (G3)
and
G4 is the residue
wherein
Ar1 and Ar2 are selected independendy from one another from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl and
G5 is the residue
—COR16 (G5)
wherein
R16 is selected from trifluoromethyl, alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, alkenyloxy, especially C3-C6-alkenyloxy, or benzyloxy,
wherein any aryl residues and/or aromatic ring systems in the substituents R1, R2, R4, R13, R14, R15, R16, Ar1 and Ar2 and/or in the ring system —NR13R15 can be substituted independently from each other by one to three of the same or different residues which are selected from halogen, cyano, alkyl, especially C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, cycloalkyl, especially C3-Cg-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, alkoxy, substituted entirely or partially by fluorine, substituted alkoxy, especially C1-C6-alkoxy, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, alkylthio, especially C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, alkoxycarbonyl, especially C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, monoalkylamino, especially mono-C1-C6-alkylamino, dialkylamino, especially di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino and methylenedioxy for two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system,
wherein each of the residues alkyl, alkenyl, alkinyl, hydroxyalkyl, alkoxy, alkenyloxy, alkinyloxy, alkanoyloxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkoxycarbonyloxy, alkylthio, alkenylthio, alkinylthio, alkylene, acyl, alkylsulfonyl, alkenylene, alkinylene, cycloalkyl, cycloalkyloxy, alkoxycarbonyl, alkylaminocarbonyl or dialkylaminocarbonyl of the substituents R1 to R14 can have 1 to 2 or 4, 6, 8, 10 or 12 C-atoms and/or 2 or 3 to 5, 7, 9, 11 or 13 and/or 15 C-atoms or 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 or 15 C-atoms depending on the structure, as well as
stereoisomers and/or mixtures thereof and pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof
for the production of medicaments for cytostatic or immunomodulatory and/or immunosuppressive treatment.
2. Use according to claim 1 , characterized in that compounds used in the production of medicaments are contained in formula (I)
wherein
R1 is a hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C1-C6-hydroxyalkyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy, C3-C6-alkinyloxy, benzyloxy, C1-C7-alkanoyloxy, C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyloxy, C1-C6-alkylthio, C3-C6-alkenylthio, C3-C6-alkinylthio, C3-C8-cycloalkyloxy, C3-C8-cycloalkylthio, C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, C2-C7-alkylaminocarbonyl, C3-C13-dialkylaminocarbonyl, carboxy, phenyl, phenoxy, phenylthio, pyridyloxy, pyridylthio, or NR5R6, wherein
R5 and
R6 are selected independently from each other from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl and C3-C6-alkinyl,
R2 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, benzyloxy or C1-C7-alkanoyloxy,
wherein R1 and R2, in case they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which is selected from the bridge members
—(CH2)4— and —(CH═CH)2— and —CH2O—CR7R8—O—, wherein
R7 and
R8 are, independently from each other, hydrogen or C1-C6-alkyl,
R3 is hydrogen, halogen, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl or C1-C6-hydroxyalkyl and
R4 is hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, C3-C6-cycloalkyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy or benzyloxy,
k is 0 or 1,
A is C1-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, C1-C3-alkoxy, fluorine or phenyl, or
1,2-cyclopropylene or
C2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, C1-C3-alkoxy, fluorine, cyano or phenyl,
C4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl
1,3,5-hexatrienylene, which is optionally substituted by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano or phenyl
ethynylene or
C2-C6-alkylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR9, CO, SO or SO2, wherein the isosteric substitution, with the exception of CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group, and
R9 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, C1-C6-acyl or C1-C6-alkylsulfonyl,
D is selected from C1-C6-alkylene, optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or C1-C6-alkoxy,
C2-C10-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or C1-C6-alkoxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
C3-C1-alkinylene, optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, or C1-C6-alkoxy, and
C1-C10-alkylene, C2-C10-alkenylene or C3-C10-alkinylene, wherein one to three methylene units are each isosterically replaced by O, S, NR10, CO, SO or SO2, wherein
R10 has the same meaning as R9, but is selected independently therefrom,
E is selected from
wherein the heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond and
n and
p can be, independently of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p≦4 and
q is 2 or 3,
R11 is hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl and
R12 hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom, wherein
R11 and R12 optionally together form a C1-C3-alkylene bridge under formation of a bi-cyclic ring system,
G is selected from hydrogen,
G1, G2, G3, G4 and G5, wherein
G1 represents the residue
—(CH2)r—(CR14R15)s—R13 (G1)
wherein
r is an integer from 1 to 3 or 0 and
s is 0 or 1,
R13 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl,
saturated, five- to seven-membered heterocycles, which can contain one or two hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O,
benzyl or phenyl,
monocyclic aromatic five or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic, ring or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
R14 has the same meaning as R13, but is selected independently thereof,
R15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein the linkage can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from N and/or S and/or O and the linkage can occur either over an aromatic ring or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
G2 is the residue
wherein the substituents R13 and R15 can have the above meaning or the grouping
—NR13R15
can also he a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O, or
saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two tirther hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O,
G3 is the residue
—SO2—(CH2)r R13 (G3)
and
G4 is the residue
wherein
Ar1 and Ar2 are selected independently from one another from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl and
G5 is the residue
COR16 (G5)
wherein
R16 is selected from trifluoromethyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy, or benzyloxy, and wherein
aromatic ring systems in the substituents R1, R2, R4, R13, R14, R15, R16 Ar1 and Ar2 and/or in the ring system —NR13R15 can be substituted independently from each other by one to three of the same or different residues which are selected from halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-Cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which can optionally be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino or di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino and methylenedioxy for two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system, their stereoisomers thereof and/or their mixtures thereof and pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts.
3. Use of the compounds according to claim 1 or 2, characterized in that the substituents R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R13, R14, R15 and R16 as well as A and D indicated for formula (I) have the following meaning in connection with the given substitutions according to this formula
wherein
halogen is fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine,
C1-C6-alkyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably a methyl-, ethyl-, propyl-, isopropyl-, butyl-, isobutyl-, sec-butyl-, tert-butyl-, cyclopropylmethyl-, pentyl-, isopentyl-, tert-pentyl-, neopentyl-, cyclopropylethyl-, cyclobutylmethyl- or a hexyl group,
alkylene is for example methylene, ethylene, propylene, tetramethylene, pentamethylene, hexamethylene, heptamethylene, octamethylene, nonamethylene or decamethylene,
C3-C6-alkenyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably an allyl-, 2-butenyl-, 3-butenyl-, 2-methyl-2-propenyl-, 2-pentenyl-, 4-pentenyl-, 2-methyl-2-butenyl-, 3-methyl-2-butenyl-, 2-hexenyl-, 5-hexenyl-, 4-methyl-3-pentenyl- or 2,2-dimethyl-3-butenyl group,
alkenylene is for example ethenylene, propenylene, butenylene, pentenylene, hexenylene, hexathenylene, heptenylene, octenylene, nonenylene or decenylene,
C3-C6-alkinyl can be straight chain or branched and is preferably a propargyl-, 2-butinyl-, 3-butinyl-, 4-pentinyl-, 5-hexinyl- or 4-methyl-2-pentinyl group,
alkinylene is for example propinylene, butinylene, pentinylene, hexinylene, heptinylene, octinylene, noninylene or decinylene,
C3-C8-cycloalkyl is preferably cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptyl or cyclooctyl,
C1-C6-hydroxyalkyl contains a hydroxyl group in one of the above-named C1-C6-alkyl residues, especially in the form of the hydroxymethyl- and hydroxyethyl group, wherein
C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy, C3-C6-alkinyloxy each contain, aside from the oxygen atom, one of the C1-C6-alkyl-, C3-C6-alkenyl- and/or C3-C6-alkinyl groups named above and the methoxy-, ethoxy-, isopropoxy-, tert-butoxy-, allyloxy- and propargyloxy groups are preferred and is to be understood as among C1-C6-alkoxy entirely or partially substituted with fluorine, for example difluormethoxy, trifluormethoxy or 2,2,2-trifluorethoxy,
C1-C6-alkylthio, C3-C6-alkenylthio, C3-C6-alkinylthio each contain, aside from the sulfur atom, one of the C1-C6-alkyl-, C3-C6-alkenyl- or C3-C6-alkinyl groups named above, especially the methylthio-, ethylthio-, isopropylthio- and tert-butylthio groups,
C3-C8-cycloalkyloxy and C3-C8-cycloalkylthio are preferred as cyclopentyloxy- and cyclopentylthio- and/or cylohexyloxy- and cyclohexylthio groups,
C1-C7-alkanoyloxy groups contain, aside from the oxygen atom, an aliphatic acyl residue with 1 to 7 carbon atoms, especially the acetoxy-, propionyloxy- and pivaloyloxy groups,
C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl groups contain, aside from the carbonyl group, one of the C1-C6-alkoxy groups mentioned above, especially the methoxycarbonyl-, ethoxycarbonyl-, isopropoxycarbonyl-, isobutoxycarbonyl-and tert-butoxycarbonyl group,
C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyloxy groups contain, aside from the oxygen atom, one of the C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl residues mentioned above, especially the methoxycarbonyloxy-, ethoxycarbonyloxy-, isopropoxycarbonyloxy-, isobutoxycarbonyloxy-and tertbutoxycarbonyl group as well as the allyloxycarbonyloxy group,
C2-C7-alkylaminocarbonyl and C3-C13-dialkylaminocarbonyl groups contain, beside the carbonyl group, an alkylamino- and/or dialkylamino residue, whose C1-C6-alkyl groups have the above meanings, wherein the dimethylaminocarbonyl-, diethylaminocarbonyl- and the diisopropylaminocarbonyl groups are preferred, and
aside from the unsubstituted amino group, one of the following C1-C6-alkylamino groups and/or di-(C1-C6-alkyl)amino groups are to be understood under the amino groups of the formula NR5R6,
C1-C6-alkylamino contains one of the C1-C6-alkyl groups mentioned above, especially in form of the methylamino-, ethylamino-, propylamino-, isopropylamino-, butylamino- and the tert-butylamino group,
di-(C1-C6-alkyl)amino carries two of the same or different of the above named C1-C6-alkyl groups on the nitrogen atom, especially in form of the dimethylamino-, diethylamino-, dipropylamino-, diisopropylamino-, isopropylmethylamino-, dibutylamino- or tert-butylmethylamino group,
C1-C6-acyl is the residue of an aliphatic saturated or unsaturated, straight chain, branched or cyclic carboxylic acid, especially in form of the formyl-, acetyl-, propionyl-acryloyl-, butyryl-, isobutyryl-, methacryloyl-, cyclopropylcarbonyl-, pentanoyl-, pivaloyl-, cyclobutylcarbonyl-, hexanoyl- and the dimethylacryloyl group,
C1-C6-alkansulfonyl is preferably the methanesulfonyl-, ethanesulfonyl-, propanesulfonyl-, butanesulfonyl-, pentanesulfonyl- and the hexanesulfonyl group, saturated rive- to seven-membered heterocycles with one or two hetero-atoms are especially tetrahydrofuryl, tetrahydrothienyl, pyrrolidinyl, tetrahydropyranyl, piperidinyl, hexahydroazepinyl, piperazinyl, hexahydrodiazepinyl or morpholinyl,
monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles with one to three heteroatoms are especially furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, imidazolyl, pyrazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl or triazinyl,
anellated bi and tricydic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocycic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring are preferably benzocyclobutyl, indanyl, indenyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, biphenylenyl, fluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, phenanthryl, dihydrophenanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocyclooctenyl or tetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenyl, wherein mono- or dioxo-derivates, wherein, the residues of indanone, tetralone, anthrone, anthraquinone, fluorenone, phenanthrone, dibenzocycloheptenone, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenone or tetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenone are, for example, also to be understood as partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems,
anellated bi- and tricyclische aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring are, for example, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, dihydrobenzofuryl, benzothienyl, dihydrobenzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, benzimidazolyl, indazolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzisoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzoisothiazolyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiadiazolyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, isothiazolopyridyl, imidazopyridyl, pyrazolopyridyl, thienopyrimidinyl, chromanyl, benzopyranyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, dihydroquinolyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, benzodioxanyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, naphthyridinyl, carbazolyl, tetrahydrocarbazolyl, pyridoindolyl, acridinyl, phenothiazinyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, benzocycloheptathienyl, dihydrothienobenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiepinyl, octahydrodibenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzazepinyl, octahydrodibenzazepinyl, benzocycloheptapyridyl, dihydropyridobenzodiazepinyl, dihydrodibenzoxazepinyl, dihydropyridobenzoxepinyl, dihydropyridobenzoxazepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiazepinyl or dihydropyridobenzothiazepinyl, wherein their mono- or dioxo-derivates and/or optionally their possible tautomeres are also to be understood as partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems, for example, the residues of indolinone, isatin, benzoxazolone and/or their tautomeres hydroxybenzoxazol, of benzisoxazolone, benzothiazolone, benzoisothiazolone and benzimidazolone and/or their tautomeres, hydroxybenzisoxazol, hydroxybenzothiazol, hydroxybenzoisothiazol and hydroxybenzimidazol, of indazolinone, of oxazolopyridinone, thiazolopyridinones, pyrazolopyridinones and imidazopyridinones and/or their tautomeres hydroxyoxazolopyridine, hydroxythiazolopyridines, hydroxypyrazolopyridines and hydroxyimidazopyridines, the residues of chromanone, chromone, quinolinone, dihydroquinolinone, tetrahydrocarbazolone, acridone, of dihydrodibenzoxepinones, benzocycloheptathiophenones, dihydrothienobenzothiepinones, dihydrodibenzothiepinones, dihydrodibenzoazepinones, benzocycloheptapyridinones, dihydropyridobenzoxazepinones, dihydrodibenzothiazepinones and of dihydropyridobenzothiazepinones,
saturated and unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles are —NR13R15 as a grouping which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from N and/or S and/or O, for example azetidine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, (1H)tetrahydropyridine, hexabydroazepine, (1H)tetrahydroazepine, octahydroazocine, pyrazolidine, piperazine, hexahydrodiazepine, morpholine, hexahydrooxazepine, thiomorpholine or thiomorpholine-1,1-dioxide,
saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, represent —NR13R15 as a grouping which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms, selected from N and/or S and/or O, for example 5-aza-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexane, 2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 7-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,5-diaza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 8-a-bicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 2,5-diaza-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 9-aza-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoxaline, (4 Hz dihydrobenzoxazine, (4H)-dihydrobenothiazine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[c]azepine, (1H)tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol, (10H)-dihydroacridine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (10H)-phenoxazine, (10H)-phenothiazine, (5H)-dibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-octahydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzodiazcpine, (11H) dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxazepine, (11H)dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]oxazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]thiazepine or (5H)-tetrahydrodibenzazocine, as well as optionally possible
tautomeres in the case of substitution of the heterocycle as such or in an anellated ring system by free hydroxy-, mercapto- and/or amino groups, and their
stereoisomers such as, if applicable, cis/trans-isomers, endo/exo-isomers, optic isomers such as enantiomers, diastereomers as pure isomers or mixtures and/or racemic mixtures as well as the pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts with inorganic or organic acids, wherein the hydrochlorides, hydrobromides, hydrolodides, sulfates and phosphates, are preferred as addition salts with suitable inorganic acids and acetates, benzoates, 4-methoxybenzoate, 2- or 4-hydroxybenzoate, 4-chlorobenzoate, ascorbate, salicylate, formiate, glutarate, tricarballylate, citrates, fumarates, gluconates, malates, maleates, methanesulfonates, lactates, oxalates, succinates, tartrates and toluolsulfonates, for example p-toluolsulfonate are preferred as addition salts of organic acids.
4. Use of compounds according to claims 1-3, characterized in that the substitutents labelled in formula (I)
have the following meanings:
R1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, C1-C4-hydroxyalkyl, hydroxy, C1-C4-alkoxy, benzyloxy, C1-C4-alkanoyloxy, C1-C4-alkylthio, C2-C5-alkoxycarbonyl, aimnocarbonyl, C3-C9-dialkylaminocarbonyl, carboxy, phenyl, phenoxy, pyridyloxy or NR5R6, wherein
R5 and
R6 are selected independently from each other form hydrogen and C1-C6-alkyl,
R2 is hydrogen, halogen, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy, wherein
R1 and R2, in the case they are adjacent, optionally form a bridge which are selected from the group of bridge members —(CH2)4— and —(CH═CH)2— and —CH2O—CR7R8—O—, wherein
R7 and
R8 can be, independently from each other, hydrogen and C1-C6-alkyl,
R3 is selected from hydrogen, halogen and C1-C6-alkyl and
R4 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy and benyloxy,
k is 0 or 1,
A is C1-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, fluorine or phenyl,
1,2-cyclopropylene,
C2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted one to three-fold by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, fluorine, cyano, or phenyl,
C4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, cyano, or phenyl,
1,3,5-hexatrienylene, which is optionally substituted by C1-C3-alkyl, fluorine, or cyano,
ethinylene or
C2-C6-alkylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NR9, CO, SO or SO2, and wherein the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ═CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group, and wherein
R9 is hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl, C1-C6-acyl or methanesulfonyl,
D is selected from C1-C10-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl or hydroxy,
C2-C10-alkenylene, optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl or hydroxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E or
C3-C10-alkinylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl or hydroxy, and can be selected as well from
C1-C10-alkylene, C2-C10-alkenylene or C3-C10-alkinylene, in which one to three methylene units are isosterically replaced by O, S, NR10, CO, SO or SO2, wherein
R10 has the same meaning as R9, but is selected independently therefrom,
E is
wherein the heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond and
n and p can be, independent of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p≦4,
q is 2 or 3,
R11 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl, carboxy or C2-C7-alkoxycarbonyl and
R12 is selected from hydrogen or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom,
G is selected from hydrogen,
G1, G2, G3, G4 and G5, wherein
G1 represents the residue
—(CH2)r—(CR14R15)s—R13 (G1)
wherein
r is 0, 1 or 2 and
s is 0 or 1,
R13 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C6-alkenyl, C3-C6-alkinyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl,
benzyl, phenyl,
monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles, which contain one to three hetero-atoms from the group N and/or S and/or O and are either bound directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, whereby the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylcne group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from the groups N and/or S and/or O and the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
R14 has the same meaning as R13, but is selected independently thereof,
R15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
monocyclic aromatic five- or six-membered heterocycles, which can contain one to three hetero-atoms selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and are bound either directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated carbocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least einem aromatic ring, wherein the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
anellated bi- and tricyclic aromatic or partially hydrated heterocyclic ring systems with 8 to 16 ring atoms and at least one aromatic ring, wherein one to three ring atoms can be selected from the group N and/or S and/or O and the bond can occur either over an aromatic or a hydrated ring and either directly or over a methylene group,
G2 is selected from the residues
wherein the substituents R13 and R15 the can have the above meaning, or the group
—NR13R15
can also be a nitrogen heterocycle bound over the nitrogen atom, selected from
saturated or unsaturated monocyclic, four- to eight-membered heterocycles, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from N and/or S and/or O, or
saturated or unsaturated bi- or tricyclic, anellated or bridged heterocycles with 8 to 16 ring atoms, which, aside from the essential nitrogen atom, can optionally contain one or two further hetero-atoms selected from N and/or S and/or O,
G3 is the residue
—SO2—(CH2)r R13 (G3),
G4 is the residue
wherein
Ar1 and
Ar2 are selected independently of each other from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl,
G5 is the residue
—COR16 (G5)
wherein
R16 is trifluoromethyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy or benzyloxy and
aromatic ring systems in which the substituents R1, R2, R4, R13, R14, R15, R16, Ar1 and Ar2 and/or in the ring system —NR13R15 can carry independently of each other one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which is optionally entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino, di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino, wherein two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system can form an additional ring over a methylenedioxy bridge.
5. The use of compounds according to claims 14, characterized in that the substiutents labelled in formula (I)
have the following meanings:
R1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, methyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, C1-C4-alkoxy, ethylthio, methoxycarbonyl, tert-butoxycarbonyl, aminocarbonyl, carboxy, and phenoxy,
R2 is hydrogen, halogen, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy,
R3 is hydrogen or halogen,
R4 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy and C1-C3-alkoxy,
k is 0 or 1,
A is C2-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy or fluorine, as well as
C2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy or fluorine,
C4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted by is C1-C3-alkyl or by one or two fluorine atoms,
1,3,5-hexatrienylene, which is optionally substituted by fluorine, or
C2-C6-alkylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S, CO or SO2, and the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ═CO cannot be adjacent to the amide group and,
D is C1-C8-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once twice by methyl or hydroxy,
C2-C8-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by methyl or hydroxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
C3-C8-alkinylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by methyl or hydroxy, as well as
C1-C8-alkylene, C2-C8-alkenylene or C3-C8-alkinylene, in which one to three methylene units can be isosterically replaced by O, S, NH, N(CH3), N(COCH3), N(SO2CH3), CO, SO or SO2,
wherein the heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond and
n and
p can be independent of each other 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p≦3,
q is 2 or 3,
R11 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl, hydroxy, hydroxymethyl and
R12 is selected from hydrogen or an oxo group which is adjacent to the nitrogen atom,
G is hydrogen or
G1, G2, G3, G4 and G5, wherein
G1 represents the residue
—(CH2)r—(CR14R15)s—R13 (G3)
wherein
r is 0, 1 or 2 and
s is 0 or 1,
R13 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C6-alkyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, benzyl or phenyl,
benzocyclobutyl, indanyl, indenyl, oxoindanyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, oxotetrahydronaphthyl, biphenylenyl, fluorenyl, oxofluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, oxodihydroanthryl, dioxodihydroanthryl, phenanthryl, dihydrophenanthryl, oxodihydrophenanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocyclooctenyl, tetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenyl and oxotetrahydrodibenzocyclooctenyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, triazinyl, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, dihydrobenzofuryl, benzothienyl, dihydrobenzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, oxoindolinyl, dioxoindolinyl, benzoxazolyl, oxobenzoxazolinyl, benzisoxazolyl, oxobenzisoxazolinyl, benzothiazolyl, oxobenzthiazolinyl, benzoisothiazolyl, oxobenzoisothiazolinyl, benzimidazolyl, oxobenzimidazolinyl, indazolyl, oxoindazolinyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiadiazolyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, oxodihydrooxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, oxodihydrothiazolopyridyl, isothiazolopyridyl, imidazopyridyl, oxodihydroimidazopyridyl, pyrazolopyridyl, oxodihydropyrazolopyridyl, thienopyrimidinyl, chromanyl, chromanonyl, benzopyranyl, chromonyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, dihydroquinolyl, oxodihydroquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, oxotetrahydroquinolinyl, benzodioxanyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, naphthyridinyl, carbazolyl, tetrahydrocarbazolyl, oxotetrahydrocarbazolyl, pyridoindolyl, acridinyl, oxodihydroacridinyl, phenothiazinyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzoxepinyl, benzocycloheptathienyl, oxobenzocycloheptathienyl, dihydrothienobenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrothienobenzothiepinyl dihydrodibenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiepinyl, octahydrodibenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzazepinyl, octahydrodibenzazepinyl, benzocycloheptapyridyl, oxobenzocycloheptapyridyl, dihydropyridobenzodiazepinyl, dihydrodibenzoxazepinyl, dihydropyridobenzoxepinyl, dihydropyridobenzoxazepinyl, oxodihydropyridobenzoxazepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiazepinyl, dihydropyridobenzothiazepinyl, oxodihydropyridobenzothiazepinyl, bound directly or over a methylene group,
R14 has the same meaning as R13, but is selected independently therefrom,
R15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
indanyl, indenyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, triazinyl, benzofuryl, benzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, benzoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzimidazolyl, chromanyl, quinolyl or tetrahydroquinolyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
G2 is selected from the residues
wherein the substituents R13 and R15 can have the above meanings, or represents the grouping
—NR13R15
each over the nitrogen-bound ring atom of azetidine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, (1H)tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, (1H)tetrahydroazepine, octahydroazocine, pyrazolidine, piperazine, hexyhydrodiazepine, morpholine, hexahydrooxazepine, thiomorpholine, thiomorpholine-1,1-dioxide, 5-aza-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexane, 2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 7-aza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,5-diaza-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2-aza-bicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 8-aza-bicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, 9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)-dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoxaline, (4H)-dihydrobenzoxazine,
(4H)-dihydrobenzothiazine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[c]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4b]indole, (10H)-dihydroacridine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (10H)-phenoxazine, (10H)-phenothiazine, (5H)-dibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-Octahydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzodiazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]oxazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]thiazepine or (5H)-tetrahydrodibenzazocine,
G3 is the residue
—SO2—(CH2)r R13 (G3),
G4 is the residue
wherein
Ar1 and
Ar2 are selected independently of each other from phenyl, pyridyl or naphthyl,
G5 is the residue
—COR16 (G5)
wherein
R16 is trifluoromethyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C3-C6-alkenyloxy or benzyloxy and
aromatic ring systems in which the substituents can be substituted independently of each other by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-Cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, can carry benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino, di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino, wherein two adjacent groups in the ring or ring system can form an additional ring over a methylenedioxy bridge.
6. The use of compounds according to claims 1-5, characterized in that the substituents labelled in formula (I)
have the following meaning:
R1 is hydrogen, halogen, cyano, methyl, trifluoromethyl, hydroxy, methoxy or methoxycarbonyl,
R2 is hydrogen or halogen,
R3 is hydrogen,
R4 is selected from hydrogen, C1-C3-alkyl or hydroxy,
k is 0 or 1,
A is selected from C2-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by hydroxy or fluorine, or
C2-C6-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted once or twice by hydroxy or fluorine,
C4-C6-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted by one or two fluorine atoms, 1,3,5-hexatrienylene or
C2-C6-alkylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, S or CO, and the isosteric substitute, with the exception of ═CO, cannot be adjacent to the amide group and,
D is C2-C8-alkylene, which is optionally substituted by methyl or hydroxy
C2-C8-alkenylene, which is optionally substituted by methyl or hydroxy, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E, or
C2-C8-alkylene, C2-C8-alkenylene, wherein one to three methylene units can be isosterically replaced by O, NH, N(CH3), N(COCH3), N(SO2CH3) or CO,
E is selected from the residues
wherein the heterocyclic ring can optionally have a double bond and
n and p can be, independent of each other, 0, 1, 2 or 3, with the proviso that n+p≦3 and
q is 2
R11 is hydrogen, methyl or hydroxyl and
R12 is hydrogen or an oxo group adjacent to the nitrogen atom,
G is selected from hydrogen, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, methoxycarbonyl, tertbutoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, trifluoracetyl, diphenylphosphinoyl or the residues
wherein
r is 0, 1 or 2 and
s is 0 or 1,
R13 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
indanyl, indenyl, oxoindanyl, naphthyl, dihydronaphthyl, tetrahydronaphtbyl, oxotetrahydronaphthyl, fluorineenyl, oxofluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, oxodihydroanthryl, dioxodihydroanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, oxodihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
furyl, thienyl, pyrrolyl, oxazolyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, isothiazolyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, triazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyridazinyl, pyrimidinyl, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, dihydrobenzofuryl, benzothienyl, dihydrobenzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, oxoindolinyl, dioxoindolinyl, benzoxazolyl, oxobenzoxazolinyl, benzisoxazolyl, oxobenzisoxazolinyl, benzothiazolyl, oxobenzthiazolinyl, benzoisothiazolyl, oxobenzoisothiazolinyl, benzimidazolyl, oxobenzimidazolinyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiadiazolyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, oxodihydrooxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, oxodihydrothiazolopyridyl, isothiazolopyridyl, imidazopyridyl, oxodihydroimidazopyridyl, pyrazolopyridyl, thienopyrimidinyl, chromanyl, chromanonyl, benzopyranyl, chromonyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, dihydroquinolyl, oxodihydroquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, oxotetrahydroquinolinyl, benzodioxanyl, quinoxalinyl, quinazolinyl, naphthyridinyl, carbazolyl, tetrahydrocarbazolyl, oxotetrahydrocarbazolyl, pyridoindolyl, acridinyl, oxodihydroacridinyl, phenothiazinyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, benzocycloheptathienyl, oxobenzocycloheptathienyl, dihydrothienobenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrothienobenzothiepinyl dihydrodibenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzazepinyl, octahydrodibenzazepinyl, benzocycloheptapyridyl, oxobenzocycloheptapyridyl, dihydropyridobenzoxepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiazepinyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
R14 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
R15 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl, phenyl,
naphthyl, furyl, thienyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, pyrazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, pyridyl, benzofuryl, benzothienyl, indolyl, indolinyl, benzoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzimidazolyl, chromanyl, quinolyl or tetrahydroquinolyl, bound directly or over a methylene group, wherein in formula (I)
the group NR13R15 can be selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, (1H)tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, Octahydroazocine, piperazine, hexahydrodiazepine, morpholine, hexahydrooxazepine, 2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 7-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, 8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)-dihydroquinoline, (1H)tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoxaline, (4H)-dihydrobenzoxazine, (4H)-dihydrobenzothiazine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (SH)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol, (10H)-dihydroacridine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (5H)-dihydrodibenzodiazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]oxazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiazepine, (10H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,f]oxaze-pine or (5H)-tetrahydrodibenzazocine.
7. The use of compounds according to claims 1-6, characterized in that the substituents in labelled the formula (I)
have the following meanings:
R1 is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, methyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy,
R2 and
R3 are hydrogen,
R4 is hydrogen or hydroxy,
k is 0 or 1,
A is selected from C2-C6-alkylene, which is optionally substitued once or twice by hydroxy or fluorine or,
C2-C4-alkylene, which is optionally substituted by fluorine,
C4-alkadienylene, which is optionally substituted by fluorine,
D is selected from C2-C6-alkylene, C2-C6-alkenylene, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E, and C2-C6-alkylene and C2-C6-alkenylene, wherein a methylene unit can be isosterically replaced by O, NH, N(CH3) or CO or an ethylene group can be isosterically replaced by NH—CO and/or CO—NH or a propylene group can be isosterically replaced by NH—CO—O and/or O—CO—NH,
E is selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, 1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine, hexahydroazepine, morpholine and hexahydro-1,4-oxazepine, wherein the heterocyclic ring optionally adjacent to the nitrogen atom, can be substituted by an oxo group,
G is selected from hydrogen, tert-butoxycarbonyl, diphenylphosphinoyl, or one of the residues
wherein
r is 0 or 1 and
s is 0 or 1,
R13 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
indenyl, oxoindanyl, naphthyl, tetrahydronaphthyl, fluorenyl, oxofluorenyl, anthryl, dihydroanthryl, oxodihydroanthryl, dioxodihydroanthryl, dibenzocycloheptenyl, dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
furyl, thienyl, oxazolyl, thiazolyl, imidazolyl, oxadiazolyl, thiadiazolyl, pyridyl, pyrazinyl, pyrimidinyl, imidazothiazolyl, benzofuryl, benzothienyl, indolyl, oxoindolinyl, dioxoindolinyl, benzoxazolyl, oxobenzoxazolinyl, benzothiazolyl, oxobenzthiazolinyl, benzimidazolyl, oxobenzimidazolinyl, benzofurazanyl, benzotriazolyl, oxazolopyridyl, oxodihydrooxazolopyridyl, thiazolopyridyl, oxodihydrothiazolopyridyl, chromanyl, chromanonyl, benzopyranyl, chromonyl, quinolyl, isoquinolyl, oxodihydroquinolinyl, tetrahydroquinolyl, oxotetrahydroquinolinyl, benzodioxanyl, quinazolinyl, acridinyl, oxodihydroacridinyl, phenothiazinyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, benzocycloheptathienyl, dihydrothienobenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzothiepinyl, dihydrodibenzazepinyl, oxodihydrodibenzazepinyl, octahydrodibenzazepinyl, benzocycloheptapyridyl, oxobenzocycloheptapyridyl, dihydrodibenzothiazepinyl bound directly or over a methylene group,
R14 is hydrogen, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
R15 is hydrogen, hydroxy, methyl, benzyl or phenyl,
naphthyl, furyl, thienyl, pyridyl, benzofuryl, benzothienyl, indolyl, benzoxazolyl, benzothiazolyl, benzimidazolyl, chromanyl, quinolyl or tetrahydroquinolyl bound directly or over a methylene group, wherein in the formula
the group NR13R15 can be selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, hexahydroazepine, morpholine, 2,5-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane, indoline, isoindoline, (1H)-dihydroquinoline, (1H)-tetrahydroquinoline, (2H)-tetrahydroisoquinoline, (1H)tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepine, (1H)-tetrahydrobenzo[d]azepine, (5H)-tetrahydrobenzo[b]oxazepine, (5H)tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiazepine, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridanone, (5H)-dihydrodibenzazepine, (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]-oxazepine or (11H)-dihydrodibenzo[b,e]thiazepine and
wherein aromatic ring systems in the substituents can be substituted, independently of each other, by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C1-C6′-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, can carry benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino or di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino, whereby two adjacent groups on the aromatic ring or ring system for an additional ring over a methylenedioxy bridge.
8. The use of compounds according to claims 1-7, characterized in that the substituents labelled in the formula (I)
have the following meanings:
R1 is hydrogen, fluorine, methyl, trifluoromethyl or hydroxy,
R2 and
R3 are hydrogen,
R4 is hydrogen or hydroxy,
k is 0,
A is ethylene, propylene or butylene which can be each optionally substituted by hydroxy or once or twice by fluorine, or
ethenylene and/or vinylene or
1,3-butadienylene
D is selected from C2-C6-alkylene or C2-C6-alkenylene, wherein the double bond can also be to ring E,
E is selected from pyrrolidine, piperidine, hexahydroazepine or morpholine,
G is selected from benzyl, phenethyl, fluorenylmethyl, anthrylmethyl, diphenylmethyl, fluorenyl or dihydrodibenzocycloheptenyl, furylmethyl, thienylmethyl, thiazotylmethyl, pyridylmethyl, benzothienylmethyl, quinolylmethyl, phenyl-thienylmethyl, phenyl-pyridylmethyl, dihydrodibenzoxepinyl, dihydrodibenzothiepinyl,
acetyl, pivaloyl, phenylacetyl, diphenylacetyl, diphenylpropionyl, naphthyl acetyl, benzoyl, naphthoyl, anthrylcarbonyl, oxofluorenylcarbonyl, oxodihydroanthrylcarbonyl or dioxodihydroanthrylcarbonyl,
furoyl, pyridylcarbonyl, chromonylcarbonyl, quinolylcarbonyl,
naphthylaminocarbonyl, dibenzylaminocarbonyl, benzylphenylaminocarbonyl, diphenylaminocarbonyl, indolinyl-1-carbenyl, dihydrodibenzazepin-N-carbonyl, tetrahydroquinolinyl-N-carbonyl, tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepinyl-N-carbonyl,
methanesulfonyl, phenylsulfonyl, p-toluolsulfonyl, naphthylsulfonyl, quinolinsulfonyl and
diphenylphosphinoyl,
wherein aromatic ring systems can be substituted independently of each other by one to three of the same or different substituents from the series halogen, cyano, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C3-C8-cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, C1-C6-alkoxy, which can be entirely or partially substituted by fluorine, benzyloxy, phenoxy, mercapto, C1-C6-alkylthio, carboxy, C1-C6-alkoxycarbonyl, benzyloxycarbonyl, nitro, amino, mono-C1-C6-alkylamino or di-(C1-C6-alkyl)-amino, wherein two adjacent groups in the ring or ring system can form an additional ring over a methylendioxy bridge.
9. Use according to one of the claims 1-8, characterized in that one or more of the following compounds and/or pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts thereof are used for the production of the medicament
N-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-ethyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
N-{2-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-ethyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
N-{2-[1-(4-phenylbutyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-ethyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
N-{2-[1-(4-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-ethyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
N-[2-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-ethyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide,
N-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide, or
N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-propionamide.
10. Use according to any one of the claims 1-8, characterized in that one or more of the following compounds and/or pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof are used for the production of a medicament
N-[4(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-{4-[1-(2-phenylethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-{4-[1-(4-biphenylylmethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-{4-[1-(1-naphthylmethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-{4-[1-(9-anthrymethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-{4-[1-(Cyclohexylphenylmethyl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide, or
N-{4-[1-(10,11-dihydro-5H-dienzo[a,d]cycloheptene-5-yl)-piperidin-4-yl]-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide.
11. Use according to any one of the claims 1-8, characterized in that one or more of the following compounds and/or pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof are used for the production of a medicament
N-[2-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-ethyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-[3-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-propyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-[5-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-pentyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-[6-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-hexyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide, or
N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-5-(pyridin-3-yl)-2,4-pentadiene acid amide.
12. Use according to any one of the claims 1-8, characterized in that one or more of the following compounds and/or pharmacologically acceptable acid addition salts thereof are used for the production of a medicament
N-(4-{1-[bis-(4-fluorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl)-butyl}-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-(4-{1-[bis-(2-chlorophenyl)-methyl]-piperidin-4-yl}-butyl)-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(2-fluoropyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide, or
N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(6-fluoropyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide.
13. Use according to any one of the claims 1-8, characterized in that one or more of the following compounds are used for the production of a medicament
N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide,
N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)-butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide dihydrochloride or,
N-[4-(1-diphenylmethylpiperidin-4-yl)butyl]-3-(pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide methanesulfonate.
14. Use according to any one of the claims 1-13 characterized in that the compounds according to the general formula (I) are combined with one or more other active ingredients for the respective indications such as cytostatic agents or immunosuppressive agents.
15. Medicament for cytostatic or immunomodulatory and/or immunosuppressive treatment in human or veterinary medicine, characterized in that it comprises a compound according to formula (I) corresponding to the substituent definitions given in claims 1-13 in combination with a cytostatic agent or an immunosuppressive agent, optionally together with further active ingredients suitable in the named indications and suitable carriers, adjuvents and additives.
16. Medicament according to claim 15 for cytostatic treatment, characterized in that together with a compound according to formula (I) and aside from pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and adjuvents, it comprises in combination one or more cytostatic agents from the series of anti-metabolites such as, cytarabine, 5-fluoruracil, 6-mercaptopurine or methotrexate, alkylating agents such as busulfan, carmustine, cisplatin, carboplatin, cyclophosphamide, dacarbazine, melphalan or thiotepa, DNA-intercalating substances and topoisomerase inhibitors such as actinomycin D, daunorubicin, doxorubicin, mitomycin C, mitoxantrone, etoposide, topotecan or irinotecan, spindle poisons such as vincristine, navelbin, taxol, or taxoter, hormonally active agents such as tamoxifen, flutiamide, formestan or goserelin or from the series of other cytostatic agents with complex modes of action such as L-asparaginase, bleomycin or hydroxyurea or from the group of the modulators of P-glycoprotein, MRP, glutathione-S-transferase, metallothionein, optionally together with futher medicines effective in these indications.
17. Medicament according to claim 15 for immunosuppressive treatment, characterized in that, together with a compounds according to formula (I) and aside from pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and adjuvents, it optionally comprises in combination one or more immunosuppressive agents from the series of the cyclosporins, such as cyclosporin A, tacrolimus, raparnycin, the group of antimetabolites such as methotrexate and azathioprine and the group of glucocorticoids, optionally together with further medicines effective in these indications.
18. Use according to one of the claims 1-14, characterized in that the production of the medicament serves for the treatment of tumors in connection with the indications gynacological tumors, ovarian carcinomas, testicle tumors, prostate carcinomas, skin cancer, kidney cancer, bladder tumors, esophagus carcinomas, stomach cancer, rectal carcinomas, pancreas carcinomas, thyroid cancer, adrenal tumors, various types of leukemia and lymphomas, Hodgkin's disease, tumor illnesses of the CNS, soft-tissue sarcomas, bone sarcomas, benign and malignant mesotheliomas, especially intestine cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, bronchial and lung carcinomas, melanomas, acute and chronic leukemias and benign papillomatosis tumors.
19. N-(4-diphenylmethyl-morpholin-2-ylmethyl)-3- (pyridin-3-yl)-acrylamide
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/208,253 US20040029861A1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 2002-07-30 | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression |
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19624668A DE19624668A1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1996-06-20 | Use of pyridylalkane, pyridylalken or pyridylalkynamides |
| PCT/EP1997/003244 WO1997048397A1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1997-06-20 | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression |
| DE19624668.7 | 1997-06-20 | ||
| US09/216,482 US6451816B1 (en) | 1997-06-20 | 1998-12-18 | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression |
| US10/208,253 US20040029861A1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 2002-07-30 | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/216,482 Continuation US6451816B1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1998-12-18 | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US20040029861A1 true US20040029861A1 (en) | 2004-02-12 |
Family
ID=8166665
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/216,482 Expired - Fee Related US6451816B1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1998-12-18 | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression |
| US10/208,253 Abandoned US20040029861A1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 2002-07-30 | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US09/216,482 Expired - Fee Related US6451816B1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1998-12-18 | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US6451816B1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6903118B1 (en) * | 1997-12-17 | 2005-06-07 | Klinge Pharma Gmbh | Piperazinyl-substituted pyridylalkane, alkene and alkine carboxamides |
| US20100040729A1 (en) * | 2006-03-21 | 2010-02-18 | Michael Sahagian | Compositions and methods for surface modification of root vegetable products |
Families Citing this family (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19624704A1 (en) * | 1996-06-20 | 1998-01-08 | Klinge Co Chem Pharm Fab | New pyridylalkanoic acid amides |
| DE19624659A1 (en) * | 1996-06-20 | 1998-01-08 | Klinge Co Chem Pharm Fab | New pyridylalkene and pyridylalkanoic acid amides |
| DE19818044A1 (en) * | 1998-04-22 | 1999-10-28 | Klinge Co Chem Pharm Fab | Reducing side effects or neutralizing action of carcinostatic or immunosuppressive agents, especially pyridine derivatives, using vitamin PP compounds, e.g. nicotinamide |
| CO5180550A1 (en) | 1999-04-19 | 2002-07-30 | Smithkline Beecham Corp | FAB I INHIBITORS |
| CO5370679A1 (en) | 1999-06-01 | 2004-02-27 | Smithkline Beecham Corp | FAB INHIBITORS 1 |
| US6762201B1 (en) | 1999-10-08 | 2004-07-13 | Affinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fab I inhibitors |
| JP4803935B2 (en) * | 1999-10-08 | 2011-10-26 | アフィニアム・ファーマシューティカルズ・インコーポレイテッド | FABI inhibitor |
| US6730684B1 (en) | 1999-10-08 | 2004-05-04 | Affinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fab I inhibitors |
| EP1560584B1 (en) * | 2001-04-06 | 2009-01-14 | Affinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fab i inhibitors |
| DK1575951T3 (en) * | 2002-12-06 | 2014-09-15 | Debiopharm Int Sa | HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS, METHODS OF PRODUCING THEREOF AND THEIR USE IN THERAPY |
| JP4880448B2 (en) | 2003-03-17 | 2012-02-22 | アフィナム ファーマシューティカルズ,インコーポレーテッド | Composition comprising a plurality of antibiotics and method of using the same |
| WO2007053131A2 (en) * | 2004-06-04 | 2007-05-10 | Affinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Acrylamide derivatives as antibiotic agents |
| PE20071159A1 (en) * | 2005-10-31 | 2007-11-30 | Schering Corp | DERIVATIVES OF TROPANE 3-MONOSUSTITUTED AS LIGANDS OF NOCICEPTIN RECEPTORS |
| US20090156578A1 (en) * | 2005-12-05 | 2009-06-18 | PAULS Henry | 3-Heterocyclylacrylamide Compounds as Fab I Inhibitors and Antibacterial Agents |
| CA2658506C (en) | 2006-07-20 | 2016-01-26 | Affinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Acrylamide derivatives as fab 1 inhibitors |
| HUP0600808A3 (en) * | 2006-10-27 | 2008-09-29 | Richter Gedeon Nyrt | New benzamide derivatives as bradykinin antagonists, process for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| HUP0600809A3 (en) * | 2006-10-27 | 2008-09-29 | Richter Gedeon Nyrt | New phenylsulfamoyl-benzamide derivatives as bradykinin antagonists, process and intermediates for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| HUP0600810A3 (en) * | 2006-10-27 | 2008-09-29 | Richter Gedeon Nyrt | New sulfonamide derivatives as bradykinin antagonists, process and intermediates for their preparation and pharmaceutical compositions containing them |
| US8263613B2 (en) | 2007-02-16 | 2012-09-11 | Affinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Salts, prodrugs and polymorphs of fab I inhibitors |
| AU2007360523A1 (en) * | 2007-10-27 | 2009-04-30 | Richter Gedeon Nyrt. | New non-peptide derivatives as bradykinin B1 antagonists |
| CA2734859A1 (en) * | 2008-08-21 | 2010-02-25 | Richter Gedeon Nyrt. | Methods for treating cns disorders |
| JP2012500800A (en) * | 2008-08-21 | 2012-01-12 | リヒター ゲデオン ニルバーノシャン ミーケデーレスベニュタールシャシャーグ | Treatment of neuropathic pain |
| WO2010114907A1 (en) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-07 | Vanderbilt University | Sulfonyl-azetidin-3-yl-methylamine amide analogs as glyt1 inhibitors, methods for making same, and use of same in treating psychiatric disorders |
| WO2011060321A1 (en) | 2009-11-16 | 2011-05-19 | Chdi, Inc. | Transglutaminase tg2 inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of use thereof |
| US8889716B2 (en) * | 2011-05-10 | 2014-11-18 | Chdi Foundation, Inc. | Transglutaminase TG2 inhibitors, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of use thereof |
| KR101720885B1 (en) | 2012-06-19 | 2017-03-28 | 데비오팜 인터네셔날 에스 에이 | Prodrug derivatives of (e)-n-methyl-n-((3-methylbenzofuran-2-yl)methyl)-3-(7-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1,8-naphthyridin-3-yl)acrylamide |
| LT3419628T (en) | 2016-02-26 | 2021-01-25 | Debiopharm International Sa | Medicament for treatment of diabetic foot infections |
| KR20190074292A (en) | 2016-10-18 | 2019-06-27 | 시애틀 지네틱스, 인크. | Targeted delivery of remedial pathway inhibitors of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides |
| MA51189A (en) | 2017-04-27 | 2020-03-04 | Seattle Genetics Inc | QUATERNARIZED NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE RECOVERY ROUTE INHIBITOR CONJUGATES |
Family Cites Families (35)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4283541A (en) | 1980-05-27 | 1981-08-11 | Usv Pharmaceutical Corporation | Pyridylacyl-hydroxamates |
| NL8005133A (en) | 1980-09-12 | 1982-04-01 | Duphar Int Res | PHENYLPIPERAZINE DERIVATIVES WITH ANTIAGRESSIVE ACTION. |
| JPS57136518A (en) | 1981-02-18 | 1982-08-23 | Eisai Co Ltd | Immunoregulator |
| US5326772A (en) | 1984-09-28 | 1994-07-05 | Byk Gulden Lomberg Chemische Fabrik Gmbh | Diaryl compounds for their use |
| US4778796A (en) | 1985-07-19 | 1988-10-18 | Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | ω-(3-pyridyl)alkenamide derivatives and anti-allergenic pharmaceutical compositions containing same |
| DE3641822A1 (en) | 1986-12-06 | 1988-06-16 | Goedecke Ag | USE OF DIHYDROPHENYLAMINOSAE DERIVATIVES AND MEDICINAL PRODUCTS CONTAINING THEM FOR IMMUNULATION AND CYTOSTASE |
| JPS63179869A (en) | 1987-01-20 | 1988-07-23 | Dainippon Pharmaceut Co Ltd | Piperidine derivative |
| JP2832979B2 (en) * | 1988-02-15 | 1998-12-09 | 武田薬品工業株式会社 | Unsaturated carboxylic acid amide derivative |
| HU206181B (en) | 1988-02-19 | 1992-09-28 | Byk Gulden Lomberg Chem Fab | Process for producing pharmaceutical compositions comprising optically pure r-(+)-niguldipin and its derivatives and suitable for treating tumoros diseases |
| EP0343307A1 (en) | 1988-05-26 | 1989-11-29 | Fabrica Espanola De Productos Quimicos Y Farmaceuticos, S.A. | 4-Piperidinealkanamine derivatives |
| IE903196A1 (en) | 1989-09-05 | 1991-03-13 | Searle & Co | Substituted n-benzylpiperidine amides |
| IE903957A1 (en) | 1989-11-06 | 1991-05-08 | Sanofi Sa | Aromatic amine compounds, their method of preparation and¹pharmaceutical compositions in which they are present |
| JPH05506027A (en) | 1990-04-10 | 1993-09-02 | ビイク グルデン ロンベルク ヒエーミツシエ フアブリーク ゲゼルシヤフト ミツト ベシユレンクテル ハフツング | New pyridine ester |
| US5352684A (en) | 1990-04-10 | 1994-10-04 | Byk Gulden Lomberg Chemische Fabrik Gmbh | Pyridines as medicaments |
| US5260323A (en) | 1990-06-28 | 1993-11-09 | Hoechst Aktiengesellschaft | 2,4- and 2,5-substituted pyridine-N-oxides, processes for their preparation and their use |
| DE4020570A1 (en) | 1990-06-28 | 1992-01-02 | Hoechst Ag | 2,4- AND 2,5-SUBSTITUTED PYRIDINE-N-OXIDES, METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION AND USE THEREOF |
| ES2069137T3 (en) | 1990-07-30 | 1995-05-01 | Takeda Chemical Industries Ltd | DERIVATIVES OF IMIDAZOPYRIDINE AND ITS USE. |
| US5229400A (en) | 1990-10-05 | 1993-07-20 | Ajinomoto Co., Inc. | Piperidine compounds and their use as antiarrhythmic agents |
| FR2676053B1 (en) | 1991-05-03 | 1993-08-27 | Sanofi Elf | NOVEL DIALKYLENEPIPERIDINO COMPOUNDS AND THEIR ENANTIOMERS, PROCESS FOR THEIR PREPARATION AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING THEM. |
| DE69209576D1 (en) | 1991-05-10 | 1996-05-09 | Takeda Chemical Industries Ltd | Pyridine derivatives, their production and use |
| US5208247A (en) | 1991-08-01 | 1993-05-04 | American Cyanamid Company | Pyridinium compounds which are useful as antagonists of platelet activating factor |
| CA2085954A1 (en) | 1991-12-24 | 1993-06-25 | Klaus Weidmann | Substituted pyridine n-oxides, processes for their preparation, and their use |
| CA2126976A1 (en) * | 1991-12-31 | 1993-07-08 | Hisashi Takasugi | Oxadiazole derivatives having acetylcholinesterase-inhibitory and muscarinic agonist activity |
| GB9200535D0 (en) | 1992-01-10 | 1992-02-26 | Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co | New compound |
| FR2686084B1 (en) | 1992-01-10 | 1995-12-22 | Bioprojet Soc Civ | NEW IMIDAZOLE DERIVATIVES, THEIR PREPARATION AND THEIR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| WO1994001402A1 (en) | 1992-07-13 | 1994-01-20 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Limited | Heterocyclic amide derivatives as tachykinin derivatives |
| IL111235A (en) | 1993-10-15 | 2001-03-19 | Schering Plough Corp | Pharmaceutical compositions for inhibition of g-protein function and for treatment of proliferative diseases containing tricyclic compounds some such compounds and process for preparing part of them |
| DE69429440T2 (en) | 1993-10-15 | 2002-08-08 | Schering Corp., Kenilworth | TRICYCLIC SULFONAMIDE DERIVATIVES FOR INHIBITING THE G-PROTEIN FUNCTION AND FOR TREATING PROLIFERATIVE DISEASES |
| ES2164716T3 (en) | 1993-10-15 | 2002-03-01 | Schering Corp | USEFUL CARBAMATE TRICICLIC COMPOUNDS TO INHIBIT THE FUNCTION OF PROTEIN-G AND FOR THE TREATMENT OF PROLIFERATIVE DISEASES. |
| AU698313B2 (en) | 1994-03-14 | 1998-10-29 | Government Of The United States Of America, As Represented By The Secretary Of The Department Of Health And Human Services, The | Use of lipoxygenase inhibitors as anti-cancer therapeutic and intervention agents |
| IL117798A (en) | 1995-04-07 | 2001-11-25 | Schering Plough Corp | Tricyclic compounds useful for inhibition of g-protein function and for treatment of proliferative diseases and pharmaceutical compositions comprising them |
| US5712280A (en) | 1995-04-07 | 1998-01-27 | Schering Corporation | Tricyclic compounds useful for inhibition of G-protein function and for treatment of proliferative diseases |
| FR2738245B1 (en) | 1995-08-28 | 1997-11-21 | Sanofi Sa | NOVEL PIPERIDINE DERIVATIVES, PROCESS FOR THEIR PRODUCTION AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING THEM |
| DE19624704A1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1998-01-08 | Klinge Co Chem Pharm Fab | New pyridylalkanoic acid amides |
| DE19624668A1 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1998-02-19 | Klinge Co Chem Pharm Fab | Use of pyridylalkane, pyridylalken or pyridylalkynamides |
-
1998
- 1998-12-18 US US09/216,482 patent/US6451816B1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2002
- 2002-07-30 US US10/208,253 patent/US20040029861A1/en not_active Abandoned
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6903118B1 (en) * | 1997-12-17 | 2005-06-07 | Klinge Pharma Gmbh | Piperazinyl-substituted pyridylalkane, alkene and alkine carboxamides |
| US20100040729A1 (en) * | 2006-03-21 | 2010-02-18 | Michael Sahagian | Compositions and methods for surface modification of root vegetable products |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US6451816B1 (en) | 2002-09-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6451816B1 (en) | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression | |
| EP0912176B1 (en) | Use of pyridyl alkane, pyridyl alkene and/or pyridyl alkine acid amides in the treatment of tumors or for immunosuppression | |
| US7241745B2 (en) | Pyridyl alkene and pyridyl alkine acid amides as cytostatics and immunosupressives | |
| EP1060163B1 (en) | New piperazinyl-substituted pyridylalkane, alkene and alkine carboxamides | |
| US6444823B1 (en) | Pyridyl alkane acid amides as cytostatics and immunosuppressives | |
| US6903118B1 (en) | Piperazinyl-substituted pyridylalkane, alkene and alkine carboxamides | |
| US6593344B1 (en) | Piperadinyl-substituted pyridylalkane, alkene and alkine carboxamides | |
| EP1042291B1 (en) | Aryl-substituted pyridylalkane, alkene, and alkine carboxamides useful as cytostatic and immunosuppressive agents | |
| KR100478405B1 (en) | Pyridylalkene- and pyridylalkyne-acidamides as cytostatic and immunosuppressive agents |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STCB | Information on status: application discontinuation |
Free format text: ABANDONED -- FAILURE TO RESPOND TO AN OFFICE ACTION |