US1856493A - Extensible chair - Google Patents
Extensible chair Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US1856493A US1856493A US70241A US7024125A US1856493A US 1856493 A US1856493 A US 1856493A US 70241 A US70241 A US 70241A US 7024125 A US7024125 A US 7024125A US 1856493 A US1856493 A US 1856493A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- switch
- brake
- chair
- motor
- lever
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 15
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000003534 oscillatory effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 3
- HAAITRDZHUANGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[2-[(7-chloro-1-benzothiophen-3-yl)methoxy]-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]imidazole;nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O.ClC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1C(OCC=1C2=CC=CC(Cl)=C2SC=1)CN1C=NC=C1 HAAITRDZHUANGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000881 depressing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- ORILYTVJVMAKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Adamantane Natural products C1C(C2)CC3CC1CC2C3 ORILYTVJVMAKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000003251 Pruritus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000027697 autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome due to CTLA4 haploinsuffiency Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000002925 dental caries Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000000994 depressogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000013372 meat Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009877 rendering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H3/00—Mechanisms for operating contacts
- H01H3/02—Operating parts, i.e. for operating driving mechanism by a mechanical force external to the switch
- H01H3/14—Operating parts, i.e. for operating driving mechanism by a mechanical force external to the switch adapted for operation by a part of the human body other than the hand, e.g. by foot
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61G—TRANSPORT, PERSONAL CONVEYANCES, OR ACCOMMODATION SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PATIENTS OR DISABLED PERSONS; OPERATING TABLES OR CHAIRS; CHAIRS FOR DENTISTRY; FUNERAL DEVICES
- A61G15/00—Operating chairs; Dental chairs; Accessories specially adapted therefor, e.g. work stands
- A61G15/02—Chairs with means to adjust position of patient; Controls therefor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01H—ELECTRIC SWITCHES; RELAYS; SELECTORS; EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE DEVICES
- H01H3/00—Mechanisms for operating contacts
- H01H3/02—Operating parts, i.e. for operating driving mechanism by a mechanical force external to the switch
- H01H3/16—Operating parts, i.e. for operating driving mechanism by a mechanical force external to the switch adapted for actuation at a limit or other predetermined position in the path of a body, the relative movement of switch and body being primarily for a purpose other than the actuation of the switch, e.g. for a door switch, a limit switch, a floor-levelling switch of a lift
Definitions
- the present invention relates to extensible chairs, and has for one object to provide improved operating and control mechanism applicable to dental, surgical, barbers and other types of chairs.
- a further object of the invention is to provide an extensible motor actuated chair or lifting mechanism having improved electric control devices for automatically rendering the motor ineffective when the parts have reached the limit of their range of adjustment, the devices being coordinated to eflect control of the different movements of the parts so as to simplify the work of the operator in the adjustments of the chair to the different working positions required from time to time.
- a further object of the invention is to provide improved operating means for the chair including a manually controlled electric switch and a brake for the driving means operatively associated with the switch for control thereby and also with certain of the movable parts of the chair whereby the brake is applied automatically when said parts are moved to a predetermined position of adj ustment.
- a further object of the invention is to provide an extensible chair having a liftin mechanism adapted to be motor driven and so constructed as to readily receive either a direct or alternating current motor without necessitating removal or adjustment of any of the circuit connections for the motor, thus requiring only the removal of one motor and the substitution of the other whereby the manufacturer may build a standard unit which can be shipped complete and ready for service with either type of motor that may be required.
- a further object of the invention is to provide an improved type of switch including yieldable means adapted to be compressed upon moving the switch to closed position whereby to afford an extremely quick release of the movable contacts of the switch in order to prevent arcing when the circuit is broken.
- a still further object of the invention is to provide in combination with a movable chair Serial N 0. 70,241.
- Another object of the invention is to provicle a simple, compact and form of chair construction embodying extensible standards or sections and lifting means therefor including a reversible electric motor and a main manually controlled reversing switch connected with the limit switch and arranged to be operated automatically by one of the chair sections as it approaches the limits of its range of adjustment.
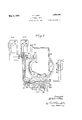
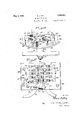
- Figure 1 is a diagrammatic view illustrating the circuit arrangement of an A. C. and D. C. motor together with the switches therefor in connection with a part sectional plan of the chair base showing the several junction boxes for the switches and a conduit for enclosing the circuit connections;
- Figure 2 is a diagrammatic View in elevation illustrating a portion of an extensible chair with the operating pins or projections for the limit switch shown on one of the adjustable sections;
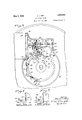
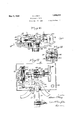
- Figure 3 is a fragmentary part sectional plan of the chair illustrating the manner of connecting the motor with the lifting mechanism and showing the brake arrangement for the motor driven shaft;
- Figure 4 is a fragmentary sectional elevation taken on line 4:ata of Figure 3, showing one of the extensible chair sections nearing its lowest position at which it effects control of the brake;
- Figure 5 is a similar view showing the section in operating position with respect to the brake tripping lever
- Figure 6 is a sectional plan through the chair base showing the construction of the extensible sections and indicating the relation of the main switch with respect to the outer section;
- Figure 7 is a detail view of a part of the brake mechanism
- Figure 8 is a similar view in which the parts are moved to release the brakes
- Figure 9 is a fragmentary sectional eleva tion illustrating the motor drive connection for the lifting mechanism and the brake control mechanism therefor;
- Figure 10 is a somewhat similar view showing the brake mechanism in release position
- Figure 11 is an elevation as viewed from the left of Figure 10, with the motor shaft removed and the brake in release position
- Figure 12 is a view in elevation similar to the upper half of Figure 11 with the brake shown applied;
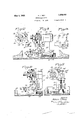
- Figure 13 is an enlarged detail view illustrating the double bell-crank for releasing the brake as shown in Figure 10;
- Figure 14 is a top plan view of the main switch with certain portions shown in section;
- Figure 15 is an elevational view of the switch looking at the side nearest the axis of the chair;
- Figure 16 is a bottom plan view of the switch
- Figure 17 is a sectional elevation taken on line 17 a17 a of Figure 16;
- Figure 18 is an enlarged detail section through one of the spring housings for the switch shown in Figure 17;
- Figure 19v is afront elevational view of the limit switch shown in Figure 1;
- Figure 20 is a side elevation of the same as viewed from the right of Figure 19;
- Figure 21 is a side elevation as viewed from the left of Figure 19;
- Figure 22 is a view in elevation somewhat similar to Figure 1.9 with parts shown in section to illustrate the construction of the re versible plunger mechanism and its retaining means;
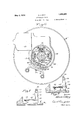
- Figure 23 is a sectional elevation taken on line 23a23a of Figure 19, showing the movable contact member in central position and illustrating one position of the switch operating projections on the outer movable section of the chair;
- Figure 24 is a similar section showing the switch after operation by the chair to one of its circuits braking positions
- Figure 25 is a sectional plan taken on line 25a25a of Figure 22.
- a chair having extensible sections and suitable raising and lowering means therefor, each of which may be of any desired or Well known construction.
- the lifting mechanism has, however, been designed in such a way as to adapt it for the ready reception of either a direct or alternating current motor, merely by the insertion of either of these types of motors in position upon the base of the chair.
- the plug and socket connections for the different types of motors are designed to interchange so that when assembling either motor no time is lost in making the necessary connections.
- the limit or safety switch for breaking the circuits when the chair sections are approach ing the limits of their adjustment in either direction serves to automatically interrupt the motor circuit while the brake for the driving mechanism, applied automatically by one of the chair sections on approaching the end of its downward stroke, prevents overrunning of the sections regardless of the fact that the operator may forget to release the pedal of the main switch at the proper time. Furthermore, the brake which is under the control of the pedal switch is automatically applied upon release of the pedal whereby to prevent coasting of the chair sections after the motor circuit is broken.
- 11 and 11 represent the upper and lower fixed or base sections of the chair, the former having an openin at one side provided with a vertically isposed flanged portion 12 for the reception either of an A. C. or D. C. motor, one of which is shown at 13 in Figures 2 and 3.
- the inner and outer extensible sections or standards are indicated generally at 14 and 15, respectively.
- the outer section is suitably guided within the base 11 by opposite sets of rollers 16, only one of which is shown, while the inner section 14 is guided within the outer section by the opposite sets of rollers 17 and 18.
- the inner section carries at its upper end a chair support, not shown, between whieh and the base member 11' is disposed any suitable form of lifting mechanism.
- This mechanism may be of the gear driven screw type arranged for operation by a gear 19 at the center of the chair base which in turn is driven by another gear 20 meshing with a third gear 21 on the bottom of a vertical shaft 22, disposed with a housing 23 carried by a base or frame 24 supported by the base plate 11.
- the housing is provided with a removable cover plate 24' as shown in Figure 3.
- the upper end of the shaft 22 is provided with a gear 25 meshing with a worm 26 on a transverse shaft 27 journaled in a suitable bearing box 27', the upper half of which is removable, the lower half of the box being preferably cast integral with the housing 23.
- the worm shaft 27 carries a disk or Wheel 28 having laterally projecting lugs 29 upon the outer ends of which is secured a flexible driving member 30.
- the latter is provided with a series of holes 31 for the reception of the reduced ends 32 of a plurality of studs 33 projecting from a disk or head 34 on the armature shaft 35 of the motor 13 as shown in Figure 3.
- a suitable driving connection is afforded between the motor and a lifting mechanism.
- the brake for the armature shaft comprises a shoe 36 adapted for engagement with the wheel or disk 28 on the worm shaft 27, the shoe being supported by a head 37 on an arm 38 pivoted at 39 upon the end of a bar 40 secured to the housing 23 of the lifting mechanism as shown in Figure 3.
- a depending rod or link 41 Connected with the inner end of the arm 38 is a depending rod or link 41 having on its lower end a head 42 through which operation of the rod is efiected.
- Projecting upwardly from the base of the housing 23 is a post or standard 43 having a laterally projecting plate 44 slotted at 45 for the passage therethrough of the brake shoe operating rod 41.
- a spring 46 is interposed between the plate 44 and the head 42 for applying the brake upon movement of the parts to the position shown in Figure 9.
- Movement of the brake to release position upon starting the motor is effected by a double acting bell crank lever 47 pivoted at 48 to the post 43 and provided with projecting pins or lugs 49 for engagement with the bottom of the head 42 of the brake rod, so that when the bell crank is swung in either direction the rod will be raised against the action of the spring as shown in Figure 10, whereby to release the brake.
- the bell crank operating means is so constructed as to be moved to brake release position whenever the operator depresses the main switch pedal, either to en ect raising or lowering of the chair, it being understood that the brakes will be held in release position aslong as the pedal remains deprssed,
- the bell crank is provided adjacent its lower end with a laterally projecting stud 5O adapted to receive the notched end of an arm 51 as shown in Figure 13.
- the arm at on side of the notch is provided with an extended portion 52 and at the opposite side of the notch with a downwardly extending operating shoulder 53.
- the stud is provided with a head 54 adapted to engage the extended arm portion 52 to guide the arm in its back and forth movement and to maintain it in the plane in which it is intended to operate.
- the arm is pivoted at 55 to a bracket 56 on the inner end of a lever 57 which in turn is pivoted at 58 to the annular upstanding por tion 59 of the chair base plate 11 as shown in Figures 3 and 9.
- the bracket 56 carries an upstanding pin on which is mounted a spring 61 disposed within a pocket formed in the outer end of the arm, as shown in Figure 10, the spring ser ing to yieldably hold the arm in normal operating position with respect to the bell crank 47.
- the lever 5'? is actuated by an ustable link 65 connected therewith for universal movement through a ball and socket connection 66 with which the lever is also adapted to have a pivotal movement.
- the link at its opposite end is connected with the lower end of a vertically disposed lever 67 through a ball and socket connection 63 pivotally engaging said lever.
- the lever 6' is pivoted at 6- to a bracket :'0 projecting upwartly from the base plate 11. Operation of lever to effect release of the brake in controlling the movements of the chair is effected by the pedal 71 for opeating the main switch, the several parts of which, including the wiring board 7 2, being disposed in a pocket or junction box 7 3 formed in the base section 11 of the chair.
- the limit switch indicated generally at 74 is removably disposed in pocket or junction box 75 in the base 11 while the line switch 76 is disposed in a pocket 77 formed in said base.
- the A. C. and D. C. motors are indicated diagrammatically at 7 8 and 7 9, respectively.
- Each of the motors is preferably provided with two plug and socket connections 80 and 81 which may be combined in a single connection if desired.
- the sockets are preterably carried by the motors and the fingers 82 which take into the sockets are adapted to project from a holder 83 on the free end of a conduit- 84 through which the circuit connections extend to the junction box 73 for connection with the switch plate 72 shown in Figure 1.
- the heavy lines indicate a closed or active circuit through the A. C. motor, while tl e light lines indicate, in part, the circuit arrangement for the D. C. motor, certain of the wires bei common to both circuits.
- the circuit for the A. C. motor is shown closed through the limit switch 74 with the latter in the position shown in Figure 24 after it has been actuated from the position shown in Figure 23 by the downward movement or" the chair to approximately its lowest position.
- the switch pedal 71 is rigidly connector with a pivot bolt 85 journaled in a hearing 86 on the s itch holding plate or.
- bracket 87 which forms a closure for the junction box 73 and which is detachably connected with the base 11 by means of the screws 87 extending through spacing lugs 83 on said plate and also through the plate 72 into the wall 88 of the junction box 73, the construction of which is indicated in Figure 6.
- a bell crank lever 90 Secured upon the pivot bolt 85 by means or" the key 89 is a bell crank lever 90 having upwardly extending and laterally projecting arms 91 and 92, respectively.
- the arm 91 carries a pin or projection 93 disposed in the to end of the brake operating lever 67 to release of the brake upon movement of 1': pedal to close the main switch when it is desired to start the motor.
- the arm 91 i connected through a link with an u: standing lever 95 pivoted 96 to the sw tcr plate 87, as shown Figures 13 and 17.
- upper end of the lever is provided wit roller 97 operable in a slot 93 formed i plunger or switch actuating rod 99 wl is guided at its opposite ends in suppo 100 and 101 carried by the plate 87.
- rod extends through a housing 102 and the end closures thereto-r against which the outer ends of a pair of springs 103 are seated as shown in Figure 17.
- tie springs engage adjacently mounted follower plates 104 which normally rests upon an in- Wardly projecting annular flange or shoulder 105 within the housing which is preferably formed integral therewith.
- the rod 99 car -ies a collar 106 rigid thereon which lies between the follower plates 104 as shown in Figure 18. From this construction it will be seen that the housing 102 may be moved in either direction merely by depressing the pedal to operate the bell crank 90 and through it the link 94 and lever 95.
- the housing carries a transversely extending bar 107 constructed of insulating material and having downwardly extending projections 108 at the opposite sides of its center adapted to engage the sides of the housing, to which they are connected by the screws .109.
- the bar 107 carries two separate plates 110 and 111, the former having two upstanding contact members 112 and the latter three similar contact members 113.
- Adjacent the switch operating plunger 99 is a plate of insulating material 114 having its ends disposed upon tne laterally extending lugs 100 and 101 of the bracket 87 to which it is secured by the screws 115 as shown in Figures 14 and
- the plate 114 is recessed to receive a plurality of fixed contact members on the 0pposite sides of the switch bar 107 carrying the movable contacts 112 and 113.
- the fixed Cfl-f. "act members, adapted for cooperation with the movable contacts 112, are indicated, two at 116 on one side of the movable contact and two at 117 on the other side thereof.
- the iixed contacts adapted for cooperation with the movable contacts 113, are indicated, three at 118 and the opposite three at 119, all being shown in Figure 15.
- the fixed contacts 117 and 119 carry a series of plugs 1 o 5 inclusive adapted to take into correspondingly arranged sockets formed in the switch plate 72 while the fixed contacts 116 and 118 carry a series of plugs 6 to 10 inclusive adapted to take into correspondingly arr .inged sockets in said plate.
- the plugs are each preferably threaded into the insulating plate 114 'iidicated at 120 in Figure 14 and are provided with nuts 121 serving to clamp the contact lingers upon said plate.
- the spring housing 102 is provided at one side with hree notches, indicated at 122, each of which is adapted to receive a'ball 123 arranged to trictionally engage the housing within the notches to hold said housing in its dii'lerent positions of adjustment under the pressure of a spring 124 mounted ina recess formed in an upstanding lug 125 on the bracket 87 between the lugs 100 and 101.
- I provide a relatively strong spring 126 of a capacity greater than that of both springs 103, each of which acts to afford the desired quick release under conditions which will be subsequently described.
- the spring 126 is preferably mounted within a bore or recess 127 formed in the base of the lug 101, as indicated in Figure 16 and 17.
- an operating stem- 128 suitably connected with the arm 92 of the bell crank 90 as by means of a roller 129 on the latter disposed within a recess 130 formed in the lower end of the stem 128.
- the stem at its upper end is provided with a head 131 engaging a follower 132 disposed within the bore 127, the follower being free to move inwardly but held against outward movement by a shoulder 133 formed as indicated in Figure 17.
- a second follower 134 normally resting upon a holder 135 in the form of a ring screwed into the lower end of the lug 101, and held against displacement by a set screw 136.
- the stem 128 is provided with lateral projections 137 operable through the ring and adapted to engage the follower 134 to move it against the action of the spring 126.
- the spring 126 is compressed by depression of the pedal in either direction so that pressure is stored up for returning the switch to normal inoperative position at the moment the pedal is released.
- the action of the spring 126 is such as to afford a quick movement of the bell-crank 90, which, through the connections provided, will. operate the plunger 99 to compress one or the other of the springs 103 against the resistance of the spring-pressed ball 123. in frictional engagement with the housing 102.
- the limit or automatic control switch 74 is adapted to be actuated by one of the adjustable sections of the chair in its up and down movements, preferably the outer section 15, through the medium of suitable parts associated therewith, such as the upper and lower pins or projections 138 and 139, respectively, in the path of which is located the controlling means for the limit switch which will presently be described.
- the limit switch embodies inner and outer switch plates 140 and 141 respectively, which are constructed of suitable insulating material and between which is disposed a metal plate 142, the several plates being connected by suitable bolts or screws 143 as shown in Figures 19 and 20.
- the inner plate 140 is provided with an undercut groove or recess 144 in which is guided a slide block 145 which is dovetailed on its outer face to receive the laterally projecting portion 146 of a holder 147 comprising a plate of insulating material having on its inner face a contact bar 148 secured by the screws 149.
- the contact bar 148 is adapted for reciprocation in an elongated recess 150 formed in the plate 141 as shown in Figures 19 and 23.
- the fixed contacts are each suitably secured to the plate 141 as by means of the studs 154 which preferably carry the binding posts for the several wires 151a, 152a and 153a connected with said contact as shown in Figure 25.
- the connection 151a leads to socketfor the plug 5 of the switch plate 72 and the opposite connection 153a to socket for the plug 10, each of said connections being adapted in conjunction with the connection 152a to complete, the motor circuit when the start ing switch is moved to closed position.
- the slide 145 is recessed to form a housing 154a for a spring 155a having its opposite ends engaging'follower plates 156 and 157 located within and being free to move inwardly of the housing.
- the followers are each held against outward movement by the end closures 158 of the housing.
- Projecting through the housing and through the spring therein is an operating stem 159 provided at one end with a head 160 engaging the fol lower 156 as shown in Figure 22.
- the stem is provided at its other end with lugs 161 disposed in engagement with the follower 157..
- the stem is recessed at its inner end to receive a roller 162 on the outer end of a lever 163 operable within a slot 164 formed by cutting away a portion of the plates 140 and 141 as shown in Figures 19 and 22.
- the lever is pivoted at 165 within the base plate 140 and'a bearing block 166 which is connected therewith by the screws 167 as shown in Figure 20.
- the lever is provided'at its in nor end with upper, lower and intermediate projecting portions 168, 169 and 170 res-pect-ively which terminatein the arc of a circle, the center of which preferably coincides with the pivotal axis of the lever.
- One or the other of these projections is at all times disposed in the path of the pins 138 and 139 on the movable chair section 15 so that if either of the pins is moved past the inner end of said lever it will engage one of the projections and shift the movable contact 148 to make or break the circuit as desired.
- the spring housing 145 is provided at one side with three notches as indicated at 171, each of which is adapted to receive a ball 172 held in frictional engagement with the housing by a spring 173 disposed in a recess formed in the base plate 140 and secured therein preferably by a screw plug 174 as shown in Figure 22.
- a spring 173 disposed in a recess formed in the base plate 140 and secured therein preferably by a screw plug 174 as shown in Figure 22.
- a base a standard adapted for reciprocation upon the base
- operating means for the standard including a reversible electric motor having circuit connections leading thereto, a reversing switch interposed in said connections, manually controlled actuating means for the switch arranged to hold it in closed position during movement of the standard, a brake for the operating means, actuating means for releasing the brake engaged by and responsive to movemen' of said manually controlled means and including a part movable to free the brake for to braking position, means for returning the brake to said position when released by said part, and release means for said part actuated by the standard in a predetermined position thereof when the switch is in circuit closing position.
- a base a movable sec tion thereon, reversible driving mechanism for moving said section in opposite directions, manually cont-rolled means for effecting reversal of the driving mechanism, a spring actuated brake for the driving mechanism normally in braking position, actuating means for the brake engaged by and responsive to movement of the manually controlled means when the latter is moved from normal to operating position, said actuating means comprising relatively movable parts one of which is movable to free the brake for return to braking position, and means actuated by said movable section in a predetermined position thereof arranged to operate said movable brake releasing part with the manually controlled means held in operating position.
- a base an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible motor, a spring actuated brake for the driving mechanism, manually controlled means for effecting reversal of the motor, a lever adapted to be actuated by said manually controlled means upon movement of the to reverse the motor, and mechanical connections interposed between the lever and the brake wl ereby the latter is moved to rease position upon starting the motor, one of 'd connections being movable to a predeternined position to free the brake for application by the spring and means actuated by the section in one position thereof for moving said connection to said position.
- a base an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible electric motor having circuit connections leading thereto, a brake for the driving mechanis comprising a pivoted shoe having an actuating member and a spring engaging the same adapted to normally apply the brake, an operating member for said actuating member adapted to effect release of the brake when moved to either of two positions, the operatmember being releasable when in either of said positions to release the actuating member a manually controlled reversing switch interposed in said connections, means operatively associated with the switch adapted to actuate said operating member upon closing the switch whereby to release the brake and means arranged to be actuated by said section in one position thereof to release said operating member whereby to release the actuating member for return to brake applying position.
- a base an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible electric motor having circuit connections leading th reto, a manually controlled reversible switch interposed in said connections, a brake for said drivin mechanism including spring actuated shoe normally held in braking position, an oscillatory member adapted upon movement in either direction to effect release of the shoe, a releasable actuating member for said oscillatory member, means interposed between said releasable actuating member and said switch adapted upon movement of the latter to either of its closing positions to op rate said releasable member whererelease of the brake, and means said actuating member adapted erated by the adjustable section in a mined position of the latter.
- a base an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible' electric motor having circuit connections leadin thereto, a manually controlled reversing switch interposed in said connections, a brake for said driving mechanism, actuating means for the brake including a releasable connection, said actuating means being ope "atively associated with the switch and adapted upon movement of the latter to either of its closing positions to effect release of the brake, and means adapted to be operated by the section in a predetermined position of the latter to effect application of the brake by moving said releasable connection to in operative position.
- a base an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible electric motor, a reversing switch for the motor circuit, a spring actuated brake for the driving mechanism normally held in braking position, an oscillatory member operatively connected with the brake and adapted when moved in diiierent directions to effect release of the same, a lever connected with the switch for operation thereby, a spring-pressed member pivoted upon the lever and adapted to effect operation, of said oscillatory member upon movement of the switch to its different closing positions, and means adapted to be actuated by the section when approaching one of its extreme positions, whereby the spring-pressed member is operated to release position to permit application of the brake.
- a reversible electric motor for operating a reciprocally mounted support between predetermined points
- a reversing switch for the motor
- a limit switch electrically connected with the reversing switch and arranged to be moved todiiierent positions by the support at said points and to an intermediate position in advance of movement of the support to said points
- the last mentioned operation of the limit switch serving to condition it for cooperation with the reversing switch in one position of the latter subsequent to operation of the limit switch by the support at one of said points
- a self applying brake for the motor arranged to be released by the reversing switch, and means for freeing the brake for return to braking position arranged for operation by the support upon movement of the latter to a'predetermined position with the reversing switch in circuit closing position.
- a base a support reciprocally mounted upon the base, operating means for the support including a reversible electric motor for moving the support to different predetermined positions, a reversing switch for the motor, a limit switch having a plurality of circuit closing positions to all of which it is moved by the support for cooperation with the reversing switch and to certain of which it is moved by the support when the latter reaches said predetermined positions while to another of which it is moved by the support when the latter is moving between said predetermined positions, a brake for the motor movable to a non-braking position by an operating portion of the reversing switch when the switch is moved to close the motor circuit, means for applying the brake when released from said position, and means actuated by the sup ort in a predetermined position thereof to ree the brake for application by said means while the reversing switch is in closed position.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Mechanisms For Operating Contacts (AREA)
- Seats For Vehicles (AREA)
- Slide Switches (AREA)
- Chairs Characterized By Structure (AREA)
- Accommodation For Nursing Or Treatment Tables (AREA)
- Dental Tools And Instruments Or Auxiliary Dental Instruments (AREA)
Description
y 3, 1932- A. J. MAY. 1,856,493
EXTENS IBLE CHAIR Filed Nov. 20, 1925 8 Sheets-Sheet 1 May 3, 1932. J MAY 7 1,856,493
EXTENS IBLE CHAIR Filed Nov. 20, 1925 8 Sheets-Sheet 2 I May 3, 1932. A. J. MAY
EXTENSIBLE CHAI'R Filed Nov. 20, 1925 8 Sheets-Sheet 5 INVENTOR.
45s ATTORNEY A. J. MAY
EXTENSIBLE CHAIR Filed Nov. 20, 1925 8 Sheets-Sheet 4 May 3, 1932.
Patented May 3, 1932 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE ADAM J. MAY, OF ROCHESTER, NEW YORK, ASSIGNOR, BY MESNE ASSIGNMENTS, TO BITTER DENTAL MANUFACTURING COMPANY, INC., OF ROCHESTER, NEW YORK, A
CORPORATION OF DELAWARE EXTENSIBLE CHAIR Application filed November 20, 1925.
The present invention relates to extensible chairs, and has for one object to provide improved operating and control mechanism applicable to dental, surgical, barbers and other types of chairs.
A further object of the invention is to provide an extensible motor actuated chair or lifting mechanism having improved electric control devices for automatically rendering the motor ineffective when the parts have reached the limit of their range of adjustment, the devices being coordinated to eflect control of the different movements of the parts so as to simplify the work of the operator in the adjustments of the chair to the different working positions required from time to time.
A further object of the invention is to provide improved operating means for the chair including a manually controlled electric switch and a brake for the driving means operatively associated with the switch for control thereby and also with certain of the movable parts of the chair whereby the brake is applied automatically when said parts are moved to a predetermined position of adj ustment.
A further object of the invention is to provide an extensible chair having a liftin mechanism adapted to be motor driven and so constructed as to readily receive either a direct or alternating current motor without necessitating removal or adjustment of any of the circuit connections for the motor, thus requiring only the removal of one motor and the substitution of the other whereby the manufacturer may build a standard unit which can be shipped complete and ready for service with either type of motor that may be required.
A further object of the invention is to provide an improved type of switch including yieldable means adapted to be compressed upon moving the switch to closed position whereby to afford an extremely quick release of the movable contacts of the switch in order to prevent arcing when the circuit is broken.-
A still further object of the invention is to provide in combination with a movable chair Serial N 0. 70,241.
section and a reversible motor for operating the same, a manually controlled two-way switch and an automatic chair controlled limit switch with circuit connections so arranged that the limit switch will have one closing position common to both closing positions of the two-way switch and two other positions, in each of which it is adapted to open the motor circuit with the main switch in one operating position and to close it with the main switch in another operating position.
Another object of the invention is to provicle a simple, compact and eficient form of chair construction embodying extensible standards or sections and lifting means therefor including a reversible electric motor and a main manually controlled reversing switch connected with the limit switch and arranged to be operated automatically by one of the chair sections as it approaches the limits of its range of adjustment.
To these and other ends the invention resides in certain improvements and combinations of parts, all as will be hereinafter more fully described, novel features being pointed out in the claims at the end of the specification.
In the drawings Figure 1 is a diagrammatic view illustrating the circuit arrangement of an A. C. and D. C. motor together with the switches therefor in connection with a part sectional plan of the chair base showing the several junction boxes for the switches and a conduit for enclosing the circuit connections;
Figure 2 is a diagrammatic View in elevation illustrating a portion of an extensible chair with the operating pins or projections for the limit switch shown on one of the adjustable sections;
Figure 3 is a fragmentary part sectional plan of the chair illustrating the manner of connecting the motor with the lifting mechanism and showing the brake arrangement for the motor driven shaft; v
Figure 4 is a fragmentary sectional elevation taken on line 4:ata of Figure 3, showing one of the extensible chair sections nearing its lowest position at which it effects control of the brake;
Figure 5 is a similar view showing the section in operating position with respect to the brake tripping lever;
Figure 6 is a sectional plan through the chair base showing the construction of the extensible sections and indicating the relation of the main switch with respect to the outer section;
Figure 7 is a detail view of a part of the brake mechanism;
Figure 8 is a similar view in which the parts are moved to release the brakes;
Figure 9 is a fragmentary sectional eleva tion illustrating the motor drive connection for the lifting mechanism and the brake control mechanism therefor;
Figure 10 is a somewhat similar view showing the brake mechanism in release position;
Figure 11 is an elevation as viewed from the left of Figure 10, with the motor shaft removed and the brake in release position Figure 12 is a view in elevation similar to the upper half of Figure 11 with the brake shown applied;
Figure 13 is an enlarged detail view illustrating the double bell-crank for releasing the brake as shown in Figure 10;
Figure 14 is a top plan view of the main switch with certain portions shown in section;
Figure 15 is an elevational view of the switch looking at the side nearest the axis of the chair;
Figure 16 is a bottom plan view of the switch;
Figure 17 is a sectional elevation taken on line 17 a17 a of Figure 16;
Figure 18 is an enlarged detail section through one of the spring housings for the switch shown in Figure 17;
Figure 19v is afront elevational view of the limit switch shown in Figure 1;
Figure 20 is a side elevation of the same as viewed from the right of Figure 19;
Figure 21 is a side elevation as viewed from the left of Figure 19;
Figure 22 is a view in elevation somewhat similar to Figure 1.9 with parts shown in section to illustrate the construction of the re versible plunger mechanism and its retaining means;
Figure 23 is a sectional elevation taken on line 23a23a of Figure 19, showing the movable contact member in central position and illustrating one position of the switch operating projections on the outer movable section of the chair;
Figure 24 is a similar section showing the switch after operation by the chair to one of its circuits braking positions, and
Figure 25 is a sectional plan taken on line 25a25a of Figure 22.
Similar reference numerals throughout the several views indicate the same parts.
In the present invention I have provided a chair having extensible sections and suitable raising and lowering means therefor, each of which may be of any desired or Well known construction. The lifting mechanism has, however, been designed in such a way as to adapt it for the ready reception of either a direct or alternating current motor, merely by the insertion of either of these types of motors in position upon the base of the chair. Furthermore, the plug and socket connections for the different types of motors are designed to interchange so that when assembling either motor no time is lost in making the necessary connections.
The limit or safety switch for breaking the circuits when the chair sections are approach ing the limits of their adjustment in either direction, serves to automatically interrupt the motor circuit while the brake for the driving mechanism, applied automatically by one of the chair sections on approaching the end of its downward stroke, prevents overrunning of the sections regardless of the fact that the operator may forget to release the pedal of the main switch at the proper time. Furthermore, the brake which is under the control of the pedal switch is automatically applied upon release of the pedal whereby to prevent coasting of the chair sections after the motor circuit is broken.
Referring to the drawings, 11 and 11 represent the upper and lower fixed or base sections of the chair, the former having an openin at one side provided with a vertically isposed flanged portion 12 for the reception either of an A. C. or D. C. motor, one of which is shown at 13 in Figures 2 and 3. The inner and outer extensible sections or standards are indicated generally at 14 and 15, respectively. The outer section is suitably guided within the base 11 by opposite sets of rollers 16, only one of which is shown, while the inner section 14 is guided within the outer section by the opposite sets of rollers 17 and 18. The inner section carries at its upper end a chair support, not shown, between whieh and the base member 11' is disposed any suitable form of lifting mechanism. This mechanism may be of the gear driven screw type arranged for operation by a gear 19 at the center of the chair base which in turn is driven by another gear 20 meshing with a third gear 21 on the bottom of a vertical shaft 22, disposed with a housing 23 carried by a base or frame 24 supported by the base plate 11. The housing is provided with a removable cover plate 24' as shown in Figure 3. The upper end of the shaft 22 is provided with a gear 25 meshing with a worm 26 on a transverse shaft 27 journaled in a suitable bearing box 27', the upper half of which is removable, the lower half of the box being preferably cast integral with the housing 23. The worm shaft 27 carries a disk or Wheel 28 having laterally projecting lugs 29 upon the outer ends of which is secured a flexible driving member 30. The latter is provided with a series of holes 31 for the reception of the reduced ends 32 of a plurality of studs 33 projecting from a disk or head 34 on the armature shaft 35 of the motor 13 as shown in Figure 3. Thus, it will be seen that upon positioning the motor upon the base the ends 32 of the studs 33 will readily take into the holes 31 of the flexible member 30 whereby a suitable driving connection is afforded between the motor and a lifting mechanism. This is of course true with respect to both types of motors, as in each case the same construction is provided at the inner end of the armature shaft.
The brake for the armature shaft comprises a shoe 36 adapted for engagement with the wheel or disk 28 on the worm shaft 27, the shoe being supported by a head 37 on an arm 38 pivoted at 39 upon the end of a bar 40 secured to the housing 23 of the lifting mechanism as shown in Figure 3. Connected with the inner end of the arm 38 is a depending rod or link 41 having on its lower end a head 42 through which operation of the rod is efiected. Projecting upwardly from the base of the housing 23 is a post or standard 43 having a laterally projecting plate 44 slotted at 45 for the passage therethrough of the brake shoe operating rod 41. A spring 46 is interposed between the plate 44 and the head 42 for applying the brake upon movement of the parts to the position shown in Figure 9. Movement of the brake to release position upon starting the motor is effected by a double acting bell crank lever 47 pivoted at 48 to the post 43 and provided with projecting pins or lugs 49 for engagement with the bottom of the head 42 of the brake rod, so that when the bell crank is swung in either direction the rod will be raised against the action of the spring as shown in Figure 10, whereby to release the brake.
The bell crank operating means is so constructed as to be moved to brake release position whenever the operator depresses the main switch pedal, either to en ect raising or lowering of the chair, it being understood that the brakes will be held in release position aslong as the pedal remains deprssed, The bell crank is provided adjacent its lower end with a laterally projecting stud 5O adapted to receive the notched end of an arm 51 as shown in Figure 13. The arm at on side of the notch is provided with an extended portion 52 and at the opposite side of the notch with a downwardly extending operating shoulder 53. The stud is provided with a head 54 adapted to engage the extended arm portion 52 to guide the arm in its back and forth movement and to maintain it in the plane in which it is intended to operate. The arm is pivoted at 55 to a bracket 56 on the inner end of a lever 57 which in turn is pivoted at 58 to the annular upstanding por tion 59 of the chair base plate 11 as shown in Figures 3 and 9. The bracket 56 carries an upstanding pin on which is mounted a spring 61 disposed within a pocket formed in the outer end of the arm, as shown in Figure 10, the spring ser ing to yieldably hold the arm in normal operating position with respect to the bell crank 47.
As a afety means for automatically eflecting application of the brake, should the operator fail to release the switch pedal as the aches its lower limit of adjustovide a trip lever 62 pivoted at 34 disposed on the base plate clret lair as shown in Figures 4 and 5. 0*. the lever extends under the bell erating arm 51 while the opposite the path of the extensible chair e l atoly returned to central position by the 45, thus permit ing the brake to be simullaneous? applied whereby to arrest further mov meat of chair sections. After return of the bell crank to central poi the chair sections raised from the position shown in Figure 5 t that shown the in 4, the spring 31 will lower the arm and the stud 5-0 will. then reengage the latter withi o notch thereof as shown in Figure 9, i understood that in this position of s the switch pedal will be in nori It will be further uniat the maximum lift of the trip is n t sufficient to raise the shoulder 53 of the arm above the stud 50, whereby retur rm to the proper position by the sprin is assured. The lever 5'? is actuated by an ustable link 65 connected therewith for universal movement through a ball and socket connection 66 with which the lever is also adapted to have a pivotal movement. The link at its opposite end is connected with the lower end of a vertically disposed lever 67 through a ball and socket connection 63 pivotally engaging said lever. The lever 6' is pivoted at 6- to a bracket :'0 projecting upwartly from the base plate 11. Operation of lever to effect release of the brake in controlling the movements of the chair is effected by the pedal 71 for opeating the main switch, the several parts of which, including the wiring board 7 2, being disposed in a pocket or junction box 7 3 formed in the base section 11 of the chair.
The limit switch indicated generally at 74 is removably disposed in pocket or junction box 75 in the base 11 while the line switch 76 is disposed in a pocket 77 formed in said base.
The A. C. and D. C. motors are indicated diagrammatically at 7 8 and 7 9, respectively. Each of the motors is preferably provided with two plug and socket connections 80 and 81 which may be combined in a single connection if desired. The sockets are preterably carried by the motors and the fingers 82 which take into the sockets are adapted to project from a holder 83 on the free end of a conduit- 84 through which the circuit connections extend to the junction box 73 for connection with the switch plate 72 shown in Figure 1. In this figure the heavy lines indicate a closed or active circuit through the A. C. motor, while tl e light lines indicate, in part, the circuit arrangement for the D. C. motor, certain of the wires bei common to both circuits. The circuit for the A. C. motor is shown closed through the limit switch 74 with the latter in the position shown in Figure 24 after it has been actuated from the position shown in Figure 23 by the downward movement or" the chair to approximately its lowest position.
The switch pedal 71 is rigidly connector with a pivot bolt 85 journaled in a hearing 86 on the s itch holding plate or. bracket 87 which forms a closure for the junction box 73 and which is detachably connected with the base 11 by means of the screws 87 extending through spacing lugs 83 on said plate and also through the plate 72 into the wall 88 of the junction box 73, the construction of which is indicated in Figure 6. Secured upon the pivot bolt 85 by means or" the key 89 is a bell crank lever 90 having upwardly extending and laterally projecting arms 91 and 92, respectively. The arm 91 carries a pin or projection 93 disposed in the to end of the brake operating lever 67 to release of the brake upon movement of 1': pedal to close the main switch when it is desired to start the motor. The arm 91 i connected through a link with an u: standing lever 95 pivoted 96 to the sw tcr plate 87, as shown Figures 13 and 17. upper end of the lever is provided wit roller 97 operable in a slot 93 formed i plunger or switch actuating rod 99 wl is guided at its opposite ends in suppo 100 and 101 carried by the plate 87. rod extends through a housing 102 and the end closures thereto-r against which the outer ends of a pair of springs 103 are seated as shown in Figure 17. The inner ends of tie springs engage adjacently mounted follower plates 104 which normally rests upon an in- Wardly projecting annular flange or shoulder 105 within the housing which is preferably formed integral therewith. The rod 99 car -ies a collar 106 rigid thereon which lies between the follower plates 104 as shown in Figure 18. From this construction it will be seen that the housing 102 may be moved in either direction merely by depressing the pedal to operate the bell crank 90 and through it the link 94 and lever 95. The housing carries a transversely extending bar 107 constructed of insulating material and having downwardly extending projections 108 at the opposite sides of its center adapted to engage the sides of the housing, to which they are connected by the screws .109. The bar 107 carries two separate plates 110 and 111, the former having two upstanding contact members 112 and the latter three similar contact members 113. Adjacent the switch operating plunger 99 is a plate of insulating material 114 having its ends disposed upon tne laterally extending lugs 100 and 101 of the bracket 87 to which it is secured by the screws 115 as shown in Figures 14 and The plate 114 is recessed to receive a plurality of fixed contact members on the 0pposite sides of the switch bar 107 carrying the movable contacts 112 and 113. The fixed Cfl-f. "act members, adapted for cooperation with the movable contacts 112, are indicated, two at 116 on one side of the movable contact and two at 117 on the other side thereof. The iixed contacts, adapted for cooperation with the movable contacts 113, are indicated, three at 118 and the opposite three at 119, all being shown in Figure 15. The fixed contacts 117 and 119 carry a series of plugs 1 o 5 inclusive adapted to take into correspondingly arranged sockets formed in the switch plate 72 while the fixed contacts 116 and 118 carry a series of plugs 6 to 10 inclusive adapted to take into correspondingly arr .inged sockets in said plate. The plugs are each preferably threaded into the insulating plate 114 'iidicated at 120 in Figure 14 and are provided with nuts 121 serving to clamp the contact lingers upon said plate.
By depressing the right side of the pedal, as viewed in Figure 6, the movable contacts 112 and 113 will engage the fixed contacts 117 and 119, respectively, whereby to release the brake and start the motor to efiect raising of the chair. Depression of the left side of the pedal will likewise release the brake and effect reversal of the motor to lower the chair when the movable contacts are shifted to engage the fixed contacts 116 and 118.
The spring housing 102 is provided at one side with hree notches, indicated at 122, each of which is adapted to receive a'ball 123 arranged to trictionally engage the housing within the notches to hold said housing in its dii'lerent positions of adjustment under the pressure of a spring 124 mounted ina recess formed in an upstanding lug 125 on the bracket 87 between the lugs 100 and 101.
As a'means for building up pressure during movement of the pedal in either direction by the operator whereby to afford a quick break between the movable and fixed con tacts of the switch to prevent arcing and the consequent burning of the parts, I provide a relatively strong spring 126 of a capacity greater than that of both springs 103, each of which acts to afford the desired quick release under conditions which will be subsequently described. The spring 126 is preferably mounted within a bore or recess 127 formed in the base of the lug 101, as indicated in Figure 16 and 17. Extending through the spring and into the bore is an operating stem- 128 suitably connected with the arm 92 of the bell crank 90 as by means of a roller 129 on the latter disposed within a recess 130 formed in the lower end of the stem 128. The stem at its upper end is provided with a head 131 engaging a follower 132 disposed within the bore 127, the follower being free to move inwardly but held against outward movement by a shoulder 133 formed as indicated in Figure 17. At the opposite end of the bore is provided a second follower 134, normally resting upon a holder 135 in the form of a ring screwed into the lower end of the lug 101, and held against displacement by a set screw 136. The stem 128 is provided with lateral projections 137 operable through the ring and adapted to engage the follower 134 to move it against the action of the spring 126. Thus, it will be seen that the spring 126 is compressed by depression of the pedal in either direction so that pressure is stored up for returning the switch to normal inoperative position at the moment the pedal is released. Upon releasing the switch from either of its closing positions the action of the spring 126 is such as to afford a quick movement of the bell-crank 90, which, through the connections provided, will. operate the plunger 99 to compress one or the other of the springs 103 against the resistance of the spring-pressed ball 123. in frictional engagement with the housing 102. Considerable pressure is required for the spring 103 to overcome the resistance of the ball and therefore the hous ng 102, carrying the movable contact, will remain inactive until the resistance of the spring-pressed ball is overcome, at which time quick action will be afforded by one or the other of the springs 103 in returning the housing and movab e contacts to central position as ind cated in Figures 14 to 16 inclusive. The same action of course takes place when moving the pedal to close the switch so that a slow movement of the two sets of contacts 112 and 113 is avoided when they are thrown either into or out of engagement with the yield-able finger contacts.
As indicated in Figure 1, certain of the sockets at one side of the switch are shown connected with certain of those at the opposite side, it being understood that the arrangement is such as to afford reversal of the motor from either operating position regardless of whether an A. C. or D. C. motor is employed. WVith the wiring arrangement shown the several circuits can be easily traced for the two types of motors with the switch in either closing position. In this connection, it will be understood that the limit switch 74 is included in the circuit, and that with the latter in central position as indicated in Fig ure 23 the motor will become operative upon moving the starting switch in either of its closing positions regardless of the type of motor used. However, with the limit switch in the position indicated in Figures 1 and 24 the circuit through the main or starting switch can only be closed with the movable contacts of the latter adjusted to engage the fixed contacts 117 and 119, the plugs 1 to 5 of which take into a series of correspondingly arranged sockets formed in the right side of the switch plate 72 while the opposite plugs 6 to 10 inclusive take into a set of correspondingly arranged sockets formed in the left side of the said plate. With the limit switch in the extreme reverse position from that shown in Figures 1 and 24 the circuit will be closed, and the motor reversed when the movable contacts of the main switch engage the fixed contacts 116 and 118. In the first named position of the switches the motor will operate to raise the chair while in the last named position it will operate to lower the same.
The limit or automatic control switch 74 is adapted to be actuated by one of the adjustable sections of the chair in its up and down movements, preferably the outer section 15, through the medium of suitable parts associated therewith, such as the upper and lower pins or projections 138 and 139, respectively, in the path of which is located the controlling means for the limit switch which will presently be described.
The limit switch embodies inner and outer switch plates 140 and 141 respectively, which are constructed of suitable insulating material and between which is disposed a metal plate 142, the several plates being connected by suitable bolts or screws 143 as shown in Figures 19 and 20. The inner plate 140 is provided with an undercut groove or recess 144 in which is guided a slide block 145 which is dovetailed on its outer face to receive the laterally projecting portion 146 of a holder 147 comprising a plate of insulating material having on its inner face a contact bar 148 secured by the screws 149. The contact bar 148 is adapted for reciprocation in an elongated recess 150 formed in the plate 141 as shown in Figures 19 and 23. Mounted on the inner face of the plate 141 are three fixed contacts 151,152 and 153, which extend within the recess in the path of the movable contact 148 for engagement therewith, the latter having three different operating positions corresponding to different positions of the chair as will be subsequently explained. The fixed contacts are each suitably secured to the plate 141 as by means of the studs 154 which preferably carry the binding posts for the several wires 151a, 152a and 153a connected with said contact as shown in Figure 25. The connection 151a leads to socketfor the plug 5 of the switch plate 72 and the opposite connection 153a to socket for the plug 10, each of said connections being adapted in conjunction with the connection 152a to complete, the motor circuit when the start ing switch is moved to closed position.
The slide 145 is recessed to form a housing 154a for a spring 155a having its opposite ends engaging'follower plates 156 and 157 located within and being free to move inwardly of the housing. The followers are each held against outward movement by the end closures 158 of the housing. Projecting through the housing and through the spring therein is an operating stem 159 provided at one end with a head 160 engaging the fol lower 156 as shown in Figure 22. The stem is provided at its other end with lugs 161 disposed in engagement with the follower 157.. The stem is recessed at its inner end to receive a roller 162 on the outer end of a lever 163 operable within a slot 164 formed by cutting away a portion of the plates 140 and 141 as shown in Figures 19 and 22. The lever is pivoted at 165 within the base plate 140 and'a bearing block 166 which is connected therewith by the screws 167 as shown in Figure 20. The lever is provided'at its in nor end with upper, lower and intermediate projecting portions 168, 169 and 170 res-pect-ively which terminatein the arc of a circle, the center of which preferably coincides with the pivotal axis of the lever. One or the other of these projections is at all times disposed in the path of the pins 138 and 139 on the movable chair section 15 so that if either of the pins is moved past the inner end of said lever it will engage one of the projections and shift the movable contact 148 to make or break the circuit as desired.
The spring housing 145 is provided at one side with three notches as indicated at 171, each of which is adapted to receive a ball 172 held in frictional engagement with the housing by a spring 173 disposed in a recess formed in the base plate 140 and secured therein preferably by a screw plug 174 as shown in Figure 22. Thus means is provided for resisting movement of the slide 145 and the movable contact 148 carried thereby until a predetermined pressure has been built up in the spring 155 sufficient to overcome the resistance of the ball, following which an extremely quick break between the movable and fixed contacts of the switch will be afforded by the action of the spring in moving the slide from one position to another,
whereby arcing is avoided and the consequent burning of the contacts prevented, which would not be the case under a slow movement of the parts. This is true regardless of the direction of movement of the operating stem 159 and the lever 163 for moving the same.
In the operation of the chair, assuming it is desired to raise it from its lowest position as indicated by the movable section 15 I p in Figure 24, the right side of the pedal as viewed in Figure 6 is depressed by the operator. This operation simultaneously releases the brake and shifts the movable contacts 112 and 113 to the right as viewed in Figure 1 and into engagement with the fixed contacts 117 and 119 and closes the motor circuit through plugs 1, 2, 8, 7, 3, 4 and 5, either for the A. C. or D. C. motor, when it is desired to raise the chair. The motor is thus started and the lifting mechanism placed in operation, it being understood that the limit switch at this time will be in the position indicated in Figures 1 and 24. As the chair sect-ion 15 is moved up the pin 138 will engage the projection 168 of the lever 163 and move the switch to the position shown in Figure 23 without breaking the circuit. The operator retains his foot upon the pedal until the chair is raised to the height desired and immediately upon release of the pedal the motor circuit is broken by return of the main switch to normal inoperative position through the action of the pedal operating spring 126. Return of the pedal also permits return of the brake through the action of the brake control spring 46 which serves to move the parts from the position shown in Figures 10 and 11 to that shown in Figures 9 and 12. In the operation just described, should the chair sections be raised to substantially their maximum height the motor circuit will be automatically broken by downward movement of the contact 148 whereby it is disengaged from the fixed contact 153. This is effected through upward movement of the lower pin 139 of the section 15 into engagement with the projection 170 of the switch operating lever. The lever 163 is thus tripped to move the projection 169 thereof into the path of the pin 139 which will again return the lever and the switch to the position shown in Figure 23 when the pedal is moved to the left to reverse the motor for the purpose of lowering the chair, it being understood that the return of the limit switch to its intermediate position does not break the circuit, which is now closed through the plugs 1, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10. Upon release of the pedal on the downward movement of the chair, coast-ing of the latter will be autoiio iis
iao
matically prevented by the simultaneous application of the brake, the latter being pro vided primarily for this purpose. This is true in any position at which the chair may be released in its downward movement. With the chair section 15 in the position shown in Figure 23, the projection 170 of the lever 163 is in position to be engaged by either of the pins 138 or 139 and it will be operated by one or the other thereof, depending upon the direction and extent of movement of the section from the position shown in said figure. The switch in this figure is in a position common to both circuits so that should the operator depress the pedal either to the right or left the motor will be started. Furthermore, should the operator fail to release the pedal to brake the circuit when the chair approaches its lower limits of adjustment the brake will be automatically applied through operation of the brake release lever 62 by chair section 15 as shown in Figure 5. The brake is thus simultaneously applied because of the fact that the arm 51 is raised to release the bell-or i lever 47 which in turn releases the pressure of the spring 46 and permits the latter to force the rod ll downwardly and apply the brake as shown in Figure 12.
I claim as my invent-ion:
1. In combination, a base, a standard adapted for reciprocation upon the base, operating means for the standard including a reversible electric motor having circuit connections leading thereto, a reversing switch interposed in said connections, manually controlled actuating means for the switch arranged to hold it in closed position during movement of the standard, a brake for the operating means, actuating means for releasing the brake engaged by and responsive to movemen' of said manually controlled means and including a part movable to free the brake for to braking position, means for returning the brake to said position when released by said part, and release means for said part actuated by the standard in a predetermined position thereof when the switch is in circuit closing position.
2. In combination, a base, a movable sec tion thereon, reversible driving mechanism for moving said section in opposite directions, manually cont-rolled means for effecting reversal of the driving mechanism, a spring actuated brake for the driving mechanism normally in braking position, actuating means for the brake engaged by and responsive to movement of the manually controlled means when the latter is moved from normal to operating position, said actuating means comprising relatively movable parts one of which is movable to free the brake for return to braking position, and means actuated by said movable section in a predetermined position thereof arranged to operate said movable brake releasing part with the manually controlled means held in operating position.
3. In combination, a base, an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible motor, a spring actuated brake for the driving mechanism, manually controlled means for effecting reversal of the motor, a lever adapted to be actuated by said manually controlled means upon movement of the to reverse the motor, and mechanical connections interposed between the lever and the brake wl ereby the latter is moved to rease position upon starting the motor, one of 'd connections being movable to a predeternined position to free the brake for application by the spring and means actuated by the section in one position thereof for moving said connection to said position.
4. In combination, a base, an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible electric motor having circuit connections leading thereto, a brake for the driving mechanis comprising a pivoted shoe having an actuating member and a spring engaging the same adapted to normally apply the brake, an operating member for said actuating member adapted to effect release of the brake when moved to either of two positions, the operatmember being releasable when in either of said positions to release the actuating member a manually controlled reversing switch interposed in said connections, means operatively associated with the switch adapted to actuate said operating member upon closing the switch whereby to release the brake and means arranged to be actuated by said section in one position thereof to release said operating member whereby to release the actuating member for return to brake applying position.
5. In combination, a base, an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible electric motor having circuit connections leading th reto, a manually controlled reversible switch interposed in said connections, a brake for said drivin mechanism including spring actuated shoe normally held in braking position, an oscillatory member adapted upon movement in either direction to effect release of the shoe, a releasable actuating member for said oscillatory member, means interposed between said releasable actuating member and said switch adapted upon movement of the latter to either of its closing positions to op rate said releasable member whererelease of the brake, and means said actuating member adapted erated by the adjustable section in a mined position of the latter. 6. In combination, a base, an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible' electric motor having circuit connections leadin thereto, a manually controlled reversing switch interposed in said connections, a brake for said driving mechanism, actuating means for the brake including a releasable connection, said actuating means being ope "atively associated with the switch and adapted upon movement of the latter to either of its closing positions to effect release of the brake, and means adapted to be operated by the section in a predetermined position of the latter to effect application of the brake by moving said releasable connection to in operative position.
7. In combination, a base, an adjustable section thereon, driving mechanism for raising and lowering the section including a reversible electric motor, a reversing switch for the motor circuit, a spring actuated brake for the driving mechanism normally held in braking position, an oscillatory member operatively connected with the brake and adapted when moved in diiierent directions to effect release of the same, a lever connected with the switch for operation thereby, a spring-pressed member pivoted upon the lever and adapted to effect operation, of said oscillatory member upon movement of the switch to its different closing positions, and means adapted to be actuated by the section when approaching one of its extreme positions, whereby the spring-pressed member is operated to release position to permit application of the brake.
8. In combination, a reversible electric motor for operating a reciprocally mounted support between predetermined points, a reversing switch for the motor, a limit switch electrically connected with the reversing switch and arranged to be moved todiiierent positions by the support at said points and to an intermediate position in advance of movement of the support to said points, the last mentioned operation of the limit switch serving to condition it for cooperation with the reversing switch in one position of the latter subsequent to operation of the limit switch by the support at one of said points, a self applying brake for the motor arranged to be released by the reversing switch, and means for freeing the brake for return to braking position arranged for operation by the support upon movement of the latter to a'predetermined position with the reversing switch in circuit closing position.
9. In combination, a base, a support reciprocally mounted upon the base, operating means for the support including a reversible electric motor for moving the support to different predetermined positions, a reversing switch for the motor, a limit switch having a plurality of circuit closing positions to all of which it is moved by the support for cooperation with the reversing switch and to certain of which it is moved by the support when the latter reaches said predetermined positions while to another of which it is moved by the support when the latter is moving between said predetermined positions, a brake for the motor movable to a non-braking position by an operating portion of the reversing switch when the switch is moved to close the motor circuit, means for applying the brake when released from said position, and means actuated by the sup ort in a predetermined position thereof to ree the brake for application by said means while the reversing switch is in closed position.
ADAM J. MAY.
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US70241A US1856493A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1925-11-20 | Extensible chair |
| US129273A US1763245A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-08-14 | Electric-circuit-control means |
| US134741A US1760763A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-09-10 | Electric-circuit-control means |
| FR626118D FR626118A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-11-19 | Elevation chair improvements |
| GB29302/26A GB261774A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-11-19 | Improvements in or relating to adjustable chairs |
| DER69362D DE494842C (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-11-21 | Adjustable operating chair |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US70241A US1856493A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1925-11-20 | Extensible chair |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US1856493A true US1856493A (en) | 1932-05-03 |
Family
ID=22094068
Family Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US70241A Expired - Lifetime US1856493A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1925-11-20 | Extensible chair |
| US129273A Expired - Lifetime US1763245A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-08-14 | Electric-circuit-control means |
| US134741A Expired - Lifetime US1760763A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-09-10 | Electric-circuit-control means |
Family Applications After (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US129273A Expired - Lifetime US1763245A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-08-14 | Electric-circuit-control means |
| US134741A Expired - Lifetime US1760763A (en) | 1925-11-20 | 1926-09-10 | Electric-circuit-control means |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US1856493A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE494842C (en) |
| FR (1) | FR626118A (en) |
| GB (1) | GB261774A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3188136A (en) * | 1962-08-27 | 1965-06-08 | Emil J Paidar Company | Electro-hydraulic system for operating elevatable chairs |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2215666A (en) * | 1937-02-04 | 1940-09-24 | Oscar H Pieper | Extensible chair |
| IT228480Y1 (en) * | 1992-07-27 | 1998-02-19 | Fast Spa | ARMCHAIR WITH MORE POSITIONS OF USE WITH ELASTIC POSITIONING MEANS |
-
1925
- 1925-11-20 US US70241A patent/US1856493A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1926
- 1926-08-14 US US129273A patent/US1763245A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1926-09-10 US US134741A patent/US1760763A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1926-11-19 GB GB29302/26A patent/GB261774A/en not_active Expired
- 1926-11-19 FR FR626118D patent/FR626118A/en not_active Expired
- 1926-11-21 DE DER69362D patent/DE494842C/en not_active Expired
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3188136A (en) * | 1962-08-27 | 1965-06-08 | Emil J Paidar Company | Electro-hydraulic system for operating elevatable chairs |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US1760763A (en) | 1930-05-27 |
| US1763245A (en) | 1930-06-10 |
| DE494842C (en) | 1930-04-01 |
| FR626118A (en) | 1927-08-30 |
| GB261774A (en) | 1928-01-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2304608A (en) | Electrical cutout for motor vehicles | |
| US1856493A (en) | Extensible chair | |
| US2352815A (en) | Electric switch | |
| US2111311A (en) | Electric switch | |
| US1815152A (en) | Electrical control mechanism | |
| US1214920A (en) | Electric switch. | |
| US1050592A (en) | Circuit-controller. | |
| US2424529A (en) | Switching arrangement for electrical apparatus | |
| US1748298A (en) | Electric-circttit-control means | |
| US1338607A (en) | Electric switch | |
| US1694613A (en) | Motor-control switch | |
| US1062728A (en) | Control means for electric switches. | |
| US1566010A (en) | Automatic electrical actuating device | |
| US785397A (en) | Power-operated switch. | |
| US1596007A (en) | Device for controlling electric circuits | |
| US1403222A (en) | Electric switch | |
| US2112510A (en) | Electrical socket | |
| US1530747A (en) | Motion-picture machine | |
| US1351184A (en) | Circuit-controller | |
| US3787789A (en) | Switching mechanism | |
| US1114149A (en) | Electric switch. | |
| US2306817A (en) | Elevator contkol system | |
| US1657688A (en) | Switching mechanism | |
| US594944A (en) | Electric switch | |
| US1738406A (en) | Electric switch and operating means therefor |