US1852394A - Method for cutting web material - Google Patents
Method for cutting web material Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US1852394A US1852394A US496122A US49612230A US1852394A US 1852394 A US1852394 A US 1852394A US 496122 A US496122 A US 496122A US 49612230 A US49612230 A US 49612230A US 1852394 A US1852394 A US 1852394A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- gum
- web
- tube
- webs
- web material
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title description 19
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title description 18
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 title description 9
- 229920000298 Cellophane Polymers 0.000 description 11
- 239000004627 regenerated cellulose Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003292 glue Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007598 dipping method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
- B31B70/14—Cutting, e.g. perforating, punching, slitting or trimming
- B31B70/16—Cutting webs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2155/00—Flexible containers made from webs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2155/00—Flexible containers made from webs
- B31B2155/001—Flexible containers made from webs by folding webs longitudinally
- B31B2155/0012—Flexible containers made from webs by folding webs longitudinally having their openings facing in the direction of movement
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2160/00—Shape of flexible containers
- B31B2160/10—Shape of flexible containers rectangular and flat, i.e. without structural provision for thickness of contents
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2160/00—Shape of flexible containers
- B31B2160/10—Shape of flexible containers rectangular and flat, i.e. without structural provision for thickness of contents
- B31B2160/106—Shape of flexible containers rectangular and flat, i.e. without structural provision for thickness of contents obtained from sheets cut from larger sheets or webs before finishing the bag forming operations
Definitions
- This invention relates to a method for cutting web material, and more definitely to a method for striking off lengths from a. multiple-walled tube formed of a plurahty of layers of web material, and particularly web material of transparent regenerated cellulose, such as known in the trades as cellophane.
- lft is an object of the invention to provide a method which eliminates the formation of and the possibility of fracture of the bag along any minute cracks such as caused by the strike off apparatus.
- a further object of the invention is to provide a method which can be readily adapted to the cutting of flat or tubed webs, of one or more layers or walls, and of substantially any web material of paper or cellophane, or any combinations thereof.
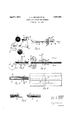
- Figure 1 is a diagrammatic sectional view of suitable apparatus whereby the embodiment of the method herein specifically described may be performed;
- FIG 2 is an enlarged view of the strike oil mechanism illustrated in Figure 1;
- Figure 3 is a vertical sectional view taken on line 33 of Figure 2;
- Figure 4 is a plan view of a portion of the tubed material illustrating in dotted lines the cuts to be made;
- Figure 5 is an enlarged view of Figure 2 taken adjacent the cutting knives.
- Figure 6 is a vertical longitudinal section of the tube after cutting with the ends of the any variety, or both reels may be of paper as will be understood.
- a gum or glue applying station where a longitudinal strip of gum isapplied along one edge of the web, and where a bar or wide strip 9 of gum is periodically applied transversely of the web.
- suitable means may include a gum pot 11, a wide gum roller 12 dipping in the pot 11, and a roll 13 journaled parallel with the roller 12.
- a disk 14 and a bar 15 respectively are secured to the roll 13.
- a roll 16 is provided about which the web material is wrapped, and with which the gum applying means cooperate.
- the web material from the reel 8 is passed to and united with the web material adjacent a roll 17.
- the longitudinal and transverse strips of gum are r of course, between the webs, as will be seen from a study of Figure 1.
- the united webs pass over rolls 18 and 19 to a suitable former 21, about which the webs are formed into a tube.
- Adjacent the roll 19 is a gum applying means, including a pot 22 and a gum applying disk 23, which means serve to apply a longitudinal strip of gum along the edge of the united webs so that when the united webs are folded about the former 21, the longitudinal strip applied by the disk 23 will secure the overlapping edges of the tube together.
- a pair of draw rolls 24 and 25 are provided beyond the former 21, as is the usual practice, and a knife 26 is secured to a suitable support 27, so that the knife 26 is held just above the surface of the tube.
- a fiat knife 28 Secured to the former 21, and extending therefrom up to a point adjacent the knife 26, is a fiat knife 28.
- Both knives 26 and 28 are formed with toothed edges, and in the embodiment shown, the edge of the knife 26 is curved concavely, and the edge of the knife 28 convexly, so that the tube is struck off or cut as indicated in dotted lines at 29 and 31 of Figure 4.
- the usual strike ofi' bar 32 mounted on any suitable means 33, cooperates with the knives 26 and 28 as will be understood and as illustrated in Figure 2.
- the arrangement of parts is such that the transverse strips 9 of gum are passing adjacent the strike off knives 26 and 28 just as the strike off bar 32 comes up to strike off the tube; thus the cuts 29 and 30 are made in the area of the gum 9.
- the formation of minute cracks and tears along the line of the cuts is substantially prevented, and even if some cracks are formed, the gum, together with the multi-ply construction of the tube, will prevent tearing of the material along such cracks as may be formed.
- the gum, glue or adhesive which is employed is preferably of a quick drying variety, which will adapt itself to the process as herein outlined.
- the gum may be applied to but a single web in order that the web can be cut without tearing. Again, the gum may be applied between more than two webs for the same purpose. It will also be obvious that the cut or strike off can be made either with the webs fiat or tubed, and that as described above, the material in the webs or tubes can be of substantially any type of paper or cellophane, or any combination thereof.
- That method of forming tubular blanks which comprises applying longitudinal and transverse strips of gum to a web of material, forming the web into a tube so that the longitudinal strips of gum will hold the web in tubular shape, and cutting off the tube in the area of the transverse strips of gum.
- That method of forming tubular blanks which comprises applying gum to a web of material, forming the web into a tube and cutting off the tube in the area of the gum.
- That method of forming multi-ply tubular blanks which comprises applying longitudinal and transverse strips of gum to a web, joining another Web to said first named web, forming the combined webs into a tube, and striking off the tube in the area of the transverse strips of gum.
- That method of forming multi-ply tubular blanks which comprises applying gum to a web, joining another web to said first named web, forming the combined webs into a tube, and striking off the tube in the area of the gum.
- That method of forming multi-ply tubular blanks of regenerated cellulose which comprises applying gum to a web of regenerated cellulose, joining another web of regenerated cellulose to said first named web, forming the combined webs into a tube, and striking off the tube in the area of the gum.
Landscapes
- Making Paper Articles (AREA)
Description
April 5, 1932. L. A. BECKER ET AL METHOD FOR CUTTING WEB MATERIAL Filed Nov. 1'7, 1930 mvemoas BECKER 7. flunson/ n N A 9 o JEN/v ATTORNEYS Patented Apr. 5, 1932 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE EOGAN A. BECKER AND JOHN M. MUNSON, F LAKEWOOD, OHIOASSIGNORS TO THE DOBECKMUN COMPANY, OF CLEVELAND, OHIO, A CORPORATION OF OHIO METHOD FOR CUTTING WEB MATERIAL Application filed November 17, 1930. Serial No. 496,122.
This invention relates to a method for cutting web material, and more definitely to a method for striking off lengths from a. multiple-walled tube formed of a plurahty of layers of web material, and particularly web material of transparent regenerated cellulose, such as known in the trades as cellophane.
llt has been found that the methods and apparatus used in cutting and strikmg ofi' webs and tubes of paper cannot be successfully used in conjunction with cellophane, due primarily to the glasslike qualities of the cellophane. Attempts to strike off cellophane have resulted in cracking and fly1ng of the cellophane, and particularly 1n the formation of minute tears or cracks along the struck off edge of the material. A sheet of cellophane, the edge of which is smooth and unbroken, will resist tearing to a very considerable degree. If a tear is started, however, the sheet offers little resistance and null tear apart with little effort. This pecuhar property of cellophane has made it impractical heretofore to adopt the rapid and efficient striking off method to the fabrication of bags or envelopes of cellophane.
It is the general object of the invention to overcome the above enumerated difficulties of the prior art by the provision of a process by which cellophane web material, particularly in the form of a multiple-walled tube, can be struck oif rapidly and effectively.
lft is an object of the invention to provide a method which eliminates the formation of and the possibility of fracture of the bag along any minute cracks such as caused by the strike off apparatus.
A further object of the invention is to provide a method which can be readily adapted to the cutting of flat or tubed webs, of one or more layers or walls, and of substantially any web material of paper or cellophane, or any combinations thereof.
The foregoing and other objects of the invention are achieved by the process described herein, and illustrated in the accompanying drawings wherein:
Figure 1 is a diagrammatic sectional view of suitable apparatus whereby the embodiment of the method herein specifically described may be performed;
Figure 2 is an enlarged view of the strike oil mechanism illustrated in Figure 1;
Figure 3 is a vertical sectional view taken on line 33 of Figure 2;
Figure 4 is a plan view of a portion of the tubed material illustrating in dotted lines the cuts to be made;
Figure 5 is an enlarged view of Figure 2 taken adjacent the cutting knives; and
Figure 6 is a vertical longitudinal section of the tube after cutting with the ends of the any variety, or both reels may be of paper as will be understood.
From the reel 7 the web material is passed by a gum or glue applying station where a longitudinal strip of gum isapplied along one edge of the web, and where a bar or wide strip 9 of gum is periodically applied transversely of the web. To this end suitable means are provided which may include a gum pot 11, a wide gum roller 12 dipping in the pot 11, and a roll 13 journaled parallel with the roller 12. To apply the longitudinal gum strip and to apply the transverse strip 9, a disk 14 and a bar 15 respectively are secured to the roll 13. A roll 16 is provided about which the web material is wrapped, and with which the gum applying means cooperate.
The web material from the reel 8 is passed to and united with the web material adjacent a roll 17. When the webs are united the longitudinal and transverse strips of gum are r of course, between the webs, as will be seen from a study of Figure 1. From the roll 17 the united webs pass over rolls 18 and 19 to a suitable former 21, about which the webs are formed into a tube. Adjacent the roll 19 is a gum applying means, including a pot 22 and a gum applying disk 23, which means serve to apply a longitudinal strip of gum along the edge of the united webs so that when the united webs are folded about the former 21, the longitudinal strip applied by the disk 23 will secure the overlapping edges of the tube together.
A pair of draw rolls 24 and 25 are provided beyond the former 21, as is the usual practice, and a knife 26 is secured to a suitable support 27, so that the knife 26 is held just above the surface of the tube. Secured to the former 21, and extending therefrom up to a point adjacent the knife 26, is a fiat knife 28. Both knives 26 and 28 are formed with toothed edges, and in the embodiment shown, the edge of the knife 26 is curved concavely, and the edge of the knife 28 convexly, so that the tube is struck off or cut as indicated in dotted lines at 29 and 31 of Figure 4. The usual strike ofi' bar 32, mounted on any suitable means 33, cooperates with the knives 26 and 28 as will be understood and as illustrated in Figure 2.
As shown in Figure 5, the arrangement of parts is such that the transverse strips 9 of gum are passing adjacent the strike off knives 26 and 28 just as the strike off bar 32 comes up to strike off the tube; thus the cuts 29 and 30 are made in the area of the gum 9. In this manner the formation of minute cracks and tears along the line of the cuts is substantially prevented, and even if some cracks are formed, the gum, together with the multi-ply construction of the tube, will prevent tearing of the material along such cracks as may be formed.
The gum, glue or adhesive which is employed is preferably of a quick drying variety, which will adapt itself to the process as herein outlined.
The steps of the process will'undoubtedly be clear from the foregoing description. However, it should be noted that the principles of the invention are applicable in a plurality of other relations for example, the gum may be applied to but a single web in order that the web can be cut without tearing. Again, the gum may be applied between more than two webs for the same purpose. It will also be obvious that the cut or strike off can be made either with the webs fiat or tubed, and that as described above, the material in the webs or tubes can be of substantially any type of paper or cellophane, or any combination thereof.
In conformity with the patent statutes, a specific embodiment only of the invention has been particularly described and illustrated, it being understood that the scope of the invention is not limited thereby, but is defined by the appended claims.
What is claimed is:
1. That method of forming tubular blanks which comprises applying longitudinal and transverse strips of gum to a web of material, forming the web into a tube so that the longitudinal strips of gum will hold the web in tubular shape, and cutting off the tube in the area of the transverse strips of gum.
2. That method of forming tubular blanks which comprises applying gum to a web of material, forming the web into a tube and cutting off the tube in the area of the gum.
3. That method of forming multi-ply tubular blanks which comprises applying longitudinal and transverse strips of gum to a web, joining another Web to said first named web, forming the combined webs into a tube, and striking off the tube in the area of the transverse strips of gum.
4:. That method of forming multi-ply tubular blanks which comprises applying gum to a web, joining another web to said first named web, forming the combined webs into a tube, and striking off the tube in the area of the gum.
5. That method of forming multi-ply tubular blanks of regenerated cellulose, which comprises applying gum to a web of regenerated cellulose, joining another web of regenerated cellulose to said first named web, forming the combined webs into a tube, and striking off the tube in the area of the gum.
LOGAN A. BECKER. JOHN M. MUNSON.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US496122A US1852394A (en) | 1930-11-17 | 1930-11-17 | Method for cutting web material |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US496122A US1852394A (en) | 1930-11-17 | 1930-11-17 | Method for cutting web material |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US1852394A true US1852394A (en) | 1932-04-05 |
Family
ID=23971333
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US496122A Expired - Lifetime US1852394A (en) | 1930-11-17 | 1930-11-17 | Method for cutting web material |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US1852394A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103240913A (en) * | 2013-04-27 | 2013-08-14 | 开化县新爱迪印刷包装有限公司 | Paper tube machine |
-
1930
- 1930-11-17 US US496122A patent/US1852394A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103240913A (en) * | 2013-04-27 | 2013-08-14 | 开化县新爱迪印刷包装有限公司 | Paper tube machine |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2334381A (en) | Method of making tear strip wrappers | |
| US2149833A (en) | Means for preparing a roll of paper for high speed pasters | |
| US2628179A (en) | Method of producing cartons having metal tearing edges | |
| US1852394A (en) | Method for cutting web material | |
| US1887680A (en) | Bag making machinery | |
| US2830506A (en) | Manufacture of semi-rigid corrugated paperboard cartons | |
| US1915626A (en) | Multi-ply paper | |
| US1848709A (en) | Pabent packaging | |
| US3551245A (en) | Method and means for forming from and securing to thin wrapper webs a reinforced tear strip | |
| US2061437A (en) | Process of making bags | |
| US1941272A (en) | Method of and apparatus for making bags | |
| US2553928A (en) | Roll web terminal | |
| US2292157A (en) | Method of making bags for sound records | |
| US1739381A (en) | Method of preparing paper rolls for the web change | |
| US2197112A (en) | Method of making bags | |
| US2001399A (en) | Machine for making shingles | |
| US205133A (en) | -porteb | |
| GB643350A (en) | Improvements in a divisible paper web | |
| US2276737A (en) | Transversely flexible corrugated paper | |
| US1906813A (en) | Manufacture of bags | |
| US1876094A (en) | Manufacture of tubes of paper or like material | |
| US1798168A (en) | Process and machine for making paper bags | |
| US2212469A (en) | Manufacture of paper and like bags, envelopes, and the like | |
| US2074992A (en) | Process of making a bag or similar article | |
| US1963571A (en) | Method and apparatus for making paper bags |