US1677458A - Stranded cable - Google Patents
Stranded cable Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US1677458A US1677458A US557677A US55767722A US1677458A US 1677458 A US1677458 A US 1677458A US 557677 A US557677 A US 557677A US 55767722 A US55767722 A US 55767722A US 1677458 A US1677458 A US 1677458A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- cable
- strands
- series
- section
- rectangular
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000011065 in-situ storage Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013021 overheating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000306 recurrent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01B—CABLES; CONDUCTORS; INSULATORS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR CONDUCTIVE, INSULATING OR DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES
- H01B9/00—Power cables
Definitions
- the present invention relates tof'helicallyV vstranded cables, that 'is'to say, cables which are'built up of anulnber of successivelayers of Wire of comparatively small section.
- the object of thepresent invention is to ⁇ provide an improved method ofmanufacturing cablesvof 'rectangular section which "shall not involve any process ofdefo-rma- 0 tion and which will, therefore, result in cables' free vfrom-the above-mentioned disadvantages. s
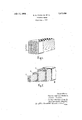
- Figure l is a diagrammatic perspective View of a conductor showing at the left-hand end the arrangement of strands
- Figure 2 is a' similar -view showing the helical laying of successive series of strandsl
- This cable is built up of three layers, A, B, C, the centre lines of which are indicated i respectively nby 'dotted lines.
- the inner layer, A comprises eight strands, theintermediate layer, B, sinteen and the outer layer', C, twenty-four strands.
- the increment in the number of strands per layer is thus seen to be eight.
- the cable in the drawing is shown as covered by a lappingv of tape, H.
- a method of manufacturing a fiat-surfaced stranded electric conductor of rectangularv cross-section which consists in helically laying in situ a basic: ⁇ series of strandssin la two-line rectangular formation as seen in cross-section at recurrent intervals lengthwise of the conductor and helically laying in situ on said, basic series a successivei strands, each series being one-strand thick and having eight more strands than the sub- 2.
- a fiat-surfaced electric conductor of rectangular,cross-section comprising a basic series of helically-laid strands in a two-line rectangular formationas seen in cross-sections taken at certain equidistant points along the length of said conductor and superimposed on said basic series a plurality of series of strands helically laid along the sides of a succession oftrectangles, each series'of said plurality being onestrand thick and havinvf eight more strands than the subjacent series.
- a method of manufacturinga Hat-sur- 1 faced multfstrand conduustcrV of rectangular cross-section,.whichl consists in providing as a core. a body substantially rectangular in cross-section and having transverse dimensions equal respectively to those of an integral number of conductor strands and heli-A cally laying in situ on saidvcore a succession of rectangularly-disposed layers of juxtaposed strands each one strand thick, the
Landscapes
- Insulated Conductors (AREA)
Description
July 17, 1928. l 1,677,458
c. A. PARSONS ET AL S TRANDED CABLE Filed May 1I 1922 /nveno/w: Char/es A/gernon @orso/7o, Jesse/ Rosen, i 1 Arf/zur Wa//ace Greyf f Y Rona la' Wa/er /V/'dg/e y, y M www r//zz Af/s,
Patented July 17,'1'7928.
UNITED STATI-:s
PATENT oFF-ica.
`CHARLES ALGERNON PARSONS,I TESSIEL4 :"ROSEN, ARTHUR WALLACE GREY, AND RONALD WALTER MIDGLEY, F NEWCASTLE-ON-TYNE, ENGLAND; SAID ROSEN,
, GREY, AND MIDGLEY AssIeNoRs rro sAID rAnsoNs.
STRANDED CABLE.
Application illed May 1, 1922, Serial No.v557,677', and in Great Britain May 17, 1921.y
The present invention relates tof'helicallyV vstranded cables, that 'is'to say, cables which are'built up of anulnber of successivelayers of Wire of comparatively small section.
While a cable of circular crosssection is often of use, as for example inv armature construction, it is frequently necessary in order, for instance, to build up a conductor to occupy a slot of a shape such as is frequently employed inv dynamo-electric machinery to modify the oval cable so that both ends of the cable section are provided with square corners, that is to say, the cable is of rectangular section.
Hitherto, in order to make a cable of such a shape it has been necessary rst toconstruct a round or oval cable and `then to deform it to the rectangular shape required.
` The crushingof the cable is undesirable, as
in this operationI theinsulationon the in. dividual wires is damaged and short circuits develop. These short circuitsfare harmful where the cable is tted in dynamo-electric machines, as they cause serious overheating ters Patent is zand also reduce the efficiency of the plant.
The object of thepresent invention is to `provide an improved method ofmanufacturing cablesvof 'rectangular section which "shall not involve any process ofdefo-rma- 0 tion and which will, therefore, result in cables' free vfrom-the above-mentioned disadvantages. s
k.The invention-consists in the improvedl 'sion of rectangularlydisposed series of cables hereinafter described and 5 pointed out in the claims.
Referring to the accompanying drawings Figure l is a diagrammatic perspective View of a conductor showing at the left-hand end the arrangement of strands, while Figure 2 is a' similar -view showing the helical laying of successive series of strandsl -This cable is built up of three layers, A, B, C, the centre lines of which are indicated i respectively nby 'dotted lines. The inner layer, A, comprises eight strands, theintermediate layer, B, sinteen and the outer layer', C, twenty-four strands. The increment in the number of strands per layer is thus seen to be eight.
particularly Owing to the helical laying of the super! I jacent series.
imposed. series of strands, cross sections .taken through the cable will showv progresfiguration of the strands will be rectangular as seen in crossl section Vfor any particular serles. C
The cable in the drawing is shown as covered by a lappingv of tape, H.
. It `will 'be seen that by the construction dei scribed we are enabled to producel a cable the section of nwhich lhas four square 4corners, that is tosay, the cable is of rectangular section, andl it is found that with the increments perlayer specified the wires'in each layerv can be easily laid in situ i. e., in the final position desired'without subsequent distortion, without any tendency to over-riding and will remain in the correct position without disturbing their` neighbours either of the same or adjacent layers.
Having now describedour invention, what we claim as new and desire to secure by Let- 1. A method of manufacturing a fiat-surfaced stranded electric conductor of rectangularv cross-section which consists in helically laying in situ a basic:` series of strandssin la two-line rectangular formation as seen in cross-section at recurrent intervals lengthwise of the conductor and helically laying in situ on said, basic series a succesi strands, each series being one-strand thick and having eight more strands than the sub- 2. A fiat-surfaced electric conductor of rectangular,cross-section, comprising a basic series of helically-laid strands in a two-line rectangular formationas seen in cross-sections taken at certain equidistant points along the length of said conductor and superimposed on said basic series a plurality of series of strands helically laid along the sides of a succession oftrectangles, each series'of said plurality being onestrand thick and havinvf eight more strands than the subjacent series.
3. A method of manufacturinga Hat-sur- 1 faced multfstrand conduustcrV of rectangular cross-section,.whichl consists in providing as a core. a body substantially rectangular in cross-section and having transverse dimensions equal respectively to those of an integral number of conductor strands and heli-A cally laying in situ on saidvcore a succession of rectangularly-disposed layers of juxtaposed strands each one strand thick, the
number of strands in said successive layers increasing by eight strands per layer.
In testimony whereof We have signed ourv names to this specification.
CHARLES ALGERNON PARSONS. JESSEL ROSEN. ARTHUR WALLACE GREY. RONALD WALTER MIDGLEY.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB1677458X | 1921-05-17 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US1677458A true US1677458A (en) | 1928-07-17 |
Family
ID=10888221
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US557677A Expired - Lifetime US1677458A (en) | 1921-05-17 | 1922-05-01 | Stranded cable |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US1677458A (en) |
-
1922
- 1922-05-01 US US557677A patent/US1677458A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE102018122680B3 (en) | Vehicle charging cable | |
| DE523047C (en) | Process for the production of slot wedges with iron sheets layered transversely to the longitudinal direction of the wedge for electrical machines | |
| DE102004003557A1 (en) | Stator for a dynamoelectric machine | |
| DE102020130647A1 (en) | Manufacturing process for manufacturing a stator with wave winding, wave winding mat and stator | |
| EP2068426B1 (en) | Electric coil conductor with rectangular cross-section | |
| DE112011104883T5 (en) | Stator for a rotary electric machine and winding method therefor | |
| DE112014004639T5 (en) | Rotating electrical machine and manufacturing process for this | |
| DE202014003291U1 (en) | cable assembly | |
| DE102014000897A1 (en) | cable assembly | |
| DE2903854C2 (en) | Triangular strand rope | |
| DE112019001797T5 (en) | Multi-core cable | |
| US1677458A (en) | Stranded cable | |
| DE102018125830A1 (en) | Stator for an electrical machine | |
| DE102012218508A1 (en) | Multi-conductor bar conductors for electrical machines | |
| DE102019107616A1 (en) | METHOD FOR FORMING A STATOR ARRANGEMENT | |
| US1677459A (en) | Stranded cable | |
| DE112014006007T5 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| EP2927912B1 (en) | Flat cable with short circuit prevention in case of fire and use and manufacture of such a flat cable | |
| DE102014203110A1 (en) | Method for producing a winding segment for electrical machine, winding segment | |
| DE102017128832A1 (en) | Multi-tooth coil winding for a 3-phase induction machine | |
| DE102019215714A1 (en) | Conductor segment of a coil arrangement of a rotating electrical machine | |
| US1655106A (en) | Electrical conductor | |
| EP4517785A1 (en) | Multi-membered conductor, use and method for producing the multi-membered conductor | |
| DE3515724C2 (en) | ||
| EP0746860B1 (en) | Twisted-conductor bundle for the windings of electric machines and equipment |