RU2791237C1 - Biocomposition based on humic acids of reed lowland peat - Google Patents
Biocomposition based on humic acids of reed lowland peat Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2791237C1 RU2791237C1 RU2022117547A RU2022117547A RU2791237C1 RU 2791237 C1 RU2791237 C1 RU 2791237C1 RU 2022117547 A RU2022117547 A RU 2022117547A RU 2022117547 A RU2022117547 A RU 2022117547A RU 2791237 C1 RU2791237 C1 RU 2791237C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- oil
- rhodococcus
- biocomposition
- humic acids
- microorganisms
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к области биотехнологии и производства биопрепаратов-нефтедеструкторов, содержащие природные полимеры -гуминовые кислоты торфа и может быть использовано в технологиях очистки от нефтяного загрязнения водных акваторий (пресных и морских), почвенных сред (песчаный грунт, различные типы нефтезагрязненных почв, галька); щебня и балластного слоя железнодорожного пути при ликвидации разливов нефтепродуктов (мазут, топливо, смазочные материалы) в различных климатических зонах. The invention relates to the field of biotechnology and the production of biopreparations-oil destructors containing natural polymers -humic acids of peat and can be used in technologies for cleaning water areas (fresh and marine) from oil pollution, soil media (sandy soil, various types of oil-contaminated soils, pebbles); crushed stone and ballast layer of the railway track during the liquidation of spills of oil products (fuel oil, fuel, lubricants) in various climatic zones.
Известно изобретение, биопрепарат «Родер» для биодеградации нефти и нефтепродуктов в почвах, почвогрунтах, пресных и высокоминерализованных водах, принятое за аналог, представляющее собой штаммы бактерий рода Rhodococcus, и содержащее R-формы родококков штаммов Rhodococcus ruber ВКМ Ас-1513Д и Rhodococcus erythropolis ВКМ Ас-1514Д, полученные путем селекции R-форм на обедненной питательной среде с концентрацией NaCl 10,0 г/л для биорекультивации загрязненных углеводородами объектов в условиях низкой минерализации или с концентрацией морской соли 30,0-50,0 г/л для биорекультивации в условиях высокой минерализациии (Мурыгина В.П., Войшвилло Н.Е., Калюжный С.В. Биопрепарат «Родер» для очистки почв, почвогрунтов, пресных и минерализованных вод от нефти и нефтепродуктов. Патент РФ МПК7 С02 F 3/34, В 09 С 1/10, С12N 1/26 // (С12N 1/26, С12R 1:01), (19) RU (11)2174496 (13) С2). Авторы предлагают использовать для биодеградации нефти и нефтепродуктов в почвах, почвогрунтах, пресных и высокоминерализованных водах только R-диссоциантов штаммов Rhodococcus ruber ВКМ Ас-1513Д и Rhodococcus erythropolis ВКМ Ас-1514Д, выращиваемых на средах с высоким содержанием морской соли и способных проводить активный процесс расщепления углеводородов нефти и нефтепродуктов в пресной и морской воде, а также в различных почвогрунтах, и создавать условия для рекультивации почв.An invention is known, the biological product "Roder" for the biodegradation of oil and oil products in soils, soils, fresh and highly mineralized waters, taken as an analogue, representing strains of bacteria of the genus Rhodococcus, and containing R-forms of rhodococcus strains of Rhodococcus ruber VKM Ac-1513D and Rhodococcus erythropolis VKM Ac-1514D, obtained by selection of R-forms on a depleted nutrient medium with a NaCl concentration of 10.0 g/l for bioremediation of objects contaminated with hydrocarbons under conditions of low salinity or with a sea salt concentration of 30.0-50.0 g/l for bioremediation in conditions of high mineralization (Murygina V.P., Voishvillo N.E., Kalyuzhny S.V. Biological preparation "Roder" for cleaning soils, soils, fresh and mineralized waters from oil and oil products. RF patent MPK 7 С02 F 3/34, B 09 C 1/10, C12N 1/26 // (C12N 1/26, C12R 1:01), (19) RU (11) 2174496 (13) C2). The authors propose to use for the biodegradation of oil and oil products in soils, soils, fresh and highly mineralized waters only R-dissociants of Rhodococcus ruber VKM Ac-1513D and Rhodococcus erythropolis VKM Ac-1514D strains grown on media with a high content of sea salt and capable of carrying out an active cleavage process. hydrocarbons, oil and oil products in fresh and sea water, as well as in various soils, and create conditions for soil reclamation.
Недостатком данного изобретения является отсутствие важных данных о способности микроорганизмов продуцировать биоэмульгаторы и отсутствие в составе биопрепарата органической матрицы, способной дополнительно связывать нефтезагрязнители и оказывать стимулирующее действие на бактерии, входящие в биопрепарат.The disadvantage of this invention is the lack of important data on the ability of microorganisms to produce bioemulsifiers and the absence of an organic matrix in the composition of the biological product, which can additionally bind oil pollutants and have a stimulating effect on the bacteria included in the biological product.
Известна биокомпозиция, принятая за прототип (Герцен М.М., Дмитриева Е.Д. Влияние гуминовых кислот на состояние капель нефтепродуктов в присутствии микроорганизмов-нефтедеструкторов рода Rhodococcus. // Вестник ТвГУ. - Серия: Химия. - 2021. - №2(44). - С. 69-79.). Признаками биокомпозиции, совпадающими с существенными признаками заявленного изобретения, является органическая часть - полимерный природный матрикс биокомпозиции, представляющая собой гуминовые кислоты тростникового низинного торфа (ТНТ), источник гуминовых кислот, из которого выделены ГК - тростниковый низинный торф, способ выделения полимерного природного матрикса и микроорганизмы рода Rhodococcus: штамм Rhodococcus erythropolis S67, заявленной биокомпозиции.Known biocomposition, adopted as a prototype (Gerzen M.M., Dmitrieva E.D. The effect of humic acids on the state of oil droplets in the presence of oil degrading microorganisms of the genus Rhodococcus. // Bulletin of TVGU. - Series: Chemistry. - 2021. - No. 2 ( 44) - pp. 69-79). The features of the biocomposition, coinciding with the essential features of the claimed invention, are the organic part - the polymeric natural matrix of the biocomposition, which is the humic acids of reed lowland peat (TNT), the source of humic acids from which HAs are isolated - reed lowland peat, the method for isolating the polymeric natural matrix and microorganisms of the genus Rhodococcus: strain Rhodococcus erythropolis S67, the declared biocomposition.
Биокомпозиции «Гуминовые кислоты тростникового низинного торфа + Rhodococcus erythropolis S67» и «Гуминовые кислоты тростникового низинного торфа + Rhodococcus erythropolis Х5», принятые за прототип, проявляют солюбилизирующую способность (значения коэффициента пропускания эмульсии нефти и нефтепродуктов в воде не более 50±2% спустя 26 часов), способны через 48 часов применения уменьшать на 30-40% площадь поверхности, занимаемой нефтепродуктами и на 50% - нефти, полная биодеградация нефти и нефтепродуктов происходит спустя 7 суток. Недостатками прототипа являются невысокая биодеградационная способность и продолжительное время полной деградации углеводородов нефти.The biocompositions “Humic acids of lowland reed peat + Rhodococcus erythropolis S67” and “Humic acids of lowland reed peat + Rhodococcus erythropolis X5”, taken as a prototype, exhibit solubilizing ability (transmission coefficient values of oil and oil products emulsion in water are not more than 50 ± 2% after 26 hours), are capable of reducing the surface area occupied by oil products by 30-40% after 48 hours of use and oil by 50%, complete biodegradation of oil and oil products occurs after 7 days. The disadvantages of the prototype are low biodegradability and a long time of complete degradation of oil hydrocarbons.
На Фиг. 1 представлено влияние биокомпозиции на состояние пленок нефти спустя 2 часа после начала эксперимента (а - комнатная температура (22°С); б - повышенная соленость (3% NaCl); в - пониженная температура (10°С)). На Фиг. 2 представлено влияние биокомпозиции на состояние пленок нефти спустя 48 часов после начала эксперимента (а - комнатная температура (22°С); б - повышенная соленость (3% NaCl); в - пониженная температура (10°С)).On FIG. Figure 1 shows the effect of the biocomposition on the state of oil films 2 hours after the start of the experiment (a - room temperature (22°C); b - high salinity (3% NaCl); c - low temperature (10°C)). On FIG. Figure 2 shows the effect of the biocomposition on the state of oil films 48 hours after the start of the experiment (a - room temperature (22°C); b - high salinity (3% NaCl); c - low temperature (10°C)).
Задача предлагаемого изобретения заключается в интенсификации процесса расщепления нефти и нефтепродуктов в пресной и морской воде, в различных почвенных средах, повышении биодеградационной способности микроорганизмов-нефтедеструктов, уменьшении времени полной деградации углеводородов нефти и создании условий для рекультивации почв в различных климатических зонах.The objective of the invention is to intensify the process of splitting oil and oil products in fresh and sea water, in various soil media, increase the biodegradation ability of oil-degrading microorganisms, reduce the time for complete degradation of oil hydrocarbons and create conditions for soil reclamation in various climatic zones.
В качестве решения поставленной задачи предлагается биокомпозиция для очистки почвы и воды от нефти инефтепродуктов на основе гуминовых кислот тростникового низинного торфа, состоящая из раствора гуминовых кислот тростникового низинного торфа концентрацией 50 мг/л, суспензии из микроорганизмов-нефтедеструкторов рода Rhodococcus штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 и Rhodococcus erythropolis Х5, в концентрации 105-106 КОЕ/мл, микроорганизмы-нефтедеструкторы рода Rhodococcus взяты в виде ассоциации в соотношении штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 и Rhodococcus erythropolis Х5 1:1, а соотношение суспензия ассоциации микроорганизмов : гуминовые кислоты тростникового низинного торфа составляет 5:3 (по объему).As a solution to this problem, a biocomposition is proposed for cleaning soil and water from oil and oil products based on humic acids of reed lowland peat, consisting of a solution of humic acids of lowland reed peat with a concentration of 50 mg/l, a suspension of oil-degrading microorganisms of the genus Rhodococcus, strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 and Rhodococcus erythropolis X5, at a concentration of 10 5 -10 6 CFU / ml, oil-degrading microorganisms of the genus Rhodococcus are taken as an association in the ratio of strains Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 and Rhodococcus erythropolis X5 1: 1, and the ratio of the suspension of the association of microorganisms: humic acids of cane lowland peat is 5 :3 (by volume).
Заявленную биокомпозицию получается следующим образом:The claimed biocomposition is obtained as follows:
Природную органическую матрицу биокомпозиции получают: навеску тростникового низинного торфа (ТНТ) обрабатывают 0,1н NaOH в соотношение торф: щелочь - 1:6, смесь кипятят в течение 2 часов при постоянном перемешивании и оставляют на сутки. Полученный раствор гумата натрия отделяют фильтрованием и подкисляют 5%-ным раствором НСl до рН=2±1. Осадок гуминовых кислот (ГК) отделяют центрифугированием в течение 20 минут при 800 об/мин и промывают дистиллированной водой до нейтрального значения среды (рН=7). Очистку ГК от низкомолекулярных примесей осуществляют путем диализа против дистиллированной воды до отрицательной реакции промывных вод на Сl- по AgNO3 в мембранных мешках с размером пор 12-14 кДа. Длительность диализа - 24 часа. Очищенный препарат гуминовых кислот сушат в сушильном шкафу при t=60°C.The natural organic matrix of the biocomposition is obtained: a sample of reed lowland peat (TNT) is treated with 0.1 N NaOH in the ratio of peat: alkali - 1:6, the mixture is boiled for 2 hours with constant stirring and left for a day. The resulting solution of sodium humate is separated by filtration and acidified with 5% HCl solution to pH=2±1. The precipitate of humic acids (HA) is separated by centrifugation for 20 minutes at 800 rpm and washed with distilled water until neutral (pH=7). Purification of HA from low molecular weight impurities is carried out by dialysis against distilled water until the wash water reacts negatively to Cl - according to AgNO 3 in membrane bags with a pore size of 12-14 kDa. The duration of dialysis is 24 hours. The purified preparation of humic acids is dried in an oven at t=60°C.
Для повышения биодеграционной способности биокомпозиции к гуминовым кислотам тростникового низинного торфа, концентрации 50 мг/л, дополнительно вносят приготовленную суспензию ассоциации микроорганизмов-нефтедеструкторов рода Rhodococcus при концентрации 105-106 КОЕ/мл (в соотношении штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 : Rhodococcus erythropolis X5=1:1 по объему), а соотношение суспензия ассоциации микроорганизмов: ГК составляет 5:3 (по объему). Маштабирование микроорганизмов проводили в жидких питательных средах в качалочных колбах на 100 мл в среде Эванса, в которую дополнительно вносили 2% н-гексадекана. Микроорганизмы культивировали в орбитальной качалке Excella Е25 при 180 об/мин при 37°С в течение шести суток.To increase the biodegradation ability of the biocomposition to humic acids of reed lowland peat, concentration 50 mg/l, additionally add the prepared suspension of the association of microorganisms-oil decomposers of the genus Rhodococcus at a concentration of 10 5 -10 6 CFU/ml (in the ratio of strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 : Rhodococcus erythropolis X5= 1:1 by volume), and the ratio of suspension association of microorganisms: HA is 5:3 (by volume). Scaling of microorganisms was carried out in liquid nutrient media in shaking flasks of 100 ml in Evans medium, to which 2% n-hexadecane was additionally added. Microorganisms were cultivated in an orbital shaker Excella E25 at 180 rpm at 37°C for six days.
Биокомпозиция на основе гуминовых кислот тростникового низинного торфа представляет собой раствор коричневого цвета. Биокомпозиция способна деградировать нефть и нефтепродукты в диапазоне солености (1-10%) (оптимальная соленость 3-7%) и температур (10-35°С) (оптимальная температура 22-26°С). Предлагаемая биокомпозиция характеризуется повышенной биодеграционной и эмульгирующей способностью по отношению к нефти и нефтепродуктам. Применение биокомпозиции на основе гуминовых кислот ТНТ и ассоциации бактерий рода Rhodococcus (штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 и Rhodococcus erythropolis Х5) снижает время необходимое для полной деструкции нефти и нефтепродуктов до 48 часов в водных средах (пресных и соленых) и при пониженной температуре (10°С).The biocomposition based on humic acids of reed lowland peat is a brown solution. The biocomposition is able to degrade oil and oil products in the range of salinity (1-10%) (optimal salinity 3-7%) and temperatures (10-35°C) (optimum temperature 22-26°C). The proposed biocomposition is characterized by increased biodegradation and emulsifying ability in relation to oil and oil products. The use of a biocomposition based on humic acids TNT and an association of bacteria of the genus Rhodococcus (strains Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 and Rhodococcus erythropolis X5) reduces the time required for the complete destruction of oil and oil products to 48 hours in aqueous media (fresh and salty) and at low temperatures (10°С). ).
Принцип работы изобретения заключается в следующем:The principle of operation of the invention is as follows:
Биокомпозиция на основе гуминовых кислот тростникового низинного торфа проявляет повышенную биодеградабельность углеводородов нефти за счет синергизма действия бактерий-нефтедеструкторов и гуминовых кислот в условиях нефтяного загрязнения. Микроорганизмы окисляют углеводородные соединения, растворяя или их эмульгируя посредством выделения биосурфактантов. Гуминовые кислоты относятся к высокомолекулярными поверхностно-активным веществам и являются эффективными стабилизирующими агентами. Гуминовые кислоты облегчают самопроизвольную адсорбцию микроорганизмов рода Rhodococcus на границе раздела нефть - вода, создавая структурно-механический барьер вокруг капель нефтепродуктов, которые начинают тонуть, переводя нефть и нефтепродукты в водную толщу. Мелкие капли углеводородов нефти, окруженные прочной пленкой адсорбционного слоя из молекул ГК и микроорганизмов, не могут сливаться друг с другом и образуют стойкие, трудно расслаивающиеся эмульсии. Высокопрочный структурно-механический барьер вокруг капель нефтепродуктов, образованный гуминовыми кислотами, предотвращает высвобождение углеводородов из состава ассоциатов. Приобретая отрицательную плавучесть капли нефтепродуктов, переходят с поверхности в толщу воды, где интенсивно разлагаются микроорганизмами-нефтедеструкторами из-за большой поверхности контакта.The biocomposition based on humic acids of reed lowland peat exhibits increased biodegradability of oil hydrocarbons due to the synergism of the action of oil degrading bacteria and humic acids under conditions of oil pollution. Microorganisms oxidize hydrocarbon compounds by dissolving or emulsifying them through the release of biosurfactants. Humic acids are high molecular weight surfactants and are effective stabilizing agents. Humic acids facilitate spontaneous adsorption of microorganisms of the genus Rhodococcus at the oil-water interface, creating a structural-mechanical barrier around oil droplets that begin to sink, transferring oil and oil products into the water column. Small drops of oil hydrocarbons, surrounded by a strong film of the adsorption layer of HA molecules and microorganisms, cannot merge with each other and form stable, difficult to separate emulsions. A high-strength structural-mechanical barrier around oil droplets, formed by humic acids, prevents the release of hydrocarbons from the composition of associates. By acquiring negative buoyancy, oil droplets pass from the surface into the water column, where they are intensively decomposed by oil degrading microorganisms due to the large contact surface.
Пример 1. Влияние биокомпозиции на основе гуминовых кислот тростникового низинного торфа на состояние пленок нефти.Example 1. Influence of a biocomposition based on humic acids of reed lowland peat on the condition of oil films.
Готовили биокомпозицию, состоящую из суспензии ассоциации микроорганизмов-нефтедеструкторов рода Rhodococcus (штаммы Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 и Rhodococcus erythropolis Х5) в концентрации 105-106 КОЕ/мл (в соотношении штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 : Rhodococcus erythropolis X5=1:1 по объему) и гуминовых кислот ТНТ (50 мг/л) а соотношение ассоциация микроорганизмов : ГК составляет 5:3 (по объему). На полученную нефтяную пленку вносили предварительно приготовленную биокомпозицию (500 мкл). Состояние пленок нефти оценивали через 2 (Фиг. 1) и 48 (Фиг. 2) часов.A biocomposition was prepared, consisting of a suspension of an association of microorganisms-oil decomposers of the genus Rhodococcus (strains Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 and Rhodococcus erythropolis X5) at a concentration of 10 5 -10 6 CFU / ml (in the ratio of strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 : Rhodococcus erythropolis X5 = 1: 1 by volume) and humic acids TNT (50 mg/l) and the ratio of association of microorganisms: HA is 5:3 (by volume). A pre-prepared biocomposition (500 µl) was added to the resulting oil film. The condition of the oil films was assessed after 2 (Fig. 1) and 48 (Fig. 2) hours.
Не зависимо от условий проведения эксперимента спустя 2 часа происходит практически полная деструкция нефтяной пленки биокомпозицией, так на поверхности воды отсутствуют даже мелкие нефтяные капли. Наблюдаются неструктурированные ансамбли, состоящие из гуминовых кислот, остатков солюбилизированной нефти и биопленки микроорганизмов. Полная деструкция углеводородов нефти происходит через 48 часов, биодеструкции не подвергается только ароматический каркас гуминовых кислот. Применение предлагаемой биокомпозиции на основе гуминовых кислот ТНТ и ассоциации бактерий рода Rhodococcus снижает время необходимое для полной деструкции нефти и нефтепродуктов до 48 часов, что обусловлено образованием и развитием более сложной по структуре биопленки из сообщества штаммов микроорганизмов, позволяющей оптимально использовать все доступные источники питания и энергии (гуминовые кислоты) и обеспечивать лучшую защищенность от воздействия токсикантов.Regardless of the conditions of the experiment, after 2 hours, the oil film is almost completely destroyed by the biocomposition, so even small oil drops are absent on the water surface. Unstructured ensembles are observed, consisting of humic acids, residues of solubilized oil, and biofilms of microorganisms. Complete destruction of oil hydrocarbons occurs after 48 hours; only the aromatic skeleton of humic acids is not subjected to biodegradation. The use of the proposed biocomposition based on humic acids TNT and the association of bacteria of the genus Rhodococcus reduces the time required for the complete destruction of oil and oil products to 48 hours, which is due to the formation and development of a more complex biofilm from the community of microorganism strains, which allows optimal use of all available sources of nutrition and energy (humic acids) and provide better protection from the effects of toxicants.
Пример 2. Ремедиационная способность предлагаемой биокомпозиции в условиях нефтезагрязненных почв.Example 2. Remediation ability of the proposed biocomposition in conditions of oil-contaminated soils.
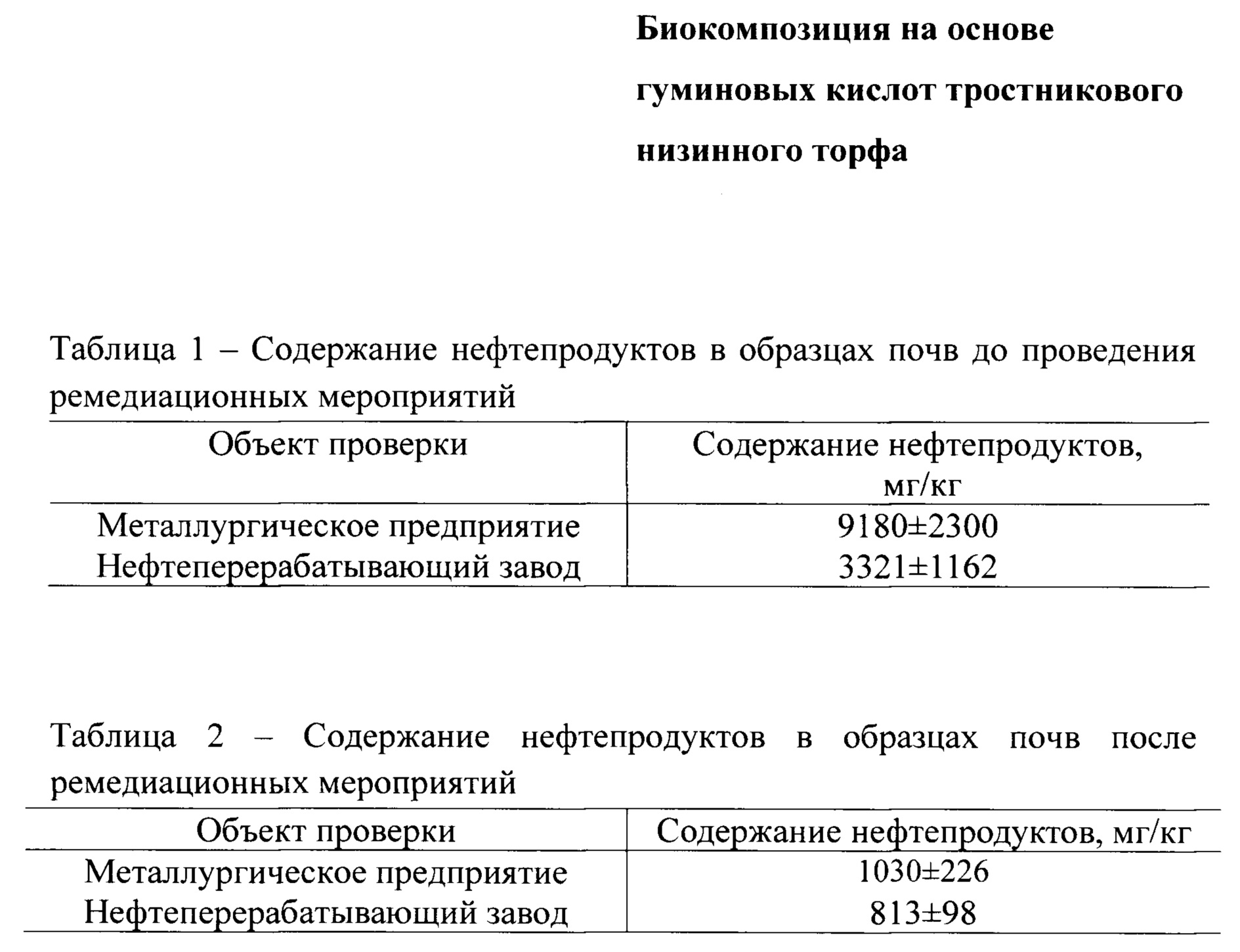
Ремедиационная эффективность предлагаемой биокомпозиции, состоящей из суспензии ассоциации микроорганизмов-нефтедеструкторов рода Rhodococcus (штаммы Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 и Rhodococcus erythropolis Х5) в концентрации 105-106 КОЕ/мл (в соотношении штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 : Rhodococcus erythropolis X5=1: 1 по объему) и гуминовых кислот ТНТ (50 мг/л), а соотношение ассоциация микроорганизмов : ГК составляет 5:3 (по объему), проанализирована на двух образцах нефтезагрязненных почв с территорий нефтеперерабатывающего завода (НПЗ) и металлургического предприятия. Исходное (Таблица 1) и остаточное (Таблица 2) содержание нефтепродуктов по окончании ремедиационных мероприятий определяли на анализаторе жидкости «Флюорат 02-3М» по методике ПНД Ф 16.1:2.21-98.The remediation efficiency of the proposed biocomposition consisting of a suspension of the association of microorganisms-oil decomposers of the genus Rhodococcus (strains Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 and Rhodococcus erythropolis X5) at a concentration of 10 5 -10 6 CFU / ml (in the ratio of Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 strains: Rhodococcus erythropolis X5 = 1: 1 according to volume) and humic acids TNT (50 mg/l), and the ratio of the association of microorganisms : HA is 5:3 (by volume), was analyzed on two samples of oil-contaminated soils from the territories of an oil refinery (refinery) and a metallurgical enterprise. The initial (Table 1) and residual (Table 2) content of oil products at the end of remediation measures was determined on the Fluorat 02-3M liquid analyzer according to the PND F 16.1:2.21-98 method.
По содержанию углеводородов нефти в исходных образцах почва с территории металлургического предприятия по уровню загрязнения соответствует почве с очень высоким уровнем загрязнения (>5000 мг/кт), с территории нефтеперерабатывающего завода - почве с высоким уровнем загрязнения (3000-5000 мг/кг) (Шагидуллин P.P. Нормирование допустимого остаточного содержания нефти и продуктов ее трансформации в почвах. / P.P. Шагидуллин [и др.] // Георесурсы. - 2011. - №5 (41). - С. 2-5). Для снижения уровня нефтяного загрязнения образцы почв обрабатывали раствором гуминовых кислот тростникового низинного торфа при концентрации 50 мг/л (почва (г): ГК (мл)=10:5) и оставляли на сутки. Затем вносили приготовленную биокомпозицию в соотношении почва (г): биокомпозиция (мл) 10:5. Образцы почв обрабатывали предлагаемой биокомпозицией, внося по 5 мл, дважды с интервалом 5 дней. Эффективность применяемой биотехнологии оценивали спустя 14 суток.According to the content of oil hydrocarbons in the initial samples, the soil from the territory of the metallurgical enterprise in terms of pollution corresponds to soil with a very high level of pollution (> 5000 mg / kt), from the territory of the oil refinery - soil with a high level of pollution (3000-5000 mg / kg) (Shagidullin P.P. Rationing of the allowable residual content of oil and products of its transformation in soils / P.R. Shagidullin [et al.] // Georesources. - 2011. - No. 5 (41), - P. 2-5. To reduce the level of oil pollution, soil samples were treated with a solution of humic acids of reed lowland peat at a concentration of 50 mg/l (soil (g): HA (ml)=10:5) and left for a day. Then the prepared biocomposition was added in the ratio of soil (g): biocomposition (ml) 10:5. Soil samples were treated with the proposed biocomposition, adding 5 ml, twice with an interval of 5 days. The effectiveness of the applied biotechnology was evaluated after 14 days.
Применение биокомпозиции позволило снизить уровень загрязнения в почве с нефтеперерабатывающего завода на 76% при этом количество нефтепродуктов в образце соответствует допустимому уровню загрязнения. В почве с металлургического предприятия уровень нефтяного загрязнения снижается на 89%, количество нефтепродуктов соответствует низкому уровню загрязнения. Эффективность заявленной биокомпозиции превышает эффективность очистки загрязненного грунта аборигенной микрофлорой (53%) и коммерческого биопрепарата «Родер» (81%).The use of the biocomposition made it possible to reduce the level of pollution in the soil from the refinery by 76%, while the amount of oil products in the sample corresponds to the permissible level of pollution. In the soil from the metallurgical enterprise, the level of oil pollution is reduced by 89%, the amount of oil products corresponds to a low level of pollution. The effectiveness of the claimed biocomposition exceeds the efficiency of cleaning contaminated soil with native microflora (53%) and the commercial biological product "Roder" (81%).
Компиляция в составе биокомпозиции гуминовых кислот тростникового низинного торфа с микроорганизмами-нефтедеструкторами рода Rhodococcus путем введения штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 и Rhodococcus erythropolis Х5 позволяет увеличить эмульгирующую, солюбилизирующую и биодеграционную способность биокомпозиции. Предлагаемый препарат обладает повышенной биодеградационной способностью по отношению к нефти и нефтепродуктам.Compilation of humic acids of cane lowland peat with oil-degrading microorganisms of the genus Rhodococcus as part of the biocomposition by introducing strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 and Rhodococcus erythropolis X5 allows increasing the emulsifying, solubilizing and biodegrading ability of the biocomposition. The proposed drug has a high biodegradability in relation to oil and oil products.
Заявленное изобретение может быть использовано в форме водной суспензии с концентрацией гуминовых кислот концентрации 50 мг/л и ассоциации микроорганизмов рода Rhodococcus штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 и Rhodococcus erythropolis Х5, способных продуцировать биоэмульгаторы, в концентрации 105-106 КОЕ/мл, взятых в соотношении штаммов Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 : Rhodococcus erythropolis X5 1:1 (по объему), а соотношение суспензия ассоциации микроорганизмов : гуминовые кислоты составляет 5:3 (по объему) в области охраны окружающей среды и природоохранных технологий, в частности очистки пресных и морских акваторий, а также различных почвенных сред (песчаный грунт, различные типы нефтезагрязненных почв, галька); щебня и балластного слоя железнодорожного пути при ликвидации разливов нефтепродуктов (мазут, топливо, смазочные материалы) в различных климатических зонах.The claimed invention can be used in the form of an aqueous suspension with a concentration of humic acids at a concentration of 50 mg/l and an association of microorganisms of the genus Rhodococcus, strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 and Rhodococcus erythropolis X5, capable of producing bioemulsifiers, at a concentration of 10 5 -10 6 CFU/ml, taken in the ratio strains of Rhodococcus erythropolis S67 : Rhodococcus erythropolis X5 1:1 (by volume), and the ratio of the suspension of the association of microorganisms : humic acids is 5:3 (by volume) in the field of environmental protection and environmental technologies, in particular the purification of fresh and marine waters, and also various soil media (sandy soil, various types of oil-contaminated soils, pebbles); crushed stone and ballast layer of the railway track during the liquidation of spills of oil products (fuel oil, fuel, lubricants) in various climatic zones.
Технический результат заявляемого решения заключается в улучшении солюбилизирующей и эмульгирующей способности гуминсодержащих продуктов на основе торфа, за счет образования активной биопленки с микроорганизмами-нефтедеструкторами рода Rhodococcus, что сопровождает увеличение биологической активности и повышение детоксицирующих свойств по отношению к нефти и нефтепродуктам.The technical result of the proposed solution is to improve the solubilizing and emulsifying ability of humin-containing products based on peat, due to the formation of an active biofilm with oil-degrading microorganisms of the genus Rhodococcus, which accompanies an increase in biological activity and an increase in detoxifying properties in relation to oil and oil products.
Claims (1)
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2791237C1 true RU2791237C1 (en) | 2023-03-06 |
Family
ID=
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2174496C2 (en) * | 1999-05-31 | 2001-10-10 | Мурыгина Валентина Павловна | Biological preparation "roder" for cleaning soils, soil grounds, sweet and mineralized waters to remove crude oil and petroleum products |
| RU2312891C1 (en) * | 2006-03-10 | 2007-12-20 | Андрей Евгеньевич Филонов | Bioemulgator-producing association microorganism strains for degradation of petroleum and petroleum products in soil, fresh and sea water |
| RU2378060C2 (en) * | 2007-07-05 | 2010-01-10 | Андрей Евгеньевич Филонов | Biological preparation for cleaning of soils from contaminations with oil and oil products, method of its production and application |
| RU2604788C1 (en) * | 2015-09-03 | 2016-12-10 | Публичное акционерное общество "Нефтяная компания "ЛУКОЙЛ" | Method of cleaning freshwater ecosystems from oil and oil products at high latitudes |
| CN107988096A (en) * | 2017-03-10 | 2018-05-04 | 厦门天邦润生物科技有限公司 | A kind of multifunctional microbial soil-repairing agent and its preparation and application |
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2174496C2 (en) * | 1999-05-31 | 2001-10-10 | Мурыгина Валентина Павловна | Biological preparation "roder" for cleaning soils, soil grounds, sweet and mineralized waters to remove crude oil and petroleum products |
| RU2312891C1 (en) * | 2006-03-10 | 2007-12-20 | Андрей Евгеньевич Филонов | Bioemulgator-producing association microorganism strains for degradation of petroleum and petroleum products in soil, fresh and sea water |
| RU2378060C2 (en) * | 2007-07-05 | 2010-01-10 | Андрей Евгеньевич Филонов | Biological preparation for cleaning of soils from contaminations with oil and oil products, method of its production and application |
| RU2604788C1 (en) * | 2015-09-03 | 2016-12-10 | Публичное акционерное общество "Нефтяная компания "ЛУКОЙЛ" | Method of cleaning freshwater ecosystems from oil and oil products at high latitudes |
| CN107988096A (en) * | 2017-03-10 | 2018-05-04 | 厦门天邦润生物科技有限公司 | A kind of multifunctional microbial soil-repairing agent and its preparation and application |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| ДМИТРИЕВА Е.Д. и др. Влияние гуминовых кислот на состояние капель нефтепродуктов в присутствии микроорганизмов-нефтедеструкторов рода Rhodococcus. Вестник Тверского государственного университета. Серия "Химия", 2021, N2 (44), с. 69-79. ДМИТРИЕВА Е.Д. и др. Влияние гуминовых веществ торфов на ростовые параметры микроорганизмов-нефтедеструкторов рода Rhodococcus в присутствии гексадекана. Ученые записки Крымского федерального университета имени В. И. Вернадского. Биология. Химия. Том 4 (70), 2018, N 2, c. 43-56. * |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Ivshina et al. | Oil desorption from mineral and organic materials using biosurfactant complexes produced by Rhodococcus species | |
| Ladousse et al. | Results of 12 years of research in spilled oil bioremediation: Inipol EAP 22 | |
| JPH0436758B2 (en) | ||
| CA2338249C (en) | Biodispersion as a method for removal of hydrocarbon oil from marine aqueous environments | |
| JP2010516233A (en) | Bioremediation method for accelerated biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in polar regions covered with sea ice, and a mixture of bacteria and enzymes as agents to perform the method | |
| Ng et al. | Recent advances of biosurfactant for waste and pollution bioremediation: Substitutions of petroleum-based surfactants | |
| Silva et al. | Oil spills: impacts and perspectives of treatment technologies with focus on the use of green surfactants | |
| Hassanshahian et al. | Crude oil pollution and biodegradation at the Persian Gulf: A comprehensive and review study | |
| Aa et al. | A critical review of oil spills in the Niger Delta aquatic environment: causes, impacts, and bioremediation assessment | |
| Jimoh et al. | Prospects in the bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants from hypersaline environments: A review | |
| FR2904248A1 (en) | Bio-assisted treatment of ground contaminated by hydrocarbons, comprises isolating and adding micro-organisms that release oil from contaminated soil, adding oil degrading micro-organisms and nitrifying and ventilating the micro-organisms | |
| Péquin et al. | Natural attenuation of oil in marine environments: A review | |
| Zaki et al. | Bioremediation of petroleum contaminants in aquatic environments | |
| RU2604788C1 (en) | Method of cleaning freshwater ecosystems from oil and oil products at high latitudes | |
| RU2791237C1 (en) | Biocomposition based on humic acids of reed lowland peat | |
| Yue et al. | Exploring the use of sodium caseinate-assisted responsive separation for the treatment of washing effluents in shoreline oil spill response | |
| Busi et al. | Biosurfactant: a promising approach toward the remediation of xenobiotics, a way to rejuvenate the marine ecosystem | |
| Singh et al. | Biosurfactant enhanced sustainable remediation of petroleum contaminated soil | |
| Rodrigues et al. | Petroleum: from basic features to hydrocarbons bioremediation in oceans | |
| Hope et al. | Biosurfactant production from Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) for applications as oil field chemical in Nigeria. | |
| Mohanrasu et al. | Bioremediation process by marine microorganisms | |
| Kaida et al. | Biodegradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons by Bacillus spp.: A Review | |
| Fokina et al. | Use of mineral sorbents for the purification of natural environments from petroleum products in the Kolsky northern region | |
| RU2571180C2 (en) | Method for purification of marine and brackish water ecosystems from oil and oil products under high latitude conditions | |
| Murphy | Environmental effects of oil pollution |