RU2669194C1 - Method for obtaining synthetic zeolite of structural type pentasil - Google Patents
Method for obtaining synthetic zeolite of structural type pentasil Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2669194C1 RU2669194C1 RU2017143507A RU2017143507A RU2669194C1 RU 2669194 C1 RU2669194 C1 RU 2669194C1 RU 2017143507 A RU2017143507 A RU 2017143507A RU 2017143507 A RU2017143507 A RU 2017143507A RU 2669194 C1 RU2669194 C1 RU 2669194C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- zeolite
- structural type
- pentasil
- catalyst
- synthetic zeolite
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J29/00—Catalysts comprising molecular sieves
- B01J29/04—Catalysts comprising molecular sieves having base-exchange properties, e.g. crystalline zeolites
- B01J29/06—Crystalline aluminosilicate zeolites; Isomorphous compounds thereof
- B01J29/40—Crystalline aluminosilicate zeolites; Isomorphous compounds thereof of the pentasil type, e.g. types ZSM-5, ZSM-8 or ZSM-11, as exemplified by patent documents US3702886, GB1334243 and US3709979, respectively
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J37/00—Processes, in general, for preparing catalysts; Processes, in general, for activation of catalysts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01B—NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS; COMPOUNDS THEREOF; METALLOIDS OR COMPOUNDS THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASS C01C
- C01B33/00—Silicon; Compounds thereof
- C01B33/20—Silicates
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Catalysts (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к получению гранулированного катализатора синтетического цеолита структурного типа пентасил с высоким содержанием цеолитной фазы. Полученный катализатор может быть использован: в нефтехимической и нефтеперерабатывающей промышленности, в частности в процессах селективной гидродепарафинизации, алкилирования, изомеризации алкилароматических углеводородов и другие.The invention relates to the production of a granular catalyst of a synthetic zeolite of the structural type pentasil with a high content of zeolite phase. The resulting catalyst can be used: in the petrochemical and oil refining industries, in particular in the processes of selective hydrodewaxing, alkylation, isomerization of alkyl aromatic hydrocarbons and others.
На эксплуатационные качества гранулированных промышленных катализаторов влияют природа и содержание активной и связующей фазы и технология их получения. Производство цеолитсодержащих катализаторов при многообразии технологических схем состоит из следующих основных стадий: подготовка цеолитного компонента (декатионирование, деалюминирования, катионного модифицирования); подготовки связующего; подготовки катализаторной массы и формования гранул; сушки и прокаливания гранул.The performance of granular industrial catalysts is influenced by the nature and content of the active and binder phases and the technology for their preparation. The production of zeolite-containing catalysts with a variety of technological schemes consists of the following main stages: preparation of a zeolite component (decationization, dealumination, cationic modification); binder preparation; preparation of the catalyst mass and the formation of granules; drying and calcining granules.
От эффективности катализатора зависит эффективность процесса, в котором он применяется, поэтому к качеству промышленного катализатора предъявляют достаточно жесткие требования: высокая активность, обеспечивающая проведение процесса в более мягком режиме и тем самым определяющая выбор технологической схемы, конструкцию и материал аппаратов; высокая селективность, обеспечивающая максимальный выход целевого продукта на сырье; высокая производительность; продолжительная эксплуатация без регенерации (или с минимальным числом регенераций); высокая термическая стабильность и способность к регенерации; повышенная механическая прочность гранул при работе в стационарном слоеThe efficiency of the process in which it is applied depends on the efficiency of the catalyst, therefore quite strict requirements are imposed on the quality of the industrial catalyst: high activity, ensuring the process is carried out in a softer mode and thereby determining the choice of the technological scheme, design and material of the apparatus; high selectivity, providing maximum yield of the target product to raw materials; high performance; continuous operation without regeneration (or with a minimum number of regenerations); high thermal stability and ability to regenerate; increased mechanical strength of the granules when working in a stationary layer
Для катализаторных систем, состоящих из активного компонента и связующего, природа связующего играет немаловажное значение на эксплуатационные характеристики будущего катализатора. Полученный катализатор в дальнейшем может быть модифицирован обменом катиона в цеолите на другие катионы с целью придания специфических эксплуатационных свойств цеолитсодержащего гранулированного катализатора.For catalyst systems consisting of an active component and a binder, the nature of the binder plays an important role in the performance of the future catalyst. The resulting catalyst can be further modified by exchanging the cation in the zeolite for other cations in order to impart specific operational properties of the zeolite-containing granular catalyst.
Порошкообразный цеолит структурного типа пентасил может быть получен гидротермальной кристаллизацией щелочных алюмокремнегелей, содержащих как правило, органическое вещество, играющее роль структурообразователя, и часто компенсирующий катион.Powdered zeolite of the structural type pentasil can be obtained by hydrothermal crystallization of alkaline aluminosilicon gels, which usually contain organic matter, which plays the role of a builder, and often compensates for the cation.
Брутто формула порошкообразного цеолита структурного типа пентасил представляет состав Na2O Al2O3 xSiO2 уН2О, где х имеет значение в интервале 20-100.The gross formula of a powdery zeolite of the structural type pentasil is the composition of Na 2 O Al 2 O 3 x SiO 2 yN 2 O, where x has a value in the range of 20-100.
В промышленной практике широкое применение нашли именно гранулированные цеолитные катализаторы из-за удобства их применения. Порошкообразный цеолит не формуется в гранулы, поэтому в дальнейшем была развита технология получения гранулированного цеолитсодержащего катализатора со связующим.In industrial practice, it is granular zeolite catalysts that have found wide application because of the convenience of their use. Powdered zeolite is not molded into granules, so the technology for producing a granular zeolite-containing catalyst with a binder was further developed.
Для цеолитсодержащих катализаторов важными показателями являются содержание цеолитной фазы в грануле, вторичная пористость, насыпной вес и механическая прочность на раздавливание, которые определяют его эксплуатационные характеристики. Для эффективного катализатора в проточном режиме важны оптимальные соотношения показателей степени кристалличности по цеолиту, вторичной пористости, насыпного веса и механической прочности на раздавливание. Важно также, чтобы связующее был инертным в каталитическом процессе.For zeolite-containing catalysts, the important indicators are the content of the zeolite phase in the granule, secondary porosity, bulk density and mechanical crushing strength, which determine its operational characteristics. For an efficient catalyst in the flow mode, the optimal ratios of the crystallinity degree of zeolite, secondary porosity, bulk density and mechanical crushing strength are important. It is also important that the binder is inert in the catalytic process.
Известен способ получения цеолитного катализатора, в котором цеолит структурного типа пентасил смешивают с гидроксидом алюминия бемитной структуры при весовм соотношении 60:40, формуют черенки, сушат и прокаливают. [Патент ФРГ №3506632, кл. С07С 667/10, 1986].A known method of producing a zeolite catalyst, in which a pentasil structural type zeolite is mixed with boehmite structure aluminum hydroxide in a weight ratio of 60:40, molded cuttings, dried and calcined. [German patent No. 3506632, class C07C 667/10, 1986].
Недостатком способа является, то что гидроксид алюминия бемитной структуры после прокалки при 500°С переходит в оксид алюминия гамма-модификации. При высоких температурах процесса оксид алюминия гамма-модификации проявляет каталитическую активность кислотно-основного типа, что снижает селективность процесса.The disadvantage of this method is that the aluminum hydroxide boehmite structure after calcination at 500 ° C is converted to alumina of gamma modification. At high process temperatures, gamma alumina exhibits a catalytic activity of the acid-base type, which reduces the selectivity of the process.
По этой же причине при получении цеолитсодержащего катализатора выбор в качестве связующего различных глин (алюмосиликатов) не лишен этих недостатков. Из литературных данных известно, что инертными материалами в качестве связующих могут быть использованы соединения оксида кремния.For the same reason, when obtaining a zeolite-containing catalyst, the choice of various clays (aluminosilicates) as a binder is not without these drawbacks. It is known from the literature that inert materials may use silicon oxide compounds as binders.
Наиболее близким по технической сущности и достигаемому результату к предлагаемому изобретению является способ получения гранулированного цеолитного катализатора [патент РФ 2099138 С1], включающего смешивание цеолита типа пентасил с аэросилем и связующим поливиниловым спиртом и увлажнение водой или уксусной кислотой, формование, сушку, прокалку и активацию.The closest in technical essence and the achieved result to the proposed invention is a method for producing a granular zeolite catalyst [RF patent 2099138 C1], comprising mixing a pentasil type zeolite with aerosil and a binder of polyvinyl alcohol and moistening with water or acetic acid, molding, drying, calcining and activation.
Недостатком этого способа является то, что для увлажнение применят в ряде случае уксусную кислоту до 30%. А также низкое содержание цеолита типа пентасил в составе катализатора до 50%.The disadvantage of this method is that in some cases, acetic acid up to 30% is used for hydration. As well as a low content of zeolite type pentasil in the composition of the catalyst up to 50%.
Целью предлагаемого изобретения является совершенствование технологии получения и улучшении свойств гранулированного катализатора со связующим содержащего в своем составе цеолит структурного типа пентасил, который бы имел меньше технологических стадий и позволил при этом сохранить высокие эксплуатационные свойства катализатора.The aim of the invention is to improve the technology for producing and improving the properties of a granular catalyst with a binder containing a zeolite of the structural type pentasil, which would have fewer process steps and would allow to maintain high performance properties of the catalyst.
Поставленная цель достигается следующим образом.The goal is achieved as follows.
Смешение компонентов порошкообразного цеолита структурного типа пентасил 70-80% масс. и модифицированного крахмала 5-10% масс, в смесителе Z-образными лопастями с паровым обогревом. При достижении однородной массы в смеситель добавляется этилсиликат-40 в пересчете по SiO2 15-20% масс. При необходимости смешиваемая масса дополнительно увлажняется. Механическая грануляция на экструдере, затем сушка при температуре 120-150°С, прокалка при температуре 500-600°С и термопаровая активация.The mixture of components of a powdery zeolite of the structural type pentasil 70-80% of the mass. and modified starch 5-10% of the mass, in the mixer Z-shaped blades with steam heating. Upon reaching a homogeneous mass, ethyl silicate-40 is added to the mixer in terms of SiO 2 15-20% of the mass. If necessary, the mixed mass is additionally moistened. Mechanical granulation on an extruder, then drying at a temperature of 120-150 ° C, calcination at a temperature of 500-600 ° C and thermocouple activation.
Промышленная применимость предлагаемого способа получения подтверждается следующими примерами.Industrial applicability of the proposed method of obtaining is confirmed by the following examples.
Сырье:Raw Material:
1. Цеолит структурного типа пентасил, порошкообразный ZSM-5. Потери при прокаливании ППП = 2-3%.1. Zeolite structural type pentasil powder ZSM-5. Loss on ignition of the SPP = 2-3%.
2. Модифицированный крахмал.2. Modified starch.
3. Этилсиликат-40, содержание SiO2 38-42%.3. Ethyl silicate-40, the content of SiO 2 38-42%.
4. Вода химически очищенная (ХОВ).4. Chemically purified water (HOV).
Оборудование:Equipment:
1. Z-образный смеситель на 100л См-2.1. Z-shaped mixer for 100l cm-2.
2. Шнековый экструдер ШЭ-1.2. Screw extruder ШЭ-1.
3. Ленточная сушильно-прокалочная печь П-1.3. Tape drying and calcining furnace P-1.
При приготовлении опытных составов адсорбента, компоненты берутся в расчете на сухое веществоIn the preparation of experimental compositions of the adsorbent, the components are taken based on dry matter
Пример 1Example 1
Для приготовления шихты на формовку в Z-образный смеситель (СМ-2) засыпают порошкообразный цеолит структурного типа пентасил 35 кг, затем при перемешивании добавляют модифицированный крахмал 5 кг. При достижении однородной массы в смеситель добавляют этилсиликат-40 10 кг. После засыпки всех компонентов, формовочную массу перемешивают в смесителе в течение 0,5-1 ч. Добавляют ХОВ до получение пластичной пасты, затем формуют на шнековом экструдере (ШЭ-1). Затем сушка при температуре 120-150°С, прокалка при температуре 500-600°С и термопаровая активация в ленточной сушильно-прокалочной печи П-1.To prepare the mixture for molding, a powdery zeolite of structural type pentasil 35 kg is poured into a Z-shaped mixer (SM-2), then 5 kg of modified starch is added with stirring. Upon reaching a homogeneous mass, ethyl silicate-40 10 kg is added to the mixer. After filling all the components, the molding material is mixed in the mixer for 0.5-1 hours. Add HOB until a plastic paste is obtained, then it is molded on a screw extruder (ШЭ-1). Then drying at a temperature of 120-150 ° C, calcining at a temperature of 500-600 ° C and thermocouple activation in a tape drying and calcination furnace P-1.
Пример 2Example 2
Катализатор готовят аналогично примеру 1, гдеThe catalyst is prepared analogously to example 1, where
цеолит структурного типа пентасил 37,5 кг,zeolite structural type pentasil 37.5 kg,
модифицированный крахмал 5 кг,modified starch 5 kg
этилсиликат-40 7,5 кг.ethyl silicate-40 7.5 kg.
Пример 3Example 3
Катализатор готовят аналогично примеру 1, гдеThe catalyst is prepared analogously to example 1, where
цеолит структурного типа пентасил 37,5 кг,zeolite structural type pentasil 37.5 kg,
модифицированный крахмал 2,5 кг,modified starch 2.5 kg,
этилсиликат-40 10 кг.ethyl silicate-40 10 kg.
Пример 4Example 4
Катализатор готовят аналогично примеру 1, гдеThe catalyst is prepared analogously to example 1, where
цеолит структурного типа пентасил 40 кг,zeolite structural type pentasil 40 kg,
модифицированный крахмал 2,5 кг,modified starch 2.5 kg,
этилсиликат-40 7,5 кг.ethyl silicate-40 7.5 kg.
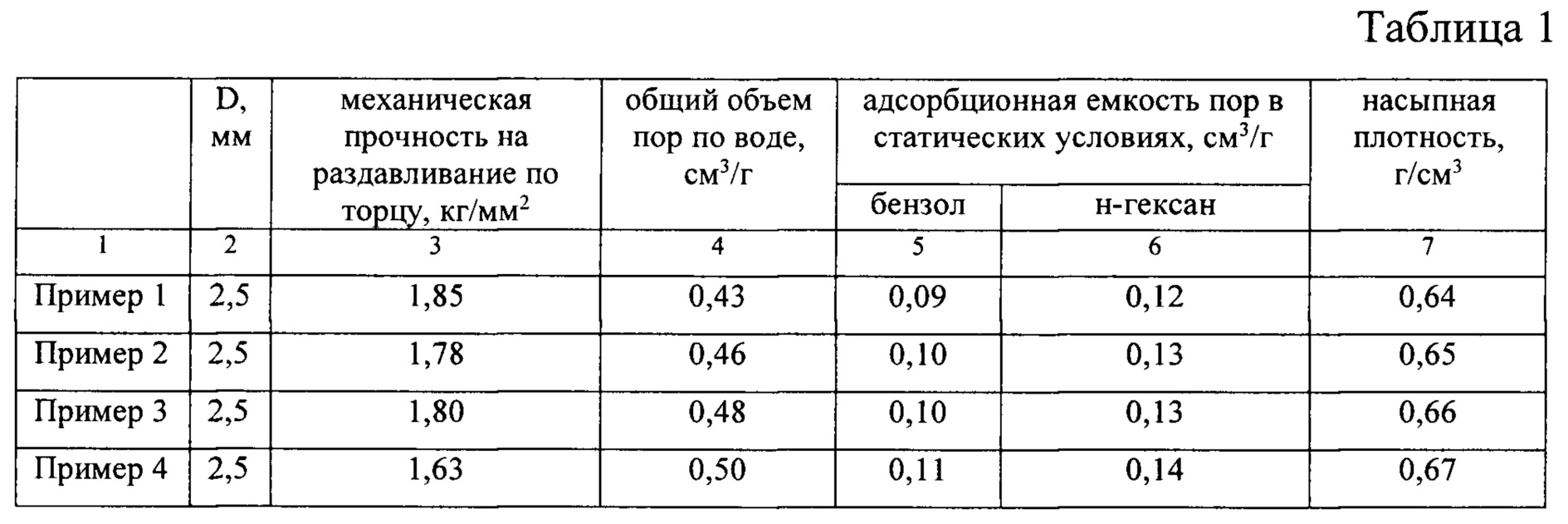
У полученных образцов затем определяли их механическую прочность на раздавливание, общий объем пор по воде, объем пор гранул в статических условиях (по бензолу и н-гексану) и насыпную плотность. Результаты определений приведены в таблице 1.The obtained samples were then determined by their mechanical crushing strength, total pore volume by water, pore volume of granules under static conditions (by benzene and n-hexane) and bulk density. The results of the determinations are shown in table 1.
В таблице 2 преведены результаты каталитических испытаний полученных образцов в процессе облагораживания прямогонной бензиновой фракции нефти. Исходный состав сырья н-алканы (С5+) - 18,7% масс, изоалканы - 54,7% масс, нафтены (С5+) - 11,4% масс, арены - 15,2% масс. Октановое число по исследовательскому методу - 52.Table 2 summarizes the results of catalytic tests of the obtained samples during the refinement of the straight-run gasoline fraction of oil. The initial composition of the raw materials n-alkanes (C5 +) - 18.7% of the mass, isoalkanes - 54.7% of the mass, naphthenes (C5 +) - 11.4% of the mass, arenes - 15.2% of the mass. The octane number according to the research method is 52.
Содержание связующего материала существенно влияет на его каталитические свойства, так как обуславливает вторичную пористую структуру, которая играет роль транспортных пор.The content of the binder material significantly affects its catalytic properties, as it determines the secondary porous structure, which plays the role of transport pores.
С ростом температуры происходит перераспределение высокооктановых компонентов в получаемых бензинах: снижается концентрация ароматических углеводородов и повышается количество изоалканов С5+. В результате этого, несмотря на высокий выход бензинов, их октановые числа остаются высокими и составляют более 75 пунктов. В газообразных продуктах реакции, полученных на всех образцах, преобладает пропан, его концентрация составляет около 40%With increasing temperature, redistribution of high-octane components in the resulting gasolines occurs: the concentration of aromatic hydrocarbons decreases and the amount of C 5+ isoalkanes increases. As a result of this, despite the high gasoline yield, their octane numbers remain high and amount to more than 75 points. Propane predominates in gaseous reaction products obtained on all samples; its concentration is about 40%
Результаты, полученные в процессе превращения прямогонной бензиновой фракции нефти, приведены ниже.The results obtained in the process of converting straight-run gasoline fraction of oil are given below.
Из результатов таблицы следует, что изменение соотношения компонентов в составе смеси для формовки, оказывает существенное влияние на механическую прочность гранул конечного катализатора, на его пористость и адсорбционные характеристики. Катализатор обладает механической прочностью на раздавливание 1,63÷1,85 кг/мм2.From the results of the table it follows that a change in the ratio of components in the composition of the molding mixture has a significant effect on the mechanical strength of the granules of the final catalyst, on its porosity and adsorption characteristics. The catalyst has a mechanical crushing strength of 1.63 ÷ 1.85 kg / mm 2 .
Анализ представленных материалов позволяет сделать вывод о том, что предлагаемое техническое решение дает возможность получать гранулированные катализаторы синтетического цеолита структурного типа пентасил с высокими показателями механической прочности и каталитической активностью.Analysis of the materials presented allows us to conclude that the proposed technical solution makes it possible to obtain granular catalysts of synthetic zeolite of the structural type pentasil with high mechanical strength and catalytic activity.
Claims (2)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017143507A RU2669194C1 (en) | 2017-12-13 | 2017-12-13 | Method for obtaining synthetic zeolite of structural type pentasil |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017143507A RU2669194C1 (en) | 2017-12-13 | 2017-12-13 | Method for obtaining synthetic zeolite of structural type pentasil |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2669194C1 true RU2669194C1 (en) | 2018-10-09 |
Family
ID=63798374
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017143507A RU2669194C1 (en) | 2017-12-13 | 2017-12-13 | Method for obtaining synthetic zeolite of structural type pentasil |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2669194C1 (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3228270A1 (en) * | 1982-07-29 | 1984-02-02 | Degussa Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | CATALYST FOR THE PRODUCTION OF HYDROCARBONS AND THE METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF |
| DE3506632A1 (en) * | 1985-02-26 | 1986-08-28 | Basf Ag, 6700 Ludwigshafen | ESTER REPLACEMENT REACTIONS ON ZEOLITHIC CATALYSTS |
| RU1615941C (en) * | 1988-05-05 | 1994-10-15 | Институт катализа СО РАН | Method of preparing of catalyst on the basis of zeolite of "pentasil" type |
| RU2099138C1 (en) * | 1996-01-23 | 1997-12-20 | Валентина Николаевна Фоменко | Esterification and reesterification catalyst and method of preparation thereof |
| RU2155099C2 (en) * | 1998-10-16 | 2000-08-27 | Каратун Ольга Николаевна | Catalyst and method for conversion of aliphatic c2-c6-hydrocarbons into high-octane gasoline or aromatic hydrocarbons |
-
2017
- 2017-12-13 RU RU2017143507A patent/RU2669194C1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3228270A1 (en) * | 1982-07-29 | 1984-02-02 | Degussa Ag, 6000 Frankfurt | CATALYST FOR THE PRODUCTION OF HYDROCARBONS AND THE METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF |
| DE3506632A1 (en) * | 1985-02-26 | 1986-08-28 | Basf Ag, 6700 Ludwigshafen | ESTER REPLACEMENT REACTIONS ON ZEOLITHIC CATALYSTS |
| RU1615941C (en) * | 1988-05-05 | 1994-10-15 | Институт катализа СО РАН | Method of preparing of catalyst on the basis of zeolite of "pentasil" type |
| RU2099138C1 (en) * | 1996-01-23 | 1997-12-20 | Валентина Николаевна Фоменко | Esterification and reesterification catalyst and method of preparation thereof |
| RU2155099C2 (en) * | 1998-10-16 | 2000-08-27 | Каратун Ольга Николаевна | Catalyst and method for conversion of aliphatic c2-c6-hydrocarbons into high-octane gasoline or aromatic hydrocarbons |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0687500B1 (en) | Catalytic composition and process for the alkylation or transalkylation of aromatic compounds | |
| US6034291A (en) | Catalytic composition and process for the alkylation and/or transalkylation of aromatic compounds | |
| JP5571950B2 (en) | Molecular sieve composition (EMM-10), production method thereof, and hydrocarbon conversion method using the composition | |
| JP5972787B2 (en) | Binderless zeolite adsorbent, method for producing binderless zeolite adsorbent, and method for adsorption separation of para-xylene from mixed xylene using binderless zeolite adsorbent | |
| RU2563648C2 (en) | Improved method of producing zeolite-based catalyst for converting methanol into olefins | |
| TWI634096B (en) | Production of para-xylene | |
| US4975402A (en) | Catalyst for aromatization of olefins and paraffins | |
| US9782758B2 (en) | Method of preparing hydrocarbon aromatization catalyst, the catalyst, and the use of the catalyst | |
| CN101208282A (en) | Selective aromatics isomerization process | |
| RU2563649C2 (en) | Method of producing zeolite-based catalyst for converting methanol into olefins | |
| US4366135A (en) | Method for preparing zeolites | |
| EP2844389A1 (en) | Catalyst for light naphtha aromatization | |
| US4548913A (en) | Catalyst, a process for its preparation and an isomerization process in the presence of this catalyst | |
| JP2006510479A5 (en) | ||
| RU2005117349A (en) | CATALYTIC COMPOSITION AND METHOD OF TRANSALKYLATION OF AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS | |
| JP5991362B2 (en) | High metal content molecular sieves and their manufacturing process | |
| US4605805A (en) | Acid-catalyzed organic compound conversion | |
| Van de Water et al. | Improved catalytic activity upon Ge incorporation into ZSM-5 zeolites | |
| RU2669194C1 (en) | Method for obtaining synthetic zeolite of structural type pentasil | |
| JP5717447B2 (en) | Large crystal molecular sieve and its manufacture | |
| RU2736077C2 (en) | Liquid catalytic cracking catalysts to increase butylene yields | |
| RU2768115C1 (en) | Catalyst and method for production thereof | |
| RU2760550C1 (en) | Catalyst and method for its production | |
| JPH04227851A (en) | Catalyst composition | |
| RU2169043C1 (en) | Catalyst and method of converting aliphatic c2-c12-hydrocarbons into high- octane gasoline or concentrate of aromatic hydrocarbons |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| HE4A | Change of address of a patent owner |
Effective date: 20191008 |
|
| QB4A | Licence on use of patent |
Free format text: LICENCE FORMERLY AGREED ON 20191105 Effective date: 20191105 |
|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20191214 |