RU2659285C1 - Sorbent based on modified graphene oxide and method of its production - Google Patents
Sorbent based on modified graphene oxide and method of its production Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2659285C1 RU2659285C1 RU2017137396A RU2017137396A RU2659285C1 RU 2659285 C1 RU2659285 C1 RU 2659285C1 RU 2017137396 A RU2017137396 A RU 2017137396A RU 2017137396 A RU2017137396 A RU 2017137396A RU 2659285 C1 RU2659285 C1 RU 2659285C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- graphene oxide
- sorbent
- production
- polyhydroquinone
- modified
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J20/00—Solid sorbent compositions or filter aid compositions; Sorbents for chromatography; Processes for preparing, regenerating or reactivating thereof
- B01J20/02—Solid sorbent compositions or filter aid compositions; Sorbents for chromatography; Processes for preparing, regenerating or reactivating thereof comprising inorganic material
- B01J20/20—Solid sorbent compositions or filter aid compositions; Sorbents for chromatography; Processes for preparing, regenerating or reactivating thereof comprising inorganic material comprising free carbon; comprising carbon obtained by carbonising processes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J20/00—Solid sorbent compositions or filter aid compositions; Sorbents for chromatography; Processes for preparing, regenerating or reactivating thereof
- B01J20/22—Solid sorbent compositions or filter aid compositions; Sorbents for chromatography; Processes for preparing, regenerating or reactivating thereof comprising organic material
- B01J20/26—Synthetic macromolecular compounds
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01J—CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROCESSES, e.g. CATALYSIS OR COLLOID CHEMISTRY; THEIR RELEVANT APPARATUS
- B01J20/00—Solid sorbent compositions or filter aid compositions; Sorbents for chromatography; Processes for preparing, regenerating or reactivating thereof
- B01J20/30—Processes for preparing, regenerating, or reactivating
- B01J20/32—Impregnating or coating ; Solid sorbent compositions obtained from processes involving impregnating or coating
Abstract
Description
Область техники. Группа изобретений относится к области органической и неорганической химии, в частности к получению сорбентов на основе модифицированного оксида графена, и может быть использована для очистки сточных вод от красителей и солей тяжелых металлов.The field of technology. The group of inventions relates to the field of organic and inorganic chemistry, in particular to the preparation of sorbents based on modified graphene oxide, and can be used to purify wastewater from dyes and heavy metal salts.
Предшествующий уровень техники. В последние годы для очистки различных сред от нефтепродуктов и других углеводородов применяют сорбенты на основе термически расширенного графита. Способ получения сорбента на основе термически расширенного графита и сорбент, патент РФ №2564354, МПК B01J 20/20, B01J 20/30, опубл. 27.09.2015. Способ получения сорбента на основе термически расширенного графита, модифицированного железосодержащими фазами с ферримагнитными свойствами, включает следующие стадии: (А) получение смеси интеркалированного графита с раствором соли 2 и/или 3 валентного железа в органической жидкости, разлагающейся при нагреве с выделением метана, где концентрация соли железа в растворе составляет от 10 до 50 масс. %; (В) отделение от полученной смеси жидкой фазы с получением твердой фазы в виде интеркалированного графита с нанесенными на него соединениями железа; (С) сушка твердой фазы до сыпучего состояния; и (D) термическое расширение интеркалированного графита с нанесенными на него соединениями железа с получением целевого продукта. Изобретение позволяет получить сорбент на основе терморасширенного графита, содержащего магнитную фазу, представленную ферримагнитными магнетитом (Fe3O4) и маггемитом (γ-Fe2O3) с улучшенными эксплуатационными свойствами.Prior art. In recent years, sorbents based on thermally expanded graphite have been used to clean various media from petroleum products and other hydrocarbons. A method of producing a sorbent based on thermally expanded graphite and a sorbent, RF patent №2564354, IPC B01J 20/20, B01J 20/30, publ. 09/27/2015. A method for producing a sorbent based on thermally expanded graphite modified with iron-containing phases with ferrimagnetic properties, includes the following steps: iron salts in solution ranges from 10 to 50 mass. %; (B) separating from the resulting mixture the liquid phase to obtain a solid phase in the form of intercalated graphite coated with iron compounds; (C) drying the solid phase to a free flowing state; and (D) thermal expansion of intercalated graphite coated with iron compounds to obtain the desired product. The invention allows to obtain a sorbent based on thermally expanded graphite containing a magnetic phase, represented by ferrimagnetic magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) and maghemite (γ-Fe 2 O 3 ) with improved performance properties.
Однако такой способ характеризуется недостаточной сорбционной емкостью материала при обработке промышленных стоков и очистке технической воды.However, this method is characterized by insufficient sorption capacity of the material during the treatment of industrial effluents and purification of industrial water.
Подлинный интерес к оксиду графена как сорбционному материалу возник в ходе исследования его свойств, основными из которых являются:Genuine interest in graphene oxide as a sorption material arose during the study of its properties, the main of which are:
- большая механическая прочность и величина удельной поверхности, что теоретически подтверждает высокую сорбционную способность;- large mechanical strength and the value of the specific surface, which theoretically confirms the high sorption capacity;
- простота получения (не требуется специальных устройств и сложных по составу каталитических систем) материала и сравнительно дешевое исходное сырье (графит).- simplicity of production (no special devices and complex in composition catalytic systems are required) of the material and relatively cheap raw materials (graphite).
Большая сорбционная способность оксида графена может быть также интерпретирована как результат хемосорбции целевых компонентов из водных растворов, основанной на различных типах взаимодействия функциональных поверхностных групп с молекулами или ионами извлекаемых веществ (установление прочных химических связей, электростатическое взаимодействие с поверхностью сорбента, ионный обмен и т.д.).The large sorption capacity of graphene oxide can also be interpreted as the result of chemisorption of target components from aqueous solutions based on various types of interaction of functional surface groups with molecules or ions of extracted substances (establishment of strong chemical bonds, electrostatic interaction with the surface of the sorbent, ion exchange, etc. .).
Гибридный наноматериал на основе оксида графена и катионного хитозана, образующего четвертичное основание, по заявке WO 2014142757 А1, МПК А61Р 31/00; B82Y 30/00; B82Y 5/00; С01В 31/00; С08В 37/08, опубл. 18.09.2014 г. Согласно способу хитозан (1 г, 6,2 ммоль) предварительно растворяют в уксусной кислоте (1%, 100 мл), затем добавляют деканаль (0.97 г, 6,2 ммоль) и перемешивают в течение 1 ч при комнатной температуре. После этого рН увеличивают до 4,5 добавлением боргидрида натрия (9.3 ммоль) и перемешивают смесь в течение 1,5 ч. Затем рН увеличивают до 10 путем добавления гидроксида натрия (раствора NaOH) (1 М). Белый осадок, образующийся в ходе реакции, отфильтровывали и промывали дистиллированной водой до достижения нейтральности среды. Дальнейшая экстракция смеси на аппарате Сокслета с использованием этанола и диэтилового эфира выполняется для удаления непрореагировавших реагентов. В результате Н-децил хитозан (1 г, 6,2 ммоль) затем добавляли к N-метил-пиролидону (МП) (50 мл) и раствору NaOH (1,5 м, 15 мл). После 30 мин перемешивания при температуре 50°С метилирование проводили следующим образом: йодид натрия (1,08 г, 7.2 ммоль) и йодистого метила (1,2 г, 78.7 ммоль) были добавлены к хитозан/NMП/NaOH в смеси, реакция происходила при перемешивании в течение 24 ч при 50°С. Затем раствор фильтровали на нутч-фильтре. После удаления фильтрата в ацетоне (400 мл) полученный осадок отфильтровывают и затем сушат под вакуумом, чтобы получить продукт.A hybrid nanomaterial based on graphene oxide and cationic chitosan, which forms a quaternary base, according to the application WO 2014142757 A1, IPC А61Р 31/00; B82Y 30/00; B82Y 5/00; СВВ 31/00; С08В 37/08, publ. September 18, 2014. According to the method, chitosan (1 g, 6.2 mmol) is pre-dissolved in acetic acid (1%, 100 ml), then decanal (0.97 g, 6.2 mmol) is added and stirred for 1 hour at room temperature. temperature After that, the pH is increased to 4.5 by adding sodium borohydride (9.3 mmol) and the mixture is stirred for 1.5 hours. Then the pH is increased to 10 by adding sodium hydroxide (NaOH solution) (1 M). The white precipitate formed during the reaction was filtered and washed with distilled water until the medium was neutral. Further extraction of the mixture on a Soxhlet apparatus using ethanol and diethyl ether is performed to remove unreacted reagents. As a result, H-decyl chitosan (1 g, 6.2 mmol) was then added to N-methyl pyrolidone (MP) (50 ml) and NaOH solution (1.5 m, 15 ml). After 30 minutes of stirring at 50 ° C., methylation was carried out as follows: sodium iodide (1.08 g, 7.2 mmol) and methyl iodide (1.2 g, 78.7 mmol) were added to chitosan / NMP / NaOH in the mixture, the reaction occurred with stirring for 24 hours at 50 ° C. Then the solution was filtered on a suction filter. After removing the filtrate in acetone (400 ml), the resulting precipitate is filtered and then dried under vacuum to obtain a product.
В данном техническом решении в качестве модифицирующего агента используют катионный полисахарид - хитозан. Технология получения материала в представленном патенте характеризуется многостадийностью, на каждом этапе используется большое количество веществ-прекурсоров органического происхождения (растворители, кислоты, восстановители и т.д.), что значительно усложняет технологию получения сорбента.In this technical solution, a cationic polysaccharide - chitosan is used as a modifying agent. The technology of obtaining material in the presented patent is characterized by multistage, at each stage a large number of organic precursors are used (solvents, acids, reducing agents, etc.), which greatly complicates the technology of sorbent production.
В качестве прототипа объекта «сорбент» выбран сорбент метил-оранжевого красителя по патенту Китая CN №104307491 А, МПК B01J 20/24, В01J 20/30, C02F 1/28, C02F 103/30, опубл. 28.01.2015 г. Согласно патенту, в сорбенте метил-оранжевого красителя в качестве эффективного модификатора оксида графена используют водорастворимую соль четвертичного аммония хитозана. Процесс модификации проводят при рН 3-11 в водном растворе в виде стабильной дисперсии. Благодаря возникновению синергетического эффекта электростатического взаимодействия четвертичной аммониевой соли и большой удельной площади поверхности графена модифицированный графен имеет очевидную высокую адсорбцию органического красителя - метилового оранжевого, адсорбция метилового оранжевого при температуре 10~50°С составляет 80% ~ 98,93%.As the prototype of the object "sorbent" selected methyl orange sorbent according to Chinese patent CN No. 104307491 A, IPC B01J 20/24, B01J 20/30, C02F 1/28, C02F 103/30, publ. 01.28.2015, according to the patent, in the methyl orange dye sorbent as an effective modifier of graphene oxide is used a water soluble quaternary ammonium salt chitosan. The modification process is carried out at pH 3-11 in an aqueous solution in the form of a stable dispersion. Due to the synergistic effect of the electrostatic interaction of the quaternary ammonium salt and a large specific surface area of graphene, the modified graphene has an obvious high adsorption of the organic dye, methyl orange, and the adsorption of methyl orange at a temperature of 10 ~ 50 ° C is 80% ~ 98.93%.
В качестве прототипа способа получения адсорбента выбрано техническое решение по патенту Китая CN №104307491 А, МПК B01J 20/24, B01J 20/30, C02F 1/28, C02F 103/30, опубл. 28.01.2015 г. Согласно патенту на полученном модифицированном графене, где используются коммерческий оксид графена и статические силы нековалетных связей хитозана с поверхностью оксида графена, путем химического восстановления оксида графена, при этом соль четвертичного аммония хитозана остается на поверхности графена; в частности, стадии модифицирования включают:As a prototype of the method of obtaining the adsorbent, the technical solution for China patent CN No. 104307491 A, IPC B01J 20/24, B01J 20/30, C02F 1/28, C02F 103/30, publ. January 28, 2015. According to the patent on the obtained modified graphene, which uses commercial graphene oxide and the static forces of non-caletic bonds of chitosan with the surface of graphene, by chemical reduction of graphene oxide, while the quaternary ammonium salt of chitosan remains on the surface of graphene; in particular, the modification steps include:
1. Во-первых, согласно методу Хаммера готовят смесь графита, оксида графита, в которую добавляют затем раствор гидроксида натрия и путем ультразвукового диспергирования получают дисперсию оксида графена с концентрацией 2~5 мг/мл.1. First, according to the Hummer method, a mixture of graphite, graphite oxide is prepared, to which sodium hydroxide solution is then added, and dispersion of graphene oxide with a concentration of 2 ~ 5 mg / ml is obtained by ultrasonic dispersion.
2. На второй стадии в дисперсию оксида графена добавляют водный раствор соли четвертичного аммония хитозана с концентрацией 3~7 мг/мл, реакционную смесь перемешивают при комнатной температуре, затем добавляют раствор гидроксида натрия с концентрацией 0,01-0,06 моль/л для регулирования значения рН до значения около 10, методом химического окисления снижают нагрев восстановителя и полученный осадок черного флокулянта фильтруют, промывают и сушат. Указанный модификатор представляет собой водорастворимые четвертичные аммониевые соли хитозана, который представляет собой 2-гидроксипропилтриметиламмоний хлорид хитозана, Н-триметил четвертичный хитозан, образующий четвертичное основание н-(4-пиридилметил) хлорида хитозана или четвертичного аммония Н-бетаин из N-(4-Н Н - два метил аминобензил) хлорида хитозана. При этом смесь подвергают ультразвуковому диспергированию в течение 1,5~2 ч. При комнатной температуре время реакции составляет 2~12 ч, время высокотемпературной реакции составляет 1~5 ч. На второй стадии восстановителем является гидрат гидразина в количестве в 2~6 раз больше оксида графита, температура нагрева 60~100°С, температура сушки 30-70°С.2. In the second stage, an aqueous solution of quaternary ammonium salt chitosan with a concentration of 3 ~ 7 mg / ml is added to the graphene oxide dispersion, the reaction mixture is stirred at room temperature, then sodium hydroxide solution is added with a concentration of 0.01-0.06 mol / l for adjusting the pH to a value of about 10, the method of chemical oxidation reduces the heating of the reducing agent and the resulting precipitate of black flocculant is filtered, washed and dried. The specified modifier is a water-soluble quaternary ammonium salts of chitosan, which is a 2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride chitosan, H-trimethyl quaternary chitosan, forming a quaternary base of n- (4-pyridylmethyl) chloride of chitosan or quaternary ammonium N-betaine of N H - two methyl aminobenzyl) chitosan chloride. The mixture is subjected to ultrasonic dispersion for 1.5 ~ 2 hours. At room temperature, the reaction time is 2 ~ 12 hours, the high-temperature reaction time is 1 ~ 5 hours. In the second stage, the reducing agent is 2 to 6 times more hydrazine hydrate graphite oxide, heating temperature 60 ~ 100 ° C, drying temperature 30-70 ° C.
Процесс адсорбции осуществляют при рН 3~11 метилового оранжевого раствора, скорости перемешивания 90~150 об/мин, времени перемешивания 0,5~24 ч и температуре адсорбции 10~50°С.The adsorption process is carried out at a pH of 3 ~ 11 methyl orange solution, a stirring speed of 90 ~ 150 rpm, a stirring time of 0.5 ~ 24 hours and an adsorption temperature of 10 ~ 50 ° C.
Применение модифицированного графена для сорбции метилового оранжевого с начальной концентрацией раствора в интервале 0,5-1,5 г/л, при температуре 10~50°С обеспечивает проведение процесса сорбции со степенью извлечения метилового оранжевого от 80 до ~98.93%.The use of modified graphene for the sorption of methyl orange with an initial concentration of the solution in the range of 0.5-1.5 g / l, at a temperature of 10 ~ 50 ° C ensures the sorption process with the degree of extraction of methyl orange from 80 to ~ 98.93%.
Раскрытие изобретенияDISCLOSURE OF INVENTION
Задачей изобретения по объекту «сорбент» является получение сорбента на основе оксида графена с улучшенными эксплуатационными свойствами за счет увеличения сорбционной емкости.The object of the invention is to obtain a sorbent based on graphene oxide with improved performance properties due to an increase in sorption capacity.
Задачей изобретения по объекту «способ получения сорбента» является упрощение технологии получения сорбента на основе оксида графена за счет сокращения номенклатуры используемых реагентов, количества операций и использования минимального количества оборудования.The object of the invention on the method of obtaining a sorbent is to simplify the technology for producing a sorbent based on graphene oxide by reducing the range of reagents used, the number of operations and the use of a minimum amount of equipment.
Поставленная задача по объекту «сорбент» решается тем, что в качестве модифицирующего вещества оксида графена применяется полигидрохинон.The task of the object "sorbent" is solved by the fact that polyhydroquinone is used as the modifying substance of graphene oxide.
Поставленная задача по объекту «способ получения сорбента» решается тем, что способ получения сорбента на основе модифицированного оксида графена включает следующие технологические стадии:The task of the method of obtaining a sorbent is solved by the fact that the method of obtaining a sorbent based on modified graphene oxide includes the following process steps:
(A) смешение исходных компонентов мас. %:(A) a mixture of initial components wt. %:
- оксид графена - 40-50;- graphene oxide - 40-50;
- хинон - 3-4- quinone - 3-4
- дистиллированная вода - остальное.- distilled water - the rest.
Смешение ведут при ультразвуковом воздействии с частотой колебаний 22±0,4 кГц в течение 40-70 мин;The mixing is carried out with ultrasonic exposure with an oscillation frequency of 22 ± 0.4 kHz for 40-70 minutes;
(B) продувка реакционного пространства инертным газом (аргоном) в течение 30 минут с последующей герметизацией;(B) purging the reaction space with an inert gas (argon) for 30 minutes, followed by sealing;
(C) нагрев исходной смеси до 95°С с последующей выдержкой в течение 6 ч с непрерывным механическим перемешиванием со скоростью 150 об/мин в среде инертного газа;(C) heating the initial mixture to 95 ° C, followed by aging for 6 hours with continuous mechanical stirring at a speed of 150 rpm in an inert gas environment;
(D) охлаждение до комнатной температуры, фильтрация полученной смеси с отделением целевого продукта в виде твердой фазы оксида графена, структура которого модифицирована полигидрохиноном;(D) cooling to room temperature, filtering the resulting mixture with the separation of the target product in the form of a solid phase of graphene oxide, the structure of which is modified with polyhydroquinone;
(Е) промывка материала предварительно нагретой до 50-70°С дистиллированной водой, вакуумирование в течение 3-7 минут для удаления влаги с поверхности и сушка при комнатной температуре 22-25°С.(E) washing the material with distilled water preheated to 50–70 ° C, evacuating for 3–7 minutes to remove moisture from the surface and drying at room temperature 22–25 ° C.
Уровень техникиThe level of technology
Качественное модифицирование поверхности оксида графена полигидрохиноном определяется делокализованной электронной системой графена, что порождает высокое сродство к ароматическим соединениям.The qualitative modification of the graphene oxide surface by polyhydroquinone is determined by the delocalized electronic system of graphene, which gives rise to a high affinity for aromatic compounds.
Осуществление изобретенияThe implementation of the invention
Для осуществления изобретения использовали следующие исходные компоненты:To implement the invention used the following source components:
оксид графена в виде 1% дисперсии в дистиллированной воде производства НаноТехЦентра, г. Тамбов;graphene oxide in the form of a 1% dispersion in distilled water produced by NanoTehCentre, Tambov;
П-бензохинон (Ч) - гранулированный сыпучий материал, полученный по ТУ 6-09-07-1638 (ООО «Лаверна»);P-benzoquinone (C) - granular bulk material obtained according to TU 6-09-07-1638 (OOO Laverna);
вода дистиллированная ГОСТ 6709-72. Настоящий стандарт распространяется на дистиллированную воду, получаемую в перегонных аппаратах и применяемую для анализа химических реактивов и приготовления растворов реактивов.distilled water GOST 6709-72. This standard applies to distilled water obtained in the distillation apparatus and used for the analysis of chemical reagents and the preparation of solutions of reagents.
Сущность изобретения состоит в следующем. Для получения сорбента на основе модифицированного полигидрохиноном оксида графена готовят смесь исходных компонентов из оксида графена, хинона и дистиллированной воды, смешение ведут при ультразвуком воздействии при частоте колебаний 22±0,4 кГц в течение 40-70 мин. Затем реакционное пространство продувают инертным газом (аргоном) в течение 30 минут с последующей герметизацией для обеспечения восстановления оксида графена, исключив доступ атмосферного кислорода, после чего исходную смесь нагревают до 95±2°С с последующей выдержкой в течение 6 ч с непрерывным механическим перемешиванием со скоростью 150 об/мин в среде инертного газа. Полученную смесь охлаждают до комнатной температуры, фильтруют с отделением целевого продукта в виде твердой фазы оксида графена, структура которого модифицирована полигидрохиноном. Целевой продукт промывают предварительно нагретой до 50-70°С дистиллированной водой, вакуумируют в течение 3-7 минут для удаления влаги с поверхности и сушат при комнатной температуре 22-25°С.The invention consists in the following. To obtain a graphene oxide modified with polyhydroquinone, a mixture of initial components is prepared from graphene oxide, quinone and distilled water, the mixture is carried out under ultrasound exposure at an oscillation frequency of 22 ± 0.4 kHz for 40-70 minutes Then the reaction space is purged with an inert gas (argon) for 30 minutes, followed by sealing to ensure the reduction of graphene oxide, excluding access of atmospheric oxygen, after which the initial mixture is heated to 95 ± 2 ° C, followed by aging for 6 hours speed of 150 rpm in inert gas. The resulting mixture is cooled to room temperature, filtered to separate the target product in the form of a solid graphene oxide phase, the structure of which is modified with polyhydroquinone. The target product is washed with pre-heated to 50-70 ° C distilled water, vacuum for 3-7 minutes to remove moisture from the surface and dried at room temperature 22-25 ° C.
Пример 1. Готовили смесь исходных компонентов из оксида графена - 250 г, хинона - 15 г и дистиллированной воды - 250 мл. Смешение вели при ультразвуковом воздействии при частоте колебаний 22±0,4 кГц в течение 40 мин, после чего проводили продувку реакционного пространства инертным газом (аргоном) в течение 30 минут с последующей герметизацией и исходную смесь нагревали до 95°С с последующей выдержкой в течение 6 ч с непрерывным механическим перемешиванием со скоростью 150 об/мин в среде инертного газа. Полученную смесь охлаждали до комнатной температуры, фильтровали с отделением целевого продукта в виде твердой фазы оксида графена, структура которого модифицирована полигидрохиноном. Целевой продукт промывали предварительно нагретой до 70°С дистиллированной водой, вакуумировали в течение 3 минут для удаления влаги с поверхности и сушили при комнатной температуре 22-25°С.Example 1. A mixture of graphene oxide starting components was prepared - 250 g, quinone - 15 g and distilled water - 250 ml. Mixing was performed under ultrasonic action at an oscillation frequency of 22 ± 0.4 kHz for 40 minutes, after which the reaction space was purged with an inert gas (argon) for 30 minutes, followed by sealing, and the initial mixture was heated to 95 ° C, followed by exposure 6 hours with continuous mechanical stirring at a speed of 150 rpm in an inert gas environment. The resulting mixture was cooled to room temperature, filtered to separate the target product as a solid phase of graphene oxide, the structure of which is modified with polyhydroquinone. The target product was washed with pre-heated to 70 ° C distilled water, was evacuated for 3 minutes to remove moisture from the surface and dried at room temperature 22-25 ° C.
Полученный продукт представляет собой пасту черного цвета, способную в контакте с водой образовывать двухкомпонентную дисперсию.The resulting product is a black paste that can form a two-component dispersion in contact with water.
Пример 2. Процесс вели аналогично примеру 1 со следующими изменениями: готовили смесь исходных компонентов из оксида графена - 200 г, хинона - 30 г и дистиллированной воды - 300 мл. Исходную смесь нагревали до 97°С с последующей выдержкой в течение 6 ч с непрерывным механическим перемешиванием со скоростью 150 об/мин в среде инертного газа. Целевой продукт промывали предварительно нагретой до 50°С дистиллированной водой, вакуумировали в течение 7 минут для удаления влаги с поверхности и сушили при комнатной температуре 22-25°С.Example 2. The process was carried out analogously to example 1 with the following changes: a mixture of graphene oxide starting components was prepared — 200 g, quinone — 30 g, and distilled water — 300 ml. The initial mixture was heated to 97 ° C, followed by aging for 6 h with continuous mechanical stirring at a speed of 150 rpm in an inert gas environment. The target product was washed with pre-heated to 50 ° C distilled water, evacuated for 7 minutes to remove moisture from the surface and dried at room temperature 22-25 ° C.
Полученный продукт представляет собой пасту черного цвета, способную в контакте с водой образовывать двухкомпонентную дисперсию.The resulting product is a black paste that can form a two-component dispersion in contact with water.
Для проведения экспериментальных исследований, направленных на установление ключевых сорбционных характеристик исследуемого образца полигидрохинона по извлечению ионов Cu+2 из водных растворов, использовали следующий порядок действий:To carry out experimental studies aimed at establishing the key sorption characteristics of the polygidroquinone sample being studied for the extraction of Cu +2 ions from aqueous solutions, the following procedure was used:
Раствор меди (сорбат) с начальной концентрацией 100 мг/л (Сисх) готовили путем разбавления в универсальной буферной системе (объемом 1 литр, рН6) рассчитанного количества Сu(NO3)2⋅3Н2O классификации ЧДА, ГОСТ 4163-78 при комнатной температуре Т=23±1°С. Масса навески полигидрохинона m=0.03 г, соответствующий объем раствора Vисх=30 мл. Для определения равновесной концентрации ионов Сu+2 использовали методы атомно-абсорбционной спектроскопии с электротермической атомизацией. Равновесная концентрация ионов Сu+2 составляла 55 мг/л.Copper solution (sorbate) with an initial concentration of 100 mg / l (C ref ) was prepared by diluting in a universal buffer system (1 liter volume, pH6) of the calculated amount of Cu (NO 3 ) 2 ⋅3H 2 O classification of analytical grade, GOST 4163-78 with room temperature T = 23 ± 1 ° С. The weight of the sample of polyhydroquinone is m = 0.03 g, the corresponding volume of solution Vex = 30 ml. To determine the equilibrium concentration of Cu + 2 ions, we used atomic absorption spectroscopy with electrothermal atomization. The equilibrium concentration of ions Cu +2 was 55 mg / l.
Для проведения экспериментальных исследований по сорбции органического красителя (метиленового синего) из воды использовали следующие режимные параметры:For experimental studies on the sorption of an organic dye (methylene blue) from water, the following regime parameters were used:
Раствор (сорбат), с начальной концентрацией 1500 мг/л (Сисх), получали разбавлением 1.5 г (±0,001 г) метиленового синего классификации ЧДА (ТУ 6-09-29-76) в одном литре дистиллированной воды ГОСТ 6709-72 (рН 6.5±0,5) при комнатной температуре Т=23±1°С. Для проведения экспериментальных исследований по сорбции органического красителя готовили навески полигидрохинона массой 0.03 г (m), а также 30 мл (Vисх) раствора начальной концентрацией 1500 мг/л. Равновесная концентрация метиленового синего в растворе составляла 780 мг/л.A solution (sorbate), with an initial concentration of 1500 mg / l (C ref ), was obtained by diluting 1.5 g (± 0.001 g) of methylene blue analytical grade classification (TU 6-09-29-76) in one liter of distilled water GOST 6709-72 ( pH 6.5 ± 0.5) at room temperature T = 23 ± 1 ° C. To carry out experimental studies on the sorption of an organic dye, we prepared samples of polyhydroquinone weighing 0.03 g (m), as well as 30 ml (V out ) of a solution with an initial concentration of 1500 mg / l. The equilibrium concentration of methylene blue in the solution was 780 mg / l.
Для проведения экспериментальных исследований по сорбции органического красителя (метиленового оранжевого) из воды использовали следующие режимные параметры:To carry out experimental studies on the sorption of organic dye (methylene orange) from water, the following regime parameters were used:
Раствор (сорбат), с начальной концентрацией 1500 мг/л (Сисх), получали разбавлением 1.5 г (±0,001 г) метиленового оранжевого классификации ЧДА (ТУ 6-09-51171-84) в одном литре дистиллированной воды ГОСТ 6709-72 (рН=6.5±0,5) при комнатной температуре Т=23±1°С. Для проведения экспериментальных исследований по сорбции органического красителя готовили навески полигидрохинона массой 0.03 г (m), раствор начальной концентрации 1500 мг/л объемом 30 мл (Vисх). Равновесная концентрация метиленового синего в растворе составляла 1095 мг/л.A solution (sorbate), with an initial concentration of 1500 mg / l (C ref ), was obtained by diluting 1.5 g (± 0.001 g) of methylene orange analytical grade classification (TU 6-09-51171-84) in one liter of distilled water GOST 6709-72 ( pH = 6.5 ± 0.5) at room temperature T = 23 ± 1 ° C. To carry out experimental studies on the sorption of an organic dye, we prepared samples of polyhydroquinone weighing 0.03 g (m), a solution of an initial concentration of 1500 mg / l with a volume of 30 ml (V out ). The equilibrium concentration of methylene blue in the solution was 1095 mg / l.
Образцы полученного продукта известной массы в виде порошка помещали в сеточную корзину с размером ячеек 1 мм2 вместе с корзиной помещали в стеклянную емкость, содержащую сорбат со слоем жидкости 5 см. После выдерживания 15 минут сеточную корзину извлекали из емкости и отстаивали в течение 30 с. Далее образец взвешивали и определяли сорбционную емкость (S) в единицах г поглощенного вещества.Samples of the obtained product of known mass in the form of powder were placed in a grid basket with a cell size of 1 mm 2 and placed in a glass container containing sorbate with a 5 cm liquid layer. After keeping for 15 minutes, the grid basket was removed from the container and settled for 30 seconds. Next, the sample was weighed and determined the sorption capacity (S) in units of g absorbed substance.
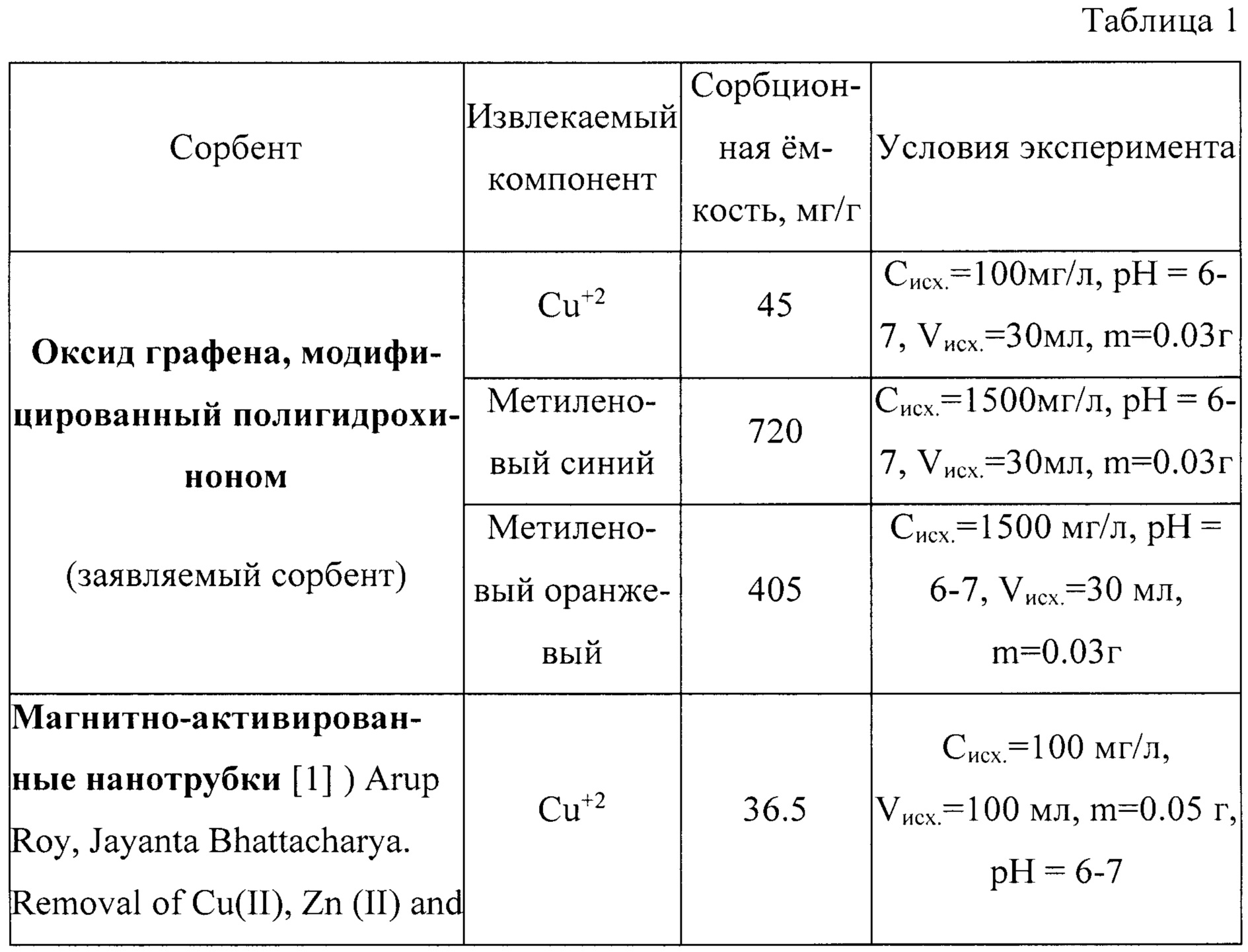
Ниже приведены полученные экспериментальные значения сорбционной емкости оксида графена, модифицированного полигидрохиноном (заявляемый сорбент) в сравнении с другими сорбентами.Below are the experimental values obtained for the sorption capacity of graphene oxide modified with polyhydroquinone (the inventive sorbent) in comparison with other sorbents.
Группа изобретений обеспечивает получение сорбента на основе оксида графена с улучшенными эксплуатационными свойствами за счет увеличения сорбционной емкости при упрощении технологии получения сорбента за счет сокращения номенклатуры используемых реагентов, количества операций и использования минимального количества оборудования.The group of inventions provides for obtaining a sorbent based on graphene oxide with improved performance properties by increasing the sorption capacity while simplifying the technology of obtaining the sorbent by reducing the range of reagents used, the number of operations and the use of a minimum amount of equipment.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017137396A RU2659285C1 (en) | 2017-10-25 | 2017-10-25 | Sorbent based on modified graphene oxide and method of its production |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017137396A RU2659285C1 (en) | 2017-10-25 | 2017-10-25 | Sorbent based on modified graphene oxide and method of its production |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2659285C1 true RU2659285C1 (en) | 2018-06-29 |
Family
ID=62815701
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017137396A RU2659285C1 (en) | 2017-10-25 | 2017-10-25 | Sorbent based on modified graphene oxide and method of its production |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2659285C1 (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2689616C1 (en) * | 2018-10-09 | 2019-05-28 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Тамбовский государственный технический университет" (ФГБОУ ВО "ТГТУ") | Method of sorption cleaning of aqueous media from organic substances and ions of heavy metals |
| RU2699634C1 (en) * | 2018-10-24 | 2019-09-06 | федеральное государственное автономное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Казанский (Приволжский) федеральный университет" (ФГАОУ ВО КФУ) | Method for detoxification of aqueous media contaminated with graphene oxide |
| CN110699703A (en) * | 2019-11-08 | 2020-01-17 | 上海纳米技术及应用国家工程研究中心有限公司 | Preparation method of reduced graphene oxide-polyhydroquinone composite electrode, product and application thereof |
| RU2725822C1 (en) * | 2019-07-09 | 2020-07-06 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Тамбовский государственный технический университет" (ФГБОУ ВО "ТГТУ") | Method of producing nanocomposite sorption material based on graphene and iron oxide nanoparticles |
| CN112264070A (en) * | 2020-10-26 | 2021-01-26 | 山东建筑大学 | Iron nitride @ nitrogen-doped graphene composite material and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN112403517A (en) * | 2020-11-26 | 2021-02-26 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Method for preparing nano enzyme by reducing graphene oxide with ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide, prepared nano enzyme and application of nano enzyme |
| CN112916045A (en) * | 2021-01-31 | 2021-06-08 | 胡国强 | Load ZnO-TiO2Preparation method of magnetic graphene oxide/chitosan composite material |
| CN115251081A (en) * | 2022-08-15 | 2022-11-01 | 安徽工业大学 | Graphene antibacterial slurry and preparation method thereof |
| RU2805525C2 (en) * | 2021-12-15 | 2023-10-18 | Федеральное Государственное Бюджетное Учреждение Науки Федеральный Исследовательский Центр Проблем Химической Физики И Медицинской Химии Российской Академии Наук (Фиц Пхф И Мх Ран) | Superhydrophobic sorbent for ecological cleaning of land and water bodies from oil and oil product spills and method for its production |
Citations (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102527333A (en) * | 2011-12-19 | 2012-07-04 | 山东大学 | Modified graphene oxide, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN103447013A (en) * | 2013-09-23 | 2013-12-18 | 青岛大学 | Method for preparing graphene/chitosan adsorbent and application method thereof |
| CN103464122A (en) * | 2013-09-23 | 2013-12-25 | 青岛大学 | Preparation method of graphene/chitosan adsorbent resin |
| CN103861564A (en) * | 2012-12-14 | 2014-06-18 | 吉首大学 | Preparation of graphene oxide adsorption material modified by dendritic polymer |
| CN103861565A (en) * | 2012-12-14 | 2014-06-18 | 吉首大学 | Preparation of linear amino modified graphene oxide adsorption material |
| CN103949218A (en) * | 2014-04-21 | 2014-07-30 | 华南理工大学 | Modified graphene adsorbent as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN104307491A (en) * | 2014-10-24 | 2015-01-28 | 武汉理工大学 | Modified graphene for efficiently adsorbing methyl orange dye and preparation method of modified graphene |
| CN104525159A (en) * | 2015-01-13 | 2015-04-22 | 张一梅 | Preparation method of heavy metal ion adsorbent |
| RU2550176C2 (en) * | 2013-05-06 | 2015-05-10 | Юрий Филиппович Гайворонский | Graphene pumice, method of its production and activation |
| WO2015075451A1 (en) * | 2013-11-21 | 2015-05-28 | The University Of Manchester | Water purification |
| CN104888725A (en) * | 2015-05-12 | 2015-09-09 | 安徽鑫昆净化设备有限公司 | Adsorbent with adsorption on heavy metals and preparation method for adsorbent |
| US20160308213A1 (en) * | 2013-12-31 | 2016-10-20 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Quinone Compound-Graphene Composite Material, Preparation Method Thereof, and Flexible Lithium Secondary Battery |
| US20170151548A1 (en) * | 2011-02-25 | 2017-06-01 | Zonko, Llc | Sorption And Separation of Various Materials By Graphene Oxides |
-
2017
- 2017-10-25 RU RU2017137396A patent/RU2659285C1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170151548A1 (en) * | 2011-02-25 | 2017-06-01 | Zonko, Llc | Sorption And Separation of Various Materials By Graphene Oxides |
| CN102527333A (en) * | 2011-12-19 | 2012-07-04 | 山东大学 | Modified graphene oxide, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN103861564A (en) * | 2012-12-14 | 2014-06-18 | 吉首大学 | Preparation of graphene oxide adsorption material modified by dendritic polymer |
| CN103861565A (en) * | 2012-12-14 | 2014-06-18 | 吉首大学 | Preparation of linear amino modified graphene oxide adsorption material |
| RU2550176C2 (en) * | 2013-05-06 | 2015-05-10 | Юрий Филиппович Гайворонский | Graphene pumice, method of its production and activation |
| CN103447013A (en) * | 2013-09-23 | 2013-12-18 | 青岛大学 | Method for preparing graphene/chitosan adsorbent and application method thereof |
| CN103464122A (en) * | 2013-09-23 | 2013-12-25 | 青岛大学 | Preparation method of graphene/chitosan adsorbent resin |
| WO2015075451A1 (en) * | 2013-11-21 | 2015-05-28 | The University Of Manchester | Water purification |
| US20160308213A1 (en) * | 2013-12-31 | 2016-10-20 | Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. | Quinone Compound-Graphene Composite Material, Preparation Method Thereof, and Flexible Lithium Secondary Battery |
| CN103949218A (en) * | 2014-04-21 | 2014-07-30 | 华南理工大学 | Modified graphene adsorbent as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN104307491A (en) * | 2014-10-24 | 2015-01-28 | 武汉理工大学 | Modified graphene for efficiently adsorbing methyl orange dye and preparation method of modified graphene |
| CN104525159A (en) * | 2015-01-13 | 2015-04-22 | 张一梅 | Preparation method of heavy metal ion adsorbent |
| CN104888725A (en) * | 2015-05-12 | 2015-09-09 | 安徽鑫昆净化设备有限公司 | Adsorbent with adsorption on heavy metals and preparation method for adsorbent |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2689616C1 (en) * | 2018-10-09 | 2019-05-28 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Тамбовский государственный технический университет" (ФГБОУ ВО "ТГТУ") | Method of sorption cleaning of aqueous media from organic substances and ions of heavy metals |
| RU2699634C1 (en) * | 2018-10-24 | 2019-09-06 | федеральное государственное автономное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Казанский (Приволжский) федеральный университет" (ФГАОУ ВО КФУ) | Method for detoxification of aqueous media contaminated with graphene oxide |
| RU2725822C1 (en) * | 2019-07-09 | 2020-07-06 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Тамбовский государственный технический университет" (ФГБОУ ВО "ТГТУ") | Method of producing nanocomposite sorption material based on graphene and iron oxide nanoparticles |
| CN110699703A (en) * | 2019-11-08 | 2020-01-17 | 上海纳米技术及应用国家工程研究中心有限公司 | Preparation method of reduced graphene oxide-polyhydroquinone composite electrode, product and application thereof |
| CN110699703B (en) * | 2019-11-08 | 2021-09-21 | 上海纳米技术及应用国家工程研究中心有限公司 | Preparation method of reduced graphene oxide-polyhydroquinone composite electrode, product and application thereof |
| CN112264070A (en) * | 2020-10-26 | 2021-01-26 | 山东建筑大学 | Iron nitride @ nitrogen-doped graphene composite material and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN112403517A (en) * | 2020-11-26 | 2021-02-26 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Method for preparing nano enzyme by reducing graphene oxide with ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide, prepared nano enzyme and application of nano enzyme |
| CN112403517B (en) * | 2020-11-26 | 2023-04-07 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Method for preparing nano enzyme by reducing graphene oxide with ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide, prepared nano enzyme and application of nano enzyme |
| CN112916045A (en) * | 2021-01-31 | 2021-06-08 | 胡国强 | Load ZnO-TiO2Preparation method of magnetic graphene oxide/chitosan composite material |
| RU2805525C2 (en) * | 2021-12-15 | 2023-10-18 | Федеральное Государственное Бюджетное Учреждение Науки Федеральный Исследовательский Центр Проблем Химической Физики И Медицинской Химии Российской Академии Наук (Фиц Пхф И Мх Ран) | Superhydrophobic sorbent for ecological cleaning of land and water bodies from oil and oil product spills and method for its production |
| CN115251081A (en) * | 2022-08-15 | 2022-11-01 | 安徽工业大学 | Graphene antibacterial slurry and preparation method thereof |
| RU2817978C1 (en) * | 2023-05-16 | 2024-04-23 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "ЛАЙФТЕХ" (ООО "ЛАЙФТЕХ") | Sorbent for removal of radionuclides from natural and waste water and method of its production |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU2659285C1 (en) | Sorbent based on modified graphene oxide and method of its production | |
| Saeed et al. | Synthesis of chitosan composite of metal-organic framework for the adsorption of dyes; kinetic and thermodynamic approach | |
| Zhao et al. | Polyethylenimine-modified chitosan materials for the recovery of La (III) from leachates of bauxite residue | |
| Zhao et al. | In-situ growth of UiO-66-NH2 onto polyacrylamide-grafted nonwoven fabric for highly efficient Pb (II) removal | |
| Zheng et al. | Design of mesoporous silica hybrid materials as sorbents for the selective recovery of rare earth metals | |
| Fan et al. | Adsorption of antimony (III) from aqueous solution by mercapto-functionalized silica-supported organic–inorganic hybrid sorbent: Mechanism insights | |
| Tirtom et al. | Comparative adsorption of Ni (II) and Cd (II) ions on epichlorohydrin crosslinked chitosan–clay composite beads in aqueous solution | |
| Nasirimoghaddam et al. | Chitosan coated magnetic nanoparticles as nano-adsorbent for efficient removal of mercury contents from industrial aqueous and oily samples | |
| Zheng et al. | Utilization of diatomite/chitosan–Fe (III) composite for the removal of anionic azo dyes from wastewater: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics | |
| Hua et al. | Fabrication and evaluation of hollow surface molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid and selective adsorption of dibenzothiophene | |
| Zhong et al. | A novel molecularly imprinted material based on magnetic halloysite nanotubes for rapid enrichment of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in water | |
| Monier et al. | Adsorption of Cu (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) ions by cross-linked magnetic chitosan-2-aminopyridine glyoxal Schiff's base | |
| Gao et al. | Preparation and chelation adsorption property of composite chelating material poly (amidoxime)/SiO2 towards heavy metal ions | |
| Cui et al. | Fast removal of Hg (II) ions from aqueous solution by amine-modified attapulgite | |
| Duan et al. | Plasma surface modification of materials and their entrapment of water contaminant: A review | |
| Saman et al. | Recovery of Au (III) from an aqueous solution by aminopropyltriethoxysilane-functionalized lignocellulosic based adsorbents | |
| Cui et al. | Preparation and application of Aliquat 336 functionalized chitosan adsorbent for the removal of Pb (II) | |
| Ragheb et al. | Magnetic solid-phase extraction using metal–organic framework-based biosorbent followed by ligandless deep-eutectic solvent-ultrasounds-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DES-USA-DLLME) for preconcentration of mercury (II) | |
| Huang et al. | Study and comparison of polydopamine and its derived carbon decorated nanoparticles in the magnetic solid-phase extraction of estrogens | |
| Kong et al. | Graphene oxide-terminated hyperbranched amino polymer-carboxymethyl cellulose ternary nanocomposite for efficient removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions | |
| Liu et al. | Construction of magnetic bifunctional β-cyclodextrin nanocomposites for adsorption and degradation of persistent organic pollutants | |
| WO2012128747A1 (en) | Graphite oxide coated particulate material and uses thereof | |
| Cheng et al. | Thiol-/thioether-functionalized porous organic polymers for simultaneous removal of mercury (II) ion and aromatic pollutants in water | |
| Hoang et al. | Coconut shell activated carbon/CoFe2O4 composite for the removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solution | |
| Chen et al. | Synthesis of magnetic carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene oxide nanocomposites for adsorption of copper from aqueous solution |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20201026 |