RU2658426C1 - Method for producing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) - Google Patents
Method for producing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2658426C1 RU2658426C1 RU2017119146A RU2017119146A RU2658426C1 RU 2658426 C1 RU2658426 C1 RU 2658426C1 RU 2017119146 A RU2017119146 A RU 2017119146A RU 2017119146 A RU2017119146 A RU 2017119146A RU 2658426 C1 RU2658426 C1 RU 2658426C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- nad
- solid phase
- concentration
- concentrate
- temperature
- Prior art date
Links
- BAWFJGJZGIEFAR-NNYOXOHSSA-N NAD zwitterion Chemical compound NC(=O)C1=CC=C[N+]([C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H](COP([O-])(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@@H]3[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H](O3)N3C4=NC=NC(N)=C4N=C3)O)O2)O)=C1 BAWFJGJZGIEFAR-NNYOXOHSSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 53
- 229940101270 nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) Drugs 0.000 title claims abstract description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 3
- 229950006238 nadide Drugs 0.000 claims abstract description 49
- 229930027945 nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide Natural products 0.000 claims abstract description 49
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 235000019441 ethanol Nutrition 0.000 claims abstract description 17
- 239000007790 solid phase Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 238000004108 freeze drying Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical group CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims abstract 3
- 239000012531 culture fluid Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000003957 anion exchange resin Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 abstract description 19
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000001963 growth medium Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 23
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 3
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004821 distillation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007791 liquid phase Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001223 reverse osmosis Methods 0.000 description 2
- 208000024827 Alzheimer disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000018737 Parkinson disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008186 active pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012267 brine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005119 centrifugation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000005515 coenzyme Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940088679 drug related substance Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008014 freezing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007710 freezing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000002216 heart Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000004255 ion exchange chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000004185 liver Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000012792 lyophilization process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004770 neurodegeneration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000015122 neurodegenerative disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229910017604 nitric acid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002773 nucleotide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003729 nucleotide group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- -1 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 description 1
- HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;chloride;hydrate Chemical compound O.[Na+].[Cl-] HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000002594 sorbent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000002784 stomach Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000000108 ultra-filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12P—FERMENTATION OR ENZYME-USING PROCESSES TO SYNTHESISE A DESIRED CHEMICAL COMPOUND OR COMPOSITION OR TO SEPARATE OPTICAL ISOMERS FROM A RACEMIC MIXTURE
- C12P19/00—Preparation of compounds containing saccharide radicals
- C12P19/26—Preparation of nitrogen-containing carbohydrates
- C12P19/28—N-glycosides
- C12P19/30—Nucleotides
- C12P19/36—Dinucleotides, e.g. nicotineamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07H—SUGARS; DERIVATIVES THEREOF; NUCLEOSIDES; NUCLEOTIDES; NUCLEIC ACIDS
- C07H1/00—Processes for the preparation of sugar derivatives
- C07H1/06—Separation; Purification
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Saccharide Compounds (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Description
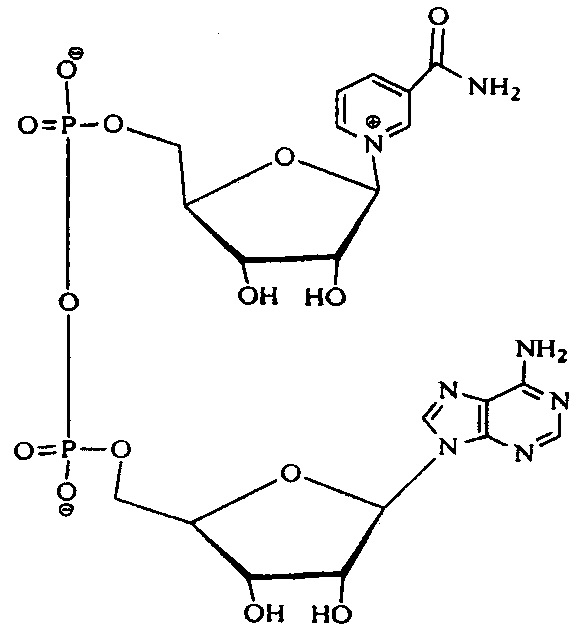
Изобретение относится к получению лекарственной субстанции - никотинамидадениндинуклеотида (НАД), соответствующего формулеThe invention relates to the production of a drug substance - nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), corresponding to the formula
Никотинамидадениндинуклеотид (НАД) является одним из важнейших коферментов, ответственных за окислительно-восстановительные процессы в клетках. В настоящее время выявлена потенциальная роль НАД в терапии нейродегенеративных заболеваний, таких как болезнь Альцгеймера и болезнь Паркинсона. Также препараты, содержащие НАД, используют в медицине при лечении заболеваний сердца, желудка и печени.Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is one of the most important coenzymes responsible for redox processes in cells. The potential role of NAD in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, has now been identified. Also, preparations containing NAD are used in medicine in the treatment of diseases of the heart, stomach and liver.
Известны методы получения НАД выделением продукта из культуральной жидкости, образующейся в процессе биосинтеза [CN 105481923, US 4515943, US 2016340378]. В способах по перечисленным патентам получение НАД из культуральной жидкости включает фильтрацию и/или ультрафильтрацию культуральной жидкости, очистку полученного раствора ионообменной хроматографией или на неионогенных сорбентах с получением малоконцентрированных растворов НАД, которые подвергаются затем концентрированию методом лиофилизации или обратного осмоса. Из полученных концентрированных растворов НАД выделяют введением в водный раствор смешивающегося с водой органического растворителя, например этилового спирта, ацетона.Known methods for producing NAD by isolating a product from a culture fluid generated during biosynthesis [CN 105481923, US 4515943, US 2016340378]. In the methods of the listed patents, the preparation of NAD from the culture fluid includes filtration and / or ultrafiltration of the culture fluid, purification of the resulting solution by ion exchange chromatography or on nonionic sorbents to obtain low concentration NAD solutions, which are then concentrated by lyophilization or reverse osmosis. From the obtained concentrated solutions, NAD is isolated by introducing into the aqueous solution a water-miscible organic solvent, for example ethyl alcohol, acetone.
Во всех известных способах для выделения НАД требуется концентрирование водных растворов НАД с низким содержанием целевого продукта (не более 3 г/л). Процесс концентрирования столь разбавленных растворов осложняется низкой термостабильностью НАД, в связи чем необходимо проведение малопроизводительного процесса лиофилизации с большим объемом раствора или обратного осмоса, сопровождающегося значительными потерями продукта.In all known methods for the isolation of NAD, concentration of aqueous NAD solutions with a low content of the target product (not more than 3 g / l) is required. The process of concentrating such dilute solutions is complicated by the low thermal stability of NAD, and therefore it is necessary to conduct a low-throughput lyophilization process with a large solution volume or reverse osmosis, accompanied by significant product losses.
Наиболее близким к заявляемому способу является способ по US 3140281, в соответствии с которым НАД выделяют из культуральной жидкости фильтрацией на воронке Бюхнера в смеси с кизельгуром, предварительной очисткой на слабоосновном анионите в ацетатной форме, хроматографией на макропористом сульфокатионите с получением разбавленного водного раствора НАД. Полученный водный раствор НАД концентрируют путем отгонки воды под вакуумом. Выделение НАД из концентрата осуществляют введением в раствор этилового спирта сначала в два приема с отделением неактивного осадка при достижении концентрации спирта около 60%, затем при добавлении спирта к фильтрату до достижении концентрации этанола 90% выпадает осадок НАД. Образовавшийся аморфный осадок отфильтровывают, промывают этанолом, затем диэтиловым эфиром и сушат в вакууме. Получают НАД с чистотой около 80-90%.Closest to the claimed method is the method according to US 3140281, in accordance with which NAD is isolated from the culture fluid by filtration on a Buchner funnel mixed with kieselguhr, preliminary purification on weakly basic anion exchange resin in acetate form, chromatography on macroporous sulfocathionite to obtain a dilute aqueous solution of NAD. The resulting NAD aqueous solution was concentrated by distillation of water under vacuum. Isolation of NAD from the concentrate is carried out by introducing ethanol into the solution, first in two doses, with the separation of the inactive precipitate when the alcohol concentration reaches about 60%, then when adding alcohol to the filtrate until the ethanol concentration reaches 90%, the NAD precipitate is precipitated. The resulting amorphous precipitate is filtered off, washed with ethanol, then with diethyl ether and dried in vacuum. Obtain NAD with a purity of about 80-90%.
Существенным недостатком способа по US 3140281 является низкий выход продукта на стадии концентрирования НАД методом отгонки воды под вакуумом. Крайне низкая термостабильность водных растворов НАД обусловливает деструкцию НАД в процессе упарки с образованием продуктов разложения. Экспериментальное воспроизведение этой стадии выявило, что даже при вакууме ниже 10 мм рт.ст. в упаренном растворе содержится не более 50% продукта, взятого на концентрирование.A significant disadvantage of the method according to US 3140281 is the low yield of the product at the stage of concentration of NAD by distillation of water under vacuum. The extremely low thermal stability of aqueous NAD solutions leads to the destruction of NAD during evaporation with the formation of decomposition products. Experimental reproduction of this stage revealed that even at a vacuum below 10 mm Hg. one stripped off solution contains not more than 50% of the product taken for concentration.
Заявляемый способ направлен на повышение выхода выделяемого из культуральной жидкости НАД, снижение затрат органических растворителей и упрощение технологического процесса.The inventive method is aimed at increasing the output allocated from the culture fluid NAD, reducing the cost of organic solvents and simplifying the process.
Поставленная задача решается получением никотинамидаденин динуклеотида из культуральной жидкости процесса биосинтеза фильтрацией культуральной жидкости, предварительной очисткой полученного раствора, его концентрированием и выделением целевого продукта из концентрированного раствора.The problem is solved by obtaining nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide from the culture fluid of the biosynthesis process by filtering the culture fluid, pre-cleaning the resulting solution, concentrating it and isolating the target product from the concentrated solution.
Отличительными признаками заявляемого способа являются:Distinctive features of the proposed method are:
Концентрирование НАД переводом раствора в твердую фазу при температуре (минус 5±1)°С, плавление образовавшейся твердой фазы при температуре 2±2°С и сбор концентрированных фракций, образующихся при плавлении твердой фазы.Concentration of NAD by transferring the solution to the solid phase at a temperature of (minus 5 ± 1) ° С, melting of the formed solid phase at a temperature of 2 ± 2 ° С and collection of concentrated fractions formed during melting of the solid phase.
Положительный результат в заявленном способе достигается за счет следующих выявленных в процессе разработки особенностей выделения НАД из культуральной жидкости:A positive result in the claimed method is achieved due to the following identified in the development process features of the allocation of NAD from the culture fluid:
• Перевод разбавленного раствора НАД в твердую фазу при температуре (минус 5±1)°С, который не сопровождается деструкцией НАД;• Translation of the diluted NAD solution into the solid phase at a temperature of (minus 5 ± 1) ° С, which is not accompanied by NAD destruction;
• Плавление твердой фазы при температуре 2±2°С происходит с селективным накоплением НАД в жидкой фазе без деструкции целевого продукта;• Melting of the solid phase at a temperature of 2 ± 2 ° C occurs with selective accumulation of NAD in the liquid phase without the destruction of the target product;
ПримерExample
Культуральную жидкость объемом 6,0 л, содержащую 15 г НАД, подвергают центрифугированию на центрифуге. Фильтрат охлаждают и смешивают с 1 кг кизельгура.A 6.0 L culture fluid containing 15 g of NAD is centrifuged in a centrifuge. The filtrate is cooled and mixed with 1 kg of kieselguhr.
Смесь фильтруют через воронку Бюхнера большого диаметра, промывают осадок водой. Получают объединенный фильтрат объемом около 8 л, представляющий собой желтый прозрачный раствор.The mixture is filtered through a large diameter Buchner funnel, and the precipitate is washed with water. A combined filtrate of about 8 L volume is obtained, which is a yellow clear solution.
Полученный раствор пропускают через колонку, содержащую слабоосновной анионит в ацетатной форме. В процессе прохождения раствора на анионите сорбируется большая часть примесей состоящих из нуклеотидных веществ и пигментов. НАД практически не сорбируется на анионит и переходит в фильтрат. Первые порции фильтрата, не содержащие НАД, отделяются от основного фильтрата. Колонка промывается небольшим количеством воды для вытеснения НАД из анионита.The resulting solution was passed through a column containing weakly basic anion exchange resin in acetate form. During the passage of the solution, most of the impurities consisting of nucleotide substances and pigments are adsorbed on the anion exchange resin. NAD is practically not adsorbed on anion exchange resin and passes into the filtrate. The first portions of the filtrate not containing NAD are separated from the main filtrate. The column is washed with a small amount of water to displace NAD from the anion exchange resin.
В результате предварительной очистки раствора НАД на анионите получают 8 л слабоокрашенного раствора, содержащего 13,5 г НАД (1,7 г/л).As a result of preliminary purification of the NAD solution on anion exchange resin, 8 L of a slightly colored solution containing 13.5 g of NAD (1.7 g / L) is obtained.
Раствор переносят в полиэтиленовую емкость и выдерживают при температуре (минус 5±1)°С в течение 5 часов. Полученную твердую фазу (ледообразную массу) подвергают дроблению и переносят в вертикальную колонну диаметром 12 см и высотой 100 см, снабженную рубашкой для подачи рассола для поддержания температуры в реакционной массе на уровне 2±2°С.The solution is transferred to a polyethylene container and kept at a temperature of (minus 5 ± 1) ° C for 5 hours. The resulting solid phase (ice mass) is crushed and transferred to a vertical column with a diameter of 12 cm and a height of 100 cm, equipped with a jacket for supplying brine to maintain the temperature in the reaction mass at a level of 2 ± 2 ° C.
Образующаяся в результате плавления жидкая фаза собирается фракциями по 500 мл. Первые 2 фракции объемом 1,0 л с концентрацией 8,5 г/л используются для дальнейшего концентрирования НАД методом лиофилизации. Последующие 3 фракции объемом 1,5 л, содержащие 4,2 г НАД (концентрация 2.8 г/л), возвращают в цикл для последующего концентрирования методом вымораживания. Выход продукта на этой стадии составляет 94%.The liquid phase formed as a result of melting is collected in fractions of 500 ml. The first 2 fractions with a volume of 1.0 l with a concentration of 8.5 g / l are used for further concentration of NAD by lyophilization. The next 3 fractions with a volume of 1.5 l containing 4.2 g of NAD (concentration of 2.8 g / l) are returned to the cycle for subsequent concentration by freezing. The product yield at this stage is 94%.
Фракция объемом 1,0 л с концентрацией 8,5 г/л передается на дальнейшее концентрирование методом лиофилизации с получением раствора НАД с концентрацией 25-30%. Полученный концентрат доводят с помощью азотной кислоты до рН 2-3 и в раствор вводят этанол до достижения концентрации по этанолу 55-60%. Выпавшие в осадок примеси, состоящие преимущественно из пептидных соединений, отделяют фильтрацией. К полученному раствору дополнительно вводят этанол до достижения концентрации по этанолу 85-90%. Образовавшийся осадок аморфного НАД отделяют центрифугированием, промывают этанолом, затем диэтиловым эфиром и сушат в вакууме. Получают 7,7 г аморфного порошка НАД с чистотой 85%.A 1.0 L fraction with a concentration of 8.5 g / L is transferred to further concentration by lyophilization to obtain a NAD solution with a concentration of 25-30%. The resulting concentrate is adjusted with nitric acid to a pH of 2-3 and ethanol is introduced into the solution to achieve an ethanol concentration of 55-60%. Precipitated impurities consisting mainly of peptide compounds are separated by filtration. Ethanol is additionally added to the resulting solution until an ethanol concentration of 85-90% is reached. The resulting amorphous NAD precipitate was separated by centrifugation, washed with ethanol, then with diethyl ether and dried in vacuum. Obtain 7.7 g of an amorphous powder NAD with a purity of 85%.
Таким образом, заявляемый способ обеспечивает 8-кратное снижение объема раствора НАД, подвергаемого лиофилизации, что обеспечивает доступность способа для промышленного применения.Thus, the inventive method provides an 8-fold reduction in the volume of the NAD solution subjected to lyophilization, which ensures the availability of the method for industrial use.
Полученный аморфный НАД может быть дополнительно очищен способом по DE 3141030 с получением кристаллического НАД с чистотой не менее 95%.The obtained amorphous NAD can be further purified by the method of DE 3141030 to obtain crystalline NAD with a purity of at least 95%.
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017119146A RU2658426C1 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2017-05-31 | Method for producing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017119146A RU2658426C1 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2017-05-31 | Method for producing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2658426C1 true RU2658426C1 (en) | 2018-06-21 |
Family
ID=62713589
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2017119146A RU2658426C1 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2017-05-31 | Method for producing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2658426C1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114437162A (en) * | 2020-10-30 | 2022-05-06 | 尚科生物医药(上海)有限公司 | Preparation method of amorphous nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3140281A (en) * | 1960-06-13 | 1964-07-07 | Sankyo Co | Process for the preparation of codehydrogenase i (diphosphopyridine nucleotide) of high purity from yeast |
| US4515943A (en) * | 1980-10-12 | 1985-05-07 | Kohjin Co., Ltd. | Crystal of beta-nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide and process for preparing the same |
| SU1693057A1 (en) * | 1989-07-02 | 1991-11-23 | Институт биохимии им.А.Н.Баха | Method for preparation of nicotinamideadenine dinucleotide (nad) |
| CN104817604A (en) * | 2015-03-16 | 2015-08-05 | 邦泰生物工程(深圳)有限公司 | Purification method for beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide |
| CN105481923A (en) * | 2015-12-30 | 2016-04-13 | 平光制药股份有限公司 | Preparation method of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
-
2017
- 2017-05-31 RU RU2017119146A patent/RU2658426C1/en active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3140281A (en) * | 1960-06-13 | 1964-07-07 | Sankyo Co | Process for the preparation of codehydrogenase i (diphosphopyridine nucleotide) of high purity from yeast |
| US4515943A (en) * | 1980-10-12 | 1985-05-07 | Kohjin Co., Ltd. | Crystal of beta-nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide and process for preparing the same |
| SU1693057A1 (en) * | 1989-07-02 | 1991-11-23 | Институт биохимии им.А.Н.Баха | Method for preparation of nicotinamideadenine dinucleotide (nad) |
| CN104817604A (en) * | 2015-03-16 | 2015-08-05 | 邦泰生物工程(深圳)有限公司 | Purification method for beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide |
| CN105481923A (en) * | 2015-12-30 | 2016-04-13 | 平光制药股份有限公司 | Preparation method of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114437162A (en) * | 2020-10-30 | 2022-05-06 | 尚科生物医药(上海)有限公司 | Preparation method of amorphous nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP4151645A2 (en) | Separation of 2'-fl from a fermentation broth | |
| RU2206613C2 (en) | Method of isolation of clavulanic acid | |
| CN103555807B (en) | Method for preparing 7-ACA (aminocephalosporanic acid) and obtaining alpha-aminoadipic acid by one-step enzymatic reaction | |
| CN103664989A (en) | Method used for preparing moxidectin using nemadectin fermentation broth | |
| KR20070119641A (en) | Isolation of galanthamine from biological material | |
| RU2658426C1 (en) | Method for producing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (nad) | |
| CN111171097A (en) | Separation and purification method for producing adenosine by fermentation | |
| CN110734467A (en) | method for extracting and purifying spinosad from fermentation liquor | |
| CN102260286B (en) | Method for separating and purifying crude product L-alpha-glycerophosphocholine | |
| KR100828706B1 (en) | A method for purifying 5'-Inosinic acid fermentation broth via crystallization process | |
| CN106366159A (en) | Carnosine extracting and purifying method | |
| KR101341033B1 (en) | Separating and Purifying Method of Coenzyme Q10 | |
| CN103113423A (en) | Method for extracting D-ribose from fermentation broth through ion exchange and membrane separation technologies | |
| JPH04360692A (en) | Production of trehalose | |
| CN100509757C (en) | Purification method of *N-L-arginine | |
| CN106883286B (en) | Extraction and purification method of tyrosine derivative | |
| CN114702487B (en) | Purification method of lysergic acid | |
| CN114213276B (en) | Method for extracting and purifying theanine from enzyme catalytic reaction | |
| TWI670278B (en) | High purity low endotoxin carbohydrate (hple) compositions, and methods of isolation thereof | |
| CN109096273A (en) | The method for separating and preparing of mezlocillin sodium impurity C, D and F | |
| CN216321130U (en) | Extraction and concentration device for clavulanic acid fermentation liquor | |
| CN109251229B (en) | Method for separating and purifying fidaxomicin | |
| KR101125538B1 (en) | Method of micelle-fractional precipitation hybrid process for the purification of paclitaxel | |
| CN112390817B (en) | Method for salting out and extracting tacrolimus fermentation liquor | |
| RU2644674C1 (en) | Method for obtaining 3,3',3'',3'''-(3,8,13,17-tetramethylporphyrin-2,7,12,18-tetrayl) tetrapropionic acid (coproporphyrin) |