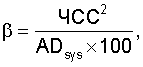RU2291663C2 - Method for measuring arterial blood pressure - Google Patents
Method for measuring arterial blood pressure Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2291663C2 RU2291663C2 RU2005105977/14A RU2005105977A RU2291663C2 RU 2291663 C2 RU2291663 C2 RU 2291663C2 RU 2005105977/14 A RU2005105977/14 A RU 2005105977/14A RU 2005105977 A RU2005105977 A RU 2005105977A RU 2291663 C2 RU2291663 C2 RU 2291663C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- blood pressure
- sys
- heart rate
- mmhg
- arterial blood
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measuring Pulse, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure Or Blood Flow (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к медицине, терапии, анестезиологии и реаниматологии, хирургии, медицине катастроф, патофизиологии.The invention relates to medicine, therapy, anesthesiology and intensive care, surgery, disaster medicine, pathophysiology.
При различных заболеваниях, повреждениях, травмах, ранениях, синдроме длительного сдавления необходимо знать величины систолического и диастолического артериального давления, а также частоты пульса.For various diseases, injuries, injuries, injuries, prolonged compression syndrome, it is necessary to know the values of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, as well as heart rate.
Экспресс-определение этих параметров системы кровообращения дает возможность немедленно установить степень тяжести состояния больного или раненого (пострадавшего) и выработать правильную тактику лечения.Rapid determination of these parameters of the circulatory system makes it possible to immediately establish the severity of the condition of the patient or wounded (injured) and develop the right treatment tactics.
Изменения в системе кровообращения немедленно отражаются на состоянии гемомикроциркуляторного русла.Changes in the circulatory system are immediately reflected in the state of the hemomicrocirculatory bed.
В настоящее время самым распространенным является аускультативный метод определения артериального давления, разработанный русским хирургом Н.С.Коротковым в 1905 г.Currently, the most common is the auscultatory method for determining blood pressure, developed by the Russian surgeon N.S. Korotkov in 1905.
Для измерения давления используется простой прибор, состоящий из механического манометра, манжеты с грушей и фонендоскопа.To measure pressure, a simple device consisting of a mechanical pressure gauge, a cuff with a pear and a phonendoscope is used.
Этот метод основан на полном пережатии манжетой плечевой артерии и выслушивании тонов, возникающих при медленном выпуске воздуха из манжеты.This method is based on the complete compression of the cuff of the brachial artery and listening to tones arising from the slow release of air from the cuff.
Известен также осциллометрический метод определения артериального давления, который основан на регистрации прибором пульсаций давления воздуха, возникающих в манжете при прохождении крови через сдавленный манжетой участок артерии (Инструментальные методы исследования сердечно-сосудистой системы. Справочник под ред. Виноградовой Т.C. М., 1986).Also known is the oscillometric method for determining blood pressure, which is based on the registration of pulsations of air pressure arising in the cuff when the blood passes through the portion of the artery squeezed by the cuff (Instrumental methods for the study of the cardiovascular system. Handbook edited by T. Vinogradova, 1986 )
Однако использование известных методов определения артериального давления требует специфических условий: доступ к верхним конечностям больного или раненого и некоторое время для выполнения исследования (3-7 минут).However, the use of known methods for determining blood pressure requires specific conditions: access to the upper limbs of a sick or wounded person and some time to complete the study (3-7 minutes).
Задачей настоящего изобретения является разработка способа определения артериального давления, позволяющего осуществить экспресс-диагностику состояния системы кровообращения немедленно (дискретно) и в динамике.The present invention is to develop a method for determining blood pressure, which allows for the rapid diagnosis of the state of the circulatory system immediately (discretely) and in dynamics.
Сущность заявленного способа заключается в следующем.The essence of the claimed method is as follows.
Инфракрасным или любым другим датчиком пульсометрии регистрируют пульсограмму на пальце, мочке или на другом доступном участке или части тела. Определяют амплитуду (А) и частоту пульсовой волны (υ).An infrared or any other heart rate monitor records a pulsogram on a finger, lobe, or other accessible area or part of the body. The amplitude (A) and the frequency of the pulse wave (υ) are determined.
По полученным величинам рассчитывают систолическое артериальное давление (ADsys) и частоту пульса (ЧСС) по формулам:Based on the obtained values, systolic blood pressure (AD sys ) and pulse rate (HR) are calculated by the formulas:
ADsys=а×А,AD sys = a × A,
где ADsys - систолическое артериальное давление, мм рт.ст.;where AD sys is systolic blood pressure, mmHg;
а - эмпирический коэффициент датчика пульсометрии;a is the empirical coefficient of the heart rate sensor;
А - амплитуда пульсовой волны (абс.ч.).A is the amplitude of the pulse wave (abs. Hours).
ЧСС=(t×υ)×60 /t,Heart rate = (t × υ) × 60 / t,
где ЧСС - частота сердечных сокращений, уд. в мин;where heart rate is the heart rate, beats. in minutes;
t - интервал времени, за который осуществлено измерение, с;t is the time interval for which the measurement was made, s;
υ - частота пульсовой волны, 1/с или с-1.υ - pulse wave frequency, 1 / s or s -1 .
Определение величины диастолического артериального давления (ADdy) осуществляют по формуле:The determination of diastolic blood pressure (AD dy ) is carried out according to the formula:
ADdy=(ADsys/е(β)),AD dy = (AD sys / е (β) ),
где ADdy - диастолическое артериальное давление, мм рт.ст.;where AD dy - diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg;
ADsys - систолическое артериальное давление, мм рт.ст.;AD sys - systolic blood pressure, mmHg;
е - постоянная, равная 2,718271;e is a constant equal to 2.718271;
Технический результат, достигаемый при использовании предложенного изобретения, заключается в возможности немедленного определения величины систолического и диастолического артериального давления, а также частоты сердечных сокращений, что, в свою очередь, дает возможность немедленно установить степень тяжести состояния больного или раненого (пострадавшего) и выработать правильную тактику лечения.The technical result achieved by using the proposed invention is the ability to immediately determine the magnitude of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, as well as heart rate, which, in turn, makes it possible to immediately establish the severity of the condition of the patient or wounded (injured) and develop the right tactics treatment.
Клинические примеры выполнения изобретения.Clinical examples of the invention.
Контрольное определение артериального давления (AD) осуществляют электронным тонометром «OMRON» (Япония)Control determination of blood pressure (AD) is carried out by an electronic tonometer "OMRON" (Japan)
Пример 1 (фиг.1).Example 1 (figure 1).
Результаты, полученные с помощью электронного тонометра «OMRON» (Япония):The results obtained using the OMRON electronic tonometer (Japan):
ADsys=119 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 119 mmHg
ADdy=75 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 75 mmHg
ЧСС=73 уд. в минHeart rate = 73 beats. in min
Математический метод:The mathematical method:
Время измерения (t) - 10 сMeasurement time (t) - 10 s
Амплитуда (А)=112Amplitude (A) = 112
Частота пульсовой волны (υ) - 1,22 с-1 Pulse wave frequency (υ) - 1.22 s -1
Частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС)=73 уд. в минHeart rate (HR) = 73 beats. in min
ЧСС=(10×1,22)×60/10=73 уд. в минHeart rate = (10 × 1.22) × 60/10 = 73 beats. in min
Коэффициент прибора К=1The coefficient of the device K = 1
ADsys=112 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 112 mmHg
ADdy=112/2,7173×73/112/100=70 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 112 / 2.71 73 × 73/112/100 = 70 mmHg
Пример 2 (фиг.2).Example 2 (figure 2).
Результаты, полученные с помощью электронного тонометра «OMRON»:The results obtained using the OMRON electronic blood pressure monitor:
ADsys=140 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 140 mmHg
ADdy=79 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 79 mmHg
ЧСС=89 уд. в минHeart rate = 89 beats. in min
Математический метод:The mathematical method:
Время измерения (t)=10 сMeasurement time (t) = 10 s
Амплитуда А=136Amplitude A = 136
Частота пульсовой волны (υ) - 1,53 с-1 Pulse wave frequency (υ) - 1.53 s -1
Частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС)=92 уд. в минHeart rate (HR) = 92 beats. in min
ЧСС=(10×1,53)×60/10=92 уд. в минHeart rate = (10 × 1.53) × 60/10 = 92 beats. in min
Коэффициент прибора К=1The coefficient of the device K = 1
ADsys=136 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 136 mmHg
ADdy=136/2,7192×92/136/100=73 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 136 / 2.71 92 × 92/136/100 = 73 mmHg
Пример 3 (фиг.3).Example 3 (figure 3).
Результаты, полученные с помощью электронного тонометра «OMRON» (Япония):The results obtained using the OMRON electronic tonometer (Japan):
ADsys=141 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 141 mmHg
ADdy=103 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 103 mmHg
ЧСС=62 уд. в минHeart rate = 62 beats. in min
Математический метод:The mathematical method:
Время измерения (t)=7 сMeasurement time (t) = 7 s
Амплитуда А=131Amplitude A = 131
Частота пульсовой волны (υ) - 1,08 с-1 Pulse wave frequency (υ) - 1.08 s -1
Частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС)=65 уд. в минHeart rate (HR) = 65 beats. in min
ЧСС=(7×1,08)×60/7=65 уд. в минHeart rate = (7 × 1.08) × 60/7 = 65 beats. in min
Коэффициент прибора К=1The coefficient of the device K = 1
ADsys=131 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 131 mmHg
ADdy=131/2,7165×65/131/100=95 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 131 / 2.71 65 × 65/131/100 = 95 mmHg
Пример 4 (фиг.4).Example 4 (figure 4).
Результаты, полученные с помощью электронного тонометра «OMRON» (Япония):The results obtained using the OMRON electronic tonometer (Japan):
ADsys=123 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 123 mmHg
ADdy=65 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 65 mmHg
ЧСС=72 уд. в минHeart rate = 72 beats. in min
Математический метод:The mathematical method:
Время измерения (t)=8 с.Measurement time (t) = 8 s.
Амплитуда А=116Amplitude A = 116
Частота пульсовой волны (υ) - 1,27 с-1 Pulse wave frequency (υ) - 1.27 s -1
Частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС)=76 уд. в минHeart rate (HR) = 76 beats. in min
ЧСС=(8×1,27)×60/8=76 уд. в минHeart rate = (8 × 1.27) × 60/8 = 76 beats. in min
Коэффициент прибора К=1The coefficient of the device K = 1
ADsys=116 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 116 mmHg
ADdy=116 /2,7176×76/116/100=70 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 116 / 2.71 76 × 76/116/100 = 70 mmHg
Пример 5 (фиг.5).Example 5 (figure 5).
Результаты, полученные с помощью электронного тонометра «OMRON» (Япония):The results obtained using the OMRON electronic tonometer (Japan):
ADsys=137 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 137 mmHg
ADdy=83 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 83 mmHg
ЧСС=75 уд. в минHeart rate = 75 beats. in min
Время измерения (t)=12 с.Measurement time (t) = 12 s.
Амплитуда А=131Amplitude A = 131
Частота пульсовой волны (υ) - 1,33 с-1 Pulse wave frequency (υ) - 1.33 s -1
Частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС)=80 уд. в минHeart rate (HR) = 80 beats. in min
ЧСС=(12×1,33)×60/12=80 уд. в минHeart rate = (12 × 1.33) × 60/12 = 80 beats. in min
Коэффициент прибора К=1The coefficient of the device K = 1
ADsys=131 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 131 mmHg
ADdy=131/2,7180×80/131/100=80 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 131 / 2.71 80 × 80/131/100 = 80 mmHg
Пример 6 (фиг.6).Example 6 (Fig.6).
Результаты, полученные с помощью электронного тонометра «OMRON» (Япония):The results obtained using the OMRON electronic tonometer (Japan):
ADsys=139 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 139 mmHg
ADdy=79 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 79 mmHg
ЧСС=82 уд. в минHeart rate = 82 beats. in min
Математический метод:The mathematical method:
Время измерения (t)=9 с.Measurement time (t) = 9 s.
Амплитуда А=132Amplitude A = 132
Частота пульсовой волны (υ) - 1,43 с-1 Pulse wave frequency (υ) - 1.43 s -1
Частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС)=86 уд. в минHeart rate (HR) = 86 beats. in min
ЧСС=(9×1,43)×60/9=86 уд. в минHeart rate = (9 × 1.43) × 60/9 = 86 beats. in min
Коэффициент прибора К=1The coefficient of the device K = 1
ADsys=132 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 132 mmHg
86×86/132/10086 × 86/132/100
AUdy=132/2,7186×86/132/100=75 мм рт.ст.AU dy = 132 / 2.71 86 × 86/132/100 = 75 mmHg
Пример 7 (фиг.7).Example 7 (Fig.7).
Результаты, полученные с помощью электронного тонометра «OMRON» (Япония):The results obtained using the OMRON electronic tonometer (Japan):
ADsys=143 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 143 mmHg
ADdy=87 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 87 mmHg
ЧСС=78 уд. в минHeart rate = 78 beats. in min
Математический метод:The mathematical method:
Время измерения (t)=3 сMeasurement time (t) = 3 s
Амплитуда А=141Amplitude A = 141
Частота пульсовой волны (υ) - 1,32 с-1 Pulse wave frequency (υ) - 1.32 s -1
Частота сердечных сокращений (ЧСС)=79 уд. в минHeart rate (HR) = 79 beats. in min
ЧСС=(3×1,32)×60/3=79 уд. в минHeart rate = (3 × 1.32) × 60/3 = 79 beats. in min
Коэффициент прибора К=1The coefficient of the device K = 1
ADsys=141 мм рт.ст.AD sys = 141 mmHg
ADdy=141/2,7179×79/141/100=90 мм рт.ст.AD dy = 141 / 2.71 79 × 79/141/100 = 90 mmHg
Предложенный способ позволяет производить немедленное определение величины систолического и диастолического артериального давления, а также частоты сердечных сокращений.The proposed method allows the immediate determination of the value of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, as well as heart rate.
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2005105977/14A RU2291663C2 (en) | 2005-03-03 | 2005-03-03 | Method for measuring arterial blood pressure |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2005105977/14A RU2291663C2 (en) | 2005-03-03 | 2005-03-03 | Method for measuring arterial blood pressure |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2005105977A RU2005105977A (en) | 2006-08-10 |
| RU2291663C2 true RU2291663C2 (en) | 2007-01-20 |
Family
ID=37059370
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2005105977/14A RU2291663C2 (en) | 2005-03-03 | 2005-03-03 | Method for measuring arterial blood pressure |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2291663C2 (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1355236A1 (en) * | 1980-12-26 | 1987-11-30 | Институт Кибернетики Ан Усср | Method of measuring blood pressure without cuff |
| RU2073482C1 (en) * | 1992-07-15 | 1997-02-20 | Анатолий Петрович Попов | Method to measure arterial pressure |
| EP0787462A1 (en) * | 1994-02-02 | 1997-08-06 | Tovarischestvo Sogranichennoi Otvetstvennostju "Russky Tsentr Perspektivnykh Tekhnology" (Russintsentr) | Oscillometric method of determining haemodynamic indicators in the arterial circulation of a patient and measuring system for applying the said method |
| RU2106792C1 (en) * | 1992-02-03 | 1998-03-20 | Клочков Виктор Александрович | Method for monitoring arterial pressure and contracting myocardial capacity |
| RU2123277C1 (en) * | 1992-07-29 | 1998-12-20 | Владимир Прокопьевич Кожемяко | Method of indirect measurement of arterial pressure and device for its realization |
-
2005
- 2005-03-03 RU RU2005105977/14A patent/RU2291663C2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1355236A1 (en) * | 1980-12-26 | 1987-11-30 | Институт Кибернетики Ан Усср | Method of measuring blood pressure without cuff |
| RU2106792C1 (en) * | 1992-02-03 | 1998-03-20 | Клочков Виктор Александрович | Method for monitoring arterial pressure and contracting myocardial capacity |
| RU2073482C1 (en) * | 1992-07-15 | 1997-02-20 | Анатолий Петрович Попов | Method to measure arterial pressure |
| RU2123277C1 (en) * | 1992-07-29 | 1998-12-20 | Владимир Прокопьевич Кожемяко | Method of indirect measurement of arterial pressure and device for its realization |
| EP0787462A1 (en) * | 1994-02-02 | 1997-08-06 | Tovarischestvo Sogranichennoi Otvetstvennostju "Russky Tsentr Perspektivnykh Tekhnology" (Russintsentr) | Oscillometric method of determining haemodynamic indicators in the arterial circulation of a patient and measuring system for applying the said method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2005105977A (en) | 2006-08-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Chung et al. | Non-invasive continuous blood pressure monitoring: a review of current applications | |
| Shriram et al. | Continuous cuffless blood pressure monitoring based on PTT | |
| US8313439B2 (en) | Calibration of pulse transit time measurements to arterial blood pressure using external arterial pressure applied along the pulse transit path | |
| JP4047282B2 (en) | Device for noninvasive measurement of hemodynamic parameters using parametrics | |
| US7192403B2 (en) | Methods, apparatus and articles-of-manufacture for noninvasive measurement and monitoring of peripheral blood flow, perfusion, cardiac output biophysic stress and cardiovascular condition | |
| US7131949B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for examining vascular endothelial functions | |
| US20090018422A1 (en) | Vital sign monitor for cufflessly measuring blood pressure using a pulse transit time corrected for vascular index | |
| US20060264771A1 (en) | Apparatus for evaluating cardiovascular functions | |
| Kazamias et al. | Blood pressure measurement with Doppler ultrasonic flowmeter. | |
| Roach et al. | Perioperative blood pressure monitoring | |
| Zahedi et al. | Finger photoplethysmogram pulse amplitude changes induced by flow-mediated dilation | |
| Nitzan | Automatic noninvasive measurement of arterial blood pressure | |
| JPH09164121A (en) | Method and device to determine overarm artery pressure wave based on finger blood pressure wave being measured by noninvasive method | |
| JP6203737B2 (en) | Finger arteriole dilatability testing method, finger arteriole dilatability testing device, and finger arteriole dilatability testing program | |
| WO2008007361A2 (en) | Wearable, ambulatory, continuous, non-invasive blood pressure measuring method and system | |
| EP1901649A2 (en) | System and method for non-invasive cardiovascular assessment from supra-systolic signals obtained with a wideband external pulse transducer in a blood pressure cuff | |
| Tsyrlin et al. | The history of blood pressure measurement: from Hales to our days | |
| JP3908783B2 (en) | Automatic operating blood pressure measuring device | |
| KR20200129811A (en) | Blood Pressure Meter And Method For Measuring Blood Pressure Using The Same | |
| RU2291663C2 (en) | Method for measuring arterial blood pressure | |
| KR20200107157A (en) | Blood Pressure Meter And Method For Measuring Blood Pressure Using The Same | |
| Meyer-Sabellek et al. | Blood pressure measurements: new techniques in automatic and in 24-hour indirect monitoring | |
| Pickering et al. | The measurement of blood pressure | |
| GB2456947A (en) | Non invasive determination of stroke volume based on incident wave suprasystolic blood pressure amplitude | |
| Stork et al. | Cuff pressure pulse waveforms: their current and prospective applications in biomedical instrumentation |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20120304 |