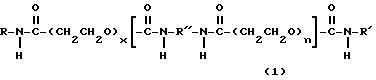RU2134704C1 - Bitumen emulsion - Google Patents
Bitumen emulsion Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2134704C1 RU2134704C1 RU93004745A RU93004745A RU2134704C1 RU 2134704 C1 RU2134704 C1 RU 2134704C1 RU 93004745 A RU93004745 A RU 93004745A RU 93004745 A RU93004745 A RU 93004745A RU 2134704 C1 RU2134704 C1 RU 2134704C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- bitumen
- emulsion
- bitumen emulsion
- thickener
- water
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
- Road Paving Structures (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к битумной эмульсии катионного типа, содержащей загуститель, к применению указанной битумной эмульсии при строительстве дорог, настиле крыш и придания водонепроницаемости и к применению ассоциативного загустителя неионного типа в указанной битумной эмульсии. The invention relates to a cationic type bitumen emulsion containing a thickener, to the use of said bitumen emulsion in road construction, roofing and waterproofing, and to the use of a non-ionic associative thickener in said bitumen emulsion.
Часто встречающейся проблемой при приготовлении холодной асфальтовой смеси каменного материала (агрегата) и катионной битумной эмульсии является то, что эмульсия стекает с камней, приводя в результате к очень тонкому слою битумного связующего на поверхности камня. Эта проблема является особенно трудной при работе с так называемыми смесями с открытой градацией, т.е. смесями на основе каменных материалов, которые имеют открытую градацию. Тонкие слои связующего приводят в результате к плохой стабильности смеси и смесь становится чувствительной к старению. A common problem when preparing a cold asphalt mixture of stone material (aggregate) and cationic bitumen emulsion is that the emulsion flows down from the stones, resulting in a very thin layer of bitumen binder on the surface of the stone. This problem is especially difficult when working with so-called mixtures with open gradation, i.e. mixtures based on stone materials that have an open gradation. Thin layers of binder result in poor stability of the mixture and the mixture becomes sensitive to aging.
Для решения этой проблемы было разработано несколько различных способов. Наиболее часто используемый способ включает смешивание наибольшего количества тонкоизмельченного каменного материала с битумной эмульсии. Недостатком этой технологии, однако, является то, что эмульсия отделяется от каменного материала, приводя в результате к смеси, которая является очень плотной и ее трудно наносить на дорогу. To solve this problem, several different methods have been developed. The most commonly used method involves mixing the largest amount of finely ground stone material with a bitumen emulsion. The disadvantage of this technology, however, is that the emulsion is separated from the stone material, resulting in a mixture that is very dense and difficult to apply on the road.
Другие способы загущения эмульсии включают загущение водной фазы с помощью добавок, таких как карбоксиметилцеллюлоза, поливинилпирролидон, метоксицеллюлоза и т. п. Однако все эти способы имеют тот недостаток, что добавка будет абсорбировать воду и/или будет оказывать отрицательное влияние на разрыв эмульсии. Предварительным требованием для загустителей, функционирующих в кислых катионных эмульсиях такого типа, который наиболее часто встречается для битумов, является то, что они должны быть неионными или по возможности катионными. Other methods for thickening the emulsion include thickening the aqueous phase with additives such as carboxymethyl cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone, methoxycellulose, etc. However, all of these methods have the disadvantage that the additive will absorb water and / or adversely affect the breaking of the emulsion. A preliminary requirement for thickeners operating in acidic cationic emulsions of the type most commonly found for bitumen is that they must be non-ionic or possibly cationic.
Другой способ, который использовался в далеком прошлом, заключается в применении анионных эмульсий, которые могут быть изготовлены с очень высокой вязкостью путем простого подбора эмульгаторов. Эмульсии этого типа называются "высоко флотирующимися эмульсиями". Недостатком эмульсий этого типа является то, что она очень медленно разбивается и по этой причине не пригодна на пространствах, где имеется большая опасность дождей (например, в Швеции). Another method that has been used in the distant past is the use of anionic emulsions, which can be made with very high viscosity by simply selecting emulsifiers. Emulsions of this type are called "high flotation emulsions." The disadvantage of this type of emulsion is that it breaks very slowly and is therefore not suitable in spaces where there is a great risk of rain (for example, in Sweden).
В соответствии с настоящим изобретением мы разработали способ, в котором используют загуститель такого типа, который взаимодействует с эмульгатором на поверхности битумных капель и образует сетку, которая придает эмульсии высокую псевдовязкость. Однако сетка не является настолько стабильной, чтобы предотвратить всплывание эмульсии на поверхность камня с образованием тонких слоев, Загуститель принадлежит к группе, которую обычно называют "ассоциативными загустителями". Такие загустители имеют обычную структуру "гидрофобный-гидрофильный-гидрофобный". Для информации об этой группе загустителей, смотри, например, "Associative Thickeners and Their Rheological Influence on Trade-Sale Formulation" by I.E.Glass. et.al, Org. Coat. Appl. Polym. Sci. Proc. In accordance with the present invention, we have developed a method in which a thickener of this type is used that interacts with an emulsifier on the surface of bitumen droplets and forms a network that gives the emulsion high pseudo viscosity. However, the grid is not so stable as to prevent the emulsion from floating onto the surface of the stone to form thin layers. The Thickener belongs to the group commonly referred to as “associative thickeners”. Such thickeners have the usual hydrophobic-hydrophilic-hydrophobic structure. For information on this group of thickeners, see, for example, "Associative Thickeners and Their Rheological Influence on Trade-Sale Formulation" by I.E. Glass. et.al, Org. Coat. Appl. Polym. Sci. Proc.
47, 1982, pp. 498-502. 47, 1982, pp. 498-502.
Следовательно, битумные эмульсии катионного типа, содержащие загуститель согласно изобретению, отличаются тем, что загуститель содержит по крайней мере одно вещество, выбранное в группе, состоящей из ассоциативных загустителей неионного типа. Therefore, cationic type bitumen emulsions containing a thickener according to the invention are characterized in that the thickener contains at least one substance selected in the group consisting of non-ionic associative thickeners.
В соответствии с вариантом битумной эмульсии согласно изобретению ассоциативные загустители неионного типа являются гидрофобно модифицированными уретанэтоксилатами, предпочтительно уретанэтоксилатами, имеющими общую формулу (1)
где R и R' являются одинаковыми или различными и каждый является прямым для разветвленным алкилом с 12 - 18 атомами углерода, R'' является насыщенной или ненасыщенной углеводородной цепью из 7-36 атомов углерода, часть из которых в цепи может быть замкнута с образованием в ней кольца, x равно 90-500, а n является целым числом 1 - 4.According to a variant of the bitumen emulsion according to the invention, non-ionic associative thickeners are hydrophobically modified urethane ethoxylates, preferably urethane ethoxylates, having the general formula (1)
where R and R 'are the same or different and each is straightforward for branched alkyl with 12 to 18 carbon atoms, R "is a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon chain of 7-36 carbon atoms, some of which in the chain can be closed to form in rings, x is 90-500, and n is an integer of 1 - 4.
Концентрация загустителя в битумной эмульсии зависит от, с одной стороны, конкретно используемого загустителя, а с другой стороны, от конкретной битумной эмульсии. Обычно концентрация загустителя будет находиться в интервале 0,05 - 1 мас.%, считая на массу битумной эмульсии. Точная концентрация в каждом индивидуальном случае предпочтительно устанавливается с помощью серии простых экспериментов с использованием различных концентраций загущающего агента. The concentration of the thickener in the bitumen emulsion depends on, on the one hand, the particular thickener used, and on the other hand, on the particular bitumen emulsion. Typically, the concentration of the thickener will be in the range of 0.05 to 1 wt.%, Based on the weight of the bitumen emulsion. The exact concentration in each individual case is preferably established using a series of simple experiments using different concentrations of thickening agent.
Битумная эмульсия согласно изобретению может быть приготовлена смешением загустителя и стандартной битумной эмульсии катионного типа при использовании традиционных способов смешения битумных продуктов. The bitumen emulsion according to the invention can be prepared by mixing a thickener and a standard cationic bitumen emulsion using conventional methods for mixing bitumen products.
Стандартные битумные эмульсии катионного типа, которые могут быть использованы в качестве исходного материала для приготовления битумных эмульсий согласно настоящему изобретению, обычно содержат битумный остаток в количестве 50 - 70 мас.%, считая на общую сумму эмульсии (стандартный материал). Standard cationic type bitumen emulsions that can be used as starting material for the preparation of bitumen emulsions according to the present invention typically contain a bitumen residue in an amount of 50 to 70 wt.%, Based on the total amount of the emulsion (standard material).
Эмульгатор, использованный в битумных эмульсиях, применяемых в качестве исходного материала для эмульсий согласно настоящему изобретению, не является критическим. Примерами эмульгаторов, встречающихся в битумных эмульсиях катионного типа, являются, например, жирные диамины, четвертичные аммониевые соединения, этоксилированные диамины, амидоамины и имидазолины. The emulsifier used in the bitumen emulsions used as the starting material for the emulsions of the present invention is not critical. Examples of emulsifiers found in cationic type bitumen emulsions are, for example, fatty diamines, quaternary ammonium compounds, ethoxylated diamines, amidoamines and imidazolines.
В соответствии с предпочтительным вариантом битумной эмульсии согласно настоящему изобретению указанная битумная эмульсия содержит разрушающую добавку, введенную в нее в виде эмульсии вода-в-масле, причем водный раствор нейтрализующего вещества диспергирован в непрерывной фазе масла. According to a preferred embodiment of the bitumen emulsion according to the present invention, said bitumen emulsion contains a destructive additive incorporated therein as a water-in-oil emulsion, wherein the aqueous solution of the neutralizing agent is dispersed in the continuous phase of the oil.
Термин "нейтрализующее вещество" используется здесь и в формуле изобретения для обозначения вещества, которое оказывает нейтрализующее действие на битумную эмульсию катионного типа при введении в нее. The term "neutralizing substance" is used here and in the claims to refer to a substance that has a neutralizing effect on the cationic type bitumen emulsion when introduced into it.
Нейтрализующее вещество предпочтительно выбирают в группе, состоящей из органических оснований, основных солей органических или неорганических кислот и гидроксидов щелочных металлов, причем основания, если или гидроксиды растворимы в воде, но недостаточно или не растворимы в масле. The neutralizing agent is preferably selected in the group consisting of organic bases, basic salts of organic or inorganic acids and alkali metal hydroxides, the base if either the hydroxides are soluble in water, but insufficiently or insoluble in oil.
Примерами таких веществ являются такие органические основания, как низкомолекулярные амины, например, моноэтаноламин, диэтаноламин, триэтаноламин и аминопропанол; основные соли органических кислот, например, тринатрий цитрат; основные соли неорганических кислот, такие как карбонат натрия, борат натрия, силикат натрия и тринатрий фосфат; и гидроксиды щелочных металлов, такие как гидроксид натрия или калия. Examples of such substances are organic bases such as low molecular weight amines, for example, monoethanolamine, diethanolamine, triethanolamine and aminopropanol; basic salts of organic acids, for example trisodium citrate; basic inorganic acid salts such as sodium carbonate, sodium borate, sodium silicate and trisodium phosphate; and alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium or potassium hydroxide.
Нейтрализующее вещество предпочтительно диспергировано в минеральном масле или в растворителе типа лигроина. The neutralizing agent is preferably dispersed in mineral oil or in a solvent such as naphtha.
Эмульгатор, использованный для эмульгирования раствора нейтрализующего вещества в масле, должен быть неионного типа и иметь ГЛБ-величину (Гидрофильно-Липофильный Баланс) в интервале 3-9, предпочтительно 5-7. The emulsifier used to emulsify a solution of a neutralizing agent in oil should be of a non-ionic type and have an HLB value (Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance) in the range of 3-9, preferably 5-7.
Подходящие количества и составы диспергирующих добавок для различных целей и эффектов легко устанавливаются в серии экспериментов. Однако обычно количество указанной добавки составляет 1-/10 предпочтительно 1,5 - 6, а особенно 2 - 4 мас.%, считая на общую массу готовой битумной эмульсии. Suitable amounts and compositions of dispersants for various purposes and effects are readily established in a series of experiments. However, usually the amount of said additive is 1- / 10, preferably 1.5-6, and especially 2-4% by weight, based on the total weight of the finished bitumen emulsion.
В соответствии с другим аспектом настоящего изобретения изобретение также относится к использованию ассоциативного загустителя неионного типа в качестве загустителя в битумной эмульсии катионного типа. In accordance with another aspect of the present invention, the invention also relates to the use of an associative thickener of non-ionic type as a thickener in a cationic type bitumen emulsion.
Ассоциативный загуститель неионного типа может быть гидрофобно модифицированным уретанэтоксилатом, предпочтительно модифицированным уретанэтоксилатом общей формулы 1, приведенной выше, где R, R1, R'', x и n имеют указанные ранее значения.The non-ionic associative thickener may be a hydrophobically modified urethane ethoxylate, preferably a modified urethane ethoxylate of the
В соответствии с другим аспектом изобретения настоящее изобретение относится к применению битумной эмульсии согласно изобретению для строительства дорог, поддержания дорог или в рабочих конструкциях, таких как настил крыш, покрытие и придание водонепроницаемости. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, the present invention relates to the use of a bitumen emulsion according to the invention for the construction of roads, maintenance of roads or in work structures such as roofing, coating and waterproofing.
В соответствии с предпочтительным вариантом этого аспекта изобретения эмульсию вода-в-масле, состоящую из водного раствора нейтрализующего вещества, диспергированного в непрерывной фазе масла, смешивают с битумной эмульсией до или во время применения указанной битумной эмульсии. According to a preferred embodiment of this aspect of the invention, a water-in-oil emulsion consisting of an aqueous solution of a neutralizing agent dispersed in a continuous oil phase is mixed with a bitumen emulsion before or during use of said bitumen emulsion.
Далее изобретение иллюстрируется следующим примерами, которые не являются ограничивающими. The invention is further illustrated by the following examples, which are not limiting.
Пример 1. Example 1
А. Средне диспергированную битумную эмульсию катионного типа, состоящую из 60 мас.%, считая на общую массу эмульсии, перегнанного битума (коммерческий продукт, торговое название BE60M фирмы Нюнес Битумен АБ, Йоханнесхоф, Швеция), загружают в емкость при перемешивании. Добавляют при перемешивании гидрообно модифицированный уретанэтоксилат (Коллакрал PU 75 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия). A. A medium dispersed cationic type bitumen emulsion consisting of 60 wt.%, Based on the total weight of the emulsion, distilled bitumen (commercial product, trade name BE60M from Nynes Bitumen AB, Johanneshof, Sweden), is loaded into the container with stirring. Hydrobially modified urethane ethoxylate (Collacral PU 75 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany) is added with stirring.
Измеряют вязкость эмульсии, содержащей добавку, на вискозиметре Брукфилда, снабженном шпинделем N 4. Образец испытывают при скорости 5 об/мин. The viscosity of the emulsion containing the additive is measured on a Brookfield viscometer equipped with
Используют четыре различные концентрации добавки, а именно 0,1, 0,2, 0,4 и 1 мас.%, считая на общую массу эмульсии. Для сравнения также проверяют вязкость эмульсии без добавки. Four different concentrations of the additive are used, namely 0.1, 0.2, 0.4 and 1 wt.%, Based on the total weight of the emulsion. For comparison, the viscosity of the emulsion without additives is also checked.
Б. повторяют процедуру раздела А, но используя другой гидрофильно модифицированный уретанэтоксилат (Коллакрал PU 85 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия) в качестве добавки. B. repeat the procedure of section A, but using another hydrophilically modified urethane ethoxylate (Collacral PU 85 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany) as an additive.
Результаты измерения вязкости приведены в табл. 1 в конце описания. The results of viscosity measurements are given in table. 1 at the end of the description.
Пример 2. Example 2
Работают по методике примера 1, но используют средне диспергированную битумную эмульсию катионного типа, состоящую из 67 мас.%, считая на общую массу эмульсии, перегнанного битума (коммерческий продукт, торговое название фирмы Нюнес Битумен АБ, Йоханнесхоф, Швеция) вместо эмульсии примера 1 и используя следующие гидрофобно модифицированные уретанэтоксилаты в различных количествах в качестве добавки. They work according to the method of Example 1, but use a medium dispersed cationic type bitumen emulsion consisting of 67 wt.%, Based on the total weight of the emulsion, distilled bitumen (commercial product, trade name of the company Nunes Bitumen AB, Johanneshof, Sweden) instead of the emulsion of Example 1 and using the following hydrophobically modified urethane ethoxylates in various amounts as an additive.
A. Коллакрал PU 75 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия. A. Collacral PU 75 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
B. Коллакрал PU 85 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия. B. Collacral PU 85 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
C. Акрисол RM 8 фирмы Ром энд Хаас, Филадельфия, США. C. Acrisol RM 8, Rom & Haas, Philadelphia, USA.
D. Бермодол PUR 2100 фирмы Берол Нобель АБ, Стокгольм, Швеция
E. Коллакрал DS 6049 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия.D. Bermodol PUR 2100 by Berol Nobel AB, Stockholm, Sweden
E. Collacral DS 6049 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
Результаты приведены в табл. 1 в конце описания. The results are shown in table. 1 at the end of the description.
Пример 3. Example 3
Работают по методике примера 1, но используют быстро разрушающуюся битумную эмульсию катионного типа, содержащую 67 мас.%, считая на общую массу эмульсии, модифицированного полимером битума (коммерческий продукт, торговое название РМЕ 89 фирмы Нюнес Битумен АБ, Йоханенсхоф, Швеция) вместо эмульсии примера 1. Используют те же самые добавки, что и в примере 1, а именно
A. Коллакрал PU 75 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия.They work according to the method of Example 1, but use a rapidly decaying cationic type bitumen emulsion containing 67 wt.%, Based on the total weight of the emulsion modified with bitumen polymer (commercial product, trade name PME 89 from Nynes Bitumen AB, Johannenshof, Sweden) instead of the emulsion of Example 1. Use the same additives as in example 1, namely
A. Collacral PU 75 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
B. Коллакрал PU 85 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия. B. Collacral PU 85 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
Результаты приведены в табл. 1 в конце описания. The results are shown in table. 1 at the end of the description.
Пример 4. Example 4
Работают по методике примера 1, но используют быстро разрушающуюся битумную эмульсию катионного типа, содержащую 77 мас.%, считая на общую массу эмульсии, перегнанного битума битума (коммерческий продукт, торговое название BE65P фирмы Нюнес Битумен АБ, Йоханенсхоф, Швеция) вместо эмульсии примера 1. Используют те же самые добавки, что и в примере 1, а именно
A. Коллакрал PU 75 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия.They work according to the procedure of Example 1, but use a rapidly decaying cationic type bitumen emulsion containing 77 wt.%, Based on the total weight of the emulsion, distilled bitumen (commercial product, trade name BE65P from Nynes Bitumen AB, Johanneshof, Sweden) instead of the emulsion of Example 1 Use the same additives as in example 1, namely
A. Collacral PU 75 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
B. Коллакрал PU 85 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия. B. Collacral PU 85 from BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany.
Результаты приведены в табл. 1 в конце описания. The results are shown in table. 1 at the end of the description.
Пример 5. Example 5
Используя процедуру примера 1, готовят смесь из исходной битумной эмульсии примера 2 (BE65M фирмы Нюнес Битумен АБ, Йоханнесхоф, Швеция), а каждую из добавок A-E, определенную в примере 2, добавляют в количестве 0,2 мас.%, считая на массу эмульсии. Using the procedure of Example 1, a mixture is prepared from the starting bitumen emulsion of Example 2 (BE65M from Nunes Bitumen AB, Johanneshof, Sweden), and each of the AE additives defined in Example 2 is added in an amount of 0.2 wt.%, Based on the weight of the emulsion .
Готовят смесь минеральных агрегатов и каждой из битумных эмульсий, содержащих добавку, используя 500 г агрегатов (Фарстагранит 0-16 мм, наполненный требуемым для асфальтовой эмульсии бетоном с размером камней 0 - 16 мм незамкнутой кривой, поставленной Дорожной Администрацией, Швеция, а "Byggnastekniska foreskrifter och allmanna rad" ("Структурные инженерные направления и общие соображения") при влажности 1 мас.% воды. Добавляют 7 мас. % (считая на массу агрегатов) битумной эмульсии и перемешивают вручную 72 секунды. Затем смесь выливают в воронку с ситом на дне для тестов "сток" и "отмывка". A mixture of mineral aggregates and each of the bitumen emulsions containing the additive is prepared using 500 g of aggregates (Farstagranit 0-16 mm filled with the concrete required for the asphalt emulsion with a stone size of 0-16 mm open curve set by the Road Administration, Sweden, and Byggnastekniska foreskrifter och allmanna rad "(Structural Engineering and General Considerations") at a moisture content of 1 wt.% water. Add 7 wt.% (based on the weight of the aggregates) of the bitumen emulsion and mix manually 72 seconds. Then the mixture is poured into a funnel with a sieve at the bottom for tests "stock" and "washing".
"Сток" представляет собой количество материала, которое собирают в тарированный алюминиевый контейнер в воронке в течение 30 минут. Контейнер сушат в печи при 110oC. Количество "стока" соответствует проценту потерь связующего, рассчитанному на массу партии агрегата.A "stock" is the amount of material that is collected in a tared aluminum container in a funnel within 30 minutes. The container is dried in an oven at 110 ° C. The amount of "runoff" corresponds to the percentage loss of binder, calculated on the weight of the batch of the unit.
Оставшийся в воронке образец затем используют для теста "отмывка", который проводят следующим образом. The sample remaining in the funnel is then used for the “washing” test, which is carried out as follows.
Через 1 час заливают в воронку 200 мл воды на образец и собирают сток в тарированный алюминиевый контейнер, содержимое сушат в печи при 110oC и высушивают. Количество "отмывки" соответствует потерям связующего в мас.%, также как и "сток". Процедура описана в "Руководстве по основным асфальтовым эмульсии". Асфальтовый институт, Колледж Парк, Мэриленд., США.After 1 hour, 200 ml of water was poured into the funnel per sample and the stock was collected in a tared aluminum container, the contents were dried in an oven at 110 ° C and dried. The amount of "washing" corresponds to the loss of binder in wt.%, As well as the "stock". The procedure is described in the Guide to Basic Asphalt Emulsions. Asphalt Institute, College Park, Maryland., USA.
Результаты приведенных выше тестов и сравнительный тест с использованием эмульсии без добавки приведены в табл. 2 в конце описания. The results of the above tests and a comparative test using an emulsion without additives are given in table. 2 at the end of the description.
Из этих результатов можно сделать вывод, что добавки предотвращают или уменьшают "сток", но не оказывают ухудшающего воздействия на разрыв эмульсии. From these results we can conclude that additives prevent or reduce the "drain", but do not have a worsening effect on the rupture of the emulsion.
Результаты указывают, что использование эмульсии в соответствии с изобретением делает возможным применение более высоких концентраций битумного связующего в холодных асфальтовых смесях и, следовательно, может быть использована техника холодного смешивания для получения асфальтовых смесей для дорог с более высокой интенсивностью дорожного движения и большего срока службы, чем это было возможно до настоящего времени. The results indicate that the use of the emulsion in accordance with the invention makes it possible to use higher concentrations of bitumen binder in cold asphalt mixtures and, therefore, the cold mixing technique can be used to produce asphalt mixtures for roads with higher traffic intensity and longer service life than it has been possible to date.
Пример 6. Example 6
К битумной эмульсии катионного типа со средним сроком разрушения, содержащей 67 мас. %, считая на общую массу эмульсии, перегнанного битума (коммерческий продукт, торговое название BE 65 М фирмы Нюнес Битумен АБ, Йохвиннесхоф, Швеция) прибавляют 2,1 мас.%, считая на массу битумной эмульсии, смеси диспергирующей добавки и гидрофобно модифицированного уретанэтоксилата (Коллакрал PU 75 фирмы БАСФ, Людвигшафен, Германия) в массовом отношении 20: 1. To a cationic type bitumen emulsion with an average fracture period of 67 wt. 2.1%, based on the total weight of the emulsion, distilled bitumen (commercial product, trade name BE 65 M, Nunes Bitumen AB, Johnshneshof, Sweden) is added, based on the weight of the bitumen emulsion, a mixture of dispersant and hydrophobically modified urethane ethoxylate ( Collacral PU 75 (BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany) in a mass ratio of 20: 1.
Диспергирующая добавка в виде эмульсии вода-в-масле, состоящей из раствора Гипермер А60 (коммерческий продукт фирмы АйСиАй Юроп Лтд., Кортенберг, Бельгия) в концентрации 6,6% (мас./мас.), Диамина BG (коммерческий продукт фирмы Сканроад АБ, Накка, Швеция) в концентрации 0,33% (мас./мас.) и Вископлекса BA-700 (коммерческий продукт фирмы Ром ГмбХ, Дарштадт, Германия) в концентрации 0,66% (мас. /мас. ) в гидрообработанном нафталиновом масле (стандартное качество Нитекс 800 фирмы Нюнес Нафтеникс АБ, Нинасхамн, Швеция), и водной фазы, состоящей из водного раствора, содержащего 8% (мас. /мас. ) карбоната натрия и 16% (мас./мас.) тринатрий цитрата, указанная эмульсия вода-в-масле содержит 70 мас.% воды. A dispersing additive in the form of a water-in-oil emulsion consisting of Hypermer A60 solution (commercial product of ICA Europe Ltd., Cortenberg, Belgium) at a concentration of 6.6% (w / w), Diamine BG (commercial product of Scanroad AB, Nakka, Sweden) at a concentration of 0.33% (wt./wt.) And Viscoplex BA-700 (commercial product of the company Rom GmbH, Darstadt, Germany) at a concentration of 0.66% (wt./wt.) In the hydrotreated naphthalene oil (Nitex 800 standard quality from Nunes Naphthenix AB, Ninashamn, Sweden), and an aqueous phase consisting of an aqueous solution, soda rzhaschego 8% (wt. / wt.) of sodium carbonate and 16% (wt. / wt.) of trisodium citrate, said water-in-oil emulsion comprising 70 wt.% water.
Смесь диспергирующей добавки и загустителя смешивают в битумной эмульсии при перемешивании стеклянным стержнем непосредственно перед добавлением 50 г эмульсии к 500 г минеральных агрегатов с так называемой незамкнутой кривой распределения. Смесь агрегаты-эмульсия перемешивают 60 секунд стальным шпателем и выливают в пластмассовую воронку с ситом на дне для тестов "сток" и "отмывка"
В этом случае не имеется "сток" в течение 30 минут. (Несколько капель прозрачной воды может быть видно, но в ней не имеется битума).A mixture of a dispersant and a thickener is mixed in a bitumen emulsion with a glass rod just before adding 50 g of the emulsion to 500 g of mineral aggregates with a so-called open distribution curve. The aggregate-emulsion mixture is stirred for 60 seconds with a steel spatula and poured into a plastic funnel with a sieve at the bottom for the "drain" and "wash" tests
In this case, there is no stock for 30 minutes. (A few drops of clear water can be seen, but there is no bitumen in it).
Через 1 час смесь испытывают на "отмывку", вливая 200 мл воды в смесь. "Отмывки" не имеется (из воронки вытекает прозрачная вода). After 1 hour, the mixture was tested for “washing” by pouring 200 ml of water into the mixture. There is no “washing” (clear water flows out of the funnel).
Пример 7. Example 7
Был повторен пример 1, но с применением медленно разрушающейся катионной битумной эмульсии, включающий 66 мас. %, считая на общую массу битумной эмульсии (торговая марка P 92-212-01 фирма Nynas Bitumen AB, Швеция) вместо эмульсии по примеру 1 и с использованием следующих ассоциативных загустителей в различных количествах как добавки:
1. Atlas Y 1822, фирма JCJ Европа Лтд, Kortenberg, Бельгия.Example 1 was repeated, but using a slowly eroding cationic bitumen emulsion, including 66 wt. %, based on the total weight of the bitumen emulsion (trademark P 92-212-01 company Nynas Bitumen AB, Sweden) instead of the emulsion according to example 1 and using the following associative thickeners in various quantities as additives:
1. Atlas Y 1822, JCJ Europe Ltd., Kortenberg, Belgium.
2. Atlas Y 1823, фирма JCJ Европа Лтд, Kortenberg, Бельгия. 2. Atlas Y 1823, JCJ Europe Ltd., Kortenberg, Belgium.
Химическая структура обоих продуктов - полиэтиленгликоль (150) дистеарат. The chemical structure of both products is polyethylene glycol (150) distearate.
Вязкость эмульсии, содержащей добавку, были измерена вискозиметром Брукфилда с шпинделем N LV2. Образец был испытан при скорости 6 об/м при to 40oC.The viscosity of the emulsion containing the additive was measured with a Brookfield viscometer with a spindle N LV2. The sample was tested at a speed of 6 rpm at t o 40 o C.
Результаты приведены в табл. 3 в конце описания. The results are shown in table. 3 at the end of the description.
Claims (6)
где R и R' являются одинаковыми или различными и каждый является прямым или разветвленным алкилом с 12 - 18 атомами углерода;
R'' является насыщенной или ненасыщенной углеводородной цепью с 7 - 36 атомами углерода, часть из которых в цепи может быть замкнута с образованием кольца в ней;
X является числом 90 - 500;
n равно целому числу 1 - 4.3. The bitumen emulsion according to claim 2, characterized in that the hydrophobically modified urethane ethoxylates have the general formula
where R and R 'are the same or different and each is straight or branched alkyl with 12 to 18 carbon atoms;
R ″ is a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon chain with 7 to 36 carbon atoms, some of which in the chain can be closed to form a ring in it;
X is the number 90 to 500;
n is an integer of 1 to 4.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU93004745A RU2134704C1 (en) | 1993-03-25 | 1993-03-25 | Bitumen emulsion |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU93004745A RU2134704C1 (en) | 1993-03-25 | 1993-03-25 | Bitumen emulsion |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU93004745A RU93004745A (en) | 1996-07-20 |
| RU2134704C1 true RU2134704C1 (en) | 1999-08-20 |
Family
ID=20136397
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU93004745A RU2134704C1 (en) | 1993-03-25 | 1993-03-25 | Bitumen emulsion |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2134704C1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112961505A (en) * | 2021-02-05 | 2021-06-15 | 辽宁省交通科学研究院有限责任公司 | Normal-temperature viscous emulsified asphalt cement and preparation method thereof |
-
1993
- 1993-03-25 RU RU93004745A patent/RU2134704C1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112961505A (en) * | 2021-02-05 | 2021-06-15 | 辽宁省交通科学研究院有限责任公司 | Normal-temperature viscous emulsified asphalt cement and preparation method thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7815725B2 (en) | Warm asphalt binder compositions containing lubricating agents | |
| ZA200601776B (en) | Process for the manufacture of a bitumen-aggregate mix suitable for road pavement | |
| JP3704077B2 (en) | Asphalt emulsion composition | |
| GB2255291A (en) | Bitumen emulsions. | |
| US20060086288A1 (en) | Bituminous emulsions, their method of preparation and their use for the production of materials and road pavements | |
| ES2215884T3 (en) | AMINA OXIDES AS ASPHALT EMULSIONANTS. | |
| FI103283B (en) | Bitumen emulsion, a process for its preparation, a disintegrant additive for use therein, and the use of said bitumen emulsion | |
| RU2134704C1 (en) | Bitumen emulsion | |
| US5521235A (en) | Bitumen emulsion and its use | |
| US4822427A (en) | Open-grade asphalt emulsion mixes | |
| EP0534039B1 (en) | Bitumen emulsion and its use | |
| US4985079A (en) | Open-graded asphalt emulsion mixes | |
| JP3841939B2 (en) | Nonionic emulsifier for asphalt | |
| JP4583336B2 (en) | Asphalt modifier | |
| KR101272531B1 (en) | Two-liquid type coating composition for preventing dust scattering and method for preventing dust scattering | |
| JP2003253134A (en) | Cationic aqueous dispersion of thermoplastic elastomer and its preparation process | |
| PL173615B1 (en) | Bituminous emulsion | |
| EP0666886A1 (en) | Bitumen emulsion, its preparation and use and breaking additive for use therein | |
| LV10630B (en) | Bitumen emulsion and its use | |
| HU212913B (en) | Bitumen emulsion and process for using the bitumen emulsion and thickeners | |
| SK280760B6 (en) | Bitumen emulsion, process for its preparation, and its use | |
| LT3233B (en) | Bitumen emulsion and use them | |
| CZ291987B6 (en) | Bituminous emulsion of cationic type and its use as well as use of associative thickening agent of non-ionic type | |
| RU2279453C1 (en) | Emulsion composition for road building | |
| Torrans et al. | Review of literature on air-entrained concrete |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20120326 |