RU202193U1 - A device for immunochromatographic highly sensitive and out-of-laboratory detection of the phytopathogenic bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis, based on an increase in the intensity of the recorded colorimetric signal due to the catalytic properties of the nanomarker - Google Patents
A device for immunochromatographic highly sensitive and out-of-laboratory detection of the phytopathogenic bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis, based on an increase in the intensity of the recorded colorimetric signal due to the catalytic properties of the nanomarker Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU202193U1 RU202193U1 RU2020119108U RU2020119108U RU202193U1 RU 202193 U1 RU202193 U1 RU 202193U1 RU 2020119108 U RU2020119108 U RU 2020119108U RU 2020119108 U RU2020119108 U RU 2020119108U RU 202193 U1 RU202193 U1 RU 202193U1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- michiganensis
- membrane
- sample
- nanoparticles
- porous
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12M—APPARATUS FOR ENZYMOLOGY OR MICROBIOLOGY; APPARATUS FOR CULTURING MICROORGANISMS FOR PRODUCING BIOMASS, FOR GROWING CELLS OR FOR OBTAINING FERMENTATION OR METABOLIC PRODUCTS, i.e. BIOREACTORS OR FERMENTERS
- C12M1/00—Apparatus for enzymology or microbiology
- C12M1/26—Inoculator or sampler
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12M—APPARATUS FOR ENZYMOLOGY OR MICROBIOLOGY; APPARATUS FOR CULTURING MICROORGANISMS FOR PRODUCING BIOMASS, FOR GROWING CELLS OR FOR OBTAINING FERMENTATION OR METABOLIC PRODUCTS, i.e. BIOREACTORS OR FERMENTERS
- C12M1/00—Apparatus for enzymology or microbiology
- C12M1/34—Measuring or testing with condition measuring or sensing means, e.g. colony counters
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/53—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor
- G01N33/543—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor with an insoluble carrier for immobilising immunochemicals
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/53—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor
- G01N33/558—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor using diffusion or migration of antigen or antibody
Abstract
Заявленное устройство предназначено для иммунохроматографической высокочувствительной, внелабораторной и экспрессной детекции фитопатогенной бактерии Clavibacter michiganensis в экстрактах листьев и клубней картофеля. Устройство представляет собой мультимембранный композит с предварительно нанесенными и высушенными иммунореагентами (тест-полоску). В состав мультимембранного композита входят рабочая нитроцеллюлозная мембрана с предварительно нанесенными иммунореагентами, закрепленная на твердой полистироловой основе, стекловолоконная мембрана с нанесенными конъюгатом пористых наночастиц типа ядро-оболочка - Au-Pt, стабилизированных поливинилпирролидоном с кроличьими поликлональными антителами, специфичными к бактериальным клеткам С.michiganensis, мембрана для впитывания и сепарации компонентов исследуемой пробы и конечной адсорбирующей мембраны для впитывания компонентов пробы после прохождения реакции и поддержания миграции жидкости по тест-полоске за счет капиллярных сил. Отличительной особенностью заявленного устройства является то, что в качестве метки использован конъюгат пористых наночастиц ядро-оболочка - Au-Pt, стабилизированных поливинилпирролидоном с поликлональными антителами против С.michiganensis. Частицы Au-Pt обладают как оптическими, так и каталитическими (пероксидаза-подобными свойствами), что позволяет использовать их в иммунохроматографическом анализе (ИХА) как наноразмерную метку с собственным оптическими сигналом, так и для снижения предела обнаружения ИХА, основанного на повышении интенсивности окрашивания при низких концентрациях антигена в пробе за счет пероксидаза-подобных свойств наночастиц, приводящих к накоплению окрашенных продуктов окисления субстрата. Высокая устойчивость частиц к химическим ингибиторам пероксидаз (азид натрия) и температуре (до 100°С) позволяет использовать наночастицы Au-Pt для амплификации сигнала даже в пробах с высокой эндогенной пероксидазной активностью после ее нивелирования. В контрольную зону (К.З.) нанесен иммуноглобулин-связывающий белок А. В тестовую зону (Т.З.) нанесены кроличьи поликлональные антитела, специфичные к бактериальным клеткам С.michiganensis. На стекловолоконную мембрану нанесен конъюгат поликлональных кроличьих антител, специфичных к детектируемым бактериальным клеткам, с пористыми наночастицами типа ядро-оболочка Au-Pt, стабилизированных поливинилпирролидоном. Для проведения анализа не требуется никаких дополнительных стационарных устройств. Продолжительность анализа составляет 15 мин, включает в себя стадии подготовки анализируемой пробы, проведение иммунохроматографического анализа с использованием тест-полоски, добавления субстратного раствора для повышения интенсивности регистрируемого колориметрического сигнала. Технической задачей заявленной полезной модели является повышение интенсивности регистрируемого окрашивания Т.З. за счет реакции, катализируемой пористыми наночастицами типа ядро-оболочка Au-Pt непосредственно на тест-полоске. Технический результат заявленной полезной модели заключается в снижении предела обнаружения фитопатогенной бактерии С.michiganensis за счет использования простой одностадийной процедуры, обеспечиваемой за счет добавления на тест-полоску субстратного раствора, содержащего смесь 3,3'-диаминобензидина, пероксида водорода и ионов Ni2+. 4 табл., 3 пр., 2 ил.The claimed device is intended for immunochromatographic highly sensitive, out-of-laboratory and express detection of the phytopathogenic bacteria Clavibacter michiganensis in extracts of leaves and tubers of potatoes. The device is a multi-membrane composite with pre-applied and dried immunoreagents (test strip). The composition of the multimembrane composite includes a working nitrocellulose membrane with preliminarily applied immunoreagents, fixed on a solid polystyrene base, a glass fiber membrane coated with a conjugate of porous core-shell nanoparticles - Au-Pt, stabilized with polyvinylpyrrolidone with rabbit cells, polyclonal antibodies against C. membrane for absorbing and separating the components of the test sample and the final adsorbent membrane for absorbing the components of the sample after the reaction and maintaining the migration of liquid along the test strip due to capillary forces. A distinctive feature of the claimed device is that a conjugate of porous core-shell nanoparticles - Au-Pt, stabilized with polyvinylpyrrolidone with polyclonal antibodies against C. michiganensis, is used as a label. Au-Pt particles possess both optical and catalytic (peroxidase-like properties), which makes it possible to use them in immunochromatographic analysis (ICA) as a nanosized label with their own optical signal, and to reduce the ICA detection limit based on an increase in the color intensity upon low concentrations of antigen in the sample due to the peroxidase-like properties of nanoparticles, leading to the accumulation of colored products of substrate oxidation. The high resistance of the particles to chemical inhibitors of peroxidases (sodium azide) and temperature (up to 100 ° C) allows the use of Au-Pt nanoparticles for signal amplification even in samples with high endogenous peroxidase activity after its leveling. In the control zone (K.Z.) applied immunoglobulin-binding protein A. In the test zone (T.Z.) applied rabbit polyclonal antibodies specific to bacterial cells of C. michiganensis. A conjugate of polyclonal rabbit antibodies specific to detectable bacterial cells with porous Au-Pt core-shell nanoparticles stabilized with polyvinylpyrrolidone is applied to the glass fiber membrane. For the analysis, no additional stationary devices are required. The duration of the analysis is 15 minutes, it includes the stages of preparing the analyzed sample, carrying out an immunochromatographic analysis using a test strip, adding a substrate solution to increase the intensity of the recorded colorimetric signal. The technical task of the claimed utility model is to increase the intensity of the recorded staining of T.Z. due to a reaction catalyzed by porous Au-Pt core-shell nanoparticles directly on the test strip. The technical result of the claimed utility model is to reduce the detection limit of the phytopathogenic bacterium C. michiganensis by using a simple one-step procedure provided by adding a substrate solution containing a mixture of 3,3'-diaminobenzidine, hydrogen peroxide and Ni2 + ions to the test strip. 4 tbl, 3 ex, 2 dwg
Description
Полезная модель относится к детекции фитопатогенной бактерии Clavibacter michiganensis (С michiganensis) и может быть использована как экспрессное лабораторное и внелабораторное средство для проведения фитосанитарного контроля специализированными службами, таможенного контроля посевного материала, мониторинга зараженности фермерскими хозяйствами.The utility model relates to the detection of the phytopathogenic bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis (C michiganensis) and can be used as an express laboratory and out-of-laboratory tool for carrying out phytosanitary control by specialized services, customs control of seed, monitoring of infection by farms.
Фитопатогенные микроорганизмы поражают широкий спектр сельскохозяйственных культур. Заражение фитопатогенными микроорганизмами приводит к существенным экономическим потерям за счет снижения урожайности растений (до 100%), ухудшению их хранимости и устойчивости к вредителям.Phytopathogenic microorganisms affect a wide range of crops. Infection with phytopathogenic microorganisms leads to significant economic losses due to a decrease in plant productivity (up to 100%), deterioration of their storage capacity and resistance to pests.
Широко распространенным на территории Российской Федерации является бактериальный фитопатоген С.michiganensis, аэробная, неспорообразующая грамположительная бактерия. Основным растением, поражаемым С.michiganensis, является картофель. Поражение картофеля приводит к загниванию его клубней (т.н. кольцевая гниль картофеля) и возникновению очагов ямчатой гнили. Заражение может происходить в период уборки урожая за счет проникновения бактерий через участки с поврежденной кожурой. Детекция низких концентраций бактерий, не вызывающих развития выраженных симптомов (латентная инфекция), представляет особый интерес для практического использования, поскольку при посадке клубней с низкой концентрацией бактерий развитие симптомов наблюдается только в процессе цветения. Таким образом, изолирование зараженных растений приведет к существенным экономическим потерям. Для предотвращения больших потерь урожая и существенных убытков необходимо диагностировать латентные инфекции в семенном материале. Согласно нормативной документации - ГОСТ 33996-2016 «Картофель семенной. Технические условия и методы определения качества» - С.michiganensis входит в список контролируемых фитопатогенных микроорганизмов картофеля. Согласно рекомендациям нормативной документации предел обнаружения для иммунохимических методов анализа составляет 104 клеток/мл. Однако для диагностики латентных инфекций необходимо достижение меньших пределов обнаружения.The bacterial phytopathogen C. michiganensis, an aerobic, non-spore-forming gram-positive bacterium, is widespread in the Russian Federation. The main plant affected by C. michiganensis is the potato. The defeat of the potato leads to rotting of its tubers (the so-called ring rot of potatoes) and the emergence of foci of pitted rot. Infection can occur during the harvest season due to the penetration of bacteria through areas with damaged skin. The detection of low concentrations of bacteria that do not cause the development of severe symptoms (latent infection) is of particular interest for practical use, since when tubers with a low concentration of bacteria are planted, symptoms develop only during the flowering process. Thus, isolating infected plants will result in significant economic losses. To prevent large crop losses and significant losses, it is necessary to diagnose latent infections in the seed. According to regulatory documents - GOST 33996-2016 “Seed potatoes. Technical conditions and methods for determining the quality "- C. michiganensis is included in the list of controlled phytopathogenic microorganisms of potatoes. According to the recommendations of the regulatory documentation, the detection limit for immunochemical methods of analysis is 10 4 cells / ml. However, to diagnose latent infections, it is necessary to achieve lower detection limits.
Для детекции С.michiganensis используются различные вариации метода полимеразной цепной реакции, иммуноферментный анализ, иммунохроматографический анализ. Несмотря на такие преимущества, как специфичность и низкий предел обнаружения, для применения методов, основанных на полимеразной цепной реакции, необходимо дорогостоящее стационарное оборудование, условия, обеспечивающие отсутствие контаминации, квалифицированный персонал. Продолжительность анализа (минимум один час без учета подготовки проб) также ограничивает применимость данных методов во внелабораторных условиях.For the detection of C. michiganensis, various variations of the polymerase chain reaction method, enzyme immunoassay, and immunochromatographic analysis are used. Despite such advantages as specificity and low detection limit, the application of methods based on polymerase chain reaction requires expensive stationary equipment, conditions that ensure the absence of contamination, and qualified personnel. The duration of the analysis (at least one hour excluding sample preparation) also limits the applicability of these methods in out-of-laboratory conditions.
Для высокочувствительной детекции С.michiganensis могут быть также использованы активно развивающиеся методы иммунохимического анализа - иммуноферментный (ИФА) и иммунохроматографический (ИХА) анализ. Возможности иммуноанализа связаны с его методической простотой, а также высокой производительностью, обеспечивающей одновременное тестирование множества проб в течение 2-3 часов. Однако выполнение ИФА включает несколько дополнительных стадий (внесение реагентов и отмывка), сопряжено с необходимостью дополнительных расходных материалов (микропланшеты, наконечники пипеток, и др.) и оборудования для регистрации результатов анализа. ИХА, в отличие от ИФА, не требует дополнительного оборудования и позволяет проводить массовый скрининг в нестерильных внелабораторных условиях с использованием минимальной подготовки проб. В классическом формате ИХА является одностадийным анализом и позволяет проводить качественный (наличие/отсутствие окрашенной Т.З.) и количественный анализ (регистрация интенсивности колориметрического сигнала в Т.З., определение количества бактерий путем сравнения интенсивности колориметрического сигнала пробы и образцов с известным количеством бактерий) по накоплению окрашенного маркера.For the highly sensitive detection of C. michiganensis, actively developing methods of immunochemical analysis can also be used - enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) and immunochromatographic (ICA) analysis. The capabilities of immunoassay are associated with its methodological simplicity, as well as high productivity, providing simultaneous testing of multiple samples for 2-3 hours. However, the performance of ELISA includes several additional stages (adding reagents and washing), associated with the need for additional consumables (microplates, pipette tips, etc.) and equipment for recording the analysis results. ICA, unlike ELISA, does not require additional equipment and allows mass screening in non-sterile out-of-laboratory conditions using minimal sample preparation. In the classical format, ICA is a one-step analysis and allows for qualitative (presence / absence of colored TZ) and quantitative analysis (registration of the intensity of the colorimetric signal in TZ, determination of the number of bacteria by comparing the intensity of the colorimetric signal of the sample and samples with a known number of bacteria ) by accumulation of the colored marker.
Однако предел обнаружения одностадийного ИХА зачастую оказывается недостаточным для высокочувствительной детекции. Один из подходов для снижения предела обнаружения ИХА основан на повышении интенсивности регистрируемого колориметрического сигнала за счет каталитической конверсии молекул субстрата в окрашенный продукт. Амплификация сигнала достигается за счет того, что единичная наночастица-катализатор приводит к конверсии большого количества молекул субстрата в регистрируемый продукт.However, the detection limit of a one-stage ICA is often insufficient for highly sensitive detection. One of the approaches to lowering the ICA detection limit is based on increasing the intensity of the recorded colorimetric signal due to the catalytic conversion of substrate molecules into a colored product. Signal amplification is achieved due to the fact that a single catalyst nanoparticle leads to the conversion of a large number of substrate molecules into a registered product.
Увеличение регистрируемой интенсивности окрашивания связано с накоплением продукта ферментативной реакции на тест-полоске. В качестве каталитической метки могут быть использованы наночастицы металлов, поскольку они обладают уникальными оптическими свойствами, могут быть легко сконъюгированы с рецепторными молекулами, показывают высокую каталитическую активность и стабильность в присутствии ингибиторов ферментов. Наиболее широко в качестве каталитически активных нанометок используются частицы Au, Pt, Pd, Ir различной формы и морфологии. Однако высокая стоимость благородных металлов-катализаторов ограничивает их применение в аналитических тест-системах.The increase in the recorded color intensity is associated with the accumulation of the product of the enzymatic reaction on the test strip. Metal nanoparticles can be used as a catalytic label, since they have unique optical properties, can be easily conjugated to receptor molecules, and show high catalytic activity and stability in the presence of enzyme inhibitors. The most widely used catalytically active nanomarkers are Au, Pt, Pd, Ir particles of various shapes and morphologies. However, the high cost of noble metal catalysts limits their use in analytical test systems.
Особенностью катализа с использованием наночастиц является множество активных центров, расположенных на поверхности частиц. Таким образом, большая часть атомов благородных металлов оказывается экранированной (внутри частиц) и не участвует в катализе. Для снижения расхода благородных металлов при синтезе каталитически активных частиц предложен подход, основанный на формировании тонкого слоя каталитически-активного металла на наночастицах носителях, благодаря чему все поверхностно экспонированные атомы металла оказываются доступны для субстрата и каталитической конверсии. Данный подход был использован в ряде работ для получения каталитически активных наночастиц Au-Pt. Например, Zhang и соавторы использовали конъюгат наночастиц Au-Pt с антителами против IgG кролика для ИХА. Gao и соавторы использовали наночастицы, состоящие из золотого ядра и монослойного платинового покрытия в качестве метки в ИХА простатического специфического антигена.A feature of catalysis using nanoparticles is the many active centers located on the surface of the particles. Thus, most of the noble metal atoms are screened (inside the particles) and do not participate in catalysis. To reduce the consumption of noble metals in the synthesis of catalytically active particles, an approach was proposed based on the formation of a thin layer of a catalytically active metal on nanoparticles, so that all surface exposed metal atoms are available for the substrate and catalytic conversion. This approach was used in a number of works to obtain catalytically active Au-Pt nanoparticles. For example, Zhang et al used a conjugate of Au-Pt nanoparticles with anti-rabbit IgG antibodies for ICA. Gao et al used nanoparticles consisting of a gold core and a monolayer platinum coating as a label in the ICA of the prostate specific antigen.
Использованные протоколы синтеза основаны на формировании платинового покрытия на наночастицах золота, однако не позволяют достичь максимального экспонирования каталитически активного платинового покрытия. Формирование пористого платинового покрытия на затравочных наночастицах золота позволит увеличить площадь поверхности каталитически-активных частиц. В литературе описан синтез пористых наночастиц Au-Pt. Так, Loynachan и соавторы для формирования пористой платиновой оболочки в качестве затравочных частиц использовали наночастицы золота, стабилизированные поливинилпирролидоном. Для синтеза пористых использовали высокие концентрации платины (до 3 мМ), высокая стоимость частиц ограничивает их применение для рутинного скрининга. Jiang и соавторы для синтеза пористых платиновых частиц использовали реакцию совместного восстановления солей платины и золота в присутствии полимера Pluronic F127. Однако в данном случае также были использованы высокие концентрации солей благородных металлов (10 мМ), а совместное восстановление не позволяет достигнуть экспонирования каталитически активных платиновых частиц на поверхности.The synthesis protocols used are based on the formation of a platinum coating on gold nanoparticles; however, they do not allow reaching the maximum exposure of the catalytically active platinum coating. The formation of a porous platinum coating on seed gold nanoparticles will increase the surface area of catalytically active particles. The literature describes the synthesis of porous Au-Pt nanoparticles. Thus, Loynachan et al. Used gold nanoparticles stabilized with polyvinylpyrrolidone as seed particles to form a porous platinum shell. High concentrations of platinum (up to 3 mM) were used for the synthesis of porous particles; the high cost of particles limits their use for routine screening. For the synthesis of porous platinum particles, Jiang et al. Used the reaction of joint reduction of platinum and gold salts in the presence of the Pluronic F127 polymer. However, in this case, high concentrations of noble metal salts (10 mM) were also used, and joint reduction does not allow achieving exposure of catalytically active platinum particles on the surface.
Таким образом, известные разработки иммунохроматографических тест-систем сфокусированы на использовании неоптимальных с точки зрения катализа непористых частиц типа ядро-оболочка, а протоколы синтеза пористых частиц требуют высоких концентраций дорогостоящих солей благородных металлов, и также не позволяют достигнуть максимального экспонирования каталитически-активных платиновых частиц на поверхности.Thus, the known developments of immunochromatographic test systems are focused on the use of non-optimal from the point of view of catalysis, non-porous particles of the core-shell type, and the protocols for the synthesis of porous particles require high concentrations of expensive salts of noble metals, and also do not allow achieving maximum exposure of catalytically active platinum particles on surface.
Отличительной особенностью предлагаемой полезной модели является использование для ИХА наночастиц типа ядро-оболочка - Au-Pt, обладающих пористой структурой каталитически активной платиновой оболочки и требующих в 3-10 раз меньшего (1 мМ) количества дорогостоящей платины для синтеза. Поливинилпирролидон (молекулярная масса 10 кДа) формирует плотный адсорбционный слой вокруг наночастиц золота (20 нм) и приводит к формированию пористой платиновой оболочки при восстановлении соли платины (Na2PtCl6, 1 мМ) в присутствии аскорбата натрия (10 мМ). Полученные пористые наночастицы Au-Pt могут быть связаны с антителами за счет физической адсорбции.A distinctive feature of the proposed utility model is the use for ICA of core-shell nanoparticles - Au-Pt, which have a porous structure of a catalytically active platinum shell and require 3-10 times less (1 mM) amount of expensive platinum for synthesis. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (molecular weight 10 kDa) forms a dense adsorption layer around gold nanoparticles (20 nm) and leads to the formation of a porous platinum shell upon reduction of a platinum salt (Na 2 PtCl 6 , 1 mM) in the presence of sodium ascorbate (10 mM). The resulting porous Au-Pt nanoparticles can be bound to antibodies through physical adsorption.
ИХА основан на миграции жидкой пробы вдоль тест-полоски под действием капиллярных сил без использования дополнительного оборудования. При прохождении пробы через иммобилизованные на тест-полоске иммуннореагенты на разных участках мембраны происходит формирование двойных иммунных комплексов при контакте пробы с конъюгатом (клетки С.michiganensis с конъюгатом антител с пористыми наночастицами Au-Pt), тройных иммунных комплексов при прохождении пробы через тестовую зону (Т.З.) (клетки С.michiganensis с конъюгатом антител с пористыми наночастицами Au-Pt - иммобилизованные в Т.З. антитела) и связывания избытка свободного конъюгата в контрольной зоне (К.З.) (конъюгат антител с пористыми наночастицами Au-Pt - иммуноглобулин-связывающий белок А в К.З.) Конъюгированный со специфическими антителами маркер (пористые наночастицы Au-Pt) распределяется по рабочей мембране за счет формирования иммунных комплексов, и его наличие или отсутствие в определенных участках мембраны приводит к возникновению окрашивания. Для снижения предела обнаружения ИХА на тест-полоску наносится субстратный раствор (10 мкл), состоящий из 0,05% 3,3'-диаминобензидина, 0,03% пероксида водорода и 0,05% сульфата никеля в 50 мМ фосфатном буфере (рН=7,2). После пятиминутной инкубации субстратного раствора н тест-полоски под действием наночастиц Au-Pt происходит конверсия неокрашенного субстрата в нерастворимый продукт, накопление которого в Т.З. и К.З. существенно увеличивает интенсивность колориметрического сигнала.ICA is based on the migration of a liquid sample along the test strip under the action of capillary forces without the use of additional equipment. When the sample passes through the immunoreagents immobilized on the test strip, double immune complexes are formed in different parts of the membrane when the sample comes into contact with the conjugate (C. michiganensis cells with conjugated antibodies with porous Au-Pt nanoparticles), triple immune complexes when the sample passes through the test zone ( T.Z.) (C. michiganensis cells with conjugate of antibodies with porous Au-Pt nanoparticles - antibodies immobilized in T.Z.) and binding of excess free conjugate in the control zone (K.Z.) (conjugate of antibodies with porous nanoparticles Au- Pt - immunoglobulin-binding protein A in K.Z.) A marker conjugated with specific antibodies (porous Au-Pt nanoparticles) is distributed over the working membrane due to the formation of immune complexes, and its presence or absence in certain areas of the membrane leads to staining. To reduce the ICA detection limit, a substrate solution (10 μl) is applied to the test strip, consisting of 0.05% 3,3'-diaminobenzidine, 0.03% hydrogen peroxide and 0.05% nickel sulfate in 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH = 7.2). After a five-minute incubation of the substrate solution n of the test strip under the action of Au-Pt nanoparticles, the unstained substrate is converted into an insoluble product, the accumulation of which in the T.Z. and K.Z. significantly increases the intensity of the colorimetric signal.
Использование ИХА для детекции фитопатогенных микроорганизмов обеспечивает достижение ряда преимуществ - проведение эффективного параллельного скрининга большого количества проб во внелабораторных условиях, экспрессность анализа (15-20 мин) при минимальной подготовке проб, простота детектирования и интерпретации результатов.The use of ICA for the detection of phytopathogenic microorganisms provides a number of advantages - effective parallel screening of a large number of samples in out-of-laboratory conditions, rapid analysis (15-20 min) with minimal sample preparation, ease of detection and interpretation of results.
Несмотря на то, что ИХА активно разрабатывается и применяется для диагностики фитопатогенов и других токсичных контаминантов, разработка иммунохроматографических тест-систем для высокочувствительной детекции С.michiganensis с целью внелабораторного выявления латентных инфекций кольцевой гнили картофеля не описана.Despite the fact that ICA is being actively developed and used for the diagnosis of phytopathogens and other toxic contaminants, the development of immunochromatographic test systems for highly sensitive detection of C. michiganensis for the purpose of out-of-laboratory detection of latent infections of potato ring rot has not been described.
Наиболее близкими аналогами заявляемой полезной модели являются иммунохроматографические тест-системы с использованием наночастиц ядро-оболочка Au-Pt, представленные в работах:The closest analogs of the claimed utility model are immunochromatographic test systems using Au-Pt core-shell nanoparticles, presented in the works:
Jiang и соавторов « Sensitive detection of Escherichia coli 0157:H7 using Pt-Au bimetal nanoparticles with peroxidase-like amplification)), Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2016, v. 77, p. 687-694.;Jiang et al., Sensitive detection of Escherichia coli 0157: H7 using Pt-Au bimetal nanoparticles with peroxidase-like amplification)), Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2016, v. 77, p. 687-694 .;
Loynachan и соавторов «Platinum nanocatalyst amplification: redefining the gold standard for lateral flow immunoassays with ultrabroad dynamic range)). ACS Nano, 2018, V. 12, p. 279-288.Loynachan et al., Platinum nanocatalyst amplification: redefining the gold standard for lateral flow immunoassays with ultrabroad dynamic range)). ACS Nano, 2018, V. 12, p. 279-288.
Технической задачей заявленной полезной модели является повышение интенсивности окрашивания Т.З. посредством реакции, катализируемой пористыми наночастицами типа ядро-оболочка Au-Pt на тест-полоске.The technical task of the claimed utility model is to increase the intensity of coloring T.Z. via a reaction catalyzed by porous Au-Pt core-shell nanoparticles on a test strip.
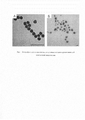
Технический результат заявленной полезной модели заключается в снижении предела обнаружения фитопатогенной бактерии С.michiganensis за счет использованием простой одностадийной процедуры, обеспечиваемой добавлением на тест-полоску субстратного раствора, содержащего смесь 3 3'-диаминобензидина, пероксида водорода и ионов Ni2+. Пористая структура наночастиц ядро-оболочка Au-Pt (Рис 1 А), отличающая их от стандартных частиц ядро-оболочка (Рис 1 Б), достигается за счет адсорбции поливинилпирролидона на поверхности затравочных наночастиц золота, что препятствует формированию монослоя плагины вокруг затравочных частиц. Пористая морфология обеспечивает большую площадь поверхности активных частиц, существенно увеличивая их удельную каталитическую активность по сравнению с непористыми частицами ядро-оболочка. Пористые наночастицы Au-Pt сохраняют до 80% пероксидазо-подобной активности в присутствии азида натрия - ингибитора пероксидаз, что позволяет использовать предложенную схему для повышения интенсивности колориметрического сигнала даже в растительных пробах с высокой эндогенной пероксидазной активностью.The technical result of the claimed utility model is to reduce the detection limit of the phytopathogenic bacterium C. michiganensis by using a simple one-step procedure, provided by adding a substrate solution containing a mixture of 3 3'-diaminobenzidine, hydrogen peroxide and Ni 2+ ions to the test strip. The porous structure of Au-Pt core-shell nanoparticles (Figure 1 A), which distinguishes them from standard core-shell particles (Figure 1 B), is achieved due to the adsorption of polyvinylpyrrolidone on the surface of the seed gold nanoparticles, which prevents the formation of a plugin monolayer around the seed particles. The porous morphology provides a large surface area for active particles, significantly increasing their specific catalytic activity as compared to non-porous core-shell particles. Porous Au-Pt nanoparticles retain up to 80% of peroxidase-like activity in the presence of sodium azide, a peroxidase inhibitor, which makes it possible to use the proposed scheme to increase the intensity of the colorimetric signal even in plant samples with high endogenous peroxidase activity.
Предлагается устройство для иммунохроматографической экспрессной лабораторной и внелабораторной высокочувствительной детекции С.michiganensis в экстрактах листьев и клубней картофеля. Устройство представляет собой мультимембранный композит с предварительно нанесенными и высушенными иммунореагентами (тест-полоску). В состав композита (рис. 2) входят рабочая нитроцеллюлозная мембрана с предварительно нанесенными иммунореагентами, закрепленная на твердой полистироловой основе, стекловолоконная мембрана с нанесенными конъюгатом пористых наночастиц типа ядро-оболочка - Au-Pt. стабилизированных поливинилпирролидоном с кроличьими поликлональными антителами специфичными к бактериальным клеткам С.michiganensis, мембрана для впитывания и сепарации компонентов исследуемой пробы и конечной адсорбирующей мембраны для впитывания компонентов пробы после прохождения реакции и поддержания миграции жидкости по тест-полоске за счет капиллярных сил.A device for express immunochromatographic laboratory and out-of-laboratory highly sensitive detection of C. michiganensis in potato leaves and tubers extracts is proposed. The device is a multi-membrane composite with pre-applied and dried immunoreagents (test strip). The composition of the composite (Fig. 2) includes a working nitrocellulose membrane with preliminarily applied immunoreagents fixed on a solid polystyrene base, a glass fiber membrane coated with a conjugate of porous core-shell nanoparticles - Au-Pt. stabilized with polyvinylpyrrolidone with rabbit polyclonal antibodies specific to C. michiganensis bacterial cells, a membrane for the absorption and separation of the components of the test sample and the final adsorbent membrane for the absorption of sample components after the reaction and maintenance of liquid migration along the test strip due to capillary forces.
Указанный технический результат достигается тем, что:The specified technical result is achieved by:
- в контрольную зону (К.З.) нанесен иммуноглобулин-связывающий белок А;- Immunoglobulin-binding protein A was applied to the control zone (K.Z.);
- в тестовую зону (Т.З.) нанесены кроличьи поликлональные антитела специфичные к клеткам С.michiganensis;- rabbit polyclonal antibodies specific to C. michiganensis cells were applied to the test zone (T.Z.);
- на стекловолоконную мембрану нанесен конъюгат пористых наночастиц Au-Pt с поликлональиыми кроличьими антителами, специфичными к С.michiganensis- a conjugate of porous Au-Pt nanoparticles with polyclonal rabbit antibodies specific to C. michiganensis is applied to the glass fiber membrane
- при добавлении смеси субстратного раствора, содержащего смесь 3,3'-диаминобензидина, пероксида водорода и ионов Ni2+ наночастицы Au-Pt катализируют реакцию окисления 3,3'-диаминобензидина пероксидом водорода, ионы никеля обеспечивают формирование нерастворимого темноокрашенного продукта реакции, прецицитирующего на рабочей нитроцеллюлозной мембране.- when adding a mixture of a substrate solution containing a mixture of 3,3'-diaminobenzidine, hydrogen peroxide and Ni 2+ ions, Au-Pt nanoparticles catalyze the oxidation reaction of 3,3'-diaminobenzidine with hydrogen peroxide, nickel ions provide the formation of an insoluble dark-colored reaction product, working nitrocellulose membrane.
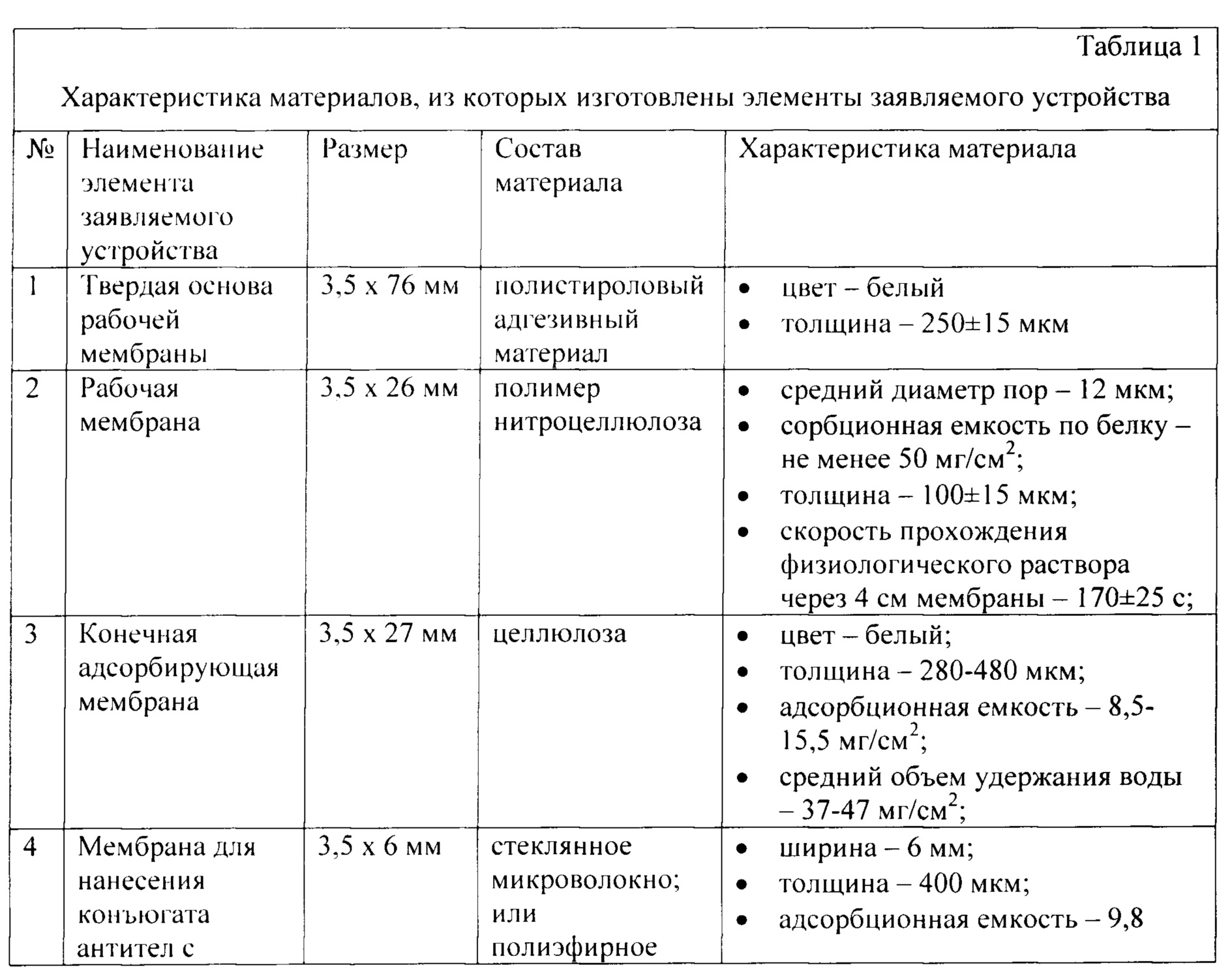
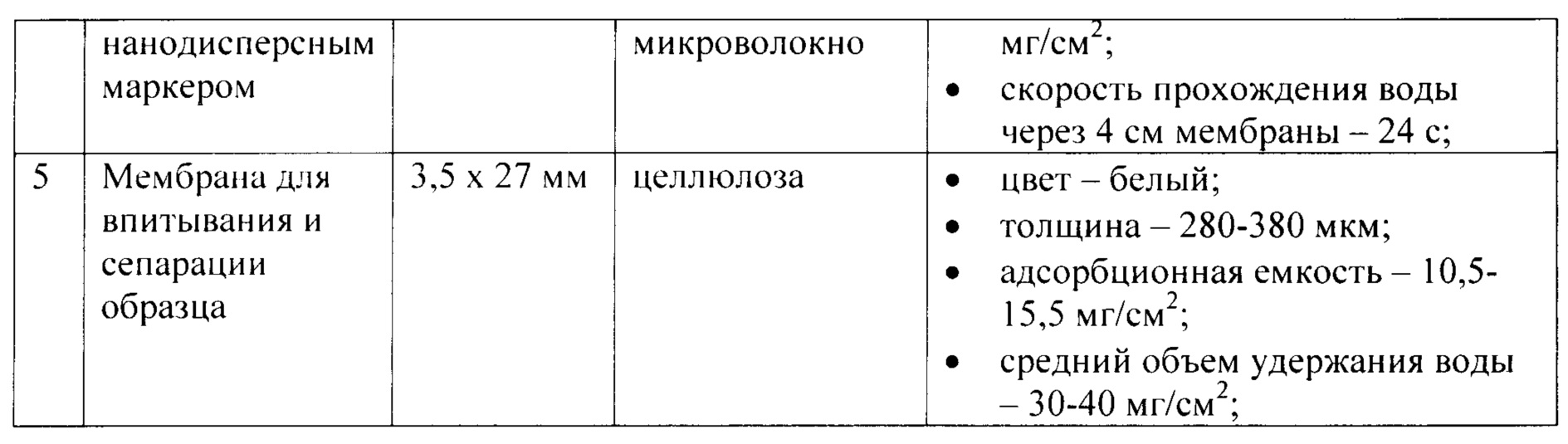
В таблице 1 приведена характеристика материалов, из которых изготовлены элементы заявляемого устройства.Table 1 shows the characteristics of the materials from which the elements of the claimed device are made.
Анализ проводят следующим образом:The analysis is carried out as follows:
1. 100 мкл анализируемого растительного экстракта (экстракт листьев или клубней картофеля) вносят в пластиковую пробирку вместимостью 1,5 мл.1. 100 μl of the analyzed plant extract (extract of leaves or tubers of potatoes) is introduced into a plastic test tube with a capacity of 1.5 ml.
2. Тест-полоску погружают вертикально нижним концом мембраны для впитывания образца в анализируемый экстракт и выдерживают при комнатной температуре в течение 5 мин.2. The test strip is immersed vertically with the lower end of the membrane to absorb the sample into the extract to be analyzed and kept at room temperature for 5 minutes.
3. Вынимают тест-полоску и помещают ее на сухую горизонтальную поверхность на 5 мин.3. Remove the test strip and place it on a dry horizontal surface for 5 minutes.
4. Через 10 мин после начала движения жидкости по тест-полоске результат анализа фиксируют визуально или с использованием детектора с видеоцифровой регистрацией.4. In 10 minutes after the beginning of the movement of the liquid along the test strip, the result of the analysis is recorded visually or using a detector with video digital recording.
5. Добавляют 20 мкл субстратного раствора, и выдерживают в течение 3 мин. Результат анализа фиксируют визуально или с использованием детектора с видеоцифровой регистрацией.5. Add 20 µl of substrate solution and incubate for 3 minutes. The result of the analysis is recorded visually or using a detector with video digital registration.
Заявляемое устройство функционирует следующим образом (см. рис. 1). Если в образце присутствуют клетки С.michiganensis, то под действием капиллярных сил они с потоком жидкости перемещаются по впитывающей мембране (5), доходят до стекловолоконной мембраны (4) и вступают в реакцию с поликлональными антителами на поверхности конъюгатов пористых наночастиц Au-Pt с образованием двойных иммунных комплексов (клетки С.michiganensis - антитела, меченные пористыми наночастицами Au-Pt). Образовавшиеся двойные иммунные комплексы под действием капиллярных сил движутся вдоль рабочей нитроцеллюлозной мембраны (2) и взаимодействуют с иммобилизованными в Т.З. поликлональными антителами к С.michiganensis с образованием тройных комплексов (иммобилизованные на мембране в Т.З. антитела - клетки С.michiganensis - антитела, меченные пористыми наночастицами Au-Pt). Избыток несвязавшихся в Т.З. конъюгатов пористых наночастиц с антителами продолжает двигаться вдоль рабочей нитроцеллюлозной мембраны (2) и взаимодействует с белком А, иммобилизованными в К.З. (А), с образованием двойных комплексов (иммобилизованные на мембране антивидовые антитела - антитела, меченные коллоидным золотом).The claimed device operates as follows (see Fig. 1). If C. michiganensis cells are present in the sample, then under the action of capillary forces they move along the absorbent membrane (5) with a liquid flow, reach the glass fiber membrane (4) and react with polyclonal antibodies on the surface of conjugates of porous Au-Pt nanoparticles to form double immune complexes (C. michiganensis cells - antibodies labeled with porous Au-Pt nanoparticles). The formed double immune complexes under the action of capillary forces move along the working nitrocellulose membrane (2) and interact with those immobilized in T.Z. polyclonal antibodies to C. michiganensis with the formation of ternary complexes (antibodies immobilized on the membrane in T.Z. - C. michiganensis cells - antibodies labeled with porous Au-Pt nanoparticles). The excess of unconnected in T.Z. conjugates of porous nanoparticles with antibodies continue to move along the working nitrocellulose membrane (2) and interact with protein A immobilized in the K.Z. (A), with the formation of double complexes (anti-species antibodies immobilized on the membrane - antibodies labeled with colloidal gold).
Интерпретация результатов анализа производится на основании наличия окрашенных Т.З. и К.З.:The interpretation of the analysis results is based on the presence of stained T.Z. and K.Z .:
1. Если через 10 мин на рабочей мембране тест-полоски появляются две темноокрашенные зоны (Т.З. и К.З.), то результат анализа считается положительным, т.е. в растительной пробе присутствуют клетки С.michiganensis. Проведения дополнительной стадии усиления сигнала в таком случае не требуется.1. If after 10 minutes two dark-colored zones (TZ and KZ) appear on the working membrane of the test strip, then the test result is considered positive, i.e. the plant sample contains C. michiganensis cells. In this case, an additional stage of signal amplification is not required.
2. Если через 10 мин на рабочей мембране тест-полоски появляется одна темноокрашенная К.З. при этом окрашивание Т.З. не наблюдается, то результат анализа считается отрицательным, т.е. в растительной пробе не содержится клеток С.michiganensis или их количество оказывается меньше предела обнаружения ИХА. В таком случае проводится дополнительная стадия усиления сигнала. Для этого на тест-полоску добавляют 20 мкл субстратного раствора. После добавления субстрата полоска выдерживается в течение 3 мин в вертикальном положении. Наличие темноокрашенной Т.З. свидетельствует о присутствии бактериальных клеток С.michiganensis в анализируемой пробе, отсутствие окрашенной Т.З. и наличие окрашенной К.З. свидетельствует об отсутствии С.michiganensis в анализируемой пробе.2. If after 10 minutes one dark-colored short circuit appears on the working membrane of the test strip. while staining T.Z. is not observed, then the result of the analysis is considered negative, i.e. the plant sample does not contain C. michiganensis cells or their number is less than the ICA detection limit. In this case, an additional stage of signal amplification is performed. To do this, add 20 μl of the substrate solution to the test strip. After adding the substrate, the strip is kept in an upright position for 3 minutes. The presence of dark-colored T.Z. indicates the presence of C. michiganensis bacterial cells in the analyzed sample, the absence of stained T.Z. and the presence of stained K.Z. indicates the absence of C. michiganensis in the analyzed sample.
3. Если через 10 мин на рабочей мембране тест-полоски не образуется ни одной окрашенной линии или происходит окрашивание только Т.З. (без формирования окраски К.З.), то результат анализа считается недействительным (рис. 2д). В таком случае необходимо повторное тестирование с использованием новой тест-полоски.3. If, after 10 minutes, no colored lines are formed on the working membrane of the test strip or only T.Z. (without color formation K.Z.), then the result of the analysis is considered invalid (Fig. 2e). If this happens, retest with a new test strip.
Эффективность данного подхода подтверждается следующими примерами:The effectiveness of this approach is confirmed by the following examples:
Пример 1 (влияние азида натрия на пероксидазную активность экстрактов клубней картофеля и конъюгата пористых наночастиц Ai-Pt с поликлональными антителами против клеток С.michiganensis)Example 1 (the effect of sodium azide on the peroxidase activity of potato tuber extracts and the conjugate of porous Ai-Pt nanoparticles with polyclonal antibodies against C. michiganensis cells)
Выбор концентрации азида натрия, обеспечивающей ингибирование эндогенных пероксидаз в растительном экстракте с сохранением высокой перикосидаза-подобной активности пористых наночастиц Au-Pt, позволяет использовать данный наноразмерный маркер для ИХА без дополнительных отмывок. В течение 5 мин инкубировали различные концентрации азида натрия (0-0,15%) с 100 мкл экстракта клубней картофеля и 95 мкл фосфатного буфера, содержащего 5 мкл пористых наночастиц. Далее добавляли 100 мкл субстратного раствора, содержащего 50 мМ 3,3'5,5'-тетраметилбензидин, 3 мМ пероксид водорода в 50 мМ цитратном буфере, рН=5,0, и выдерживали в течение 10 мин. Ферментативную реакцию останавливали добавлением 50 мкл 1 М серной кислоты. Интенсивность окрашивания при длине волны 450 нм фиксировали с помощью фотометра в трех повторностях. Результаты представлены в таблице 2.The choice of the sodium azide concentration, which ensures the inhibition of endogenous peroxidases in the plant extract while maintaining the high pericosidase-like activity of porous Au-Pt nanoparticles, makes it possible to use this nano-sized marker for ICA without additional washes. For 5 min, various concentrations of sodium azide (0-0.15%) were incubated with 100 μl of potato tuber extract and 95 μl of phosphate buffer containing 5 μl of porous nanoparticles. Then, 100 μl of a substrate solution containing 50 mM 3,3'5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine, 3 mM hydrogen peroxide in 50 mM citrate buffer, pH = 5.0 was added and kept for 10 min. The enzymatic reaction was stopped by the addition of 50 μl of 1 M sulfuric acid. The intensity of staining at a wavelength of 450 nm was recorded using a photometer in triplicate. The results are shown in Table 2.
Наночастицы Au-Pt сохраняют до 82% пероксидаза-подобной активности в условиях, обеспечивающих полную инактивацию эндогенных пероксидаз. Таким образом, добавление 0,05% азида натрия позволяет проводить амплификацию сигнала с использованием каталитической активности пористых наночастиц даже при анализе проб с высокой эндогенной пероксидазной активностью.Au-Pt nanoparticles retain up to 82% of the peroxidase-like activity under conditions that ensure complete inactivation of endogenous peroxidases. Thus, the addition of 0.05% sodium azide makes it possible to amplify the signal using the catalytic activity of porous nanoparticles even when analyzing samples with high endogenous peroxidase activity.
Пример 2 (выявление клеток С.michiganensis в экстракте клубней картофеля без проведения стадии амплификации сигнала).Example 2 (detection of C. michiganensis cells in potato tuber extract without performing a signal amplification step).
С использованием заявляемого устройства проводят анализ экстрактов клубней картофеля, с добавлением 103- 106 клеток/мл (кл/мл) С.michiganensis и экстракта клубней картофеля, не содержащего бактериальных клеток. Анализируемую аликвоту (100 мкл экстракта) вносят в пробирку, после чего тест-полоску погружают вертикально нижним концом мембраны для впитывания образца на глубину 0,5 см в образец и инкубируют при комнатной температуре в течение 5 мин. Вынимают тест-полоску и помещают ее на горизонтальную поверхность. Результат анализа оценивают через 5 мин с помощью программного обеспечения видеоцифрового детектора. Анализ проводят в трех повторностях, используя тест-полоски разных серий. Результаты анализа приведены в таблице 3.Using the proposed device, the analysis of potato tubers extracts is carried out, with the addition of 103-106 cells / ml (cells / ml) of C. michiganensis and an extract of potato tubers that does not contain bacterial cells. An aliquot to be analyzed (100 μl of the extract) is added to a test tube, after which the test strip is immersed vertically with the lower end of the membrane to absorb the sample to a depth of 0.5 cm into the sample and incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes. Remove the test strip and place it on a horizontal surface. The analysis result is evaluated after 5 minutes using the video digital detector software. The analysis is carried out in triplicate using test strips from different batches. The analysis results are shown in Table 3.
Пределом обнаружения ИХА считали количество клеток С.michiganensis, обеспечивающих колориметрический сигнал в Т.З. превосходящий сумму среднего значения колориметрического сигнала и трех стандартных отклонений для отрицательной пробы (здоровый экстракт). Для ИХА без проведения амплификации сигнала сумма среднего значения колориметрического сигнала и трех стандартных отклонений для отрицательной пробы была равна 0,85. Таким образом, предел обнаружения для данной системы составлял 104 кл/мл С.michiganensis. Из приведенных данных видно, что регистрируемая интенсивность колориметрического сигнала в тестовой зоне позволяет достоверно детектировать 104 кл/мл С.michiganensis в экстракте клубней картофеля в рамках заявленного времени анализа (10 мин).The limit of ICA detection was the number of C. michiganensis cells providing a colorimetric signal in T.Z. exceeding the sum of the mean of the colorimetric signal and three standard deviations for the negative sample (healthy extract). For ICA without signal amplification, the sum of the mean value of the colorimetric signal and three standard deviations for the negative sample was 0.85. Thus, the detection limit for this system was 104 cells / ml C. michiganensis. It can be seen from the data presented that the recorded intensity of the colorimetric signal in the test zone makes it possible to reliably detect 104 cells / ml of C. michiganensis in the extract of potato tubers within the stated analysis time (10 min).
Пример 3 (выявление клеток С.michiganensis в экстракте клубней картофеля без проведения стадии амплификации сигнала).Example 3 (detection of C. michiganensis cells in potato tuber extract without carrying out the signal amplification step).
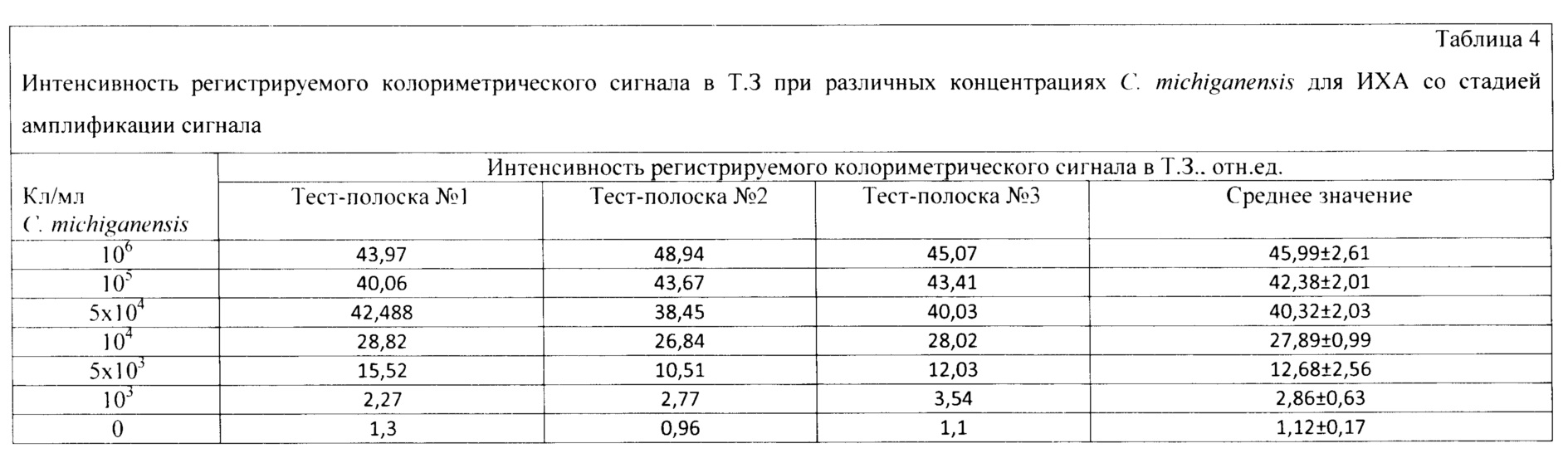
С использованием заявляемого устройства проводят анализ экстрактов клубней картофеля, с добавлением 103-106 клеток/мл (кл/мл) С.michiganensis и экстракта клубней картофеля, не содержащего бактериальных клеток. Анализируемую аликвоту (100 мкл экстракта) вносят в пробирку, после чего тест-полоску погружают вертикально нижним концом мембраны для впитывания образца на глубину 0,5 см в образец и инкубируют при комнатной температуре в течение 5 мин. Вынимают тест-полоску и помещают ее на горизонтальную поверхность. Спустя 5 мин добавляют 20 мкл субстратного раствора. Результат анализа оценивают через 5 мин с помощью видеоцифрового детектора. Анализ проводят в трех повторностях, используя тест-полоски разных серий. Результаты анализа приведены в таблице 4.Using the proposed device, an analysis of potato tubers extracts is carried out, with the addition of 10 3 -10 6 cells / ml (cells / ml) C. michiganensis and an extract of potato tubers that does not contain bacterial cells. An aliquot to be analyzed (100 μl of the extract) is added to a test tube, after which the test strip is immersed vertically with the lower end of the membrane to absorb the sample to a depth of 0.5 cm into the sample and incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes. Remove the test strip and place it on a horizontal surface. After 5 minutes, 20 μl of the substrate solution is added. The analysis result is evaluated after 5 minutes using a video digital detector. The analysis is carried out in triplicate using test strips from different batches. The analysis results are shown in Table 4.
Пределом обнаружения ИХА считали количество клеток С.michiganensis, обеспечивающих колориметрический сигнал в Т.З. превосходящий сумму среднего значения колориметрического сигнала и трех стандартных отклонений для отрицательной пробы (здоровый экстракт). Для ИХА без проведения амплификации сигнала сумма среднего значения колориметрического сигнала и трех стандартных отклонений для отрицательной пробы была равна 1,63. Таким образом, предел обнаружения для данной системы составлял 103 кл/мл С.michiganensis. Из приведенных экспериментальных данных видно, что регистрируемая интенсивность колориметрического сигнала в тестовой зоне позволяет достоверно детектировать 103 кл/мл С.michiganensis в экстракте клубней картофеля в рамках заявленного времени анализа (10 мин).The limit of ICA detection was the number of C. michiganensis cells providing a colorimetric signal in T.Z. exceeding the sum of the mean of the colorimetric signal and three standard deviations for the negative sample (healthy extract). For ICA without signal amplification, the sum of the mean value of the colorimetric signal and three standard deviations for the negative sample was 1.63. Thus, the detection limit for this system was 103 cells / ml C. michiganensis. From the experimental data presented, it can be seen that the recorded intensity of the colorimetric signal in the test zone makes it possible to reliably detect 10 3 cells / ml C. michiganensis in the extract of potato tubers within the stated analysis time (10 min).
По сравнению с системой без амплификации сигнала получено десятикратное снижение предела обнаружения, достигаемое за короткое время (дополнительных 5 мин), и не требующее сложных методических решений (добавление капли готового к использованию субстратного раствора на тест-полоску).Compared to the system without signal amplification, a tenfold decrease in the detection limit was obtained, which was achieved in a short time (additional 5 min) and did not require complex methodological solutions (adding a drop of a ready-to-use substrate solution to the test strip).
Краткое описание чертежей.Brief description of the drawings.
На рис. 1 представлены микрофотографии наночастиц, полученные методом просвечивающей электронной микроскопии. А - наночастицы типа ядро-оболочка Au-Pt. Б - пористые наночастицы типа ядро-оболочка Au-Pt, стабилизированные поливинилпирролидоном.In fig. 1 shows micrographs of nanoparticles obtained by transmission electron microscopy. A - Au-Pt core-shell nanoparticles. B - porous Au-Pt core-shell nanoparticles stabilized with polyvinylpyrrolidone.
На рис. 2 изображена схема заявляемого устройства для иммунохроматографической экспрессной лабораторной и внелабораторной детекции С.michiganensis. 1 - твердая полистирольная основа рабочей нитроцеллюлозной мембраны; 2 - рабочая нитроцеллюлозная мембрана; 3 - конечная адсорбирующая мембрана для впитывания компонентов образца после прохождения реакции; 4 - стекловолоконная мембрана с нанесенным и высушенным конъюгатом пористых наночастиц Au-Pt с поликлональными кроличьими антителами, специфичными к С.michiganensis; 5 - мембрана для впитывания и сепарации исследуемого образца; 6 - Т.З. с нанесенными поликлональными кроличьими антителами к С.michiganensis; 7 - К.З. с нанесенным иммуноглобулин-связывающим белком А.In fig. 2 shows a diagram of the proposed device for immunochromatographic express laboratory and out-of-laboratory detection of C. michiganensis. 1 - solid polystyrene base of a working nitrocellulose membrane; 2 - working nitrocellulose membrane; 3 - final adsorbent membrane for absorbing sample components after the reaction; 4 - glass fiber membrane coated and dried with a conjugate of porous Au-Pt nanoparticles with polyclonal rabbit antibodies specific to C. michiganensis; 5 - membrane for absorption and separation of the test sample; 6 - T.Z. with applied polyclonal rabbit antibodies to C. michiganensis; 7 - K.Z. with applied immunoglobulin-binding protein A.
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2020119108U RU202193U1 (en) | 2020-06-09 | 2020-06-09 | A device for immunochromatographic highly sensitive and out-of-laboratory detection of the phytopathogenic bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis, based on an increase in the intensity of the recorded colorimetric signal due to the catalytic properties of the nanomarker |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2020119108U RU202193U1 (en) | 2020-06-09 | 2020-06-09 | A device for immunochromatographic highly sensitive and out-of-laboratory detection of the phytopathogenic bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis, based on an increase in the intensity of the recorded colorimetric signal due to the catalytic properties of the nanomarker |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU202193U1 true RU202193U1 (en) | 2021-02-05 |
Family
ID=74550983
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2020119108U RU202193U1 (en) | 2020-06-09 | 2020-06-09 | A device for immunochromatographic highly sensitive and out-of-laboratory detection of the phytopathogenic bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis, based on an increase in the intensity of the recorded colorimetric signal due to the catalytic properties of the nanomarker |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU202193U1 (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2523393C1 (en) * | 2013-03-19 | 2014-07-20 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение науки Институт биохимии имени А.Н. Баха РАН Российской академии наук (ИНБИ РАН) | Test strip for highly sensitive immunochromatographic analysis |
| US9739773B1 (en) * | 2010-08-13 | 2017-08-22 | David Gordon Bermudes | Compositions and methods for determining successful immunization by one or more vaccines |
| RU2642588C1 (en) * | 2017-03-14 | 2018-01-25 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Вятский государственный университет" | Immunochromatographic test system for pathogenic helicobacter pylori strains detection |
| RU192778U1 (en) * | 2018-12-26 | 2019-10-01 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Федеральный исследовательский центр "Фундаментальные основы биотехнологии" Российской академии наук" (ФИЦ Биотехнологии РАН) | Device for immunochromatographic express off-laboratory diagnostics of grape disease caused by leaf curling virus |
-
2020
- 2020-06-09 RU RU2020119108U patent/RU202193U1/en active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9739773B1 (en) * | 2010-08-13 | 2017-08-22 | David Gordon Bermudes | Compositions and methods for determining successful immunization by one or more vaccines |
| RU2523393C1 (en) * | 2013-03-19 | 2014-07-20 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение науки Институт биохимии имени А.Н. Баха РАН Российской академии наук (ИНБИ РАН) | Test strip for highly sensitive immunochromatographic analysis |
| RU2642588C1 (en) * | 2017-03-14 | 2018-01-25 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Вятский государственный университет" | Immunochromatographic test system for pathogenic helicobacter pylori strains detection |
| RU192778U1 (en) * | 2018-12-26 | 2019-10-01 | Федеральное государственное учреждение "Федеральный исследовательский центр "Фундаментальные основы биотехнологии" Российской академии наук" (ФИЦ Биотехнологии РАН) | Device for immunochromatographic express off-laboratory diagnostics of grape disease caused by leaf curling virus |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CA1251382A (en) | Use of substituted quinone electron transfer agents in analytical determinations | |
| Yulaev et al. | Development of a potentiometric immunosensor for herbicide simazine and its application for food testing | |
| JPS6329247A (en) | Composition for analysis, analytic element and method of measuring substance to be analyzed | |
| US4525452A (en) | Enzyme immunoassay with step of immersing sample in deionized water | |
| WO1986004421A1 (en) | Enzyme immunoassay with two-part solution of tetramethylbenzidine as chromogen | |
| CH627281A5 (en) | ||
| JPS63271160A (en) | Composition and method of immunoassay of feces sample | |
| KR101990301B1 (en) | Optical biosensor | |
| JPS6367864B2 (en) | ||
| Yang et al. | Comparison of soybean peroxidase with horseradish peroxidase and alkaline phosphatase used in immunoassays | |
| CN113721024A (en) | Fluorescence immunoassay rapid detection kit and detection method for enrofloxacin carbon quantum dots in animal derived food | |
| RU202193U1 (en) | A device for immunochromatographic highly sensitive and out-of-laboratory detection of the phytopathogenic bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis, based on an increase in the intensity of the recorded colorimetric signal due to the catalytic properties of the nanomarker | |
| US4687736A (en) | Detection of biological substances by specific labelling techniques | |
| US5063151A (en) | Immunoassay method and kit | |
| Gotoh et al. | Micro-FET biosensors using polyvinylbutyral membrane | |
| US20100209941A1 (en) | Method, device and kit for determining conditions related to a dysfunction of the renal proximal tubule | |
| US20090053694A1 (en) | Photochemically Amplified Bioassay | |
| Cembella et al. | In vitro assays for phycotoxins | |
| RU201487U1 (en) | Device for multiplex immunochromatographic analysis of viral and bacterial pathogens with an additional stage of signal amplification | |
| Monroe | Amperometric immunoassay | |
| CN107923907A (en) | Immunologic measure reagent composition and application thereof | |
| EP0903410B1 (en) | Method for detection and determination of enzymatic reactions in urine | |
| Patra et al. | Biosensors involved in dairy industries | |
| Głowacka et al. | Photometric flow system for the determination of serum lactate dehydrogenase activity | |
| CN110296972B (en) | Quantitative detection method for staphylococcus aureus based on SERS technology |