NL2011815C2 - Hot melt adhesive composition. - Google Patents
Hot melt adhesive composition. Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- NL2011815C2 NL2011815C2 NL2011815A NL2011815A NL2011815C2 NL 2011815 C2 NL2011815 C2 NL 2011815C2 NL 2011815 A NL2011815 A NL 2011815A NL 2011815 A NL2011815 A NL 2011815A NL 2011815 C2 NL2011815 C2 NL 2011815C2
- Authority
- NL
- Netherlands
- Prior art keywords
- hot melt
- composition according
- styrene
- resins
- polymer
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 30
- 239000004831 Hot glue Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 24
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 47
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 239000012943 hotmelt Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 24
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 27
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 18
- 150000002894 organic compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000001993 wax Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- -1 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 claims description 9
- QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene Natural products CC=C QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 150000003505 terpenes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 9
- 235000007586 terpenes Nutrition 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000004805 propylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 claims description 6
- 229920001059 synthetic polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229920001585 atactic polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- IANQTJSKSUMEQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-benzofuran Chemical compound C1=CC=C2OC=CC2=C1 IANQTJSKSUMEQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- YBYIRNPNPLQARY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-indene Chemical compound C1=CC=C2CC=CC2=C1 YBYIRNPNPLQARY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- RSWGJHLUYNHPMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Abietic-Saeure Natural products C12CCC(C(C)C)=CC2=CCC2C1(C)CCCC2(C)C(O)=O RSWGJHLUYNHPMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butadiene Chemical compound C=CC=C KAKZBPTYRLMSJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000013032 Hydrocarbon resin Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Naphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- KHPCPRHQVVSZAH-HUOMCSJISA-N Rosin Natural products O(C/C=C/c1ccccc1)[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 KHPCPRHQVVSZAH-HUOMCSJISA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920006270 hydrocarbon resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920003049 isoprene rubber Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000005011 phenolic resin Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920006132 styrene block copolymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920000468 styrene butadiene styrene block copolymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- KHPCPRHQVVSZAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-cinnamyl beta-D-glucopyranoside Natural products OC1C(O)C(O)C(CO)OC1OCC=CC1=CC=CC=C1 KHPCPRHQVVSZAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000001336 alkenes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000004945 aromatic hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002480 mineral oil Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000012188 paraffin wax Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- WTARULDDTDQWMU-RKDXNWHRSA-N (+)-β-pinene Chemical compound C1[C@H]2C(C)(C)[C@@H]1CCC2=C WTARULDDTDQWMU-RKDXNWHRSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- WTARULDDTDQWMU-IUCAKERBSA-N (-)-Nopinene Natural products C1[C@@H]2C(C)(C)[C@H]1CCC2=C WTARULDDTDQWMU-IUCAKERBSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GRWFGVWFFZKLTI-IUCAKERBSA-N 1S,5S-(-)-alpha-Pinene Natural products CC1=CC[C@@H]2C(C)(C)[C@H]1C2 GRWFGVWFFZKLTI-IUCAKERBSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- KJQMOGOKAYDMOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(=C)C=C.CC(=C)C=C Chemical compound CC(=C)C=C.CC(=C)C=C KJQMOGOKAYDMOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 244000043261 Hevea brasiliensis Species 0.000 claims description 2
- CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N O-Xylene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1C CTQNGGLPUBDAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- WTARULDDTDQWMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pseudopinene Natural products C1C2C(C)(C)C1CCC2=C WTARULDDTDQWMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000001335 aliphatic alkanes Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- XCPQUQHBVVXMRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-Fenchene Natural products C1CC2C(=C)CC1C2(C)C XCPQUQHBVVXMRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229930006722 beta-pinene Natural products 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920001400 block copolymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- GJKZSOHUVOQISW-UHFFFAOYSA-N buta-1,3-diene;2-methylbuta-1,3-diene;styrene Chemical compound C=CC=C.CC(=C)C=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 GJKZSOHUVOQISW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- LCWMKIHBLJLORW-UHFFFAOYSA-N gamma-carene Natural products C1CC(=C)CC2C(C)(C)C21 LCWMKIHBLJLORW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920001519 homopolymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920003052 natural elastomer Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920001194 natural rubber Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000346 polystyrene-polyisoprene block-polystyrene Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920003048 styrene butadiene rubber Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920001935 styrene-ethylene-butadiene-styrene Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920003051 synthetic elastomer Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000008096 xylene Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- GRWFGVWFFZKLTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N α-pinene Chemical compound CC1=CCC2C(C)(C)C1C2 GRWFGVWFFZKLTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- MVNCAPSFBDBCGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-pinene Natural products CC1=CCC23C1CC2C3(C)C MVNCAPSFBDBCGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- 238000006555 catalytic reaction Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 150000002825 nitriles Chemical class 0.000 claims 1
- 229920013639 polyalphaolefin Polymers 0.000 claims 1
- 229920001083 polybutene Polymers 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003292 glue Substances 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000007598 dipping method Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 229940095050 propylene Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 230000009477 glass transition Effects 0.000 description 5
- XPVIQPQOGTVMSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-acetamidophenyl)arsenic Chemical compound CC(=O)NC1=CC=C([As])C=C1 XPVIQPQOGTVMSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VXNZUUAINFGPBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Butene Chemical compound CCC=C VXNZUUAINFGPBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229920013640 amorphous poly alpha olefin Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 3
- VSKJLJHPAFKHBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylbuta-1,3-diene;styrene Chemical compound CC(=C)C=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 VSKJLJHPAFKHBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- FACXGONDLDSNOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N buta-1,3-diene;styrene Chemical compound C=CC=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 FACXGONDLDSNOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IAQRGUVFOMOMEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N butene Natural products CC=CC IAQRGUVFOMOMEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 235000010446 mineral oil Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 229920005996 polystyrene-poly(ethylene-butylene)-polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009736 wetting Methods 0.000 description 2
- LIKMAJRDDDTEIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-hexene Chemical compound CCCCC=C LIKMAJRDDDTEIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JMMZCWZIJXAGKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpent-2-ene Chemical compound CCC=C(C)C JMMZCWZIJXAGKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001643597 Evas Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000005662 Paraffin oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002367 Polyisobutene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004820 Pressure-sensitive adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006125 amorphous polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000084 colloidal system Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011096 corrugated fiberboard Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004132 cross linking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- BXOUVIIITJXIKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethene;styrene Chemical group C=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 BXOUVIIITJXIKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920006228 ethylene acrylate copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005038 ethylene vinyl acetate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002193 fatty amides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012968 metallocene catalyst Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004200 microcrystalline wax Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019808 microcrystalline wax Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003607 modifier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011087 paperboard Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001200 poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- YWAKXRMUMFPDSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N propyl ethylene Natural products CCCC=C YWAKXRMUMFPDSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000012776 robust process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003673 urethanes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012855 volatile organic compound Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09J—ADHESIVES; NON-MECHANICAL ASPECTS OF ADHESIVE PROCESSES IN GENERAL; ADHESIVE PROCESSES NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE; USE OF MATERIALS AS ADHESIVES
- C09J123/00—Adhesives based on homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers
- C09J123/02—Adhesives based on homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after-treatment
- C09J123/10—Homopolymers or copolymers of propene
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G59/00—Polycondensates containing more than one epoxy group per molecule; Macromolecules obtained by polymerising compounds containing more than one epoxy group per molecule using curing agents or catalysts which react with the epoxy groups
- C08G59/18—Macromolecules obtained by polymerising compounds containing more than one epoxy group per molecule using curing agents or catalysts which react with the epoxy groups ; e.g. general methods of curing
- C08G59/40—Macromolecules obtained by polymerising compounds containing more than one epoxy group per molecule using curing agents or catalysts which react with the epoxy groups ; e.g. general methods of curing characterised by the curing agents used
- C08G59/50—Amines
- C08G59/504—Amines containing an atom other than nitrogen belonging to the amine group, carbon and hydrogen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09J—ADHESIVES; NON-MECHANICAL ASPECTS OF ADHESIVE PROCESSES IN GENERAL; ADHESIVE PROCESSES NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE; USE OF MATERIALS AS ADHESIVES
- C09J153/00—Adhesives based on block copolymers containing at least one sequence of a polymer obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds; Adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Adhesives Or Adhesive Processes (AREA)
Abstract
The present invention is in the field of a hot melt adhesive composition, use of said hot melt composition and products comprising said composition. A hot melt adhesive (HMA), also known as a hot glue is a form of thermoplastic adhesive. It is commonly supplied in solid form, as blocks, pillows, powders, films or sticks designed to be melted e.g. in an dedicated hot melt melter and to be applied using a hot melt applicator. Such a glue i tacky when hot, and solidifies in a relatively short time, typically from a few seconds to one a few minutes. Hot melt adhesives can also be applied by dipping or spraying.
Description
Title Hot melt adhesive composition FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is in the field of a hot melt adhesive composition, use of said hot melt composition and products comprising said composition.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION A hot melt adhesive (HMA), also known as a hot glue, is a form of thermoplastic adhesive. It is commonly supplied in solid form, as blocks, pillows, powders, films or sticks designed to be melted e.g. in an dedicated-hot melt melter and to be applied using a hot melt applicator. Such a glue is tacky when hot, and solidifies in a relatively short time, typically from a few seconds to a few minutes exceptionally. Hot melt adhesives can also' be applied by dipping or spraying.
Hot melt adhesives provide several advantages. Volatile organic compounds are reduced or eliminated, a drying or curing step is eliminated, they have a long shelf life, they do not lose thickness during solidifying, and usually can be disposed of without special precautions. They also have some disadvantages, such as a thermal load (due to hot application) of a substrate, loss of bond strength at higher temperatures, and complete melting of the adhesive.
General properties of hot melt adhesives are open time (working time to make a bond, where the surface still retains sufficient tack, can range from seconds for fast-setting adhesives to infinity for pressure-sensitive adhesives), set time (time to form a bond of acceptable strength), tack (degree of surface stickiness of the adhesive, and surface energy (influences wetting of different kind of surfaces).
Hot melt glues often consist of one base material with various additives. The composition is then formulated to have a glass transition temperature (onset of brittleness) below a lowest service temperature and a suitably high melt temperature as well. Hot melt adhesives can be tailored for a given application, e.g. the melt viscosity, tack, strength and the crystallization rate (and corresponding open time) and crystallization level. It is considered that a lower level of crystallization, such as can be reached by using amorphous polymers will lead to softer adhesives such as which can be used for bonding soft and flexible materials.
Some of the possible base materials, each having advantages and disadvantages, are ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) copolymers, ethylene-acrylate copolymers, polyamides and polyesters, polyurethanes (PUR), or reactive urethanes, styrene block copolymers (SBC), also called styrene copolymer adhesives and various other copolymers.
Polyolefins, such as polyethylene, suffer from various disadvantages, e.g. from cohesive failure, and relative high cost price.
In physical and organic chemistry, the dispersity is a measure of the heterogeneity of sizes of molecules or particles in a mixture. A collection of objects is called monodis-perse or uniform if the objects have the same size, shape, or mass. A sample of objects that have an inconsistent size, shape and mass distribution is called polydisperse or non-uniform. The objects can be in any form of chemical dispersion, such as particles in a colloid, and polymer molecules in a solvent. Polymers can possess a distribution of molecular mass; and particles often possess a wide distribution of size, surface area and mass.
The term dispersity, represented by the symbol B, can refer to either molecular mass or degree of polymerization. It can be calculated using the equation DM = Mw/Mn, where Mw is the weight-average molar mass and Mn is the number-average molar mass.
Many of the prior art adhesives need to be bonded directly, typically within a few seconds, as an open time is relatively short. That characteristics makes such an adhesive not suited for larger surfaces to be adhered.
It is also preferred to have an adhesive that has a long transferability.
It is often also important to have a high initial strength. For many prior art adhesive initial strength is not sufficient. One has to wait before making the bond thus reducing open time.
For many applications a strong initial bond is required. Inherently it is difficult to provide a strong bond with an adhesive, especially with hot melt adhesives.
Adhesives are preferably also temperature stable.
It is therefore an object of the present invention to provide a hot melt adhesive which overcomes one or more of the above disadvantages, without jeopardizing functionality and advantages.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a hot melt adhesive according to claim 1, a use thereof according to claim 12 and a product according to claim 14. The present hot melt is considered to be a relatively slow hot melt.
The present adhesive surprisingly provides a high initial strength, suitable viscoelastic properties, strong bonding, long transferability, good wetting, low-temperature flexibility, good anti-blocking, good stability, long shelf life, stress release during formation of a bond, applicability over a broad temperature range, application on a variety of substrates, such as porous flexible substrates, good cohesive strength, and long open time, and which can be used in combination with a broad range of additives, organic compounds and elastomers, respectively, compared to other adhesives, especially hot melt adhesives. The present hot melt adhesive provides an open time of at least 10 seconds, more typically at least 3 minutes, and often at least 5 minutes. It is therefore especially suited for application on relatively large surfaces, such as in a matrass, in foam and in furniture. It is very suited for difficult-to-bond plastics. It provides a very good adhesion, such as to polypropylene and products comprising polypropylene, such as foam, as well as for wood and metal bonding.
The present adhesive comprises a C5-C50 organic compound, such as a C6-C25 organic compound. This organic compound can unexpectedly be added in high amounts to the present adhesive, without jeopardizing functionality thereof; in fact it has been found that the organic compound even improves the functionality. The organic compound is preferably a liquid compound.
The present adhesive comprises a synthetic thermoplastic polymer having weight average molecular weight of · 80,000 to 200,000 and a dispersity of 1-4.2, preferably from 1-3.5, more preferably from 1-3, even more preferably from 1- 2.5, such as from 1.1-2, wherein the dispersity is defined as above (DM = Mw/Mn, where Mw is the weight-average molar mass and Mn is the number-average molar mass). For prior art adhesive it is considered necessary to have a high dispersity polymer, typically a DM of about 5 or higher, in order to obtain required characteristics, such as good adhesive properties. It therefore came as a surprise that relatively low dispersity polymers could be used. In fact these low dispersity polymers, albeit available on the market, are put on the market for very different uses, such as non-woven fabrics, resin modifiers, elastics and pigment-dispersing agent.
The present adhesive further comprises an elastomer and preferably a wax.
In view of the present invention the following is considered relevant.
Amorphous polyolefin (APO/APAO) polymers are compatible with many solvents, tackifiers, waxes, and polymers; they find wide use in many adhesive applications. APO hot melts have good fuel and acid resistance, moderate heat resistance, are tacky, soft and flexible, have good adhesion and longer open times than crystalline polyolefins. APOs tend to have lower melt viscosity, better adhesion, longer open times and slow set times than comparable EVAs. Some APOs can be used alone, but often they are compounded with tackifiers, waxes, and plasticizers (e.g., mineral oil, poly-butene oil). Examples of APOs include amorphous (atactic) propylene (APP), amorphous propylene/ethylene (APE), amorphous propylene/butene (APB), amorphous propylene/hexene (APH), amorphous propyl-ene/ethylene/butene. APOs show relatively low cohesion, the entangled polymer chains have fairly high degree of freedom of movement. Under mechanical load, most of the strain is dissipated by elongation and disentanglement of polymer chains.
Thereby the present invention provides a solution to one or more of the above mentioned problems.
Advantages of the present description are detailed throughout the description.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates in a first aspect to a hot melt adhesive composition according to claim 1.
The elastomer is present in a relative low amount. It preferably has a molecular weight of 20-150 kg/mole, more preferably 30-100 kg/mole, such as 50-70 kg/mole. It has been found that especially this molecular weight range provides good characteristics to the present adhesive.
In an example of the present adhesive the organic compound is selected from liquid alkanes, alkenes, aromatic hydrocarbons having 1-5 aromatic groups, such as 3-4 aromatic groups, such as naphthalene, oils, such as light and middle weight oils, mineral oil, naphthenic oils, poly-butene oil, and combinations thereof. Naphthenic oils may relate to hydrotreated heavy naphthenic distillate. It may have' less than 50% non-aromatic hydrocarbons. A broad range of organic compounds may be used in the present adhesive.
In an example of the present adhesive the organic compounds is present in an amount of 5-60 wt.%, preferably 10-50 wt. %, more preferably 20-45 wt. %, such as 30-40 wt.%.
Such is considered a very high amount. As noted addition of an organic compound is thereby hardly limited; further the characteristics of the present adhesive remain good.
In an example of the present adhesive the synthetic polymer is one or more atactic polymers, preferably a metallocene catalyst based atactic polymer, more preferably a poly(alfa)alkene polymer, such as poly(alfa)propylene, poly(alfa)butadiene, poly(alfa)methylpentene, most preferably more than 80 wt.% polypropylene. It is even more preferred to use 85 wt.%-99.99 wt.% polypropylene, such as 90 wt.%-99 wt.% polypropylene. Small amounts of other polymers may be present.
In an example of the present adhesive the synthetic polymer is present in an amount of 10-40 wt.%, preferably 12-30 wt. %, more preferably 15-25 wt. %, such as 18-22 wt.%.
Best performances in terms as described above are found for these adhesives.
In an example of the present adhesive the synthetic polymer is 70-100% atactic, preferably 90-99.99% atactic, more preferably 95-99.9% atactic, such as 98-99% atactic. Surprisingly highly atactic polymers with low polydispersity may be used in adhesives, especially in relative high amounts.
In an example of the present adhesive the elastomer is one or more of a copolymer, a block polymer, and a homopolymer, preferably a styrene block polymer.
These elastomers preferably have a tri-block structure, such as an A-B-A or A-B-C structure. A central block B is preferably chemically more flexible whereas block A and C are chemically more inflexible. The A- and/or C-block preferably have a glass transition temperature that is above ambient temperature, preferably a glass transition temperature somewhat lower than a temperature of application, whereas B-blocks preferably have a glass transition temperature that is around or below ambient temperature. The present elastomer preferably has one or more of the characteristics: being macromolecular; a glass transition temperature (of at least a part thereof) Tg is below a temperature of application; being amorphous; having a moderate degree of crosslinking; and having low secondary forces between molecules.
In an example of the present adhesive the elastomer is present in an amount of 1-15 wt.%, preferably 2-10 wt. %, more preferably 3-8 wt. %, such as 4-6 wt.%.
In an example of the present adhesive the elastomer is one or more of a natural rubber, an-artificial rubber, such as a styrene-isoprene-styrene block copolymer, a styrene-butadiene-rubber, a styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer, a styrene-ethylene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer, a sty-rene-isoprene- butadiene-styrene block copolymer, a nitril-isoprene rubber, and isoprene-isoprene rubber.
Examples are styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS), providing high-strength, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) providing low-viscosity and high initial strength, styrene-ethylene/butylene-styrene (SEBS) providing low self-adhering, and styrene-ethylene/propylene (SEP).
In an example the present adhesive comprises one or more additives.
Additives may relate to a wax, such as microcrystalline waxes, fatty amide waxes, PE-waxes, and PP-waxes; to a plasticizer, such as a paraffin oil, polyisobutylene, naphthenic oil, and a chlorinated paraffin; to an antioxidant and stabilizer; to a pigment and dye; and to a tackifying resin, such as a terpene-phenol resin, a rosins, a terpene and a modified terpene, an aliphatic, cycloaliphatic and aromatic resin, a hydrogenated hydrocarbon resin, tackifier resin emulsion, modified rosin resin, polymerized rosin resin, a-pinene resins, β-pinene resins, terpene resins, terpene phenol resins, alkylphenol resins, styrene resins, xylene resins, couma-rone resins, indene resins, hydrocarbon resins and combinations thereof, and their derivates, and their mixtures.
In an example the present adhesive comprises 0.01-30 wt. % wax, preferably 1-2 wt. %, such as paraffin. The wax is preferably high crystalline short chain was, such as a C2-C5 polymer wax, wherein a melting point of the wax is preferably lower than 100 °C, more preferably lower than 90 °C.
In an example of the present adhesive comprises 0.01-50 wt. % resin, preferably 1-30 wt. %.
In an example of the present adhesive comprises 0.01-5 wt. % plasticizer, preferably 1-2 wt. %.
In an example of the present adhesive comprises 0.01-5 wt. % stabilizer, preferably 0.1-1 wt. %.
In a second aspect the present invention relates to a use of the present adhesive composition for one or more of obtaining a high initial strength, low quantity, long transferability, and long open time.
The present hot melt adhesives may be used for corrugated fiberboard boxes, disposable diaper, paperboard cartons, assembly of parts in manufacturing, and in electronic devices .
In an example the present adhesive composition is used in one-sided or two-sided bonding, especially of bonding of large surfaces of 0.5-10 m2, such as 1-5 m2, such as in a matrass, in foam and in furniture.
In a third aspect the present invention relates to a product comprising an adhesive composition according to the invention.
The invention is further detailed by the accompanying figures and examples, which are exemplary and explanatory of nature and are not limiting the scope of the invention. To the person skilled in the art it may be clear that many variants, being obvious or not, may be conceivable falling within the scope of protection, defined by the present claims.
EXAMPLES/EXPERIMENTS
The invention although described in detailed explanatory context may be best understood in conjunction with the accompanying examples and figures.
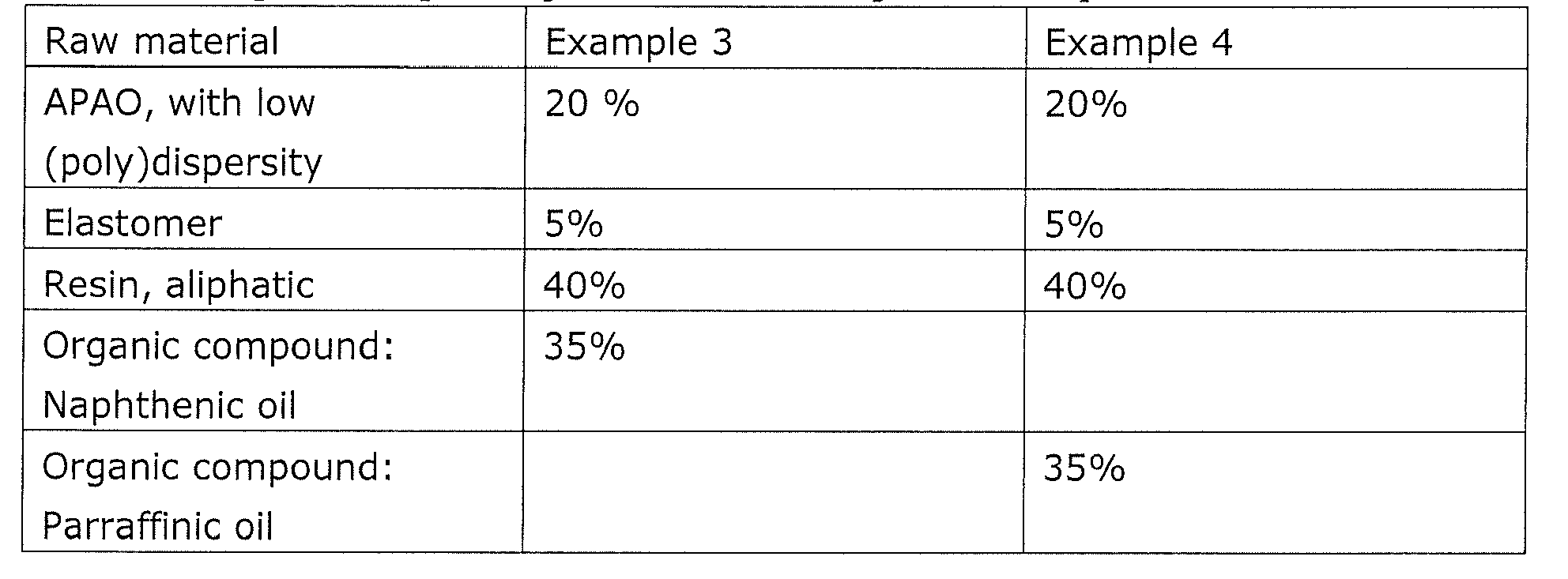
Example 1: 4910 comparison with commercial hot melt based on APAO with high (poly)dispersity
The performance of the present adhesive was compared with a standard APAO based hot melt, i.c. Sabamelt 4910. The test involved using a spray gun to glue together foam under tension at different open times. The present adhesive is bonded securely within 15 seconds and typically less, and was substantially faster than the commercial hot melt which required 30 seconds till 1 minute. The open time of the present adhesive averaged 3 minutes, substantially longer than the commercial hot melt (2 minutes). Thus showing that the use of a APAO of low (poly)dispersity in combination with a elastomer and an organic compound creates at the customer a much broader application window, which is less dependent on mass (e.g. beads of 1,5-5 g/m) and settings, generating a robust process.
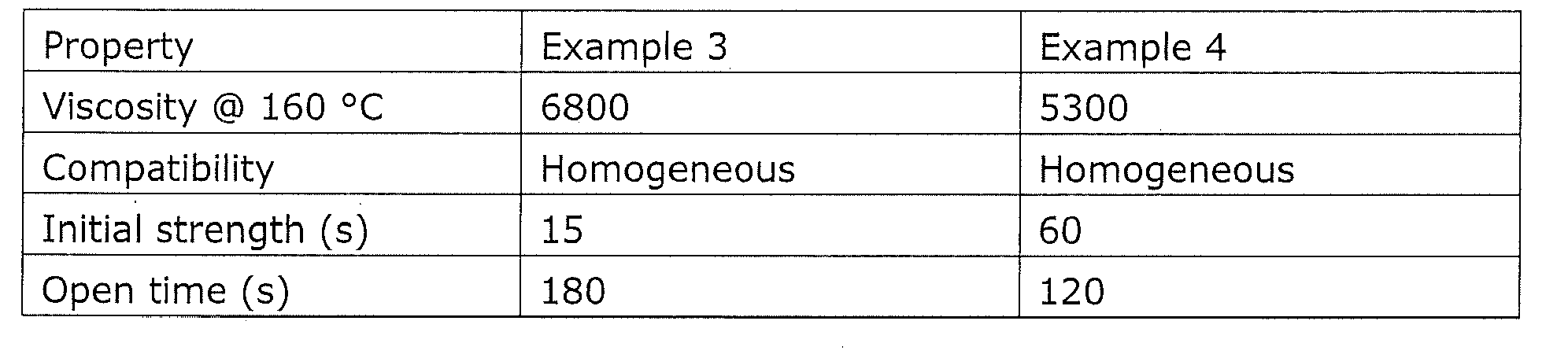
Example 2:
Example comparing different organic compounds:
Properties like viscosity, compatibility, initial strength, open time, were tested.
Examples 3 and 4 demonstrate the importance of the organic compound and the chemical nature of this compound.
It should be appreciated that for commercial applica- tion it may be preferable to use one or more variations of the present system, which would similar be to the ones disclosed in the present application and are within the spirit of the invention .
Claims (14)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| NL2011815A NL2011815C2 (en) | 2013-11-18 | 2013-11-18 | Hot melt adhesive composition. |
| PCT/NL2014/050791 WO2015072860A1 (en) | 2013-11-18 | 2014-11-18 | Hot melt adhesive composition |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| NL2011815 | 2013-11-18 | ||
| NL2011815A NL2011815C2 (en) | 2013-11-18 | 2013-11-18 | Hot melt adhesive composition. |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| NL2011815C2 true NL2011815C2 (en) | 2015-05-19 |
Family
ID=50190649
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| NL2011815A NL2011815C2 (en) | 2013-11-18 | 2013-11-18 | Hot melt adhesive composition. |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| NL (1) | NL2011815C2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2015072860A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110157365A (en) * | 2019-04-15 | 2019-08-23 | 安徽绿谷新材料有限公司 | A kind of rubber glue and preparation method thereof that volatility is low |
| CN110157366A (en) * | 2019-06-11 | 2019-08-23 | 恩平市盈嘉丰胶粘制品有限公司 | A kind of environmentally-friendly sanitary articles hot-fusible pressure-sensitive adhesive and preparation method thereof |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3635861A (en) * | 1968-06-28 | 1972-01-18 | Flintkote Co | Pressure-sensitive hot-melt adhesives |
| US20040081795A1 (en) * | 2002-10-28 | 2004-04-29 | Baoyu Wang | Hot melt adhesive composition based on a random copolymer of isotactic polypropylene |
| US6767424B1 (en) * | 1998-10-20 | 2004-07-27 | Henkel Kommanditgesellschaft Auf Aktien | Hot-melt adhesive for glueing DVDs |
| US20070117907A1 (en) * | 2005-11-18 | 2007-05-24 | Clariant Produkte (Deutschland) Gmbh | Use of polyolefin waxes in hot melt compositions |
-
2013
- 2013-11-18 NL NL2011815A patent/NL2011815C2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2014
- 2014-11-18 WO PCT/NL2014/050791 patent/WO2015072860A1/en not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3635861A (en) * | 1968-06-28 | 1972-01-18 | Flintkote Co | Pressure-sensitive hot-melt adhesives |
| US6767424B1 (en) * | 1998-10-20 | 2004-07-27 | Henkel Kommanditgesellschaft Auf Aktien | Hot-melt adhesive for glueing DVDs |
| US20040081795A1 (en) * | 2002-10-28 | 2004-04-29 | Baoyu Wang | Hot melt adhesive composition based on a random copolymer of isotactic polypropylene |
| US20070117907A1 (en) * | 2005-11-18 | 2007-05-24 | Clariant Produkte (Deutschland) Gmbh | Use of polyolefin waxes in hot melt compositions |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2015072860A1 (en) | 2015-05-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5709749B2 (en) | Hot melt adhesives based on metallocene-catalyzed olefin-α-olefin copolymers | |
| US9732258B2 (en) | PSA containing olefin block copolymers and styrene block copolymers | |
| CN105308141B (en) | Hot-melt adhesive based on low melting point polypropylene homopolymer | |
| CN103476888A (en) | Stretch Film Lamination Adhesives | |
| JP2001523285A (en) | Hot melt adhesive with high peel strength and high shear strength for nonwoven fabric | |
| TWI553076B (en) | Hot melt adhesive | |
| EP3847221B1 (en) | Hot melt adhesive compositions | |
| JP6682525B2 (en) | Hot melt adhesive for polyolefin film | |
| NL2011815C2 (en) | Hot melt adhesive composition. | |
| JP7431910B2 (en) | Permanent adhesive pressure sensitive adhesive with improved environmental compatibility | |
| JP6657123B2 (en) | Promoting adhesion of hot melt adhesives to difficult substrates | |
| BR112019019934B1 (en) | ADHESIVE COMPOSITION AND METHOD FOR BONDING TWO SUBSTRATES | |
| JP2001040315A (en) | Method for bonding polyolefin based resin-made pad to carpet | |
| ES2350441B2 (en) | HOT ADHESIVE FORMULATION FOR THE PLACEMENT OF PLASTIC MATERIALS | |
| CN115975560A (en) | A kind of self-adhesive TPO waterproof membrane hot melt adhesive and preparation method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM | Lapsed because of non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20161201 |