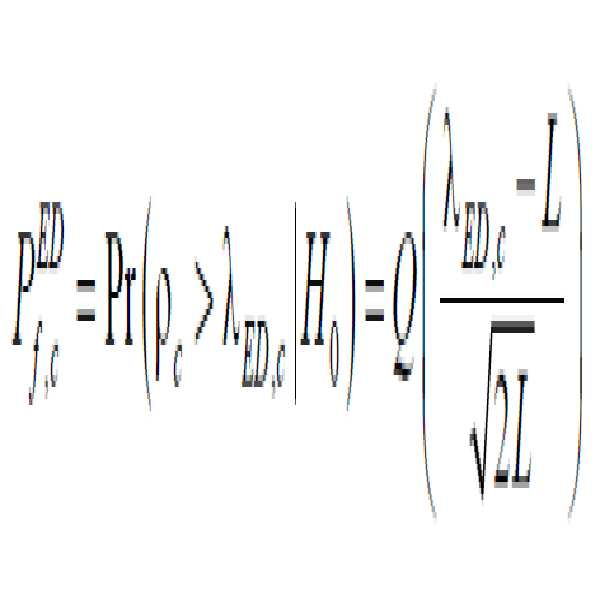KR20170090805A - A Soft-Hard Combination-Based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Scheme for Cognitive Radio Networks - Google Patents
A Soft-Hard Combination-Based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Scheme for Cognitive Radio Networks Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20170090805A KR20170090805A KR1020160011608A KR20160011608A KR20170090805A KR 20170090805 A KR20170090805 A KR 20170090805A KR 1020160011608 A KR1020160011608 A KR 1020160011608A KR 20160011608 A KR20160011608 A KR 20160011608A KR 20170090805 A KR20170090805 A KR 20170090805A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- cluster
- spectrum sensing
- header
- fusion
- hard
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 39
- 230000001149 cognitive effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 25
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 57
- 238000003657 Likelihood-ratio test Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 37
- 230000004927 fusion Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 37
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 241000854291 Dianthus carthusianorum Species 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000007500 overflow downdraw method Methods 0.000 abstract description 5
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008034 disappearance Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005562 fading Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R23/00—Arrangements for measuring frequencies; Arrangements for analysing frequency spectra
- G01R23/16—Spectrum analysis; Fourier analysis
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R23/00—Arrangements for measuring frequencies; Arrangements for analysing frequency spectra
- G01R23/02—Arrangements for measuring frequency, e.g. pulse repetition rate; Arrangements for measuring period of current or voltage
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W16/00—Network planning, e.g. coverage or traffic planning tools; Network deployment, e.g. resource partitioning or cells structures
- H04W16/02—Resource partitioning among network components, e.g. reuse partitioning
- H04W16/10—Dynamic resource partitioning
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W16/00—Network planning, e.g. coverage or traffic planning tools; Network deployment, e.g. resource partitioning or cells structures
- H04W16/14—Spectrum sharing arrangements between different networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/08—Testing, supervising or monitoring using real traffic
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합 기반의 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법에 관한 것이다.
본 발명에 따른 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법은 인지 라디오 네트워크(Cognitive Radio Networks)에서의 스펙트럼 센싱 방법에 있어서, 복수의 클러스터(cluster)로 구성된 인지 라디오 네트워크에서, 각 클러스터 헤더(CHs)에서 LRT(Likelihood Ratio Test) 기반 소프트 융합(soft combination)을 사용하여 1차 사용자(PU ; primary user) 출현에 기반한 클러스터 결정을 수행하는 단계와, 상기 클러스터를 구성하는 FU(Fusion Center)에서 각 클러스터 헤더(CHs)로부터 클러스터 결정을 제공받아, 가중치 결정 퓨전룰(weighted decision fusion rule) 기반의 하드 융합(hard combination)을 사용하여 전체 결정을 수행하는 단계;를 포함하여 이루어져, 인지 라디오 네트워크에서 소프트-하드 융합 방법을 사용함으로써 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 성능을 향상시킬 수 있도록 제공된다.The present invention relates to a cooperative spectrum sensing method based on soft-hard convergence for a cognitive radio network.
A cooperative spectrum sensing method according to the present invention is a spectrum sensing method in a cognitive radio network, wherein in a cognitive radio network composed of a plurality of clusters, a Likelihood Ratio Test (LRT) Performing a cluster decision based on the appearance of a primary user (PU) using a soft combination based on a cluster of the cluster headers (CHs) And performing a full decision using a hard combination based on a weighted decision fusion rule, the decision being made by using a soft-hard fusion method in a cognitive radio network And is provided to improve cooperative spectrum sensing performance.
Description
본 발명은 인지 라디오 네트워크에서의 스펙트럼 센싱 방법에 관한 것으로, 특히 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합 기반의 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to a spectral sensing method in a cognitive radio network, and more particularly to a soft-hard convergence based cooperative spectrum sensing method for cognitive radio networks.
인지 라디오(Cognitive Radio)는 스펙트럼 환경을 인지하여 통신 가능한 주파수를 지능적으로 찾아내어 학습하고, 이를 이용하여 기존 서비스에 간섭을 주지 않고 통신을 수행하는 지능형 무선통신 기술을 의미한다. 이러한 인지 라디오는 스펙트럼 센싱을 지원할 수 있는 기술로서, 많은 나라에서 부족한 스펙트럼 문제를 해결할 수 있는 방법으로 대두되고 있다. 따라서, 인지 라디오는 미래 무선 통신을 위한 가장 발전 전망이 기대되는 기술들 중 하나라 할 수 있다. Cognitive Radio means an intelligent wireless communication technology that intelligently detects and communicates with available frequencies by recognizing a spectrum environment and uses it to perform communication without interfering with existing services. This cognitive radio is a technology that can support spectrum sensing and is emerging as a way to solve the spectrum problem that is lacking in many countries. Therefore, cognitive radio is one of the most promising technologies for future wireless communication.
스펙트럼 센싱은 인가된 사용자들과의 해로운 간섭을 막고, 스펙트럼 사용률을 향상시키기 위한 인지 라디오의 주요한 기능이다. 일반적으로 센싱 성능을 더 향상시키기 위해서 SUs(Secondary users)의 공간 다이버시티를 사용하는 협력 스펙트럼 센싱이 사용되는데, 협력을 사용함으로써 SUs는 개인적인 결정들보다 더 정확한 결정들을 만들기 위해서 그들의 로컬 센싱 정보를 공유할 수 있다. Spectrum sensing is a key function of cognitive radio to prevent harmful interference with authorized users and to improve spectrum utilization. In general, cooperative spectrum sensing using spatial diversity of secondary users (SUs) is used to further improve sensing performance. By using cooperation, SUs can share their local sensing information to make more accurate decisions than individual decisions can do.
협력 SUs가 네트워크에서 센싱 데이터를 공유하는 방법에 따라서 협력 스펙트럼 센싱은 centralized, distributed, relay-assisted 와 같이 3개의 종류로 나누어진다. 먼저, 첫 번째 Centralized cooperative sensing에서는 FC(fusion center)가 협력 센싱을 컨트롤 하게 된다. 한편, 두 번째 Distributed cooperative sensing은 FC에 의존하지 않는다. 반면에 SUs는 그들 사이에 로컬 스펙트럼 결정을 교환하고, 그리고 PUs(Primary users)의 출현과 비출현에 대한 결정을 보도한다. 세 번째 협력 스펙트럼 센싱인 relay-assisted cooperative sensing 방법이다. 이러한 방법들에 따라서 약한 센싱 채널과 강한 레포팅 채널을 가지는 어떤 SU와 강한 센싱 채널과 약한 레포팅 채널을 가지는 어떤 SU는 협력 스펙트럼의 성능을 향상시키기 위해서 서로 협력을 할 수 있게 된다. Cooperative Spectrum Sensing is divided into three types as centralized, distributed, and relay-assisted depending on how the SUs share the sensing data in the network. First, in the first centralized cooperative sensing, FC (fusion center) controls cooperative sensing. On the other hand, the second distributed cooperative sensing does not depend on FC. SUs, on the other hand, exchange local spectral decisions between them, and report decisions about the emergence and disappearance of PUs (Primary users). A third cooperative spectral sensing is relay-assisted cooperative sensing. According to these methods, some SU having a weak sensing channel and a strong reporting channel, and some SU having a strong sensing channel and a weak reporting channel can cooperate with each other to improve the performance of the cooperative spectrum.
이러한 인지 라디오 네트워크에서 협력 스펙트럼 센싱을 위해서 일반적으로 LRT(Likelihood Ratio Test) 기반의 소프트 융합(soft combination) 방법이 주로 적용되는데, 이 LRT 기반의 소프트 융합 방법은 협력 검출 과정이 복잡하고 검출 확률이 떨어지는 문제점이 있다. In this cognitive radio network, a soft combination method based on LRT (Likelihood Ratio Test) is generally applied for cooperative spectrum sensing. This LRT-based soft fusion method has a problem that the cooperative detection process is complicated and the detection probability is low There is a problem.
본 발명은 종래 인지 라디오 네트워크에서의 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법에서 발생하는 문제점을 해결하기 위하여 제안된 것으로서, 본 발명의 목적은 인지 라디오 네트워크에서의 협력 스펙트럼 센싱에서 소프트 융합과 하드 융합을 함께 사용하여 협력 검출의 복잡성을 줄이고 센싱 성능이 우수한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법을 제공하는 데 있다. The present invention has been made in order to solve the problems occurring in the cooperative spectrum sensing method in the conventional cognitive radio network, and it is an object of the present invention to provide cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks, And to provide a method for sensing a cooperative spectrum based on a soft-hard fusion, which has a high sensing performance.
상기 목적을 달성하기 위한 본 발명에 따른 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법은 인지 라디오 네트워크에서의 스펙트럼 센싱 방법에 있어서, 복수의 클러스터로 구성된 인지 라디오 네트워크에서, 각 클러스터 헤더에서 LRT 기반 소프트 융합을 사용하여 1차 사용자 출현에 기반한 클러스터 결정을 수행하는 단계와, 상기 클러스터를 구성하는 FU에서 각 클러스터 헤더로부터 클러스터 결정을 제공받아, 가중치 결정 퓨전룰 기반의 하드 융합을 사용하여 전체 결정을 수행하는 단계;를 포함하여 이루어진다. According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method for sensing spectrum in a cognitive radio network, the method comprising the steps of: Performing a cluster determination based on the appearance of a primary user using an LRT-based soft fusion; and receiving cluster decision from each cluster header in an FU constituting the cluster, and using a hard fusion based on a weight determination fusion rule, And performing a determination.
상기 클러스터 결정을 수행하는 단계는 각 클러스터에 존재하는 SUs에서 샘플 센싱 시간 동안 1차 사용자가 전송하는 신호를 수신하여, 수신된 신호의 에너지를 나타내는 실험 통계 값을 생성하고 이를 클러스터 헤더에 전송하는 단계와; 클러스터 헤더에서 해당 클러스터에 존재하는 모든 SUs의 실험 통계 값을 합하여 LRT를 수행하고, 1차 사용자 출현에 기반하여 클러스터 결정을 one bit 하드 결정(Dc=1 또는 Dc=0)으로 만드는 단계;를 포함하여 이루어진다. The step of performing the cluster determination includes receiving a signal transmitted by a primary user during a sample sensing time in SUs existing in each cluster, generating an experimental statistical value indicating energy of the received signal, and transmitting the generated experimental statistic value to a cluster header Wow; The LRT is performed by adding the experimental statistic values of all the SUs existing in the cluster header in the cluster header, and the cluster decision is made one-bit hard decision (Dc = 1 or Dc = 0) based on the appearance of the primary user .
여기에서, 상기 클러스터 헤더는 모든 SUs의 실험 통계 값을 합한 클러스터 실험 통계값을 산출하고, 상기 클러스터 헤드의 1차 사용자 신호의 평균 SNR를 계산하고, 이를 통하여 클러스터 실험 통계값의 분포를 계산하며, 상기 클러스터 실험 통계값에 대한 LRT를 수행하여, PU의 출현 또는 비출현에 대한 클러스터 결정을 수행하게 된다.Here, the cluster header calculates a cluster experimental statistic value by adding experimental statistic values of all SUs, calculates an average SNR of a primary user signal of the cluster head, calculates a distribution of cluster experimental statistical values through the calculation, LRT for the cluster experimental statistical value is performed to perform cluster determination for appearance or non-appearance of PU.
상기 FC는 각 클러스터에서 복수의 SU 중 어느 하나의 SU를 클러스터 헤더로 선택하고, 주기적으로 스펙트럼 센싱 과정을 수행하며, 전체결정을 네트워크에 존재하는 모든 SU들에게 브로드캐스트 하게 된다. The FC selects one of a plurality of SUs as a cluster header in each cluster, periodically performs a spectrum sensing process, and broadcasts the entire decision to all SUs present in the network.
또한, 상기 FC는 모든 클러스터 결정을 모아 가중치 결정 퓨전룰에 따라 전체 결정을 수행하는데, 상기 가중치 결정 퓨전률은 다음의 수학식으로 표현된다. Also, FC collects all cluster crystals and performs a full determination according to a weight determination fusion rule, and the weight determination fusion ratio is expressed by the following equation.
(여기서, c는 클러스터 순번(c-th 클러스터)으로 1, 2, … , K 값을 갖고, Dc는 각 클러스터 헤더에 의해 전송된 클러스터 결정(Dc=1 또는 Dc=0)이며, P0=Pr(H0)와 P1=Pr(H1)는 각각 1차 사용자(PU) 신호의 출현(H1)과 비출현(H0)에 대한 사전 확률이며, ωc는 가중치 요소(weighted factors)를 나타낸다.(Here, c is the cluster sequence (c-th cluster) by 1, 2, ..., has a K value, D c is the clustered crystals (Dc = 1 or Dc = 0) transmitted by each cluster header, P 0 = P r (H 0) and P 1 = P r (H 1 ) is a priori probability for each of the primary user (PU) appearance (H1) and the non-appearance (H0) of the signal is, ω c is the weight element (weighted factors.
여기에서, 상기 가중치 요소 ωc는 다음의 수학식을 통하여 선택된다.Here, the weight factor? C is selected through the following equation.
(여기에서 Pf,c는 각 클러스터 헤더의 거짓 알림 확률(false alarm probability)을, Pd,c는 검출 확률(detection probability)을 나타낸다)(Where P f, c is the false alarm probability of each cluster header, and P d and c are the detection probabilities)
한편, 상기 FC는 클러스터 헤더들을 위한 최적의 클러스터 경계값을 얻기 위하여, 상기 클러스터 실험 통계값에 대한 LRT 값의 pdf(probability density function)를 전개하고, 상기 pdf 전개 값을 이용하여 각 클러스터 헤더의 거짓 알림 확률 및 검출 확률을 결정하여, 최적의 클러스터 경계값을 결정하게 된다. In order to obtain an optimal cluster boundary value for cluster headers, the FC develops a probability density function (pdf) of an LRT value for the cluster experimental statistical value, The notification probability and the detection probability are determined, and the optimal cluster boundary value is determined.
상기 각 클러스터 헤더의 거짓 알림 확률 및 검출 확률은 다음의 수학식으로 결정된다.The false notification probability and detection probability of each cluster header are determined by the following equation.
(여기에서, Λc는 클러스터 헤더에 의해 수행된 LRT 값, λc는 클러스터 경계값을 나타낸다)(Here, Λ c shows the LRT value, λ c is a cluster boundary value performed by the cluster header)
또한, 상기 최적의 클러스터의 경계값은 최소 에러 확률 기준에 따라 다음의 수학식을 통하여 결정된다.Also, the boundary value of the optimal cluster is determined by the following equation according to the minimum error probability criterion.
본 발명에 따르면, 인지 라디오 네트워크에서 소프트-하드 융합 방법을 사용함으로써 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 성능을 향상시킬 수 있는 효과가 있다. 즉, 본 발명에 따른 소프트-하드 융합 방법은 클러스터 기반 네트워크를 구성하는데, 클러스터에서 LRT 기반 소프트 융합이 적용되고, 퓨전 센터에서 가중치 결정 퓨전룰 기반 하드 융합을 사용하여 종래 소프트 융합 방법들이 가지고 있는 한계점인 협력 검출의 복잡성을 줄일 수 있는 효과를 기대할 수 있다. According to the present invention, cooperative spectrum sensing performance can be improved by using a soft-hard convergence method in a cognitive radio network. That is, the soft-hard convergence method according to the present invention constitutes a cluster-based network, in which soft convergence based on LRT is applied in a cluster, and weight convergence based fusion rules are used in a fusion center, It is possible to reduce the complexity of the cooperative detection.
또한, LRT를 사용하여 낮은 SNR 체계(약 15 dB)에서 1차 신호들을 검출할 수 있으며. LRT 값의 확률밀도 함수에 대한 closed-form을 사용하기 때문에 LRT 계산의 복잡성을 줄일 수 있다. 이와 같이, 기존의 소프트 융합 방법들에 비해서 LRT를 사용함으로써 레포팅 시간 측면에서 센싱 오버헤드를 줄이는 효과를 기대할 수 있다. In addition, LRT can be used to detect primary signals at low SNR (about 15 dB). The use of closed-form for the probability density function of the LRT value reduces the complexity of the LRT computation. As described above, the use of the LRT in comparison with the existing soft fusion methods can reduce the sensing overhead in terms of the reporting time.
도 1은 본 발명에 따른 인지 라디오 네트워크에서 협력 스펙트럼 센싱을 위한 소프트-하드 융합 개념도,
도 2는 본 발명에 따른 SHC 방법의 레포팅 메카니즘을 나타낸 개념도이다. 1 is a soft-hard fusion concept diagram for cooperative spectrum sensing in a cognitive radio network according to the present invention;
2 is a conceptual diagram showing a reporting mechanism of the SHC method according to the present invention.
이하, 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 바람직한 실시예를 상세히 설명하기로 한다 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings
도 1은 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 인지 라디오 네트워크에서 협력 스펙트럼 센싱을 위한 소프트-하드 융합 개념을 나타낸 것이다. 1 illustrates a soft-hard convergence concept for cooperative spectrum sensing in a cognitive radio network according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 1에서, 인지 라디오 네트워크는 K 개의 클러스터(cluster)로 구성되어 있으며, 각 클러스터는 같은 수 N 개의 SUs(secondary users)를 가지고 있다. 인지 라디오 네트워크에서 FC(Fusion Center)는 클러스터들을 구성하고, 클러스터 헤더(CHc)를 선택하며, 네트워크에 있는 모든 SUs를 협력하게 한다. 2차 시스템(secondary system)은 1차 사용자(PU ; primary user) P의 라디오 범위 내에서 동작한다. 여기에서, 1차 사용자 P는 나타나거나 사리질 수 있지만, 상태는 하나의 센싱 인터벌 시간 동안 변하지 않는다. 각 클러스터에 있는 모든 SUs는 수신된 1차 신호(primary signal)와 같은 평균 SNR(signal-to-noise ratio)을 가진다. 이러한 가정은 클러스터들이 똑같이 작은 영역에 위치하는 이웃한 SUs를 그룹핑에 의해서 이루어지므로 합당한 과정이다. 그러나 각 클러스터는 1차 사용자 P와의 사이에 다른 링크 채널 조건을 가진다. 따라서 각 클러스터는 1차 신호와 독립적이고 다른 평균 SNR을 가진다. In FIG. 1, the Cognitive Radio Network is composed of K clusters, and each cluster has the same number of SUs (secondary users). In a cognitive radio network, a Fusion Center (FC) configures clusters, selects a cluster header (CHc), and cooperates with all SUs in the network. The secondary system operates within the radio range of the primary user P (PU). Here, the primary user P may appear or disappear, but the state does not change during one sensing interval time. All SUs in each cluster have the same average signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as the received primary signal. This assumption is reasonable because the clusters are grouped into neighboring SUs that are equally small. However, each cluster has different link channel conditions with the primary user P. Therefore, each cluster is independent of the primary signal and has a different average SNR.
도 1에서 설명하고 있는 것처럼 본 발명에서 제안된 소프트-하드 융합(soft-hard combination, 이하 'SHC'로 약칭한다) 방법의 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 과정은 다음과 같이 2단계로 구성된다.As shown in FIG. 1, the cooperative spectrum sensing process of the soft-hard combination (SHC) method proposed in the present invention is composed of two steps as follows.
[ [ 1 단계Stage 1 ] ]
클러스터 헤더들은 소프트 융합(soft combination)을 사용하여 1차 활동에 근거하여 어떤 클러스터 결정을 다음처럼 수행한다. 먼저, 센싱 과정의 시작지점에서 SU ci (i-th SU in the c-th cluster)는 1차 신호를 듣고, 수신된 신호의 에너지를 나타내는 지역적인 실험 통계 자료(test statistics) ρ ci 를 만든다. 각 SU는 M 개의 1차 신호 샘플을 지역 실험 통계자료를 만들기 위해서 사용한다. 그리고 지역 실험 통계자료 ρ ci 는 클러스터 헤더로 전송된다. Cluster headers perform some cluster decision based on the first activity using a soft combination as follows. First, at the beginning of the sensing process, SU ci (i-th SU in the c-th cluster) hears the primary signal and produces a regional test statistic ρ ci that represents the energy of the received signal. Each SU uses M primary signal samples to generate local experimental statistics. And the regional experimental statistical data ρ ci is transmitted to the cluster header.
각 클러스터는 하나의 클러스터 헤더를 가지고 있으며, 클러스터 헤더는 그 클러스터 내에 있는 모든 SUs들과 협력할 수 있다. c-th 클러스터의 클러스터 헤더는 다음처럼 나타낸다. CHc(c= 1, 2, …,K,)는 c-th 클러스터의 클러스터 헤더를 나타낸다. 클러스터 헤더 선택은 다음과 같이 이루어진다. Each cluster has one cluster header, and the cluster header can cooperate with all the SUs in the cluster. The cluster header of the c- th cluster is shown as follows. CH c ( c = 1, 2, ..., K ,) represents the cluster header of the c- th cluster. Cluster header selection is done as follows.
먼저, 1차 사용자(PU) P의 출현을 감지하기 위해서 인지 라디오(CR) 시스템은 스펙트럼 센싱 과정을 주기적으로 수행한다. 일반적으로 CR 시스템의 구조는 하나의 센싱 슬롯과 하나의 데이터 전송 슬롯으로 구성되어 있다. 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 과정은 센싱 슬롯 내에서 FC(Fusion Center)에 의해서 주기적으로 수행된다. 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 주기는 응용요구 조건에 따라서 시스템 설계자에 의해서 스펙트럼 센싱과 스펙트럼 분할 사이의 조절에 의해서 이루어진다. FC는 각 클러스터에서 어떤 SU(secondary user)를 하나의 클러스터 헤더로서 선택한다. 클러스터 헤더들은 클러스터에 존재하는 모든 SUs의 실험 통계자료에 기반하여 LRT(Likelihood Ratio Test)를 수행하고, 1차 사용자(PU) P의 출현에 기반하여 클러스터 결정을 one bit 하드 결정(one bit hard decision)으로 만든다. Dc(c= 1, 2,…,K)는 c-th 클러스터의 클러스터 결정(즉, Dc = 1 혹은 Dc = 0 은 각각 PU의 출현 혹은 비출현)을 각각 나타낸다. First, a cognitive radio (CR) system performs a spectrum sensing process periodically to detect the appearance of a primary user (PU) P. In general, the structure of CR system is composed of one sensing slot and one data transmission slot. The cooperative spectrum sensing process is performed periodically by FC (Fusion Center) in the sensing slot. The cooperative spectrum sensing period is achieved by the system designer by adjusting the spectrum sensing and spectral division according to application requirements. The FC selects an SU (secondary user) as one cluster header in each cluster. The cluster headers perform Likelihood Ratio Test (LRT) based on experimental statistical data of all SUs existing in the cluster, and determine one-bit hard decision ). D c ( c = 1, 2, ..., K) represents the cluster decision of the c- th cluster (ie, D c = 1 or D c = 0, respectively.
[ [ 2 단계Step 2 ] ]
모든 클러스터 헤더는 그들의 클러스터 결정 정보 Dc를 FC에 에러-프리 레포팅 채널(error-free reporting channels)을 통해서 전송한다. FC는 모든 클러스터 결정들을 모아서 전체 결정을 가중치 결정 퓨전룰(weighted decision fusion rule)을 사용하여 만든다. 앞에서 언급한 것처럼 클러스터들은 수신된 1차 신호와 다른 평균 SNR을 사용하므로 전체 결정에 대한 기여도는 다르다. 그러나 기존의 퓨전룰(k-out-of-N, e.g., OR rule, AND rule 혹은 MAJORITY rule)은 이러한 측면을 고려하지 않는다. 따라서 기존 k-out-of-N rule은 본 발명의 SHC 방법에 적용될 수 없다. 반면에 본 발명에 따른 가중치 결정 퓨전룰(weighted decision fusion rule)은 다른 가중치들(weighted factors)을 센싱 신뢰성에 따라서 클러스터 결정에 할당한다. All cluster headers send their cluster determination information D c to FC via error-free reporting channels. FC aggregates all cluster decisions and makes the entire decision using a weighted decision fusion rule. As mentioned earlier, clusters use a different average SNR than the received primary signal, so the contribution to the overall decision is different. However, existing fusion rules ( k-out-of-N , eg, OR rule, AND rule or MAJORITY rule) do not consider this aspect. Therefore, the existing k-out-of-N rule can not be applied to the SHC method of the present invention. On the other hand, the weighted decision fusion rule according to the present invention assigns other weighted factors to cluster determination according to sensing reliability.
도 2는 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 SHC 방법의 레포팅 메카니즘을 나타낸 개념도이다. 2 is a conceptual diagram showing a reporting mechanism of the SHC method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2에 도시된 바와 같이, 기존의 소프트 융합 방법(Conventional soft combination scheme)에서는 SUs가 순차적으로 센싱 데이터를 FC에 전송한다. 여기에서, ts는 하나의 SU가 센싱 데이터를 FC에 전송하기 위해서 필요한 전송 시간을 나타낸다. As shown in FIG. 2, in a conventional soft combination scheme, SUs sequentially transmit sensing data to the FC. Here, t s represents the transmission time required for one SU to transmit the sensing data to the FC.
이에 반해, 본 발명의 SHC 방법에서 같은 클러스터에 존재하는 SUs는 센싱 데이터를 클러스터 헤더에 전송한다. 기존의 방법들과 합리적인 비교를 위해서 어떤 SU가 센싱 데이터를 클러스터 헤더에 전송하는데 필요한 시간을 ts로 나타내기로 한다. 클러스터 헤더는 one bit로 클러스터 결정을 하고, 순차적으로 FC에 전송한다. 클러스터 헤더가 결정을 FC에 전송하는데 필요한 시간은 th로 나타낸다. 컨드롤 채널의 주어진 대역폭과 전송율에서 SU가 클러스터 헤더에 보고해야 할 데이터가 많을수록 더 많은 시간이 필요하다. SU에 의해서 모아진 소프트 센싱 데이터의 전송 시간과 클러스터 헤더에 의해서 만들어진 one bit 결정의 전송 시간 사이의 상관계수를 ε(ε<0)로 나타내기로 한다. 즉, ts = εth가 된다. On the other hand, in the SHC method of the present invention, SUs existing in the same cluster transmit sensing data to the cluster header. For a reasonable comparison with the existing methods, let us denote the time required for an SU to transmit the sensing data to the cluster header as t s . The cluster header makes a cluster decision with one bit, and sequentially transmits it to the FC. The time required for the cluster header to send the decision to the FC is denoted by t h . The more data the SU has to report in the cluster header at a given bandwidth and transmission rate of the control channel, the more time it takes. Let ε (ε <0) be the correlation coefficient between the transmission time of the soft sensing data collected by the SU and the transmission time of the one bit decision made by the cluster header. That is, t s = 竜 t h .
최종적으로 전체 결정은 FC에 의해서 만들어진다. 각 센싱 주기 동안 만들어진 전체 결정을 Dg로 나타낸다. 즉, Dg=1 혹은 Dg= 0는 각각 1차 사용자의 출현과 사라짐을 나타낸다. 스펙트럼 센싱 과정의 마지막 단계에서 FC는 전체결정을 네트워크에 존재하는 모든 SUs들에게 브로드캐스트 한다. 본 발명에서 Pr(A)은 임의의 사건 A의 확률을 나타낸다. 또한, LRT는 Likelihood Ratio Test를, L-LRT는 Log-Likelihood Ratio Test를 각각 나타낸다. Finally, the entire decision is made by FC. The total crystal made during each sensing period is denoted by D g . That is, D g = 1 or D g = 0 indicates the occurrence and disappearance of the primary user, respectively. At the end of the spectrum sensing process, the FC broadcasts the entire decision to all SUs present in the network. In the present invention, P r (A) represents the probability of an arbitrary event A. Likelihood Ratio Test is used for LRT and Log-Likelihood Ratio Test is used for L-LRT.
이하에서는 본 발명의 SHC 방법에서, 각 클러스터의 클러스터 헤더에서 소프트 융합을 진행하는 과정에 대하여 설명한다. Hereinafter, in the SHC method of the present invention, the process of soft fusion in the cluster header of each cluster will be described.
먼저, 클러스터 SUci(i-th secondary user of c-th cluster)는 M 샘플 센싱 기간 동안 수신된 신호 rci를 측정한다. 1차 사용자에 의해서 전송된 신호는 Sci이다. 이 신호는 플랫 페이딩 채널(flat fading channel)을 통하여 SUci로 전파된다. 2차 사용자 SUci에서 수신된 이산신호의 m-th 샘플 rci(m)은 다음의 수학식 1과 같이 나타낸다.First, the cluster SU ci (i-th secondary user of c-th cluster) measures the received signal r ci during the M sample sensing period. The signal transmitted by the primary user is S ci . This signal propagates to SU ci through a flat fading channel. The m-th sample r ci (m) of the discrete signal received in the secondary user SU ci is expressed as Equation (1) below.
여기서 H0, H1 은 SUs 인근에 PU의 비출현(absent)과 출현(present)을 각각 나타낸다. 또한, rci는 c-th 클러스터에서 1차 수신된 신호를 나타낸다. 노이즈는 (additive white and Gaussian (AWGN) with zero-mean)를 가정한다. hci는 채널 이득, sci는 전송된 1차 신호를 각각 나타내고, 서로 독립이다. 1차 사용자의 상태는 하나의 센싱 기간 동안 일정하다. Where H 0 and H 1 represent the absent and present of PU near SUs, respectively. Also, r ci represents the primary received signal in the c-th cluster. The noise (additive white and Gaussian (AWGN) with zero-mean). h ci denotes a channel gain, and s ci denotes a transmitted primary signal, and are independent of each other. The state of the primary user is constant during one sensing period.
지역 실험 통계값(local test statistics) ρci(estimation of received primary signal power of the SUci)는 다음의 수학식 2와 같이 나타낸다. The local test statistics ρ ci (estimation of received primary signal power of the SU ci ) is expressed by the following equation (2).
여기서 M = 2TW 로, 하나의 센싱 기간 동안 각 SU에서 모아진 샘플들의 수를 나타낸다. T와 W는 검출 시간과 신호의 대역폭을 각각 나타낸다. 본 발명에서 제안된 SHC 방법에서는 한 번에 하나의 채널이 센싱된다. Where M = 2 TW, which represents the number of samples collected in each SU during a sensing period. T and W represent the detection time and the bandwidth of the signal, respectively. In the SHC method proposed in the present invention, one channel is sensed at a time.
SUs의 실험 통계값(test statistics(TS))은 Equal Gain Combining(EGC)를 사용하여 클러스터 헤더에서 합쳐진다. 클러스터 실험 통계값(cluster test statistic) ρc(the estimation of received primary signal power at the cluster head of the c-th cluster)는 다음의 수학식 3과 같이 나타낸다.The test statistics (TS) of SUs are combined in the cluster headers using Equal Gain Combining (EGC). The cluster test statistic ρ c (the estimation of received primary signal power at the cluster head of the c-th cluster) is expressed by the following equation (3).
H0 가정 하에서 실험 통계값 ρc는 독립변수이고, 확률밀도함수는 L(L = NM) degrees of freedom을 가지는 Chi-square 분포를 가진다. H1 가정 하에서 ρc는 L degrees of freedom과 non-central parameter γcL를 가지는 독립 non-central chi-square 랜덤 변수이다. The experimental statistical value ρ c is an independent variable under the assumption of H 0 , and the probability density function has a Chi-square distribution with degrees (L = L) degrees of freedom. Under H 1 assumption, ρ c is an independent non-central chi-square random variable with L degrees of freedom and a non-central parameter γ cL .
클러스터 헤더 CHc에서 측정된 1차 사용자 신호의 평균 SNR은 다음의 수학식 4와 같이 나타낸다. 여기에서, 같은 클러스터 내에 있는 모든 SUs는 같은 SNR을 가지는 것으로 가정한다.The average SNR of the primary user signal measured in the cluster header CH c is expressed by Equation (4) below. Here, it is assumed that all SUs in the same cluster have the same SNR.
앞에서 언급한 것처럼 SNR은 SU의 위치 정보를 사용하여 얻어진다. 분석의 간편함을 위해서 노이즈는 unit variance를 가지는 것으로 가정하고, Central Limit Theorem(CLT)을 사용함에 의해서 실험 통계자료 ρc의 분포는 H0 혹은 H1 두 조건(H0 혹은 H1) 하에서 가우시안 분포에 의해서 나타낼 수 있다. 따라서 ρc의 분포는 다음의 수학식 5와 같이 나타낼 수 있다. As mentioned earlier, the SNR is obtained using the SU location information. Distribution for ease of analysis noise test statistics by assumed that the unit variance, and using the Central Limit Theorem (CLT) ρ c is a Gaussian distribution under H 0 or H 1 two conditions (H 0 or H 1) As shown in FIG. Therefore, the distribution of ρ c can be expressed by the following equation (5).
여기에서, L = NM은 수신된 1차 신호의 샘들의 수이며, 이러한 샘플들은 클러스터 헤더에서 소프트 융합을 사용하여 수집된다. 각 클러스터의 클러스터 헤더는 ρc를 클러스터 결정을 만들기 위한 클러스터 관측 수단으로 사용한다. 클러스터 헤더는 LRT를 수행하여 1차 사용자의 출현 혹은 비출현에 대한 클러스터 결정을 한다. 상술한 수학식 1에서 주어진 2진 hypothesis 실험에 대한 L-LRT(log-likelihood ratio test)는 다음의 수학식 6과 같이 표현될 수 있다.Where L = NM is the number of samples of the primary signal received, and these samples are collected using soft fusion in the cluster header. The cluster headers of each cluster use ρ c as a cluster observing means for making a cluster decision. The cluster header performs the LRT to determine the clusters for the appearance or non-occurrence of the primary user. The log-likelihood ratio test (L-LRT) for the binary hypothesis experiment given in Equation (1) can be expressed as Equation (6).
여기서 fp(ρc│H1), fp(ρc│H0)는 H1과 H0 가정 하에서 각각 클러스터 실험 통계자료 ρc의 확률밀도 함수이며, log는 자연로그를 의미한다. 하나의 클러스터 내에서 수신된 1차 신호들의 SNRs이 같기 때문에, Ac(conducted at a certain secondary user i-th in c-th cluster SUci and also at a cluster head)는 같은 분포 fΛ(Λc)로부터 전개되는 것으로 고려된다. 따라서 클러스터 결정 Dc(0,1)은 L-LRT에 기반을 두고 다음의 수학식 7과 같이 나타낼 수 있다.Here, f p (ρ c │H 1 ) and f p (ρ c │H 0 ) are the probability density functions of the cluster experimental statistical data ρ c under the assumption of H 1 and H 0 , respectively, and log means natural logarithm. Because equal a 1 SNRs of the difference signal received within a cluster, A c (conducted at a certain secondary user i-th in c-th cluster SUci and also at a cluster head) distribution as is f Λ (Λ c) . ≪ / RTI > Therefore, the cluster decision D c (0, 1) can be expressed by Equation (7) based on L-LRT.
이하에서는 FU(Fusion Center)에서 하드 융합을 진행하는 과정에 대하여 설명한다. Hereinafter, the process of hard fusion at the FU (Fusion Center) will be described.
도 1에서와 같이, 네트워크는 K 개의 클러스터로 구성되어 있으며, 각 클러스터에는 N SUs가 존재한다.As shown in FIG. 1, the network is composed of K clusters, and N SUs exists in each cluster.
FC(fusion center)는 1차 사용자(PU)의 상태를 결정하기 위해서 클러스터 결정을 받고 합한다. 여기서 가중치 결정 퓨전룰(weighted decision fusion rule(WDFR))이 퓨전 룰(fusion rule)로서 사용된다. D = [D1,D2.…,DK]는 FC에서 수신된 클러스터 결정의 집합을 나타낸다. FC는 LRT를 사용하여 전체 결정을 다음의 수학식 8과 같이 만든다.The fusion center (FC) receives and aggregates the cluster decisions to determine the state of the primary user (PU). Here, a weighted decision fusion rule (WDFR) is used as a fusion rule. D = [D 1 , D 2 . , D K ] denote the set of cluster decisions received at the FC. FC uses the LRT to make the overall decision as shown in equation (8).
여기서 P0=Pr(H0)와 P1=Pr(H1)는 각각 PU 신호의 출현과 비출현에 대한 사전 확률이다. 클러스터 헤더들의 결정은 독립적으로 이루어지고, L-LRT는 다음의 수학식 9와 같이 전개된다. Where P 0 = P r ( H 0 ) and P 1 = P r ( H 1 ) are prior probabilities for the appearance and non-occurrence of PU signals, respectively. The determination of the cluster headers is performed independently, and the L-LRT is developed as shown in the following Equation (9).
따라서 가중치 결정 퓨전룰(weighted decision fusion rule)은 다음의 수학식 10과 같이 표현될 수 있다.Therefore, the weighted decision fusion rule can be expressed by Equation (10). &Quot; (10) "
여기서 가중치(weighted factors)는 다음의 수학식 11을 사용하여 선택된다.Here, the weighted factors are selected using the following equation (11).
여기에서, Pf,c는 각 클러스터 헤더의 거짓 알림 확률(false alarm probability), Pd,c는 검출 확률(detection probability)을 나타낸다. 상기 수학식 10은 최적의 결정 퓨전룰로서, 마지막으로 FC는 전체 결정을 네트워크에 있는 모든 SUs에게 브로드캐스트 한다. Here, P f, c denotes a false alarm probability of each cluster header, and P d, c denotes a detection probability. (10) is an optimal decision fusion rule, and finally FC broadcasts the entire decision to all SUs in the network.
이하에서는 FC에서 클러스터 헤더들을 위한 최적의 클러스터 경계값을 산출하는 방법에 대하여 설명하기로 한다. 먼저, 가장 일반적인 기존의 센싱 방법인 Energy Detector(ED)를 소개하고, 다음으로 본 발명에 따른 SHC 방법에서 클러스터 헤더들을 위한 최적의 클러스터 경계값을 얻기 위한 방법을 설명하기로 한다. Hereinafter, a method for calculating an optimal cluster boundary value for cluster headers in the FC will be described. First, an energy detector (ED), which is the most common conventional sensing method, is introduced, and a method for obtaining an optimal cluster boundary value for cluster headers in the SHC method according to the present invention will be described.
[ ED (Energy Detector) ][ED (Energy Detector)]
기존의 센싱 방법인 ED의 동작을 설명하기 위해서, ED가 어떤 클러스터 헤더 에서 사용되고 있는 것으로 가정한다. 이러한 경우에 CHc는 에너지 경계값 λED,c에 기반 하여 다음의 수학식 12와 같이 결정을 수행한다.In order to explain the operation of ED, which is an existing sensing method, it is assumed that ED is used in some cluster headers. In this case, CH c performs the determination according to the following equation (12) based on the energy boundary value? ED, c .
여기서 ρc는 상술한 수학식 3에서 설명한 실험 통계값이다. DED,c=1 혹은 DED,c=0은 ED를 사용하여 CHc에서 H1 혹은 H0 추정이 이루어짐을 의미한다. Local false alarm probability(LFP) 와 local detection probability(LDP) 는 다음의 수학식 13 및 14와 같이 결정된다.Here,? C is an experimental statistic value described in Equation (3). D ED, c = 1 or D ED, c = 0 means that H 1 or H 0 estimation is done in CH c using ED. Local false alarm probability (LFP) And local detection probability (LDP) Is determined according to the following equations (13) and (14).
여기서 γc는 CHc에서 평균 SNR이다. L은 각 CHc에서 수집되고 수신된 1차 샘플들의 수이다. 또한, 로 Q-function을 나타낸다..Where γ c is the average SNR in CH c . L is the number of primary samples collected and received at each CH c . Also, Represents a Q-function.
[ 최적의 클러스터 [Optimal cluster 경계값Boundary value 계산 ] Calculation ]
본 발명의 SHC 방법에서는 클러스터 헤더들을 위한 최적의 클러스터 경계값을 계산하기 위해서 LRT 값 Λc의 pdf(Probability Density Function(확률밀도함수))를 전개한다. In the SHC method of the present invention, the pdf (Probability Density Function) of the LRT value Λ c is developed to calculate an optimal cluster boundary value for the cluster headers.
ρ=[ρ1,ρ2,…,ρc,…,ρK], μc,j(j=0 or j=1)는 상술한 수학식 5의 분산을 의미한다. ρc는 클러스터 헤더 CHc에서 LRT를 위한 실험 통계값(test statistic)을 나타내는 랜덤 변수이다. 상기 수학식 5 및 6으로부터 LRT 값은 다음의 수학식 15와 같이 전개된다.ρ = [ρ 1 , ρ 2 , ... , ρ c , ... , ρ K ], μ c, j (j = 0 or j = 1) means the variance of Equation (5). ρ c is a random variable representing the test statistic for the LRT in the cluster header CH c . From Equations (5) and (6), the LRT value is developed as shown in the following Equation (15).
수학식 5에 있는 평균값과 분산값을 상기 수학식 15에 대입하고, 기번적인 이론을 적용하여 LRT의 pdf는 다음의 수학식 16과 같이 전개된다.The mean value and the variance value in Equation (5) are substituted into Equation (15), and the pdf of the LRT is developed as Equation (16) by applying the opportunistic theory.
여기서, here,
그리고, And,
여기서, here,
따라서, 각 클러스터 헤더의 거짓 알림 확률(false alarm probability) Pf,c와 검출 확률(detection probability) Pd,c는 다음의 수학식 20 및 21과 같이 나타낸다.Therefore, the false alarm probability P f, c and the detection probability P d, c of each cluster header are expressed by the following equations (20) and (21).
상기 수학식 20 및 21의 값들은 MATLAB을 사용하여 편리하게 얻어질 수 있다. 지금까지의 설명으로부터 각 클러스터의 거짓 알림 확률(false alarm probability)(Pf,c)과 검출 확률(detection probability)(Pd,c)은 채널 조건, 즉 평균 SNR 및 클러스터 경계값에 의해서 결정됨을 알 수 있다. 고정된 채널 조건하에서 전체 센싱 에러를 최소화하는 최적의 지역적인 센싱 경계값을 찾는 것은 매우 의미가 있다는 것을 알 수 있다. The values of the above equations 20 and 21 can be conveniently obtained using MATLAB. It can be seen from the foregoing description that the false alarm probability (P f, c ) and the detection probability (P d, c ) of each cluster are determined by the channel conditions, that is, the average SNR and the cluster boundary value Able to know. It is very meaningful to find an optimal local sensing boundary value that minimizes the overall sensing error under fixed channel conditions.
본 발명에서 c-th 클러스터의 클러스터 경계값인 λopt,c 를 결정하기 위해서 최소 에러 확률 기준(minimum error probability criterion)를 사용하며, 이는 다음의 수학식 22와 같이 나타낼 수 있다. In the present invention, a minimum error probability criterion is used to determine the cluster boundary value λ opt, c of the c-th cluster, which can be expressed by the following equation (22).
상기 수학식 20 내지 22로부터 알 수 있는 것처럼, 최적의 클러스터 경계값 λopt,c 는 LRT 값의 pdf를 기반으로 하여 얻어질 수 있음을 알 수 있다. 따라서 수학식 16의 pdf를 사용하여 클러스터 헤더 CHc는 최적의 클러스터 경계값 λopt,c 을 얻을 수 있으며, 이는 수학식 7에서 비교를 위해서 사용된다. As can be seen from the above equations (20) to (22), it can be seen that the optimal cluster boundary value? Opt, c can be obtained based on the pdf of the LRT value. Therefore, by using pdf in Equation 16, the cluster header CHc can obtain the optimal cluster boundary value [lambda] opt, c , which is used for comparison in Equation (7).
이와 같이 본 발명에 따른 소프트-하드 융합 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법은 소프트 융합과 하드 융합을 함께 사용하여 스펙트럼을 센싱함으로써 센싱 성능을 향상시킬 수 있다. As described above, the soft-hard fused cooperative spectrum sensing method according to the present invention can enhance the sensing performance by sensing the spectrum using the soft fusion and the hard fusion together.
즉, 본 발명의 SHC 방법은 각 클러스터에서 클러스터 헤더(CHc)가 다른 SUs의 실험 통계값을 융합하고, 최소 에러 확률 기준에 의해서 결정되는 최적의 클러스터 경계값을 가지고 LRT를 수행한다. 최적의 클러스터 경계값은 LRT 값의 pdf의 closed-form 표현을 사용하여 전개되는데, 이러한 시뮬레이션 결과는 특히 낮은 SNR 체계에서 기존의 ED와 비교해 볼 때 LRT가 보다 우수한 성능을 보여 주게 된다. 또한, Weighted Decision Fusion Rule(WDFR)을 사용하여 FC는 다른 클러스터 헤더들의 기여도를 구별할 수 있고, SHC 방법은 기존의 하드 융합 방법들, 예를 들면“AND 룰, OR 룰, MAJORITY 룰, LRT”등을 사용하는 각각의 경우와 비교해 볼 때 각각의 경우에 대해서 보다 우수한 센싱 성능을 얻을 수 있게 된다. 반면에 SHC 방법의 레포팅 메카니즘은 기존의 소프트 융합 방법과 비교해 볼 때 레포팅 시간을 줄일 수 있게 된다. That is, in the SHC method of the present invention, cluster headers CHc in each cluster fuse experimental statistical values of other SUs and perform LRT with optimal cluster boundary values determined by a minimum error probability criterion. The optimal cluster boundary value is developed using a closed-form representation of the pdf of the LRT value. This simulation result shows that the LRT performs better in comparison with the existing ED, especially in the low SNR system. In addition, the Weighted Decision Fusion Rule (WDFR) can be used by the FC to distinguish the contribution of the other cluster headers. The SHC method can be applied to existing hard fusion methods such as "AND Rule, OR Rule, MAJORITY Rule, LRT" It is possible to obtain a better sensing performance for each case as compared with the case of using each of them. On the other hand, the reporting mechanism of the SHC method can reduce the reporting time compared to the existing soft fusion method.
이러한 본 발명은 상술한 실시예에 한정되는 것은 아니며 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 갖는 자에 의해 본 발명의 기술사상과 아래에 기재될 특허청구 범위의 균등범위 내에서 다양한 수정 및 변형이 이루어질 수 있음은 물론이다. It is to be understood that the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and that various modifications and changes may be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the appended claims. Of course, can be achieved.
CH : 클러스터 헤더(Cluster header)
PU : 1차 사용자(Primary User)
SU : 2차 사용자(Secondary user)
FC : 퓨전 센터(Fusion Center)CH: Cluster header
PU: Primary User
SU: Secondary user
FC: Fusion Center
Claims (9)
(a) 복수의 클러스터(cluster)로 구성된 인지 라디오 네트워크에서, 각 클러스터 헤더(CHs)에서 LRT(Likelihood Ratio Test) 기반 소프트 융합(soft combination)을 사용하여 1차 사용자(PU ; primary user) 출현에 기반한 클러스터 결정을 수행하는 단계와;
(b) 상기 클러스터를 구성하는 FU(Fusion Center)에서 각 클러스터 헤더(CHs)로부터 클러스터 결정을 제공받아, 가중치 결정 퓨전룰(weighted decision fusion rule) 기반의 하드 융합(hard combination)을 사용하여 전체 결정을 수행하는 단계;를 포함하여 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
A method for spectral sensing in Cognitive Radio Networks,
(a) In a cognitive radio network composed of a plurality of clusters, a soft combination based on a Likelihood Ratio Test (LRT) based on each cluster header (CHs) is used for the appearance of a primary user (PU) Based cluster determination;
(b) a cluster decision is received from each cluster header (CHs) in a fusion center (FU) constituting the cluster, and a cluster determination is performed using a hard combination based on a weighted decision fusion rule And performing a soft-hard fusion-based cooperative spectrum sensing method for a cognitive radio network.
상기 클러스터 결정을 수행하는 단계(a)는
(a-1) 각 클러스터에 존재하는 SUs(Secondary Users)에서 샘플 센싱 시간 동안 1차 사용자(PU)가 전송하는 신호(Sci)를 수신하여, 수신된 신호(rci)의 에너지를 나타내는 실험 통계 값(test statistics)(ρci)을 생성하고 이를 클러스터 헤더에 전송하는 단계와;
(a-2) 클러스터 헤더에서 해당 클러스터에 존재하는 모든 SUs의 실험 통계 값(ρci)을 합하여 LRT를 수행하고, 1차 사용자(PU) 출현에 기반하여 클러스터 결정을 one bit 하드 결정(one bit hard decision)(Dc=1 또는 Dc=0)으로 만드는 단계;를 포함하여 이루어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
The step (a) of performing the cluster determination
(a-1) to receive signals (S ci) by the sample sensing time the primary user (PU) for a transmission from the SUs (Secondary Users) present in each cluster, the experiment representing the energy of the received signal (r ci) Generating test statistics (? Ci ) and transmitting them to the cluster header;
(LRT) is performed by adding the experimental statistical values (ρ ci ) of all the SUs present in the cluster in the cluster header (a-2), and one-bit hard decision hard decision (Dc = 1 or Dc = 0) for the soft-hard convergence-based cooperative spectrum sensing method.
상기 클러스터 헤더는
상기 모든 SUs의 실험 통계 값(ρci)을 합한 클러스터 실험 통계값(ρc)을 산출하고,
상기 클러스터 헤드의 1차 사용자 신호(Sci)의 평균 SNR(Signal to noise ratio)(γc)를 계산하고, 이를 통하여 클러스터 실험 통계값(ρc)의 분포를 계산하며,
상기 클러스터 실험 통계값(ρc)에 대한 LRT를 수행하여, PU의 출현(Dc=1) 또는 비출현(Dc=0)에 대한 클러스터 결정을 수행하는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
3. The method of claim 2,
The cluster header
Calculating a cluster test statistic value (ρ c) the sum of the test statistic value (ρ ci) of the all SUs and
Calculating an average signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) (γ c ) of the primary user signal (S ci ) of the cluster head, calculating a distribution of the cluster experimental statistical value (ρ c )
Characterized in that the LRT for the cluster test statistic (r c ) is performed to perform a cluster decision on the appearance of the PU (Dc = 1) or the non-appearance (Dc = 0) HARD Fusion - based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Method.
상기 FC는 각 클러스터에서 복수의 SU 중 어느 하나의 SU를 클러스터 헤더로 선택하고, 주기적으로 스펙트럼 센싱 과정을 수행하며, 전체결정을 네트워크에 존재하는 모든 SU들에게 브로드캐스트 하는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
3. The method according to claim 1 or 2,
Wherein the FC selects one of a plurality of SUs as a cluster header in each cluster, periodically performs a spectrum sensing process, and broadcasts the entire decision to all SUs present in the network. Soft - Hard Fusion - based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Method for Networks.
상기 FC는 모든 클러스터 결정을 모아 가중치 결정 퓨전룰에 따라 전체 결정을 수행하되, 상기 가중치 결정 퓨전률은 다음의 수학식으로 표현되는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
(여기서, c는 클러스터 순번(c-th 클러스터)으로 1, 2, … , K 값을 갖고, Dc는 각 클러스터 헤더에 의해 전송된 클러스터 결정(Dc=1 또는 Dc=0)이며, P0=Pr(H0)와 P1=Pr(H1)는 각각 1차 사용자(PU) 신호의 출현(H1)과 비출현(H0)에 대한 사전 확률이며, ωc는 가중치 요소(weighted factors)를 나타낸다)
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the FC performs a full determination according to a weight determination fusion rule by collecting all cluster decisions, and the weight determination fusion ratio is expressed by the following equation: < EMI ID = Way.
(Here, c is the cluster sequence (c-th cluster) by 1, 2, ..., has a K value, D c is the clustered crystals (Dc = 1 or Dc = 0) transmitted by each cluster header, P 0 = P r (H 0) and P 1 = P r (H 1 ) is a priori probability for each of the primary user (PU) appearance (H1) and the non-appearance (H0) of the signal is, ω c is the weight element (weighted factors)
상기 가중치 요소 ωc는 다음의 수학식을 통하여 선택되는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
(여기에서 Pf,c는 각 클러스터 헤더의 거짓 알림 확률(false alarm probability)을, Pd,c는 검출 확률(detection probability)을 나타낸다)
6. The method of claim 5,
Wherein the weight factor? C is selected through the following equation:? C ?
(Where P f, c is the false alarm probability of each cluster header, and P d and c are the detection probabilities)
상기 FC는 클러스터 헤더들을 위한 최적의 클러스터 경계값을 얻기 위하여,
상기 클러스터 실험 통계값(ρc)에 대한 LRT 값(Λc)의 pdf(probability density function)를 전개(fΛ(Λc))하고, 상기 pdf 전개 값을 이용하여 각 클러스터 헤더의 거짓 알림 확률(false alarm probability)(Pf,c) 및 검출 확률(detection probability)(Pd,c)을 결정하여, 최적의 클러스터 경계값을 결정하는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
7. The method according to claim 1 or 6,
In order to obtain an optimal cluster boundary value for cluster headers,
The probability density function pdf of the LRT value Λ c with respect to the cluster experimental statistical value ρ c is developed (f Λ (Λ c )), and the false notification probability of each cluster header (P f, c ) and a detection probability (P d, c ) to determine an optimal cluster boundary value. Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Method.
상기 각 클러스터 헤더의 거짓 알림 확률(false alarm probability)(Pf,c) 및 검출 확률(detection probability)(Pd,c)은 다음의 수학식으로 결정되는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
(여기에서, Λc는 클러스터 헤더에 의해 수행된 LRT 값, λc는 클러스터 경계값을 나타낸다)
8. The method of claim 7,
Wherein a false alarm probability (P f, c ) and a detection probability (P d, c ) of each cluster header are determined by the following equation: - HARD Fusion - based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Method.
(Here, Λ c shows the LRT value, λ c is a cluster boundary value performed by the cluster header)
상기 최적의 클러스터의 경계값은 최소 에러 확률 기준(minimum error probability criterion)에 따라 다음의 수학식을 통하여 결정되는 것을 특징으로 하는 인지 라디오 네트워크를 위한 소프트-하드 융합기반 협력 스펙트럼 센싱 방법.
9. The method of claim 8,
Wherein the boundary value of the optimal cluster is determined by the following equation according to a minimum error probability criterion. ≪ RTI ID = 0.0 > 11. < / RTI >
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160011608A KR20170090805A (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2016-01-29 | A Soft-Hard Combination-Based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Scheme for Cognitive Radio Networks |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160011608A KR20170090805A (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2016-01-29 | A Soft-Hard Combination-Based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Scheme for Cognitive Radio Networks |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170090805A true KR20170090805A (en) | 2017-08-08 |
Family
ID=59652956
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020160011608A KR20170090805A (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2016-01-29 | A Soft-Hard Combination-Based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Scheme for Cognitive Radio Networks |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20170090805A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108494510A (en) * | 2018-03-16 | 2018-09-04 | 西安电子科技大学 | Decision fusion method under non-ideal report channel based on optimal weighting coefficients |
| CN109150623A (en) * | 2018-09-13 | 2019-01-04 | 重庆大学 | Malicious user SSDF attack method and system are resisted based on repeating query credit value |
| KR102032518B1 (en) * | 2018-09-18 | 2019-10-15 | 국방과학연구소 | Secondary user coordinator included in cognitive radio networks |
| CN111800229A (en) * | 2020-07-21 | 2020-10-20 | 浙江大学 | Cooperative receiving method and system based on air interface information fusion |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101277816B1 (en) * | 2007-04-23 | 2013-06-21 | 링나 홀딩스 피티이., 엘엘씨 | Cluster-based cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio systems |
| KR101535251B1 (en) * | 2013-06-26 | 2015-07-24 | 성균관대학교산학협력단 | Cooperative spectrum sensing apparatus and cooperative spectrum sensing method |
-
2016
- 2016-01-29 KR KR1020160011608A patent/KR20170090805A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101277816B1 (en) * | 2007-04-23 | 2013-06-21 | 링나 홀딩스 피티이., 엘엘씨 | Cluster-based cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio systems |
| KR101535251B1 (en) * | 2013-06-26 | 2015-07-24 | 성균관대학교산학협력단 | Cooperative spectrum sensing apparatus and cooperative spectrum sensing method |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| A cluster-based selective cooperative spectrum sensing scheme in cognitive radio * |
| A cluster-based selective cooperative spectrum sensing scheme in cognitive radio(EURASIP 저널, 2013.6.공개) * |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108494510A (en) * | 2018-03-16 | 2018-09-04 | 西安电子科技大学 | Decision fusion method under non-ideal report channel based on optimal weighting coefficients |
| CN109150623A (en) * | 2018-09-13 | 2019-01-04 | 重庆大学 | Malicious user SSDF attack method and system are resisted based on repeating query credit value |
| CN109150623B (en) * | 2018-09-13 | 2020-08-21 | 重庆大学 | A method to defend against malicious user SSDF attacks based on round-robin reputation values |
| KR102032518B1 (en) * | 2018-09-18 | 2019-10-15 | 국방과학연구소 | Secondary user coordinator included in cognitive radio networks |
| CN111800229A (en) * | 2020-07-21 | 2020-10-20 | 浙江大学 | Cooperative receiving method and system based on air interface information fusion |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. | Cooperative spectrum sensing optimization in energy-harvesting cognitive radio networks | |
| Visser et al. | Multinode spectrum sensing based on energy detection for dynamic spectrum access | |
| Zou et al. | Outage probability analysis of cognitive transmissions: Impact of spectrum sensing overhead | |
| Kozal et al. | Spectrum sensing-energy tradeoff in multi-hop cluster based cooperative cognitive radio networks | |
| KR20170090805A (en) | A Soft-Hard Combination-Based Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Scheme for Cognitive Radio Networks | |
| Wan et al. | Energy-efficient cooperative spectrum sensing scheme based on spatial correlation for cognitive internet of things | |
| CN101753232A (en) | Method and system for detecting cooperative frequency spectrum | |
| Arora et al. | Cooperative spectrum sensing using hard decision fusion scheme | |
| Rai et al. | Spectrum sensing and allocation schemes for cognitive radio | |
| CN105246082B (en) | A kind of perception information fusion method based on energy measuring | |
| Zhao et al. | Scheduling of collaborative sequential compressed sensing over wide spectrum band | |
| Khanikar et al. | Incorporating primary user interference for enhanced spectrum sensing | |
| Hariharan et al. | Average detection probability analysis for cooperative-MIMO spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks | |
| Zhao et al. | Cooperative sequential compressed spectrum sensing over wide spectrum band | |
| Sharma et al. | Performance comparison of hard and soft fusion techniques for energy efficient CSS in cognitive radio | |
| Kaligineedi et al. | Distributed detection of primary signals in fading channels for cognitive radio networks | |
| Nallagonda et al. | Performance of Generalized $\alpha-\mu $ Fading for Energy Detection Based Spectrum Sensing in Presence of Channel Errors | |
| Wang et al. | Interference management for smart grid communication under cognitive wireless network | |
| Perez et al. | Adaptive EM-based algorithm for cooperative spectrum sensing in mobile environments | |
| Karami et al. | Cluster size optimization in cooperative spectrum sensing | |
| Cardoso et al. | Spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks | |
| Rop et al. | Spectrum Sensing on High Density Cognitive Radio Vehicular Ad Hoc Network. | |
| PeiPei et al. | Joint temporal and spatial sensing based cooperative cognitive networks | |
| Wang et al. | Cooperative spectrum sensing based on matrix rank minimization | |
| Li et al. | A resource-efficient green paradigm for crowdsensing based spectrum detection in internet of things networks |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| PA0109 | Patent application |
Patent event code: PA01091R01D Comment text: Patent Application Patent event date: 20160129 |
|
| PA0201 | Request for examination | ||
| PG1501 | Laying open of application | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| PE0902 | Notice of grounds for rejection |
Comment text: Notification of reason for refusal Patent event date: 20170919 Patent event code: PE09021S01D |
|
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| PE0601 | Decision on rejection of patent |
Patent event date: 20180621 Comment text: Decision to Refuse Application Patent event code: PE06012S01D Patent event date: 20170919 Comment text: Notification of reason for refusal Patent event code: PE06011S01I |