KR20170018072A - Methods of treating or ameliorating migraine - Google Patents
Methods of treating or ameliorating migraine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20170018072A KR20170018072A KR1020177001848A KR20177001848A KR20170018072A KR 20170018072 A KR20170018072 A KR 20170018072A KR 1020177001848 A KR1020177001848 A KR 1020177001848A KR 20177001848 A KR20177001848 A KR 20177001848A KR 20170018072 A KR20170018072 A KR 20170018072A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- migraine
- once
- patient
- compound
- headache
- Prior art date
Links
- ZBKFQNDDWBCYLQ-ZALCBRDASA-N C[C@H]([C@@H](C(C(CCC1)C1C(C)=O)=C)N)C(C)=C Chemical compound C[C@H]([C@@H](C(C(CCC1)C1C(C)=O)=C)N)C(C)=C ZBKFQNDDWBCYLQ-ZALCBRDASA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K38/00—Medicinal preparations containing peptides
- A61K38/04—Peptides having up to 20 amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- A61K38/07—Tetrapeptides
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/40—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil
- A61K31/401—Proline; Derivatives thereof, e.g. captopril
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/0012—Galenical forms characterised by the site of application
- A61K9/0019—Injectable compositions; Intramuscular, intravenous, arterial, subcutaneous administration; Compositions to be administered through the skin in an invasive manner
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/02—Suppositories; Bougies; Bases therefor; Ovules
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/06—Antimigraine agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Dermatology (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Acyclic And Carbocyclic Compounds In Medicinal Compositions (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
소정의 실시형태에서, 본 발명은 펩타이드 NMDAR 부분 작용제를 투여함으로써 편두통(예를 들어, 발작적 편두통, 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통, 무전조 편두통, 편두통양 장애, 월경 편두통, 복부 편두통, 아동기 주기적 증후군 또는 군발성 두통)을 치료하는 방법에 관한 것이다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 본 발명은 또한 펩타이드 NMDAR 부분 작용제를 투여함으로써 환자에서 장기간 편두통 후 후유증을 치료 또는 경감시키는 방법에 관한 것이다. 소정의 다른 실시형태에서, 본 발명은, 펩타이드 NMDAR 부분 작용제를 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 피질 확산성 억제 또는 피질 확산성 억제에 의해 생긴 질환 또는 병태를 치료, 억제 또는 예방하는 방법에 관한 것이다. 예를 들어, 간질, 외상성 뇌 손상, 및/또는 뇌졸중을 치료하는 방법이 본 명세서에 제공된다.In certain embodiments, the present invention provides a method of treating migraine (e.g., epilepsy, chronic migraine, retinal migraine, ocular migraine migraine, migraine migraine, migraine headache disorder, menstrual migraine, Childhood periodic syndrome or cluster headache). In certain embodiments, the present invention is also directed to a method of treating or alleviating a long-term post-migraine episode in a patient by administering a peptide NMDAR partial agonist. In certain other embodiments, the invention provides a method of treating, inhibiting or preventing a disease or condition caused by inhibiting cortical spreading or inhibiting cortical spread in a patient in need thereof, comprising administering a peptide NMDAR partial agonist . For example, methods of treating epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, and / or stroke are provided herein.
Description
관련 출원에 대한 상호 참조Cross-reference to related application
본원은 2014년 6월 23일자로 출원된 미국 가출원 제62/015,727호, 및 2015년 1월 29일자로 출원된 미국 가출원 제62/109,386호(이들 각각은 그들의 전문이 참고로 본 명세서에 포함됨)의 이익 및 우선권을 주장한다. This application claims the benefit of US Provisional Application No. 62 / 015,727, filed June 23, 2014, and U.S. Provisional Application No. 62 / 109,386, filed January 29, 2015, each of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety, To the benefit and priority of.
편두통은 재발하고, 혈관 촉발물질에 초점을 두는 기존의 약물요법에 의해 대개 불량하게 제어되는 허약성 공격과 연관된 일차성 삽화성 두통 통증 장애이다. 편두통 공격의 발병은, 피질 확산성 억제(spreading depression; SD)의 현상에 의해 발생한, 섬광 암점, 또는 편두통 조짐에 의해 대개 전조가 된다(문헌[Ayata, Headache, 50:725-30, 2010; Eikerman-Haerter et al., Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep., 10:167-73, 2010; 및 -del-Rio et al., Curr. Opin. Neurol., 17(3):289-93, 2004] 참조). SD는, 세포외 칼륨의 국소 증가 및 피질의 큰 구역에 걸쳐 느린 탈분극의 자가 전파하는 파를 생성하는 글루타메이트의 방출에 의해 촉발된, 뇌파 측정 활성의 느리게 전파하는 억제이다. 대략 15 내지 30%의 편두통 환자가 조짐 편두통(migraine with aura)을 경험한다. Migraine is a primary episodic headache pain disorder associated with a relapsing and fragile attack that is usually poorly controlled by existing drug therapy focusing on vascular trigger substances. The onset of a migraine attack is predominantly predated by flash scotia or migraine symptoms caused by the development of a spreading depression (SD) (Ayata, Headache, 50: 725-30, 2010; Eikerman Haerter et al., Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep., 10: 167-73, 2010; And -del-Rio et al., Curr. Opin. Neurol., 17 (3): 289-93, 2004). SD is a slow-spreading inhibition of EEG activity triggered by local increases in extracellular potassium and release of glutamate, which produces self-propagating waves of slow depolarization across large areas of the cortex. Approximately 15 to 30% of migraine patients experience migraine with aura.
포유류의 중추 신경계(central nervous system; CNS)는 신경활성 펩타이드 소마토스타틴, 콜레사이스토키닌, VIP, 물질 P, 엔케팔린, 신경펩타이드 Y(NPY), 뉴로텐신, TRH, CCK 및 다이노르핀을 포함하는 뇌 및 척수 내의 특별한 신호전달을 발생시키는 많은 신경활성 펩타이드를 사용한다. (일반적으로 문헌[The Biochemical Basis of Neuropharmacology, Cooper, Bloom and Roth, 5th ed., Oxford University Press, New York, 1986] 참조). CNS에서 운영되는 복잡한 신호전달 경로의 조심스런 설명은 CNS와 연관된 다양한 장애에 대한 중요한 치료학적 표적을 제시하는 이 신경활성 펩타이드에 의해 조절되는 특별한 수용체를 확인시켰다. The mammalian central nervous system (CNS) is the brain that contains the neuroactive peptides somatostatin, choleseitokinin, VIP, substance P, enkephalin, neuropeptide Y (NPY), neurotensin, TRH, CCK, And many neuroactive peptides that generate special signaling in the spinal cord. (See generally The Biochemical Basis of Neuropharmacology, Cooper, Bloom and Roth, 5th ed., Oxford University Press, New York, 1986). Careful explanations of the complex signaling pathways operating in the CNS have identified specific receptors that are regulated by these neuroactive peptides that present important therapeutic targets for the various disorders associated with the CNS.
N-메틸-D-아스파르테이트(NMDA) 수용체(NMDAR)는 뇌졸중 관련 뇌 세포 사멸, 경련 장애, 및 학습 및 기억을 포함하는 신경퇴행성 장애에 연루된 하나의 수용체이다. NMDAR은 중추 신경계에서 정상 시냅스 전달, 시냅스 가소성 및 흥분세포독성을 조절하는 데 있어서 중심적인 역할을 또한 한다. NMDAR은 장기간 강화(long-term potentiation; LTP)에 추가로 관여된다. LTP는 학습 및 기억의 기초를 이루는 뉴런 연결의 지속적 강화이다(문헌[Bliss and Collingridge, 1993, Nature 361:31-39] 참조).The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor (NMDAR) is a receptor involved in stroke-related brain cell death, convulsive disorders, and neurodegenerative disorders including learning and memory. NMDAR also plays a central role in regulating normal synaptic transmission, synaptic plasticity and excitatory cytotoxicity in the central nervous system. NMDAR is further involved in long-term potentiation (LTP). LTP is a sustained enhancement of neuronal connections underlying learning and memory (see Bliss and Collingridge, 1993, Nature 361: 31-39).
글루타메이트 수용체의 2개의 일반 종류는 중추 신경계(CNS)를 특징으로 한다. 이들은 신호전달 단백질의 G-단백질 커플링된 수용체 패밀리, 및 이온자극성 글루타메이트 수용체에 속하는 대사자극성 글루타메이트 수용체이다(Muir and Lees, Stroke, 1995, 26, 503-513). 이온자극성 종류는 이들을 활성화하는 선택적 리간드에 의해 AMPA, 카이네이트 및 NMDA 수용체 하위유형으로 추가로 세분된다.Two common classes of glutamate receptors are characterized by the central nervous system (CNS). These are G-protein coupled receptor families of signaling proteins, and metabotropic glutamate receptors belonging to ion-stimulating glutamate receptors (Muir and Lees, Stroke, 1995, 26, 503-513). Ion-stimulating classes are further subdivided into AMPA, kainate and NMDA receptor subtypes by selective ligands that activate them.
NMDA 매개 소분자 작용제 및 길항제 화합물은 잠재적 치료학적 용도를 위해 개발되었다. 그러나, 이들 중 대부분은 매우 좁은 치료학적 지수 및 환각, 운동실조, 불합리한 행동 및 상당한 독성(이들 모두 이의 유효성 및/또는 안전성을 제한함)을 포함하는 원치 않는 부작용과 관련된다. NMDA mediated molecular agonists and antagonist compounds have been developed for potential therapeutic applications. However, most of these are associated with very narrow therapeutic indices and unwanted side effects including hallucinations, ataxia, irrational behavior and considerable toxicity, all of which limit its effectiveness and / or safety.
따라서, 증가한 효율 및 감소한 원치 않는 부작용을 제공하는 화합물에 의한 편두통 및 다른 관련 질환의 개선된 치료에 대한 요구가 여전하다.Thus, there remains a need for improved treatment of migraine and other related disorders by compounds that provide increased efficacy and reduced undesirable side effects.
소정의 실시형태에서, 본 개시내용은 약제학적 유효량의 GLYX 펩타이드를 이를 필요로 하는 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 편두통을 치료하는 방법에 관한 것이다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 발작적 편두통(episodic migraine), 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통(ophthalmoplegic migraine), 무전조 편두통(acephalgic migraine), 편두통양 장애(migrainous disorder), 월경 편두통, 복부 편두통, 아동기 주기적 증후군(childhood periodic syndrome) 및/또는 군발성 두통(cluster headache)일 수 있다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 무조짐 편두통(일반 편두통)이다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 조짐 편두통(고전적 편두통)이다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 이질통이 동반된다. In certain embodiments, the present disclosure relates to a method of treating migraine comprising administering a pharmaceutically effective amount of a GLYX peptide to a patient in need thereof. In certain embodiments, the migraine is selected from the group consisting of episodic migraine, chronic migraine, retina migraine, ophthalmoplegic migraine, acephalgic migraine, migrainous disorder, menstrual migraine, Migraine, childhood periodic syndrome and / or cluster headache. In certain embodiments, the migraine headache is a non-migraine migraine (general migraine headache). In certain embodiments, the migraine headache is a headache migraine (classic migraine headache). In certain embodiments, the migraine head is accompanied by allodynia.
예를 들어, 개시된 화합물은 편두통(예를 들어, 발작적 편두통, 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통, 무전조 편두통, 편두통양 장애, 월경 편두통, 복부 편두통, 아동기 주기적 증후군 또는 군발성 두통)의 치료를 위해 기능적으로 NMDAR의 글라이신 부위의 작용과 상호작용하거나 이것을 조절할 수 있다.For example, the disclosed compounds are useful for the treatment of migraine (e.g., seizure, migraine, chronic migraine, retinal migraine, ocular migraine, migraine migraine, migraine headache, menstrual migraine, abdominal migraine, childhood periodic syndrome or cluster headache) It can interact with or regulate the action of the glycine site of NMDAR functionally for treatment.
소정의 실시형태에서, 본 개시내용은 약제학적 유효량의 GLYX 펩타이드를 이를 필요로 하는 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 피질 확산성 억제(SD)를 치료, 억제 및/또는 예방하는 방법에 관한 것이다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 본 개시내용은 약제학적 유효량의 GLYX 펩타이드를 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 장기간 편두통 후 후유증을 치료 또는 경감시키는 것에 관한 것이다. In certain embodiments, the present disclosure is directed to a method of treating, inhibiting and / or preventing cortical spread inhibition (SD) comprising administering a pharmaceutically effective amount of a GLYX peptide to a patient in need thereof. In certain embodiments, the disclosure relates to treating or ameliorating a long-term post-migraine episode in a patient in need thereof, comprising administering to the patient a pharmaceutically effective amount of a GLYX peptide.
소정의 실시형태에서, GLYX 펩타이드는 하기 구조를 가지거나, NMDAR 부분 작용제 활성을 가지는 이의 약제학적으로 허용되는 염, 또는 이의 유도체이다:In certain embodiments, the GLYX peptide is a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, or derivative thereof, having the following structure, or having NMDAR partial agonist activity:
. .
일 양태에서, 본 발명은 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 편두통을 치료하는 방법에 관한 것이고, 상기 방법은 약제학적 유효량의 하기로 표시되는 화합물 또는 이의 약제학적으로 허용되는 염을 상기 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함한다:In one aspect, the invention is directed to a method of treating migraine in a patient in need thereof, which method comprises administering to said patient a pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound represented by the formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, Includes:
. .
또 다른 양태에서, 본 발명은 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 피질 확산성 억제를 치료, 억제 및/또는 예방하는 방법에 관한 것이고, 상기 방법은 약제학적 유효량의 하기로 표시되는 화합물 또는 이의 약제학적으로 허용되는 염을 상기 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함한다:In another aspect, the invention is directed to a method of treating, inhibiting and / or preventing cortical diffusing inhibition in a patient in need thereof, which method comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound represented by the following formula ≪ / RTI > to said patient: < RTI ID = 0.0 >
. .
또 다른 양태에서, 본 발명은 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 장기간 편두통 후 후유증을 치료 또는 경감시키는 방법에 관한 것이고, 상기 방법은 약제학적 유효량의 하기로 표시되는 화합물 또는 이의 약제학적으로 허용되는 염을 상기 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함한다:In another embodiment, the invention is directed to a method of treating or alleviating a long-term post-migraine episode in a patient in need thereof, which method comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound represented by the following, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, Comprising administering to a patient:
. .
하기 더 자세히 기재된 바대로, 조짐에서 투여될 때 효과적인 약물은 예를 들어 편두통의 조기 단계에서 중재를 허용함으로써 환자에게 유리할 것이다. 본 명세서에 기재된 방법이 조짐에서 GLYX 펩타이드의 투여를 포함하는 조짐 편두통의 치료에 적용 가능하다는 것이 고려된다.As described in more detail below, drugs that are effective when administered in the symptoms will be beneficial to the patient, for example, by allowing intervention in the early stages of migraine. It is contemplated that the methods described herein are applicable in the treatment of symptom migraine including administration of GLYX peptides in the context.
도 1은 해마회 슬라이스의 필드 CA1에서의 병소적 높은 [K+] 유도된 확산성 억제(SD)를 보여주어, 뉴런 및 신경교의 많은 탈분극의 분산 파를 반영하는 휘도의 변화를 발생시킨다.
도 2는 뇌 슬라이스에서 발생한 SD에 대한 데이터를 보여주고; 개시 부위에서 SD의 개별 순차적 삽화의 기준 구역 사이의 상당한 차이가 없어서(본페로니 다중 비교 시험((Bonferroni Multiple Comparison Test)), P>0.20), GLYX-13이 SD의 개시를 변경하지 않는다는 것을 나타낸다.
도 3은 GLYX-13이 SD 개시에 대한 불응 기간을 증가시킨다는 것을 입증하는 데이터를 보여준다. SD는 대조군 슬라이스(대조군)에서의 이전의 SD 후 5분에 성공적으로 일어날 수 있지만, GLYX-13(GLYX-13 30')에 의해 처리된 슬라이스에서는 일어날 수 없었다.
도 4A는 증가한 휘도의 SD "조짐"이 개시 피펫으로부터 확산하고 슬라이스에 걸쳐 전파하고, SD 전도 속도를 계산하기 위해 사용될 수 있다는 것을 보여주다(도 4B).
도 5는, GLYX-13이 SD 전도 속도에 영향을 미치는 경우 SD의 반복 삽화가 안정한 속도를 유지시키는지 시험하기 위해, 6회 후속 SD를 분석하기 위한 반복 측정에 의한, 변량의 1방향 분석(ANOVA)을 보여준다.
도 6A는 대조군 피라미드 뉴런에서 SD의 2개의 삽화에 반응한 가시 수축을 보여주지만, 도 6B는 10μM GLYX-13의 존재 하의 동일한 과정을 예시하고; 도 6C는 GLYX-13이 SD 후 가시 크기의 회복을 구제한다는 것을 나타낸다.
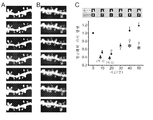
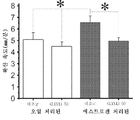
도 7A는 확산 거리를 보여주고, 도 7B는 (에스트로겐 치료된 및 비오일 치료된) 랫트에서의 확산성 억제의 확산 속도를 보여주어, 확산 속도가 오일 치료된 랫트와 비교하여 더 빠르다는 것을 나타낸다.
도 8은 에스트로겐 처리된 랫트로부터의 슬라이스에서의 SD가 오일 처리된 랫트보다 길게 이동한다는 것을 보여준다.
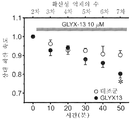
도 9A는 랫트 실험에서의 SD와 연관된 휘도 변화가 GLYX-13의 존재 하에 지연된다는 것을 보여주고; 도 9B는 SD가 GLYX-13의 존재 하에 유발된다는 것을 보여준다.
도 10은 GLYX-13의 적용 전에 및 후에 에스트로겐 치료된 랫트에 걸친 SD 전파 속도에 대한 GLYX-13의 영향(F(1,8)=3.1;p<0.05); 및 2개의 군 사이의 GLYX-13의 예비노출(F(1,8)=4.2; p<0.05)을 보여준다.
도 11A 내지 도 11B는 블라스트 후 24시간에 PEL 시험에서 라파스티넬(3㎎/㎏ IV; 블라스트 후 1시간)의 블라스트 유도된 학습 결함의 구제를 보여준다. 도 11A는 블라스트 회복 시간(정상 보행에 대한 잠재력) 데이터를 보여준다. 도 11B는 대상체 간 설계를 사용한 블라스트 후 24시간에 수행된 단일 3분 긍정적 정서 학습(PEL) 시험 세션의 결과를 보여준다. N = 군마다 4 내지 6. * P<0.05(도 11A) ANOVA, 또는 (도 11B) 피셔의 PLSD 사후 시험, 라파스티넬 + TBI 대 비히클 + TBI.Figure 1 shows the lesion high [K + ] induced diffuse suppression (SD) in the field CA1 of the hippocampal slice, resulting in a change in brightness reflecting the dispersive wave of many depolarizations of neurons and glia.
Figure 2 shows the data for the SD that occurred in the brain slice; There was no significant difference between the reference regions of the individual sequential illustrations of SD at the initiation site (Bonferroni Multiple Comparison Test, P > 0.20), indicating that GLYX-13 did not alter the onset of SD .
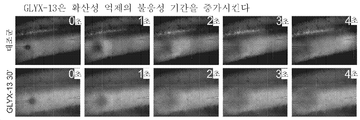
Figure 3 shows data demonstrating that GLYX-13 increases the refractory period for SD initiation. SD could be successful at 5 minutes after the previous SD in the control slice (control), but could not occur at the slice treated by GLYX-13 (GLYX-13 30 ').
4A shows that the SD "signature" of increased brightness can be used to diffuse from the initiation pipette, propagate across the slice, and calculate the SD conduction velocity (FIG. 4B).
Figure 5 shows a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) by repeated measurements to analyze six subsequent SDs to test whether GLYX-13 affects the SD conduction velocity and whether the SD repeatedly maintains a stable rate ).
Figure 6A shows the visible contraction in response to two illustrations of SD in control pyramidal neurons, Figure 6B illustrates the same procedure in the presence of 10 [mu] M GLYX-13; Figure 6C shows that GLYX-13 rescues the recovery of visible size after SD.
Figure 7A shows the diffusion distance and Figure 7B shows the diffusion rate of diffusion inhibition in rats (estrogen treated and non-oil treated), indicating that the diffusion rate is faster compared to the oil treated rats .
Figure 8 shows that SD at the slice from the estrogen treated rats migrates longer than the oil treated rats.
Figure 9A shows that the brightness change associated with SD in rat experiments is delayed in the presence of GLYX-13; Figure 9B shows that SD is induced in the presence of GLYX-13.
Figure 10 shows the effect of GLYX-13 (F (1,8) = 3.1; p < 0.05) on SD propagation velocity across estrogen-treated rats before and after application of GLYX-13; And preliminary exposure of GLYX-13 (F (1,8) = 4.2; p < 0.05) between the two groups.
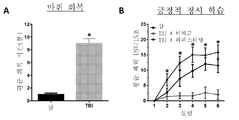
Figures 11A-11B show the relief of blast induced learning defects of rapastinel (3 mg / kg IV; 1 hour after blasting) in the PEL test 24 hours after blast. FIG. 11A shows the blast recovery time (potential for normal walking) data. FIG. 11B shows the results of a single 3-minute positive emotional learning (PEL) test session performed 24 hours after blasting using inter-subject design. Each group N = 4 to 6. * P <0.05 (FIG. 11A) ANOVA, or (FIG. 11B) of the Fisher PLSD post-test, Rapa styryl Ner + TBI vs. vehicle + TBI.
편두통 분류Migraine Classification
편두통은 1988년에 처음에 포괄적으로 분류되었다. 국제 두통 협회(International Headache Society)는 가장 최근에 2004년에 두통의 이의 분류를 업데이트하였다. 이 분류에 따르면, 편두통은 무엇보다도 긴장형 두통 및 군발성 두통과 함께 원발성 두통이다Migraine was first categorized first in 1988. The International Headache Society recently updated its classification of headaches in 2004. According to this classification, migraine is primarily a primary headache with tension-type headache and cluster headache
편두통은 7개의 하위분류로 분류된다(이들 중 몇몇은 추가의 하위분류를 포함한다): Migraine is classified into seven subclasses (some of which include additional subclasses):
무조짐 편두통, 또는 "일반 편두통"은 조짐을 동반하지 않는 편두통성 두통을 포함한다.Migraine, or "generalized migraine" includes migraine headaches that do not accompany symptoms.
조짐 편두통, 또는 "전통적 편두통"은 보통 조짐을 동반하는 편두통성 두통을 포함한다. 덜 흔하게는, 조짐은 두통 없이 또는 비편두통성 두통과 함께 발생할 수 있다. 2개의 다른 변형은 가족성 반신불수 편두통 및 산발적 반신불수 편두통이고, 여기서 사람은 조짐 편두통을 가지고 운동 장애를 동반한다. 근친이 동일한 병태를 가지는 경우, 이것은 "가족성"이라 불리고, 그렇지 않으면 이것은 "산발적"이라 불린다. 또 다른 변형은 두개기부형 편두통(basilar-type migraine)이고, 여기서 두통 및 조짐은 운동 장애가 아니라 말하기의 어려움, 세상의 회전, 귀의 울림, 또는 다수의 다른 뇌간 관련 증상이 동반된다. 이 유형은 뇌간에 공급하는 동맥인 두개기부 동맥의 경련으로 인한 것으로 초기에 생각되었다. 조짐 편두통의 진단을 위한 가이드라인은 예를 들어 문헌[Eriksen et al., European Journal of Neurology 11:583-591, 2004 및 국제 두통 장애 분류, 2판(International Classification of Headache Disorders, Second Edition)(ICHD-II)]에서 발견된다. 조짐 편두통의 하위유형은 ICHD-II에 기재된 것, 예컨대 편두통성 두통을 가지는 통상적인 조짐(IHS 1.2.1), 비편두통성 두통을 가지는 통상적인 조짐(IHS 1.2.2), 두통이 없는 통상적인 조짐(IHS 1.2.3), 가족성 반신불수 편두통(IHS 1.2.4), 산발적 반신불수 편두통(IHS 1.2.5) 및 두개기부형 편두통(IHS 1.2.6)을 포함한다.Signs Migraine, or "traditional migraine", includes migraine headaches usually accompanied by signs. Less commonly, the symptoms can occur with or without a headache. Two other variants are familial hemiparesis syndrome and sporadic hemiparesis syndrome, in which a person is accompanied by movement disorders with an ocular migraine. If an ancestor has the same condition, it is called "familial", otherwise it is called "sporadic". Another variant is basilar-type migraine, where headaches and signs are not motor disorders but are accompanied by difficulties in speaking, world rotation, ringing in the ears, or many other brain-related symptoms. This type was initially thought to be due to seizures of the cranial base arteries, the arteries supplying the brainstem. Guidelines for the diagnosis of migraine headache can be found in, for example, Eriksen et al., European Journal of Neurology 11: 583-591, 2004 and International Classification of Headache Disorders, Second Edition -II). ≪ / RTI > Signs Subtypes of migraine include those described in ICHD-II, such as the usual signs with migraine headaches (IHS 1.2.1), common signs with non-migraine headaches (IHS 1.2.2), headache- Includes signs (IHS 1.2.3), familial hemiparesis involuntary migraine (IHS 1.2.4), sporadic hemiparesis involuntary migraine (IHS 1.2.5), and two donor migraine (IHS 1.2.6).
흔히 편두통의 선구자인 아동기 주기적 증후군은 주기적 구토(때때로의 강한 구토 기간), 복부 편두통(복부 통증, 보통 구역이 동반됨) 및 아동기의 양성 발작성 현기증(때때로의 현기증의 도짐)을 포함한다.Childhood periodic syndrome, often a pioneer of migraine, includes periodic vomiting (sometimes a period of strong vomiting), abdominal migraine (accompanied by abdominal pain, common areas), and childhood benign paroxysmal vertigo (occasional dizziness).
망막 편두통은 시각 장애 또는 심지어 한쪽 눈의 일시적인 실명을 동반하는 편두통성 두통을 포함한다.Retinal migraine includes migraine headaches with visual impairment or even temporary blindness in one eye.
편두통의 합병증은 드문 긴 또는 드문 빈번한, 또는 발작 또는 뇌 병변과 연관된 편두통성 두통 및/또는 조짐을 기술한다.Complications of migraine describe rare or rare frequent, or migraine headaches and / or signs associated with seizures or brain lesions.
개연성 편두통은 편두통의 약간의 특징을 가지지만, (동반 약제 과다사용의 존재의 경우에) 이것을 편두통으로 확실히 진단하기 위한 충분한 증거가 없는 경우의 상태를 기술한다.Possible migraine has some characteristics of migraine, but describes a condition in the absence of sufficient evidence to diagnose it with migraine (in the presence of concomitant drug overuse).
만성 편두통은 편두통의 합병증이고, 편두통성 두통에 대한 진단학적 기준을 충족시키고 더 긴 시간 간격 동안 발생하는 두통이다. 구체적으로, 3개월 초과 동안 15일/개월 이상.Chronic migraine is a complication of migraine, a headache that meets the diagnostic criteria for migraine headaches and occurs over a longer time interval. Specifically, more than 15 days / month for more than 3 months.
편두통에 4가지 가능한 단계가 존재하지만, 단계 모두가 필수적으로 경험되지 않는다: (1) 두통 전의 시간 또는 일에 생기는 전구증상; (2) 두통을 즉시 진행시키는 조짐; (3) 두통 단계로 또한 공지된 통증 단계; 및 (4) 편두통 공격의 종료 후 경험하는 효과인 후구증상.There are four possible stages of migraine, but not all of the stages are necessarily experienced: (1) global symptoms that occur in the hours or days before the headache; (2) an indication that the headache progresses immediately; (3) a pain stage also known as a headache stage; And (4) epigastric symptoms that are experienced after the end of the migraine attacks.
전구 또는 전조 증상은 통증 또는 조짐의 시작 전에 2시간 내지 2일의 발병으로 편두통을 가지는 사람의 약 60%에서 발생한다. 이 증상은 변경된 기분, 과민증, 우울증 또는 희열, 피로, 특정 음식에 대한 갈망, (특히 목에서의) 근육 경직, 변비 또는 설사, 및 냄새 또는 소음에 대한 민감성을 포함하는 매우 다양한 현상을 포함할 수 있다. 이것은 조짐 편두통 또는 무조짐 편두통을 가지는 사람에서 발생할 수 있다.Bulbous or precursor symptoms occur in about 60% of people with migraine with a 2 to 2 day outbreak before the onset of pain or symptoms. The symptoms may include a wide variety of symptoms including altered mood, irritability, depression or bliss, fatigue, craving for certain foods, muscle stiffness (especially in the neck), constipation or diarrhea, and sensitivity to odor or noise have. This can occur in people with an ocular migraine or no ocular migraine.
조짐은 두통 전에 또는 동안에 발생하는 일시적 병소적 신경학적 현상이다. 이것은 수 분에 걸쳐 점진적으로 나타나고, 일반적으로 60분 미만으로 지속한다. 증상은 성질 상 시각, 감각 또는 운동일 수 있고, 많은 사람들이 하나 초과를 경험한다. 시각 효과가 가장 흔히 발생하고; 이것은 사례의 99% 이하에서 발생하고, 사례 중 50% 초과에서 감각 또는 운동 효과가 동반되지 않는다. 시각 장애는 대개 섬광 암점으로 이루어진다(깜박거리고 읽거나 운전하는 사람의 능력을 방해할 수 있는 시야의 부분 변경의 구역.) 이것은 통상적으로 시야 중심 주위에서 시작하고 이후 축성 또는 성의 벽과 같이 보이는 것으로 기재되는 지그재그 선으로 측면으로 확산한다. 보통 선은 검정 및 흰색이지만, 몇몇 사람들은 또한 색상이 있는 선을 본다. 몇몇 사람들은 이들의 시야(반맹으로 공지됨) 중 일부를 잃는 반면, 다른 사람들은 흐려짐을 경험한다.Symptoms are a temporary lesional neurological phenomenon that occurs before or during a headache. This is gradual over several minutes and generally lasts less than 60 minutes. Symptoms can be visual, sensory or motor in nature, and many people experience more than one. Visual effects are most common; This occurs at less than 99% of cases and is not accompanied by sensory or motor effects in more than 50% of cases. Blindness usually consists of scintillation (a zone of partial change of vision that can interfere with the ability of a person to blink and read or drive). This usually begins around the visual field center and then looks like a wall of casting or sexuality And spread to the side by a zigzag line. Usually lines are black and white, but some people also see lines with colors. Some people lose some of their visions (known as anti-Semitic), while others experience blurring.
감각 조짐은 제2의 가장 흔한 유형이고; 이들은 조짐을 가지는 사람들 중 30 내지 40%에서 발생한다. 대개 저리는(pin-and-needle) 느낌은 손 및 팔의 한 측에서 시작하고, 동일한 측면에서 코-입 부위로 확산한다. 저림은 보통 위치 감각의 소실로 아린감이 지나간 후에 발생한다. 조짐 단계의 다른 증상은 말하기 또는 언어 장애, 세상의 회전, 및 덜 흔하게는 운동 문제를 포함할 수 있다. 운동 증상은 이것이 반신불수 편두통이라는 것을 나타내고, 허약은 대개 다른 조짐과 달리 1시간보다 길게 지속된다.Sensory sign is the second most common type; These occur in 30% to 40% of people with symptoms. Usually a pin-and-needle feel starts from one side of the hand and arm and spreads from the same side to the nose. The lower limb usually occurs after the perception of the position is lost due to the perception of the position. Other symptoms of the indication stage may include speech or language impairment, rotation of the world, and less commonly, exercise problems. Exercise symptoms indicate that this is a hemiplegic migraine, and weakness usually lasts longer than one hour, unlike other symptoms.
조짐은 또한 후속하는 두통 없이 발생할 수 있다. 침묵 편두통으로 또한 공지된 무전조 편두통은 비교적 희귀하고, 후속하는 두통(즉, 통증 단계 무) 없이 조짐 및 다른 증상을 포함한다.Symptoms can also occur without a subsequent headache. Also known as silent migraine headache, migraine headache is relatively rare and involves signs and other symptoms without subsequent headache (ie, no pain stages).
통증 단계 동안, 두통은 보통 일측성이고, 두근거리고, 강도가 보통 내지 경증이다. 이것은 보통 점진적으로 오고, 신체 활동에 의해 악화된다. 그러나, 사례 중 40% 초과에서, 통증은 이측성일 수 있고, 목 통증은 흔히 연관된다. 이측성 통증은 무조짐 편두통을 가지는 사람에서 특히 흔하다. 덜 흔하게는, 통증은 주로 머리의 뒤 또는 상부에서 발생할 수 있다. 통증은 보통 성인에서 4 내지 72시간 지속하지만, 어린 어린이에서 흔하게 1시간 미만 지속한다. 공격의 빈도는 가변적이고, 수명이 아주 적거나 수주일이고 평균 약 1개월이다.During the pain phase, the headache is usually unilateral, puffy, and usually mild in intensity. This usually comes gradually, and is exacerbated by physical activity. However, in over 40% of cases, pain may be bilateral, and neck pain is often associated. Bilateral pain is especially common in people with no symptoms of migraine. Less commonly, pain can occur primarily in the back or upper part of the head. Pain usually lasts 4 to 72 hours in adults, but usually lasts less than an hour in young children. The frequency of attacks is variable, life span is very small or several weeks and average is about one month.
통증은 흔히 구역, 구토, 광에 대한 민감성, 소리에 대한 민감성, 냄새에 대한 민감성, 피로 및 과민성을 동반한다. 뇌간과 관련된 신경학적 증상 또는 신체의 양측에서의 신경학적 증상을 가지는 편두통인 두개기부 편두통에서, 흔한 효과는 세상의 회전의 감각, 변덕스러움 및 혼란을 포함한다. 구역은 사람의 거의 90%에서 발생하고, 구토는 약 1/3에서 발생한다. 다른 증상은 시야 혼탁, 비 강직, 설사, 빈번한 배뇨, 창백함 또는 발한을 포함할 수 있다. 종창 또는 두피의 압통은 목 강직이 발생하면서 생길 수 있다.Pain is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, sensitivity to sound, sensitivity to odor, fatigue and irritability. In migraine with craniofacial migraine, which has neurological symptoms associated with brain stem or neurological symptoms on both sides of the body, a common effect involves sensation, whim and confusion of the world's rotation. Zone occurs in almost 90% of people, and vomiting occurs in about 1/3. Other symptoms may include visual acuity, non-rigidity, diarrhea, frequent urination, pale or sweating. Tenderness or tenderness of the scalp can occur when neck stiffness occurs.
편두통의 효과는 주요 두통이 끝난 후 수 일 동안 지속할 수 있고; 이것은 편두통 후구증상이라 불리다. 많은 것들이 편두통이 있는 부위에서의 아픈 느낌을 보고하고, 일부는 두통이 지나간 후 수 일 동안 생각의 손상을 보고한다. 환자는 피곤하게 느낄 수 있고, 머리 통증, 인지 장애, 위장관 증상, 기분 변화 및 허약을 가진다.The effect of migraine can last for several days after the main headache is over; This is called migraine headache symptoms. Many report a sick feeling at the site of migraine, and some report a loss of thought for a few days after the headache has passed. The patient may feel tired, have headache, cognitive impairment, gastrointestinal symptoms, mood swings and weakness.
GLYX 펩타이드GLYX peptide
GLYX-13은, N-메틸-D-아스파르테이트 글루타메이트 수용체(NMDAR)의 활성화에 전례없는 조절 작용을 가지는 새로 개발된 신속한 작용하는, 장기간 지속되는 항우울제이다. 이것이 활성화될 것을 요하는 NMDA 수용체에서의 의무적인 공동작용제 글라이신 부위에서 작용하는 이 물질은 이 중요한 수용체의 활성화를 정상화시켜서, 이것이 매우 낮을 때 이것을 증가시키고, 이것이 매우 높을 때 이것을 억제한다. 이 작용을 통해, GLYX-13은 시냅스 강도의 LTD를 억제하면서 장기간 강화(LTP)의 유도를 증대시키고, 늙은 동물로부터 해마회 슬라이스에서의 정상 LTP를 복원한다. GLYX-13 is a newly developed, fast acting, long-lasting antidepressant with an unprecedented regulatory action on the activation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor (NMDAR). This material, acting at the obligatory synergist glycine site at the NMDA receptor that needs to be activated, normalizes the activation of this important receptor, increasing it when it is very low and inhibiting it when it is very high. Through this action, GLYX-13 increases the induction of long-term fortification (LTP) while inhibiting LTD of synaptic strength and restores normal LTP from hippocampus slices from old animals.
본 명세서에 사용되는 바대로, 용어 "GLYX 펩타이드"는 NMDAR 글라이신 부위 부분 작용제/길항제 활성을 가지는 펩타이드이다. GLYX 펩타이드는 널리 공지된 재조합 또는 합성 방법, 예컨대 US 특허 5,763,393 및 4,086,196(본 명세서에 참조로 포함됨)에 기재된 것에 의해 얻어질 수 있다. 몇몇 실시형태에서, GLYX는 아미노산 서열 Thr-Pro-Pro-Thr을 가지는 테트라펩타이드, 또는 L-트레오닐-L-프롤릴-L-프롤릴-L-트레오닌 아마이드를 의미한다.As used herein, the term "GLYX peptide" is a peptide having the NMDAR glycine site partial agonist / antagonist activity. GLYX peptides can be obtained by well known recombinant or synthetic methods, such as those described in US Pat. Nos. 5,763,393 and 4,086,196 (incorporated herein by reference). In some embodiments, GLYX means a tetrapeptide having the amino acid sequence Thr-Pro-Pro-Thr, or L-threonyl-L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-threonine amide.
예를 들어, GLYX-13은 하기한 바대로 도시된 화합물을 의미한다:For example, GLYX-13 means a compound shown as follows:
. .
GLYX-13의 다형, 동족체, 수화물, 용매화물, 유리 염기 및/또는 적합한 염, 예컨대 아세테이트 염(이것으로 제한되지는 않음)이 또한 고려된다. 펩타이드는 US 5,763,393에 추가로 기재된 바대로 환형 또는 비환형 형태일 수 있다. 몇몇 실시형태에서, GLYX-13 유사체는 Thr 또는 Pro기의 하나 이상에서 모이어티의 삽입 또는 결실, 예컨대 CH2, OH 또는 NH2 모이어티의 결실을 포함할 수 있다. 다른 실시형태에서, GLYX-13은 하나 이상의 할로겐, C1-C3 알킬(임의로 할로겐 또는 아미노에 의해 치환됨), 하이드록실 및/또는 아미노에 의해 임의로 치환될 수 있다. NMDAR의 글라이신 부위 부분 작용제는 US 5,763,393, US 6,107,271, 및 문헌[Wood et al., NeuroReport, 19, 1059-1061, 2008](이의 전체 내용은 참조로 본 명세서에 포함됨)에 개시되어 있다.Polymorphs, homologs, hydrates, solvates, free bases and / or suitable salts of GLYX-13 such as, but not limited to, acetate salts are also contemplated. The peptide may be in the form of a cyclic or acyclic, as further described in US 5,763,393. In some embodiments, GLYX-13 analogs may include Thr or insertion of one or more moieties from the group of Pro, or deleted, for example, CH 2, deletion of the OH or NH 2 moieties. In another embodiment, GLYX-13 may be optionally substituted by one or more halogen, (optionally substituted by halogen or amino) C 1 -C 3 alkyl, hydroxyl and / or amino. The glycine site partial agonists of NMDAR are disclosed in US 5,763,393, US 6,107,271, and Wood et al., NeuroReport, 19, 1059-1061, 2008, the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference.
본 명세서에 개시된 펩타이드가 천연 및 비천연 아미노산 둘 다, 예를 들어 모든 천연 아미노산(또는 이의 유도체), 모든 비천연 아미노산(또는 이의 유도체), 또는 천연 및 비천연 아미노산의 혼합물을 포함할 수 있는 것으로 이해될 수 있다. 예를 들어, GLYX-13에서의 1개, 2개, 3개 이상의 아미노산은 각각 독립적으로 D- 또는 L-구성을 가질 수 있다.It is contemplated that the peptides disclosed herein may include both natural and unnatural amino acids, for example, all natural amino acids (or derivatives thereof), all unnatural amino acids (or derivatives thereof), or mixtures of natural and unnatural amino acids Can be understood. For example, one, two, three or more amino acids in GLYX-13 may each independently have a D- or L- configuration.
GLYX-13은 NR2B 함유 NMDAR에서 주로 작용할 수 있고, 공지된 NMDAR 조절제, 예컨대 CPC-101,606 및 케타민의 전통적인 부작용을 나타내지 않을 수 있다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 필수적으로 진정이 없는 항편두통 또는 다른 치료학적 효과는 치료학적 유효량으로 대상체에게 투여될 때 GLYX-13에 의해 생성될 수 있다. 훨씬 다른 실시형태에서, GLYX-13은 남용 가능성을 가지지 않을 수 있다(예를 들어, 습관 형성이지 않을 수 있다).GLYX-13 may act predominantly in NR2B containing NMDAR and may not exhibit the traditional side effects of known NMDAR modulators, such as CPC-101,606 and ketamine. In certain embodiments, essentially non-sedating anti-migraine or other therapeutic effect can be produced by GLYX-13 when administered to a subject in a therapeutically effective amount. In a much different embodiment, GLYX-13 may not have the potential for abuse (e.g., it may not be habit-forming).
몇몇 실시형태에서, GLYX-13은 AMPA GluR1 세린-845 인산화를 증가시킬 수 있다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 글라이코겐 신타제 키나제 3β(GSK-3β)는 GLYX-13에 의해 활성화될 수 있다. 몇몇 경우에, β-카테닌의 수준은 GLYX-13의 투여 후 변경될 수 있다.In some embodiments, GLYX-13 can increase AMPA GluR1 serine-845 phosphorylation. In certain embodiments, the
몇몇 실시형태에서, GLYX-13 또는 GLYX-13을 포함하는 조성물은 혈장 수준에 비해 더 우수한 i.v. 생체내 효력 및/또는 뇌 수준 농도를 제공할 수 있다.In some embodiments, a composition comprising GLYX-13 or GLYX-13 is administered in combination with an i.v. In vivo potency and / or brain level concentration.
추가적으로, GLYX-13은 글라이신 부위 길항제, 예컨대 L-701,324, 또는 좁은 치료 지수를 가지는 다른 글라이신 부위 길항제와 비교하여 넓은 치료 지수를 가질 수 있어서, 치료학적 효과와 운동실조 사이에 매우 좁은 범위의 용량을 발생시킨다. 예를 들어, L-701,324는 운동실조를 생성시키는 용량에서 항경련 효과를 가졌다(Bristow, et al, JPET 279:492-501, 1996). 유사하게, 일련의 Merz 화합물은 운동실조를 생성시키는 용량에서 항경련 효과를 가졌다(Parsons, et al., JPET283:1264-1275, 1997). In addition, GLYX-13 can have a broad therapeutic index compared to glycine site antagonists such as L-701,324, or other glycine site antagonists with a narrow therapeutic index, thus providing a very narrow range of capacity between therapeutic effect and ataxia . For example, L-701,324 had an anticonvulsant effect on the capacity to produce ataxia (Bristow, et al, JPET 279: 492-501, 1996). Similarly, a series of Merz compounds had an anticonvulsant effect in the capacity to produce ataxia (Parsons, et al., JPET283: 1264-1275, 1997).
방법Way
일 양태에서, 본 발명은 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 편두통을 치료하는 방법에 관한 것이고, 상기 방법은 약제학적 유효량의 하기로 표시되는 화합물 또는 이의 약제학적으로 허용되는 염을 상기 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함한다:In one aspect, the invention is directed to a method of treating migraine in a patient in need thereof, which method comprises administering to said patient a pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound represented by the formula: or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, Includes:
. .
소정의 실시형태에서, 화합물은 약 0.01㎎/㎏ 내지 약 1000㎎/㎏ 또는 약 1㎎/㎏ 내지 약 500㎎/㎏의 화합물의 용량으로 환자에게 투여된다.In certain embodiments, the compound is administered to a patient at a dose of about 0.01 mg / kg to about 1000 mg / kg or about 1 mg / kg to about 500 mg / kg of the compound.
소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 발작적 편두통, 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통, 무전조 편두통, 편두통양 장애, 월경 편두통, 복부 편두통, 아동기 주기적 증후군 또는 군발성 두통이다.In certain embodiments, the migraine headache is seizure-like migraine, chronic migraine, retinal migraine, ocular migraine migraine, migraine headache, migraine headache disorder, menstrual migraine, abdominal migraine, childhood periodic syndrome or cluster headache.
소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 발작적 편두통, 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통, 무전조 편두통 또는 군발성 두통이다.In certain embodiments, the migraine is a seizure type migraine, a chronic migraine, a retina migraine, an ophthalmoplegia migraine, an electroless migraine or a cluster headache.
소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 조짐 편두통(고전적 편두통)이다. In certain embodiments, the migraine headache is a headache migraine (classic migraine headache).
소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 무조짐 편두통(일반 편두통)이다. In certain embodiments, the migraine headache is a non-migraine migraine (general migraine headache).
소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 이질통이 수반된다.In certain embodiments, the migraine head is accompanied by allodynia.
소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 방법은 약 1 내지 10㎎/㎏, 약 10㎎/㎏ 내지 약 250㎎/㎏, 약 20㎎/㎏ 내지 약 150㎎/㎏, 약 30㎎/㎏ 내지 약 125㎎/㎏, 약 40㎎/㎏ 내지 약 110㎎/㎏, 약 50㎎/㎏ 내지 약 100㎎/㎏, 약 60㎎/㎏ 내지 약 90㎎/㎏, 또는 약 70㎎/㎏ 내지 약 90㎎/㎏의 화합물을 투여하는 단계를 포함한다. In certain embodiments, the method comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the invention in an amount of about 1 to 10 mg / kg, about 10 mg / kg to about 250 mg / kg, about 20 mg / kg to about 150 mg / Kg, from about 40 mg / kg to about 110 mg / kg, from about 50 mg / kg to about 100 mg / kg, from about 60 mg / kg to about 90 mg / Kg of the compound.
소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 방법은 약 1㎎/㎏, 약 2.5㎎/㎏, 약 5㎎/㎏, 약 10㎎/㎏, 약 15㎎/㎏, 약 20㎎/㎏, 약 25㎎/㎏, 약 30㎎/㎏, 약 50㎎/㎏, 약 70㎎/㎏, 또는 약 100㎎/㎏의 화합물을 투여하는 단계를 포함한다.In certain embodiments, the method comprises administering to a subject in need of treatment a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula I in an amount of about 1 mg / kg, about 2.5 mg / kg, about 5 mg / kg, about 10 mg / kg, about 15 mg / , About 30 mg / kg, about 50 mg / kg, about 70 mg / kg, or about 100 mg / kg of the compound.
소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 방법은 1일 약 2회, 1일 약 1회, 2일 1회, 3일 1회, 4일 1회, 5일 1회, 1주 약 1회, 2주 약 1회, 또는 4주 약 1회 화합물을 투여하는 단계를 포함한다. In certain embodiments, the method comprises administering to a subject in need thereof at least one dose per day, at least once per day, at once per day, once per day, once per day, once per day, once per day, once per day, once per day, once per week, 1, or about once every 4 weeks.
또 다른 양태에서, 본 발명은 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 피질 확산성 억제 또는 피질 확산성 억제에 의해 발생한 질환 또는 병태를 치료 또는 억제 또는 예방하는 방법에 관한 것이고, 상기 방법은 약제학적 유효량의 하기로 표시되는 화합물 또는 이의 약제학적으로 허용되는 염을 상기 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함한다:In another aspect, the invention is directed to a method of treating, inhibiting or preventing a disease or condition caused by inhibiting cortical spreading or inhibiting cortical spread in a patient in need thereof, said method comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of Comprising administering to the patient a compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof that is displayed:
. .
또 다른 양태에서, 본 발명은 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 장기간 편두통 후 후유증을 치료 또는 경감시키는 방법에 관한 것이고, 상기 방법은 약제학적 유효량의 하기로 표시되는 화합물 또는 이의 약제학적으로 허용되는 염을 상기 환자에게 투여하는 단계를 포함한다:In another embodiment, the invention is directed to a method of treating or alleviating a long-term post-migraine episode in a patient in need thereof, which method comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound represented by the following, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, Comprising administering to a patient:
. .
소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 화합물은 약 0.01㎎/㎏ 내지 약 1000㎎/㎏의 화합물의 용량으로 환자에게 투여된다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 화합물은 약 1㎎/㎏ 내지 약 500㎎/㎏의 용량으로 환자에게 투여된다.In certain embodiments, the compound is administered to a patient at a dose of about 0.01 mg / kg to about 1000 mg / kg of compound. In certain embodiments, the compound is administered to a patient at a dose of about 1 mg / kg to about 500 mg / kg.
소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 방법은 약 1㎎/㎏ 내지 10㎎/㎏, 약 1㎎/㎏ 내지 20㎎/㎏; 약 10㎎/㎏ 내지 약 250㎎/㎏, 약 20㎎/㎏ 내지 약 150㎎/㎏, 약 30㎎/㎏ 내지 약 125㎎/㎏, 약 40㎎/㎏ 내지 약 110㎎/㎏, 약 50㎎/㎏ 내지 약 100㎎/㎏, 약 60㎎/㎏ 내지 약 90㎎/㎏, 또는 약 70㎎/㎏ 내지 약 90㎎/㎏의 화합물을 투여하는 단계를 포함한다. In certain embodiments, the method comprises administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound selected from the group consisting of about 1 mg / kg to 10 mg / kg, about 1 mg / kg to 20 mg / kg; From about 10 mg / kg to about 250 mg / kg, from about 20 mg / kg to about 150 mg / kg, from about 30 mg / kg to about 125 mg / Kg to about 100 mg / kg, about 60 mg / kg to about 90 mg / kg, or about 70 mg / kg to about 90 mg / kg of the compound.
소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 방법은 약 20㎎/㎏, 약 25㎎/㎏, 약 30㎎/㎏, 약 50㎎/㎏, 약 70㎎/㎏, 1㎎/㎏, 5㎎/㎏, 10㎎/㎏, 15㎎/㎏, 20㎎/㎏ 또는 약 100㎎/㎏의 화합물을 투여하는 단계를 포함한다.In certain embodiments, the method comprises administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of at least one of the following: about 20 mg / kg, about 25 mg / kg, about 30 mg / kg, about 50 mg / kg, about 70 mg / Mg / kg, 15 mg / kg, 20 mg / kg or about 100 mg / kg of the compound.
소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 방법은 1일 약 2회, 1일 약 1회, 2일 1회, 3일 1회, 4일 1회, 5일 1회, 1주 약 1회 또는 2주 약 1회 또는 예를 들어 1개월 1회 화합물을 투여하는 단계를 포함한다. In certain embodiments, the method comprises administering to a subject about two times per day, about once per day, once per day, once per day, once per day, once per day, once per day, once per day, once per week, Once or once a month for example.
소정의 실시형태에서, 상기 방법은 오피오이드, 항우울제, 항간질제, 비스테로이드 소염 약물(NSAID), 세로토닌 5HT1B/1D 작용제, N-메틸-D-아스파르테이트 길항제 또는 소염 화합물과의 병용투여를 추가로 포함한다.In certain embodiments, the method further comprises the co-administration of an opioid, an antidepressant, an antiepileptic agent, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), a serotonin 5HT1B / 1D agonist, an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, do.
NMDAR 활성화는 많은 실험 모의에서 SD의 현상을 촉진하거나 심지어 이것에 필수일 수 있다. 따라서, NMDAR의 과활성화를 방지하는 화합물은 편두통 공격의 발병을 감소시키고 심지어 예방하기 위한 중요한 새로운 치료제일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 하기 기재된 GLYX-13은 시험관내 해마회 슬라이스에서 SD의 생성 및 전파를 억제한다. 소정의 실험에서, GLYX-13은 세포외 칼륨 농도의 국소 증가에 의해 SD의 유도를 완전히 예방할 수 있고/있거나, 차단되지 않는 경우, 이것은 완전히 SD 전파의 속도를 느리게 할 수 있다. 더욱이, GLYX-13은 SD 이후 이의 원래 크기로 수상돌기 가시의 복원을 개선할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 예방학적으로 및/또는 급성 기준으로 환자에서 편두통을 치료하는 방법이 본 명세서에 제공된다. 이러한 투여는 환자에서 중증도(또는 몇몇 실시형태에서, 중지) 편두통 공격을 완화할 수 있다.NMDAR activation may promote or even require the development of SD in many experimental simulations. Thus, compounds that prevent overactivation of NMDAR can be an important new therapeutic agent to reduce or even prevent the onset of migraine attacks. For example, GLYX-13, described below, inhibits the generation and propagation of SD in the in vitro hippocampal slice. In certain experiments, GLYX-13 can completely prevent the induction of SD by local increase in extracellular potassium concentration and / or if it is not blocked, this can completely slow the rate of SD propagation. Furthermore, GLYX-13 can improve the restoration of dendritic visibility to its original size after SD. For example, methods for treating migraine in a patient on a prophylactic and / or acute basis are provided herein. Such administration can alleviate the severity (or, in some embodiments, halting) migraine attacks in the patient.
소정의 실시형태에서, 환자는 인간이다. 고려되는 환자는 여성 환자 및/또는 청소년 환자를 포함한다. In certain embodiments, the patient is a human. Patients considered include female patients and / or adolescent patients.
치료 내성 환자에서 편두통(예를 들어, 발작적 편두통, 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통, 무전조 편두통, 편두통양 장애, 월경 편두통, 복부 편두통, 아동기 주기적 증후군 또는 군발성 두통) 또는 예를 들어 적어도 1개, 또는 적어도 2개의, 다른 화합물 또는 치료제의 적절한 과정에 반응하지 않고/않거나 않고 있는 편두통을 겪는 환자에서 불응성 편두통을 치료하는 방법이 본 명세서에 또한 제공된다. 예를 들어, a) 임의로 치료 내성으로 환자를 확인하는 단계 및 b) 상기 환자에게 GLYX-13의 유효 용량을 투여하는 단계를 포함하는, 치료 내성 환자에서 편두통(예를 들어, 발작적 편두통, 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통, 무전조 편두통, 편두통양 장애, 월경 편두통, 복부 편두통, 아동기 주기적 증후군 또는 군발성 두통)을 치료하는 방법이 본 명세서에 제공된다. 소정의 실시형태에서, 편두통은 조짐 편두통이다.Migraine headache, migraine headache disorder, menstrual migraine, abdominal migraine, childhood periodic syndrome, or cluster headache), or in the treatment of a migraine headache, for example, in migraine-resistant patients (e.g., seizure disorders, chronic migraine, chronic migraine, Methods for treating refractory migraine in a patient suffering from migraine without, or not responding to, appropriate treatment of at least one, or at least two, other compounds or therapeutic agents, are also provided herein. (E. G., Seizure type migraine, chronic migraine, chronic migraine headache) in a patient who is resistant to therapy, comprising the steps of: a) identifying the patient with a therapeutic tolerance, and b) administering an effective dose of GLYX- , Retinal migraine, ocular muscle palsy migraine, migraine migraine, migraine headache disorder, menstrual migraine, abdominal migraine, childhood periodic syndrome or cluster headache) are provided herein. In certain embodiments, the migraine is an ataxia migraine.
일 실시형태에서, 예를 들어 단일 단위 용량으로 GLYX 펩타이드의 유효량을 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 편두통(예를 들어, 발작적 편두통, 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통, 무전조 편두통, 편두통양 장애, 월경 편두통, 복부 편두통, 아동기 주기적 증후군 또는 군발성 두통)을 급성으로 치료하는 방법이 본 명세서에 제공된다. 예를 들어, 본 명세서에 일 실시형태에서 GLYX-13의 유효량을 급성으로(예를 들어, 단일 용량) 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 편두통 공격의 발병에서 이를 필요로 하는 환자에서 편두통을 치료하는 방법이 고려된다. 이러한 방법은 상기 투여 후 약 2주 이하, 1주 이하, 1일 이하 또는 1시간 이하(예를 들어 15분 이하, 1시간 반 이하) 동안 편두통의 적어도 하나의 증상의 환자를 경감시킬 수 있다. 몇몇 실시형태에서, 이러한 방법은 상기 투여 후 약 1일 이상, 1주 이상 또는 2주 이상 동안 편두통의 적어도 하나의 증상의 환자를 경감시킬 수 있다. 예를 들어, 편두통을 겪는 환자에게 GLYX 펩타이드의 유효량을 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 방법이 본 명세서에 제공되고, 상기 환자는 편두통을 치료하기 위한 또 다른 약제가 투여된 동일한 환자와 비교하여 GLYX 펩타이드의 제1 투여 후 실질적으로 초기에 편두통의 적어도 하나의 증상이 실질적으로 경감된다. 당해 분야의 당업자는 급성 투여의 이러한 방법이 병원 또는 외래 환자 환경에서 유리할 수 있다는 것을 이해할 것이다. 본 명세서에 기재된 방법은 조짐 편두통 동안 발생하는 이질통의 치료 동안 또한 유용할 수 있다. In one embodiment, there is provided a method of treating a migraine headache comprising administering an effective amount of a GLYX peptide, e. G., In a single unit dose, to a patient in need thereof for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment or prevention of migraine (e. G., Seizure migraine, chronic migraine, retina migraine, Methods for acutely treating a migraine headache, migraine headache disorder, migraine headache disorder, menstrual migraine, abdominal migraine, childhood periodic syndrome or cluster headache headache are provided herein. For example, a method of treating migraine in a patient in need thereof in the onset of a migraine attack comprising administering an effective amount of GLYX-13 in an acute (e. G., Single dose) . Such a method may alleviate the patient of at least one symptom of migraine for less than about 2 weeks, less than 1 week, less than 1 day, or less than 1 hour (e.g., less than 15 minutes, less than 1.5 hours) after the administration. In some embodiments, the method may alleviate a patient having at least one symptom of migraine for at least about 1 day, at least 1 week, or more than 2 weeks after the administration. For example, a method is provided herein that includes administering an effective amount of a GLYX peptide to a patient suffering from migraine, wherein the patient is administered an effective amount of a GLYX peptide as compared to the same patient to which another agent for treating migraine is administered At least one symptom of migraine is substantially relieved substantially early after the first administration. One of ordinary skill in the art will appreciate that this method of acute administration may be beneficial in a hospital or outpatient setting. The methods described herein may also be useful during the treatment of allodynia occurring during an ocular migraine.
본 방법은 우울증을 가지거나, 외상성 뇌 손상, 간질을 겪거나, 뇌졸중의 위험에 있는 환자의 치료에서 또한 사용될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 일 실시형태에서, GLYX 펩타이드, 예를 들어 GLYX-13의 유효량을 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 외상성 뇌 손상을 치료하는 방법이 본 명세서에 제공된다. 또 다른 실시형태에서, GLYX 펩타이드, 예를 들어 GLYX-13의 유효량을 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 간질을 치료하는 방법이 제공된다.The method may also be used in the treatment of patients with depression, traumatic brain injury, epilepsy, or at risk of stroke. For example, in one embodiment, a method of treating a traumatic brain injury comprising administering an effective amount of a GLYX peptide, such as GLYX-13, is provided herein. In another embodiment, a method of treating epilepsy comprising administering an effective amount of a GLYX peptide, e. G., GLYX-13, is provided.
심혈관 병태 이외에, 조짐 편두통 환자는 다른 신경학적 및/또는 정신적인 병태 및 장애에 대한 위험이 증가할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 주우울증 또는 자살 시도와 함께 조짐 편두통의 동시발생이 자발적 경련을 발생시킬 위험을 증가시키는 것으로 나타났다(Hesdorffer et al., Epilepsy Res. 75(2-3):220-223, 2007). 조짐 편두통과 연관된 다른 병태는 NO 활성의 상당히 더 높은 마커, 우울증의 발병률의 증가, 및 일반 집단의 것보다 실질적으로 더 높은 뇌졸중에 대한 유전적 바이오마커 상관관계를 포함한다(Etminan et al., #MJ330(7482):63, 2005). 임의의 이들 병태를 가지거나 이의 위험이 있는 편두통 환자는 이 질환을 치료하거나 관리하기 위한 약제를 취할 수 있고, 이들 약제는 조짐 편두통의 치료를 위한 현재 사용되는 약제와 부정적으로 상호작용할 수 있다. 본 명세서에 기재된 바대로, 이들 병태 중 몇몇은 트립탄 치료(예를 들어, 뇌졸중 및 수마트립탄 치료)에 금기이다. 더구나, FDA는 세로토닌 재흡수 저해제(SSRI) 또는 선택적 세로토닌/노르에피네프린 재흡수 저해제(SNRI)인 소정의 항우울제와 함께 트립탄이 사용될 때 발생할 수 있는 생명을 위협하는 증상인 세로토닌 증후군과 관련하여 2006년에 공중 건강 권고를 발행하였다. 따라서, 본 명세서에 기재된 방법은 우울증을 가지는 환자 또는 뇌졸중을 겪거나 이의 위험에 있는 환자의 치료에 유용할 수 있다. In addition to cardiovascular disease, patients with sign migraine may be at increased risk for other neurological and / or mental conditions and disorders. For example, coincidence of major migraine with major depression or suicide attempts has been shown to increase the risk of spontaneous seizures (Hesdorffer et al., Epilepsy Res. 75 (2-3): 220-223, 2007) . Other conditions associated with the sign migraine include a significantly higher marker of NO activity, an increased incidence of depression, and a genetically biomarker correlation to a stroke substantially greater than that of the general population (Etminan et al., ≪ RTI ID = 0.0 & MJ 330 (7482): 63, 2005). Migraine sufferers having or at risk for any of these conditions may take medicines to treat or manage the disease and these medicines may interact negatively with currently used medications for the treatment of migraine headache. As described herein, some of these conditions are contraindicated for tryptic therapy (e.g., stroke and hydatidactate treatment). In addition, the FDA has concluded that in relation to serotonin syndrome, a life-threatening symptom that may occur when a tryptan is used with a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or a selective serotonin / norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) And published public health recommendations. Thus, the methods described herein may be useful in the treatment of patients with depression or those suffering from or at risk of stroke.
투약량Dosage
본 개시내용의 임의의 조성물의 투약량은 증상, 환자의 연령 및 체중, 치료하거나 예방하고자 하는 장애의 성질 및 중증도, 투여의 경로, 및 본 조성물의 형태에 따라 변할 것이다. 임의의 본 제제는 단일 용량 또는 분할 용량으로 투여될 수 있다. 본 개시내용의 조성물을 위한 투약량은 당해 분야에서 당업자에게 공지된 기법에 의해 또는 본 명세서에 교시된 바대로 용이하게 결정될 수 있다. 일반적으로, 화합물이 예를 들어, 0.05㎎ 내지 3000mg(고체 형태로서 측정된), 예를 들어 약 10㎎ 내지 약 500㎎, 또는 예를 들어, 약 1 내지 약 200㎎/㎏의 일일 투약량으로 인간에게 투여될 때 성공적인 결과가 얻어질 수 있다. 용량 범위는 예를 들어 10 내지 1000mg(예를 들어, 50 내지 800mg)을 포함한다. 몇몇 실시형태에서, 50, 100, 150, 200, 225, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500, 550, 600, 650, 700, 750, 800, 850, 900, 950, 또는 1000㎎의 화합물이 투여된다. 대안적으로, 투약량은 환자의 체중을 사용하여 계산될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 환자에게 투여되는 화합물, 또는 이의 약제학적 조성물의 용량은 1 내지 500㎎/㎏(예를 들어, 5 내지 250㎎/㎏)의 범위일 수 있다. 예시적인 비제한적인 실시형태에서, 용량은 5 내지 200㎎/㎏(예를 들어, 1, 2, 2.5, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 또는 50㎎/㎏) 또는 15 내지 100㎎/㎏(예를 들어, 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 또는 200㎎/㎏)의 범위일 수 있다. 예시적인 비제한적인 실시형태에서, 용량은 1 내지 15㎎/㎏, 50 내지 100㎎/㎏, 60 내지 90㎎/㎏, 또는 70 내지 80㎎/㎏의 범위일 수 있다. The dosage of any composition of the disclosure will vary depending on the symptom, the age and weight of the patient, the nature and severity of the disorder to be treated or prevented, the route of administration, and the form of the composition. Any of the present agents may be administered in a single dose or in divided doses. Dosages for the compositions of this disclosure can be readily determined by techniques known to those skilled in the art or as taught herein. Generally, the compound is administered in a daily dose of, for example, 0.05 mg to 3000 mg (measured as a solid form), e.g., from about 10 mg to about 500 mg, or, for example, from about 1 to about 200 mg / A successful result can be obtained. The dose range includes, for example, 10 to 1000 mg (e.g., 50 to 800 mg). In some embodiments, the compound of Formula I is administered at a dose of 50, 100, 150, 200, 225, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500, 550, 600, 650, 700, 750, 800, 850, 900, 950, Lt; / RTI > Alternatively, the dosage can be calculated using the patient ' s body weight. For example, the dose of a compound administered to a patient, or a pharmaceutical composition thereof, may range from 1 to 500 mg / kg (e.g., 5 to 250 mg / kg). In an exemplary non-limiting embodiment, the dose is in the range of 5 to 200 mg / kg (e.g., 1, 2, 2.5, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, (For example, 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, or 200 mg / kg). In an exemplary non-limiting embodiment, the dose may range from 1 to 15 mg / kg, 50 to 100 mg / kg, 60 to 90 mg / kg, or 70 to 80 mg / kg.
GLYX-13은 높은 치료 지수를 제공할 수 있다. 예를 들어, GLYX-13은 약 1 내지 약 10㎎/㎏, 약 10 내지 약 200㎎/㎏, 예를 들어 약 30㎎/㎏, 약 75㎎/㎏, 또는 약 100㎎/㎏의 i.v. 또는 피하 용량 범위로 치료학적으로 효과적일 수 있다. 몇몇 실시형태에서, 예를 들어 500㎎/㎏(i.v)의 용량에서 운동실조가 발생하지 않는다.GLYX-13 can provide a high therapeutic index. For example, GLYX-13 may be administered at a dose of about 1 to about 10 mg / kg, about 10 to about 200 mg / kg, such as about 30 mg / kg, about 75 mg / kg, or about 100 mg / kg i.v. Or < / RTI > subcutaneous dose range. In some embodiments, no ataxia occurs at a dose of, for example, 500 mg / kg (i.v).
치료의 용도에 필요한 GLYX 펩타이드의 치료학적 유효량은 치료되는 병태의 형태, 원하는 치료 시간의 기간, 환자의 연령 및 병태에 따라 변하고, 궁극적으로 주치의에 의해 결정된다. 원하는 용량은 2주, 1주, 6주, 5주, 4주, 3주, 2주 또는 1일 동안 효과적인 단일 용량으로, 또는 적절한 간격으로 투여되는 수회 용량, 예를 들어 매일 2회, 3회, 4회 이상의 하위용량으로 편리하게 투여될 수 있다.The therapeutically effective amount of GLYX peptide required for therapeutic use will vary depending upon the type of condition being treated, the duration of the desired treatment time, the age and condition of the patient, and ultimately determined by the attending physician. The desired dose may be administered in single effective doses for 2 weeks, 1 week, 6 weeks, 5 weeks, 4 weeks, 3 weeks, 2 weeks, or 1 day, or several doses administered at appropriate intervals, , ≪ / RTI > may be conveniently administered at least four sub-doses.
유효 용량 또는 양, 및 제제의 투여의 시기에 대한 임의의 가능한 효과는 본 개시내용의 임의의 특정한 조성물에 대해 확인될 필요가 있을 수 있다. 이것은 동물의 하나 이상의 군(바람직하게는 군마다 적어도 5마리의 동물)을 사용하여 본 명세서에 기재된 바와 같은 일상 실험에 의해 또는 적절한 경우 인간 실험에서 달성될 수 있다. 임의의 본 조성물의 유효성 및 치료 또는 예방의 방법은 조성물을 투여하고, 하나 이상의 적용 가능한 지수를 측정하고, 이 지수의 치료 후의 값을 치료 전의 동일한 지수의 값과 비교함으로써 투여의 효과를 평가함으로써 평가될 수 있다.The effective dose or amount, and any possible effect on the timing of administration of the agent, may need to be ascertained for any particular composition of the present disclosure. This can be accomplished by routine experimentation as described herein using at least one group of animals (preferably at least five animals per group) or, if appropriate, in a human experiment. The effectiveness and the method of treatment or prevention of any of the present compositions can be assessed by assessing the effect of the administration by administering the composition, measuring one or more applicable indices, and comparing the post-treatment value of the index to the value of the same index prior to treatment .
소정의 환자에서 가장 효과적인 치료를 생성하는 임의의 특정한 본 조성물의 투여의 정확한 시간 및 양은 본 조성물의 활성, 약동학, 및 생체이용률, 환자의 생리학적 상태(연령, 성별, 질환 유형 및 단계, 일반 신체 상태, 소정의 투약량에 대한 반응성 및 약제의 유형 포함), 투여의 경로 등에 따라 달라질 것이다. 본 명세서에 제시된 가이드라인은 치료를 최적화하기 위해 사용될 수 있어서, 예를 들어 대상체의 모니터링 및 투약량 및/또는 시기의 조정으로 이루어진 단지 일상적 실험을 필요로 하는, 투여의 최적 시간 및/또는 양을 결정한다.The exact time and amount of administration of any particular composition that will produce the most effective treatment in a given patient will depend upon a variety of factors including the activity, pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the composition, the physiological condition of the patient (age, sex, disease type and stage, Condition, responsiveness to a given dosage, and type of drug), route of administration, and the like. The guidelines set forth herein may be used to optimize treatment, for example, to determine the optimal time and / or amount of administration, which requires only routine experimentation with monitoring of the subject and adjustment of dosage and / or timing do.
대상체가 치료되면서, 환자의 건강은 치료 기간 동안 미리 결정된 시간에 하나 이상의 관련 지수를 측정함으로써 모니터링될 수 있다. 조성물, 양, 투여의 시간 및 제제를 포함하는 치료는 이러한 모니터링의 결과에 따라 최적화될 수 있다. 동일한 매개변수를 측정함으로써 개선의 정도를 결정하기 위해 환자를 주기적으로 재평가할 수 있다. 투여되는 본 조성물의 양(들) 및 가능하게는 투여의 시간의 조정은 이 재평가에 기초하여 이루어질 수 있다.As the subject is being treated, the patient ' s health can be monitored by measuring one or more relevant indices at a predetermined time during the treatment period. The compositions, amounts, times of administration, and treatments comprising the agents can be optimized according to the results of such monitoring. The patient can be periodically reassessed to determine the degree of improvement by measuring the same parameters. Adjustment of the amount (s) of the composition to be administered and possibly the time of administration may be made based on this reassessment.
치료는 화합물의 최적 용량보다 낮은 더 작은 투약량으로 개시될 수 있다. 이후, 투약량은 최적 치료학적 효과가 획득될 때까지 작은 증분으로 증가할 수 있다.The treatment may be initiated with a smaller dose lower than the optimal dose of the compound. Thereafter, the dosage can be increased in small increments until an optimal therapeutic effect is obtained.
상이한 물질의 효과의 발생 및 기간이 상보성일 수 있으므로, 본 조성물의 사용은 조성물에 함유된 임의의 개별 물질에 필요한 투약량을 감소시킬 수 있다.Since the occurrence and duration of effects of different substances may be complementary, the use of the present compositions may reduce the dosage required for any individual substance contained in the composition.
본 조성물의 독성 및 치료 효율은 예를 들어 LD50 및 ED50을 결정하기 위해 세포 배양물 또는 실험 동물에서 표준 약제학적 절차에 의해 결정될 수 있다.The toxicity and therapeutic efficacy of the present compositions may be determined by standard pharmaceutical procedures in cell cultures or experimental animals, for example to determine LD50 and ED50.
세포 배양 검정 및 동물 연구로부터 얻은 데이터는 인간에서 사용하기 위한 투약량의 범위를 제제화하는 데 사용될 수 있다. 임의의 본 조성물의 투약량은 바람직하게는 아주 적은 독성으로 또는 독성 없이 ED50을 포함하는 순환 농도의 범위 내에 있다. 투약량은 이용된 투약량 형태 및 사용된 투여의 경로에 따라 이 범위 내에 변할 수 있다. 본 개시내용의 조성물의 경우, 치료학적 유효 용량은 세포 배양 검정으로부터 초기에 예측될 수 있다.Data from cell culture assays and animal studies can be used to formulate a range of dosage for use in humans. The dosage of any of the present compositions is preferably in the range of circulating concentrations that include ED50 with little or no toxicity. Dosages may vary within this range depending on the dosage form employed and the route of administration used. For compositions of this disclosure, the therapeutically effective dose can be initially predicted from cell culture assays.
소정의 실시형태에서, GLYX 펩타이드는 예방학적 조치로서(즉, 전구증상 단계 전에) 투여된다. 소정의 실시형태에서, GLYX 펩타이드는 전구증상 동안 투여된다. 소정의 실시형태에서, GLYX 펩타이드는 조짐에서 투여된다. "조짐에서"란 조짐의 발병 후 및 편두통 통증의 발병 전의 임의의 시간을 의미한다. 소정의 실시형태에서, GLYX 펩타이드는 편두통 통증의 발병 후에 투여된다. 소정의 실시형태에서, GLYX 펩타이드는 예를 들어 이의 증상을 감소시키기 위해 후구증상 동안 투여된다.In certain embodiments, the GLYX peptide is administered as a prophylactic measure (i. E., Prior to the pre-symptomatic phase). In certain embodiments, the GLYX peptide is administered during prodromal symptoms. In certain embodiments, the GLYX peptide is administered in an indication. By "on indication" is meant any time after onset of symptoms and before the onset of migraine pain. In certain embodiments, the GLYX peptide is administered after the onset of migraine pain. In certain embodiments, the GLYX peptide is administered during a glomeruloneal condition to, for example, reduce its symptoms.
용어 "치료한다"는, 본 명세서에 사용되는 바대로, 예방학적 치료 또는 본 명세서에 기재된 질환, 장애, 또는 병태의 하나 이상의 증상 또는 컨디션을 예방하는 치료(예를 들어, 통증 또는 조짐 편두통 및 이질통 동반 또는 부재)를 의미한다. 예방학적 치료는 예를 들어 (예를 들어, 편두통 조짐에서) 질환, 장애 또는 병태의 발병에 선행하는 사건 전에("예비노출 예방") 또는 후에("노출 후 예방") 개시될 수 있다. 본 명세서에 기재된 GLYX 펩타이드, 또는 이의 약제학적으로 허용되는 염 또는 용매화물, 또는 이의 약제학적 조성물의 투여를 포함하는 예방적 치료는 급성, 단기간 또는 만성일 수 있다. 투여되는 용량은 예방학적 치료의 과정 동안 변할 수 있다. 또한 문헌[Kaniecki et al., "Treatment of Primary Headache: Preventive Treatment of Migraine." In: Standards of Care for Headache Diagnosis and Treatment. Chicago (IL): National Headache Foundation; 2004, p. 40-52]을 참조한다.The term "treat ", as used herein, refers to a prophylactic treatment or treatment to prevent one or more symptoms or conditions of the disease, disorder or condition described herein (e.g., pain or signs of migraine and allodynia Accompanied or absent). Prophylactic treatment may be initiated prior to (e. G., Pre-exposure prevention) or after (e. G., Post-exposure prevention) an event prior to the onset of a disease, disorder or condition (e. Prophylactic treatment, including administration of a GLYX peptide, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, or a pharmaceutical composition thereof, as described herein, may be acute, short term or chronic. The dose administered may vary during the course of prophylactic treatment. See also Kaniecki et al., "Treatment of Primary Headache: Preventive Treatment of Migraine." In: Standards of Care for Headache Diagnosis and Treatment. Chicago (IL): National Headache Foundation; 2004, p. 40-52].
제제Formulation
본 개시내용의 GLYX 펩타이드는 당해 분야에 널리 공지된 바대로 이의 의도하는 용도에 따라 다양한 수단에 의해 투여될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 본 개시내용의 조성물이 경구로 투여되는 경우, 이것은 정제, 캡슐, 과립제, 산제 또는 시럽으로서 제제화될 수 있다. 대안적으로, 본 개시내용의 제제는 주사(정맥내, 근육내 또는 피하), 드랍 점적주사 제제 또는 좌제로서 비경구로 투여될 수 있다. 안과용 점막 경로에 의한 도포를 위해, 본 개시내용의 조성물은 점안액 또는 안연고로서 제제화될 수 있다. 이 제제는 종래의 수단에 의해 제조될 수 있고, 원하는 경우, 조성물은 임의의 종래의 첨가제, 예컨대 부형제, 결합제, 붕괴제, 활택제, 교정제, 가용화제, 현탁 조제, 유화제 또는 코팅제와 함께 사용될 수 있다.The GLYX peptides of the present disclosure can be administered by various means depending on the intended use thereof as is well known in the art. For example, when the compositions of the present disclosure are administered orally, it can be formulated as tablets, capsules, granules, powders or syrups. Alternatively, the formulation of the present disclosure can be administered parenterally as an injection (intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous), drop-on injection, or as a suppository. For application by ocular mucosal route, the compositions of the present disclosure may be formulated as eye drops or ointments. The formulation can be prepared by conventional means and, if desired, the composition can be used with any conventional additives such as excipients, binders, disintegrants, lubricants, correctives, solubilizers, suspending aids, emulsifiers or coatings .
발현 벡터로 편입된, GLYX 펩타이드를 코딩하는 DNA가 생체내 GLYX 펩타이드를 발현시키기 위해 임의의 공지된 투여 방법을 사용하여 또한 투여될 수 있다.DNA encoding a GLYX peptide, incorporated into an expression vector, may also be administered using any known method of administration to express the GLYX peptide in vivo.
본 발명의 제제에서, 습윤제, 유화제 및 활택제, 예컨대 황산 라우릴 나트륨 및 스테아르산마그네슘, 및 착색제, 이형제, 코팅제, 감미료, 향료 및 향료제, 보존제 및 항산화제는 제제화제로서 존재할 수 있다.In the formulations of the present invention, wetting agents, emulsifiers and lubricants, such as sodium lauryl sulfate and magnesium stearate, and colorants, release agents, coatings, sweeteners, flavoring and perfuming agents, preservatives and antioxidants may be present as formulatory agents.
본 조성물은 경구, 국소(협측 및 설하 포함), 직장, 질내, 에어로졸 및/또는 비경구 투여에 적합할 수 있다. 제제는 단위 투약량 형태로 편리하게 제시될 수 있고, 약학의 분야에 널리 공지된 임의의 방법에 의해 제조될 수 있다. 단일 용량을 생성하기 위해 담체 재료와 조합될 수 있는 조성물의 양은 치료되는 대상체, 및 특정한 투여 방식에 따라 변한다.The compositions may be suitable for oral, topical (including buccal and sublingual), rectal, vaginal, aerosol and / or parenteral administration. The formulations may conveniently be presented in unit dosage form and may be prepared by any of the methods well known in the art of pharmacy. The amount of composition that can be combined with the carrier material to produce a single dose will vary depending upon the subject being treated, and the particular mode of administration.
이 제제의 제조 방법은 본 개시내용의 회합 조성물을 담체 및 임의로 하나 이상의 보조 성분과 놓는 단계를 포함한다. 일반적으로, 제제는 균일하게 친밀하게 액체 담체, 또는 미분된 고체 담체, 또는 둘 다와 회합 물질이 되게 하고, 이후 필요한 경우 생성물을 성형함으로써 제조된다.The method of manufacture of this preparation comprises the step of placing the associative composition of the present disclosure with the carrier and optionally one or more accessory ingredients. In general, the formulations are prepared by uniformly and intimately bringing into liquid carriers, or finely divided solid carriers, or both, and associative materials, and then, if necessary, shaping the product.
경구 투여에 적합한 제제는 캡슐, 카세, 환제, 정제, 로젠지(가향 기제, 보통 수크로스 및 아카시아 또는 트라가칸스를 사용), 분말, 과립의 형태로, 또는 수성 또는 비수성 액체 중의 용액 또는 현탁액으로서, 또는 수중유 또는 유중수 액체 에멀션으로서, 또는 엘릭시르제 또는 시럽으로서, 또는 파스틸로서(불활성 기제, 예컨대 젤라틴 및 글라이세린, 또는 수크로스 및 아카시아를 사용) 사용될 수 있고, 각각은 활성 성분으로서 이의 본 조성물의 미리 결정된 양을 함유한다. 본 개시내용의 조성물은 볼루스, 연약 또는 페이스트로서 또한 투여될 수 있다.Formulations suitable for oral administration may be in the form of capsules, cachets, pills, tablets, lozenges (using a base, usually sucrose and acacia or tragacanth), powders, granules, or as solutions or suspensions in aqueous or non- , Or as an oil-in-water or water-in-oil liquid emulsion, or as an elixir or syrup, or as pastilles (using an inert base such as gelatin and glycerin, or sucrose and acacia) Of the present composition. The composition of the present disclosure may also be administered as a bolus, soft or paste.
경구 투여를 위한 고체 투약량 형태(캡슐, 정제, 환제, 드라제, 산제, 과립제 등)의 경우에, 본 조성물은 하나 이상의 약제학적으로 허용되는 담체, 예컨대 시트르산나트륨 또는 인산이이칼슘, 및/또는 하기 중 임의와 혼합될 수 있다: (1) 충전제 또는 증량제, 예컨대 전분, 락토스, 수크로스, 글루코스, 만니톨 및/또는 규산; (2) 결합제, 예컨대 카복시메틸셀룰로스, 알기네이트, 젤라틴, 폴리비닐 피롤리돈, 수크로스 및/또는 아카시아 등; (3) 습윤제, 예컨대 글라이세롤; (4) 붕괴제, 예컨대 한천-한천, 탄산칼슘, 감자 또는 타피오카 전분, 알긴산, 특정 규산염, 및 탄산나트륨; (5) 용액 지연제, 예컨대 파라핀; (6) 흡수 가속제, 예컨대 4차 암모늄 화합물; (7) 습윤제, 예컨대 아세틸 알코올 및 글라이세롤 모노스테아레이트 등; (8) 흡수제, 예컨대 고령토 및 벤토나이트 점토; (9) 활택제, 이러한 탈크, 스테아르산칼슘, 스테아르산마그네슘, 고체 폴리에틸렌 글라이콜, 황산 라우릴 나트륨, 및 이의 혼합물; 및 (10) 착색제. 캡슐, 정제 및 환제의 경우에, 조성물은 완충제를 또한 포함할 수 있다. 유사한 유형의 고체 조성물은 락토스 또는 유당과 같은 부형제, 및 고분자량 폴리에틸렌 글라이콜 등을 사용하여 연질 및 경질 충전 젤라틴 캡슐에서 충전제로서 또한 사용될 수 있다.In the case of solid dosage forms (capsules, tablets, pills, dragees, powders, granules, etc.) for oral administration, the compositions may contain one or more pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, such as sodium citrate or di-calcium phosphate, and / (1) fillers or extenders such as starch, lactose, sucrose, glucose, mannitol and / or silicic acid; (2) binders such as carboxymethylcellulose, alginate, gelatin, polyvinylpyrrolidone, sucrose and / or acacia; (3) wetting agents such as glycerol; (4) disintegrators such as agar-agar, calcium carbonate, potato or tapioca starch, alginic acid, specific silicates, and sodium carbonate; (5) solution retarders such as paraffin; (6) absorption accelerators such as quaternary ammonium compounds; (7) wetting agents such as acetyl alcohol and glycerol monostearate; (8) absorbents such as kaolin and bentonite clay; (9) lubricants, such as talc, calcium stearate, magnesium stearate, solid polyethylene glycol, sodium lauryl sulfate, and mixtures thereof; And (10) a colorant. In the case of capsules, tablets and pills, the composition may also comprise buffering agents. Solid compositions of a similar type may also be used as fillers in soft and hard-filled gelatin capsules using excipients such as lactose or lactose, and high molecular weight polyethylene glycols and the like.
정제는 임의로 하나 이상의 보조 성분에 의해 압축 또는 성형에 의해 제조될 수 있다. 압축 정제는 결합제(예를 들어, 젤라틴 또는 하이드록시프로필메틸 셀룰로스), 활택제, 불활성 희석제, 보존제, 붕괴제(예를 들어, 나트륨 전분 글라이콜레이트 또는 가교결합된 나트륨 카복시메틸 셀룰로스), 표면-활성 또는 분산제를 사용하여 제조될 수 있다. 성형 정제는 적합한 기계에서 불활성 액체 희석제에 의해 습윤된 본 조성물의 혼합물을 성형함으로써 제조될 수 있다. 정제, 및 다른 고체 투약량 형태, 예컨대 드라제, 캡슐, 환제 및 과립제는 임의로 빗금 표시되거나 코팅 및 쉘, 예컨대 장용 코팅 및 약제 제제 분야에 널리 공지된 다른 코팅에 의해 제조될 수 있다.Tablets may optionally be made by compression or molding with one or more accessory ingredients. Compressed tablets may be prepared by conventional means such as binding agents (e.g., gelatin or hydroxypropylmethylcellulose), lubricants, inert diluents, preservatives, disintegrants (e. G., Sodium starch glycolate or crosslinked sodium carboxymethylcellulose) May be prepared using an active or dispersing agent. Molded tablets may be prepared by molding a mixture of the present composition wetted by an inert liquid diluent in a suitable machine. Tablets, and other solid dosage forms, such as dragees, capsules, pills, and granules, may optionally be prepared by shading or other coatings well known in the art of coatings and shells such as enteric coatings and pharmaceutical formulations.
경구 투여를 위한 액체 투약량 형태는 약제학적으로 허용되는 에멀션, 마이크로에멀션, 용액, 현탁액, 시럽 및 엘릭시르제를 포함하다. 본 조성물 이외에, 액체 투약량 형태는 당해 분야에서 흔히 사용되는 불활성 희석제, 예를 들어 물 또는 다른 용매, 가용화제 및 유화제, 예컨대 에틸 알코올, 아이소프로필 알코올, 에틸 카보네이트, 에틸 아세테이트, 벤질 알코올, 벤질 벤조에이트, 프로필렌 글라이콜, 1,3-뷰틸렌 글라이콜, 오일(특히, 면실유, 땅콩유, 옥수수유, 배아유, 올리브유, 캐스터유 및 참깨유), 글라이세롤, 테트라하이드로퓨릴 알코올, 소르비탄의 폴리에틸렌 글라이콜 및 지방산 에스터, 사이클로덱스트린 및 이들의 혼합물을 함유할 수 있다.Liquid dosage forms for oral administration include pharmaceutically acceptable emulsions, microemulsions, solutions, suspensions, syrups and elixirs. In addition to the present compositions, the liquid dosage forms may be formulated with inert diluents commonly used in the art such as water or other solvents, solubilizing agents and emulsifiers such as ethyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, ethyl carbonate, ethyl acetate, benzyl alcohol, benzyl benzoate (Especially cottonseed oil, peanut oil, corn oil, germ oil, olive oil, castor oil and sesame oil), glycerol, tetrahydrofuryl alcohol, sorbitol, Polyethylene glycols of fatty acids, fatty acid esters, cyclodextrins, and mixtures thereof.
현탁액은, 본 조성물 이외에, 예를 들어 에톡실화 아이소스테아릴 알코올, 폴리옥시에틸렌 소르비톨 및 소르비탄 에스터, 미결정질 셀룰로스, 알루미늄 메타하이드록사이드, 벤토나이트, 한천-한천 및 트라가칸스, 및 이들의 혼합물과 같은 현탁제를 함유할 수 있다.Suspensions may contain, in addition to the present compositions, suspensions of the active ingredient, such as, for example, ethoxylated isostearyl alcohols, polyoxyethylene sorbitol and sorbitan esters, microcrystalline cellulose, aluminum metahydroxide, bentonite, agar-agar and tragacanth, , ≪ / RTI > and the like.
직장 또는 질내 투여를 위한 제제는, 본 조성물을 예를 들어 코코아 버터, 폴리에틸렌 글라이콜, 좌약 왁스 또는 살리실레이트를 포함하는 하나 이상의 적합한 비자극 부형제 또는 담체와 혼합함으로써 제조될 수 있고, 실온에서 고체이지만, 신체 온도에서 액체이고, 따라서 체강에서 용융하고 활성제를 방출하는, 좌제로서 제시될 수 있다. 질내 투여에 적합한 제제는 적절한 것으로 당해 분야에 공지된 바와 같은 담체를 함유하는 파세리, 탐폰, 크림, 겔, 페이스트, 폼(foam) 또는 스프레이 제제를 또한 포함한다.Formulations for rectal or vaginal administration may be prepared by mixing the compositions with one or more suitable non-excipient excipients or carriers, including, for example, cocoa butter, polyethylene glycol, suppository wax or salicylate, , But may be presented as a suppository that is liquid at body temperature and therefore melts in the body cavity and releases the active agent. Formulations suitable for vaginal administration also include parcels, tampons, creams, gels, pastes, foams or spray formulations containing carriers as are known in the art as being suitable.
본 조성물의 경피 투여를 위한 투약량 형태는 분말, 스프레이, 연고, 페이스트, 크림, 연고, 겔, 용액제 및 패치를 포함한다.Dosage forms for transdermal administration of the compositions include powders, sprays, ointments, pastes, creams, ointments, gels, solutions and patches.
국소 눈 투여를 위해, 본 발명의 조성물은, 병용 치료의 경우에 단위 투약량이 치료학적 유효량의 활성 성분 또는 이의 일부 멀티플을 포함하도록 제제화된, 용액, 겔, 연고제, 현탁액 또는 고체 인서트의 형태를 취할 수 있다.For topical ocular administration, the compositions of the present invention may take the form of solutions, gels, ointments, suspensions or solid inserts in unit dosage amounts formulated to contain a therapeutically effective amount of the active ingredient, .
비경구 투여에 적합한 본 발명의 약제학적 조성물은 사용 바로 전에 무균 주사용 용액 또는 분산액으로 재구성될 수 있고, 항산화제, 완충제, 세균발육저지제, 제제가 의도되는 수혜자의 혈액과 등장성이 되게 하는 용질 또는 현탁제 또는 증점제를 함유할 수 있는, 하나 이상의 약제학적으로 허용되는 무균 등장성 수성 또는 비수성 용액, 분산액, 현탁액 또는 에멀션, 또는 무균 분말과 조합하여 본 조성물을 포함한다.The pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention suitable for parenteral administration may be reconstituted with an aseptic injectable solution or dispersion immediately prior to use and may be formulated to contain an antioxidant, a buffering agent, a bacterial growth inhibiting agent, an agent that is isotonic with the blood of the intended recipient Dispersions, suspensions or emulsions, or sterile powders, which may contain one or more pharmaceutically acceptable sterile isotonic aqueous or nonaqueous solutions, solubilizers or suspending agents or thickening agents.
본 발명의 약제학적 조성물에서 사용될 수 있는 적합한 수성 및 비수성 담체의 예는 물, 에탄올, 폴리올(예컨대 글라이세롤, 프로필렌 글라이콜, 폴리에틸렌 글라이콜 등), 및 적합한 이들의 혼합물, 식물성 오일, 예컨대 올리브유 및 주사용 유기 에스터, 예컨대 에틸 올레에이트 및 사이클로덱스트린을 포함한다. 적절한 유동성은 예를 들어 코팅 재료, 예컨대 레시틴의 사용에 의해, 분산액의 경우에 필요한 입자 크기의 유지에 의해, 및 계면활성제의 사용에 의해 유지될 수 있다.Examples of suitable aqueous and nonaqueous carriers that may be used in the pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention include water, ethanol, polyols (such as glycerol, propylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, etc.), and mixtures thereof, vegetable oils , Such as olive oil and injectable organic esters such as ethyl oleate and cyclodextrin. Proper fluidity can be maintained, for example, by the use of coating materials such as lecithin, by the maintenance of the required particle size in the case of dispersions, and by the use of surfactants.
병용 치료Combination therapy
본 명세서에 기재된 임의의 GLYX 펩타이드(예를 들어, GLYX-13)는 단독으로 또는 본 명세서에 기재된 임의의 질환 또는 병태를 치료하거나 예방하는 다른 물질과 조합되어 사용될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 몇몇 병용 치료에서, 치료학적 화합물의 하나 이상의 투약량은 단독으로 투여될 때 표준 투약량으로부터 감소할 수 있다.Any of the GLYX peptides described herein (e. G., GLYX-13) may be used alone or in combination with other substances to treat or prevent any of the diseases or conditions described herein. For example, in some combination therapies, one or more dosages of the therapeutic compound may be decreased from a standard dosage when administered alone.
본 발명의 방법은 또한 GLYX 펩타이드와 오피오이드, 항우울제, 항간질제, 비-스테로이드 소염 약물(NSAID), 세로토닌 5HT1B/1D 작용제, N-메틸-D-아스파르테이트 길항제 또는 소염 화합물의 병용 투여를 포함한다.The methods of the invention also include the concomitant administration of GLYX peptides with opioids, antidepressants, antiepileptics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), serotonin 5HT1B / 1D agonists, N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists or anti-inflammatory compounds.
본 개시내용은 소정의 실시형태에서 단독의 또는 하나 이상의 다른 항우울제 치료, 예컨대 트라이사이클릭 항우울제, MAO-I, SSRI, 및 이중 및 삼중 재흡수 저해제 및/또는 편두통(예를 들어, 발작적 편두통, 만성 편두통, 망막 편두통, 안구근육마비 편두통, 무전조 편두통, 편두통양 장애, 월경 편두통, 복부 편두통, 아동기 주기적 증후군 또는 군발성 두통)을 치료하기 위한 약제의 제조를 위한 불안완화 약물과 조합된 GLYX 펩타이드 또는 펩타이드의 사용에 관한 것이다. GLYX 펩타이드와 조합되어 사용될 수 있는 예시적인 약물은 아나프라닐, 아다핀, 아벤틸, 엘라빌, 노르프라민, 파멜라, 페르토프란, 시네퀀, 수르몬틸, 토프라닐, 비박틸, 파르네이트, 나르딜, 마르플란, 셀렉사, 렉사프로, 루복스, 팍실, 프로작, 졸로프트, 웰부트린, 이펙사, 레메론, 사임발타, 데시렐(트라조돈) 및 루디오밀을 포함한다.This disclosure is based, in some embodiments, on the use of single or more than one other antidepressant treatment such as tricyclic antidepressant, MAO-I, SSRI, and dual and triple reabsorption inhibitors and / or migraine A GLYX peptide in combination with an anxiolytic drug for the manufacture of a medicament for treating a migraine headache, a migraine headache, a retinal migraine headache, an ocular migraine headache, a migraine headache disorder, a migraine headache disorder, a menstrual migraine headache, Lt; / RTI > peptide. Exemplary drugs that may be used in combination with the GLYX peptide include anapranil, adapine, avenyl, elabyl, And include rheumatoid, desirel (trazodone), and rudiodmil. In addition, the compounds of the present invention can be used in combination with other drugs.
소정의 실시형태에서, 오피오이드는 알펜타닐, 부토르파놀, 부프레노르핀, 덱스트로모다마이드, 데조신, 덱스트로프로폭시펜, 코데인, 다이하이드로코데인, 다이펜옥실레이트, 에토르핀, 펜타닐, 하이드로코돈, 하이드로모르폰, 케토베미돈, 로페라마이드, 레보르파놀, 레보메타돈, 메프타지놀, 메타돈, 모르핀, 모르핀-6-글루코로나이드, 날부핀, 날록손, 옥시코돈, 옥시모르폰, 펜타조신, 페티딘, 피리트라마이드, 프로폭시펜, 레미펜타닐, 술펜타닐, 틸리딘 및 트라마돌로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된다. In certain embodiments, the opioid is selected from the group consisting of alfentanil, butorphanol, buprenorphine, dextromodamide, dezocine, dextrorphoxifene, codeine, dihydrocodeine, diphenoxylate, , Hydrocodone, hydro morphone, ketobemidone, loperamide, levorphanol, levomadone, mettazinol, methadone, morphine, morphine-6-glucononide, nalbuphine, naloxone, oxycodone, oxymorphone, penta Is selected from the group consisting of benzoic acid, benzoic acid, benzoic acid, benzoic acid, benzoic acid, benzoic acid, benzoic acid, benzoic acid,
소정의 실시형태에서, 항우울제는 아디나졸람, 알라프로클레이트, 아민프틴, 아미트립틸린/클로르디아제폭사이드 배합물, 아티파메졸, 아자미안세린, 바지나프린, 베푸랄린, 비페멜란, 비노달린, 비페나몰, 브로파로민, 카복사존, 세리클라민, 시아노프라민, 시목사톤, 시탈로프람, 셀레프롤, 클로복사민, 다제피닐, 데아놀, 데멕시프틸린, 다이벤제핀, 도티에핀, 드록시도파, 에넥페신, 에스타졸람, 에토페리돈, 페목세틴, 펜가빈, 페졸라민, 플루오트라센, 이다족산, 인델록사진, 이프린돌, 레보프로틸린, 리튬, 리톡세틴, 로페프라민, 메디폭사민, 메타프라민, 메트랄린돌, 미안세린, 밀나시프란, 미나프린, 미르타자핀, 몬티렐린, 네브라세탐, 네포팜, 니알라마이드, 노미펜신, 노르플루옥세틴, 오로티렐린, 옥사플로잔, 피나제팜, 피를린돌, 피조틸린, 리탄세린, 롤리프람, 세르클로레민, 세티프틸린, 시부트라민, 술부티아민, 술피리드, 테닐록사진, 토졸리논, 티롤리베린, 티아네프틴, 티플루카르빈, 트라조돈, 토페나신, 토파미소팜, 톨록사톤, 토목세틴, 베랄리프리드, 빌록사진, 비쿠알린, 지멜리딘 및 조메타핀으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된다.In certain embodiments, the antidepressant is selected from the group consisting of adinazolam, allproclaite, aminethytin, amitriptyline / chlorodiaxanthoxide combination, atipamozole, azamylancerin, vasinaprin, befuralin, bipemelan, , Biphenamol, broparomine, carpazone, sericramine, cianoframine, cymoxatone, citalopram, celefrole, clofammin, tadafinil, decanol, But are not limited to, ziprin, ditinepine, droxidopa, enecethexine, esthazolam, etoparidone, femetecine, fengabine, But are not limited to, but are not limited to, thiazolidinediones, thiazolidinediones, thiazolidinediones, thiazolidinediones, thiazolidinediones, Norfloxacin, orotrielin, oxaflozan, pinazepam, pirolindol, pizotillin, ri Wherein the compound is selected from the group consisting of serine, thiamine, threonine, threonine, threonine, serine, threonine, threonine, threonine, threonine, threonine, threonine, Tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol, tocopherol and tocopherol.
소정의 실시형태에서, 항간질제는 카르바마제핀, 플루피르틴, 가바펜틴, 라모트리긴, 옥스카르바제핀, 페니토인, 레티가빈, 토피라메이트 및 발프로에이트로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된다.In certain embodiments, the anti-epileptic agent is selected from the group consisting of carbamazepine, flupirtine, gabapentin, ramotrygin, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, retigavine, topiramate, and valproate.
소정의 실시형태에서, NSAID는 아세메타신, 아스피린, 셀레콕시브, 데라콕시브, 디클로페낙, 디플루니살, 에텐자마이드, 에토페나메이트, 에토리콕시브, 페노프로펜, 플루페남산, 플루르비프로펜, 로라졸락, 로르녹시캄, 이부프로펜, 인도메타신, 이속시캄, 케부존, 케토프로펜, 케토롤락, 나프록센, 나부메톤, 니플룸산, 술린닥, 톨메틴, 피록시캄, 메클로페남산, 메페남산, 멜록시캄, 메타미졸, 모페부타존, 옥시펜부타존, 파레콕시브, 페니돈, 페닐부타존, 피록시캄, 프로파세타몰, 프로피페나존, 로페콕시브, 살리실아마이드, 수프로펜, 티아프로펜산, 테녹시캄, 발데콕시브, 4-(4-사이클로헥실-2-메틸옥사졸-5-일)-2-플루오로벤젠설폰아마이드, N-[2-(사이클로헥실옥시)-4-나이트로페닐]메탄설폰아마이드, 2-(3,4-다이플루오로페닐)-4-(3-하이드록시-3-메틸뷰톡시)-5-[4-(메틸설포닐)페닐]-3(2H)-피리다지논, 및 2-(3,5-다이플루오로페닐)-3-[4-(메틸설포닐)페닐]-2-사이클로펜텐-1-온으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된다.In certain embodiments, the NSAID is selected from the group consisting of acetemethicone, aspirin, celecoxib, deracoxib, diclofenac, diflunisal, ethenamicide, etopenamate, etoricoxib, fenoprofen, flufenamic acid, Norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, norepinephrine, But are not limited to, camphor, camphor, camphor, camphor, camphor, camphor, camphor, camphor, camphor, camphor, camphoric acid, (4-cyclohexyl-2-methyloxazol-5-yl) -2-fluorobenzenesulfonamide < / RTI > 4- (3-hydroxy-3-methylbutoxy) -4-nitrophenyl] methanesulfonamide, N- [2- (cyclohexyloxy) Phenyl] -3 (2H) -pyridazinone, and 2- (3,5-difluorophenyl) -3- [4- (methylsulfonyl) phenyl] 2-cyclopenten-l-one.
소정의 실시형태에서, 세로토닌 5HT1B/1D 작용제는 엘레트립탄, 프로바트립탄, 나라트립탄, 리자트립탄, 수마트립탄 및 졸미트립탄으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된다.In certain embodiments, the serotonin 5HT1B / 1D agonist is selected from the group consisting of eletriptan, probutriptan, narutriptan, lizatriptan, sumatriptan and zolmitriptan.
소정의 실시형태에서, N-메틸-D-아스파르테이트 길항제는 아만타딘, 압티가넬, 베손프로딜, 부디핀, 코난토킨 G, 델루세민, 덱사나비놀, 덱스트로메토르판, 덱스트로프로폭시펜, 펠바메이트, 플루오로펠바메이트, 가시클리딘, 글라이신, 이페녹사존, 카이토세팔린, 케타민, 케토베미돈, 라니세민, 리코스티넬, 미다포텔, 메만틴, D-메타돈, D-모르핀, 밀나시프란, 네라멕산, 오르페나드린, 레마세미드, 술파조신, FPL-12,495(라세마이드 대사물질), 토피라메이트, (αR)-α-아미노-5-클로로-1-(포스포노메틸)-1H-벤즈이미다졸-2-프로판산, 1-아미노사이클로펜탄-카복실산, [5-(아미노메틸)-2-[[[(5S)-9-클로로-2,3,6,7-테트라하이드로-2,3-다이옥소-1H-,5H-피리도[1,2,3-데]퀴녹살린-5-일]아세틸]아미노]페녹시]-아세트산, α-아미노-2-(2-포스포노에틸)-사이클로헥산프로판산, α-아미노-4-(포스포노메틸)-벤젠아세트산, (3E)-2-아미노-4-(포스포노메틸)-3-헵텐산, 3-[(1E)-2-카복시-2-페닐에테닐]-4,6-다이클로로-1H-인돌-2-카복실산, 2-하이드록시-N,N,N-트라이메틸-에타나미눔과의 8-클로로-2,3-다이하이드로피리다지노[4,5-b]퀴놀린-1,4-다이온 5-옥사이드 염, N'-[2-클로로-5-(메틸티오)페닐]-N-메틸-N-[3-(메틸티오)페닐]-구아니딘, N'-[2-클로로-5-(메틸티오)페닐]-N-메틸-N-[3-[(R)-메틸설피닐]페닐]-구아니딘, 6-클로로-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-9-메틸-2,3-다이옥소-1H-인데노[1,2-b]피라진-9-아세트산, 7-클로로티오키누렌산, (3S,4aR,6S,8aR)-데카하이드로-6-(포스포노메틸)-3-아이소퀴놀린카복실산, (-)6,7-다이클로로-1,4-다이하이드로-5-[3-(메톡시메틸)-5-(3-피리디닐)-4-H-1,2,4-트리아졸-4-일]-2,3-퀴녹살린다이온, 4,6-다이클로로-3-[(E)-(2-옥소-1-페닐-3-피롤리디닐리덴)메틸]-1H-인돌-2-카복실산, (2R,4S)-rel-5,7-다이클로로-1,2,3,4-테트라하이드로-4-[[(페닐아미노)카보닐]아미노]-2-퀴놀린카복실산, (3R,4S)-rel-3,4-다이하이드로-3-[4-하이드록시-4-(페닐메틸)-1-피페리디닐]-2H-1-벤조피란-4,7-다이올, 2-[(2,3-다이하이드로-1H-인덴-2-일)아미노]-아세트아마이드, 1,4-다이하이드로-6-메틸-5-[(메틸아미노)메틸]-7-나이트로-2,3-퀴녹살린다이온, [2-(8,9-다이옥소-2,6-다이아자바이사이클로[5.2.0]비-1(7)-엔-2-일)에틸]-포스폰산, (2R,6S)-1,2,3,4,5,6-헥사하이드로-3-[(2S)-2-메톡시프로필]-6,11,11-트라이메틸-2,6-메타노-3-벤자조신-9-올, 2-하이드록시-5-[[(펜타플루오로페닐)메틸]아미노]-벤조산, 1-[2-(4-하이드록시페녹시)에틸]-4-[(4-메틸페닐)메틸]-4-피페리디놀, 1-[4-(1H-이미다졸-4-일)-3-뷰티닐]-4-(페닐메틸)-피페리딘, 2-메틸-6-페닐에티닐)-피리딘, 3-(포스포노메틸)-L-페닐알라닌, 및 3,6,7-테트라하이드로-2,3-다이옥소-N-페닐-1H,5H-피리도[1,2,3-데]퀴녹살린-5-아세트아마이드로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된다. In certain embodiments, the N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist is selected from the group consisting of amantadine, attitergen, verson prodyl, todipine, conanthone G, delulcamine, dexanthinol, dextromethorphan, dextrope D-methadone, D-methadone, D-mannitol, D-mannitol, D-mannitol, D-mannitol, (Α) -α-amino-5-chloro-1- (phosgene), morphine, milnacipran, neramexane, orphenadrine, remasemide, sulfamazone, FPL-12,495 (racemate metabolite), topiramate (5S) -9-chloro-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-naphthalen-2-ylmethyl) 5-yl] acetyl] amino] phenoxy] -acetic acid, a-amino-2 - (2-phosphonoethyl) -cyclohexanepropanoic acid, -amino 3-heptenoic acid, 3 - [(1E) -2-carboxy-2-phenylethenyl] Chloro-2,3-dihydropyridazino [4, 5-dichloro-lH-indole-2-carboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-N, N, , 5-b] quinoline-1,4-dione 5-oxide salt and N '- [2-chloro-5- (methylthio) - [2 - [(R) -methylsulfinyl] phenyl] -guanidine, 6-chloro-2,3 (3S, 4aR, 6S, 6S) -7-methyl-2,3-dioxo-1H-indeno [1,2- b] pyrazine- (6,7-dichloro-1,4-dihydro-5- [3- (methoxymethyl) -5- (3-pyridinyl) -4-H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl] -2,3-quinoxalindane, Oxo-1-phenyl-3-pyrrolidinylidene) methyl] -1H-indole Carboxylic acid, (2R, 4S) -rel-5,7-dichloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-4 - [[(phenylamino) carbonyl] amino] -2-quinolinecarboxylic acid, Dihydro-3- [4-hydroxy-4- (phenylmethyl) -1-piperidinyl] -2H-1-benzopyran-4,7-diol Dihydro-6-methyl-5 - [(methylamino) methyl] -7-nitro (8,9-dioxo-2,6-diazabicyclo [5.2.0] non-1 (7) -en-2-yl) ethyl] -phosphate (2R, 6S) -1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydro-3 - [(2S) -2-methoxypropyl] -6,11,11-trimethyl- 1- [2- (4-hydroxyphenoxy) ethyl] - methano-3-benzazocin-9-ol and 2-hydroxy-5 - [[(pentafluorophenyl) (4-methylphenyl) methyl] -4-piperidinol, 1- [4- (1H- Methyl-6-phenylethynyl) -pyridine, 3- (phosphonomethyl) -L-phenylalanine, And 3,6,7-tetrahydro-2,3-dioxo-N-phenyl-1H, 5H-pyrido [1,2,3-de] quinoxaline-5-acetamide.
소정의 실시형태에서, 소염 화합물은 아스피린, 셀레콕시브, 코르티손, 데라콕시브, 에라콕시브, 디플루니살, 에토리콕시브, 페노프로펜, 이부프로펜, 케토프로펜, 나프록센, 프레드니솔론, 술린닥, 톨메틴, 피록시캄, 메페남산, 멜록시캄, 페닐부타존, 로페콕시브, 수프로펜, 발데콕시브, 4-(4-사이클로헥실-2-메틸옥사졸-5-일)-2-플루오로벤젠설폰아마이드, N-[2-(사이클로헥실옥시)-4-나이트로페닐]메탄설폰아마이드, 2-(3,4-다이플루오로페닐)-4-(3-하이드록시-3-메틸뷰톡시)-5-[4-(메틸설포닐)페닐]-3(2H)-피리다지논 및 2-(3,5-다이플루오로페닐)-3-[4-(메틸설포닐)페닐]-2-사이클로펜텐-1-온으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택된다.In certain embodiments, the anti-inflammatory compound is selected from the group consisting of aspirin, celecoxib, cortisone, deracoxib, eracoxib, diflunisal, etoricoxib, fenoprofen, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen, (4-cyclohexyl-2-methyloxazol-5-yl) benzoic acid, lauric acid, linalk, tolmetin, piroxycam, mefenamic acid, meloxicam, phenylbutazone, rofecoxib, 2- (3,4-difluorophenyl) -4- (3-hydroxymethyl) -2-fluorobenzenesulfonamide, N- [2- (cyclohexyloxy) -3-methylbutoxy) -5- [4- (methylsulfonyl) phenyl] -3 (2H) -pyridazinone and 2- (3,5- difluorophenyl) -3- [4- Methylsulfonyl) phenyl] -2-cyclopenten-l-one.
본 개시내용은 하기 비제한적인 예에 의해 예시된 다수의 양태를 가진다.The present disclosure has a number of aspects exemplified by the following non-limiting examples.
실시예 Example
실시예 1Example 1
본 명세서에 기재된 연구는 시험관내 해마회 슬라이스에서 수상돌기 가시 크기의 SD 유발 변화의 실시간 영상화를 위해 전파의 SD 속도, 및 2-광자 레이저 스캐닝 현미경검사의 세포외 다부위 전기생리학적 모니터링을 이용하였다. GLYX-13인 신규한 NMDAR 수용체 기능적 글라이신 부위 부분 작용제의 효과를 SD의 전파의 속도 및 한계치, 및 수상돌기 가시 형태에 대한 SD의 실시간 효과에서 대해 조사하였다. GLYX-13은 세포외 칼륨 농도의 국소 증가에 의해 SD의 유도를 때때로 완벽하게 방지하고, 지속적으로 이의 전파 속도를 늦추었다. 해마회 CA1 구역을 통한 SD의 통과는 뉴런 탈분극이 회복된 후 역전되는 수상돌기 가시의 신속한 수축을 생성시켰다. GLYX-13은 SD 후 이의 원래 크기 및 위치로의 수상돌기 가시의 복귀의 속도 및 정도를 개선하여서, 약물 및 NMDA 수용체 활성을 조절하는 기타가 반복 편두통 공격으로부터의 가능한 손상으로부터 뇌에서의 시냅스 연결을 보호할 수 있다는 것을 나타낸다.The studies described herein used SD velocities of radio waves and extracellular multi-site electrophysiologic monitoring of 2-photon laser scanning microscopy for real-time imaging of SD-induced changes in dendritic visibility size in in vitro hippocampal slices . The effect of the novel NMDAR receptor functional glycine site partial agonists of GLYX-13 was investigated in the real time effects of SD on the rate and threshold of propagation of SD and on the dendritic visibility form. GLYX-13 prevented the induction of SD from time to time by locally increasing the extracellular potassium concentration, and slowed its propagation rate constantly. The passage of SD through the hippocampal CA1 region produced a rapid contraction of the dendritic spines that reversed after neuronal depolarization was restored. GLYX-13 improves the rate and extent of the return of dendritic spines to the original size and position of the posterior segment of the SD, allowing the other to regulate drug and NMDA receptor activity from synaptic connections in the brain from possible damage from repeated migraine attacks Protection.
일반 방법General method
약물drug
모든 외부 및 패치 피펫 용액을 탈이온화 증류수(18 ㏁㎝-2 초과의 저항; Milli-Q 시스템)에 의해 만들었다. 세포외 및 세포내 용액을 만들기 위한 화학물질을 시그마-알드리치(Sigma-Aldrich)(미국 미조리주 세인트 루이스)로부터 구입하였다. 알렉사플루오르 594를 모레큘러 프로브즈(Molecular Probes)로부터 구입하였다.All external and patch pipette solutions were made with deionized distilled water (resistance greater than 18 MΩ cm -2 ; Milli-Q system). Chemicals for making extracellular and intracellular solutions were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Alexa Fluor 594 was purchased from Molecular Probes.
슬라이스 제조 및 세포외 기록Slice preparation and extracellular recording
14일 내지 21일령의 스프라그-다울리(등록상표) 랫트(Taconic Farms(뉴욕주 허드슨))로부터 해마회 슬라이스에서 실험을 수행하였다. 랫트를 아이소플루오란에 의해 깊게 마취시키고, 희생시키고, 뇌를 빨리 제거하고, 126 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 2.6 CaCl2, 1.3 MgCl2, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 26 NaHCO3, 및 11 글루코스(mM 단위)를 함유하는, 산소화된(95%의 O2 - 5%의 CO2), 얼음 냉각된 인공 뇌척수액(ACSF)에 위치시켰다. 뇌를 2등분하고, 이마엽을 절단하고, 슬라이싱 동안 계속해서 산소화된 얼음 냉각된 ACSF에서 액침된 스테이지에 부착된 사이아노아크릴레이트를 사용하여 개별 반구를 접착시켰다. 해마를 함유하는 400㎛ 두께의 두정 슬라이스를 바이브라톰(Leica 1200s)을 사용하여 절단하고, 최소 1시간 동안 실온에서 항온처리를 위해 계면 보유 챔버로 옮긴 후, 32℃에서 기록을 위해 Haas 스타일 계면 챔버로 옮겼다. 슬라이스를 실험의 시작 전에 95% O2/5% CO2에 의해 포화된 ACSF(4㎖/분; ACSF mM: NaCl 126; KCl 3; NaH2PO4 1.25; MgCl 1.3; CaCl2 2.5; NaHCO3 26; 글루코스 10)에 의해 관류시키고, 모든 약물을 욕 적용하였다.Experiments were performed on hippocampus slices from Sprague-Dawley (TM) rats (Taconic Farms, Hudson, NY) between 14 and 21 days of age. Anesthetic depth by a rat in iso-fluoran and, expense and, removing the brain quickly and, 126 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 2.6
세포외 기록을 Clampex(v. 9)에 의해 MultiClamp 700B(Axon Instruments)를 사용하여 수행하고, 1kHz에서 여과시키고, 3kHz에서 디지털화하였다. 저저항(ACSF에 의해 충전된 후 1 내지 2㏁) 기록 전극을 SD 개시 피펫으로부터 대략 150㎜ 거리 간격으로 CA1 구역의 방사층에서의 샤퍼 측부 말단 필드(Schaffer collateral termination field)의 정점 수지상 구역으로 삽입된 얇은 벽의 붕규산염 유리로부터 만들어서, SD의 속도를 모니터링하였다. 적외선 차등 간섭 대비(DIC) 광학부품이 장착된 Zeiss Axioskop 2FS 수직 현미경에 액침된 기록 챔버를 탑재하였다. 10x 대물렌즈를 사용하여 SD에 의해 발생한 슬라이스 휘도 변화를 영상화하였다. 휘도 변화를 PTI 마스터 시스템에 의해 제어되는 냉각된 CCD 카메라(CoolSNAP HQ)에 의해 100㎳마다 영상화하였다. 전기생리학적 데이터를 Clampfit 9에 의해 분석하였다. 영상화 데이터를 디지털화하고, ImageJ(NIH)에 의해 재구성하였다.Extracellular recordings were performed by Clampex (v. 9) using MultiClamp 700B (Axon Instruments), filtered at 1 kHz and digitized at 3 kHz. A low resistance (1 to 2 M OMEGA after being charged by ACSF) recording electrode was inserted into the apical dendritic zone of the Schaffer collateral termination field in the emissive layer of the CA1 zone at intervals of about 150 mm from the SD initiation pipette ≪ / RTI > was made from a thin walled borosilicate glass and the rate of SD was monitored. A recording chamber immersed in a
양극성 스테인리스 강 자극 전극(FHC(메인주 보도인))을 CA3 구역에서 샤퍼 측부-맞교 섬유(Schaffer collateral-commissural fiber)에 위치시키고, 각각 30초마다 최대 fEPSP의 대략 50%를 유발하도록(50 내지 100pA; 100㎲ 기간) 조정된 자극 강도에 의해 전류 펄스를 적용하였다. ISO-Flex 아이솔레이터로부터의 전기 자극을 마스터 8개 펄스 생성기(AMPI(이스라엘 예루살렘))에 의해 제어하고, Multiclamp 700B(모레큘러 디바이시스(Molecular Devices)(캘리포니아주 서니베일))에 의해 촉발하였다. 신호를 Digidata 1322에 의해 디지털화하고, Multiclamp 700B 증폭기를 사용하여 기록하였다. fEPSP 기울기를 최대 음성 편향의 20 내지 80%로부터 선형 외삽에 의해 측정하고, 기울기는 실험을 시작하기 전에 적어도 15분 동안 10% 내에로 안정한 것으로 확인시켜주었다. IBM 호환 개인용 컴퓨터에서 Clampfit(Version 9; Axon Instrument)를 사용하여 데이터를 분석하였다. 유발된 fEPSP(최대 진폭의 50%, 2 내지 4mV)를 적어도 30분의 안정한 기준 기간 동안 방사층에서의 정점 수지상 필드에서 기록하였다.Place a bipolar stainless steel stimulation electrode (FHC (Main State Press)) in a Schaffer collateral-commissural fiber in the CA3 area and force each 50 seconds to produce approximately 50% of the maximum fEPSP every 30 seconds 100 pA; 100 기간 period). Current pulses were applied by the adjusted stimulus intensity. Electrical stimulation from an ISO-Flex isolator was controlled by a master eight pulse generator (AMPI, Israel Jerusalem) and triggered by Multiclamp 700B (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, Calif.). Signals were digitized by Digidata 1322 and recorded using a Multiclamp 700B amplifier. The fEPSP slope was measured by linear extrapolation from 20-80% of the maximal sound deflection and the slope was confirmed to be stable within 10% for at least 15 minutes before starting the experiment. Data was analyzed using Clampfit (Version 9; Axon Instrument) on IBM compatible personal computers. The induced fEPSP (50% of maximum amplitude, 2 to 4 mV) was recorded in the peak dendritic field in the emissive layer for a stable baseline period of at least 30 minutes.
해마회 확산성 억제의 유도Induction of hippocampal diffusion inhibition
해마의 급성 두정 슬라이스를 현미경 스테이지에서 액침된 기록 챔버로 옮기고, 가온된 ACSF(32℃)에 의해 관류시키고, 여기서 세포외 [K+]를 3㎖/분의 관류 속도에서 8mM으로 상승시켰다. 유리 피펫을 통해 3M KCl의 압력 주입 퍼프에 의해 확산성 억제를 개시시켰다. 50 내지 100㎳ 지속한 8 내지 10psi의 압력 펄스를 Picospritzer II(Parker Hannifin(뉴햄프셔주 홀리스))에 의해 구동하였다. 피펫 저항은 3M KCl에 의해 충전될 때 2±0.2㏁이었다. The hippocampal acute parietal slice was transferred to a recording chamber immersed in a microscope stage and perfused with warmed ACSF (32 ° C) where the extracellular [K + ] was elevated to 8 mM at a perfusion rate of 3 ml / min. Diffusion inhibition was initiated by a pressure injection puff of 3M KCl through a glass pipette. A pressure pulse of 8-10 psi lasting 50-100 ms was driven by Picospritzer II (Parker Hannifin, Holliss, NH). The pipette resistance was 2 ± 0.2 MΩ when filled with 3M KCl.
수상돌기Dendrite 가시 수축/회복의 동적 영상화 분석 Dynamic visualization analysis of visual contraction / recovery
15분 동안 알렉사 플루오르 594(100μM)에 의해 해마회 슬라이스에서 CA1 피라미드 뉴런을 로딩한 후, 상기 기재된 바대로 60x/1.1 nA 물 액침 적외선 대물렌즈와 4x 디지털 룸이 장착된 커스텀화 2-광자 레이저-스캐닝 Olympus BX61WI 현미경을 사용하여 3차 수상돌기를 영상화하였다(Zhang et al., 2008). 이동 바이어스를 피하기 위해 포커싱된 층으로부터의 ±3㎛의 범위의 XYZ 스캐닝 모드를 0.5㎛의 z 스테이지 간격으로 사용하고, 7초의 단일 깊이 프로필 시간에 대해 각각의 영상은 종료까지 0.45초가 걸렸다. 너무 많은 여기 광으로부터 작은 수상돌기 가시에 대한 광독성의 임의의 징후 및 형광의 포화를 피하기 위해 많은 관심을 취했다. 깊이 프로필을 5분 간격으로 반복하여 가능한 염료 광퇴색 및 광독성을 감소시켰다. 810nm으로 조정된 Mai/Tai 레이저(Solid-State Laser(캘리포니아주 마운틴 뷰))를 여기에 사용하고, 영상 획득을 Olympus FluoviewFV300 소프트웨어(Olympus America(뉴욕주 멜빌))에 의해 제어하였다. 최대로 오픈된 핀홀 및 배경에 대해 신호에 최적화된 방출 스펙트럼 창으로 공초점 레이저의 스캔 헤드 광전자증배관 관에 의해 동시형광을 검출하였다. 트랜스형광 경로에서, 565㎚의 색선별 거울을 사용하여 녹색 및 적색 형광을 분리시키고, 각각 HQ525/50 및 HQ605/50 방출 필터를 통해 통과시켜, 투과된 또는 반사된 여기 광(Chroma Technology(버몬트주 록킹햄))을 제거하고, 2개의 광전자증배관 관에 의해 동시에 검출하였다. 도면은 전체 6㎛ Z-프로필의 붕괴된 영상을 보여주고, 이 투영은 가시 용적의 지수로서 강도를 계산하기 위해 사용되었다.CA1 pyramidal neurons were loaded in hippocampal slices by Alexa Fluor 594 (100 [mu] M) for 15 minutes, then customized two-photon laser-equipped with 60x / 1.1 nA water immersion infrared objective and 4x digital room as described above, Scanning A third dendrite projection was imaged using an Olympus BX61WI microscope (Zhang et al., 2008). An XYZ scanning mode in the range of +/- 3 mu m from the focused layer was used at z stage intervals of 0.5 mu m from the focused layer to avoid movement bias and each image took 0.45 seconds to the end for a single depth profile time of 7 seconds. I took a lot of attention to avoid random indications of phototoxicity and saturation of fluorescence for small dendritic spines from too much excitation light. Depth profiles were repeated at 5 minute intervals to reduce possible dye fade and phototoxicity. Mai / Tai lasers (Solid-State Laser, Mountain View, CA) adjusted to 810 nm were used here and image acquisition was controlled by the Olympus FluoviewFV300 software (Olympus America, Melville, NY). Simultaneous fluorescence was detected by a scanhead photomultiplier tube of a confocal laser with a maximally open pinhole and an emission-optimized spectrum window for the signal to background. In the transfluorescent path, green and red fluorescence were separated using a 565 nm color-picking mirror and passed through HQ525 / 50 and HQ605 / 50 emission filters, respectively, to transmit or reflected excitation light (Chroma Technology Locking ham)) were removed and detected simultaneously by two photomultiplier tubes. The figure shows a collapsed image of the entire 6 탆 Z-profile, which projection was used to calculate the intensity as an exponent of the visible volume.
데이터 분석Data Analysis
기록 신호를 1kHz 컷오프 주파수에 의해 8개-극 베셀(Bessel) 저역 통과 필터를 통해 여과시키고, 100㎲의 간격으로 Clampex(V. 9)에 의해 샘플링하였다. fEPSP 기울기를 Clampfit(V.9)에 의해 계산한 후, 데이터를 Origin 6.1(Microcal Software(메사추세츠주))에 의해 추가로 처리하고, CorelDraw 10(Corel, Ottawa(캐나다 온타리오)에 의해 제시하였다. 모든 데이터를 변량의 일방향 분석(ANOVA), 또는 SPSS 소프트웨어(SPSS Inc.(일리노이주 시카고))를 사용하여 스튜던트 t 시험에 의해 분석하였다. 유의 수준을 P<0.05로 설정하였다. 데이터는 실험에 걸쳐 평균±SEM으로 제시된다.The recording signal was filtered by a 1 kHz cutoff frequency through an eight-pole Bessel low-pass filter and sampled by Clampex (V.9) at intervals of 100 μs. After the fEPSP slope was calculated by Clampfit (V.9), the data was further processed by Origin 6.1 (Microcal Software, MA) and presented by CorelDraw 10 (Corel, Ottawa, Ontario, Data were analyzed by Student's t test using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or SPSS software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) .The significance level was set at P < ± SEM.
결과result
해마회 슬라이스의 필드 CA1에서의 In the field CA1 of the seahorse slice 병소적Lesional 높은 [K+] 유도된 High [K +] induced 확산성Diffusibility 억제 control
[K+]o가 32℃에서 8mM으로 상승한 인공 뇌척수액(ACSF)에서, CA1 방사층에서의 필드로의 3M [K+]o의 단일 국소 퍼프(100㎳)(도 1, 상부 왼쪽)는, 해마의 전체 CA1 구역에 걸쳐 9±5.4㎜/분(n = 16)의 전파 속도로 분산하는, SD를 신뢰성 있게 유도하였다. 음성 필드 전위 이동(도 1, 상부 오른쪽)을 특징으로 하는 SD는 통상적으로 45초 초과로 지속하는 해마회 CA1 구역의 방사층 시냅스 층에서 -8±1.5 mV(n=30)의 최대 이동을 나타냈다.(Fig. 1, upper left) of 3M [K + ] o into the field in the CA1 emissive layer in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) where [K + ] o rose to 8 mM at 32 [ SD was reliably induced, spreading across the entire CA1 region of the hippocampus at a propagation velocity of 9 ± 5.4 mm / min (n = 16). SD characterized by a negative field potential shift (Fig. 1, upper right) showed a maximum shift of -8 ± 1.5 mV (n = 30) in the radial layer synaptic layer of the hippocampus CA1 region, which typically lasted more than 45 seconds .
SD를 10분마다 유도하여 K+의 세포외 공간 전도의 기간 및 유효 규모의 측정치인 음성 전위 이동의 면적(도 1, 상부 오른쪽, 빗금 구역)이 반복 SD에 의해 안정한지를 시험하였다. 개시 전극으로부터 기록된 음성 전위 이동의 면적이 600㎛ 멀리 원위 기록 전극에서보다 높지만(도 1, 하부), 부위 어느 하나에서 10분 간격으로 발생한 반복된 순차적 SD의 개별 삽화의 진폭 또는 전파 속도에 상당한 차이가 없었다(본페로니 다중 비교 시험, P>0.20). 이 결과는 재현 가능한 SD 음성 전위 이동이 적어도 처음 10 동안 해마의 필드 CA1에서 안정하게 반복하여 발생할 수 있다는 것을 나타낸다.SD was induced every 10 minutes to test whether the area of the negative potential transfer (Fig. 1, upper right, hatched area), which is a measure of the period of extracellular space conduction and the effective scale of K + , was stable by repeated SD. The area of the voice potential shift recorded from the start electrode is 600 占 퐉 far higher than in the distal recording electrode (Fig. 1, lower), but the amplitude or propagation speed of individual illustrations of repeated sequential SD There was no difference (multiple comparison of this ferroni, P > 0.20). This result indicates that the reproducible SD speech potential shift can occur stably and repeatedly in the field CA1 of the hippocampus for at least the first ten.
GLYX-13은 전파를 억제하고, 해마회 확산성 억제의 불응 기간을 증가시킨다GLYX-13 inhibits propagation and increases the refractory period of hippocampal spread inhibition
신규한 NMDA 수용체 글라이신 동시작용제 부위 부분 작용제 GLYX-13이 생리학적 범위 내에 NMDA 수용체 활성화를 조절하고 과도한 활성화를 방지함으로써 SD에 대한 한계치를 상승시키거나 이를 방지할 수 있다는 가설을 시험하기 위해, CA1 구역μ의 방사층으로 높은 [K+](패치 피펫 중의 1mM)의 간단한 분사 전에 GLYX-13을 1, 10, 또는 50㎛에서 해마회 슬라이스에 30분 동안 욕 적용하고, SD를 유발하도록 시도하였다. 용량-반응 관계를 처음에 나이브 슬라이스에서 높은 [K+] 분사의 시간에 기초하여 작도하고, 이후 30분 후 SD를 검출하기 위해 DC 전위를 기록하면서 3회의 시험 농도(1, 10 또는 50μM)의 각각에서 GLYX-13의 욕 적용하였다.To test the hypothesis that the novel NMDA receptor glycine co-agonist site partial agonist GLYX-13 can raise or prevent the limit on SD by regulating NMDA receptor activation within the physiological range and preventing excessive activation, Prior to the simple injection of high [K +] (1 mM in the patch pipette) into the emissive layer of μ, GLYX-13 was applied to the hippocampal slice at 1, 10, or 50 μm for 30 min and attempted to induce SD. The dose-response relationship was initially plotted on the basis of the time of high [K +] injection on the Naïve slice, and after 30 minutes thereafter, each of the three test concentrations (1, 10 or 50 μM) Was applied with a bath of GLYX-13.
적어도 3개의 SD를 약물 비함유 ACSF에서 초기에 유발한 후, 슬라이스를 GLYX-13에 의해 관류시키고 10분마다 SD를 유발하도록 계속하였다. 도 2, 상부에 예시된 바대로, 10μM의 GLYX-13의 경우, 개시 부위에서 SD의 개별 순차적 삽화의 기준 구역 사이의 상당한 차이가 없어서(본페로니 다중 비교 시험, P>0.20), GLYX-13이 SD의 개시를 변경하지 않는다는 것을 나타낸다.At least three SDs were induced initially in drug-free ACSF, and then the slice was perfused with GLYX-13 and continued to induce SD every 10 minutes. In the case of GLYX-13 at 10 [mu] M as illustrated in Figure 2 above, there was no significant difference between the reference regions of the individual sequential illustrations of SD at the initiation site (this ferroni multiple comparison test, P > 0.20) 13 does not change the start of SD.
반복 SD에 의해 근처(근위) 및 먼(원위) 기록 부위에서 SD 진폭의 관계에 영향을 미치는지를 GLYX-13을 다음에 시험하였다. 슬라이스를 10μM의 GLYX-13에 의해 관류하고, 10분마다 SD를 계속해서 유발하였다(도 2, 하부). 본페로니 다중 비교 시험(P>0.20)은 다시 대조군 슬라이드에서 SD의 개별 순차적 삽화의 구역 사이에 상당한 차이를 나타내지 않았다. GLYX-13은 근위 기록 부위에서 SD의 음성 전위 이동의 개시에 영향을 미치지 않았다.GLYX-13 was then tested to see if it affected the SD amplitude relationship at the near (proximal) and distant (distal) recording sites by repeated SD. The slice was perfused with 10 [mu] M GLYX-13 and SD was continuously induced every 10 minutes (Fig. 2, lower). This Peroni multiple comparison test ( P > 0.20) again did not show any significant differences between the zones of the individual sequential illustrations of SD in the control slides. GLYX-13 did not affect the initiation of the SD negative-potential translation at the proximal recording site.
개시 부위에서의 SD 진폭을 원격 부위(도 2, 하부)에서 SD의 음성 전위 부위의 구역과 상관시켰다. 따라서, GLYX-13의 부재 및 존재 하의 근위/원위 면적 비율을 비교하였다. 도 2, 하부에 예시된 바대로, 원격 부위와 개시 부위 사이의 면적 비율은 6번째 SD(6번째 SD)의 적용에 의해 10μM의 GLYX-13의 존재 하에 극적으로 감소하였다. 2방향 ANOVA는 3개의 상당한 효과를 나타냈다: 1) 모든 관찰에 비해 동일한 슬라이스에서 시간 효과 반복 SD(F(1, 12)=5.17, p<0.05); 2) 약물 치료로부터의 효과(F(1,12)=5.07, p<0.05); 및 3) 치료와의 시간의 상호작용(F(1,12)=30.91, p<0.01). 이 결과는 SD의 재발 음성 전위 이동이 원격 부위와 개시 부위 사이의 진폭 비율을 변경하고; 이 감소가 GLYX-13에 의해 현저히 증대된다는 것을 나타낸다. 이 발견은 GLYX-13이 특히 다수의 SD 사건 후에 뇌를 통한 SD의 전파를 상당히 억제할 수 있다는 것을 보여준다.The amplitude of SD at the initiation site was correlated with the region of the negative potential site of SD at the remote site (Fig. 2, bottom). Therefore, the ratio of proximal / distal area in the absence and presence of GLYX-13 was compared. As illustrated in Figure 2, lower, the area ratio between the remote site and the initiation site decreased dramatically in the presence of 10 μM GLYX-13 by application of the 6 th SD (6 th SD). Two-way ANOVA showed three significant effects: 1) Time effect repeat SD (F (1, 12) = 5.17, p <0.05) on the same slice compared to all observations; 2) Effect from medication (F (1,12) = 5.07, p <0.05); And 3) interaction of treatment with time (F (1,12) = 30.91, p <0.01). This result suggests that recurrent negative displacement of SD changes the amplitude ratio between the remote site and the initiation site; Indicating that this reduction is markedly enhanced by GLYX-13. This finding suggests that GLYX-13 can significantly inhibit the spread of SD through the brain, especially after multiple SD events.
이전의 연구에서, GLYX-13이 음성 필드 전위 이동의 진폭을 감소시키고 다수의 SD 후 가장 큰 효과인 전도 속도를 느리게 함으로써 SD의 전파를 제한할 수 있다는 것이 입증되었다. 각각의 SD 개시 사이의 간격을 짧게 함으로써, 대조군 슬라이스에서의 각각의 SD가 다음의 성공적인 SD 동안 3-4분의 절대 불응 기간을 가진다는 것이 발견되었다(n = 7). 10μM의 GLYX-13은 5-6분으로 이 불응 기간을 연장시켰다(n = 6). 도 3에 도시된 바대로, SD는 대조군 슬라이스(대조군)에서의 이전의 SD 후 5분에 성공적으로 일어날 수 있지만, GLYX-13(GLYX-13 30')에 의해 처리된 슬라이스에서는 일어날 수 없었다.Previous studies have demonstrated that GLYX-13 can limit the propagation of SD by reducing the amplitude of the speech field potential shift and slowing the conduction rate, the greatest effect after multiple SDs. By shortening the interval between each SD initiation, it was found that each SD in the control slice had an absolute refractory period of 3-4 minutes during the next successful SD (n = 7). 10 μM GLYX-13 prolonged this refusal period by 5-6 min (n = 6). As shown in FIG. 3, SD could successfully occur at 5 minutes after the previous SD in the control slice (control), but could not occur at the slice treated by GLYX-13 (GLYX-13 30 ').
SDSD 유도 Judo 세포외Extracellular 공간 용적 이동에 의해 생성된 광학 밀도의 고유 변화를 사용한 Using the intrinsic variation of the optical density produced by the space displacement SDSD 전파의 측정 Measurement of radio wave
유체가 탈분극된 세포로 돌진하고 이것이 팽윤되면서 SD는 세포외 공간 용적의 심오한 수축을 유발하고, 이것은 생체내 고유 광학 밀도의 변화로서 보일 수 있다. 이러한 휘도 강도 변화는 전파된 광 DIC 현미경검사를 사용하여 뇌 슬라이스에서 또한 용이하게 검출될 수 있다. 도 4A는 증가한 휘도의 SD "조짐"이 개시 피펫으로부터 확산하고 슬라이스에 걸쳐 전파하고, SD 전도 속도를 계산하기 위해 사용될 수 있다는 것을 보여주다(도 4B). 증가한 휘도의 시간 과정은 전기생리학적 기록을 사용하여 SD의 최대 음성 전위 이동과 잘 상관된다. 따라서, 거리에 의한 휘도 변화의 시간 과정의 계산은 SD 전도 속도를 측정하기 위한 정확하고 편리한 방식을 제공한다.As the fluid rushes into the depolarized cells and it swells, SD causes profound contraction of extracellular space volume, which can be seen as a change in intrinsic optical density in vivo. This intensity intensity change can also be easily detected in brain slices using propagated optical DIC microscopy. 4A shows that the SD "signature" of increased brightness can be used to diffuse from the initiation pipette, propagate across the slice, and calculate the SD conduction velocity (FIG. 4B). The time course of the increased luminance is well correlated with the maximum voice potential shift of SD using electrophysiological recordings. Thus, the calculation of the time course of the luminance change by distance provides an accurate and convenient way to measure the SD conduction velocity.
반복된 SD가 동일한 전도 속도를 나타내는지를 결정하기 위해, 도 4A의 상부에서 프로그래밍된 바대로 150㎛에 의해 분리된 5점에 걸쳐 휘도 변화를 모니터링하였다. 반복 측정에 의한 1방향 ANOVA는 SD가 P1로부터 P5로 개별 슬라이스 내에 정상 투과 속도를 유지시킨다(F(5, 35)=2.42, p>0.05)는 것을 나타낸다. 따라서, 투과 속도는 연속 삽화에 걸쳐 SD 안정성을 시험하고 연속적인 삽화에 걸쳐 시험하기 위해 P1로부터 P5로 사용될 수 있다. SD의 평균 전파 속도는 9.07±0.55㎜/분이고, 7.54 내지 11.14㎜/분(n=16) 범위이다.To determine if repeated SDs exhibited the same conduction rate, the luminance change was monitored over five points separated by 150 [mu] m as programmed at the top of Fig. 4A. One-way ANOVA by repeated measurements shows that SD maintains the normal permeation rate within the individual slice from P1 to P5 (F (5, 35) = 2.42, p> 0.05). Thus, the permeation rate can be used from P1 to P5 to test SD stability over successive illustrations and to test over successive illustrations. The average propagation velocity of SD is 9.07 0.55 mm / min, and is in the range of 7.54-11.14 mm / min (n = 16).
SD의 반복 삽화가 안정한 속도를 유지시키는지 및 GLYX-13이 SD 전도 속도에 영향을 미치는지를 시험하기 위해, 도 5에 예시된 바대로 6개의 후속 SD를 분석하기 위해 ANOVA 시험을 반복 측정에 의해 사용하였다. 분석은 대조군과 GLYX-13 처리된 슬라이스 사이에 상당한 차이를 나타냈다(F(1,50)=3.66, p <0.01). SD 서열은 전체 변량의 38.5%를 차지하여서, SD 전파 속도가 상당히 증가하는 SD 수에 의해 느려진다는 것(F(5,50)=14.01, p<0.01)을 나타낸다. 모든 반복 SD에 걸쳐 SD 전파 속도에 대한 GLYX-13 효과가 2방향 ANOVA에서 유의도에 도달하지 않더라도, SD의 수와 GLYX-13 처리 사이에 상당한 상호작용가 존재하여서(F(5,50)=2.53, P<0.05), GLYX-13(채워진 원)이 7번째 SD에 의해서만 SD 전파 속도를 상당히 감소시킨다는 것을 반영한다.To test whether the repeated illustrations of SD maintain stable rates and whether GLYX-13 affects SD conduction velocity, the ANOVA test is used by repeated measurements to analyze six subsequent SDs as illustrated in Figure 5 Respectively. The analysis showed a significant difference between the control and the GLYX-13 treated slice (F (1,50) = 3.66, p <0.01). The SD sequence accounts for 38.5% of the total variance, indicating that the SD propagation velocity is slowed by the significantly increasing number of SDs (F (5,50) = 14.01, p <0.01). There was a significant interaction between the number of SDs and the GLYX-13 treatment (F (5,50) = 2.53), even though the GLYX-13 effect on SD propagation rate across all repeats SD did not reach significance in the two-way ANOVA , P <0.05), reflecting that GLYX-13 (filled circle) significantly reduces the SD propagation rate only by the 7th SD.
확산성Diffusibility 억제는 CA1 피라미드 뉴런 Inhibition is the CA1 pyramidal neuron 수상돌기Dendrite 가시가 용적에서 가역적으로 수축하도록 한다 Allow thorns to shrink reversibly in volume
뇌에서의 피라미드 뉴런 수지세포의 해부학적 마이크로구조는 다양한 자극에 대해 반응하여 놀랍게도 신뢰도가 있다. 탈분극, 산소/포도당 박탈 및 N-메틸-D-아스파르테이트는 모두 시험관내 해마회 CA1 피라미드 뉴런에서 수상돌기 가시의 수축을 생성하는 것으로 나타났다. SD에 대한 가시의 반응을 조사하기 위해, 단일 CA1 피라미드 뉴런을 형광성 염료 알렉사플루오르-594에 의해 충전하고, 2-광자 레이저 스캐닝 현미경검사로부터 수집된 시리얼 z-스택 절편(0.2㎛ 단계 스패닝 5㎛)을 사용하여 수상돌기 가시 형상을 영상화하였다. CA1 피라미드로의 알렉사플루오르-594의 로딩이 뉴런 내에 평형 분포에 도달한 30분 후, SD를 해마회 슬라이스의 CA1 구역의 방사층(CA1 피라미드 뉴런의 정점 수지세포에서 샤펴 측부 액손 시냅스)으로 높은 [K+](패치 피펫에서의 1M)의 간단한 분사에 의해 개시시켰다. 도 6A 및 도 6B에 예시된 바대로, SD에 의해 생성된 탈분극은 붕괴된 z-스택 형광 진폭에 의해 측정된 바대로 실질적인 가시 수축을 유발하지 않고, 가시 용적은 제1 SD 후 20-30분에 완전히 회복하였다. 이것은 SD 유도된 탈분극의 후유증 중 하나가 수상돌기 가시 형태의 변형이라는 것을 확인시켜준다.The anatomic microstructure of the pyramidal neuron resin cells in the brain is surprisingly reliable in response to various stimuli. Depolarization, oxygen / glucose deprivation and N-methyl-D-aspartate all produced shrinkage of dendritic spines in CA1 pyramidal neurons in hippocampal hippocampus. To investigate the response of visibility to SD, a single CA1 pyramidal neuron was filled with fluorescent dye Alexa Fluor-594, and a serial z-stack slice (0.2 탆 step spanning 5 탆) collected from a 2-photon laser scanning microscopy examination Was used to image the thorn morphology. After 30 minutes of loading of the Alexa fluoro-594 into the CA1 pyramid reached equilibrium distribution in the neurons, SD was elevated to the radial layer of the CA1 region of the hippocampus slice (capillary side axon synapses in CA1 pyramidal neurons) K +] (1M on a patch pipette). As illustrated in Figures 6A and 6B, the depolarization produced by SD does not cause substantial visible shrinkage as measured by the collapsed z-stack fluorescence amplitude, and the visual volume is 20-30 minutes after the first SD . This confirms that one of the consequences of SD-induced depolarization is a deformation of the dendritic spine morphology.
GLYXGLYX -13은 -13 is 확산성Diffusibility 억제 이후 After inhibition 수상돌기Dendrite 가시 회복을 Thorn recovery 개선한다Improve
마지막으로, SD에 대한 수상돌기 가시의 동적 형태학적 반응에 대해 GLYX-13의 효과를 검사하였다. GLYX-13이 SD에 대해 반응하여 가시의 수축을 감소시키거나, 이의 회복을 개선하는지를 이것을 조사하였다. 도 6A는 대조군 피라미드 뉴런에서의 SD의 2개의 삽화에 반응한 가시 수축을 예시하는 반면, 도 6B는 10μM의 GLYX-13의 존재 하에 동일한 과정을 예시한다. 반복 측정에 대한 ANOVA는 도 6C의 상부에 예시된 것과 같은 수상돌기 가시로부터 측정된 형광성 강도에 대한 유의성(F(8,64)=17.53, p<0.001)에 도달하고, 이 유의성은 SD 후 시간 과정으로부터 주로 생겨서(F(8,64)=6.18, p<0.01), GLYX-13(채워진 원)이 SD에 의해 생긴 수축을 변경하지 않지만, 이것이 SD 후 가시 크기의 회복을 구제한다는 것을 나타낸다(F(8,64)=2.81, p<0.05).Finally, the effect of GLYX-13 on the dynamic morphological response of dendritic spines to SD was examined. It was investigated whether GLYX-13 responded to SD to reduce visual contraction or to improve its recovery. Figure 6A illustrates the visible contraction in response to two illustrations of SD in control pyramidal neurons, while Figure 6B illustrates the same procedure in the presence of 10 [mu] M GLYX-13. ANOVA for repeated measurements reached significance (F (8,64) = 17.53, p < 0.001) for the fluorescent intensity measured from the dendrite visibility as illustrated at the top of Figure 6C, (F (8,64) = 6.18, p < 0.01), indicating that GLYX-13 (filled circle) does not alter the shrinkage caused by SD, but this rescues the recovery of visible size after SD F (8,64) = 2.81, p < 0.05).
실시예 2Example 2
해마회 슬라이스 제조: 14일 내지 21일령의 스프라그-다울리(등록상표) 랫트(Taconic Farms)를 사용하여 실험을 수행하였다. 랫트를 아이소플루오란에 의해 깊게 마취시키고, 희생시키고, 뇌를 빨리 제거하고, 126 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 2.6 CaCl2, 1.3 MgCl2, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 26 NaHCO3, 및 11 글루코스(mM 단위)를 함유하는, 산소화된(95%의 O2 - 5%의 CO2), 얼음 냉각된 인공 뇌척수액(ACSF)에 위치시켰다. 뇌를 2등분하고, 이마엽을 절단하고, 슬라이싱 동안 계속해서 산소화된 얼음 냉각된 ACSF에서 액침된 스테이지에 부착된 사이아노아크릴레이트를 사용하여 개별 반구를 접착시켰다. 해마를 함유하는 400㎛의 두께의 두정 슬라이스를 바이브라톰(Leica 1200s)을 사용하여 절단하고, 실험을 시작하기 전 최소 1시간 동안 실온에서 항온처리를 위해 계면 보유 챔버로 옮겼다.Preparation of hippocampus slices: Experiments were performed using Sprague-Dawley (TM) rats (Taconic Farms) between 14 and 21 days of age. Anesthetic depth by a rat in iso-fluoran and, expense and, removing the brain quickly and, 126 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 2.6
해마회 확산성 억제의 유도: 해마의 급성 두정 슬라이스를 현미경 스테이지에서 액침된 기록 챔버로 옮기고, 가온된 ACSF(32℃)에 의해 관류시키고, 여기서 세포외 [K+]를 3㎖/분의 관류 속도에서 8mM으로 상승시켰다. 유리 피펫을 통해 3M KCl의 압력 주입 퍼프에 의해 확산성 억제를 개시시켰다. 보통 50㎳ 지속한 8 내지 10psi의 압력 펄스를 피코스프리쳐(picospritzer)에 의해 구동하였다. 피펫 저항은 3M KCl에 의해 충전될 때 2±0.2㏁이었다.Induction of hippocampal diffusibility inhibition: The hippocampal acute parietal slice was transferred to a recording chamber immersed in a microscope stage and perfused with warmed ACSF (32 ° C), where extracellular [K +] was perfused at a perfusion rate of 3 ml / min To 8 mM. Diffusion inhibition was initiated by a pressure injection puff of 3M KCl through a glass pipette. Pressure pulses of 8-10 psi, which lasted for 50 ms, were driven by a picospritzer. The pipette resistance was 2 ± 0.2 MΩ when filled with 3M KCl.
전기생리학적 기록 방법: 세포외 기록을 Clampex(v. 9)에 의해 MultiClamp 700B(Axon Instruments)를 사용하여 수행하고, 1kHz에서 여과시키고, 3kHz에서 디지털화하였다. 저저항(ACSF에 의해 충전된 후 1 내지 2㏁) 기록 전극을 SD 개시 피펫으로부터 대략 150㎜ 거리 간격으로 CA1 구역의 방사층에서의 샤퍼 측부 말단 필드의 정점 수지상 구역으로 삽입된 얇은 벽의 붕규산염 유리로부터 만들어서, SD의 속도를 모니터링하였다. 적외선 차등 간섭 대비(DIC) 광학부품이 장착된 Zeiss Axioskop 2FS 수직 현미경에 액침된 기록 챔버를 탑재하였다. 10x 대물렌즈를 사용하여 SD에 의해 발생한 슬라이스 휘도 변화를 영상화하였다. 휘도 변화를 PTI 마스터 시스템에 의해 제어되는 냉각된 CCD 카메라(CoolSNAP HQ)에 의해 100㎳마다 영상화하였다. 전기생리학적 데이터를 Clampfit 9에 의해 분석하였다. 영상화 데이터를 디지털화하고, ImageJ(NIH)에 의해 재구성하였다. 모든 실험을 국립 보건원 가이드라인을 준수하여 승인된 프로토콜 하에 수행하였다.Electrophysiological recording method: Extracellular recordings were performed by Clampex (v. 9) using MultiClamp 700B (Axon Instruments), filtered at 1 kHz and digitized at 3 kHz. A low resistance (1 to 2 M OMEGA after being charged by ACSF) recording electrode was applied to the apical dendritic region of the capillary side end field in the emissive layer of the CA1 region at approximately 150 mm distance from the SD initiation pipette to the thin walled borosilicate Made from glass, the rate of SD was monitored. A recording chamber immersed in a
실시예 1의 발견은 여성 및 청소년 환자와 관련하여 조사되었다. 시험관내 뇌 슬라이스에서 해마의 CA1 구역에서 확산성 탈분극(SD)을 개시시키도록 실험 프로토콜을 사용하였다. 가시적으로 더 긴 범위에 걸쳐 개시 부위로부터 확산성 억제의 거리 및 SD 전파 속도를 더 잘 관찰하기 위해, 실시예 1의 10x 대물렌즈를 1.6㎜로 조망 도메인을 확대하기 위해 4x 대물렌즈에 의해 대체하였다. 기록 챔버를 변형시켜 측면 둘 다로부터 슬라이스를 관류시키고, 더 많은 효과적인 관류가 뇌 슬라이스에 충분한 산소를 제공할 뿐만 아니라, 확산성 억제의 각각의 삽화가 세포외 및 세포내 둘 다에서 극적인 이온 조성물 변화를 발생시키므로 안정한 세포외 환경을 유지시키는 것을 돕는다.The findings of Example 1 have been investigated in connection with female and adolescent patients. Experimental protocols were used to initiate diffuse depolarization (SD) in the CA1 region of the hippocampus in vitro brain slices. To better observe the distance of diffusion suppression and the SD propagation velocity from the initiation site over a longer range of visibility, the 10x objective of Example 1 was replaced by a 4x objective to magnify the viewing domain to 1.6 mm . The recording chamber is modified so that the slice is perfused from both sides and that more effective perfusion not only provides sufficient oxygen to the brain slice but also allows each illustration of diffusing inhibition to produce dramatic ion composition changes both extracellularly and intracellularly Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > extracellular < / RTI > environment.
2개월령의 난소절제된 스프라그-다울리(등록상표) 암컷 랫트의 2개의 군은 현재의 코호트 연구에 포함되었다. 난소절제된 랫트 중 하나의 군은 7번째 수술 일 후로 7일 동안 에스트로겐의 매일 주사에 의해 제공된 반면, 다른 것은 실험을 수행하기 전 7일 동안 대조군으로서 오일 비히클만이 주사되었다.Two groups of 2 month old ovariectomized Sprague-Dawley (R) female rats were included in the current cohort study. One group of ovariectomized rats was provided with daily injections of estrogen for 7 days after the 7th surgical day while the other was only injected with oil vehicle as the control group for 7 days before the experiment.
휘도 변화를 실패(<100㎜), 국소 확산(>100㎜; <800㎜); 또는 완전 확산(>800㎜)으로서 3M 칼륨의 퍼프에 따라 가시적으로 분류화하였다. SD 유도는 8마리의 오일 처리된 랫트로부터의 39개의 슬라이스 및 7마리의 에스트로겐 처리된 랫트로부터의 35개의 슬라이스에서 시도되었다. 표 1은 2개의 군에서 동일한 방법에 의해 유발된 SD의 발생의 빈도의 요약이다. 오일 치료 군에서, 실패율은 에스트로겐 치료 군에서보다 상당히 높아서(카이 제곱 시험, P=0.014), 에스트로겐 자체가 병소 탈분극에 SD를 나타내는 뇌 조직의 경향을 증대시킨다는 것을 나타낸다.Change in luminance was failed (<100 mm), local diffusion (> 100 mm; <800 mm); Or < / RTI > complete diffusion (> 800 mm). SD induction was attempted on 39 slices from 8 oil-treated rats and 35 slices from 7 estrogen-treated rats. Table 1 summarizes the frequency of occurrence of SD caused by the same method in the two groups. In the oil-treated group, the failure rate was significantly higher than in the estrogen-treated group (chi-square test, P = 0.014), indicating that estrogen itself increases the tendency of brain tissue to exhibit SD in lesion depolarization.
하기 도 7에 도시된 바대로 확산성 억제의 전파 속도를 예측하도록 휘도 변화를 사용하였다. SD가 이 관찰 부위 사이를 이동하는 데 걸리는 시간으로 관찰 부위 사이의 SD의 거리를 나눔으로써 병소 3M 칼륨 퍼프에 의해 유도된 국소화 및 완전 SD 둘 다로부터 전파 속도를 계산하였다. 도 7에 예시된 바대로, 에스트로겐 처리된 랫트로부터의 슬라이스에서의 평균 확산 속도는 오일 처리된 랫트로부터의 슬라이스에서의 확산 속도(0.083±0.005㎜/초, P<0.05, 스튜던트 t 시험)보다 상당히 빠른 0.121± 0.013㎜/초이었다. 이 데이터는 에스트로겐이 해마에서, 그리고 가능하게는 또한 신생피질에서의 SD의 경향 및 속도 둘 다를 증대시키는 데 있어서 상당한 역할을 한다는 것을 나타낸다.The luminance change was used to predict the propagation speed of the diffusion suppression as shown in FIG. The propagation velocity was calculated from both the localization and full SD induced by the lesion 3M potassium puff by dividing the distance of SD between the sites of observation by the time it took for the SD to travel between these sites. As illustrated in Figure 7, the average diffusion rate at the slice from the estrogen treated rats was significantly greater than the diffusion rate at the slice from the oil treated rats (0.083 0.005 mm / sec, P < 0.05, Student t test) Fast 0.121 ± 0.013 mm / sec. This data indicates that estrogens play a significant role in increasing both the tendency and speed of SD in the hippocampus, and possibly also in the neocortex.
개시 부위로부터 멀리 SD의 전파의 최대 거리를 측정함으로써 에스트로겐이 SD의 중증도에 어떻게 영향을 미치는지의 시험을 수행하였다. 8에 도시된 바대로, 검출 불가능한 휘도 변화를 나타낸 가까운 이웃하는 관찰 부위의 거리에 의해 개시 부위로부터 최소 검출 가능한 휘도 변화(기준치로부터 >5% 변화)를 나타낸 관찰 부위의 거리를 평균하고, 개시 부위로부터 이 거리를 측정함으로써 예측된 샤퍼 측부 경로를 따른 확산 종말점. 도 8에 도시된 바대로, 에스트로겐 처리된 랫트로부터의 슬라이스에서의 SD는 오일 처리된 랫트로부터의 슬라이스에서의 SD(0.394±0.051㎜; n=16, P<0.05, 스튜던트 t 시험)보다 상당히 더 긴 거리(0.594±0.071㎜; n=18)를 이동하였다. 그러므로, 에스트로겐 처리된 랫트에서의 SD는 더 용이하게 유발될 뿐만 아니라, 더 긴 거리 전파되었다.A test was conducted to determine how estrogen affects the severity of SD by measuring the maximum distance of SD propagation far from the onset site. As shown in FIG. 8, the distance of the observation region showing the minimum detectable brightness change (> 5% change from the reference value) from the start position was averaged by the distance of the near neighbor observation region showing the undetectable luminance change, Lt; / RTI > along the predicted path of the sharper side by measuring this distance from the diffusion endpoint. As shown in Figure 8, the SD at the slice from the estrogen treated rats was significantly higher than the SD at the slice from the oil treated rats (0.394 0.051 mm; n = 16, P <0.05, Student t test) The long distance (0.594 ± 0.071 mm; n = 18) was moved. Therefore, SD in estrogen-treated rats was not only more easily induced, but also propagated longer distances.
10μM의 GLYX-13은 이후 2개의 Sd가 10분 떨어져 유도된 후 관류물에 첨가되고, 10분마다 SD를 계속해서 유도하여 SD의 속도 및 스케일이 영향을 받는지를 결정하였다. 도 9는 GLYX-13의 적용 전 및 10μM의 욕 적용된 GLYX-13에 대한 50분 노출 후 에스트로겐 치료된 랫트로부터 슬라이스에서 유발된 SD의 통상적인 차이를 보여준다. SD에 대한 GLYX-13의 효과를 평가하기 위해 10개의 관찰 부위에서의 휘도 변화를 측정하였다. 도 9B에 도시된 바대로 SD가 여전히 용이하게 유발되지만, 도 9A는 SD와 연관된 휘도 변화가 GLYX-13의 존재 하에 지연된다는 것을 명확히 보여준다. 쌍 지은 t 시험은 GLYX-13이 6.56± 0.57㎜/분으로부터 4.96±0.28㎜/분으로 평균 SD 전파 속도를 상당히 감소시킨다는 것을 나타낸다(n=5, P<0.01, 쌍 지은 t 시험). 오일 처리된 랫트로부터의 해마회 슬라이스에서 동일한 실험을 수행하였다. GLYX-13이 평균 SD 전파 속도를 5.09±0.61㎜/분으로부터 4.50±0.39㎜/분으로 감소시키면서(n=5), 이 감소는 통계 유의성에 도달하지 않았다.10 μM of GLYX-13 was then added to the perfusate after two Sd's were induced 10 minutes apart and continued to induce SD every 10 minutes to determine if the rate and scale of SD were affected. Figure 9 shows the typical difference in slice-induced SD from estrogen-treated rats before application of GLYX-13 and after 50 min exposure to 10 μM bath-applied GLYX-13. To evaluate the effect of GLYX-13 on SD, the change in luminance at 10 observation sites was measured. Although SD is still easily induced as shown in FIG. 9B, FIG. 9A clearly shows that the brightness change associated with SD is delayed in the presence of GLYX-13. The twin-t test indicates that GLYX-13 significantly reduces the mean SD propagation velocity from 6.56 ± 0.57 mm / min to 4.96 ± 0.28 mm / min (n = 5, P <0.01, paired t test). The same experiment was performed on hippocampal slices from oil-treated rats. This decrease did not reach statistical significance while GLYX-13 reduced the mean SD propagation velocity from 5.09 ± 0.61 mm / min to 4.50 ± 0.39 mm / min (n = 5).
2개의 군에 걸쳐 SD 전파 속도에 대한 GLYX-13의 효과를 조사하기 위해 2방향 반복된 ANOVA를 또한 수행하였다. 도 10이 예시하는 것처럼, 제1 유의성은 GLYX-13의 적용 전 및 후에 에스트로겐 치료된 랫트로부터 생기고(F(1,8)=3.1; p<0.05); 제2 유의성은 2개의 군 사이의 GLYX-13의 노출 간에 생겼다(F(1,8)=4.2; p<0.05). 이 결과는 GLYX-13이 에스트로겐 치료된 랫트에서 더 강한 효과를 가져서, 오일 치료된 랫트의 수준으로 SD의 전파 속도를 상당히 느리게 한다는 것을 나타낸다.Two-way repeated ANOVA was also performed to investigate the effect of GLYX-13 on SD propagation velocities across the two groups. As illustrated in Figure 10, the first significance arises from estrogen-treated rats (F (1,8) = 3.1; p < 0.05) before and after the application of GLYX-13; The second significance occurred between the exposure of GLYX-13 between the two groups (F (1,8) = 4.2; p < 0.05). These results indicate that GLYX-13 has a stronger effect in estrogen-treated rats, which significantly slows the spreading rate of SD to the level of oil-treated rats.
실시예Example 3 3
방법Way
동물animal
성체 수컷(2-3개월령) 스프라그-다울리(등록상표)(SD) 랫트를 할란(Harlan)(미국)으로부터 구입하였다. 랫트를 백양나무 목재 침구를 가지는 Lucite 우리에서 감금하고, 12시간:12시간 광:암 사이클(5AM에서의 광)에서 유지시키고, 연구에 걸쳐 Purina(등록상표) 랫트 음식(미국) 및 수돗물에 자유로이 접근이 제공되었다Adult male (2-3 month old) Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were purchased from Harlan (USA). The rats were housed in a Lucite cage that had white wood bedding and kept in 12 hours: 12 hours light: cancer cycle (light at 5AM) and were free to study Purina (R) rat food (US) Access was provided
외상성 뇌 손상 유도 Induce traumatic brain injury
단일 블라스트 유도된 외상성 뇌 손상을 유도하고, 골드스테인(Goldstein) 등의 프로토콜에 따라 랫트에서 사용하도록 변형시켰다(Goldstein, L.E., et al. (2012) "Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in blast-exposed military veterans and a blast neurotrauma mouse model," Science Translational Medicine 4:134ra160.) 성체 수컷 스프라그-다울리(등록상표) 랫트를 아이소플루란에 의해 마취시키고, 귀마개를 랫트의 귀 둘 다로 삽입하고, 랫트는 폴리에스터 필름의 0.014 인치를 펀칭함으로써 생성된 헬륨의 단일 약 42 PSI 블라스트를 받았다. 샴 대조군을 블라스트 반경의 바깥에 위치시켰다. 하기한 바대로 동물이 블라스트 후 1시간 라파스티넬(3㎎/㎏ IV) 또는 0.9% 무균 식염수 비히클(1㎖/㎏ IV)에 의해 투약되면서, 랫트를 처음에 3.5-4% 아이소플루란을 사용하여 마취시키고, 이후 이의 귀를 1.5 x 1.5㎜ 폼 플러그(Pura-Fit ear plugs, Moldex-Metric INC(캘리포니아주 쿨버 시티))에 의해 보호하였다. 랫트를 두부 접근 설치류 가슴 억제제(thoracic restrainer)(Stoelting(미국))에 위치시켜 두부가 자유로이 이동하게 허용하면서 이의 신체를 보호하고, 머리는 알루미늄 쇼크 관(183 x 61㎝; L-3 Applied Technologies(미국))의 말단으로부터 10㎝에 있다. 랫트는 폴리에스터 필름의 0.014 인치 천공에 의해 생성된 헬륨의 단일 약 42 PSI 블라스트를 받았다. 샴 대조군을 블라스트 반경의 바깥에 위치시켰다. 동물은 블라스트 후 1시간에 라파스티넬(3㎎/㎏ IV) 또는 0.9% 무균 식염수 비히클(1㎖/㎏ IV)이 투약되었다. 마취로부터 회복하는 잠재력을 기록하였다(도 11A). 회복은 눈 깜빡임 및 체위반사, 및 일반 보행(정상 리듬 게이트, 비순환 게이트, 체중 완전 지지, 약간의 코 훌쩍임 및 탐구 행동의 증거)을 나타나는 것으로 정의된다. 동물은 블라스트 후 1시간에 GLYX-13(3㎎/㎏ IV) 또는 0.9% 무균 식염수 비히클(1㎖/㎏ IV)이 투약되었다. N = 군마다 4-6; * P<0.05(도 11A) ANOVA.Induced blunt-traumatic brain injury and modified for use in rats according to protocols such as Goldstein et al. (Goldstein, LE, et al. (2012) "Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in blast-exposed military veterans and a male adult Sprague-Dawley (TM) rats were anesthetized with isoflurane, the earplugs were inserted into both ears of the rats, and rats were anesthetized with polyester film < RTI ID = 0.0 >Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > PSI < / RTI > Siam controls were placed outside the blast radius. The rats were initially injected with 3.5-4% isoflurane (1 mg / kg IV), while the animals were dosed with 1 hour of rabastin (3 mg / kg IV) or 0.9% sterile saline vehicle And their ears were then protected by 1.5 x 1.5 mm foam plugs (Pura-Fit ear plugs, Moldex-Metric INC, Coolvertshire, Calif.). The rats were placed in a thoracic restrainer (Stoelting (USA)) to protect their bodies while allowing the head to move freely, and the head was placed in an aluminum shock tube (183 x 61 cm; L-3 Applied Technologies USA). ≪ / RTI > The rats received a single approximately 42 PSI blast of helium produced by 0.014 inch punching of the polyester film. Siam controls were placed outside the blast radius. Animals were dosed with either rafastinol (3 mg / kg IV) or 0.9% sterile saline vehicle (1 ml / kg IV) at 1 hour after blast. The potential for recovery from anesthesia was noted (Figure 11A). Recovery is defined as blinking and positional reflexes and evidence of normal gait (evidence of normal rhythm gating, acyclic gating, full weight gain, slight nasal congestion, and inquisitive behavior). Animals were dosed with GLYX-13 (3 mg / kg IV) or 0.9% sterile saline vehicle (1 ml / kg IV) at 1 hour after blast. N = 4-6 per group; * P < 0.05 (FIG. 11A) ANOVA.
양성 감정 학습( PEL ) 도 11B는 대상체 간 설계를 사용한 블라스트 후 24시간에 수행된 단일 3분 긍정적 정서 학습(PEL) 시험 세션의 결과를 보여준다. N = 군마다 4-6. 피셔 PLSD 사후 시험을 이용하여 결과(라파스티넬 + TBI 대 비히클 + TBI)를 평가하였다. Positive Emotional Learning ( PEL ) Figure 11B shows the results of a single 3-minute positive emotional learning (PEL) test session performed 24 hours after blast using inter-subject design. N = 4-6 per group. Fisher PLSD post-test was used to evaluate the results (Rapastinel + TBI vs. Vehicle + TBI).
이종연합 거친 신체 놀이(rough-and-tumble play)가 문헌(Burgdorf, J., et al. (2011) "Positive emotional learning is regulated in the medial prefrontal cortex by GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors," Neuroscience 192:515-523)에 이전에 기재된 바대로 수행되었고, 투약 후 3시간 및 2주에 시험이 발생했다. 이종연합 거친 신체 놀이 자극은 실험자의 오른쪽 손에 의해 투여되었다. 동물은 교대하는 이종연합 거친 신체 놀이의 15초 차단 및 비자극의 15초로 이루어진 3분의 이종연합 거친 신체 놀이를 받았다. 높은 빈도의 초음파 발성(USV)을 기록하고, 이전에 기재된 바대로(Id.) Avasoft SASlab Pro(독일)에 의해 소노그램에 의해 분석하였다. 각각의 비-자극 기간 동안 발생한 주파수 변조된 50-kHz USV를 정량화하여 PEL을 측정하였다. 동물은 시험 전에 자극을 놀이하도록 습관되지 않았다.A heterogeneous rough-and-tumble play has been described by Burgdorf, J., et al. (2011) Positive emotional learning is regulated in the medial prefrontal cortex by GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors, Neuroscience 192: 515 -523), and the test occurred at 3 and 2 weeks after dosing. The heterogeneous coarse body play stimuli were administered by the right hand of the experimenter. The animals received a three-minute union coarse body play consisting of 15 seconds of alternating union coarse body play and 15 seconds of unenchanted play. A high frequency of ultrasound (USV) was recorded and analyzed by Sonogram as previously described (Id.) By Avasoft SASlab Pro (Germany). The frequency-modulated 50-kHz USV generated during each non-stimulation period was quantified to measure the PEL. Animals were not allowed to play stimuli before testing.
결과result
도 11A에 도시된 바대로, TBI를 받은 동물은 샴 대조군 동물과 비교하여 마취로부터 더 긴 회복 시간을 나타냈다[F(1, 13) = 41.7, P<0.05]. 도 11B에 도시된 바대로, 라파스티넬(3㎎/㎏ IV)은 양성 감정 학습의 TBI 유도 억제를 구제하였다[F(2, 12) = 10.0, P<.05; 피셔 PLSD 사후 시험 라파스티넬 + TBI 대 비히클 + TBI, 샴 대 비히클 + TBI 대, P<0.05]. 또한, 마취 회복 시간은 PEL의 속도와 상당히 상관되지 않았다[r(15) = -0.14, P>.05]. 양성 감정 학습 시험에서, 라파스티넬의 단일 용량(3㎎/㎏ IV)은 TBI에 의해 유도된 학습 및 감정의 결함을 완전히 구제하였다. 따라서, 이 전임상 모델에서, 라파스티넬은 주요 인지를 치료하는 데 효과적이고, TBI 및 라파스티넬의 정서적인 증상은 PTSD의 치료에 치료학적 잠재력을 가지는 것으로 나타났다. As shown in FIG. 11A, animals receiving TBI showed a longer recovery time from anesthesia as compared to Siam control animals [F (1, 13) = 41.7, P <0.05]. As shown in Figure 11B, rapastinel (3 mg / kg IV) relieved TBI induced inhibition of positive emotional learning [F (2, 12) = 10.0, P < Fisher PLSD post-test Rupastatin + TBI vs. Vehicle + TBI, Sham vs Vehicle + TBI vs. P <0.05]. In addition, the anesthetic recovery time was not significantly correlated with the rate of PEL [r (15) = -0.14, P > .05]. In the positive emotional learning test, a single dose of rapamystel (3 mg / kg IV) completely relieved the learning and emotion deficiencies induced by TBI. Thus, in this preclinical model, Rapastelnell is effective in treating major cognitions, and emotional symptoms of TBI and Rapastinel have therapeutic potential in the treatment of PTSD.
균등물Equalization
본 개시내용의 특정한 실시형태가 기재되어 있지만, 상기 명세서가 예시적이고 제한적이 아니다. 본 개시내용의 많은 변형은 본 명세서의 검토 시 당해 분야의 당업자에게 명확할 것이다. 본 개시내용의 완전한 범위는 청구항과 균등물의 이의 완전한 범위와 함께, 그리고 명세서와 이러한 변형과 함께 참조로 결정되어야 한다.Although specific embodiments of the present disclosure have been described, the foregoing description is illustrative and not restrictive. Many modifications of the present disclosure will be apparent to those skilled in the art upon examination of this specification. The full scope of the disclosure should be determined by reference to the claims and their full scope of equivalents, together with the specification and such modifications.
달리 표시되지 않은 한, 성분의 분량, 반응 조건, 매개변수, 기술적 특징 및 명세서 및 청구항에 사용된 기타 등등을 나타내는 모든 숫자는 모든 경우에 용어 "약"에 의해 변형되는 것으로 이해되어야 한다. 따라서, 반대로 표시되지 않은 한, 명세서 및 첨부된 청구항에 기재된 숫자 매개변수는 본 개시내용에 의해 얻어지는 추구되는 원하는 특성에 따라 달라질 수 있는 대략치이다.Unless otherwise indicated, all numbers expressing quantities of ingredients, reaction conditions, parameters, technical characteristics and the like used in the specification and claims, and the like are to be understood as being modified in all instances by the term "about. &Quot; Thus, unless indicated to the contrary, the numerical parameters set forth in the specification and the appended claims are approximations that may vary depending upon the desired properties sought to be obtained by this disclosure.
하기 기재된 항목을 포함하는 본 명세서에 언급된 모든 공보 및 특허는, 각각의 개별 공보 또는 특허가 참조로 구체적으로 및 개별적으로 표시된 것처럼, 이의 전문이 참조로 본 명세서 포함된다. 상충의 경우에, 본 명세서에서의 임의의 정의를 포함하는 본 출원이 우세할 것이다.All publications and patents mentioned in this specification, including the items listed below, are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety, as if each individual publication or patent was specifically and individually indicated by reference. In the case of a conflict, the present application, including any definitions herein, will prevail.
Claims (26)
A method of treating migraine in a patient in need of treatment for migraine comprising administering to said patient a pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound as shown below or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
.A method of treating, inhibiting and / or preventing cortical spreading inhibition in a patient in need of such treatment, inhibition and / or prevention of a cortical spreading depression comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound represented by the formula A method for treating, inhibiting and / or preventing cortical diffusibility inhibition, comprising administering to said patient a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
.
.A method of treating or alleviating a long-term migraine after-effect in a patient in need of treatment or alleviation of a long-term migraine headache, comprising administering to said patient a pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound represented by the following formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof: A method of treating or alleviating a long-term post-migraine episode, comprising:
.
.A method of treating or alleviating traumatic brain injury in a patient in need of such treatment or alleviation of traumatic brain injury comprising administering to said patient a pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound represented by the following formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof: How to treat or relieve traumatic brain injury:
.
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201462015727P | 2014-06-23 | 2014-06-23 | |
| US62/015,727 | 2014-06-23 | ||
| US201562109386P | 2015-01-29 | 2015-01-29 | |
| US62/109,386 | 2015-01-29 | ||
| PCT/US2015/037177 WO2015200322A1 (en) | 2014-06-23 | 2015-06-23 | Methods of treating or ameliorating migraine |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20170018072A true KR20170018072A (en) | 2017-02-15 |
Family
ID=54938737
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020177001848A KR20170018072A (en) | 2014-06-23 | 2015-06-23 | Methods of treating or ameliorating migraine |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP3157943A4 (en) |
| JP (2) | JP6688748B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20170018072A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN106661085A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2015280108B2 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112016030375A8 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2953170A1 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX2016017388A (en) |
| RU (1) | RU2721401C2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2015200322A1 (en) |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1995006468A1 (en) * | 1993-09-01 | 1995-03-09 | Smithkline Beecham Corporation | Method for treating migraine headaches |
| EP1365787B1 (en) * | 2000-08-25 | 2007-03-21 | Research Corporation Technologies, Inc | Use of amino acid anticonvulsants for treatment of pain |
| US20040053835A1 (en) * | 2000-11-17 | 2004-03-18 | Sophia Kossida | Regulation of human nmda receptor |
| MXPA05009425A (en) * | 2003-03-06 | 2006-02-10 | Botulinum Toxin Res Ass Inc | Treatment of sinusitis related chronic facial pain and headache with botulinum toxin. |
| CN102105168A (en) * | 2008-07-23 | 2011-06-22 | 协和发酵麒麟株式会社 | Therapeutic agent for migraine |
| WO2011003064A2 (en) * | 2009-07-02 | 2011-01-06 | Naurex, Inc. | Methods of treating neuropathic pain |
| PL2985032T3 (en) * | 2009-10-05 | 2019-07-31 | Northwestern University | Glyx for use in the treatment of alzheimer's disease, parkinson's disease or huntington's disease |
| US8951968B2 (en) * | 2009-10-05 | 2015-02-10 | Northwestern University | Methods of treating depression and other related diseases |
| MX2012009388A (en) * | 2010-02-11 | 2012-10-01 | Univ Northwestern | Secondary structure stabilized nmda receptor modulators and uses thereof. |
| CA2834286A1 (en) * | 2011-04-27 | 2012-11-01 | Northwestern University | Methods of treating alzheimer's disease, huntington's disease, autism, and other disorders |
| SG11201502860UA (en) * | 2012-10-12 | 2015-05-28 | Univ Northwestern | Methods of identifying compounds for treating depression and other related diseases |
-
2015
- 2015-06-23 BR BR112016030375A patent/BR112016030375A8/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2015-06-23 CA CA2953170A patent/CA2953170A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2015-06-23 MX MX2016017388A patent/MX2016017388A/en unknown
- 2015-06-23 JP JP2016575106A patent/JP6688748B2/en active Active
- 2015-06-23 WO PCT/US2015/037177 patent/WO2015200322A1/en active Application Filing
- 2015-06-23 CN CN201580033913.6A patent/CN106661085A/en active Pending
- 2015-06-23 AU AU2015280108A patent/AU2015280108B2/en not_active Ceased
- 2015-06-23 EP EP15811633.5A patent/EP3157943A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2015-06-23 KR KR1020177001848A patent/KR20170018072A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2015-06-23 RU RU2017101410A patent/RU2721401C2/en active
-
2020
- 2020-04-06 JP JP2020068289A patent/JP2020114863A/en active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| MX2016017388A (en) | 2018-02-19 |
| WO2015200322A1 (en) | 2015-12-30 |
| BR112016030375A2 (en) | 2017-08-15 |
| BR112016030375A8 (en) | 2021-07-13 |
| JP2020114863A (en) | 2020-07-30 |
| RU2721401C2 (en) | 2020-05-19 |
| JP6688748B2 (en) | 2020-04-28 |
| CN106661085A (en) | 2017-05-10 |
| CA2953170A1 (en) | 2015-12-30 |
| AU2015280108B2 (en) | 2019-11-28 |
| JP2017519778A (en) | 2017-07-20 |
| AU2015280108A1 (en) | 2017-01-19 |
| EP3157943A1 (en) | 2017-04-26 |
| RU2017101410A3 (en) | 2019-01-21 |
| RU2017101410A (en) | 2018-07-24 |
| EP3157943A4 (en) | 2018-01-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| ES2750728T3 (en) | Use of cannabinoids in combination with Aripriprazole | |
| US20220160655A1 (en) | Anxiolytic composition, formulation and method of use | |
| ES2824552T3 (en) | Tradipitant treatment method | |
| AU2020210168B2 (en) | Methods and compositions for improving cognitive function | |
| JP2023169413A (en) | Methods and compositions for treating psychotic disorders | |
| JP5030553B2 (en) | Pharmaceuticals for treating dry mice and / or salivary secretion disorders | |
| TW201605443A (en) | Methods of treating fragile X syndrome and related disorders | |
| US20190298740A1 (en) | Methods and compositions for treating hallucinations and conditions related to the same | |
| US20200046687A1 (en) | Methods and compositions for treating pain | |
| US20220273662A1 (en) | Use of sildenafil and rock inhibitors for treating stroke or sequelae following stroke | |
| TW544311B (en) | Therapeutic or preventive agent for intractable epilepsies | |
| KR20170018072A (en) | Methods of treating or ameliorating migraine | |
| US8975298B2 (en) | Therapeutic agent for pain | |
| US12042505B2 (en) | Compositions and methods for treating dry eye | |
| US20240325324A1 (en) | Compositions and methods for treating dry eye | |
| KR20210060489A (en) | Improve sleep or post-sleep behavior | |
| Liu et al. | Locus coeruleus activation contributes to masseter muscle overactivity induced by chronic restraint stress in mice | |
| Niveditha et al. | Current Updates on Migrane: Diagnosis and Management | |
| Goodfellow | Altered NMDA Receptor Composition and Function Contribute to Deficits in Forebrain-Dependent Learning and Memory in Adult Rats Exposed to Ethanol as Neonates | |
| TW201103546A (en) | New use of 5H-dibenz/b,f/azepine-5-carboxamide derivatives |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application |