KR101699869B1 - Preparation method of food container - Google Patents
Preparation method of food container Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101699869B1 KR101699869B1 KR1020140167740A KR20140167740A KR101699869B1 KR 101699869 B1 KR101699869 B1 KR 101699869B1 KR 1020140167740 A KR1020140167740 A KR 1020140167740A KR 20140167740 A KR20140167740 A KR 20140167740A KR 101699869 B1 KR101699869 B1 KR 101699869B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- magnesium
- compound
- group
- carbon atoms
- transition metal
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F10/00—Homopolymers and copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond
- C08F10/02—Ethene
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D1/00—Containers having bodies formed in one piece, e.g. by casting metallic material, by moulding plastics, by blowing vitreous material, by throwing ceramic material, by moulding pulped fibrous material, by deep-drawing operations performed on sheet material
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F4/00—Polymerisation catalysts
- C08F4/02—Carriers therefor
- C08F4/022—Magnesium halide as support anhydrous or hydrated or complexed by means of a Lewis base for Ziegler-type catalysts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F4/00—Polymerisation catalysts
- C08F4/42—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors
- C08F4/44—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors selected from light metals, zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper, silver, gold, boron, gallium, indium, thallium, rare earths or actinides
- C08F4/60—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors selected from light metals, zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper, silver, gold, boron, gallium, indium, thallium, rare earths or actinides together with refractory metals, iron group metals, platinum group metals, manganese, rhenium technetium or compounds thereof
- C08F4/62—Refractory metals or compounds thereof
- C08F4/64—Titanium, zirconium, hafnium or compounds thereof
- C08F4/642—Component covered by group C08F4/64 with an organo-aluminium compound
- C08F4/6423—Component of C08F4/64 containing at least two different metals
- C08F4/6425—Component of C08F4/64 containing at least two different metals containing magnesium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F4/00—Polymerisation catalysts
- C08F4/42—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors
- C08F4/44—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors selected from light metals, zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper, silver, gold, boron, gallium, indium, thallium, rare earths or actinides
- C08F4/60—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors selected from light metals, zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper, silver, gold, boron, gallium, indium, thallium, rare earths or actinides together with refractory metals, iron group metals, platinum group metals, manganese, rhenium technetium or compounds thereof
- C08F4/62—Refractory metals or compounds thereof
- C08F4/64—Titanium, zirconium, hafnium or compounds thereof
- C08F4/65—Pretreating the metal or compound covered by group C08F4/64 before the final contacting with the metal or compound covered by group C08F4/44
- C08F4/651—Pretreating with non-metals or metal-free compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F4/00—Polymerisation catalysts
- C08F4/42—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors
- C08F4/44—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors selected from light metals, zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper, silver, gold, boron, gallium, indium, thallium, rare earths or actinides
- C08F4/60—Metals; Metal hydrides; Metallo-organic compounds; Use thereof as catalyst precursors selected from light metals, zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper, silver, gold, boron, gallium, indium, thallium, rare earths or actinides together with refractory metals, iron group metals, platinum group metals, manganese, rhenium technetium or compounds thereof
- C08F4/62—Refractory metals or compounds thereof
- C08F4/64—Titanium, zirconium, hafnium or compounds thereof
- C08F4/65—Pretreating the metal or compound covered by group C08F4/64 before the final contacting with the metal or compound covered by group C08F4/44
- C08F4/652—Pretreating with metals or metal-containing compounds
- C08F4/654—Pretreating with metals or metal-containing compounds with magnesium or compounds thereof
- C08F4/6546—Pretreating with metals or metal-containing compounds with magnesium or compounds thereof organo-magnesium compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J5/00—Manufacture of articles or shaped materials containing macromolecular substances
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L23/00—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L23/02—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after-treatment
- C08L23/04—Homopolymers or copolymers of ethene
- C08L23/06—Polyethene
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L23/00—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L23/02—Compositions of homopolymers or copolymers of unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers not modified by chemical after-treatment
- C08L23/04—Homopolymers or copolymers of ethene
- C08L23/08—Copolymers of ethene
- C08L23/0807—Copolymers of ethene with unsaturated hydrocarbons only containing more than three carbon atoms
- C08L23/0815—Copolymers of ethene with aliphatic 1-olefins
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 40%이상의 공극율을 갖는 지글러-나타 중합 촉매의 존재 하에, 에틸렌 단량체를 단독으로 중합하거나 또는 에틸렌 단량체를 α-올레핀과 공중합하여 160㎡/g 이상의 비표면적을 가지는 폴리올레핀 수지를 제조하는 단계; 및 상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하는 단계;를 포함하는 식품 용기의 제조 방법에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to a process for producing a polyolefin resin having a specific surface area of 160 m 2 / g or more by polymerizing an ethylene monomer alone or copolymerizing an ethylene monomer with an? -Olefin in the presence of a Ziegler-Natta catalyst having a porosity of 40% ; And molding the polyolefin resin.
Description
본 발명은 식품 용기의 제조 방법에 관한 것으로서, 보다 상세하게는 낮은 휘발성 화합물 수치를 가지며 우수한 관능 안정성으로 식품, 생수 및 음료의 이취 또는 맛에 영향을 주는 부분을 최소화할 수 있는 식품 용기의 제조 방법에 관한 것이다. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a food container capable of minimizing a portion affecting the odor or flavor of foods, bottled water and beverages with a low volatile compound value and excellent sensory stability .
최근 생수 및 음료 시장의 성장에 따라 이취와 맛에 대한 민감성이 크게 대두되는 추세이다. 이에 따라 용기로 주로 사용되는 폴리에틸렌 테레프탈레이트와 병마개로 주로 사용되는 폴리에틸렌과 폴리프로필렌 수지가 용기 내 내용물의 이취 또는 맛의 변화를 유발할 수 있는지에 대한 가능성의 지표로서 수지 고유의 관능 평가가 중요해 지고 있다.The recent trend of bottled water and beverages market is very sensitive to odor and taste. Accordingly, the inherent sensory evaluation of the resin has become important as an index of the possibility of polyethylene terephthalate, which is mainly used as a container, and polyethylene or polypropylene resin, which is mainly used as a bottle cap, .
본 발명은 낮은 휘발성 화합물 수치를 가지며 우수한 관능 안정성으로 식품, 생수 및 음료의 이취 또는 맛에 영향을 주는 부분을 최소화할 수 있는 식품 용기의 제조 방법을 제공하기 위한 것이다. The present invention is to provide a method of manufacturing a food container which has a low volatile compound value and is excellent in sensory stability and can minimize a portion affecting odor or flavor of food, bottled water and beverage.
본 명세서에서는, 40 % 이상의 공극율을 갖는 지글러-나타 중합 촉매의 존재 하에, 에틸렌 단량체를 단독으로 중합하거나 또는 에틸렌 단량체를 α-올레핀과 공중합하여 160㎡/g 이상의 비표면적을 가지는 폴리올레핀 수지를 제조하는 단계; 및 상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하는 단계;를 포함하는, 식품 용기의 제조 방법이 제공된다. In the present specification, the ethylene monomer is polymerized singly or in the presence of a Ziegler-Natta catalyst having a porosity of 40% or more or a copolymer of an ethylene monomer and an? -Olefin to prepare a polyolefin resin having a specific surface area of 160 m 2 / g or more step; And molding the polyolefin resin. A method of manufacturing a food container, comprising the steps of:
이하 발명의 구체적인 구현예에 따른 식품 용기의 제조 방법에 대하여 보다 상세하게 설명하기로 한다.
Hereinafter, a method of manufacturing a food container according to a specific embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail.
상술한 바와 같이, 발명의 일 구현예의 식품 용기의 제조 방법은 40% 이상의 공극율을 갖는 지글러-나타 중합 촉매의 존재 하에, 에틸렌 단량체를 단독으로 중합하거나 또는 에틸렌 단량체를 α-올레핀과 공중합하여 160㎡/g 이상의 비표면적을 가지는 폴리올레핀 수지를 제조하는 단계; 및 상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하는 단계;를 포함할 수 있다. As described above, the method of manufacturing a food container according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises polymerizing an ethylene monomer alone or copolymerizing an ethylene monomer with an alpha -olefin in the presence of a Ziegler-Natta catalyst having a porosity of 40% / g; < / RTI > And molding the polyolefin resin.
본 발명자들은 40%이상, 또는 45% 내지 70%의 공극율을 갖는 지글러-나타 촉매를 이용하여 제조되는 폴리에틸렌 수지가 내부에 소정의 공극을 가지게 되며, 이러한 폴리에틸렌 수지를 이용하여 식품 용기를 제조하는 과정에서 이취를 발생시키거나 관능성을 저하하는 휘발성 화합물들이 쉽게 제거되어 최종 제품인 식품 용기가 낮은 휘발성 화합물 수치를 가지며 우수한 관능 안정성으로 식품, 생수 및 음료의 이취 또는 맛에 영향을 주는 부분을 최소화할 수 있다는 점을 실험을 통하여 확인하고 발명을 완성하였다. The present inventors have found that a polyethylene resin produced using a Ziegler-Natta catalyst having a porosity of 40% or more, or 45% to 70% has a predetermined void in the interior thereof, and a process of manufacturing a food container using such a polyethylene resin The volatile compounds that generate odor and deteriorate the sensibility are easily removed, and the final product, the food container, has low volatile compound values and the excellent sensory stability can minimize the influence on the odor or taste of food, bottled water and beverage And the invention was completed through experiments.
구체적으로, 상기 공극율을 갖는 지글러-나타 촉매를 이용하여 에틸렌 단량체를 단독으로 중합하거나 또는 에틸렌 단량체를 α-올레핀과 공중합하면, 160 ㎡/g 이상, 또는 190 ㎡/g 내지 300 ㎡/g 의 비표면적을 가지는 폴리올레핀 수지 분말을 제공할 수 있는데, 이러한 폴리올레핀 수지 분말 각각은 미세한 기공을 포함하는 입체상일 수 있으며, 이에 따라 상술한 비표면적을 가질 수 있다. 상기 비표면적을 갖는 폴리올레핀 수지 분말의 구체적인 입체 형상의 특징으로 인하여 후단의 성형 공정이나 또는 선택적으로 적용될 수 있는 건조 및 탈기 공정 등에서 이취를 발생시키거나 관능성을 저하하는 휘발성 화합물들이 보다 쉽게 제거될 수 있다.Specifically, when the ethylene monomer is polymerized singly by using the Ziegler-Natta catalyst having the above porosity or when the ethylene monomer is copolymerized with the alpha -olefin, a ratio of 160 m 2 / g or more, or 190 m 2 / g to 300 m 2 / g Each of the polyolefin resin powders may have a surface area, and each of the polyolefin resin powders may be a three-dimensional phase containing fine pores, and thus may have the above-mentioned specific surface area. Since the polyolefin resin powder having the specific surface area has a specific three-dimensional shape, it is possible to easily remove volatile compounds that generate odor or deteriorate the functionality in the subsequent molding step or selectively applied drying and degassing processes have.
40% 미만의 공극율을 갖거나 실질적으로 공극이 존재하지 않는 지글러-나타 계열 촉매를 사용하는 경우, 낮은 비표면적을 갖거나 상술한 미세한 기공이 충분히 분포하지 않는 폴리올레핀 수지가 제조될 수 있으며, 이러한 폴리올레핀 수지로부터 제공되는 성형품 또는 식품 용기는 상대적으로 높은 휘발성 화합물 함량을 가져서 이취를 발생시키거나 관능성이 저하될 수 있다. When a Ziegler-Natta catalyst having a porosity of less than 40% or substantially no voids is used, a polyolefin resin having a low specific surface area or in which the above-described fine pores are not sufficiently distributed can be produced, The molded article or the food container provided from the resin may have a relatively high volatile compound content and may generate bad odor or deteriorate the functionality.
상기 공극율은 지글러-나타 계열 촉매 전체 부피 중 기공 또는 빈 공간이 차지하는 부피의 비율로 정의될 수 있으며, BET측정기를 통하여 측정할 수 있다. The porosity can be defined as the ratio of volume occupied by pores or voids in the total volume of the Ziegler-Natta catalyst, and can be measured using a BET meter.
상기 식품 용기는 식음료 용기 또는 식음료 용기의 마개일 수 있다. The food container may be a food or beverage container or a stopper of a food and beverage container.
구체적으로, 상기 식품 용기는 ASTM D 1238에 따라 190℃, 2.16 kgf/㎠ 하중 하에서 측정했을 때 0.8 내지 15 g/10분의 용융지수을 갖는 폴리올레핀 수지를 포함할 수 있고, 휘발성 화합물의 함량이 0.075 중량%이하일 수 있다. 용융지수가 0.8 g/10분 미만일 경우 낮은 흐름성 및 높은 압출부하로 인하여 성형에 바람직하지 않으며, 15 g/10분 초과일 경우 내환경응력저항성 등의 물성이 저하되므로 바람직하지 않다.Specifically, the food container may include a polyolefin resin having a melt index of 0.8 to 15 g / 10 min measured at 190 占 폚 under a load of 2.16 kgf / cm2 according to ASTM D 1238, and the content of volatile compounds is 0.075 wt% % ≪ / RTI > When the melt index is less than 0.8 g / 10 min, it is not preferable for molding due to low flowability and high extrusion load, and when it exceeds 15 g / 10 min, physical properties such as environmental stress resistance are lowered.
또한, 상기 제조되는 폴리올레핀 수지는 ASTM D 1505에 따른 평균 밀도가 0.945 내지 0.970 g/㎤ 일 수 있다. 평균밀도가 0.945 미만일 경우 낮은 강성 물성 및 용기마개 성형시 커팅 문제가 있을 수 있으며, 0.970 초과일 경우 충격 물성이 현격히 저하되므로 바람직하지 않다. In addition, the polyolefin resin may have an average density of 0.945 to 0.970 g / cm < 3 > according to ASTM D 1505. When the average density is less than 0.945, there may be a problem of low rigidity property and a cutting problem when forming the container stopper, and when the average density is more than 0.970, the impact property is significantly deteriorated.
상기 제조된 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하는 단계에서는 통상적으로 알려진 성형 방법을 사용할 수 있으나, 보다 용이하게 식음료 용기 또는 식음료 용기의 마개를 제조하기 위하여 사출 및 압축 공정을 적용할 수 있다. 구체적으로, 상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하는 단계는 상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 식음료 용기 또는 식음료 용기의 마개로 사출 성형 및 압축 공정을 수행하는 단계를 포함할 수 있다. In the step of molding the polyolefin resin, a known molding method can be used. However, injection and compression processes can be applied to manufacture a food or beverage container cap more easily. Specifically, the step of molding the polyolefin resin may include a step of performing the injection molding and compression processing of the polyolefin resin with a stopper of a food or beverage container or a food and beverage container.
상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하여 식품 용기를 제조하는 과정에서, 상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 소정의 조건에서 건조 및 탈기하는 과정을 추가로 적용하면 상기 폴리올레핀에 잔류하는 휘발성 화합물 함량을 보다 낮출 수 있다. 구체적으로, 상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하는 단계는 상기 160㎡/g 이상의 비표면적을 가지는 폴리올레핀 수지를 1 ppmw이하의 수분을 포함하고 50℃ 내지 105 ℃의 온도를 갖는 기체를 이용하여 건조 및 탈기 하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다. When the process of drying and degassing the polyolefin resin in a process of forming the polyolefin resin to form a food container is further applied, the content of the volatile compound remaining in the polyolefin can be further reduced. Specifically, the step of molding the polyolefin resin comprises a step of drying and degassing the polyolefin resin having a specific surface area of 160 m 2 / g or more with a gas containing a water content of 1 ppmw or less and having a temperature of 50 ° C to 105 ° C As shown in FIG.
상기 사용 되는 기체는 일반 공기나 질소로 필터를 통하여 수분 관리를 하며 1 ppmw 이하의 수분을 포함하는 것이 바람직하며, 상기 건조 및 탈기의 온도는 30℃ 이상에서부터 폴리에틸렌 수지의 물성에 영향을 주지 않을 범위 내일 수 있으며, 폴리에틸렌 수지의 녹는점 보다 20℃ 낮은 온도 조건까지로 일반적으로 50℃ 내지 105 ℃가 바람직하다. 기체의 유량은 가능한 높을수록 바람직하며 시간은 3 내지 24시간 동안 지속될 수 있다. It is preferable that the gas used is a general air or nitrogen gas which controls moisture through a filter and contains moisture of 1 ppmw or less. The temperature of the drying and degassing ranges from 30 ° C or higher to a range that does not affect the physical properties of the polyethylene resin And preferably 50 ° C to 105 ° C to a temperature condition lower than the melting point of the polyethylene resin by 20 ° C. The flow rate of the gas is preferably as high as possible, and the time may last for 3 to 24 hours.
한편, 상기 일 구현예의 식품 용기의 제조 방법은 상기 에틸렌 단량체를 단독으로 중합 시 또는 에틸렌 단량체를 α-올레핀과 공중합 시에 아마이드계 활제를 첨가하는 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다. Meanwhile, the method of manufacturing a food container according to one embodiment may further include adding an amide-based lubricant when the ethylene monomer is polymerized singly or when the ethylene monomer is copolymerized with an alpha -olefin.
구체적으로, 상기 제조된 폴리에틸렌 수지 분말은 압출기를 이용하여 폴리에틸렌 수지 100 중량부에 대하여 용도에 따라 적정한 토크를 위한 에루카아마이드 또는 베헨아마이드 화합물 등의 아마이드계 활제 0 내지 0.3 중량부, 중화제 0.01 내지 0.2 중량부 및 산화방지제 0.01 내지 0.2 중량부를 균일하게 분산 후, 150∼220℃의 온도에서 용융 압출하여 혼합하여 펠렛으로 제조 후 사일로에 저장되고, 그 후 기체를 흘려 보내며 휘발성 물질을 배출시키는 탈기 및 건조 공정을 선택적으로 진행하여 식품 용기로 성형할 수 있다. Specifically, the polyethylene resin powder is prepared by kneading 0 to 0.3 parts by weight of an amide-based lubricant such as an erucamide or behenamide compound for an appropriate torque for 100 parts by weight of a polyethylene resin using an extruder, 0.01 to 0.2 And 0.01 to 0.2 parts by weight of an antioxidant are uniformly dispersed and then melt extruded at a temperature of 150 to 220 캜 to prepare a pellet which is then stored in a silo and then degassed and dried to discharge a gas and discharge a volatile substance The process can be selectively performed to form a food container.
한편, 상기 에틸렌 단량체의 단독 중합 또는 에틸렌 단량체 및 α-올레핀 간의 공중합에서는 폴리올레핀 합성에 적용되는 반응 조건이 별 다른 제한 없이 사용할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 상기 에틸렌 단량체의 단독 중합 또는 에틸렌 단량체 및 α-올레핀 간의 공중합은 60℃ 내지 90 ℃의 온도 및 10 psi 내지 150psi의 압력 조건 하에서 수행될 수 있다. On the other hand, in the case of the homopolymerization of the ethylene monomer or the copolymerization between the ethylene monomer and the? -Olefin, the reaction conditions applied to the synthesis of the polyolefin may be used without limitation. For example, the homopolymerization of the ethylene monomer or the copolymerization between the ethylene monomer and the alpha -olefin can be carried out at a temperature of 60 DEG C to 90 DEG C and a pressure of 10 psi to 150 psi.
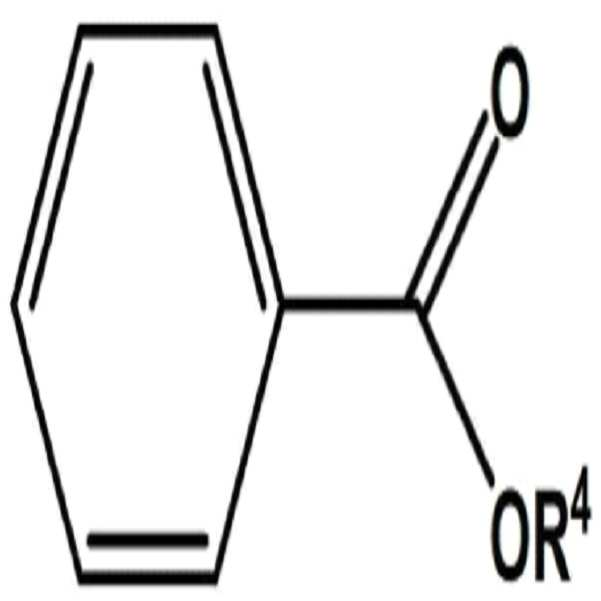
상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 제조하는 단계에서는 폴리올레핀 수지의 합성에 사용될 수 있는 것으로 알려진 지글러-나타 중합 촉매를 큰 제한 없이 사용할 수 있으나, 상기 지글러-나타 중합 촉매는 마그네슘 화합물; 하기 화학식1의 알킬 알루미늄 화합물; 전이 금속 화합물; 하기 화학식 2의 화합물 및 화학식3의 화합물로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 1종 이상의 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자 공여체를 포함하는 것이 바람직하다. In the step of preparing the polyolefin resin, a Ziegler-Natta catalyst which is known to be usable for the synthesis of a polyolefin resin can be used without limitation, but the Ziegler-Natta catalyst can be a magnesium compound; An alkyl aluminum compound of formula (1); Transition metal compounds; It is preferable to include an internal electron donor including at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a compound represented by the following formula (2) and a compound represented by the following formula (3).
[화학식1][Chemical Formula 1]
R1AlX3 -l R 1 AlX 3 -l
상기 화학식 1에서, R1는 탄소수 1 내지 10의 직쇄 또는 분지쇄의 알킬기이며, l은 1 내지 3 의 정수이고, X는 할로겐이다. In Formula 1, R 1 is a straight or branched alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, 1 is an integer of 1 to 3, and X is halogen.
[화학식2](2)
[화학식3] (3)
상기 화학식2내지3에서, R2, R3 및 R4는 서로 같거나 다를 수 있으며, 각각 수소, 탄소수 1내지 20의 직쇄, 분지형 또는 고리형알킬기(Alkyl), 탄소수 2내지 20의 알케닐기 (Alkenyl), 탄소수 3내지 20의 시클로알킬기 (Cycloalkyl), 탄소수 3내지 20의 아릴기 (Aryl), 탄소수 1내지 20의 알킬실릴기 (Alkylsilyl), 탄소수 7내지 20의 아릴알킬기 (Arylalkyl), 탄소수 7내지 20의 알킬아릴기 (Alkylaryl)기, 또는 탄소수 2내지 20의 헤테로원자를 포함하는 알킬기이다.R 2 , R 3 and R 4 may be the same or different and are each a hydrogen, a straight chain, branched or cyclic alkyl group (Alkyl) having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkenyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms An alkenyl group having 3 to 20 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 3 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 3 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkylsilyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an arylalkyl group having 7 to 20 carbon atoms, An alkylaryl group of 7 to 20 carbon atoms, or an alkyl group containing a hetero atom of 2 to 20 carbon atoms.
상기 마그네슘 화합물은 마그네슘 할라이드, 알콕시 마그네슘, 알킬마그네슘할라이드, 알콕시할로겐화마그네슘 및 알릴옥시할로겐화마그네슘으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 1종 이상을 포함할 수 있다. The magnesium compound may include at least one member selected from the group consisting of magnesium halide, alkoxy magnesium, alkyl magnesium halide, alkoxy halide magnesium, and allyloxy halide magnesium.
상기 마그네슘 화합물의 구체적인 예로는, 염화마그네슘, 이염화마그네슘, 브롬화마그네슘, 불화마그네슘, 또는 요드화마그네슘 등의 할로겐화마그네슘; 메톡시염화마그네슘, 에톡시염화마그네슘, 이소프록시염화마그네슘, 부톡시염화마그네슘, 또는 옥톡시염화마그네슘 등의 알콕시할로겐화마그네슘; 페녹시염화마그네슘 등의 알릴옥시할로겐화마그네슘; 및 에톡시마그네슘, 이소프록시마그네슘, 또는 부톡시마그네슘 등의 알콕시마그네슘; 등이 사용될 수 있으며, 마그네슘 할라이드를 사용하는 것이 촉매의 활성을 증가시켜 바람직하다. 또한, 그 중에서도 이염화마그네슘을 사용하는 것이 주 활성금속인 전이금속 화합물과 구조적, 배위적으로 안정하고 높은 활성을 나타내어 바람직하다.Specific examples of the magnesium compound include magnesium halides such as magnesium chloride, magnesium dichloride, magnesium bromide, magnesium fluoride, and magnesium iodide; Magnesium alkoxy halides such as magnesium methoxide chloride, magnesium ethoxy chloride, magnesium isopropoxy chloride, magnesium chloride butoxide, or magnesium octoxy chloride; Allyloxyhalogenated magnesium such as phenoxy magnesium chloride; And alkoxy magnesium such as ethoxy magnesium, isopropoxy magnesium, or butoxy magnesium; Etc., and it is preferable to use magnesium halide because it increases the activity of the catalyst. Among them, magnesium dichloride is preferably used because it exhibits stable and high activity in terms of structure and coordination with the transition metal compound, which is the main active metal.
상기 전이 금속 화합물은 하기 화학식4의 전이 금속 화합물을 포함할 수 있다. 상기 전이 금속 화합물은 IVB, VB, 또는 VIB족의 전이 금속 또는 이러한 전이 금속을 함유한 유기 화합물을 포함하는 의미이며, 상기 전이 금속의 구체적인 예로는 Ti, Zr, Hf, Rf, V, Nb, Ta, Db, Cr, Mo, W, Sg을 들 수 있다.The transition metal compound may include a transition metal compound represented by the following formula (4). The transition metal compound means a transition metal of Group IVB, VB, or VIB or an organic compound containing such a transition metal. Specific examples of the transition metal include Ti, Zr, Hf, Rf, V, Nb, Ta , Db, Cr, Mo, W, and Sg.
[화학식4][Chemical Formula 4]
MXn(OR5)4-n MX n (OR 5 ) 4-n
상기 화학식 4에서, M은 주기율표 IVB, VB및 VIB족의전이 금속 원소로 이루어진 군에서 선택되고, X는 할로겐, R5는 탄소수 1내지 10의 알킬기, n은 금속의 산화수로 0 내지 4이다.In the formula (4), M is selected from the group consisting of transition metal elements of Group IVB, VB and VIB of the periodic table, X is halogen, R 5 is an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, and n is 0 to 4 as an oxidation number of metal.
상기 지글러-나타 중합 촉매는, 마그네슘 화합물을 알코올과 반응시켜 마그네슘 화합물 용액을 제조하는 단계; 및 상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 상기 화학식1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 알킬알루미늄, 전이금속 화합물, 및 상기 화학식 2내지3로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자공여체를 반응시키는 단계를 통하여 얻어질 수 있다. The Ziegler-Natta catalyst may be prepared by reacting a magnesium compound with an alcohol to prepare a magnesium compound solution; And an inner electron donor including the alkyl magnesium compound, the transition metal compound, and the compound represented by Chemical Formulas 2 to 3, wherein the magnesium compound solution includes the compound represented by Chemical Formula 1.
상기 폴리올레핀 합성용 촉매의 제조에서, 마그네슘 화합물을, 알코올과 반응시켜 마그네슘 화합물 용액을 제조할 수 있다.In the production of the polyolefin synthesis catalyst, a magnesium compound solution can be prepared by reacting a magnesium compound with an alcohol.
상기 알코올은 폴리올레핀 합성용 지글러-나타 촉매의 제조에 사용되는 것으로 알려진 알코올이라면 제한 없이 사용 할 수 있다. 구체적으로 에탄올, n-프로판올, 이소프로판올, n-부탄올, 이소부탄올, n-펜탄올, 이소펜탄올, 네오펜탄올, 시클로펜탄올, n-헥산올, n-헵탄올, n-옥탄올, 데칸올, 도데칸올, 2-메틸펜탄올, 2-에틸부탄올, 2-에틸헥산올 등의 지방족 또는 지환족 알코올; 시클로헥산올, 메틸시클로헥산올 등의 아릴사이클릭 알코올; 또는 벤질알코올, 메틸벤질알코올, 이소프로필벤질알코올, α-메틸벤질알코올 등의 아로마틱 알코올; 이 사용될 수 있고, 이 중에서 지방족 또는 지환족 알코올을 사용하는 것이 바람직하며, 시클릭또는 벤젠 고리를 가진 알코올은 분자 자체가 커서 때문에 반응성이 떨어지고 반응이 느리게 진행되기 때문에 비교적 사슬길이가 짧은 에탄올을 사용하는 것이 더욱 바람직하다. The alcohol can be used without limitation as long as it is an alcohol known to be used in the production of a Ziegler-Natta catalyst for synthesizing polyolefins. Specific examples of the solvent include ethanol, n-propanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, isobutanol, n-pentanol, isopentanol, neopentanol, cyclopentanol, n- Aliphatic or alicyclic alcohols such as dodecanol, 2-methylpentanol, 2-ethylbutanol and 2-ethylhexanol; Aryl cyclic alcohols such as cyclohexanol and methylcyclohexanol; Or aromatic alcohols such as benzyl alcohol, methylbenzyl alcohol, isopropylbenzyl alcohol and? -Methylbenzyl alcohol; Among them, it is preferable to use an aliphatic or alicyclic alcohol. Since the alcohol having a cyclic or benzene ring has a large molecular size, the reactivity is poor and the reaction proceeds slowly, so ethanol having a relatively short chain length is used .
상기 알코올은 마그네슘 화합물과 반응하여 마그네슘 화합물을 용해시킬 수 있고, 마그네?? 화합물을 성글게 팽창시켜 표면적을 넓히는 역할을 수행한다. 또한, 상기 알코올을 첨가하여 마그네?? 화합물을 팽창시킬 수 있어, 고온에서 균질 용액을 제조하는 단계가 필요 없고, 0 내지 40℃의 온도에서 30분 내지 2시간 정도 충분히 교반하고, 마그네슘 화합물과 알코올을 반응시켜 활성이 높은 촉매를 제조할 수 있다. The alcohol may react with the magnesium compound to dissolve the magnesium compound, The compound swells to expand the surface area. Further, by adding the above alcohol, The compound can be swollen and there is no need to prepare a homogeneous solution at a high temperature. The solution is sufficiently stirred at a temperature of 0 to 40 ° C for about 30 minutes to 2 hours, and a magnesium compound is reacted with an alcohol to prepare a highly active catalyst .
상기 마그네슘 화합물 및 알코올의 반응 몰비는 1:0.5 내지 1:10, 바람직하게는 1:2 내지 1:8일 수 있다. 상기 알코올의 반응 몰비가 마그네슘 화합물 대비 10몰을 초과하는 경우 높은 활성을 나타내기 위하여 마그네슘 화합물과 반응시키는 전이금속 화합물의 양을 증가시켜야 하여 경제성 측면에서 바람직하지 못하고, 0.5몰 미만인 경우 제조되는 촉매의 수율이 작을 수 있어 바람직하지 못하다.The reaction molar ratio of the magnesium compound and the alcohol may be 1: 0.5 to 1:10, preferably 1: 2 to 1: 8. When the reaction molar ratio of the alcohol is more than 10 moles relative to the magnesium compound, the amount of the transition metal compound to be reacted with the magnesium compound must be increased in order to exhibit high activity, which is not preferable from the economical point of view. The yield may be small, which is undesirable.
또한, 상기 마그네슘 용액을 제조하는 단계는 탄화수소의 용매의 존재 하에서 상기 마그네슘 화합물 및 알코올을 반응시킬 수 있다. 상기와 같이 탄화수소 용매 하에서 반응하는 경우, 적은 양의 알코올을 사용하면서도 마그네슘 화합물과 알코올의 균질 용액을 얻을 수 있어 바람직하다.The magnesium solution may be prepared by reacting the magnesium compound with an alcohol in the presence of a hydrocarbon solvent. When the reaction is carried out in the presence of a hydrocarbon solvent as described above, a homogeneous solution of a magnesium compound and an alcohol can be obtained while using a small amount of alcohol.
상기 탄화수소 용매의 구체적인 예로는 탄소수가 5 내지 20인 지방족 또는 지환족 탄화수소를 들 수 있으며, 그 중에서도 탄소수가8 내지17인 지방족 또는 지환족 탄화수소 용매가 가장 바람직하다. 보다 구체적인 예로는 헥산, 헵탄, 옥탄, 데칸, 도데칸, 테트라데칸, 미네랄 오일 등의 지방족 탄화수소; 시클릭헥산, 시클릭옥탄, 메틸시클릭펜탄, 메틸시클릭헥산 등의 지환족 탄화수소; 벤젠, 톨루엔, 자일렌, 에틸벤젠, 큐멘 등의 방향족 탄화수소 등을 들 수 있다. Specific examples of the hydrocarbon solvent include aliphatic or alicyclic hydrocarbons having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, and aliphatic or alicyclic hydrocarbon solvents having 8 to 17 carbon atoms are most preferred. More specific examples include aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, octane, decane, dodecane, tetradecane, and mineral oil; Alicyclic hydrocarbons such as cyclic hexane, cyclic octane, methyl cyclic pentane and methyl cyclic hexane; And aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene, toluene, xylene, ethylbenzene, and cumene.
상기 탄화수소 용매는 상기 마그네슘 화합물 1몰에 대하여 5내지 20몰 비율로 반응시키는 것이 바람직하다. 탄화수소 용매의 사용량이 상기 범위 미만일 경우에는 낮은 온도에서 균질한 마그네슘 할라이드 화합물 용액을 얻기 어렵고, 상기 범위를 초과하면 공정상 반응기 용량이 커지고 온도를 조절하기 어려울 수 있기 때문에 바람직하지 못하다.The hydrocarbon solvent is preferably reacted at a rate of 5 to 20 mol per 1 mol of the magnesium compound. If the amount of the hydrocarbon solvent is less than the above range, it is difficult to obtain a homogeneous solution of the magnesium halide compound at a low temperature. If the amount is larger than the above range, the reactor capacity may increase in the process and the temperature may be difficult to control.
상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과, 상기 화학식1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 알킬알루미늄, 전이금속 화합물, 및 상기 화학식2내지3로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자공여체를 반응시키는 단계에서, 상기 반응물을 반응시키는 순서나 투입순서는 크게 제한되지 않는다. 예를 들어 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 알킬알루미늄, 전이금속 화합물, 및 내부전자공여체를 동시에 반응시킬 수도 있고, 상기 성분들을 순차적으로 투입하여 반응시킬 수도 있다. In the step of reacting the magnesium compound solution with the internal electron donor comprising the alkyl aluminum, the transition metal compound and the compound represented by the above formulas 2 to 3 containing the compound represented by the formula 1, The sequence or order of insertion is not limited. For example, the magnesium compound solution, the alkyl aluminum, the transition metal compound, and the internal electron donor may be reacted simultaneously, or the components may be sequentially added to react.
다만, 촉매의 활성을 증가시키기 위하여, 상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과, 상기 화학식1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 알킬알루미늄, 전이금속 화합물, 및 상기 화학식2내지3로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자공여체를 반응시키는 단계는, 상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 상기 화학식1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 알킬알루미늄을 반응시키는 단계 및 상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 상기 알킬알루미늄의 반응 결과물을 전이 금속 화합물 및 상기 화학식2내지3로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자공여체와 순차적으로 반응시키는 단계를 포함하여 반응시키는 것이 바람직하다. However, in order to increase the activity of the catalyst, an inner electron donor including the magnesium compound solution, the alkylaluminum including the compound represented by the formula (1), the transition metal compound, and the compound represented by the formula (2) Reacting the magnesium compound solution with an alkylaluminum compound including the compound represented by Formula 1, and reacting the magnesium compound solution and the reaction product of the alkylaluminum with a transition metal compound represented by Formula 2 to Formula 3 With an internal electron donor comprising a compound of formula < RTI ID = 0.0 > (I) < / RTI >
보다 구체적으로, 알코올과 마그네?? 화합물의 반응에서, 알코올이 마그네슘 화합물을 성글게 팽창시켜 활성점이 많이 생성될 수 있는 공간을 확보하고, 이에 바로 알킬 알루미늄과 반응을 시켜, 마그네슘 화합물에 붙어 있던 알코올을 떼어내면서 활성점을 다량 생성시킬 수 있다. 즉, 상기 알킬알루미늄 화합물은 상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 반응시켜, 최종적으로 제조된 폴리올레핀 중합용 촉매의 활성이 증대되고, 이러한 촉매를 이용하여 폴리올레핀을 중합하면 분자량 분포가 넓은 폴리올레핀을 얻을 수 있다. More specifically, alcohol and magnesia In the reaction of the compound, it is possible to generate a large amount of active sites by allowing alcohol to sparse and expand the magnesium compound to secure a space in which a large number of active sites can be generated, and then reacting with the alkyl aluminum to remove the alcohol attached to the magnesium compound have. That is, the alkylaluminum compound is reacted with the magnesium compound solution to increase the activity of the finally prepared polyolefin polymerization catalyst. When the polyolefin is polymerized using such a catalyst, a polyolefin having a broad molecular weight distribution can be obtained.
상기 알킬알루미늄은 상기 화학식1로 표시되는 화합물을 1종이상 포함할 수 있고, 화학식1로 표시되는 화합물의 구체적인 예로는 트리에틸알루미늄, 트리메틸알루미늄, 트리이소프로필알루미늄, 트리옥틸알루미늄, 디에틸알루미늄클로라이드, 디에틸알루미늄브로마이드, 디에틸알루미늄아이오다이드, 디에틸알루미늄플로라이드, 에틸알루미늄디클로라이드, 디메틸알루미늄클로라이드, 메틸알루미늄디클로라이드 등을 들 수 있다.The alkyl aluminum may include at least one compound represented by the formula (1), and specific examples of the compound represented by the formula (1) include triethyl aluminum, trimethyl aluminum, triisopropyl aluminum, trioctyl aluminum, diethyl aluminum chloride , Diethylaluminum bromide, diethylaluminum iodide, diethylaluminum fluoride, ethylaluminum dichloride, dimethylaluminum chloride, methylaluminum dichloride, and the like.
상기 마그네슘 화합물 및 알킬알루미늄은 1:0.01 내지 1:5의 몰 비로 반응할 수 있고, 바람직하게는 1:0.5 내지 1:10의 몰비로 반응시킬 수 있다. 알킬알루미늄 화합물의 사용량이 마그네슘 화합물 1몰당 0.01 몰 미만인 경우에는 제조되는 폴리올레핀의 분자량 분포가 증가하지 않을 수 있고, 50몰을 초과하는 경우에는 촉매 활성이 급격하게 떨어질 수 있다. The magnesium compound and the alkylaluminum can be reacted at a molar ratio of 1: 0.01 to 1: 5, preferably at a molar ratio of 1: 0.5 to 1:10. When the amount of the alkyl aluminum compound used is less than 0.01 mol per 1 mol of the magnesium compound, the molecular weight distribution of the produced polyolefin may not increase, and when it exceeds 50 mol, the catalytic activity may drop sharply.
상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 알킬알루미늄 화합물의 반응온도는 -50 내지 150℃가 바람직하며, 특히 0 내지 100℃가 바람직하다. 상기 온도범위를 벗어나는 경우, 반응물이 충분히 반응하지 못하여 활성이 떨어지거나, 부반응이 증가하여 바람직하지 못하다. 또한, 반응시간은 반응이 시작되는 시점에서부터 0.5 내지 24시간 동안 충분히 수행하는 것이 바람직하다.The reaction temperature of the magnesium compound solution and the alkylaluminum compound is preferably -50 to 150 ° C, more preferably 0 to 100 ° C. If the temperature is out of the above range, the reactants do not sufficiently react to deteriorate the activity or the side reaction increases, which is not preferable. In addition, the reaction time is preferably sufficiently performed for 0.5 to 24 hours from the start of the reaction.
그리고, 상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 알킬알루미늄을 반응시킨 용액을, 전이금속 화합물, 및 상기 화학식 2 내지 3으로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자공여체와 순차적으로 반응시켜 폴리올레핀 합성용 촉매를 제조할 수 있다.Then, a solution obtained by reacting the magnesium compound solution with alkyl aluminum may be sequentially reacted with a transition metal compound and an internal electron donor including the compounds represented by the above formulas 2 to 3, thereby preparing a polyolefin synthesis catalyst.
상기 마그네슘 화합물 및 전이금속 화합물은 1:0.1 내지 1:50의 몰 비로 반응할 수 있고, 바람직하게는 1:1 내지 1:10의 몰비로 반응시킬 수 있다. 전이금속 화합물의 사용량이 마그네슘 화합물 1몰당 0.1몰 미만인 경우에는 제조되는 촉매의 활성이 떨어지거나, 이를 이용하여 합성되는 폴리올레핀의 입체규칙성이 저하 될 수 있어 바람직하지 못하다.The magnesium compound and the transition metal compound may be reacted at a molar ratio of 1: 0.1 to 1:50, preferably at a molar ratio of 1: 1 to 1:10. When the amount of the transition metal compound to be used is less than 0.1 mole per 1 mole of the magnesium compound, the activity of the catalyst to be produced deteriorates or the stereoregularity of the synthesized polyolefin may be lowered, which is not preferable.
상기 전이금속 화합물을 상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 알킬알루미늄을 반응시킨 용액에 투여하는 온도는 -50℃ 내지 150℃에서 이루어질 수 있고, 바람직하게는 -20℃ 내지 100℃일 수 있다. 반응 과정은 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 알킬알루미늄의 반응물을 반응기에서 교반하고, 일정한 양의 전이금속 화합물을 약 2시간 동안 조금씩 가하는 형태로 진행할 수 있다. 전이금속 화합물을 천천히 투여하는 것은 전이금속 화합물이 다른 화합물과 급격히 반응을 진행하여 생길 수 있는 부 반응을 방지할 수 있어 바람직하다. The temperature at which the transition metal compound is added to the solution obtained by reacting the magnesium compound solution with the alkylaluminum may be -50 ° C to 150 ° C, preferably -20 ° C to 100 ° C. The reaction process can be carried out by stirring the magnesium compound solution and the reaction product of the alkylaluminum in the reactor and adding a certain amount of the transition metal compound to the reaction product for about 2 hours. The slow administration of the transition metal compound is preferable because the transition metal compound can prevent the side reaction that may occur due to rapid reaction with other compounds.
그리고, 전이금속 화합물을 투여하여 반응을 시킨 다음, 그 반응물의 온도를 높이고 내부전자공여체를 투여하여 반응시킬 수 있다. Then, the reaction can be carried out by administering a transition metal compound, raising the temperature of the reaction product, and administering an internal electron donor.
상기 내부전자공여체는 폴리올레핀 합성용 중합 촉매 내부에서 전이금속 화합물에 전자를 공여하여, 촉매의 활성점을 형성하는 역할을 하며, 이를 통해 촉매 활성이 증가하고, 입체규칙성이 개선된 폴리올레핀을 합성할 수 있다. 구체적으로, 상기 에틸벤조에이트, 또는 디아이소부틸 프탈레이트는 벤젠고리에 하나 또는 두개의 아실기를 포함하고, 상술한 R2 내지 R4의 특정 작용기가 특정 위치에 결합되어 있는 구조를 갖는다. 즉, 이러한 화학 구조는 촉매 활성점에 강하게 결합할 수 있으며, 결정화도를 높이는 핵제의 역할을 할 수 있다. 이에 따라, 상기 화학식2내지3로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자공여체는 보다 효과적으로 촉매의 활성을 증가시킬 수 있고, 핵제의 역할을 통해 미분량을 감소시킬 수 있다.The internal electron donor serves to form an active site of the catalyst by donating electrons to the transition metal compound within the polymerization catalyst for polyolefin synthesis, thereby increasing the catalytic activity and synthesizing a polyolefin having improved stereoregularity . Specifically, the ethylbenzoate or diisobutylphthalate has one or two acyl groups in the benzene ring, and has a structure in which the above-mentioned specific functional groups of R 2 to R 4 are bonded at specific positions. That is, this chemical structure can strongly bind to the catalytic active site and can act as a nucleating agent for increasing the degree of crystallization. Accordingly, the internal electron donor including the compounds represented by Chemical Formulas 2 to 3 can more effectively increase the activity of the catalyst, and can reduce the amount of the internal electron donor through the role of the nucleating agent.
상기 내부전자공여체는 상기 마그네슘 화합물 1몰당 0.1 내지 5몰 반응시킬 수 있고, 바람직하게는 0.1 내지 1몰 반응시킬 수 있다. 상기 범위를 벗어나게 내부전자공여체를 반응시키는 경우, 최종적으로 얻어지는 폴리올레핀 합성용 촉매의 활성점의 균일도가 낮아질 수 있기 때문에 바람직하지 못하다.The internal electron donor may be reacted with 0.1 to 5 moles, preferably 0.1 to 1 mole, per mole of the magnesium compound. When the internal electron donor is reacted outside the above range, the uniformity of the active sites of the polyolefin synthesis catalyst finally obtained may be lowered, which is not preferable.
그리고, 상기 내부전자공여체를 반응시킨 생성물을 탄화수소 용매로 세정하고, 촉매 입자만을 침전시킨 후 상층액을 제거하는 과정을 수 차례 반복하고, 전이금속 화합물이 제거된 촉매 입자를 흐르는 질소 하에 2시간 이상 환기시키고, 건조하여 최종 폴리올레핀 중합용 촉매를 제조할 수 있다.The process in which the product obtained by reacting the internal electron donor is washed with a hydrocarbon solvent and only the catalyst particles are precipitated and then the supernatant is removed are repeated several times and the catalyst particles having the transition metal compound removed therefrom under nitrogen And then the catalyst for polymerization of the final polyolefin can be prepared.
한편, 보다 우수한 굴곡강도 및 충격강도 등의 우수한 기계적 물성을 가지면서도 높은 내환경 응력 균열성 및 높은 용융 장력을 확보하여 수지 성형성 또는 수지 가공성을 향상시키기 위하여, 상기 담체상에 결합된 전이금속의 할로겐화 화합물은 다양한 크기를 갖는 입자를 포함하거나, 넓은 입자 크기 분포를 가질 수 있다. On the other hand, in order to secure a high environmental stress cracking property and a high melt tension while having excellent mechanical properties such as excellent bending strength and impact strength and the like, and to improve resin moldability or resin processability, The halogenated compound may include particles having various sizes, or may have a broad particle size distribution.
구체적으로, 상기 지글러-나타 중합 촉매는 최대 직경이 500㎛ 초과인 입자 2 wt% 내지 40 wt%; 최대 직경이 120㎛ 미만인 입자 10 wt% 내지 35 wt%; 및 잔량의 120㎛ 내지 500㎛의 최대 직경을 갖는 입자를 포함할 수 있다. 또한, 상기 담체상에 결합된 전이금속의 할로겐화 화합물은 최대 직경이 500㎛ 초과 1000㎛이하인 입자 2 내지 40wt%, 최대 직경이 50㎛ 이상 120㎛ 미만인 입자 10 wt% 내지 35 wt%; 및 잔량의 120㎛ 내지 500㎛의 최대 직경을 갖는 입자를 포함할 수 있다. Specifically, the Ziegler-Natta catalyst comprises 2 wt% to 40 wt% of particles having a maximum diameter of more than 500 탆; 10 wt% to 35 wt% of particles having a maximum diameter of less than 120 탆; And particles having a maximum diameter of 120 [mu] m to 500 [mu] m of the remaining amount. Further, the halogenated compound of the transition metal bonded on the carrier may contain 2 to 40 wt% of particles having a maximum diameter of 500 탆 to 1000 탆 and 10 wt% to 35 wt% of particles having a maximum diameter of 50 탆 to less than 120 탆; And particles having a maximum diameter of 120 [mu] m to 500 [mu] m of the remaining amount.
상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 제조하는 단계에서 사용 가능한 상기 α-올레핀으로는 1-부텐, 1-펜텐, 1-헥센, 4-메틸, 1-펜텐, 1-헵텐 및 1-옥텐으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 1종 이상의 단량체를 들 수 있다. Examples of the? -Olefin which can be used in the step of preparing the polyolefin resin include 1-butene, 1-pentene, 1-hexene, 4-methyl, 1-pentene, And the like.
본 발명에 따르면, 낮은 휘발성 화합물 수치를 가지며 우수한 관능 안정성으로 식품, 생수 및 음료의 이취 또는 맛에 영향을 주는 부분을 최소화할 수 있는 식품 용기의 제조 방법 및 이러한 제조 방법으로부터 제공되는 식품 용기가 제공될 수 있다. According to the present invention, there is provided a method of manufacturing a food container capable of minimizing a portion affecting odor or taste of foods, bottled water and beverages with a low volatile compound value and excellent sensory stability, and a food container provided from such a manufacturing method .
발명을 하기의 실시예에서 보다 상세하게 설명한다. 단, 하기의 실시예는 본 발명을 예시하는 것일 뿐, 본 발명의 내용이 하기의 실시예에 의하여 한정되는 것은 아니다.
The invention will be described in more detail in the following examples. However, the following examples are illustrative of the present invention, and the present invention is not limited by the following examples.
[[ 제조예Manufacturing example : : 지글러Ziegler -- 나타Appear 촉매의 제조] Preparation of Catalyst]
제조예1Production Example 1
교반기와 오일 순환 히터가 장착된 300 ml 크기의 내압용 유리반응기를 질소로 충분히 환기시키고, 질소분위기하에서 반응기 내에 헥산 110 ml를 채웠다. 반응기에 무수 이염화마그네슘 5.71 g을 투입하고 상온에서 교반하였다. 에탄올 17.8 ml를 1시간에 걸쳐 서서히 투입하고 무수 이염화마그네슘과 에탄올이 충분히 반응하도록 300 rpm의 회전 속도로 1시간 이상 교반하였다. A 300 ml pressure-resistant glass reactor equipped with a stirrer and an oil circulating heater was sufficiently evacuated with nitrogen and 110 ml of hexane was charged into the reactor under a nitrogen atmosphere. 5.71 g of anhydrous magnesium dichloride was added to the reactor and stirred at room temperature. 17.8 ml of ethanol was slowly added thereto over 1 hour and stirred at 300 rpm for 1 hour or more to sufficiently react the anhydrous magnesium dichloride and ethanol.
디에틸알루미늄 클로라이드 16 ml에 헥산 16 ml를 혼합하여 50%로 희석한 알킬알루미늄 화합물을 상기 무수 이염화마그네슘과 에탄올의 혼합물에, 25℃에서 400 rpm의 회전 속도로 교반하면서, 4시간에 걸쳐 서서히 투입하였다. 투입이 완료된 후에는 교반 속도를 500 rpm으로 올려 2시간 동안 반응시켰다. 16 ml of diethylaluminum chloride and 16 ml of hexane were mixed and the alkylaluminum compound diluted to 50% was slowly added to the mixture of magnesium anhydrous magnesium dichloride and ethanol at 25 ° C at a rotation speed of 400 rpm for 4 hours Respectively. After completion of the addition, the stirring speed was increased to 500 rpm and reacted for 2 hours.
그리고, 이렇게 만들어진 불균일 혼합액에 사염화티탄 20 ml를 25℃에서 서서히 투입하고, 30분간 유지해 준 뒤 서서히 가열하였다. 73℃에서 내부 전자공여체로 에틸벤조에이트 0.26 ml를 주입한 후 3시간 동안 반응시켰다. 반응이 완료되면 온도를 50℃로 낮추어 교반을 멈추고, 만들어진 촉매를 침전시켜 상층액을 제거하고 헥산 200 ml를 넣은 다음 충분히 헹구어 냈다. 이 과정을 6회 이상 반복하여 폴리에틸렌 합성용 촉매를 제조하였다.
Then, 20 ml of titanium tetrachloride was gradually added to the thus prepared heterogeneous mixed solution at 25 占 폚, held for 30 minutes, and then slowly heated. At 73 ° C, 0.26 ml of ethyl benzoate was injected as an internal electron donor and reacted for 3 hours. When the reaction was completed, the temperature was lowered to 50 ° C, stirring was stopped, the catalyst was precipitated, the supernatant was removed, 200 ml of hexane was added, and the mixture was thoroughly rinsed. This process was repeated 6 times or more to prepare a catalyst for synthesizing polyethylene.
제조예2Production Example 2
1) 상기 에탄올 17.8 ml 대신에 에탄올 21ml를 사용한 점 및 2) 디에틸알루미늄 클로라이드 16 ml에 헥산 16 ml를 혼합하는 대신에 디에틸알루미늄 클로라이드 20ml에 헥산 20ml를 혼합한 점 제외하고, 제조예1과 동일한 방법으로 폴리에틸렌 합성용 촉매를 제조하였다.
1) except that 21 ml of ethanol was used instead of 17.8 ml of ethanol and 2) 16 ml of diethylaluminum chloride was mixed with 16 ml of hexane, and 20 ml of diethylaluminum chloride was mixed with 20 ml of hexane. A catalyst for synthesizing polyethylene was prepared in the same manner.
제조예3Production Example 3
1) 상기 에탄올 17.8 ml 대신에 에탄올 28ml를 사용한 점 및 2) 디에틸알루미늄 클로라이드 16 ml에 헥산 16 ml를 혼합하는 대신에 디에틸알루미늄 클로라이드 20ml에 헥산 20ml를 혼합한 점 제외하고, 제조예1과 동일한 방법으로 폴리에틸렌 합성용 촉매를 제조하였다.
1) except that 28 ml of ethanol was used instead of 17.8 ml of ethanol and 2) 16 ml of diethylaluminum chloride was mixed with 20 ml of hexylic acid instead of 20 ml of diethylaluminum chloride instead of 16 ml of hexane. A catalyst for synthesizing polyethylene was prepared in the same manner.
[[ 실시예Example 1 내지 2 및 1 to 2 and 비교예1Comparative Example 1 : : 폴리올레핀Polyolefin 수지의 제조] Preparation of resin]
비교예1Comparative Example 1
상기 제조예1에서 제조된 지글러-나타 촉매 및 수소의 존재 하에, 에틸렌 단량체를 80℃의 온도 및 70psi 의 압력하에서 약 2시간 동안 중합 반응시켜서 폴리에틸렌 수지를 제조하였다. 이때, 상기 지글러-나타 촉매는 무수 이염화마그네슘, 에탄올, 디에틸알루미늄 클로라이드, 사염화티탄을 1:5.1:2.1:3의 몰비로 포함하였다.
In the presence of the Ziegler-Natta catalyst and hydrogen prepared in Preparation Example 1, the ethylene monomer was polymerized at a temperature of 80 ° C and a pressure of 70 psi for about 2 hours to prepare a polyethylene resin. At this time, the Ziegler-Natta catalyst contained anhydrous magnesium dichloride, ethanol, diethylaluminum chloride and titanium tetrachloride in a molar ratio of 1: 5.1: 2.1: 3.
실시예1Example 1
상기 제조예2에서 제조된 지글러-나타 촉매 및 수소의 존재 하에, 에틸렌 단량체를 80℃의 온도 및 70psi 의 압력하에서 약 2시간 동안 중합 반응시켜서 폴리에틸렌 수지를 제조하였다. 이때, 상기 지글러-나타 촉매는 무수 이염화마그네슘, 에탄올, 디에틸알루미늄 클로라이드, 사염화티탄을 1:6:2.6:3 의 몰비로 포함하였다.
In the presence of the Ziegler-Natta catalyst and hydrogen prepared in Preparation Example 2, the ethylene monomer was polymerized at a temperature of 80 ° C and a pressure of 70 psi for about 2 hours to prepare a polyethylene resin. At this time, the Ziegler-Natta catalyst contained anhydrous magnesium dichloride, ethanol, diethylaluminum chloride and titanium tetrachloride in a molar ratio of 1: 6: 2.6: 3.
실시예2Example 2
상기 제조예2에서 제조된 지글러-나타 촉매 및 수소의 존재 하에, 에틸렌 단량체를 80℃의 온도 및 70psi 의 압력하에서 약 2시간 동안 중합 반응시켜서 폴리에틸렌 수지를 제조하였다. 이때, 상기 지글러-나타 촉매는 무수 이염화마그네슘, 에탄올, 디에틸알루미늄 클로라이드, 사염화티탄을 1:8:2.6:3 의 몰비로 포함하였다.
In the presence of the Ziegler-Natta catalyst and hydrogen prepared in Preparation Example 2, the ethylene monomer was polymerized at a temperature of 80 ° C and a pressure of 70 psi for about 2 hours to prepare a polyethylene resin. At this time, the Ziegler-Natta catalyst contained anhydrous magnesium dichloride, ethanol, diethylaluminum chloride and titanium tetrachloride in a molar ratio of 1: 8: 2.6: 3.
상기 비교예1 및 실시예 1 및 2 제조된 폴리에틸렌 수지 분말의 비표면적은 분말에 질소를 흡착시켜 흡착된 질소가스의 양을 측정하여 BET식으로 계산하였다.
The specific surface area of the polyethylene resin powder prepared in Comparative Example 1 and Examples 1 and 2 was calculated by the BET equation by measuring the amount of adsorbed nitrogen gas by adsorbing nitrogen in the powder.
[식음료 용기 마개의 제조][Manufacturing of food and beverage container stopper]
상기 비교예1 및 실시예 1 및 2 제조된 폴리에틸렌 수지를 각각 이용하여 30mm규격의 48캐비티를 가진 사출성형기를 이용하여 230℃ 사출 조건으로 용기 마개를 제조하였다. Using the polyethylene resin prepared in Comparative Example 1 and Examples 1 and 2, a container cap was manufactured under the conditions of injection molding at 230 캜 using an injection molding machine having 48 cavities of 30 mm size.
상기 제조된 용기 마개에 포함된 휘발성 화합물의 함량은 105℃ 하에서 1시간동안 열을 가하였을 때 수지 무게 감소 비율을 측정하였다.
The content of the volatile compounds contained in the above-mentioned container stopper was determined by measuring the resin weight loss ratio when heat was applied at 105 DEG C for 1 hour.
휘발성 화합물 (wt%)In the container cap
Volatile compounds (wt%)
상기 표1에 나타난 바와 같이, 49% 및 65%의 공극율을 갖는 지글러-나타 중합 촉매를 사용하여 제조되는 폴리에틸렌 수지가 각각 200 및 270 ㎡/g의 비표면적을 가지며, 이러한 폴리에틸렌 수지를 사용하여 제조된 용기 마개는 0.080 wt% 미만의 휘발성 화합물을 포함한다는 점이 확인되었다.
As shown in Table 1, the polyethylene resin prepared using the Ziegler-Natta catalyst having a porosity of 49% and 65% had a specific surface area of 200 and 270 m 2 / g, respectively. It has been found that the container closure contains less than 0.080 wt% volatile compounds.
[[ 실시예Example 3 내지 6: 3 to 6: 폴리올레핀Polyolefin 수지의 제조] Preparation of resin]
실시예1과 동일한 방법으로 폴리에틸렌 수지를 제조하였다. A polyethylene resin was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1.
상기 제조된 폴리에틸렌 수지 분말의 비표면적은 분말에 질소를 흡착시켜 흡착된 질소가스의 양을 측정하여 BET식으로 계산하였으며, 휘발성 화합물의 함량은 105℃ 하에서 1시간동안 열을 가하였을 때 수지 무게 감소 비율을 측정하였다.The specific surface area of the prepared polyethylene resin powder was calculated by BET equation by measuring the amount of nitrogen gas adsorbed by adsorbing nitrogen in the powder, and the volatile compound content was calculated by subtracting the weight of the resin when heat was applied at 105 DEG C for 1 hour The ratio was measured.
또한, 상기 제조된 폴리에틸렌 수지 분말의 용융흐름지수은 ASTM D 1238에 따라 190℃, 2.16㎏f/㎤ 하중 하에서 측정하였고, 밀도는 ASTM D 1505에 따라 측정하였다. The melt flow index of the polyethylene resin powder thus prepared was measured under a load of 2.16 kgf / cm 3 at 190 캜 according to ASTM D 1238, and the density was measured according to ASTM D 1505.
그리고, GC/MS 는 200℃에서 20분동안 헤드스페이스법으로 휘발분을 포집 후, 이 혼합 기체를 3단계로 승온 시키며 분류하여 정성 및 정량 분석하였다 [ 1단계 : 50℃, 2분 유지, 2단계 : 10℃/분 속도로 250℃까지 승온 후 5분 유지, 3단계 : 10℃/분 속도로 320℃까지 승온 후 5분 유지]
The GC / MS was subjected to qualitative and quantitative analysis by collecting volatile components by headspace method at 200 ° C for 20 minutes, then heating the mixture to three stages, and qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing it. [Step 1: : The temperature was raised to 250 ° C at a rate of 10 ° C / minute and maintained for 5 minutes, the third stage: the temperature was raised to 320 ° C at a rate of 10 ° C / minute and then maintained for 5 minutes]
(펠렛)division
(Pellets)
3Example
3
4Example
4
5Example
5
6Example
6
물성Suzy
Properties
(g/㎤)density
(g / cm3)
상기 표2에 나타난 바와 같이, 실시예1에서 제조된 폴리에틸렌을 80℃의 질소 가스에 노출시키면서 건조함에 따라서 잔류하는 휘발성 화합물의 함량 및 탄화수소의 함량이 점차 낮아진다는 점이 확인되었다. 또한, 상기 제조되는 폴리올레핀 수지는 190℃ 및 2.16㎏f/㎤ 의 조건에서 4.0 g/10분 의 용융 지수를 가져서 우수한 성형성을 갖는다.
As shown in the above Table 2, it was confirmed that the content of residual volatile compounds and the content of hydrocarbons gradually decreased as the polyethylene produced in Example 1 was dried while being exposed to nitrogen gas at 80 ° C. In addition, the polyolefin resin to be produced has a melt index of 4.0 g / 10 min under the conditions of 190 ° C and 2.16 kgf / cm 3, and has excellent moldability.
Claims (13)
상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 식음료 용기 또는 식음료 용기의 마개로 사출 성형하는 단계를 포함하는 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하는 단계;를 포함하고,
상기 지글러-나타 중합 촉매는 마그네슘 화합물; 하기 화학식1의 알킬 알루미늄 화합물; 전이 금속 화합물; 하기 화학식 2의 화합물 및 화학식3의 화합물로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 1종 이상의 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자 공여체를 포함하고,
상기 지글러-나타 중합 촉매는, 마그네슘 화합물을 알코올과 반응시켜 마그네슘 화합물 용액을 제조하는 단계; 및 상기 마그네슘 화합물 용액과 상기 화학식1로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 알킬알루미늄, 전이금속 화합물, 및 상기 화학식 2내지3로 표시되는 화합물을 포함하는 내부전자공여체를 반응시키는 단계를 통하여 제조되며,
상기 마그네슘 화합물을 알코올과 반응시켜 마그네슘 화합물 용액을 제조하는 단계에서 상기 마그네슘 화합물 및 알코올의 반응 몰비는 1:6 내지 8이며,
휘발성 화합물의 함량이 0.075 중량%이하인 식품 용기의 제조 방법:
[화학식1]
R1AlX3-l
상기 화학식 1에서, R1는 탄소수 1 내지 10의 직쇄 또는 분지쇄의 알킬기이며, l은 1 내지 3 의 정수이고, X는 할로겐이고,
[화학식2]
[화학식3]
상기 화학식 2 내 지3에서,
R2, R3 및 R4는 서로 같거나 다를 수 있으며, 각각 수소, 탄소수 1내지 20의 직쇄, 분지형 또는 고리형알킬기(Alkyl), 탄소수 2내지 20의 알케닐기 (Alkenyl), 탄소수 3내지 20의 시클로알킬기 (Cycloalkyl), 탄소수 3내지 20의 아릴기 (Aryl), 탄소수 1내지 20의 알킬실릴기 (Alkylsilyl), 탄소수 7내지 20의 아릴알킬기 (Arylalkyl), 탄소수 7내지 20의 알킬아릴기 (Alkylaryl)기, 또는 탄소수 2내지 20의 헤테로원자를 포함하는 알킬기이다.
In the presence of a Ziegler-Natta catalyst having a porosity of 45% to 70%, the ethylene monomer is polymerized singly or the ethylene monomer is copolymerized with an -olefin to obtain a polyolefin having a specific surface area of 190 m 2 / g to 300 m 2 / g Producing a resin; And
And molding the polyolefin resin by injection-molding the polyolefin resin into a food or beverage container or a stopper of a food and beverage container,
The Ziegler-Natta catalyst may be a magnesium compound; An alkyl aluminum compound of formula (1); Transition metal compounds; An internal electron donor comprising at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a compound represented by the following formula (2) and a compound represented by the following formula (3)
The Ziegler-Natta catalyst may be prepared by reacting a magnesium compound with an alcohol to prepare a magnesium compound solution; And an inner electron donor including the alkyl magnesium compound, the transition metal compound, and the compound represented by Chemical Formula 2 to 3, wherein the magnesium compound solution includes the compound represented by Chemical Formula 1,
The reaction mole ratio of the magnesium compound to the alcohol in the step of reacting the magnesium compound with the alcohol in the step of preparing the magnesium compound solution is 1: 6 to 8,
Wherein the content of the volatile compound is 0.075% by weight or less:
[Chemical Formula 1]
R 1 AlX 3-l
Wherein R 1 is a straight or branched alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, 1 is an integer of 1 to 3, X is halogen,
(2)
(3)
In Formulas 2 and 3 above,
R 2 , R 3 and R 4 may be the same or different and each represents hydrogen, a straight chain, branched or cyclic alkyl group (Alkyl) having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkenyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms (Alkenyl) A cycloalkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 3 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkylsilyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an arylalkyl group having 7 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkylaryl group having 7 to 20 carbon atoms (Alkylaryl) group, or an alkyl group containing a hetero atom having 2 to 20 carbon atoms.
상기 식품 용기는 식음료 용기 또는 식음료 용기의 마개인, 식품 용기의 제조 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the food container is a food or beverage container or a food and beverage container.
상기 식품 용기는 ASTM D 1238에 따라 190℃, 2.16 kgf/㎠ 하중 하에서 측정했을 때 0.8 내지 15 g/10분의 용융지수을 갖는 폴리올레핀 수지를 포함하고,
식품 용기의 제조 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Said food container comprising a polyolefin resin having a melt index of 0.8 to 15 g / 10 min measured at 190 占 폚 under a load of 2.16 kgf / cm2 according to ASTM D 1238,
A method of manufacturing a food container.
상기 폴리올레핀 수지를 성형하는 단계는 상기 160 ㎡/g 이상의 비표면적을 가지는 폴리올레핀 수지를 1 ppmw이하의 수분을 포함하고 50℃ 내지 105 ℃의 온도를 갖는 기체를 이용하여 건조 및 탈기하는 단계를 더 포함하는, 식품 용기의 제조 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
The step of molding the polyolefin resin further comprises a step of drying and degassing the polyolefin resin having a specific surface area of at least 160 m < 2 > / g using a gas containing not more than 1 ppmw of water and having a temperature of from 50 DEG C to 105 DEG C Wherein the method comprises the steps of:
상기 에틸렌 단량체의 단독 중합 또는 에틸렌 단량체 및 α-올레핀 간의 공중합은 60℃ 내지 90 ℃의 온도 및 10 psi 내지 150 psi의 압력 조건 하에 이루어지는,
식품 용기의 제조 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
The homopolymerization of the ethylene monomer or the copolymerization between the ethylene monomer and the? -Olefin is carried out at a temperature of 60 ° C to 90 ° C and a pressure of 10 psi to 150 psi.
A method of manufacturing a food container.
상기 마그네슘 화합물은 마그네슘 할라이드, 알콕시 마그네슘, 알킬마그네슘할라이드, 알콕시할로겐화마그네슘 및 알릴옥시할로겐화마그네슘으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 1종 이상을 포함하는, 식품 용기의 제조 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the magnesium compound comprises at least one member selected from the group consisting of magnesium halide, alkoxy magnesium, alkyl magnesium halide, magnesium alkoxy magnesium halide and magnesium allyloxy halide.
상기 전이 금속 화합물은 하기 화학식4의 전이 금속 화합물을 포함하는, 식품 용기의 제조 방법:
[화학식4]
MXn(OR5)4-n
상기 화학식 4에서, M은 주기율표 IVB, VB및 VIB족의전이 금속 원소로 이루어진 군에서 선택되고, X는 할로겐, R5는 탄소수 1내지 10의 알킬기, n은 금속의 산화수로 0 내지 4이다.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the transition metal compound comprises a transition metal compound represented by the following formula (4): < EMI ID =
[Chemical Formula 4]
MX n (OR 5 ) 4-n
In the formula (4), M is selected from the group consisting of transition metal elements of Group IVB, VB and VIB of the periodic table, X is halogen, R 5 is an alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, and n is 0 to 4 as an oxidation number of metal.
상기 α-올레핀은 1-부텐, 1-펜텐, 1-헥센, 4-메틸, 1-펜텐, 1-헵텐 및 1-옥텐으로 이루어진 군에서 선택된 1종 이상의 단량체를 포함하는, 식품 용기의 제조 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Wherein the? -Olefin comprises at least one monomer selected from the group consisting of 1-butene, 1-pentene, 1-hexene, 4-methyl, 1-pentene, 1-heptene and 1-octene .
상기 에틸렌 단량체를 단독으로 중합 시 또는 에틸렌 단량체를 α-올레핀과 공중합 시에 아마이드계 활제를 첨가하는 단계를 더 포함하는, 식품 용기의 제조 방법.
The method according to claim 1,
Further comprising the step of adding an amide-based lubricant when the ethylene monomer alone is polymerized or when the ethylene monomer is copolymerized with? -Olefins.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020140167740A KR101699869B1 (en) | 2014-11-27 | 2014-11-27 | Preparation method of food container |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020140167740A KR101699869B1 (en) | 2014-11-27 | 2014-11-27 | Preparation method of food container |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20160063889A KR20160063889A (en) | 2016-06-07 |
| KR101699869B1 true KR101699869B1 (en) | 2017-01-25 |
Family
ID=56192949
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020140167740A KR101699869B1 (en) | 2014-11-27 | 2014-11-27 | Preparation method of food container |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101699869B1 (en) |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100601146B1 (en) | 1999-11-12 | 2006-07-13 | 삼성토탈 주식회사 | Polyethylene resin composition for plastic closure and its article |
| KR100362208B1 (en) | 2000-11-09 | 2002-11-23 | 에스케이 주식회사 | Polypropylene composition for closure |
| EP1310436A1 (en) * | 2001-11-09 | 2003-05-14 | SOLVAY POLYOLEFINS EUROPE - BELGIUM (Société Anonyme) | Screw cap comprising a multimodal polyethylene composition |
| US6806313B2 (en) | 2003-03-05 | 2004-10-19 | W. R. Grace & Co.-Conn. | Erucamide-free closure and liner compositions |
| KR100922179B1 (en) | 2003-04-11 | 2009-10-19 | 삼성토탈 주식회사 | Polyethylene Composition for Plastic Bottle Cap and the Molded Article |
| EP1674523A1 (en) * | 2004-12-22 | 2006-06-28 | Total Petrochemicals Research Feluy | Caps and closures |
| EP2402391B1 (en) | 2010-06-29 | 2013-07-31 | Borealis AG | Bimodal polyethylene composition for injection moulded articles |
| KR20140014656A (en) | 2012-07-25 | 2014-02-06 | 동우 화인켐 주식회사 | Calculation method of boric acid in polarizing plate |
| KR101553203B1 (en) * | 2012-09-26 | 2015-09-14 | 롯데케미칼 주식회사 | Preparation method for polyethylene resin and polyethylene resin having high escr and melt tension |
| KR101420017B1 (en) | 2012-11-12 | 2014-07-15 | 삼성토탈 주식회사 | Polyethylene Resine Composition for Plastic Closure and Article Produced with the Same |
| KR101433234B1 (en) * | 2012-11-23 | 2014-08-22 | 롯데케미칼 주식회사 | Preparing method of catalystfor polymerization of polyolefinand process for polymerization of polyolefin using the same |
-
2014
- 2014-11-27 KR KR1020140167740A patent/KR101699869B1/en active IP Right Grant
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20160063889A (en) | 2016-06-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1403292B1 (en) | Process for preparing an olefin polymerisation catalyst component with improved high temperature activity | |
| EP3307820B1 (en) | Process for manufacture of low emission polypropylene | |
| EP2812362B1 (en) | Immobilization of single site catalyst on inorganic oxide support for preparation of uhmwpe | |
| EP3353146B1 (en) | Synthesis of substituted amidobenzoate compounds, the compounds obtained and the use thereof as phthalate free internal electron donor for polymerization of olefins | |
| KR102288988B1 (en) | Process for preparing polypropylene | |
| EP2520591B1 (en) | Catalyst for polyolefin polymerisation and a production method for the same | |
| CN106459539B (en) | Polymer composition based on propylene | |
| EP2520592B1 (en) | Production method for a catalyst for polyolefin polymerisation, a catalyst obtained by means of the same, and a production method for polyolefins by using the same | |
| EP3683243B1 (en) | Process of manufacture of catalyst and propylene polymer that use this or copolymer for propylene polymerization | |
| KR102291554B1 (en) | Process for preparing polypropylene | |
| KR101699869B1 (en) | Preparation method of food container | |
| KR101735447B1 (en) | method of preparing polyolefin nanocomposite including dispersed carbon support on the polyolefin and nanocomposite prepared thereby | |
| KR101553203B1 (en) | Preparation method for polyethylene resin and polyethylene resin having high escr and melt tension | |
| KR102156075B1 (en) | Ziegler-Natta procatalyst compositions AND OLEFINE polymerization process | |
| KR101433234B1 (en) | Preparing method of catalystfor polymerization of polyolefinand process for polymerization of polyolefin using the same | |
| KR101686178B1 (en) | Preparation method for polyolefin resin having high escr and excellent workability | |
| KR102225972B1 (en) | Process for preparing polypropylene | |
| KR102467598B1 (en) | Catalyst COMPOSITION for Polymerization of oleFin, METHOD OF PRODUCING THE SAME, AND METHOD OF PRODUCING POLYOLEFIN USING THE SAME METHOD | |
| EP3421510B1 (en) | Ethylene/1-hexene copolymer having excellent processability and mechanical properties | |
| KR100822616B1 (en) | Catalyst for polymerization of ultra high molecular weight polyolefin which has narrow molecular weight distribution and the preparation thereof | |
| KR101473354B1 (en) | Catalyst composition for polymerization of olefin, preparing method of the same, and process for polymerization of olefin using the same | |
| KR101495780B1 (en) | Method for preparation of catalyst for olefin polymerization, catalyst produced therefrom, and method for preparation of polyolefin using the same | |
| KR102287924B1 (en) | Method for producing catalyst for synthesis of high density polyethylene | |
| KR20190050436A (en) | Method for producing catalyst composition for polymerization of high density polyolefin | |
| KR102467589B1 (en) | Method for producing catalyst for polymerization of ethylene and method for producing polyethylene using the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| X091 | Application refused [patent] | ||
| AMND | Amendment | ||
| X701 | Decision to grant (after re-examination) | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20200102 Year of fee payment: 4 |