KR100955914B1 - Device and Method for Producing Drinking Water by Treating Waste Water - Google Patents
Device and Method for Producing Drinking Water by Treating Waste Water Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100955914B1 KR100955914B1 KR1020070120880A KR20070120880A KR100955914B1 KR 100955914 B1 KR100955914 B1 KR 100955914B1 KR 1020070120880 A KR1020070120880 A KR 1020070120880A KR 20070120880 A KR20070120880 A KR 20070120880A KR 100955914 B1 KR100955914 B1 KR 100955914B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- activated carbon
- water
- tank
- treating
- drinking water
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F9/00—Multistage treatment of water, waste water or sewage
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D61/00—Processes of separation using semi-permeable membranes, e.g. dialysis, osmosis or ultrafiltration; Apparatus, accessories or auxiliary operations specially adapted therefor
- B01D61/02—Reverse osmosis; Hyperfiltration ; Nanofiltration
- B01D61/025—Reverse osmosis; Hyperfiltration
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/28—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by sorption
- C02F1/283—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by sorption using coal, charred products, or inorganic mixtures containing them
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/42—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by ion-exchange
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/44—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by dialysis, osmosis or reverse osmosis
- C02F1/441—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by dialysis, osmosis or reverse osmosis by reverse osmosis
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/02—Aerobic processes
- C02F3/12—Activated sludge processes
- C02F3/1236—Particular type of activated sludge installations
- C02F3/1268—Membrane bioreactor systems
- C02F3/1273—Submerged membrane bioreactors
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/30—Aerobic and anaerobic processes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F2303/00—Specific treatment goals
- C02F2303/24—Separation of coarse particles, e.g. by using sieves or screens
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02W—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO WASTEWATER TREATMENT OR WASTE MANAGEMENT
- Y02W10/00—Technologies for wastewater treatment
- Y02W10/10—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
Abstract
본 발명은 하/폐수 처리를 통한 음용수 생산 장치 및 방법에 관한 것으로, 분리막 생물 반응부, 고도 처리부 및 정수부를 포함하며, 발생 폐수 전량을 모두 활용할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 폐수를 처리하여 중수도(건물용수, 조경용수, 습지 조성 용수 등) 및 음용수/상수를 각각 그 유량을 조절하면서 동시에 얻을 수 있는 장점을 갖는다.The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for producing drinking water through sewage / wastewater treatment, including a membrane bioreactor, an advanced treatment unit, and a water purification unit, which can utilize all of the generated wastewater, as well as treating the wastewater for heavy water (building water). , Landscaping water, wetland composition water, etc.) and drinking water / constant water, respectively.
폐수, 분리막 생물 반응, 고도 처리, 정수, 중수, 상수/음용수 Wastewater, Membrane Bioreaction, Advanced Treatment, Purified Water, Heavy Water, Constant / Drinking Water
Description
본 발명은 하/폐수 처리 장치 및 방법에 관한 것이다. 보다 구체적으로, 본 발명은 발생하는 폐수 전량을 처리하고 재활용하여 상수/음용수를 얻을 수 있는 고효율의 무방류 하/폐수 처리 장치 및 방법에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to a sewage / wastewater treatment apparatus and method. More specifically, the present invention relates to a high efficiency non-discharge sewage / wastewater treatment apparatus and method capable of treating and recycling the total amount of generated wastewater to obtain water / drinking water.
산업이 다양화·고도화·대형화됨에 따라 각 분야에서 다양하고 많은 양의 오염물질들이 방출되고 있으며, 인구 밀집도가 높아짐에 따라 생활 폐수 역시 지속적으로 증가하고 있는 실정이다. 반면, 산업 현장, 생활에서 요구되는 물의 량은 급격히 증가하고 있어 배출되는 오수, 하수 등의 폐수를 적절히 처리하여 이를 재활용하는 방안이 절실히 요구되고 있다. As the industry diversifies, advances and enlarges, various and large amounts of pollutants are emitted in each field, and as the population density increases, household wastewater also continues to increase. On the other hand, the amount of water required in industrial sites and living places is rapidly increasing, and there is an urgent need for a method of appropriately treating wastewater such as discharged sewage and sewage and recycling it.
통상적으로, 수질 환경 개선을 위한 처리 공법 및 장치는 폐수처리(waste water treatment system) 또는 하수처리(sewage treatment system)로 불리기도 하며, 그 기능은 생활 오.폐수 및 공장 용수와 축산 폐수를 정화하여 하천으로 방류하거나 다시 재활용하기 위함이다. Conventionally, treatment methods and devices for improving the water quality are also called waste water treatment systems or sewage treatment systems, and their function is to purify domestic wastewater, factory water and livestock wastewater. It is to be discharged to the stream or recycled again.
기존에 알려진 대표적인 폐수 처리 공정으로는 활성 슬러지 처리 방식이 알 려져 있다. 상기 공정은 대표적인 생물학적 처리 방식으로서 활성슬러지(하수를 폭기시켜 흡착성 및 침전성을 갖게 한 슬러지로서, 유기물을 영양원으로 하여 번식하는 호기성 세균, 원생동물, 편충 등의 생물 및 유기, 무기의 비생물성 슬러지의 집합체) 및 하수를 혼합하여 폭기조에서 폭기 및 교반함으로써 콜로이드 및 용해성 유기물을 활성슬러지에 흡착시켜 침전 형성이 용이하도록 한다.Known representative wastewater treatment processes are known as activated sludge treatment. The process is a representative biological treatment method of activated sludge (a sludge that aerated and sedimented by sewage to aerated water, and abiotic bacteria, protozoa, worms, etc., which reproduce organic matter as a nutrient source, and abiotic organisms such as organic and inorganic). Aggregate of sludge) and sewage are mixed and aerated and stirred in an aeration tank to adsorb colloid and soluble organic matter to activated sludge to facilitate precipitation formation.
그러나, 상기 공정은 주로 유기물 제거를 목적으로 하고 있으며, 질소 및 인 제거에는 적합하지 않다. 이러한 문제점을 해결하기 위하여, 바르덴포 공법(Bardenpho; 2개의 무산소조 및 2개의 호기조) 공법, A/O 공법(2개의 반응조를 이용한 탄화수소 및 인 제거) 및 A2/O 공법(질소 및 인을 동시 처리), 연속 회분식법(sequencing batch reactor; SBR) 등이 개발되었다.However, the process is primarily aimed at removing organics and is not suitable for nitrogen and phosphorus removal. To solve this problem, the Bardenpho process (two anoxic and two aerobic tanks), the A / O process (removing hydrocarbons and phosphorus using two reactors) and the A 2 / O process (nitrogen and phosphorus simultaneously) Treatment), sequencing batch reactor (SBR), and the like.
한편, 폐수 처리 분야에 있어서, 처리 효율 증대, 공간 활용성, 공정의 단순화, 운전비 절감 등을 고려하여 기술의 개선이 이루어지고 있으며, 최근에는 고농도의 미생물을 반응조에 유지하여 부지 절감 및 폐수 처리 효율을 개선하기 위하여 중공사막과 같은 재질의 막(membrane)을 적용하는 막 분리조(MBR) 기술도 알려져 있다. 이와 관련한 종래 기술은 하기와 같다.Meanwhile, in the field of wastewater treatment, technology has been improved in consideration of increased treatment efficiency, space utilization, process simplification, and operation cost reduction. In recent years, high-density microorganisms are maintained in a reactor to reduce site and wastewater treatment efficiency. MBR technology is also known in which a membrane of a material such as a hollow fiber membrane is applied to improve the efficiency. The related art in this regard is as follows.
국내특허번호 제447039호는 오수를 포기 침전조에 유입시키는 단계, 유기물 분해 후 침전시키는 단계, 상등액을 전해조로 통과시키는 단계, 중금속을 제거하고 여과기를 통과한 후 볼타 전지 효과장치 및 세라믹체가 구비된 유통관을 통과시켜 배출시키는 단계로 이루어지는 하수 정화 처리방법을 개시하고 있다.Korean Patent No. 447039 discloses a step of introducing wastewater into a sedimentation tank, precipitating after decomposition of organic matter, passing the supernatant into an electrolytic bath, removing heavy metals and passing through a filter, and then passing a voltaic battery effector and a ceramic body. Disclosed is a sewage treatment method comprising a step of passing through a wastewater.
국내특허번호 제515849호는 막 분리를 이용한 하수 및 침출수의 순수화 재이용 방법에 관한 것으로, 침출수 집수조로부터 공급펌프에 의해 전처리 투과수조로 공급하여 전처리하는 전처리공정; 상기 전처리된 처리수를 역삼투막 분리 모듈을 통과시켜 처리하는 역삼투막 분리공정; 및 미생물 제거 및 이온교환을 위한 폴리싱 공정으로 이루어지며, 특히 전처리 공정의 공급펌프를 통해 공급되는 원수가 스크린 필터 및 회전막 분리장치를 통과한 후 전처리 투과수조로 공급되고; 회전막 분리 장치의 막 재질을 폴리에테르설폰 또는 재생형 셀룰로오스로 사용하는 점을 그 기술적 특징으로 하고 있다. Korean Patent No. 515849 relates to a method for repurifying sewage and leachate using membrane separation, and comprising: a pretreatment step of pretreatment by supplying a leachate collection tank to a pretreatment permeation tank by a feed pump; A reverse osmosis membrane separation process of treating the pretreated treated water through a reverse osmosis membrane separation module; And a polishing process for removing microorganisms and ion exchange, and in particular, raw water supplied through a feed pump of a pretreatment process is passed to a pretreatment permeation tank after passing through a screen filter and a rotary membrane separator; The technical feature is that the membrane material of the rotary membrane separator is used as polyether sulfone or regenerated cellulose.
국내특허번호 제603631호는 응집제를 이용한 응집처리-특수여과보조제를 이용한 응집처리-심층여재필터를 이용한 응집물의 제거-나권형 저압 역삼투막 처리를 통한 유기물질 및 이온물질 제거 순으로 구성되는 하수처리공정을 개시하고 있다.Korean Patent No. 606331 is a sewage treatment process consisting of flocculation treatment using flocculant, flocculation treatment using special filtration aid, removal of flocculant using depth filter, and removal of organic and ionic substances through spiral wound low pressure reverse osmosis membrane treatment. Is starting.
국내특허번호 제711259호는 오존처리-자화처리-정밀여과 처리-광촉매 처리-한외여과처리 순으로 이루어지는 오수 또는 폐수의 처리 장치를 개시하고 있는 바, 한외 여과부를 투과하지 못한 슬러리의 처리부를 구비하고 있으며, 광촉매 처리부, 한외 여과부 및 슬러리 처리부를 하나의 설비 내에 포함하고 있다.Korean Patent No. 711259 discloses an apparatus for treating sewage or wastewater in the order of ozone treatment, magnetization treatment, fine filtration treatment, photocatalyst treatment and ultrafiltration treatment. The photocatalyst treatment unit, the ultrafiltration unit, and the slurry treatment unit are included in one facility.
그러나, 상기 언급된 선행기술은 발생 폐수 전부를 처리하기에는 처리 용량면에서 한계가 있거나, 폐수를 상수 또는 음용수 수준으로 정화 처리하기에는 만족스럽지 않다. 더욱이, 처리수의 수질은 고정될 수밖에 없기 때문에, 그 활용 면에서 경직되어 있다. However, the above-mentioned prior art has limitations in terms of treatment capacity for treating all of the generated wastewater, or is not satisfactory for purifying wastewater to a constant or drinking water level. Moreover, since the water quality of the treated water has to be fixed, it is rigid in terms of its utilization.
상기 종래 기술의 한계를 극복하기 위하여, 본 발명자들은 지속적으로 연구를 진행한 결과, 발생 폐수의 전량을 처리하면서 상수 및 음용수 수준까지 정수 효율을 높일 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 처리수의 활용 목적(건물 용수, 조경 용수 등과 같은 중수도; 또는 상수 및 음용수)에 따라, 조업 모드(operation mode)에 유연성을 부여할 수 있는 공정을 개발하게 된 것이다.In order to overcome the limitations of the prior art, the present inventors continue to study, as a result of treating the entire amount of wastewater generated, as well as to improve the water purification efficiency up to the constant and drinking water level, the purpose of utilizing the treated water (building water Or water, such as landscaping water, or constant and drinking water), to develop a process that can give flexibility to an operation mode.
따라서, 본 발명의 목적은 발생 폐수의 전량을 처리함과 동시에 음용수 수준으로 정수 효율을 향상시킬 수 있는 폐수 처리 장치를 제공하는 것이다.Accordingly, it is an object of the present invention to provide a wastewater treatment apparatus capable of treating the entire amount of wastewater generated and improving water purification efficiency at the level of drinking water.
본 발명의 다른 목적은 처리수의 활용 목적에 따라 조업 모드에 유연성을 부여할 수 있는 폐수 처리 장치를 제공하는 것이다.Another object of the present invention is to provide a wastewater treatment apparatus capable of giving flexibility to the operation mode according to the purpose of utilizing the treated water.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은 상기 장치에 의한 폐수 처리 방법을 제공하는 것이다. Another object of the present invention is to provide a wastewater treatment method by the above apparatus.
본 발명의 제1 면에 따르면, According to the first aspect of the invention,
(A) (a1) 제올라이트 분말의 존재 하에서 하수 또는 폐수를 처리하며, 상기 제올라이트에 의한 이온 교환을 수반하는 무산소조, (a2) 상기 이온 교환된 제올라이트 및 슬러지를 고액분리하는 막 분리조 및 (a3) 상기 분리된 슬러지 및 제올라이트의 적어도 일부분을 산소의 공급 및 미생물의 존재 하에서 처리하여 상기 무산소조로 이송하는 호기조를 포함하며, 상기 막 분리조로부터 분리된 액상 흐름을 후속 단계로 이송하는 분리막 생물반응부(membrane bio-reactor; MBR);(A) (a1) an anoxic tank for treating sewage or wastewater in the presence of zeolite powder, and (a2) a membrane separation tank for solid-liquid separation of the ion exchanged zeolite and sludge, and (a3) A membrane bioreactor for treating at least a portion of the separated sludge and zeolite in the presence of microorganisms and supplying oxygen to the oxygen-free tank, and transferring the liquid stream separated from the membrane separation tank to a subsequent step ( membrane bio-reactor (MBR);
(B) (b1) 오존의 공급 하에서 상기 분리막 생물 반응부로부터 이송된 액상 흐름을 처리하는 오존 반응조, 및 (b2) 활성탄의 존재 하에서 상기 오존 처리된 액상 흐름을 흡착 처리하는 제1 활성탄 여과기를 포함하며, 상기 활성탄 여과액의 적어도 일부분을 후속 단계로 이송하는 고도처리부; 및(B) (b1) an ozone reactor for treating the liquid flow transferred from the membrane bioreactor under supply of ozone, and (b2) a first activated carbon filter for adsorbing the ozone treated liquid stream in the presence of activated carbon. And an advanced processor for transferring at least a portion of the activated carbon filtrate to a subsequent step; And
(C) (c1) 마이크로필터(micro-filter)를 이용하여 상기 이송된 활성탄 여과액을 처리하는 미세여과기, (c2) 역삼투막을 이용하여 상기 미세여과액을 처리하는 역삼투 여과기, (c3) 활성탄의 존재 하에서 상기 역삼투 여과액을 흡착 처리하는 제2 활성탄 여과기; 및 (c4) 상기 흡착 처리액을 상수/음용수 수준에 도달하기까지 자외선으로 처리하는 자외선 살균기를 포함하는 정수부;(C) (c1) a microfilter for treating the transferred activated carbon filtrate using a micro-filter, (c2) a reverse osmosis filter for treating the microfiltrate using a reverse osmosis membrane, (c3) activated carbon A second activated carbon filter for adsorbing the reverse osmosis filtrate in the presence of; And (c4) a water purification unit including an ultraviolet sterilizer for treating the adsorption treatment liquid with ultraviolet rays until reaching a constant / drinking water level.
를 포함하는, 하/폐수 처리를 통한 음용수 생산 장치가 제공된다.Provided is a drinking water production apparatus through sewage / wastewater treatment.
본 발명의 제2 면에 따르면, According to a second aspect of the invention,
(A) (a1) 하수 또는 폐수와 함께 제올라이트 분말을 공급하여 무산소 유입의 조건 하에서 이온 교환 처리하는 단계, (a2) 상기 이온 교환된 제올라이트 및 슬러지를 고액분리하는 단계 및 (a3) 상기 분리된 슬러지 및 제올라이트의 적어도 일부분을 산소의 공급 및 미생물의 존재 하에서 처리하여 상기 무산소조로 이송하는 단계를 포함하며, 상기 고액 분리를 통하여 남은 액상 흐름을 후속 단계로 이송하는 분리막 생물 반응 단계;(A) (a1) supplying zeolite powder with sewage or wastewater to ion exchange treatment under conditions of anoxic inflow, (a2) solid-liquid separation of the ion exchanged zeolite and sludge, and (a3) the separated sludge And treating at least a portion of the zeolite in the presence of oxygen and in the presence of microorganisms and transferring the same to the anoxic tank, wherein the membrane bioreaction step of transferring the remaining liquid flow through the solid-liquid separation to a subsequent step;
(B) (b1) 오존의 공급 하에서 상기 단계 (A)로부터 이송된 액상 흐름을 처리하는 오존 처리 단계, 및 (b2) 활성탄의 존재 하에서 상기 오존 처리된 액상 흐름을 흡착 처리하는 제1 활성탄 흡착 처리 단계를 포함하고, 상기 제1 활성탄 처리된 액의 적어도 일부분을 후속 단계로 이송하는 고도처리 단계; 및(B) (b1) an ozone treatment step of treating the liquid stream transferred from step (A) under the supply of ozone, and (b2) a first activated carbon adsorption treatment of adsorption treatment of the ozone treated liquid stream in the presence of activated carbon And an advanced treatment step of transferring at least a portion of the first activated carbon treated liquid to a subsequent step; And
(C) (c1) 마이크로필터(micro-filter)를 이용하여 상기 이송된 활성탄 여과액을 처리하는 단계, (c2) 역삼투막을 이용하여 상기 미세여과액을 처리하는 단계, (c3) 활성탄의 존재 하에서 상기 역삼투 여과액을 흡착 처리하는 제2 활성탄 흡착 처리 단계; 및 (c4) 상기 제2 활성탄 처리된 액을 상수/음용수 수준에 도달하기 까지 자외선으로 처리하는 단계를 포함하는 정수 처리 단계;(C) (c1) treating the transferred activated carbon filtrate with a micro-filter, (c2) treating the microfiltrate with a reverse osmosis membrane, (c3) in the presence of activated carbon A second activated carbon adsorption treatment step of adsorbing the reverse osmosis filtrate; And (c4) treating the second activated carbon treated liquid with ultraviolet rays until reaching a constant / drinking water level;
를 포함하는 하/폐수 처리를 통한 음용수 생산 방법이 제공된다.Drinking water production method is provided through the sewage / wastewater treatment comprising a.
본 발명에 따른 폐수 처리 장치 및 방법은 폐수 처리량 및 효율 면에서 우수할 뿐만 아니라, 조업 모드를 용이하게 변경하여 정화도가 다른 처리수를 원하는 량으로 하나의 공정 내에서 동시에 얻을 수 있는 장점을 갖는다. 따라서, 예를 들면, 청정 지역에 독립적으로 위치하는 시설 내에서 자체적으로 발생하는 하/폐수를 전량 처리하여 중수도 및 상수/음용수로 재활용함으로써 수질 오염을 근본적으로 차단할 수 있다.The wastewater treatment apparatus and method according to the present invention not only have excellent wastewater throughput and efficiency, but also have an advantage of easily changing the operation mode to simultaneously obtain a desired amount of treated water having a different degree of purification in one process. . Thus, for example, it is possible to fundamentally block water pollution by completely treating sewage / wastewater generated in a facility located independently in a clean area and recycling it to heavy water and drinking water / drinking water.
이하, 본 발명은 첨부된 도면을 참고로 하여 하기의 설명에 의하여 모두 달성될 수 있다. 하기의 설명은 본 발명의 바람직한 태양을 기술하는 것으로 이해되어야 하며, 본 발명이 반드시 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.Hereinafter, the present invention can be achieved by the following description with reference to the accompanying drawings. The following description is to be understood as describing preferred embodiments of the invention, but the invention is not necessarily limited thereto.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 구체예에 따른 폐수(하수) 처리 공정을 개략적으로 도 시하는 공정도이다.1 is a process diagram schematically showing a wastewater (sewage) treatment process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명에 따른 처리 공정은 특별히 제한되지 않고 각종 산업 폐수 및/또는 생활 하수를 원수로서 처리할 수 있다. The treatment process according to the present invention is not particularly limited and various industrial wastewater and / or domestic sewage can be treated as raw water.
상기 도면에서 상기 원수는 제올라이트를 이용한 막 생물 반응부로 이송되는 바, 이러한 막 생물 반응부는 본 발명의 출원인의 국내특허출원번호 제2005-68837호에 기본적인 원리가 개시되어 있으며, 상기 선행기술은 본 발명의 참고자료로서 포함된다. In the drawing, the raw water is transferred to the membrane bioreactor using zeolite. The membrane bioreactor is disclosed in Korean Patent Application No. 2005-68837 of Applicant of the present invention, and the prior art discloses the present invention. It is included as a reference.
이때, 선택적으로 균등조(equalization tank; 1) 및 스크린 분리기(2)를 거치게 된다. 균등조는 유입 폐수의 유량 및 수질의 변동을 흡수하여 균등화함으로써 후속 공정의 효율을 높일 수 있으며, 바람직하게는 2 이상의 조를 이용한다. 스크린 분리기는 수처리 시 수중에 부유하는, 비교적 대형인 고형물을 철망 및 철제 격자 등의 스크린(약 0.5∼50㎜의 평균 직경을 갖는 것이 바람직함)을 사용해서 제거할 수 있다. 상기 스크린은 바-로드, 와이어, 그랜팅, 와이어매쉬, 퍼훼레이티드, 플레이트 등으로 구성될 수 있다.At this time, it is optionally subjected to an equalization tank (1) and the screen separator (2). The equalization tank can increase the efficiency of the subsequent process by absorbing and equalizing the fluctuations in the flow rate and the water quality of the influent wastewater, and preferably, two or more tanks are used. Screen separators can remove relatively large solids suspended in water during water treatment using screens (preferably having an average diameter of about 0.5 to 50 mm) such as wire mesh and steel grids. The screen may be composed of bar rods, wires, grants, wire meshes, perforated plates, and the like.
스크린(2)을 거친 하수는 제올라이트 분말과 함께 무산소조(4)로 이송되어 산소 공급 없이 처리되며, 경우에 따라서는 교반 하에서 처리하는 것이 바람직하다. 상기 무산소조(4)에서, 제올라이트 분말은 폐수의 흐름에 따라 이동하고 원수 내에 함유된 암모니아성 질소(NH4 +-N)는 제올라이트의 Na+ 등의 양이온과 이온 교환이 이루어짐으로써 폐수 내의 질소가 제거된다. 이때, 무산소조의 온도는 특별히 한정되는 것은 아니나, 약 5℃∼35℃으로 함이 바람직하고, 무산소조 내의 용존 산소량(dissolved oxygen; DO)은 약 0.2mg/L 이하인 것이 바람직하다. The sewage having passed through the
이때, 상기 무산소조(2)에 투입되는 제올라이트 분말로서 천연 또는 합성 제올라이트가 모두 사용될 수 있고, 전술한 이온 교환 반응을 가능하게 하는 한, 특별한 종류로 제한되는 것은 아니다. 또한, 제올라이트 분말의 투입량은 상기 무산소조(2)로 유입되는 폐수에 함유된 암모니아성 질소의 농도에 따라 정하여지며, 상기 제올라이트 투입량의 결정 방법은 본 출원인의 국내특허출원번호 제2005-68837호에 개시되어 있다. 본 발명의 전형적인 태양에 따르면, 상기 제올라이트 분말은 약 30∼100 nm의 기공 크기(pore size), 그리고 약 80∼100 m2/g의 비표면적을 갖는 다.At this time, both natural or synthetic zeolites may be used as the zeolite powder to be injected into the oxygen-
무산소조(2)로부터 배출된, 탈질 처리된 하수는 막 분리조(5)로 유입되어 그 내부에 설치된 분리막(적어도 1 이상 설치됨)을 통하여 고액 분리가 이루어지게 된다. 이때, 제올라이트 분말 및 슬러지(고형)는 분리막을 통과하지 못하게 되고, 고형분이 분리되고 남은 원수는 후속 단계로 이송된다. 바람직하게는 배출 펌프(도시되지 않음)를 분리막과 연결시켜 이송을 용이하게 한다. The denitrified sewage discharged from the
반면, 막 분리조(5)에서 분리막의 표면에 남게 되는 이온 교환된 제올라이트 분말 및 슬러지(고형)는 막 분리조(5)로부터 슬러지 형태로 배출되는 바, 이를 위하여 바람직하게는 상기 막 분리조(5)의 하부에 위치하는 폭기 장치(도시되지 않음)를 사용하여 폭기하여, 분리막으로부터 이탈이 용이하게 한다. On the other hand, the ion-exchanged zeolite powder and sludge (solid) remaining on the surface of the membrane in the
또한, 상기 구체예에 따르면, 막 분리조로부터 배출되는 제올라이트 분말 및 슬러지의 약 95%∼98%는 호기조(3)로 반송되는 것이 바람직하다. 이때, 반송 펌프(도시되지 않음)가 상기 막 분리조(5)와 연결되어 있어 반송을 용이하게 한다. 반송되지 않은 잉여 슬러지는 바람직하게는 슬러지 저류조(6)에서 농축된 다음, 농축물은 별도로 처리(예를 들면, 위탁 처리)되고, 잔류물은 다시 균등조(1)로 이송한다.Further, according to the above embodiment, it is preferable that about 95% to 98% of the zeolite powder and sludge discharged from the membrane separation tank is returned to the
상기 호기조(3)는 질산화 반응조로서, 질산화 미생물에 의하여 이온 교환된 제올라이트 분말을 재생한다. 구체적으로, 슬러지와 함께 이송된 제올라이트는 질산화 반응에 의하여 암모니아성 질소 이온의 평형이 깨짐에 따라 용액 상으로 암모니아성 질소를 지속적으로 질산성 질소(NO3-N)로 전환시킨다. 이와 같이, 호기조의 배출물(특히, 재생된 제올라이트)은 신규 제올라이트 및 스크린을 거쳐 유입되는 원수와 함께 무산소조(4)로 이송됨으로써 신규 제올라이트의 투입량을 감소시킬 수 있다. 상기 호기조의 온도는 특별히 한정되는 것은 아니나, 약 5∼35℃이 바람직하고, 호기조 내의 용존 산소량(dissolved oxygen; DO)은 약 1mg/L 이상인 것이 바람직하다.The
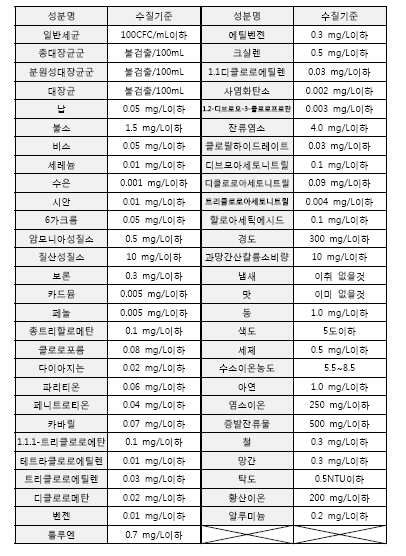
한편, 본 발명에 있어서, 상기 분리막 생물 반응부의 막 분리조(5)로부터 배출되는 액상 흐름은 하기 표 1의 수질 기준을 만족시키는 것이 바람직하며, 이를 위하여 전술한 분리막 생물 반응부의 공정 조건이 적절하게 조절될 수 있다. 상기 배출되는 액상 흐름은 이후 고도 처리 단계를 거치게 된다. On the other hand, in the present invention, it is preferable that the liquid flow discharged from the
[표 1]TABLE 1
단위: ㎎/ℓUnit: mg / l
1: 부유 고형 물질(suspended solid) 1 : suspended solid
2: 총질소 2 : total nitrogen
3: 총인 3 : total person
한편, 고도 처리 단계에 앞서, 액상 흐름은 1차 처리수조(7)를 거치도록 하고, 상기 1차 처리수조(7) 내의 처리수 일부를 막 분리조로 이송하여 역세수로서 분리막으로부터 제올라이트 분말 및 슬러지를 분리하는데 활용할 수도 있다(도 1의 점선 참조).On the other hand, prior to the advanced treatment step, the liquid flow is passed through the primary treatment tank (7), and a portion of the treated water in the primary treatment tank (7) is transferred to the membrane separation tank to remove the zeolite powder and sludge from the separation membrane as backwash water It can also be used to separate (see dashed line in Figure 1).
고도처리 단계에 있어서, 상기 1차 처리수조(7)로부터 이송된 액상 흐름은 먼저 오존 반응조(8) 내에서 오존 발생기(11)로부터 생성된 오존에 의하여 처리된다. 오존 처리를 통하여 용액 내의 세균, 바이러스의 살균, 유기성 착색성분의 분해, 악취 물질의 분해, COD 감소, 유독성분의 분해 등의 효과를 달성할 수 있다. 이외에도, 암모니아성 질소 및 용존 유기물의 제거 효과를 갖기 때문에 후속의 제1 활성탄 여과 단계의 전처리로서 효과적이다. In the advanced treatment step, the liquid flow sent from the primary treatment tank 7 is first treated by ozone generated from the
구체적으로, 오존은 공기 중 산소 또는 순산소를 이용하여 가스 상태로 발생시키며, 이를 수처리에 응용할 경우에는 액상에 용해시켜 사용한다. 액체 상태의 잔류오존은 불안정하여 비교적 단시간 내에 산소 및 물로 전환되며, HO2 -, O2 -, O3 - 등의 중간 생성물을 거쳐 OH 라디칼을 생성하는 바, 이러한 OH 라디칼은 오존 그 자체보다 높은 전위차를 갖고 있기 때문에 상당수의 유기물과 빠른 속도로 반응하는 특성을 갖는다. 오존 발생기(1)의 종류는 자외선식 오존 발생기, 전해식 오존 발생기, 무성방전식 오존 발생기 등이 특별한 제한 없이 사용가능하다.Specifically, ozone is generated in the gas state using oxygen or pure oxygen in the air, and when it is applied to water treatment, it is used by dissolving in a liquid phase. In a relatively short time the residual ozone in the liquid state is unstable and the oxygen, and is converted with water, HO 2 -, O 2 - , O 3 - , through an intermediate product such as a bar, these OH radicals to generate OH radical is higher than the ozone itself Because of the potential difference, it has a characteristic of reacting with a large number of organic substances at high speed. The type of ozone generator 1 can be used without particular limitations such as an ultraviolet ozone generator, an electrolytic ozone generator, an silent discharge ozone generator, and the like.
한편, 오존 처리된 액상 흐름은 제1 활성탄 여과기로 이송되어 전단에서 제거되지 않은 기타 오염물질을 흡착을 통하여 제거한다. 즉, 액상 흐름에 함유되어 있는 현탁 물질, 이온성 용해물질, 비이온성 용해물 등은 통상적인 응집 침전법 또는 모래여과법으로 제거하기 곤란한 바, 본 발명에서는 활성탄 여과 방식으로 상기 오염물질을 효과적으로 제거한다. On the other hand, the ozonated liquid stream is sent to the first activated carbon filter to remove other contaminants not removed at the front end by adsorption. That is, suspended solids, ionic dissolved substances, nonionic dissolved substances, etc. contained in the liquid stream are difficult to remove by conventional flocculation or sand filtration, and in the present invention, the contaminants are effectively removed by activated carbon filtration. .
제1 활성탄 여과에 앞서, 선택적으로 2차 처리수조(9)를 거치게 한 다음, 제1 활성탄 여과기로 이송할 수 있다. 활성탄은 주로 야자나무의 껍질, 목재, 석탄 등을 원료로 사용하여 고온에서 소성시켜 제조되는 바, 원료에 따라 크게 식물계 및 광물계로 분류되며, 형상에 따라 입상탄 및 분말탄으로 분류되기도 한다. Prior to filtration of the first activated carbon, it may optionally be subjected to a secondary treatment tank 9 and then transferred to the first activated carbon filter. Activated carbon is mainly manufactured by firing at high temperature using bark of wood, wood, coal, etc. as a raw material, and is classified into plant-based and mineral-based according to raw materials, and also classified into granular and powdered coal according to shape.
본 발명에서 사용가능한 활성탄은 당업계에서 알려진 종류가 특별히 제한됨이 없이 사용될 수 있는 바, 바람직하게는 약 8∼30 메쉬의 입도, 약 800∼1500㎡/g의 비표면적, 약 100∼1000㎚의 기공 크기, 그리고 약 0.4∼0.5g/㎤의 밀도를 갖는 것을 사용한다. Activated carbon usable in the present invention can be used without particular limitation to the kind known in the art, preferably about 8 to 30 mesh particle size, specific surface area of about 800 to 1500
전형적으로, 과립형으로 성형돤 입상 활성탄(Granular Activated Carbon)을 충진한 탱크 내에 오존 처리된 액상 흐름을 하향식으로 통과시켜 유기물 등을 효과적으로 흡착할 수 있다. Typically, the tank filled with granular activated carbon (Granular Activated Carbon) formed into a granular form can be passed through the ozone-treated liquid flow in a top-down manner to effectively adsorb organic matter and the like.
도 1에 도시된 구체예에서, 고도처리된 액상 흐름은 하기 표 2의 수질 기준을 맞추도록 각각의 공정이 조절되는 것이 바람직하며, 상기 액상 흐름의 적어도 일부는 후속 단계인 정수부로 이송되고, 나머지는 건물 용수, 조경 용수, 습지 조성용수 등의 중수도로 활용될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 상수/음용수에 대한 요구량이 많은 경우에는 정수부로 이송되는 고도 처리수의 량을 증가시키는 반면, 중수도에 대한 요구량이 많은 경우에는 정수부로 이송되는 고도 처리수의 량을 감소시킬 수 있다. 이러한 조업 모드의 유연성을 보다 용이하게 달성하기 위하여, 바람직하게는 재활용 수조(12)를 활용할 수 있는 바, 후속의 정수부로 이송되지 않은 액상 흐름은 상기 재활용 수조를 통하여 경우에 따라서는 제1 활성탄 여과기 내에서 활성탄에 흡착된 물질을 탈착시키기 위한 역세수로 활용할 수도 있으며, 후속의 정수부 내의 제2 활성탄 여과기(15)에서도 역세수로 활용할 수 있으며, 역세(back washing) 처리 후의 탈착 오염물질-함유 흐름은 균등조(1)로 반송할 수도 있다(도 1에서 점선 참조). In the embodiment shown in FIG. 1, the highly treated liquid stream is preferably each process adjusted to meet the water quality criteria of Table 2 below, at least a portion of the liquid stream being sent to a subsequent stage water purification unit, the remainder being Can be used as heavy water such as building water, landscape water, wetland water. For example, if the demand for water / drinking water is high, the amount of highly treated water delivered to the water purification unit may be increased, while if the demand for heavy water is high, the amount of highly treated water delivered to the water purification unit may be reduced. . In order to more easily achieve this flexibility of the operation mode, it is preferable to utilize the
[표 2]TABLE 2
상기 고도 처리부로부터 이송된 액상 흐름, 즉 제1 활성탄 여과액은 마이크로필터(micro-filter)가 구비된 미세여과기(13) 내에서 여과되어 일부 부유물질이 분리 제거된다. 특히, 미세여과기는 역삼투(R/O) 여과 설비의 전처리로서 후단 설비의 효율에 큰 영향을 미친다. 즉, 역삼투 여과 설비의 경우, 조업 시간의 경과에 따라 막의 오염이 점점 증가하여 처리 효율이 저하되기 때문에, 역삼투막의 오염을 최소화하기 위하여 미세 여과기를 전단에 배치하는 것이다.The liquid flow, ie, the first activated carbon filtrate, transferred from the advanced processing unit is filtered in a
미세여과액은 그 다음 역삼투 여과기(reverse osmosis filter; 14)로 이송되는 바, 상기 과정은 막 분리를 위하여 막에 압력을 가하는 방식으로서 삼투압보다 큰 압력을 농도가 높은 쪽에서 낮은 쪽으로 가함으로써 삼투현상과는 반대로 농도가 높은 쪽에서 낮은 쪽으로 투과시키게 된다. The microfiltrate is then transferred to a reverse osmosis filter (14), which is a method of pressurizing the membrane for membrane separation by osmosis by applying a pressure greater than osmotic pressure from the higher to the lower concentration. In contrast, the concentration is transmitted from the higher side to the lower side.
상기 역삼투 막의 재질로서 지지층(바람직하게는 약 30∼70㎛의 두께를 가지며, 다공 성 재질임) 상에 분리 효과를 위한 분리층(바람직하게는 0.1∼0.4㎛의 두께)으로 형성된 비대칭형 셀룰로오스 아세테이트 또는 방향족 폴리아미드가 전형적으로 사용될 수 있다. 보다 바람직하게는, 폴리아미드계 막이 사용된다. Asymmetric cellulose formed as a separation layer (preferably 0.1 to 0.4 ㎛ thickness) for the separation effect on the support layer (preferably having a thickness of about 30 ~ 70 ㎛, porous material) as a material of the reverse osmosis membrane Acetate or aromatic polyamides can typically be used. More preferably, polyamide based membranes are used.
본 발명의 구체예에 있어서, 역삼투막으로 사용 가능한 셀룰로오스계 막과 폴리아미드계 막의 전형적인 성상은 하기 표 3에 기재하였으나, 본 발명이 반드시 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.In the embodiment of the present invention, typical properties of the cellulose-based membrane and the polyamide-based membrane which can be used as the reverse osmosis membrane are described in Table 3 below, but the present invention is not necessarily limited thereto.
[표 3][Table 3]
본 발명에 따르면, 역삼투 여과기는 다양한 타입이 사용될 수 있으며, 대표적으로는 관형(tublar type), 나선형(spiral type), 중공사형(hollow fiber type), 평판형(plate and fram type), 회전판형(rotary disk type) 등이 있다. According to the present invention, the reverse osmosis filter can be used in various types, typically tubular (spiral type), spiral (spiral type), hollow fiber type, plate and fram type, rotating plate type (rotary disk type).
상기 역삼투 여과기(14)에 의한 여과액은 후술하는 제2 활성탄 여과기(15)로 이송되는 한편, 여과되고 남은 농축수는 배출되어 바람직하게는 증발 농축기(17) 내에서 고형화되고 대기방지부 또는 대기방지시설(18)에서 처리된다. The filtrate by the
상기 제2 활성탄 여과기(15)는 전술한 제1 활성탄 여과기(10)와 동일한 방식으로 여과되며, 제1 활성탄여과기와 차이점으로는 역삼투 여과기 처리수의 물맛을 향상시키고 냄새 및 색도를 제거하며 역삼투막에 의한 pH 저하를 상승시키는 역할을 한다. 전술한 바와 같이 재활용 수조(12)로부터 유입되는 역세수에 의하여 흡착된 물질이 탈착될 수 있으며, 탈착된 물질을 함유하는 처리수는 균등조(1)로 이송될 수 있다. 즉, 제1 및 제2 활성탄 여과기는 여과기 내에 침적된 물질을 제거하기 위하여 역세 처리되는 바, 처리 후 발생하는 역세수는 균등조로 이송된다. 이러한 역세 과정은 정상운전 시에는 수행되지 않으며, 유지 목적으로 주기적으로 수 행될 수 있다.The second activated
제2 활성탄 여과기로부터 배출되는 처리액은 자외선 살균기(16)로 이송되어 자외선 처리되는 바, 상기 방식은 예를 들면 살균 파장 254㎚의 파장으로 세균 및 바이러스의 DNA를 변성시켜 사멸시킨다. 이와 같은 자외선 살균 처리에 의하여 음용수/상수에 적합하도록 세균류 등을 99.9% 이상의 수준까지 살균할 수 있다. 특히, 물의 맛, 색, 성질, 미네랄 등의 유효성분에 영향을 주지 않을 뿐만 아니라, 배관 라인에 직접 연결하여 유수 상태 그대로 사용할 수 있다. The treatment liquid discharged from the second activated carbon filter is transferred to the
상기 정수부로부터 배출되는 처리수의 수질은 상수/음용수로 활용하기에 적합한 정도에 도달할 필요가 있는 바, 이를 고려하여 각각의 구성 단계(즉, 미세여과, 역삼투막 여과, 제2 활성탄 여과, 및 자외선 살균)에서의 공정 조건이 조절될 수 있다. 예를 들면, 하기 표 4에 나타낸 음용수 수질 기준을 만족하는 것이 바람직하나, 본 발명이 반드시 이에 한정되는 것은 아니다.The water quality of the treated water discharged from the water purification unit needs to reach a degree suitable for use as constant / drinking water, and considering each of the constituent steps (ie, microfiltration, reverse osmosis membrane filtration, second activated carbon filtration, and ultraviolet light). Process conditions in sterilization) can be controlled. For example, it is preferable to satisfy the drinking water quality standards shown in Table 4 below, but the present invention is not necessarily limited thereto.
[표 4] TABLE 4
본 발명에 따른 폐수 처리 장치 및 방법의 가장 큰 장점은 전술한 바와 같이 발생 폐수 전량을 모두 활용할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 폐수를 중수(건물용수, 조경용수, 습지 조성 용수 등) 및 음용수/상수를 동시에, 그리고 각 유량을 조절하면서 얻을 수 있다는 것이다. 따라서, 청정 지역, 예를 들면 상수원 보호 구역에 위치하는 산업 또는 주거 환경으로부터 배출된 폐수 전량을 처리하여 재활용하여 중수도 및 상수/음용수를 얻을 수 있기 때문에 상용화 측면에서 우수하다. The greatest advantage of the wastewater treatment apparatus and method according to the present invention is not only can utilize all of the generated wastewater as described above, but also wastewater in heavy water (building water, landscaping water, wetland composition water, etc.) and drinking water / water at the same time. And by adjusting each flow rate. Therefore, it is excellent in terms of commercialization because it is possible to process and recycle the total amount of wastewater discharged from an industrial or residential environment located in a clean area, for example, a water source protection zone, to obtain water and drinking water / drinking water.
이하 실시예를 통해 본 발명을 좀 더 구체적으로 살펴보지만, 하기 예에 본 발명의 범주가 한정되는 것은 아니다.Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to Examples, but the scope of the present invention is not limited to the following Examples.
실시예 1Example 1
도 1에 도시된 바와 같이, 폐수를 3단계, 즉 분리막 생물 반응부, 고도처리부 및 정수부에 따라 처리하였다.As shown in Figure 1, the wastewater was treated according to three stages, namely the membrane bioreactor, advanced treatment and water purification.
상기 공정은 하기의 표 5∼7에 기재된 세부 조업 조건의 범위를 갖는 장치를 이용하여 수행되었다.The process was carried out using an apparatus having a range of detailed operating conditions as described in Tables 5 to 7 below.
[표 5]TABLE 5
생물 반응부Biological reaction part
[표 6]TABLE 6
고도 처리부Advanced processing unit
[표 7]TABLE 7
정수 장치Water purifier
폐수 및 분리막 생물 반응부 및 고도 처리부로부터 배출되는 처리수의 수질을 하기 표 8에 나타내었다.The quality of the treated water discharged from the wastewater and the membrane bioreactor and the advanced treatment unit is shown in Table 8 below.
[표 8] TABLE 8
단위: ㎎/ℓUnit: mg / l
상기 고도처리부로부터 배출되는 처리수는 중수도로서 적합한 수질 기준을 충족하고 있음을 알 수 있다. It can be seen that the treated water discharged from the advanced treatment unit satisfies the appropriate water quality standard as the heavy water.
한편, 정수부에서 배출된 수질 평가 항목에 대하여 각각 측정한 결과, 상기 표 5에 기재된 기준을 충족하고 있음을 확인하였다. On the other hand, as a result of measuring each of the water quality evaluation items discharged from the water purification unit, it was confirmed that the criteria described in Table 5 above.
본 발명에 따른 폐수 처리 장치 및 방법은 폐수 처리량 및 효율 면에서 우수할 뿐만 아니라, 조업 모드를 용이하게 변경하여 정화도가 다른 처리수를 원하는 량으로 하나의 공정 내에서 동시에 얻을 수 있는 장점을 갖기 때문에 향후 다양한 장소에서 상용화가 기대된다.Wastewater treatment apparatus and method according to the present invention is not only excellent in terms of wastewater treatment and efficiency, but also has the advantage that it is possible to easily change the operation mode to obtain a desired amount of treated water with different degrees of purification in one process at the same time. Therefore, commercialization is expected in various places in the future.
본 발명의 단순한 변형 내지 변경은 모두 본 발명의 영역에 속하는 것으로, 본 발명의 구체적인 보호범위는 첨부된 특허청구범위에 의하여 명확해질 것이다.All simple modifications and variations of the present invention fall within the scope of the present invention, and the specific scope of the present invention will be apparent from the appended claims.
도 1은 본 발명의 일 구체예에 따른 폐수(하수) 처리 공정을 개략적으로 도시하는 공정도이다.1 is a process diagram schematically showing a wastewater (sewage) treatment process according to an embodiment of the present invention.
<도면 부호에 대한 설명><Description of Drawing>
1: 균등조 2: 스크린1: equalizer 2: screen
3: 호기조 4: 무산소조3: aerobic tank 4: anaerobic tank
5: 막 분리조 6: 슬러지 저류조5: membrane separation tank 6: sludge storage tank
7: 1차 처리수조 8: 오존 반응조7: Primary treatment tank 8: Ozone reactor
9: 2차 처리수조 10: 제1 활성탄 여과기9: secondary treatment tank 10: first activated carbon filter
11: 오존 발생기 12: 재활용 수조11: ozone generator 12: recycling tank
13: 미세여과기 14: 역삼투 여과기13: microfilter 14: reverse osmosis filter
15: 제2 활성탄 여과기 16: 자외선 살균기15: second activated carbon filter 16: ultraviolet sterilizer
17: 증발 농축기 18: 대기방지시설17: evaporator 18: air barrier
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070120880A KR100955914B1 (en) | 2007-11-26 | 2007-11-26 | Device and Method for Producing Drinking Water by Treating Waste Water |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070120880A KR100955914B1 (en) | 2007-11-26 | 2007-11-26 | Device and Method for Producing Drinking Water by Treating Waste Water |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20090054151A KR20090054151A (en) | 2009-05-29 |
| KR100955914B1 true KR100955914B1 (en) | 2010-05-04 |
Family
ID=40861370
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020070120880A KR100955914B1 (en) | 2007-11-26 | 2007-11-26 | Device and Method for Producing Drinking Water by Treating Waste Water |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100955914B1 (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101236467B1 (en) * | 2011-10-27 | 2013-02-22 | 김성종 | Apparatus and method for treating rainwater |
| KR101335668B1 (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2013-12-05 | (주) 영동엔지니어링 | Multiple waste water processing filtration device having advanced disinfecting and backwashing function |
| CN103466881A (en) * | 2013-09-04 | 2013-12-25 | 常州友达环保科技有限公司 | Two-stage submerged membrane bio-reactor (MBR) |
| KR101355866B1 (en) | 2013-08-06 | 2014-01-28 | (주)한국주조기계 | Smart wastewater reusing system using rainwater and graywater |
| KR101898135B1 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2018-10-31 | (주)로터스엔지니어링 | Biological hydrogen wastewater treatment system |
| KR20200087397A (en) * | 2019-01-11 | 2020-07-21 | 이에스티 주식회사 | Treatment system of waste water using oxidation preprocess |
| KR102213273B1 (en) * | 2020-07-14 | 2021-02-05 | 국진산업개발(주) | water treating apparatus for reuse of dirty water and waste water and sea water |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100983312B1 (en) * | 2009-09-28 | 2010-09-20 | 에이네스트(주) | Apparatus for reusing sewage waste water using separation membrane and ozone |
| CN103319048A (en) * | 2013-06-29 | 2013-09-25 | 惠州市众惠环保工程有限公司 | Method for recycling moisture from high-concentration organic sewage |
| KR101481075B1 (en) * | 2014-02-20 | 2015-01-13 | 주식회사 포스코건설 | Continuous flow type apparatus for water treatment using submerged type membrane filtration and method for backwashing membrane thereof |
| KR101445748B1 (en) * | 2014-07-04 | 2014-10-07 | 주식회사 프로솔 | a wastewater treatment system using ozone |
| KR20160123822A (en) * | 2015-04-17 | 2016-10-26 | 한국과학기술연구원 | Apparatus for treatment of a high temperature wastewater by using a membrane distillation process |
| CN105399280B (en) * | 2015-12-17 | 2018-07-17 | 李秋芬 | A kind of sewage disposal system |
| KR102154604B1 (en) * | 2019-08-05 | 2020-09-11 | (주)쓰리에스 | Purifying and uncycling system for livestock wastewater |
| CN111875088A (en) * | 2020-06-16 | 2020-11-03 | 湖北鑫来利陶瓷发展有限公司 | Treatment method of ceramic production wastewater |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100430071B1 (en) | 2001-06-01 | 2004-05-10 | 김홍민 | Facility supplying extinguish water and living water by recycling waste water |
| KR100515849B1 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2005-09-21 | 아주환경 주식회사 | Leachate and Sewage Recycling Method |
| KR100825518B1 (en) | 2005-07-29 | 2008-04-25 | 주식회사 미래엔지니어링 | Device and method for Biological Treatment of Wastewater using MBR and Zeolite Powder |
-
2007
- 2007-11-26 KR KR1020070120880A patent/KR100955914B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100430071B1 (en) | 2001-06-01 | 2004-05-10 | 김홍민 | Facility supplying extinguish water and living water by recycling waste water |
| KR100515849B1 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2005-09-21 | 아주환경 주식회사 | Leachate and Sewage Recycling Method |
| KR100825518B1 (en) | 2005-07-29 | 2008-04-25 | 주식회사 미래엔지니어링 | Device and method for Biological Treatment of Wastewater using MBR and Zeolite Powder |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101236467B1 (en) * | 2011-10-27 | 2013-02-22 | 김성종 | Apparatus and method for treating rainwater |
| KR101335668B1 (en) * | 2013-04-30 | 2013-12-05 | (주) 영동엔지니어링 | Multiple waste water processing filtration device having advanced disinfecting and backwashing function |
| KR101355866B1 (en) | 2013-08-06 | 2014-01-28 | (주)한국주조기계 | Smart wastewater reusing system using rainwater and graywater |
| CN103466881A (en) * | 2013-09-04 | 2013-12-25 | 常州友达环保科技有限公司 | Two-stage submerged membrane bio-reactor (MBR) |
| KR101898135B1 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2018-10-31 | (주)로터스엔지니어링 | Biological hydrogen wastewater treatment system |
| KR20200087397A (en) * | 2019-01-11 | 2020-07-21 | 이에스티 주식회사 | Treatment system of waste water using oxidation preprocess |
| KR102208641B1 (en) * | 2019-01-11 | 2021-01-28 | 이에스티 주식회사 | Treatment system of waste water using oxidation preprocess |
| KR102213273B1 (en) * | 2020-07-14 | 2021-02-05 | 국진산업개발(주) | water treating apparatus for reuse of dirty water and waste water and sea water |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20090054151A (en) | 2009-05-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100955914B1 (en) | Device and Method for Producing Drinking Water by Treating Waste Water | |
| Tansel | New technologies for water and wastewater treatment: A survey of recent patents | |
| Stoquart et al. | Hybrid membrane processes using activated carbon treatment for drinking water: a review | |
| CN102107994B (en) | Device for filtering various water sources into direct drinking water | |
| Gedda et al. | Introduction to conventional wastewater treatment technologies: limitations and recent advances | |
| CN105384316B (en) | A kind of processing method of the fluorine-containing nitrogen-containing wastewater of electronics industry | |
| KR100611171B1 (en) | Advanced water treatment using membrane Filtration | |
| Guo et al. | Experimental investigation of adsorption–flocculation–microfiltration hybrid system in wastewater reuse | |
| CN103787525B (en) | A kind of method of municipal effluent secondary biochemical effluent advanced treatment | |
| JP2002011498A (en) | Device for treating leachate | |
| Tian et al. | Hybrid process of BAC and sMBR for treating polluted raw water | |
| KR200383096Y1 (en) | Advanced water treatment using membrane Filtration | |
| KR100711259B1 (en) | Purification treatment apparatus | |
| ZA200201560B (en) | Method and device for purifying and treating waste water in order to obtain drinking water. | |
| JP5055746B2 (en) | Water circulation system using membrane | |
| CN1344690A (en) | Water treating method and treater for producing pure health water | |
| Thiel et al. | Activated carbon vs anthracite as primary dual media filters–a pilot plant study | |
| KR101054613B1 (en) | Apparatus for waste water single reactor composed of biological and membrane process | |
| JPH0119959B2 (en) | ||
| JP3831055B2 (en) | Public water supply | |
| WO2007105974A1 (en) | Biological process for wastewater treatment | |
| Nthunya et al. | Emerging nanoenhanced membrane-based hybrid processes for complex industrial wastewater treatment | |
| CN220703463U (en) | Recycling system of acid-base wastewater in semiconductor industry | |
| CN217947914U (en) | System for recycling wastewater generated in process of synthesizing ammonia and ethylene glycol by coal gasification | |
| Pellegrin et al. | Membrane processes |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20130311 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20140421 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20150422 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20160418 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20170426 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20180523 Year of fee payment: 9 |