JP7638136B2 - INFORMATION PROVIDING SERVER, INFORMATION PROVIDING SYSTEM, INFORMATION PROVIDING METHOD, AND PROGRAM - Google Patents
INFORMATION PROVIDING SERVER, INFORMATION PROVIDING SYSTEM, INFORMATION PROVIDING METHOD, AND PROGRAM Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7638136B2 JP7638136B2 JP2021069235A JP2021069235A JP7638136B2 JP 7638136 B2 JP7638136 B2 JP 7638136B2 JP 2021069235 A JP2021069235 A JP 2021069235A JP 2021069235 A JP2021069235 A JP 2021069235A JP 7638136 B2 JP7638136 B2 JP 7638136B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information
- operator
- image
- terminal
- operation terminal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Manipulator (AREA)
- User Interface Of Digital Computer (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
本発明は、情報提供サーバ、情報提供システム、情報提供方法、およびプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to an information providing server, an information providing system, an information providing method, and a program.
従来、モニタ用端末または別の端末から送信されたデータにより、ロボットを遠隔操作して実験器具または実験装置を操作する技術が知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。また、従来では、クラスメイトの実写画像を各人の評価エリアに配列して表示させたり、視線方向の座席を表示することに関する技術が知られている(例えば、特許文献2、3参照)。
Conventionally, there is known technology for remotely controlling a robot to operate experimental equipment or devices using data sent from a monitor terminal or another terminal (see, for example, Patent Document 1). Conventionally, there is also known technology for displaying live images of classmates in an array in each person's evaluation area, or displaying the seat in the line of sight (see, for example,
しかしながら、遠隔操作中は、一人の作業であるため孤独感を生じる場合があった。また、遠隔操作中に、他の人が動いている様子等をあたかも実際にいるかのように感じさせることについては検討されていなかった。 However, remote operation can sometimes create a sense of loneliness because it is a task performed by one person. Also, no consideration has been given to making the user feel as if other people are actually present during remote operation.
本発明の態様は、このような事情を考慮してなされたものであり、遠隔操作時であっても、作業空間にいるかのように感じさせる情報を提供することができる情報提供サーバ、情報提供システム、情報提供方法、およびプログラムを提供することを目的の一つとする。 The aspects of the present invention have been made in consideration of these circumstances, and one of the objectives is to provide an information providing server, information providing system, information providing method, and program that can provide information that makes the user feel as if they are in the work space, even when operating remotely.
この発明に係る情報提供サーバ、情報提供システム、情報提供方法、およびプログラムは、以下の構成を採用した。
(1):この発明の一態様に係る情報提供サーバは、一以上の操作端末とネットワークを介して通信する通信部と、前記操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報を取得する取得部と、空間上における前記操作者の配置場所を管理する管理部と、前記管理部によって管理された前記操作者の空間上における配置場所に、前記操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置し、配置した情報を前記操作端末に出力する出力制御部と、を備える情報提供サーバである。
An information providing server, an information providing system, an information providing method, and a program according to the present invention employ the following configuration.
(1): An information providing server according to one embodiment of the present invention is an information providing server including a communication unit that communicates with one or more operating terminals via a network, an acquisition unit that acquires information relating to the behavior of an operator of the operating terminal, a management unit that manages the location of the operator in space, and an output control unit that arranges information based on information representing the operator and information relating to the behavior at the location of the operator in space managed by the management unit, and outputs the arranged information to the operating terminal.
(2):上記(1)の態様において、前記管理部は、前記操作者が配置場所を選択する画像を生成し、生成した画像を前記操作端末に送信し、前記画像を用いて選択された配置場所に基づいて、前記操作者の配置場所を管理するものである。 (2): In the aspect of (1) above, the management unit generates an image in which the operator selects a placement location, transmits the generated image to the operation terminal, and manages the placement location of the operator based on the placement location selected using the image.
(3):上記(1)または(2)の態様において、前記操作端末は、一以上のロボット装置を遠隔操作する端末を含むものである。 (3): In the above embodiment (1) or (2), the operation terminal includes a terminal that remotely controls one or more robot devices.
(4):上記(1)から(3)のうち何れか1つの態様において、前記管理部は、実空間上において、前記操作者によって操作されるロボット装置の配置位置を取得し、取得した配置位置に配置されたロボット装置を含む画像を前記操作端末に出力する場合に、前記ロボット装置の表示領域に前記操作者を表す画像を重畳させるものである。 (4): In any one of the above aspects (1) to (3), the management unit acquires the position of the robot device operated by the operator in real space, and when outputting an image including the robot device placed at the acquired position to the operation terminal, superimposes an image representing the operator on the display area of the robot device.
(5):上記(1)~(3)の態様において、前記管理部は、予め仮想空間上に割り当てられ座席情報に対応付けて、前記操作者の配置場所を管理し、前記仮想空間を示す画像を前記操作端末に出力させる場合に、前記仮想空間上の座席の画像の位置に対応付けて、前記操作者を表す画像を重畳させるものである。 (5): In the above aspects (1) to (3), the management unit manages the location of the operator by associating it with seat information that has been assigned in advance in the virtual space, and when an image showing the virtual space is output to the operation terminal, an image representing the operator is superimposed in association with the position of the image of the seat in the virtual space.
(6):上記(1)~(5)のうち何れか一つに記載の態様において、前記出力制御部は、前記操作者の音声を取得し、取得した音声を前記配置場所に音像定位させて出力させるものである。 (6): In the aspect described in any one of (1) to (5) above, the output control unit acquires the voice of the operator, localizes the acquired voice as a sound image at the placement location, and outputs the voice.
(7):本発明の他の態様は、上記(1)~(6)うち何れか一つに記載された情報提供サーバと、前記一以上の操作端末と、前記一以上の操作端末によって遠隔操作される一以上のロボット装置と、を備える情報提供システムである。 (7): Another aspect of the present invention is an information provision system comprising an information provision server described in any one of (1) to (6) above, the one or more operation terminals, and one or more robot devices remotely operated by the one or more operation terminals.
(8):本発明の他の態様は、コンピュータが、一以上の操作端末とネットワークを介して通信し、前記操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報を取得し、空間上における前記操作者の配置場所を管理し、管理した前記操作者の空間上における配置場所に、前記操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置し、配置した情報を前記操作端末に出力する、情報提供方法である。 (8): Another aspect of the present invention is an information provision method in which a computer communicates with one or more operation terminals via a network, acquires information related to the behavior of an operator of the operation terminal, manages the location of the operator in space, arranges information based on information representing the operator and information related to the behavior at the managed location of the operator in space, and outputs the arranged information to the operation terminal.
(9):本発明の他の態様は、コンピュータに、一以上の操作端末とネットワークを介して通信させ、前記操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報を取得させ、空間上における前記操作者の配置場所を管理させ、管理した前記操作者の空間上における配置場所に、前記操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置し、配置した情報を前記操作端末に出力させる、プログラムである。 (9): Another aspect of the present invention is a program that causes a computer to communicate with one or more operation terminals via a network, acquire information related to the actions of an operator of the operation terminal, manage the location of the operator in space, arrange information based on information representing the operator and information related to the actions at the managed location of the operator in space, and output the arranged information to the operation terminal.
上記(1)~(9)の態様によれば、遠隔操作時であっても、作業空間にいるかのように感じさせる情報を提供することができる。 According to the above aspects (1) to (9), it is possible to provide information that makes the user feel as if they are in the work space, even during remote operation.
上記(2)の態様によれば、空間上の操作者が所望する位置に、操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置させることができる。 According to the above aspect (2), information based on information representing the operator and information related to the action can be placed in a position in space desired by the operator.
上記(3)、(4)の態様によれば、ロボット装置200が表示される位置に、操作者を表す画像が表示されるため、孤独感が生じることを防止することができる。
According to the above aspects (3) and (4), an image representing the operator is displayed at the position where the
上記(5)の態様によれば、仮想空間上の作業場所であっても、周囲の状況を把握することができ、作業空間にいるかのように感じさせる情報を提供することができる。 According to the above aspect (5), even if the work location is in a virtual space, it is possible to grasp the surrounding situation and provide information that makes the user feel as if they are in the work space.
上記(6)の態様によれば、配置場所に応じた音声を操作者に聞かせることができるため、より現実的に作業空間にいるかのように感じさせることができる。 According to the above aspect (6), the operator can hear a sound that corresponds to the placement location, making the operator feel as if he or she is in a more realistic working space.
以下、図面を参照し、本発明の情報提供サーバ、情報提供システム、情報提供方法、およびプログラムの実施形態について説明する。 Below, with reference to the drawings, an embodiment of the information providing server, information providing system, information providing method, and program of the present invention will be described.
[システム構成]
図1は、実施形態に係る情報提供システム1の構成の一例を示す図である。図1に示す情報提供システム1は、例えば、情報提供サーバ100と、ロボット装置200と、操作端末300と、を備える。また、情報提供サーバ100は、上記構成に加えて、ロボットメーカ端末400と、通信企業端末500とを備えていてもよい。情報提供サーバ100は、ロボット装置200、操作端末300、ロボットメーカ端末400、および通信企業端末500と、ネットワークNWを介して通信可能に接続されている。ネットワークNWは、例えば、インターネット、セルラー網、Wi-Fi(登録商標)網、WAN(Wide Area Network)、LAN(Local Area Network)、プロバイダ装置、無線基地局等を含む。情報提供システム1において、ロボット装置200および操作端末300は、それぞれが一以上備えていてもよい。図1の例では、ロボット装置200A、200B、および200Cが示されているが、ロボット装置の数や種類についてはこれに限定されない。また、図1の例では、複数の操作端末300-1~300-n(nは2以上の自然数)が示されている。以下、ロボット装置および操作端末のそれぞれを特に識別しない場合は、単に「ロボット装置200」、「操作端末300」と称して説明する。情報提供サーバ100は、「サーバ」の一例である。
[System configuration]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of an
情報提供サーバ100は、一以上の操作端末300と、操作対象の一以上のロボット装置200とを対応付けて管理する。この場合、情報提供サーバ100は、操作端末300ごとに1台のロボット装置200を対応付けてもよく、複数の操作端末300に1台のロボット装置200を対応付けてもよく、1つの操作端末300に複数のロボット装置200を対応付けてもよい。また、情報提供サーバ100は、操作端末300から入力された操作内容を取得し、操作内容に対応する動作制御情報をロボット装置200に送信することで、ロボット装置200の遠隔操作を実行させる。また、情報提供サーバ100は、ロボット装置200によって取得した情報を操作端末300に送信する。また、情報提供サーバ100は、遠隔操作時であっても、作業空間(例えば、遠隔操作するロボット装置200の周囲)にいるかのように感じさせるための情報を生成し、生成した情報を操作端末300に提供する。
The
ロボット装置200は、ネットワークNWを介して情報提供サーバ100から送信された制御情報に基づいて、所定の動作を実行する。ロボット装置200は、例えば、例えば、車輪や台車、クローラー、クレーン等を駆動させることによって移動することができる移動機構を備える。図1の例において、ロボット装置200Aは、少なくともクレーンによって移動可能な両腕を備えるロボットである。ロボット装置200Bは、下部に設けられた車輪によって移動可能な両腕を備えるロボットである。ロボット装置200Cは、二足歩行動作よって移動可能な両腕を備えるロボットである。また、ロボット装置200は、物体に対して、把持や移動、操作等の作業を実行するアーム部を備える。また、ロボット装置200には、振動や温度、圧力、触覚センサ等の各種のセンサが複数設けられ、各センサによって検出されたデータを所定周期または要求を受け付けたタイミングで情報提供サーバ100に送信する。また、ロボット装置200は、周辺を撮像するカメラや、画像を表示するモニタ、音声を出力するスピーカ、周辺の音を取得するマイク等を備えていてもよい。
The
操作端末300は、ロボット装置200の操作内容を入力したり、ロボット装置200により取得された情報を、操作者に通知する。操作端末300は、1台または複数のロボット装置200を操作可能である。また、操作端末300は、ロボット装置200の一部のパーツ(例えば、右手アームまたは左手アーム等)を操作してもよい。また、操作端末300は、例えば、HMD(ヘッドマウントディスプレイ)等の視覚装置や操作装置、操作者の動きを検出する環境センサが設けられていてもよい。なお、操作端末300は、例えば、企業内に設けられているものに限定されず、操作者の自宅に設けられた端末でもよく、駅やデパート、公共施設、ネットカフェ等に設置されたテレワークステーションに設けられた端末でもよい。
The
ロボットメーカ端末400は、例えば、ロボット装置200の製造業者や管理会社が利用する端末である。ロボットメーカ端末400は、例えば、各ロボット装置200に搭載されたソフトウェア(プログラム)のバージョンを更新したり、ロボット装置200からのエラー情報を取得し、取得したエラー情報に基づいて、ロボット装置200の遠隔操作や停止制御等を行う。
The
通信企業端末500は、例えば、ネットワークNW上の通信を管理する通信事業者等が利用する端末である。通信企業端末500は、情報提供システム1に対し、遠隔操作のために通信されるデータ量を管理したり、通信の遅延等を管理し、システム内の通信環境のメンテナンス等を行う。また、通信企業端末500は、ネットワークNW上に障害が発生した場合の対応等を行ってもよい。
The
次に、情報提供サーバ100、ロボット装置200、および操作端末300の機能について具体的に説明する。
[情報提供サーバ]
図2は、実施形態に係る情報提供サーバ100の構成の一例を示す図である。情報提供サーバ100は、例えば、通信部110と、通信制御部120と、取得部130と、管理部140と、制御部150と、記憶部170とを備える。通信制御部120と、取得部130と、管理部140と、制御部150とは、それぞれ、例えばCPU(Central Processing Unit)等のハードウェアプロセッサがプログラム(ソフトウェア)を実行することにより実現される。これらの構成要素のうち一部または全部は、LSI(Large Scale Integration)やASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit)、FPGA(Field-Programmable Gate Array)、GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)等のハードウェア(回路部;circuitryを含む)によって実現されてもよいし、ソフトウェアとハードウェアの協働によって実現されてもよい。これらの構成要素の機能のうち一部または全部は、専用のLSIによって実現されてもよい。プログラムは、予め情報提供サーバ100が備えるHDD(Hard Disk Drive)やフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置(非一過性の記憶媒体を備える記憶装置)に格納されていてもよいし、DVDやCD-ROM等の着脱可能な記憶媒体(非一過性の記憶媒体)に格納されており、記憶媒体が、情報提供サーバ100が備えるドライブ装置に装着されることで情報提供サーバ100が備えるHDDやフラッシュメモリにインストールされてもよい。情報提供サーバ100は、クラウドコンピューティングシステムに組み込まれたサーバ装置や記憶装置に実現されてもよい。この場合、クラウドコンピューティングシステムにおける複数のサーバ装置や記憶装置によって、情報提供サーバ100の機能が実現されてもよい。
Next, the functions of the
[Information server]
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of the
通信部110は、通信制御部120の制御により、ネットワークNWを介して、一以上のロボット装置200、一以上のロボット装置200を遠隔操作する操作端末300、その他の外部装置と通信する。通信制御部120は、通信部110における通信を制御する。
Under the control of the
通信制御部120は、通信部110における通信を制御する。通信制御部120は、例えば、操作端末300から入力されたロボット装置200の操作内容を受信したり、操作内容に応じた動作制御情報を、ロボット装置200に送信する。また、通信制御部120は、ロボット装置200から送信されたセンサ等の検出結果やカメラ画像等の情報を受信したり、受信した情報に基づく提供情報を、操作端末に送信する。
The
取得部130は、ロボット装置200または操作端末300から各種情報を取得する。例えば、取得部130は、操作端末300からロボット装置200を操作するための操作情報を取得する。また、取得部130は、操作端末300から操作者の行動に関する情報を取得する。行動に関する情報には、例えば、操作者の動作に関する情報や、操作者の音声に関する情報等が含まれる。また、取得部130は、ロボット装置200に設けられたセンサやカメラからの情報を取得する。また、取得部130は、ネットワークNWに接続された外部装置から情報を取得してもよい。
The
管理部140は、例えば、認証管理部142と、情報管理部144と、利用状況管理部146とを備える。認証管理部142は、ロボット装置200を操作する操作者(システム利用者)の認証や利用権限等を管理する。また、認証管理部142は、認証結果に基づいて、操作端末300が操作するロボット装置200を対応付けて管理する。
The
情報管理部144は、利用者ごとに利用可能な情報を管理する。例えば、情報管理部144は、ロボットを制御するためのロボット制御情報や、ロボット装置200に設けられたセンサから取得された情報(センサ情報)を記憶部に170に記憶させると共に、それぞれ異なるアクセス権を設定し、設定されたアクセス権が確認されたときに、対応する提供可能な権限を有する操作端末300に情報を送信する。これにより、データの機密性が守られる。したがって、例えば、アクセス権を持たない他人に情報を盗まれたり、改ざんされたりすることを防止することができ、システム全体のセキュリティを向上させることができる。また、アクセス権によって提供する情報を管理することで、様々な利用者等に安心して情報提供システム1を利用させることができる。
The
利用状況管理部146は、利用者ごとの情報提供システム1の利用状況を管理する。例えば、利用状況管理部146は、利用者ごとに空間上における配置場所を管理する。空間上とは、例えば、作業空間であり、実空間上でもよく、仮想空間上でもよい。以下では、主に実空間を中心として説明する。また、利用状況管理部146は、空間上に予め割り当てられた座席に対する操作者の配置位置を管理したり、操作端末300に提供する情報の利用状況等を管理する。
The usage
制御部150は、例えば、ロボット情報制御部151と、カスタマイズデータ制御部と、意図推定部153と、動作制御部154と、動作キャンセル部155と、出力制御部156とを備える。ロボット情報制御部151は、例えば、動作制御部154により生成されたロボット装置200に対する動作制御情報に対して、実際にロボット装置200がどのような操作を行ったのか等を管理する。また、ロボット情報制御部151は、記憶部170に記憶されたロボット制御情報173に基づいて、ロボット装置200に基本的な動作を実行させる。基本的な動作とは、例えば、ロボット装置200を移動させたり、姿勢を変えたり、物体を持ったり置いたりする動作である。これらの基本的な動作の制御情報がロボット制御情報173に格納されている。
The
カスタマイズデータ制御部152は、例えば、特定の動作(例えば、物を組み立てる作業や半田付け作業、ネジ止めしたり、料理における各種工程作業等)をロボット装置200に実行させるためのカスタマイズデータを生成する。
The customization
意図推定部153は、操作端末300により入力される操作内容の少なくとも一部の情報から操作者の意図を推定する。操作者の意図には、例えば、操作者がロボット装置200に行わせたい行動(動作)の意図だけでなく、行動等を予測することや、ロボット装置200の駆動をアシストさせることも含まれる。例えば、遠隔操作では通信等によって操作者が指示している感じとロボット装置200の動作にズレが生じる。そのため、意図推定部153は、操作者からの操作内容をそのままロボット装置200に実行させるのではなく、操作内容に基づいて操作者の意図を推定し、推定結果に基づいてロボット装置200の動作制御情報を生成することで、ロボット装置200の動きをより適切にアシストし、違和感の少ない遠隔操作を実現することができる。意図推定部153は、例えば、教師データを用いて学習させた学習モデル(意図推定情報174)を参照し、操作内容に対応する意図を推定する。なお、学習の際には、例えば、操作内容を入力し、その操作内容に対する作業者等が設定した正解の意図情報を出力するための教師データを用いて学習を行う。
The
また、意図推定部153は、操作者から入力された操作内容およびロボット装置200の実際の動作内容を示す履歴情報に基づいて、意図推定情報174を更新してもよい。これにより、より適切な意図推定を実現できる。
The
また、意図推定部153は、例えば、グラスプタクソノミー(GRASP Taxonomy)手法(例えば、参考文献1参照)によって、操作者の動作意図を推定してもよい。実施形態では、例えばグラスプタクソノミー手法によって操作者あるいはロボット装置200の姿勢すなわち把持姿勢を分類することで操作者状態を分類して、操作者の動作意図を推定する。
参考文献1;Thomas Feix, Javier Romero,他,“The GRASP Taxonomy of Human GraspTypes” IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems ( Volume: 46, Issue: 1, Feb.2016),IEEE,p66-77.
Furthermore, the
Reference 1: Thomas Feix, Javier Romero, et al., “The GRASP Taxonomy of Human GraspTypes” IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems (Volume: 46, Issue: 1, Feb.2016), IEEE, p66-77.
動作制御部154は、意図推定部153により推定された操作者の意図に基づいて対象のロボット装置200を動作させるための動作制御情報を生成し、生成した動作制御情報を操作対象のロボット装置200に送信し、ロボット装置200の動作を制御する。また、動作制御部154は、操作者の意図に加えて(または代えて)、ロボット情報制御部151やカスタマイズデータ制御部152等により得られるロボット装置200の動作に関する情報を取得し、取得した情報に基づいて、動作制御情報を生成してもよい。また、動作制御部154は、例えば、複数の操作者が、同時に2つのアーム部を操作する場合に、触覚等のセンサ情報等に基づいて、力の足し算や引き算等の合成処理を行い、協調して作業するための動作制御を行ってもよい。これにより、複数の操作者により1台のロボット装置200が操作された場合であってもバランスの良い動作を実現することができる。
The
動作キャンセル部155は、動作制御部154によりロボット装置200に実行させる動作のうち、操作者の意図と異なる動作を選択し、選択した動作の実行をキャンセルする。この場合、動作キャンセル部155は、操作者から入力された操作内容が、ロボット装置200に動作させる内容であるか否かを操作者に問い合わせ、問い合わせ結果に基づいて、動作制御部154に動作制御情報を生成させたり、意図推定情報174を更新させたりする。
The
出力制御部156は、ロボット装置200から取得した音声や画像に基づいて、操作端末300を操作する操作者に提供する情報を生成する。提供する情報には、画像や音声が含まれる。また、出力制御部156は、認証管理部142による認証処理の結果に基づいて、センサ情報等を出力する。また、出力制御部156は、利用状況管理部146により管理された内容に基づいて、ユーザごとに提供する情報を生成する。
The
記憶部170は、上記の各種記憶装置、或いはSSD(Solid State Drive)、EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)、ROM(Read Only Memory)、またはRAM(Random Access Memory)等により実現されてもよい。記憶部170に、例えば、利用者情報171、利用状況情報172、ロボット制御情報173、意図推定情報174、センサ情報175、プログラム、およびその他の情報が格納される。
The
図3は、利用者情報171の内容を説明するための図である。利用者情報171は、例えば、情報提供システム1によるサービス利用時等に利用者を認証する認証情報に、氏名、権限、優先度、画像情報等の情報が対応付けられたものである。認証情報には、例えば、利用者を識別する識別情報である利用者IDやパスワード等が含まれる。また、認証情報には、指紋情報や虹彩情報等の生体認証情報が含まれてもよい。権限には、例えば、利用者に割り当てられたアクセス権等の権限情報が含まれる。この権限情報に基づいて、ロボット装置200により取得されたセンサ情報等を取得することができる。情報管理部144は、権限に格納された情報を参照することで、誰がどのデータにアクセス可能であるか、どのデータにアクセスできないのか等を管理することができる。優先度情報は、例えば、複数の操作者がロボット装置200を遠隔操作している場合であって、それぞれの操作内容が同一または類似する場合の優先度が格納されている。画像情報とは、利用者を表す画像情報である。画像情報には、例えば、利用者の顔画像や全体画像、利用者が識別できるように利用者に似せて作成されたアバター画像やイラスト画像等が含まれる。また、画像情報は、利用者を360度から撮影した画像や、各パーツ(例えば腕や足)のみの画像が含まれてもよい。
3 is a diagram for explaining the contents of the
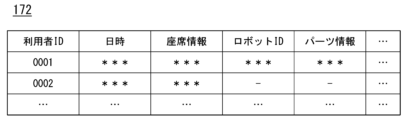
図4は、利用状況情報172の内容を説明するための図である。利用状況情報172は、例えば、利用者IDに、日時、座席情報、ロボット装置200を識別する識別情報であるロボットIDと、パーツ情報とが対応付けられている。日時は、例えば、利用開始日時でもよく、利用時間等の情報が含まれてもよい。座席情報は、ロボット装置200が作業を行う空間に配置された座席のうち、利用者が利用する座席情報である。この座席は、ロボット装置200ではない実際の作業者が作業を行っている場所(座席)の情報が格納されてもよい。パーツ情報は、ロボット装置を複数の利用者(操作者)によって動作させる場合の担当パーツに関する情報である。利用状況情報172は、利用状況管理部146によって、管理され状況に応じて更新される。
Figure 4 is a diagram for explaining the contents of the
図5は、意図推定情報174の内容について説明するための図である。意図推定情報174は、例えば、操作端末300から取得した操作内容に、推定意図に関する情報が対応付けられている。これらの情報は、操作者ごとに管理されてよく、複数の操作者の意図推定情報174を統合して、頻度の高い意図推定に関する情報のみが格納されてもよく、履歴情報等に基づいて更新されてもよい。
Figure 5 is a diagram for explaining the contents of the
図6は、センサ情報175の内容について説明するための図である。センサ情報175には、ロボット装置200を識別する識別情報であるロボットIDに、日時、操作者ID、操作パーツ、センサ情報等が格納されている。操作者IDには、操作した操作者の利用者IDが格納される。操作パーツには、操作者が操作したロボットIDのパーツが格納される。これにより、1台のロボット装置200が複数の操作者によって操作される場合であっても、それぞれの操作履歴(センサ情報)を管理することができる。
Figure 6 is a diagram for explaining the contents of the
[ロボット装置]
図7は、実施形態に係るロボット装置200の構成の一例を示す図である。ロボット装置200は、例えば、例えば、通信部202と、センサ204と、カメラ(撮像部の一例)206と、マイク208と、駆動部210と、モニタ214と、スピーカ216と、制御装置240と、記憶部260とを備える。駆動部210は、例えば、アーム部210Aと、移動用駆動部210Bとを備える。制御装置240は、例えば、通信制御部242と、取得部244と、駆動制御部246と、出力制御部248とを備える。通信制御部242と、取得部244と、駆動制御部246と、出力制御部248とは、それぞれ、例えばCPU等のハードウェアプロセッサがプログラム(ソフトウェア)を実行することにより実現される。これらの構成要素のうち一部または全部は、LSIやASIC、FPGA、GPU等のハードウェア(回路部;circuitryを含む)によって実現されてもよいし、ソフトウェアとハードウェアの協働によって実現されてもよい。これらの構成要素の機能のうち一部または全部は、専用のLSIによって実現されてもよい。プログラムは、予めロボット装置200が備えるHDDやフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置(非一過性の記憶媒体を備える記憶装置)に格納されていてもよいし、DVDやCD-ROM等の着脱可能な記憶媒体(非一過性の記憶媒体)に格納されており、記憶媒体が、ロボット装置200が備えるドライブ装置に装着されることでロボット装置200が備えるHDDやフラッシュメモリにインストールされてもよい。
[Robot device]
7 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of the
通信部202は、後述する。通信制御部242の制御により、ネットワークNWを介して、情報提供サーバ100、その他の外部装置と通信する。また、通信部202は、他のロボット装置200と通信してもよく、操作端末300と通信を行ってもよい。
The
センサ204は、ロボット装置200の位置を検出する位置センサ、速度を検出する速度センサ、ロボット装置200の周辺またはアーム部210Aの先端部等の特定の位置の温度を検出する温度センサ等を含む。位置センサは、例えば、GPS(Global Positioning System)受信装置から情報を受信して、受信した情報に基づいて位置情報(経度・緯度情報)を求める。また、センサ204は、周囲の湿度を検出する湿度センサや、ロボット装置200によって操作される物体の振動を検出する振動センサを含んでいてもよい。また、センサ204は、周辺の物体を検知する物体検知センサを含んでいてもよい。周辺の物体とは、例えば、他のロボット装置200や人物、障害物等である。
The
カメラ206は、例えば、CCD(Charge Coupled Device)やCMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)等の固体撮像素子を利用したデジタルカメラである。カメラ206は、例えば、所定のタイミングでロボット装置200の周辺を撮像する。カメラ206は、一台に限らず、複数台がロボット装置200に設けられてもよい。例えば、カメラ206は、ロボット装置200の頭部に設けられる。また、カメラ206は、アーム部210Aの先端付近に設けられてもよい。これにより、作業対象の物体を近い距離で撮影することができるため、より細かい作業を行い易くすることができる。
The
マイク208には、ロボット装置200の周辺の音が入力される。マイク208は、入力された音声に基づく情報を制御装置240に出力する。
Sounds around the
アーム部210Aは、対象物体を把持したり、対象物体に対して所定の作業を行う。アーム部210Aは、例えば、多関節ロボットアームであり、例えば、アクチュエータ、ギア、人工筋等を備える。例えば、アーム部210Aは、多関節ロボットアームの一端がロボット装置本体の右側付近に接続された第1アーム部と、他の多関節ロボットアームの一端がロボット装置本体の左側付近に接続された第2アーム部とを備える。また、アーム部210Aには、第1アーム部および第2アーム部に加えて他のアーム部を備えていてもよい。以下、それぞれのアームを区別しない場合は、単に「アーム部210A」と称する。アーム部の他端は、所定の物を把持可能な把持部が構成されている。アーム部210Aは、制御装置220の制御に基づいて駆動する。また、アーム部は、人の腕の動きと同等の動きが可能である。 The arm unit 210A grasps a target object and performs a predetermined task on the target object. The arm unit 210A is, for example, a multi-joint robot arm, and includes, for example, an actuator, a gear, an artificial muscle, and the like. For example, the arm unit 210A includes a first arm unit in which one end of the multi-joint robot arm is connected near the right side of the robot device main body, and a second arm unit in which one end of the other multi-joint robot arm is connected near the left side of the robot device main body. The arm unit 210A may also include other arm units in addition to the first arm unit and the second arm unit. Hereinafter, when there is no need to distinguish between the respective arms, they will simply be referred to as "arm unit 210A". The other end of the arm unit is configured with a gripping unit capable of gripping a predetermined object. The arm unit 210A is driven based on the control of the control device 220. The arm unit is capable of movement equivalent to that of a human arm.
移動用駆動部210Bは、ロボット装置200が床面や地面を移動するための駆動部である。移動用駆動部210Bは、例えば、2つの脚部であってもよいし、車輪、台車、クローラー等の移動機構が設けられていてもよい。例えば、移動用駆動部210Bが脚部の場合、脚部は、制御装置220の制御に基づいて、ロボット装置200を歩行させるように動作する。また、移動用駆動部210Bは、クレーン等を駆動させることによって天井またはレールに沿って移動可能な構造であってもよい。これらの構成によりロボット装置200は、所望の方向に移動することができる。なお、駆動部210は、アーム部210Aまたは移動用駆動部210B以外にも腰や頭等の他の関節等を駆動させる機構が設けられてもよい。駆動部210は、駆動制御部246よる制御に基づいて駆動が実行される。
The moving
モニタ214は、例えば、LCD(Liquid Crystal Display)や有機EL(Electro Luminescence)表示装置等である。モニタ214は、出力制御部248によって出力された情報を画像として表示する。モニタ214は、ロボット装置200に複数設けられてよい。モニタ214は、例えば、頭部に設けられていてもよく、腹部や背面に設けられていてもよい。スピーカ216は、出力制御部248によって出力された情報を音声として出力する。
The
制御装置240は、例えば、通信制御部242と、取得部244と、駆動制御部246と、出力制御部248とを備える。通信制御部242と、取得部244と、駆動制御部246と、出力制御部248とは、例えば、CPU等のハードウェアプロセッサがプログラム(ソフトウェア)を実行することにより実現される。これらの構成要素のうち一部または全部は、LSIやASIC、FPGA、GPU等のハードウェア(回路部)によって実現されてもよいし、ソフトウェアとハードウェアの協働によって実現されてもよい。プログラムは、予めHDDやフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置(非一過性記憶媒体)に格納さいてもよいし、DVDやCD-ROM等の着脱可能な記憶媒体(非一過性記憶媒体)に格納されており、記憶媒体がドライブ装置に装着されることでインストールされてもよい。
The
通信制御部242は、例えば、通信部202を介して無線通信によって、情報提供サーバ100と通信し、情報の送受信を行う。また、通信制御部242は、通信部202を介して他のロボット装置200と通信を行ってもよい。
The
取得部244は、ロボット装置200に設けられたセンサ204の検出結果(センサ情報)を取得する。また、取得部244は、カメラ206により撮像された画像を取得する。また、取得部244は、マイク208から入力された音に基づく情報を取得する。
The
駆動制御部246は、情報提供サーバ100から取得した動作制御情報に基づいて、アーム部210Aおよび移動用駆動部210Bを動作させる。また、駆動制御部246は、動作制御情報に基づいて、ロボット装置200の他のパーツ(例えば、頭、胴、腰等)を駆動させて、姿勢等を変更させる。また、駆動制御部246は、記憶部260に記憶された基本動作情報262およびカスタマイズ動作情報264に基づいて、ロボット装置200を駆動させてもよい。基本動作情報262は、ロボット装置200の種類等に応じて基本的な動作を実行させるための駆動制御情報である。カスタマイズ動作情報264とは、例えば、操作者ごとに予め登録された特定の動作をロボット装置200に実行させるための駆動制御情報である。
The
出力制御部248は、情報提供サーバ100から取得した情報に基づく画像をモニタ214に出力させる。また、出力制御部248は、情報提供サーバ100から取得した情報に基づく音声や警告音等をスピーカ216に出力させる。
The
記憶部260は、例えば、HDD、フラッシュメモリ、EEPROM、ROM、またはRAM等により実現される。記憶部260には、例えば、基本動作情報262、カスタマイズ動作情報264、プログラム、その他の情報が格納されている。
The
[操作端末]
図8は、実施形態に係る操作端末300の構成の一例を示す図である。操作端末300は、例えば、通信部310と、視覚装置320と、操作装置330と、環境センサ340と、制御装置360と、記憶部380とを備える。視覚装置320と、操作装置330と、環境センサ340は、「HMI(Human Machine Interface)」の一例である。
[Operation terminal]
8 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of the
通信部310は、制御装置360による制御によりネットワークNWを介して情報提供サーバ100と通信を行う。また、通信部310は、他の操作端末300やロボット装置200と通信を行ってもよい。
The
視覚装置320は、例えば、HMDでもよく、メガネ型の装置やディスプレイにセンサ等が設けられた構成であってもよい。視覚装置320は、例えば、画像表示部322と、視線検出部324と、センサ326と、マイク327と、スピーカ328と、制御部329とを備える。視覚装置320は、制御装置360が情報提供サーバ100から受信したロボット装置200の状態画像や音声等を出力示したり、操作者の視線の動き等を検出する。
The
画像表示部322は、例えば、LCDや有機ELディスプレイ等である。画像表示部は、制御部329の制御に応じて、後述する出力制御部368により出力された画像を表示する。
The
視線検出部324は、制御部329の制御により視覚装置320を利用する操作者の視線を検出し、検出した視線情報(操作者センサ値)を制御装置360に出力する。視線情報とは、例えば、視線ベクトルを含む情報である。
The
センサ326は、例えば、加速度センサ、ジャイロスコープセンサ、磁力センサ等である。センサ326は、視覚装置320を装着した操作者の頭部の傾き、頭部の回転を検出し、検出した頭部動作情報(操作者センサ値)を制御装置360に出力する。
The
マイク327は、操作者の音声の入力を受け付ける。スピーカ328は、出力制御部368により出力された音声や警告音等を出力する。
The
制御部329は、制御装置360からの制御情報に基づいて視線検出部324による視線検出の実行を制御したり、センサ326による検出を制御したり、画像表示部322への画像表示を制御したり、視覚装置320を介した操作者からの情報の入力を受け付けたりする。
The
操作装置330は、例えば、センサ(操作者センサ)332と、制御部334と、フィードバック部336と、入力部338とを備える。操作装置330には、例えば、操作者の手に装着される触覚データグローブが含まれる。
The
センサ332は、例えば、加速度センサ、ジャイロスコープセンサ、磁力センサ等である。なお、センサ332は、複数のセンサを備える。センサ332は、例えば2つのセンサによって各指の動きをトラッキングする。センサ332は、例えば、制御部334の制御により、操作者の各指の方位や動き、手の動き等の操作者の腕部の姿勢や位置に関する情報である操作者腕部情報(操作者センサ値)を検出する。なお、操作者腕部情報(操作者センサ値)には、手先位置・姿勢情報、各指の角度情報、肘の位置・姿勢情報、各部の動きをトラッキングした情報等のヒトの腕部全般におよぶ情報が含まれる。
The
制御部334は、センサ332が検出した操作者腕部情報を、制御装置360に出力する。また、制御部334は、制御装置360から取得したフィードバック情報に基づいて、フィードバック部336を制御する。
The
フィードバック部336は、制御部334の制御に応じて、操作者にフィードバック情報をフィードバックする。フィードバック部336は、フィードバック情報に応じて、例えば、ロボット装置200のアーム部210Aに取り付けられている振動を与える手段(不図示)や空気圧を与える手段(不図示)や手の動きを拘束する手段(不図示)や温度を感じさせる手段(不図示)や堅さや柔らかさを感じさせる手段(不図示)、振動を感じさせる手段(不図示)等によって操作者に感覚をフィードバックする。
The
入力部338は、例えば、触覚データグローブ以外のキーボードやマウス、レバー、タッチパネル、マイク等の各入力装置である。入力部338は、各入力装置によってロボット装置200に対する操作内容の入力を受け付ける。
The
環境センサ340は、例えば、操作者の動作を検出する。環境センサ340は、例えば、カメラ(撮像部の一例)342と、センサ344と、物体位置検出部346とを備える。カメラ342は、操作者を含む画像を撮像する。カメラ342は、例えば、RGBカメラである。カメラ342は、撮影した画像を物体位置検出部346に出力する。なお、環境センサ340において、カメラ342とセンサ344の位置関係が既知である。
The
センサ344は、例えば深度センサである。センサ344は、検出結果を物体位置検出部346に出力する。なお、カメラ342とセンサ344は、距離センサであってもよい。
物体位置検出部346は、カメラ342によって撮影された画像とセンサ344によって検出された検出結果とに基づいて、撮影された画像における対象物体の三次元位置と大きさ形状等を周知の手法で検出する。物体位置検出部346は、物体位置検出部346が記憶するパターンマッチングのモデル等を参照して、カメラ342が撮影した画像に対して画像処理(エッジ検出、二値化処理、特徴量抽出、画像強調処理、画像抽出、パターンマッチング処理等)を行って物体の位置を推定する。なお、物体位置検出部346は、撮影された画像から複数の物体が検出された場合、物体毎に位置を検出する。物体位置検出部346は、検出した物体位置情報を、制御装置360に送信する。なお、環境センサ340が送信するデータは、例えば位置情報を有する点群であってもよい。
Based on the image captured by the
制御装置360は、例えば、通信制御部362と、取得部364と、操作内容生成部366と、出力制御部368とを備える。通信制御部362と、取得部364と、操作内容生成部366と、出力制御部368とは、例えば、CPU等のハードウェアプロセッサがプログラム(ソフトウェア)を実行することにより実現される。これらの構成要素のうち一部または全部は、LSIやASIC、FPGA、GPU等のハードウェア(回路部)によって実現されてもよいし、ソフトウェアとハードウェアの協働によって実現されてもよい。プログラムは、予めHDDやフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置(非一過性記憶媒体)に格納さいてもよいし、DVDやCD-ROM等の着脱可能な記憶媒体(非一過性記憶媒体)に格納されており、記憶媒体がドライブ装置に装着されることでインストールされてもよい。
The
通信制御部362は、例えば、通信部310を介して無線通信によって、情報提供サーバ100と通信し、情報の送受信を行う。また、通信制御部362は、通信部310を介して他の操作端末300と通信を行ってもよい。また、通信制御部362は、視覚装置320や操作装置330、環境センサ340との通信を行う。
The
取得部364は、視覚装置320、操作装置330、環境センサ340から得られた除法を取得する。操作内容生成部366は、取得部364により取得された情報に基づいて、ロボット装置200に対する操作内容を生成する。例えば、操作内容生成部366は、視覚装置320から取得された情報に基づいて視線情報や頭の向きに関する操作内容を生成する。また、操作内容生成部366は、操作装置330から取得された情報に基づいて、ロボット装置200のアーム部210Aの動作に関する操作内容を生成する。また、操作内容生成部366は、環境センサ340から取得された情報に基づいて、ロボット装置200の姿勢や移動方向、移動量に関する操作内容を生成する。操作内容生成部366により生成された情報は、通信部310を介して、情報提供サーバ100に送信される。
The
出力制御部368は、情報提供サーバ100から取得した提供情報を、視覚装置320や操作装置330に出力する。例えば、情報提供サーバ100から取得した画像や視覚装置320の画像表示部322に出力させる。また、出力制御部368は、情報提供サーバ100から取得した情報に基づく音声や警告音等をスピーカ328に出力させる。また、出力制御部368は、情報提供サーバ100から取得した触覚に関する情報を操作者に伝えるためのフィードバック情報を操作装置330に出力させる。
The
記憶部380は、例えば、HDD、フラッシュメモリ、EEPROM、ROM、またはRAM等により実現される。記憶部380には、例えば、プログラム、その他の情報が格納されている。
The
[実施形態に係るロボット装置の遠隔操作について]
次に、実施形態に係る情報提供システム1によるロボット装置200の遠隔操作について具体的に説明する。図9は、実施形態に係るロボット装置200の遠隔操作について説明するための図である。図9では、2人の操作者U1、U2が交代で1台のロボット装置200を操作する例を示している。操作者U1およびU2は、それぞれ、図9に示すように、視覚装置320と操作装置330とを装着している。操作端末300-1、300-2は、異なる場所に設置されてもよい。
[Regarding remote control of the robot device according to the embodiment]
Next, remote operation of the
また、操作者U1とU2には、操作者の動作や周辺環境を測定する環境センサ340が設置されている。なお、環境センサ340と同様の構成は、例えば、ロボット装置200に取り付けられていてもよい。また、操作装置330は、例えば、操作者の左手に装着される操作装置330aと、右手に装着される操作装置330bとを含む。操作装置330a、330bのそれぞれから入力される操作内容は、ロボット装置200の左手LHおよび右手RHの動作制御に用いられる。操作者の腕の位置や顔の向き等は、環境センサ340により検出される。それぞれの検出したデータは、ネットワークを介して情報提供サーバ100に送信される。
In addition, the operators U1 and U2 are provided with
情報提供サーバ100は、操作端末300-1、300-2のうち、ロボット装置200を操作する端末から得られる操作内容に基づいて操作者の意図を推定する。ここで、意図推定部153が推定する情報例について、具体的に説明する。意図推定部153は、取得した操作者からの操作内容に基づいて、操作者の動作意図を推定する。例えば、意図推定部153は、操作端末300の操作者センサ値に基づいて、操作者の腕部の姿勢を分類することで、ロボット装置の把持部を含むアームの姿勢を分類する。また、意図推定部153は、分類結果に基づいて、操作者がロボット装置200に行わせたい動作意図を推定する。意図推定部153は、例えば、時刻毎の手や指の動き、ロボット装置200に行わせたい作業目的、作業内容、時刻毎の手や指の動き等を操作者の動作意図として推定する。作業目的は、例えば、物体の把持、物体の移動等である。作業内容は、例えば、物体を把持して持ち上げる、物体を把持して移動させる等である。
The
また、意図推定部153は、例えば、記憶部170に記憶された学習済みモデルや意図推定情報174に操作内容を入力して、操作者の動作意図を推定してもよい。実施形態では、把持姿勢の分類によって意図推定を行うことで、精度良く操作者の動作意図を推定することができる。なお、把持姿勢の分類には、他の手法を用いてもよい。
The
また、意図推定部153は、視線と腕部の動きを用いて統合的に推定してもよい。この場合、意図推定部153は、視線情報と、手の動き情報とテーブルTB上の物体OBの位置情報とを学習済みのモデルに入力して、操作者の動作意図を推定するようにしてもよい。
The
図9の例において、意図推定部153は、例えば、視線情報に基づいて把持させた物体を推定する。次に、意図推定部153は、推定した把持させたい物体に基づいて、操作者の手の姿勢を推定する。また、意図推定部153は、例えば、操作内容に基づいて、まず操作者の手の姿勢を推定し、次に推定した操作者の手の姿勢から、把持したい物体を推定してもよい。また、操作者U1、U2ごとに異なる部位の操作が割り当てられている場合には、意図推定部153は、それぞれの操作内容に基づく意図を推定してもよい。
In the example of FIG. 9, the
例えば、図9に示すテーブルTB上に物体OBが置かれている場合、意図推定部153は、手の姿勢に基づいて、物体OBを把持すると推定する。また、意図推定部153は、操作内容と、ロボット装置200の状態情報とに基づいて、操作者が意図する手先の将来軌道を、事前に推定してもよい。なお、意図推定部153は、センサにより検出された検出結果、環境センサ340が撮影した画像を画像処理した結果等も用いて、把持したい物体と、物体の位置を推定するようにしてもよい。
For example, when an object OB is placed on the table TB shown in FIG. 9, the
また、操作者が操作する環境とロボット動作環境では座標系が異なるため、例えば、ロボット装置200の起動時に、操作者の操作環境とロボット動作環境とのキャリブレーションを行ってもよい。また、把持の際、情報提供サーバ100は、ロボット装置の把持力と、物体と把持部との摩擦力等に基づいて、把持時の把持位置の誤差を考慮して、把持位置を決定してもよい。
In addition, since the coordinate system is different between the environment in which the operator operates and the robot operating environment, for example, calibration between the operator's operating environment and the robot operating environment may be performed when the
ロボット装置200は、遠隔操作されていない場合は、制御装置240の制御に応じて動作が制御され、遠隔操作されている場合、情報提供サーバ100が推定された意図等に基づいて生成した動作制御情報に応じて動作が制御される。
When the
ロボット装置200の制御装置240は、情報提供サーバ100からの動作制御情報に基づいて駆動部210を制御する。また、ロボット装置200は、センサ204により検出されたセンサ情報や、カメラ206で撮像された画像、マイク208により出力された音声等の情報を情報提供サーバ100に出力する。情報提供サーバ100は、取得したセンサ情報、画像、音声等に基づいて操作端末300-1、300-2に提供する提供情報を生成する。この場合、情報提供サーバ100は、画像にセンサ情報の少なくとも一部を重畳した画像を生成してもよい。情報提供サーバ100は、触覚により伝達させるための情報も含めた提供情報を生成する。また、ロボット装置200は、複数の操作者により操作することが可能であるため、ロボット装置200の各部位の操作者を特定するための情報をカメラ画像に重畳した画像を生成してもよい。操作端末300は、情報提供サーバ100から出力された画像を表示させる。これにより、複数の操作者がロボット装置200を操作する場合に、他の操作者によって操作されたロボットの状況を把握することができる。
The
また、上述のような遠隔操作を実行する場合、操作者は、それぞれ異なる場所の操作端末300を操作しているため、孤独を感じてしまう場合がある。そのため、情報提供サーバ100は、ロボット装置200が存在する作業空間に操作者がいると感じさせる(錯覚させる、疑似体験させる)情報を生成し、生成した画像を操作端末300に提供する。
When performing remote operation as described above, the operators may feel lonely because they are operating the
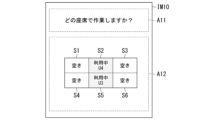
例えば、情報提供サーバ100は、利用者からロボット装置200の遠隔操作の指示があった場合に、ロボット装置200を作業させる空間上の配置場所を選択させるための情報(画像)を操作端末300に送信する。配置場所は、例えば、空間上の座席情報に基づいて位置付けられる。図10は、利用者に座席を選択させるための画像IM10の一例を示す図である。なお、画像IM10のレイアウトや表示内容等の表示態様については、図10の例に限定されるものではない。以降に説明する他の画像の表示態様についても同様とする。また、画像IM10の内容は、例えば、出力制御部156により生成される。
For example, when a user instructs to remotely operate the
画像IM10には、例えば、文字表示領域A11と、座席選択領域A12とが含まれる。文字表示領域A11には、利用者に座席の選択を促す文字情報が表示される。図10の例では、「どの座席で作業しますか?」といった文字情報が表示されている。なお、情報提供サーバ100は、文字情報に相当する音声データを生成し、生成したデータを操作端末300から出力させてもよい。
Image IM10 includes, for example, a text display area A11 and a seat selection area A12. Text information that prompts the user to select a seat is displayed in text display area A11. In the example of FIG. 10, text information such as "Which seat would you like to work at?" is displayed. Note that the
座席選択領域A12には、例えば、利用者が操作するロボット装置200が操作する作業空間に存在する座席の利用状況に関する情報が表示されている。図10の例では、6つの座席S1~S6が、例えば実空間の座席の位置に対応させて表示されている。なお、仮想空間上で座席を設定する場合、このような座席位置は、例えば通常の業務モード、会議モード等に応じて、座席の配置や大きさ、数等を異なるようにしてもよい。座席配置は、例えば会議モードでは、座席を円形に配置するようにしてもよい。また、座席配置は、例えば会社の座席配置と同じ配置を用いても良く、出社している社員の座席には出社中等の表示をすることで現実世界と仮想世界を混合させてもよい。情報提供サーバ100は、利用状況管理部146によって管理されている利用状況情報172を参照し、利用中の座席に関する情報も含めて座席選択領域A12に表示させる。図10の例において、座席選択領域A12には、座席S2、S5が利用中であり、座席S1、S3、S4、S6が空席であることを示す画像が表示されている。また、情報提供サーバ100は、座席選択領域A12に、現在利用中である利用者を識別する情報を表示させてもよい。図10の例では、座席S2を利用者U4が利用し、座席S5を利用者U3が利用していることを示している。これにより、利用者は、利用中の状況に基づいて、自分が所望する座席を選択することができる。以下、利用者が、座席S4を選択したものとして説明する。
In the seat selection area A12, for example, information on the use status of seats in the work space where the
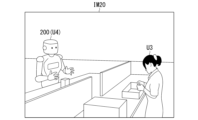
情報提供サーバ100は、座席が特定されると、利用状況情報172を更新すると共に、座席S4の位置に利用者が移動するロボット装置200を移動させる動作制御情報を生成し、生成した動作制御情報をロボット装置200に送信する。ロボット装置200は、受信した動作制御情報に基づいて、S4の位置に移動し、カメラ206によって撮像された画像等を情報提供サーバ100に送信する。情報提供サーバ100は、ロボット装置200から得られた画像を、操作端末300に送信し、視覚装置320に表示させる。
When the seat is identified, the
図11は、ロボット装置200により撮像された画像IM20の一例を示す図である。画像IM20は、座席S4から右側を見た仮想空間上の図である。図11の例では、利用者U3と、利用者U4が操作する他のロボット装置200(U4)が表示されている。これにより、周辺に存在する作業者または他のロボット装置を把握することができる。
Figure 11 is a diagram showing an example of an image IM20 captured by the
また、画像IM20を直接みた限りでは、他のロボット装置200(U4)が誰によって操作しているのかを把握することができない。更に、他のロボット装置200を用いたリモートワークが今後進んでいくと、周辺には、複数のロボット装置200しか存在しない場合もあり、孤独感を生じる場合がある。そこで、情報提供サーバ100は、他のロボット装置200(U4)を操作している利用者U4を表す画像を、利用者情報171に格納されている画像情報から取得し、取得した画像を他のロボット装置200(U4)に重畳させた画像を生成する。
In addition, by looking directly at the image IM20, it is not possible to know who is operating the other robotic device 200 (U4). Furthermore, as remote work using other
図12は、周辺に存在する他のロボット装置200(U4)に利用者の画像情報を重畳させることについて説明するための図である。図12の例では、画像IM20に他のロボット装置200(U4)を操作する利用者U4の画像IM(U4)を重畳した画像IM30が生成されている。例えば、情報提供サーバ100は、ロボット装置200のカメラ206で撮像された画像に含まれる他のロボット装置200(U4)の向きを検出し、検出した角度に対応する角度で撮影された画像情報を利用者情報171から取得する。また、取得した画像に対して拡大や縮小等を行い、画像IM20に含まれる他のロボット装置200(U4)の大きさに対応させて他のロボット装置200(U4)が隠れるように重畳させる。また、情報提供サーバ100は、他のロボット装置200(U4)の行動(腕や足の動作)等に応じて、利用者U4の画像の腕や足の位置等を部分的に動かして、操作者の行動に関する情報を表示させる。上述したように、操作端末300に提供する画像に他のロボット装置200が含まれる場合に、他のロボット装置200を操作する利用者を表す画像を行動に合わせて動かしながら重畳表示させることで、あたかもその位置に操作者がいて動作しているように感じさせることができ、遠隔操作中であっても、孤独感なく、周囲の作業者の様子を把握しながら作業を行うことができる。また、行動に関する情報を表示されるため、忙しい状態は、暇そうな状態を画像から判別することができる。
FIG. 12 is a diagram for explaining superimposing image information of a user on other robotic devices 200 (U4) existing in the vicinity. In the example of FIG. 12, an image IM30 is generated by superimposing an image IM (U4) of a user U4 operating another robotic device 200 (U4) on an image IM20. For example, the
また、情報提供サーバ100は、画像だけでなく、図12に示すように、周辺の会話等の音声を取得し、取得した音声を操作端末300に提供する。この場合、情報提供サーバ100は、例えば、他のロボット装置200(U4)を操作する操作端末から取得した音声を、他のロボット装置200(U4)の配置場所に音像定位させて出力させる。また、作業者U3の音声は、マイク208により入力されたものが出力される。これにより、配置場所に応じた音声を操作者に聞かせることができるため、より現実的に作業空間にいるかのように感じさせることができる。また、実空間上において、他のロボット装置200(U4)や作業員が行った作業は、画像から認識することができるため、利用者は、他の作業員の作業状況を直接確認しながら、自分の作業や進捗を管理することができる。
In addition, the
また、情報提供サーバ100は、ロボット装置の視線方向(顔の向き)が変わった場合に変わった方向にある座席に配置された他のロボット装置に対しても、上述した画像や音声等の情報を提供する。これにより、左右に振り向くだけでなく、後ろを振り返った場合にも周辺に存在するロボット装置200を操作する操作者を表示させることができる。
In addition, when the line of sight (face direction) of the robot device changes, the
また、作業中に他の作業者の画像や音声が提供されると、それらの情報を煩わしいと感じる場合もあり得る。そこで、情報提供サーバ100は、操作端末300から要求があった場合に、周辺に存在する作業員やロボット装置を削除した画像を提供してもよい。図13は、周辺に存在する作業員やロボット装置200の画像が削除された画像IM40の一例を示す図である。図13の例では、領域A41、A42内に表示されていた他のロボット装置200や作業員が削除された画像IM40が表示されている。削除した領域A41、A42には、他のロボット装置200や作業員が存在しないときに撮影された背景画像が重畳されていてもよく、他のマスク画像が表示されていてもよい。また、情報提供サーバ100は、利用者の要求に応じて、他のロボット装置のみを削除してもよく、特定の利用者(作業者)のみを削除してもよい。また、画像に加えて、対応する音声を削除してもよい(ミュート機能)。これにより、作業状況等に応じて周辺状況の提供内容を切り替え、自分の好きな環境下で作業を行うことができる。
In addition, when images and sounds of other workers are provided during work, the information may be perceived as annoying. Therefore, the
なお、実施形態において、仮想区間上に予め座席が割り当てられている場合には、割り当てられた座席情報に対応付けて、操作者の配置場所を管理し、管理された仮想空間を示す画像を操作端末に出力させてもよい。図14は、仮想空間上に操作者を表す情報と行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置した例を示す図である。情報提供サーバ100は、図14に示すように仮想空間上の座席の位置を示す画像に、操作者U3、U4を表す画像IM(U3)、画像IM(U4)を、それぞれが利用する座席を示す画像の位置に対応付けられた位置に重畳させた画像IM50を生成する。また、情報提供サーバ100は、画像IM(U3)、画像IM(U4)が重畳された位置に、それぞれの操作者の音声を音像定位させた情報を操作端末300から出力させる。これにより、仮想空間上においても作業空間にいるかのように感じさせる情報を提供することができる。
In the embodiment, when seats are assigned in advance on the virtual section, the location of the operator may be managed in association with the assigned seat information, and an image showing the managed virtual space may be output to the operation terminal. FIG. 14 is a diagram showing an example of arranging information based on information representing the operator and information related to the action in the virtual space. As shown in FIG. 14, the
[処理シーケンス]
次に、実施形態における情報提供システムによって実行される処理について、シーケンス図を用いて説明する。図15は、実施形態における情報提供システム1によって実行される処理について説明するためのシーケンス図である。図15の例では、情報提供サーバ100と、ロボット装置200と、操作端末300を用いて説明するものとする。
[Processing sequence]
Next, the process executed by the information providing system in the embodiment will be described with reference to a sequence diagram. Fig. 15 is a sequence diagram for explaining the process executed by the
操作端末300は、ロボット装置200を遠隔操作するために、情報提供サーバ100にアクセスする(ステップS100)。情報提供サーバ100は、操作端末300から入力される認証情報等に基づいて情報提供システム1を利用可能であるか否かの認証処理を行う(ステップS102)。以下では、認証により利用が許可された場合について説明する。利用が許可された場合、情報提供サーバ100は、座席を選択させる画像(例えば、画像IM10)を生成し(ステップS104)。生成した画像IM10を操作端末300に表示させる(ステップS106)。また、情報提供サーバ100は、操作端末300によって選択された座席情報を取得し(ステップS108)、利用状況を管理する(ステップS110)。また、情報提供サーバ100は、選択された座席に移動するような動作制御情報を生成し、生成した動作制御情報をロボット装置200に送信する(ステップS112)。
The
ロボット装置200は、情報提供サーバ100からの動作制御情報に基づいて、選択された座席の位置に移動し(ステップS114)。ロボット装置200のセンサの検出結果や、カメラにより撮像された画像等の情報提供サーバ100に出力する(ステップS116)。
The
情報提供サーバ100は、ロボット装置200から送信された情報を取得し、取得した情報に基づいて、操作端末300に提供する情報(提供情報)を生成する(ステップS118)。そして、情報提供サーバ100は、生成した提供情報を、操作端末300に送信する(ステップS120)。
The
操作端末300は、情報提供サーバ100から送信された提供情報を受信し、受信した情報を視覚装置320および操作装置330等から出力して、情報を提供する(ステップS122)。次に、操作端末300は、ロボット装置200に関する操作内容を情報提供サーバ100に送信する(ステップS124)。
The
情報提供サーバ100は、操作端末300のそれぞれから得られる操作内容に基づいて意図推定を行い(ステップS126)、意図推定結果に基づく動作制御情報を生成し(ステップS128)、生成した動作制御情報をロボット装置200に送信する(ステップS130)。
The
ロボット装置200は、動作制御情報に基づいて動作を行い(ステップS132)、動作中または動作結果で、センサ等から得られる情報(センサ情報)やカメラ画像等を情報提供サーバ100に送信する(ステップS134)。
The
情報提供サーバ100は、受信した情報を記憶部170に記憶させ(ステップS136)、取得した情報を操作端末300に送信するための提供情報を生成し(ステップS138)、生成した提供情報を、操作端末300に送信する(ステップS140)。操作端末300は、得られた情報出力して、操作者に情報提供を行う(ステップS142)。以降、ステップS124~S142の処理が、ロボット装置200への操作が完了するまで継続して行われる。
The
<変形例>
実施形態における情報提供サーバ100、ロボット装置200、および操作端末300の処理の一部または全部は、AI(Artificial Intelligence)技術によって実現されてもよい。また、情報提供サーバ100、ロボット装置200、および操作端末300に含まれる機能部または記憶部に記憶される情報のうち、一部または全部の機能部または情報は、他の装置に含まれてもよい。
<Modification>
A part or all of the processes of the
また、上述の実施形態では、空間上に配置された場所に操作者を表す情報や行動に関する情報等を配置して出力させたが、例えば、WEB会議モード等において仮想空間上の座席に利用者が配置されている場合に、指定した人物のみが自分から見て前方に存在するように配置の変更を行ってもよい。 In addition, in the above embodiment, information representing the operator and information regarding their actions are arranged and output at locations arranged in space, but for example, when users are seated in a virtual space in a web conference mode or the like, the arrangement may be changed so that only the designated person is present in front of the user.
また、情報提供サーバ100は、操作に関する履歴情報や意図推定情報等をロボットメーカ端末400に送信してもよい。これにより、ロボットメーカ端末400や商品の開発や、プログラムのアップデート等に利用することができる。この場合、ロボット装置200のエコ運転(例えば、低電力運転や低負荷運転、低通信量運転)を行った企業、または、操作者若しくはテレワーク特性に適したロボット制御の方法を提供した企業等に対して、システム利用の割引や減額サービスを行ってもよい。これにより、利用者からの情報提供を推進することができるため、サービスの向上に役立てることができる。
The
また、上述の実施形態では、1台のロボット装置200を複数の操作者で操作する場合に、それぞれの操作意図や作業状況を表示させる例を示したが、例えば、所定距離以内に存在する複数のロボット装置200や、共同作業を行っているロボット装置間で、上述した意図推定結果や、作業状況、操作者に関する情報を提供してもよい。これにより、ロボット同士の意図推定機能を用いることで、人間同士で行うよりもより意識の共有が可能となる。また、周辺のロボット装置200の状況まで取得することができるため、グループワーク等も円滑に行うことができる。
In addition, in the above embodiment, when multiple operators operate one
以上説明した実施形態は、情報提供サーバ100において、一以上の操作端末300とネットワークNWを介して通信する通信部110と、操作端末300の操作者の行動に関する情報を取得する取得部130と、空間上における操作者の配置場所を管理する管理部140と、管理部140によって管理された操作者の空間上における配置場所に、操作者を表す情報と行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置し、配置した情報を操作端末300に出力する出力制御部156と、を備えることにより、遠隔操作時であっても、作業空間にいるかのように感じさせる情報を提供することができる。
The embodiment described above includes an
具体的には、上述の実施形態によれば、例えば、仮想空間(職場)における操作者の位置(配置場所)をコーディネートし、その位置に基づき仮想空間に操作者が作業をしている様子を表す情報を配置することで、操作者の見ている画像(視覚装置の画像)に仮想空間上の自己位置から見える様子(同じ空間内で働く人の働いている様子)を出力することができる。また、上述した実施形態によれば、ロボット装置を遠隔操作することによってテレワークを行うにあたり、より汎用的に様々な装置を使用したり、それをチームで運用することができる。また、従来は遠隔操作を行うにしても限られた専用ロボットでの限られた作業しかできなかったが、本実施形態によれば、汎用性の高いロボット装置によって誰もが簡単にテレワークを行うことが可能になる。 Specifically, according to the above-mentioned embodiment, for example, by coordinating the position (location) of the operator in the virtual space (workplace) and arranging information showing the state of the operator working in the virtual space based on that position, it is possible to output the state seen from the operator's own position in the virtual space (the state of people working in the same space) in the image seen by the operator (image of the visual device). Furthermore, according to the above-mentioned embodiment, when performing telework by remotely operating a robot device, it is possible to use various devices more generally and operate them in a team. Furthermore, while in the past, only limited tasks could be performed with limited dedicated robots even when remotely operated, according to this embodiment, anyone can easily perform telework using a highly versatile robot device.
また、実施形態によれば、ロボット情報とセンサ情報(企業の機密を含みうる情報)分けて管理することができ、機密対応可能なサーバを提供することができる。また、遠隔操作する操作者は同一サーバにアクセス可能であり、同一ロボット、あるいは別ロボットの操縦権やセンサ情報を共有することができる。例えば、同一ロボット装置を操作する場合には、複数の操作者が違う腕を操作することで、同一ロボットの同一腕を先輩と後輩が同時に操作し、触覚などのセンサ情報も共有した上で力の足し算、引き算ができる。また、別ロボット操縦の場合に、意図推定機能を共有し、他者の意図を開示することにより以心伝心が可能となる。また、実施形態によれば、1人の操縦者が2台のロボットを操縦することが可能である。この場合、例えば大きい机を2台のロボットで運ぼうとした場合、予め一台のロボットを机の端に連れていき、別ロボットと同期処理をする。また、別ロボットをもう一端に連れていき、持ち上げる動作をしようとすると同期処理により一緒に持ち上げる。更に、実施形態では、人間同士で掛け声をかけて動作させるよりも正確な作業が可能となる。また、実施形態では、一人の操縦者が同じ作業をたくさんのロボットにさせる場合に、サポーティッドテレオペレーション機能によって、ロボット個体差と作業対象物の個体差を吸収することができる。 According to the embodiment, robot information and sensor information (information that may include corporate secrets) can be managed separately, and a server capable of handling confidential information can be provided. Remote operators can access the same server and can share the control rights and sensor information of the same robot or different robots. For example, when operating the same robot device, multiple operators can operate different arms, allowing a senior and a junior to simultaneously operate the same arm of the same robot and add or subtract force while sharing sensor information such as touch. In addition, when operating different robots, telepathy is possible by sharing the intention estimation function and disclosing the intention of others. According to the embodiment, one operator can operate two robots. In this case, for example, if two robots are to carry a large desk, one robot is brought to the edge of the desk in advance and synchronized with the other robot. Also, when the other robot is brought to the other end and an operation to lift it is performed, the robots are lifted together by synchronization processing. Furthermore, in the embodiment, more accurate work is possible than when humans call out to each other to perform the operation. In addition, in the embodiment, when one operator has multiple robots perform the same work, the supported teleoperation function can absorb individual differences between robots and individual differences between work objects.
上記説明した実施形態は、以下のように表現することができる。
移動体と、前記移動体の利用者の携帯端末との通信を行うサーバのコンピュータが、
プログラムを記憶した記憶装置と、
ハードウェアプロセッサと、を備え、
前記ハードウェアプロセッサが前記記憶装置に記憶されたプログラムを実行することにより、
一以上の操作端末とネットワークを介して通信し、
前記操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報を取得し、
空間上における前記操作者の配置場所を管理し、
管理した前記操作者の空間上における配置場所に、前記操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置し、配置した情報を前記操作端末に出力する、
ように構成されている、情報提供サーバ。
The above-described embodiment can be expressed as follows.
A server computer that communicates with a mobile object and a mobile terminal of a user of the mobile object,
A storage device storing a program;
a hardware processor;
The hardware processor executes the program stored in the storage device,
Communicating with one or more operation terminals via a network;
Acquire information regarding the behavior of an operator of the operation terminal;
Managing the location of the operator in space;
arranging information based on information representing the operator and information related to the action at a location in the space of the managed operator, and outputting the arranged information to the operation terminal;
An information providing server configured to:
以上、本発明を実施するための形態について実施形態を用いて説明したが、本発明はこうした実施形態に何等限定されるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲内において種々の変形及び置換を加えることができる。 The above describes the form for carrying out the present invention using an embodiment, but the present invention is not limited to such an embodiment, and various modifications and substitutions can be made without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
1…情報提供システム、100…情報提供サーバ、110、202、310…通信部、120…通信制御部、130…取得部、140…管理部、150…制御部、170…記憶部、200…ロボット装置、204…センサ、206…カメラ、208…マイク、210…駆動部、214…モニタ、216…スピーカ、240…制御装置、260…記憶部、300…操作端末、320…視覚装置、330…操作装置、340…環境センサ、360…制御装置、380…記憶部 1... Information providing system, 100... Information providing server, 110, 202, 310... Communication unit, 120... Communication control unit, 130... Acquisition unit, 140... Management unit, 150... Control unit, 170... Storage unit, 200... Robot device, 204... Sensor, 206... Camera, 208... Microphone, 210... Driving unit, 214... Monitor, 216... Speaker, 240... Control device, 260... Storage unit, 300... Operation terminal, 320... Visual device, 330... Operation device, 340... Environmental sensor, 360... Control device, 380... Storage unit
Claims (7)
前記複数の操作端末のうち、第1の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報と、前記第1の操作端末以外の他の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報とを取得する取得部と、
一以上のロボット装置が存在する空間を撮像部で撮影した画像の仮想空間上における前記他の操作端末の操作者の配置場所を管理する管理部と、
前記管理部によって管理された前記他の操作端末の操作者の仮想空間上における配置場所に、前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置し、配置した情報を前記第1の操作端末に出力する出力制御部と、を備え、
前記他の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報は、前記一以上のロボット装置を遠隔操作するための操作内容を含み、
前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報は、前記撮像部により撮像された画像に存在する前記一以上のロボット装置のうち前記他の操作端末の操作者が操作するロボット装置が存在する位置に前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す画像を重畳させた情報と、前記他の操作端末の操作者の音声を音像定位させた情報と、を含み、
前記出力制御部は、前記第1の操作端末からの要求により、前記撮像部により撮像された画像から前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す画像と前記ロボット装置を表す画像とのうち少なくとも一方を削除した画像を生成して前記第1の操作端末に提供する、
情報提供サーバ。 A communication unit that communicates with a plurality of operation terminals via a network;
an acquisition unit that acquires information regarding an action of an operator of a first operation terminal among the plurality of operation terminals and information regarding an action of an operator of an operation terminal other than the first operation terminal;
a management unit that manages the location of the operator of the other operation terminal in a virtual space of an image captured by an imaging unit of a space in which one or more robot devices exist;
an output control unit that arranges information based on information representing the operator of the other operating terminal and information regarding the behavior at an arrangement location in a virtual space of the operator of the other operating terminal managed by the management unit, and outputs the arranged information to the first operating terminal;
the information about the actions of the operators of the other operation terminals includes operation content for remotely operating the one or more robot devices;
the information based on the information representing the operator of the other operating terminal and the information relating to the behavior includes information in which an image representing the operator of the other operating terminal is superimposed at a position where a robot device operated by the operator of the other operating terminal is present among the one or more robot devices present in the image captured by the imaging unit, and information in which a sound image is localized for a voice of the operator of the other operating terminal ,
the output control unit, in response to a request from the first operation terminal, generates an image by deleting at least one of an image representing an operator of the other operation terminal and an image representing the robot device from an image captured by the imaging unit, and provides the image to the first operation terminal.
Information server.
請求項1に記載の情報提供サーバ。 the management unit generates an image that allows an operator of the first operation terminal to select a location, transmits the generated image to the first operation terminal, and manages the location of the operator of the first operation terminal based on the location selected using the image.
2. The information providing server according to claim 1.
請求項1または2に記載の情報提供サーバ。 the plurality of operation terminals include a terminal for remotely operating one or more robot devices,
3. The information providing server according to claim 1 or 2.
請求項1から3のうち何れか1項に記載の情報提供サーバ。 the output control unit acquires a voice of an operator of the other operation terminal , and outputs the acquired voice by localizing a sound image at a location of the operator of the other operation terminal .
4. The information providing server according to claim 1.
前記複数の操作端末と、
前記複数の操作端末によって遠隔操作される一以上のロボット装置と、
を備える情報提供システム。 An information providing server according to any one of claims 1 to 4 ;
The plurality of operation terminals;
one or more robot devices remotely operated by the plurality of operation terminals;
An information provision system comprising:
複数の操作端末とネットワークを介して通信し、
前記複数の操作端末のうち、第1の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報と、前記第1の操作端末以外の他の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報とを取得し、
一以上のロボット装置が存在する空間を撮像部で撮影した画像の仮想空間上における前記他の操作端末の操作者の配置場所を管理し、
管理した前記他の操作端末の操作者の仮想空間上における配置場所に、前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置し、配置した情報を前記第1の操作端末に出力し、
前記他の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報は、前記一以上のロボット装置を遠隔操作するための操作内容を含み、
前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報は、前記撮像部により撮像された画像に存在する前記一以上のロボット装置のうち前記他の操作端末の操作者が操作するロボット装置が存在する位置に前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す画像を重畳させた情報と、前記他の操作端末の操作者の音声を音像定位させた情報と、を含み、
前記第1の操作端末からの要求により、前記撮像部により撮像された画像から前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す画像と前記ロボット装置を表す画像とのうち少なくとも一方を削除した画像を生成して前記第1の操作端末に提供する、
情報提供方法。 The computer
Communicate with multiple operation terminals via a network,
acquiring information regarding an action of an operator of a first operation terminal among the plurality of operation terminals and information regarding an action of an operator of another operation terminal other than the first operation terminal;
managing locations of operators of the other operation terminals in a virtual space of an image captured by an imaging unit of a space in which one or more robot devices exist;
arranging information representing the operator of the other operation terminal and information related to the behavior at a location in a virtual space of the operator of the other operation terminal that is managed, and outputting the arranged information to the first operation terminal;
the information about the actions of the operators of the other operation terminals includes operation content for remotely operating the one or more robot devices;
the information based on the information representing the operator of the other operating terminal and the information relating to the behavior includes information in which an image representing the operator of the other operating terminal is superimposed at a position where a robot device operated by the operator of the other operating terminal is present among the one or more robot devices present in the image captured by the imaging unit, and information in which a sound image is localized for a voice of the operator of the other operating terminal ,
generating an image obtained by deleting at least one of an image representing the operator of the other operation terminal and an image representing the robot device from an image captured by the imaging unit in response to a request from the first operation terminal, and providing the image to the first operation terminal;
How to provide information.
複数の操作端末とネットワークを介して通信させ、
前記複数の操作端末のうち、第1の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報と、前記第1の操作端末以外の他の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報とを取得させ、
一以上のロボット装置が存在する空間を撮像部で撮影した画像の仮想空間上における前記他の操作端末の操作者の配置場所を管理させ、
管理された前記他の操作端末の操作者の仮想空間上における配置場所に、前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報を配置し、配置した情報を前記第1の操作端末に出力させ、
前記他の操作端末の操作者の行動に関する情報は、前記一以上のロボット装置を遠隔操作するための操作内容を含み、
前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す情報と前記行動に関する情報とに基づく情報は、前記撮像部により撮像された画像に存在する前記一以上のロボット装置のうち前記他の操作端末の操作者が操作するロボット装置が存在する位置に前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す画像を重畳させた情報と、前記他の操作端末の操作者の音声を音像定位させた情報と、を含み、
前記第1の操作端末からの要求により、前記撮像部により撮像された画像から前記他の操作端末の操作者を表す画像と前記ロボット装置を表す画像とのうち少なくとも一方を削除した画像を生成して前記第1の操作端末に提供させる、
プログラム。 On the computer,
Communicating with multiple operation terminals via a network,
acquiring information on an action of an operator of a first operation terminal among the plurality of operation terminals and information on an action of an operator of another operation terminal other than the first operation terminal;
managing locations of operators of the other operation terminals in a virtual space of an image captured by an imaging unit of a space in which one or more robot devices exist;
arranging information representing the operator of the other operation terminal and information related to the behavior at a location in a virtual space of the operator of the other operation terminal being managed, and outputting the arranged information to the first operation terminal;
the information about the actions of the operators of the other operation terminals includes operation content for remotely operating the one or more robot devices;
the information based on the information representing the operator of the other operating terminal and the information relating to the behavior includes information in which an image representing the operator of the other operating terminal is superimposed at a position where a robot device operated by the operator of the other operating terminal is present among the one or more robot devices present in the image captured by the imaging unit, and information in which a voice of the operator of the other operating terminal is localized as a sound image,
generating an image obtained by deleting at least one of an image representing the operator of the other operation terminal and an image representing the robot device from an image captured by the imaging unit in response to a request from the first operation terminal, and providing the image to the first operation terminal;
program.
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021069235A JP7638136B2 (en) | 2021-04-15 | 2021-04-15 | INFORMATION PROVIDING SERVER, INFORMATION PROVIDING SYSTEM, INFORMATION PROVIDING METHOD, AND PROGRAM |
| CN202210195963.6A CN115225682B (en) | 2021-04-15 | 2022-03-01 | Management server, remote operation system, remote operation method, and storage medium |
| CN202311388284.1A CN117336337A (en) | 2021-04-15 | 2022-03-01 | Remote operation system and method and storage medium |
| US17/720,271 US20220331967A1 (en) | 2021-04-15 | 2022-04-13 | Management server, remote operation system, remote operation method, and storage medium |
| US18/655,333 US20240286290A1 (en) | 2021-04-15 | 2024-05-06 | Remote operation control system, remote operation control method, and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021069235A JP7638136B2 (en) | 2021-04-15 | 2021-04-15 | INFORMATION PROVIDING SERVER, INFORMATION PROVIDING SYSTEM, INFORMATION PROVIDING METHOD, AND PROGRAM |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2022164029A JP2022164029A (en) | 2022-10-27 |
| JP7638136B2 true JP7638136B2 (en) | 2025-03-03 |
Family
ID=83742771
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021069235A Active JP7638136B2 (en) | 2021-04-15 | 2021-04-15 | INFORMATION PROVIDING SERVER, INFORMATION PROVIDING SYSTEM, INFORMATION PROVIDING METHOD, AND PROGRAM |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7638136B2 (en) |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000244886A (en) | 1999-01-20 | 2000-09-08 | Canon Inc | Computer conference system, computer processing device, method for performing computer conference, processing method in computer processing device, video conference system, method for performing video conference, headphones |
| JP2019168971A (en) | 2018-03-23 | 2019-10-03 | 国立大学法人電気通信大学 | Same room feeling communication system |
| US20200078950A1 (en) | 2017-05-17 | 2020-03-12 | Telexistence Inc. | Sensation imparting device, robot control system, and robot control method |
-
2021
- 2021-04-15 JP JP2021069235A patent/JP7638136B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000244886A (en) | 1999-01-20 | 2000-09-08 | Canon Inc | Computer conference system, computer processing device, method for performing computer conference, processing method in computer processing device, video conference system, method for performing video conference, headphones |
| US20200078950A1 (en) | 2017-05-17 | 2020-03-12 | Telexistence Inc. | Sensation imparting device, robot control system, and robot control method |
| JP2019168971A (en) | 2018-03-23 | 2019-10-03 | 国立大学法人電気通信大学 | Same room feeling communication system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2022164029A (en) | 2022-10-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Delmerico et al. | Spatial computing and intuitive interaction: Bringing mixed reality and robotics together | |
| JP7760023B2 (en) | Server, remote control system, remote control method, and program | |
| EP3425481B1 (en) | Control device | |
| US20210346557A1 (en) | Robotic social interaction | |
| US12248635B2 (en) | Spatially aware computing hub and environment | |
| US12416967B2 (en) | Spatially aware computing hub and environment | |
| US20240286290A1 (en) | Remote operation control system, remote operation control method, and storage medium | |
| JP7375770B2 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method, and program | |
| TW202105129A (en) | Artificial reality systems with personal assistant element for gating user interface elements | |
| CN109153122A (en) | Vision-Based Robot Control System | |
| CN112569607A (en) | Display method, device, equipment and medium for pre-purchased prop | |
| Hauser et al. | Analysis and perspectives on the ana avatar xprize competition | |
| JP5659787B2 (en) | Operation environment model construction system and operation environment model construction method | |
| JP2010257081A (en) | Image processing method and image processing apparatus | |
| JP6950192B2 (en) | Information processing equipment, information processing systems and programs | |
| Marques et al. | Commodity telepresence with the AvaTRINA nursebot in the ANA Avatar XPRIZE semifinals | |
| KR102010023B1 (en) | Method and system for providing mixed reality service | |
| JP7638136B2 (en) | INFORMATION PROVIDING SERVER, INFORMATION PROVIDING SYSTEM, INFORMATION PROVIDING METHOD, AND PROGRAM | |
| JP2019207572A (en) | Information processing device and program | |
| Renner et al. | Facilitating HRI by mixed reality techniques | |
| JP7588545B2 (en) | Remote operation control system, remote operation control method, and program | |
| CN108304062A (en) | Virtual environment exchange method, equipment and system | |
| Zhao et al. | Adaptable Mixed-Reality Sensorimotor Interface for Human-Swarm Teaming: Person with Limb Loss Case Study and Field Experiments | |
| KR20220108417A (en) | Method of providing practical skill training using hmd hand tracking | |
| JP2016218830A (en) | Tactile sensation presentation system, tactile sensation presentation method, and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20231128 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20240612 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20240806 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20240918 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20241022 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20241219 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20250121 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20250218 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7638136 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |