JP7623935B2 - Car t細胞の若返り - Google Patents
Car t細胞の若返り Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7623935B2 JP7623935B2 JP2021506492A JP2021506492A JP7623935B2 JP 7623935 B2 JP7623935 B2 JP 7623935B2 JP 2021506492 A JP2021506492 A JP 2021506492A JP 2021506492 A JP2021506492 A JP 2021506492A JP 7623935 B2 JP7623935 B2 JP 7623935B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- car
- cells
- receptor
- module
- fitc
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
- A61K47/55—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound the modifying agent being also a pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent, i.e. the entire conjugate being a codrug, i.e. a dimer, oligomer or polymer of pharmacologically or therapeutically active compounds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/335—Heterocyclic compounds having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin
- A61K31/35—Heterocyclic compounds having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin having six-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/352—Heterocyclic compounds having oxygen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. fungichromin having six-membered rings with one oxygen as the only ring hetero atom condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. methantheline
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/38—Heterocyclic compounds having sulfur as a ring hetero atom
- A61K31/381—Heterocyclic compounds having sulfur as a ring hetero atom having five-membered rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/4353—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/437—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems the heterocyclic ring system containing a five-membered ring having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. indolizine, beta-carboline
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/4427—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/444—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof containing further heterocyclic ring systems containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring heteroatom, e.g. amrinone
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/445—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine
- A61K31/4523—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine containing further heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/4535—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine containing further heterocyclic ring systems containing a heterocyclic ring having sulfur as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pizotifen
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
- A61K31/445—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine
- A61K31/4523—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine containing further heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/4545—Non condensed piperidines, e.g. piperocaine containing further heterocyclic ring systems containing a six-membered ring with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. pipamperone, anabasine
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/47—Quinolines; Isoquinolines
- A61K31/4738—Quinolines; Isoquinolines ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems
- A61K31/4745—Quinolines; Isoquinolines ortho- or peri-condensed with heterocyclic ring systems condensed with ring systems having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. phenantrolines
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K31/7042—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings
- A61K31/7052—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides
- A61K31/706—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides containing six-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom
- A61K31/7064—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides containing six-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom containing condensed or non-condensed pyrimidines
- A61K31/7076—Compounds having saccharide radicals and heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. nucleosides, nucleotides containing six-membered rings with nitrogen as a ring hetero atom containing condensed or non-condensed pyrimidines containing purines, e.g. adenosine, adenylic acid
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/10—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the cell type used
- A61K40/11—T-cells, e.g. tumour infiltrating lymphocytes [TIL] or regulatory T [Treg] cells; Lymphokine-activated killer [LAK] cells
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/30—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by the recombinant expression of specific molecules in the cells of the immune system
- A61K40/31—Chimeric antigen receptors [CAR]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K40/00—Cellular immunotherapy
- A61K40/40—Cellular immunotherapy characterised by antigens that are targeted or presented by cells of the immune system
- A61K40/41—Vertebrate antigens
- A61K40/42—Cancer antigens
- A61K40/4202—Receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- A61K40/421—Immunoglobulin superfamily
- A61K40/4211—CD19 or B4
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
- A61K47/55—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound the modifying agent being also a pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent, i.e. the entire conjugate being a codrug, i.e. a dimer, oligomer or polymer of pharmacologically or therapeutically active compounds
- A61K47/551—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound the modifying agent being also a pharmacologically or therapeutically active agent, i.e. the entire conjugate being a codrug, i.e. a dimer, oligomer or polymer of pharmacologically or therapeutically active compounds one of the codrug's components being a vitamin, e.g. niacinamide, vitamin B3, cobalamin, vitamin B12, folate, vitamin A or retinoic acid
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/62—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being a protein, peptide or polyamino acid
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/68—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment
- A61K47/6835—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an antibody, an immunoglobulin or a fragment thereof, e.g. an Fc-fragment the modifying agent being an antibody or an immunoglobulin bearing at least one antigen-binding site
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K49/00—Preparations for testing in vivo
- A61K49/001—Preparation for luminescence or biological staining
- A61K49/0013—Luminescence
- A61K49/0017—Fluorescence in vivo
- A61K49/0019—Fluorescence in vivo characterised by the fluorescent group, e.g. oligomeric, polymeric or dendritic molecules
- A61K49/0021—Fluorescence in vivo characterised by the fluorescent group, e.g. oligomeric, polymeric or dendritic molecules the fluorescent group being a small organic molecule
- A61K49/0041—Xanthene dyes, used in vivo, e.g. administered to a mice, e.g. rhodamines, rose Bengal
- A61K49/0043—Fluorescein, used in vivo
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K49/00—Preparations for testing in vivo
- A61K49/001—Preparation for luminescence or biological staining
- A61K49/0013—Luminescence
- A61K49/0017—Fluorescence in vivo
- A61K49/005—Fluorescence in vivo characterised by the carrier molecule carrying the fluorescent agent
- A61K49/0052—Small organic molecules
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/435—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from animals; from humans
- C07K14/705—Receptors; Cell surface antigens; Cell surface determinants
- C07K14/70503—Immunoglobulin superfamily
- C07K14/7051—T-cell receptor (TcR)-CD3 complex
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K16/00—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies
- C07K16/18—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans
- C07K16/28—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants
- C07K16/2803—Immunoglobulins [IGs], e.g. monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against material from animals or humans against receptors, cell surface antigens or cell surface determinants against the immunoglobulin superfamily
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2239/00—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K40/00
- A61K2239/46—Indexing codes associated with cellular immunotherapy of group A61K40/00 characterised by the cancer treated
- A61K2239/48—Blood cells, e.g. leukemia or lymphoma
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2319/00—Fusion polypeptide
- C07K2319/01—Fusion polypeptide containing a localisation/targetting motif
- C07K2319/03—Fusion polypeptide containing a localisation/targetting motif containing a transmembrane segment
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
Description
本開示は、癌抗原によって消耗したキメラ抗原受容体T(CAR T)細胞を若返らせるためのシステムを提供する。特に、前記システムは古典的CAR構築物の中に融合受容体を含み、融合受容体は、高親和性リガンド-ペイロード薬物結合体を認識して、消耗したCAR Tの阻害シグナル伝達をブロックするかまたは抗原非依存性経路を介してCAR Tを再活性化するように設計された薬物ペイロードを送達するリガンド結合モジュールを提供する。
キメラ抗原受容体(CAR)T細胞療法の分野は過去20年間にわたってかなりの進歩を遂げてきた。CAR構築物は、4つの部分:(1)腫瘍特異的抗原に対する細胞外結合部分、(2)ヒンジドメイン、(3)膜貫通ドメイン、ならびに(4)様々な活性化ドメイン、例えば、CD28、4-1BB、およびCD3ζ鎖の組み合わせからなる。CD19陽性B細胞白血病に対するCAR T療法において最も印象的な成功が見られ、いくつかの臨床試験において80%を超える完全寛解率が成し遂げられた。
(a) 消耗したCAR T細胞に、結合体を含む第1の成分を提供する工程であって、前記結合体が、遊離可能なリンカーまたは遊離不可能なリンカーを介して薬物ペイロードと共有結合により連結された標的リガンドを含む、工程;
(b) 前記消耗したCAR T細胞に、消耗したCAR構築物と連結された融合受容体を含む第2の成分を提供する工程であって、前記融合受容体が、標的リガンド結合モジュールと膜アンカーモジュールを含む、工程;
(c) 第2の成分の標的リガンド結合モジュールを第1の成分中の標的リガンドと結合させて複合体を形成する工程;
(d) 膜アンカーモジュールに、消耗したCAR T細胞の中への複合体の内部移行を媒介させる工程;
(e) ペイロード薬物に、消耗したCAR Tの阻害シグナル伝達をブロックさせるか、または抗原非依存性経路を介して前記CAR Tを再活性化させる工程
を含む。
少なくとも2成分を含む、消耗した古典的CAR T細胞を若返らせるためのシステムであって、第1の成分が、ペイロード薬物と共有結合により連結された標的リガンドを含む結合体であり、第2の成分が、膜アンカーモジュールと連結された標的リガンド結合モジュールであり、第2の成分の標的リガンド結合モジュールが、第1の成分中の標的リガンドを高親和性で認識して複合体を形成し、ペイロード薬物が、消耗した古典的CAR Tの阻害シグナル伝達をブロックするか、または抗原非依存性経路を介して該CAR Tを再活性化し、膜アンカーモジュールが、消耗したCAR T細胞の中への2成分複合体の内部移行を媒介する、前記システム。
[本発明1002]
第1の成分の標的リガンドが、葉酸、FITC、またはFK506である、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1003]
第2の成分の標的リガンド結合モジュールが、抗FITC抗体断片、FKBP、または葉酸受容体である、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1004]
膜アンカーモジュールが葉酸受容体である、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1005]
第1の成分が、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物との間に遊離可能なリンカーを含む、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1006]
第1の成分が、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物との間に遊離不可能なリンカーを含む、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1007]
標的リガンドとリガンド結合モジュールとの間の結合親和性がnM以下の範囲である、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1008]
薬物ペイロードが、Toll様受容体7(TLR7)アゴニストまたはインターフェロン遺伝子刺激因子(Simulator of interferon genes)(STING)アゴニストである、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1009]
薬物ペイロードが、以下のタンパク質: SHP1/2、TC-PTPまたはDGKα、TGFβに対するインヒビターである、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1010]
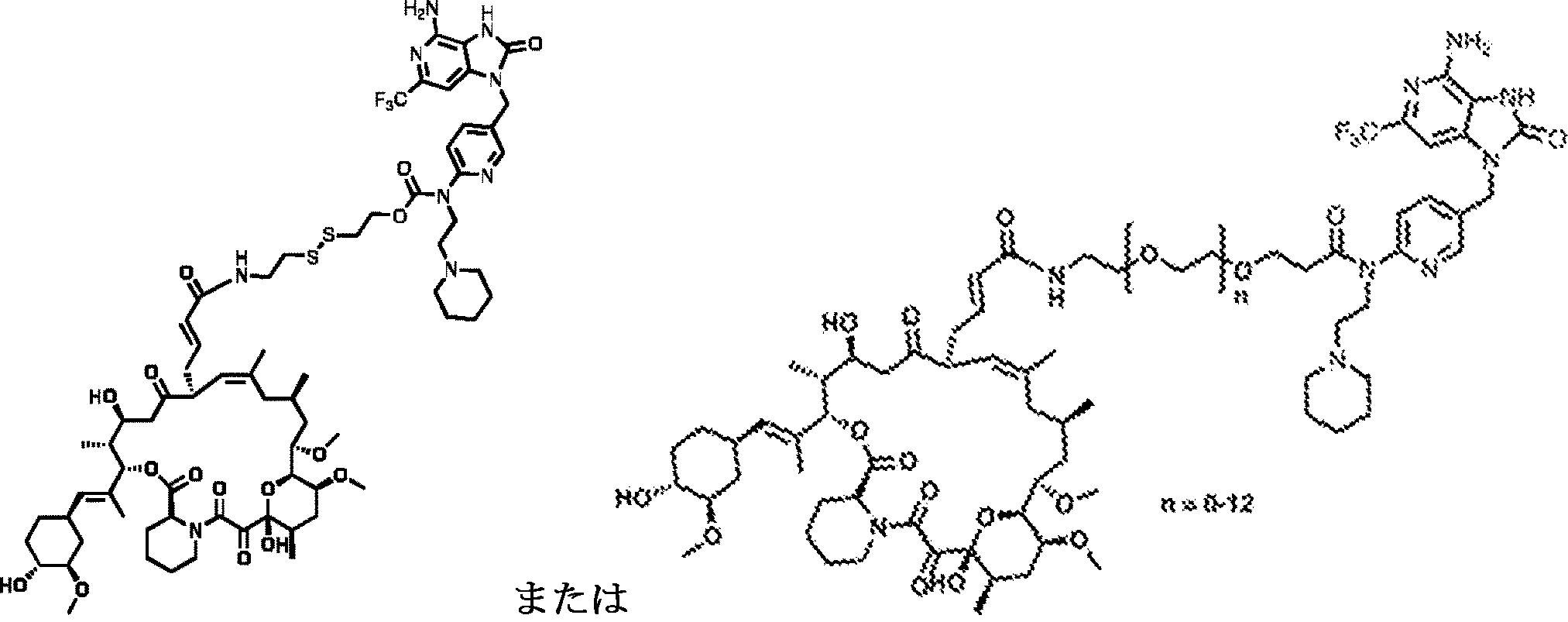
TLR7アゴニストが、
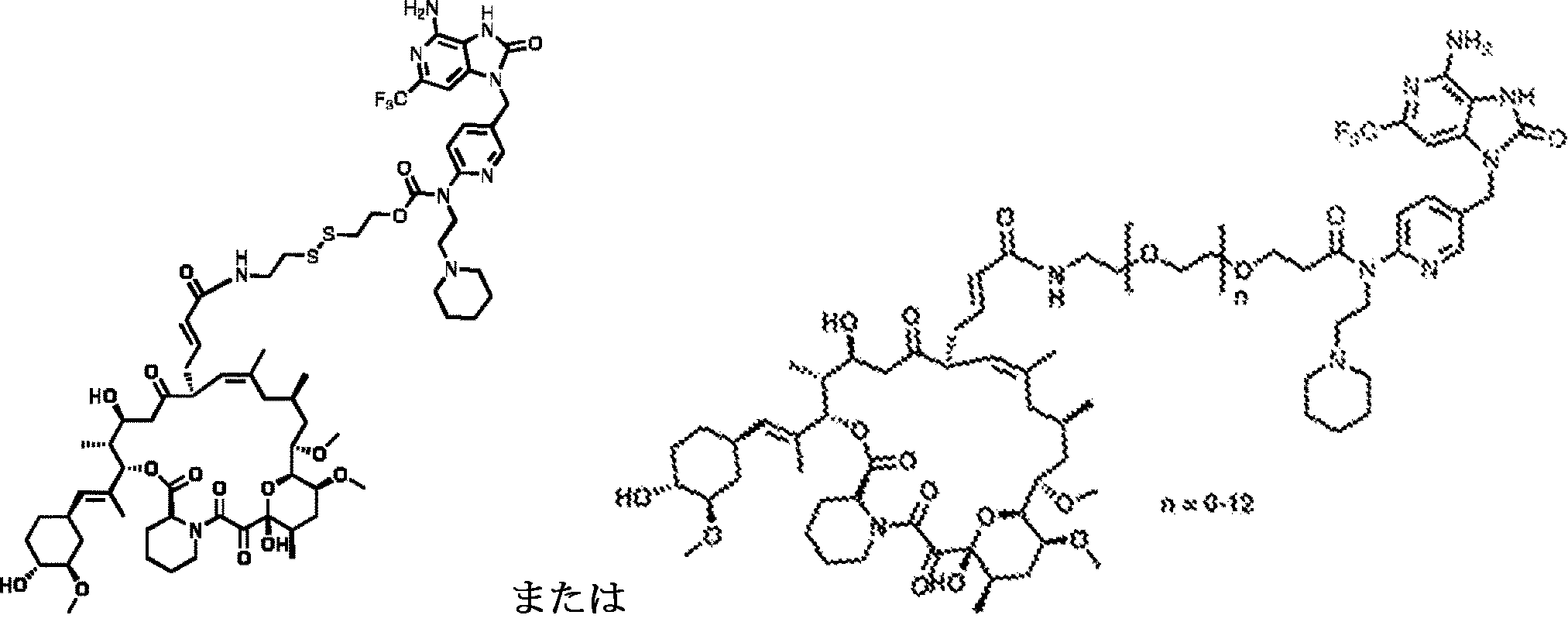
の構造を有する、本発明1008のシステム。
[本発明1011]
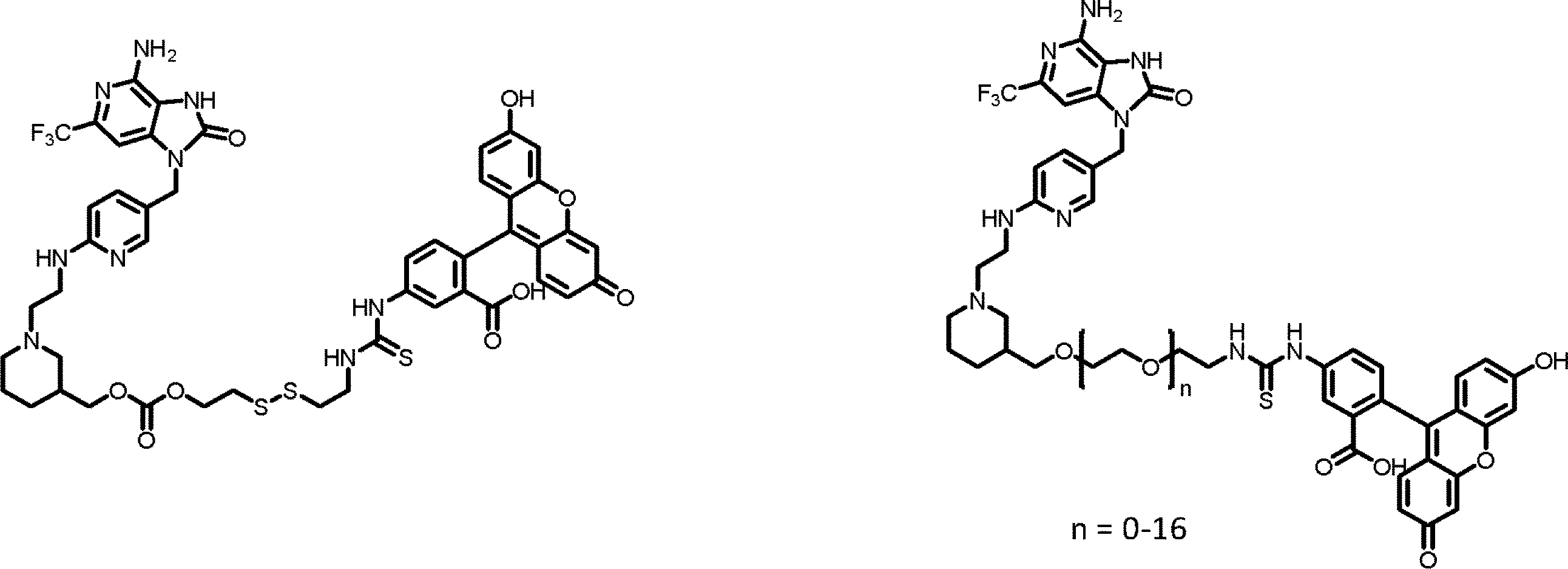
第1の成分が、
の構造を有するフルオレセイン-TLR7アゴニストである、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1012]
第1の成分が、
の構造を有するFK506-TLR7アゴニストである、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1013]
第1の成分が、以下:
のうちの1つである、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1014]
第1の成分が、以下のTC-PTPホスファターゼインヒビター:
からなる群より選択されるペイロード薬物を含む、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1015]
ホスファターゼインヒビターが、以下の構造:
を形成するようにフルオレセインまたはFK506(タクロリムス)と連結されている、本発明1014のシステム。
[本発明1016]
第1の成分中のペイロード薬物が、以下の構造:
のうちの1つのSTINGアゴニストを含む、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1017]
第1の成分が、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物との間に、以下の構造:
からなる群より選択されるスペーサーを含む、本発明1001のシステム。
[本発明1018]
消耗したCAR T細胞を若返らせるための方法であって、
(a) 消耗したCAR T細胞に、結合体を含む第1の成分を提供する工程であって、該結合体が、遊離可能なリンカーまたは遊離不可能なリンカーを介して薬物ペイロードと共有結合により連結された標的リガンドを含む、工程;
(b) 該消耗したCAR T細胞に、消耗したCAR構築物と連結された融合受容体を含む第2の成分を提供する工程であって、該融合受容体が、標的リガンド結合モジュールと膜結合型受容体モジュールを含む、工程;
(c) 第2の成分の標的リガンド結合モジュールを第1の成分中の標的リガンドと結合させて複合体を形成する工程;
(d) 膜結合型CARモジュールに、消耗したCAR T細胞の中への複合体の内部移行を媒介させる工程;
(e) ペイロード薬物に、消耗したCAR Tの阻害シグナル伝達をブロックさせるか、または抗原非依存性経路を介して該CAR Tを再活性化させる工程
を含む、前記方法。
[本発明1019]
ペイロード薬物が、その機能を、消耗したCAR Tのエンドソームの中で果たし、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物が、遊離不可能なリンカーによって連結されている、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1020]
ペイロード薬物が、その機能を、消耗したCAR Tのサイトゾルの中で遊離薬物として果たし、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物が、遊離可能なリンカーによって連結されている、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1021]
第1の成分の標的リガンドが、葉酸、FITC、またはFK506である、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1022]
第2の成分の標的リガンド結合モジュールが、抗FITC、葉酸受容体、またはFKBPである、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1023]
リガンド結合モジュールが葉酸受容体α(FRa)である、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1024]
薬物ペイロードが、Toll様受容体7(TLR7)アゴニストまたはインターフェロン遺伝子刺激因子(STING)アゴニストである、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1025]
薬物ペイロードが、以下のタンパク質: SHP1/2、TC-PTPまたはDGKα、TGFβに対するインヒビターである、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1026]
TLR7アゴニストが、
の構造を有する、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1027]
第1の成分が、
の構造を有するフルオレセイン-TLR7アゴニストである、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1028]
第1の成分が、
の構造を有するFK506-TLR7アゴニストである、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1029]
第1の成分が、以下:
のうちの1つである、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1030]
第1の成分が、以下のTC-PTPホスファターゼインヒビター:
からなる群より選択されるペイロード薬物を含む、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1031]
ホスファターゼインヒビターが、以下の構造:
を形成するようにフルオレセインまたはFK506(タクロリムス)と連結されている、本発明1030の方法。
[本発明1032]
第1の成分中のペイロード薬物が、以下の構造:
のうちの1つのSTINGアゴニストを含む、本発明1018の方法。
[本発明1033]
第1の成分が、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物との間に、以下の構造:
からなる群より選択されるスペーサーを含む、本発明1018の方法。
本発明のこれらの、および他の特徴、局面、および利点は、以下の図面、関連する説明、および特許請求の範囲を参照すればさらに深く理解される。
本開示の概念が本明細書中での図面および説明において詳細に例示および説明されるが、図面およびその説明の中での結果は例示であり、特徴を制限するものではないと考えなくてはならない。例示的な態様だけが示され、かつ説明され、本開示の精神の範囲内にある全ての変更および修正が保護されることが望ましいと理解される。
抗CD19 CAR T細胞の消耗および薬物処理:
6ウェルプレートの中で抗CD19 CAR T細胞をRajiと1:1比で共培養したが、新鮮なRaji細胞を12時間ごとに同じウェルに添加した。死滅作用および共抑制マーカーをフローサイトメトリーカウンティングによって定量した。薬物処理のために、Raji細胞で4回刺激した後、消耗した抗CD19 CAR Tを異なる濃度の薬物と12時間さらにインキュベートし、次いで、同様に定量した。
融合受容体陽性細胞を、様々な濃度のある特定のリガンド-色素分子と4℃で30分間インキュベートした。インキュベーション後に、細胞をPBSで2回洗浄し、次いで、フローサイトメトリーに提出した。結合曲線およびKd計算にはMFIまたはシフト(shift)パーセントを使用した。
細胞株およびヒトT細胞
MDAMB-231細胞とMDA-MB-231 CD19+細胞を培養するために、10%熱失活胎仔ウシ血清および1%ペニシリン-ストレプトマイシンを含有するDMEM(Gibco)を使用した。健常ボランティアから入手したヒト全血から末梢血単核球(PBMC)をフィコール密度勾配遠心分離法(GE Healthcare Lifesciences, #17-5442-02)によって単離した。PBMCから純粋なCD3+T細胞を、EasySep(商標)Human T Cell Isolation Kit(STEM CELL technologies, #17951)を用いて濃縮した。
12ウェルプレートの中で抗CD19 CAR T細胞をCD19+ Raji細胞と1:1比で、1ウェルにつき2x106個のCAR Tおよび2x106個のRajiの密度でコインキュベートした。新たなRaji細胞を12時間ごとに3回添加し、次いで、CAR T細胞の消耗を確認するためにRaji細胞集団、溶解効果、および共抑制性受容体を試験した。フローサイトメトリーとルシフェラーゼベースのアッセイを用いて溶解効果を定量した。次いで、潜在的なペイロードの若返り効力を試験するために、この細胞混合物を96ウェルプレートに1ウェルにつき約2x105個の細胞で移し、異なる濃度の薬物を添加した。12時間後に、Raji細胞集団、溶解効果、および共抑制性受容体を再試験し、PBS処理群と比較した。
本実施例では、本発明者らは、消耗したCAR T細胞のモデルを示した。簡単に述べると、図1aは、方法のセクションで記載したように、Bリンパ腫細胞の一種であるRaji細胞を、抗CD19 CAR T細胞の一種であるFMC63 CAR T細胞と共培養し、連続3日間にわたって12時間ごとに新鮮なRaji細胞を共培養物に添加したことを示す。図1bは、インビトロで新鮮なRaji細胞で3回刺激した後に、これらのCAR T細胞が死滅作用の減少によって示されるように消耗状態になったことを示す。共培養されたK562細胞は負の対照として役立った。
本実施例では、本発明者らは、標的となる細胞タイプへの送達ペイロード薬物の秘密経路の図を示す。FKBPまたは抗FITCは融合受容体としてFRaと連結される。融合受容体は、特定の薬物ペイロードと連結された標的リガンドFK506またはFITCと結合することができる。FRaの性質により、融合受容体は、FK506またはFITCと連結されたペイロードをCAR T細胞の中に絶え間無く内部移行させ、かつ送達する。従って、CAR TがCARを介して標的細胞と結合した時、本実施例では、CAR T表面にある抗CD19分子は癌細胞のCD19に結合し、CAR Tの中にある送達ペイロード薬物はその機能を発揮し得る、すなわち、ペイロード機能に基づいてCAR T活性を調節し得る。例えば、必要に応じてCAR Tを若返らせるために、一部のペイロード薬物が、PD-1、CTLA4、またはLAG3 T細胞機能調節分子に作用するように向けられ得る。
本実施例では、本発明者らは、標的リガンドFK506またはFITCは、それぞれの融合受容体(G4Sによって葉酸受容体と連結したFKBPまたはFITC-AF647)と首尾よく結合することを示す。本実施例では、ペイロード薬物は、融合受容体でトランスフェクトされたジャーカット細胞におけるペイロード分布を示すためのイメージング剤ローダミンである。FK506およびFITCの結合親和性を競合的結合によって計算した。FK506-ローダミンはFKBP-FR融合受容体に対してKd=3.39nMを示すのに対して、FITC-AF647は抗FITC-FRに対してKd=8.03nMを示す。
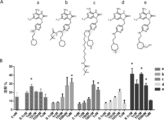
本実施例では、本発明者らは、消耗したCAR T細胞を処理するために、以下の構造を有するToll様受容体7アゴニストと結合体化した標的リガンドFK506を提供した。消耗したCAR T細胞にTLR7アゴニストペイロード薬物が標的化された時に、死滅作用が増大する用量依存的パターンが観察される。従って、CAR T活性の指標であるIFNγ発現レベルはペイロード薬物濃度と比べて用量依存的に増大した。T細胞効果の阻害分子であるTim3の発現レベルは逆の用量依存性を示した。すなわち、ペイロード薬物の濃度が増加するとTim3発現は減少した。
本実施例では、本発明者らは、低ナノモル濃度範囲の抗力で、CAR T消耗を元に戻す可能性がある他の潜在的なペイロードの構造のリストを提供する。
固形腫瘍におけるCAR T細胞療法の大きな制約の1つは、癌抗原で繰り返し刺激された後に消耗状態になる傾向があることである。しかしながら、この現象はCAR T細胞に特有ではなく、慢性ウイルス感染4と腫瘍浸潤リンパ球5の両方で述べられている。抗原から一晩離された後に(「休養」後に)再刺激されると、固形腫瘍組織から単離されたT細胞が多量のINFγ分泌と死滅作用を示した研究において、T細胞の消耗表現型の可逆性が判明している57。しかしながら、もっと臨床に関係するやり方で、阻害シグナル伝達をブロックするか、または他の経路を介してT細胞を活性化する市販の治療剤を用いて若返らせることができれば魅力が高まるだろう。チェックポイントインヒビター(すなわち、PD-1、CTLA-4など)を標的とする抗体が診療所において、固形腫瘍において、ある程度の成功を示している151。しかしながら、2種類以上の標的の組み合わせが必要だと見出されることが多い。さらに、抗体療法は固形腫瘍に十分に浸透しないという欠点も持つ。このことが、固形腫瘍におけるCAR T細胞とチェックポイントブロッケード(checkpoint blockade)(ICB)の併用療法の報告の少なさにつながった可能性がある。
の構造を有する。
TLR7アゴニスト以外に、以下で説明するように、CAR T細胞の消耗を元に戻す/阻止する可能性がある他のいくつかの潜在的なペイロードがある。標的のいくつかは、今のところ本発明者らの標的化薬物送達アプローチに適したIC50をもつアゴニストもインヒビターも無い場合があるが、依然として注目する価値があり、CRISPRまたは標的化マイクロRNA送達アプローチなどの他の阻害機構によって探求される可能性がある。
Simulator of IFN Genes(STING)は、サイトゾルDNAセンシング(sensing)と以下のIFN-β産生に関与するマスターアダプターである。STINGはsdDNAと弱く結合するが、cGMP-AMP合成酵素(sGAS)によって合成された内因性サイクリックジヌクレオチドGMP-AMP(cGAMP)に強く結合する。これは主にマクロファージ、T細胞、様々なDC、内皮細胞、ならびに選ばれた線維芽細胞および上皮細胞において発現している。STINGの試験は主にマクロファージおよび樹状細胞における機能に焦点を合わせており、最近、いくつかのグループがT細胞におけるSTING活性化の直接的な効果を認めた40。STINGアゴニストはT細胞に対して同様の炎症促進効果を有する可能性がある。ADU-S100は、診療所において探求されてきた多くのSTINGアゴニストの1つである。
ジアシルグリセロールキナーゼ-α(DGK-α)は、IP3と一緒になって、TCRシグナル伝達のセカンドメッセンジャーであるジアシルグリセロール(DAG)をホスファチジン酸(PA)に変換する。DGKはCD8-NILよりもCD8TILにおいて高発現しており、DGKを阻害するとERKリン酸化と溶解性脱顆粒が促進される41。これはまた、インビボから単離されたCAR TILの溶解機能も回復させる5。一部のDGKインヒビター構造は以下の通りである。
TGFβは、T細胞、B細胞、およびマクロファージなどの多くの免疫細胞において免疫抑制機能があることで知られている。T細胞においてTGFβI型受容体(TGFβRI。ALK5とも知られる)を遮断すると腫瘍の免疫抑制環境が元に戻る42。低分子インヒビターが探求されており、ガルニセルチブ(LY2157299一水和物)およびEW-7197が診療所において試験されている43-44。
zesteホモログ2エンハンサー(Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2)(EZH2)は、Treg機能と強い相関関係(correv)があるヒストンH3K27メチルトランスフェラーゼである。EZH2の遺伝子破壊または薬理学的破壊によって腫瘍浸潤性Tregの炎症誘発機能が得られた45。慢性ウイルス感染における消耗したCTLはまた、ユニークなエピジェネティック変化でも特徴付けられるので174、EZH2インヒビターはこの消耗状態を逆転できる可能性がある。CPI1205、EPZ6438、およびGSK126を含む、EZH2インヒビターのいくつかの低分子が開発されている。
Claims (21)
- 少なくとも以下の2成分:
ペイロード薬物と共有結合により連結された標的リガンドを含む結合体である、第1の成分;および
膜アンカーモジュールと連結された標的リガンド結合モジュールを含む融合受容体である、第2の成分
を含む、消耗したキメラ抗原受容体(CAR)T細胞を若返らせるためのシステムであって、
融合受容体がCAR T細胞の表面上で発現し、
ペイロード薬物がToll様受容体7(TLR7)アゴニストであり、
標的リガンドおよび標的リガンド結合モジュールが、それぞれフルオレセインイソチオシアネート(FITC)および抗FITC scFvであるか、または、それぞれタクロリムス(FK506)およびFK506結合タンパク質(FKBP)であり、
膜アンカーモジュールが葉酸受容体であり、
第2の成分の標的リガンド結合モジュールが、第1の成分中の標的リガンドを高親和性で認識して複合体を形成し、
ペイロード薬物が、抗原非依存性経路を介して消耗したCAR T細胞を再活性化し、
膜アンカーモジュールが、消耗したCAR T細胞の中への2成分複合体の内部移行を媒介する、
前記システム。 - 膜アンカーモジュールが葉酸受容体α(FRα)である、請求項1記載のシステム。
- 第1の成分が、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物との間に遊離可能なリンカーを含む、請求項1または2記載のシステム。
- 第1の成分が、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物との間に遊離不可能なリンカーを含む、請求項1または2記載のシステム。
- 標的リガンドとリガンド結合モジュールとの間の結合親和性がnM以下の範囲である、請求項1~4のいずれか一項記載のシステム。
- 遊離可能なリンカーまたは遊離不可能なリンカーを介してペイロード薬物と共有結合により連結された標的リガンドを含む、結合体
を含む、消耗したCAR T細胞を若返らせるための方法において使用するための薬学的組成物であって、
消耗したCAR T細胞が、標的リガンド結合モジュールと膜結合型受容体モジュールとを含む融合受容体を発現しており、
ペイロード薬物がTLR7アゴニストであり、
標的リガンドおよび標的リガンド結合モジュールが、それぞれFITCおよび抗FITC scFvであるか、または、それぞれFK506およびFKBPであり、
膜結合型受容体モジュールが葉酸受容体であり、
標的リガンド結合モジュールは、標的リガンドと結合して複合体を形成し、
膜結合型受容体モジュールは、CAR T細胞の中への複合体の内部移行を媒介し、
ペイロード薬物は、抗原非依存性経路を介してCAR T細胞を再活性化させる、
前記薬学的組成物。 - 融合受容体を発現するCAR T細胞であって、該融合受容体が、標的リガンド結合モジュールと膜結合型受容体モジュールとを含む、CAR T細胞
を含む、消耗したCAR T細胞を若返らせるための方法において使用するための薬学的組成物であって、
該薬学的組成物が、
遊離可能なリンカーまたは遊離不可能なリンカーを介してペイロード薬物と共有結合により連結された標的リガンドを含む、結合体
と組み合わせて用いられ、
該結合体が、融合受容体を発現するCAR T細胞の消耗後に投与され、
ペイロード薬物がTLR7アゴニストであり、
標的リガンドおよび標的リガンド結合モジュールが、それぞれFITCおよび抗FITC scFvであるか、または、それぞれFK506およびFKBPであり、
膜結合型受容体モジュールが葉酸受容体であり、
標的リガンド結合モジュールは、標的リガンドと結合して複合体を形成し、
膜結合型受容体モジュールは、CAR T細胞の中への複合体の内部移行を媒介し、
ペイロード薬物は、抗原非依存性経路を介してCAR T細胞を再活性化させる、
前記薬学的組成物。 - CARおよび融合受容体を含む構築物であって、該融合受容体が、標的リガンド結合モジュールと膜結合型受容体モジュールとを含む、構築物
を含む、消耗したCAR T細胞を若返らせるための方法において使用するための薬学的組成物であって、
該方法が、
該構築物を用いてT細胞をトランスフェクトし、CARおよび融合受容体を発現するCAR T細胞を作製する工程と、
該CAR T細胞の消耗後、CAR T細胞に、
遊離可能なリンカーまたは遊離不可能なリンカーを介してペイロード薬物と共有結合により連結された標的リガンドを含む、結合体
を接触させる工程と
を含み、
ペイロード薬物がTLR7アゴニストであり、
標的リガンドおよび標的リガンド結合モジュールが、それぞれFITCおよび抗FITC scFvであるか、または、それぞれFK506およびFKBPであり、
膜結合型受容体モジュールが葉酸受容体であり、
標的リガンド結合モジュールは、標的リガンドと結合して複合体を形成し、
膜結合型受容体モジュールは、CAR T細胞の中への複合体の内部移行を媒介し、
ペイロード薬物は、抗原非依存性経路を介してCAR T細胞を再活性化させ、これによって該CAR T細胞を若返らせる、
前記薬学的組成物。 - ペイロード薬物が、その機能を、消耗したCAR T細胞のエンドソームの中で果たし、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物が、遊離不可能なリンカーによって連結されている、請求項11~13のいずれか一項記載の薬学的組成物。
- ペイロード薬物が、その機能を、消耗したCAR T細胞のサイトゾルの中で遊離薬物として果たし、標的リガンドとペイロード薬物が、遊離可能なリンカーによって連結されている、請求項11~13のいずれか一項記載の薬学的組成物。
- 膜結合型受容体モジュールが葉酸受容体α(FRa)である、請求項11~15のいずれか一項記載の薬学的組成物。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201862715666P | 2018-08-07 | 2018-08-07 | |
| US62/715,666 | 2018-08-07 | ||
| PCT/US2019/042726 WO2020033129A1 (en) | 2018-08-07 | 2019-07-21 | Rejuvenation of car t cell |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021533166A JP2021533166A (ja) | 2021-12-02 |
| JPWO2020033129A5 JPWO2020033129A5 (ja) | 2022-07-28 |
| JP7623935B2 true JP7623935B2 (ja) | 2025-01-29 |
Family
ID=69415080
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021506492A Active JP7623935B2 (ja) | 2018-08-07 | 2019-07-21 | Car t細胞の若返り |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20210308267A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3833400A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP7623935B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20210042125A (ja) |
| CN (2) | CN112543651B (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU2019317278B2 (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA3108710A1 (ja) |
| SG (1) | SG11202100616VA (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2020033129A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014100615A1 (en) | 2012-12-20 | 2014-06-26 | Purdue Research Foundation | Chimeric antigen receptor-expressing t cells as anti-cancer therapeutics |
| US12144850B2 (en) | 2016-04-08 | 2024-11-19 | Purdue Research Foundation | Methods and compositions for car T cell therapy |
| ES3010559T3 (en) | 2017-02-28 | 2025-04-03 | Endocyte Inc | Compositions and methods for car t cell therapy |
| JP7549303B2 (ja) | 2018-01-22 | 2024-09-11 | エンドサイト・インコーポレイテッド | Car t細胞の使用方法 |
| CN112105382A (zh) | 2018-02-23 | 2020-12-18 | 恩多塞特公司 | 用于car t细胞疗法的顺序方法 |
| JP7721436B2 (ja) | 2018-04-12 | 2025-08-12 | ウモジャ バイオファーマ インコーポレイテッド | ウイルスベクター及びパッケージング細胞株 |
| WO2021178887A1 (en) * | 2020-03-06 | 2021-09-10 | Purdue Research Foundation | Methods, compounds, and compositions for modifying car-t cell activity |
| CN116096861A (zh) * | 2020-04-03 | 2023-05-09 | 赛立维公司 | 过继性细胞转移的增强 |
| US20240293456A1 (en) * | 2020-11-30 | 2024-09-05 | Purdue Research Foundation | Combinations of small molecule drug conjugate and car-expressing cytotoxic lymphocytes and methods of treating cancer using the same |
| AU2022340551A1 (en) * | 2021-08-30 | 2024-03-07 | Purdue Research Foundation | Conjugates, compositions, and methods for rejuvenation of car t-cells |
| CN118696234A (zh) * | 2022-02-18 | 2024-09-24 | 豪夫迈·罗氏有限公司 | 用于检测样品中的目标分析物的方法 |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRPI0815416A2 (pt) * | 2007-08-15 | 2014-10-21 | Amunix Inc | Composições e métodos para modificar propriedades de polipeptídeos biologicamente ativos |
| KR102357968B1 (ko) * | 2013-10-15 | 2022-02-03 | 더 스크립스 리서치 인스티튜트 | 키메라 항원 수용체 t 세포 스위치 및 이의 용도 |
| AU2014337367B2 (en) * | 2013-10-15 | 2020-04-30 | The Scripps Research Institute | Peptidic chimeric antigen receptor T cell switches and uses thereof |
| US10640569B2 (en) * | 2013-12-19 | 2020-05-05 | Novartis Ag | Human mesothelin chimeric antigen receptors and uses thereof |
| AU2014368383B2 (en) * | 2013-12-20 | 2020-01-16 | Cellectis | Method of engineering multi-input signal sensitive T cell for immunotherapy |
| WO2015142675A2 (en) * | 2014-03-15 | 2015-09-24 | Novartis Ag | Treatment of cancer using chimeric antigen receptor |
| US20170158749A1 (en) * | 2014-04-23 | 2017-06-08 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Chimeric antigen receptors (car) and methods for making and using the same |
| US20180243340A1 (en) * | 2015-08-24 | 2018-08-30 | University Of Houston System | Combination therapy combining car + t cells with appropriately timed immunodulatory antibodies |
| EP3440191A4 (en) * | 2016-04-07 | 2019-12-11 | Bluebird Bio, Inc. | CHIMERIC ANTIGEN RECEPTOR T-CELL COMPOSITIONS |
| US12144850B2 (en) * | 2016-04-08 | 2024-11-19 | Purdue Research Foundation | Methods and compositions for car T cell therapy |
| JP7278777B2 (ja) * | 2016-05-25 | 2023-05-22 | パーデュー・リサーチ・ファウンデイション | 骨髄由来サプレッサー細胞のターゲティングにより癌を処置する方法 |
| CN116474108A (zh) * | 2016-12-14 | 2023-07-25 | 普渡研究基金会 | 成纤维细胞活化蛋白(fap)-靶向成像和治疗 |
| EP3583218B1 (en) * | 2017-02-17 | 2025-04-16 | Purdue Research Foundation | Targeted ligand-payload based drug delivery for cell therapy |
-
2019
- 2019-07-21 JP JP2021506492A patent/JP7623935B2/ja active Active
- 2019-07-21 CN CN201980052586.7A patent/CN112543651B/zh active Active
- 2019-07-21 KR KR1020217006445A patent/KR20210042125A/ko not_active Ceased
- 2019-07-21 SG SG11202100616VA patent/SG11202100616VA/en unknown
- 2019-07-21 EP EP19847190.6A patent/EP3833400A4/en active Pending
- 2019-07-21 US US17/266,509 patent/US20210308267A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2019-07-21 AU AU2019317278A patent/AU2019317278B2/en active Active
- 2019-07-21 CA CA3108710A patent/CA3108710A1/en active Pending
- 2019-07-21 WO PCT/US2019/042726 patent/WO2020033129A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2019-07-21 CN CN202310525133.XA patent/CN116763943A/zh active Pending
-
2023
- 2023-12-21 US US18/392,939 patent/US20240148880A1/en active Pending
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| GHONEIM, H.E. et al.,Trends in Molecular Medicine,2016年,Vol. 22,No. 12,pp.1000-1011. |
| KIM, M.S., et al.,Journal of the American Chemical Society,2015年,Vol. 137,No. 8,pp.2832-2835. |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN116763943A (zh) | 2023-09-19 |
| CA3108710A1 (en) | 2020-02-13 |
| US20240148880A1 (en) | 2024-05-09 |
| JP2021533166A (ja) | 2021-12-02 |
| CN112543651A (zh) | 2021-03-23 |
| EP3833400A1 (en) | 2021-06-16 |
| SG11202100616VA (en) | 2021-03-30 |
| US20210308267A1 (en) | 2021-10-07 |
| EP3833400A4 (en) | 2022-06-15 |
| KR20210042125A (ko) | 2021-04-16 |
| WO2020033129A1 (en) | 2020-02-13 |
| CN112543651B (zh) | 2023-06-02 |
| AU2019317278B2 (en) | 2025-05-22 |
| AU2019317278A1 (en) | 2021-03-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7623935B2 (ja) | Car t細胞の若返り | |
| Pesce et al. | PD/1-PD-Ls checkpoint: insight on the potential role of NK cells | |
| JP7288402B2 (ja) | 細胞医療用の標的リガンド-ペイロードによる薬剤デリバリー | |
| Zhu et al. | Patient-derived glioblastoma stem cells are killed by CD133-specific CAR T cells but induce the T cell aging marker CD57 | |
| KR102889007B1 (ko) | T 세포 악성종양의 면역요법을 위한 키메라 항원 수용체 및 cd7 발현의 차단 | |
| CN107750167B (zh) | 用于治疗癌症和感染的免疫检查点调节剂的抑制剂 | |
| JP2021078514A (ja) | 血液系腫瘍を標的としたキメラ抗体受容体(CARs)の構成およびその使用方法 | |
| ES2918501T3 (es) | Receptores de antígenos quiméricos de mesotelina humana y usos de los mismos | |
| Hillerdal et al. | Chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T cells for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer | |
| JP2021176863A (ja) | 免疫細胞の能力を増強する方法 | |
| CN111601823B (zh) | 用car-t或car-nk细胞在癌症治疗中靶向lilrb4 | |
| CN112203661A (zh) | 包含双氟烷基-1,4-苯并二氮杂*酮化合物与免疫治疗剂的组合物和其使用方法 | |
| KR20150080507A (ko) | 면역 반응의 향상 | |
| KR20180030879A (ko) | 복막암을 치료하기 위한 조성물 및 방법 | |
| Mews et al. | Multivalent, bispecific αB7-H3-αCD3 chemically self-assembled nanorings direct potent T cell responses against medulloblastoma | |
| AU2021392655A9 (en) | Methods and materials for treating t cell cancers | |
| EP3436829A1 (en) | Lymphocytes expressing cd73 in cancerous patient dictates therapy | |
| Huang et al. | Checkpoint CD24 function on tumor and immunotherapy | |
| AU2017224499A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating regulatory T cell-mediated diseases | |
| US11702632B2 (en) | Ex vivo method of generating super regulatory T cells for the prevention of autoimmune disease | |
| HK40049545A (en) | Rejuvenation of car t cell | |
| Cao et al. | An inherent T cell-activating mRNA delivery platform for in vivo CAR T generation | |
| HK40049545B (en) | Rejuvenation of car t cell | |
| Didi-Zurinam et al. | Potentiating T cell tumor targeting using a combination of TCR with a Siglec-7 based CSR | |
| Beke | T cell receptor-and calcium-induced Gli signalling in CD8+ T cell effector function |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220629 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220720 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20220720 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20230807 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20231024 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20231031 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20231213 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20240401 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20240627 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20240927 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20241226 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20250117 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7623935 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |