JP7586855B2 - Dental treatment equipment - Google Patents
Dental treatment equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7586855B2 JP7586855B2 JP2022095571A JP2022095571A JP7586855B2 JP 7586855 B2 JP7586855 B2 JP 7586855B2 JP 2022095571 A JP2022095571 A JP 2022095571A JP 2022095571 A JP2022095571 A JP 2022095571A JP 7586855 B2 JP7586855 B2 JP 7586855B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- cutting tool
- drive
- root canal
- load
- control unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Dental Tools And Instruments Or Auxiliary Dental Instruments (AREA)
Description
本開示は、ハンドピースを備えた歯科用治療装置に関し、特に、歯の根管(以下、単に根管ともいう)の内壁を切削拡大する歯科用治療装置に関する。 This disclosure relates to a dental treatment device equipped with a handpiece, and in particular to a dental treatment device that cuts and enlarges the inner wall of a tooth's root canal (hereinafter simply referred to as the root canal).
歯科治療において、根管を切削拡大する治療が行われることがある。当該治療には、ハンドピースのヘッド部にファイル或いはリーマと称される切削工具を取付けた歯科用治療装置が用いられる。歯科用治療装置は、モータなどの駆動部で切削工具を回転駆動することで根管を切削拡大している。切削工具には、例えば、時計回り方向の回転駆動で切削を行うように刃が形成されている。そのため、歯科用治療装置は、切削工具を時計回り方向に回転駆動すると根管壁に切削工具の刃が食い込み根管を切削拡大することができる。 Dental treatment may involve cutting and enlarging the root canal. For this treatment, a dental treatment device is used that has a cutting tool called a file or reamer attached to the head of a handpiece. The dental treatment device cuts and enlarges the root canal by rotating the cutting tool with a drive unit such as a motor. The cutting tool has a blade that cuts when rotated clockwise, for example. Therefore, when the dental treatment device rotates the cutting tool clockwise, the blade of the cutting tool bites into the root canal wall, cutting and enlarging the root canal.
国際公開第2012/164875号(特許文献1)に記載の歯科用治療装置では、一定時間毎にモータの回転方向を反転させて、切削工具の回転駆動を一定時間毎に正転駆動と逆転駆動とを繰り返すツイスト駆動を行っている。ここで、歯科用治療装置において、時計回り方向の回転駆動を正転駆動、反時計回り方向の回転駆動を逆転駆動とする。 In the dental treatment device described in International Publication No. 2012/164875 (Patent Document 1), the rotation direction of the motor is reversed at regular intervals to perform twist drive, in which the cutting tool is rotated in a forward and reverse direction repeatedly at regular intervals. Here, in the dental treatment device, clockwise rotation is referred to as forward drive, and counterclockwise rotation is referred to as reverse drive.
歯科用治療装置は、正転駆動で根管を切削する場合、切削工具を所定の回転速度で回転駆動させている。そのため、歯科用治療装置は、停止状態から所定の回転速度に達するまでの時間を短くするほど切削効率が高くなる。しかし、停止状態から所定の回転速度に達するまでの時間を短くするには、回転加速度を速くする必要があるが、回転加速度を速くすると駆動部であるモータの振動が大きくなる。逆に、歯科用治療装置は、停止状態から所定の回転速度に達するまでの時間を長くすると、モータの振動は小さくなるが切削効率は低下する。 When cutting a root canal with forward drive, the dental treatment device rotates and drives the cutting tool at a predetermined rotational speed. Therefore, the shorter the time it takes for the dental treatment device to reach the predetermined rotational speed from a stopped state, the higher the cutting efficiency. However, to shorten the time it takes for the dental treatment device to reach the predetermined rotational speed from a stopped state, it is necessary to increase the rotational acceleration, but increasing the rotational acceleration increases the vibration of the motor, which is the drive unit. Conversely, if the time it takes for the dental treatment device to reach the predetermined rotational speed from a stopped state is increased, the vibration of the motor decreases but the cutting efficiency decreases.
つまり、歯科用治療装置では、切削効率を高めるとモータの振動が大きくなり、逆に切削効率を低下させるとモータの振動は小さくなる。そのため、切削効率とモータの振動との間には二律背反の関係が存在し、歯科用治療装置では、モータの振動を抑えつつ、切削効率の良い切削工具の回転駆動を行うことは困難であった。特に、特許文献1のようなツイスト駆動をする歯科用治療装置では、正転駆動と逆転駆動とを繰り返して切削工具の回転駆動を行うため切削工具5の回転の加速、減速を繰り返し行う必要から、モータの振動を抑えつつ、切削効率の良い切削工具の回転駆動を行うことは困難であった。
In other words, in dental treatment devices, increasing the cutting efficiency increases the motor vibration, and conversely, decreasing the cutting efficiency decreases the motor vibration. Therefore, there is a trade-off between cutting efficiency and motor vibration, and in dental treatment devices, it has been difficult to perform rotational driving of the cutting tool with good cutting efficiency while suppressing motor vibration. In particular, in dental treatment devices with twist drive such as those in
本開示は、上記問題点を解決するためになされたものであり、駆動部の振動を抑えつつ、切削効率の良い切削工具の回転駆動を行うことができる歯科用治療装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present disclosure has been made to solve the above problems, and aims to provide a dental treatment device that can rotate and drive a cutting tool with good cutting efficiency while suppressing vibration in the drive unit.
本開示に係る歯科用治療装置は、歯牙の根管を治療する歯科用治療装置である。歯科用治療装置は、ハンドピースのヘッド部に保持した、根管を切削するための切削工具を回転駆動する駆動部と、切削工具を回転駆動する駆動部を制御する制御部と、切削工具に加わる負荷を検出する負荷検出部と、を備える。制御部は、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上である場合、切削工具が切削対象物を切削する正転駆動、または正転の駆動量が大きいツイスト駆動を、逆転駆動、または逆転の駆動量が大きいツイスト駆動に切り替え、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷未満である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の切削工具の回転加速度の大きさを第3値とし、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の切削工具の回転加速度の大きさを第3値より大きい第4値として駆動部を制御する。 The dental treatment device according to the present disclosure is a dental treatment device for treating a root canal of a tooth. The dental treatment device includes a drive unit that rotates and drives a cutting tool for cutting a root canal held in a head unit of a handpiece, a control unit that controls the drive unit that rotates and drives the cutting tool, and a load detection unit that detects a load applied to the cutting tool. When the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit is equal to or greater than a second reference load, the control unit switches the forward drive or twist drive with a large forward drive amount for the cutting tool to cut a cutting object to a reverse drive or twist drive with a large reverse drive amount, and controls the drive unit to set the magnitude of the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during the start and stop periods to a third value when the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit is less than the second reference load, and to set the magnitude of the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during the start and stop periods to a fourth value greater than the third value when the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit is equal to or greater than the second reference load .
本発明に係る別の歯科用治療装置は、歯牙の根管を治療する歯科用治療装置である。歯科用治療装置は、ハンドピースのヘッド部に保持した切削工具を回転駆動する駆動部と、切削工具を回転駆動する駆動部を制御する制御部と、電気的根管長測定で得られる切削工具の先端の根管内での位置を検出する位置検出部と、を備える。制御部は、位置検出部で検出した切削工具の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖に近い場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の切削工具の回転加速度を、基準位置より根尖から遠い場合に比べて大きくして駆動部を制御する。 Another dental treatment device according to the present invention is a dental treatment device for treating a root canal of a tooth. The dental treatment device includes a drive unit that rotates and drives a cutting tool held in a head unit of a handpiece, a control unit that controls the drive unit that rotates and drives the cutting tool, and a position detection unit that detects the position of the tip of the cutting tool in the root canal obtained by electrical root canal length measurement. When the position of the tip of the cutting tool detected by the position detection unit is closer to the root apex than a reference position, the control unit controls the drive unit by increasing the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during the start period and the stop period compared to when the tip is farther from the root apex than the reference position .
本開示に係る歯科用治療装置は、切削工具に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具の回転加速度を変更するように駆動部を制御するので、駆動部の振動を抑えつつ、切削効率の良い切削工具の回転駆動を行うことができる。 The dental treatment device disclosed herein controls the drive unit to change the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool according to the load applied to the cutting tool, so that the cutting tool can be rotated with good cutting efficiency while suppressing vibration in the drive unit.
(概要)
根管を切削拡大する治療は、人により根管が湾曲している程度や根管が石灰化して閉塞している状況などが異なっており、非常に難しい治療である。歯科用治療装置である根管治療器を用いて根管を切削拡大する場合において、根管口から根尖位置に至るまでの根管を切削拡大する必要があるが、その位置に応じて切削工具に加わる負荷が異なり、一般的に、根尖位置に近づくほど根管が細くなるので切削工具に加わる負荷が大きくなる。
(overview)
The treatment of cutting and enlarging the root canal is very difficult because the degree of curvature of the root canal and the condition of the root canal being blocked by calcification vary from person to person. When cutting and enlarging the root canal using a root canal treatment device, which is a dental treatment device, it is necessary to cut and enlarge the root canal from the root canal opening to the root apex position, but the load applied to the cutting tool varies depending on the position. In general, the closer to the root apex position, the thinner the root canal is, so the load applied to the cutting tool increases.
ここで、根管治療器は、回転駆動として、例えば正転駆動、逆転駆動、および正転と逆転とを繰り返すツイスト駆動を行うことができる。正転駆動は、切削対象物である根管壁を切削する方向の回転駆動で、例えば時計回り方向の回転駆動である。逆転駆動は、正転駆動の逆方向の回転駆動で、例えば反時計回り方向の回転駆動である。切削工具は、時計回り方向の回転駆動で切削が行えるように刃が形成されているので、時計回り方向の回転駆動を正転駆動として駆動すると、ネジが食い込んでいくように根管壁に切削工具の刃が食い込み根管を切削拡大することができる。逆に、切削工具は、反時計回り方向の回転駆動を逆転駆動として駆動すると、ネジを緩めるように切削工具の刃の根管壁への食い込みが解除され、切削工具に加わる負荷が低下する。 Here, the root canal treatment device can perform, for example, forward drive, reverse drive, and twist drive that repeats forward and reverse rotation as the rotation drive. Forward drive is a rotation drive in a direction that cuts the root canal wall, which is the cutting target, for example, clockwise drive. Reverse drive is a rotation drive in the opposite direction to the forward drive, for example, counterclockwise drive. The cutting tool has a blade that can perform cutting with clockwise rotation drive, so when the cutting tool is driven with clockwise rotation drive as the forward drive, the cutting tool blade bites into the root canal wall like a screw biting in, and the root canal can be cut and enlarged. Conversely, when the cutting tool is driven with counterclockwise rotation drive as the reverse drive, the cutting tool blade is released from biting into the root canal wall like a screw being loosened, and the load on the cutting tool is reduced.
根管治療器は、根管を切削拡大する場合、切削工具を所定の回転速度で正転駆動させているが、切削効率を高めるためには停止状態から所定の回転速度に達するまでの時間を短くする必要があり回転加速度を速く(回転加速度の大きさを大きく)する。しかし、根管治療器は、回転加速度を速くすると駆動部であるモータの振動が大きくなる。逆に、根管治療器は、停止状態から所定の回転速度に達するまでの時間を長くすると、モータの振動は小さくなるが切削効率は低下する。 When cutting and enlarging a root canal, a root canal treatment instrument drives the cutting tool in the forward direction at a predetermined rotational speed, but to improve cutting efficiency, it is necessary to shorten the time it takes to reach the predetermined rotational speed from a stopped state, and this is done by increasing the rotational acceleration (increasing the magnitude of the rotational acceleration). However, in a root canal treatment instrument, increasing the rotational acceleration increases the vibration of the motor, which is the drive unit. Conversely, if the time it takes for a root canal treatment instrument to reach the predetermined rotational speed from a stopped state is increased, the vibration of the motor decreases but the cutting efficiency decreases.
つまり、根管治療器では、切削効率を高めることとモータの振動を小さくすることとは二律背反の関係であり、モータの振動を抑えつつ、切削効率の良い切削工具の回転駆動を行うことは困難であった。そこで、本開示に係る根管治療器では、根管を切削拡大するとき切削工具に加わる負荷が大きくなり、逆に根管を切削しないとき切削工具に加わる負荷が小さくなることから、切削工具に加わる負荷に着目して回転加速度を制御する回転駆動を行っている。これにより、本開示に係る根管治療器では、モータの振動を抑えつつ、切削効率の良い切削工具の回転駆動を行うことが可能となっている。以下、図を用いて具体的な実施の形態について詳しく説明する。
(実施の形態1)
[根管治療器の構成]
図1は、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100の構成を示す概略図である。図2は、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器の機能の構成を示すブロック図である。なお、実施の形態1に係る歯科用治療装置は、歯科用根管治療のためのハンドピース1に根管拡大および根管長測定などのシステムを含めて根管治療器100として説明する。しかし、本開示に係る歯科用治療装置は、根管治療器100に限定されるものではなく、同様の構成を有する歯科用治療装置について適用することができる。また、根管長測定の構成を有しない根管治療器100であってもよい。
In other words, in a root canal treatment instrument, increasing cutting efficiency and reducing motor vibration are in a trade-off relationship, and it has been difficult to perform rotational driving of a cutting tool with good cutting efficiency while suppressing motor vibration. Therefore, in a root canal treatment instrument according to the present disclosure, since the load applied to the cutting tool increases when cutting and enlarging a root canal, and the load applied to the cutting tool decreases when the root canal is not cut, the rotational driving is performed by controlling the rotational acceleration by focusing on the load applied to the cutting tool. As a result, in a root canal treatment instrument according to the present disclosure, it is possible to perform rotational driving of a cutting tool with good cutting efficiency while suppressing motor vibration. Specific embodiments will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings.
(Embodiment 1)
[Configuration of root canal treatment device]
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of a root
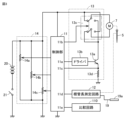
図1に示す根管治療器100は、歯科用根管治療のためのハンドピース1、モータユニット6、制御ボックス9をハンドピース1の内部に含んでいる。つまり、図1に示す根管治療器100は、ハンドピース1が、ホースを介して、制御ボックスに連結されている構成ではなく、コードレスタイプの根管治療器である。
The root
歯科用根管治療のハンドピース1は、ヘッド部2と、ヘッド部2に連接される細径のネック部3と、該ネック部3に連接され手指によって把持される把持部4とを備えている。そして、把持部4には、ヘッド部2に保持される切削工具5(ファイル或いはリーマなど)を回転駆動させるためのモータユニット6や制御ボックス9を内蔵している。
The
モータユニット6は、図2に示すようにマイクロモータ7を内蔵し、該マイクロモータ7へ電源を供給する電源供給用リード線71および、後述する根管長測定回路12へ信号を伝送する信号用リード線8などを介して、制御ボックス9に接続してある。ここで、信号用リード線8は、モータユニット6及びハンドピース1内を経て切削工具5と電気的に導通し、電気信号を伝達する導電体の一部である。なお、切削工具5は、根管長測定回路12の一方の電極となる。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
制御ボックス9は、制御部11、比較回路110、根管長測定回路12、モータドライバ13、設定部14、操作部15、表示部16および報知部17などを備えている。なお、リード線19は、図1に図示していないが、たとえば把持部4より導出するよう構成してもよい。リード線19は、一方を根管長測定回路12に連結し、他方の先端に患者の唇に掛けられる口腔電極19aを電気的に導通する状態で取付けてある。なお、口腔電極19aは、根管長測定回路12の他方の電極となる。
The
制御部11は、根管拡大及び根管長測定システム全体の制御を行うもので、主要部はマイクロコンピュータで構成されている。制御部11には、比較回路110、根管長測定回路12、モータドライバ13、設定部14、操作部15、表示部16、および報知部17を接続してある。制御部11は、切削対象物を切削する切削工具5の回転方向を制御している。具体的に、制御部11は、切削工具5を時計回り(右回りともいう)方向に回転させる時計回り駆動、切削工具5を反時計回り(左回りともいう)方向に回転させる反時計回り駆動、時計回り駆動と反時計回り駆動とを繰り返すツイスト駆動などの制御を行う。ここで、切削工具の回す方向(時計回り方向や反時計回り方向)は、ヘッド部2に取付ける切削工具5の側から切削工具5の先端方向を向いた場合を基準に考えるものとする。さらに、制御部11は、時計回りの回転角度、回転速度あるいは回転角速度(回転数)、回転加速度、反時計回りの回転角度、回転速度あるいは回転角速度(回転数)、回転加速度、繰り返し数などのパラメータを変更して、切削工具5を回転させる駆動の制御を行うことができる。
The
ここで、回転角度は、切削工具5を時計回り方向または反時計回り方向に回す大きさを表す回転量であり、回転速度あるいは回転角速度(回転数)を一定にした場合の回転時間(駆動期間ともいう)などで規定してもよい。また、回転角度は、駆動電流量やトルク量などの切削工具5の回転駆動に関連する量で規定してもよい。厳密には切削工具やモータのかかる負荷によって、たとえば制御上の回転時間と実際の回転角度とは対応関係を補正しなければならない場合があるが、補正量は極めて小さく本開示の実施においては無視することができる。さらに、回転加速度は、単位時間当たりの回転速度あるいは回転角速度(回転数)の増減で規定される。回転加速度は、単位時間当たりの回転回数が増加する場合、正の値となり、単位時間当たりの回転回数が減少する場合、負の値となるが、本開示において「回転加速度の大きさ」と記載する場合、回転加速度の絶対値を規定している。
Here, the rotation angle is the amount of rotation that represents the amount of rotation of the
比較回路110は、切削工具5に加わる負荷を検出するために必要な構成であり、当該負荷の検出が必要な場合に選択して設けることが可能な構成である。比較回路110は、モータドライバ13により切削工具5を時計回り方向または反時計回り方向に回転させているいずれかの時点で、負荷の比較を行うことが可能である。具体的に、比較回路110は、切削工具5を時計回り方向または反時計回り方向に所定の回転角度(たとえば180度)回転させた後に、切削工具5に加わる負荷と基準負荷とを比較することができる。
The
根管長測定回路12は、切削工具5の先端の根管内での位置を検出するために必要な構成であり、当該位置の検出が必要な場合に選択して設けることが可能な構成である。根管長測定回路12は、根管内に挿入した切削工具5を一方の電極、患者の唇に掛けた口腔電極19aを他方の電極として閉回路を構成する。そして、根管長測定回路12は、切削工具5と口腔電極19aとの間に測定電圧を印加し、切削工具5と口腔電極19aとの間のインピーダンスを計測することによって、歯の根尖位置から切削工具5の先端までの距離を測定することができる。切削工具5の先端が根尖位置に到達したことを根管長測定回路12が検出したとき、切削工具の挿入量、すなわち根管口から切削工具の先端までの距離を根管長とすることができる。なお、切削工具5と口腔電極19aとの間のインピーダンスを計測して、根管長を測定する電気的根管長測定方法は公知のものであり、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100には、公知になっているすべての電気的根管長測定方法を適用することができる。
The root canal
モータドライバ13は、電源供給用リード線71を介してマイクロモータ7に接続し、制御部11からの制御信号に基づいて、マイクロモータ7に供給する電源を制御している。モータドライバ13は、マイクロモータ7に供給する電源を制御することで、マイクロモータ7の回転方向、回転数および回転加速度など、つまり切削工具5の回転方向、回転数および回転加速度などを制御することができる。なお、主にマイクロモータ7およびモータドライバ13により駆動部を構成している。
The
設定部14は、把持部4の表面に設定変更するための選択ボタン15b(図1参照)を有しており、操作者(術者)が当該選択ボタン15bを操作することで切削工具5の回転方向、回転数、回転角度、および回転加速度などを制御する基準を設定する。また、設定部14は、切削工具5の回転数、回転角度および回転加速度のパラメータを設定する他、根管長測定を行うか否かの選択、駆動モードの選択なども設定することができる。さらに、設定部14は、切削工具5に加わる負荷と比較回路110おいて比較する基準負荷(回転方向、回転加速度などを切り替えるための基準)、タイミングなどを設定する。
The setting
操作部15は、把持部4の表面に駆動開始・停止ボタン15a(図1参照)を有しており、操作者が当該駆動開始・停止ボタン15aを操作することで切削工具5の回転駆動を開始または停止することができる。つまり、切削工具5の回転駆動が停止しているときに駆動開始・停止ボタン15aを操作すると、操作部15は、制御部11に対して切削工具5の回転駆動を開始する指示信号を送信する。切削工具5の回転駆動中に駆動開始・停止ボタン15aを操作すると、操作部15は、制御部11に対して切削工具5の回転駆動を停止する指示信号を送信する。
The
表示部16は、根管内での切削工具5の先端の位置や切削工具5の回転方向、回転数および回転角度などを表示する。さらに、報知部17が使用者に対して報知するための情報を、表示部16に表示することもできる。コードレスタイプの根管治療器100では、把持部4に表示部16が設けてある。そのため、使用者は、視線を大きく変えることなく、切削工具5を切削方向に駆動しているのか、非切削方向に駆動しているのか、現在の切削工具5の位置はどの程度か、切削工具5にかかっている負荷はどの程度か、回転数はいくらか、といった情報を確認することができる。
The
報知部17は、現在、制御部11で行っている切削工具5の回転駆動状態を、光、音や振動などにより報知する。具体的に、報知部17は、切削工具5の回転駆動状態を報知するために、必要に応じてLED(Light Emitting Diode),スピーカーや振動子などを設け、時計回り方向の回転駆動と反時計回り方向の回転駆動とで発光するLEDの色を変えたり、スピーカーから出力する音を変えたりする。なお、報知部17は、表示部16で、使用者に対して切削工具5の回転駆動状態を表示することができる場合、LED,スピーカーや振動子など別途設けなくてもよい。
The
次に、切削工具5の回転駆動制御を行う根管治療器100の回路構成について、さらに詳しく説明する。図3は、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100の回路構成を示す回路図である。図3に示す根管治療器100には、切削工具5の回転駆動制御に関わるマイクロモータ7、制御部11、比較回路110、根管長測定回路12、モータドライバ13、および設定部14の部分について図示してある。
Next, the circuit configuration of the root
さらに、モータドライバ13は、トランジスタスイッチ13a、トランジスタドライバ回路13b、回転方向切替スイッチ13c、および負荷検出用抵抗13dを含んでいる。なお、回転方向切替スイッチ13cは、リレー素子として説明するが、FETなどの半導体のスイッチ素子でモータ駆動回路を構成してもよい。設定部14は、基準負荷設定用の可変抵抗14a、デューティ設定用の可変抵抗14b、および基準位置設定用の可変抵抗14cを含んでいる。なお、設定部14には、比較回路110において検出した負荷と基準負荷とを比較するタイミングを示す回転角度(または回転時間)を設定する構成なども含まれるが、当該構成については図3に図示していない。また、図3に示す根管治療器100には、主電源20およびメインスイッチ21に接続してある。切削工具5は、図示していないが適宜の歯車機構等を介してマイクロモータ7に保持してある。
The
トランジスタドライバ回路13bは、制御部11のポート11aから出力する制御信号で作動し、トランジスタスイッチ13aのオン・オフを制御してマイクロモータ7を駆動する。マイクロモータ7は、回転方向切替スイッチ13cの状態に応じて時計回り方向または反時計回り方向に回転する。制御部11のポート11aから出力する制御信号が、たとえば一定の周期で繰返されるパルス波形である場合、そのパルス波形の幅、すなわちデューティ比は、設定部14のデューティ設定用の可変抵抗14bによって調整される。マイクロモータ7は、このデューティ比に対応した回転数で切削工具5を駆動する。
The
回転方向切替スイッチ13cは、制御部11のポート11bから出力する制御信号で、切削工具5を時計回り方向に駆動するか、反時計回り方向に駆動するかを切替える。制御部11は、ポート11cに入力される負荷検出用抵抗13dの電流量(または電圧値)に基づき、切削工具5に加わる負荷を検出する。そのため、負荷検出用抵抗13dは、切削工具5に加わる負荷を検出する負荷検出部として機能している。なお、負荷検出部は、負荷検出用抵抗13dの電流量(または電圧値)に基づいて切削工具5に加わる負荷を検出する構成に限定されるものではなく、たとえば切削工具5の回転駆動部分にトルクセンサを設けて切削工具5に加わる負荷を検出する構成など別の構成であってもよい。検出される負荷は、たとえば切削工具5に加わるトルク値に制御部11で換算され、表示部16に表示される。また、比較回路110では、制御部11で換算されたトルク値と、基準負荷設定用の可変抵抗14aを用いて設定したトルク値とを比較している。もちろん、比較回路110は、トルク値に換算せずに負荷検出用抵抗13dの電流量(または電圧値)と可変抵抗14aの電流量(または電圧値)とを直接比較する構成でもよい。
The
さらに、制御部11は、根管長測定回路12で測定した根管長をポート11dに入力する。そのため、根管長測定回路12は、切削工具5の先端の根管内での位置を検出する位置検出部として機能している。また、制御部11は、負荷検出部で検出した切削工具5に加わる負荷をポート11eから比較回路110へ出力し、比較回路110が基準負荷と比較した比較結果をポート11eから入力する。そのため、比較回路110は、負荷検出部で検出した負荷と基準負荷とを比較する負荷比較部として機能している。なお、制御部11は、上記アナログ回路で説明した構成を、ひとつのマイクロコンピュータにソフトウェアとしてまとめてもよい。
Furthermore, the
図4は、切削工具5の回転方向を示した模式図である。図4に示す切削工具5の回転方向では、ヘッド部2に取付ける切削工具5の側から切削工具5の先端方向を向いて切削工具5を右回りに回転させる時計回り方向5aの回転駆動と、左回りに回転させる反時計回り方向5bの回転駆動とが図示されている。切削工具5の刃5Aが時計回り方向の回転駆動をすることで根管を切削する場合、時計回り方向5aの回転駆動が正転駆動で、反時計回り方向5bの回転駆動が逆転駆動である。なお、予め定められた回転角度で時計回り方向5aに切削工具5を回転させる駆動と、予め定められた回転角度で反時計回り方向5bに切削工具5を回転させる駆動とを交互に行う駆動が、ツイスト駆動である。また、ツイスト駆動では、時計回り方向と反時計回り方向との交互回転を、等しい駆動量に行うものであってもよいし、異なる駆動量だけ行うものであってもよい。
[回転駆動の制御]
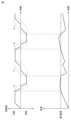
次に、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100における回転駆動の制御について説明する。図5は、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100における回転駆動の制御について説明するためのフローチャートである。図6は、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器における回転数および負荷の変化について説明するための図である。図6に示すグラフは、上段が回転数の変化を示すグラフで、下段が切削工具5に加わる負荷の変化を示すグラフである。回転数の変化を示すグラフは、縦軸が回転数で、横軸が時間である。切削工具5に加わる負荷の変化を示すグラフ、縦軸が切削工具5に加わる負荷で、横軸が時間である。実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100では、ツイスト駆動で切削工具5の回転駆動を行っているため、正転駆動と逆転駆動とを繰り返して行い切削工具5の回転の加速、減速を繰り返し行っている。そのため、単純に、回転加速度の大きさを大きくすると、切削効率は高くなるが、駆動部であるマイクロモータ7の振動も大きくなってしまう。
FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram showing the rotation direction of the
[Rotation drive control]
Next, the control of the rotation drive in the root
そこで、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100では、切削工具5に加わる負荷に着目して、切削工具5の回転加速度を制御する。具体的に、制御部11は、図5に示すように、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上か否かを判断する(ステップS101)。切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷未満の場合(ステップS101でNO)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第1値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS102)。一方、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上の場合(ステップS101でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第2値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS103)。なお、第2値は、第1値より大きい。
Therefore, in the root
つまり、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷より小さいとき、根管壁に切削工具5の刃が食い込んでいない、または食い込みが少ないので根管の切削への寄与が小さい。そのため、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度を遅く(回転加速度の大きさを小さく)して、起動する期間および停止させる期間が長くなっても切削効率を低下させる虞は少ない。また、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度を遅くすることで、マイクロモータ7の振動を小さく抑制することができる。
In other words, when the load applied to the
一方、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上のとき、根管壁に切削工具5の刃が食い込んでいるので根管の切削への寄与が大きい。そのため、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度を速く(回転加速度の大きさを大きく)して、起動する期間および停止させる期間を短くすることで高い切削効率を維持できる。ただ、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度を速くするので、マイクロモータ7の振動は大きくなる。
On the other hand, when the load applied to the
図6に示すように、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷未満において、切削工具5の回転駆動が切り替わる際に、正転から停止までの減速、および停止から逆転までの加速の期間A、逆転から停止までの減速、および停止から正転までの加速の期間Bの回転加速度の大きさを第1値(<第2値)と小さくする。
As shown in FIG. 6, when the load applied to the
一方、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上において、切削工具5の回転駆動が切り替わる際に、正転から停止までの減速、および停止から逆転までの加速の期間C、逆転から停止までの減速、および停止から正転までの加速の期間Dの回転加速度の大きさを第2値(>第1値)と大きくする。
On the other hand, when the load applied to the
第1値は、第2値の1/3~2/3の大きさであることが望ましい。マイクロモータ7の種類やハンドピース1の構造により第1値および第2値は変化するが、マイクロモータ7の振動を抑えつつ、切削効率の良い切削工具の回転駆動を行うことができる最適な第1値および第2値を複数回実験の実験結果から決定してもよい。
It is desirable that the first value be 1/3 to 2/3 of the second value. The first and second values vary depending on the type of
図5に示すフローチャートでは、制御部11で停止操作を受け付けたか否かを判断する(ステップS104)。駆動開始・停止ボタン15aが押下されて、停止操作を受け付けた場合(ステップS104でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転駆動を停止する。一方、停止操作を受け付けていない場合(ステップS104でNO)、制御部11は、処理をステップS101に戻す。つまり、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上か否かで、切削工具5の回転加速度を切り替えてツイスト駆動を行う。
In the flowchart shown in FIG. 5, the
図6に示した例では、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上か否かで、切削工具5の回転加速度を第1値か第2値かに切り替えていたが、基準負荷を複数設け、切削工具5の回転加速度を複数の値に切り替えてもよい。これにより、制御部11は、マイクロモータ7の振動をより抑えつつ、より切削効率の良い切削工具の回転駆動を行うことができる。
In the example shown in FIG. 6, the
実際の切削工具5の回転駆動では、負荷検出部において切削工具5に加わる負荷を検出してから切削工具5の回転加速度の切り替え制御までの間に数msec程度のタイムラグが生じる。しかし、図6に示すグラフでは、当該タイムラグは小さいとして当該タイムラグを無視して図示していない。
In the actual rotational drive of the
以上のように、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100は、歯牙の根管を治療する歯科用治療装置である。根管治療器100は、ハンドピース1のヘッド部2に保持した、根管を切削するための切削工具5を回転駆動するマイクロモータ7と、切削工具5を回転駆動するマイクロモータ7を制御する制御部11と、切削工具5に加わる負荷を検出する負荷検出部(負荷検出用抵抗13d)と、を備える。制御部11は、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具5に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御する。
As described above, the root
具体的に、制御部11は、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷未満である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第1値とし、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第1値より大きい第2値としてマイクロモータ7を制御する。これにより、実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100は、切削工具5に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御するので、マイクロモータ7の振動を抑えつつ、切削効率の良い切削工具5の回転駆動を行うことができる。
(実施の形態2)
実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100では、切削工具5をツイスト駆動する場合に、切削工具5に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御する構成について説明した。実施の形態2に係る根管治療器では、所定の負荷が切削工具に加わった場合に切削工具を逆転させる駆動において、切削工具に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータを制御する構成について説明する。なお、実施の形態2に係る根管治療器100でも、図1~図3に示した実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100と同じ構成を用いるため、同じ構成には同じ符号を用いて詳しい説明を繰返さない。
Specifically, the
(Embodiment 2)
In the root
図7は、実施の形態2に係る根管治療器100における回転駆動の制御について説明するためのフローチャートである。図8は、実施の形態2に係る根管治療器100における回転数および負荷の変化について説明するための図である。図7に示すグラフは、上段が回転数の変化を示すグラフで、下段が切削工具5に加わる負荷の変化を示すグラフである。回転数の変化を示すグラフは、縦軸が回転数で、横軸が時間である。切削工具5に加わる負荷の変化を示すグラフ、縦軸が切削工具5に加わる負荷で、横軸が時間である。実施の形態2に係る根管治療器100では、正転駆動で切削工具5の回転駆動を行っているが、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上になると、切削工具5の破損を防止するため逆転駆動に切り替える制御を行っている。第2基準負荷は、切削工具5の材質や形状などにより予め設定してある。
Figure 7 is a flow chart for explaining the control of the rotation drive in the root
実施の形態2に係る根管治療器100においても、切削工具5に加わる負荷に着目して、切削工具5の回転加速度を制御する。具体的に、制御部11は、図7に示すように、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上か否かを判断する(ステップS201)。切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷未満の場合(ステップS201でNO)、制御部11は、回転駆動を正転駆動に切り替える(ステップS202)。なお、ステップS202において、制御部11が、正転駆動で切削工具5の回転駆動を行っている場合、正転駆動を継続することになる。次に、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第3値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS203)。
In the root
一方、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上の場合(ステップS201でYES)、制御部11は、回転駆動を逆転駆動に切り替える(ステップS204)。なお、ステップS202において、制御部11が、逆転駆動で切削工具5の回転駆動を行っている場合、逆転駆動を継続することになる。次に、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第4値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS205)。なお、第4値は、第3値より大きい。
On the other hand, if the load applied to the
つまり、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷より小さいとき、制御部11は、マイクロモータ7の振動を小さく抑えつつ、根管を切削拡大することができる程度の回転加速度で切削工具5を回転駆動する。一方、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上のとき、根管壁に切削工具5の刃が食い込んで動かなくなっているので、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度を速くして、切削工具の刃の根管壁への食い込みを素早く解除する。
In other words, when the load applied to the
実施の形態2に係る根管治療器100は、切削工具の刃の根管壁への食い込みを素早く解除して、根管を切削拡大する切削工具5の回転駆動に戻すことができれば、高い切削効率を維持することができる。ただ、制御部11は、切削工具の刃の根管壁への食い込みを解除する期間、切削工具5の回転加速度を速くするので、マイクロモータ7の振動は大きくなる。
The root
図7に示すように、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上になると、切削工具5の回転駆動を切り替え、切削工具5に加わる負荷を緩和する駆動を行っている。そのため、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上になり、正転から停止までの減速、および停止から逆転までの加速の期間E,Gの回転加速度の大きさを第4値(>第3値)と大きくする。
As shown in FIG. 7, when the load applied to the
切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷未満になるまで、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転駆動を逆転駆動のまま維持することになる。切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷未満になり、切削工具5の回転駆動を逆転駆動から正転駆動に切り替える場合、逆転から停止までの減速、および停止から正転までの加速の期間F,Hの回転加速度の大きさを第3値(<第4値)と小さくする。
The
図7に示すフローチャートでは、制御部11で停止操作を受け付けたか否かを判断する(ステップS206)。駆動開始・停止ボタン15aが押下されて、停止操作を受け付けた場合(ステップS206でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転駆動を停止する。一方、停止操作を受け付けていない場合(ステップS206でNO)、制御部11は、処理をステップS201に戻す。つまり、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上か否かで、切削工具5の回転駆動を逆転駆動に切り替える駆動を行う。
In the flowchart shown in FIG. 7, the
実施の形態2に係る切削工具5の回転駆動は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷未満において正転駆動であると説明したがツイスト駆動であってもよい。切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷未満において切削工具5をツイスト駆動させる場合、実施の形態1で説明した駆動を実施の形態2で説明した駆動に組み合わせてもよい。
The rotational drive of the
以上のように、実施の形態2に係る根管治療器100は、制御部11が、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上である場合、切削工具5が切削対象物を切削する正転駆動とは逆方向の逆転駆動に切り替え、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷未満である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第3値とし、負荷検出部で検出する切削工具5に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第3値より大きい第4値としてマイクロモータ7を制御する。
(実施の形態3)
実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100では、切削工具5に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御する構成について説明した。実施の形態3に係る根管治療器では、切削工具5に加わる負荷以外の値に応じて切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御する構成について説明する。なお、実施の形態3に係る根管治療器100でも、図1~図3に示した実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100と同じ構成を用いるため、同じ構成には同じ符号を用いて詳しい説明を繰返さない。
As described above, in the root
(Embodiment 3)
In the root
図9は、実施の形態3に係る根管治療器100における回転駆動の制御について説明するためのフローチャートである。まず、実施の形態3に係る根管治療器100では、切削工具5の回転速度に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御する構成について説明する。切削工具5の回転速度は、選択ボタン15bを操作することで設定することができるが、設定した切削工具5の回転速度が速いと、起動する期間および停止させる期間が長くなり切削効率が低下する虞がある。
Figure 9 is a flow chart for explaining the control of the rotation drive in the root
そこで、実施の形態3に係る根管治療器100では、切削工具5の回転速度に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を制御する。具体的に、制御部11は、図9に示すように、切削工具5の回転速度を設定する(ステップS301)。制御部11は、設定した切削工具5の回転速度が基準回転速度以上か否かを判断する(ステップS302)。切削工具5の回転速度が基準速度未満の場合(ステップS302でNO)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第5値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS303)。一方、設定した切削工具5の回転速度が基準速度以上の場合(ステップS302でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第6値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS304)。なお、第6値は、第5値より大きい。
Therefore, in the root
つまり、設定した切削工具5の回転速度が基準速度より小さいとき、設定した切削工具5の回転速度に達するまでの期間(起動する期間)および設定した切削工具5の回転速度から停止するまでの期間(停止させる期間)が短い。しかし、設定した切削工具5の回転速度が基準速度以上のとき、設定した切削工具5の回転速度に達するまでの期間(起動する期間)および設定した切削工具5の回転速度から停止するまでの期間(停止させる期間)が長くなるので、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを大きくしなければ切削効率を低下させる虞が生じる。なお、設定した切削工具5の回転速度が基準速度より小さいときは切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを小さくすることで、マイクロモータ7の振動を小さく抑制することができる。
In other words, when the set rotational speed of the
図9に示すフローチャートでは、制御部11で停止操作を受け付けたか否かを判断する(ステップS305)。駆動開始・停止ボタン15aが押下されて、停止操作を受け付けた場合(ステップS305でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転駆動を停止する。一方、停止操作を受け付けていない場合(ステップS305でNO)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転速度を変更する操作を受け付けたか否かを判断する(ステップS306)。回転速度を変更する操作を受け付けた場合(ステップS306でYES)、制御部11は、処理をステップS301に戻す。つまり、制御部11は、新たに切削工具5の回転速度を設定する。回転速度を変更する操作を受け付けた場合(ステップS306でYES)、制御部11は、処理をステップS305に戻す。つまり、制御部11は、同じ回転速度で切削工具5の回転駆動を継続する。
In the flowchart shown in FIG. 9, the
図9に示した例では、制御部11は、設定した切削工具5の回転速度が基準速度以上か否かで、切削工具5の回転加速度を第5値か第6値かで切り替えていたが、基準速度を複数設け、切削工具5の回転加速度を複数の値に切り替えてもよい。また、図9に示した例では、制御部11は、設定した切削工具5の回転速度に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御するが、他の実施の形態で説明した制御と組み合わせ制御してもよい。
In the example shown in FIG. 9, the
さらに、図10は、実施の形態3に係る根管治療器における回転駆動の別の制御について説明するためのフローチャートである。図10に示すフローチャートでは、切削工具5の先端の位置に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御する構成について説明する。根尖位置に近づくほど根管は細くなるので切削工具に加わる負荷が大きくなるため、切削効率を低下させないために切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを大きくすることか好ましい。
Furthermore, FIG. 10 is a flowchart for explaining another control of the rotational drive in the root canal treatment device according to
そこで、根管治療器100では、切削工具5の先端の位置に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を制御する。具体的に、制御部11は、図10に示すように、制御部11は、根管長測定回路12から得た切削工具5の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖に近いか否かを判断する(ステップS401)。切削工具5の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖から遠い場合(ステップS401でNO)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第7値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS402)。一方、切削工具5の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖に近い場合(ステップS401でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第8値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS403)。なお、第8値は、第7値より大きい。
Therefore, in the root
つまり、切削工具5の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖から遠い場合、切削工具5に加わる負荷は小さいが、切削工具5の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖に近い場合、切削工具5に加わる負荷は大きくなる。そのため、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が小さくなる位置では、切削工具5の回転加速度を遅くすることで、マイクロモータ7の振動を小さく抑制することができる。一方、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が大きくなる位置では、切削工具5の回転加速度を速くするので、高い切削効率を維持できる。
In other words, when the position of the tip of the
図10に示した例では、制御部11は、切削工具5の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖に近いか否かで、切削工具5の回転加速度を第7値か第8値かで切り替えていたが、基準位置を複数設け、切削工具5の回転加速度を複数の値に切り替えてもよい。また、図10に示した例では、制御部11は、切削工具5の先端の位置に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御するが、他の実施の形態で説明した制御を組み合わせて制御してもよい。また、切削工具5の先端の位置は、切削工具5に加わる負荷に対応するため、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷を測定することに代えて、切削工具5の先端の位置に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更するようにマイクロモータ7を制御してもよい。
In the example shown in FIG. 10, the
図10に示した例では、制御部11は、切削工具5の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖に近い場合、高い切削効率を維持するため切削工具5の回転加速度を速くして切削工具5に加わる負荷を大きすると説明した。しかし、根尖付近で過剰な切削を防ぐ必要がある場合、根尖付近に閾値をさらに設けて当該閾値より根尖に切削工具5の先端の位置が近づいたとき、切削工具5の回転加速度を遅くして回転数を低下させて切削工具5に加わる負荷を小さくしてもよい。もちろん、他の実施の形態に係る根管治療器においても、根管長測定回路12を有し切削工具5の先端の位置を得ることができるのであれば、根尖付近で過剰な切削を防ぐために切削工具5の回転数を低下させてもよい。
In the example shown in FIG. 10, the
(変形例)
(1)実施の形態1に係る根管治療器100では、切削工具5に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更する構成を説明した。しかし、切削工具5に加わる負荷に関わらず、同じ回転加速度で切削工具を回転駆動する駆動モードと、切削工具5に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更する駆動モードを切り替えることができるようにしてもよい。
(Modification)
(1) In the root
図11は、駆動モードの切り替えについて説明するためのフローチャートである。まず、操作者(術者)は選択ボタン15bを操作することで駆動モードの選択することができ、制御部11は、選択された駆動モードが第1モードか否かを判断する(ステップS501)。ここで、第1モードは、切削工具5に加わる負荷に関わらず、同じ回転加速度で切削工具を回転駆動する駆動モードであり、第2モードは、切削工具5に加わる負荷に応じて、切削工具5の回転加速度を変更する駆動モードである。
Figure 11 is a flowchart for explaining the switching of the drive mode. First, the operator (surgeon) can select the drive mode by operating the
駆動モードが第1モードである場合(ステップS501でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷に関わらず、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第1値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS502)。なお、第1モードでは、操作者が予め切削工具5の回転加速度を第1値に設定(または初期設定)してあり、切削効率を高めるよりマイクロモータ7の振動を小さく抑制する回転加速度に設定してある。もちろん、操作者が予め切削工具5の回転加速度を第2値(>第1値)に設定(または初期設定)して、第1モードにおいて、マイクロモータ7の振動の抑制を犠牲にして切削効率を高める回転加速度に設定してもよい。
When the drive mode is the first mode (YES in step S501), the
駆動モードが第1モードでなく第2モードである場合(ステップS501でNO)、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上か否かを判断する(ステップS503)。切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷未満の場合(ステップS503でNO)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第1値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS504)。一方、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上の場合(ステップS503でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転加速度の大きさを第2値として切削工具5を回転駆動する(ステップS505)。
If the drive mode is not the first mode but the second mode (NO in step S501), the
つまり、第2モードの回転駆動は、実施の形態1で説明した回転駆動であり、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷未満のとき、切削工具5の回転加速度を遅くすることで、マイクロモータ7の振動を小さく抑制することができる。一方、制御部11は、切削工具5に加わる負荷が第1基準負荷以上のとき、切削工具5の回転加速度を速くして、起動する期間および停止させる期間を短くすることで高い切削効率を維持している。
In other words, the second mode of rotational drive is the rotational drive described in
図11に示すフローチャートでは、制御部11で停止操作を受け付けたか否かを判断する(ステップS506)。駆動開始・停止ボタン15aが押下されて、停止操作を受け付けた場合(ステップS506でYES)、制御部11は、切削工具5の回転駆動を停止する。一方、停止操作を受け付けていない場合(ステップS506でNO)、制御部11は、処理をステップS501に戻す。つまり、制御部11は、選択された駆動モードの判断を行う。
In the flowchart shown in FIG. 11, the
図11に示した例では、制御部11は、駆動モードが第1モードか第2モードかを切り替えていたが、他に複数のモードを設け、操作者が選択ボタン15bを操作することで複数のモードから駆動モードを選択できるようにしてもよい。他のモードは、例えば、実施の形態2で説明した駆動や実施の形態3で説明した駆動である。
In the example shown in FIG. 11, the
(2) 実施の形態1~3に係る根管治療器100では、コードレスタイプの根管治療器でモータユニット6や制御ボックス9を内蔵している構成について説明したが、これに限定されるものではなく、ハンドピース1が、ホース61を介して、外部に設けた制御ボックス9に連結される構成でもよい。図12は、ハンドピース1の外に設けた制御ボックス9とコードで接続された根管治療器100aの構成を示す概略図である。当該根管治療器100aの構成において、図1~図3に示した構成と同じ構成については、同じ符号を付して詳しい説明は繰り返さない。
(2) In the root
図12に示す根管治療器100aは、歯科用根管治療のためのハンドピース1、モータユニット6、制御ボックス9を含んでいる。歯科用根管治療のハンドピース1は、把持部4の基部には、ヘッド部2に保持される切削工具5(ファイル或いはリーマなど)を回転駆動させるためのモータユニット6が着脱自在に接続される。ハンドピース1にモータユニット6が連結された状態で歯科用のインスツルメント10を構成する。
The root canal treatment device 100a shown in FIG. 12 includes a
モータユニット6は、マイクロモータ7を内蔵し、該マイクロモータ7へ電源を供給する電源供給用リード線71および、根管長測定回路12へ信号を伝送する信号用リード線8などを内装するホース61を介して、制御ボックス9に連結してある。
The
制御ボックス9は、図12に示すように、本体側部にインスツルメント10を不使用時に保持するためのホルダ10aを取付けてある。また、制御ボックス9には、フートコントローラ18を制御部11に連結し、リード線19を根管長測定回路12に連結してある。リード線19は、制御ボックス9から引き出されているが、ホース61の途中から分岐するように引き出してもよい。
As shown in FIG. 12, the
設定部14は、制御ボックス9の表面に設定変更するための選択ボタン15bを有しており、当該選択ボタン15bを操作することで切削工具5の回転方向、回転数および回転角度などを制御する基準を設定する。
The setting
操作部15は、制御ボックス9の表面に駆動開始・停止ボタン15aを有しており、当該駆動開始・停止ボタン15aを操作することで切削工具5の駆動を開始または停止することができる。
The
フートコントローラ18は、マイクロモータ7による切削工具5の駆動制御を足踏操作によって行う操作受付部である。なお、マイクロモータ7による切削工具5の駆動制御は、フートコントローラ18に限定されるものではなく、ハンドピース1の把持部4に操作スイッチ(図示せず)を設け、この操作スイッチとフートコントローラ18とを併用して切削工具5の駆動制御を行うようにしてもよい。また、たとえば、フートコントローラ18の足踏操作がなされている状態で、さらに切削工具5が根管内に挿入されたことを根管長測定回路12が検出したことで、切削工具5の回転を開始するようにしてもよい。
The foot controller 18 is an operation reception unit that controls the driving of the
なお、根管治療器100aの制御ボックス9は、歯科用診療台の側部に設置するトレーテーブルやサイドテーブル上に載置して使用する構成について説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されず、トレーテーブルやサイドテーブル内に制御ボックス9を組込んだ構成であってもよい。
The
(3) 実施の形態1~3に係る根管治療器100では、切削工具5を駆動する動力源にマイクロモータ7を用いる場合について説明したが、これに限定されるものではなく、エアモータなどの別の駆動源であってもよい。
(3) In the root
今回開示された実施の形態はすべての点で例示であって制限的なものではないと考えられるべきである。本開示の範囲は、上記した説明ではなく、特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。 The embodiments disclosed herein should be considered to be illustrative and not restrictive in all respects. The scope of the present disclosure is indicated by the claims, not by the above description, and is intended to include all modifications within the meaning and scope of the claims.
1 ハンドピース、2 ヘッド部、3 ネック部、4 把持部、5 切削工具、6 モータユニット、7 マイクロモータ、8 信号用リード線、9 制御ボックス、10 インスツルメント、10a ホルダ、11 制御部、12 根管長測定回路、13 モータドライバ、13a トランジスタスイッチ、13b トランジスタドライバ回路、13c 回転方向切替スイッチ、13d 負荷検出用抵抗、14 設定部、14a,14b,14c 可変抵抗、15 操作部、15a 駆動開始・停止ボタン、15b 選択ボタン、16 表示部、17 報知部、18 フートコントローラ、19 リード線、19a 口腔電極、100,100a 根管治療器、110 比較回路。 1 handpiece, 2 head, 3 neck, 4 grip, 5 cutting tool, 6 motor unit, 7 micromotor, 8 signal lead, 9 control box, 10 instrument, 10a holder, 11 control section, 12 root canal length measurement circuit, 13 motor driver, 13a transistor switch, 13b transistor driver circuit, 13c rotation direction switch, 13d load detection resistor, 14 setting section, 14a, 14b, 14c variable resistor, 15 operation section, 15a drive start/stop button, 15b selection button, 16 display section, 17 notification section, 18 foot controller, 19 lead, 19a oral cavity electrode, 100, 100a root canal treatment device, 110 comparison circuit.
Claims (9)
ハンドピースのヘッド部に保持した、根管を切削するための切削工具を回転駆動する駆動部と、
前記切削工具を回転駆動する前記駆動部を制御する制御部と、
前記切削工具に加わる負荷を検出する負荷検出部と、を備え、
前記制御部は、
前記負荷検出部で検出する前記切削工具に加わる負荷が第2基準負荷以上である場合、前記切削工具が切削対象物を切削する正転駆動、または正転の駆動量が大きいツイスト駆動を、逆転駆動、または逆転の駆動量が大きい前記ツイスト駆動に切り替え、
前記負荷検出部で検出する前記切削工具に加わる負荷が前記第2基準負荷未満である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度の大きさを第3値とし、
前記負荷検出部で検出する前記切削工具に加わる負荷が前記第2基準負荷以上である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度の大きさを前記第3値より大きい第4値として前記駆動部を制御する、歯科用治療装置。 A dental treatment device for treating a root canal of a tooth, comprising:
A drive unit that rotates a cutting tool for cutting a root canal, the cutting tool being held in a head portion of the handpiece;
a control unit that controls the drive unit that rotates the cutting tool;
a load detection unit that detects a load applied to the cutting tool,
The control unit is
when the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit is equal to or greater than a second reference load, switching from a forward drive in which the cutting tool cuts an object to be cut or a twist drive having a large amount of forward drive to a reverse drive or the twist drive having a large amount of reverse drive;
when the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit is less than the second reference load, a magnitude of the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during a start period and a stop period is set to a third value;
A dental treatment device that controls the drive unit to set the magnitude of rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during the start-up period and the stop period to a fourth value greater than the third value when the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit is equal to or greater than the second reference load .
前記負荷検出部で検出する前記切削工具に加わる負荷が前記第2基準負荷より小さい第1基準負荷未満である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度の大きさを第1値とし、
前記負荷検出部で検出する前記切削工具に加わる負荷が前記第1基準負荷以上である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度の大きさを前記第1値より大きい第2値として前記駆動部を制御する、請求項1に記載の歯科用治療装置。 The control unit is
when the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit is less than a first reference load that is less than the second reference load, a magnitude of rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during a start period and a stop period is set to a first value;
The dental treatment device of claim 1, wherein when the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit is equal to or greater than the first reference load, the magnitude of the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during the start-up period and the stop period is controlled to a second value greater than the first value, and the drive unit is controlled.
前記切削工具を回転駆動する回転速度を設定することができ、
設定した回転速度に応じて前記切削工具の回転加速度を変更するように前記駆動部を制御する、請求項1~請求項3のいずれか1項に記載の歯科用治療装置。 The control unit is
A rotation speed at which the cutting tool is rotated can be set,
The dental treatment apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the drive unit is controlled so as to change the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool in accordance with a set rotational speed.
設定した回転速度が基準回転速度以上である場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度を、前記基準回転速度未満である場合に比べて大きくして前記駆動部を制御する、請求項4に記載の歯科用治療装置。 The control unit is
5. The dental treatment device according to claim 4, wherein when the set rotational speed is equal to or higher than a reference rotational speed, the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during the start-up and stop periods is controlled to be greater than when the set rotational speed is less than the reference rotational speed , thereby controlling the drive unit.
前記制御部は、
前記位置検出部で検出する前記切削工具の先端の位置に応じて前記切削工具の回転加速度を変更するように前記駆動部を制御する、請求項1~請求項3のいずれか1項に記載の歯科用治療装置。 a position detection unit that detects a position of a tip of the cutting tool in the root canal obtained by electrical root canal length measurement;
The control unit is
The dental treatment device according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the drive unit is controlled so as to change the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool depending on the position of the tip of the cutting tool detected by the position detection unit.
前記位置検出部で検出した前記切削工具の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖に近い場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度を、前記基準位置より前記根尖から遠い場合に比べて大きくして前記駆動部を制御する、請求項6に記載の歯科用治療装置。 The control unit is
The dental treatment device according to claim 6, wherein when the position of the tip of the cutting tool detected by the position detection unit is closer to the apex than a reference position, the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during the start-up period and the stop period is controlled to be greater than when the tip position is farther from the apex than the reference position.
前記負荷検出部で検出する前記切削工具に加わる負荷に応じて、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度を変更しない第1モードと、
前記負荷検出部で検出する前記切削工具に加わる負荷に応じて、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度を変更する第2モードと、を切り替えることができる、請求項1~請求項3のいずれか1項に記載の歯科用治療装置。 The control unit is
a first mode in which the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during a start period and a stop period is not changed in response to a load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit;
A dental treatment device as described in any one of claims 1 to 3, capable of switching between a first mode in which the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during a start-up period and a stop period is changed depending on the load applied to the cutting tool detected by the load detection unit.
ハンドピースのヘッド部に保持した切削工具を回転駆動する駆動部と、
前記切削工具を回転駆動する前記駆動部を制御する制御部と、
電気的根管長測定で得られる前記切削工具の先端の根管内での位置を検出する位置検出部と、を備え、
前記制御部は、
前記位置検出部で検出した前記切削工具の先端の位置が基準位置より根尖に近い場合、起動する期間および停止させる期間の前記切削工具の回転加速度を、前記基準位置より前記根尖から遠い場合に比べて大きくして前記駆動部を制御する、歯科用治療装置。 A dental treatment device for treating a root canal of a tooth, comprising:
a drive unit that rotates a cutting tool held in a head portion of the handpiece;
a control unit that controls the drive unit that rotates the cutting tool;
a position detection unit that detects a position of the tip of the cutting tool in the root canal obtained by electrical root canal length measurement,
The control unit is
A dental treatment device that controls the drive unit by increasing the rotational acceleration of the cutting tool during the start-up and stop periods when the position of the tip of the cutting tool detected by the position detection unit is closer to the apex than a reference position, compared to when the tip is farther from the apex than the reference position .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022095571A JP7586855B2 (en) | 2022-06-14 | 2022-06-14 | Dental treatment equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022095571A JP7586855B2 (en) | 2022-06-14 | 2022-06-14 | Dental treatment equipment |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2023182143A JP2023182143A (en) | 2023-12-26 |
| JP7586855B2 true JP7586855B2 (en) | 2024-11-19 |
Family
ID=89310260
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022095571A Active JP7586855B2 (en) | 2022-06-14 | 2022-06-14 | Dental treatment equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7586855B2 (en) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012164875A1 (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2012-12-06 | 株式会社ナカニシ | Dental handpiece control device |
| JP2020202896A (en) | 2019-06-14 | 2020-12-24 | 株式会社モリタ製作所 | Dental treatment device |
-
2022
- 2022-06-14 JP JP2022095571A patent/JP7586855B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012164875A1 (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2012-12-06 | 株式会社ナカニシ | Dental handpiece control device |
| JP2020202896A (en) | 2019-06-14 | 2020-12-24 | 株式会社モリタ製作所 | Dental treatment device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2023182143A (en) | 2023-12-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9463076B2 (en) | Dental treating apparatus | |
| JP5870154B2 (en) | Dental treatment apparatus and driving method thereof | |
| EP3597139B1 (en) | Root canal treatment device | |
| JP6826202B2 (en) | Dental treatment equipment and its driving method | |
| US10813717B2 (en) | Dental treatment apparatus and method of driving the same | |
| JP2016198191A (en) | Dental treatment device and driving method thereof | |
| JP6711771B2 (en) | Dental treatment apparatus and driving method thereof | |
| JP7586855B2 (en) | Dental treatment equipment | |
| EP3922206B1 (en) | Dental therapy device and method for driving same | |
| US11925516B2 (en) | Dental treatment apparatus and method of driving the same | |
| JP7057320B2 (en) | Dental treatment equipment | |
| JP2018143631A (en) | Root canal former | |
| JP2019195719A (en) | Dental treatment device and driving method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20231025 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20240628 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20240702 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20240828 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20241105 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20241107 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7586855 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |