JP7399720B2 - X-ray CT device - Google Patents
X-ray CT device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7399720B2 JP7399720B2 JP2020006504A JP2020006504A JP7399720B2 JP 7399720 B2 JP7399720 B2 JP 7399720B2 JP 2020006504 A JP2020006504 A JP 2020006504A JP 2020006504 A JP2020006504 A JP 2020006504A JP 7399720 B2 JP7399720 B2 JP 7399720B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- data
- ray
- transmission
- communication unit
- partial
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 117
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 114
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 59
- NJPPVKZQTLUDBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N novaluron Chemical compound C1=C(Cl)C(OC(F)(F)C(OC(F)(F)F)F)=CC=C1NC(=O)NC(=O)C1=C(F)C=CC=C1F NJPPVKZQTLUDBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000013480 data collection Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims 3
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 claims 3
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 129
- 238000002591 computed tomography Methods 0.000 description 86
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 68
- 238000007781 pre-processing Methods 0.000 description 64
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 19
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 15
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 11
- 239000002872 contrast media Substances 0.000 description 10
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000001015 abdomen Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002238 attenuated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005316 response function Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
Description
本明細書及び図面に開示の実施形態は、X線コンピュータ断層撮影(CT:Computed Tomography)装置に関する。 Embodiments disclosed in this specification and the drawings relate to an X-ray computed tomography (CT) apparatus.
X線CT装置において、フォトンカウンティング(Photon Counting)CTと呼ばれる技術が知られている。フォトンカウンティングCTでは、複数のビンそれぞれでX線フォトンの数をカウントすることにより画像化を行うので、膨大な量のデータが架台装置からコンソール装置に伝送される。例えば、スキャンの実施で得られる情報量が増えると、コンソール装置に送信されるデータ量は大きくなり、データ伝送時間が長くなってしまう。 In X-ray CT apparatuses, a technique called photon counting CT is known. In photon counting CT, imaging is performed by counting the number of X-ray photons in each of a plurality of bins, so a huge amount of data is transmitted from the gantry device to the console device. For example, if the amount of information obtained by performing a scan increases, the amount of data sent to the console device will increase, resulting in a longer data transmission time.
本明細書及び図面に開示の実施形態が解決しようとする課題の一つは、必要な画像を即時的に参照可能にすることである。ただし、本明細書及び図面に開示の実施形態により解決される課題は上記課題に限られない。後述する実施形態に示す各構成による各効果に対応する課題を他の課題として位置づけることもできる。 One of the problems to be solved by the embodiments disclosed in this specification and the drawings is to make necessary images available for immediate reference. However, the problems solved by the embodiments disclosed in this specification and the drawings are not limited to the above problems. Problems corresponding to the effects of each configuration shown in the embodiments described later can also be positioned as other problems.
実施形態に係るX線CT装置は、回転部と、第1の通信部と、第2の通信部と、画像生成部と、を備える。前記回転部は、架台に設けられ、被検体を透過したX線に基づいて、ビュー毎に投影データを収集するデータ収集部を含む。前記第1の通信部は、前記架台に設けられ、前記回転部を支持する固定部、又は前記架台の外部に設けられている。前記第2の通信部は、前記回転部に設けられ、前記投影データのうち、リアルタイム再構成に必要な部分データを優先的に含む送信用データを生成し、前記送信用データを前記第1の通信部に順次送信する。前記画像生成部は、前記第2の通信部が受信した前記送信用データに含まれる前記部分データに基づいて、前記リアルタイム再構成を実行する。 The X-ray CT apparatus according to the embodiment includes a rotating section, a first communication section, a second communication section, and an image generation section. The rotation unit includes a data collection unit that is provided on the pedestal and collects projection data for each view based on the X-rays that have passed through the subject. The first communication unit is provided on the pedestal, and is provided on a fixed part that supports the rotating part, or outside the pedestal. The second communication unit is provided in the rotating unit, generates transmission data that preferentially includes partial data necessary for real-time reconstruction out of the projection data, and transmits the transmission data to the first communication unit. Send sequentially to the communication department. The image generation unit executes the real-time reconstruction based on the partial data included in the transmission data received by the second communication unit.
以下、図面を参照して、X線CT装置の実施形態について詳細に説明する。以下の実施形態で説明するX線CT装置は、フォトンカウンティングCTを実行可能な装置である。すなわち、以下の実施形態で説明するX線CT装置は、フォトンカウンティング方式の検出器を用いて被検体を透過したX線を計数することで、X線CT画像データを再構成可能な装置である。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the X-ray CT apparatus will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. The X-ray CT apparatus described in the following embodiments is an apparatus capable of performing photon counting CT. That is, the X-ray CT apparatus described in the following embodiments is an apparatus that can reconstruct X-ray CT image data by counting the X-rays that have passed through the subject using a photon-counting detector. .
(第1の実施形態)
図1は、第1の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1の構成の一例を示す図である。図1に示すように、第1の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1は、架台装置10と、寝台装置30と、コンソール装置40とを有する。
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of an
なお、本実施形態では、非チルト状態での回転フレーム13の回転軸又は寝台装置30の天板33の長手方向をZ軸方向とする。また、Z軸方向に直交し、床面に対し水平である軸方向をX軸方向とする。また、Z軸方向に直交し、床面に対し垂直である軸方向をY軸方向とする。なお、図1は、説明のために架台装置10を複数方向から描画したものであり、X線CT装置1が架台装置10を1つ有する場合を示す。
In this embodiment, the rotation axis of the rotating
架台装置10は、被検体P(患者)にX線を照射し、被検体Pを透過したX線を検出して、検出したX線に対応するデータをコンソール装置40に出力する装置である。図1に示すように、架台装置10は、X線管11と、X線検出器12と、回転フレーム13と、X線高電圧装置14と、制御装置15と、ウェッジ16と、コリメータ17と、DAS(Data Acquisition System)18とを有する。
The
X線管11は、熱電子を発生する陰極(フィラメント)と、熱電子の衝突を受けてX線を発生する陽極(ターゲット)とを有する真空管である。X線管11は、X線高電圧装置14からの高電圧の印加により、陰極から陽極に向けて熱電子を照射することで、被検体Pに対し照射するX線を発生する。例えば、X線管11には、回転する陽極に熱電子を照射することでX線を発生させる回転陽極型のX線管がある。
The
X線高電圧装置14は、変圧器(トランス)及び整流器等の電気回路を有し、X線管11に印加する高電圧を発生する高電圧発生装置と、X線管11が発生するX線に応じた出力電圧の制御を行うX線制御装置とを有する。高電圧発生装置は、変圧器方式であってもよいし、インバータ方式であってもよい。
The X-ray
ウェッジ16は、X線管11から照射されたX線量を調節するためのフィルタである。具体的には、ウェッジ16は、X線管11から被検体Pへ照射されるX線が、予め定められた分布になるように、X線管11から照射されたX線を透過して減衰するフィルタである。例えば、ウェッジ16は、ウェッジフィルタ(wedge filter)やボウタイフィルタ(bow-tie filter)であり、所定のターゲット角度や所定の厚みとなるようにアルミニウム等を加工したフィルタである。
The
コリメータ17は、ウェッジ16を透過したX線の照射範囲を絞り込むための鉛板等であり、複数の鉛板等の組み合わせによってスリットを形成する。なお、コリメータ17は、X線絞りと呼ばれる場合もある。また、図1においては、X線管11とコリメータ17との間にウェッジ16が配置される場合を示すが、X線管11とウェッジ16との間にコリメータ17が配置される場合であってもよい。この場合、ウェッジ16は、X線管11から照射され、コリメータ17により照射範囲が制限されたX線を透過して減衰させる。
The
X線検出器12は、複数の検出素子を有する光子計数型検出器である。X線検出器12における各検出素子は、X線管11から照射されて被検体Pを通過したX線を検出し、検出したX線の入射に応じて信号をDAS18へと出力する。各検出素子は、X線フォトンが入射するごとに、当該X線フォトンのエネルギー値を計測可能な信号を出力する。X線フォトンは、例えば、X線管11から照射され被検体Pを透過したX線の光子である。各検出素子は、X線フォトンが入射するごとに、1パルスの電気信号(アナログ信号)を出力する。
The
例えば、X線検出器12は、シンチレータアレイと、光センサアレイとを有する間接変換型の検出器である。シンチレータアレイは、複数のシンチレータを有する。シンチレータは、入射したX線フォトンをシンチレータ光に変換する。光センサアレイは、例えば、フォトダイオード等の光センサを有する。光センサは、シンチレータ光を電気信号に変換する。なお、X線検出器12は、入射したX線フォトンを、直接、電気信号に変換する直接変換型の検出器であっても構わない。
For example, the
例えば、図1に示すX線検出器12は、検出素子が、チャンネル方向(X線検出器12の回転方向に沿った方向)にN列、架台装置10が非チルト時の状態における回転フレーム13の回転中心軸方向(図1中のZ軸方向)(列方向、row方向)にM列配置された検出器である。検出素子は、光子が入射すると、1パルスの電気信号を出力する。X線CT装置1は、検出素子が出力した個々のパルスを弁別することで、検出素子に入射したX線フォトンの数を計数することができる。また、X線CT装置1は、パルスの強度に基づく演算処理を行うことで、計数したX線フォトンのエネルギー値を計測することができる。
For example, in the
DAS18は、ビュー(View)毎に、X線検出器12から出力されるデータを収集するデータ収集回路である。X線検出器12から出力されるデータは、計数処理の結果である計数結果を表し、後述する前処理を施す前の投影データである。例えば、DAS18は、X線検出器12の各検出素子から出力される電気信号に対して増幅処理を行う増幅器と、電気信号をデジタル信号に変換するA/D変換器とを有する。DAS18は、例えば、プロセッサにより実現される。DAS18は、X線管11から照射されて被検体Pを透過したX線に由来する光子(X線フォトン)を計数し、当該計数した光子のエネルギーを弁別した結果を計数結果として収集する。例えば、回転フレーム13の回転中に、X線管11からX線が連続曝射されている場合、DAS18は、全周囲分(360度分)の計数結果を収集する。そして、DAS18は、計数結果をコンソール装置40に送信する。
The
例えば、DAS18は、X線検出器12の検出素子が出力した各パルスを弁別して計数したX線フォトンの入射位置(検出位置)と、当該X線フォトンのエネルギー値とを計数結果として、X線管11の位置(管球位置)ごとに収集する。入射位置は、例えば、計数に用いたパルスが出力された際の検出素子の位置である。また、DAS18は、例えば、パルスのピーク値とシステム固有の応答関数とからエネルギー値を演算する。或いは、DAS18は、例えば、パルスの強度を積分することで、エネルギー値を演算する。DAS18は、演算したエネルギー値を、例えば、比較器(コンパレータ)を用いて、複数のエネルギー弁別域(エネルギービン)に振り分ける。複数のエネルギー弁別域(エネルギービン)に振り分けられた計数結果は、エネルギーに応じた光子数の分布を示すエネルギースペクトルとなる。以下、エネルギービンを、単に、ビンと記載する。
For example, the
回転フレーム13は、X線管11とX線検出器12とを対向支持し、制御装置15によってX線管11とX線検出器12とを回転させる円環状のフレームである。例えば、回転フレーム13は、アルミニウムを材料とした鋳物である。なお、回転フレーム13は、X線管11及びX線検出器12に加えて、X線高電圧装置14やウェッジ16、コリメータ17、DAS18等を更に支持することもできる。更に、回転フレーム13は、図1において図示しない種々の構成を更に支持することもできる。
The rotating
制御装置15は、CPU(Central Processing Unit)等を有する処理回路と、モータ及びアクチュエータ等の駆動機構とを有する。制御装置15は、後述する入力インターフェース43からの入力信号を受けて、架台装置10及び寝台装置30の動作制御を行う。例えば、制御装置15は、回転フレーム13の回転や架台装置10のチルト、寝台装置30及び天板33の動作等について制御を行う。一例を挙げると、制御装置15は、架台装置10をチルトさせる制御として、入力された傾斜角度(チルト角度)情報により、X軸方向に平行な軸を中心に回転フレーム13を回転させる。なお、制御装置15は架台装置10に設けられてもよいし、コンソール装置40に設けられてもよい。
The
寝台装置30は、撮影対象の被検体Pを載置、移動させる装置である。図1に示すように、寝台装置30は、基台31と、寝台駆動装置32と、天板33と、支持フレーム34とを有する。基台31は、支持フレーム34を鉛直方向に移動可能に支持する筐体である。寝台駆動装置32は、被検体Pが載置された天板33を、天板33の長軸方向に移動する駆動機構であり、モータ及びアクチュエータ等を含む。支持フレーム34の上面に設けられた天板33は、被検体Pが載置される板である。なお、寝台駆動装置32は、天板33に加え、支持フレーム34を天板33の長軸方向に移動してもよい。
The
コンソール装置40は、操作者によるX線CT装置1の操作を受け付けるとともに、架台装置10によって収集されたデータ(計数結果)を用いてX線CT画像データを再構成する装置である。図1に示すように、コンソール装置40は、メモリ41と、ディスプレイ42と、入力インターフェース43と、処理回路44とを有する。なお、コンソール装置40は架台装置10とは別体として説明するが、架台装置10にコンソール装置40又はコンソール装置40の各構成要素の一部が含まれてもよい。
The
メモリ41は、例えば、RAM(Random Access Memory)、フラッシュメモリ等の半導体メモリ素子、ハードディスク、光ディスク等により実現される。メモリ41は、例えば、投影データやCT画像データを記憶する。また、例えば、メモリ41は、X線CT装置1に含まれる回路がその機能を実現するためのプログラムを記憶する。なお、メモリ41は、X線CT装置1とネットワークを介して接続されたサーバ群(クラウド)により実現されることとしてもよい。
The
ディスプレイ42は、各種の情報を表示する。例えば、ディスプレイ42は、処理回路44によって生成された各種の画像を表示したり、操作者から各種の操作を受け付けるためのGUI(Graphical User Interface)を表示したりする。例えば、ディスプレイ42は、液晶ディスプレイやCRT(Cathode Ray Tube)ディスプレイである。なお、ディスプレイ42は、架台装置10に設けられてもよい。また、ディスプレイ42は、デスクトップ型でもよいし、コンソール装置40本体と無線通信可能なタブレット端末等で構成されることにしても構わない。
The display 42 displays various information. For example, the display 42 displays various images generated by the
入力インターフェース43は、操作者から各種の入力操作を受け付けて、受け付けた入力操作を電気信号に変換して処理回路44に出力する。例えば、入力インターフェース43は、X線CT画像データの撮影条件や、CT画像データを再構成する際の再構成条件や、CT画像データから後処理画像を生成する際の画像処理条件等の入力操作を操作者から受け付ける。例えば、入力インターフェース43は、マウスやキーボード、トラックボール、スイッチ、ボタン、ジョイスティック、操作面へ触れることで入力操作を行うタッチパッド、表示画面とタッチパッドとが一体化されたタッチスクリーン、光学センサを用いた非接触入力回路、音声入力回路等により実現される。なお、入力インターフェース43は、架台装置10に設けられてもよい。また、入力インターフェース43は、コンソール装置40本体と無線通信可能なタブレット端末等で構成されることにしても構わない。また、入力インターフェース43は、マウスやキーボード等の物理的な操作部品を備えるものだけに限られない。例えば、コンソール装置40とは別体に設けられた外部の入力機器から入力操作に対応する電気信号を受け取り、この電気信号を処理回路44へ出力する電気信号の処理回路も入力インターフェース43の例に含まれる。
The input interface 43 receives various input operations from an operator, converts the received input operations into electrical signals, and outputs the electrical signals to the
処理回路44は、X線CT装置1全体の動作を制御する。例えば、処理回路44は、システム制御機能440、スキャン制御機能441、前処理機能442、再構成処理機能443、及び、表示制御機能444を実行する。
The
システム制御機能440は、入力インターフェース43を介して操作者から受け付けた入力操作に基づいて、処理回路44の各種機能を制御する。
The system control function 440 controls various functions of the
スキャン制御機能441は、当該被検体Pに対してX線を利用したスキャンを実行する。例えば、スキャン制御機能441は、入力インターフェース43を介して操作者から受け付けた入力操作に基づいて、スキャンを制御する。具体的には、スキャン制御機能441は、入力操作に基づいて、X線高電圧装置14に制御信号を送信することで、高電圧発生装置からの出力電圧を制御する。また、スキャン制御機能441は、DAS18に制御信号を送信することで、DAS18によるデータ収集を制御する。
The scan control function 441 executes a scan of the subject P using X-rays. For example, the scan control function 441 controls scanning based on an input operation received from an operator via the input interface 43. Specifically, the scan control function 441 controls the output voltage from the high voltage generator by transmitting a control signal to the X-ray
前処理機能442は、DAS18から送信されたデータ(計数結果)に対して前処理を行うことで、前処理を施したデータを生成する。具体的には、前処理機能442は、対数変換処理や、オフセット補正、感度補正、ビームハードニング補正等の補正処理を行なうことで、前処理を施したデータを生成する。また、前処理機能442は、生成したデータをメモリ41に格納する。以下、DAS18から送信されたデータを、単に、投影データと称し、前処理機能442によって前処理を施した投影データを、前処理後の投影データと称する。前処理機能442は、合成部の一例である。
The
再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された前処理後の投影データを種々の再構成法(例えば、FBP(Filtered Back Projection)などの逆投影法や、逐次近似法など)によって再構成することでCT画像データを生成する。また、再構成処理機能443は、生成したCT画像データをメモリ41に格納する。再構成処理機能443は、画像生成部の一例である。
The
ここで、フォトンカウンティングCTで得られる計数結果から生成された投影データには、被検体Pを透過することで減弱されたX線のエネルギースペクトルの情報が含まれている。このため、再構成処理機能443は、例えば、特定のエネルギー成分を画像化したX線CT画像データ(エネルギー弁別画像データ)を再構成することができる。また、再構成処理機能443は、例えば、複数のエネルギー成分それぞれのX線CT画像データを再構成することができる。
Here, the projection data generated from the counting results obtained by photon counting CT includes information on the energy spectrum of the X-rays attenuated by passing through the subject P. Therefore, the
また、再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された前処理後の投影データから、確認用のCT画像データを生成することができる。ここで、確認用のCT画像データは、リアルタイム再構成画像とも呼ばれる。
Further, the
表示制御機能444は、処理回路44によって生成された各種の画像をディスプレイ42に表示させる。例えば、表示制御機能444は、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたCT画像データをディスプレイ42に表示させる。
The display control function 444 causes the display 42 to display various images generated by the
図1に示すX線CT装置1においては、各処理機能がコンピュータによって実行可能なプログラムの形態でメモリ41へ記憶されている。処理回路44は、メモリ41からプログラムを読み出して実行することで各プログラムに対応する機能を実現するプロセッサである。換言すると、各プログラムを読み出した状態の処理回路44は、読み出したプログラムに対応する機能を有することとなる。
In the
なお、上記説明において用いた「プロセッサ」という文言は、例えば、CPU(Central Processing Unit)、GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)、特定用途向け集積回路(Application Specific Integrated Circuit:ASIC)、プログラマブル論理デバイス(例えば、単純プログラマブル論理デバイス(Simple Programmable Logic Device:SPLD)、複合プログラマブル論理デバイス(Complex Programmable Logic Device:CPLD)、及びフィールドプログラマブルゲートアレイ(Field Programmable GateArray:FPGA))等の回路を意味する。プロセッサが例えばCPUである場合、プロセッサは記憶回路に保存されたプログラムを読み出し実行することで機能を実現する。一方、プロセッサが例えばASICである場合、記憶回路にプログラムを保存する代わりに、プロセッサの回路内にプログラムを直接組み込まれる。なお、本実施形態の各プロセッサは、プロセッサごとに単一の回路として構成される場合に限らず、複数の独立した回路を組み合わせて1つのプロセッサとして構成し、その機能を実現するようにしてもよい。さらに、図1における複数の構成要素を1つのプロセッサへ統合してその機能を実現するようにしてもよい。 Note that the word "processor" used in the above description refers to, for example, a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), an Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC), a programmable logic device (for example, Refers to circuits such as a simple programmable logic device (SPLD), a complex programmable logic device (CPLD), and a field programmable gate array (FPGA). When the processor is, for example, a CPU, the processor realizes its functions by reading and executing a program stored in a storage circuit. On the other hand, if the processor is, for example, an ASIC, the program is directly incorporated into the processor's circuitry instead of storing the program in a memory circuit. Note that each processor of this embodiment is not limited to being configured as a single circuit for each processor, but may also be configured as a single processor by combining multiple independent circuits to realize its functions. good. Furthermore, a plurality of components in FIG. 1 may be integrated into one processor to realize its functions.
図2は、第1の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1のデータ伝送を説明するための図である。例えば、DAS18が生成した投影データは、通信機52から通信機51に送信され、コンソール装置40へと転送される。ここで、通信機51は、第1の通信部の一例であり、通信機52は、第2の通信部の一例である。
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining data transmission of the
通信機52は、例えば、架台装置10の回転フレーム13に設けられている。例えば、通信機52は、回転フレーム13に設けられたDAS18に搭載されている。通信機51は、例えば、架台装置10の固定フレーム19に設けられている。固定フレーム19は、架台装置10の非回転部分であり、回転フレーム13を回転可能に支持する。又は、通信機51は、例えば、架台装置10の外部に設けられている。なお、通信機51は、別のところに設けられてもよく、例えば、制御装置15に搭載されてもよい。
The
ここで、回転フレーム13は、回転部の一例であり、固定フレーム19は、固定部の一例である。具体的には、架台装置10は、回転部側ユニットと、固定部側ユニットとに分けられる。回転部側ユニットは、例えば、回転フレーム13、X線管11、X線検出器12、X線高電圧装置14、ウェッジ16、コリメータ17、DAS18、通信機52などを含む。固定部側ユニットは、例えば、固定フレーム19、制御装置15、通信機51などを含む。
Here, the rotating
例えば、スキャンが実施される場合、コンソール装置40のスキャン制御機能441から架台装置10の固定部側ユニットの通信機51に制御信号が送信される。そして、架台装置10において、当該制御信号が固定部側ユニットの通信機51から図示しないスリップリングを介して回転部側ユニットの通信機52に送信される。ここで、コンソール装置40から架台装置10への伝送径路を、アップリンクと記載する場合がある。
For example, when a scan is performed, a control signal is transmitted from the scan control function 441 of the
例えば、架台装置10において、スキャンの実施により、回転部側ユニットのDAS18により投影データが収集される。このとき、DAS18により収集された投影データが、回転部側ユニットの通信機52からスリップリングを介して固定部側ユニットの通信機51に送信される。そして、当該投影データが固定部側ユニットの通信機51からコンソール装置40に送信される。ここで、架台装置10からコンソール装置40への伝送径路を、ダウンリンクと記載する場合がある。
For example, in the
以上、本実施形態に係るX線CT装置1の全体構成について説明した。かかる構成のもと、第1の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1は、フォトンカウンティングCTによりX線CT画像データを再構成する。
The overall configuration of the
ところで、フォトンカウンティングCTでは、膨大な量の投影データが架台装置10の回転部側ユニットからスリップリング、固定部側ユニットを経由してコンソール装置40に伝送される。例えば、スキャンの実施で得られる情報量が増えると、コンソール装置40に送信される投影データのデータ量は大きくなり、コンソール装置40に投影データを送りきる時間が長くなる。例えば、フォトンカウンティングCTでは、従来型の積分型検出器を用いたX線CT装置に比べてビン数が増えるため、データ量は大幅に大きくなり、データ伝送時間が長くなってしまう。データ伝送時間を短くする方法として、ダウンリンクのレーン数を増やすなどの方法がある。しかし、スリップリングのレーン数も増やす必要があり、コストアップや装置の大型を招いてしまう。
By the way, in photon counting CT, a huge amount of projection data is transmitted from the rotating section side unit of the
そこで、本実施形態に係るX線CT装置1は、膨大な量の投影データを伝送する際に必要な画像を即時的に参照可能にするために、以下の処理を実行する。本実施形態に係るX線CT装置1は、回転部側ユニットと、通信機51と、通信機52と、再構成処理機能443とを備える。回転部側ユニットは、架台装置10に設けられ、被検体Pを透過したX線に基づいて、ビュー毎に投影データを収集するDAS18を含む。通信機51は、架台装置10に設けられ、回転部側ユニットを支持する固定部側ユニット、又は、架台装置10の外部に設けられている。通信機52は、回転部側ユニットに設けられ、投影データのうち、リアルタイム再構成に必要な部分データを優先的に含む送信用データを生成し、送信用データを通信機51に順次送信する。再構成処理機能443は、通信機51が受信した送信用データに含まれる部分データに基づいて、リアルタイム再構成を実行する。
Therefore, the
本実施形態に係るX線CT装置1による処理について具体的に説明する。本実施形態に係るX線CT装置1は、DAS18により収集される投影データのデータ量に応じて、データ伝送方式を、投影データのうち、リアルタイム再構成に必要な部分データを優先的に送信する第1のデータ伝送方式、又は、投影データを送信する第2のデータ伝送方式に切り替える。
Processing by the
具体的には、まず、検査技師等の操作者は、コンソール装置40を用いて、入力操作を行う。このとき、スキャン制御機能441は、入力インターフェース43を介して操作者から受け付けた当該入力操作に基づいて、検査が行われる患者の患者情報を取得し、取得した患者情報を表す画面をディスプレイ42に表示させる。このとき、スキャン制御機能441は、スキャン計画の設定を受け付ける。次に、操作者は、取得した患者情報を基に、例えば被検体P(患者)の腹部を撮影するスキャン計画を作成する。ここで、スキャン計画の設定を受け付けた際にディスプレイ42に表示される画面は、リアルタイム再構成を実行するか否かを選択するためのチェックボックス等のボタンを含む。操作者が当該ボタンを操作した場合、スキャン制御機能441は、スキャン計画にリアルタイム再構成を設定する。
Specifically, first, an operator such as a laboratory technician performs an input operation using the
次に、コンソール装置40のスキャン制御機能441から制御信号が架台装置10の固定部側ユニットに送信される。当該制御信号は、例えば、X線高電圧装置14が発生する出力電圧を制御したり、DAS18にデータ収集を実行させたりする信号である。また、当該制御信号は、リアルタイム再構成が設定されたスキャン計画を表す情報を含む。固定部側ユニットにおいて、例えば通信機51を搭載する制御装置15は、当該制御信号に含まれるスキャン計画に基づいて、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集される投影データのデータ量を計算する。DAS18によりビュー毎に収集される投影データは、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データである。そして、制御装置15は、スキャン計画から、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tvを計算し、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビューに対応する期間Tv以内で送りきれるか否かを判定する。
Next, a control signal is transmitted from the scan control function 441 of the
ここで、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビュー以内で送りきれると判定された場合、通信機51は、第2のデータ伝送方式に切り替えるための切替信号を当該制御信号に組み込んで、回転部側ユニットに送信する。この場合、回転部側ユニットにおいて、通信機52は、当該制御信号に含まれる切替信号に応じて、実行するデータ伝送方式を、第2のデータ伝送方式に切り替える。
Here, if it is determined that the projection data of each view obtained by performing the scan can be transmitted within one view, the
一方、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビュー以内で送りきれないと判定された場合、通信機51は、第1のデータ伝送方式に切り替えるための切替信号を当該制御信号に組み込んで、回転部側ユニットに送信する。この場合、回転部側ユニットにおいて、通信機52は、当該制御信号に含まれる切替信号に応じて、実行するデータ伝送方式を、第1のデータ伝送方式に切り替える。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the projection data of each view obtained by scanning cannot be sent within one view, the
図3は、第1の実施形態における第2のデータ伝送方式の一例を示す図である。図3に示す処理は、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビュー以内で送りきれる場合に実行される処理である。ここで、図3に示すように、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tvは、例えば、DAS18を実現するプロセッサのクロック周期CLKに対応する期間であるものとする。
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating an example of the second data transmission method in the first embodiment. The process shown in FIG. 3 is a process that is executed when the projection data of each view obtained by scanning can be sent within one view. Here, as shown in FIG. 3, it is assumed that the period Tv corresponding to one view is, for example, a period corresponding to the clock cycle CLK of the processor that implements the
架台装置10において、スキャンの実施により、回転部側ユニットのDAS18によりビュー毎に投影データが収集される。回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、第2のデータ伝送方式を実行することにより、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集された投影データを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に順次送信する。上記パケットは、投影データと、当該投影データを識別するために付与されたヘッダー及びフッターとを含む。投影データは、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tv内に送信される。
In the
コンソール装置40において、前処理機能442は、架台装置10から送信された投影データを受信し、受信した投影データに対して前処理を行うことで、前処理後の投影データを生成する。再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された前処理後の投影データを再構成することにより、CT画像データを生成する。表示制御機能444は、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたCT画像データをディスプレイ42に表示させる。
In the
図4は、第1の実施形態における第1のデータ伝送方式の一例を示す図である。図4に示す処理は、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビュー以内で送りきれない場合に実行される処理である。ここで、図4に示すように、図3と同様に、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tvは、例えば、DAS18を実現するプロセッサのクロック周期CLKに対応する期間であるものとする。
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of the first data transmission method in the first embodiment. The process shown in FIG. 4 is a process that is executed when the projection data of each view obtained by scanning cannot be sent within one view. Here, as shown in FIG. 4, similarly to FIG. 3, it is assumed that the period Tv corresponding to one view is, for example, a period corresponding to the clock cycle CLK of the processor that implements the
図4において、第1のデータ伝送方式としては、例えば、データを間引く方式が挙げられる。例えば、データを間引く対象として、チャンネル、列、ビン、ビューなどが挙げられる。 In FIG. 4, the first data transmission method includes, for example, a data thinning method. For example, data can be thinned out by channels, columns, bins, views, etc.
架台装置10において、スキャンの実施により、回転部側ユニットのDAS18によりビュー毎に投影データが収集される。回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、第1のデータ伝送方式を実行することにより、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集された投影データのうち、リアルタイム再構成に必要な部分データを優先的に含む送信用データを生成し、生成した送信用データを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に順次送信する。上記パケットは、送信用データと、当該送信用データを識別するために付与されたヘッダー及びフッターとを含む。送信用データは、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tv内に送信される。
In the
また、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集された投影データのうち、部分データ以外のデータを、パケットにより、当該部分データを優先的に送信した時間とは異なる時間に、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。上記パケットは、部分データ以外のデータと、当該部分データ以外のデータを識別するために付与されたヘッダー及びフッターとを含む。
In addition, the
ここで、回転部側ユニットのDAS18により収集される投影データのデータ量は、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tv内において回転部側ユニットの通信機52が固定部側ユニットの通信機51へ送信できるデータ量の上限より大きく、送信用データのデータ量は、上記送信できるデータ量の上限以下である。又は、上記送信できるデータ量よりも小さい。
Here, the amount of projection data collected by the
具体的には、図4に示す処理では、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、スキャン実施中において、部分データを含む送信用データを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に順次送信する。例えば1ビュー目から5ビュー目において、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、部分データを含む送信用データを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に順次送信する。
Specifically, in the process shown in FIG. 4, the
コンソール装置40において、前処理機能442は、架台装置10から送信された送信用データを受信し、受信した送信用データに対して前処理を行うことで、前処理後の送信用データを生成する。ここで、前処理機能442は、生成した前処理後の送信用データをメモリ41に格納する。再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された前処理後の送信用データに基づいて、リアルタイムに再構成することにより、リアルタイム再構成画像を生成する。ここで、再構成処理機能443は、生成したリアルタイム再構成画像をメモリ41に格納する。また、表示制御機能444は、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたリアルタイム再構成画像をディスプレイ42に表示させる。これにより、操作者は、例えば、スキャンが正しく行われているか否かを確認することができる。
In the
ここで、送信用データ(部分データ)は、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tv内において回転部側ユニットの通信機52が固定部側ユニットの通信機51へ送信できるデータ量よりも小さい。
Here, the transmission data (partial data) is smaller than the amount of data that can be transmitted from the
この場合、例えば1ビュー目から5ビュー目において、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、後から送っても影響がないデータとして、部分データ以外のデータを、期間Tv内で部分データを送信した時間の後の時間に、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。すなわち、部分データ以外のデータを、1ビュー目から5ビュー目に送信用データを送るパケットの空いている部分を用いて送信する。
In this case, for example, from the first view to the fifth view, the
ここで、部分データ以外のデータのうち、例えば1ビュー目から5ビュー目に送信できないデータが存在するものとする。この場合、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、部分データ以外のデータのうち、例えば1ビュー目から5ビュー目に送信できないデータを、DAS18または回転部側ユニット内に設けられたメモリに格納しておく。そして、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、スキャン実施後において、次のスキャンの実施前までに、メモリに格納されたデータを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。
Here, it is assumed that among the data other than the partial data, there is data that cannot be transmitted from the first view to the fifth view, for example. In this case, the
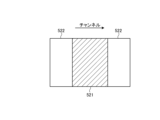
図5~図11は、第1の実施形態における部分データを説明するための図である。第1の実施形態では、第1のデータ伝送方式において、例えば、チャンネルのデータ、及び、列のデータの少なくとも1つを間引く場合や、ビンのデータを間引く場合について説明する。 5 to 11 are diagrams for explaining partial data in the first embodiment. In the first embodiment, a case will be described in which, in the first data transmission method, for example, at least one of channel data and column data is thinned out, or bin data is thinned out.
部分データは、例えば、リアルタイム再構成に必要なデータとして、投影データのうち、チャンネル単位、列単位で少なくとも1つを間引いたデータである。 The partial data is, for example, data necessary for real-time reconstruction, which is data obtained by thinning out at least one of the projection data in units of channels and units of columns.
例えば、部分データが列単位で間引いたデータである場合、図5に示すように、部分データ501は、列方向のデータのうち、例えば、奇数列のデータである。すなわち、部分データ501以外のデータ502として、偶数列のデータが間引かれる。
For example, when the partial data is data thinned out in columns, as shown in FIG. 5, the
例えば、部分データが列単位で間引いたデータである場合、図6に示すように、部分データ511は、列方向のデータのうち、スキャン計画により撮影される被検体Pの腹部に対応する中央部分の列のデータである。すなわち、部分データ511以外のデータ512として、当該中央部分の列のデータ以外のデータが間引かれる。
For example, when the partial data is data thinned out in columns, as shown in FIG. This is the data in the column. That is, as
例えば、部分データがチャンネル単位で間引いたデータである場合、図7に示すように、部分データ521は、チャンネル方向のデータのうち、スキャン計画により撮影される被検体Pの腹部に対応する中央部分のデータである。すなわち、部分データ521以外のデータ522として、当該中央部分のチャンネルのデータ以外のデータが間引かれる。
For example, when the partial data is data thinned out in units of channels, as shown in FIG. This is the data. That is, as
例えば、部分データがチャンネル単位及び列単位で間引いたデータである場合、図8に示すように、部分データ531は、チャンネル方向のデータ、及び、列方向のデータのうち、スキャン計画により撮影される被検体Pの腹部に対応する中央部分のデータである。すなわち、部分データ531以外のデータ532として、当該中央部分のチャンネル及び列のデータ以外のデータが間引かれる。
For example, when the partial data is data thinned out in channel units and column units, as shown in FIG. This is data of the central portion corresponding to the abdomen of the subject P. That is, as
また、投影データは、複数のビンそれぞれで収集されたデータであるため、部分データは、例えば、リアルタイム再構成に必要なデータとして、ビン単位で間引いたデータである。 Furthermore, since the projection data is data collected in each of a plurality of bins, the partial data is, for example, data thinned out in units of bins as data necessary for real-time reconstruction.
例えば、部分データがビン単位で間引いたデータである場合、部分データは、基本となるビンのデータである。すなわち、基本となるビンのデータ以外のデータが間引かれる。 For example, when the partial data is data thinned out in units of bins, the partial data is the data of the basic bin. That is, data other than the data in the basic bin is thinned out.
例えば、撮影に造影剤が用いられる場合、基本となるビンは、造影剤の種類に応じて決定される。具体的には、図9に示すように、造影剤の種類と基本となるビンとを対応付けるテーブルにより決定される。例えば、造影剤の種類として造影剤Aが使用される場合、基本となるビンは、造影剤Aを描出するために適したビンとして、図9に示す3番目のビン「ビン3」が選ばれる。例えば、造影剤の種類として造影剤Bが使用される場合、基本となるビンは、造影剤Bを描出するために適したビンとして、図9に示す4番目のビン「ビン4」が選ばれる。造影剤に関する情報は、例えば、スキャン制御機能441によって、スキャン計画に組み込まれる。 For example, when a contrast agent is used for imaging, the basic bin is determined according to the type of contrast agent. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 9, it is determined by a table that associates the type of contrast agent with the basic bin. For example, when contrast medium A is used as the type of contrast medium, the third bin "bin 3" shown in FIG. 9 is selected as the basic bin suitable for depicting contrast medium A. . For example, when contrast medium B is used as the type of contrast medium, the fourth bin "bin 4" shown in FIG. 9 is selected as the basic bin suitable for depicting contrast medium B. . Information regarding the contrast agent is incorporated into the scan plan, for example by the scan control function 441.
あるいは、通常の撮影を行う場合は、基本となるビンは、X線フォトンのカウント数が多く見込まれるビンが選ばれる。例えば、X線管11から照射されるエネルギースペクトルは、管電圧により変化するため、基本となるビンは、管電圧に応じて決定される。具体的には、図10に示すように、管電圧と基本となるビンとを対応付けるテーブルにより決定される。例えば、管電圧が120keVの場合では、基本となるビンは、図10に示す4番目のビン「ビン4」が選ばれる。例えば、管電圧が80keVの場合では、基本となるビンは、図10に示す3番目のビン「ビン3」が選ばれる。管電圧に関する情報は、例えば、スキャン制御機能441によって、スキャン計画に組み込まれる。
Alternatively, when performing normal imaging, a bin that is expected to have a large number of X-ray photon counts is selected as the basic bin. For example, since the energy spectrum emitted from the
ここで、コンソール装置40において、前処理機能442は、架台装置10から送信された送信用データ(部分データ)と部分データ以外のデータとを受信した場合、パケットのヘッダー及びフッターを参照して、データの形式を整える。具体的には、前処理機能442は、送信用データに含まれる部分データと部分データ以外のデータとを用いて、投影データを合成する。すなわち、前処理機能442は、データを間引く前の投影データを生成する。
Here, in the
例えば、部分データがチャンネル及び列のデータを間引いたデータである場合(図8を参照)では、前処理機能442は、図11に示すように、送信用データに含まれる部分データ531と、部分データ531以外のデータ532とを用いて、投影データを合成する。すなわち、前処理機能442は、チャンネル及び列のデータを間引く前の投影データ530を生成する。
For example, when the partial data is data obtained by thinning out the channel and column data (see FIG. 8), the
また、部分データが列のデータを間引いたデータである場合(図5、図6を参照)では、前処理機能442は、送信用データに含まれる部分データと、部分データ以外のデータとを用いて、投影データを合成する。すなわち、前処理機能442は、列のデータを間引く前の投影データを生成する。
Furthermore, when the partial data is data obtained by thinning out column data (see FIGS. 5 and 6), the
また、部分データがチャンネルのデータを間引いたデータである場合(図7を参照)では、前処理機能442は、送信用データに含まれる部分データと、部分データ以外のデータとを用いて、投影データを合成する。すなわち、前処理機能442は、チャンネルのデータを間引く前の投影データを生成する。
In addition, when the partial data is data obtained by thinning out channel data (see FIG. 7), the
また、部分データがビンのデータを間引いたデータである場合(図9、図10を参照)では、前処理機能442は、送信用データに含まれる部分データと、部分データ以外のデータとを用いて、投影データを合成する。すなわち、前処理機能442は、ビンのデータを間引く前の投影データを生成する。
Furthermore, when the partial data is data obtained by thinning out the bin data (see FIGS. 9 and 10), the
前処理機能442は、合成した投影データに対して前処理を行うことで、前処理後の投影データを生成する。ここで、前処理機能442は、メモリ41に格納された前処理後の送信用データを削除し、生成した前処理後の投影データをメモリ41に格納する。すなわち、送信用データを投影データに置き換える。再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された投影データを再構成することでCT画像データを生成する。ここで、再構成処理機能443は、メモリ41に格納されたリアルタイム再構成画像を削除し、生成したCT画像データをメモリ41に格納する。すなわち、リアルタイム再構成画像をCT画像データに置き換える。表示制御機能444は、必要に応じて、例えば操作者の操作に応じて、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたCT画像データをディスプレイ42に表示させる。
The
図12は、第1の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1による処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing the procedure of processing by the
図12のステップS101では、スキャン制御機能441は、スキャン計画の設定を受け付ける。具体的には、スキャン制御機能441は、入力インターフェース43を介して操作者から受け付けた入力操作に基づいて、検査が行われる患者の患者情報を取得し、取得した患者情報を表す画面をディスプレイ42に表示させる。操作者は、取得した患者情報を基に、例えば被検体P(患者)の腹部を撮影するスキャン計画を作成する。 In step S101 in FIG. 12, the scan control function 441 receives settings for a scan plan. Specifically, the scan control function 441 acquires patient information of the patient to be examined based on input operations received from the operator via the input interface 43, and displays a screen representing the acquired patient information on the display 42. to be displayed. The operator creates a scan plan for photographing the abdomen of the subject P (patient), for example, based on the acquired patient information.
図12のステップS102では、スキャン制御機能441は、受け付けたスキャン計画にリアルタイム再構成が設定されているか否かを判定する。 In step S102 of FIG. 12, the scan control function 441 determines whether real-time reconfiguration is set in the received scan plan.
ここで、受け付けたスキャン計画にリアルタイム再構成が設定されていると判定された場合(ステップS102;Yes)、コンソール装置40のスキャン制御機能441から架台装置10の固定部側ユニットに送信される制御信号は、リアルタイム再構成が設定されたスキャン計画を表す情報を含む。その後、図12のステップS103が実行される。
Here, if it is determined that real-time reconfiguration is set in the received scan plan (step S102; Yes), control is transmitted from the scan control function 441 of the
一方、受け付けたスキャン計画にリアルタイム再構成が設定されていないと判定された場合(ステップS102;No)、コンソール装置40のスキャン制御機能441から架台装置10の固定部側ユニットに送信される制御信号は、リアルタイム再構成が設定されていないスキャン計画を表す情報を含む。その後、図12のステップS104が実行される。
On the other hand, if it is determined that real-time reconfiguration is not set in the received scan plan (step S102; No), a control signal is sent from the scan control function 441 of the
図12のステップS103では、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビュー以内で流しきれるか否かの判定が行われる。具体的には、固定部側ユニットにおいて、例えば通信機51を搭載する制御装置15は、当該制御信号に含まれるスキャン計画に基づいて、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集される投影データのデータ量を計算する。すなわち、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データのデータ量を計算する。そして、制御装置15は、スキャン計画から、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tvを計算し、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビューに対応する期間Tv以内で送りきれるか否かを判定する。
In step S103 of FIG. 12, it is determined whether the projection data of each view obtained by performing the scan can be passed through within one view. Specifically, in the fixed unit, for example, the
ここで、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビュー以内で送りきれると判定された場合(ステップS103;Yes)、図12のステップS104が実行される。 Here, if it is determined that the projection data of each view obtained by performing the scan can be sent within one view (step S103; Yes), step S104 in FIG. 12 is executed.
一方、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビュー以内で送りきれないと判定された場合(ステップS103;No)、図12のステップS105が実行される。 On the other hand, if it is determined that the projection data of each view obtained by scanning cannot be sent within one view (step S103; No), step S105 in FIG. 12 is executed.
図12のステップS104では、第2のデータ伝送方式が実行される。具体的には、固定部側ユニットの通信機51は、第2のデータ伝送方式に切り替えるための切替信号を当該制御信号に組み込んで、回転部側ユニットに送信する。この場合、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、当該制御信号に含まれる切替信号に応じて、実行するデータ伝送方式を、第2のデータ伝送方式に切り替える。
In step S104 of FIG. 12, the second data transmission method is executed. Specifically, the
例えば、架台装置10において、スキャンの実施により、回転部側ユニットのDAS18によりビュー毎に投影データが収集される。回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、第2のデータ伝送方式を実行することにより、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集された投影データを、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に順次送信する。コンソール装置40において、前処理機能442は、架台装置10から送信された投影データを受信し、受信した投影データに対して前処理を行うことで、前処理後の投影データを生成する。再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された前処理後の投影データを再構成することにより、CT画像データを生成する。表示制御機能444は、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたCT画像データをディスプレイ42に表示させる。その後、図12のステップS107が実行される。
For example, in the
図12のステップS105では、第1のデータ伝送方式が実行される。具体的には、固定部側ユニットの通信機51は、第1のデータ伝送方式に切り替えるための切替信号を当該制御信号に組み込んで、回転部側ユニットに送信する。この場合、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、当該制御信号に含まれる切替信号に応じて、実行するデータ伝送方式を、第1のデータ伝送方式に切り替える。その後、図12のステップS106が実行される。
In step S105 of FIG. 12, the first data transmission method is executed. Specifically, the
図12のステップS106では、リアルタイム再構成に必要なデータを最優先で送り、その後、残りのデータを送る処理が行われる。 In step S106 in FIG. 12, the data necessary for real-time reconfiguration is sent with the highest priority, and then the remaining data is sent.
具体的には、例えば、架台装置10において、スキャンの実施により、回転部側ユニットのDAS18によりビュー毎に投影データが収集される。回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、第1のデータ伝送方式を実行することにより、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集された投影データのうち、リアルタイム再構成に必要な部分データを優先的に含む送信用データを生成し、生成した送信用データを、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に順次送信する。
Specifically, for example, in the
コンソール装置40において、前処理機能442は、架台装置10から送信された送信用データを受信し、受信した送信用データに対して前処理を行うことで、前処理後の送信用データを生成する。ここで、前処理機能442は、生成した前処理後の送信用データをメモリ41に格納する。再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された前処理後の送信用データに基づいて、リアルタイムに再構成することにより、リアルタイム再構成画像を生成する。ここで、再構成処理機能443は、生成したリアルタイム再構成画像をメモリ41に格納する。また、表示制御機能444は、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたリアルタイム再構成画像をディスプレイ42に表示させる。これにより、操作者は、例えば、スキャンが正しく行われているか否かを確認することができる。
In the
また、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集された投影データのうち、部分データ以外のデータ(残りのデータ)を、当該部分データを優先的に送信した時間とは異なる時間に、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。
Furthermore, the
図12のステップS107では、次のスキャンがあるか否かの判定が行われる。例えば、固定部側ユニットにおいて、通信機51を搭載する制御装置15は、当該制御信号に含まれるスキャン計画に次のスキャンがあるか否かを判定する。
In step S107 of FIG. 12, it is determined whether there is a next scan. For example, in the fixed unit, the
ここで、次のスキャンがあると判定された場合(ステップS106;Yes)、ステップS102が実行される。 Here, if it is determined that there is a next scan (step S106; Yes), step S102 is executed.
一方、次のスキャンがないと判定された場合(ステップS106;No)、処理が終了する。 On the other hand, if it is determined that there is no next scan (step S106; No), the process ends.
ここで、コンソール装置40において、前処理機能442は、架台装置10から送信された送信用データ(部分データ)と部分データ以外のデータとを受信した場合、パケットのヘッダー及びフッターを参照して、データの形式を整える。すなわち、前処理機能442は、送信用データに含まれる部分データと部分データ以外のデータとを用いて、投影データを合成する。前処理機能442は、合成した投影データに対して前処理を行うことで、前処理後の投影データを生成する。ここで、前処理機能442は、メモリ41に格納された前処理後の送信用データを削除し、生成した前処理後の投影データをメモリ41に格納する。すなわち、送信用データを投影データに置き換える。再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された投影データを再構成することでCT画像データを生成する。ここで、再構成処理機能443は、メモリ41に格納されたリアルタイム再構成画像を削除し、生成したCT画像データをメモリ41に格納する。すなわち、リアルタイム再構成画像をCT画像データに置き換える。表示制御機能444は、必要に応じて、例えば操作者の操作に応じて、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたCT画像データをディスプレイ42に表示させる。
Here, in the
以上、説明したとおり、第1の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1では、架台装置10において、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集される投影データのうち、リアルタイム再構成に必要な部分データを優先的に含む送信用データを生成し、送信用データを固定部側ユニットの通信機51に順次送信する。コンソール装置40において、再構成処理機能443は、通信機51が受信した送信用データに含まれる部分データに基づいて、リアルタイム再構成を実行する。そのため、第1の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1では、部分データを優先的に送信する処理等を行うことにより、必要な画像を即時的に参照可能にすることができる。また、第1の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1では、上記構成により、ダウンリンクのレーン数を増やしたり、スリップリングのレーン数も増やしたりする必要がない。
As described above, in the
(第2の実施形態)
第1の実施形態では、第1のデータ伝送方式において、例えば、チャンネル単位、列単位でデータを間引く場合や、ビン単位でデータを間引く場合について説明した。第2の実施形態では、第1のデータ伝送方式において、例えば、ビュー単位でデータを間引く場合について説明する。以下では、第2の実施形態では、第1の実施形態とは異なる処理を中心に説明する。
(Second embodiment)
In the first embodiment, a case has been described in which, in the first data transmission method, data is thinned out in units of channels or columns, or data is thinned out in units of bins, for example. In the second embodiment, a case will be described in which, for example, data is thinned out in units of views in the first data transmission method. In the following, the second embodiment will be described with a focus on processing that is different from the first embodiment.
図13は、第2の実施形態における第1のデータ伝送方式の一例を示し、第2の実施形態における部分データを説明するための図である。図13に示す処理は、スキャンの実施によって得られる各ビューの投影データが1ビュー以内で送りきれない場合に実行される処理である。ここで、図13に示すように、図4と同様に、1ビュー分に対応する期間Tvは、例えば、DAS18を実現するプロセッサのクロック周期CLKに対応する期間であるものとする。
FIG. 13 shows an example of the first data transmission method in the second embodiment, and is a diagram for explaining partial data in the second embodiment. The process shown in FIG. 13 is a process that is executed when the projection data of each view obtained by scanning cannot be sent within one view. Here, as shown in FIG. 13, similarly to FIG. 4, it is assumed that the period Tv corresponding to one view is a period corresponding to the clock cycle CLK of the processor implementing the
部分データは、例えば、リアルタイム再構成に必要なデータとして、ビュー単位で間引いたデータである。 Partial data is, for example, data that is thinned out in units of views as data necessary for real-time reconstruction.
例えば、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、スキャン計画に基づいて、1ビュー分のデータを送りきるのに要する時間を予測し、当該時間に基づいて、間引くビュー数を決定する。具体的には、例えば、1ビュー分のデータを送りきるのに要する時間Tpが、2ビュー分に対応する期間(2Tv)を超えるが、3ビュー分に対応する期間(3Tv)に達しないものとする(2Tv<Tp<3Tv)。この場合、1ビュー分のデータを送りきるのに、少なくとも3ビュー分に対応する期間を要する。そこで、通信機52は、間引くビュー数を2とし、1ビュー目のデータ、4ビュー目のデータ、7ビュー目のデータ、・・・を部分データとする。すなわち、部分データ以外のデータとして、2ビュー目のデータ、3ビュー目のデータ、5ビュー目のデータ、6ビュー目のデータ、8ビュー目のデータ、9ビュー目のデータ、・・・が間引かれる。
For example, the
具体的には、図13に示す処理では、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、スキャン実施中の1ビュー目のデータ、4ビュー目のデータ、7ビュー目のデータ、・・・を部分データとし、当該部分データを含む送信用データを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。例えば1ビュー目から3ビュー目において、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、部分データである1ビュー目のデータを含む送信用データを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。例えば4ビュー目から6ビュー目において、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、部分データである4ビュー目のデータを含む送信用データを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。例えば7ビュー目から9ビュー目において、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、部分データである7ビュー目のデータを含む送信用データを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。
Specifically, in the process shown in FIG. 13, the
コンソール装置40において、前処理機能442は、架台装置10から送信された送信用データを受信し、受信した送信用データに対して前処理を行うことで、前処理後の送信用データを生成する。ここで、前処理機能442は、生成した前処理後の送信用データをメモリ41に格納する。再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された前処理後の送信用データに基づいて、リアルタイムに再構成することにより、リアルタイム再構成画像を生成する。ここで、再構成処理機能443は、生成したリアルタイム再構成画像をメモリ41に格納する。また、表示制御機能444は、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたリアルタイム再構成画像をディスプレイ42に表示させる。これにより、操作者は、例えば、スキャンが正しく行われているか否かを確認することができる。
In the
ここで、3ビュー目、6ビュー目、9ビュー目において、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、後から送っても影響がないデータとして、部分データ以外のデータを、期間Tv内で部分データを送信した時間の後の時間に、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。すなわち、部分データ以外のデータを、3ビュー目、6ビュー目、9ビュー目に送信用データを送るパケットの空いている部分を用いて送信する。
Here, in the third view, the sixth view, and the ninth view, the
また、部分データ以外のデータのうち、例えば3ビュー目、6ビュー目、9ビュー目に送信できないデータが存在するものとする。この場合、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、部分データ以外のデータのうち、例えば3ビュー目、6ビュー目、9ビュー目に送信できないデータを、DAS18または回転部側ユニット内に設けられたメモリに格納しておく。そして、回転部側ユニットの通信機52は、スキャン実施後において、次のスキャンの実施前までに、メモリに格納されたデータを、パケットにより、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信する。
Furthermore, it is assumed that among the data other than the partial data, there is data that cannot be transmitted in, for example, the third view, the sixth view, and the ninth view. In this case, the
ここで、コンソール装置40において、前処理機能442は、架台装置10から送信された送信用データ(部分データ)と部分データ以外のデータとを受信した場合、パケットのヘッダー及びフッターを参照して、データの形式を整える。具体的には、前処理機能442は、送信用データに含まれる部分データと部分データ以外のデータとを用いて、投影データを合成する。すなわち、前処理機能442は、データを間引く前の投影データを生成する。
Here, in the
例えば、部分データがビューのデータを間引いたデータである場合では、前処理機能442は、送信用データに含まれる部分データと、部分データ以外のデータとを用いて、投影データを合成する。すなわち、前処理機能442は、ビューのデータを間引く前の投影データを生成する。
For example, if the partial data is data obtained by thinning out view data, the
前処理機能442は、合成した投影データに対して前処理を行うことで、前処理後の投影データを生成する。ここで、前処理機能442は、メモリ41に格納された前処理後の送信用データを削除し、生成した前処理後の投影データをメモリ41に格納する。すなわち、送信用データを投影データに置き換える。再構成処理機能443は、前処理機能442により生成された投影データを再構成することでCT画像データを生成する。ここで、再構成処理機能443は、メモリ41に格納されたリアルタイム再構成画像を削除し、生成したCT画像データをメモリ41に格納する。すなわち、リアルタイム再構成画像をCT画像データに置き換える。表示制御機能444は、必要に応じて、例えば操作者の操作に応じて、再構成処理機能443によって生成されたCT画像データをディスプレイ42に表示させる。
The
以上、説明したとおり、第2の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1では、部分データを優先的に送信する処理等を行うことにより、必要な画像を即時的に参照可能にすることができる。また、第2の実施形態に係るX線CT装置1では、上記構成により、ダウンリンクのレーン数を増やしたり、スリップリングのレーン数も増やしたりする必要がない。
As described above, in the
(その他の実施形態)
これまで第1、第2の実施形態について説明したが、上述した第1、第2の実施形態以外にも、種々の異なる形態にて実施されてよいものである。
(Other embodiments)
Although the first and second embodiments have been described so far, the present invention may be implemented in various different forms in addition to the first and second embodiments described above.
上述した実施形態では、チャンネル単位で間引く方法、列単位で間引く方法、ビュー単位で間引く方法、ビン単位で間引く方法について説明したが、これらの方法を組み合わせてもよい。例えば、部分データは、投影データのうち、チャンネル単位、列単位、ビュー単位、ビン単位で少なくとも1つを間引いたデータであってもよい。 In the embodiments described above, the methods of thinning out channels, columns, views, and bins have been described, but these methods may be combined. For example, the partial data may be data obtained by thinning out at least one of the projection data in units of channels, units of columns, units of views, and units of bins.
また、上述した実施形態では、固定部側ユニットの通信機51と回転部側ユニットの通信機52とのデータ伝送は、図示しないスリップリングを介して行われているが、これに限定されない。例えば、固定部側ユニットの通信機51と回転部側ユニットの通信機52とのデータ伝送の手段として、光通信が用いられてもよい。
Further, in the embodiment described above, data transmission between the
また、上述した実施形態では、リアルタイム再構成の設定は、スキャン計画の設定を受け付ける画面で行われているが、これに限定されない。例えば、リアルタイム再構成の設定は、スキャン計画の設定を受け付ける画面とは別の画面で行われてもよい。具体的には、スキャン制御機能441は、スキャン計画の設定を受け付けた際に、スキャン計画の設定を受け付ける画面とは別の画面をディスプレイ42に表示する。ディスプレイ42に表示された別の画面は、リアルタイム再構成を実行するか否かを選択するためのチェックボックス等のボタンを含む。操作者が当該ボタンを操作した場合、スキャン制御機能441は、スキャン計画にリアルタイム再構成を設定する。 Furthermore, in the embodiments described above, the real-time reconfiguration settings are performed on the screen that accepts scan plan settings, but the invention is not limited thereto. For example, real-time reconfiguration settings may be performed on a screen that is separate from the screen that accepts scan plan settings. Specifically, when scan plan settings are accepted, scan control function 441 displays a screen on display 42 that is different from the screen for accepting scan plan settings. Another screen displayed on display 42 includes buttons such as checkboxes for selecting whether to perform real-time reconstruction. When the operator operates the button, the scan control function 441 sets real-time reconstruction in the scan plan.
また、上述した実施形態では、架台装置10が、スキャン計画に基づいて、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集される投影データのデータ量を計算する処理等を行うことによって、実行するデータ伝送方式を決定しているが、これに限定されない。例えば、コンソール装置40が、スキャン計画に基づいて、DAS18によりビュー毎に収集される投影データのデータ量を計算する処理等を行うことによって、実行するデータ伝送方式を決定してもよい。
Furthermore, in the embodiment described above, the
また、上述した実施形態では、回転部側ユニットの通信機52が、スキャン実施後において、次のスキャンの実施前までに、メモリに格納されたデータ(残りのデータ)を、固定部側ユニットの通信機51を介してコンソール装置40に送信しているが、これに限定されない。例えば、回転部側ユニットの通信機52が、次のスキャンの実施までに残りのデータの送信が終わらない場合、次のスキャンの実施中において、残りのデータの送信を引き続き行ってもよい。この場合、通信機52は、残りのデータを、次のスキャンの実施中の期間Tv内において、部分データを送信した時間の後の時間に送信する。
Furthermore, in the above-described embodiment, the
上述した実施形態では、X線CT装置1として、フォトンカウンティングCTを実行可能な装置を例に挙げて説明したが、これに限定されず、例えば、高精細のX線CT装置(以下、高精細CT装置と記載する)に適用してもよい。
In the above-described embodiment, the
高精細CT装置では、X線検出器12として、0.25mm×160列の検出素子を体軸方向に配列することにより、従来型のX線CT装置(例えば、0.5mm×80列の検出素子)に比べてスライス幅が1/2となり、体軸方向において、従来よりも2倍の空間分解能が得られる。また、高精細CT装置では、X線検出器12として、従来型のX線CT装置の2倍のチャンネル数である1792チャンネルの検出素子を面内方向に配列することにより、面内方向において、従来よりも2倍の空間分解能が得られる。ここで、高精細CT装置は、従来型のX線CT装置より高い空間分解能を有するX線検出器12を搭載することにより、X線検出器12により収集される信号が増加する。このため、X線検出器12が信号処理を行うデータ量が増加する。例えば、高精細CT装置では、従来型のX線CT装置に比べてピクセル数が増えるため、データ量は大幅に大きくなり、データ伝送時間が長くなってしまう。したがって、上述した実施形態によるX線CT装置1は、高精細CT装置である場合であっても有効である。すなわち、部分データを優先的に送信する処理等を行うことにより、必要な画像を即時的に参照可能にすることができる。
In a high-definition CT device, the
また、処理回路44は、ネットワークを介して接続された外部装置のプロセッサを利用して、機能を実現することとしてもよい。例えば、処理回路44は、メモリ41から各機能に対応するプログラムを読み出して実行するとともに、X線CT装置1とネットワークを介して接続された外部のワークステーションやクラウドを計算資源として利用することにより、図1に示す各機能を実現する。
Furthermore, the
上述した実施形態に係る各装置の各構成要素は機能概念的なものであり、必ずしも物理的に図示の如く構成されていることを要しない。即ち、各装置の分散・統合の具体的形態は図示のものに限られず、その全部又は一部を、各種の負荷や使用状況などに応じて、任意の単位で機能的又は物理的に分散・統合して構成することができる。更に、各装置にて行われる各処理機能は、その全部又は任意の一部が、CPU及び当該CPUにて解析実行されるプログラムにて実現され、あるいは、ワイヤードロジックによるハードウェアとして実現されうる。 Each component of each device according to the embodiments described above is functionally conceptual, and does not necessarily need to be physically configured as shown in the drawings. In other words, the specific form of distributing and integrating each device is not limited to what is shown in the diagram, and all or part of the devices can be functionally or physically distributed or integrated in arbitrary units depending on various loads and usage conditions. Can be integrated and configured. Furthermore, all or any part of each processing function performed by each device can be realized by a CPU and a program that is analyzed and executed by the CPU, or can be realized as hardware using wired logic.
また、上述した実施形態で説明した制御方法は、予め用意された制御プログラムをパーソナルコンピュータやワークステーション等のコンピュータで実行することによって実現することができる。この制御プログラムは、インターネット等のネットワークを介して配布することができる。また、この制御プログラムは、ハードディスク、フレキシブルディスク(FD)、CD-ROM、MO、DVD等のコンピュータで読み取り可能な記録媒体に記録され、コンピュータによって記録媒体から読み出されることによって実行することもできる。 Further, the control method described in the above-described embodiments can be realized by executing a control program prepared in advance on a computer such as a personal computer or a workstation. This control program can be distributed via a network such as the Internet. Further, this control program can also be executed by being recorded on a computer-readable recording medium such as a hard disk, flexible disk (FD), CD-ROM, MO, DVD, etc., and being read from the recording medium by the computer.
以上説明した少なくとも1つの実施形態によれば、必要な画像を即時的に参照可能にすることができる。 According to at least one embodiment described above, necessary images can be instantly referenced.
いくつかの実施形態を説明したが、これらの実施形態は、例として提示したものであり、発明の範囲を限定することは意図していない。これら実施形態は、その他の様々な形態で実施されることが可能であり、発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲で、種々の省略、置き換え、変更、実施形態同士の組み合わせを行うことができる。これら実施形態やその変形は、発明の範囲や要旨に含まれると同様に、特許請求の範囲に記載された発明とその均等の範囲に含まれるものである。 Although several embodiments have been described, these embodiments are presented by way of example and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. These embodiments can be implemented in various other forms, and various omissions, substitutions, changes, and combinations of embodiments can be made without departing from the gist of the invention. These embodiments and their modifications are included within the scope and gist of the invention as well as within the scope of the invention described in the claims and its equivalents.
1 X線CT装置
10 架台装置
13 回転フレーム
18 DAS
19 固定フレーム
51 通信機
52 通信機
443 再構成処理機能
1
19
Claims (8)
前記架台に設けられ、前記回転部を支持する固定部、又は前記架台の外部に設けられた第1の通信部と、
前記回転部に設けられ、前記投影データのうち、リアルタイム再構成に必要な部分データを優先的に含む送信用データを生成し、前記送信用データを前記第1の通信部に順次送信する第2の通信部と、
前記第1の通信部が受信した前記送信用データに含まれる前記部分データに基づいて、前記リアルタイム再構成を実行する画像生成部と、
を備え、
前記投影データのデータ量は、1ビュー分に対応する期間において前記第2の通信部が前記第1の通信部へ送信できるデータ量の上限より大きく、
前記送信用データのデータ量は、前記送信できるデータ量の上限以下である、又は、前記送信できるデータ量よりも小さい、
X線CT装置。 a rotating part that is provided on the mount and includes a data collection part that collects projection data for each view based on the X-rays that have passed through the subject;
a fixed part provided on the pedestal and supporting the rotating part; or a first communication part provided outside the pedestal;
a second communication unit provided in the rotation unit, which generates transmission data that preferentially includes partial data necessary for real-time reconstruction among the projection data, and sequentially transmits the transmission data to the first communication unit; communications department and
an image generation unit that performs the real-time reconstruction based on the partial data included in the transmission data received by the first communication unit;
Equipped with
The data amount of the projection data is larger than the upper limit of the data amount that the second communication unit can transmit to the first communication unit in a period corresponding to one view,
The amount of data for transmission is less than or equal to the upper limit of the amount of data that can be transmitted, or is smaller than the amount of data that can be transmitted.
X-ray CT device.
前記架台に設けられ、前記回転部を支持する固定部、又は前記架台の外部に設けられた第1の通信部と、a fixed part provided on the pedestal and supporting the rotating part; or a first communication part provided outside the pedestal;
前記回転部に設けられ、前記投影データのうち、リアルタイム再構成に必要な部分データを優先的に含む送信用データを生成し、前記送信用データを前記第1の通信部に順次送信する第2の通信部と、a second communication unit provided in the rotation unit, which generates transmission data that preferentially includes partial data necessary for real-time reconstruction among the projection data, and sequentially transmits the transmission data to the first communication unit; communications department and
前記第1の通信部が受信した前記送信用データに含まれる前記部分データに基づいて、前記リアルタイム再構成を実行する画像生成部と、an image generation unit that performs the real-time reconstruction based on the partial data included in the transmission data received by the first communication unit;
合成部と、a synthesis section;
を備え、Equipped with
前記第2の通信部は、前記投影データのうち、前記部分データ以外のデータを、前記部分データを優先的に送信した時間とは異なる時間に送信し、The second communication unit transmits data other than the partial data among the projection data at a time different from a time when the partial data was preferentially transmitted,
前記合成部は、前記第1の通信部が受信した前記送信用データに含まれる前記部分データと前記部分データ以外のデータとを用いて前記投影データを合成する、The synthesis unit synthesizes the projection data using the partial data included in the transmission data received by the first communication unit and data other than the partial data.
X線CT装置。X-ray CT device.
前記送信用データのデータ量は、前記送信できるデータ量の上限以下である、又は、前記送信できるデータ量よりも小さい、
請求項2に記載のX線CT装置。 The data amount of the projection data is larger than the upper limit of the data amount that the second communication unit can transmit to the first communication unit in a period corresponding to one view,
The amount of data for transmission is less than or equal to the upper limit of the amount of data that can be transmitted, or is smaller than the amount of data that can be transmitted.
The X-ray CT apparatus according to claim 2 .
請求項1~3のいずれか一項に記載のX線CT装置。 The partial data is data obtained by thinning out at least one of the projection data in units of channels, units of columns, units of views, and units of bins.
The X-ray CT apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 3 .
請求項1~4のいずれか一項に記載のX線CT装置。 The second communication unit switches between a first data transmission method that preferentially transmits the partial data and a second data transmission method that transmits the projection data.
The X-ray CT apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 4 .
請求項5に記載のX線CT装置。 The second communication unit switches a data transmission method to be executed to the first data transmission method or the second data transmission method according to a scan plan.
The X-ray CT apparatus according to claim 5 .
請求項1に記載のX線CT装置。 The second communication unit transmits data other than the partial data among the projection data at a time different from a time when the partial data was preferentially transmitted.
The X-ray CT apparatus according to claim 1 .
を更に備えた請求項7に記載のX線CT装置。 a synthesis unit that synthesizes the projection data using the partial data included in the transmission data received by the first communication unit and data other than the partial data;
The X-ray CT apparatus according to claim 7 , further comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020006504A JP7399720B2 (en) | 2020-01-20 | 2020-01-20 | X-ray CT device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020006504A JP7399720B2 (en) | 2020-01-20 | 2020-01-20 | X-ray CT device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021112380A JP2021112380A (en) | 2021-08-05 |
| JP7399720B2 true JP7399720B2 (en) | 2023-12-18 |
Family
ID=77076270
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020006504A Active JP7399720B2 (en) | 2020-01-20 | 2020-01-20 | X-ray CT device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7399720B2 (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006288458A (en) | 2005-04-06 | 2006-10-26 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image diagnostic device and image reconstruction method |
| JP2007037782A (en) | 2005-08-03 | 2007-02-15 | Toshiba Medical Systems Corp | X-ray computer tomographic imaging system |
| US20160189402A1 (en) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-06-30 | General Electric Company | Methods and systems for contrast enhanced imaging with single energy acquisition |
| JP2017131336A (en) | 2016-01-26 | 2017-08-03 | 東芝メディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Photon counting type X-ray CT apparatus |
| JP2020005795A (en) | 2018-07-05 | 2020-01-16 | キヤノンメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Medical image processing apparatus and X-ray CT apparatus |
-
2020
- 2020-01-20 JP JP2020006504A patent/JP7399720B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006288458A (en) | 2005-04-06 | 2006-10-26 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image diagnostic device and image reconstruction method |
| JP2007037782A (en) | 2005-08-03 | 2007-02-15 | Toshiba Medical Systems Corp | X-ray computer tomographic imaging system |
| US20160189402A1 (en) | 2014-12-30 | 2016-06-30 | General Electric Company | Methods and systems for contrast enhanced imaging with single energy acquisition |
| JP2017131336A (en) | 2016-01-26 | 2017-08-03 | 東芝メディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Photon counting type X-ray CT apparatus |
| JP2020005795A (en) | 2018-07-05 | 2020-01-16 | キヤノンメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Medical image processing apparatus and X-ray CT apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021112380A (en) | 2021-08-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7348376B2 (en) | Medical processing equipment, X-ray CT system and processing program | |
| JP7341721B2 (en) | Radiation detector and X-ray CT device | |
| US11328460B2 (en) | X-ray CT system and processing method | |
| JP7179479B2 (en) | X-ray CT device | |
| JP7106392B2 (en) | Sensitivity correction method and photon counting detector | |
| JP2024017481A (en) | X-ray ct apparatus, data collection system, data collection method, and program | |
| JP7399720B2 (en) | X-ray CT device | |
| JP7466401B2 (en) | Medical imaging diagnostic equipment | |
| JP7490333B2 (en) | X-ray CT system and processing program | |
| JP7391499B2 (en) | Radiation detector, radiation diagnostic equipment, and charge sharing determination method | |
| JP7292938B2 (en) | X-ray CT device, X-ray CT system and control program | |
| JP7118798B2 (en) | X-ray computed tomography device | |
| JP7321798B2 (en) | Reconstruction device and radiological diagnosis device | |
| JP2020199086A (en) | X-ray CT system | |
| US20230346323A1 (en) | X-ray ct apparatus | |
| JP7495318B2 (en) | X-ray CT scanner | |
| JP7233911B2 (en) | X-ray CT system and processing program | |
| JP7534123B2 (en) | X-ray detector and X-ray CT device | |
| EP4307015A1 (en) | Photon counting detector (pcd) apparatus and overlapping micro-pixel summing method | |
| JP7555218B2 (en) | X-ray CT apparatus and data transfer method | |
| JP7206163B2 (en) | X-ray CT apparatus, medical information processing apparatus, and medical information processing program | |
| JP2024036754A (en) | X-ray ct apparatus, data processing method and data processing program | |
| JP7199920B2 (en) | X-ray computed tomography device | |
| US20240016459A1 (en) | Overlapping pixel summing scheme in the full size photon counting computed tomography (ct) | |
| JP2022092932A (en) | X-ray computer tomographic apparatus, medical image processing apparatus, and data processing method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20221124 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20230628 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20230801 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20231002 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20231107 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20231206 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 7399720 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |