JP7188738B2 - game machine - Google Patents
game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7188738B2 JP7188738B2 JP2018161494A JP2018161494A JP7188738B2 JP 7188738 B2 JP7188738 B2 JP 7188738B2 JP 2018161494 A JP2018161494 A JP 2018161494A JP 2018161494 A JP2018161494 A JP 2018161494A JP 7188738 B2 JP7188738 B2 JP 7188738B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- game
- data
- area
- main control
- processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
- Slot Machines And Peripheral Devices (AREA)
Description
本発明は、ぱちんこ遊技機(一般的に「パチンコ機」とも称する)や回胴式遊技機(一般に「パチスロ機」とも称する)等の遊技機に関する。 The present invention relates to a game machine such as a pachinko game machine (generally called a "pachinko machine") or a reel-type game machine (generally called a "pachislot machine").
パチンコ機では、遊技領域を転動する遊技球が発生するノイズによって、電子回路へ影響が生じることがある。このため、リセット手段から複数の制御手段へリセット信号を出力する場合に、ノイズによる悪影響を抑えて各制御手段を正確にリセットすることが検討されている。例えば、特許文献1に記載された遊技機では、リセット信号の信号線には、各制御基板毎にバッファがそれぞれ設けられているので、リセット信号を停電監視回路からすべての制御基板へ出力する場合に、ノイズの影響を抑えてリセット信号を正確に出することができる。即ち、停電監視回路と各制御基板とは、ケーブル等により接続されており、その信号線は長くなるが、ノイズの影響を抑えて、リセット信号を確実に出力し、各制御基板に確実にリセットをかけると共に、誤ったリセット信号の出力を防止し、各制御基板が誤ってリセットされることを防止することができる遊技機が記載されている。 In a pachinko machine, noise generated by game balls rolling in a game area may affect electronic circuits. Therefore, when a reset signal is output from a reset means to a plurality of control means, it has been studied to suppress the adverse effects of noise and to accurately reset each control means. For example, in the gaming machine described in
しかし、前述した遊技機ではノイズの影響を抑制し、基板間で信号を確実に伝送するこHowever, in the game machines mentioned above, it is necessary to suppress the effects of noise and reliably transmit signals between boards.
とは考慮されていなかった。was not considered.
本発明は、ノイズによる影響を低減できる遊技機の提供を課題とする。An object of the present invention is to provide a game machine capable of reducing the influence of noise.
本上記課題を解決するために、本発明は、 抽選制御を行い抽選結果に基づいて遊技の進行に係る制御を行う主制御手段と、
前記主制御手段に制御されて遊技に関する情報を表示する表示装置と、
前記表示装置に表示信号を出力する表示信号出力手段と、
リセット信号を出力する初期化手段とを備える遊技機であって、
前記リセット信号は、前記主制御手段と前記表示信号出力手段とへ出力され、
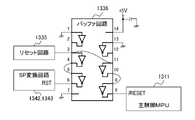
前記初期化手段から前記主制御手段と前記表示信号出力手段に向けて出力される前記リセット信号の経路から分岐した経路であって、前記表示信号出力手段に向かう経路上に信号方向を規制可能に構成された第2の信号方向規制手段を設け、
前記初期化手段から前記主制御手段への前記リセット信号の経路上に前記第2の信号方向規制手段に入力されて前記表示信号出力手段に出力されるリセット信号に同期して前記主制御手段にリセット信号が出力可能に構成された第1の信号方向規制手段を設け、
前記第1の信号方向規制手段は、前記第2の信号方向規制手段と同じようにバッファ回路が複数直列に接続された回路であり、
前記第1の信号方向規制手段と前記第2の信号方向規制手段は、複数のバッファ回路と該バッファ回路の入力と出力に電気的に接続された複数の接続端子を有する同一のワンチップの集積回路である
ことを特徴とする遊技機である。(例えば、段落2413~段落2551、図257~図265などを参照)。
In order to solve the above problems, the present invention provides main control means for performing lottery control and controlling the progress of a game based on the result of the lottery ;
a display device controlled by the main control means to display information about a game;
display signal output means for outputting a display signal to the display device;
A gaming machine comprising initialization means for outputting a reset signal,
the reset signal is output to the main control means and the display signal output means;
A path branched from a path of the reset signal output from the initialization means to the main control means and the display signal output means, the signal direction being able to be regulated on the path toward the display signal output means. a configured second signal direction regulating means;
In synchronism with the reset signal input to the second signal direction regulating means on the path of the reset signal from the initialization means to the main control means and output to the display signal output means, providing first signal direction regulation means configured to output a reset signal;
The first signal direction regulating means is a circuit in which a plurality of buffer circuits are connected in series like the second signal direction regulating means,
Said first signal direction regulating means and said second signal direction regulating means are integrated on the same one chip having a plurality of buffer circuits and a plurality of connection terminals electrically connected to the inputs and outputs of said buffer circuits. is a circuit
It is a gaming machine characterized by (See, eg, paragraphs 2413-2551, FIGS. 257-265, etc.).
本発明によれば、ノイズによる影響を低減できる。According to the present invention, the influence of noise can be reduced.
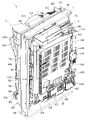
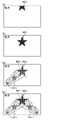
本発明の一実施形態であるパチンコ機1について、図面を参照して詳細に説明する。まず、図1乃至図9を参照して本実施形態のパチンコ機1の全体構成について説明する。図1は本発明の一実施形態であるパチンコ機の正面図である。図2はパチンコ機の右側面図であり、図3はパチンコ機の平面図であり、図4はパチンコ機の背面図である。図5はパチンコ機を前から見た斜視図であり、図6はパチンコ機を後ろから見た斜視図である。図7は本体枠から扉枠3を開放させると共に、外枠2から本体枠4を開放させた状態で前から見たパチンコ機の斜視図である。図8はパチンコ機を扉枠3、遊技盤5、本体枠4、及び外枠2に分解して前から見た分解斜視図であり、図9はパチンコ機を扉枠3、遊技盤5、本体枠4、及び外枠2に分解して後ろから見た分解斜視図である。
A
本実施形態のパチンコ機1は、遊技ホールの島設備(図示しない)に設置される枠状の外枠2と、外枠2の前面を開閉可能に閉鎖する扉枠3と、扉枠3を開閉可能に支持していると共に外枠2に開閉可能に取付けられている本体枠4と、本体枠4に前側から着脱可能に取付けられると共に扉枠3を通して遊技者側から視認可能とされ遊技者によって遊技球
が打込まれる遊技領域5aを有した遊技盤5と、を備えている。
The
パチンコ機1の外枠2は、図8及び図9等に示すように、上下に離間しており左右に延びている上枠部材10及び下枠部材20と、上枠部材10及び下枠部材20の両端同士を連結しており上下に延びている左枠部材30及び右枠部材40と、を備えている。上枠部材10、下枠部材20、左枠部材30、及び右枠部材40は、前後の幅が同じ幅に形成されている。また、上枠部材10及び下枠部材20の左右の長さに対して、左枠部材30及び右枠部材40の上下の長さが、長く形成されている。
As shown in FIGS. 8 and 9, the
また、外枠2は、左枠部材30及び右枠部材40の下端同士を連結し下枠部材20の前側に取付けられる幕板部材50と、上枠部材10の正面視左端部側に取付けられている外枠側上ヒンジ部材60と、幕板部材50の正面視左端側上部と左枠部材30とに取付けられている外枠側下ヒンジ部材70と、を備えている。外枠2の外枠側上ヒンジ部材60と外枠側下ヒンジ部材70とによって、本体枠4及び扉枠3が開閉可能に取付けられている。
The
パチンコ機1の扉枠3は、正面視の外形が四角形で前後に貫通している貫通口111を有した枠状の扉枠ベースユニット100と、扉枠ベースユニット100の前面下部に取付けられ遊技球を貯留可能な上皿201及び下皿202を有した皿ユニット200と、扉枠ベースユニット100の前面上部に取付けられるトップユニット350と、扉枠ベースユニット100の前面左部に取付けられる左サイドユニット400と、扉枠ベースユニット100の前面右部に取付けられる右サイドユニット450と、扉枠ベースユニット100の前面右下部に皿ユニット200を貫通して取付けられ上皿201に貯留された遊技球を遊技盤5の遊技領域内へ打込むために遊技者が操作可能なハンドルユニット500と、扉枠ベースユニット100の後面下部に取付けられ遊技領域内へ打ち損じた遊技球を受けて皿ユニット200の下皿202へ排出するファールカバーユニット520と、扉枠ベースユニット100の後面下部に取付けられ上皿201の遊技球を球発射装置680へ送るための球送りユニット540と、扉枠ベースユニット100の後面に取付けられ貫通口111を閉鎖するガラスユニット560と、ガラスユニット560の後面下部を覆う防犯カバー580と、を備えている。
The
パチンコ機1の本体枠4は、一部が外枠2の枠内に挿入可能とされると共に遊技盤5の外周を支持可能とされた枠状の本体枠ベース600と、本体枠ベース600の正面視左側の上下両端に取付けられ外枠2の外枠側上ヒンジ部材60及び外枠側下ヒンジ部材70に夫々回転可能に取付けられると共に扉枠3の扉枠側上ヒンジ部材140及び扉枠側下ヒンジ部材150が夫々回転可能に取付けられる本体枠側上ヒンジ部材620及び本体枠側下ヒンジ部材640と、本体枠ベース600の正面視左側面に取付けられる補強フレーム660と、本体枠ベース600の前面下部に取付けられており遊技盤5の遊技領域5a内に遊技球を打込むための球発射装置680と、本体枠ベースの正面視右側面に取付けられており外枠2と本体枠4、及び扉枠3と本体枠4の間を施錠する施錠ユニット700と、本体枠ベース600の正面視上辺及び左辺に沿って後側に取付けられており遊技者側へ遊技球を払出す逆L字状の払出ユニット800と、本体枠ベース600の後面下部に取付けられている基板ユニット900と、本体枠ベース600の後側に開閉可能に取付けられ本体枠ベース600に取付けられた遊技盤5の後側を覆う裏カバー980と、を備えている。
The
裏カバー980の内部には、パチンコ機1で行われる遊技の進行にかかる制御を行う主制御ユニット1300が設けられる。主制御ユニット1300には役物比率表示器1317が設けられる。役物比率表示器1317は、例えば、4桁の7セグメントLEDによって構成される。液晶表示装置によって役物比率表示器1317を構成してもよい。なお、役物比率表示器1317を主制御ユニット1300ではなく、払出制御基板ユニット95
0に設けられてもよい。
Inside the
It may be set to 0.
また、役物比率を表示する表示装置を別に設けず、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244に役物比率を表示してもよい。この場合、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244のいずれかに役物比率を常時表示すると、役物比率を遊技者に報知でき、遊技者がパチンコ機の調子を確認できてよい。
Also, the character product ratio may be displayed on the liquid
役物比率は、後述するように、役物獲得球数÷総獲得球数で計算でき、例えば役物比率の数値が高い(例えば、90%)のパチンコ機は、大当たりによって多くの賞球が得られているので、調子がよいといえる。一方、役物比率の数値が低い(例えば、10%)のパチンコ機は、大当たり遊技が少なく、大当たり中の賞球が少ないので、調子が悪いといえる。したがって、遊技者は、役物比率の数値を考慮して、遊技するパチンコ機を選択できる。 As will be described later, the role ratio can be calculated by dividing the number of balls won by the total number of balls won. Since it is obtained, it can be said that it is in good condition. On the other hand, a pachinko machine with a low accessory ratio (for example, 10%) has few jackpot games and few prize balls during the jackpot, so it can be said to be in poor condition. Therefore, the player can select the pachinko machine to play in consideration of the value of the accessory ratio.
遊技者に役物比率を報知する態様として、役物比率の数値をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示してもよい。例えば、役物比率が70%以上の場合は赤色で数値を表示し、枠ランプを赤点灯または点滅し、69%~30%の場合は緑色で数値を表示し、枠ランプを緑点灯または点滅する。役物比率の数値は、装飾図柄と間違えないような態様で表示するとよい。例えば、変動していないときの装飾図柄の表示位置と重ならない位置に表示したり、役物比率を示す数字の大きさを装飾図柄より小さくするなどの態様で表示するとよい。表示態様は何段階に分けてもよい。
As a mode for notifying the player of the role ratio, the numerical value of the role ratio may be displayed on the main liquid
また、役物比率の数値によってメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される装飾図柄の態様を変えて、役物比率を遊技者に報知してもよい。例えば、役物比率が70%以上の場合は赤色で装飾図柄を表示し、枠ランプを赤点灯または点滅し、69%~30%の場合は緑色で装飾図柄を表示し、枠ランプを緑点灯または点滅する。表示態様は何段階に分けてもよい。
Also, the aspect of the decorative pattern displayed on the main liquid
また、扉枠3に備わる液晶表示装置244に表示してもよい。その際、上述した表示態様を変えてもよいし、役物比率だけでなく、他の情報とともに表示してもよい。他の情報とは、大当たり回数や大当たりの連続回数(所謂、連チャン回数)や持ち球数、残り残金などである。
Alternatively, the information may be displayed on the liquid
また、役物比率に限らず、後述する連続役物比率やベース値などを、前述したように態様を変化させて表示してもよい。役物比率、連続役物比率、ベース値は、各々表示態様を変えてもよい。 Further, not only the character product ratio, but also a continuous character product ratio, a base value, and the like, which will be described later, may be displayed by changing the mode as described above. The character product ratio, the continuous character product ratio, and the base value may be displayed in different ways.
主制御ユニット1300は、図13に示すように、一度閉めたら破壊せずに開けることができない構造で封印された透明の樹脂製の主制御基板ボックス1320に封入されており、プリント基板上に配置された部品を外部から見ることができる。さらに、例えば、裏カバー980が透明な樹脂で形成されている場合、パチンコ機1の裏面側から主制御ユニット1300を見ることができ、主制御ユニット1300に設けられる役物比率表示器1317をパチンコ機1の裏面側から見ることができる。役物比率表示器1317を主制御基板ボックス1320内に封入することによって、パチンコ機1の射幸性を低く見せるための役物比率表示器1317の不正な改造を防止でき、パチンコ機1の正確な射幸性を表示できる。
As shown in FIG. 13, the
なお、裏カバー980が不透明な樹脂で形成されている場合、役物比率表示器1317の位置の裏カバー980に穴を開けたり、役物比率表示器1317の位置を透明にすることによって、パチンコ機1の裏面側から役物比率表示器1317を見られるようにしても
よい。
If the
また、裏カバー980が透明な樹脂で形成されている場合でも、役物比率表示器1317の位置の裏カバー980の表面を平坦に形成したり、裏カバー980を薄く形成することによって、役物比率表示器1317をパチンコ機1の裏面側から見やすくしてもよい。
Further, even when the
パチンコ機1の裏面下方には、アウト口1111や入賞口2001、2005、2006などを経由して遊技領域5aから流出した遊技球を集合し、パチンコ機1の外部に排出する排出口が設けられている。なお、排出口から排出された遊技球は、島設備を通じて球タンク802に供給される。本実施例のパチンコ機1には、排出口から排出される遊技球を検出する排出球センサ3060を設ける。
At the bottom of the back surface of the
図13に示すように、主制御ユニット1300には表示スイッチ1318が設けられる。主制御基板ボックス1320には、表示スイッチ1318が操作可能な穴が設けられる。表示スイッチ1318の近傍のプリント基板上又は主制御基板ボックス1320に、役物比率の表示を操作するためのスイッチであることを表示(印刷、刻印、シールなど)するとよい。なお、表示スイッチ1318は、役物比率表示器1317の近くに設けることが望ましいが、主制御ユニット1300ではなくても、操作が容易な場所であれば、他の基板(例えば、演出制御基板4700、電源装置4112)や筐体4100や前面部材4200に設けてもよい。周辺制御ユニット1500や、主制御ユニット1300とは別体で設けられた中継基板や、枠側の電源基板ボックス930内の電源基板や、払出制御基板ユニット950に設けられてもよい。また、後述するように、表示スイッチ1318はRAMクリアスイッチと兼用してもよい。表示スイッチ1318を遊技者が操作できない位置に設けることで、遊技者が誤って操作することを防止できる。
As shown in FIG. 13, the
本体枠4の払出ユニット800は、本体枠ベース600の後側に取付けられる逆L字状の払出ユニットベース801と、払出ユニットベース801の上部に取付けられており上方へ開放された左右に延びた箱状で図示しない島設備から供給される遊技球を貯留する球タンク802と、球タンク802の下側で払出ユニットベース801に取付けられており球タンク802内の遊技球を正面視左方向へ誘導する左右に延びたタンクレール803と、払出ユニットベース801における正面視左側上部の後面に取付けられタンクレール803からの遊技球を蛇行状に下方へ誘導する球誘導ユニット820と、球誘導ユニット820の下側で払出ユニットベース801から着脱可能に取付けられており球誘導ユニット820により誘導された遊技球を払出制御基板ユニット950に収容された払出制御基板951(図17を参照)からの指示に基づいて一つずつ払出す払出装置830と、払出ユニットベース801の後面に取付けられ払出装置830によって払出された遊技球を下方へ誘導すると共に皿ユニット200における上皿201での遊技球の貯留状態に応じて遊技球を通常放出口又は満タン放出口の何れかから放出させる上部満タン球経路ユニット850と、払出ユニットベース801の下端に取付けられ上部満タン球経路ユニット850の通常放出口から放出された遊技球を前方へ誘導して前端から扉枠3の貫通球通路526へ誘導する通常誘導路及び満タン放出口から放出された遊技球を前方へ誘導して前端から扉枠3の満タン球受口530へ誘導する満タン誘導路を有した下部満タン球経路ユニット860と、を備えている。
The dispensing
本体枠4の基板ユニット900は、本体枠ベース600の後側に取付けられる基板ユニットベース910と、基板ユニットベース910の正面視左側で本体枠ベース600の後側に取付けられ内部に低音用のスピーカ921を有したスピーカユニット920と、基板ユニットベース910の後側で正面視右側に取付けられ内部に電源基板が収容されている電源基板ボックス930と、スピーカユニット920の後側に取付けられており内部にインターフェイス制御基板が収容されているインターフェイス制御基板ボックス940と、
電源基板ボックス930及びインターフェイス制御基板ボックス940に跨って取付けられており内部に遊技球の払出しを制御する払出制御基板951が収容された払出制御基板ユニット950と、を備えている。
The
A payout
パチンコ機1の遊技盤5は、図8及び図9等に示すように、遊技球が打込まれる遊技領域5aの外周を区画し球発射装置680から発射された遊技球を遊技領域5aの上部に案内する外レール1001及び内レール1002を有した前構成部材1000と、前構成部材1000の後側に取付けられると共に遊技領域5aの後端を区画する平板状の遊技パネル1100と、遊技パネル1100の後側の下部に取付けられており上方に開放された箱状の基板ホルダ1200と、基板ホルダ1200の後側に取付けられておりパチンコ機1の遊技を制御するための主制御基板1310を有している主制御ユニット1300と、遊技パネル1100の前側で遊技領域5a内に取付けられ遊技領域5a内に打込まれた遊技球を受入可能な複数の入賞口を有した表ユニット(図示は省略)と、基板ホルダ1200の上側で遊技パネル1100の後側に取付けられている裏ユニット3000と、を備えている。
As shown in FIGS. 8 and 9, the
本実施形態のパチンコ機1は、上皿201に遊技球を貯留した状態で、遊技者がハンドルレバー504を回転操作すると、球発射装置680によってハンドルレバー504の回転角度に応じた強さで遊技球が遊技盤5の遊技領域5a内へ打込まれる。そして、遊技領域5a内に打込まれた遊技球が、図示しない入賞口に受入れられると、受入れられた入賞口に応じて、所定数の遊技球が払出装置830によって上皿201に払出される。この遊技球の払出しによって遊技者の興趣を高めることができるため、上皿201内の遊技球を遊技領域5a内へ打込ませることができ、遊技者に遊技を楽しませることができる。
In the
[2.遊技盤の全体構成]
次に、パチンコ機1の遊技盤5の全体構成について、図10乃至図16を参照して詳細に説明する。図10は、遊技盤の正面図である。図11は遊技盤を右前から見た斜視図であり、図12は遊技盤を左前から見た斜視図であり、図13は遊技盤を後ろから見た斜視図である。また、図14は遊技盤を主な構成毎に分解して前から見た分解斜視図であり、図15は遊技盤を主な構成毎に分解して後ろから見た分解斜視図である。更に、図16は、遊技盤における前構成部材及び表ユニットを遊技領域内の前後方向の略中央で切断した正面図である。
[2. Overall configuration of the game board]
Next, the overall configuration of the
本実施形態の遊技盤5は、遊技者がハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504を操作することで遊技球が打込まれる遊技領域5aを有している。また、遊技盤5は、遊技領域5aの外周を区画し外形が正面視略四角形状とされた前構成部材1000と、前構成部材1000の後側に取付けられており遊技領域5aの後端を区画する板状の遊技パネル1100と、遊技パネル1100の後側下部に取付けられている基板ホルダ1200と、基板ホルダ1200の後面に取付けられており遊技球を遊技領域5a内へ打込むことで行われる遊技内容を制御する主制御基板1310(図17を参照)を有している主制御ユニット1300と、を備えている。遊技パネル1100の前面において遊技領域5a内となる部位には、遊技球と当接する複数の障害釘が所定のゲージ配列で植設されている(図示は省略)。
The
また、遊技盤5は、主制御基板1310からの制御信号に基づいて遊技状況を表示し前構成部材1000の左下隅に遊技者側へ視認可能に取付けられている機能表示ユニット1400と、遊技パネル1100の後側に取付けられている周辺制御ユニット1500と、正面視において遊技領域5aの中央に配置されており所定の演出画像を表示可能なメイン液晶表示装置1600と、遊技パネル1100の前面に取付けられる表ユニット2000と、遊技パネル1100の後面に取付けられる裏ユニット3000と、を更に備えている
。裏ユニット3000の後面にメイン液晶表示装置1600が取付けられていると共に、メイン液晶表示装置1600の後面に周辺制御ユニット1500が取付けられている。
The
遊技パネル1100は、外周が枠状の前構成部材1000の内周よりもやや大きく形成されていると共に透明な平板状のパネル板1110と、パネル板1110の外周を保持しており前構成部材1000の後側に取付けられると共に後面に裏ユニット3000が取付けられる枠状のパネルホルダ1120と、を備えている。
The
表ユニット2000は、遊技領域5a内に打込まれた遊技球を受入可能に常時開口している複数の一般入賞口2001と、複数の一般入賞口2001とは遊技領域5a内の異なる位置で遊技球を受入可能に常時開口している第一始動口2002と、遊技領域5a内の所定位置に取付けられており遊技球の通過を検知するゲート部2003と、遊技球がゲート部2003を通過することにより抽選される普通抽選結果に応じて遊技球の受入れが可能となる第二始動口2004と、第一始動口2002又は第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れにより抽選される第一特別抽選結果又は第二特別抽選結果に応じて遊技球の受入れが何れかにおいて可能となる第一大入賞口2005及び第二大入賞口2006と、を備えている。第二大入賞口2006は、遊技球が流通する一つの流路に配置された第二上大入賞口2006aと第二下大入賞口2006bとの二つの大入賞口により構成されている(図16を参照)。
The
また、表ユニット2000は、遊技領域5a内の左右方向中央でアウト口1111の直上に取付けられており第一始動口2002及び第一大入賞口2005を有している始動口ユニット2100と、始動口ユニット2100の正面視左方で内レール1002に沿って取付けられており三つの一般入賞口2001を有しているサイドユニット下2200と、サイドユニット下2200の正面視左端上方に取付けられているサイドユニット上2300と、遊技領域5a内の略中央に取付けられており一つの一般入賞口2001、ゲート部2003、第二始動口2004、及び第二大入賞口2006を有している枠状のセンター役物2500と、を備えている。
In addition, the
裏ユニット3000は、パネルホルダ1120の後面に取付けられ前方が開放されている箱状で後壁に四角い開口部3010aを有している裏箱3010と、裏箱3010内の所定位置に配置されており表ユニット2000の一般入賞口2001に受入れられた遊技球を検知する複数の一般入賞口センサ3015と、裏箱3010の後面に取付けられておりメイン液晶表示装置1600を着脱可能に取付けるためのロック機構3020と、裏箱3010内の正面視右端に取付けられておりセンター役物2500の一般入賞口2001や第二始動口2004に受入れられた遊技球を排出するための右球通路ユニット3030と、裏箱3010内の正面視右下隅の前端付近に取付けられておりセンター役物2500の第二大入賞口2006や第二アウト口2543cに受入れられた遊技球を排出するための右下球通路ユニット3035と、を備えている。
The
また、裏ユニット3000は、裏箱3010の後面に取付けられている上中継基板3040と、上中継基板3040の後側を覆う上中継基板カバー3041と、裏箱3010の後面に回動可能に取付けられている箱状の演出駆動基板ボックス3042と、演出駆動基板ボックス3042内に収容されている演出駆動基板3043と、裏箱3010の後面に取付けられているパネル中継基板3044と、パネル中継基板3044の後側を覆うパネル中継基板カバー3045と、を備えている。
The
更に、裏ユニット3000は、裏箱3010内の前端で正面視左辺側の上下方向中央から上寄りに取付けられている裏左中装飾ユニット3050と、裏箱3010内における開口部3010aの下方で裏箱3010の後壁付近に取付けられている裏下後可動演出ユニ
ット3100と、裏箱3010内における開口部3010aの上方で正面視左側に取付けられている裏上左可動演出ユニット3200と、裏箱3010内で開口部3010aの正面視左側に取付けられている裏左可動演出ユニット3300と、裏箱3010内における開口部3010aの上方で左右方向中央から正面視右端までにかけて取付けられている裏上中可動演出ユニット3400と、裏箱3010内における開口部3010aの下方で裏下後可動演出ユニット3100の前方に取付けられている裏下前可動演出ユニット3500と、を備えている。
Further, the
[2-1.前構成部材]
次に、前構成部材1000について、主に図14及び図15を参照して説明する。前構成部材1000は、正面視の外形が略正方形とされ、内形が略円形状に前後方向へ貫通しており、内形の内周によって遊技領域5aの外周を区画している。この前構成部材1000は、正面視で左右方向中央から左寄りの下端から時計回りの周方向へ沿って円弧状に延び正面視左右方向中央上端を通り過ぎて右斜め上部まで延びた外レール1001と、外レール1001に略沿って前構成部材1000の内側に配置され正面視左右方向中央下部から正面視左斜め上部まで円弧状に延びた内レール1002と、内レール1002の下端の正面視右側で遊技領域5aの最も低くなった位置に形成されており後方へ向かって低くなるように傾斜しているアウト誘導部1003と、を備えている。
[2-1. Front component]
Next, the front
また、前構成部材1000は、アウト誘導部1003の正面視右端から前構成部材1000の右辺付近まで右端側が僅かに高くなるように直線状に傾斜している右下レール1004と、右下レール1004の右端から前構成部材1000の右辺に沿って外レール1001の上端の下側まで延びており上部が前構成部材1000の内側へ湾曲している右レール1005と、右レール1005の上端と外レール1001の上端とを繋いでおり外レール1001に沿って転動して来た遊技球が当接する衝止部1006と、を備えている。
In addition, the
また、前構成部材1000は、内レール1002の上端に回動可能に軸支され、外レール1001との間を閉鎖するように内レール1002の上端から上方へ延出した閉鎖位置と正面視時計回りの方向へ回動して外レール1001との間を開放した開放位置との間でのみ回動可能とされると共に閉鎖位置側へ復帰するように図示しないバネによって付勢された逆流防止部材1007を、備えている。
The front
レール1001、1002の出口付近(望ましくは、逆流防止部材1007を通過した直後)の遊技盤5の裏面側には、遊技領域5aに打ち込まれた遊技球を検出する発射球センサ1020を設ける。例えば、発射球センサ1020は、磁気センサで構成し、逆流防止部材1007を通過して遊技領域5aに流入した遊技球を検出すると、信号を出力する。なお、発射球センサ1020は、遊技領域内で遊技球が必ず通過する位置に設けてもよい。遊技盤5における発射球センサ1020の位置を固定化することによって、複数機種間で仕様を共通化でき、製造現場での検査やホールでの設置後検査が容易になる。
A
また、レール1001、1002の出口付近などの遊技領域5aの上流に設けた発射球センサ1020は、入賞口センサが遊技球の入賞を検出する前にアウト球を検出する。すなわち、アウト球、賞球の順で遊技球を検出するので、アウト球として計数されていない遊技球に起因した賞球を検出せず、正確にベース値を計算できる。
A
[2-2.遊技パネル]
次に、遊技パネル1100について、主に図14及び図15を参照して説明する。遊技パネル1100は、外周が枠状の前構成部材1000の内周よりもやや大きく形成されていると共に透明な合成樹脂で形成されている平板状のパネル板1110と、パネル板1110の外周を保持しており前構成部材1000の後側に取付けられると共に後面に裏ユニ
ット3000が取付けられる枠状のパネルホルダ1120と、を備えている。遊技パネル1100のパネル板1110は、遊技領域5a内において最も低い位置となる部位に前後に貫通しているアウト口1111が形成されている。また、パネル板1110には、前後に貫通しており表ユニット2000を取付けるための開口部1112が複数形成されている。
[2-2. Game panel]
Next, the
遊技パネル1100のパネルホルダ1120は、パネル板1110を後側から着脱可能に保持している。また、パネルホルダ1120は、裏ユニット3000を取付けるための取付孔と、位置決め孔とが後面に複数形成されている。
The
遊技パネル1100を前構成部材1000の後側に取付けた状態では、前構成部材1000のアウト誘導部1003の後側にパネル板1110のアウト口1111が開口した状態となる。これにより、遊技領域5aの下端へ流下した遊技球が、アウト誘導部1003によって後側のアウト口1111へ誘導され、アウト口1111を通って遊技パネル1100の後側へ排出される。
When the
[2-3.基板ホルダ]
次に、基板ホルダ1200について、図11乃至図15を参照して説明する。基板ホルダ1200は、上方及び前方が開放された横長の箱状に形成されており、底面が左右方向中央へ向かって低くなるように傾斜している。この基板ホルダ1200は、遊技盤5に組立てた状態では、遊技パネル1100の後側に取付けられている裏ユニット3000の下部を下側から覆うことができる。これにより、アウト口1111を通って遊技パネル1100の後側へ排出された遊技球、及び、表ユニット2000及び裏ユニット3000から下方へ排出された遊技球、を全て受けることができ、底面に形成された排出部1201(図14を参照)から下方へ排出させることができる。
[2-3. Substrate holder]
Next, the
[2-4.主制御基板ユニット]
次に、主制御ユニット1300について、図11乃至図15、及び図17を参照して説明する。主制御ユニット1300は、基板ホルダ1200の後面に着脱可能に取付けられている。この主制御ユニット1300は、遊技内容及び遊技球の払出し等を制御する主制御基板1310と、主制御基板1310を収容しており基板ホルダ1200に取付けられる主制御基板ボックス1320と、を備えている。
[2-4. Main control board unit]
Next, the
主制御基板ボックス1320は、複数の封印機構を備えており、一つの封印機構を用いて主制御基板ボックス1320を閉じると、次に、主制御基板ボックス1320を開けるためにはその封印機構を破壊する必要があり、主制御基板ボックス1320の開閉の痕跡を残すことができる。従って、開閉の痕跡を見ることで、主制御基板ボックス1320の不正な開閉を発見することができ、主制御基板1310への不正行為に対する抑止力が高められている。
The main
[2-5.機能表示ユニット]
次に、機能表示ユニット1400について、図10乃至図12を参照して説明する。機能表示ユニット1400は、図示するように、遊技領域5aの外側で前構成部材1000の左下隅に取付けられている。この機能表示ユニット1400は、遊技盤5をパチンコ機1に組立てた状態で、扉枠3の貫通口111を通して前方(遊技者側)から視認することができる(図1を参照)。この機能表示ユニット1400は、主制御基板1310からの制御信号に基づき複数のLEDを用いて、遊技状態(遊技状況)や、普通抽選結果や特別抽選結果等を表示するものである。
[2-5. Function display unit]
Next, the
機能表示ユニット1400は、詳細な図示は省略するが、遊技状態を表示する一つのL
EDからなる状態表示器と、ゲート部2003に対する遊技球の通過により抽選される普通抽選結果に基づいて二つのLEDを点滅制御することにより普通図柄を変動表示した後にこれら二つのLEDを普通抽選結果に応じた点灯態様で表示させる普通図柄表示器と、ゲート部2003に対する遊技球の通過に係る普通図柄の変動表示のうち未だ変動表示の開始条件が成立していない変動表示の個数である保留数を表示する二つのLEDからなる普通保留表示器と、第一始動口2002への遊技球の受入れ(始動入賞の発生)により抽選された第一特別抽選結果に基づいて八つのLEDを点滅制御することにより第一特別図柄を変動表示した後にこれら八つのLEDを第一特別抽選結果に応じた点灯態様で表示させる第一特別図柄表示器と、第一始動口2002への遊技球の受入れに係る第一特別図柄の変動表示のうち未だ変動表示の開始条件が成立していない変動表示の個数である保留数を表示する二つのLEDからなる第一特別保留数表示器と、第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れ(始動入賞の発生)により抽選された第二特別抽選結果に基づいて八つのLEDを点滅制御することにより第二特別図柄を変動表示した後にこれら八つのLEDを第二特別抽選結果に応じた点灯態様で表示させる第二特別図柄表示器と、第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れに係る第二特別図柄の変動表示のうち未だ変動表示の開始条件が成立していない変動表示の個数である保留数を表示する二つのLEDからなる第二特別保留数表示器と、第一特別抽選結果又は第二特別抽選結果が「大当り」等の時に、第一大入賞口2005や第二大入賞口2006の開閉パターンの繰返し回数(ラウンド数)を表示する二つのLEDからなるラウンド表示器と、を主に備えている。なお、機能表示ユニット1400の一部の表示器(例えば、第一特別図柄表示器)を7セグメントLEDで構成してもよい。
Although detailed illustration is omitted, the
A status indicator consisting of an ED and two LEDs are controlled to flash based on the result of the ordinary lottery drawn by the passage of the game ball through the
この機能表示ユニット1400では、備えられているLEDを、適宜、点灯、消灯、及び、点滅、等させることにより、保留数や図柄等を表示することができる。
In this
[2-6.周辺制御ユニット]
次に、周辺制御ユニット1500について、図13及び図15を参照して説明する。周辺制御ユニット1500は、裏ユニット3000の裏箱3010の後面に取付けられている。周辺制御ユニット1500は、主制御基板1310からの制御信号に基づいて遊技者に提示する演出を制御する周辺制御基板1510(図17を参照)と、周辺制御基板1510を収容している周辺制御基板ボックス1520と、を備えている。周辺制御基板1510は、発光演出、サウンド演出、及び可動演出、等を制御するための周辺制御部1511と、演出画像を制御するための液晶表示制御部1512と、を備えている(図17を参照)。
[2-6. Peripheral control unit]
Next, the
[2-7.メイン液晶表示装置]
次に、メイン液晶表示装置1600について、図10乃至図16を参照して説明する。メイン液晶表示装置1600は、正面視において遊技領域5aの中央に配置されており、遊技パネル1100の後側に裏ユニット3000の裏箱3010を介して取付けられている。詳述すると、メイン液晶表示装置1600は、裏箱3010の後壁の略中央の後面に対して、着脱可能に取付けられている。このメイン液晶表示装置1600は、遊技盤5を組立てた状態で、枠状のセンター役物2500の枠内を通して、前側(遊技者側)から視認することができる。このメイン液晶表示装置1600は、白色LEDをバックライトとしたフルカラーの表示装置であり、静止画像や動画を表示することができる。
[2-7. Main liquid crystal display device]
Next, the main liquid
メイン液晶表示装置1600は、図14及び図15に示すように、正面視左側面から外方へ突出している二つの左固定片1601と、正面視右側面から外方へ突出している右固定片1602と、を備えている。このメイン液晶表示装置1600は、液晶画面を前方へ向けた状態で、後述する裏箱3010の枠状の液晶取付部内の正面視左内周面に開口している二つの固定溝3010cに、裏箱3010の斜め後方から二つの左固定片1601を
挿入した上で、右固定片1602側を前方へ移動させて、右固定片1602をロック機構3020の開口部内に挿入し、ロック機構3020を下方へスライドさせることにより、裏箱3010に取付けられる。
As shown in FIGS. 14 and 15, the main liquid
[2-8.表ユニットの全体構成]
次に、表ユニット2000について、主に図10乃至図12、図14乃至図16を参照して説明する。遊技盤5の表ユニット2000は、遊技パネル1100のパネル板1110に、前方から取付けられており、前端がパネル板1110の前面よりも前方へ突出していると共に、後端が開口部1112を貫通してパネル板1110の後面よりも後方へ突出している。本実施形態の表ユニット2000は、遊技領域5a内に打込まれた遊技球を受入可能としており常時開口している複数の一般入賞口2001と、複数の一般入賞口2001とは遊技領域5a内の異なる位置で遊技球を受入可能に常時開口している第一始動口2002と、遊技領域5a内の所定位置に取付けられており遊技球の通過を検知するゲート部2003と、遊技球がゲート部2003を通過することにより抽選される普通抽選結果に応じて遊技球の受入れが可能となる第二始動口2004と、第一始動口2002又は第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れにより抽選される第一特別抽選結果又は第二特別抽選結果に応じて何れかにおいて遊技球の受入れが可能となる第一大入賞口2005及び第二大入賞口2006と、を備えている。
[2-8. Overall configuration of table unit]
Next, the
複数(ここでは四つ)の一般入賞口2001は、三つが遊技領域5a内の下部に配置されており、残りの一つが遊技領域5a内における正面視右上付近に配置されている。第一始動口2002は、遊技領域5a内の左右方向中央でアウト口1111の直上に配置されている。ゲート部2003は、遊技領域5a内における正面視右上で衝止部1006の略直下に配置されている。第二始動口2004は、ゲート部2003の直下から正面視右寄りに配置されている。上述した複数の一般入賞口2001のうち遊技領域5a内の正面視右上付近に配置されている一般入賞口2001は、第二始動口2004の直上に配置されている。第一大入賞口2005は、第一始動口2002とアウト口1111との間に配置されている。第二大入賞口2006は、第一始動口2002の正面視右方で第一大入賞口2005よりも上方に配置されている。
Three of the plurality (here, four) of the general winning
表ユニット2000における第二大入賞口2006は、図16に示すように、遊技球が流通する一つの流路に沿って配置された第二上大入賞口2006aと第二下大入賞口2006bとにより構成されている。第二大入賞口2006は、第二上大入賞口2006aが遊技領域5a内における正面視右下付近に配置されており、第二下大入賞口2006bが第二上大入賞口2006aの正面視左側で下方に配置されている。
As shown in FIG. 16, the second large winning
また、表ユニット2000は、遊技領域5a内の左右方向中央でアウト口1111の直上に取付けられており第一始動口2002及び第一大入賞口2005を有している始動口ユニット2100と、始動口ユニット2100の正面視左方で内レール1002に沿って取付けられており三つの一般入賞口2001を有しているサイドユニット下2200と、サイドユニット下2200の正面視左端上方に取付けられているサイドユニット上2300と、遊技領域5a内の略中央に取付けられており一つの一般入賞口2001、ゲート部2003、第二始動口2004、及び第二大入賞口2006を有している枠状のセンター役物2500と、を備えている。
In addition, the
[2-8a.始動口ユニット]
次に、表ユニット2000の始動口ユニット2100について、説明する。始動口ユニット2100は、遊技領域5a内において、左右方向中央の下端部付近でアウト口1111の直上に配置されており、パネル板1110に前方から取付けられている。この始動口ユニット2100は、第一始動口2002及び第一大入賞口2005を有している。
[2-8a. starting unit]
Next,
始動口ユニット2100は、パネル板1110の前面に取付けられ左右に延びた矩形状で前後に貫通している第一大入賞口2005を有した平板状のユニットベース2101と、ユニットベース2101における第一大入賞口2005の上方で左右方向略中央の上部から前方へ突出しており第一始動口2002を形成している球受部2102と、ユニットベース2101の後側に取付けられており第一始動口2002に受入れられた遊技球を下方へ誘導する球誘導部2103と、球誘導部2103に取付けられており第一始動口2002に受入れられた遊技球を検知する第一始動口センサ2104と、第一大入賞口2005を閉鎖するようにユニットベース2101の後面に取付けられている第一アタッカユニット2110と、を備えている。
The starting
始動口ユニット2100の第一アタッカユニット2110は、第一大入賞口2005を後方から閉鎖するようにユニットベース2101の後面に取付けられ前端が第一大入賞口2005と略同じ大きさで前方に開放されている箱状のユニットケース2111と、第一大入賞口2005を開閉可能にユニットケース2111の前端で下辺が回動可能に支持されている横長矩形状で平板状の第一大入賞口扉部材2112と、ユニットケース2111内に取付けられており第一大入賞口扉部材2112を開閉駆動させる第一アタッカソレノイド2113と、ユニットケース2111内に取付けられており第一大入賞口2005に受入れられた遊技球を検知する第一大入賞口センサ2114と、ユニットケース2111の上面に取付けられており第一始動口センサ2104、第一アタッカソレノイド、及び第一大入賞口センサ2114と主制御基板1310との接続を中継する始動口ユニット中継基板2115と、ユニットケース2111の下部に取付けられており第一大入賞口2005を発光装飾させるための始動口ユニット装飾基板(図示は省略)と、を備えている。
The first attacker unit 2110 of the starting
第一始動口2002を形成している球受部2102は、遊技球を一度に一つのみ受入可能な大きさで上方に向かって開口している。ユニットベース2101を貫通している第一大入賞口2005は、遊技球を一度に複数(例えば、4個~6個)受入可能な大きさで前方に向かって開口している。
The
始動口ユニット2100は、球受部2102により形成されている第一始動口2002が上方に向かって開口しており、第一始動口2002に受入れられた遊技球を、球誘導部2103によりユニットベース2101の後側で下方へ誘導し、第一始動口センサ2104に検知させた後に、第一アタッカユニット2110を貫通して下方へ排出させることができる。本実施形態では、第一始動口センサ2104が二つ備えられており、主制御基板1310では、所定の時間範囲内で二つの第一始動口センサ2104が遊技球を検知すると、第一始動口2002に遊技球が受入れられたと判断するようになっている。これにより、第一始動口2002への不正な工具の挿入による不正行為を検知することができる。
In the starting
始動口ユニット2100では、ユニットベース2101の後面に第一アタッカユニット2110を取付けることにより、第一アタッカユニット2110の第一大入賞口扉部材2112が、ユニットベース2101に開口している第一大入賞口2005内に後方から挿入されて、第一大入賞口2005を閉鎖している。この第一大入賞口扉部材2112は、第一大入賞口2005を閉鎖している直立した状態で、下辺の左右両端部がユニットケース2111によって回動可能に取付けられており、上辺が前方且つ下方へ移動するように回動させることで第一大入賞口2005を閉状態から開状態とすることができる。
In the starting
第一アタッカユニット2110の第一大入賞口扉部材2112は、通常の状態(第一アタッカソレノイド2113が非通電の状態)では直立して、第一大入賞口2005を閉鎖している。そして、第一アタッカソレノイド2113が遊技状態に応じて通電されると、上辺が前方且つ下方へ移動するように第一大入賞口扉部材2112が回動して、上辺が下
辺よりもやや上方へ位置した状態となる。つまり、第一大入賞口扉部材2112が、第一大入賞口2005の下辺から前方へ向かって高くなるように傾斜した状態となる。
The first large prize winning
この状態で第一大入賞口2005の前方を遊技球が流下して第一大入賞口扉部材2112に当接すると、第一大入賞口扉部材2112の傾斜により遊技球の流通方向が下方から後方へと変化し、第一大入賞口2005に受入れられてユニットケース2111内に進入することとなる。そして、第一大入賞口2005に受入れられた遊技球は、第一大入賞口センサ2114により検知された後に、ユニットケース2111の下面から下方へ排出される。
In this state, when the game ball flows down in front of the first big
[3.制御構成]
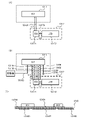
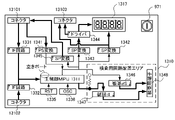
次に、パチンコ機1の各種制御を行う制御構成について、図17を参照して説明する。図17は、パチンコ機の制御構成を概略的に示すブロック図である。パチンコ機1の主な制御構成は、図示するように、遊技盤5に取付けられる主制御基板1310及び周辺制御基板1510と、本体枠4に取付けられる払出制御基板951と、から構成されており、夫々の制御が分担されている。主制御基板1310は、遊技動作(遊技の進行)を制御する。周辺制御基板1510は、主制御基板1310からのコマンドに基いて遊技中の各種演出装置を制御する周辺制御部1511と、周辺制御部1511からのコマンドに基いてメイン液晶表示装置1600や上皿液晶表示装置244等での演出画像の表示を制御する液晶表示制御部1512と、を備えている。払出制御基板951は、遊技球の払出し等を制御する払出制御部952と、ハンドルレバー504の回転操作による遊技球の発射を制御する発射制御部953と、を備えている。
[3. Control configuration]
Next, a control configuration for performing various controls of the
[3-1.主制御基板]
遊技の進行を制御する主制御基板1310は、各種処理プログラムや各種コマンドを記憶するROM1313や一時的にデータを記憶するRAM1312等が内蔵されるマイクロプロセッサである主制御MPU1311と、入出力デバイス(I/Oデバイス)としての主制御I/Oポート1314と、各種検出スイッチからの検出信号が入力される主制御入力回路1315と、各種ソレノイドを駆動するための主制御ソレノイド駆動回路1316と、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されているRAMに記憶された情報を完全に消去するためのRAMクリアスイッチと、を備えている。主制御MPU1311は、その内蔵されたROMやRAMのほかに、その動作(システム)を監視するウォッチドッグタイマや不正を防止するための機能等も内蔵されている。
[3-1. Main control board]
The
主制御基板1310の主制御MPU1311は、第一始動口2002に受入れられた遊技球を検出する第一始動口センサ2104、第二始動口2004に受入れられた遊技球を検出する第二始動口センサ2551、一般入賞口2001に受入れられた遊技球を検出する一般入賞口センサ3015、ゲート部2003を通過した遊技球を検知するゲートセンサ2547、第一大入賞口2005に受入れられた遊技球を検知する第一大入賞口センサ2114、第二大入賞口2006としての第二上大入賞口2006a及び第二下大入賞口2006bに受入れられた遊技球を検知する第二上大入賞口センサ2554及び第二下大入賞口センサ2557、排出球センサ3060、発射球センサ1020及び遊技領域5a内における不正な磁気を検知する磁気検出センサ、等からの検出信号が夫々主制御I/Oポート1314を介して入力される。
The
主制御MPU1311は、これらの検出信号に基づいて、主制御I/Oポート1314から主制御ソレノイド駆動回路に制御信号を出力することにより、始動口ソレノイド2550、第一アタッカソレノイド2113、第二上アタッカソレノイド2553、及び第二下アタッカソレノイド2556に駆動信号を出力したり、主制御I/Oポート1314から機能表示ユニット1400の第一特別図柄表示器、第二特別図柄表示器、第一特別図柄
記憶表示器、第二特別図柄記憶表示器、普通図柄表示器、普通図柄記憶表示器、遊技状態表示器、ラウンド表示器、等に駆動信号を出力したりする。
Based on these detection signals, the
なお、本実施形態おいて、第一始動口センサ2104、第二始動口センサ2551、ゲートセンサ2547、第一大入賞口センサ2114、第二上大入賞口センサ2554、及び第二下大入賞口センサ2557には、非接触タイプの電磁式の近接スイッチを用いているのに対して、一般入賞口センサ3015には、接触タイプのON/OFF動作式のメカニカルスイッチを用いている。これは、遊技球が、第一始動口2002や第二始動口2004に頻繁に入球すると共に、ゲート部2003を頻繁に通過するため、第一始動口センサ2104、第二始動口センサ2551、及びゲートセンサ2547による遊技球の検出も頻繁に発生する。このため、第一始動口センサ2104、第二始動口センサ2551、及びゲートセンサ2547には、耐久性が高く寿命の長い近接スイッチを用いている。また、遊技者にとって有利となる有利遊技状態(「大当り」遊技、等)が発生すると、第一大入賞口2005や第二大入賞口2006が開放(又は、拡大)されて遊技球が頻繁に入球するため、第一大入賞口センサ2114、第二上大入賞口センサ2554、及び第二下大入賞口センサ2557による遊技球の検出も頻繁に発生する。このため、第一大入賞口センサ2114、第二上大入賞口センサ2554、及び第二下大入賞口センサ2557にも、耐久性が高く寿命の長い近接スイッチを用いている。これに対して、遊技球が頻繁に入球しない一般入賞口2001には、一般入賞口センサ3015による検出も頻繁に発生しない。このため、一般入賞口センサ3015には、近接スイッチより寿命が短いメカニカルスイッチを用いている。
In addition, in this embodiment, the first
また、主制御MPU1311は、遊技に関する各種情報(遊技情報)及び払出しに関する各種コマンド等を払出制御基板951に送信したり、この払出制御基板951からのパチンコ機1の状態に関する各種コマンド等を受信したりする。更に、主制御MPU1311は、メイン液晶表示装置1600等で実行される遊技演出の制御に関する各種コマンド及びパチンコ機1の状態に関する各種コマンドを、主制御I/Oポート1314を介して周辺制御基板1510の周辺制御部1511に送信したりする。なお、主制御MPU1311は、払出制御基板951からパチンコ機1の状態に関する各種コマンドを受信すると、これらの各種コマンドを整形して周辺制御部1511に送信する。
In addition, the
主制御基板1310には、電源基板ボックス930内の電源基板から各種電圧が供給されている。この主制御基板1310に各種電圧を供給する電源基板は、電源遮断時にでも所定時間、主制御基板1310に電力を供給するためのバックアップ電源としての電気二重層キャパシタ(以下、単に「キャパシタ」と記載する。)を備えている。このキャパシタにより主制御MPU1311は、電源遮断時にでも電源断時処理において各種情報をRAM1312に記憶することができる。この記憶した各種情報は、電源投入時に主制御基板1310のRAMクリアスイッチが操作されると、RAM1312から完全に消去(クリア)される。このRAMクリアスイッチの操作信号(検出信号)は、払出制御基板951にも出力される。
Various voltages are supplied to the
また、主制御基板1310には、停電監視回路が設けられている。この停電監視回路は、電源基板から供給される各種電圧の低下を監視しており、それらの電圧が停電予告電圧以下となると、停電予告として停電予告信号を出力する。この停電予告信号は、主制御I/Oポート1314を介して主制御MPU1311に入力される他に、払出制御基板951等にも出力されている。
Further, the
主制御基板1310には、パチンコ機1の裏面側から視認可能な位置に役物比率表示器1317が取り付けられる。役物比率表示器1317は、主制御MPU1311が計算した役物比率を表示する。
A
また、主制御基板1310には、表示スイッチ1318が設けられる。表示スイッチ1318は、モーメンタリ動作をする押ボタンスイッチで構成するとよいが、他の形式のスイッチでもよい。表示スイッチ1318を操作すると、役物比率表示器1317に役物比率を表示する。なお、役物比率表示器1317は常時、役物比率を表示し、表示スイッチ1318の操作によって表示内容を切り替えてもよい。
A
図18は、主制御MPU1311内の構成を示す図である。
FIG. 18 is a diagram showing the internal configuration of the
主制御MPU1311は、CPU13111、RAM1312、ROM1313、乱数発生回路13112、パラレル入力ポート13113、シリアル通信回路13114、タイマ回路13115、割込コントローラ13116、外部バスインターフェイス13117、クロック回路13118、照合用ブロック13119、固有情報13120、演算回路13121及びリセット回路13122を有する。
The
CPU13111は、ROM1313に記憶されたプログラムを実行する。RAM1312は、プログラム実行時に必要なデータを記憶する。
The
主制御MPU1311には、一つ以上の乱数発生回路13112が設けられている。乱数発生回路13112は、変動表示ゲームの結果(第一特別抽選結果、第二特別抽選結果)の抽選結果や変動表示ゲームの演出内容を決定するための乱数を提供する。乱数発生回路13112は、例えば、主制御MPU1311に供給されるクロック周期(又は、該クロック周期を分周した信号)のタイミングで更新した乱数を出力する、いわゆるハード乱数生成手段である。乱数発生回路13112が生成するハード乱数は、特別図柄の当たりの抽選や、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの当たり図柄の抽選や、普通図柄の当たりの抽選に用いられる。
One or more random
パラレル入力ポート13113は、主制御入力回路1315を経由して各種検出スイッチからの検出信号が入力されるポートである。
A
シリアル通信回路13114は、主制御I/Oポート1314を介して、遊技演出の制御に関する各種コマンド及びパチンコ機1の状態に関する各種コマンドを周辺制御基板1510の周辺制御部1511と送受信する。また、シリアル通信回路13114は、主制御I/Oポート1314を介して、遊技に関する各種情報(遊技情報)及び遊技球の払い出しに関する各種コマンド等を払出制御基板951と送受信する。さらに、シリアル通信回路13114は、役物比率を表示するためのデータを役物比率表示器1317に送信する。シリアル通信回路13114の詳細な構成は、図20を参照して後述する。
The
タイマ回路13115は、タイマ割り込みや各種時間制御のためのタイマである。割込コントローラ13116は、CPU13111に対する各種の割り込み(一般割り込み、ソフトウェアでマスク不可能なNMI)を制御する。すなわち、割込コントローラ13116が割り込みを検出した場合、割り込みの種類毎に定められたベクターテーブルを参照し、ベクターテーブルに設定されたアドレスにジャンプする。
A
外部バスインターフェイス13117は、主制御MPU1311の内部バスを外部のデバイスと接続するためのインターフェイスである。外部バスインターフェイス13117からは、I/Oリクエスト(IORQ)、リード(RD)、ライト(WR)、16ビットのアドレス(A0~A15)、8ビットのデータ(D0~D7)が入出力できる。
The
クロック回路13118は、入力された外部クロック信号(例えば、32MHz)から
主制御MPU1311の内部クロックを生成する。また、クロック回路13118は、入力されたクロック信号に、設定された数の分周をして、CLKO端子から外部に出力する。例えば、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171(図28参照)に供給するクロック信号を出力してもよい。
A
照合用ブロック13119は、ROM1313が不正に改造されていないかを所定のコードを用いて照合する機能ブロックである。固有情報13120は、主制御MPU1311に固有のIDであり、チップの製造時に書き換え不能に書き込まれている。
A
演算回路13121は、ROM1313に記録されたプログラムによらない演算機能を提供する。この演算機能は、チップの製造時に固定的に書き込まれている。
The
リセット回路13122は、指定外走行禁止回路、ウォッチドッグタイマ及びユーザリセット機能を有する。指定外走行禁止回路は、ROM1313の所定外のアドレスにCPU13111がアクセスした場合、不正なプログラムによるアクセスであると推定し、主制御MPU1311の動作をリセットする。ウォッチドッグタイマは、所定のタイマ時間が経過した際にタイムアウト信号を出力し、主制御MPU1311の動作をリセットする。ユーザリセット機能は、SRST端子に入力されたリセット信号によって、主制御MPU1311の動作をリセットする。
The
図19は、演算回路13121の詳細な構成を示すブロック図である。
FIG. 19 is a block diagram showing the detailed configuration of the
演算回路13121は、演算結果についてプログラムによらない演算機能を提供するものであり、乗算回路131211及び除算回路131215を有する。
The
乗算回路131211は、所定ビット数(例えば、16ビット)の二つの値を乗じて、32ビットの積を出力する演算回路であり、乗算関数によって入力値(乗数、被乗数)を積に変換して出力する変換回路として機能する。
The
主制御MPU1311のCPU13111は、乗算入力レジスタA131212及び乗算入力レジスタB131213に16ビット以下の乗数及び被乗数を格納する。乗算回路131211は、二つの16ビットの乗算入力レジスタ131212、131213に格納された値を所定のタイミングで読み出し、二つの値を乗じた結果を乗算結果レジスタ131214に格納する。CPU13111は、乗算結果レジスタ131214から乗算結果を取得する。乗算入力レジスタ131212、131213への値の書き込みから乗算結果レジスタ131214への演算結果の格納までは、所定の時間(例えば1クロック)で完了するように構成されており、CPU13111は、乗算入力レジスタ131212、131213に値を格納して、所定のクロック数が経過した後に、乗算結果レジスタ131214を参照して乗算結果を取得できる。
The
除算回路131215は、所定ビット数(例えば、32ビット)の被除数を所定ビット数(例えば、32ビット)の除数で割って、32ビットの商と32ビットの剰余を出力する演算回路であり、除算関数によって入力値(除数、被除数)を商及び剰余変換して出力する変換回路として機能する。
The
主制御MPU1311のCPU13111は、除算入力レジスタA131216に32ビット以下の被除数を格納し、除算入力レジスタB131217に32ビット以下の除数を格納する。除算回路131215は、二つの32ビットの除算入力レジスタ131216、131217の両方に値が格納されことを検出すると、格納された値を所定のタイミングで読み出し、被除数を除数で割った結果である商を除算結果レジスタA131218
に格納し、剰余を除算結果レジスタB131219に格納する。また、除算回路131215は、除算入力レジスタ131216、131217に格納された値を読み込むと、読み込んだ値を消去し、当該レジスタをクリアするとよい。また、除算回路131215は、スタート命令が入力されたタイミングで、除算入力レジスタ131216、131217に格納された値を読み出し、除算結果を除算結果レジスタ131218、131219に格納してもよい。この場合、除算入力レジスタ131216、131217に格納された値を、読み込みタイミングで消去しなくてもよい。また、除算入力レジスタ131216、131217は、既に値が格納されていても(格納されている値をクリアせずに)、さらに、値を上書き可能でもよい。
The
, and the remainder is stored in the division result register B131219. In addition, when the
CPU13111は、除算結果レジスタ131218、131219から除算結果を取得する。除算入力レジスタ131216、131217への値の書き込みから除算結果レジスタ131218、131219への演算結果の格納までは、所定の時間(例えば32クロック)で完了するように構成されており、CPU13111は、除算入力レジスタ131216、131217に値を格納して、所定のクロック数が経過した後に、除算結果レジスタ131218、131219をそれぞれ参照して商及び剰余を取得できる。
The
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、後述するように、ベース値を計算するために除算処理が必要であり、CPU13111がプログラムを実行する除算は複数の乗算及び減算で実行されるので相当の時間がかかるものである。このため、タイマ割込み処理毎にベース計算処理を実行するのは困難であり、遅滞ないベース値の表示は困難であった。これに対し、演算回路13121を用いて除算処理を行うことによって、ベース値の計算に必要な時間を短縮でき、一つのタイマ割込み処理において複数回ベース値を計算できる(図75、図80参照)。また、演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタ131216、131217への値の書き込みから除算結果レジスタA131218からの演算結果の読み出しまでの間、CPU13111は除算処理のために占有されないので、他の処理を実行でき、タイマ割込み処理中のベース算出処理を効率的に実行できる。
In the
図20は、シリアル通信回路13114の構成を示す図である。
FIG. 20 shows a configuration of the
シリアル通信回路13114は、四つのデータ送受信回路を有しており、各データ送受信回路が1チャネル分のデータを所定のデバイスと送受信する。なお、図20では、データ送信回路のみを図示し、データ受信回路(例えば、1チャネル分が実装)の説明は省略する。
The
本実施例の遊技機では、シリアル通信回路13114は、前述したように、周辺制御基板1510との通信に使用されるチャネル0、払出制御基板951との通信に使用されるチャネル1、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171との通信に使用されるチャネル2の三つのチャネルが使用され、チャネル3は未使用である。
In the gaming machine of the present embodiment, the
シリアル通信回路13114は、データレジスタ3141、送信データレジスタ3142、パリティ生成回路3143、送信用シフトレジスタ3144、コマンドステータスレジスタ3145、通信設定レジスタ3146、送信トリガ設定レベルレジスタ3147、ボーレートレジスタ3148及びボーレート生成回路3149を有する。
The
CPU13111から入力されたデータは、データレジスタ3141に格納された後、送信データレジスタ3142に格納される。送信データレジスタ3142は、所定の容量(例えば、64バイト)のFIFOで構成される。送信データレジスタ3142は、パリティ生成回路3143がデータの送信単位毎に生成した誤り検出符号を、送信すべきデータに付加し、送信用シフトレジスタ3144に格納する。
Data input from the
ボーレート生成回路3149は、クロック回路13118から供給されるクロック信号から、ボーレートレジスタ3148に設定されたレートでデータを送信するための送信用クロック信号を生成する。そして、送信用シフトレジスタ3144は、送信用クロック信号に従って、データを送信する。
The baud
コマンドステータスレジスタ3145は、送信状態を確認するために参照されるレジスタである。
A
通信設定レジスタ3146は、データの送信を制御するためのコマンドを格納する。送信トリガ設定レベルレジスタ3147は、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOが割り込みを発生させるデータ量を制御するための閾値を格納する。ボーレートレジスタ3148は、データの送信レートを規定するためのボーレートの設定を格納する。通信設定レジスタ3146、送信トリガ設定レベルレジスタ3147及びボーレートレジスタ3148は、図21のステップS28において初期設定として、4チャネルの各々について設定される。
以下、これらの設定について詳しく説明する。通信設定レジスタには、各チャネルの通信フォーマットが設定される。具体的には、FIFOの使用の有無(FIFOモード、ノーマルモード)、ストップビットのビット数、パリティ(パリティを使用するか、偶数パリティか奇数パリティか)を設定する。例えば、周辺制御基板1510との通信に使用されるチャネル0及び払出制御基板951との通信に使用されるチャネル1では、FIFOモード、ストップビット=1ビット、偶数パリティを意味する1×××1010Bを設定し、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171との通信に使用されるチャネル2では、FIFOモード、ストップビット=1ビット、パリティ未使用を意味する1×××1000Bを設定する。
These settings are described in detail below. A communication format for each channel is set in the communication setting register. Specifically, whether or not to use FIFO (FIFO mode, normal mode), the number of stop bits, and parity (whether parity is used, even parity or odd parity) are set. For example, in
FIFOモードでは、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOを使用してデータを送信する。また、遊技機はノイズが多い環境にあることから、主制御基板1310の外に高速でデータを送信する際は、パリティを設定することが望ましい。
In FIFO mode, the FIFO of transmit data register 3142 is used to transmit data. In addition, since the game machine is in a noisy environment, it is desirable to set parity when transmitting data to the outside of the
役物比率表示器1317は主制御基板1310に実装されるので、通信用の電線を経由する他の基板との通信と比較し、ノイズの影響は少ない。また、送受信するデータ量が少ないので、通信速度は低くてよく、パリティを使用する必要性は乏しい。なお、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171と主制御MPU1311との間で信号を伝達するパターンに沿って(例えば、プリント基板の表面又は内層に設けられた信号線の左右及び/又は厚み方向に隣接する層)にグランドパターンを設け、グランドパターンによるシールド効果によって、当該信号伝達パターンに重畳するノイズを低減できる。
Since the character
送信トリガ設定レベルレジスタ3147は、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOが割り込みを発生させるデータ量を定める。具体的には、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOに格納されている送信データの量が設定したバイト数より小さい場合、各チャンネルに対応したステータスレジスタの所定ビットがセットされる。ステータスレジスタの当該ビットを判定することによって、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOに空きがあるか否かを確認でき、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOに格納されたデータの送信タイミングを判定できる。
The transmission trigger
なお、送信FIFOに異常があるかを判定するために、ステータスレジスタの当該ビットを利用できる。例えば、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOに所定の期間データが書き込まれない場合でも、ステータスレジスタの当該ビットがセットされない場合、送信
データレジスタ3142のFIFOに空きが生じていないことから、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOからデータが送信されていないと判定して、エラー処理(例えば、エラー報知)を実行してもよい。
Note that the bit in the status register can be used to determine whether there is an abnormality in the transmission FIFO. For example, even if data is not written to the FIFO of the transmission data register 3142 for a predetermined period of time, if the corresponding bit of the status register is not set, the FIFO of the transmission data register 3142 does not have an empty space. It may be determined that data has not been transmitted from the FIFO, and error processing (for example, error notification) may be performed.
ボーレートレジスタ3148は、データ送信レートを定める。例えば、周辺制御基板1510との通信に使用されるチャネル0では19200bpsを設定し、払出制御基板951との通信に使用されるチャネル1では1200bpsを設定し、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171との通信に使用されるチャネル2では1200bpsを設定する。
このように、各チャネルで送信されるデータによって送信レートを変えている。これは、遊技機の内部は遊技球が転動しており、遊技機の電子回路はノイズの影響を受けやすい環境下にある。このため、遊技者に付与される利益に直接関係する出球を制御するためのデータは確実に送信されるように、低速で払出制御基板951にデータを送信する。一方、周辺制御基板1510は、送信されるデータ量が多く、出球に関係がないので、高いレートでデータを送信する。また、周辺制御基板1510は、受信したコマンドが異常かを検証しており、異常であると判定した場合、周辺制御基板1510を動作させない又は異常処理(例えば、通信エラー報知)を実行し、コマンドの再送を要求する。そして、再送されたコマンドが正常であると判定された場合、該正常コマンドを用いて周辺制御基板1510の状態が復旧される。このため、周辺制御基板1510との通信は、高いレートでデータを送信できる。さらに、周辺制御基板1510との通信レートを低くすると、始動口の入賞から図柄の変動開始までの遅延を遊技者が認識できるようになり、興趣を低下させる可能性がある。
In this way, the transmission rate is changed according to the data transmitted on each channel. This is because game balls are rolling inside the gaming machine, and the electronic circuits of the gaming machine are in an environment susceptible to noise. For this reason, the data for controlling the output of balls directly related to the profit given to the player is transmitted at a low speed to the
役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171との通信は、高いレート(周辺制御基板1510とのデータ送信レートである19200bps)でも、低いレート(払出制御基板951とのデータ送信レートである1200bps)でもよい。また、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171との通信は、高いレート(周辺制御基板1510とのデータ送信レートである19200bps)と低いレート(払出制御基板951とのデータ送信レートである1200bps)との間のレートを採用してもよい。これは、データ送信レートを高くすると、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171のトランジスタのスイッチングノイズ等により他の回路に誤動作を起こさせる可能性がある。一方、ノイズにより送信されたデータに異常が生じても、送信データが更新されない限りタイマ割込みごとに同じデータを再送し、再送されたコマンドが正常であれは、役物比率表示器1317の表示内容は正常に戻るので、送信レートを極端に低速にする必要はないためである。
The communication with the
コマンドステータスレジスタ3145は、送信状態を確認するために参照されるレジスタであり、例えば、各ビットは以下のように定義される。
ビット7:SnTC 送信完了を示すフラグであり、0は送信中、1は送信完了を示す。ビット6:SnTDBE ノーマルモード(FIFOを使用しない通信モード)においては、送信データエンプティを示すフラグであり、0は送信用シフトレジスタに未転送、1は送信用シフトレジスタに転送済みを示す。すなわち、送信データレジスタ3142から送信用シフトレジスタ3144にデータが転送され、送信データレジスタ3142に送信データが格納されていない状態になると、セットされる。
Bit 7: SnTC This is a flag indicating completion of transmission, 0 indicating that transmission is in progress, and 1 indicating completion of transmission. Bit 6: SnTDBE In normal mode (a communication mode that does not use FIFO), this is a flag indicating that transmission data is empty. That is, it is set when data is transferred from the transmission data register 3142 to the
SnTFTL FIFOモードにおいては、送信FIFOトリガレベルを示すフラグであり、0は送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOに格納されている送信データの量がトリガレベル以上、1は送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOに格納されている送信データの量がトリガレベル未満を示す。すなわち、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOに
格納されている送信データの量が、送信トリガレベル設定レジスタに設定されたバイト数より少ないときにセットされる。このため、FIFOモードでの通信時には、当該ビットが1であることを確認した後、送信データレジスタ3142のFIFOにデータを書き込む。
ビット5~2:未使用(0固定)
ビット1:SnTCL 送信バッファ、ブレークコード送信をクリアし、送信データを空にして、又は送信FIFOトリガレベルを(SnTFL)を設定するためのビットであり、外部から書き込まれる。例えば、バッファの内容を強制的にクリアする場合、当該ビットに1をセットする。より具体的には、FIFOにコマンドを書き込んだが、なんらかの事情(例えば、異常発生)によって、書き込んだコマンドの送信を中止する場合に使用される。なお、ビット1が設定されても、送信用シフトレジスタのデータはクリアされない。
In the SnTFTL FIFO mode, the flag indicates the transmission FIFO trigger level. amount of transmitted data is below the trigger level. That is, it is set when the amount of transmission data stored in the FIFO of the transmission data register 3142 is less than the number of bytes set in the transmission trigger level setting register. Therefore, during communication in the FIFO mode, after confirming that the bit is 1, data is written in the FIFO of the
Bits 5-2: Not used (fixed to 0)
Bit 1: SnTCL Bit to clear transmit buffer, break code transmit, empty transmit data, or set transmit FIFO trigger level (SnTFL), written externally. For example, when forcibly clearing the contents of the buffer, 1 is set to the relevant bit. More specifically, it is used when a command is written to the FIFO, but transmission of the written command is canceled due to some circumstances (for example, occurrence of an abnormality). Note that even if
以上に説明した構成で、シリアル通信回路13114は、調歩同期通信(非同期通信)が可能であるが、図示しない同期通信用のクロック信号を出力する。この場合、通信相手方(役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171)に供給するクロック信号は、クロック回路13118ではなく、シリアル通信回路13114から出力される。シリアル通信回路13114の各送受信回路は、少なくとも一つのチャネルが設定によって同期通信が可能でもよく、調歩同期用シリアル通信回路と同期通信用シリアル通信回路とを別に設けてもよい。
With the configuration described above, the
また、図示を省略したが、シリアル通信回路13114は、同期通信時に使用されるデータ取り込みタイミングを示す信号(LOAD)を出力する。
Although not shown, the
[3-2.払出制御基板]
図17に戻って、パチンコ機の制御構成の説明を続ける。遊技球の払出し等を制御する払出制御基板951は、詳細な図示は省略するが、払出しに関する各種制御を行う払出制御部952と、発射ソレノイド682による発射制御を行うとともに、球送りソレノイド551による球送り制御を行う発射制御部953と、パチンコ機1の状態を表示するエラーLED表示器と、エラーLED表示器に表示されているエラーを解除するためのエラー解除スイッチと、球タンク802、タンクレール803、球誘導ユニット820、及び払出装置830内の遊技球を、パチンコ機1の外部へ排出して球抜き動作を開始するための球抜きスイッチと、を備えている。
[3-2. Payout control board]
Returning to FIG. 17, the description of the control configuration of the pachinko machine is continued. Although not shown in detail, a
[3-2a.払出制御部]
払出制御基板951における払出しに関する各種制御を行う払出制御部952は、詳細な図示は省略するが、各種処理プログラムや各種コマンドを記憶するROMや一時的にデータを記憶するRAM等が内蔵されるマイクロプロセッサである払出制御MPUと、I/Oデバイスとしての払出制御I/Oポートと、払出制御MPUが正常に動作しているか否かを監視するための外部WDT(外部ウォッチドッグタイマ)と、払出装置830の払出モータ834に駆動信号を出力するための払出モータ駆動回路と、払出しに関する各種検出スイッチからの検出信号が入力される払出制御入力回路と、を備えている。払出制御MPUには、その内蔵されたROMやRAMのほかに、不正を防止するため機能等も内蔵されている。
[3-2a. Payout control unit]
Although detailed illustration is omitted, the
払出制御部952の払出制御MPUは、主制御基板1310からの遊技に関する各種情報(遊技情報)及び払い出しに関する各種コマンドを払出制御I/Oポートを介してシリアル方式で受信したり、主制御基板1310からのRAMクリアスイッチの操作信号(検出信号)が払出制御I/Oポートを介して入力されたりする他に、満タン検知センサ535からの検出信号が入力されたり、球切れ検知センサ827、払出検知センサ842、及
び羽根回転検知センサ840からの検出信号が入力される。
The payout control MPU of the
払出装置830の球切れ検知センサ827、払出検知センサ842、及び羽根回転検知センサ840からの検出信号は、払出制御入力回路に入力され、払出制御I/Oポートを介して払出制御MPUに入力される。
Detection signals from the out-of-
また、本体枠4に対する扉枠3の開放を検出する扉枠開放スイッチ、及び外枠2に対する本体枠4の開放を検出する本体枠開放スイッチからの検出信号は、払出制御入力回路に入力され、払出制御I/Oポートを介して払出制御MPUに入力される。
Detection signals from the door frame open switch for detecting the opening of the
また、ファールカバーユニット520の満タン検知センサ535からの検出信号は、払出制御入力回路に入力され、払出制御I/Oポートを介して払出制御MPUに入力される。
Further, a detection signal from the full
払出制御MPUは、払出モータ834を駆動するための駆動信号を、払出制御I/Oを介して払出モータ834に出力したり、パチンコ機1の状態をエラーLED表示器に表示するための信号を、払出制御I/Oポートを介してエラーLED表示器に出力したり、パチンコ機1の状態を示すためのコマンドを、払出制御I/Oポートを介して主制御基板1310にシリアル方式で送信したり、実際に払出した遊技球の球数を払出制御I/Oポートを介して外部端子板784に出力したりする。この外部端子板784は、遊技ホール側に設置されたホールコンピュータに接続されている。このホールコンピュータは、パチンコ機1が払出した遊技球の球数やパチンコ機1の遊技情報等を把握することにより遊技者の遊技を監視している。外部端子板784から出力する信号のうち主制御基板1310が生成する信号は、主制御基板1310から払出制御基板951を経由して外部端子板784から出力する。なお、主制御基板1310が生成する信号を、払出制御基板951を経由せずに外部端子板784から出力してもよい。
The payout control MPU outputs a drive signal for driving the payout motor 834 to the payout motor 834 via the payout control I/O, and outputs a signal for displaying the state of the
エラーLED表示器は、セグメント表示器であり、英数字や図形等を表示してパチンコ機1の状態を表示している。エラーLED表示器が表示して報知する内容としては、次のようなものがある。例えば、図形「-」が表示されているときには「正常」である旨を報知し、数字「0」が表示されているときには「接続異常」である旨(具体的には、主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951との基板間の電気的な接続に異常が生じている旨)を報知し、数字「1」が表示されているときには「球切れ」である旨(具体的には、球切れ検知センサ827からの検出信号に基づいて払出装置830内に遊技球がない旨)を報知し、数字「2」が表示されているときには「球がみ」である旨(具体的には、羽根回転検知センサ840からの検出信号に基づいて払出装置830の払出通路において払出羽根と遊技球とがかみ合って払出羽根が回転困難となっている旨)を報知し、数字「3」が表示されているときには「計数スイッチエラー」である旨(具体的には、払出検知センサ842からの検出信号に基づいて払出検知センサ842に不具合が生じている旨)を報知し、数字「5」が表示されているときには「リトライエラー」である旨(具体的には、払出し動作のリトライ回数が予め設定された上限値に達した旨)を報知し、数字「6」が表示されているときには「満タン」である旨(具体的には、満タン検知センサ535からの検出信号に基づいてファールカバーユニット520内に貯留された遊技球で満タンである旨)を報知し、数字「7」が表示されているときには「CR未接続」である旨(払出制御基板951からCRユニットまでに亘るいずれかにおいて電気的な接続が切断されている旨)を報知し、数字「9」が表示されているときには「ストック中」である旨(具体的には、まだ払出していない遊技球の球数が予め定めた球数に達している旨)を報知している。
The error LED indicator is a segment indicator, and displays the status of the
球貸ボタンからの遊技球の球貸要求信号、及び返却ボタンからのプリペイドカードの返却要求信号は、CRユニットに入力される。CRユニットは、球貸要求信号に従って貸し
出す遊技球の球数を指定した信号を、払出制御基板951にシリアル方式で送信し、この信号が払出制御I/Oポートで受信されて払出制御MPUに入力される。またCRユニットは、貸出した遊技球の球数に応じて挿入されたプリペイドカードの残度を更新するとともに、その残度を表示部に表示するための信号を出力し、この信号が表示部に入力されて表示される。
A game ball lending request signal from the ball lending button and a prepaid card return requesting signal from the return button are input to the CR unit. The CR unit transmits a signal designating the number of game balls to be lent according to the ball lending request signal to the
[3-2b.発射制御部]
発射ソレノイド682による発射制御と、球送りソレノイド551による球送制御と、を行う発射制御部953は、詳細に図示は省略するが、発射に関する各種検出スイッチからの検出信号が入力される発射制御入力回路と、定時間毎にクロック信号を出力する発振回路と、このクロック信号に基づいて遊技球を遊技領域5aに向かって打ち出すための発射基準パルスを出力する発射タイミング制御回路と、この発射基準パルスに基づいて発射ソレノイド682に駆動信号を出力する発射ソレノイド駆動回路と、発射基準パルスに基づいて球送りソレノイド551に駆動信号を出力する球送りソレノイド駆動回路と、を備えている。発射タイミング制御回路は、発振回路からのクロック信号に基づいて、1分当たり100個の遊技球が遊技領域5aに向かって打ち出されるよう発射基準パルスを生成して発射ソレノイド駆動回路に出力するとともに、発射基準パルスを所定数倍した球送基準パルスを生成して球送りソレノイド駆動回路に出力する。
[3-2b. Launch control unit]
Although not shown in detail, a
ハンドルユニット500関係では、ハンドルレバー504に手のひらや指が触れているか否かを検出する接触検知センサ509、及び遊技者の意志によって遊技球の打ち出しを強制的に停止するか否かを検出するストップボタンからの検出信号は、発射制御入力回路に入力された後に、発射タイミング制御回路に入力される。またCRユニットとCRユニット接続端子板とが電気的に接続されると、CR接続信号として発射制御入力回路に入力され、発射タイミング制御回路に入力される。ハンドルレバー504の回転位置に応じて遊技球を遊技領域5aに向かって打ち出す強度を電気的に調節するハンドル操作センサ507からの信号は、発射ソレノイド駆動回路に入力される。
In relation to the
この発射ソレノイド駆動回路は、ハンドル操作センサ507からの信号に基づいて、ハンドルレバー504の回転位置に見合う打ち出し強度で遊技球を遊技領域5aに向かって打ち出すための駆動電流を、発射基準パルスが入力されたことを契機として、発射ソレノイド682に出力する。一方、球送りソレノイド駆動回路は、球送基準パルスが入力されたことを契機として、球送りソレノイド551に一定電流を出力することにより、皿ユニット200の上皿201に貯留された遊技球を球送りユニット540内に1球受入れ、その球送基準パルスの入力が終了したことを契機として、その一定電流の出力を停止することにより受入れた遊技球を球発射装置680側へ送る。このように、発射ソレノイド駆動回路から発射ソレノイド682に出力される駆動電流は可変に制御されるのに対して、球送りソレノイド駆動回路から球送りソレノイド551に出力される駆動電流は一定に制御されている。
This firing solenoid drive circuit receives a drive current for firing a game ball toward the
なお、払出制御基板951に各種電圧を供給する電源基板は、電源遮断時にでも所定時間、主制御基板1310に電力を供給するためのバックアップ電源としてのキャパシタを備えている。このキャパシタにより払出制御MPUは、電源遮断時にでも電源断時処理において各種情報を払出制御基板951のRAMに記憶することができる。この記憶した各種情報は、電源投入時に主制御基板1310のRAMクリアスイッチが操作されると、払出制御基板951のRAMから完全に消去(クリア)される。
In addition, the power board that supplies various voltages to the
[3-3.周辺制御基板]
周辺制御基板1510は、図17に示すように、主制御基板1310からのコマンドに基づいて演出制御を行う周辺制御部1511と、この周辺制御部1511からの制御デー
タに基づいてメイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244の描画制御を行う液晶表示制御部1512と、を備えている。
[3-3. Peripheral control board]
As shown in FIG. 17, the peripheral control board 1510 includes a
[3-3a.周辺制御部]
周辺制御基板1510における演出制御を行う周辺制御部1511は、詳細な図示は省略するが、マイクロプロセッサとしての周辺制御MPUと、各種処理プログラムや各種コマンドを記憶する周辺制御ROMと、高音質の演奏を行う音源ICと、この音源ICが参照する音楽及び効果音等の音情報が記憶されている音ROMと、を備えている。
[3-3a. Peripheral control unit]
Although detailed illustration is omitted, the
周辺制御MPUは、パラレルI/Oポート、シリアルI/Oポート等を複数内蔵しており、主制御基板1310から各種コマンドを受信すると、この各種コマンドに基づいて、遊技盤5の各装飾基板に設けられたカラーLED等への点灯信号、点滅信号又は階調点灯信号を出力するための遊技盤側発光データをランプ駆動基板用シリアルI/Oポートから演出駆動基板3043に送信したり、遊技盤5に設けられた各種演出ユニットを作動させる駆動モータへの駆動信号を出力するための遊技盤側駆動データを遊技盤装飾駆動基板用シリアルI/Oポートから演出駆動基板3043に送信したり、扉枠3に設けられた加振装置242や扉右下駆動モータ272等の電気的駆動源への駆動信号を出力するための扉側駆動データと、扉枠3の各装飾基板に設けられたカラーLED等への点灯信号、点滅信号又は階調点灯信号を出力するための扉側発光データと、から構成される扉側駆動発光データを枠装飾駆動基板用シリアルI/Oポートから扉枠3側に送信したり、メイン液晶表示装置1600や上皿液晶表示装置244に表示させる画面を示す制御データ(表示コマンド)を液晶制御部用シリアルI/Oポートから液晶表示制御部1512に送信したり、するほかに、音ROMから音情報を抽出するための制御信号(音コマンド)を音源ICに出力したりする。 The peripheral control MPU incorporates a plurality of parallel I/O ports, serial I/O ports, etc. When various commands are received from the main control board 1310, based on these various commands, each decoration board of the game board 5 The game board side light emission data for outputting a lighting signal, a blinking signal or a gradation lighting signal to the provided color LED etc. is transmitted from the serial I / O port for the lamp driving board to the effect driving board 3043, or the game board The game board side drive data for outputting the drive signal to the drive motor that operates the various production units provided in 5 is transmitted from the game board decoration drive board serial I / O port to the production drive board 3043, and the door Door-side drive data for outputting a drive signal to an electric drive source such as the vibrating device 242 provided on the frame 3 and the door lower right drive motor 272; door-side drive light-emission data for outputting a lighting signal, a blinking signal, or a gradation lighting signal to an LED or the like; or to transmit control data (display command) indicating a screen to be displayed on the main liquid crystal display device 1600 or the upper liquid crystal display device 244 from the serial I/O port for the liquid crystal control section to the liquid crystal display control section 1512, In addition, it outputs a control signal (sound command) for extracting sound information from the sound ROM to the sound source IC.
遊技盤5に設けられた各種演出ユニットの位置を検出するための各種位置検出センサからの検出信号は、裏箱の後面に取付けられた演出駆動基板3043を介して周辺制御MPUに入力されている。また、扉枠3に設けられた演出操作ユニット220のタッチパネル246、演出ボタン押圧センサ258からの検出信号は、周辺制御MPUに入力されている。
Detection signals from various position detection sensors for detecting the positions of various effect units provided on the
また周辺制御MPUは、液晶表示制御部1512が正常に動作している旨を伝える信号(動作信号)が液晶表示制御部1512から入力されており、この動作信号に基づいて液晶表示制御部1512の動作を監視している。
Further, the peripheral control MPU receives a signal (operation signal) from the liquid crystal
音源ICは、周辺制御MPUからの制御データ(音コマンド)に基づいて音ROMから音情報を抽出し、扉枠3や本体枠4等に設けられたスピーカ921等から各種演出に合せた音楽及び効果音等が流れるように制御を行う。なお、周辺制御基板1510が収容された周辺制御基板ボックス1520から後方へ突出しているボリュームを回転操作することで、音量を調整することができるようになっている。本実施形態では、扉枠3側の複数のスピーカと本体枠4の低音用のスピーカ921とに、音情報としての音響信号(例えば、2chステレオ信号、4chステレオ信号、2.1chサラウンド信号、或いは、4.1chサラウンド信号、等)を送ることで、従来よりも臨場感のある音響効果(音響演出)を提示することができる。
The sound source IC extracts sound information from the sound ROM based on the control data (sound command) from the peripheral control MPU, and outputs music and sounds in accordance with various effects from the
なお、周辺制御部1511は、周辺制御MPUに内蔵された内蔵WDT(ウォッチドッグタイマ)のほかに、図示しない、外部WDT(ウォッチドッグタイマ)も備えており、周辺制御MPUは、内蔵WDTと外部WDTとを併用して自身のシステムが暴走しているか否かを診断している。
The
この周辺制御MPUから液晶表示制御部1512に出力される表示コマンドはシリアル入出力ポートにより行われ、本実施形態では、ビットレート(単位時間あたりに送信できるデータの大きさ)として19.2キロ(k)ビーピーエス(bits per second、以下、「bps」と記載する)が設定されている。一方、周辺制御MPUから裏箱の後面に取付けられた演出駆動基板3043に出力される、初期データ、扉枠側点灯点滅コマンド、遊技盤側点灯点滅コマンド、可動体駆動コマンド、表示コマンドと異なる複数のシリアル入出力ポートにより行われ、本実施形態では、ビットレートとして250kbpsが設定されている。
A display command output from the peripheral control MPU to the liquid crystal
この演出駆動基板3043は、受信した扉枠側点灯点滅コマンドに基いた点灯信号又は点滅信号を、扉枠3に備えられた各装飾基板のLEDに出力したり、受信した遊技盤側点灯点滅コマンドに基いた点灯信号又は点滅信号を遊技盤5に備えられた各装飾基板のLEDに出力したりする。
This
また、演出駆動基板3043は、受信した駆動コマンドに基いた駆動信号を、扉枠3に備えられた加振装置242及び扉右下駆動モータ272や、遊技盤5に備えられた各駆動モータ等に出力したりする。
In addition, the
[3-3b.周辺制御部の各種制御処理]
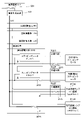
まず、周辺制御部電源投入時処理について、図60を参照して説明する。パチンコ機1に電源が投入されると、図17に示した周辺制御部1511の周辺制御MPU(図示省略)は、図60に示すように、周辺制御部電源投入時処理を行う。この周辺制御部電源投入時処理が開始されると、演出制御プログラムが周辺制御MPUの制御の下、初期設定処理を行う(ステップS1000)。この初期設定処理では、演出制御プログラムが、周辺制御MPU自身を初期化する処理と、ホットスタート/コールドスタートの判定処理と、リセット後のウェイトタイマを設定する処理等を行う。周辺制御MPUは、まず自身を初期化する処理を行うが、この周辺制御MPUを初期化する処理にかかる時間は、マイクロ秒(μs)オーダーであり、極めて短い時間で周辺制御MPUを初期化することができる。これにより、周辺制御MPUは、割り込み許可が設定された状態となることによって、例えば、後述する周辺制御部コマンド受信割り込み処理において、主制御基板1310から出力される、遊技演出の制御に関するコマンドやパチンコ機1の状態に関するコマンド等の各種コマンドを受信することができる状態となる。
[3-3b. Various control processing of the peripheral control unit]
First, the peripheral controller power-on process will be described with reference to FIG. When the power is turned on to the
ステップS1000に続いて、演出制御プログラムは現在時刻情報取得処理を行う(ステップS1002)。この現在時刻情報取得処理では、RTC制御部から、年月日を特定するカレンダー情報と時分秒を特定する時刻情報とを取得して、周辺制御RAMに、現在のカレンダー情報としてカレンダー情報記憶部にセットするとともに、現在の時刻情報として時刻情報記憶部にセットする。 Following step S1000, the effect control program performs current time information acquisition processing (step S1002). In this current time information acquisition process, calendar information specifying the year, month, day and time information specifying the hour, minute, and second are acquired from the RTC control unit, and stored in the peripheral control RAM as the current calendar information in the calendar information storage unit. , and set it in the time information storage unit as the current time information.
ステップS1002に続いて、演出制御プログラムは、Vブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGに値0をセットする(ステップS1006)。このVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGは、後述する周辺制御部定常処理を実行するか否かを決定するためのフラグであり、周辺制御部定常処理を実行するとき値1、周辺制御部定常処理を実行しないとき値0にそれぞれ設定される。Vブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGは、周辺制御MPUからの画面データを受け入れることができる状態である旨を伝えるVブランク信号が入力されたことを契機として実行される後述する周辺制御部Vブランク信号割り込み処理において値1がセットされるようになっている。このステップS1006では、Vブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGに値0をセットすることによりVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGを一度初期化している。
Following step S1002, the effect control program sets the
ステップS1006に続いて、演出制御プログラムは、Vブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGが値1であるか否かを判定する(ステップS1008)。このVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGが値1でない(値0である)ときには、再びステップS1008に戻ってVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGが値1であるか否かを繰り返し判定する。このような判定を繰り返すことにより、周辺制御部定常処理を実行するまで待機する状態となる。 Following step S1006, the effect control program determines whether or not the V blank signal detection flag VB-FLG is value 1 (step S1008). When the V blank signal detection flag VB-FLG is not 1 (is 0), the process returns to step S1008 to repeatedly determine whether the V blank signal detection flag VB-FLG is 1 or not. By repeating such a determination, a standby state is established until the peripheral controller steady-state processing is executed.
ステップS1008でVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGが値1であるとき、つまり周辺制御部定常処理を実行するときには、まず定常処理中フラグSP-FLGに値1をセットする(ステップS1009)。この定常処理中フラグSP-FLGは、周辺制御部定常処理を実行中であるとき値1、周辺制御部定常処理を実行完了したとき値0にそれぞれセットされる。 When the V blank signal detection flag VB-FLG is 1 in step S1008, that is, when the peripheral controller steady-state processing is executed, the steady-state processing flag SP-FLG is set to 1 (step S1009). The steady-processing flag SP-FLG is set to a value of 1 when the peripheral control unit steady processing is being executed, and set to a value of 0 when the peripheral control unit steady processing is completed.
ステップS1009に続いて、演出制御プログラムは1ms割り込みタイマ起動処理を行う(ステップS1010)。この1ms割り込みタイマ起動処理では、後述する周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理を実行するための1ms割り込みタイマを起動するとともに、この1ms割り込みタイマが起動して周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理が実行された回数をカウントするための1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNに値1をセットして1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNの初期化も行う。この1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNは周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理で更新される。
Following step S1009, the effect control program performs 1 ms interrupt timer activation processing (step S1010). In this 1 ms interrupt timer start processing, a 1 ms interrupt timer for executing
ステップS1010に続いて、演出制御プログラムは、ランプデータ出力処理を行う(ステップS1012)。このランプデータ出力処理では、演出制御プログラムが図119に示したランプ駆動基板4170へのDMAシリアル連続送信を行う。ここでは、周辺制御MPUの周辺制御DMAコントローラを利用してランプ駆動基板用シリアルI/Oポート連続送信を行う。 Following step S1010, the effect control program performs lamp data output processing (step S1012). In this lamp data output process, the effect control program performs continuous DMA serial transmission to the lamp driving board 4170 shown in FIG. In this case, the peripheral control DMA controller of the peripheral control MPU is used to perform continuous transmission to the serial I/O port for the lamp driving board.
ステップS1012に続いて、演出制御プログラムは、演出操作ユニット監視処理を行う(ステップS1014)。この演出操作ユニット監視処理では、後述する周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理における演出操作ユニット情報取得処理において、演出操作ユニット220に設けられた各種検出スイッチからの検出信号に基づいて操作ボタン220Cの操作等を取得した各種情報に基づいて、操作ボタン220Cの操作有無を監視し、操作ボタン220Cの操作の状態を遊技演出に反映するか否かを適宜決定する。
Following step S1012, the production control program performs production operation unit monitoring processing (step S1014). In this effect operation unit monitoring process, in the effect operation unit information acquisition process in the peripheral control unit 1ms timer interrupt process described later, the operation of the
ステップS1014に続いて、演出制御プログラムは、表示データ出力処理を行う(ステップS1016)。この表示データ出力処理では、後述する表示データ作成処理で音源内蔵VDPの内蔵VRAM上に生成した1画面分(1フレーム分)の描画データを音源内蔵VDPが遊技盤側装飾基板3053及び扉枠側装飾基板233に出力する。これにより、遊技盤側装飾基板3053及び扉枠側装飾基板233にさまざまな画面が描画される。
Following step S1014, the effect control program performs display data output processing (step S1016). In this display data output process, drawing data for one screen (one frame) generated on the built-in VRAM of the built-in sound source VDP in the display data creation process described later is transferred to the VDP built-in sound source on the game board side
ステップS1016に続いて、演出制御プログラムは、音データ出力処理を行う(ステップS1018)。この音データ出力処理では、演出制御プログラムが、後述する音データ作成処理で音源内蔵VDPに設定された音楽及び効果音等の音データをスピーカ921に出力したり、音楽及び効果音のほかに報知音や告知音の音データをスピーカ921に出力したりする。
Following step S1016, the effect control program performs sound data output processing (step S1018). In this sound data output process, the production control program outputs sound data such as music and sound effects set in the sound source built-in VDP in the sound data creation process to be described later to the
ステップS1018に続いて、演出制御プログラムはスケジューラ更新処理を行う(ステップS1020)。このスケジューラ更新処理では、演出制御プログラムが周辺制御RAMにセットされた各種スケジュールデータを更新する。例えば、スケジューラ更新処理では、画面生成用スケジュールデータを構成する時系列に配列された画面データのうち、
先頭の画面データから何番目の画面データを音源内蔵VDPに出力するのかを指示するために、ポインタを更新する。
Following step S1018, the effect control program performs scheduler update processing (step S1020). In this scheduler update process, the performance control program updates various schedule data set in the peripheral control RAM. For example, in the scheduler update process, of the screen data arranged in time series that constitutes the schedule data for screen generation,
The pointer is updated to indicate which screen data from the first screen data is to be output to the tone generator built-in VDP.
またスケジューラ更新処理では、発光態様生成用スケジュールデータを構成する時系列に配列された発光データのうち、先頭の発光データから何番目の発光データを各種LEDの発光態様とするのかを指示するために、ポインタを更新する。 Further, in the scheduler update process, among the light emission data arranged in time series constituting the light emission mode generation schedule data, the number of the light emission data from the top light emission data is to be used as the light emission mode of each LED. , to update the pointer.
またスケジューラ更新処理では、音生成用スケジュールデータを構成する時系列に配列された、音楽や効果音等の音データ、報知音や告知音の音データを指示する音指令データのうち、先頭の音指令データから何番目の音指令データを音源内蔵VDPに出力するのかを指示するために、ポインタを更新する。 In the scheduler update process, among the sound data such as music and sound effects arranged in time series, and the sound command data indicating the sound data of the notification sound and notification sound, the first sound A pointer is updated in order to indicate what number of sound command data is to be output from the command data to the tone generator built-in VDP.
またスケジューラ更新処理では、電気的駆動源スケジュールデータを構成する時系列に配列されたモータやソレノイド等の電気的駆動源の駆動データのうち、先頭の駆動データから何番目の駆動データを出力対象とするのかを指示するために、ポインタを更新する。 Further, in the scheduler update process, among the drive data of the electric drive sources such as motors and solenoids arranged in time series that constitute the electric drive source schedule data, the drive data of which order from the head drive data is to be output. Update the pointer to indicate what to do.
ステップS1020に続いて、演出制御プログラムは、受信コマンド解析処理を行う(ステップS1022)。この受信コマンド解析処理では、演出制御プログラムが、遊技盤側装飾基板3053から送信された情報や、主制御基板1310から送信された各種コマンドであって、後述する周辺制御部コマンド受信割り込み処理(コマンド受信手段)において受信した各種コマンドの解析を行う(コマンド解析手段)。
Following step S1020, the effect control program performs received command analysis processing (step S1022). In this received command analysis process, the effect control program is information transmitted from the game board
ステップS1022に続いて、演出制御プログラムが警告処理を行う(ステップS1024)。この警告処理では、さらに、演出制御プログラムが、上述のようにステップS1022の受信コマンド解析処理で解析したコマンドに、所定の報知表示に区分される各種コマンドが含まれているときには、各種異常報知を実行するための異常表示態様に設定されている、画面生成用スケジュールデータ、発光態様生成用スケジュールデータ、音生成用スケジュールデータ、及び電気的駆動源スケジュールデータ等を、周辺制御部1511の周辺制御ROM又は周辺制御RAMから抽出して周辺制御RAMにセットする。なお、警告処理では、複数の異常が同時に発生した場合には、予め登録した優先度の高い順から異常報知から行われ、その異常が解決して残っている他の異常報知に自動的に遷移するようになっている。これにより、一の異常が発生した後であってその異常を解決する前に他の異常が発生して一の異常が発生しているという情報を失うことなく、複数の異常を同時に監視することができる。
Following step S1022, the effect control program performs warning processing (step S1024). In this warning process, furthermore, when the commands analyzed by the received command analysis process of step S1022 as described above include various commands classified into predetermined notification displays, the effect control program issues various abnormal notifications. The schedule data for screen generation, the schedule data for light emission mode generation, the schedule data for sound generation, the electric drive source schedule data, etc., which are set in the abnormal display mode for execution, are stored in the peripheral control ROM of the
またさらに、この警告処理では、電源投入時から所定時間が経過した後に、演出制御プログラムが、上述した受信コマンド解析処理(ステップS1022)において解析したコマンドが、状態表示に区分される各種コマンド、例えばエラー解除ナビコマンド(第2のエラー解除コマンド)である場合、演出動作に伴う通常の演出態様とは異なる態様に制御することにより、例えば、遊技盤側装飾基板3053(演出装置)、扉枠側装飾基板233(演出装置)、ランプ(演出装置)を用いて視覚的に外部に警告したり、スピーカを用いて聴覚的に外部に警告する(エラー報知手段)。このようにすると、悪意のある遊技者が、遊技状態であるにも拘わらず払出制御基板951の操作スイッチを操作することにより主制御基板1310にエラー解除ナビコマンドを入力しようと試行した際に、パチンコ機1が外部に警告を行う構成となっているため、遊技の進行に影響を及ぼしかねない主制御基板1310に対する不正行為が抑止されるようになる。
Furthermore, in this warning process, after a predetermined time has elapsed since the power was turned on, the command analyzed by the effect control program in the received command analysis process (step S1022) described above is classified into various commands for status display, such as In the case of the error cancellation navigation command (second error cancellation command), by controlling in a mode different from the normal presentation mode accompanying the presentation operation, for example, the game board side decoration board 3053 (drawing device), the door frame side A decorative substrate 233 (rendering device) and a lamp (rendering device) are used to visually warn the outside, and a speaker is used to audibly warn the outside (error notification means). In this way, when a malicious player tries to input an error cancellation navigation command to the
次に、上述したステップS1024に続いて、演出制御プログラムはRCT取得情報更新処理を行う(ステップS1026)。このRTC取得情報更新処理では、演出制御プログラムが、ステップS1002の現在時刻情報取得処理で取得して周辺制御RAMにセッ
トした、カレンダー情報記憶部に記憶されたカレンダー情報と時刻情報記憶部に記憶された時刻情報とを更新する。このRCT取得情報更新処理により、時刻情報記憶部に記憶される時刻情報である時分秒が更新され、この更新される時刻情報に基づいてカレンダー情報記憶部に記憶されるカレンダー情報である年月日が更新される。
Next, following step S1024 described above, the effect control program performs RCT acquisition information update processing (step S1026). In this RTC acquisition information update process, the effect control program stores the calendar information stored in the calendar information storage unit and the time information storage unit acquired in the current time information acquisition processing of step S1002 and set in the peripheral control RAM. update the time information. By this RCT acquisition information update processing, the hour, minute, and second, which are the time information stored in the time information storage unit, are updated, and based on the updated time information, the year, month, and month, which are the calendar information stored in the calendar information storage unit. date is updated.
ステップS1026に続いて、演出制御プログラムはランプデータ作成処理を行う(ステップS1028)。このランプデータ作成処理では、この演出制御プログラムが、ステップS1020のスケジューラ更新処理においてポインタが更新されて、発光態様生成用スケジュールデータを構成する時系列に配列された発光データのうち、そのポインタが指示する発光データに基づいて、遊技盤5に設けた各種装飾基板の複数のLEDへの点灯信号、点滅信号、又は階調点灯信号を出力するための遊技盤側発光データSL-DATを、周辺制御部1511の周辺制御ROM又は周辺制御RAMから抽出して作成するとともに、周辺制御RAMにセットするとともに、扉枠3に設けた各種装飾基板の複数のLEDへの点灯信号、点滅信号又は階調点灯信号を出力するための扉側発光データSTL-DATを、周辺制御部1511の周辺制御ROM又は周辺制御RAMから抽出して作成して、周辺制御RAMにセットする。
Following step S1026, the effect control program performs lamp data creation processing (step S1028). In this lamp data creation process, the effect control program updates the pointer in the scheduler update process of step S1020, and the pointer is designated among the light emission data arranged in time series constituting the light emission mode generation schedule data. Peripheral control of game board side light emission data SL-DAT for outputting a lighting signal, a blinking signal, or a gradation lighting signal to a plurality of LEDs of various decorative boards provided on the
ステップS1028に続いて、演出制御プログラムは表示データ作成処理を行う(ステップS1030)。この表示データ作成処理では、演出制御プログラムが、ステップS1020のスケジューラ更新処理においてポインタが更新されて、画面生成用スケジュールデータを構成する時系列に配列された画面データのうち、そのポインタが示す画面データを、周辺制御部1511の周辺制御ROM又は周辺制御RAMから抽出して音源内蔵VDPに出力する。音源内蔵VDPは、周辺制御MPUから画面データが入力されると、この入力された画面データに基づいて液晶及び音制御ROM1512bからキャラクタデータを抽出してスプライトデータを作成して遊技盤側装飾基板3053及び扉枠側装飾基板233に表示する1画面分(1フレーム分)の描画データを内蔵VRAM上に生成する。
Following step S1028, the effect control program performs display data creation processing (step S1030). In this display data creation process, the presentation control program updates the pointer in the scheduler update process of step S1020, and out of the screen data arranged in time series constituting the schedule data for screen generation, the screen data indicated by the pointer. is extracted from the peripheral control ROM or peripheral control RAM of the
ステップS1030に続いて、演出制御プログラムは音データ作成処理を行う(ステップS1032)。この音データ作成処理では、演出制御プログラムが、ステップS1020のスケジューラ更新処理においてポインタが更新されて、音生成用スケジュールデータを構成する時系列に配列された音指令データのうち、そのポインタが指示する音指令データを、周辺制御部1511の周辺制御ROM又は周辺制御RAMから抽出して音源内蔵VDPに出力する。音源内蔵VDPは、周辺制御MPUから音指令データが入力されると、液晶及び音制御ROMに記憶されている音楽や効果音等の音データを抽出して内蔵音源を制御することにより、音指令データに規定された、トラック番号に従って音楽及び効果音等の音データを組み込むとともに、出力チャンネル番号に従って使用する出力チャンネルを設定する。
Following step S1030, the effect control program performs sound data creation processing (step S1032). In this sound data creation process, the presentation control program updates the pointer in the scheduler update process of step S1020, and the pointer points out of the sound instruction data arranged in time series constituting the schedule data for sound generation. The sound command data is extracted from the peripheral control ROM or peripheral control RAM of the
ステップS1032に続いて、演出制御プログラムはバックアップ処理を行う(ステップS1034)。このバックアップ処理では、演出制御プログラムが、周辺制御MPUと外付けされる周辺制御RAMに記憶されている内容を、バックアップ第1エリアと、バックアップ第2エリアと、にそれぞれコピーしてバックアップするとともに、周辺制御MPUと外付けされる周辺制御SRAMに記憶されている内容を、バックアップ第1エリアと、バックアップ第2エリアと、にそれぞれコピーしてバックアップする。 Following step S1032, the effect control program performs backup processing (step S1034). In this backup process, the performance control program copies and backs up the contents stored in the peripheral control MPU and the peripheral control RAM externally attached to the first backup area and the second backup area, respectively. The contents stored in the peripheral control MPU and the externally attached peripheral control SRAM are copied and backed up in the first backup area and the second backup area, respectively.
ステップS1034に続いて、WDTクリア処理を行う(ステップS1036)。このWDTクリア処理では、周辺制御内蔵WDT1511afと、周辺制御外部WDT1511eと、にクリア信号を出力して周辺制御MPUにリセットがかからないようにしている。 Following step S1034, WDT clear processing is performed (step S1036). In this WDT clearing process, a clear signal is output to the peripheral control built-in WDT 1511af and the peripheral control external WDT 1511e so that the peripheral control MPU is not reset.
ステップS1036に続いて、演出制御プログラムが、周辺制御部定常処理の実行完了として定常処理中フラグSP-FLGに値0をセットし(ステップS1038)、再びステップS1006に戻り、Vブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGに値0をセットして初期化し、後述する周辺制御部Vブランク信号割り込み処理においてVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGに値1がセットされるまで、ステップS1008の判定を繰り返し行う。つまりステップS1008では、Vブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGに値1がセットされるまで待機し、ステップS1008でVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGが値1であると判定されると、ステップS1009~ステップS1038の処理を行い、再びステップS1006に戻る。このように、ステップS1008でVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGが値1であると判定されると、ステップS1009~ステップS1038の処理を行うようになっている。ステップS1009~ステップS1038の処理を「周辺制御部定常処理」という。
Following step S1036, the effect control program sets the
この周辺制御部定常処理は、演出制御プログラムが、まずステップS1009で周辺制御部定常処理を実行中であるとして定常処理中フラグSP-FLGに値1をセットすることから開始し、ステップS1010で1ms割り込みタイマ起動処理を行い、ステップS1012、ステップS1014、・・・、そしてステップS1036の各処理を行って最後にステップS1038において周辺制御部定常処理の実行完了として定常処理中フラグSP-FLGに値0をセットすると、完了することとなる。周辺制御部定常処理は、ステップS1008でVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGが値1であるときに実行される。このVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGは、上述したように、周辺制御MPUからの画面データを受け入れることができる状態である旨を伝えるVブランク信号が音源内蔵VDPから入力されたことを契機として実行される後述する周辺制御部Vブランク信号割り込み処理において値1がセットされるようになっている。本実施形態では、遊技盤側装飾基板3053及び扉枠側装飾基板233のフレーム周波数(1秒間あたりの画面更新回数)として、上述したように、概ね秒間30fpsに設定しているため、Vブランク信号が入力される間隔は、約33.3ms(=1000ms÷30fps)となっている。つまり、周辺制御部定常処理は、約33.3msごとに繰り返し実行されるようになっている。
This peripheral control unit steady processing, effect control program, first step S1009 peripheral control unit steady processing is being executed and starts from setting the
次に、図61に示した、周辺制御部1511の周辺制御MPUからの画面データを受け入れることができる状態である旨を伝えるVブランク信号が液晶表示制御部1512の音源内蔵VDPから入力されたことを契機として実行する周辺制御部Vブランク信号割り込み処理について説明する。この周辺制御部Vブランク信号割り込み処理が開始されると、周辺制御部1511の周辺制御MPUは、図61に示すように、定常処理中フラグSP-FLGが値0であるかを判定する(ステップS1045)。この定常処理中フラグSP-FLGは、上述したように、図60の周辺制御部電源投入時処理におけるステップS1009~ステップS1038の周辺制御部定常処理を実行中であるとき値1、周辺制御部定常処理を実行完了したとき値0にそれぞれセットされる。
Next, as shown in FIG. 61, the V blank signal indicating that the screen data from the peripheral control MPU of the
ステップS1045で定常処理中フラグSP-FLGが値0でない(値1である)とき、つまり周辺制御部定常処理を実行中であるときには、そのままこのルーチンを終了する。一方、ステップS1045で定常処理中フラグSP-FLGが値0であるとき、つまり周辺制御部定常処理を実行完了したときには、Vブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGに値1をセットし(ステップS1050)、このルーチンを終了する。このVブランク信号検出フラグVB-FLGは、上述したように、周辺制御部定常処理を実行するか否かを決定するためのフラグであり、周辺制御部定常処理を実行するとき値1、周辺制御部定常処理を実行しないとき値0にそれぞれ設定される。 When the steady-state processing flag SP-FLG is not 0 (is 1) in step S1045, that is, when the peripheral control section steady-state processing is being executed, this routine ends. On the other hand, when the steady-state processing flag SP-FLG is 0 in step S1045, that is, when the execution of the peripheral control unit steady-state processing is completed, the V blank signal detection flag VB-FLG is set to 1 (step S1050), Exit this routine. As described above, the V blank signal detection flag VB-FLG is a flag for determining whether or not to execute the peripheral control unit steady processing. They are each set to a value of 0 when no routine processing is executed.
次に、図60の周辺制御部電源投入時処理の周辺制御部定常処理におけるステップS1
010で1ms割り込みタイマの起動により1ms割り込みタイマが発生するごとに繰り返し実行する周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理について説明する。この周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理が開始されると、周辺制御部1511の周辺制御MPUは、図62に示すように、1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNが33回より小さいか否かを判定する(ステップS1100)。この1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNは、上述したように、図60の周辺制御部電源投入時処理の周辺制御部定常処理におけるステップS1010の1ms割り込みタイマ起動処理で1ms割り込みタイマが起動して本ルーチンである周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理が実行された回数をカウントするカウンタである。本実施形態では、遊技盤側装飾基板3053及び扉枠側装飾基板233のフレーム周波数(1秒間あたりの画面更新回数)として、上述したように、概ね秒間30fpsに設定しているため、Vブランク信号が入力される間隔は、約33.3ms(=1000ms÷30fps)となっている。つまり、周辺制御部定常処理は、約33.3msごとに繰り返し実行されるようになっているため、周辺制御部定常処理におけるステップS1010で1ms割り込みタイマを起動した後、次の周辺制御部定常処理が実行されるまでに、周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理が32回だけ実行されるようになっている。具体的には、周辺制御部定常処理におけるステップS1010で1ms割り込みタイマが起動されると、まず1回目の1msタイマ割り込みが発生し、2回目、・・・、そして32回目の1msタイマ割り込みが順次発生することとなる。
Next, step S1 in the peripheral controller steady-state processing of the peripheral controller power-on processing in FIG.
In 010, the peripheral control unit 1ms timer interrupt processing that is repeatedly executed each time the 1ms interrupt timer is generated by activating the 1ms interrupt timer will be described. When this
ステップS1100で1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNが33回より小さくないとき、つまり33回目の1msタイマ割り込みが発生してこの周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理が開始されたときには、そのままこのルーチンを終了する。33回目の1msタイマ割り込みの発生が次回のVブランク信号の発生よりたまたま先行した場合には、本実施形態では、割り込み処理の優先順位として、周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理の方が周辺制御部Vブランク割り込み処理と比べて高く設定されているものの、この33回目の1msタイマ割り込みによる周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理の開始を強制的にキャンセルするようになっている。換言すると、本実施形態では、Vブランク信号が周辺制御基板1510のシステム全体を支配する信号であるため、33回目の1msタイマ割り込みの発生が次回のVブランク信号の発生よりたまたま先行した場合には、周辺制御部Vブランク割り込み処理を実行するために33回目の1msタイマ割り込みによる周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理の開始が強制的にキャンセルさせられている。そして、Vブランク信号の発生により周辺制御部定常処理におけるステップS1010で1ms割り込みタイマを再び起動した後、新たに1回目の1msタイマ割り込みの発生による周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理を開始するようになっている。
When the 1ms timer interrupt execution count STN is not less than 33 times in step S1100, that is, when the 33rd 1ms timer interrupt occurs and this peripheral control unit 1ms timer interrupt processing is started, this routine ends. If the occurrence of the 33rd 1ms timer interrupt happens to precede the next occurrence of the V blank signal, in the present embodiment, the peripheral control unit 1ms timer interrupt processing is prioritized over the peripheral control unit V Although it is set higher than the blank interrupt processing, the start of the
一方、ステップS1100で1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNが33回より小さいときには、1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNに値1だけ足す(インクリメントする、ステップS1102)。この1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNに値1が足されることにより、図60の周辺制御部電源投入時処理の周辺制御部定常処理におけるステップS1010の1ms割り込みタイマ起動処理で1ms割り込みタイマが起動して本ルーチンである周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理が実行された回数が1回分だけ増えることとなる。
On the other hand, when the 1 ms timer interrupt execution count STN is smaller than 33 in step S1100, the
ステップS1102に続いて、モータ及びソレノイド駆動処理を行う(ステップS1104)。このモータ及びソレノイド駆動処理では、周辺制御MPUと周辺制御RAMにセットされた電気的駆動源スケジュールデータを構成する時系列に配列されたモータやソレノイド等の電気的駆動源の駆動データのうち、ポインタが指示する駆動データに従って、各種モータやソレノイド等の電気的駆動源を駆動するとともに、時系列に規定された次の駆動データにポインタを更新し、このモータ及びソレノイド駆動処理を実行するごとに、ポインタを更新する。 Following step S1102, motor and solenoid drive processing is performed (step S1104). In this motor and solenoid drive processing, pointer drives various motors, solenoids, and other electrical drive sources according to the drive data indicated by , updates the pointer to the next drive data specified in chronological order, and executes this motor and solenoid drive process each time, Update the pointer.
ステップS1104に続いて、可動体情報取得処理を行う(ステップS1106)。この可動体情報取得処理では、遊技盤5に設けた各種検出スイッチからの検出信号が入力されているか否かを判定することにより各種検出スイッチからの検出信号の履歴情報(例えば、原位置履歴情報、可動位置履歴情報など。)を作成し、周辺制御RAMにセットする。この周辺制御RAMにセットされる各種検出スイッチからの検出信号の履歴情報から遊技盤5に設けた各種可動体の原位置や可動位置等を取得することができる。
Following step S1104, movable body information acquisition processing is performed (step S1106). In this movable object information acquisition process, history information (for example, original position history information) of detection signals from various detection switches is determined by determining whether or not detection signals from various detection switches provided on the
ステップS1106に続いて、演出操作ユニット情報取得処理を行う(ステップS1108)。この演出操作ユニット情報取得処理では、演出操作ユニット220に設けられた各種検出スイッチからの検出信号が入力されているか否かを判定することにより各種検出スイッチからの検出信号の履歴情報(例えば、操作ボタン220Cの操作履歴情報など)を作成し、周辺制御RAMにセットする。この周辺制御RAMにセットされる各種検出スイッチからの検出信号の履歴情報から操作ボタン220Cの操作有無を取得することができる。
Following step S1106, effect operation unit information acquisition processing is performed (step S1108). In this production operation unit information acquisition process, history information (for example, operation operation history information of the
ステップS1108に続いて、描画状態情報取得処理を行う(ステップS1110)。この描画状態情報取得処理では、扉枠側装飾基板233の扉枠側演出用レシーバICから出力されるLOCKN信号の履歴情報を作成し、周辺制御RAMにセットする。LOCKN信号は、前述したように、扉枠側装飾基板233の扉枠側演出用レシーバICSDIC0が、周辺制御基板1510に備える扉枠側演出用トランスミッタIC1512dから受信した描画データが異常なデータであると判断すると、その旨を伝えるために出力する信号である。
Following step S1108, drawing state information acquisition processing is performed (step S1110). In this drawing state information acquisition process, the history information of the LOCKN signal output from the door frame side performance receiver IC of the door frame
ステップS1110に続いて、バックアップ処理を行い(ステップS1112)、このルーチンを終了する。このバックアップ処理では、周辺制御RAMに記憶されている内容を、バックアップ第1エリアと、バックアップ第2エリアと、にそれぞれコピーしてバックアップするとともに、周辺制御SRAMに記憶されている内容を、バックアップ第1エリアと、バックアップ第2エリアと、にそれぞれコピーしてバックアップする。 Following step S1110, backup processing is performed (step S1112), and this routine ends. In this backup process, the contents stored in the peripheral control RAM are copied to the first backup area and the second backup area for backup, and the contents stored in the peripheral control SRAM are copied to the backup second area. 1 area and the backup second area, respectively, to be backed up.
このように、周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理では、1msという期間内において、演出の進行として上述したステップS1104~ステップS1108の演出に関する各種処理を実行している。これに対して、図60の周辺制御部電源投入時処理における周辺制御部定常処理では、約33.3msという期間内において、演出の進行として上述したステップS1012~ステップS1032の演出に関する各種処理を実行している。周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理では、ステップS1100で1msタイマ割り込み実行回数STNが値33より小さくないとき、つまり33回目の1msタイマ割り込みが発生してこの周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理が開始されたときには、そのままこのルーチンを終了するようになっているため、仮に、33回目の1msタイマ割り込みの発生が次回のVブランク信号の発生よりたまたま先行した場合でも、この33回目の1msタイマ割り込みによる周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理の開始を強制的にキャンセルし、Vブランク信号の発生により周辺制御部定常処理におけるステップS1010で1ms割り込みタイマを再び起動した後、新たに1回目の1msタイマ割り込みの発生による周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理を開始するようになっている。つまり、周辺制御部定常処理による演出の進行状態とタイマ割り込み制御である周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理による演出の進行状態との整合性が崩れないようになっている。したがって、演出の進行状態を確実に整合させることができる。
As described above, in the peripheral control unit 1ms timer interrupt process, various processes related to the effects of steps S1104 to S1108 described above are executed within a period of 1ms as the progress of the effects. On the other hand, in the peripheral control unit steady-state processing in the peripheral control unit power-on processing of FIG. is doing. In the peripheral controller 1ms timer interrupt processing, when the 1ms timer interrupt execution count STN is not less than the
また、上述したように、Vブランク信号が出力される間隔は、遊技盤側装飾基板3053及び扉枠側装飾基板233の液晶サイズによって多少変化するし、周辺制御MPUと音
源内蔵VDPとが実装された周辺制御基板1510の製造ロットにおいてもVブランク信号が出力される間隔が多少変化する場合もある。本実施形態では、Vブランク信号が周辺制御基板1510のシステム全体を支配する信号であるため、33回目の1msタイマ割り込みの発生が次回のVブランク信号の発生よりたまたま先行した場合には、周辺制御部Vブランク割り込み処理を実行するために33回目の1msタイマ割り込みによる周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理の開始が強制的にキャンセルさせられている。つまり本実施形態では、Vブランク信号が出力される間隔が多少変化する場合であっても、33回目の1msタイマ割り込みによる周辺制御部1msタイマ割り込み処理の開始を強制的にキャンセルすることによって、このVブランク信号が出力される間隔が多少変化することによる時間ズレを吸収することができるようになっている。
Also, as described above, the interval at which the V blank signal is output varies somewhat depending on the liquid crystal size of the game board
[3-4.液晶表示制御部]
次に、周辺制御基板1510におけるメイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244の描画制御を行う液晶表示制御部1512は、詳細な図示は省略するが、マイクロプロセッサとしての表示制御MPUと、各種処理プログラム、各種コマンド及び各種データを記憶する表示制御ROMと、メイン液晶表示装置1600や上皿液晶表示装置244を表示制御するVDP(Video Display Processorの略)と、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に表示される画面の各種データを記憶する画像ROMと、この画像ROMに記憶されている各種データが転送されてコピーされる画像RAMと、を備えている。
[3-4. Liquid crystal display control section]
Next, the liquid crystal
この表示制御MPUは、パラレルI/Oポート、シリアルI/Oポート等を内蔵しており、周辺制御部1511からの制御データ(表示コマンド)に基づいてVDPを制御してメイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244の描画制御を行っている。なお、表示制御MPUは、正常に動作していると、その旨を伝える動作信号を周辺制御部1511に出力する。また表示制御MPUは、VDPから実行中信号が入力されており、この実行中信号の出力が16msごとに停止されたことを契機として、割り込み処理を行っている。
This display control MPU incorporates a parallel I/O port, a serial I/O port, etc., and controls the VDP based on control data (display commands) from the
表示制御ROMは、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に描画する画面を生成するための各種プログラムのほかに、周辺制御部1511からの制御データ(表示コマンド)と対応するスケジュールデータ、その制御データ(表示コマンド)と対応する非常駐領域転送スケジュールデータ等を複数記憶している。スケジュールデータは、画面の構成を規定する画面データが時系列に配列されて構成されており、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に描画する画面の順序が規定されている。非常駐領域転送スケジュールデータは、画像ROMに記憶されている各種データを画像RAMの非常駐領域に転送する際に、その順序を規定する非常駐領域転送データが時系列に配列されて構成されている。この非常駐領域転送データは、スケジュールデータの進行に従ってメイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に描画される画面データを、前もって、画像ROMから画像RAMの非常駐領域に各種データを転送する順序が規定されている。
The display control ROM stores control data (display commands) from the
表示制御MPUは、周辺制御部1511からの制御データ(表示コマンド)と対応するスケジュールデータの先頭の画面データを表示制御ROMから抽出してVDPに出力した後に、先頭の画面データに続く画面データを表示制御ROMから抽出してVDPに出力する。このように、表示制御MPUは、スケジュールデータに時系列に配列された画面データを、先頭の画面データから1つずつ表示制御ROMから抽出してVDPに出力する。
The display control MPU extracts the top screen data of the schedule data corresponding to the control data (display command) from the
VDPは、表示制御MPUから出力された画面データが入力されると、この入力された画面データに基づいて画像RAMからスプライトデータを抽出してメイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に表示する描画データを生成し、この生成した描画データを、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に出力する。またVDPは、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244が、表示制御MPUからの画面データを受入れないときに、その旨を伝える実行中信号を表示制御MPUに出力する。なお、VDPは、ラインバッファ方式が採用されている。この「ラインバッファ方式」とは、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244の左右方向を描画する1ライン分の描画データをラインバッファに保持し、このラインバッファに保持した1ライン分の描画データを、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に出力する方式である。
When screen data output from the display control MPU is input, the VDP extracts sprite data from the image RAM based on the input screen data, and displays it on the main liquid
画像ROMには、極めて多くのスプライトデータが記憶されており、その容量が大きくなっている。画像ROMの容量が大きくなると、つまり、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に描画するスプライトの数が多くなると、画像ROMのアクセス速度が無視できなくなり、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に描画する速度に影響することとなる。そこで、本実施形態では、アクセス速度の速い画像RAMに、画像ROMに記憶されているスプライトデータを転送してコピーし、この画像RAMからスプライトデータを抽出している。なお、スプライトデータは、スプライトをビットマップ形式に展開する前のデータである基データであり、圧縮された状態で画像ROMに記憶されている。
The image ROM stores an extremely large amount of sprite data and has a large capacity. When the capacity of the image ROM increases, that is, when the number of sprites to be drawn on the main liquid
ここで、「スプライト」について説明すると、「スプライト」とは、メイン液晶表示装置1600や上皿液晶表示装置244に、纏まった単位として表示されるイメージである。例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に、種々の人物(キャラクタ)を表示させる場合には、夫々の人物を描くためのデータを「スプライト」と呼ぶ。これにより、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に複数人の人物を表示させる場合には、複数のスプライトを用いることとなる。また人物のほかに、背景を構成する家、山、道路等もスプライトであり、背景全体を1つのスプライトとすることもできる。これらのスプライトは、画面に配置される位置やスプライト同士が重なる場合の上下関係(以下、「スプライトの重ね合わせの順序」と記載する。)が設定されてメイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244に描画される。
A "sprite" is an image displayed as a unit on the main liquid
なお、スプライトは縦横それぞれ64画素の矩形領域を複数張り合わせて構成されている。この矩形領域を描くためのデータを「スプライトキャラクタ」と呼ぶ。小さなスプライトの場合には1つのスプライトキャラクタを用いて表現することができるし、人物など比較的大きいスプライトの場合には、例えば横2×縦3などで配置した合計6個のスプライトキャラクタを用いて表現することができる。背景のように更に大きいスプライトの場合には更に多数のスプライトキャラクタを用いて表現することができる。このように、スプライトキャラクタの数及び配置は、スプライトごとに任意に指定することができるようになっている。 Note that the sprite is constructed by gluing together a plurality of rectangular areas of 64 pixels each in length and width. The data for drawing this rectangular area is called a "sprite character". A small sprite can be expressed using one sprite character, and a relatively large sprite such as a person can be expressed using a total of 6 sprite characters, for example, arranged horizontally by 2×vertically 3. can be expressed. Larger sprites such as backgrounds can be represented using more sprite characters. In this way, the number and arrangement of sprite characters can be arbitrarily specified for each sprite.
メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244は、その正面から見て左から右に向かって順次、画素に沿った一方向に画素ごとの表示状態を設定する主走査と、その一方向と交差する方向に主走査を繰り返し行う副走査と、によって駆動される。メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244は、液晶表示制御部1512から出力された1ライン分の描画データが入力されると、主走査としてメイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿
液晶表示装置244の正面から見て左から右に向かって順次、1ライン分の画素にそれぞれ出力する。そして1ライン分の出力が完了すると、メイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244は、副走査として直下のラインに移行し、同様に次ライン分の描画データが入力されると、この次ライン分の描画データに基づいて主走査としてメイン液晶表示装置1600、サブ液晶表示装置3114や上皿液晶表示装置244の正面から見て左から右に向かって順次、1ライン分の画素にそれぞれ出力する。
The main liquid
[4.遊技内容]
次に、本実施形態のパチンコ機1による遊技内容について、主に図10、図16及び図17等を参照して説明する。本実施形態のパチンコ機1は、扉枠3の前面右下隅に配置されたハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504を遊技者が回転操作することで、皿ユニット200の上皿201に貯留された遊技球が、遊技盤5における外レール1001と内レール1002との間を通って遊技領域5a内の上部へと打ち込まれて、遊技球による遊技が開始される。遊技領域5a内の上部へ打ち込まれた遊技球は、その打込強さによってセンター役物2500の左側、或いは、右側の何れかを流下する。なお、遊技球の打込み強さは、ハンドルレバー504の回転量によって調整することができ、時計回りの方向へ回転させるほど強く打込むことができ、連続で一分間に最大100個の遊技球、つまり、0.6秒間隔で遊技球を打込むことができる。
[4. Game content]
Next, game contents by the
また、遊技領域5a内には、適宜位置に所定のゲージ配列で複数の障害釘(図示は省略)が遊技パネル1100(パネル板1110)の前面に植設されており、遊技球が障害釘に当接することで、遊技球の流下速度が抑制されると共に、遊技球に様々な動きが付与されて、その動きを楽しませられるようになっている。また、遊技領域5a内には、障害釘の他に、遊技球の当接により回転する風車(図示は省略)が適宜位置に備えられている。
In addition, in the
センター役物2500の上部へ打込まれた遊技球は、センター役物2500の前周壁部2512の外周面のうち、最も高くなった部位よりも正面視左側へ進入すると、図示しない複数の障害釘に当接しながら、センター役物2500よりも左側の領域を流下することとなる。そして、センター役物2500の左側の領域を流下する遊技球が、センター役物2500の前周壁部2512の外周面に開口しているワープ入口2520に進入すると、ワープ通路2521を通ってセンター役物2500の枠内に開口しているワープ出口2522から誘導路2523を通ってステージ2530に供給される。
When the game ball hit to the top of the
ワープ出口2522からステージ2530に供給された遊技球は、ステージ2530上を転動して左右に行ったり来たりして、左右方向中央の中央誘導部2531、又は、その左右にあるサイド誘導部2532の何れかから後方に放出される。ステージ2530の中央誘導部2531から遊技球が遊技領域5a内に放出されと、この中央誘導部2531が第一始動口2002の直上に位置していることから、中央誘導部2531から放出された遊技球は、高い確率で第一始動口2002に受入れられる。この第一始動口2002に遊技球が受入れられると、主制御基板1310及び払出制御基板951を介して払出装置830から所定数(例えば、3個)の遊技球が、上皿201に払出される。
The game ball supplied to the
ステージ2530を転動している遊技球が、サイド誘導部2532から遊技領域5a内に放出されと、始動口ユニット2100へ向かって流下する。センター役物2500のステージ2530から遊技領域5a内に放出された遊技球は、始動口ユニット2100の第一始動口2002や、開状態の第一大入賞口2005等に受入れられる可能性がある。
When the game ball rolling on the
ところで、センター役物2500の左側へ流下した遊技球が、ワープ入口2520に進入しなかった場合、サイドユニット上2300の棚部2302により左右方向中央側へ寄
せられ、サイドユニット下2200の一般入賞口2001や第一始動口2002等に受入れられる可能性がある。そして、一般入賞口2001に遊技球が受入れられると、主制御基板1310及び払出制御基板951を介して払出装置830から所定数(例えば、10個)の遊技球が、上皿201に払出される。
By the way, if the game ball that has flowed down to the left side of the
一方、遊技領域5a内においてセンター役物2500の上部に打込まれた遊技球が、センター役物2500の前周壁部2512の外周面の最も高くなった部位よりも右側に進入する(打込まれる)と、右打遊技領域2540の右上流通空間2541内に進入する。この右上流通空間2541内には、図示は省略するが、複数の障害釘が植設されており、遊技球が障害釘に当接してその流下方向を様々に変化させながら流通する。この右上流通空間3541内には、上部にゲート部2003が、下部に一般入賞口2001と通常は第二始動口扉部材2549により閉鎖されている第二始動口2004が備えられている。
On the other hand, the game ball hit to the upper part of the
右上流通空間2541内を流下した遊技球は、その下流側の右流通路2542を通って右下流通空間2543内に進入する。この右下流通空間2543に進入した遊技球は、第二大入賞口2006として左右に並んだ第二上大入賞口2006aと第二下大入賞口2006bを閉鎖している第二上大入賞口扉部材2552と第二下大入賞口扉部材2555の上面が底面を形成している第二アタッカ通路2543aを通り、低くなっている正面視左側の放出板部2559の左端から遊技領域5a内に放出される。第二アタッカ通路2543aの下流端(放出板部2559)は、始動口ユニット2100の第一大入賞口2005へ遊技球が向かうように開口しており、第一大入賞口2005が開状態の時に、第二アタッカ通路2543aから遊技領域5a内に遊技球が放出されると、高い確率で遊技球が第一大入賞口2005に受入れられる。
The game ball flowing down in the upper
この右流通路2542及び右下流通空間2543を流通する遊技球は、複数の減速リブ2546により、流通速度の増加が抑制されながら流下する。なお、ごくまれに、右下流通空間2543内において、第二アタッカ通路2543aの上流端付近で分岐している排出通路2543bに進入することがあり、排出通路2543bに進入した遊技球は遊技領域5a内に戻されることなく第二アウト口2543cから遊技盤5外に排出される。
A game ball that circulates in the right circulation path 2542 and the lower
右打して右上流通空間2541内に進入した遊技球が、ゲート部2003を通過してゲートセンサ2547により検知されると、主制御基板1310において予め決められている数値範囲で更新される普通乱数の中から一の普通乱数を取得し、この取得した普通乱数を予め決められた普通当り判定テーブルと照合することで普通抽選を行う。後述する時短制御を実行していない場合にこの普通抽選の結果が「普通当り」となると第二始動口扉部材2549が1回だけ正面視反時計回りの方向に回動して第二始動口2004を開状態とし、所定時間(この例では0.5秒)の間に亘り第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れが可能となる。一方、時短制御を実行している場合には普通抽選にて「普通当り」として「第一普通当り」、「第二普通当り」、「第三普通当り」のいずれとなったかを抽選する。そして、時短制御を実行している場合に普通抽選の普通抽選結果が「第一普通当り」、「第二普通当り」、「第三普通当り」のいずれかとなると第二始動口扉部材2549が正面視反時計回りの方向へ回動して第二始動口2004を開状態とすることで所定期間に亘って第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れが可能な状態とした後、正面視反時計回りの方向へ回動して第二始動口2004を閉状態とすることで第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れが不可能な状態にする開閉制御を所定回数(この例では5回)に亘って繰り返す。なお、普通抽選の普通抽選結果が「第一普通当り」となった場合には第二始動口2004が遊技球の受入れを可能な状態とされる5回夫々の期間として「0.3秒」、「0.28秒」、「0.3秒」、「0.28秒」、「0.3秒」とされ、普通抽選の普通抽選結果が「第二普通当り」となった場合には第二始動口2004が遊技球の受入れを可能な状態とされる5回夫々の期間として「0.3秒」、「0.28秒」、「1.1秒」、「0.2
8秒」、「0.3秒」とされ、普通抽選の普通抽選結果が「第三普通当り」となった場合には第二始動口2004が遊技球の受入れを可能な状態とされる5回夫々の期間として「0.3秒」、「0.28秒」、「0.3秒」、「0.28秒」、「1.1秒」とされ、「第二普通当り」及び「第三普通当り」では「第一普通当り」よりも遊技者に有利(第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れが容易)な当りとなっている。また、第二始動口2004に遊技球が受入れられると、主制御基板1310及び払出制御基板951を介して払出装置830から所定数(例えば、3個)の遊技球が、上皿201に払出される。
When a game ball that hits right and enters the upper
8 seconds", "0.3 seconds", and when the ordinary lottery result of the ordinary lottery is "3rd ordinary win", the
本実施形態では、ゲート部2003を遊技球が通過したことに基づいて機能表示ユニット1400の普通図柄表示器で行われる普通図柄の変動表示において、普通図柄の変動表示を開始してから普通図柄を停止表示するまで(普通抽選結果を示唆するまで)にある程度の時間を設定している(例えば、0.01~60秒、普通変動時間とも称す)。第二始動口2004では、普通変動時間の経過後に第二始動口扉部材2549が回動して開状態となる。なお、後述する時短制御の実行中には通常(時短制御を実行していない状態)よりも普通変動時間を短縮させる制御を実行するようになっている。また、第二始動口扉部材2549を回動して第二始動口2004を開状態とする開放時間については、遊技状態に応じて変化させるようにしても良く、例えば、時短制御を実行していない場合には時短制御を実行している場合に比べて、第二始動口2004の開放時間を長い時間に変更するようにしても良い。
In this embodiment, in the variable display of the normal symbols performed by the normal symbol display device of the
また、遊技球がゲート部2003を通過してから普通図柄表示器に変動表示される普通図柄を停止表示するまで(普通抽選結果が示唆されるまで)の間に、新たな遊技球がゲート部2003を通過すると、普通図柄表示器にて新たに普通図柄の変動表示を開始することができないため、普通図柄の変動表示開始を、先の普通図柄の変動表示が終了するまで(普通抽選結果の示唆が終了するまで)保留するようにしている。具体的にはゲートセンサ2547によりゲート部2003を通過した遊技球を検知したことに基づいて主制御基板1310にて取得した普通乱数を記憶しておき、普通図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態になるまで普通図柄の変動表示開始を保留する。なお、主制御基板1310にて記憶可能な普通乱数の保留数は、4つまでを上限とし、それ以上については、ゲート部2003を遊技球が通過しても、保留せずに破棄している。これにより、保留が貯まることで遊技ホール側の負担の増加を抑制している。
In addition, after the game ball passes through the
本実施形態のパチンコ機1は、第一始動口2002に受入れられた遊技球が第一始動口センサ2104により検知されると、主制御基板1310において予め決められている数値範囲で更新される第一特別乱数の中から一の第一特別乱数を取得し、この取得した第一特別乱数を予め決められた大当り判定テーブルと照合することで遊技者に有利な有利遊技状態(例えば、「大当り」、「小当り」、等)を発生させる第一特別抽選結果の抽選が行われる。そして、抽選された第一特別抽選結果に基づいて第一特別図柄表示器の八つのLEDを所定の変動時間(例えば、0.1~360秒)に亘って点滅制御した後に第一特別抽選結果に応じた点灯態様で表示する(第一特別図柄を変動表示した後に第一特別抽選結果に応じた停止図柄を表示する)ことにより第一特別抽選結果を遊技者に示唆する。なお、第一始動口2002に遊技球が受入れられることで抽選される第一特別抽選結果には、「はずれ」、「小当り」、「2R大当り」、「8R大当り」、「10R大当り」があり、取得した第一特別乱数を大当り判定テーブルと照合することでこれらのうち何れであるかが判別され、さらには大当り遊技後に通常(低確率状態:本例では約395分の1の確率で大当りに当選する)よりも大当りに当選する確率(当選確率)を向上させる確率向上制御(高確率状態(確変状態ともいう):本例では約44分の1の確率で大当りに当選する)を実行するか否か(確変大当りか否か)と、少なくとも第一特別抽選結果がはずれの場合に通常よりも変動時間を短縮させる時短制御(時短状態)を実行するか否か(時短大当りか否か)及び時短制御を実行する期間(時短回数:特別図柄(第一特別打図柄及び第二
特別図柄の変動回数))と、も判別されるようになっている。なお、「小当り」の当選確率は遊技状態に関わらず常に一定とされる(本例では約300分の1)。
In the
また、第二始動口2004に受入れられた遊技球が第二始動口センサ2551により検知されると、主制御基板1310において予め決められている数値範囲で更新される第二特別乱数の中から一の第二特別乱数を取得し、この取得した第二特別乱数を予め決められた大当り判定テーブルと照合することで遊技者に有利な有利遊技状態(例えば、「大当り」、「小当り」、等)を発生させる第二特別抽選結果の抽選が行われる。そして、抽選された第二特別抽選結果に基づいて第二特別図柄表示器の八つのLEDを所定の変動時間(例えば、0.1~360秒)に亘って点滅制御した後に第二特別抽選結果に応じた点灯態様で表示する(第二特別図柄を変動表示した後に第二特別抽選結果に応じた停止図柄を表示する)ことにより第二特別抽選結果を遊技者に示唆する。なお、第二始動口2004に遊技球が受入れられることで抽選される第二特別抽選結果には、「はずれ」、「2R大当り」、「4R大当り」、「5R大当り」、「6R大当り」、「7R大当り」、「8R大当り」、「16R大当り」があり、取得した第二特別乱数を大当り判定テーブルと照合することでこれらのうち何れであるかが判別され、さらには大当り遊技後に通常(低確率状態:本例では約395分の1の確率で大当りに当選する)よりも大当りに当選する確率(当選確率)を向上させる確率向上制御(高確率状態(確変状態ともいう):本例では約44分の1の確率で大当りに当選する)を実行するか否か(確変大当りか否か)と、少なくとも第二特別抽選結果がはずれの場合に通常よりも変動時間を短縮させる時短制御(時短状態)を実行するか否か(時短大当りか否か)及び時短制御を実行する期間(時短回数:特別図柄(第一特別打図柄及び第二特別図柄の変動回数))と、も判別されるようになっている。
In addition, when the game ball accepted in the
第一始動口2002及び第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れにより抽選された特別抽選結果(第一特別抽選結果及び第二特別抽選結果)が、有利遊技状態を発生させる特別抽選結果の場合、所定の変動時間の経過後に特別図柄表示器(第一特別図柄表示器、第二特別図柄表示器)の8つのLEDを特別抽選結果に応じた点灯態様で表示させ、その後第一大入賞口2005及び第二大入賞口2006の何れが所定の開閉パターンで遊技球の受入れが可能な状態となる。第一大入賞口2005や第二大入賞口2006が開状態の時に、第一大入賞口2005や第二大入賞口2006に遊技球が受入れられると、主制御基板1310及び払出制御基板951によって払出装置830から所定数(例えば、第一大入賞口2005に遊技球が受入れられた場合には11個、又は、第二大入賞口2006に遊技球が受入れられた場合には15個)の遊技球が、上皿201に払出される。従って、第一大入賞口2005や第二大入賞口2006が遊技球を受入可能としている時に、第一大入賞口2005や第二大入賞口2006に遊技球を受入れさせることで、多くの遊技球を払出させることができ、遊技者を楽しませることができる。
If the special lottery result (first special lottery result and second special lottery result) drawn by accepting the game ball into the
特別抽選結果が「小当り」や「2R大当り」の場合には、第一大入賞口2005が、所定短時間(例えば、0.2秒~0.6秒の間)の間、遊技球を受入可能な開状態となってから閉鎖する開閉パターンを複数回(例えば、2回)繰返す。一方、特別抽選結果が「4R大当り」、「5R大当り」、「6R大当り」、「7R大当り」、「8R大当り」、「10R大当り」、「16R大当り」の場合には、第一大入賞口2005又は第二大入賞口2006が、遊技球を受入可能な開状態となった後に、所定時間(例えば、約30秒)経過するか、或いは、第一大入賞口2005へ予め決められている個数(例えば、7個)の遊技球が受入れられるか又は第二大入賞口2006へ予め決められている個数(例えば、10個)の遊技球が受入れられるか、の何れかの条件が充足すると、遊技球を受入不能な閉状態とする開閉パターン(一回の開閉パターンを1ラウンドと称す)を、所定回数(所定ラウンド数)繰返す。例えば、「4R大当り」であれば4ラウンド、「5R大当り」であれば5ラウンド、「16R大当り」であれば16ラウンド、夫々繰返して、遊技者に有利
な有利遊技状態を発生させる。また、特別抽選結果が「小当り」や「2R大当り」の場合に実行される開閉パターン(第一大入賞口2005が所定短時間(例えば、0.2秒~0.6秒の間)の間、遊技球を受入可能な開状態となってから閉鎖する開閉パターン)では実質的に第一大入賞口2005へ遊技球を入球させることは困難である。これに対して特別抽選結果が「4R大当り」、「5R大当り」、「6R大当り」、「7R大当り」、「8R大当り」、「10R大当り」、「16R大当り」の場合に実行される開閉パターン(第一大入賞口2005又は第二大入賞口2006が、遊技球を受入可能な開状態となった後に、所定時間(例えば、約30秒)経過するか、或いは、第一大入賞口2005へ予め決められている個数(例えば、7個)の遊技球が受入れられるか又は第二大入賞口2006へ予め決められている個数(例えば、10個)の遊技球が受入れられるか、の何れかの条件が充足すると、遊技球を受入不能な閉状態とする開閉パターン)では第一大入賞口2005又は第二大入賞口2006へ遊技球を入球させることは容易となっている。なお、特別抽選結果が「4R大当り」、「5R大当り」、「6R大当り」、「7R大当り」、「8R大当り」、「10R大当り」、「16R大当り」の場合には、上記第一大入賞口2005又は第二大入賞口2006が、遊技球を受入可能な開状態となった後に、所定時間(例えば、約30秒)経過するか、或いは、第一大入賞口2005へ予め決められている個数(例えば、7個)の遊技球が受入れられるか又は第二大入賞口2006へ予め決められている個数(例えば、10個)の遊技球が受入れられるか、の何れかの条件が充足すると、遊技球を受入不能な閉状態とする開閉パターンが実行されるラウンド数を実質的な特別抽選結果としてもよく、特別抽選結果として第一大入賞口2005へ予め決められている個数(例えば、7個)の遊技球が受入れられるか又は第二大入賞口2006へ予め決められている個数(例えば、10個)の遊技球が受入れられるか、の何れかの条件が充足すると、遊技球を受入不能な閉状態とする開閉パターンと特別抽選結果が「小当り」や「2R大当り」の場合に実行される開閉パターン(第一大入賞口2005が所定短時間(例えば、0.2秒~0.6秒の間)の間、遊技球を受入可能な開状態となってから閉鎖する開閉パターン)とを含む複数のラウンドを実行するものを設けるようにしてもよい。例えば、特別抽選結果として「実質4Rとする8R大当り」を設けて、第一大入賞口2005へ予め決められている個数(例えば、7個)の遊技球が受入れられるか又は第二大入賞口2006へ予め決められている個数(例えば、10個)の遊技球が受入れられるか、の何れかの条件が充足すると、遊技球を受入不能な閉状態とする開閉パターンを4回繰り返した後、特別抽選結果が「小当り」や「2R大当り」の場合に実行される開閉パターン(第一大入賞口2005が所定短時間(例えば、0.2秒~0.6秒の間)の間、遊技球を受入可能な開状態となってから閉鎖する開閉パターン)を4回繰り返すようにしてもよい。
When the special lottery result is a "small win" or "2R big win", the first
ところで、本実施形態では第二大入賞口2006が、左右に並んだ第二上大入賞口2006aと第二下大入賞口2006bとで構成されており、第二大入賞口2006が用いられる「大当り」の場合、例えば、初めのラウンド(1R目)は第二上大入賞口2006aが開いて遊技球を受入可能とし、受入不能とする条件の充足により閉鎖されて、次に受入可能とするまでの間(インターバルの間)、第二下大入賞口2006bを開いて遊技球を受入可能とする次のラウンド(2R目)を開始させ、第二下大入賞口2006bが受入不能となると、その間にインターバルの期間が経過しているため、第二上大入賞口2006aを再び開いて遊技球を受入可能とする。そして、第二上大入賞口2006aと第二下大入賞口2006bとを、所定ラウンド数の消化まで交互に開閉させる。これにより、第二アタッカ通路2543a内では、「大当り」中は第二上大入賞口2006a及び第二下大入賞口2006bの何れかが遊技球を受入可能な状態となっているため、この状態で右打して第二アタッカ通路2543a内に遊技球を流通させると、その遊技球が必ず第二大入賞口2006に受入れられることとなり、遊技球の取りこぼしをなくして、遊技者を楽しませることができる。
By the way, in the present embodiment, the second
また、本実施形態では上記した複数種類の大当りのうち一部の大当りでは、大当り当選
時の遊技状態に応じて大当り遊技の終了後に上記時短制御を実行するか否かを異ならせている。例えば、非時短状態(時短制御を実行していない状態)で第一特別抽選結果が大当り遊技後に確率向上制御を実行しない8R通常大当りである場合には、大当り遊技後に時短制御を実行しない。一方、時短状態(時短制御を実行している状態)で第一特別抽選結果が8R通常大当りである場合には、大当り遊技後に時短制御を実行するようになっている。また、非時短状態(時短制御を実行していない状態)で第二特別抽選結果が大当り遊技後に確率向上制御を実行しない2R通常大当りである場合には、大当り遊技後に時短制御を実行しない。一方、時短状態(時短制御を実行している状態)で第二特別抽選結果が2R通常大当りである場合には、大当り遊技後に時短制御を実行するようになっている。また、低確率非時短状態(確率向上制御と時短制御との両方ともに実行していない状態:通常状態ともいう)で第一特別抽選結果及び第二特別抽選結果が大当り遊技後に確率向上制御を実行する2R確変大当りである場合には、大当り遊技後に時短制御を実行しない。一方、確率向上制御を実行しているか又は時短制御を実行している状態、即ち通常状態以外の状態で第一特別抽選結果及び第二特別抽選結果が大当り遊技後に確率向上制御を実行する2R確変大当りである場合には、大当り遊技後に時短制御を実行するようになっている。
In addition, in the present embodiment, for some of the above-described multiple types of big wins, whether or not the time saving control is executed after the end of the big win game is differentiated according to the game state at the time of winning the big win. For example, when the result of the first special lottery is an 8R normal jackpot in which the probability improvement control is not executed after the big win game in a non-time saving state (a state where the time saving control is not executed), the time saving control is not executed after the big win game. On the other hand, when the first special lottery result is the 8R normal jackpot in the time saving state (the time saving control is being executed), the time saving control is executed after the jackpot game. When the result of the second special lottery is a 2R normal jackpot in which the probability improvement control is not executed after the big win game in a non-time saving state (a state where the time saving control is not executed), the time saving control is not executed after the big win game. On the other hand, when the result of the second special lottery is the 2R normal jackpot in the time saving state (when the time saving control is being executed), the time saving control is executed after the big win game. In addition, the first special lottery result and the second special lottery result in the low probability non-time-saving state (both probability improvement control and time-saving control are not executed: normal state) Execute the probability improvement control after the big hit game In the case of the 2R probability variable jackpot, the time saving control is not executed after the jackpot game. On the other hand, the 2R probability improvement control is executed after the first special lottery result and the second special lottery result are big hits in a state other than the normal state where the probability improvement control is executed or the time reduction control is executed. In the case of a big hit, time saving control is executed after the big hit game.
本実施形態では、第一始動口2002への遊技球の受入れにより第一特別図柄表示器にて実行される第一特別図柄の変動表示と、第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れにより第二特別図柄表示器にて実行される第二特別図柄の変動表示と、は同時に実行されず、いずれか一方のみを実行するようにしている。そのため、第一始動口2002への遊技球の受入れにより第一特別図柄表示器に変動表示される第一特別図柄を停止表示するまで(第一特別抽選結果が示唆されるまで)の間と第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れにより第二特別図柄表示器に変動表示される第二特別図柄を停止表示するまで(第二特別抽選結果が示唆されるまで)の間に、第一始動口2002や第二始動口2004に新たな遊技球が受入れられると、第一特別図柄表示器や第二特別図柄表示器にて新たに第一特別図柄や第二特別図柄の変動表示を開始することができないため、特別図柄(第一特別図柄、第二特別図柄)の変動表示開始を先の特別図柄(第一特別図柄、第二特別図柄)の変動表示が終了するまで(第一特別抽選結果や第二特別抽選結果の示唆が完了するまで)保留するようにしている。具体的には、第一始動口センサ2104により第一始動口2002に受入れられた遊技球を検知したことに基づいて主制御基板1310にて取得した第一特別乱数と、第二始動口センサ2551により第二始動口2004に受入れられた遊技球を検知したことに基づいて主制御基板1310にて取得した第二特別乱数と、を記憶しておき、特別図柄(第一特別図柄、第二特別図柄)の変動表示を開始できる状態になるまで特別図柄(第一特別図柄、第二特別図柄)の変動表示開始を保留する。なお、主制御基板1310にて記憶可能な第一特別乱数及び第二特別乱数の保留数は夫々4つまでを上限とし、それ以上については、第一始動口2002及び第二始動口2004に遊技球が受入れられても保留せずに、破棄している。これにより、保留が貯まることで遊技ホール側の負担の増加を抑制している。また、主制御基板1310に記憶されている第一特別乱数及び第二特別乱数は、第二特別乱数の方を優先して消化させるようになっている。つまり、第一始動口2002及び第二始動口2004への遊技球の受入れタイミングに関わらず、第二特別乱数が記憶されて第二特別図柄の変動表示開始が保留されていれば、第一特別図柄よりも第二特別図柄の変動表示が優先して実行されるようになっている。
In this embodiment, the variation display of the first special symbol executed by the first special symbol display device by accepting the game ball to the
この特別抽選結果の示唆は、機能表示ユニット1400(第一特別図柄表示器、第二特別図柄表示器)とメイン液晶表示装置1600とで行われる(サブ液晶表示装置3114も用いても良い)。機能表示ユニット1400では、主制御基板1310によって直接制御されて特別抽選結果の示唆が行われる。機能表示ユニット1400での特別抽選結果の示唆は、特別図柄表示器(第一特別図柄表示器、第二特別図柄表示器)を構成する上記した八つのLEDを、点灯・消灯を繰返して所定時間点滅させ、その後に、所定の点灯態様
で停止して、この停止時に点灯しているLEDの組み合わせによって特別抽選結果を示唆する。
This special lottery result is suggested by the function display unit 1400 (first special symbol display device, second special symbol display device) and the main liquid crystal display device 1600 (the sub liquid
一方、メイン液晶表示装置1600では、主制御基板1310からの制御信号(変動パターンコマンド、判定結果通知コマンド等)に基いて、周辺制御基板1510によって間接的に制御され、演出画像によって特別抽選結果の示唆が行われる。具体的には、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、複数の異なる図柄からなる一連の装飾図柄列が複数列(例えば、左装飾図柄・中装飾図柄・右装飾図柄の三列)表示された状態で各装飾図柄列の変動表示が開始され、その後に、順次停止表示され(本例では左装飾図柄→右装飾図柄→中装飾図柄の順に停止表示される)、最終的に全ての装飾図柄列が停止表示されると、停止表示された図柄の組合せによって抽出された特別乱数(第一特別乱数、第二特別乱数)の抽選結果が遊技者側に示唆されるようになっている。つまり、始動入賞発生時に取得した特別乱数(第一特別乱数、第二特別乱数)に基づく特別抽選結果(第一特別抽選結果、第二特別抽選結果)に応じて、複数の装飾図柄列が変動表示された後に特別抽選結果(第一特別抽選結果、第二特別抽選結果)を示唆するように停止表示される演出画像が表示されるようになっている。なお、第一特別図柄表示器に変動表示される第一特別図柄や第二特別図柄表示器に変動表示される第二特別図柄よりも、メイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される装飾図柄の方が大きく見易いため、一般的に遊技者はメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示された装飾図柄に注目することとなる。
On the other hand, the main liquid
なお、機能表示ユニット1400での特別抽選結果を示唆する時間(LEDの点滅時間(変動時間))と、メイン液晶表示装置1600での特別抽選結果を示唆する時間(図柄列が変動して確定画像が表示されるまでの時間)とは、異なっており、機能表示ユニット1400の方が短い時間に設定されている。
Note that the time indicating the special lottery result on the function display unit 1400 (blinking time of the LED (fluctuation time)) and the time indicating the special lottery result on the main liquid crystal display device 1600 (the symbol row fluctuates to indicate the final image). is displayed), and the
また、周辺制御基板1510では、メイン液晶表示装置1600による特別抽選結果を示唆するための演出画像の表示の他に、抽選された特別抽選結果に応じて、センター役物2500の装飾体、裏左中装飾ユニット3050、裏下後可動演出ユニット3100、裏上左可動演出ユニット3200、裏左可動演出ユニット3300、裏上中可動演出ユニット3400、及び裏下前可動演出ユニット3500、等を適宜用いて、発光演出、可動演出、表示演出、等を行うことが可能であり、各種の演出によっても遊技者を楽しませることができ、遊技者の遊技に対する興趣が低下するのを抑制することができる。
Further, in the peripheral control board 1510, in addition to the display of the effect image for suggesting the result of the special lottery by the main liquid
[5.主制御基板の各種制御処理]
次に、パチンコ機1の遊技の進行に応じて、主制御基板1310によって実行される処理について説明する。具体的には、遊技機の電源投入時に実行されるシステム/ユーザリセット処理と、システム/ユーザリセット処理で起動されるタイマによって所定周期(本実施形態では、4ms)で実行されるタイマ割込み処理について説明する。
[5. Various control processing of the main control board]
Next, processing executed by the
[5-1.初期化処理]
図21及び図22は、本発明の実施形態における主制御基板の初期化処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[5-1. Initialization process]
21 and 22 are flowcharts showing the procedure of initialization processing of the main control board in the embodiment of the present invention.
パチンコ機1に電源が投入されると、主制御基板1310の主制御MPU1311が主制御プログラムを実行することによって初期化処理を行う。初期化処理が開始されると、主制御MPU1311は、まず、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたRAM1312のプロテクトを書き込み許可に設定し、RAM1312への書き込みができる状態にする(ステップS10)。具体的には、RAMプロテクトレジスタに書き込み許可を示す”00H”を出力する。
When the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、内蔵されたウォッチドッグタイマを起動する(ステップS12)。具体的には、まず、ウォッチドッグタイマコントロールレジスタに、モード設定を示す”03H”を書き込み、さらに、ウォッチドッグタイマの起動を示す”03H”を書き込む。さらに、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアして、リセットする(ステップS14)。
Subsequently, the
続いて、所定のウェイト時間が経過したかを判定する(ステップS16)。パチンコ機1の電源を投入してから所定電圧となるまでの間は電圧がすぐに上昇しないため、電源投入時から所定電圧に上がるまでの間に電圧が停電予告電圧より小さくなると、停電監視回路から停電予告信号が入力される。ウェイト処理では、所定の監視ウェイト値を設定し、ウォッチドッグタイマを起動させながら所定時間(例えば、200ミリ秒)処理を待機させる。
Subsequently, it is determined whether or not a predetermined wait time has elapsed (step S16). Since the voltage does not rise immediately after turning on the power of the
所定のウェイト時間が経過していれば、サブ基板(周辺制御基板1510など)が起動するために必要な時間が経過しているので、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されているかを判定する(ステップS18)。RAMクリアスイッチが操作されている場合、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータのうち役物比率算出用ワークエリア(役物比率算出用領域13128)以外の領域のデータを消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されていない場合、内蔵RAM1312にバックアップされているデータを消去せず、停電フラグが設定されているかを判定する(ステップS20)。停電フラグは、停電発生など、パチンコ機1の電源が正常な処理を経て遮断された場合にセットされるフラグである(図22のステップS56参照)。
If the predetermined wait time has passed, the time required for starting the sub-board (peripheral control board 1510, etc.) has passed, so it is determined whether the RAM clear switch has been operated (step S18). . When the RAM clear switch is operated, the data in the area other than the role product ratio calculation work area (the role product ratio calculation area 13128) among the data backed up in the work area of the built-in
その結果、停電フラグが設定されていなければ、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータ(役物比率算出用領域13128以外)を消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、停電フラグが設定されていれば、停電フラグをクリアし、前回の電源遮断時に計算されたチェックサムを用いて内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータから算出したチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとを比較(検証)する(ステップS22)。
As a result, if the power failure flag is not set, the data in the work area of the built-in
その結果、バックアップデータから算出されたチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとが一致しなければ、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータ(役物比率算出用領域13128以外)を消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、バックアップデータから算出されたチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとが一致すれば、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しいので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータを消去せず、ステップS24に進む。
As a result, if the checksum calculated from the backup data does not match the checksum stored in step S48, the data in the work area of the
続いて、チェックコードを用いて役物比率算出用ワークエリア(役物比率算出用領域13128)が正常かを判定する(ステップS24)。異常であると判定された場合、役物比率算出用ワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、役物比率算出用ワークエリアに格納されているデータを消去する(ステップS26)。 Subsequently, using the check code, it is determined whether or not the work area for character product ratio calculation (area for character product ratio calculation 13128) is normal (step S24). If it is determined to be abnormal, the data in the role product ratio calculation work area may not be correct, so the data stored in the role product ratio calculation work area is deleted (step S26).
なお、役物比率算出用領域13128に、1又は複数のバックアップ領域を設ける場合、最初に、チェックコードを用いてメイン領域を判定し、メイン領域が異常であると判定された場合、バックアップ領域1、2、Nの順で判定し、最初に正常であると判定されたバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製するとよい。その後、バックアップ領域のデータは消去しても、そのまま残してもよい。メイン領域が正常であると判定された場合
、バックアップ領域のデータは消去しても、そのまま残してもよい。
In addition, when one or more backup areas are provided in the character product
役物比率算出用領域については、電源投入時によるチェックコードの判定結果とは別に、所定時間毎に役物比率算出用領域13128のデータを消去してもよい。また、所定の稼動量毎(例えば、所定の発射球数毎、所定の入賞球数毎、所定数の特別図柄変動表示ゲーム毎、所定数の特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当り毎など)に役物比率算出用領域13128のデータを消去してもよい。
As for the area for calculating the role product ratio, the data in the area for calculating the
このように、本実施形態のパチンコ機では、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータを、データの種別毎に(遊技制御用データ13132と役物比率算出・表示用データ13136とを)異なる条件で消去する。すなわち、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって、バックアップされた遊技制御用データ13132は消去されるが、バックアップされた役物比率算出・表示用データ13136は消去されない。RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって役物比率算出・表示用データ13136が消去できると、パチンコ機1が算出した役物比率を任意のタイミングで消去できる。このため、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって、バックアップされた役物比率算出・表示用データ13136は消去されないようにして、遊技場の係員の操作による役物比率算出・表示用データ13136の消去を防止し、役物比率が異常な状態の隠蔽を防止できる。このため、役物比率が高い状態や低い状態へ改造された遊技機を容易に検出できる。
Thus, in the pachinko machine of this embodiment, the data backed up in the work area of the built-in
主制御MPU1311は、RAM作業領域の復電時設定又はRAM初期化処理が実行されると、主制御MPU1311(CPU13111)の各種設定レジスタに設定するための初期設定を実行する(ステップS28)。主制御MPU1311の初期設定では、まず、CTC(Counter/Timer Circuit)の初期設定を行い、割り込みを許可する。さらに、
シリアル通信ポート及び試験信号出力ポートの初期設定を行う。ハードウェア乱数の生成回路を起動する。そして、周辺制御基板1510、払出制御基板951及び役物比率表示器1317との通信に使用するシリアル通信回路13114の設定を行う。さらに、シリアル通信回路13114の動作開始後に、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171の初期設定を行う。
The
Initialize the serial communication port and test signal output port. Start the hardware random number generator. Then, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板1510に送信するための電源投入時コマンドを設定する処理を実行する(ステップS32)。電源投入時コマンド作成処理では、遊技バックアップ情報から遊技情報を読み出して、遊技情報に応じた各種コマンドを主制御内蔵RAM1312の所定記憶領域に記憶する。電源投入時コマンドの生成は、電源投入時状態基準コマンドを基準コマンドデータとしてセットし、生成するコマンドに対応するコマンド加算データを加算する。
Subsequently, the
電源投入時のコマンドには、電源投入時状態バッファコマンドや特別図柄・電動役物動作番号コマンドが含まれる。電源投入時状態バッファコマンドは、電源断後の復帰時に遊技状態を通知するコマンドであり、特別抽選の当選確率及び普通電動役物の動作態様を通知する。一方、特別図柄・電動役物動作番号コマンドは、特別図柄の変動表示の実行状況を通知する。 The power-on command includes a power-on state buffer command and a special symbol/electric accessory operation number command. The state buffer command at power-on is a command for notifying the game state at the time of restoration after power-off, and notifies the winning probability of the special lottery and the operation mode of the normal electric accessory. On the other hand, the special symbol/electric accessary product operation number command notifies the execution status of the variable display of the special symbol.
その後、主制御MPU1311は、タイマ割込み処理をはじめとする割り込み処理の実行を許可する(ステップS34)。パチンコ機1の電源投入からステップS34までの処理によりパチンコ機1の初期設定が完了する(初期設定手段)。
After that, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、停電予告信号を取得し(ステップS36)、停電予告信号がONであるか否かを判定する(ステップS38)。停電予告信号がONでない場合(ステップS38の結果が「No」)、すなわち、乱数更新処理を実行する(ステップ
S40)。ステップS46の乱数更新処理では、主として特別抽選や普通抽選において当選判定を行うための乱数以外の乱数を更新する。なお、特別抽選や普通抽選において当選判定を行うための乱数の更新処理は、後述するタイマ割込み処理で実行される。停電予告信号が検出されるまでステップS36からステップS40までの処理を実行し、これらの処理を主制御側メイン処理とする(初期設定後通常手段)。
Subsequently, the
一方、停電予告信号を検出した場合には(ステップS38の結果が「Yes」)、主制御MPU1311は、電源断時処理を実行する(電断時設定手段)。電源断時処理では、停電発生前の状態に復帰させるためのデータをバックアップする処理を実行する。具体的には、まず、割込み処理の実行を禁止する(ステップS42)。これにより後述するタイマ割り込み処理が行われなくなり、主制御内蔵RAM1312への書き込みを防ぎ、遊技情報の書き換えを保護することができる。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、出力ポートをクリアして、各ポートからの出力によって制御される機器の動作を停止する(ステップS44)。具体的には、ソレノイド・停電クリア・ACK出力ポートに停電クリア信号OFFビットデータを設定する。なお、全ての出力ポートがクリアされなくてもよく、例えば、電力消費が大きいソレノイドやモータを制御するための出力ポートをクリアすればよい。これらの出力ポートをクリアすることによって、主基板側電源断時処理が終了するまでの時間の消費電力を低減し、主基板側電源断時処理を確実に終了できるようになる。
On the other hand, when the power failure warning signal is detected (the result of step S38 is "Yes"), the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、バックアップされるワークエリアに格納されたデータが正常に保持されたか否かを判定するためのチェックサムを計算する(ステップS46)。さらに、チェックサムの計算結果をRAM1312のチェックサムエリアに格納する(ステップS48)。このチェックサムはワークエリアにバックアップされたデータが正常かの判定に使用される。
Subsequently, the
続いて、役物比率算出用ワークエリア(役物比率算出用領域13128)のデータからチェックコード(例えば、チェックサム)算出する(ステップS50)。チェックコードが固定値である場合には、ステップS50においてチェックコードを算出する必要はない。なお、チェックコードは、主基板電源断時処理ではなく、役物比率算出・表示処理でデータの更新の都度、算出し、記憶してもよい。 Subsequently, a check code (for example, a checksum) is calculated from the data in the role product ratio calculation work area (the role product ratio calculation area 13128) (step S50). If the check code is a fixed value, there is no need to calculate the check code in step S50. It should be noted that the check code may be calculated and stored each time the data is updated in the character product ratio calculation/display process instead of the main board power-off process.
続いて、算出したチェックコード(又は、チェックコードとして用いる所定値)を役物比率算出用領域13128の所定の領域に格納する(ステップS52)。 Subsequently, the calculated check code (or a predetermined value used as the check code) is stored in a predetermined area of the character product ratio calculation area 13128 (step S52).
続いて、役物比率算出用ワーク(役物比率算出用領域13128)のメイン領域のデータを各バックアップ領域に複製する(ステップS54)。このとき、計算されたチェックコードも複製する。バックアップは、主基板側電源断時処理ではなく、役物比率算出・表示処理で適宜(例えば、データの更新の都度)、実行してもよい。 Subsequently, the data in the main area of the role product ratio calculation work (area for role product ratio calculation 13128) is copied to each backup area (step S54). At this time, the calculated check code is also duplicated. The backup may be executed as appropriate (for example, each time data is updated) in the character product ratio calculation/display process instead of the process when the power is turned off on the main board side.
このように、役物比率の算出に使用するデータを、計算された(又は、所定値の)チェックコードと共にバックアップ領域に格納することによって、電源遮断時にも役物比率算出用のデータを保持し、長期間の稼動における役物比率を算出できる。 In this way, by storing the data used for calculating the character ratio in the backup area together with the calculated (or predetermined value) check code, the data for calculating the character ratio can be retained even when the power is cut off. , the function ratio in long-term operation can be calculated.
さらに、停電フラグとしてバックアップフラグエリアに正常にバックアップされたことを示す値を格納する(ステップS56)。これにより、遊技バックアップ情報の記憶が完了する。最後に、RAMプロテクトレジスタに書き込み禁止を示す”01H”を出力することでRAM1312の書き込みを禁止し(ステップS58)、停電から復旧するまでの間、待機する(無限ループ)。
Furthermore, a value indicating normal backup is stored in the backup flag area as a power failure flag (step S56). This completes the storage of the game backup information. Finally, by outputting "01H" indicating write prohibition to the RAM protect register, writing to the
[5-2.タイマ割込み処理]
次に、タイマ割込み処理について説明する。タイマ割込み処理は、図21及び図22に示した初期化処理において設定された割り込み周期(本実施形態では、4ms)ごとに繰り返し行われる。図23はタイマ割込み処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
[5-2. Timer interrupt processing]
Next, timer interrupt processing will be described. The timer interrupt processing is repeatedly performed for each interrupt cycle (4 ms in this embodiment) set in the initialization processing shown in FIGS. 21 and 22 . FIG. 23 is a flow chart showing an example of timer interrupt processing.
タイマ割込み処理が開始されると、主制御MPU1311は、主制御プログラムを実行することによって、まず、プログラムステータスワードのRBS(レジスタバンク選択フラグ)に1を設定し、レジスタを切り替える(ステップS70)。本実施形態における主制御基板1310には、バンク0とバンク1を有しており、タイマ割込み処理が実行されるたびに切り替えて使用される。
When timer interrupt processing is started, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理を実行する(ステップS74)。スイッチ入力処理では、主制御MPU1311の各種入力ポートの入力端子に入力されている各種信号を読み取り、入力情報として主制御内蔵RAM1312の入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。具体的には、一般入賞口などの入賞口に入球した遊技球を検出する各種センサからの検出信号、磁石を用いた不正行為を検出する磁気検出スイッチ3024からの検出信号、賞球制御処理で送信した賞球コマンドを払出制御基板951が正常に受信した旨を伝える払出制御基板951からの払主ACK信号などをそれぞれ読み取り、入力情報として入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。また、スイッチ入力処理では、排出球センサ3060や発射球センサ1020からの検出信号を読み取って、アウト球数を計数する。
Next, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、タイマ更新処理を行う(ステップS76)。タイマ更新処理では、例えば、後述する特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理で決定される変動表示パターンに従って特別図柄表示器1185が点灯する時間、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理で決定される普通図柄変動表示パターンに従って普通図柄表示器1189が点灯する時間のほかに、主制御基板1310(主制御MPU1311)が送信した各種コマンドを払出制御基板951が正常に受信した旨を伝える払主ACK信号が入力されているか否かを判定する際にその判定条件として設定されているACK信号入力判定時間等の時間管理を行う。具体的には、変動表示パターン又は普通図柄変動表示パターンの変動時間が5秒間であるときには、タイマ割り込み周期が4msに設定されているので、このタイマ減算処理を行うごとに変動時間を4msずつ減算し、その減算結果が値0になることで変動表示パターン又は普通図柄変動表示パターンの変動時間を正確に計測している。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、乱数更新処理1を実行する(ステップS78)。乱数更新処理1では、大当り判定用乱数、大当り図柄用乱数、及び小当り図柄用乱数を更新する。またこれらの乱数に加えて、図に示したシステム/ユーザリセット処理(主制御側メイン処理)におけるステップS40の非当落乱数更新処理で更新される、大当り図柄用初期値決定用乱数、及び小当り図柄用初期値決定用乱数も更新する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、賞球制御処理を実行する(ステップS80)。賞球制御処理では、入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、読み出した入力情報に基づいて払い出される遊技球(賞球)の数を計算し、主制御内蔵RAM1312に書き込む。また、賞球数の計算結果に基づいて、遊技球を払い出すための賞球コマンドを作成したり、主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951との基板間の接続状態を確認するためのセルフチェックコマンドを作成したりする。主制御MPU1311は、作成した賞球コマンドやセルフチェックコマンドを主払シリアルデータとして払出制御基板951に送信する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、現在の遊技状態を判定し、遊技価値として払い出される賞球数を現在の遊技状態に対応した領域に加算して、主制御内蔵RAM1312の役物比率算出用領域13128(図26参照)を更新する(ステップS81)。ステップS81の処理は、ステップS80で払い出されるべき賞球がない場合にはスキップでき、パ
チンコ機1の負荷を軽減できる。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、枠コマンド受信処理を実行する(ステップS82)。払出制御基板951では、払出制御プログラムによって、状態表示に区分される1バイト(8ビット)の各種コマンド(例えば、枠状態1コマンド、エラー解除ナビコマンド、及び枠状態2コマンド)を送信する。一方、後述するように、払出制御プログラムによって、払出動作にエラーが発生した場合にエラー発生コマンドを出力したり、操作スイッチの検出信号に基づいてエラー解除報知コマンドを出力する。枠コマンド受信処理では、各種コマンドを払主シリアルデータとして正常に受信すると、その旨を払出制御基板951に伝える情報を、出力情報として主制御内蔵RAM1312の出力情報記憶領域に記憶する。また、主制御MPU1311は、払主シリアルデータとして正常に受信したコマンドを2バイト(16ビット)のコマンドに整形し(例えば、枠状態表示コマンド、エラー解除報知コマンドなど)、送信情報として上述した送信情報記憶領域に記憶する。また、賞球排出処理では、役物比率算出用領域13128の遊技状態により定められた記憶領域(図27参照)に賞球排出数を記録する。
Subsequently, the
役物比率算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)は、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)の後で役物比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の前であれば、どの順序で実行してもよい。 The character ratio calculation area update process (step S81) may be executed in any order as long as it is after the prize ball control process (step S80) and before the character ratio calculation/display process (step S89). .
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、不正行為検出処理を実行する(ステップS84)。不正行為検出処理では、賞球に関する異常状態を確認する。例えば、上述した入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、大当り遊技状態でない場合にカウントスイッチによって大入賞口2005,2006に遊技球が入球していると検知されたとき等には、主制御プログラムは、異常状態として報知表示に区分される入賞異常表示コマンドを作成し、送信情報として上述した送信情報記憶領域に記憶する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理を実行する(ステップS86)。特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理では、大当り用乱数値が主制御内蔵ROMに予め記憶されている当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定する。さらに、大当り図柄乱数値に基づいて確率変動状態に移行させるか否かを判定する。そして、確変移行条件が成立している場合には、その後、確率変動状態に移行させる一方、確変移行条件が成立していない場合には当該確率変動状態以外の遊技状態に移行させる。ここで、「確率変動状態」とは、上述した特別抽選の当選確率が通常遊技状態(低確率状態)と比較して相対的に高く設定された状態(高確率状態)をいう。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理を実行する(ステップS88)。普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理では、上述した入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、ゲートスイッチ2352からの検出信号が入力端子に入力されていたか否かを判定する。検出信号が入力端子に入力されていた場合には、普通図柄当り判定用乱数を抽出し、主制御内蔵ROMに予め記憶されている普通図柄当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定する(「普通抽選」という)。そして、普通抽選による抽選結果に応じて第二始動口扉部材2549を開閉動作させるか否かを決定する。この決定により開閉動作をさせる場合、第二始動口扉部材2549が開放(又は、拡大)状態となることで始動口2004に遊技球が受け入れ可能となる遊技状態となって遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態に移行させる。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、表示スイッチ1318が操作されているかを判定し、表示スイッチ1318が操作されていれば、役物比率算出・表示処理(図24、図25)を呼び出し、役物比率算出用領域13128に格納された賞球数を参照して役物比率を
算出する。そして、算出された役物比率を役物比率表示器1317に表示する(ステップS89)。このように、タイマ割込み処理において役物比率算出・表示処理を呼び出して、役物比率を算出することによって、直近のデータによる役物比率(パチンコ機1の射幸性)を確認できる。
Subsequently, the
なお、表示スイッチ1318が操作されているかにかかわらず、本体枠4が外枠2から開放したことを本体枠開放スイッチ(図示省略)が検出していれば、役物比率を表示してもよい。また、本体枠4が外枠2から開放したことを本体枠開放スイッチ(図示省略)が検出中に表示スイッチ1318が操作された場合に、役物比率表示器1317に役物比率を表示してもよい。表示スイッチ1318は、遊技盤の裏面側に設けられていることから、表示スイッチ1318が表示されていれば、通常、本体枠4が開放しており、遊技の進行が停止している。このように、遊技の進行が停止したタイミングで役物比率を算出すると、遊技中に役物比率の算出のための除算や減算によってCPUリソースを消費することがなく、CPUの負荷を軽減できる。
Regardless of whether the
役物比率算出・表示処理の詳細は、図24、図25において後述する。また、役物比率の表示方法の具体例は後述する。なお、表示スイッチ1318が操作されていると、全ての種類の値(役物比率、連続役物比率、累計、総累計)を計算してもよいが、表示スイッチ1318の操作毎に、表示される値のみを計算してもよい。また、表示スイッチ1318が操作されているかにかかわらず役物比率を計算し、表示スイッチ1318が操作されていれば、算出された役物比率を役物比率表示器1317に表示してもよい。
Details of the character product ratio calculation/display processing will be described later with reference to FIGS. 24 and 25 . A specific example of the display method of the character product ratio will be described later. In addition, when the
なお、パチンコ機1が不正を検出して遊技を中止した場合でも、役物比率算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)及び役物比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)を実行する。不正が検出されたか否かにかかわらず、これらの処理を実行することによって、不正報知中でも役物比率を確認できる。
Note that even when the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、出力データ設定処理を実行する(ステップS90)。出力データ設定処理では、主制御MPU1311の各種出力ポートの出力端子から各種信号を出力する。例えば、出力情報に基づいて主制御MPU1311の所定の出力ポートの出力端子から、払出制御基板951からの各種コマンドを正常に受信したときには主払ACK信号を払出制御基板951に出力したり、大当り遊技状態であるときには大入賞口2005、2006の開閉部材2107の開閉動作を行うアタッカソレノイド(第一アタッカソレノイド2113、第二上アタッカソレノイド2553、第二下アタッカソレノイド2556)に駆動信号を出力したり、始動口(第二始動口扉部材2549)の開閉動作を行う始動口ソレノイド2550に駆動信号を出力したりするほかに、確率変動中情報出力信号、特別図柄表示情報出力信号、普通図柄表示情報出力信号、時短中情報出力情報、始動口入賞情報出力信号等の遊技に関する各種情報(遊技情報)信号及びセキュリティ信号を払出制御基板951に出力したりする。
Subsequently, the
また、出力データ設定処理では、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で計数されたアウト球数に対応する信号を外部端子板784から出力する。例えば、所定のアウト球数(10個など)毎に外部端子板784から所定長のパルス信号を出力してもよい。
Also, in the output data setting process, a signal corresponding to the number of out balls counted in the switch input process (step S74) is output from the external
また、出力データ設定処理では、パチンコ機1に接続された検査装置に出力するための試験信号の設定を行う。試験信号には、例えば、遊技状態を示す信号や普通図柄、特別図柄の停止図柄を示す信号が含まれる(情報信号出力手段)。
In the output data setting process, a test signal to be output to the inspection device connected to the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板コマンド送信処理を実行する(ステップS92)。周辺制御基板コマンド送信処理では、上述した送信情報記憶領域からコマン
ドやデータなどの送信情報を読み出し、送信情報を主周シリアルデータとして周辺制御基板1510に送信する。送信情報には、本ルーチンであるタイマ割込み処理で作成した各種コマンドが記憶されている。主周シリアルデータは、1パケットが3バイトに構成されている。具体的には、主周シリアルデータは、1バイト(8ビット)の記憶容量を有するコマンドの種類を示すステータスと、1バイト(8ビット)の記憶容量を有する演出のバリエーションを示すモードと、ステータス及びモードを数値とみなしてその合計を算出したサム値と、から構成されており、このサム値は、送信時に作成されている。
Subsequently, the
最後に、主制御MPU1311は、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットする(ステップS96)。ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値がセットされることにより、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLがクリア設定される。また、最後に、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンクを切り替える(復帰する)。以上の処理が終了すると、タイマ割込み処理を終了し、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。
Finally, the
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、主制御MPU1311が、タイマ割込み処理において、役物比率や連続役物比率の計算処理を実行するが、払出制御部952の払出制御MPUが役物比率や連続役物比率の計算処理を実行してもよい。この場合、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510の周辺制御部1511に役物比率や連続役物比率を表示するためのコマンドを送信してもよいし、払出制御部952から周辺制御部1511に役物比率や連続役物比率を表示するためのコマンドを送信してもよい。
In the
[5-3.役物比率算出・表示処理]
図24及び図25は、役物比率算出・表示処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。役物比率算出・表示処理は、主制御MPU1311が実行する。なお、周辺制御基板1510の周辺制御部1511が役物比率算出・表示処理を実行してもよい。周辺制御部1511が役物比率を算出する場合、算出された役物比率はメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示してもよい。例えば、算出された役物比率が所定の範囲内(又は、範囲外)である場合、遊技における演出を変えてもよい。具体的には、役物比率が所定の閾値(基準値より小さい閾値)を超えている場合に、予告演出を変えて、通常の予告演出より興趣が高まる予告演出を行ってもよい。
[5-3. Character ratio calculation/display processing]
24 and 25 are flowcharts showing an example of character product ratio calculation/display processing. The
まず、主制御MPU1311のRAM1312の役物比率算出用領域13128のメイン領域からチェックコードを算出し(ステップS140)、算出したチェックコードが、役物比率算出用領域13128に格納されているチェックコードと一致しているかを判定する(ステップS142)。算出したチェックコードと役物比率算出用領域13128に格納されているチェックコードとが一致していれば、メイン領域のデータは正常なので、役物比率算出処理を実行し、メイン領域のデータから役物比率及び連続役物比率を算出し、役物比率算出用領域13128に格納する(ステップS156)。具体的には、役物獲得球数÷総獲得球数で役物比率を計算し、連続役物獲得球数÷総獲得球数で連続役物比率を計算する。計算された役物比率及び連続役物比率の小数部分(小数点以下の値)は切り捨てるか、四捨五入するとよい。そして、ステップS160に進む。
First, a check code is calculated from the main area of the role product
なお、ステップS156において、役物比率算出用領域13128の役物比率及び/又は連続役物比率の更新毎に、更新された値をバックアップ領域に複製してもよい。
In step S156, each time the character product ratio and/or the continuous character product ratio in the character product
獲得球数が格納されるビット数が大きく、主制御MPU1311で演算可能なビット数が不足する場合、役物比率の演算において、獲得球数の下位ビットを省略して除算をして役物比率を算出してもよい。例えば、獲得球数の格納領域が32ビットであれば、0~42億9496万7295までの数値を記憶できる。しかし、主制御MPUが8ビットプロ
セッサであり、8又は16ビットの演算ができる場合、32ビットで格納された獲得球数のうち、値が1の最上位ビットから下の16ビットを取り出して演算用レジスタ(16ビット)に格納して除算するとよい。なお、獲得球数が演算に使用可能なビット数の最大値(16ビットの最大値である32767)以下である場合、下位16ビットを取り出して演算に使用すればよい。
If the number of bits in which the number of acquired balls is stored is large and the number of bits that can be calculated by the
また、総獲得球数を100で除して(小数点以下を切り捨てて)、被除数(割られる数)として用いて役物比率を計算すると、小数での計算を避けることができる。 Also, if the total number of acquired balls is divided by 100 (rounded down to the decimal point) and used as the dividend (divided number) to calculate the character ratio, calculation using decimal numbers can be avoided.
また、役物比率の上限を99に設定し、役物比率の計算結果が100以上となった場合には99としてもよい。 Also, the upper limit of the character product ratio may be set to 99, and may be set to 99 when the calculation result of the character product ratio is 100 or more.
一方、算出したチェックコードと役物比率算出用領域13128に格納されているチェックコードとが一致していなければ、メイン領域のデータは異常なので、バックアップ領域1のデータからの役物比率の算出を試みる。具体的には、役物比率算出用領域13128のバックアップ領域1からチェックコードを算出し(ステップS144)、算出したチェックコードが、役物比率算出用領域13128に格納されているチェックコードと一致しているかを判定する(ステップS146)。算出したチェックコードと役物比率算出用領域13128に格納されているチェックコードとが一致していれば、バックアップ領域1のデータは正常なので、バックアップ領域1のデータをメイン領域に複製し(ステップS148)、役物比率算出処理を実行し、メイン領域のデータから役物比率及び連続役物比率を算出する(ステップS156)。そして、ステップS160に進む。
On the other hand, if the calculated check code and the check code stored in the character product
一方、算出したチェックコードと役物比率算出用領域13128に格納されているチェックコードとが一致していなければ、バックアップ領域1のデータは異常なので、バックアップ領域2のデータからの役物比率の算出を試みる。具体的には、役物比率算出用領域13128のバックアップ領域2からチェックコードを算出し(ステップS150)、算出したチェックコードが、役物比率算出用領域13128に格納されているチェックコードと一致しているかを判定する(ステップS152)。算出したチェックコードと役物比率算出用領域13128に格納されているチェックコードとが一致していれば、バックアップ領域1のデータは正常なので、バックアップ領域2のデータをメイン領域に複製し(ステップS154)、役物比率算出処理を実行し、メイン領域のデータを読み出して役物比率及び連続役物比率を算出する(ステップS156)。そして、ステップS160に進む。
On the other hand, if the calculated check code and the check code stored in the character product
他にバックアップ領域があれば、同様に、当該バックアップ領域のデータが正常かを判定し、正常なバックアップ領域のデータから役物比率及び連続役物比率を算出する。 If there is another backup area, it is similarly determined whether the data in the backup area is normal, and the character product ratio and the continuous character product ratio are calculated from the data in the normal backup area.
メイン領域及び全てのバックアップ領域のデータが異常であれば、役物比率算出用ワークエリア(役物比率算出用領域13128)を初期化し、異常を報知する(ステップS158)。 If the data in the main area and all the backup areas are abnormal, the character product ratio calculation work area (character product ratio calculation area 13128) is initialized, and the abnormality is notified (step S158).
続いて、メイン領域からチェックコードを算出し(ステップS160)、算出したチェックコードを役物比率算出用領域13128に格納する(ステップS162)。役物比率算出・表示処理でチェックコードを算出するのは、主基板側電源断時処理の途中でリセットされた場合、停電フラグやチェックサムが算出されていないために、初期化処理においてRAM1312にバックアップされたデータが初期化されるが、役物比率算出・表示処理で定期的にチェックコードを算出して記憶すれば、パチンコ機の電源が再投入されても、役物比率算出用ワークエリア(役物比率算出用領域13128)のデータは消去されずに残すことができるためである。 Subsequently, a check code is calculated from the main area (step S160), and the calculated check code is stored in the role product ratio calculation area 13128 (step S162). The reason why the check code is calculated in the character ratio calculation/display process is that if it is reset in the middle of the power failure process on the main board side, the power failure flag and checksum are not calculated. Although the backed-up data is initialized, if the check code is calculated and stored periodically in the character ratio calculation/display process, the work area for calculating the character ratio can be saved even if the pachinko machine is turned on again. This is because the data in (character product ratio calculation area 13128) can be left without being erased.
続いて、バックアップ領域振り分けカウンタ値に1を加算して更新し(ステップS164)、バックアップ領域振り分けカウンタ値が奇数かを判定する(ステップS166)。バックアップ領域振り分けカウンタ値が奇数であれば、メイン領域のデータをバックアップ領域1に複製する(ステップS168)。一方、バックアップ領域振り分けカウンタ値が偶数であれば、メイン領域のデータをバックアップ領域2に複製する(ステップS170)。バックアップ領域振り分けカウンタ値によって、メイン領域のデータの複製先を振り分けて、一部のバックアップ領域のみにデータを書き込むことによって、異常な値が複数のバックアップ領域に書き込まれることを防止できる。 Subsequently, the backup area allocation counter value is updated by adding 1 (step S164), and it is determined whether the backup area allocation counter value is an odd number (step S166). If the backup area allocation counter value is an odd number, the data in the main area is copied to the backup area 1 (step S168). On the other hand, if the backup area allocation counter value is an even number, the data in the main area is copied to the backup area 2 (step S170). It is possible to prevent an abnormal value from being written to a plurality of backup areas by sorting the copy destinations of the data in the main area according to the backup area allocation counter value and writing the data only to a part of the backup areas.
なお、3以上のバックアップ領域を設ける場合、バックアップ領域振り分けカウンタ値をバックアップ領域の数で除した余りによって、データを書き込むバックアップ領域を振り分ければよい。 When three or more backup areas are provided, the backup areas to which data is written may be allocated according to the remainder obtained by dividing the backup area allocation counter value by the number of backup areas.
続いて、算出された役物比率を役物比率表示器1317に表示する(ステップS172)。具体的には、算出した役物比率の種類と算出された値とを用いて、変換表(図示省略)を参照して、役物比率表示器1317の各桁に表示するデータを取得し、取得したデータを役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171に送る。例えば、役物比率の種類が役物比率(累計)であれば、上2桁にA7を表示し、算出された役物比率が66%であれば、下2桁に66を表示する。
Subsequently, the calculated role product ratio is displayed on the role product ratio display 1317 (step S172). Specifically, using the calculated type of role product ratio and the calculated value, a conversion table (not shown) is referenced to acquire data to be displayed on each digit of the role
役物比率算出・表示処理の役物比率算出処理(ステップS156)は、役物比率算出用領域13128(すなわち、図27に示す役物比率算出用ワークエリア)から獲得球数のデータを読み出すが、役物比率算出用領域13128の獲得球数に関わる記憶領域にデータを書き込むことはできない。すなわち、後述するように、ステップS156、S172の処理を共通プログラムモジュールで構成した場合、当該共通プログラムモジュールは、役物比率算出用領域13128の獲得球数に関わる記憶領域にデータを書き込む権限がなく、算出した役物比率及び連続役物比率の記憶領域にはデータを書き込むことができる。
The character ratio calculation process (step S156) of the character ratio calculation/display process reads the number of acquired balls from the character ratio calculation area 13128 (that is, the work area for calculating the character ratio shown in FIG. 27). , Data cannot be written in the storage area related to the number of winning balls in the role product
以上に説明したように、役物比率算出・表示処理において役物比率を算出するためのデータをバックアップ領域に複製するので、異常リセット等により、正常な電源断時処理が実行されなかった場合に、役物比率を算出するためのデータを保護できる。 As explained above, the data for calculating the character product ratio in the character product ratio calculation/display process is duplicated in the backup area. , the data for calculating the character ratio can be protected.
なお、ステップS156、S172の処理は、遊技機の種類によらず共通であるため、一つ又は複数の共通プログラムモジュールで構成するとよい。この場合、メイン領域のチェックコード及びバックアップ領域のチェックコードが間違っていないかを判定する処理は、共通プログラムモジュールとは別に非共通側に構成するとよい。これは、データのチェック、バックアップ方法は機種ごとに異なるためである。しかし、データのチェック、バックアップ方法を機種間で共通化すれば、共通プログラムモジュールに配置してもよい。 It should be noted that the processes of steps S156 and S172 are common regardless of the type of gaming machine, and thus may be configured with one or a plurality of common program modules. In this case, the process of determining whether the check code in the main area and the check code in the backup area are correct may be configured on the non-common side separately from the common program module. This is because the data check and backup methods differ from model to model. However, if the data check and backup methods are shared among the models, they may be arranged in a common program module.
[6.記憶領域の構成]
続いて、ROM1313に格納されたプログラム及びデータの配置について説明する。図26(A)は、主制御基板1310の主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたROM1313及びRAM1312に格納されたプログラム(コード)及びデータの配置の一例を示す図である。
[6. Storage area configuration]
Next, the arrangement of programs and data stored in the
ROM1313には、遊技制御用コード13131、遊技制御用データ13132、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133、デバッグ(検査機能)用データ13134、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135及び役物比率算出・表示用データ13136を格納
する領域が含まれている。本実施形態のROM1313には、遊技制御用コード13131及び遊技制御用データ13132などのパチンコ機1に関わるプログラムやデータを格納する遊技制御領域(第一記憶領域)と、デバッグ(検査機能)コード13133及びデバッグ(検査機能)データ13134などの、パチンコ機1のデバッグ(検査機能)に必要な信号の出力を目的として使用されるプログラムやデータを格納するデバッグ(検査機能)領域(第二記憶領域)と、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135及び役物比率算出・表示用データ13136などの、役物比率の算出を目的として使用されるプログラムを格納する役物比率算出領域(第三記憶領域)が割り当てられている。
遊技制御用データ13132の最終アドレスと、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の先頭アドレスとの間には16バイト以上の空き領域(未使用空間)が設けられており、ダンプリスト形式で表示した場合に遊技制御領域とデバッグ(検査機能)領域とが容易に区別できるようになっている。同様に、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の最終アドレスと、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135の先頭アドレスとの間には16バイト以上の空き領域(未使用空間)が設けられており、ダンプリスト形式で表示した場合にデバッグ(検査機能)領域と役物比率算出用領域とが容易に区別できるようになっている。なお、空き領域に格納される値は、同一の値である固定値とし、かつ、遊技領域、デバッグ領域で設定される値とは異なる値又は頻度が低い値で設定されるとよい。また、空き領域に格納される値は、No OperationコードなどCPUが何もしない命令でもよい。このようにすると、ダンプリスト形式で表示される場合、遊技制御領域、デバッグ(検査機能)領域、役物比率算出領域が容易に区別できるようになる。
Between the end address of the
また、デバッグ(検査機能)領域と役物比率算出領域とを分けずに、デバッグ領域の一部に役物比率算出・表示用コード13135や役物比率算出・表示用データ13136を格納してもよい。すなわち、遊技制御領域と他の領域とが明確に区別されていればよい。このように、遊技制御領域と他の領域とを明確に区別することによって、遊技の進行の制御に直接関わらない処理である役物比率算出領域(役物比率算出・表示用コード13135や役物比率算出・表示用データ13136)を遊技制御領域と分けて配置して、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135の不具合(バグ等)が遊技制御に影響を及ぼす危険性を回避している。
Alternatively, the
なお、デバッグ(検査機能)領域には、遊技に直接関連しない目的のプログラムやデータが格納されており、例えば、パチンコ機1の遊技制御以外のパチンコ機1のデバッグ時のみに使用される各種機能検査信号を出力するためのコード13133が格納される。これらデバッグ用(検査機能)コード13133は、デバッグ用(検査機能)信号を出力するためのプログラムである。また、役物比率算出領域には、遊技の進行に直接関係しない、役物比率を算出する目的のプログラムが格納される。
The debug (inspection function) area stores programs and data for purposes not directly related to the game. A
また、遊技制御用コード13131は、主制御MPU1311によって実行される。また、遊技制御用コード13131は、RAM1312に対して適宜読み書きが可能であるが、遊技制御用コード13131で使用する遊技制御用領域13126に対しては、デバッグ(検査機能)用コードから読み出しのみが実行可能となるように構成されており、当該領域に対する書き込みが実行できないように構成されている。このように、遊技制御用領域13126は、遊技制御用コード13131のみからアクセス可能な、遊技領域を構成する。デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133に基づく処理は、遊技制御用コード13131の実行中において、一方的に呼び出して実行することが可能であるが、デバッグ(検査機能)用コードから遊技制御用コード13131を呼び出して実行することができないように構成している。これにより、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の独立性を高められるので、遊技制御用コード13131を変更した場合であってもデバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の変更を最小限にとどめることができる。
Also, the
また、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135は、遊技制御用コード13131から呼び出され(例えば、図23に示すタイマ割込み処理のステップS89)、主制御MPU1311によって実行される。役物比率算出・表示用コード13135によって計算された役物比率は、RAM1312の役物比率算出用領域13128に格納される。役物比率算出用領域13128は、図示するように、遊技制御用領域13126とは別に(遊技制御領域外に)設けられる。このように、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135を遊技制御用コード13131と別に設計し、別の領域に格納することによって、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135の検査と遊技制御用コード13131の検査とを別に行うことができ、パチンコ機1の検査の手間を減少できる。また、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135を、機種に依存せず、複数の機種で共通に使用できる。
Also, the role product ratio calculation/
図26(B)は、役物比率算出用領域13128の詳細を示す図である。役物比率算出用領域13128は、役物比率の算出結果が格納されるメイン領域の他、メイン領域に格納されたデータの複製が格納されるバックアップ領域1及びバックアップ領域2とを設けてもよい。バックアップ領域は一つでも複数でもよい。各領域には、データの誤りを検出するためのチェックコードが付加される。チェックコードは、各領域のデータのチェックサムでも予め定めた値でもよい。チェックコードは、パチンコ機1の電源投入時に初期化処理で設定したり、役物比率算出・表示処理においてメイン領域のデータが更新される毎に設定したり、主制御側電源断時処理(図22のステップS50~S54)において設定してもよい。特に、チェックコードが固定値である場合、初期化処理で正常と判定した又はデータを消去した際にチェックコードを初期化し、主制御側電源断時処理(図20のステップS50)において固定値をセットしてもよい。チェックコードは、停電フラグと兼用してもよい。すなわち、メイン領域のチェックコードに所定値が設定されていれば、停電フラグが設定されていると判定してもよい。また、停電フラグに所定値が設定されていれば、各領域のチェックコードが正しい値である(すなわち、各領域のデータが正常である)と判定してもよい。
FIG. 26B is a diagram showing details of the character product
なお、メイン領域が異常であると判定された場合にバックアップ領域が正常であるかを判定し、正常であると判定されたバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製してもよい(図21のステップS24)。また、主制御側電源断時処理において、メイン領域の値を各バックアップ領域に複製してもよい(図22のステップS54)。また、役物比率算出・表示処理において、メイン領域の値が更新される毎に、更新されたデータをバックアップ領域に複製してもよい(図25のステップS168、S170)。 Incidentally, if it is determined that the main area is abnormal, it may be determined whether or not the backup area is normal, and the data in the backup area determined to be normal may be copied to the main area (step in FIG. 21). S24). Also, in the main control side power-off process, the values in the main area may be duplicated in each backup area (step S54 in FIG. 22). Also, in the role product ratio calculation/display process, every time the value in the main area is updated, the updated data may be copied to the backup area (steps S168 and S170 in FIG. 25).
メイン領域とバックアップ領域1との間、及びバックアップ領域1とバックアップ領域2との間には、未使用空間が設けられる。各領域の間に未使用空間を設けることによって、各領域のアドレスを遠ざけることができ、アドレスの上位桁で各領域を区別できる。
Unused space is provided between the main area and the
図27は、役物比率算出用領域13128における各データを格納するためのワークエリアの具体的な構造を示す図である。役物比率算出用領域13128の獲得球数のデータは、主制御MPU1311が時刻するタイマ割り込み処理(図23)において書き込まれ、役物比率算出・表示処理の役物比率算出処理(図24のステップS156)において読み出される。このように、役物比率算出・表示処理が役物比率算出用領域13128から獲得球数のデータを読み出し、タイマ割り込み処理(遊技制御プログラム)が役物比率算出用領域13128に獲得球数のデータを書き込むことによって、遊技制御プログラムと役物比率算出・表示処理を実行するプログラムとを完全に分けることができ、異なる仕様の遊技機でも役物比率算出・表示処理のためのプログラムを共通化できる。
FIG. 27 is a diagram showing a specific structure of a work area for storing each data in the character product
なお、役物比率算出・表示処理の役物比率算出処理(図24のステップS156)は、
算出した役物比率及び連続役物比率を役物比率算出用領域13128の役物比率及び連続役物比率の記憶領域に書き込む。算出された役物比率及び連続役物比率のデータは、役物比率を表示する際、役物比率算出・表示処理の役物比率表示処理(図25のステップS170)において読み出される。遊技制御プログラムは、役物比率算出用領域13128の役物比率及び連続役物比率の記憶領域にアクセスしない。
Note that the role product ratio calculation process (step S156 in FIG. 24) of the role product ratio calculation/display process is
The calculated role product ratio and continuous role product ratio are written in the storage area for the role product ratio and continuous role product ratio of the area for calculating the
図27(A)は、最も簡単な方法のワークエリアの構造を示す。図27(A)に示すワークエリアの構造では、役物獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、総獲得球数、役物比率及び連続役物比率を格納する。役物獲得球数は、動作中の役物(例えば、開放中の大入賞口2005、2006、第二始動口扉部材2549が開放中の第二始動口2004)への入賞による賞球数である。連続役物獲得球数は、役物が連続して動作中(例えば、大当りの連チャン中で入賞口が開放中)の役物への入賞による賞球数である。総獲得球数は、遊技者に払い出された全賞球数である。役物比率は、役物獲得球数÷総獲得球数で計算できる。連続役物比率は、連続役物獲得球数÷総獲得球数で計算できる。役物獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、及び総獲得球数は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS81で更新され、役物比率及び連続役物比率は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS91で計算され、格納される。
FIG. 27A shows the structure of the work area of the simplest method. In the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 27(A), the number of winning ball, the number of continuous winning balls, the total number of winning balls, the ratio of the winning role, and the ratio of the continuous winning role are stored. The number of prize balls obtained is the number of prize balls obtained by winning prizes for the prizes in operation (for example, the
図27(A)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、役物獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数及び総獲得球数は、後述する図27(B)の総累計に相当し、各々3又は4バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215又は4294967295までの数値を記憶できる。これらのデータはデータに異常が生じない限り消去されないことから、長期間のデータを格納できるように大きな記憶領域を用意している。また、役物比率及び連続役物比率は、1バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で255までの数値を記憶できる。 Among the structure of the work area shown in FIG. It is a 4-byte storage area and can store numeric values up to 16777215 or 4294967295 in decimal. Since these data will not be erased unless an abnormality occurs in the data, a large storage area is provided so that long-term data can be stored. Also, the role product ratio and the continuous role product ratio are storage areas of 1 byte, and can store numerical values up to 255 in decimal.
図27(B)は、リングバッファを用いたワークエリアの構造を示す。図27(B)に示すワークエリアの構造では、役物獲得球数、その他獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、合計獲得球数、役物比率及び連続役物比率を格納する。また各データの記憶領域は、所定数の賞球毎にn個の記憶領域(例えば、賞球6000個毎にn=10個の記憶領域)を持つリングバッファによって構成されており、合計獲得球数が所定数(6000個)になると全てのデータの書き込みポインタが移動して、データが更新される記憶領域が変わる。そして、n番目の記憶領域に所定数の賞球分のデータが格納された後、書き込みポインタは1番目の記憶領域に移動し、1番目の記憶領域にデータを格納する。なお、合計獲得球数以外のデータ(役物獲得球数、発射球数、入賞球数、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム数、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当り回数など)が所定数となった場合に、書き込みポインタを移動してもよい。 FIG. 27B shows the structure of a work area using a ring buffer. In the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 27(B), the number of winning balls, the number of other winning balls, the number of successive winning balls, the total number of winning balls, the role ratio and the continuous role ratio are stored. Each data storage area is configured by a ring buffer having n storage areas for each predetermined number of prize balls (for example, n=10 storage areas for every 6000 prize balls). When the number reaches a predetermined number (6000), the write pointers for all the data are moved, and the storage area where the data is updated changes. After the data for the predetermined number of prize balls is stored in the n-th storage area, the write pointer moves to the first storage area and stores the data in the first storage area. In addition, when the data other than the total number of acquired balls (number of acquired balls, number of fired balls, number of winning balls, number of special symbol variation display games, number of special symbol variation display games, etc.) reaches a predetermined number, You may move the write pointer.
なお、リングバッファの書き込みポインタ及び読み出しポインタは全てのデータに共通であり、所定の賞球数毎に全てのデータ列の書き込みポインタが移動する。また、書き込みポインタの移動に伴い、読み出しポインタも移動する。読み出しポインタは、書き込みポインタより一つ前の記憶領域を指す。これは、賞球6000個分の直近のデータを用いて役物比率を計算するためである。 The write pointer and read pointer of the ring buffer are common to all data, and the write pointers of all data strings are moved for each predetermined number of winning balls. Further, the read pointer also moves along with the movement of the write pointer. The read pointer points to the storage area one before the write pointer. This is for calculating the character ratio using the most recent data for 6000 prize balls.
各データの累計は、リングバッファのn個の記憶領域に格納されているデータの累計値であり、役物比率、連続役物比率の累計の値は各データの累計値から算出された値であり、リングバッファが一巡して、新たなデータを書き込むためにリングバッファの一つの記憶領域がクリアされると、当該クリアされた領域のデータを除外して累計値が計算される。各データの総累計は、過去に収集したデータの累計値であり、当該累計値から計算された役物比率、連続役物比率の総累計の値は各データの総累計値から算出された値であり、リングバッファが一巡して、新たなデータを書き込むためにリングバッファの一つの記憶領域がクリアされても、当該クリアされた領域のデータを含めて総累計値が計算される。 The cumulative total of each data is the cumulative value of the data stored in the n storage areas of the ring buffer. Yes, when the ring buffer is cycled and one storage area of the ring buffer is cleared for writing new data, the cumulative value is calculated excluding the data in the cleared area. The total cumulative value of each data is the cumulative value of the data collected in the past, and the total cumulative value of the role ratio and continuous role ratio calculated from the cumulative value is the value calculated from the total cumulative value of each data. Even if one storage area of the ring buffer is cleared in order to write new data after the ring buffer completes one cycle, the total accumulated value is calculated including the data in the cleared area.
図27(B)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、役物獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、役物比率、連続役物比率は、図27(A)における説明と同じである。その他獲得球数は、役物以外(開閉しない入賞口、例えば一般入賞口2001)への入賞による賞球数である。合計獲得球数は、遊技者に払い出された全賞球数であり、この値が所定数になると書き込みポインタが移動する。役物獲得球数、その他獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、及び合計獲得球数は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS81で書き込みポインタがある記憶領域のデータが更新され、役物比率及び連続役物比率は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS91で計算され、格納される。 Of the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 27(B), the number of winning character balls, the number of consecutive winning ball, the character ratio, and the continuous character ratio are the same as those explained in FIG. 27(A). The number of other won balls is the number of prize balls obtained by winning prizes other than accessories (a winning opening that does not open and close, for example, the general winning opening 2001). The total number of won balls is the total number of prize balls paid out to the player, and when this value reaches a predetermined number, the write pointer moves. As for the number of winning balls, the number of other winning balls, the number of continuous winning balls, and the total number of winning balls, the data in the storage area with the write pointer is updated in step S81 of the timer interrupt processing, and the role ratio and the continuous winning balls are updated. The product ratio is calculated and stored in step S91 of timer interrupt processing.
図27(C)は、リングバッファを用いたワークエリアの構造を示す。図27(C)に示すワークエリアの構造では、図27(B)に示すものより詳細なデータを取得でき、普通電動役物獲得球数、特別電動役物獲得球数、始動口獲得球数、その他入賞口獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、合計獲得球数、役物比率及び連続役物比率を格納する。また各データの記憶領域は、所定数の賞球毎にn個の記憶領域(例えば、賞球6000個毎に10個の記憶領域)を持つリングバッファによって構成されており、合計獲得球数が所定数(6000個)になると書き込みポインタが移動して、データが更新される記憶領域が変わる。そして、n番目の記憶領域に所定数の賞球分のデータが格納された後、書き込みポインタは1番目の記憶領域に移動し、1番目の記憶領域にデータを格納する。なお、合計獲得球数以外のデータ(特別電動役物獲得球数、発射球数、入賞球数、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム数、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当り回数など)が所定数となった場合に、書き込みポインタを移動してもよい。 FIG. 27C shows the structure of a work area using a ring buffer. In the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 27(C), it is possible to obtain more detailed data than that shown in FIG. 27(B). , other winning hole winning ball number, continuous role winning ball number, total winning ball number, role ratio and continuous role ratio are stored. Each data storage area is configured by a ring buffer having n storage areas for each predetermined number of prize balls (for example, 10 storage areas for every 6000 prize balls), and the total number of winning balls is When the predetermined number (6000) is reached, the write pointer moves and the storage area where the data is updated changes. After the data for the predetermined number of prize balls is stored in the n-th storage area, the write pointer moves to the first storage area and stores the data in the first storage area. In addition, when data other than the total number of acquired balls (number of special electric accessory acquired balls, number of fired balls, number of winning balls, number of special symbol variation display games, number of special symbol variation display games, etc.) reaches a predetermined number You may move the write pointer to
各データの累計は、リングバッファのn個の記憶領域に格納されているデータの累計値であり、役物比率、連続役物比率の累計の値は各データの累計値から算出された値であり、リングバッファが一巡して、新たなデータを書き込むためにリングバッファの一つの記憶領域にクリアされると、当該クリアされた領域のデータを除外して累計値が計算される。各データの総累計は、過去に収集したデータの累計値であり、役物比率、連続役物比率の累計の値は各データの累計値から算出された値であり、リングバッファが一巡して、新たなデータを書き込むためにリングバッファの一つの記憶領域にクリアされても、当該クリアされた領域のデータを含めて総累計値が計算される。 The cumulative total of each data is the cumulative value of the data stored in the n storage areas of the ring buffer. When the ring buffer is cycled and one storage area of the ring buffer is cleared for writing new data, the cumulative value is calculated excluding the data in the cleared area. The total cumulative value of each data is the cumulative value of the data collected in the past, and the cumulative value of the character ratio and the continuous component ratio is the value calculated from the cumulative value of each data. Even if one storage area of the ring buffer is cleared for writing new data, the total cumulative value is calculated including the data in the cleared area.
図27(B)(C)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、リングバッファ内の役物獲得球数、その他獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、合計獲得球数、普通電動役物獲得球数、特別電動役物獲得球数、始動口獲得球数、その他入賞口獲得球数は、各々2バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で65535までの数値を記憶できる。役物獲得球数、その他獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、合計獲得球数、普通電動役物獲得球数、特別電動役物獲得球数、始動口獲得球数及びその他入賞口獲得球数の累計は、各々3バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215までの数値を記憶できる。累計は賞球6000個×n(n=10の場合は60000個の賞球)分のデータの合計であることから、大きな記憶領域を用意している。役物獲得球数、その他獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、合計獲得球数、役物比率、連続役物比率、普通電動役物獲得球数、特別電動役物獲得球数、始動口獲得球数及びその他入賞口獲得球数の総累計は、各々3又は4バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215又は4294967295までの数値を記憶できる。総累計はデータに異常が生じない限り消去されないことから、長期間のデータを格納できるように、さらに大きな記憶領域を用意している。また、役物比率及び連続役物比率の累計及び総累計は、各々1バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で255までの数値を記憶できる。 Of the structure of the work area shown in FIGS. 27(B) and (C), the number of winning balls in the ring buffer, the number of other winning balls, the number of continuous winning balls, the total number of winning balls, and the normal electric winning balls Each of the number, the number of winning balls for the special electric accessory, the number of winning balls for the starting opening, and the number of winning openings is a storage area of 2 bytes, and can store numerical values up to 65,535 in decimal. Number of winning balls, number of other winning balls, number of continuous winning balls, total number of winning balls, number of normal electric winning balls, number of special electric winning balls, number of starting balls and other winning balls The cumulative total of numbers is a storage area of 3 bytes each, and can store numerical values up to 16777215 in decimal. Since the cumulative total is the sum of data for 6000 prize balls×n (60000 prize balls when n=10), a large storage area is provided. Number of acquired balls, number of other acquired balls, number of continuous acquired balls, total number of acquired balls, ratio of role, ratio of continuous roles, number of normal electric accessories acquired, number of special electric accessories acquired, starting point The number of winning balls and the total cumulative number of winning balls are each a storage area of 3 or 4 bytes, and can store numerical values up to 16,777,215 or 4,294,967,295 in decimal. Since the total cumulative total is not deleted unless an abnormality occurs in the data, a larger storage area is provided so that long-term data can be stored. Also, the sum total and total sum of the role ratio and the continuous role ratio are each a storage area of 1 byte, and can store numerical values up to 255 in decimal.
図27(C)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、合計獲得球数、役物比率、連続役物比率は、図27(B)における説明と同じである。その他獲得球数は、役物以外(開閉しな
い入賞口)への入賞による賞球数である。普通電動役物獲得球数は、普通図柄による抽選の結果によって動作中の普通電動役物(第二始動口扉部材2549が開放中の第二始動口2004)への入賞により獲得される賞球数である。特別電動役物獲得球数は、特別図柄による抽選の結果によって動作中の特別電動役物(例えば、開放中の大入賞口2005、2006)への入賞による賞球数である。始動口獲得球数は、始動口(第一始動口2002)への入賞により獲得される賞球数である。その他入賞口獲得球数は、役物ではなく(動作せず)、特別図柄の抽選の契機とならない入賞口(一般入賞口2001)への入賞により獲得される賞球数である。普通電動役物獲得球数、特別電動役物獲得球数、始動口獲得球数、その他入賞口獲得球数、連続役物獲得球数、及び合計獲得球数は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS81で書き込みポインタがある記憶領域のデータが更新され、役物比率及び連続役物比率は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS91で計算され、格納される。
In the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 27(C), the total number of acquired balls, the character ratio, and the continuous character ratio are the same as those explained in FIG. 27(B). The number of other winning balls is the number of prize balls obtained by winning prizes other than accessories (a winning opening that does not open and close). The number of winning balls of the normal electric accessory is the prize balls obtained by winning the normal electric accessory in operation (the
図27(A)に示すデータ構造では、格納されている値が異常であると判定された場合に、初期化処理のステップS116で役物比率算出用領域13128のデータが消去されるが、他の契機でデータは消去されない。このため、所定期間(例えば、1日、1週間、1月など)毎に役物比率算出用領域13128のデータを消去してもよい。同様に、図25(B)(C)の総累計を所定期間毎に消去してもよい。
In the data structure shown in FIG. 27A, when the stored value is determined to be abnormal, the data in the role product
また、役物比率算出用領域13128のデータや、算出された役物比率が異常値である(例えば、役物比率が100%超、役物比率の算出結果が前回の算出値から大きく変化した、役物獲得球数>総獲得球数など)場合、当該異常値を消去してもよい。当該異常値だけでなく、役物比率算出用領域13128の全データを消去してもよい。また、役物比率算出用領域13128のデータや、算出された役物比率が異常値である場合、異常であることを報知してもよい。また、チェックコードを用いてバックアップ領域のデータを検査し、正常なバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製後に、再度役物比率を計算してもよい。
Also, the data in the character product
[7.役物比率表示器の構成]
図28は、役物比率表示器1317の構成を示す図である。
[7. Configuration of character ratio indicator]
FIG. 28 is a diagram showing the configuration of the character
役物比率表示器1317は、ドライバ回路13171及び複数の7セグメントLED13172によって構成される。例えば、7セグメントLED13172は4桁で構成される。
The
ドライバ回路13171と7セグメントLED13172とは、一体として一つのパッケージに収容されるとよいが、両者が別のパッケージに収容されてもよい。
The
ドライバ回路13171と主制御MPU1311とは、3本の信号線(DATA、LOAD、CLOCK)によって接続される。
The
DATA線は、役物比率表示器1317に表示するデータや役物比率表示器1317の動作状態を設定する信号を転送し、主制御MPU1311のシリアル通信回路13114に接続される。LOAD線は、データの取り込みタイミングを示す信号を転送し、主制御MPU1311のシリアル通信回路13114に接続される。CLOCK線は、ドライバ回路13171の動作周期を規定するクロック信号を転送し、主制御MPU1311のシリアル通信回路13114に接続される。
The DATA line transfers data to be displayed on the
ドライバ回路13171と7セグメントLED13172とは、4本の桁選択信号線IDIG-0~IDIG-3と、8本のセグメント点灯信号線ISEG-a~ISEG-Dpとで接続される。セグメント点灯信号線ISEG-a~ISEG-Dpは、7セグメン
トLED13172の各LED素子(7セグメント及び小数点)を点灯させる信号を伝達する。桁選択信号線IDIG-0~IDIG-3は、セグメント点灯信号線ISEG-a~ISEG-Dpで伝送される信号が、7セグメントLED13172のどの桁の信号かを示す制御信号を伝達する。なお、図示した信号(電流)の向きは7セグメントLED13172がアノードコモン型かカソードコモン型かで異なるが、アノードコモン型の例を図示した。
The
ドライバ回路13171のR-EXT端子には、7セグメントLED13172の各LED素子に流す電流値を定める抵抗13174が接続される。抵抗13174の抵抗値の変更によって、7セグメントLED13172の各LED素子の発光輝度を変えることができる。
The R-EXT terminal of the
図29は、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171の構成を示す図である。
FIG. 29 is a diagram showing the configuration of the
ドライバ回路13171は、16ビットシフトレジスタ3171、16ビットデータラッチ3172、8ビットデータラッチ3173A~D、8×4データセレクタ3174、デコーダ3175、2×8データセレクタ3176、定電流ドライバ3178、ドライバ3179、ラッチセレクタ・ロードパルス分配器3180、Digit-Limit制御部3181、デューティ比制御部3182、データセレクタ制御部3183、スタンバイモード制御部3184及び発振器3185を有する。
The
16ビットシフトレジスタ3171は、DATA IN端子に入力されたシリアルデータを取り込み、16ビット分のデータを保持し、パラレルデータとして16ビットデータラッチ3172に送る。なお、D15(MSB)~D12の4ビットは、ドライバ回路13171の動作モード(図35参照)を選択するためのデータであり、D11~D8の4ビットは動作モードと対応するレジスタを選択させるデータであり(図33参照)、D7~D0(LSB)は、その詳細設定のデータである。
The 16-
16ビットデータラッチ3172は、LOAD信号のタイミングでデータをラッチし、D15~D8を各制御部(ラッチセレクタ・ロードパルス分配器3180、Digit-Limit制御部3181、デューティ比制御部3182、データセレクタ制御部3183、スタンバイモード制御部3184)に送り、D7~D0を8ビットデータラッチ3173A~Dに送る。
The 16-bit data latch 3172 latches data at the timing of the LOAD signal, and D15 to D8 are controlled by each control section (latch selector/
具体的には、図30に示すように、16ビットシフトレジスタ3171は、CLOCK信号の立ち上がりタイミングでDATA IN端子に入力されたシリアルデータを取り込み、データをシフトする。16ビットデータラッチ3172は、LOAD信号の立ち上がりタイミングで、16ビット分のデータをパラレルデータとして16ビットシフトレジスタ3171から取得し、データをラッチする。そして、D15~D8を各制御部(ラッチセレクタ・ロードパルス分配器3180、Digit-Limit制御部3181、デューティ比制御部3182、データセレクタ制御部3183、スタンバイモード制御部3184)に送る。また、16ビットデータラッチ3172は、LOAD信号の立ち下がりタイミングで、ラッチしたデータのうちD7~D0を8ビットデータラッチ3173A~Dに送る。
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 30, the 16-
LOAD信号はラッチセレクタ・ロードパルス分配器3180にも入力される。ラッチセレクタ・ロードパルス分配器3180は、D15~D8を取得し、表示データ(D7~D0の8ビット)を格納する8ビットデータラッチ3173を選択する。具体的には、ロードレジスタ選択テーブル(図33参照)に示すように、D15~D8が00100010Bであれば、ラッチセレクタ・ロードパルス分配器3180は、データレジスタ0、す
なわち、Digit-Aの8ビットデータラッチ3173Aがデータを格納するように、8ビットデータラッチ3173を選択する信号を送る。
The LOAD signal is also input to the latch selector/
8ビットデータラッチ3173は、7セグメントLED13172の数(表示桁数)だけ設けられており、ラッチセレクタ・ロードパルス分配器3180からの選択信号に従って、各7セグメントLEDに表示するためのデータを取り込み、保持する。8ビットデータラッチ3173は、保持したデータを8×4データセレクタ3174に送る。
The 8-bit data latches 3173 are provided for the number of 7-segment LEDs 13172 (the number of display digits), and according to the selection signal from the latch selector/
8×4データセレクタ3174は、各8ビットデータラッチ3173A~Dから送られたデータを、予め定められた各桁の表示タイミングで選択し、デコーダ3175及び2×8データセレクタ3176に送る。
The 8×4
デコーダ3175は、キャラクタジェネレータデコードテーブル(図34参照)を用いて、入力されたデータを7セグメントLED13172に表示するキャラクタに変換し、各セグメントを点灯させるためのデータを生成する。生成されたデータは、2×8データセレクタ3176に入力される。
The
2×8データセレクタ3176は、デコード設定を参照して、デコーダを使用するモードに設定されている場合はデコーダ3175からのデータを選択し、デコーダを使用しないモードに設定されている場合は8×4データセレクタ3174からのデータを選択する。選択されたデータは、定電流ドライバ3178に入力される。
The 2×8
定電流ドライバ3178は、2×8データセレクタ3176からのデータを用いて、各セグメントを点灯させるための電流信号をデータ出力端子OUTa~OUTDpから出力する。定電流ドライバ3178から出力される電流は、前述したように、R-EXT端子に接続された抵抗の抵抗値によって制御される。
The constant
ドライバ3179は、7セグメントLED13172の各セグメントを点灯させるために定電流ドライバ3178から出力された電流のシンク電流を受け入れる。ドライバ3179が、端子DIG-0~DIG-3の電流吸い込みタイミングを制御することによって、どの7セグメントLED(桁)を表示するかが決まる。
Digit-Limit制御部3181は、ドライバ回路13171が制御する7セグメントLED13172の表示桁数を制御する。すなわち、ドライバ回路13171は、外部からの設定によって、点灯する桁数を1から4桁に制御できる。具体的には、D15~D8を00100001Bとし、D7~D0を××××0011Bとしたデータを入力することによって、Digit-Limit制御部3181の桁レジスタ(DIGITREGISTER)に4桁全てを使用する設定が書き込まれる。なお、×はH又はLのいずれのデータでもよいことを示し、入力データがHかLかは真理表には影響しない。
Digit-
デューティ比制御部3182は、7セグメントLED13172を点灯させる際のデューティ比を制御する。すなわち、ドライバ回路13171は、外部からの設定によってデューティ比を制御でき、7セグメントLED13172が点灯する明るさを制御する。デューティ比制御部3182は、定電流ドライバ3178及びドライバ3179に送るタイミング信号のうち少なくとも一方のパルス幅を制御することによって、デューティ比を制御する。具体的には、D15~D8を00100000Bとし、D3~D0に任意のデータを入力することによって、デューティ比制御部3182のデューティレジスタ(DUTY REGISTER)に0/16~15/16の16段階のデューティ比の設定が書き込まれる。
The duty
データセレクタ制御部3183は、デコーダの設定を制御する。すなわち、ドライバ回路13171は、外部からの設定によってデコーダ3175を使用するか否かを制御する。具体的には、D15~D8を00100001Bとし、D7~D0を0001××××Bとしたデータを入力することによって、デコーダを使用する設定がデコードレジスタに書き込まれ、D7~D0を0000××××Bとしたデータを入力することによって、デコーダを使用しないNO DECODERの設定が書き込まれる。データセレクタ制御部3183は、デコーダを使用する設定がされている場合、2×8データセレクタ3176がデコーダ3175からのデータを選択するように制御し、デコーダを使用しない設定がされている場合、2×8データセレクタ3176が8×4データセレクタ3174からのデータを選択するように制御する。
A data
スタンバイモード制御部3184は、スタンバイモードの設定、データクリアの設定を制御する。すなわち、ドライバ回路13171は、外部からの設定によってスタンバイモードに移行できる。具体的には、D15~D12を0100Bとし、D3~D0を0000Bとしたデータを入力することによって、スタンバイモードに設定できる。スタンバイモードでは、その時点での設定をそのまま維持し、7セグメントLED13172へ出力される電流を遮断して、ドライバ回路13171の消費電力を抑制する。
The standby
また、ドライバ回路13171は、外部からの設定によって、内部に保持された全てのデータをクリアできる。具体的には、D15~D12を0100Bとし、D3~D0を0001Bとしたデータを入力することによって、レジスタやラッチに保持された全てのデータをクリアして初期化する。
In addition, the
発振器3185は、ドライバ回路13171内で使用されるクロックを生成する。
図31は、主制御基板1310の実装例を示す図である。なお、本図において、主制御基板ボックス1320の構成を実線で示し、主制御基板1310上の構成を点線で示す。
FIG. 31 is a diagram showing a mounting example of the
図31(A)は、実装例1の主制御基板ボックス1320を示す。主制御基板ボックス1320は、一度閉めたら破壊せずに開けることができない構造で封印可能に主制御基板1310を収容する透明の樹脂によって構成されおり、その表面には、主制御基板1310の型番表示(シール貼付、刻印、印刷など)や開封シールが貼付されている。開封シールは、主制御基板1310の封印を開封した履歴を記録するシールである。
FIG. 31(A) shows the main
図31(B)に示す実装例1は、(A)に示す主制御基板ボックス1320に主制御基板1310を収容した状態を示す。実装例1では、主制御基板1310上に主制御MPU1311が実装されている。なお、主制御基板1310の長手方向と主制御MPU1311の長手方向が同じ方向になるように、主制御MPU1311が実装されるとよい。
Mounting example 1 shown in FIG. 31(B) shows a state in which the
主制御基板1310は、主制御基板ボックス1320に封入され、主制御ユニット1300を構成している。主制御MPU1311は、不適切な改造がされていないことを外部から確認可能な位置に配置されている。また、主制御MPU1311は、その周囲に部品を配置しないことによって、不適切な改造がされていないことを外部から容易に確認できるように配置されている。
The
役物比率表示器1317は、主制御基板1310上で、外部から視認可能な位置に配置される。役物比率表示器1317に表示される数字の向きは、主制御MPU1311の型番表示や主制御基板ボックスに1320の型番表示と同一方向にするとよい。また、役物比率表示器1317の長手方向と主制御基板1310の長手方向と主制御MPU1311の長手方向が同じ方向になるように実装されるとよい。なお、主制御基板1310が横長
の向きで遊技機に実装される場合には、役物比率表示器1317の長手方向や主制御MPU1311の長手方向と主制御基板1310の長手方向とが同じ向きになるように役物比率表示器1317や主制御MPU1311を実装するとよい。また、主制御基板1310が縦長の向きで遊技機に実装される場合には、役物比率表示器1317の長手方向や主制御MPU1311の長手方向と主制御基板1310の長手方向とが90度の向きになるように役物比率表示器1317や主制御MPU1311を実装するとよい。
The
また、主制御基板1310から信号線を引き出すためのコネクタCN1、CN2は、役物比率表示器1317と長手が揃う方向で、主制御基板1310の長辺に沿った端部(図では上側の長辺に沿った上端部であるが、下側の長辺に沿った下端部や、左右辺に沿った端部でもよい)に実装されるとよい。すなわち、コネクタCN1、CN2に接続される配線(ハーネス)が役物比率表示器1317と重なって、役物比率表示器1317の視認を妨げない位置に、コネクタCN1、CN2が配置されることが望ましい。
Connectors CN1 and CN2 for drawing out signal lines from the
さらに、主制御基板ボックス1320の型番表示や主制御基板ボックス1320に貼付された開封シールは、主制御MPU及び役物比率表示器1317のいずれとも重ならない位置に貼付される。
Furthermore, the model number display of the main
このように役物比率表示器1317を実装することによって、役物比率表示器1317や主制御MPU1311の型番表示が正しい向きで表示され、これらの視認性を向上し、製造過程や、遊技場に設置後の検査においても、無理な姿勢を取ることなく、役物比率や主制御MPU1311の改造の有無を確認できる。
By mounting the
図31(C)に示す別の実装例では、主制御MPU1311の型番表示と役物比率表示器1317の数字表示の向きは同じ方向となるように実装されているが、主制御MPU1311以外の回路モジュール(例えばIC)の型番表示の向きが、主制御MPU1311の型番表示や役物比率表示器1317の数字表示の向きと異なる。また、主制御MPU1311以外の回路モジュールは、主制御基板ボックス1320の型番表示や主制御基板ボックス1320に貼付された開封シールと重なる位置に配置されてもよい。これは、主制御MPU1311以外の回路モジュールは、不正な改造を検査する際の重要性が低いので、主制御基板1310上に配置される向きを同じにする意義が薄いためである。
In another implementation example shown in FIG. 31(C), the model number display of the
図32は、主制御MPU1311と役物比率表示器1317との位置関係を示す図である。
FIG. 32 is a diagram showing the positional relationship between the
図32(A)に示すように、役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171と7セグメントLED13172との間の信号線13173は、ノイズによる影響で、信号が不安定になる場合がある。このため、ドライバ回路13171と7セグメントLED13172とは可能な限り近づけて配置することが望ましい。
As shown in FIG. 32A, the
例えば、図示したように、ドライバ回路13171と7セグメントLED13172との距離(配線13173の長さL2)は、主制御MPU1311と役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171との距離(配線13101の長さL1)より短くなるように配置する。すなわち、L1がL2より大きくなる。
For example, as illustrated, the distance between the
また、前述したように、主制御MPU1311の周囲には、点線で示すように、不適切な改造がされていないことを外部から容易に確認するために、部品を配置しない。このため、配線長L1はある程度の長さになってしまうが、L2は可能な限り短くする。
Also, as described above, no parts are arranged around the
なお、ドライバ回路13171と7セグメントLED13172とは、一つのパッケー
ジに収容されても、別のパッケージに収容されてもよく、いずれの場合でも、L1がL2より大きくなるように実装される。
The
図32(B)は、別の実装例において、主制御MPU1311と役物比率表示器1317との位置関係を示す図であり、図32(C)は、図32(B)に示す実装例におけるプリント基板の断面図である。
FIG. 32(B) is a diagram showing the positional relationship between the
図32(B)に示すように、主制御MPU1311と役物比率表示器1317のドライバ回路13171との間の信号線13101の両側にグランドパターン13102を設けている。さらに、プリント基板において、信号線13101の裏面及び内層には信号パターンを設けない禁止領域13106を設ける。禁止領域13106のプリント基板の裏面及び内層の少なくとも一方にガードパターンとしてのグランドパターン13107又は電源パターンを設けるとよい。
As shown in FIG. 32B,
本実装例における他の信号線の配置を説明すると、例えば、発振器から主制御MPU1311にクロック信号を供給する信号線13103は、禁止領域13106を避けて(すなわち、信号線13103と信号線13101とが交差しないように)配置される。また、主制御MPU1311に接続される信号線13104は、スルーホール13105によって裏面又は内層に抜けるように配置してもよい。この場合も、信号線13104は禁止領域13106を避けて(すなわち、信号線13104と信号線13101とが交差しないように)配置される。
To explain the arrangement of other signal lines in this implementation example, for example, the
なお、主制御基板1310は、不正な改造を防止する観点から、一般的に、表面及び裏面にパターンを有し、内層を有さない二層基板で構成されるが、前述した実装例は、内層を有する(4層、6層などの)多層基板にも適用できる。
In addition, from the viewpoint of preventing unauthorized modification, the
図33は、ドライバ回路13171のロードレジスタ選択テーブルを示す図である。
FIG. 33 shows a load register selection table of the
ロードレジスタ選択テーブルは、ドライバ回路13171に入力されたデータを格納するレジスタを決定するためのテーブルである。
A load register selection table is a table for determining a register for storing data input to the
本実施例のドライバ回路13171は、7個のレジスタを有する。デューティレジスタは、デューティ比制御部3182によって使用され、7セグメントLED13172を点灯するデューティ比が設定される。例えば、D15~D8が00100000Bである場合、D7~D0にセットされたデータは、デューティ比を設定するためのデータであり、デューティ比制御部3182のデューティレジスタに書き込まれる。
The
デコードレジスタは、データセレクタ制御部3183又はDigit-Limit制御部3181によって使用され、デコーダ3175の使用、すなわちデコードの有無及び表示桁数が設定される。デコードレジスタと桁数レジスタとを一つのレジスタとして構成してもよい。例えば、D15~D8が00100001Bである場合、D7~D0にセットされたデータは、デコードの有無を設定するためのデータ又は表示桁数を設定するためのデータであり、データセレクタ制御部3183のデコードレジスタ又はDigit-Limit制御部3181の桁レジスタに書き込まれる。
The decode register is used by the data
データレジスタは、8ビットデータラッチ3173A~Dによって使用され、7セグメントLED13172の各桁に表示するデータが設定される。例えば、D15~D8が00100010B~00100101Bである場合、D7~D0にセットされたデータは、7セグメントLEDを点灯するためのデータであり、8ビットデータラッチ3173A~D内のデータレジスタに書き込まれる。
The data registers are used by 8-bit data latches 3173A-D to set the data to be displayed on each digit of the 7-
以上に説明したレジスタに設定される、デューティ比、デコードの有無及び表示桁数は、役物比率を表示する都度設定する必要がなく、一度設定すればよいので、図21のステップS28において初期設定として設定される。なお、初期設定で1度のみ設定した場合には、初期設定後にノイズ等の影響で設定が変更される可能性があるため、所定条件(例えば、本体枠4の開放を検出するごと、切替ボタンが押下されるごと)に再設定してもよい。これにより、ノイズで設定が切り替わってしまっても、正しい表示を常に行うことができるようになる。 The duty ratio, the presence/absence of decoding, and the number of display digits, which are set in the registers described above, do not need to be set every time the character ratio is displayed. is set as Note that if the setting is made only once in the initial setting, there is a possibility that the setting will be changed due to the influence of noise after the initial setting. is pressed). As a result, correct display can always be performed even if the settings are switched due to noise.
図34は、キャラクタジェネレータデコードテーブルを示す図である。キャラクタジェネレータデコードテーブルは、デコーダ3175が、入力データを7セグメントLED13172に表示するキャラクタのデータに変換するために使用される。キャラクタジェネレータデコードテーブルを用いることによって、数字や一部のアルファベットなどの文字を、字体を考えることなく表示できる。また、数字を表示する場合、D5~D0は表示される数字と一致するので、演算結果を変換することなくドライバ回路13171に入力して、7セグメントLED13172に表示できる。
FIG. 34 is a diagram showing a character generator decode table. The character generator decode table is used by
なお、7セグメントLED13172の各桁の小数点の点灯はD6によって制御される。
The lighting of the decimal point of each digit of the 7-
図35は、ドライバ回路13171の状態遷移図であり、図36は、役物比率表示器1317の表示例を示す図である。
FIG. 35 is a state transition diagram of the
本実施例のドライバ回路13171には、五つの状態、すなわち、初期状態、データ入力済状態、LED点灯状態(0000)、LED点灯状態(入力データに応じた点灯)、LED点灯状態(全点灯)が準備されている。
The
この五つの状態を制御するために、ブランク、通常動作、レジスタ書込、全点灯、スタンバイのモード設定命令がある。ブランク命令は、定電流ドライバ3178の出力とドライバ3179の出力を遮断する。通常動作命令は、各設定の終了後に7セグメントLED13172の表示を行う。表示データを設定しないで通常動作命令を入力すると、7セグメントLED13172は全桁で数字の0を表示する。レジスタ書き込み命令は、使用桁数の設定、デューティ比の設定、デコーダの使用又は未使用の設定、表示データの入力を行う。D11~D8でデータを書き込むレジスタを選択し、D7~D0でレジスタへ設定する内容を入力する(図33参照)。全点灯命令はデータ側の定電流ドライバ3178の出力をオンにして、7セグメントLED13172の全セグメントを点灯する。スタンバイ命令には、パラメータによって二つに分かれ、スタンバイ状態に遷移するスタンバイ命令と、初期状態に遷移するクリア命令とがある。スタンバイ命令は、その時点での設定を維持し、定電流ドライバ3178及びドライバ3179の動作を停止し、7セグメントLED13172へ出力される電流を遮断して、ドライバ回路13171の消費電力を抑制する。また、クリア命令は、レジスタやラッチに保持された全てのデータをクリアして初期化し、表示も消灯する。
To control these five states, there are mode setting instructions for blank, normal operation, register write, full lighting, and standby. A blank command shuts off the output of constant
なお、ブランク命令も表示命令の一種であることから、本明細書において、「表示」は、7セグメントLEDの全点灯、一部のセグメントの点灯及び全消灯のいずれの状態も含むものである。 Note that the blank command is also a kind of display command, so in this specification, "display" includes any state of full lighting of the 7-segment LEDs, lighting of some segments, and complete extinguishing of the segments.
図36を参照して、前述した各状態における表示例を説明する。 A display example in each state described above will be described with reference to FIG.
遊技機の電源投入時は、ドライバ回路13171の初期設定が完了していない又は表示
データが設定されていないため、初期状態(ALL BLANK)であり、図36(A)に示すように7セグメントLED13172の全セグメントが消灯する非点灯状態となる。また、本体枠4が閉鎖され遊技が可能な状態では、役物比率表示器1317を視認できないので、スタンバイモードに設定して、7セグメントLED13172を消灯し、遊技機の消費電力を低減するとよい。
When the gaming machine is powered on, the initial setting of the
そして、ドライバ回路13171に各種制御用のレジスタに制御用データを設定して初期設定が完了した後、表示データを入力すると、7セグメントLED13172に所定の表示をする。この所定の表示は、図36(B)に示すように、全桁に「-」を表示したり、全セグメントを点灯してもよい。この所定の表示によって、役物比率表示器1317の正常動作を確認できるようにするとよい。
After initial setting is completed by setting control data in various control registers in the
また、本体枠4が開放された場合には、役物比率表示器1317が正常に動作していることを確認できるように、全桁に所定の表示をするとよい。例えば、図36(B)に示すように全桁に「-」を表示したり、全セグメントを点灯してもよい。
Further, when the
そして、表示スイッチ1318が操作され表示データがドライバ回路13171に入力されると、LED点灯状態(入力データに応じた点灯)となる。具体的には、役物比率表示状態となり、7セグメントLED13172の左2桁に表示内容を示すコードを表示し、右2桁に役物比率の数値を表示する。図36(C)に示す例では、「y175」が表示されており、役物比率1が75%であることを示している。なお、表示される役物比率が規定範囲外の異常値である場合、その旨を識別できる表示をするとよい。例えば、全桁(または、数字)を点滅して表示したり、小数点を点灯又は点滅させる。
When the
さらに表示スイッチ1318が操作され表示データがドライバ回路13171に入力されると、7セグメントLED13172の表示内容が変更される。すなわち、別な種類の役物比率を表示する。この場合も、左2桁に表示内容を示すコードを、右2桁に役物比率の数値を表示する。図36(D)に示す例では、「y263」が表示されており、役物比率2が63%であることを示している。なお、この場合も、前述と同様に、表示される役物比率が規定範囲外の異常値である旨を識別できる表示をするとよい。役物比率のより具体的な表示例は、図37を用いて後述する。
Further, when the
そして本体枠4が閉鎖されると、役物比率表示器1317の正常動作を確認できる所定の表示を行い(図36(E))、所定時間(例えば、30秒)経過後、7セグメントLED13172を消灯し、遊技機の消費電力を低減するとよい。この役物比率非表示状態は、初期設定完了後と同じ態様であるが、異なる態様でもよく、役物比率表示と区別可能な態様であればよい。
Then, when the
図36(E)は、役物比率表示器1317や主制御MPU1311に異常があり、役物比率を表示できない場合の表示例である。小数点は点灯でも点滅でも、桁毎に異なる表示でもよい。また、異常表示は、図示したものと異なる態様でもよく、役物比率表示ができない状態であることを示すために正常な役物比率表示と区別可能な態様であればよい。
FIG. 36(E) is a display example when the
また、いずれかの状態において、全点灯命令を入力すると、7セグメントLED13172の全セグメントが点灯する。また、いずれかの状態において、ブランク命令又はスタンバイ命令を入力すると、データを保持したまま、7セグメントLED13172の全セグメントが消灯する。また、いずれかの状態において、データクリア命令を入力すると、レジスタやラッチに保持された全てのデータをクリアし、7セグメントLED13172の全セグメントを点灯して、初期状態に戻る。
In addition, when an all-lighting command is input in any state, all the segments of the 7-
[8.役物比率の表示]
次に、役物比率の算出及び表示の方法を説明する。
[8. Display of character ratio]
Next, a method of calculating and displaying the character product ratio will be described.
前述したように、役物比率は、主制御基板1310に設けられた役物比率表示器1317に表示される。前述したように、役物比率表示器1317は、例えば、4桁の7セグメントLEDや、液晶表示装置によって構成され、下2桁に役物比率の数値を表示し、上2桁に数値の種類を表示する。
As described above, the character ratio is displayed on the
また、2桁の7セグメントLEDで役物比率表示器1317を構成してもよい。この場合、役物比率の数値と当該数値の種類とを交互に表示するとよい。
Also, the
役物比率の数値の表示態様は、役物比率と所定の基準値との比較結果によって異なる表示態様で表示してもよい。例えば、役物比率が所定の基準値を超えた場合に、数値を点滅させたり、色を変えたり(通常時は緑色で、基準超時は赤色など)して表示する。基準値との比較結果により表示態様を変えることによって、役物比率が異常であることを容易に認識できる。 The display mode of the numerical value of the role product ratio may be displayed in a different display mode depending on the result of comparison between the role product ratio and a predetermined reference value. For example, when the role product ratio exceeds a predetermined reference value, the numerical value is blinked or the color is changed (green when normal, red when exceeding the reference value, etc.). By changing the display mode according to the result of comparison with the reference value, it is possible to easily recognize that the character ratio is abnormal.
役物比率表示器1317を、一つ又は複数のLEDランプで構成してもよい。役物比率表示器1317を一つのLEDランプで構成した場合、役物比率と所定の基準値との比較結果を異なる態様で表示する。例えば、役物比率が基準値より小さい場合は緑色、役物比率が基準値より大きい場合は赤色で表示する。また、役物比率が基準値より小さい場合は点灯、役物比率が基準閾値より大きい場合は点滅で表示する。
The
役物比率表示器1317を複数(例えば、10個)のLEDランプで構成した場合、一つのLEDランプを10%として役物比率を表示する。例えば、役物比率が70%以上80%未満であれば、7個のLEDを点灯させる。この場合、表示内容(役物比率か連続役物比率か、直近データ表示か中期データ表示かなど)によって、異なる表示態様(表示色)で表示してもよい。
When the
また、総獲得球数が6000個より小さい場合、賞球データの収集期間が短く、役物比率の値が収束していない可能性があるため、異なる表示態様(表示色、点滅など)で表示してもよい。総獲得球数が閾値より少ない場合の表示態様と、前述した基準値を超えた場合の表示態様とは異なる態様とすることが望ましい。 In addition, if the total number of acquired balls is less than 6000, the period for collecting prize ball data is short, and the value of the character ratio may not have converged, so it is displayed in a different display mode (display color, blinking, etc.) You may It is desirable that the display mode when the total number of acquired balls is less than the threshold is different from the display mode when the total number of acquired balls exceeds the above-described reference value.
役物比率表示器1317は、直近データ表示と中期データ表示と長期データ表示とを切り替えて表示してもよい。直近データ表示は、図27(B)(C)に示すリングカウンタにおいて、現在書き込み中の一つ前のカウンタ値を用いて計算した役物比率である。中期データ表示は、図27(B)(C)に示すリングカウンタにおいて、累計を用いて計算した役物比率である。長期データ表示は、図27(B)(C)に示すリングカウンタにおいて、総累計を用いて計算した役物比率である。
The character
役物比率表示器1317を機能表示ユニット1400で兼用してもよい。機能表示ユニット1400は通常は主制御基板1310からの制御信号に基づいて遊技状況を表示するが、本体枠4が外枠2から開放したことを本体枠開放スイッチ(図示省略)が検出すると、主制御基板1310は、機能表示ユニット1400が役物比率を表示するように表示を切り替える。本体枠4の開放によって機能表示ユニット1400の表示を切り替えるが、遊技の進行は継続するとよい。遊技の進行を継続することによって、本体枠4が閉鎖すると役物比率表示から遊技状態の表示に迅速に切り替えることができる。例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中に本体枠4が開放すると役物比率が表示されるが、変動時間の経過前に本体枠4が閉鎖されると、残りの時間分の変動表示を行うことができる。機能表示ユニッ
ト1400に表示される特別図柄はメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される装飾図柄と同期しているので、機能表示ユニット1400の特別図柄変動表示が停止するタイミングで装飾図柄が停止する。このため、機能表示ユニット1400が役物比率を表示しても、遊技者に違和感を与えないように構成できる。
The
役物比率表示器1317は、役物比率以外を表示してもよい。例えば、単位時間あたりの入賞口の種類毎の入賞数や払い出された賞球数を表示してもよい。単位時間は、1分、10分、1時間、10時間など、表示スイッチ1318の操作によって切り替えて表示するとよい。
The character
役物比率表示器1317は、ベースを表示してもよい。ベースは、特賞中(大当り中)を除いた通常時の出玉率であり、セーフ球数÷アウト球数で計算できる。発射球数(アウト球数)は、発射球センサ1020によって検出する。前述したように、発射球センサ1020は、球発射装置から遊技領域5aに遊技球を導くレール1001、1002の出口(逆流防止部材1007)付近に設ける(図10、図16参照)。また、アウト球数を、排出球センサ3060によって検出してもよい。前述したように、排出球センサ3060は、遊技領域5aから流出した遊技球をパチンコ機1の外部に排出する排出口に設ける(図4参照)。また、遊技領域5aの下部に設けられるアウト口1111を通過する遊技球を検出するアウト口通過球センサ1021(図53参照)を設け、アウト口通過球センサ1021が検出した遊技球の数と、始動口センサ2104、2551が検出した遊技球の数と、各種入賞口センサ3015、2114、2554、2557が検出した遊技球の数との合計によって、アウト球数を検出してもよい。さらに、球発射装置680へ供給される遊技球を検出する発射供給球センサ(図示省略)と、球発射装置680から打ち出されたが遊技領域5aに到達しなかった遊技球(いわゆる、ファール球)を検出するファール球センサ(図示省略)とを設け、発射供給球センサが検出した球発射装置680へ供給された遊技球の数からファール球数を減じて、アウト球数(発射球数)を検出してもよい。
The
アウト球数は、前述したいずれかの方法で計数すればよい。すなわち、図示したセンサのうち、排出球センサ3060か発射球センサ1020のいずれかが設けられれば足りる。
The number of out balls may be counted by any of the methods described above. That is, it is sufficient to provide either the discharged
また、セーフ球数は払い出した賞球数に等しい。また、ベースを、遊技状態毎(通常遊技中、電サポ中、確率変動中、時間短縮中)の出玉率と定義し、遊技状態毎のセーフ球数÷アウト球数で計算してもよい。役物比率表示器1317にベースを表示することによって、稼動中における出球性能の設計値からのズレを遊技機ごとにその場で確認できる。また、ホールコンを使用せずに出球性能を確認できるので、遊技場の立入検査時に遊技機毎の検査が容易になる。
Also, the number of safe balls is equal to the number of awarded balls. Also, the base may be defined as the ball output rate for each game state (during normal play, during power supply, during probability fluctuation, during time reduction), and calculated by the number of safe balls / the number of out balls for each game state. . By displaying the base on the
役物比率表示器1317は、ベースの他の入賞や賞球に関する情報(一般入賞口2001への入賞数や当該入賞による賞球数、始動口2002への入賞数や当該入賞による賞球数、大入賞口2005、2006への入賞数や当該入賞による賞球数など)を表示してもよい。
The
役物比率表示器1317は、常に役物比率を表示しても、表示スイッチ1318の操作によって役物比率を表示してもよい。例えば、押ボタンスイッチである表示スイッチ1318を押すと、役物比率の表示を開始し、所定時間表示した後に表示を消す。なお、本体枠4が外枠2から開放したことを本体枠開放スイッチ(図示省略)が検出中に表示スイッチ1318が操作されると、役物比率表示器1317に役物比率を表示してもよい。すなわち、本体枠開放中でなければ表示スイッチ1318が操作されても、役物比率表示器1317は役物比率を表示しない。
The character
また、表示スイッチ1318の操作毎に、表示内容を変えてもよい。例えば、図37に示すように、表示スイッチ1318を1回操作すると、役物比率(累計)を意味するA7を上2桁に表示し、所定数(例えば、60000個)の賞球に対する役物比率を下2桁に表示する。表示スイッチ1318を、もう1回操作すると、上2桁の表示が連続役物比率(累計)を意味するA6に切り替わり、所定数(例えば、60000個)の賞球に対する連続役物比率を下2桁に表示してもよい(図37(B))。さらに、表示スイッチ1318を1回操作すると役物比率(賞球6000個)を意味するy7を上2桁に表示し、直近のデータによる役物比率を下2桁に表示(直近データ表示)をする(図37(C))。表示スイッチ1318を、もう1回操作すると、上2桁の表示が役物比率(累計)を意味するy6に切り替わり、所定数(例えば、60000個)の賞球に対する役物比率を下2桁に表示(中期データ表示)をしてもよい(図37(D))。
Also, the display content may be changed for each operation of the
表示スイッチ1318は、独立したスイッチとして設けなくても、主制御基板1310又は周辺制御基板1510に設けられるRAMクリアスイッチと兼用してもよい。すなわち、当該スイッチは、電源投入時に操作されるとRAMクリアスイッチとして機能し、パチンコ機1の動作中に操作されると表示スイッチ1318として機能する。RAMクリアスイッチと表示スイッチ1318とを一つのスイッチに機能を集約することによって、遊技場の係員が操作するスイッチは一つとなり、経験が浅い係員による誤操作を減少できる。
The
以上のように、本実施形態によれば、稼働中の遊技機の役物比率を正確に計算でき、稼働中の遊技機の射幸性を確認できる。 As described above, according to the present embodiment, it is possible to accurately calculate the accessory ratio of the gaming machine in operation, and to check the gambling nature of the gaming machine in operation.
また、賞球数のデータを役物比率算出・表示用データ13136として蓄積し、チェックコードが異常である場合に役物比率算出・表示用データ13136を消去するので、誤った役物比率の表示を避けることができる。
In addition, since the data of the number of winning balls is accumulated as the character ratio calculation/
また、主制御MPU1311のRAM1312にバックアップされた遊技の進行に関係するデータの消去条件と別の条件で役物比率算出・表示用データ13136を消去するので、正確な賞球数のデータを保持し、正確な役物比率を計算できる。
In addition, since the
また、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によっては役物比率算出・表示用データ13136を消去しないので、遊技場の係員の操作により、誤って役物比率算出・表示用データ13136を消去することがなく、役物比率算出・表示用データがRAMクリアスイッチの操作によって消去されないので、遊技場の係員の誤操作によって、当該データが消去されないように構成されている。また、遊技場が意図的に役物比率算出・表示用データを消去できないので、表示される役物比率の信頼性が高まり、役物比率が高い状態の隠蔽を防止できる。
In addition, since the role product ratio calculation/
[9.ベースの表示]
[9-1.ベースを表示する遊技機の基本構成]
ここまで、役物比率を計算し表示するパチンコ機の実施例を説明したが、次に、ベース値を計算し表示するパチンコ機の実施例を説明する。なお、本実施例では、専ら、ベース値を計算し表示するパチンコ機を説明するが、ベース値と共に役物比率を計算し表示してもよい。
[9. Show Base]
[9-1. Basic Configuration of Game Machine Displaying Base]
So far, the embodiment of the pachinko machine that calculates and displays the character ratio has been described. Next, the embodiment of the pachinko machine that calculates and displays the base value will be described. In this embodiment, the pachinko machine that calculates and displays the base value will be described exclusively, but the character ratio may be calculated and displayed together with the base value.
以下に説明するパチンコ機では、前述したように、始動口(第一始動口2002、第二始動口2004)に遊技球が入賞すると、乱数による抽選が行われ、特別図柄変動表示ゲームを実行する。特別図柄変動表示ゲームの変動パターン(変動時間)は、相対的に短い
時間の変動パターン(10秒程度の通常変動パターン、保留数が多いときに選択されやすい2~5秒程度の短縮変動パターン)や、相対的に長い時間の変動パターン(1分を超えるスーパーリーチなどの変動パターン)がある。パチンコ機でベース値を計算する場合、ベース値の報知はエラーの報知より緊急性を要さないことから、特別図柄変動表示ゲームが次の変動表示ゲームに切り替わるタイミングで報知できる。しかし、変動表示時間が長い場合は、一つの特別図柄変動表示ゲームの終了を待たずに、所定の条件を満たしたときに(例えば、アウト球数(発射球数)や賞球数(払出球数)が変化した場合に)、ベース値を計算し表示を更新する方が望ましい。このため、本実施例のパチンコ機では、遊技中(例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中でも)に所定の条件を満たしたとき(例えば、アウト球数(発射球数)や賞球数(払出球数)が変化した場合)に、ベース値を計算し、表示する。次に、このような動作をするパチンコ機の具体的な構成を説明する。
In the pachinko machine described below, as described above, when a game ball wins at the starting port (the
図38は、ベース値を計算し表示するパチンコ機1の主制御基板1310の周辺の構成を示すブロック図である。
FIG. 38 is a block diagram showing the configuration around the
図38に示すパチンコ機1は、図17に示すパチンコ機1とほぼ同様の構成を有するが、符号1317で表される構成が、役物比率表示器ではなくベース表示器である。本実施例のパチンコ機1のベース表示器1317は、例えば、図4や図28に示すように、4桁の7セグメントLEDを使用してもよく、他の桁数(例えば、2桁)の7セグメントLEDを使用してもよい。
The
本実施例のパチンコ機1は、主制御MPU1311が実行するタイマ割込み処理(図23)の役物比率算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)において、賞球数やアウト球数のデータを取得し、役物比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)において、ベース値を計算して表示する。なお、以下の説明では、図23のステップS81の「役物比率算出用領域更新処理」を「ベース算出用領域更新処理」と読み替え、ステップS89の「役物比率算出・表示処理」を「ベース算出・表示処理」と読み替えて説明する。また、図26に示す「役物比率算出用領域13128」を「ベース算出用領域13128」と読み替え、「役物比率算出・表示用コード13135」を「ベース算出・表示用コード13135」と読み替え、「役物比率算出・表示用データ13136」を「ベース算出・表示用データ13136」と読み替えて説明する。
The
図39は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の一例を示すフローチャートである。ベース算出用領域更新処理は、現在の遊技状態を判定し、遊技価値として払い出される賞球数を現在の遊技状態に対応した領域に加算して、主制御内蔵RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128を更新する。特に、図39に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、タイマ割込み周期ごとに毎回ベース値を計算するために、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で算出された賞球数を用いて総賞球数を直接更新し(ステップS814)、アウト球数を用いて総アウト球数を直接更新する(ステップS822)。
FIG. 39 is a flow chart showing an example of base calculation region update processing (step S81). In the base calculation area update process, the current game state is determined, the number of prize balls to be paid out as game value is added to the area corresponding to the current game state, and the
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。遊技状態が特賞中であるとは、大入賞口2005、2006が開放しており、遊技者が多くの賞球を獲得できる時間中であるが、大当り遊技のオープニングやエンディングの時間を含めてもよい。一つの大当り中で大入賞口2005、2006が開放と閉鎖を繰り返す場合、大入賞口の閉鎖から次の開放までの間(閉鎖インターバル)の時間を含んでもよい。すなわち、ステップS810における特賞中は、条件装置作動中を意味し、例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当たり図柄の確定からエンディング終了までである。また、右打ち指示中の全ての時間を含んでもよい。
First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). When the game state is during the special prize, it means that the
さらに、始動口2002、2004においては、時短中、確変中(ST中)、電サポ中
を特賞中に含めてもよい。さらに、時短中、確変中(ST中)、電サポ中以外の遊技状態において、始動口2004の開放から閉鎖後の所定時間(例えば、始動口に入賞した球がアウト球として検出されるまでに必要な数秒)までの間を特賞中に含めてもよい。
Furthermore, in the starting
本実施例のパチンコ機1に設けられる電動作動役物は、ベース値の計算の観点から2種類に分けられる。前述したように、本実施例の遊技機における、大入賞口2005、2006に関する特賞中とは、条件装置作動中(例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当たり図柄の確定からエンディング終了まで)であり、ベース値は特賞中以外の賞球およびアウト球数で計算されるので、大入賞口2005、2006への正常な(いわゆる大当り中の)入賞はベース値の算出に使用されない。一方、開閉部材を有する始動口2004(いわゆる、電動チューリップ)は、特賞中以外(低確率時や非時短時)の入賞球および賞球がベース値の算出に使用される。つまり、電動作動役物のうち、一部の役物(大入賞口2005、2006)は、遊技状態(特賞中か否か)に関係なく、入賞球数および賞球数をベース値の計算に使用せず、他の役物(始動口2004)は、入賞球数および賞球数をベース値の計算に使用するか使用しないかが、遊技状態(特賞中か否か)に応じて切り替えられることになる。入賞球数および賞球数をベース値の計算に使用しないとは、払い出された賞球をイン(ベース値の計算における被除数である特賞中以外の賞球数)に計数しないことの他、入賞信号が入力されても、当該入賞信号によって賞球を払い出すためのエッジ情報を作成しないことも含まれる。
The electrically operated accessories provided in the
また、大入賞口2005、2006は、条件装置が作動しない場合でも(いわゆる小当たりとして)開放するときがある。一般的に小当りは時短中に発生し、短時間開放のため遊技球が入賞する可能性が低いので、ベース値の計算には影響しない。しかし、特賞中以外(通常時)に小当たりを発生させ、遊技球が入賞する可能性が高くなる時間だけ開放してもよい。この場合、特賞中以外に発生した小当りにおける大入賞口2005、2006への入賞球および賞球はベース値の計算に使用してもよい。このようにすると、特賞中以外の小当たりの発生確率を制御することによって、ベース値の期待値(設計値)を変更できる。すなわち、ベース値の規格に対し柔軟に対応できるパチンコ機を提供でき、設計の自由度を向上できる。
Also, the
遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しない賞球であるため、賞球数やアウト球数を更新せずに、ベース算出用領域更新処理を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で入力情報に基づいて算出された賞球数を取得する(ステップS811)。ベース算出用領域更新処理で取得する賞球数は、払い出しが決定した賞球数でもよい。また、作成済みの払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。また、送信済の払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。また、主制御基板1310が払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信し、払出制御基板951から受信確認(ACK)を受信した払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。さらに、主制御基板1310が払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信し、払出制御基板951から払出完了の報告を受けた賞球数(払出済み賞球数)でもよい。このバリエーションは図41から図44を用いて説明する。
If the game state is during a special prize, the prize balls are not related to the calculation of the base value, so the base calculation region updating process is terminated without updating the number of prize balls or the number of out balls. On the other hand, if the game state is not during the special prize, the number of prize balls calculated based on the input information in the prize ball control process (step S80) is acquired (step S811). The number of prize balls acquired in the base calculation region updating process may be the number of prize balls determined to be put out. Alternatively, the number of prize balls corresponding to the prepared payout command may be used. Alternatively, it may be the number of prize balls corresponding to the payout command that has already been sent. Moreover, the
そして、取得した賞球数を総賞球数に加算して、総賞球数を更新する(ステップS814)。なお、賞球があるかを判定し、賞球がなければ、総賞球数を更新する処理をスキップしてもよい。また、始動口2002、2004に遊技球が入賞したが、保留が上限値であり、始動口への入賞が保留されなかった場合でも賞球は払い出されるので、総賞球数が更新される。また、入賞口に遊技球が入賞しても賞球が発生しない遊技状態(例えば、特定のエラー発生時など)においては、当該入賞に起因する賞球が発生せず、取得する賞球数が0であるため、総賞球数は更新されない。総賞球数は、主制御内蔵RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128に設けられる総賞球数格納領域(図52参照)に記録される
。すなわち、図39に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、賞球数が計算される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総賞球数が更新される。
Then, the acquired number of prize balls is added to the total number of prize balls to update the total number of prize balls (step S814). It should be noted that it is possible to determine whether or not there are prize balls, and if there are no prize balls, the process of updating the total number of prize balls may be skipped. In addition, although the game balls enter the starting
その後、アウト球数を取得し(ステップS818)、取得したアウト球数を総アウト球数に加算するように、総アウト球数を更新する(ステップS822)。アウト球数は、前述したように、発射球センサ1020や排出球センサ3060などによって検出され、ステップS74のスイッチ入力処理で、これらのセンサの検出信号を読み取って、センサの検出信号があればアウト球数=1を取得する。総アウト球数は、主制御内蔵RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128に設けられる総アウト球数格納領域(図52参照)に記録される。すなわち、図39に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、アウト球が検出される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総アウト球数が更新される。このように、タイマ割込み処理ごとにベース算出処理を実行して、総アウト球数を更新し、ベース算出表示処理(図40)にてベース値を計算し表示するので、ベース値を遅滞なく表示でき、ベースが正常か異常かを遅滞なく判断できる。
After that, the number of out-balls is acquired (step S818), and the total number of out-balls is updated so that the acquired number of out-balls is added to the total number of out-balls (step S822). As described above, the number of out balls is detected by the
なお、後述するベース算出用領域更新処理(図46)のステップS815からS817のように、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットしてもよい。さらに、ステップS824からS825のように、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止してもよい。 As in steps S815 to S817 of the base calculation area updating process (FIG. 46), which will be described later, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated. , You may reset the timer for prize ball abnormality notification. Further, as in steps S824 to S825, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize notification has timed up. may be stopped.
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、主制御MPU1311が、タイマ割込み処理においてベース値の計算処理を実行するが、払出制御部952の払出制御MPUがベース値の計算処理を実行してもよい。この場合、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510の周辺制御部1511にベースを報知するためのコマンドを送信してもよいし、払出制御部952から周辺制御部1511にベースを報知するためのコマンドを送信してもよい。
In the
また、一つのタイマ割込み処理において、入賞口への入賞とアウト球との両方の情報を取得しても、賞球数を総賞球数(または、後述する実施例では賞球数バッファ)に加算し、アウト球数を総アウト球数(または、後述する実施例ではアウト球数バッファ)に加算する。また、一つのタイマ割込み処理において、複数の入賞口への入賞の情報を取得しても、複数の入賞による賞球数の合計を総賞球数(または、後述する実施例では賞球数バッファ)に加算する。このため、ベース値を正確に計算し、表示できる。例えば、賞球数が5個の入賞口の入賞口センサと賞球数が3個の入賞口の入賞口センサとへの入賞を検出した場合は、合計8個の賞球を総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算する。 Also, in one timer interrupt process, even if the information of both the winning ball to the winning hole and the out ball is acquired, the number of prize balls is set to the total number of prize balls (or the number of prize balls buffer in the embodiment described later). The number of out-balls is added to the total number of out-balls (or the number of out-balls buffer in the embodiment described later). Also, in one timer interrupt process, even if information on winning to a plurality of winning holes is acquired, the total number of winning balls due to a plurality of winnings is calculated as the total number of winning balls (or ). Therefore, the base value can be accurately calculated and displayed. For example, if a prize-winning sensor detects a prize-winning hole with 5 prize balls and a prize-winning hole sensor with 3 prize balls, a total of 8 prize balls are detected as the total number of prize balls. (or add to the prize number buffer).
また、遊技球の発射が検出されている場合にのみ、賞球数を総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算してもよい。すなわち、発射球センサ1020の検出から所定時間以内に検出した入賞に関する賞球数のみを総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算してもよい。また、発射制御部953または球発射装置680の動作を検出し、発射制御部953または球発射装置680が動作している間(さらに、発射制御部953または球発射装置680が動作を停止してから所定時間(例えば、5秒)後まで)に検出した入賞に関する賞球数のみを総賞球数または賞球数バッファに加算してもよい。また、遊技者が発射ハンドルを操作している場合に、賞球数を総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算してもよい。すなわち、ハンドルユニット500の接触検知センサ509に手のひらや指が触れていることが検出されている時間から所定時間(例えば、5秒)以内に検出した入賞に関する賞球数のみを総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算してもよい。このようにすると、遊技球が発射されていない状態で賞球を検出する異常や不正行為による賞球のベース値への反映を防止でき、不正確なベース値の表示を防止できる。また、接触検知セン
サ509を用いると、遊技球の発射を検出するセンサを新たに設けなくてもよいので、パチンコ機1のコストの上昇を抑制できる。
Also, the number of prize balls may be added to the total number of prize balls (or the number of prize balls buffer) only when the shooting of game balls is detected. That is, only the number of winning balls detected within a predetermined time from the detection of the
図39に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、特賞中の賞球数およびアウト球数を除外してベースを計算したが、特賞中でも一般入賞口及び始動口への入賞による賞球数を計数し、大入賞口へ入賞した球数を除外してアウト球数を計数して、ベース値を計算してもよい。 In the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 39, the base is calculated by excluding the number of winning balls and the number of out balls during the special prize, but the number of winning balls due to the winning of the general winning opening and the starting opening are not counted even during the special prize. Alternatively, the base value may be calculated by counting the number of out-balls, excluding the number of balls that have entered the big prize pool.
図40は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の一例を示すフローチャートである。図40に示すベース算出・表示処理では、毎回(タイマ割込み周期ごと)にベース値を計算する。 FIG. 40 is a flowchart showing an example of base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 40, the base value is calculated each time (every timer interrupt cycle).
まず、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS902)。総アウト球数が0であれば、ベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。なお、総賞球数が0である場合はベース値として0が計算されるが、ベース値を計算しなくてもよい。さらに、異常なベース値が計算される場合(例えば、総賞球数が総アウト数より大きく、ベース値として1(100%)以上の値が計算される場合)、ベース値を計算しなくてもよい。ベース値を百分率で表す場合、総賞球数÷総アウト球数に100を乗じてベース値を計算する。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。 First, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S902). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base value is not calculated and the base calculation/display process is terminated. On the other hand, if the total number of out balls is not 0, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). When the total number of winning balls is 0, 0 is calculated as the base value, but the base value does not have to be calculated. In addition, if an abnormal base value is calculated (e.g., if the total number of balls won is greater than the total number of outs and a value of 1 (100%) or more is calculated as the base value), the base value must not be calculated. good too. When the base value is expressed as a percentage, the base value is calculated by multiplying the total number of awarded balls divided by the total number of out balls by 100. Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217.
除算入力レジスタA131216に格納される総賞球数に乗じられる所定数は、計算されるベース値の桁数を制御する。例えば、この所定数を100とすれば、ベース値は100分率で1の位まで計算され、少数以下は計算されない。また、この所定数を10000とすれば、ベース値は100分率で小数2桁まで計算される。すなわち、演算回路から出力された商を100で除すると、小数2桁の100分率のベース値が計算できる。 The predetermined number by which the total number of balls stored in divide input register A131216 is multiplied controls the number of digits of the calculated base value. For example, if this predetermined number is 100, the base value is calculated up to the 1's place in the hundredth fraction, and the fractions below the decimal point are not calculated. Also, if this predetermined number is 10000, the base value is calculated to two decimal places in a fraction of 100. That is, by dividing the quotient output from the arithmetic circuit by 100, the base value of the fraction of 100 with two decimal places can be calculated.
そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、除算入力レジスタ131216、131217へのデータの書き込みから除算結果レジスタA131218からデータを読み出すまでの32クロックのウェイト時間には、主制御MPU1311は、処理を行わずに待機しても、他の処理を行ってもよい。例えば、除算入力レジスタ131216、131217へのデータの書き込みから除算結果レジスタA131218からデータを読み出すまでの間に大当たりの当落を判定する乱数を更新してもよい。より具体的には、乱数発生回路13112で生成されるハード乱数は、主制御MPU1311に供給されるクロック周期(又は、該クロック周期を分周した信号)のタイミングで更新されるので、該ウェイト時間にもハード乱数が更新される。
Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. During the 32-clock wait time from writing data to the division input registers 131216 and 131217 to reading data from the division result register A131218, the
すなわち、本実施例の遊技機では、演算回路13121がベース演算処理を実行中においても、遊技にかかる他の処理を並行して実行可能となっている。遊技にかかる他の処理は、少なくとも、当落を判定するための乱数を更新する処理が含まれる。また、演算回路13121における演算(除算)処理中に、遊技の結果に影響を与える乱数の更新が1回以上行われる。
That is, in the gaming machine of this embodiment, even while the
また、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラーとなるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
Also, if the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。ベース報知コマンドは、単にベース値を報知するものでも、ベース値の異常を報知するものでもよい。ベース値の異常とは、例えば、計算されたベース値が設計値(正常値)から所定の許容範囲を超えて大きくまたは小さくなった場合などである。なお、複数段階の許容範囲を設けてベース値の乖離の程度によって異常の程度を複数段階で判定してもよい。 Thereafter, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees. The base notification command may simply notify the base value or may notify an abnormality of the base value. Abnormality of the base value is, for example, when the calculated base value becomes larger or smaller than the design value (normal value) beyond a predetermined allowable range. In addition, a plurality of stages of allowable ranges may be provided, and the degree of abnormality may be determined in a plurality of stages according to the degree of divergence of the base values.
ベースの報知は、様々な方法があり、以下に説明する方法の一つでも、二つ以上を組み合わせてもよい。例えば、ベース表示器(7セグメントLED)1317、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244などでベースの値を常時または所定のタイミングで報知してもよい。遊技者にベース値を報知すると、遊技者がパチンコ機の調子を確認できてよい。その際、役物比率で説明した表示態様をベース値に適用してもよい。ベースの値を報知する場合、計算されたベース値をパーセンテージ表記として、前述した表示器や表示装置に表示する。なお、小数点以下の値は切り捨て、四捨五入、切り上げのいずれでもよいし、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244など画像を表示可能な表示装置では、小数点以下第1位まで表示し、より詳細に表示してもよい。
There are various methods for base notification, and one or more of the methods described below may be used in combination. For example, the base value may be notified by the base display (7-segment LED) 1317, the liquid
7セグメントLEDで構成されるベース表示器1317にベース値を表示する場合、主制御MPU1311がベース表示器1317のドライバ回路13171に設けられた所定のレジスタに表示データを入力する。すなわち、主制御MPU1311は、ベース報知コマンドとして、ドライバ回路13171のレジスタに設定される表示データを生成する。より具体的には、主制御MPU1311は、図33、図34に示すように、D15~D8に数値を表示する桁を「データn設定」で指定し、D7~D0に表示内容を指定したデータを生成し、シフトレジスタ3171に書き込む。
When displaying a base value on the
また、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244にベース値を表示する場合、ベース値に所定の基準値(例えば、50%など)を設け、当該基準値を超えた場合は、表示態様を変更するとよい。例えば、数値を点滅させたり、色を変えたり(通常時は緑色で、基準超時は赤色など)して表示する。さらに、複数段階でベース値の表示態様を変えてもよい。具体的には、表示されるベース値が、30%以上、25%以上30%未満、20%以上25%未満、15%以上20%未満、10%以上15%未満、10%未満のように複数の段階に分けて、各段階で白、青、黄のように発光色を変えて表示してもよい。また、各段階で「調子いいね」「調子が下がってきてるよ」「やばいんじゃない」「ある意味凄いね」など、ベース値が低いときには自虐的なコメントを表示してもよい。ベース値が基準値を超えている場合、パチンコ機が想定とは異なる動作をしており、不正が行われている可能性がある。このため、赤色などの警告を示す態様による表示が望ましい。また、遊技の進行を停止しない程度の弱いエラーと同一又は同様の表示態様でもよい。ここで、同様とは、表示、ランプ、音の少なくとも一つが同じことを意味する。
In addition, when the base value is displayed on the liquid
また、各種ランプ、液晶表示装置、音などでベース値がどの範囲にあるか(ベース値が高いのか低いのか、異常値か正常値か、など)を報知してもよい。また、ベースが計算できず(ステップS902でYes)、かつ、過去に計算されたベース値がない場合、ベース報知不可を液晶表示装置に表示するためのベース報知コマンドを生成してもよい。報知コマンドを生成したサブ基板に送信することによって、サブ基板が制御する演出装置でベースの状態を報知することができるので、主基板で報知するより多種多様の報知ができ、主基板の負荷を軽減できる。また、ベース表示器1317に何も表示されていないときにベース表示不可を報知することによって、ベース表示器1317の故障と、表示するベース値がないこととを切り分けることができる。さらに、ベース値の異常を液晶表示装置に表示することによって、ベース表示器1317が設けられた遊技盤の裏面側を見ることなく、ベース値の異常を知ることができる。
In addition, various lamps, a liquid crystal display device, sound, etc. may be used to notify the range of the base value (whether the base value is high or low, whether it is an abnormal value or a normal value, etc.). Further, if the base cannot be calculated (Yes in step S902) and there is no previously calculated base value, a base notification command may be generated for displaying on the liquid crystal display that base notification is not possible. By transmitting the notification command to the generated sub-board, the effect device controlled by the sub-board can notify the state of the base. can be reduced. Further, by informing that the base display is impossible when nothing is displayed on the
機能表示ユニット1400がベース表示器1317を兼ねてもよい。この場合、機能表示ユニット1400の特定のLEDランプ(または7セグメントLED)を使用して常時報知するとよい。また、所定のタイミング(例えば、本体枠4の開放時、特別図柄変動表示ゲームが実行されていない間、特別図柄変動表示ゲームが終了したタイミング)で報知するとよい。
The
外部端子板784から遊技場に設置されたホールコンピュータにベースの情報を出力してもよい。この場合、後述するベース算出・表示処理(図47、図49など)のように、所定のタイミングで(所定の賞球数ごとに、所定のアウト球数ごとに)、ベースの情報を出力するとよい。
Base information may be output from the external
外部端子板784から出力するベースの情報は、算出されたベース値が所定の閾値に対して高いか低いかを表す2値(ハイ、ロー)の信号でもよい。また、算出されたベース値の概略を示す長さの信号を出力してもよい(例えば、ベース値が30%以上40%未満は、30ミリ秒のパルス)。また、算出されたベース値の概略を示す数の連続パルスを出力してもよい(例えば、ベース値が30%以上40%未満は、3個の連続パルス)。
The base information output from the external
なお、ベース値が更新されない場合でも、ベース報知コマンドを生成してもよく、ベース値が更新されない場合には、ベース報知コマンドを生成しなくてもよい。ベース報知コマンドを生成しなくても、ベース値の表示は継続される。 The base notification command may be generated even when the base value is not updated, and the base notification command may not be generated when the base value is not updated. The display of the base value continues even if the base notification command is not generated.
また、図56などで後述するように、計算されたベース値が異常であるかを判定し、ベース値の異常を報知するベース報知コマンドを生成し、遊技者やホール従業員にベースの異常を報知してもよい。 In addition, as will be described later with reference to FIG. 56, etc., it determines whether the calculated base value is abnormal, generates a base notification command for notifying the abnormality of the base value, and notifies the player or the hall employee of the abnormality of the base value. may be notified.
また、遊技者へのベースを報知するかを、遊技状態(遊技状況)に応じて決定してもよい。これは、ベース値を遊技者に常時報知すると、パチンコ機の本来の楽しみである特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出に対する遊技者の注意が疎かになり、遊技者の意識が分散する可能性があるためである。 Also, whether or not to inform the player of the base may be determined according to the game state (game situation). This is because, if the base value is constantly reported to the player, the player's attention to the performance of the special symbol variation display game, which is the original enjoyment of the pachinko machine, may be neglected and the player's consciousness may be dispersed. is.
また、計算されたベース値に基づいて、実行中や今後実行される特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出を変化させてもよい。例えば、複数の表示選択テーブルを準備し、ベース値によって異なる表示選択テーブル(図64~図68参照)から演出を選択するとよい。 Also, based on the calculated base value, the effect of the special symbol variation display game being executed or to be executed in the future may be changed. For example, it is preferable to prepare a plurality of display selection tables and select an effect from different display selection tables (see FIGS. 64 to 68) depending on the base value.
また、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中に、ベース値が所定の閾値(例えば、30%)を越えたり下回ることもある。このため、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中に閾値を越えたり、下回ったときに、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出を変化させてもよい。ベース値が所定の閾値を超えて上昇したときと下降したときで、演出を同じ態様で変化させてもよいし、演出を異なる態様で変化させてもよい。 Also, the base value may exceed or fall below a predetermined threshold value (for example, 30%) during the special symbol variation display game. Therefore, when the threshold value is exceeded or fallen below during the special symbol variation display game, the effect of the special symbol variation display game may be changed. When the base value rises above a predetermined threshold value and when it falls, the effect may be changed in the same manner, or the effect may be changed in different manners.
図41は、賞球数の更新タイミングとベース値の計算タイミングの一例を示す図である。図23に示すように、本実施例ではステップS81のベース算出用領域更新処理で賞球数を更新し、ステップS89のベース比率算出・表示処理でベース値を計算する。 FIG. 41 is a diagram showing an example of the update timing of the number of prize balls and the calculation timing of the base value. As shown in FIG. 23, in this embodiment, the number of winning balls is updated in the base calculation area update process of step S81, and the base value is calculated in the base ratio calculation/display process of step S89.
このため、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で遊技球の入賞を検出し、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で入賞口毎に定められた賞球数を計算し、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)で賞球数バッファを更新する。その後、ベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)でベース値を更新し、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)で払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信する。
Therefore, the
払出制御基板951は、受信した払出コマンドをメモリに格納すると、払出コマンド受信確認を主制御基板1310に送信する。そして、払出制御基板951は、払出コマンドに従って賞球を払い出すと、球払出完了を主制御基板1310に通知する。なお、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で計算された賞球数のうち未払出し賞球数は、主制御基板1310又は払出制御基板951でバックアップされる。払出制御基板951で未払出し賞球数をバックアップする場合、払出制御基板951が払出コマンド受信確認を主制御基板1310に送信する必要があるが、球払出完了を主制御基板1310に通知する必要はない。一方、主制御基板1310で未払出し賞球数をバックアップする場合、払出制御基板951が球払出完了を主制御基板1310に通知する必要があるが、払出コマンド受信確認を主制御基板1310に送信する必要はない。
After storing the received payout command in the memory, the
以上に説明した実施例にかかるパチンコ機では、遊技中にベース値が遅滞なく計算され、遊技機の状態をリアルタイムで知ることができる。このため、遊技機の異常を早期に発見できる。例えば、ベース値が所定の閾値より低いまたは高いとベースが異常であると判定する場合、一つの特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中にベース値が複数回計算され、所定の閾値を跨いで上下して異常であると判定されても遊技を止めることなく、異常の判定にかかわらずベース値の計算処理は継続して実行する。例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームには、通常変動などの短時間のものや、リーチ変動などの長時間のものがあり、一つの特別図柄変動表示ゲームの開始から終了までの間にベース値を計算する条件を複数回満たした場合、その都度ベース値を計算し、その都度ベース値を更新して表示するとよい。これは、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中のベース値の計算を制限すると(例えば、変動表示終了時に1回だけベース値を計算し更新する)、ベース値の計算タイミングによっては、ベース値の変化に長時間気が付かず、ホール運営に必要な情報が適切なタイミングで出力されず、ホールが迷惑を被る可能性があるからである。 In the pachinko machine according to the embodiment described above, the base value is calculated without delay during the game, and the state of the game machine can be known in real time. Therefore, an abnormality in the gaming machine can be detected early. For example, when it is determined that the base value is abnormal when the base value is lower or higher than a predetermined threshold, the base value is calculated multiple times during one special symbol variation display game, and the predetermined threshold is exceeded. The game is not stopped even if it is determined as such, and the calculation processing of the base value is continuously executed regardless of the abnormality determination. For example, the special symbol variation display game includes short-time games such as normal variation and long-time games such as reach variation, and the base value is calculated from the start to the end of one special symbol variation display game. If the condition is met multiple times, the base value should be calculated each time, and the base value should be updated and displayed each time. This is because if the calculation of the base value during the special symbol variation display game is restricted (for example, the base value is calculated and updated only once at the end of the variation display), depending on the calculation timing of the base value, it may take a long time to change the base value. This is because there is a possibility that the information necessary for hall operation will not be output at an appropriate timing, causing inconvenience to the hall.
また、発射された遊技球が始動口や一般入賞口に入賞していなければ、ベース値が低下する。この状態では、遊技者は損をしているので、例えば、液晶で行われている演出に追加演出(例えば、ベース値の変化に関連しない当落に関する演出や、ベース値の変化に伴って現出する特定の演出)を付加したり、大当りの期待度が高い予告演出(ベース値の変化に関連しない演出のうち、次回予告演出などの期待度が高い予告演出や、ベース値の変化に伴って現出する特定の演出のうち期待度が高い予告演出(例えば、ベース値をレインボー表示で表示))を行ってもよい。これによって、遊技者は、始動口および一般入賞口に入賞しないことにより感じる不快感を軽減し、遊技を継続する動機づけを与えることができる。 Also, if the launched game ball does not enter the starting opening or the general winning opening, the base value is lowered. In this state, the player is at a loss, so for example, additional effects to the effects performed on the liquid crystal (for example, effects related to wins and losses that are not related to changes in the base value, and effects that appear with changes in the base value) (Specific effects to be added), and notice effects with high expectations for big hits (among the effects that are not related to changes in the base value, notice effects with high expectations such as the next notice effect, and changes in the base value Of the specific effects that appear, a highly anticipated advance notice effect (for example, displaying the base value in a rainbow display) may be performed. As a result, the player can be motivated to continue the game by alleviating the discomfort caused by not winning the starting slot and the general winning slot.
一方、発射された遊技球の多くが始動口や一般入賞口に入賞すれば(過去の入賞数の平均値より多く入賞すれば)、ベース値が上昇する。この状態では、大当り抽選の結果がはずれでも、遊技者には通常より多くの遊技球の払い出しを受けているため、遊技者のがっかり感は軽減される。変動表示ゲームの演出を、期待度が低い演出に変えてもよい。 On the other hand, if most of the launched game balls enter the start hole or the general winning hole (if more than the average number of past winnings wins), the base value increases. In this state, even if the result of the jackpot lottery is a loss, the player receives more game balls than usual, so the player's disappointment is alleviated. The effect of the variable display game may be changed to a less expected effect.
[9-2.賞球数の更新タイミングとベース値の計算タイミングのバリエーション]
次に、図42から図44を用いて、賞球数の更新タイミングとベース値の計算タイミングのバリエーションを説明する。各バリエーションにおける賞球数の更新タイミング、ベース値の計算タイミングの概要は以下の通りである。
・図41:賞球数計算→賞球数更新→ベース値計算→払出コマンド送信
・図42:賞球数計算→賞球数更新→払出コマンド送信→ベース値計算
・図43:賞球数計算→払出コマンド送信→賞球数更新→ベース値計算
・図44:賞球数計算→払出コマンド送信→コマンド受信確認→賞球数更新→ベース値計算
・図45:賞球数計算→払出コマンド送信→払出完了通知→賞球数更新→ベース値計算
なお、上記図41から図44のバリエーションは、図39に示すベース算出用領域更新処理および図40に示すベース算出・表示処理だけでなく、後述するいずれのベース算出用領域更新処理およびベース算出・表示処理にも適用可能である。
[9-2. Variation of the update timing of the number of prize balls and the calculation timing of the base value]
Next, with reference to FIGS. 42 to 44, variations of the update timing of the number of awarded balls and the calculation timing of the base value will be described. An overview of the update timing of the number of prize balls and the calculation timing of the base value in each variation is as follows.
・Figure 41: Number of prize balls calculated → Number of prize balls updated → Base value calculated → Payout command sent ・Figure 42: Number of prize balls calculated → Number of prize balls updated → Payout command sent → Base value calculated ・Figure 43: Number of prize balls calculated → Send payout command → Update number of prize balls → Calculate base value ・Fig. 44: Calculate number of prize balls → Send payout command → Confirm command reception → Update number of prize balls → Calculate base value ・Fig. →notification of payout completion→update of the number of prize balls→calculation of the base value Note that the variations shown in FIGS. It is applicable to any base calculation area update process and base calculation/display process.
図42に示す手順では、図23に示すタイマ割込み処理の手順と異なり、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)は図示した位置で実行し、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)の後にベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)を実行する。 In the procedure shown in FIG. 42, unlike the procedure of timer interrupt processing shown in FIG. - Execute the display process (step S89).
すなわち、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で遊技球の入賞を検出し、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で入賞口毎に定められた賞球数を計算し、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)で総賞球数(または、後述する実施例では賞球数バッファ)を更新する。その後、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)で払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信し、ベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)でベース値を更新する。
That is, the
払出制御基板951は、受信した払出コマンドをメモリに格納すると、払出コマンド受信確認を主制御基板1310に送信する。そして、払出制御基板951は、払出コマンドに従って賞球を払い出すと、球払出完了を主制御基板1310に通知する。前述したように、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で計算された賞球数のうち未払出し賞球数を主制御基板1310又は払出制御基板951のいずれでバックアップするかによって、払出コマンド受信確認又は球払出完了のいずれかを省略してもよい。
After storing the received payout command in the memory, the
図43に示す手順では、図23に示すタイマ割込み処理の手順と異なり、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)の後にベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)及びベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)を実行する。 In the procedure shown in FIG. 43, unlike the procedure of timer interrupt processing shown in FIG. to run.
すなわち、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で遊技球の入賞を検出し、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で入賞口毎に定められた賞球数を計算し、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)で払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信する。その後、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)で、送信した払出コマンドに対応する賞球数で総賞球数(または、後述する実施例では賞球数バッファ)を更新し、ベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)でベース値を更新する。なお、送信した払出コマンドに対応する賞球数ではなく、作成した払出コマンドに対応する賞球数で(払出コマンドが未送信であっても)賞球数バッファを更新してもよい。
That is, the
払出制御基板951は、受信した払出コマンドをメモリに格納すると、払出コマンド受信確認を主制御基板1310に送信する。そして、払出制御基板951は、払出コマンドに従って賞球を払い出すと、球払出完了を主制御基板1310に通知する。前述したように、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で計算された賞球数のうち未払出し賞球数を主制御基板1310又は払出制御基板951のいずれでバックアップするかによって、払出コマンド受信確認又は球払出完了のいずれかを省略してもよい。
After storing the received payout command in the memory, the
なお、主制御MPU1311が、払出制御基板951からコマンド受信確認や球払出完了通知を受信するタイミングは、払出制御基板951の処理速度や払出装置830の動作速度によるので、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)やベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)との順序は問わない。
In addition, the timing at which the
図44に示す手順では、図23に示すタイマ割込み処理の手順と異なり、払出制御基板951から払出コマンド受信確認を受信した後に、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップ
S81)及びベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)を実行する。
In the procedure shown in FIG. 44, unlike the procedure of the timer interrupt process shown in FIG. (Step S89) is executed.
すなわち、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で遊技球の入賞を検出し、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で入賞口毎に定められた賞球数を計算し、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)で払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信する。
That is, the
払出制御基板951は、受信した払出コマンドをメモリに格納すると、払出コマンド受信確認を主制御基板1310に送信する。
After storing the received payout command in the memory, the
主制御MPU1311は、払出制御基板951から払出コマンド受信確認を受信すると、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)で、コマンド受信確認を受信した払出コマンドに対応する賞球数で総賞球数(または、後述する実施例では賞球数バッファ)を更新し、ベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)でベース値を更新する。
When the
そして、払出制御基板951は、払出コマンドに従って賞球を払い出すと、球払出完了を主制御基板1310に通知する。なお、図44に示す手順では、停電発生時に未払出し賞球数のデータを消失しないため、払出制御基板951で未払出し賞球数のデータバックアップしている。このため、払出制御基板951から主制御基板1310へのコマンド受信確認は必要であるが、球払出完了通知は省略してもよい。
When the
図45に示す手順では、図23に示すタイマ割込み処理の手順と異なり、払出制御基板951から球払出完了通知を受信した後に、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)及びベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)を実行する。 In the procedure shown in FIG. 45, unlike the procedure of timer interrupt processing shown in FIG. (Step S89) is executed.
すなわち、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で遊技球の入賞を検出し、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で入賞口毎に定められた賞球数を計算し、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)で払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信する。
That is, the
払出制御基板951は、受信した払出コマンドをメモリに格納すると、払出コマンド受信確認を主制御基板1310に送信する。そして、払出制御基板951は、払出コマンドに従って賞球を払い出すと、球払出完了を主制御基板1310に通知する。
After storing the received payout command in the memory, the
主制御MPU1311は、払出制御基板951から球払出完了通知を受信すると、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)で、払い出しが完了した賞球数で総賞球数(または、後述する実施例では賞球数バッファ)を更新し、ベース比率算出・表示処理(ステップS89)でベース値を更新する。
When the
なお、図44に示す手順では、停電発生時に未払出し賞球数のデータを消失しないため、主制御基板1310で未払出し賞球数のデータバックアップしている。このため、払出制御基板951から主制御基板1310への球払出完了通知は必要であるが、コマンド受信確認は省略してもよい。
In the procedure shown in FIG. 44, the
以上に説明したように、本実施例のパチンコ機は、所定の条件が満たされた場合に、ベース値の計算に使用するパラメータである賞球数やアウト球数を更新する。例えば、図41や図42に示す処理では、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で入賞口センサが遊技球の入賞を検出すると賞球数を更新する。また、図43に示す処理では、払い出しコマンドを送信すると賞球数を更新する。また、図44に示す処理では、払い出しコマンドの受信を確認すると賞球数を更新する。また、図45に示す処理では、賞球の払い出しが完了
すると賞球数を更新する。
As described above, the pachinko machine of this embodiment updates the number of winning balls and the number of out balls, which are the parameters used for calculating the base value, when a predetermined condition is satisfied. For example, in the processes shown in FIGS. 41 and 42, the number of winning balls is updated when the winning opening sensor detects winning of game balls in the switch input process (step S74). Also, in the process shown in FIG. 43, when the payout command is transmitted, the number of prize balls is updated. Also, in the processing shown in FIG. 44, the number of prize balls is updated when the reception of the payout command is confirmed. Also, in the processing shown in FIG. 45, the number of prize balls is updated when the payout of prize balls is completed.
なお、本実施例のパチンコ機では、遊技状態が特賞中であるかの判定タイミングと賞球数の更新タイミングとのズレによって、特賞中の賞球数を正確に計数できない可能性がある。特に、入賞口への入賞から賞球数の更新までの時間が長い場合に問題が大きくなる。このため、特賞中の入賞にフラグを付し、当該入賞による賞球数、払出コマンド、受信確認および払出完了通知に当該フラグを引き継ぐ。そして、当該フラグを用いて、各段階で特賞中の賞球であるかを判定する。このようにすると、入賞口への入賞から賞球数の更新までの時間が長くても、特賞中の賞球数を正確に計数して更新できる。 In the pachinko machine of this embodiment, there is a possibility that the number of prize balls during the special prize cannot be counted accurately due to the difference between the timing of determining whether the game state is the special prize and the timing of updating the number of prize balls. In particular, the problem becomes serious when it takes a long time to update the number of prize balls after winning a prize in the prize opening. For this reason, a flag is attached to the winning prize during the special prize, and the flag is inherited to the number of winning balls, the payout command, the reception confirmation, and the payout completion notification. Then, using the flag, it is determined at each stage whether the ball is in the middle of a grand prize. In this way, even if it takes a long time to update the number of prize balls after entering the winning hole, the number of prize balls during the special prize can be accurately counted and updated.
また、本実施例のパチンコ機では、これらの契機で賞球数やアウト球数を更新して、ベース値を計算して表示する。すなわち、遊技機単体でベース値を知ることができるので、製造工程や検査工程での釘調整に必要な時間を短縮でき、効率良く遊技機を製造できる。 Further, in the pachinko machine of the present embodiment, the number of winning balls and the number of out balls are updated at these opportunities, and the base values are calculated and displayed. That is, since the base value can be known from the game machine alone, the time required for nail adjustment in the manufacturing process and the inspection process can be shortened, and the game machine can be efficiently manufactured.
また、本実施例のパチンコ機では、パチンコ機が球切れ状態で賞球を払い出せない場合、主制御基板1310又は払出制御基板951が未払出球の数を保持する。
Further, in the pachinko machine of this embodiment, when the pachinko machine is out of balls and the prize balls cannot be paid out, the
主制御基板1310が未払出球の数を保持する場合、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で入賞口センサが遊技球の入賞を検出すると、入賞が検出された入賞口に対応する賞球数を未払出球数に加算する。なお、この未払出球数には、所定の上限を設けてもよいが、上限を設けなくてもよい。この場合、払い出される賞球数が計算される都度、ベース値を計算するための賞球数バッファまたは総賞球数を更新するとよい。また、主制御基板1310から払出制御基板951に払出コマンドの送信後に賞球数を更新してもよい。
When the
一方、払出制御基板951が未払出球の数を保持する場合、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で入賞口センサが遊技球の入賞を検出すると、入賞が検出された入賞口に対応する賞球数の払出コマンドを払出制御基板951に送信する。パチンコ機が球切れ状態で賞球を払い出せない場合でも払出コマンドが送信され、未払出球数は払出制御基板951で保持される。この場合、払出コマンドが送信される都度、ベース値を計算するための賞球数バッファまたは総賞球数を更新するとよい。
On the other hand, when the
また、払出制御基板951が払出コマンドを受信すると、ベース値を計算するための賞球数を更新してもよい。なお、この賞球数には、所定の上限を設けてもよいが、上限を設けなくてもよい。また、実際に賞球が払い出される都度、ベース値を計算するための賞球数を更新してもよい。払出制御基板951はベース値を計算するための賞球数を主制御基板1310に送信し、主制御基板1310は、受信した賞球数を用いてベース値を計算する。
Also, when the
また、図47において後述するように、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較せずに、所定回数(例えば、10回)の入賞毎に、または、所定時間(例えば、5秒)毎に、ステップS891およびS892を実行してもよい。 Also, as will be described later with reference to FIG. 47, without comparing the winning balls buffer value with the threshold value Th1, every predetermined number of wins (for example, 10 times) or every predetermined time (for example, 5 seconds) , steps S891 and S892 may be performed.
以上に説明したように、ベース値を計算するための賞球数の更新は様々なタイミングで行うことができるが、賞球数を更新すると遅滞なくベース値を計算し、ベース表示器1317にリアルタイムに表示してもよいし、所定のタイミング(例えば、1分ごと)にベース値を計算し、表示してもよい。 As described above, the number of prize balls for calculating the base value can be updated at various times. Alternatively, the base value may be calculated and displayed at a predetermined timing (for example, every minute).
[9-3.賞球数の更新とベース値の計算のタイミング]
次に、図46から図51を用いて、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)、ベース算出表示処理(ステップS89)のバリエーションを説明する。各バリエーションに
おけるベース値の計算タイミングの概要は以下の通りである。
・図39及び図40:タイマ割込み周期ごとに毎回ベース値を計算
・図46及び図47:所定賞球数ごとにベース値を計算
・図48及び図49:所定アウト球数ごとにベース値を計算
・図50及び図51:賞球数及びアウト球数の一方が所定数に達したらベース値が更新
[9-3. Timing of updating the number of prize balls and calculating the base value]
Next, variations of the base calculation area update process (step S81) and the base calculation display process (step S89) will be described with reference to FIGS. 46 to 51. FIG. The outline of the calculation timing of the base value in each variation is as follows.
・Figures 39 and 40: Calculate the base value every timer interrupt cycle ・Figures 46 and 47: Calculate the base value for each predetermined number of winning balls ・Figures 48 and 49: Calculate the base value for each predetermined number of out balls Calculation ・Figure 50 and Figure 51: When either the number of awarded balls or the number of out balls reaches a predetermined number, the base value is updated.
図46は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図46に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、賞球数が所定の条件を満たしたタイミングでベース値を計算するために、賞球数を賞球数バッファに記録する(ステップS813)。なお、図46において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理(図39)と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 46 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation area updating process (step S81). In the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 46, the number of prize balls is recorded in the number of prize balls buffer in order to calculate the base value at the timing when the number of prize balls satisfies a predetermined condition (step S813). In FIG. 46, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation area updating process (FIG. 39), and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しない賞球であるため、賞球数やアウト球数を更新せずに、ステップS824に進む。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で入力情報に基づいて算出された賞球数を取得する(ステップS811)。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded. If the game state is during a special prize, the prize balls are not related to the calculation of the base value, so the process proceeds to step S824 without updating the number of prize balls or the number of out balls. On the other hand, if the game state is not during the special prize, the number of prize balls calculated based on the input information in the prize ball control process (step S80) is obtained (step S811).
そして、賞球があるか、すなわち、取得した賞球数が1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS812)。その結果、賞球がなければ、賞球数を更新せずにステップS818に進む。一方、賞球があれば、取得した賞球数を賞球数バッファに加算する(ステップS813)。なお、賞球数バッファに加算する都度、外部端子板784から遊技場に設置されたホールコンピュータに賞球数を出力してもよいし、後述する賞球数が所定の閾値Th1以上となった場合に当該閾値Th1を外部端子板784からホールコンピュータに出力してもよい。ここで賞球数バッファは、ベース値を計算するために主制御内蔵RAM1312に設けられる領域であり、パチンコ機1が払い出す賞球数が一時的に格納される。
Then, it is determined whether there is a prize ball, that is, whether the number of prize balls obtained is one or more (step S812). As a result, if there are no prize balls, the process proceeds to step S818 without updating the number of prize balls. On the other hand, if there are prize balls, the acquired number of prize balls is added to the number of prize balls buffer (step S813). Each time the number of prize balls is added to the number of prize balls buffer, the number of prize balls may be output from the external
そして、賞球数に異常があるかを判定する(ステップS815)。例えば、賞球数の異常とは、特賞中以外の所定時間に多くの賞球(例えば、一般入賞口や始動口の賞球数から考えて、1分間に10発以上の入賞に相当する賞球)が得られている場合などである。なお、複数段階の許容範囲を設けて賞球数の基準値からの乖離の程度によって異常の程度を複数段階で判定してもよい。また、賞球数に異常がある場合、ステップS813において、取得した賞球数を賞球数バッファに加算しなくてもよく、ステップS813において賞球数バッファに加算した賞球数を減算してもよい。 Then, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls (step S815). For example, an abnormality in the number of prize balls is defined as a number of prize balls in a predetermined time period other than during the special prize (for example, considering the number of prize balls in the general prize opening and the start opening, a prize corresponding to 10 or more prizes per minute) sphere) is obtained. It should be noted that the degree of abnormality may be determined in a plurality of stages according to the degree of deviation from the reference value of the number of prize balls provided with a plurality of stages of allowable ranges. Also, if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, it is not necessary to add the number of prize balls acquired to the number of prize balls buffer in step S813. good too.
その結果、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS816)、遊技者やホール従業員に賞球が異常であることを報知する。異常の報知は、様々な方法があり、以下に説明する方法の一つでも、二つ以上を組み合わせてもよい。例えば、各種ランプ、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244、音などで賞球数の異常を報知してもよい。また、外部端子板784から遊技場に設置されたホールコンピュータに賞球数の異常を出力してもよい。さらに、当該異常と判定された賞球数をベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。この場合、遊技者に賞球を払い出してもよい。また、賞球数が異常と判定され且つ前述した報知手段(音、ランプ、LED、液晶表示装置、外部端子板784からの情報出力など)によって報知する場合、異常と判定された賞球数をベース値の計算に使用してもよい。さらに、遊技を一時的に停止してもよい。具体的には、主制御基板1310は、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されなくても、主制御内蔵RAM1312の全データを初期化し、周辺制御部1511のRAMの全データを初期化する。そして、初期状態で動作確認から遊技を開始する。遊技を停止する他の方法として、遊技を一旦停止(例えば、特別図柄の変動表示を停止)した後、エラー報知停止後に元の状態に復帰して遊技を再開する。このため、停電監視回路が電源電圧の低下を検出しなくても停電検知信号を出力し、
主制御MPU1311は主制御内蔵RAM1312の全データをバックアップして、遊技を停止する。そして、エラー報知終了後に、主制御内蔵RAM1312のデータをバックアップ領域からリストアして、遊技を再開する。このとき、周辺制御部1511は、そのままの状態で、主制御基板1310からのコマンドを待つので、主制御基板1310の動作の再開によって、中断していた遊技を再開する。とはいえ、100個の遊技球(すなわち、アウト球)が遊技領域5aに発射され、全ての遊技球が一般入賞口や始動口に入賞する可能性があるので、賞球数の異常を報知する態様は、通常のエラー(磁気センサエラーなど)より緊急度が低い、おとなしい態様(例えば、通常のエラー報知より小音量や低光量)が望ましい。また、表示時間も通常のエラーと同じか、短時間でもよい。場合によっては、報知時間を0秒にして報知しなくてもよい。
As a result, if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated (step S816) to notify the player or hall employee that the number of prize balls is abnormal. There are various methods for announcing an abnormality, and one of the methods described below or a combination of two or more methods may be used. For example, various lamps, liquid
The
そして、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットし(ステップS817)、賞球異常報知時間の計数を開始する。 Then, the prize ball abnormality notification timer is reset (step S817), and counting of the prize ball abnormality notification time is started.
その後、アウト球数を取得し(ステップS818)、取得したアウト球数を総アウト球数に加算するように、総アウト球数を更新する(ステップS822)。 After that, the number of out-balls is acquired (step S818), and the total number of out-balls is updated so that the acquired number of out-balls is added to the total number of out-balls (step S822).
その後、ステップS817で起動した賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定する(ステップS824)。そして、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止する(ステップS825)。なお、ステップS824では、所定時間だけ賞球異常を報知するためのタイマの時間によって報知の終了を判定したが、所定の発射球数だけ賞球異常を報知しするように報知の終了を判定してもよい。また、ホール従業員が確認するまで異常を報知し続けてもよい。 After that, it is determined whether the timer for announcing abnormal prize balls started in step S817 has timed up (step S824). Then, when the timer for prize ball abnormality notification times up, a prize ball abnormality notification stop command is generated, and the prize ball abnormality notification is stopped (step S825). In step S824, the end of the notification is determined by the time of the timer for notifying the abnormality of the prize ball for a predetermined time, but the end of the notification is determined so that the abnormality is notified only for the predetermined number of shot balls. may Alternatively, the anomaly may continue to be reported until a hall employee confirms it.
図46に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、ステップS985で賞球数に異常があるかを判定したが、アウト球数を取得した後に、アウト球数との比較において賞球数に異常があるか(すなわち、ベース値に異常があるか)を判定してもよい。例えば、所定の時間においてアウト球数を超える賞球数が計数された場合や、一般入賞口や始動口の賞球数から考えて、アウト球が高い割合(例えば、50%以上)で入賞している場合などである。 In the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 46, it is determined whether or not there is an abnormality in the number of awarded balls in step S985. (ie, whether there is an abnormality in the base value). For example, if the number of winning balls exceeds the number of out-balls in a predetermined time, or if the number of winning balls in the general winning opening and the starting opening is considered, a high percentage of out-balls (for example, 50% or more) wins. For example, if
図47は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図47に示すベース算出・表示処理では、賞球数が所定の条件を満たすタイミングでベース値が更新される。なお、図47において、前述したベース算出・表示処理(図40)と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 47 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display process shown in FIG. 47, the base value is updated when the number of prize balls satisfies a predetermined condition. In FIG. 47, the same step numbers are assigned to the same parts as in the base calculation/display processing (FIG. 40) described above, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、賞球数バッファに格納されている賞球数が予め定められている閾値Th1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS890)。賞球数バッファ値が所定の閾値Th1以上であるかの判定には様々な方法がとり得る。例えば、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較したり、賞球数の格納領域の所定のビットの値で判定してもよい(具体的には、賞球数の格納領域を8ビットで構成し、最上位ビットが1になればアウト球数が128以上であると判定できる)。またベース算出用領域更新処理(図46)で賞球数と閾値Th1とを比較した判定結果をフラグに記録し、ベース算出・表示処理(図47)では、当該フラグによって、賞球数バッファ値が所定の閾値Th1以上であるかを判定してもよい。 First, it is determined whether or not the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th1 (step S890). Various methods can be used to determine whether the prize ball number buffer value is greater than or equal to the predetermined threshold value Th1. For example, the value of the number of prize balls buffer may be compared with the threshold value Th1, or the value of a predetermined bit in the number of prize balls storage area may be used for determination. If the most significant bit becomes 1, it can be determined that the number of out balls is 128 or more). Also, in the base calculation region update process (Fig. 46), the determination result of comparing the number of prize balls and the threshold value Th1 is recorded in a flag, and in the base calculation/display process (Fig. is greater than or equal to a predetermined threshold value Th1.
そして、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1より小さければ、ベース値を計算するタイミングではないので、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。 Then, if the number-of-balls buffered value is smaller than the threshold value Th1, it is not the time to calculate the base value, so the base calculation/display process ends.
一方、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上であれば、総賞球数に閾値Th1を加算し(ステップS891)、賞球数バッファから閾値Th1を減算する(ステップS892)。すなわち、所定の起点から計数した賞球数が所定の条件を満たす(賞球数バッファに格納
された賞球数が閾値Th1以上となる)遊技状況であれば、当該賞球数の端数部分を残し(賞球数バッファから閾値Th1を減算した端数を賞球数バッファに残し)、他の部分をメモリに格納して(総賞球数に閾値Th1を加算し)、ベース値の計算に使用する処理を実行する。具体的には、閾値Th1が100個である場合に、賞球数バッファ値が99個であり、一般入賞口に入賞して5個の賞球が発生すると、賞球数バッファ値は104個となるが、100個を総賞球数に移動してベース値の計算に使用し、残り4個は賞球数バッファに残す。この場合、賞球数バッファに残された4個の賞球のカウントは、次に賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上となった場合にベース値の計算に使用される。また、閾値Th1=100個で説明したが、1000個など他の数値でもよい。しかし、大当たりが得られてもベースが計算されないような大きな閾値Th1を設定すると、不正の発見が遅延する可能性があるので、閾値Th1は1回の大当たりで払い出される賞球数以下(複数種類の大当たり(例えば、4ラウンドと8ラウンドの大当たり)がある場合、大当たりの賞球数の最小値以下)に設定するとよい。また、早期に不正を発見する観点から、頻繁にベース値を更新するとよい。例えば、閾値Th1が100個ではなく10個の方が、頻繁にベース値が更新される点で好ましい。
On the other hand, if the winning ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1, the threshold Th1 is added to the total winning ball number (step S891), and the threshold Th1 is subtracted from the winning ball number buffer (step S892). That is, if the number of prize balls counted from a predetermined starting point satisfies a predetermined condition (the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1), the fractional portion of the number of prize balls is calculated. Retain (leave the fraction obtained by subtracting the threshold Th1 from the number of prize balls buffer in the number of prize balls buffer), store the other part in memory (add the threshold Th1 to the total number of prize balls), and use it to calculate the base value process. Specifically, when the threshold value Th1 is 100, the prize ball number buffer value is 99, and if 5 prize balls are generated by entering the general winning hole, the prize ball number buffer value is 104. However, 100 are moved to the total number of balls to be used for calculating the base value, and the remaining 4 are left in the number of winning balls buffer. In this case, the count of the four prize balls left in the prize ball buffer is used for calculating the base value when the prize ball buffer value becomes equal to or greater than the threshold value Th1 next time. Also, although the threshold value Th1 has been described as 100, other numerical values such as 1000 may be used. However, if a large threshold Th1 is set so that the base is not calculated even if a big win is obtained, the detection of fraud may be delayed. If there are jackpots (e.g., 4-round and 8-round jackpots), it should be set to less than or equal to the minimum number of prize balls for the jackpot. In addition, from the viewpoint of detecting fraud at an early stage, it is preferable to update the base value frequently. For example, it is preferable to set the threshold Th1 to 10 instead of 100 because the base value is updated frequently.
なお、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較せずに、所定回数(例えば、10回)の入賞毎に、ステップS891およびS892を実行してもよい。さらに、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較せずに、所定時間(例えば、5秒)毎に、ステップS891およびS892を実行してもよい。この所定時間は、主制御MPU1311で動作するタイマで計測しても、RTC(リアルタイムクロック)の出力で計測してもよい。
It should be noted that steps S891 and S892 may be executed every predetermined number of wins (for example, 10 times) without comparing the buffer value for the number of winning balls with the threshold value Th1. Furthermore, Steps S891 and S892 may be executed at predetermined time intervals (for example, 5 seconds) without comparing the winning ball number buffer value with the threshold value Th1. This predetermined time may be measured by a timer operated by the
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS902)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラー(又は、不定)となるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S902). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base value is not calculated and the base calculation/display process is terminated. On the other hand, if the total number of out balls is not 0, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217. Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. Note that if the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
また、総アウト球数が0である場合の他、算出されるベース値が異常値となる場合に、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出用領域13128を更新しなくてもよい。例えば、総アウト球数が総賞球数以下である場合、ベース値は100%以上となり、発射球数(アウト球)と同数以上の賞球が得られており、通常に遊技が行われている状態ではないので、除算入力レジスタ131216、131217に数値を格納せず、ベース値を計算しなくてもよい。また、ベース値を計算して、除算結果レジスタA131218から読み出した値が100%以上である場合、除算結果レジスタA131218から読み出した値でベース算出用領域13128を更新しなくてもよい。
In addition, when the total number of out balls is 0, or when the calculated base value is an abnormal value, the base value may not be calculated and the
また、ベース値の異常は、1500%を閾値として判定してもよい。入賞口に対する最大賞球数が15個であるパチンコ機の理論的なベース値の上限値は1500%なので、1500%を超えているベース値は、あり得ない値であり、遊技機が異常であると判定できる。この場合も、ベース値を計算しないくてもよい、又は、除算結果レジスタA131218から読み出した値でベース算出用領域13128を更新しなくてもよい。
Also, the abnormality of the base value may be determined with a threshold of 1500%. Since the theoretical upper limit of the base value of a pachinko machine in which the maximum number of prize balls per winning hole is 15 is 1500%, a base value exceeding 1500% is an impossible value and the gaming machine is abnormal. It can be determined that there is Also in this case, the base value may not be calculated, or the
また、ベース値の異常を判定する閾値は他の値でもよい。パチンコ機の通常の稼働におけるベース値の正常値(例えば、30%~50%)を定めて、当該正常値の範囲外であれ
ば、除算結果レジスタA131218から読み出した値でベース算出用領域13128を更新せず、ベース値の表示を更新しなくてもよい。
Also, the threshold for determining whether the base value is abnormal may be another value. A normal value (for example, 30% to 50%) of the base value in normal operation of the pachinko machine is determined, and if it is outside the range of the normal value, the value read from the division result register A 131218 is used to fill the
以上にベース値を表示しない場合を説明したが、計算されたベース値が異常な値であっても、当該異常なベース値を表示してもよい。 Although the case where the base value is not displayed has been described above, even if the calculated base value is an abnormal value, the abnormal base value may be displayed.
なお、総賞球数と総アウト球数は、図52で後述するように、パチンコ機1が稼働を開始したときからの累計の数値であるが、総賞球数と総アウト球数を同じタイミングで(例えば、所定の賞球数毎、所定のアウト球数毎に)初期化してもよい。
As will be described later with reference to FIG. 52, the total number of prize balls and the total number of out balls are cumulative values from when the
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。 Thereafter, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees.
以上に説明したように、本実施例のパチンコ機は、賞球数を取得する毎に賞球数が異常でないかを判定するので、不正行為を早期に発見できる。これは、通常の遊技中では、一般入賞口2001や始動口2002、2004に、高い確率で相当数の遊技球(例えば発射球数の50%)が入賞することはない。そこで、常に開口している入賞口(一般入賞口2001や始動口2002、2004)への入賞の異常を判定し、報知する。
As described above, the pachinko machine of the present embodiment determines whether the number of prize balls is abnormal each time the number of prize balls is obtained, so that fraud can be detected early. This is because during a normal game, a considerable number of game balls (for example, 50% of the number of shot balls) do not enter the general
また、本実施例のパチンコ機では、賞球数が所定の条件を満たした場合にベース値を計算するので、適切なタイミングで正確なベース値を表示できる。 Further, in the pachinko machine of the present embodiment, the base value is calculated when the number of winning balls satisfies a predetermined condition, so an accurate base value can be displayed at an appropriate timing.
図46、図47に示す例では、賞球数が所定数の達したタイミングでベース値を計算するので、賞球毎にベース値を計算する場合より、ベース値の計算に要する演算量(例えば主制御MPU1311の負荷)を低減できる。なお、新たなベース値が計算されると、計算されたベース値を報知するためのベース報知コマンドが生成されて新たなベース値が報知されるが、それまでの間は従来のベース値が報知される。
In the examples shown in FIGS. 46 and 47, the base value is calculated when the number of prize balls reaches a predetermined number. load on the
図48は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図48に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、アウト球数が所定の条件を満たしたタイミングでベース値を計算するために、アウト球数をアウト球数バッファに記録する(ステップS819)。なお、図48において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 48 is a flowchart showing another example of the base calculation area updating process (step S81). In the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 48, the number of out balls is recorded in the number of out balls buffer in order to calculate the base value at the timing when the number of out balls satisfies a predetermined condition (step S819). In FIG. 48, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation area updating process, and the detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、特賞中以外の賞球数を取得し(ステップS811)、賞球があるかを判定する(ステップS812)。そして、ステップS812における判定の結果、賞球があれば、取得した賞球数を総賞球数に加算する(ステップS814)。すなわち、図48に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、賞球数が計算される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総賞球数が更新される。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded. Then, the number of prize balls other than the special prize is obtained (step S811), and it is determined whether there are prize balls (step S812). Then, as a result of determination in step S812, if there are prize balls, the acquired number of prize balls is added to the total number of prize balls (step S814). That is, in the base calculation region updating process shown in FIG. 48, the total number of prize balls used for calculating the base value is updated each time the number of prize balls is calculated.
そして、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し(ステップS815)、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS816)、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットする(ステップS817)。 Then, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls (step S815), and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated (step S816), and an abnormality notification timer for prize balls is reset (step S817). ).
その後、アウト球数を取得し(ステップS818)。取得したアウト球数をアウト球数バッファに加算する(ステップS819)。 After that, the number of out balls is acquired (step S818). The acquired number of out balls is added to the number of out balls buffer (step S819).
その後、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し(ステップS824)、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球
異常報知を停止する(ステップS825)。
After that, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize ball notification has timed up (step S824). step S825).
また、本実施例のパチンコ機では、所定の賞球数毎にベース値を計算する。このため、例えば、始動口に遊技球が入賞して、先読み演出を発生させることが決定され、保留表示の表示態様を通常とは異なる態様(点滅表示や赤色保留など)で表示する場合に、遊技者は先読みされた保留に対応する特別図柄変動表示ゲームが大当りになることを期待するが、当該特別図柄変動表示ゲームがハズレであると、遊技者は落胆する。このような場合でも、本実施例のように、所定の賞球数毎にベース値を計算すると、前述したような遊技者の落胆を低減できる。これは、賞球発生タイミングよりベース値の計算が遅延するので、始動口に入賞したことによる賞球によって高くなったベース値が報知されるためである。すなわち、始動口への入賞時に先読み演出を実行すると判定された場合でも、当該始動口への入賞時に払い出される賞球数を加算しても上述した所定数(例えば、閾値Th1=100個)に達しない場合にはベース値は更新されない。つまり、遊技者に表示されるベース値は変化していない。しかし、賞球を得られたので、ベース値は上昇するはずである(表示桁数の関係で下位の数値しか変わらず、表示は変わらない場合がある)。このため、前述した先読み演出がはずれであっても、遊技者は、後にベース値が上昇する(すなわち、調子がよい)と思い、興趣の低下が抑制できる。換言すると、先読み演出を実行すると判定された場合でも、賞球バッファ値が所定数(閾値Th1)に達していない場合にはベース値が更新されない。また、先読み演出を実行すると判定された場合で且つ賞球バッファ値が所定数に達した場合には、次に賞球バッファ値が所定数に達するまで、ベース値の計算が遅延させてもよい。 Also, in the pachinko machine of this embodiment, the base value is calculated for each predetermined number of winning balls. For this reason, for example, when it is determined that a game ball wins a prize in the starting hole and a look-ahead effect is generated, and the display mode of the pending display is displayed in a mode different from the normal one (blinking display, red pending, etc.), The player expects that the special symbol variation display game corresponding to the prefetched hold will be a big hit, but the player will be disappointed if the special symbol variation display game fails. Even in such a case, if the base value is calculated for each predetermined number of winning balls as in this embodiment, the disappointment of the player as described above can be reduced. This is because the calculation of the base value is delayed from the timing of generating the prize ball, so that the base value increased by the prize ball that has entered the starting hole is reported. That is, even if it is determined to execute the look-ahead effect at the time of winning the starting hole, even if the number of prize balls paid out at the time of winning the starting hole is added, the above-mentioned predetermined number (for example, threshold value Th1 = 100) If not reached, the base value is not updated. That is, the base value displayed to the player has not changed. However, since the prize ball was obtained, the base value should increase (in some cases, only the lower value changes due to the number of display digits, and the display does not change). Therefore, even if the above-described look-ahead effect is missed, the player thinks that the base value will rise later (that is, the player is in good shape), and the loss of interest can be suppressed. In other words, even if it is determined to execute the look-ahead effect, the base value is not updated if the prize ball buffer value has not reached the predetermined number (threshold value Th1). In addition, when it is determined to execute the look-ahead effect and when the prize ball buffer value reaches a predetermined number, the calculation of the base value may be delayed until the prize ball buffer value reaches the predetermined number next time. .
なお、ベース値の計算を遅延させるか、遅滞なく計算するかを遊技者が選択できるようにしてもよい。例えば、遊技の開始時に操作ボタン220Cによって選択できるようにする。また、抽選によって、ベース値の計算タイミングを決定してもよい。また、先読み演出を行うことが決定されると、ベース値の計算の遅延を報知可能な演出を実行するとよい。なお、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの保留記憶が上限に到達している場合、始動口に入賞しても大当たり抽選は実行されない。この場合でも、始動口への入賞に伴い賞球が払い出されるので、当該賞球数は計数され、ベース値の計算に使用される。なお、特定のエラー時に、始動口や一般入賞口に入賞しても、入賞がなかったと取り扱われて、賞球が払い出されない場合は、賞球数は計数されず、当該入賞によってはベース値は更新されない。
It should be noted that the player may be allowed to select whether to delay the calculation of the base value or to calculate it without delay. For example, at the start of the game, the
図49は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図49に示すベース算出・表示処理では、アウト球数が所定の条件を満たすタイミングでベース値が更新される。なお、図49において、前述したベース算出・表示処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 49 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 49, the base value is updated at the timing when the number of out balls satisfies a predetermined condition. In FIG. 49, the same step numbers are assigned to the same parts as in the base calculation/display processing described above, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、アウト球数バッファに格納されているアウト球数が予め定められている閾値Th2以上であるかを判定する(ステップS895)。アウト球数バッファ値が所定の閾値Th2以上であるかの判定には様々な方法がとり得る。例えば、アウト球数と閾値Th2とを比較したり、アウト球数の格納領域の所定のビットの値で判定してもよい(具体的には、アウト球数の格納領域を8ビットで構成し、最上位ビットが1になればアウト球数が128以上であると判定できる)。またベース算出用領域更新処理(図48)でアウト球数と閾値Th2とを比較した判定結果をフラグに記録し、ベース算出・表示処理(図49)では、当該フラグによって、アウト球数が所定の閾値Th2以上であるかを判定してもよい。 First, it is determined whether or not the number of out balls stored in the number of out balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th2 (step S895). Various methods can be used to determine whether the out-ball number buffer value is greater than or equal to the predetermined threshold value Th2. For example, the number of out-balls may be compared with the threshold value Th2, or the value of a predetermined bit in the storage area for the number of out-balls may be used for determination (specifically, the storage area for the number of out-balls is composed of 8 bits). , if the most significant bit becomes 1, it can be determined that the number of out balls is 128 or more). Also, in the base calculation area updating process (Fig. 48), the determination result of comparing the number of out balls and the threshold value Th2 is recorded in a flag, and in the base calculation/display process (Fig. 49), the number of out balls is specified by the flag. is equal to or greater than a threshold value Th2.
そして、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2より小さければ、ベース値を計算するタイミングではないので、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。 Then, if the out-ball number buffer value is smaller than the threshold Th2, it is not the timing to calculate the base value, so the base calculation/display processing ends.
一方、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2以上であれば、総アウト球数に閾値Th2を加算し(ステップS899)、アウト球数バッファから閾値Th2を減算する(ステップS900)。なお、アウト球数バッファ値と閾値Th2とを比較せずに、所定時間(例えば、1分)毎に、ステップS899およびS900を実行してもよい。 On the other hand, if the out-ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th2, the threshold Th2 is added to the total out-ball number (step S899), and the threshold Th2 is subtracted from the out-ball number buffer (step S900). Steps S899 and S900 may be executed at predetermined time intervals (for example, one minute) without comparing the out-ball number buffer value with the threshold value Th2.
その後、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラーとなるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
Thereafter, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217. Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. If the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
なお、総賞球数と総アウト球数は、パチンコ機1が稼働を開始したときからの累計の数値であるが、総賞球数と総アウト球数を同じタイミングで(例えば、所定の賞球数毎、所定のアウト球数毎に)初期化してもよい。
The total number of awarded balls and the total number of out-balls are cumulative values from when the
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。ベース報知コマンドは、単にベース値を報知するものでも、特定の演出でベース値を報知するものでも、ベース値の異常を報知するものでもよい。 Thereafter, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees. The base notification command may simply notify the base value, may notify the base value with a specific effect, or may notify an abnormality of the base value.
以上に説明したように、本実施例のパチンコ機では、アウト球数(発射球数)が所定数に達する毎にベース値を更新し表示できる。このため、適切なタイミングでベース値を表示できる。また、面白さが追求された遊技機を提供できる。 As described above, in the pachinko machine of this embodiment, the base value can be updated and displayed each time the number of out balls (the number of shot balls) reaches a predetermined number. Therefore, the base value can be displayed at appropriate timing. Also, it is possible to provide a gaming machine that pursues amusement.
また、賞球(入賞検出、払出コマンド送信、払出コマンド到達、賞球払出完了など)の都度、賞球数を総賞球数に加算する。これは、賞球数を加算する際に所定の条件を満たしているか(例えば、賞球に対応するアウト球があるか)を確認すると、ベース値を正しく計算できないおそれがあるためである。例えば、発射が所定時間(1分程度)行われなくても、遊技領域に配設された釘に遊技球が引っ掛かって生じる玉掛り(ぶどう)状態が解消し、遅れて入賞口に遊技球が入賞する場合があるからである。このため、アウト球の有無にかかわらず賞球数を更新することが望ましい。 In addition, each time a prize ball is detected (detection of a prize, transmission of a payout command, arrival of a payout command, completion of payout of prize balls, etc.), the number of prize balls is added to the total number of prize balls. This is because there is a possibility that the base value cannot be calculated correctly if it is checked whether a predetermined condition is satisfied when adding the number of prize balls (for example, whether there is an out ball corresponding to the prize ball). For example, even if the shot is not performed for a predetermined time (about one minute), the slinging (grape) state caused by the game ball being caught on a nail arranged in the game area is resolved, and the game ball is delayed in the winning opening. This is because they may win prizes. Therefore, it is desirable to update the number of prize balls regardless of the presence or absence of out balls.
アウト球数およびアウト球数バッファ値のいずれもが閾値Th2より小さい場合、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2より小さい端数であることを表示したり、アウト球数バッファ値を表示してもよい。 If both the number of out balls and the buffer value of the number of out balls are smaller than the threshold Th2, it may be displayed that the buffer value of the number of out balls is a fraction smaller than the threshold Th2, or the buffer value of the number of out balls may be displayed.
図48、図49に示す例では、アウト球数が所定数の達したタイミングでベース値を計算するので、アウト球が検出される毎にベース値を計算する場合より、ベース値の計算に要する演算量(例えば主制御MPU1311の負荷)を低減できる。なお、新たなベース値が計算されると、計算されたベース値を報知するためのベース報知コマンドが生成されて新たなベース値が報知されるが、それまでの間は従来のベース値が報知される。 In the examples shown in FIGS. 48 and 49, the base value is calculated when the number of out balls reaches a predetermined number. The amount of calculation (for example, the load of the main control MPU 1311) can be reduced. When a new base value is calculated, a base notification command for notifying the calculated base value is generated and the new base value is notified, but until then, the conventional base value is notified. be done.
図50は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図50に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、賞球数とアウト球数のいずれかが所定の条件を満たしたタイミングでベース値を計算するために、賞球数を賞球数バッファに記録し、アウト球数をアウト球数バッファに記録する。なお、図50において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 50 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation area updating process (step S81). The base calculation area update process shown in FIG. 50 records the number of prize balls in the number of prize balls buffer in order to calculate the base value at the timing when either the number of prize balls or the number of out balls satisfies a predetermined condition. , records the number of out pitches in the number of out pitches buffer. In FIG. 50, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation area updating process, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、特賞中以外の賞球数を取得し(ステップS811)、賞球があるかを判定する(ステップS812)。そして、賞球があれば、取得した賞球数を賞球数バッファに加算する(ステップS813)。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded. Then, the number of prize balls other than the special prize is obtained (step S811), and it is determined whether there are prize balls (step S812). Then, if there are prize balls, the acquired number of prize balls is added to the number of prize balls buffer (step S813).
そして、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し(ステップS815)、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS816)、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットする(ステップS817)。 Then, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls (step S815), and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated (step S816), and an abnormality notification timer for prize balls is reset (step S817). ).
その後、アウト球数を取得し(ステップS818)、取得したアウト球数をアウト球数バッファに加算する(ステップS819)。 After that, the number of out balls is acquired (step S818), and the acquired number of out balls is added to the number of out balls buffer (step S819).
その後、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し(ステップS824)、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止する(ステップS825)。 After that, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize notification has timed up (step S824), and when the timer for abnormal notification of prize ball has timed up, a command to stop the abnormal notification of prize ball is generated, and the abnormal notification of prize ball is stopped ( step S825).
図51は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図51に示すベース算出・表示処理では、賞球数とアウト球数のいずれかが所定の条件を満たすタイミングでベース値が更新される。なお、図51において、前述したベース算出・表示処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 51 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display process shown in FIG. 51, the base value is updated when either the number of winning balls or the number of out balls satisfies a predetermined condition. In FIG. 51, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the base calculation/display processing described above, and the detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、賞球数バッファに格納されている賞球数が予め定められている閾値Th1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS890)。賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1より小さければ、総賞球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS895に進む。一方、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上であれば、総賞球数に閾値Th1を加算し(ステップS891)、賞球数バッファから閾値Th1を減算する(ステップS892)。そして、総アウト球数にアウト球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS893)、アウト球数バッファを0にする(ステップS894)。なお、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較せずに、所定回数の入賞毎や所定時間毎に、ステップS891からS894を実行してもよい。 First, it is determined whether or not the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th1 (step S890). If the buffer value for the number of prize balls is smaller than the threshold value Th1, it is not time to update the total number of prize balls, so the process proceeds to step S895. On the other hand, if the winning ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1, the threshold Th1 is added to the total winning ball number (step S891), and the threshold Th1 is subtracted from the winning ball number buffer (step S892). Then, the out-ball number buffer value is added to the total out-ball number (step S893), and the out-ball number buffer is set to 0 (step S894). Steps S891 to S894 may be executed every predetermined number of wins or every predetermined time without comparing the buffer value for the number of winning balls with the threshold value Th1.
その後、アウト球数バッファに格納されているアウト球数が予め定められている閾値Th2以上であるかを判定する(ステップS895)。アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2より小さければ、総アウト球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS902に進む。一方、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2以上であれば、総賞球数に賞球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS897)、賞球数バッファを0にする(ステップS898)。そして、総アウト球数に閾値Th2を加算し(ステップS899)、アウト球数バッファから閾値Th2を減算する(ステップS900)。 After that, it is determined whether or not the number of out balls stored in the number of out balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th2 (step S895). If the buffer value for the number of out balls is smaller than the threshold Th2, it is not time to update the total number of out balls, so the process proceeds to step S902. On the other hand, if the out ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th2, the prize ball number buffer value is added to the total prize ball number (step S897), and the prize ball number buffer is set to 0 (step S898). Then, the threshold Th2 is added to the total number of out balls (step S899), and the threshold Th2 is subtracted from the buffer for the number of out balls (step S900).
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS902)。総アウト球数が0であれば、ベース値を計算できないので、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラーとなるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S902). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base calculation/display process ends. On the other hand, if the total number of out balls is not 0, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217. Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. If the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。ベース報知コマンドは、単にベース値を報知するものでも、ベース値の異常を報知するものでもよい。なお、ベース値を計算する毎にベース報知コマンドを生成しても、ベース値を計算してもベース報知コマンドを生成しなくてもよい。 Thereafter, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees. The base notification command may simply notify the base value or may notify an abnormality of the base value. Note that the base notification command may be generated each time the base value is calculated, or the base notification command may not be generated even if the base value is calculated.
図51に示すベース算出・表示処理では、総賞球数や総アウト球数が更新されなくても、毎回ベース値を計算している。すなわち、総賞球数および総アウト球数が更新されなければ、ベース値として同じ値が計算され、ベース値は同じ値を維持する。一方、総賞球数または総アウト球数が更新されれば、ベース値は違う値に更新される。 In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 51, the base value is calculated every time even if the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls are not updated. That is, if the total number of won balls and the total number of out balls are not updated, the same value is calculated as the base value, and the base value remains the same value. On the other hand, if the total number of awarded balls or the total number of out-balls is updated, the base value is updated to a different value.
図52は、ベース算出用領域13128における各データを格納するためのワークエリアの具体的な構造を示す図である。
FIG. 52 is a diagram showing the specific structure of the work area for storing each data in the
ベース算出用領域13128の総賞球数および総アウト球数のデータは、主制御MPU1311が実行するベース算出用領域更新処理およびベース算出・表示処理(図39、図46、図47、図48、図49、図51など)で書き込まれ、ベース算出・表示処理(図40、図47、図49、図51など)で読み出される。また、ベース算出用領域13128の賞球数バッファおよびアウト球数バッファのデータは、主制御MPU1311が実行するベース算出用領域更新処理(図46、図48、図50など)で書き込まれ、ベース算出・表示処理(図47、図49、図51など)で読み出される。このため、ベース算出用領域更新処理およびベース算出・表示処理をタイマ割込み処理(遊技制御プログラム)と分けて構成でき、異なる仕様の遊技機でも役物比率算出・表示処理のためのプログラムを共通化できる。
The data of the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls in the
図52(A)は、最も簡単な方法のワークエリアの構造の一例を示す。図52(A)に示すワークエリアの構造では、賞球数バッファ、総賞球数、アウト球数バッファ、入賞球数バッファ、特定入賞球数バッファ、総アウト球数及びベースを格納する。賞球数バッファは、特賞中以外に遊技者に払い出された賞球数を一時的に格納し、賞球数が所定の条件を満たした場合(例えば、所定数の賞球ごと)にベースを計算するために用いられる。総賞球数は、特賞中以外に遊技者に払い出された全賞球数である。アウト球数バッファは、特賞中以外に遊技者が発射した遊技球数であり、アウト球数が所定の条件を満たした場合(例えば、所定数のアウト球ごと)にベースを計算するために用いられる。入賞球数バッファは、一般入賞口や始動口に入賞した球数を一時的に格納する。特定入賞球数バッファは、特定の一般入賞口や始動口に入賞した球数を一時的に格納する。入賞球数バッファは、アウト口通過球数によってアウト球数を計数する場合(図55、図56)に使用される。特定入賞球数バッファは、特定一般入賞口への入賞球数でアウト球数を補正する場合(図71、図72)に使用される。総アウト球数は、特賞中以外に遊技者が発射した全遊技球数である。ベースは、総賞球数÷総アウト球数×100で計算され、パーセンテージで表された数値であり、ベース算出・表示処理のステップS903で計算される。 FIG. 52(A) shows an example of the structure of the work area of the simplest method. In the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 52(A), winning ball number buffer, total winning ball number, out ball number buffer, winning ball number buffer, specific winning ball number buffer, total out ball number and base are stored. The number of prize balls buffer temporarily stores the number of prize balls paid out to the player other than during the special prize, and when the number of prize balls meets a predetermined condition (for example, every predetermined number of prize balls) is used to calculate The total number of prize balls is the total number of prize balls paid out to the player except during the special prize. The number of out balls buffer is the number of game balls shot by the player other than during the special prize, and is used to calculate the base when the number of out balls meets a predetermined condition (for example, every predetermined number of out balls). be done. The winning ball number buffer temporarily stores the number of winning balls in the general winning opening and the starting opening. The specific winning ball number buffer temporarily stores the number of balls that have won a specific general winning hole or starting hole. The winning ball number buffer is used when counting the number of out balls by the number of balls passing through the out hole (FIGS. 55 and 56). The specific winning ball number buffer is used when correcting the number of out balls with the number of winning balls into a specific general winning hole (FIGS. 71 and 72). The total number of out balls is the total number of game balls shot by the player except during the special prize. The base is calculated by dividing the total number of winning balls/total number of out balls×100, and is a numerical value expressed as a percentage, and is calculated in step S903 of the base calculation/display processing.
図52(A)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、総賞球数及び総アウト球数は、後述する図52(B)の総累計の各領域に相当し、各々3又は4バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215又は4294967295までの数値を記憶できる。これらのデータはデータに異常が生じない限り消去されないことから、長期間のデータを格納できるように大きな記憶領域を用意する。また、ベースは、後述する図52(B)のベースの総累計に相当する1バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で255までの数値を記憶できる。なお、ベース値が小数で記録できる容量を割り当ててもよい。 Of the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 52(A), the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls correspond to each area of the total accumulation shown in FIG. 52(B), which will be described later. and can store values up to 16777215 or 4294967295 in decimal. Since these data will not be erased unless an abnormality occurs in the data, a large storage area is prepared so that long-term data can be stored. The base is a 1-byte storage area corresponding to the total sum of bases in FIG. 52(B), which will be described later. It should be noted that a capacity that can be recorded with a decimal base value may be allocated.
図52(B)は、リングバッファを用いたワークエリアの構造の別の一例を示す。図52(B)に示すワークエリアの構造では、賞球数バッファ、総賞球数、アウト球数バッフ
ァ、入賞球数バッファ、特定入賞球数バッファ、総アウト球数及びベースを格納する。各データ項目は、図52(A)における説明と同じである。総賞球数および総アウト球数の記憶領域は、所定数の賞球毎(または、所定数のアウト球数毎、所定時間毎)にn個の記憶領域(例えば、賞球6000個毎にn=10個の記憶領域)を持つリングバッファによって構成されており、賞球数が所定数(6000個)になると全てのデータの書き込みポインタが移動して、データが更新される記憶領域が変わる。そして、n番目の記憶領域に所定数の賞球分のデータが格納された後、書き込みポインタは1番目の記憶領域に移動し、1番目の記憶領域にデータを格納する。なお、賞球数以外のデータ(アウト球数、所定時間など)が所定数となった場合に、書き込みポインタを移動してもよい。
FIG. 52B shows another example of a work area structure using a ring buffer. The structure of the work area shown in FIG. 52(B) stores winning balls buffer, total winning balls, out balls buffer, winning balls buffer, specific winning balls buffer, total out balls and base. Each data item is the same as described in FIG. 52(A). The storage areas for the total number of prize balls and the total number of out balls are stored in n storage areas for each predetermined number of prize balls (or for each predetermined number of out balls or for each predetermined time) (for example, each 6000 prize balls). n = 10 storage areas), and when the number of prize balls reaches a predetermined number (6000), the write pointer for all data moves and the storage area where the data is updated changes. . After the data for the predetermined number of prize balls is stored in the n-th storage area, the write pointer moves to the first storage area and stores the data in the first storage area. Note that the write pointer may be moved when data other than the number of winning balls (the number of out balls, a predetermined time period, etc.) reaches a predetermined number.
なお、リングバッファの書き込みポインタ及び読み出しポインタは全てのデータに共通であり、所定の賞球数毎に全てのデータ列の書き込みポインタが移動する。また、書き込みポインタの移動に伴い、読み出しポインタも移動する。読み出しポインタは、書き込みポインタより一つ前の記憶領域を指す。これは、賞球6000個分の直近のデータを用いてベース値を計算するためである。 The write pointer and read pointer of the ring buffer are common to all data, and the write pointers of all data strings are moved for each predetermined number of winning balls. Further, the read pointer also moves along with the movement of the write pointer. The read pointer points to the storage area one before the write pointer. This is for calculating the base value using the most recent data for 6000 prize balls.
総賞球数及び総アウト球数の累計は、リングバッファのn個の記憶領域に格納されているデータの累計値であり、ベースの累計の値は総賞球数及び総アウト球数の累計値から算出された値であり、リングバッファが一巡して、新たなデータを書き込むためにリングバッファの一つの記憶領域がクリアされると、当該クリアされた領域のデータを除外して累計値が再計算される。各データの総累計は、過去に収集した全データの累計値であり、当該累計値から計算されたベースの総累計の値は各データの総累計値から算出された値であり、リングバッファが一巡して、新たなデータを書き込むためにリングバッファの一つの記憶領域がクリアされても、当該クリアされた領域の元のデータを含めて総累計値が計算される。 The total number of prize balls and the total number of out balls is the accumulated value of the data stored in the n storage areas of the ring buffer, and the base total value is the total of the total number of prize balls and the total number of out balls. is a value calculated from the values of recalculated. The total cumulative value of each data is the cumulative value of all data collected in the past, and the base total cumulative value calculated from the relevant cumulative value is the value calculated from the total cumulative value of each data, and the ring buffer is Even if one storage area of the ring buffer is cleared in order to write new data, the total cumulative value is calculated including the original data of the cleared area.
図52(B)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、リングバッファ内の総賞球数、総アウト球数は、各々2バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で65535までの数値を記憶できる。累計は賞球6000個×n(n=10の場合は60000個の賞球)分のデータの合計であることから、大きな記憶領域を用意する。総賞球数および総アウト球数の累計は、各々3又は4バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215又は4294967295までの数値を記憶できる。総累計はデータに異常が生じない限り消去されないことから、長期間のデータを格納できるように、さらに大きな記憶領域を用意する。また、ベースの累計及び総累計は、各々1バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で255までの数値を記憶できる。なお、ベース値が小数で記録できる容量を割り当ててもよい。 In the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 52(B), the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls in the ring buffer are storage areas of 2 bytes each, and can store numerical values up to 65535 in decimal. Since the cumulative total is the sum of the data for 6000 prize balls.times.n (60000 prize balls when n=10), a large storage area is prepared. The total number of winning balls and the total number of out-balls are storage areas of 3 or 4 bytes, respectively, and can store numerical values up to 16777215 or 4294967295 in decimal. Since the total sum is not deleted unless an abnormality occurs in the data, a larger storage area is prepared so that long-term data can be stored. Also, each of the base total and the total total is a 1-byte storage area, and can store numerical values up to 255 in decimal. It should be noted that a capacity that can be recorded with a decimal base value may be allocated.
図52(A)に示すデータ構造では、格納されているデータは消去されないので、所定期間(例えば、1日、1週間、1月など)毎にベース算出用領域13128のデータを消去してもよい。同様に、図52(B)の総累計を所定期間毎に消去してもよい。
In the data structure shown in FIG. 52(A), stored data is not erased, so even if the data in the
また、ベース算出用領域13128のデータや、算出されたベース値が異常値である場合、当該異常値を消去してもよい。当該異常値だけでなく、ベース算出用領域13128の全データを消去してもよい。また、ベース算出用領域13128のデータや、算出されたベース値が異常であることを報知してもよい。また、チェックコードを用いてバックアップ領域のデータを検査し、正常なバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製後に、再度ベース値を計算してもよい。
Also, if the data in the
[9-4.ベース値の表示]
前述したように計算されたベース値は、パチンコ機1の電源が投入されている間は表示し続けてもよいが、本体枠4が閉鎖され遊技が可能な状態では、ベース表示器1317を
視認できないので、7セグメントLED13172を消灯し、遊技機の消費電力を低減してもよい。当然ながら、7セグメントLED13172の消灯中でも、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)及びベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)は実行される。
[9-4. Base value display]
The base value calculated as described above may continue to be displayed while the
また、ベース表示器1317は、ベース値を常に表示しても、表示スイッチ1318の操作によってベース値を表示してもよい。例えば、押ボタンスイッチである表示スイッチ1318を押すと、ベース値の表示を開始し、所定時間表示した後に表示を消す。なお、本体枠4が外枠2から開放したことを本体枠開放スイッチ(図示省略)が検出中に表示スイッチ1318が操作されると、ベース表示器1317にベース値を表示してもよい。すなわち、本体枠4の開放中でなければ表示スイッチ1318が操作されても、ベース表示器1317は役物比率を表示しない。
Also, the
また、本体枠4が開放された場合には、ベース表示器1317が正常に動作していることを確認できるように、全桁に所定の表示をするとよい。例えば、図36(B)に示すように全桁に「-」を表示したり、全セグメントを点灯してもよい。
Further, when the
そして本体枠4が閉鎖されると、ベース表示器1317の正常動作を確認できる所定の表示を行い(図36(E))、所定時間(例えば、30秒)経過後、7セグメントLED13172を消灯し、遊技機の消費電力を低減するとよい。このベース非表示状態は、初期設定完了後(図36(B))と同じ態様であるが、異なる態様でもよく、表示されるベース値と区別可能な態様であればよい。
Then, when the
ベース表示器1317を機能表示ユニット1400で兼用してもよい。機能表示ユニット1400は通常は主制御基板1310からの制御信号に基づいて遊技状況を表示するが、本体枠4が外枠2から開放したことを本体枠開放スイッチ(図示省略)が検出すると、主制御基板1310は、機能表示ユニット1400がベース値を表示するように表示を切り替える。本体枠4の開放によって機能表示ユニット1400の表示を切り替えても、遊技の進行は継続するとよい。遊技の進行を継続することによって、本体枠4が閉鎖するとベース表示から遊技状態の表示に迅速に切り替えることができる。例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中に本体枠4が開放するとベース値が表示されるが、変動時間の経過前に本体枠4が閉鎖されると、残りの時間分の変動表示を行うことができる。機能表示ユニット1400に表示される特別図柄はメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される装飾図柄と同期しているので、機能表示ユニット1400の特別図柄変動表示が停止するタイミングで装飾図柄が停止する。このため、機能表示ユニット1400がベース値を表示しても、遊技者に違和感を与えないように構成できる。
The
また、本体枠4の閉鎖中でも、計算されたベース値(前述した実施例では、役物比率)をベース表示器(役物比率表示器)1317に表示してもよい。このようにすると、本体枠4を開けずにベース値(役物比率)を確認できるので、遊技機の稼働の低下を抑制できる。また、本体枠4が開放しているかの判定が不要である。また、パチンコ機が両側に設置される島設備では、片側のパチンコ機の本体枠4を開放すると、反対側に設置されたパチンコ機の裏面を見ることができる。このような遊技機において、片側のパチンコ機の本体枠4を開放することによって、背中合わせに設置された2台のパチンコ機のベース(役物比率)を確認できる。また、本体枠4の閉鎖中でもベース値を表示する場合、遊技者が認識できる形態で(例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出を表示する表示装置や枠に取り付けられた表示装置などに)ベース値を表示するとよい。ベース値は、パチンコ機の調子を表すバロメータとして利用可能であり、遊技者が見る価値があるからである。主制御基板1310でベース値を計算する場合にはベース値を表示するための信号を主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510に送信すればよい。払出制御基板951でベース値を
計算する場合にはベース値を表示するための信号を払出制御基板951から周辺制御基板1510に送信すればよい。また、ベース値を表示するための信号を中継基板を介して送信してもよい。
Further, even when the
また、本実施例のパチンコ機では、省エネモードに移行してもベース表示器1317の光量(輝度)を変化させない。省エネモード中にベース表示器1317の光量を低下させると、開店時間以外にパチンコ機を調整する場合にベース表示器1317によるベース値の確認が困難になるからである。
Further, the pachinko machine of this embodiment does not change the amount of light (brightness) of the
具体的には、本実施例の遊技機は、いずれの入賞口にも遊技球が入賞せず、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの保留記憶が消化された後、所定時間が経過すると、待機状態になる。待機状態において、周辺制御部1511は、いわゆる通常変動で出力するBGMを継続して出力する。さらに、待機状態で所定時間(例えば、30秒)が経過するとデモ状態に移行する。デモ状態では、遊技機のモチーフが分かる動画を再生したり、遊技機の説明が行われたりする。さらに、デモ状態で所定時間(例えば、30秒)が経過すると省エネモードに移行する(なお、デモ状態と省エネモードとを区別しなくてもよい)。省エネモードでは、電力消費を抑制するために、周辺制御部1511が制御する液晶表示装置1600、3114、244や各種ランプの光量を低減する。しかし、主制御基板1310が制御する表示装置(機能表示ユニット1400やベース表示器1317)の消費電力は、パチンコ機全体の消費電力と比べて小さいので、これらの表示装置の光量を低減しなくてもよい。また、機能表示ユニット1400の光量を低減しなければ、空き台で遊技しようとする遊技者が前回の抽選の結果を容易に視認できる。
Specifically, the gaming machine of the present embodiment enters a standby state when a predetermined time elapses after the game ball does not enter any of the winning holes and the reserved memory of the special symbol variation display game is consumed. . In the standby state, the
また、始動口や一般入賞口に遊技球が入賞しなくても、遊技球が遊技領域に向けて発射されアウト球が検出されると、表示されているベース値が再計算され更新される可能性がある。遊技球が発射されアウト球数が増加しても賞球数が増えなければ、計算されるベース値は低下するが、リベンジに燃える遊技者もいる。 In addition, even if a game ball does not enter the starting gate or general winning gate, when a game ball is launched toward the game area and an out ball is detected, the displayed base value can be recalculated and updated. have a nature. If game balls are shot and the number of out balls increases, but the number of prize balls does not increase, the calculated base value will decrease, but some players will take revenge.
このような遊技者に、ベース表示器1317を兼ねた機能表示ユニット1400で遊技の状態を報知することによって、遊技の興趣を再興できる。すなわち、デモモードや省エネモードに移行しても、ベース値が表示される表示器の表示態様をデモモードや省エネモードに移行する前の光量を維持するか、光量を上昇させて、遊技者がベース値をきちんと確認できるようにするとよい。
By informing such a player of the state of the game with the
このようにベース値が表示される表示器の光量の維持または上昇について説明したが、消費エネルギーの低減という観点を重視して、ベース値が表示される表示器の光量を下降または消灯してもよい。例えば、省エネモード中に所定の操作(発射を強制的に停止させる発射停止ボタン、現出される演出に変化を与える操作ボタン、RAMの内容をクリアするRAMクリアボタン、遊技機への電力の供給の有無を切り替える供給調整ボタンなどの遊技機に備わる操作手段の操作)を検出すると、ベース値が表示される表示器の光量を低減するとよい。さらに、省エネモード中に限らず、前述した所定の操作を行うと、省エネモード中に消費電力を低減するランプ等とベース値が表示される表示器との両方の光量を低減したり消灯してもよい。 In this way, maintaining or increasing the light intensity of the display that displays the base value has been explained, but from the viewpoint of reducing energy consumption, even if the light intensity of the display that displays the base value is decreased or extinguished good. For example, during the energy saving mode, predetermined operations (fire stop button to forcibly stop firing, operation button to change the effect that appears, RAM clear button to clear the contents of RAM, power supply to the game machine It is preferable to reduce the amount of light of the display on which the base value is displayed when the operation of the operation means provided in the gaming machine, such as a supply adjustment button for switching between the presence and absence of the base value, is detected. Furthermore, not only during the energy saving mode, if the above-mentioned predetermined operation is performed, the light amount of both the lamp that reduces power consumption and the display that displays the base value will be reduced or turned off during the energy saving mode. good too.
ランプ等とベース値が表示される表示器との両方の光量を低減や消灯する場合、ベース値が表示される表示器より先に、省エネモード中に消費電力を低減するランプ等の光量を低減したり消灯してもよく、この場合、消費電力が大きいランプ等の光量を先に低減して消費電力を大きく減少させる効果を奏する。また、ベース値が表示される表示器をランプ等より先に、ベース値が表示される表示器の光量を低減したり消灯してもよく、この場合、省エネモード中でも遊技機の華やかさを維持する効果を奏する。また、省エネモード中
に消費電力を低減するランプ等とベース値が表示される表示器とを同時に低減したり消灯してもよく、この場合、消費電力の低減量を大きくでき、省エネ効果が高い。なお、これらの説明における時間の前後(「先に」や「同時に」の意味)は、内部的な処理のタイミングの順序や、遊技者からの見た目の順序も含む。
When reducing or turning off the light intensity of both the lamp, etc. and the display that displays the base value, the light intensity of the lamp, etc. that reduces power consumption during energy saving mode is reduced before the display that displays the base value. In this case, the light amount of a lamp or the like, which consumes a large amount of power, is first reduced, thereby greatly reducing the power consumption. In addition, the light amount of the display on which the base value is displayed may be reduced or turned off prior to the lamp or the like. It works. In addition, the lamp or the like that reduces power consumption and the display that displays the base value may be reduced or turned off at the same time during the energy saving mode. . Note that the terms before and after time (meaning "before" or "at the same time") in these descriptions include the order of internal processing timings and the order of appearance from the player's point of view.
また、ベース値の表示態様を複数段階に設定し、各段階の表示態様を変えてもよい。具体的には、表示されるベース値が、30%以上、25%以上30%未満、20%以上25%未満、15%以上20%未満、10%以上15%未満、10%未満のように複数の段階に分ける。ベース値を表示する表示器をマルチカラーLEDで構成して、各段階で白、青、黄のように発光色を変えて表示してもよい。また、ベース値を表示する表示器を液晶表示装置で構成して、各段階で「調子いいね」「調子が下がってきてるよ」「やばいんじゃない」「ある意味凄いね」など、ベース値が低いときには自虐的なコメントを表示してもよい。さらに、ベース値を表示する表示器の表示態様は変えずに、装飾図柄が表示されるメイン液晶表示装置1600に前述したようなコメントを付加する演出を実行してもよい。
Moreover, the display mode of the base value may be set in multiple stages, and the display mode of each stage may be changed. Specifically, the displayed base value is 30% or more, 25% or more and less than 30%, 20% or more and less than 25%, 15% or more and less than 20%, 10% or more and less than 15%, or less than 10%. divided into multiple stages. The indicator for displaying the base value may be composed of a multi-color LED, and may be displayed by changing the emission color such as white, blue, and yellow at each stage. In addition, the display unit that displays the base value is configured with a liquid crystal display device, and at each stage, the base value is low Occasionally it may display self-deprecating comments. Further, an effect of adding a comment as described above may be performed on the main liquid
[9-5.アウト口通過球数を用いるベース値の計算]
次に、図53から図56を用いて、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)、ベース算出表示処理(ステップS89)のさらなるバリエーションを説明する。図54から図56で説明する処理では、入賞球数とアウト口通過球数を用いてアウト球数を計算し、ベース値を計算する。各バリエーションにおけるベース値の計算タイミングの概要は以下の通りである。
・図54及び図40:タイマ割込み周期ごとに毎回ベース値を計算
・図55及び図56:所定賞球数ごとおよび所定アウト球数ごとにベース値を計算
なお、所定賞球数ごとにベース値を計算するパターン、所定アウト球数ごとにベース値を計算するパターンの説明は省略するが、図54から図56を組み合わせることによって実現できる。
[9-5. Calculation of base value using the number of balls passing through the out mouth]
Next, further variations of the base calculation region updating process (step S81) and the base calculation display process (step S89) will be described with reference to FIGS. 53 to 56. FIG. In the processing described in FIGS. 54 to 56, the number of out balls is calculated using the number of winning balls and the number of balls passing through the out port, and the base value is calculated. The outline of the calculation timing of the base value in each variation is as follows.
・Figures 54 and 40: Base value is calculated every timer interrupt cycle ・Figure 55 and Figure 56: Base value is calculated for each predetermined number of prize balls and for each predetermined number of out balls The base value is calculated for each predetermined number of prize balls and the pattern for calculating the base value for each predetermined number of out-balls will be omitted, but they can be realized by combining FIGS.
アウト球を、アウト口1111付近に設けたアウト口通過球センサ1021で検出すると、正確なアウト球数を計数できない問題がある。これは、遊技領域5aに向けて打ち出された遊技球は、アウト口1111の他、一般入賞口2001、始動口2002、大入賞口2005、2006を経由して遊技領域5aから流出する。このため、アウト口通過球センサ1021では、遊技領域5aに向けて発射された遊技球の数を正確に計数できない。そこで、本実施例のパチンコ機では、入賞球数とアウト口通過球数を用いて正確にアウト球数を計算し、ベース値を正確に計算する。
If out balls are detected by the
図53は、遊技盤の別の一例を示す正面図である。 FIG. 53 is a front view showing another example of the game board.
本実施例のパチンコ機の遊技盤は、図10に示す遊技盤と概ね同じ構造であるが、遊技領域5aの下部に設けられアウト口1111を通過して遊技領域5aから流出する遊技球(アウト口通過球数)を検出するアウト口通過球センサ1021を設ける。アウト口通過球センサ1021は、遊技者がアウト口1111を通して見える位置に設置するとよい。遊技者がアウト口1111を通して見える位置にアウト口通過球センサ1021を設置することによって、アウト球が計数されていること、すなわち、ベースが計算されていることを意識させることができる。
The game board of the pachinko machine of this embodiment has substantially the same structure as the game board shown in FIG. Out mouth passing
また、アウト口通過球センサ1021を、遊技領域5aからアウト口1111を通過して流下する遊技球が整列する集合樋など、遊技者から見ない位置に設置してもよい。遊技者が視認不可能な位置に設置すると、アウト球の計数を遊技者に意識させなくてよい。また、アウト口通過球センサ1021をアウト口1111の奥側に設けることによって、液
晶表示装置や役物(可動体)を配置する場所を十分に確保でき、遊技盤5の設計の自由度を向上できる。また、遊技球の二重カウントを防止するため、アウト口通過球センサ1021を通過した遊技球が跳ね返らないように、アウト口通過球センサ1021を通過した遊技球が転動する転動面に傾斜をつけたり、曲面にするとよい。
In addition, the out-hole passing
図54は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図54に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、タイマ割込み周期ごとにアウト口通過球数を用いてベース値を計算するために、賞球数、アウト口通過球数および入賞球数を取得する。なお、図54において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 54 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation area updating process (step S81). The base calculation area update process shown in FIG. 54 acquires the number of prize balls, the number of balls passed through the out hole, and the number of winning balls in order to calculate the base value using the number of balls passed through the out hole at each timer interrupt cycle. In FIG. 54, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation area updating process, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、特賞中以外の賞球数を取得し(ステップS811)、取得した賞球数を総賞球数に加算する(ステップS814)。すなわち、図54に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、賞球数が計算される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総賞球数が更新される。なお、賞球があるかを判定し、賞球がなければ、総賞球数を更新する処理をスキップしてもよい。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded. Then, the number of prize balls other than the special prize is obtained (step S811), and the obtained number of prize balls is added to the total number of prize balls (step S814). That is, in the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 54, the total number of prize balls used to calculate the base value is updated each time the number of prize balls is calculated. It should be noted that it is possible to determine whether there are prize balls or not, and if there are no prize balls, the process of updating the total number of prize balls may be skipped.
その後、アウト口通過球数を取得し(ステップS818)、入賞球数を取得する(ステップS820)。そして、アウト口通過球数と入賞球数の和を総アウト球数に加算する(ステップS822)。すなわち、図54に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、アウト球や入賞球が検出される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総アウト球数が更新される。 After that, the number of balls passing through the outlet is obtained (step S818), and the number of winning balls is obtained (step S820). Then, the sum of the number of balls passing through the out hole and the number of winning balls is added to the total number of out balls (step S822). That is, in the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 54, the total number of out balls used for calculating the base value is updated each time an out ball or winning ball is detected.
なお、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理(図46)のステップS815からS817のように、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットしてもよい。さらに、図46のステップS824からS825のように、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止してもよい。 As in steps S815 to S817 of the base calculation area updating process (FIG. 46) described above, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated. , You may reset the timer for prize ball abnormality notification. Furthermore, as in steps S824 to S825 in FIG. 46, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize ball notification has timed up. You may stop ball abnormality information.
図54に示すベース算出用領域更新処理で総賞球数および総アウト球数を記録した後、図40に示すベース算出・表示処理によってベース値を計算できる。 After recording the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls in the base calculation area update process shown in FIG. 54, the base value can be calculated by the base calculation/display process shown in FIG.
図55は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図55に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、賞球数とアウト球数のいずれかが所定の条件を満たしたタイミングでベース値を計算するために、賞球数を賞球数バッファに記録し、アウト口通過球数をアウト球数バッファに記録し、入賞球数を入賞球数バッファに記録する。なお、図55において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 55 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation area updating process (step S81). The base calculation area update process shown in FIG. 55 records the number of prize balls in the number of prize balls buffer in order to calculate the base value at the timing when either the number of prize balls or the number of out balls satisfies a predetermined condition. , the number of balls passing through the out-hole is recorded in the out-ball number buffer, and the number of prize-winning balls is recorded in the prize-winning ball number buffer. In FIG. 55, the same step numbers are assigned to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation area updating process, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、特賞中以外の賞球数を取得し(ステップS811)、賞球があるかを判定する(ステップS812)。そして、賞球があれば、取得した賞球数を賞球数バッファに加算する(ステップS813)。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded. Then, the number of prize balls other than the special prize is obtained (step S811), and it is determined whether there are prize balls (step S812). Then, if there are prize balls, the acquired number of prize balls is added to the number of prize balls buffer (step S813).
そして、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し(ステップS815)、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS816)、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットする(ステップS817)。 Then, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls (step S815), and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated (step S816), and an abnormality notification timer for prize balls is reset (step S817). ).
その後、アウト口通過球数を取得し(ステップS818)、取得したアウト口通過球数をアウト球数バッファに加算する(ステップS819)。そして、入賞球数を取得し(ステップS820)、取得した入賞球数を入賞球数バッファに加算する(ステップS821)。 After that, the number of balls passing through the out hole is acquired (step S818), and the acquired number of balls passing through the out hole is added to the out ball number buffer (step S819). Then, the number of winning balls is acquired (step S820), and the acquired number of winning balls is added to the number of winning balls buffer (step S821).
その後、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し(ステップS824)、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止する(ステップS825)。 After that, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize notification has timed up (step S824), and when the timer for abnormal notification of prize ball has timed up, a command to stop the abnormal notification of prize ball is generated, and the abnormal notification of prize ball is stopped ( step S825).
図54に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、取得したアウト口通過球数と入賞球数の和を一つの記憶領域(総アウト球数)に加算し、図55に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、取得したアウト口通過球数と入賞球数を、別の記憶領域(アウト球数バッファ、入賞球数バッファ)に加算する。このように、アウト口通過球数と入賞球数を一つの記憶領域に記録しても、別の記憶領域に記録してもよい。 In the base calculation area update process shown in FIG. 54, the sum of the acquired number of balls passing through the out hole and the number of winning balls is added to one storage area (total number of out balls), and the base calculation area update process shown in FIG. Then, the obtained number of balls passing through the out-hole and the number of winning balls are added to separate storage areas (out-ball number buffer, winning ball number buffer). In this way, the number of balls passing through the outlet and the number of winning balls may be recorded in one storage area or in separate storage areas.
また、図55に示すベース算出用領域更新処理で、取得したアウト口通過球数と入賞球数を別の記憶領域に記録する場合、入賞口に入賞したときにアウト球数が1増えるので、アウト口通過球数の計数と入賞球数の計数が同時に(一つのタイマ割込み処理内で)実行されるが、アウト球数バッファと入賞球数バッファの両方を更新した後にベース値を計算する。その際、一つのタイマ割込み処理内でアウト球数バッファと入賞球数バッファの両方を更新できない場合に、アウト口通過球数を優先して計数するか、入賞球数を優先して計数するかを、適宜抽選によって決定するのではなく、予め定めておいたほうがよい。その際、賞球に関する処理を他の処理より優先すると、賞球の払出処理を迅速に実行できるが、遊技機の仕様に応じて適宜決定すればよい。 Also, in the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 55, if the acquired number of balls passing through the out hole and the number of winning balls are recorded in separate storage areas, the number of out balls increases by 1 when the winning hole is won. Counting the number of balls passing through the out hole and the number of winning balls are simultaneously executed (within one timer interrupt processing), but the base value is calculated after updating both the out ball number buffer and the winning ball number buffer. At that time, if both the buffer for the number of out balls and the buffer for the number of winning balls cannot be updated within one timer interrupt processing, whether the number of balls passing through the out port is preferentially counted or the number of winning balls is preferentially counted. should be determined in advance rather than being determined by lottery. In this case, if the process related to the prize balls is prioritized over other processes, the payout process of the prize balls can be executed quickly.
図56は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図56に示すベース算出・表示処理では、賞球数とアウト球数のいずれかが所定の条件を満たすタイミングでベース値が更新される。なお、図56において、前述したベース算出・表示処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 56 is a flowchart showing another example of the base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display process shown in FIG. 56, the base value is updated when either the number of winning balls or the number of out balls satisfies a predetermined condition. In FIG. 56, the same step numbers are assigned to the same parts as in the base calculation/display processing described above, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、賞球数バッファに格納されている賞球数が予め定められている閾値Th1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS890)。賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1より小さければ、総賞球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS896に進む。一方、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上であれば、総賞球数に閾値Th1を加算し(ステップS891)、賞球数バッファから閾値Th1を減算する(ステップS892)。そして、総アウト球数にアウト球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS893)、アウト球数バッファを0にする(ステップS894)。なお、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較せずに、所定回数の入賞毎や所定時間毎に、ステップS891からS894を実行してもよい。 First, it is determined whether or not the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th1 (step S890). If the buffer value for the number of prize balls is smaller than the threshold value Th1, it is not time to update the total number of prize balls, so the process proceeds to step S896. On the other hand, if the winning ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1, the threshold Th1 is added to the total winning ball number (step S891), and the threshold Th1 is subtracted from the winning ball number buffer (step S892). Then, the out-ball number buffer value is added to the total out-ball number (step S893), and the out-ball number buffer is set to 0 (step S894). Steps S891 to S894 may be executed every predetermined number of wins or every predetermined time without comparing the buffer value for the number of winning balls with the threshold value Th1.
その後、アウト球数バッファに格納されているアウト口通過球数と入賞球数バッファに格納されている入賞球数との和が予め定められている閾値Th2以上であるかを判定する(ステップS896)。アウト口通過球数と入賞球数の合計が遊技領域に流入した遊技球の数でありアウト球数となる。判定の結果、計算されたアウト球数が閾値Th2より小さければ、総アウト球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS902に進む。一方、計算されたアウト球数が閾値Th2以上であれば、総賞球数に賞球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS897)、賞球数バッファを0にする(ステップS898)。そして、総アウト球数に閾値Th2を加算し(ステップS899)、入賞球数バッファを0に設定し、アウト球数バッファに入賞球数バッファ値を加算し、閾値Th2を減算する(ステップS901)。なお、アウト球数(アウト球数バッファ値+入賞球数バッファ値)と閾値
Th2とを比較せずに、所定回数の入賞毎や所定時間毎に、ステップS896からS901を実行してもよい。
After that, it is determined whether or not the sum of the number of passing balls stored in the out ball number buffer and the number of winning balls stored in the winning ball number buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th2 (step S896). ). The sum of the number of balls passing through the out port and the number of winning balls is the number of game balls flowing into the game area, which is the number of out balls. As a result of the determination, if the calculated number of out-balls is smaller than the threshold Th2, it is not the time to update the total number of out-balls, so the process proceeds to step S902. On the other hand, if the calculated number of out balls is equal to or greater than the threshold Th2, the number of prize balls buffer value is added to the total number of prize balls (step S897), and the number of prize balls buffer is set to 0 (step S898). Then, the threshold value Th2 is added to the total number of out balls (step S899), the winning ball number buffer is set to 0, the winning ball number buffer value is added to the out ball number buffer, and the threshold value Th2 is subtracted (step S901). . Steps S896 to S901 may be executed every predetermined number of wins or at predetermined time intervals without comparing the number of out balls (buffer value for number of out balls + buffer value for number of winning balls) with the threshold value Th2.
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS902)。総アウト球数が0であれば、ベース値を計算できないので、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラーとなるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S902). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base calculation/display process ends. On the other hand, if the total number of out balls is not 0, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217. Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. If the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。 Thereafter, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees.
図56に示すベース算出・表示処理では、総賞球数や総アウト球数が更新されなくても、毎回ベース値を計算している。すなわち、総賞球数および総アウト球数が更新されなければ、ベース値として同じ値が計算され、ベース値は同じ値を維持する。一方、総賞球数または総アウト球数が更新されれば、ベース値は違う値に更新される。 In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 56, the base value is calculated every time even if the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls are not updated. That is, if the total number of won balls and the total number of out balls are not updated, the same value is calculated as the base value, and the base value remains the same value. On the other hand, if the total number of awarded balls or the total number of out-balls is updated, the base value is updated to a different value.
以上に説明したように本実施例のパチンコ機では、アウト口通過球数に入賞球数を加算してアウト球数を計算するので、アウト球数を正確に計数し、ベース値を正確に計算できる。さらに、遊技機の製造工程や検査工程において、ベース値を確認することによって、入賞口スイッチ、ベース表示器1317およびベース値を計算する処理が正常かを確認できる。
As described above, in the pachinko machine of this embodiment, the number of out balls is calculated by adding the number of winning balls passed through the out hole, so the number of out balls is counted accurately, and the base value is calculated accurately. can. Furthermore, by confirming the base value in the manufacturing process and inspection process of the gaming machine, it is possible to confirm whether the prize winning opening switch, the
[9-6.ベースの異常の報知]
以上に説明した処理は、計算されたベース値を報知するためのコマンドを生成するものであるが、次に、ベース値の異常を判定し、該異常を報知する処理を説明する。
・図57:タイマ割込み周期ごとに毎回ベース値を計算
・図58:所定賞球数ごとおよび所定アウト球数ごとにベース値を計算
なお、所定賞球数ごとにベース値を計算するパターン、所定アウト球数ごとにベース値を計算するパターンの説明は省略するが、図57と図58を組み合わせることによって実現できる。
[9-6. Base Abnormality Notification]
The processing described above is for generating a command for notifying the calculated base value. Next, the processing for determining an abnormality in the base value and notifying the abnormality will be described.
・Figure 57: Base value is calculated every timer interrupt cycle. ・Figure 58: Base value is calculated for each predetermined number of prize balls and for each predetermined number of out balls. Although the explanation of the pattern for calculating the base value for each number of out pitches is omitted, it can be realized by combining FIG. 57 and FIG.
図57は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図57に示すベース算出・表示処理では、毎回(タイマ割込み周期ごと)にベース値を計算する。 FIG. 57 is a flowchart showing another example of the base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 57, the base value is calculated each time (every timer interrupt cycle).
まず、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS902)。総アウト球数が0であれば、ベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラーとなるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
First, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S902). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base value is not calculated and the base calculation/display process is terminated. On the other hand, if the total number of out balls is not 0, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217. Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. If the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
その後、計算されたベース値が異常であるかを判定する(ステップS907)。ベース値の異常とは、例えば、計算されたベース値が設計値(正常値)から所定の許容範囲を超えて大きくまたは小さくなった場合などである。なお、複数段階の許容範囲を設けてベース値の乖離の程度によって異常の程度を複数段階で判定してもよい。そして、ベース値が異常であれば、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。一方、ベース値が異常でなければ、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。ベースの異常を報知する方法は、前述したベースの報知と同じ方法を採用できる。 After that, it is determined whether the calculated base value is abnormal (step S907). Abnormality of the base value is, for example, when the calculated base value becomes larger or smaller than the design value (normal value) beyond a predetermined allowable range. In addition, a plurality of stages of allowable ranges may be provided, and the degree of abnormality may be determined in a plurality of stages according to the degree of divergence of the base values. Then, if the base value is abnormal, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the player or hall employee. On the other hand, if the base value is not abnormal, the base calculation/display process is terminated. The same method as the above-described base notification can be adopted as the method of notifying the abnormality of the base.
例えば、以下に説明する方法の一つでも、二つ以上を組み合わせてもよい。具体的には、ベース表示器(7セグメントLED)1317、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244などでベース値の異常を報知してもよい。遊技者にベース値の異常を報知すると、遊技者がパチンコ機の異常を確認できてよい。計算されたベース値をパーセンテージ表記として、前述した表示器や表示装置に表示して、ベース値の異常を報知してもよい。なお、小数点以下の値は切り捨て、四捨五入、切り上げのいずれでもよいし、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244など画像を表示可能な表示装置では、小数点以下第1位まで表示し、より詳細に表示してもよい。
For example, one or a combination of two or more of the methods described below may be used. Specifically, base display (7-segment LED) 1317, liquid
また、液晶表示装置1600、3114、244にベース値を表示する場合、ベース値が異常である場合は、表示態様を変更するとよい。例えば、数値を点滅させたり、色を変えたり(通常時は緑色で、異常時は赤色など)して表示する。さらに、複数段階でベース値の表示態様を変えてもよい。具体的には、表示されるベース値が、30%以上、25%以上30%未満、20%以上25%未満、15%以上20%未満、10%以上15%未満、10%未満のように複数の段階に分けて、各段階で白、青、黄のように発光色を変えて表示してもよい。
Further, when the base values are displayed on the liquid
また、各種ランプ、液晶表示装置、音などでベース値がどの範囲にあるか(ベース値が高いのか低いのか、異常値か正常値か、など)を報知してもよい。機能表示ユニット1400でベース値の異常を報知してもよい。また、外部端子板784から遊技場に設置されたホールコンピュータにベースの異常の情報を出力してもよい。
In addition, various lamps, a liquid crystal display device, sound, etc. may be used to notify the range of the base value (whether the base value is high or low, whether it is an abnormal value or a normal value, etc.). The
なお、図57に示すベース算出・表示処理は、例えば、図50、図55に示すような、賞球数やアウト球数が所定の条件を満たすタイミングで総賞球数や総アウト球数を更新するベース算出用領域更新処理と組み合わせて使用するとよい。 Note that the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 57 calculates the total number of awarded balls and the total number of out-balls at the timing when the number of awarded balls and the number of out-balls satisfy predetermined conditions as shown in FIGS. 50 and 55, for example. It is preferable to use it in combination with the base calculation region update processing to be updated.
図58は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図58に示すベース算出・表示処理では、賞球数とアウト球数のいずれかが所定の条件を満たすタイミングでベース値が更新される。なお、図58において、前述したベース算出・表示処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 58 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 58, the base value is updated at the timing when either the number of winning balls or the number of out balls satisfies a predetermined condition. In FIG. 58, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the base calculation/display processing described above, and the detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、賞球数バッファに格納されている賞球数が予め定められている閾値Th1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS890)。賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1より小さければ、総賞球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS895に進む。一方、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上であれば、総賞球数に閾値Th1を加算し(ステップS891)、賞球数バッファから閾値Th1を減算する(ステップS892)。そして、総アウト球数にアウト球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS893)、アウト球数バッファを0にする(ステップS894)。なお、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較せずに、所定回数の入賞毎や所定時間毎に、ステップS891からS894を実行してもよい。 First, it is determined whether or not the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th1 (step S890). If the buffer value for the number of prize balls is smaller than the threshold value Th1, it is not time to update the total number of prize balls, so the process proceeds to step S895. On the other hand, if the winning ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1, the threshold Th1 is added to the total winning ball number (step S891), and the threshold Th1 is subtracted from the winning ball number buffer (step S892). Then, the out-ball number buffer value is added to the total out-ball number (step S893), and the out-ball number buffer is set to 0 (step S894). Steps S891 to S894 may be executed every predetermined number of wins or every predetermined time without comparing the buffer value for the number of winning balls with the threshold value Th1.
その後、アウト球数バッファに格納されているアウト球数が予め定められている閾値Th2以上であるかを判定する(ステップS895)。アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2より小さければ、総アウト球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS902に進む。一方、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2以上であれば、総賞球数に賞球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS897)、賞球数バッファを0にする(ステップS898)。そして、総アウト球数に閾値Th2を加算し(ステップS899)、アウト球数バッファから閾値Th2を減算する(ステップS900)。 After that, it is determined whether or not the number of out balls stored in the number of out balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th2 (step S895). If the buffer value for the number of out balls is smaller than the threshold Th2, it is not time to update the total number of out balls, so the process proceeds to step S902. On the other hand, if the out ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th2, the prize ball number buffer value is added to the total prize ball number (step S897), and the prize ball number buffer is set to 0 (step S898). Then, the threshold Th2 is added to the total number of out balls (step S899), and the threshold Th2 is subtracted from the buffer for the number of out balls (step S900).
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS902)。総アウト球数が0であれば、ベース値を計算できないので、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラーとなるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S902). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base calculation/display process ends. On the other hand, if the total number of out balls is not 0, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217. Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. If the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
その後、計算されたベース値が異常であるかを判定する(ステップS907)。ベース値の異常とは、例えば、計算されたベース値が設計値(正常値)から所定の許容範囲を超えて大きくまたは小さくなった場合などである。なお、複数段階の許容範囲を設けてベース値の乖離の程度によって異常の程度を複数段階で判定してもよい。そして、ベース値が異常であれば、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。一方、ベース値が異常でなければ、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。 After that, it is determined whether the calculated base value is abnormal (step S907). Abnormality of the base value is, for example, when the calculated base value becomes larger or smaller than the design value (normal value) beyond a predetermined allowable range. In addition, a plurality of stages of allowable ranges may be provided, and the degree of abnormality may be determined in a plurality of stages according to the degree of divergence of the base values. Then, if the base value is abnormal, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the player or hall employee. On the other hand, if the base value is not abnormal, the base calculation/display process is terminated.
図58に示すベース算出・表示処理では、総賞球数や総アウト球数が更新されなくても、毎回ベース値を計算している。すなわち、総賞球数および総アウト球数が更新されなければ、ベース値として同じ値が計算され、ベース値は同じ値を維持する。一方、総賞球数または総アウト球数が更新されれば、ベース値は違う値に更新される。 In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 58, the base value is calculated every time even if the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls are not updated. That is, if the total number of won balls and the total number of out balls are not updated, the same value is calculated as the base value, and the base value remains the same value. On the other hand, if the total number of awarded balls or the total number of out-balls is updated, the base value is updated to a different value.
なお、図58に示すベース算出・表示処理は、例えば、図39や図54に示すように、取得した賞球数やアウト球数を用いて直接、総賞球数や総アウト球数を更新するベース算出用領域更新処理と組み合わせて使用するとよい。 Note that the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 58 directly updates the total number of prize balls and total number of out balls using the acquired number of prize balls and number of out balls, as shown in, for example, FIG. 39 and FIG. It is preferable to use it in combination with the base calculation area update process.
以上に説明したように、本実施例のパチンコ機では、計算されたベース値が異常である場合に当該異常を報知するので、遊技者は遊技機の状態を知ることができ、ホール従業員は遊技機への不正な操作の可能性を知ることができる。また、従来のエラー検出では発見できない遊技機の異常を検出し報知できる。 As described above, in the pachinko machine of this embodiment, if the calculated base value is abnormal, the abnormality is notified, so that the player can know the state of the gaming machine, and the hall staff can It is possible to know the possibility of illegal operation to the game machine. In addition, it is possible to detect and report abnormalities in gaming machines that cannot be detected by conventional error detection.
[9-7.ベースの変化の報知]
次に、計算されたベース値の変化を報知する遊技機の実施例を説明する。
[9-7. Notification of base change]
Next, an embodiment of a gaming machine that notifies changes in calculated base values will be described.
パチンコ機で計算されるベース値は、当然ながら上下する。ベース値は遊技機の調子を表すため、遊技中の遊技者はベース値そのものの他、ベース値の変化を気にする。このため、遊技者へのベース値の変化の報知が望まれる。ベース値の上下の目安となる表示が出現すると、遊技者は安心して遊技を行うことができる。 The base value calculated by pachinko machines naturally fluctuates. Since the base value indicates the condition of the gaming machine, the player during the game cares not only about the base value itself but also about changes in the base value. Therefore, it is desirable to inform the player of the change in the base value. The player can play the game with peace of mind when the display that serves as a reference for the upper and lower levels of the base value appears.
図59は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図59に示すベース算出・表示処理では、現在のベース値と過去のベース値の履
歴とを比較するために、計算されたベース値の履歴を記録する。なお、図59において、前述したベース算出・表示処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。
FIG. 59 is a flowchart showing another example of the base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display process shown in FIG. 59, the history of calculated base values is recorded in order to compare the current base value with the history of past base values. In FIG. 59, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the base calculation/display processing described above, and the detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、賞球数バッファに格納されている賞球数が予め定められている閾値Th1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS890)。賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1より小さければ、総賞球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS895に進む。一方、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上であれば、総賞球数に閾値Th1を加算し(ステップS891)、賞球数バッファから閾値Th1を減算する(ステップS892)。そして、総アウト球数にアウト球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS893)、アウト球数バッファを0にする(ステップS894)。なお、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較せずに、所定回数の入賞毎や所定時間毎に、ステップS891からS894を実行してもよい。 First, it is determined whether or not the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th1 (step S890). If the buffer value for the number of prize balls is smaller than the threshold value Th1, it is not time to update the total number of prize balls, so the process proceeds to step S895. On the other hand, if the winning ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1, the threshold Th1 is added to the total winning ball number (step S891), and the threshold Th1 is subtracted from the winning ball number buffer (step S892). Then, the out-ball number buffer value is added to the total out-ball number (step S893), and the out-ball number buffer is set to 0 (step S894). Steps S891 to S894 may be executed every predetermined number of wins or every predetermined time without comparing the buffer value for the number of winning balls with the threshold value Th1.
その後、アウト球数バッファに格納されているアウト球数が予め定められている閾値Th2以上であるかを判定する(ステップS895)。アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2より小さければ、総アウト球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS902に進む。一方、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2以上であれば、総賞球数に賞球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS897)、賞球数バッファを0にする(ステップS898)。そして、総アウト球数に閾値Th2を加算し(ステップS899)、アウト球数バッファから閾値Th2を減算する(ステップS900)。 After that, it is determined whether or not the number of out balls stored in the number of out balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th2 (step S895). If the buffer value for the number of out balls is smaller than the threshold Th2, it is not time to update the total number of out balls, so the process proceeds to step S902. On the other hand, if the out ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th2, the prize ball number buffer value is added to the total prize ball number (step S897), and the prize ball number buffer is set to 0 (step S898). Then, the threshold Th2 is added to the total number of out balls (step S899), and the threshold Th2 is subtracted from the buffer for the number of out balls (step S900).
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS902)。総アウト球数が0であれば、ベース値を計算できないので、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラーとなるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S902). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base calculation/display process ends. On the other hand, if the total number of out balls is not 0, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217. Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. If the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
その後、ベース値管理タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定する(ステップS904)。ベース値管理タイマがタイムアップしていなければ、ベース値をベース履歴に格納するタイミングではないので、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、ベース値管理タイマがタイムアップしていれば、ベース値をベース履歴に格納し(ステップS905)、ベース値管理タイマをリセットする(ステップS906)。 After that, it is determined whether or not the base value management timer has expired (step S904). If the base value management timer has not timed out, it is not the time to store the base value in the base history, so the base calculation/display process is terminated. On the other hand, if the base value management timer has timed out, the base value is stored in the base history (step S905), and the base value management timer is reset (step S906).
ベース値管理タイマは、所定時間(例えば、10分)毎にベース値を記録するために使用されるタイマで、ベース値管理タイマがタイムアップする毎に現在のベース値をベース履歴に格納する。ベース履歴は、ベース算出用領域13128に格納される。ベース履歴は、一つのみをベース算出用領域13128に格納しても、複数をベース算出用領域13128に格納してもよい。複数のベース履歴をベース算出用領域13128に格納する場合、ベース算出用領域13128にリングバッファを構成し、例えば所定時間×10個のベース値を格納してもよい。また、図52に示すように、ベース算出用領域13128に総賞球数と総アウト球数のリングバッファを構成し、例えば所定時間×n個の賞球数と総アウト球数を格納し、必要に応じてベース値を計算してもよい。
The base value management timer is a timer used to record a base value every predetermined time (for example, 10 minutes), and every time the base value management timer times up, the current base value is stored in the base history. The base history is stored in
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。 Thereafter, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees.
図63は、表示選択処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。表示選択処理は、周辺制御部電源投入時処理(図60)の表示データ作成処理(ステップS1030)から呼び出される。 FIG. 63 is a flowchart illustrating an example of display selection processing. The display selection process is called from the display data creation process (step S1030) of the peripheral controller power-on process (FIG. 60).
まず、周辺制御部1511のMPUは、ベース算出用領域13128に格納された特定のベース履歴(例えば、直近の過去のベース値)を選択し、選択されたベース履歴値が現在のベース値より小さいかを判定する(ステップS10301)。その結果、選択されたベース履歴値が現在のベース値より小さければ、ベース低下継続時間計測タイマを参照し、ベース値の低下開始から所定時間(例えば、30秒)が経過しているかを判定する(ステップS10302)。そして、ベースの低下開始から所定時間が経過していなければ、ベース低下中の演出テーブルを選択する(ステップS10303)。一方、ベースの低下開始から所定時間が経過していれば、ベース低下継続中の演出テーブルを選択する(ステップS10304)。
First, the MPU of the
一方、選択されたベース履歴値が現在のベース値より小さくなければ(等しいまたは大きい)、ベース低下継続時間計測タイマをリセットし(ステップS10305)、ベース上昇中の表示選択テーブルを選択する(ステップS10306)。 On the other hand, if the selected base history value is not smaller than (equal to or larger than) the current base value, the timer for measuring the duration of the base decrease is reset (step S10305), and the display selection table during base increase is selected (step S10306). ).
以上に説明した表示選択処理では、ステップS10301において、現在のベース値がベース履歴値より小さいかを判定したが、現在のベース値とベース履歴値とを比較して、大きい、等しい、小さいを判定してもよい。ベース値は除算で求まることから一般的に小数値である。このため、所定の許容範囲(例えば、3%)を考慮してベース履歴値と現在のベース値とが等しいかを判定するとよい。 In the display selection process described above, in step S10301, it is determined whether the current base value is smaller than the base history value. You may Since the base value is obtained by division, it is generally a decimal value. Therefore, it is preferable to determine whether the base historical value and the current base value are equal in consideration of a predetermined allowable range (eg, 3%).
図64から図68は、表示選択テーブルの一例を示す図である。これらの表示選択テーブルは、始動口への入賞を契機として(または、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの開始前に)選択された乱数によって、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出を選択するために用いられる。図64から図66に示す表示選択テーブル1はベース値の上昇中またはベース値に変化がない場合に選択され、図67、図68に示す表示選択テーブル2、3は、ベース値の低下中に選択される。特に、図68に示す表示選択テーブル3は、ベース値が低下し始めてから所定時間(例えば30秒)の経過後に選択される。 64 to 68 are diagrams showing examples of display selection tables. These display selection tables are used to select the effect of the special symbol variation display game with a random number selected upon winning a prize in the starting port (or before the start of the special symbol variation display game). The display selection table 1 shown in FIGS. 64 to 66 is selected when the base value is increasing or when the base value does not change, and the display selection tables 2 and 3 shown in FIGS. 67 and 68 are selected during the base value decrease. selected. In particular, the display selection table 3 shown in FIG. 68 is selected after a predetermined period of time (for example, 30 seconds) has elapsed since the base value started to decrease.
各表示選択テーブルは、演出番号、演出内容、変動時間、備考、振り分けの各項目を含む。演出番号は、表示選択テーブルで選択される演出を一意に識別するための識別子である。演出内容は、当該演出の名称である。変動時間は、当該演出により特別図柄の変動が開始してから終了するまでの時間である。備考は、当該演出の概要を設計者が理解可能なように記載した情報である。振り分けは、当該演出が選択される確率であり、65536を分母とした分子で定義されている。 Each display selection table includes items of effect number, effect content, variable time, remarks, and distribution. The effect number is an identifier for uniquely identifying the effect selected in the display selection table. The effect content is the name of the effect. The variation time is the time from when the variation of the special symbol starts to when it ends due to the effect. The remarks are information describing the outline of the presentation so that the designer can understand it. Distribution is the probability that the effect is selected, and is defined by the numerator with 65536 as the denominator.
図64に示す表示選択テーブル1(はずれ)は、大当り抽選の結果がはずれであって、ベース値の上昇中または変化がない場合に選択される、図65に示す表示選択テーブル1(当たり1)は、大当り抽選の結果が確変状態を導出しない通常大当りであって、ベース値の上昇中または変化がない場合に選択される。図66に示す表示選択テーブル1(当たり2)は、大当り抽選の結果が確変状態を導出する確変大当りであって、ベース値の上昇中または変化がない場合に選択される。 The display selection table 1 (lost) shown in FIG. 64 is selected when the result of the jackpot lottery is a loss and the base value is increasing or remains unchanged, and the display selection table 1 (win 1) shown in FIG. is selected when the result of the jackpot lottery is a normal jackpot that does not lead to a variable probability state and the base value is increasing or not changing. The display selection table 1 (win 2) shown in FIG. 66 is selected when the result of the jackpot lottery is a variable probability big win that derives a variable probability state and the base value is increasing or not changing.
図67に示す表示選択テーブル2は、ベース値の低下中に選択される。また、図68に示す表示選択テーブル3は、ベース値が低下し始めてから所定時間(例えば30秒)が経過しても、ベース値が低下している場合に選択される。 The display selection table 2 shown in FIG. 67 is selected while the base value is decreasing. Further, the display selection table 3 shown in FIG. 68 is selected when the base value has decreased even after a predetermined time (for example, 30 seconds) has elapsed since the base value started to decrease.
図示するように、表示選択テーブル2、3には、図柄が変動しない演出であるフリーズ演出1、2が含まれており、高い確率でフリーズ演出が選択される。フリーズ演出は、演出決定後所定時間(例えば5秒)が経過すると表示される。
As shown, the display selection tables 2 and 3 include
また、ベース値が低下し始めてから所定時間(例えば30秒)が経過しても、ベース値が低下している場合には、表示選択テーブル3を用いて演出を選択し、選択された演出に切り替えてもよい。 In addition, if the base value has decreased even after a predetermined time (for example, 30 seconds) has passed since the base value started to decrease, the display selection table 3 is used to select an effect, and the selected effect is displayed. You can switch.
また、ベース値の変化を報知する特定の演出を表示するかを、遊技状態(遊技状況)に応じて決定してもよい。これは、ベース値の変化を遊技者に常時報知すると、パチンコ機の本来の楽しみである特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出に対する遊技者の注意が疎かになり、遊技者の意識が分散する可能性があるためである。 Further, whether or not to display a specific effect for notifying the change of the base value may be determined according to the game state (game situation). This is because if the player is always notified of the change in the base value, the player's attention to the performance of the special symbol variation display game, which is the original enjoyment of the pachinko machine, may be neglected and the player's consciousness may be dispersed. Because there is
例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの実行中(大当たり抽選の結果が示されていない遊技状況)においては、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出を優先して実行し、変動中でないときは、ベース値の上昇時または下降時に特定の演出(ベース値の変化の目安となる演出)を表示するとよい。 For example, during the execution of the special symbol variation display game (game situation in which the result of the jackpot lottery is not shown), the effect of the special symbol variation display game is preferentially executed, and when the variation is not in progress, the base value is increased. It is preferable to display a specific effect (an effect that serves as a guideline for a change in the base value) at the time of hour or at the time of descent.
当該特定の演出は、特別図柄変動表示ゲームが実行されない時間が所定時間継続したタイミングで表示するとよい。こでは、当該特定の演出を特別図柄変動表示ゲーム終了後直ちに表示すると、遊技者の緊張感が持続し、疲労が蓄積されるからである。当該特定の演出が表示されている状態で、始動口に遊技球が入賞すると、当該特定の演出の表示を中止して、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出を実行する。これは、始動口への入賞を契機に、大当たり抽選が行われ、特別図柄変動表示ゲームが開始するので、遊技者を特別図柄変動表示ゲームに注視させる方がよいためである。 The specific effect may be displayed at the timing when the special symbol variation display game is not executed for a predetermined period of time. This is because if the specific effect is displayed immediately after the special symbol variation display game ends, the player's sense of tension continues and fatigue accumulates. When the game ball wins in the starting hole while the specific effect is being displayed, the display of the specific effect is stopped and the effect of the special symbol variation display game is executed. This is because the winning of the start slot triggers a big winning lottery and the special symbol variation display game is started, so it is better to make the player pay attention to the special symbol variation display game.
当該特定の演出は、賞球数が所定数(閾値Th1)に達していない状況、または、アウト球数が所定数(閾値Th2)に達していない状況でも表示されるとよい。また、当該特定の演出を抽選の結果に応じて表示してもよいが、同一条件を満たせば必ず実行されるようにしてもよい。 The specific effect may be displayed even when the number of prize balls does not reach a predetermined number (threshold Th1) or when the number of out balls does not reach a predetermined number (threshold Th2). Also, the specific effect may be displayed according to the result of the lottery, or may be executed without fail if the same conditions are met.
また、当該特定の演出は、ベース値の上昇時には表示せず、ベース値の下降時にのみ表示するとよい。これは、ベース値の上昇を遊技者に報知すると、遊技者の期待が高まり、遊技者が期待する程度にベース値が上昇しなければ、期待とのギャップによって、遊技者は落胆する可能性がある。一方、ベース値の下降を遊技者に報知すると、ベース値を上昇させるべく闘争心を高める遊技者もいるためである。 Moreover, it is preferable that the specific effect is not displayed when the base value is increased, and is displayed only when the base value is decreased. This is because when a player is notified of a rise in the base value, the player's expectations rise, and if the base value does not rise to the extent that the player expects, the player may be disappointed due to the gap between expectations and expectations. be. On the other hand, if the player is notified of the decrease in the base value, some players will increase their fighting spirit in order to increase the base value.
また、本実施例では、ベース値の低下中とそれ以外(上昇中、定常中)で表示選択テーブルを変えたが、ベース値の低下中と定常中と上昇中との3状態に分けて表示選択テーブルを定義して、ベースの上昇中を遊技者に報知してもよい。この場合、所定の許容範囲(例えば、3%)を考慮してベース値が定常中か(ベース履歴値と現在のベース値とが等しいか)を判定するとよい。 In addition, in this embodiment, the display selection table is changed depending on whether the base value is decreasing or not (increasing, steady state), but the display is divided into three states: decreasing base value, steady state, and increasing base value. A selection table may be defined to inform the player that the base is rising. In this case, it is preferable to determine whether the base value is steady (whether the base history value and the current base value are equal) in consideration of a predetermined allowable range (for example, 3%).
また、当該特定の演出を特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中に表示してもよい。この場合、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中に表示されたときより、特別図柄変動表示ゲーム中以外で表示されたときの方が、ベース値が下降するする可能性が高くなっている。 Also, the specific effect may be displayed during the special symbol variation display game. In this case, the base value is more likely to decrease when displayed outside the special symbol variation display game than when displayed during the special symbol variation display game.
なお、始動口へ遊技球が入賞せず、特別図柄変動表示ゲームが行われない状態では、通常、ベース値は低下する。また、特別図柄変動表示ゲームが所定時間行われなければ、メイン液晶表示装置1600にはデモ画面が表示される。
In addition, when no game ball enters the starting hole and the special symbol variation display game is not performed, the base value usually decreases. Also, if the special symbol variation display game is not performed for a predetermined time, the main liquid
図69は、本実施例のパチンコ機の表示画面の一例を示す図である。 FIG. 69 is a diagram showing an example of the display screen of the pachinko machine of this embodiment.
図69(A)は、ノーマルリーチの表示例であり、左図柄と右図柄とが7で停止しており、中図柄が変動している。図69(B)は、スペシャルリーチ1の表示例であり、画面左上に表示される左図柄と右図柄とが7で停止しており、中図柄が変動している。画面中央部では、遊技者と相手がじゃんけんで対戦しており、じゃんけんの結果によって中図柄が決定される。図69(C)は、スペシャルリーチ2の表示例であり、画面左上に表示される左図柄と右図柄とが7で停止しており、中図柄が変動している。画面中央部では、遊技者と相手が対戦しており、対戦の結果によって中図柄が決定される。
FIG. 69(A) is a display example of normal reach, in which the left and right symbols are stopped at 7, and the middle symbol is fluctuating. FIG. 69(B) is a display example of
図69(D)は、フリーズ演出1の表示例であり、停止した装飾図柄が画面中央部に表示されており、装飾図柄の認識を邪魔しない位置(例えば、画面右下部)にベース値の低下を認識可能な表示をする。図69(E)は、フリーズ演出2の表示例であり、停止した装飾図柄が画面中央部に表示されており、装飾図柄の認識を邪魔しない位置(例えば、画面下部)にベース値の低下の継続を認識可能な表示をする。フリーズ演出において、ベース値の低下を示す表示は装飾図柄の認識を邪魔しない位置であれば任意の位置でよい。また、ベース値の低下を示す表示は装飾図柄と重なる位置に表示してもよい。例えば、表示画面の中央にポップアップする表示でもよい。
FIG. 69(D) is a display example of
以上にベース値の変化の程度をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示する例を説明したが、装飾ランプの点灯態様を変更してもよい。また、ベース値の上下の傾向ではなく、ベース値の変化を数値で表示してもよい。
An example of displaying the degree of change in the base value on the main liquid
表示されるベース値の変化は、所定時間前の時間区間で計算されたベース値と現在の時間区間で計算されたベース値との比較結果でも、所定時間前に計算されたベース値の総累計と最新のベース値の総累計との比較結果でもよい。 The change in the displayed base value is the result of comparing the base value calculated in the time interval before the specified time and the base value calculated in the current time interval. and the total cumulative sum of the latest base values.
[9-8.特定の一般入賞口を考慮したベースの計算]
次に、特定の一般入賞口への入賞を考慮してベース値を正確に計算する処理を説明する。
[9-8. Calculation of Base Considering Specific General Entrances]
Next, the process of accurately calculating the base value in consideration of the winning in a specific general winning slot will be described.
パチンコ機では、遊技者は、大当たり中に遊技球が入賞しやすい状態となった特定の入賞口(例えば、開放状態となった大入賞口2005、2006)への入賞を狙って、遊技球の発射の強さを調整する。大当り中でも、いわゆる通常打ちと同じ箇所を狙って遊技球を発射させて大入賞口2005を狙ったり、発射の強さを最大まで強めた、いわゆる右打ちによって大入賞口2006を狙ったりする遊技のバリエーションがある。このようなバリエーションがある中で、大入賞口の下流に始動口や一般入賞口を配置して、大入賞口からこぼれた球を拾うように遊技盤を設計することがある。
In a pachinko machine, a player shoots a game ball with the aim of winning a prize in a specific winning hole (for example, the big winning
ここで、大当り中に右打ちさせるパチンコ機における、下流(下部)について詳しく説明する。大当り中には開放した大入賞口に遊技球を入賞させるため、遊技者は右打ちを行う。遊技領域に向けて発射された遊技球の多くは開放中の大入賞口2006に入賞する。前述したように、本実施例のパチンコ機は、図10や図16に示すように、大入賞口2005の右側に一般入賞口2001が設けられており、右打ちをした遊技球が開放中の大入賞口2006に入賞しなかったときに、この一般入賞口2001に入賞する。すなわち、大入賞口2005の右側の一般入賞口2001は、右打ちをした遊技球が開放中の大入賞口2006に入賞しなかったときにのみ入賞するといえる。
Here, the downstream (lower part) of a pachinko machine that hits to the right during a big win will be described in detail. During the big win, the player hits to the right in order to win the game ball into the opened big winning hole. Most of the game balls shot toward the game area enter the large winning
ベース値は100発の遊技球を遊技領域5aに向けて発射したときに、始動口および一
般入賞口への入賞によって払い出された賞球数(すなわち、100個のアウト球数に対して払い出された賞球数の割合)を示すため、遊技領域に流入したが始動口および一般入賞口に入賞する可能性が低い(大入賞口に入賞する可能性が高い)遊技球を発射球数(アウト球数)に計数すると、ベース値として計算したときに、実際のベース値と乖離することが想定される。
The base value is the number of prize balls paid out by winning the starting opening and the general winning opening when 100 game balls are fired toward the
このため、本実施例では、大入賞口2005の右側の一般入賞口2001を特定の一般入賞口と定義し、特賞中に該特定の一般入賞口に入賞した球数をアウト球数から除外してベース値を計算する。
Therefore, in this embodiment, the general winning
特定の一般入賞口を考慮してベース値を計算する遊技機の各バリエーションにおけるベース値の計算タイミングの概要は以下の通りである。
・図70及び図40:タイマ割込み周期ごとに毎回ベース値を計算
・図71及び図72:所定賞球数ごとおよび所定アウト球数ごとにベース値を計算
なお、所定賞球数ごとにベース値を計算するパターン、所定アウト球数ごとにベース値を計算するパターンの説明は省略するが、図70から図72を組み合わせることによって実現できる。
An overview of the calculation timing of the base value in each variation of the gaming machine that calculates the base value in consideration of a specific general winning hole is as follows.
・Figures 70 and 40: Calculate the base value every timer interrupt cycle ・Figures 71 and 72: Calculate the base value for each predetermined number of prize balls and for each predetermined number of out balls Note that the base value is calculated for each predetermined number of prize balls and the pattern for calculating the base value for each predetermined number of out balls will be omitted, but they can be realized by combining FIGS. 70 to 72 .
図70は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図70に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、タイマ割込み周期ごとに特定の一般入賞口への入賞球数で補正されたアウト球数を用いてベース値を計算するために、賞球数、アウト球数および特定入賞球数を取得する。なお、図70において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 70 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation area updating process (step S81). The base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. Get the number of balls and the number of specific winning balls. In FIG. 70, the same step numbers are assigned to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation area updating process, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、特賞中以外の賞球数を取得し(ステップS811)、取得した賞球数を総賞球数に加算する(ステップS814)。すなわち、図70に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、賞球数が計算される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総賞球数が更新される。なお、賞球があるかを判定し、賞球がなければ、総賞球数を更新する処理をスキップしてもよい。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded. Then, the number of prize balls other than the special prize is obtained (step S811), and the obtained number of prize balls is added to the total number of prize balls (step S814). That is, in the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 70, the total number of prize balls used to calculate the base value is updated each time the number of prize balls is calculated. It should be noted that it is possible to determine whether there are prize balls or not, and if there are no prize balls, the process of updating the total number of prize balls may be skipped.
その後、アウト球数を取得し(ステップS818)、特定の一般入賞口への入賞球数(特定入賞球数)を取得する(ステップS820)。そして、アウト球数から特定入賞球数を減じた値を総アウト球数に加算する(ステップS822)。すなわち、図70に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、アウト球や入賞球が検出される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総アウト球数が更新される。 After that, the number of out balls is acquired (step S818), and the number of winning balls into a specific general winning hole (specific number of winning balls) is acquired (step S820). Then, the value obtained by subtracting the specific number of winning balls from the number of out balls is added to the total number of out balls (step S822). That is, in the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 70, the total number of out balls used to calculate the base value is updated each time an out ball or winning ball is detected.
なお、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理(図46)のステップS815からS817のように、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットしてもよい。さらに、図46のステップS824からS825のように、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止してもよい。 As in steps S815 to S817 of the base calculation area updating process (FIG. 46) described above, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated. , You may reset the timer for prize ball abnormality notification. Furthermore, as in steps S824 to S825 in FIG. 46, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize ball notification has timed up. You may stop ball abnormality information.
図70に示すベース算出用領域更新処理で総賞球数および総アウト球数を記録した後、図40に示すベース算出・表示処理によってベース値を計算できる。 After recording the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls in the base calculation area update process shown in FIG. 70, the base value can be calculated by the base calculation/display process shown in FIG.
図71は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図71に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、賞球数とアウト球数が所定の条
件を満たしたタイミングでベース値を計算するために、賞球数を賞球数バッファに記録し、アウト球数をアウト球数バッファに記録する。なお、図71において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。
FIG. 71 is a flowchart showing another example of the base calculation area updating process (step S81). In the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 71, in order to calculate the base value at the timing when the number of prize balls and the number of out balls satisfy a predetermined condition, the number of prize balls is recorded in the number of prize balls buffer, and the number of out balls is stored. Record the number in the out pitches buffer. In FIG. 71, the same step numbers are assigned to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation area updating process, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、特賞中以外の賞球数を取得し(ステップS811)、賞球があるかを判定する(ステップS812)。そして、賞球があれば、取得した賞球数を賞球数バッファに加算する(ステップS813)。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded. Then, the number of prize balls other than the special prize is obtained (step S811), and it is determined whether there are prize balls (step S812). Then, if there are prize balls, the acquired number of prize balls is added to the number of prize balls buffer (step S813).
そして、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し(ステップS815)、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS816)、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットする(ステップS817)。 Then, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls (step S815), and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated (step S816), and an abnormality notification timer for prize balls is reset (step S817). ).
その後、アウト球数を取得し(ステップS818)、取得したアウト球数をアウト球数バッファに加算する(ステップS819)。そして、入賞球数を取得し、取得した入賞球数にかかる入賞口が特定の一般入賞口であるかを判定し、特定の一般入賞口への入賞球数を取得する(ステップS820)。そして、取得した特定の一般入賞口への入賞球数を特定入賞球数バッファに加算する(ステップS823)。 After that, the number of out balls is acquired (step S818), and the acquired number of out balls is added to the number of out balls buffer (step S819). Then, the number of winning balls is acquired, and it is determined whether the winning hole corresponding to the acquired number of winning balls is a specific general winning hole, and the number of winning balls to the specific general winning hole is acquired (step S820). Then, the acquired number of winning balls to the specific general winning hole is added to the specific winning ball number buffer (step S823).
その後、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し(ステップS824)、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止する(ステップS825)。 After that, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize notification has timed up (step S824), and when the timer for abnormal notification of prize ball has timed up, a command to stop the abnormal notification of prize ball is generated, and the abnormal notification of prize ball is stopped ( step S825).
図72は、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図72に示すベース算出・表示処理では、特定入賞球数バッファに記録された特定入賞球数を考慮してベース値を計算する。なお、図72において、前述したベース算出・表示処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 72 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation/display processing (step S89). In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 72, the base value is calculated in consideration of the specific winning ball number recorded in the specific winning ball number buffer. In FIG. 72, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation/display processing, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、賞球数バッファに格納されている賞球数が予め定められている閾値Th1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS890)。賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1より小さければ、総賞球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS895に進む。一方、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上であれば、総賞球数に閾値Th1を加算し(ステップS891)、賞球数バッファから閾値Th1を減算する(ステップS892)。そして、総アウト球数にアウト球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS893)、アウト球数バッファを0にする(ステップS894)。なお、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較せずに、所定回数の入賞毎や所定時間毎に、ステップS891からS894を実行してもよい。 First, it is determined whether or not the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th1 (step S890). If the buffer value for the number of prize balls is smaller than the threshold value Th1, it is not time to update the total number of prize balls, so the process proceeds to step S895. On the other hand, if the winning ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1, the threshold Th1 is added to the total winning ball number (step S891), and the threshold Th1 is subtracted from the winning ball number buffer (step S892). Then, the out-ball number buffer value is added to the total out-ball number (step S893), and the out-ball number buffer is set to 0 (step S894). Steps S891 to S894 may be executed every predetermined number of wins or every predetermined time without comparing the buffer value for the number of winning balls with the threshold value Th1.
その後、アウト球数バッファに格納されているアウト口通過球数と入賞球数バッファに格納されている入賞球数との和が予め定められている閾値Th2以上であるかを判定する(ステップS895)。アウト口通過球数と入賞球数の合計が遊技領域に流入した遊技球の数でありアウト球数となる。判定の結果、計算されたアウト球数が閾値Th2より小さければ、総アウト球数を更新するタイミングではないので、ステップS902に進む。一方、計算されたアウト球数が閾値Th2以上であれば、総賞球数に賞球数バッファ値を加算し(ステップS897)、賞球数バッファを0にする(ステップS898)。そして、総アウト球数から特定入賞球数を減算し、閾値Th2を加算する(ステップS899)、入賞球数バッファを0に設定し、アウト球数バッファから閾値Th2を減算する(ステップS900)。 After that, it is determined whether or not the sum of the number of passing balls stored in the out ball number buffer and the number of winning balls stored in the winning ball number buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th2 (step S895). ). The sum of the number of balls passing through the out port and the number of winning balls is the number of game balls flowing into the game area, which is the number of out balls. As a result of the determination, if the calculated number of out-balls is smaller than the threshold Th2, it is not the time to update the total number of out-balls, so the process proceeds to step S902. On the other hand, if the calculated number of out balls is equal to or greater than the threshold Th2, the number of prize balls buffer value is added to the total number of prize balls (step S897), and the number of prize balls buffer is set to 0 (step S898). Then, the specific number of winning balls is subtracted from the total number of out balls and the threshold value Th2 is added (step S899), the winning ball number buffer is set to 0, and the threshold value Th2 is subtracted from the out ball number buffer (step S900).
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS902)。総アウト球数が0であれば、ベース値を計算できないので、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数を総アウト球数で除してベース値を計算する(ステップS903)。具体的には、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じて除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する。そして、32クロック経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から商を読み出して、ベース値とする。なお、総アウト球数が0である場合、ベース値を計算しても、演算回路13121からの返り値はエラーとなるので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納しなくてよい。この場合、ベース表示器1317に表示されるベース値は更新されない。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S902). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base calculation/display process ends. On the other hand, if the total number of out balls is not 0, the base value is calculated by dividing the total number of awarded balls by the total number of out balls (step S903). Specifically, the total number of winning balls is multiplied by a predetermined number (for example, 100) and stored in the division input register A131216, and the total number of out balls is stored in the division input register B131217. Then, after 32 clocks have passed, the quotient is read from the division result register A131218 and used as the base value. If the total number of out balls is 0, even if the base value is calculated, the return value from the
その後、計算されたベース値が異常であるかを判定する(ステップS907)。ベース値の異常とは、例えば、計算されたベース値が設計値(正常値)から所定の許容範囲を超えて大きくまたは小さくなった場合などである。なお、複数段階の許容範囲を設けてベース値の乖離の程度によって異常の程度を複数段階で判定してもよい。そして、ベース値が異常であれば、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS908)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。一方、ベース値が異常でなければ、ベース算出・表示処理を終了する。 After that, it is determined whether the calculated base value is abnormal (step S907). Abnormality of the base value is, for example, when the calculated base value becomes larger or smaller than the design value (normal value) beyond a predetermined allowable range. In addition, a plurality of stages of allowable ranges may be provided, and the degree of abnormality may be determined in a plurality of stages according to the degree of divergence of the base values. Then, if the base value is abnormal, a base notification command is generated (step S908), and the base is notified to the player or hall employee. On the other hand, if the base value is not abnormal, the base calculation/display process is terminated.
図72に示すベース算出・表示処理では、総賞球数や総アウト球数が更新されなくても、毎回ベース値を計算している。すなわち、総賞球数および総アウト球数が更新されなければ、ベース値として同じ値が計算され、ベース値は同じ値を維持し、総賞球数または総アウト球数が更新されれば、ベース値は違う値に更新される。なお、総賞球数および総アウト球数の一方が更新されたタイミングでベース値を計算してもよく、両方が更新されたタイミングでベース値を計算してもよい。 In the base calculation/display processing shown in FIG. 72, the base value is calculated every time even if the total number of winning balls and the total number of out balls are not updated. That is, if the total number of awarded balls and the total number of out balls are not updated, the same value is calculated as the base value, the base value remains the same value, and if the total number of awarded balls or the total number of out balls is updated, Base value is updated to a different value. The base value may be calculated at the timing when one of the total number of awarded balls and the total number of out-balls is updated, or at the timing when both are updated.
また、本実施例のパチンコ機では、遊技領域に流入したが始動口および一般入賞口に入賞する可能性が低い遊技球を除外してベース値を計算するので、実際のベース値との乖離が少ないベース値を正確に計算できる。 In addition, in the pachinko machine of this embodiment, since the base value is calculated by excluding game balls that have flowed into the game area but are unlikely to enter the starting hole or the general winning hole, deviation from the actual base value is calculated. A small base value can be calculated accurately.
また、大当り中に右打ちするパチンコ機で大入賞口2006の下流に一般入賞口2001がある場合を説明したが、本実施例にかかる発明は、大当り中に通常打ちで大入賞口2005を狙うパチンコ機でも、大入賞口2005の下流に始動口または一般入賞口が配設されている遊技機にも適用できる。
In addition, the pachinko machine that hits to the right during the big win has explained the case where the
また、遊技領域5aには、通常は遊技球を受け入れないが、大当たり抽選結果に応じて遊技球の受け入れが可能となる大入賞口2005、2006が配置されている。この大入賞口2005、2006への入賞による賞球をベース値の計算から除外してもよい。この場合、遊技球が始動口2002、2004に入賞して特別図柄変動表示ゲームが開始し、特別図柄が確定してから大入賞口2005、2006が開放するまで(大当たりオープニング)から、大入賞口2005、2006が閉鎖してから次の特別図柄変動表示ゲームが開始するまで(大当たりエンディング)の間を特賞中として、検出されたアウト球をアウト球数から除外する。このようにすれば、図39などのステップS810で特賞中であるかを判定せずに特賞中の賞球数およびアウト球数を計数できる。なお、一つの大当たりで大入賞口2005、2006が開放と閉鎖を繰り返す場合、大入賞口2005、2006の閉鎖から次の開放までの間(閉鎖インターバル)の時間を特賞中に含めてもよい。すなわち、特賞中は、条件装置作動中を意味し、例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当たり図柄の確定からエンディング終了までである。また、右打ち指示中の全ての時間を含んでもよい。さらに、始動口2002、2004においては、時短中、確変中(ST中)、電サポ中を特賞中に含めてもよい。さらに、時短中、確変中(ST中)、電サポ中以外の遊技状態において、始動口2004の開放から閉鎖後の所定時間(例えば、始動口に入賞し
た球がアウト球として検出されるまでに必要な数秒)までの間を特賞中に含めてもよい。
Also, in the
また、遊技領域5aには、通常は遊技球を受け入れないが、普通図柄の抽選結果に応じて遊技球の受け入れが可能となる第二始動口2004が配置されている。この第二始動口2004への入賞による賞球をベース値の計算から除外してもよい。この場合、遊技球がゲート部2003を通過して普通図柄の抽選が行われ、普通図柄変動表示ゲームが開始し、普通図柄が確定してから開放するまで(オープニング)から、第二始動口2004が閉鎖してから次の普通図柄変動表示ゲームが開始するまで(エンディング)の間を特賞中として、検出されたアウト球をアウト球数から除外する。なお、第二始動口2004が普通図柄の抽選結果によって開放と閉鎖を繰り返す場合、第二始動口2004の閉鎖から次の開放までの間(閉鎖インターバル)の時間を特賞中に含めてもよい。このようにすると、時短中だけでなく、第二始動口2004への全ての入賞をベース値の計算から除外できる。
Also, in the
前述のようにすれば、図39などのステップS810で特賞中であるかを判定せずに特賞中(大当たり、時短など)以外の賞球数およびアウト球数を正確に計数できる。 As described above, it is possible to accurately count the number of prize balls and the number of out balls other than those during special prizes (jackpots, short working hours, etc.) without determining in step S810 of FIG.
このようにすると、遊技者が右打ちをしている間のアウト球数、賞球数を正確に除外し、ベース値を正確に計算できる。 In this way, the number of out balls and the number of winning balls while the player is hitting right can be accurately excluded, and the base value can be calculated accurately.
また、パチンコ機によっては、大当り中でも時短中でもない状態(いわゆる通常状態)では左打ちで遊技を行い、大当り中または時短中は右打ちで遊技を行うことが推奨される。このような遊技機では、左打ち時に入賞する一般入賞口2001、第一始動口2002および右打ち時に入賞する一般入賞口2001、第二始動口2004が設けられている。このような遊技機において、遊技領域5aの左側から中央(左打ち時に遊技球が転動する領域)および遊技領域5aの右側(右打ち時に遊技球が転動する領域)における入賞口の数や配置、釘の配設位置によって、各入賞口への入球率が異なる。言い換えると左打ちのときのベース値と右打ちのときのベース値が異なる。
Also, depending on the pachinko machine, it is recommended to play the game with the left hand when neither the big win nor the time saving is in progress (so-called normal state), and to play the game with the right hand during the big win or the time saving. In such a game machine, a general
パチンコ機のベース値は、通常状態において遊技者が左打ちを行うことを想定して設定されている。ところが、前述した理由のように、左打ち時と右打ち時とでベース値が異なる場合(例えば、通常状態における右打ち時のベース値は左打ち時より低くなるように設計されている場合)、通常状態において遊技者が右打ちをすると、低いベース値が計算される。 The base value of the pachinko machine is set on the assumption that the player hits to the left in the normal state. However, if the base value differs between left-handed and right-handed for the reason described above (for example, the base value for right-handed is designed to be lower than that for left-handed in normal conditions). , a low base value is calculated when the player hits right in normal conditions.
ホールは、ベース値が低いパチンコ機は、異常があると考え点検をするか、出玉性能が悪い遊技機であると判断する。出玉性能が悪い(想定されるベースより低い)と判断されたパチンコ機においても、ホールは、遊技者が左打ちを行っていると判断するので、左打ち時のベースに作用する始動口や一般入賞口の入球率を高める調整を行う。そして、異常がある釘を調整して、ベース値を高めるようにする。このように調整された遊技機で左打ちをすると、通常状態でも多くの賞球が得られる。換言すると少額で多くの抽選を受けられることになる。つまり、左打ち時のベースがホールが想定していたものと相違がなくても、ホールが勘違いして、左打ち時に入賞する始動口や一般入賞口の入球率を高める調整を行う。このような遊技者の悪意によってホールが不利益を被る可能性があることから、左打ち時のベース値と右打ち時のベース値とを正確に計算する必要がある。 A pachinko machine with a low base value is considered to be abnormal and should be inspected or judged to be a machine with poor ball output performance. Even in a pachinko machine that is judged to have poor ball output performance (lower than the expected base), the hole judges that the player is hitting left, so the starting opening that affects the base when hitting left Make adjustments to increase the ball entry rate of the general winning entrance. Then, adjust the abnormal nail to increase the base value. When the game machine adjusted in this way hits to the left, many prize balls can be obtained even in the normal state. In other words, many lotteries can be received with a small amount. In other words, even if the base when hitting left-handed is not different from what the hole has assumed, the hole misunderstands and adjusts to increase the ball entry rate of the starting opening and the general winning opening that wins when hitting left-handed. Since there is a possibility that the hole may be disadvantaged by such malice of the player, it is necessary to accurately calculate the base value for hitting left and the base value for hitting right.
ところで、時短中に右打ちを行うパチンコ機は、遊技状態によって開閉する第二始動口2004と、第二始動口2004を開放させるための普通図柄抽選を行うためのゲート部2003は、右打ち時に遊技球が転動する領域に配置されている。また、通常状態に右打ちしてゲート部2003を遊技球が通過した場合、普通図柄の抽選は行っても普図当選確
率を極めて低くして第二始動口2004が開かないようにしたり、普通図柄抽選に当選しても第二始動口2004の開放時間を短くして、通常状態では第二始動口2004への入賞を困難にしている。
By the way, in a pachinko machine that hits to the right during time saving, the
ここで、通常状態で右打ちした状態でベース値を高めるためには、第二始動口2004への入球率を高めることになる。しかし、一般に第一始動口2002より第二始動口2004は有利に設定されていることから、第二始動口2004への入球率を高めるとホールの利益を圧迫する。そこで、通常状態にゲート部2003を通過した遊技球を計数し、ベース値を計算する際に、ゲート部2003の通過球数を用いて補正したベース値を計算するとよい。
Here, in order to increase the base value in the normal state of hitting to the right, the rate of entry into the
具体的には、通常状態においてゲート部2003を通過した遊技球数を特定入賞球数としてアウト球数(遊技領域5aに向けて打ち込まれた遊技球数)から減算する。アウト球数の減少によって、高いベースの計算値を得ることができる。例えば、相当数の遊技球がゲート部2003を通過した場合、には極めて高いベース値が計算されることになる。なお、補正処理の程度は、遊技機の設計値(性能)に基づいて、適宜決定すればよい。
Specifically, the number of game balls passing through the
さらに、ゲート部2003の通過を監視し、遊技球がゲート部2003を通過した場合(始動口に入賞せずに所定数(例えば、3個)の遊技球がゲート部2003を通過した場合などの条件をつけてもよい)、ゲート部2003を通過した後(または、前後)の所定時間または所定発射数において計数されたアウト球数をベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。このようにすると、より正確にベース値を計算できる。ゲート部2003の通過を検出すると、ベース値の計算結果に反映されないことを積極的に遊技者に報知せずに、「左打ちに戻してください」などの表示や音声を出力してもよい。また、ゲート部2003の通過の検出時に、右打ちがされていることをホールに報知してもよい。例えば、特定のランプを点灯させたり、点灯態様を変えたり、外部端子板784から遊技場に設置されたホールコンピュータに右打ち中であることを出力してもよい。
Furthermore, the passage of the
以上に説明したように、遊技領域5aの右側(右打ち時に遊技球が転動する領域)に設けられたゲート部2003の通過球数をアウト球数から除外することによって、通常状態で右打ち時のベース値を大きい値へ補正できる。このため、遊技者の遊技スタイルによるベースの計算値の変動を防止できる。
As described above, by excluding the number of balls passing through the
[9-9.ベース値の初期化]
パチンコ機1の稼働状況を確認するというベース値の役割を鑑みると、算出されたベース値は長期間保持されることが望ましい。また、算出されたベース値は容易に消去できないことが望ましい。このため、主制御MPU1311のRAM1312にバックアップされた遊技の進行に関係するデータの消去条件と別の条件でベース算出・表示用データ13136を消去する。これにより、正確な賞球数のデータを保持し、正確な役物比率を計算できる。
[9-9. Initialize base value]
Considering the role of the base value of confirming the operation status of the
具体的には、RAMクリアスイッチの操作(第1の操作)によってはベース算出・表示用データ13136を消去しないが、主制御MPU1311に供給されるバックアップ電源を遮断し、かつパチンコ機1の電源の遮断する第2の操作によって、主制御MPU1311のRAM1312にバックアップされた全てのデータを消去できる。第2の操作は、この操作を実現する一つのスイッチを設けてもよいし、遊技店の従業員が主制御基板1310に供給されるバックアップ用の電源線のコネクタを抜去して、パチンコ機1の電源の遮断してもよい。
Specifically, the operation of the RAM clear switch (first operation) does not erase the base calculation/
換言すると、主制御MPU1311のRAM1312を消去するために二つの操作が準
備されており、第1の操作では遊技の進行に関係するデータのみを消去するが、第2の操作では算出されたベース値や遊技の進行に関係するデータを含む全てのデータを消去する。
In other words, two operations are prepared for erasing the
このように構成することによって、遊技場の係員の誤操作によってベース算出・表示用データ13136が消去されないので、表示される役物比率の信頼性が高まり、役物比率が高い状態の隠蔽を防止できる。
By configuring in this way, the base calculation/
[9-10.入賞異常を考慮したベースの計算]
図73、図74は、入賞異常を考慮したベース算出領域更新処理のフローチャートである。
[9-10. Calculation of Base Considering Winning Abnormality]
73 and 74 are flowcharts of the base calculation area update process in consideration of the winning abnormality.
パチンコ機1においては、前述したステップS815で判定される賞球数の異常の他、入賞異常が検出される場合がある。例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームで大当たりが導出されたことによる大入賞口2005、2006の開放中以外に入賞が検出された場合や、普通図柄変動表示ゲームで当たりが導出されたことによる始動口2004の開放中以外に入賞が検出された場合は入賞異常である。すなわち、ステップS815で判定される賞球数の異常は、賞球数から検出される異常な動作であり、主に所定時間に多くの賞球が得られている場合である。一方、入賞異常は、入賞球数から検出される異常な動作であり、主に入賞不可能な状態における入賞や、所定時間に多くの入賞が検出される場合である。
In the
この入賞異常にかかる入賞球はアウト球としてカウントされるので、この分を補正してベースを正確に計算することが望ましい。このため、入賞異常を考慮したベース算出領域更新処理では、検出した入賞異常にかかる入賞球数を減じるように総アウト球数を補正する。 Since the winning ball related to this winning abnormality is counted as an out ball, it is desirable to calculate the base accurately by correcting this amount. Therefore, in the base calculation area update process considering the winning abnormality, the total number of out balls is corrected so as to reduce the number of winning balls related to the detected winning abnormality.
なお、通常は大入賞口2005、2006や始動口2004へは特賞中にのみ入賞するので、これらの入賞口への入賞球はベースを計算するためのアウト球として計数されることがなく、入賞異常を考慮する必要がない。
It should be noted that normally the
図73は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の一例を示すフローチャートである。ベース算出用領域更新処理は、現在の遊技状態を判定し、遊技価値として払い出される賞球数を現在の遊技状態に対応した領域に加算して、主制御内蔵RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128を更新する。特に、図73に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、図39に示すベース算出用領域更新処理と同様に、タイマ割込み周期ごとに毎回ベース値を計算するために、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で算出された賞球数を用いて総賞球数を直接更新し(ステップS814)、アウト球数を用いて総アウト球数を直接更新する(ステップS822)。なお、図73において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。
FIG. 73 is a flow chart showing an example of base calculation area update processing (step S81). In the base calculation area update process, the current game state is determined, the number of prize balls to be paid out as game value is added to the area corresponding to the current game state, and the
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded.
遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しない賞球であるため、賞球数やアウト球数を更新せずに、ベース算出用領域更新処理を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で入力情報に基づいて算出された賞球数を取得する(ステップS811)。ベース算出用領域更新処理で取得する賞球数は、払い出しが決定した賞球数でもよい。また、作成済みの払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。また、送信済の払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。また、主制御基板1310が払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信し、払出制御基板951から受信確認(ACK
)を受信した払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。さらに、主制御基板1310が払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信し、払出制御基板951から払出完了の報告を受けた賞球数(払出済み賞球数)でもよい。このバリエーションは図41から図44を用いて説明済みである。
If the game state is during a special prize, the prize balls are not related to the calculation of the base value, so the base calculation region updating process is terminated without updating the number of prize balls or the number of out balls. On the other hand, if the game state is not during the special prize, the number of prize balls calculated based on the input information in the prize ball control process (step S80) is obtained (step S811). The number of prize balls acquired in the base calculation region updating process may be the number of prize balls determined to be put out. Alternatively, the number of prize balls corresponding to the prepared payout command may be used. Alternatively, it may be the number of prize balls corresponding to the payout command that has already been sent. In addition, the
) may be the number of prize balls corresponding to the received payout command. Furthermore, the
そして、取得した賞球数を総賞球数に加算して、総賞球数を更新する(ステップS814)。なお、賞球があるかを判定し、賞球がなければ、総賞球数を更新する処理をスキップしてもよい。また、始動口2002、2004に遊技球が入賞したが、保留が上限値であり、始動口への入賞が保留されなかった場合でも賞球は払い出されるので、総賞球数が更新される。また、入賞口に遊技球が入賞しても賞球が発生しない遊技状態(例えば、特定のエラー発生時など)においては、当該入賞に起因する賞球が発生せず、取得する賞球数が0であるため、総賞球数は更新されない。総賞球数は、主制御内蔵RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128に設けられる総賞球数格納領域(図52参照)に記録される。すなわち、図73に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、賞球数が計算される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総賞球数が更新される。
Then, the acquired number of prize balls is added to the total number of prize balls to update the total number of prize balls (step S814). It should be noted that it is possible to determine whether there are prize balls or not, and if there are no prize balls, the process of updating the total number of prize balls may be skipped. In addition, although the game balls enter the starting
その後、アウト球数を取得する(ステップS818)。そして、入賞異常が検出されているかを判定する(ステップS826)。そして、異常と判定された入賞に対応する遊技球数を取得する(ステップS827)。具体的には、前述したように、特別図柄変動表示ゲームで大当たりが導出されたことにより生起する特賞中(条件装置作動中)以外に大入賞口2005、2006への入賞が検出された場合や、普通図柄変動表示ゲームで当たりが導出されたことによる開放中ではないのに始動口2004への入賞が検出された場合は入賞異常であると判定する。
After that, the number of out balls is acquired (step S818). Then, it is determined whether or not a winning abnormality is detected (step S826). Then, the number of game balls corresponding to the winning determined to be abnormal is acquired (step S827). Specifically, as described above, when a winning to the
入賞異常にかかる入賞球が一つ検出されると入賞異常と判定してもよいし、入賞異常にかかる入賞球が所定数検出されると入賞異常と判定してもよい。また、入賞異常にかかる入賞球が連続して所定数検出されると入賞異常と判定してもよいし、入賞異常にかかる入賞球が所定の時間内に所定数検出されると入賞異常と判定してもよい。 It may be determined that the winning ball is abnormal when one winning ball related to the winning abnormality is detected, or it may be determined that the winning ball is abnormal when a predetermined number of winning balls related to the winning abnormality are detected. Further, when a predetermined number of winning balls related to the winning abnormality are continuously detected, it may be determined as a winning abnormality, and when a predetermined number of winning balls related to the winning abnormality are detected within a predetermined time, it is determined as a winning abnormality. You may
そして、取得したアウト球数を総アウト球数に加算するように、総アウト球数を更新する(ステップS822)。アウト球数は、前述したように、発射球センサ1020や排出球センサ3060などによって検出され、ステップS74のスイッチ入力処理で、これらのセンサの検出信号を読み取って、取得する。このとき、取得したアウト球数から入賞異常にかかる入賞球数を減じた値を総アウト球数に加算してもよく、また、取得したアウト球数を総アウト球数に加算した後に、入賞異常にかかる入賞球数を総アウト球数から減じてもよい。総アウト球数は、主制御内蔵RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128に設けられる総アウト球数格納領域(図52参照)に記録される。すなわち、図73に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、アウト球が検出される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総アウト球数が更新される。このように、タイマ割込み処理ごとにベース算出処理を実行して、総アウト球数を更新し、ベース算出表示処理(図40)にてベース値を計算し表示するので、ベース値を遅滞なく表示でき、ベース値が正常か異常かを遅滞なく判断できる。
Then, the total number of out-balls is updated so that the acquired number of out-balls is added to the total number of out-balls (step S822). The number of out balls is detected by the
なお、後述するベース算出用領域更新処理(図74)のステップS815からS817のように、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットしてもよい。さらに、ステップS824からS825のように、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止してもよい。 As in steps S815 to S817 of the base calculation area updating process (FIG. 74), which will be described later, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated. , You may reset the timer for prize ball abnormality notification. Further, as in steps S824 to S825, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize notification has timed up. may be stopped.
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、主制御MPU1311が、タイマ割込み処理においてベース値の計算処理を実行するが、払出制御部952の払出制御MPUがベース値の計算処理を実行してもよい。この場合、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510の周辺制御部1511にベースを報知するためのコマンドを送信してもよいし、払出制御部952から周辺制御部1511にベースを報知するためのコマンドを送信してもよい。
In the
また、一つのタイマ割込み処理において、入賞口への入賞とアウト球との両方の情報を取得しても、賞球数を総賞球数(または、後述する実施例では賞球数バッファ)に加算し、アウト球数を総アウト球数(または、後述する実施例ではアウト球数バッファ)に加算する。また、一つのタイマ割込み処理において、複数の入賞口への入賞の情報を取得しても、複数の入賞による賞球数の合計を総賞球数(または、後述する実施例では賞球数バッファ)に加算する。このため、ベース値を正確に計算し、表示できる。例えば、賞球数が5個の入賞口の入賞口センサと賞球数が3個の入賞口の入賞口センサとへの入賞を検出した場合は、合計8個の賞球を総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算する。 Also, in one timer interrupt process, even if the information of both the winning ball to the winning hole and the out ball is acquired, the number of prize balls is set to the total number of prize balls (or the number of prize balls buffer in the embodiment described later). The number of out-balls is added to the total number of out-balls (or the number of out-balls buffer in the embodiment described later). Also, in one timer interrupt process, even if information on winning to a plurality of winning holes is acquired, the total number of winning balls due to a plurality of winnings is calculated as the total number of winning balls (or ). Therefore, the base value can be accurately calculated and displayed. For example, if a prize-winning sensor detects a prize-winning hole with 5 prize balls and a prize-winning hole sensor with 3 prize balls, a total of 8 prize balls are detected as the total number of prize balls. (or add to the prize number buffer).
また、遊技球の発射が検出されている場合にのみ、賞球数を総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算してもよい。すなわち、発射球センサ1020の検出から所定時間以内に検出した入賞に関する賞球数のみを総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算してもよい。また、発射制御部953または球発射装置680の動作を検出し、発射制御部953または球発射装置680が動作している間(さらに、発射制御部953または球発射装置680が動作を停止してから所定時間(例えば、5秒)後まで)に検出した入賞に関する賞球数のみを総賞球数または賞球数バッファに加算してもよい。また、遊技者が発射ハンドルを操作している場合にのみ、賞球数を総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算してもよい。すなわち、ハンドルユニット500の接触検知センサ509に手や指が触れていることが検出されている時間から所定時間(例えば、5秒)以内に検出した入賞に関する賞球数のみを総賞球数(または、賞球数バッファ)に加算してもよい。このようにすると、遊技球が発射されていない状態で賞球を検出する異常や不正行為による賞球のベース値への反映を防止でき、不正確なベース値の表示を防止できる。この場合、接触検知センサ509を用いると、遊技球の発射を検出するセンサを新たに設けなくてもよいので、パチンコ機1のコストの上昇を抑制できる。
Also, the number of prize balls may be added to the total number of prize balls (or the number of prize balls buffer) only when the shooting of game balls is detected. That is, only the number of winning balls detected within a predetermined time from the detection of the
図74は、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS81)の別の一例を示すフローチャートである。図74に示すベース算出用領域更新処理は、アウト球数が所定の条件を満たしたタイミングでベース値を計算するために、アウト球数をアウト球数バッファに記録する(ステップS819)。なお、図74において、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理と同じ部分には同じステップ番号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 74 is a flowchart showing another example of the base calculation area updating process (step S81). In the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 74, the number of out balls is recorded in the number of out balls buffer in order to calculate the base value at the timing when the number of out balls satisfies a predetermined condition (step S819). In FIG. 74, the same step numbers are given to the same parts as in the above-described base calculation area updating process, and the detailed description thereof will be omitted.
まず、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS810)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、特賞中以外の賞球数を取得し(ステップS811)、賞球があるかを判定する(ステップS812)。そして、ステップS812における判定の結果、賞球がなければ、賞球数を更新せずにステップS818に進む。一方、賞球があれば、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し(ステップS815)、賞球数に異常がなければ、取得した賞球数を総賞球数に加算する(ステップS814)。すなわち、図74に示すベース算出用領域更新処理では、賞球数が計算される都度、ベース値の計算に用いられる総賞球数が更新される。 First, it is determined whether the game state is a special prize (step S810). The same criteria as those described with reference to FIG. 39 can be used as the criteria for judging whether or not a special prize is being awarded. Then, the number of prize balls other than the special prize is obtained (step S811), and it is determined whether there are prize balls (step S812). If the result of determination in step S812 is that there are no prize balls, the process proceeds to step S818 without updating the number of prize balls. On the other hand, if there are prize balls, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls (step S815), and if there is no abnormality in the number of prize balls, the acquired number of prize balls is added to the total number of prize balls (step S814). . That is, in the base calculation area updating process shown in FIG. 74, the total number of prize balls used for calculating the base value is updated each time the number of prize balls is calculated.
一方、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS816)、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットする(ステップS817)。 On the other hand, if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated (step S816), and the timer for prize abnormality notification is reset (step S817).
その後、アウト球数を取得し(ステップS818)。取得したアウト球数をアウト球数
バッファに加算する(ステップS819)。そして、入賞異常が検出されているかを判定し(ステップS826)、異常と判定された入賞に対応する遊技球数を取得する(ステップS827)。
After that, the number of out balls is acquired (step S818). The acquired number of out balls is added to the number of out balls buffer (step S819). Then, it is determined whether or not a winning abnormality is detected (step S826), and the number of game balls corresponding to the winning determined as abnormal is obtained (step S827).
その後、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し(ステップS824)、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止する(ステップS825)。 After that, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize notification has timed up (step S824), and when the timer for abnormal notification of prize ball has timed up, a command to stop the abnormal notification of prize ball is generated, and the abnormal notification of prize ball is stopped ( step S825).
図73、図74に示すベース算出領域更新処理では、入賞異常にかかる全ての入賞球数分アウト球を補正したが、特定の種類の入賞異常にかかる入賞球ではアウト球を補正して、他の特定の種類の入賞異常にかかる入賞球ではアウト球を補正しなくてもよい。例えば、入賞異常にかかる入賞球の種類によっては、当該入賞球に対する賞球を払い出すことや払い出さないことがある。この入賞異常に対して賞球を払い出すかは入賞口毎に定められているとよい。この場合、賞球が払い出されない入賞異常については、入賞球を総アウト球として計数せず、ベース値の計算に使用しないとよい。一方、賞球が払い出される入賞異常については、入賞球を総アウト球として計数し、払い出される賞球も総賞球数として計数して、ベース値の計算に使用するとよい。なお、賞球が払い出される入賞異常でも、入賞球を総アウト球として計数せず、払い出される賞球も総賞球数として計数せず、ベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。 In the base calculation area updating process shown in FIGS. 73 and 74, the out balls are corrected for all the winning balls related to the winning abnormality. It is not necessary to correct the out ball for the winning ball related to the specific type of winning abnormality. For example, depending on the type of winning ball related to the winning abnormality, the winning ball may or may not be paid out. It is preferable that whether or not a prize ball is to be paid out in response to this prize winning abnormality is determined for each prize winning opening. In this case, in the case of a prize-winning abnormality in which no prize balls are paid out, the prize-winning balls should not be counted as total-out balls and should not be used in the calculation of the base value. On the other hand, as for the prize winning abnormality in which prize balls are paid out, the winning balls are counted as total out balls, and the paid out prize balls are also counted as the total number of prize balls, and used for calculating the base value. Note that even in the case of a prize winning abnormality in which prize balls are paid out, the winning balls may not be counted as the total out balls, the paid out prize balls may not be counted as the total number of prize balls, and may not be used in the calculation of the base value.
例えば、遊技機の故障をメンテナンス(球詰まりの解除等)した結果、ホール従業員が手で始動口に遊技球を入れて、遊技者が損しないように出球を補償することがあり、この場合は当該始動口への入賞に対して賞球が払い出される。この始動口への入賞は入賞異常として検出されるが、賞球が払い出される。このように賞球が払い出される場合は、ベース値に反映すべきなので、入賞異常と判定しないとよい。この場合、ベース値の計算に反映する入賞口(始動口2002、2004)においては賞球を払い出し、入賞異常を判定せず、他の入賞口(大入賞口2005、2006)においては賞球を払い出さずに、入賞異常を判定するとよい。入賞異常を判定する入賞口は、入賞異常を判定しない入賞口より、入賞により払い出される賞球の数が少ないものである(始動口は3個賞球、大入賞口は15個賞球)。このため、大入賞口において入賞異常を判定するが、始動口において異常入賞を判定しなくても、不正行為に対する防御の観点からは、大きなセキュリティホールにはならない。このように、入賞異常を判定することによって、アウト球と賞球数との不整合を防止できる。特に、賞球を発生しない入賞異常にかかる入賞球数を用いてアウト球数を補正することによって、賞球数と当該賞球の原因となるアウト球とを整合させることができる。
For example, as a result of maintenance (removal of jammed balls, etc.) for a game machine malfunction, a hall employee may manually insert a game ball into the starting hole to compensate for the ball output so that the player does not lose money. In that case, a prize ball is paid out for winning a prize to the start hole. Winning to this starting port is detected as a prize winning abnormality, but prize balls are paid out. When prize balls are paid out in this way, it should be reflected in the base value, so it should not be determined as a prize winning abnormality. In this case, in the winning openings (starting
前述したように様々な入賞口で入賞異常を判定できるが、パチンコ機への具体的な実装例について説明する。 As described above, it is possible to determine a winning abnormality in various winning ports, but a specific implementation example for a pachinko machine will be described.
まず、一般入賞口2001では入賞異常を判定せず、一般入賞口2001以外の入賞口(大入賞口2005、2006、始動口2002、2004)で入賞異常を判定してもよい。一般入賞口は、複数の遊技球の同時入賞が困難であることから、不正行為に対する遊技機のセキュリティ耐性を向上しつつ、開閉する電動役物である大入賞口2005、2006や始動口2002(合計3個)より数多く設けられている一般入賞口2001(合計4個)への入球によって遊技者に出球を補償できる。また、一般入賞口2001は、ホールの従業員が容易に識別できることから、パチンコ機1のメンテナンスや出球補償のための操作が容易である。ホールの従業員が一般入賞口2001を容易に識別できる理由としては、一般入賞口2001は遊技領域にまとめて(分かれた領域に)配置されることが多く、また、電動役物(大入賞口2005、2006、始動口2002、2004)と飾り部材(外観)が異なったりするためである。また、一般入賞口の1球の入賞に対する賞球
数が少ない場合には、不正行為に対する遊技機のセキュリティ耐性が向上する効果がある。なお、特定の一般入賞口(例えば、左端)のみで入賞異常を判定せず、他の一般入賞口では入賞異常を判定してもよい。
First, the
また、賞球数が多い大入賞口2005、2006では入賞異常を判定せず、大入賞口2005、2006以外の入賞口(賞球数が少ない一般入賞口2001、始動口2002、2004)で入賞異常を判定してもよい。大入賞口は、1球の入賞に対する賞球数が多いので、少ない入賞球でもベース値が大きく変化する。このため、パチンコ機の検査時にベース値の変化を容易に検査できて便利である。なお、特定の大入賞口(例えば、遊技球を手で入れやすい大入賞口2005)のみで入賞異常を判定せず、他の大入賞口(例えば、2006)では入賞異常を判定してもよい。
In addition, no prize-winning abnormalities are determined in the large prize-winning
また、始動口2002、2004では入賞異常を判定せず、始動口2002、2004以外の入賞口(一般入賞口2001、大入賞口2005、2006)で入賞異常を判定してもよい。始動口は、1球の入賞に対する賞球数が大入賞口より少ないので、ゴトに対する遊技機のセキュリティ耐性を向上しつつ、遊技者に出球を補償できる。なお、特定の始動口(例えば、遊技盤の中央に設けられた始動口2002は位置が分かりやすい)のみで入賞異常を判定せず、他の始動口2004では入賞異常を判定してもよい。
Further, the winning abnormality may not be determined at the starting
さらに、大入賞口や始動口においては、当該入賞口の開閉部材がパチンコ機の正面から視認可能な位置にある、すなわち、ホールの従業員が開閉部材を操作容易な入賞口では入賞異常を判定せず、当該入賞口の開閉部材がパチンコ機の正面から視認できない位置にある、すなわち、ホールの従業員が開閉部材を操作困難な入賞口では入賞異常を判定してもよい。例えば、閉状態で垂直に位置する開閉部材が斜め位置に傾斜することによって、開閉部材が遊技球を拾う構造の入賞口(いわゆる、電動チューリップ)ではホールの従業員が操作容易である。一方、閉状態では平板状部材で入賞口が塞がれており、該平板状部材が奥に引っ込むことによって、入賞口への入口が開く構造の入賞口(いわゆる、ベロチュー)ではホールの従業員が操作困難である。このようにすると、遊技者への出球補償に使用される入賞口に限定してセキュリティレベルを緩和するので、ホールの従業員に分かりやすく、かつ、遊技機のセキュリティ耐性を向上できる。 Furthermore, in the case of the big winning opening and the start opening, the opening/closing member of the winning opening is located in a position that can be seen from the front of the pachinko machine, that is, the opening/closing member can be easily operated by hall employees. Instead, the opening/closing member of the winning opening is located at a position that cannot be visually recognized from the front of the pachinko machine, that is, the opening/closing member may be difficult for hall employees to operate. For example, by tilting the opening and closing member that is positioned vertically in the closed state to an oblique position, it is easy for hall employees to operate a winning opening (so-called electric tulip) in which the opening and closing member picks up game balls. On the other hand, in the closed state, the winning opening is closed with a flat plate member, and when the flat member is retracted, the entrance to the winning opening opens (so-called Velochu). is difficult to operate. In this way, the security level is relaxed only for the winning holes used to compensate the player for putting out balls, so it is easy for hall employees to understand, and the security resistance of the gaming machine can be improved.
また、検出された入賞異常を報知してもよい。入賞異常の報知の方法は、前述した賞球数異常の報知の方法と同じでよい(例えば、外部端子板へのセキュリティ信号の出力、液晶等の表示装置への警告表示、遊技盤又は枠の装飾ランプの点灯や点滅、音声や効果音、警告音の出力など)が、入賞異常の報知は他の異常の報知より緩い報知にするとよい。具体的には、異常報知の時間が短かったり、異常を報知する文字が小さかったり、異常報知時にランプが点灯しなかったり、異常報知音を他の異常時の報知音の音量よりも小さく(抑制)するとよい。 Also, the detected winning abnormality may be notified. The method of notifying the abnormal prize may be the same as the method of notifying the abnormal number of prize balls described above (for example, outputting a security signal to an external terminal board, displaying a warning on a display device such as a liquid crystal, Lighting or flashing of decorative lamps, output of voice, sound effect, warning sound, etc.) should be looser than other abnormalities. Specifically, the abnormal notification time is short, the characters that notify the abnormality are small, the lamp does not light up when the abnormality is notified, and the abnormality notification sound is set to a lower volume than other abnormal notification sounds (suppressed). ).
また、入賞異常の報知では、入賞異常を検出してから所定時間の異常報知をし、当該所定時間中にさらに入賞異常を検出しても、当該所定時間を延長せずに、最初に設定された所定時間で報知を終了したり、報知の態様を変えるとよい。このように、入賞異常が所定の時間(例えば、数分間)連続して発生する場合、遊技者による不正行為ではなく、ホールが遊技機をメンテナンスしていると判断できる。このため、所定時間だけ入賞異常を報知して、その後は報知を継続しないようにすると、ホールによる遊技機のメンテナンス作業を妨害せず、作業効率を向上できる。また、所定時間後に報知の態様を変えることによって、遊技機のメンテナンス作業を妨害せず、正しく作業が継続して行われていることが分かる。具体的には、表示装置やランプによる報知は継続するが、音による報知を停止する(又は、音量を低下する)とよい。 In addition, in the notification of the winning abnormality, the abnormality is notified for a predetermined time after the detection of the winning abnormality. It is preferable to end the notification after a predetermined time or change the mode of notification. In this way, when the winning abnormality occurs continuously for a predetermined time (for example, several minutes), it can be determined that the hall is performing maintenance on the gaming machine, not the player's fraudulent act. Therefore, if the winning abnormality is notified only for a predetermined time and the notification is not continued after that, the work efficiency can be improved without interfering with the maintenance work of the game machine by the hall. In addition, by changing the mode of notification after a predetermined time, it can be seen that the maintenance work of the game machine is not hindered and the work is continued correctly. Specifically, it is preferable to stop the sound notification (or reduce the volume) while continuing the notification by the display device or the lamp.
纏めると、本実施例の遊技機は、入賞球数によってアウト球数を補正する補正手段を有し、該補正手段は、複数の入賞口を複数の種別(始動口、大入賞口)に区分し、第1の種別の入賞口については、所定の条件の成立中(特賞中)以外に検出した入賞球に基づいてアウト球数を補正し、第2の種別の入賞口については、所定の条件の成立中(特賞中)以外に検出した入賞球に基づいてアウト球数を補正しない。これによって、前述したように、遊技機のメンテナンスによる遊技者への補償の際のアウト球数のズレを防止でき、アウト球数を正確に計算できる。また、遊技機の誤動作により異常なベース値が計算されることがあり、その調整(メンテナンス)としてベース値の調整が可能となる。これにより、正確なベース値を計算し、表示できる。 In summary, the gaming machine of the present embodiment has correcting means for correcting the number of out balls according to the number of winning balls, and the correcting means classifies a plurality of winning holes into a plurality of types (starting hole, big winning hole). However, for the first type of winning opening, the number of out balls is corrected based on the winning balls detected while a predetermined condition is not satisfied (during the special prize), and for the second type of winning opening, a predetermined number of winning balls are detected. The number of out balls is not corrected based on the winning balls detected except when the condition is established (during the special prize). As a result, as described above, it is possible to prevent deviation of the number of out balls when compensating the player for maintenance of the gaming machine, and to accurately calculate the number of out balls. In addition, an abnormal base value may be calculated due to a malfunction of the game machine, and the base value can be adjusted as the adjustment (maintenance). This allows an accurate base value to be calculated and displayed.
ここまで、入賞異常の検出や、入賞異常の検出の例外的な取り扱い(検出しない場合)について説明したが、入賞異常と判定される遊技球は、遊技において取得した賞球ではなく、パチンコ機のメンテナンス(ベース値の調整)に用いられる可能性が高いので、望ましくは、入賞異常を判定された入賞球はアウト球数に反映せず、ベース値の計算に使用しないとよい。 Up to this point, we have explained the detection of a winning abnormality and the exceptional handling of the detection of a winning abnormality (when it is not detected). Since there is a high possibility that the winning balls will be used for maintenance (adjustment of the base value), it is desirable that the winning balls determined to be abnormal should not be reflected in the number of out balls and should not be used in the calculation of the base value.
また、図73、図74に示すベース算出領域更新処理において検出された入賞異常を報知してもよい。例えば、タイマ割込み処理の不正行為検出処理(ステップS84)において、入賞異常を異常状態として入賞異常表示コマンドを作成し、周辺制御基板コマンド送信処理(ステップS92)において送信する。この入賞異常の報知は、入賞異常にかかる入賞球が一つ検出されると行ってもよいし、入賞異常にかかる入賞球が所定数検出されると行ってもよい。また、入賞異常にかかる入賞球が連続して所定数検出されると入賞異常の報知を行ってもよいし、入賞異常にかかる入賞球が所定の時間内に所定数検出されると入賞異常の報知を行ってもよい。 In addition, the winning abnormality detected in the base calculation area updating process shown in FIGS. 73 and 74 may be reported. For example, in the fraudulent act detection process (step S84) of the timer interrupt process, a winning abnormality display command is created with the winning abnormality as an abnormal state, and is transmitted in the peripheral control board command transmission process (step S92). The notification of the abnormal winning may be performed when one abnormal winning ball is detected, or when a predetermined number of abnormal winning balls are detected. Further, when a predetermined number of winning balls related to the abnormal winning are continuously detected, the notification of the abnormal winning may be performed, and when a predetermined number of the winning balls related to the abnormal winning are detected within a predetermined time, the abnormal winning is notified. Notification may be made.
さらに、入賞異常の報知は、所定時間の経過後に終了してもよいし、次に当該入賞口が開放した(条件装置が作動した)場合に終了してもよい。 Further, the notification of the winning abnormality may be ended after a predetermined time has elapsed, or may be ended when the winning opening is opened next time (the condition device is activated).
なお、入賞異常を報知しなくてもよい。 It should be noted that it is not necessary to report the winning abnormality.
[9-11.演算回路の特性を生かしたベース値の算出処理]
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、ベース値を計算する除算処理を演算回路13121が行うので、CPU13111がプログラムによって除算を実行するより他の処理を妨げることなくベース値を計算できる。ここまで説明したベース算出処理は、この特性を生かしたものではなかった。
[9-11. Base Value Calculation Processing Utilizing Characteristics of Arithmetic Circuit]
In the
すなわち、ベース値の計算に関連し、前述したタイマ割込み処理(図23)では、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)において、排出球センサ3060や発射球センサ1020からの検出信号を読み取って、アウト球数を計数し、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)において、払い出される遊技球(賞球)の数を計算する。その後、ベース算出用領域更新処理(ステップS98)において、ベース算出用領域13128の賞球数とアウト球数を更新する。
That is, in relation to the calculation of the base value, in the above-described timer interrupt processing (FIG. 23), in the switch input processing (step S74), detection signals from the ejected
その後、ベース算出・表示処理(ステップS89)において、ベース算出用領域13128に格納された賞球数とアウト球数を参照してベース値を算出し、算出されたベース値をベース表示器1317に表示する。
Thereafter, in the base calculation/display process (step S89), the base value is calculated by referring to the number of winning balls and the number of out balls stored in the
タイマ割込み処理は、所定時間毎に実行されるものであるところ、タイマ割込み毎に所定の処理が必ず終了する必要があるので、プログラムによる遅い除算処理では、時間がかかる処理をタイマ割込み処理に含める、すなわち、複数回のベース計算処理をタイマ割込
み処理に含めるのは困難であった。一方、演算回路13121を用いて除算処理を行うことによって、ベース値の計算に必要な時間を短縮でき、一つのタイマ割込み処理において複数回ベース値を計算でき、遅滞なくベース値を表示できる。
Although timer interrupt processing is executed at predetermined intervals, it is necessary to complete the predetermined processing for each timer interrupt. Therefore, in the slow division processing by the program, the timer interrupt processing includes the time-consuming processing. In other words, it was difficult to include base calculation processing multiple times in timer interrupt processing. On the other hand, by performing division processing using the
また、演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタ131216、131217への値の書き込みから除算結果レジスタA131218からの演算結果の読み出しまでの間、CPU13111は除算処理のために占有されない。すなわち、被除数及び除数の入力タイミングから商の出力タイミングまでの32クロックのウェイト時間を有効に活用でき、この間に他の処理を行うことができる。換言すると、被除数及び除数の入力タイミングと商の出力タイミングとが別になるので、タイマ割込み処理におけるベース値計算処理の自由度が向上する。
In addition, the
図75は、演算回路の特性を生かしたタイマ割込み処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。図75に示すタイマ割込み処理は、ベース算出処理(ステップS97、S98)を除いて前述したタイマ割込み処理(図23)と同じなので、同一の処理の説明は省略する。 FIG. 75 is a flow chart showing an example of timer interrupt processing that takes advantage of the characteristics of the arithmetic circuit. The timer interrupt processing shown in FIG. 75 is the same as the above-described timer interrupt processing (FIG. 23) except for the base calculation processing (steps S97 and S98), so description of the same processing will be omitted.
タイマ割込み処理が開始されると、主制御MPU1311は、主制御プログラムを実行することによって、まず、レジスタを切り替える(ステップS70)。
When timer interrupt processing is started, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理を実行する(ステップS74)。スイッチ入力処理では、主制御MPU1311の各種入力ポートの入力端子に入力されている各種信号を読み取り、入力情報として主制御内蔵RAM1312の入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。具体的には、入賞球を検出するセンサからの検出信号や、不正行為を検出するスイッチからの検出信号や、排出球センサ3060や、発射球センサ1020からの検出信号を読み取って、アウト球数を計数する。
Next, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出処理1を実行する(ステップS97)。ベース算出処理1では、ステップS74で計数されたアウト球数を用いて総アウト球数を更新し、ベース値を計算する。ベース算出処理1の詳細は、図76、図78を用いて後述する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、タイマ更新処理(ステップS76)と、乱数更新処理1(ステップS78)を実行する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、賞球制御処理を実行する(ステップS80)。賞球制御処理では、入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、読み出した入力情報に基づいて払い出される遊技球(賞球)の数を計算し、主制御内蔵RAM1312に書き込む。また、賞球数の計算結果に基づいて、遊技球を払い出すための賞球コマンドを作成する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出処理2を実行する(ステップS98)。ベース算出処理2では、ステップS80で算出された賞球数を用いて総賞球数を更新し、ベース値を計算する。ベース算出処理2の詳細は、図77、図79を用いて後述する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、枠コマンド受信処理(ステップS82)と、不正行為検出処理(ステップS84)と、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理(ステップS86)と、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理(ステップS88)とを実行する。続いて、主制御MPU1311は、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)と、周辺制御基板コマンド送信処理(ステップS92)とを実行する。最後に、主制御MPU1311は、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットする(ステップS96
)。ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値がセットされることにより、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLがクリア設定される。また、最後に、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンクを切り替える(復帰する)。以上の処理が終了すると、タイマ割込み処理を終了し、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。
Subsequently, the
). By setting a predetermined value in the watchdog timer clear register WCL, the watchdog timer clear register WCL is cleared. Finally, the
図76は、ベース算出処理1(ステップS97)の一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 76 is a flowchart showing an example of base calculation processing 1 (step S97).
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS9701)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しないアウト球であるため、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理1を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で検出されたアウト球数を取得し(ステップS9702)、取得したアウト球数を総アウト球数に加算するように、総アウト球数を更新する(ステップS9705)。なお、アウト球数が取得できない又は取得したアウト球数が0である場合、ベース算出処理1を直ちに終了してもよい。このようにすると、無駄にベース値を計算することなく、主制御MPU1311の負荷を低減できる。
First, the
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS9707)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出処理1を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じた値を演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する(ステップS9708)。そして、所定時間(32クロック)経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から演算結果(総賞球数÷総アウト球数)を読み出して、ベース値とする(ステップS9709)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S9707). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base
その後、前述したステップS908と同様に、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS9710)、遊技者やホール従業員にベース(ベース値や、ベース値の異常)を報知する。ベース報知コマンドは、周辺制御部1511や液晶表示制御部1512が制御する表示装置(液晶表示装置1600、3114、244)やスピーカ921でベース値を報知する場合には、周辺制御部1511に対する表示コマンドや音出力コマンドである。また、主制御基板1310が制御するベース表示器1317や機能表示ユニット1400で報知する場合、これらの表示装置は7セグメントLEDやLEDランプで構成されていることから、ベース報知コマンドはLED素子への駆動信号である。具体的には、7セグメントLEDがドライバによって駆動される場合、ドライバ(ドライバ内のキャラクタジェネレータ)に設定された文字コードを含む駆動信号がベース報知コマンドである。また、7セグメントLEDが直接駆動される場合、各LED素子を点灯するための駆動信号がベース報知コマンドである。
After that, similarly to step S908 described above, a base notification command is generated (step S9710), and the base (base value or base value abnormality) is notified to the player or hall employee. The base notification command is a display command for the
図77は、ベース算出処理2(ステップS98)の一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 77 is a flowchart showing an example of base calculation processing 2 (step S98).
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS9801)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。
First, the
その結果、遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しない賞球であるため、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で算出された賞球数を取得し(ステップS9802)、取得した賞球数を総賞球数に加算するように、総賞球数を更新する(ステップS9809)。なお、賞球数が取得できない又は取得した賞球数が0である場合、ベース算出処理2を直ちに終了してもよい。このようにすると、無駄にベース値を計算することなく、主制
御MPU1311の負荷を低減できる。
As a result, if the game state is during the special prize, the base
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS9810)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じた値を演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する(ステップS9812)。なお、総賞球数が0である場合はベース値として0が計算されるが、ベース値を計算しなくてもよい。さらに、総賞球数が総アウト数より大きい場合はベース値として1(100%)以上の値が計算されるが、ベース値を計算しなくてもよい。そして、所定時間(32クロック)経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から演算結果(総賞球数÷総アウト球数)を読み出して、ベース値とする(ステップS9813)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S9810). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS9814)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。 After that, a base notification command is generated (step S9814), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees.
図76、図77に示すベース算出処理は、タイマ割込み処理毎に実行されるので、遅滞なくベース値を計算し表示できる。なお、ベース算出処理1、ベース算出処理2をタイマ割込み処理毎に実行せずに、所定時間(例えば、タイマ割込み処理より長い周期の1分)毎のタイマ割込み処理において実行してもよい。タイマ割込み処理毎にベース算出表示処理を実行しないことによって、タイマ割込み処理毎にベース値を計算する場合より、ベース値の計算に要する演算量(例えば主制御MPU1311の負荷)を低減できる。
Since the base calculation processing shown in FIGS. 76 and 77 is executed for each timer interrupt processing, the base value can be calculated and displayed without delay. Note that
次に、図78から図79を用いて、ベース算出処理(ステップS97、S98)の別な例を説明する。図78、図79に示すベース算出処理は、所定アウト球数毎、所定賞球数毎にベース値を計算する。 Next, another example of the base calculation process (steps S97 and S98) will be described with reference to FIGS. 78 and 79. FIG. The base calculation process shown in FIGS. 78 and 79 calculates a base value for each predetermined number of out balls and for each predetermined number of winning balls.
図78は、ベース算出処理1(ステップS97)の別な一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 78 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation process 1 (step S97).
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS9701)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しないアウト球であるため、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理1を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で検出されたアウト球数を取得し(ステップS9702)、取得したアウト球数をアウト球数バッファに加算するように、アウト球数バッファを更新する(ステップS9703)。なお、アウト球数が取得できない又は取得したアウト球数が0である場合、ベース算出処理1を直ちに終了してもよい。このようにすると、無駄にベース値を計算することなく、主制御MPU1311の負荷を低減できる。
First, the
その後、アウト球数バッファに格納されているアウト球数が予め定められている閾値Th2以上であるかを判定する(ステップS9704)。アウト球数が所定の閾値Th2以上であるかの判定には様々な方法がとり得る。例えば、アウト球数バッファ値と閾値Th2とを比較したり、アウト球数の格納領域の所定のビットの値で判定してもよい(具体的には、アウト球数の格納領域を8ビットで構成し、最上位ビットが1になればアウト球数が128以上であると判定できる)。 After that, it is determined whether or not the number of out balls stored in the number of out balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th2 (step S9704). Various methods can be used to determine whether the number of out balls is equal to or greater than the predetermined threshold Th2. For example, the buffer value for the number of out-balls may be compared with the threshold value Th2, or the value of a predetermined bit in the storage area for the number of out-balls may be used for determination (specifically, the storage area for the number of out-balls is 8 bits). If the most significant bit becomes 1, it can be determined that the number of out balls is 128 or more).
そして、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2より小さければ、ベース値を計算するタイミングではないので、ベース算出処理1を終了する。
Then, if the out-ball number buffer value is smaller than the threshold Th2, it is not the timing to calculate the base value, so the
一方、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2以上であれば、総アウト球数にアウト球数バッファ値を加算するように、総アウト球数を更新し(ステップS9705)、アウト球数バッファを0に設定する(ステップS9706)。 On the other hand, if the buffer value for the number of out balls is equal to or greater than the threshold Th2, the total number of out balls is updated so as to add the buffer value for the number of out balls to the total number of out balls (step S9705), and the buffer for the number of out balls is set to 0. set (step S9706).
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS9707)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出処理1を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じた値を演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する(ステップS9708)。そして、所定時間(32クロック)経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から演算結果(総賞球数÷総アウト球数)を読み出して、ベース値とする(ステップS9709)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S9707). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS9710)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。 After that, a base notification command is generated (step S9710), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees.
図79は、ベース算出処理2(ステップS98)の別な一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 79 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation process 2 (step S98).
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS9801)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しない賞球であるため、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で算出された賞球数を取得し(ステップS9802)、賞球があるか、すなわち、取得した賞球数が1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS9803)。その結果、賞球がなければ、賞球数を更新せずにステップS9808に進む。一方、賞球があれば、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し(ステップS9805)、賞球数に異常がなければ、取得した賞球数を賞球数バッファに加算するように、賞球数バッファを更新する(ステップS9804)。
First, the
一方、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS9806)、遊技者やホール従業員に賞球が異常であることを報知する。異常の報知は、様々な方法があり、以下に説明する方法の一つでも、二つ以上を組み合わせてもよい。具体的には、図46のステップS816で説明した様々な方法をとりうる。 On the other hand, if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated (step S9806) to notify the player or hall employee that the number of prize balls is abnormal. There are various methods for announcing an abnormality, and one of the methods described below or a combination of two or more methods may be used. Specifically, various methods described in step S816 of FIG. 46 can be used.
賞球数の異常とは、例えば、特賞中以外の所定時間に多くの賞球(例えば、一般入賞口や始動口の賞球数から考えて、1分間に10発以上の入賞に相当する賞球)が得られている場合などである。なお、複数段階の許容範囲を設けて賞球数の基準値からの乖離の程度によって異常の程度を複数段階で判定してもよい。 Abnormality in the number of prize balls is, for example, a lot of prize balls in a predetermined time other than during the special prize (for example, considering the number of prize balls in the general prize opening and the start opening, a prize corresponding to 10 or more prizes per minute sphere) is obtained. It should be noted that the degree of abnormality may be determined in a plurality of stages according to the degree of deviation from the reference value of the number of prize balls provided with a plurality of stages of allowable ranges.
そして、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットし(ステップS9807)、賞球異常報知時間の計数を開始する。 Then, the timer for prize ball abnormality notification is reset (step S9807), and counting of the prize ball abnormality notification time is started.
そして、賞球数バッファに格納されている賞球数が予め定められている閾値Th1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS9808)。賞球数バッファ値が所定の閾値Th1以上であるかの判定には様々な方法がとり得る。例えば、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較したり、賞球数の格納領域の所定のビットの値で判定してもよい(具体的には、賞球数の格納領域を8ビットで構成し、最上位ビットが1になればアウト球数が128以上であると判定できる)。 Then, it is determined whether or not the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th1 (step S9808). Various methods can be used to determine whether the prize ball number buffer value is greater than or equal to the predetermined threshold value Th1. For example, the value of the number of prize balls buffer may be compared with the threshold value Th1, or the value of a predetermined bit in the number of prize balls storage area may be used for determination. If the most significant bit becomes 1, it can be determined that the number of out balls is 128 or more).
そして、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1より小さければ、ベース値を計算するタイミングではないので、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。
Then, if the winning ball number buffer value is smaller than the threshold value Th1, it is not the timing to calculate the base value, so the
一方、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上であれば、総賞球数に賞球数バッファ値を加算するように、総賞球数を更新し(ステップS9809)、賞球数バッファを0に設定する(ステップS9810)。 On the other hand, if the prize ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1, the total prize ball number is updated so as to add the prize ball number buffer value to the total prize ball number (step S9809), and the prize ball number buffer is set to 0. Set (step S9810).
なお、賞球数バッファに加算する都度、外部端子板784から遊技場に設置されたホールコンピュータに賞球数を出力してもよいし、後述する賞球数が所定の閾値Th1以上となった場合に当該閾値Th1を外部端子板784からホールコンピュータに出力してもよい。ここで賞球数バッファは、ベース値を計算するために主制御内蔵RAM1312に設けられる領域であり、パチンコ機1が払い出す賞球数が一時的に格納される。
Each time the number of prize balls is added to the number of prize balls buffer, the number of prize balls may be output from the external
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS9811)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じた値を演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納する(ステップS9812)。そして、所定時間(32クロック)経過後に、除算結果レジスタA131218から演算結果(総賞球数÷総アウト球数)を読み出して、ベース値とする(ステップS9813)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S9811). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base
その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS9814)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。 After that, a base notification command is generated (step S9814), and the base is notified to the players and hall employees.
その後、ステップS9807で起動した賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定する(ステップS9815)。そして、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止する(ステップS9816)。なお、ステップS9815では、所定時間だけ賞球異常を報知するためのタイマの時間によって報知の終了を判定したが、所定の発射球数だけ賞球異常を報知しするように報知の終了を判定してもよい。また、ホール従業員が確認するまで異常を報知し続けてもよい。 After that, it is determined whether the timer for announcing abnormal prize balls started in step S9807 has timed up (step S9815). Then, when the timer for prize ball abnormality notification times up, a prize ball abnormality notification stop command is generated, and the prize ball abnormality notification is stopped (step S9816). In step S9815, the end of the notification is determined by the time of the timer for notifying the abnormality of the prize ball for a predetermined time, but the end of the notification is determined so that the abnormality is notified only for the predetermined number of shot balls. may Alternatively, the anomaly may continue to be reported until a hall employee confirms it.
図80は、タイマ割込み処理の別な一例を示すフローチャートである。図80に示すタイマ割込み処理は、ベース算出処理(ステップS93、S94)とベース表示処理(ステップS95)を除いて前述したタイマ割込み処理(図23、図75)と同じなので、同一の処理の説明は省略する。 FIG. 80 is a flow chart showing another example of timer interrupt processing. The timer interrupt processing shown in FIG. 80 is the same as the above-described timer interrupt processing (FIGS. 23 and 75) except for the base calculation processing (steps S93 and S94) and the base display processing (step S95). are omitted.
タイマ割込み処理が開始されると、主制御MPU1311は、主制御プログラムを実行することによって、まず、レジスタを切り替える(ステップS70)。
When timer interrupt processing is started, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理を実行する(ステップS74)。スイッチ入力処理では、排出球センサ3060や発射球センサ1020からの検出信号を読み取って、アウト球数を計数する。
Next, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出処理3を実行する(ステップS93)。ベース算出処理3では、ステップS74で計数されたアウト球数を用いて総アウト球数を更新し、ベース値を計算するためのパラメータを演算回路13121に書き込む。ベース算出処理3の詳細は、図81、図84を用いて後述する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、タイマ更新処理(ステップS76)と、乱数更新処
理1(ステップS78)を実行する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、賞球制御処理を実行する(ステップS80)。賞球制御処理では、入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、読み出した入力情報に基づいて払い出される遊技球(賞球)の数を計算し、主制御内蔵RAM1312に書き込む。また、賞球数の計算結果に基づいて、遊技球を払い出すための賞球コマンドを作成する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出処理4を実行する(ステップS94)。ベース算出処理2では、ステップS80で計数された賞球数を用いて総賞球数を更新し、ベース値を計算するためのパラメータを演算回路13121に書き込む。ベース算出処理4の詳細は、図82、図85を用いて後述する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、枠コマンド受信処理(ステップS82)と、不正行為検出処理(ステップS84)と、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理(ステップS86)と、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理(ステップS88)とを実行する。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、演算回路13121から読み出し、ベースを報知するためのコマンドを生成するベース表示処理を実行する(ステップS95)。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)と、周辺制御基板コマンド送信処理(ステップS92)とを実行する。最後に、主制御MPU1311は、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットする(ステップS96)。ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値がセットされることにより、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLがクリア設定される。また、最後に、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンクを切り替える(復帰する)。以上の処理が終了すると、タイマ割込み処理を終了し、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。
Subsequently, the
図81は、ベース算出処理3(ステップS93)の一例を示すフローチャートである。図81に示すベース算出処理3は、図76に示すベース算出処理1からステップS9709以後を取り除いたものである。
FIG. 81 is a flowchart showing an example of base calculation processing 3 (step S93).
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS9701)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しないアウト球であるため、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理1を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で検出されたアウト球数を取得し(ステップS9702)、取得したアウト球数を総アウト球数に加算するように、総アウト球数を更新する(ステップS9705)。なお、アウト球数が取得できない又は取得したアウト球数が0である場合、ベース算出処理3を直ちに終了してもよい。このようにすると、無駄にベース値を計算することなく、主制御MPU1311の負荷を低減できる。
First, the
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS9707)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出処理3を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタB131217に総アウト球数を格納する(ステップS9708)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S9707). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base
図82は、ベース算出処理4(ステップS94)の一例を示すフローチャートである。図82に示すベース算出処理4は、図77に示すベース算出処理2からステップS9813以後を取り除いたものである。
FIG. 82 is a flowchart showing an example of base calculation processing 4 (step S94).
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS9801)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しない賞球であるため、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で算出された賞球数を取得し(ステップS9802)、取得した賞球数を総賞球数に加算するように、総賞球数を更新する(ステップS9809)。なお、賞球数が取得できない又は取得した賞球数が0である場合、ベース算出処理1を直ちに終了してもよい。このようにすると、無駄にベース値を計算することなく、主制御MPU1311の負荷を低減できる。
First, the
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS9810)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じた値を演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタA131216に格納する(ステップS9812)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S9810). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base
なお、図81のステップS9708で、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納せず、図82のステップS9812で、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じた値を除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納してもよい。 In step S9708 of FIG. 81, the total number of out balls is not stored in the division input register B131217, and in step S9812 of FIG. , and the total number of out balls may be stored in the division input register B131217.
図83は、ベース表示処理(ステップS95)の一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 83 is a flow chart showing an example of the base display process (step S95).
主制御MPU1311は、除算結果レジスタA131218から演算結果(総賞球数÷総アウト球数)を読み出して、ベース値とする(ステップS8901)。その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS8902)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。
The
図81、図82に示すベース算出処理と、図83に示すベース表示処理は、タイマ割込み処理毎に実行されるので、遅滞なくベース値を計算し表示できる。なお、ベース算出処理1、ベース算出処理2をタイマ割込み処理毎に実行せずに、所定時間(例えば、1分)毎のタイマ割込み処理において実行してもよい。
Since the base calculation processing shown in FIGS. 81 and 82 and the base display processing shown in FIG. 83 are executed for each timer interrupt processing, the base value can be calculated and displayed without delay. Note that the
次に、図84から図85を用いて、ベース算出処理(ステップS97、S98)の別な例を説明する。図84、図85に示すベース算出処理は、所定アウト球数毎、所定賞球数毎にベース値を計算する。 Next, another example of the base calculation process (steps S97 and S98) will be described with reference to FIGS. 84 and 85. FIG. The base calculation process shown in FIGS. 84 and 85 calculates a base value for each predetermined number of out balls and for each predetermined number of winning balls.
図84は、ベース算出処理3(ステップS93)の別な一例を示すフローチャートである。図84に示すベース算出処理3は、図78に示すベース算出処理1からステップS9709以後を取り除いたものである。
FIG. 84 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation process 3 (step S93).
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS9701)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しないアウト球であるため、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理1を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で検出されたアウト球数を取得し(ステップS9702)、取得したアウト球数をアウト球数バッファに加算するように、アウト球数バッファを更新する(ステップS9703)。なお、アウト球数が取得できない又は取得したアウト球数が0である場合、ベース算出処理3を直ちに終了してもよい。このようにすると、無駄にベース値を計算することなく、主制御MPU1311の負荷を低減でき
る。
First, the
その後、アウト球数バッファに格納されているアウト球数が予め定められている閾値Th2以上であるかを判定する(ステップS9704)。アウト球数が所定の閾値Th2以上であるかの判定には様々な方法がとり得る。例えば、アウト球数バッファ値と閾値Th2とを比較したり、アウト球数の格納領域の所定のビットの値で判定してもよい(具体的には、アウト球数の格納領域を8ビットで構成し、最上位ビットが1になればアウト球数が128以上であると判定できる)。 After that, it is determined whether or not the number of out balls stored in the number of out balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th2 (step S9704). Various methods can be used to determine whether the number of out balls is equal to or greater than the predetermined threshold Th2. For example, the buffer value for the number of out-balls may be compared with the threshold value Th2, or the value of a predetermined bit in the storage area for the number of out-balls may be used for determination (specifically, the storage area for the number of out-balls is 8 bits). If the most significant bit becomes 1, it can be determined that the number of out balls is 128 or more).
そして、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2より小さければ、ベース値を計算するタイミングではないので、ベース算出処理1を終了する。
Then, if the out-ball number buffer value is smaller than the threshold Th2, it is not the timing to calculate the base value, so the
一方、アウト球数バッファ値が閾値Th2以上であれば、総アウト球数にアウト球数バッファ値を加算するように、総アウト球数を更新し(ステップS9705)、アウト球数バッファを0に設定する(ステップS9706)。 On the other hand, if the buffer value for the number of out balls is equal to or greater than the threshold Th2, the total number of out balls is updated so as to add the buffer value for the number of out balls to the total number of out balls (step S9705), and the buffer for the number of out balls is set to 0. set (step S9706).
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS9707)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出処理1を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタB131217に総アウト球数を格納する(ステップS9708)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S9707). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base
図85は、ベース算出処理4(ステップS94)の別な一例を示すフローチャートである。図85に示すベース算出処理4は、図79に示すベース算出処理2からステップS9813以後を取り除いたものである。
FIG. 85 is a flow chart showing another example of the base calculation process 4 (step S94).
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS9801)。特賞中であるかの判定基準は図39で説明したものと同じものを用いることができる。そして、遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しない賞球であるため、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)で算出された賞球数を取得し(ステップS9802)、賞球があるか、すなわち、取得した賞球数が1以上であるかを判定する(ステップS9803)。その結果、賞球がなければ、賞球数を更新せずにステップS9808に進む。一方、賞球があれば、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し(ステップS9805)、賞球数に異常がなければ、取得した賞球数を賞球数バッファに加算するように、賞球数バッファを更新する(ステップS9804)。
First, the
一方、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS9806)、遊技者やホール従業員に賞球が異常であることを報知する。異常の報知は、様々な方法があり、以下に説明する方法の一つでも、二つ以上を組み合わせてもよい。具体的には、図46のステップS816で説明した様々な方法をとりうる。 On the other hand, if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated (step S9806) to notify the player or hall employee that the number of prize balls is abnormal. There are various methods for announcing an abnormality, and one of the methods described below or a combination of two or more methods may be used. Specifically, various methods described in step S816 of FIG. 46 can be used.
賞球数の異常とは、例えば、特賞中以外の所定時間に多くの賞球(例えば、一般入賞口や始動口の賞球数から考えて、1分間に10発以上の入賞)が得られている場合などである。なお、複数段階の許容範囲を設けて賞球数の基準値からの乖離の程度によって異常の程度を複数段階で判定してもよい。 An abnormality in the number of prize balls is, for example, when a large number of prize balls are obtained in a predetermined time period other than during the special prize (for example, considering the number of prize balls at the general prize opening and the start opening, 10 or more prizes are won per minute). For example, if It should be noted that the degree of abnormality may be determined in a plurality of stages according to the degree of deviation from the reference value of the number of prize balls provided with a plurality of stages of allowable ranges.
そして、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットし(ステップS9807)、賞球異常報知時間の計数を開始する。 Then, the timer for prize ball abnormality notification is reset (step S9807), and counting of the prize ball abnormality notification time is started.
そして、賞球数バッファに格納されている賞球数が予め定められている閾値Th1以上
であるかを判定する(ステップS9808)。賞球数バッファ値が所定の閾値Th1以上であるかの判定には様々な方法がとり得る。例えば、賞球数バッファ値と閾値Th1とを比較したり、賞球数の格納領域の所定のビットの値で判定してもよい(具体的には、賞球数の格納領域を8ビットで構成し、最上位ビットが1になればアウト球数が128以上であると判定できる)。
Then, it is determined whether or not the number of prize balls stored in the number of prize balls buffer is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold value Th1 (step S9808). Various methods can be used to determine whether the prize ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the predetermined threshold value Th1. For example, the buffer value of the number of prize balls may be compared with the threshold value Th1, or the value of a predetermined bit in the number of prize balls storage area may be used for determination (specifically, the number of prize balls may be stored in 8 bits). If the most significant bit becomes 1, it can be determined that the number of out balls is 128 or more).
そして、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1より小さければ、ベース値を計算するタイミングではないので、ベースを計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。
Then, if the winning ball number buffer value is smaller than the threshold value Th1, it is not the timing to calculate the base value, so the
一方、賞球数バッファ値が閾値Th1以上であれば、総賞球数に賞球数バッファ値を加算するように、総賞球数を更新し(ステップS9809)、賞球数バッファを0に設定する(ステップS9810)。 On the other hand, if the prize ball number buffer value is equal to or greater than the threshold Th1, the total prize ball number is updated so as to add the prize ball number buffer value to the total prize ball number (step S9809), and the prize ball number buffer is set to 0. Set (step S9810).
なお、賞球数バッファに加算する都度、外部端子板784から遊技場に設置されたホールコンピュータに賞球数を出力してもよいし、後述する賞球数が所定の閾値Th1以上となった場合に当該閾値Th1を外部端子板784からホールコンピュータに出力してもよい。ここで賞球数バッファは、ベース値を計算するために主制御内蔵RAM1312に設けられる領域であり、パチンコ機1が払い出す賞球数が一時的に格納される。
Each time the number of prize balls is added to the number of prize balls buffer, the number of prize balls may be output from the external
その後、総アウト球数が0であるかを判定する(ステップS9811)。総アウト球数が0であればベース値を計算できないので、ベース値を計算せず、ベース算出処理2を終了する。一方、総アウト球数が0でなければ、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じた値を演算回路13121の除算入力レジスタA131216に格納する(ステップS9812)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the total number of out balls is 0 (step S9811). If the total number of out balls is 0, the base value cannot be calculated, so the base
なお、図84のステップS9708で、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納せず、図85のステップS9812で、総賞球数に所定数(例えば100)を乗じた値を除算入力レジスタA131216に格納し、総アウト球数を除算入力レジスタB131217に格納してもよい。 In step S9708 of FIG. 84, the total number of out balls is not stored in the division input register B131217, and in step S9812 of FIG. , and the total number of out balls may be stored in the division input register B131217.
図86は、ベース表示処理(ステップS95)の別な一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 86 is a flow chart showing another example of the base display process (step S95).
主制御MPU1311は、除算結果レジスタA131218から演算結果(総賞球数÷総アウト球数)を読み出して、ベース値とする(ステップS8901)。その後、ベース報知コマンドを生成し(ステップS8902)、遊技者やホール従業員にベースを報知する。
The
その後、ベース算出処理4のステップS9807で起動した賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定する(ステップS8903)。そして、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止する(ステップS8904)。なお、ステップS8903では、所定時間だけ賞球異常を報知するためのタイマの時間によって報知の終了を判定したが、所定の発射球数だけ賞球異常を報知するように報知の終了を判定してもよい。また、ホール従業員が確認するまで異常を報知し続けてもよい。
After that, it is determined whether the timer for announcing abnormal prize balls started in step S9807 of
図75、図80に示すように、本実施例のタイマ割込み処理では、タイマ割込み処理が終了する前に(タイマ割り込み周期が経過して、次のタイマ割込み処理が開始する前に)、演算回路13121から除算結果を読み出せるタイミングで、演算回路13121への入力値(除数、被除数)を書き込む。具体的には、演算回路13121への入力値(除数
、被除数)の書き込みタイミングは、タイマ割込み処理の前半であったり、乱数更新処理(ステップS78)より前であったり、特別図柄や普通図柄の制御処理(ステップS86、S88)より前がよい。
As shown in FIGS. 75 and 80, in the timer interrupt processing of this embodiment, before the timer interrupt processing ends (before the timer interrupt cycle elapses and the next timer interrupt processing starts), the arithmetic circuit Input values (divisor, dividend) to the
また、遊技者に付与する遊技媒体(賞球)の数によって、ベース値を計算する処理の実行の有無を判定してもよい。すなわち、入賞口毎に定められた賞球数の観点から、賞球数やアウト球数をベース値の計算に使用するかを切り替えてもよい。例えば、一つの入賞球に対して最大の賞球を付与する入賞口の賞球は、ベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。 Further, whether or not to execute the process of calculating the base value may be determined based on the number of game media (prize balls) given to the player. That is, from the viewpoint of the number of prize balls determined for each winning hole, it may be switched whether to use the number of prize balls or the number of out balls for calculating the base value. For example, the winning ball in the winning hole that gives the maximum winning ball to one winning ball may not be used in the calculation of the base value.
具体的には、遊技領域に設けられた入賞口毎に定められた遊技媒体が入賞したときに付与する賞遊技媒体(1つの入賞球に対して払い出される賞球)の数が1個、3個、5個の3種類である場合、最大である5個の賞球数及びこれに対応するアウト球数をベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。これは、賞球数が大きい入賞をベース値の計算に使用すると、計算されたベース値の変化が大きくなり、計算されたベース値の下位桁を加工手段によって丸めて(四捨五入、切り上げ、切り捨て等をして)表示しても、表示される値が頻繁に変化する場合が生じる。このような場合、パチンコ機が所定の性能を発揮しているか(例えば、設定した出玉率通りなのか)のホールによる判断が困難になるからである。 Specifically, the number of prize game media (prize balls paid out for one prize ball) given when a game medium determined for each prize winning port provided in the game area wins is 1, 3, or 3. In the case of three types of 1 and 5, the maximum number of 5 winning balls and the number of out balls corresponding thereto may not be used for calculation of the base value. This is because if a prize with a large number of prize balls is used to calculate the base value, the calculated base value will change greatly, and the lower digits of the calculated base value will be rounded (rounded off, rounded up, rounded down, etc.) ), the displayed value may change frequently. This is because, in such a case, it is difficult for the pachinko hall to determine whether the pachinko machine is exhibiting a predetermined performance (for example, whether the ball output rate is as set).
また、最小である1個の賞球数及びこれに対応するアウト球数をベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。これは、賞球数が小さい入賞によるベース値の変化は小さいことから、当該1個の賞球をベース値の計算に使用しなくても、加工手段によって計算されたベース値の下位桁を丸めて(四捨五入、切り上げ、切り捨て等をして)表示すると、表示されるベース値は変化しない場合が生じるので、表示の変化に貢献しない処理は省略してもよいからである。 Also, the minimum number of one winning ball and the corresponding number of out balls may not be used for calculating the base value. Since the change in the base value due to winning with a small number of prize balls is small, the lower digits of the base value calculated by the processing means are rounded off even if the single prize ball is not used in the calculation of the base value. This is because the displayed base value may not change if the displayed value is rounded (rounded off, rounded up, rounded down, etc.), and processing that does not contribute to the change in display may be omitted.
また、賞球数が最大の場合と最小の場合で説明したが、最大と最小の間にある中間値の賞球数をベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。この場合、最大と最小の賞球数はベース値の計算に使用するため、最大と最小が平均化されることによってパチンコ機全体の動作を表す賞球数やアウト球数が示され、適切なベース値を示すことができる。 In addition, although the case where the number of prize balls is the maximum and the case where the number of prize balls is the minimum have been described, it is not necessary to use an intermediate number of prize balls between the maximum and the minimum for calculation of the base value. In this case, since the maximum and minimum numbers of winning balls are used to calculate the base value, the number of winning balls and the number of out-balls representing the operation of the pachinko machine as a whole are shown by averaging the maximum and minimum values, A base value can be indicated.
なお、3種類の賞球数のパターンで説明したが、3種類に限らず、5種類や7種類など他の種類の賞球数のパターンでもよい。 Although three types of prize ball number patterns have been described, the patterns are not limited to three types, and other types of prize ball number patterns such as five types and seven types may be used.
さらに、特定の種類(前述した最小値の1個や、中間値の3個や、最大値の5個など)の賞球数の入賞をベース値の計算に使用しなかった場合、当該入賞が検出された際の遊技状態における全ての入賞はベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。例えば、5個の賞球を付与する入賞口への入賞をベース値の計算に使用しない場合、当該入賞口への入賞が検出された遊技状態においては、当該遊技状態の終了までは、当該入賞口や他の入賞口への入賞をベース値の計算に使用しない。また、当該遊技状態の開始以後についても、当該入賞口や他の入賞口への入賞は遡ってベース値の計算に使用しない。 In addition, if a particular type of winning ball (such as the minimum value of 1, the middle value of 3, the maximum value of 5, etc.) is not used in the calculation of the base value, such winning will be All winnings in the game state when detected need not be used in calculating the base value. For example, if the winning to a winning hole that gives five balls is not used for calculating the base value, in the game state in which the winning to the winning hole is detected, until the game state ends, the winning Winnings in mouths or other winnings should not be used to calculate base values. Moreover, even after the start of the game state, winnings in the relevant winning opening and other winning openings are not retroactively used for calculation of the base value.
また、当該入賞が検出された際の遊技状態が再び生じた場合における入賞はベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよく、当該入賞が検出された際の遊技状態が他の遊技状態に遷移するまでの入賞をベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。これは、計算されるベース値の変化が大きい遊技状態の賞球数とアウト球数をベース値の計算に使用しないことによって、パチンコ機が正常か(例えば、設定した出玉率通りなのか)の判断が遅延する可能性を排除するためである。 In addition, when the game state when the winning is detected occurs again, the winning may not be used for calculating the base value, and the game state when the winning is detected transitions to another game state. Winnings up to 2000 do not have to be used to calculate the base value. This is done by not using the number of winning balls and the number of out balls in the game state in which the base value to be calculated changes greatly, in calculating the base value. This is to eliminate the possibility of a delay in the judgment of
なお、遊技状態によって賞球数が変化する場合に1個の入賞球に対して最大(又は、最小、中間)となる賞球について、ベース値の計算に使用しなくてもよい。 When the number of prize balls changes depending on the game state, the maximum (or minimum or intermediate) prize ball for one winning ball may not be used for calculating the base value.
次に、前述した遊技媒体(賞球)の数によって、賞球数及びアウト球数をベース値の計算に使用しない具体的な処理を説明する。 Next, a specific process of not using the number of prize balls and the number of out balls for calculating the base value will be described, depending on the number of game media (prize balls) described above.
スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)において、各入賞口センサからの検出信号が主制御基板1310に入力されたときに、主制御MPU1311が当該入賞をベース値の計算に使用するかを判定してもよい。そして、ベース値の計算に使用しないと判定される入賞については、ベース値を計算するための総賞球数や総アウト球数の更新をしなかったり、ベース値の計算処理を実行しなかったりする。より具体的には、例えば、図75に示すタイマ割込み処理で、ベース算出処理1(ステップS97)において、ベース値の計算から除外する入賞球数を0にしてアウト球数から除外し、ベース算出処理2(ステップS98)において、ベース値の計算から除外する賞球数を0にして総賞球数に加算しないとよい。また、検出された全ての入賞がベース値の計算に使用しない場合、図75のベース算出処理1(ステップS97)及びベース算出処理2(ステップS98)を実行しなくてもよい。
In the switch input process (step S74), when the detection signal from each winning opening sensor is input to the
また、図80に示すタイマ割込み処理では、ベース算出処理3(ステップS93)において、ベース値の計算から除外する入賞球数を0にしてアウト球数から除外し、ベース算出処理4(ステップS94)において、ベース値の計算から除外する賞球数を0にして総賞球数に加算しないとよい。また、検出された全ての入賞がベース値の計算に使用しない場合、図80のベース算出処理3(ステップS93)、ベース算出処理4(ステップS94)及びベース表示処理(ステップS95)を実行しなくてもよい。 Further, in the timer interrupt process shown in FIG. 80, in the base calculation process 3 (step S93), the number of winning balls to be excluded from the calculation of the base value is set to 0 to be excluded from the number of out balls, and the base calculation process 4 (step S94). , the number of prize balls excluded from the calculation of the base value should be set to 0 and not added to the total number of prize balls. If none of the detected prize winnings are used for calculating the base value, base calculation processing 3 (step S93), base calculation processing 4 (step S94) and base display processing (step S95) of FIG. 80 are not executed. may
ベース値の計算に使用しないと判定された入賞球数をアウト球数から除外する方法は、図73や図74で説明した異常入賞によるアウト球の補正と同様の方法を採用してもよい。 The method of excluding the number of winning balls determined not to be used in the calculation of the base value from the number of out balls may adopt the same method as the correction of out balls due to abnormal winning explained in FIGS. 73 and 74.
なお、この場合、検出された入賞をベース値の計算に使用するかを入賞球数から判定するので、ベース算出処理1(ステップS97)、ベース算出処理2(ステップS98)、ベース算出処理3(ステップS93)及びベース算出処理4(ステップS94)において、特賞中かを判定しなくてもよい。 In this case, it is determined from the number of winning balls whether the detected winning prize is to be used for calculating the base value. In step S93) and base calculation processing 4 (step S94), it is not necessary to determine whether a prize is being awarded.
このように、所定の入賞にかかるアウト球数及び入賞球数をベース値の計算から除外することによって、処理を飛ばさずに実行するので、特に開発段階において処理が正確に実行されているかを容易に確認できる。また、ベース値を計算する処理を実行せずに、ベース値を更新しないことによって、主制御MPU1311の処理が軽減され、他の処理(抽選処理や変動パターンを決定する処理など)を正確に実行できる。
In this way, by excluding the number of out balls and the number of winning balls for a predetermined prize from the calculation of the base value, the processing can be executed without skipping. can be confirmed. In addition, by not executing the processing for calculating the base value and not updating the base value, the processing of the
すなわち、有利度合いが異なる複数の賞がある中で、最大の賞は遊技者に付与されても、ベース値の計算には使用されず、当該賞の付与によってベース値は変化せずに表示される。さらに、当該最大となる賞を付与した遊技状態が少なくとも終了するまでは、計算されるベース値は変化せずに表示される。 That is, even if there are multiple prizes with different degrees of advantage, even if the largest prize is awarded to the player, it is not used for calculating the base value, and the base value is displayed without any change due to the awarding of the prize. be. Further, the calculated base value is displayed without change until at least the gaming state in which the maximum prize is given is terminated.
[9-12.ベースを表示する遊技機の別な構成]
図87は、本実施例のパチンコ機の制御構成を概略的に示すブロック図である。
[9-12. Another configuration of the game machine displaying the base]
FIG. 87 is a block diagram schematically showing the control configuration of the pachinko machine of this embodiment.
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、図17に示すパチンコ機の制御構成と異なり、排出球センサ3060として、盤側排出球センサ3060Aが遊技盤5に設けられ、枠側排出球センサ3060Bが本体枠4に設けられる。なお、盤側排出球センサ3060A及び枠側排出球センサ3060Bのいずれか一方が設けられても、両方が設けられてもよい。
In the
盤側排出球センサ3060Aは、前述したように、遊技領域5aの下部に設けられるアウト口1111を通過する遊技球を検出するアウト口通過球センサ1021である(図53参照)。盤側排出球センサ3060Aの出力信号は、図92を用いて後述するように、主制御基板1310に入力され、主制御MPU1311に入力される。この場合、アウト口通過球センサ1021が検出した遊技球の数と、始動口センサ2104、2551が検出した遊技球の数と、各種入賞口センサ3015、2114、2554、2557が検出した遊技球の数との合計をアウト球数とする。
The board-side discharged
枠側排出球センサ3060Bは、前述したように、遊技領域5aから流出した遊技球をパチンコ機1の外部に排出する排出口に設けられる(図4参照)。枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力信号は、払出制御基板951や、本体枠4と遊技盤5とを接続するコネクタを経由して主制御基板1310に入力される。
As described above, the frame-side
盤側排出球センサ3060Aと枠側排出球センサ3060Bとの両方を設けた場合、盤側排出球センサ3060Aの計数結果と枠側排出球センサ3060Bの計数結果とを比較して、二つの計数結果に所定以上の差が生じた場合にエラーを報知してもよい。また、所定時間内の二つの計数結果に所定以上の差が生じた場合に、エラーを報知してもよい。
When both the board-side discharged
なお、本実施例のパチンコ機では、表示スイッチ1318は必須の構成ではなく、後述するように所定の時間間隔でベース表示器1317の表示内容(暫定区間表示と確定区間表示)が切り替えられるが(図99参照)、表示スイッチ1318の操作によって、ベース値を表示したり、表示内容を切り替えてもよい。
In addition, in the pachinko machine of the present embodiment, the
前述した以外の構成は、図17に示すパチンコ機の制御構成と同じである。 Configurations other than those described above are the same as the control configuration of the pachinko machine shown in FIG.
図88、図89は、枠側排出球センサ3060Bの配置を示す図である。
88 and 89 are diagrams showing the arrangement of the frame-side discharged
図88は、遊技盤の裏面側の本体枠4に設けられる球流路960においてアウト球を1条に整列させて、一つの枠側排出球センサ3060Bでアウト球を計数する機構の例を示す。遊技領域5aを転動する遊技球は、アウト口1111、一般入賞口2001、大入賞口2005、2006を経由して遊技盤5の裏面側の本体枠4に流入する。本体枠4には、排出された遊技球を正面視の右側に流下させ、1条に整列させる球流路960が設けられている。枠側排出球センサ3060Bは、1条に整列した遊技球を計数する。
FIG. 88 shows an example of a mechanism for aligning out-balls in a row in the
図89は、遊技盤の裏面に設けられる球流路960において整列させたアウト球を2条で流下させ、複数の排出球センサ3060で計数する機構の例を示す。遊技領域5aを転動する遊技球は、アウト口1111、一般入賞口2001、始動口2002、2004、大入賞口2005、2006を経由して遊技盤5の裏面側の本体枠4に流入する。本体枠4には、排出された遊技球を左右から中央付近に流下させ、2条に整列させる球流路960が設けられている。二つ設けられた枠側排出球センサ3060Bの各々は、各条に整列した遊技球を計数する。
FIG. 89 shows an example of a mechanism in which out balls aligned in a
枠側排出球センサ3060Bは、図53、図88、図89に示す位置に設けられるが、球流路960と共にユニット化して、本体枠4から着脱可能に構成してもよい。また、枠側排出球センサ3060Bを本体枠4から着脱可能に構成してもよい。
The frame-side discharged
図90は、排出球センサと主制御基板との接続例を示す図である。 FIG. 90 is a diagram showing an example of connection between the ejected ball sensor and the main control board.
盤側排出球センサ3060Aの出力線は、中継基板を経由して主制御基板1310に設
けられたコネクタ13101に接続され、盤側排出球センサ3060Aの出力信号が主制御MPU1311に入力される。枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線は、主制御基板1310に設けられたコネクタ13102に接続され、枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力信号が主制御MPU1311に入力される。
The output line of board-side ejected
盤側排出球センサ3060Aの出力線が接続されるコネクタ13101は、主制御基板1310の上側に設けられるとよく、枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線が接続されるコネクタ13102は、主制御基板1310の下側に設けられるとよい。
A
盤側排出球センサ3060Aの出力線が接続されるコネクタ13101と、枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線が接続されるコネクタ13102とは別に設けられるが、破線で示すように、盤側排出球センサ3060Aの出力線と枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線とが一つのコネクタ(例えば、13102)に接続されてもよい。
A
なお、盤側排出球センサ3060Aの出力線を、中継基板を経由せずに主制御基板1310に接続してもよい。枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線を、直接、主制御基板1310に接続してもよい。枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線を払出制御基板951を経由して主制御基板1310に接続してもよい。枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線を中継基板(図示省略)を経由して主制御基板1310に接続してもよい。枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線を払出制御基板951又は中継基板に接続後、遊技盤5と本体枠4とを接続するコネクタ(例えば、フローティングコネクタ)を経由して、主制御基板1310に接続してもよい。
Note that the output line of the board-side ejected
また、本実施例のパチンコ機には複数の磁気検出センサ1030が設けられる。磁気検出センサ1030の出力信号は、図92を用いて後述するように、主制御MPU1311に入力される。
Also, the pachinko machine of this embodiment is provided with a plurality of
図91は、遊技盤5の一例を示す正面図であり、特に、遊技盤5に設けられた磁気検出センサ1030の配置を示す。
FIG. 91 is a front view showing an example of the
磁気検出センサ1030は、遊技領域5a内における不正な磁気を検知するセンサであり、各種入賞口2001、2002、2004、2005、2006への入賞を検出するセンサの近傍(図において星印の位置)に設けられる。磁気検出センサ1030の検出範囲は遊技盤5上の破線で示し、一部重複している。
The
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、アウト口1111の付近にも磁気検出センサ1030が設けられる。これは、不正なベース値の計算を防止するためである。すなわち、遊技者がアウト口1111に磁石を近づけて排出球センサ3060を動作させた場合、アウト球数が実際より多く計数され、ベース値が低下する。このため、遊技店では、ベース値を所定の規格値に戻すようにパチンコ機1のメンテナンス作業を行うことがある。実際と異なるベース値に基づいてメンテナンス作業がされたパチンコ機では通常状態の出球が増加することになり、遊技者が通常より有利な状態で遊技でき、多くの出球を獲得できる。正確なベース値を計算し、このように不正な出球の払い出しを防止するために、アウト口1111の付近に磁気検出センサ1030を設ける。なお、アウト口1111の付近以外にも排出球センサ3060が磁気によって誤動作する可能性がある箇所には磁気検出センサ1030を設けるとよい。
In the
アウト口1111付近に設けられる磁気検出センサ1030は、図示したように、他の磁気検出センサ1030より検出範囲が広い方がよい。これは、図89に示したように、複数の排出球センサ3060でアウト球を検出する場合、複数の排出球センサ3060を
カバー可能な十分な範囲で磁気を検出するためである。また、アウト口1111付近に設けられる磁気検出センサ1030の磁気検出範囲は、他の入賞口(例えば、アウト口1111の上部に設けられる大入賞口2005)を含んでもよい。
The
図92は、主制御入力回路1315の構成を示す図である。主制御入力回路1315は、排出球センサ3060や入賞口センサ(一般入賞口センサ3015、第一始動口センサ2104、第二始動口センサ2551、第一大入賞口センサ2114、第二上大入賞口センサ2554、第二下大入賞口センサ2557など)、磁気検出センサ1030の出力信号を受け、主制御MPU1311に入力する。
FIG. 92 shows a structure of main
主制御入力回路1315は、インターフェイス回路1331及びバッファ回路1332を含む。インターフェイス回路1331は、各種センサから入力された信号をレベル変換や整形(例えば、チャタリング除去)して出力する。バッファ回路1332は、主制御MPU1311から指示されたタイミングで、入力された信号をデータバスに出力する。
Main
具体的には、各センサからの出力信号はインターフェイス回路1331のA1~A8のいずれかの端子に入力され、インターフェイス回路1331でレベル変換や整形がされた信号がY1~Y8端子から出力され、バッファ回路1332のA1~A8のいずれかの端子に入力される。バッファ回路1332は、主制御MPU1311のチップセレクト信号CS4、CS5が入力されたタイミングで、Y1~Y8端子に入力された信号をデータバスに出力する。これによって、各センサによる検出結果が主制御MPU1311に取り込まれる。
Specifically, the output signal from each sensor is input to one of terminals A1 to A8 of the
インターフェイス回路1331は、異常検出回路及び電源監視回路を含む。インターフェイス回路1331の異常検出回路は、A1~A8端子の入力を監視しており、各端子への入力信号が所定の閾値(例えば、4V)より低いレベルや、所定の閾値(例えば、電源電圧-0.1V)より高いレベルになると、スイッチへの接続線の断線やスイッチの短絡を検出し、いずれかの端子の入力が前記所定の閾値によって定義される正常範囲を超えた場合、異常信号Eを出力するとともに、A1~A8端子の入力信号とは無関係に、各センサがOFFであるレベルの信号をY1~Y8端子から出力する。インターフェイス回路1331の電源監視回路は、電源電圧VSを監視しており、電源電圧が所定の閾値(例えば、12V-20%)より低いレベルとなり、電源の異常を検出すると、異常信号Eを出力するとともに、A1~A8端子の入力信号とは無関係に、各センサがOFFであるレベルの信号をY1~Y8端子から出力する。つまり、センサからONレベルの信号が入力されても、当該入力に対するインターフェイス回路の出力はOFFレベルとなる。このため、主制御MPU1311は、当該センサから出力された信号を有効なものとして判定しない(当該センサの出力は無効とされる)。これにより、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチの電源が低下したか否かによって、入力信号の処理を実行するか否かを判定する必要がなくなり、処理負荷を軽減できるとともに、Y1~Y8の出力信号を入力信号A1~8の状態に無関係に、各センサがOFFとなるレベルの信号を出力できる。
The
後述するように、主制御MPU1311は、異常信号を検出すると、ベース値の計算を行わない(図105参照)。インターフェイス回路1331には、ベース値の計算に使用されるセンサからの信号(排出球数、賞球数)とベース値の計算に使用されないセンサからの信号(ゲートセンサ2547など)とが入力される。インターフェイス回路1331は、いずれかの入力信号が異常となった場合に異常信号を出力する。このため、ベースの計算に関係ないセンサに異常が検出されても、ベースの計算が実行されずに、ベース表示器1317の表示内容は維持されて変化しないことになる。
As will be described later, when the
すなわち、主制御入力回路1315は、ベース値の計算に使用されるセンサからの信号
とベース値の計算に使用されないセンサからの信号とを監視して、いずれかの信号が異常となった場合、ベースの計算を停止するために異常信号を出力する。
That is, the main
図93、図94、図95は、主制御基板1310の実装例を示す図である。図93(A)は、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とが異なるドライバ回路1334に接続される例を示し、図93(B)は、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とが一つのドライバ回路1334に接続される例を示す。図94は、主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317と主制御基板1310上の配置を示す。図95(A)は、主制御基板ボックス1320に収容された主制御基板1310の正面図であり、図95(B)は下面図であり、図95(C)は右側面図である。
93, 94, and 95 are diagrams showing examples of mounting the
図93(A)、(B)に示すように、主制御I/Oポート1314は、ラッチ回路1333及びドライバ回路1334を含む。
As shown in FIGS. 93A and 93B, the main control I/
図93(A)に示す例において、機能表示ユニット1400の表示データとベース表示器1317の表示データとは、主制御MPU1311から出力され、異なるラッチ回路1333に取り込まれる。そして、異なるドライバ回路1334から表示データが機能表示ユニット1400及びベース表示器1317に出力される。
In the example shown in FIG. 93(A), the display data of the
図93(B)に示す例において、機能表示ユニット1400の表示データとベース表示器1317の表示データとは、主制御MPU1311から出力され、一つのラッチ回路1333に取り込まれる。そして、一つのドライバ回路1334から表示データが機能表示ユニット1400及びベース表示器1317に出力される。
In the example shown in FIG. 93(B), the display data of the
図93(A)及び(B)に示す例において、主制御MPU1311には、リセット回路1335からのリセット信号や、クロック発振器1336からのクロック信号が入力される。主制御MPU1311から機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317の表示データが出力される信号線と、リセット信号やクロック信号の信号線とは交差しないように配置されるとよい。
In the examples shown in FIGS. 93A and 93B, the
コネクタ13101は、盤側排出球センサ3060Aの出力線が接続されるコネクタであり、主制御基板1310の上側に設けられるとよい。コネクタ13101には、盤側排出球センサ3060Aからの出力線だけでなく、他の入賞口センサ3015、2104等や、磁気検出センサ1030からの出力線が接続される。コネクタ13102は、枠側排出球センサ3060Bの出力線が接続されるコネクタであり、主制御基板1310の下側に設けられるとよい。コネクタ13101、13102に入力された排出球センサ3060からの信号は、インターフェイス回路1331及びバッファ回路1332を介して、主制御MPU1311に入力される。
図94は、主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317との間に配置される部品の主制御基板1310上の配置を示す図である。図94は、主制御基板1310を構成するプリント基板を裏面側から示した図であり、実線が裏面側のパターン、破線が部品面側のパターン、点線がプリント基板の部品面に実装された部品を示す。なお、グランドパターンと電源パターンの図示は省略した。
FIG. 94 is a diagram showing the arrangement of components on the
主制御MPU1311から出力されるデータ線(D1~D8)は、ラッチ2(1333)に入力され、ドライバ2(1334)を経由してベース表示器1317の7セグメントLEDの各桁のカソード側のセグメント端子に接続される。
The data lines (D1 to D8) output from the
また、主制御MPU1311から出力されるデータ線の一部(D1~D4)は、ラッチ
1(1333)に入力され、ドライバ1(1334)を経由してベース表示器1317の7セグメントLEDの各桁のアノード側のコモン端子に接続される。
Some of the data lines (D1 to D4) output from the
主制御MPU1311からは、ラッチ回路1333の動作タイミングを制御するチップセレクト信号が出力されている、具体的には、ラッチ回路2(1333)は、主制御MPU1311のチップセレクト信号CS2が入力されたタイミングで、各セグメントの点滅を制御するためのデータをデータ線(D1~D8)から取り込む。また、ラッチ回路1(1333)は、主制御MPU1311のチップセレクト信号CS3が入力されたタイミングで、各桁の点滅を制御するためのデータをデータ線(D1~D4)から取り込む。
A chip select signal that controls the operation timing of the
主制御MPU1311には、リセット回路1335からのリセット信号や、クロック発振器1336からのクロック信号が入力される。また、リセット信号はリセット回路1335から各ラッチ回路1333にも入力される、ラッチ回路1333は、リセット信号によって、ラッチされたデータをクリアする。
A reset signal from a
主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317との間のデータ線(D1~D8)と、リセット信号やクロック信号の信号線とは交差しないように配置される。同様に、図示は省略するが、主制御MPU1311と機能表示ユニット1400との間のデータ線(D1~D8)と、リセット信号やクロック信号の信号線とは交差しないように配置される。
The data lines (D1 to D8) between the
これは、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、ダイナミック点灯によってベース表示器1317を制御することから、主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317との間のデータ線ではパルス信号が伝達され、主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317との間のデータ線では、頻繁にレベルが変化する。特に、ドライバ回路1334とベース表示器1317との間はLED素子を駆動するために必要な大きな電流が流れる。このため、主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317との間(特に、ドライバ回路1334とベース表示器1317との間)のデータ線はノイズの発生要因となる。そして、主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317との間のデータ線と、リセット信号やクロック信号の信号線とが交差すると、リセット信号やクロック信号の信号線にノイズが載って、パチンコ機1が誤動作する可能性がある。この信号線の交差は、プリント基板の表面と裏面における配線パターンの交差や、内層と表面層(表面、裏面)の配線パターンの交差でも生じうる。
This is because, in the
具体的には、本来生じ得ないタイミングで主制御MPU1311にリセット信号が入力されることによって、遊技中に主制御MPU1311がリセットされ、遊技が停止したり、遊技状態が消去されることが生じ得る。なお、本来生じ得ないタイミングで遊技状態が消去されると、正常な電源断時処理が実行されずにリセットされるので、RAM1312に記憶されたデータがクリアされ、大当りが終了したり、変動表示ゲームが途中で終了したり、特別図柄変動表示ゲームや普通図柄変動表示ゲームの保留が消去されたりする。
Specifically, when a reset signal is input to the
主制御基板ボックス1320は、主制御基板1310に取り付けられた部品の高さや、組み付けたときの他の部材との干渉に応じて、部分的に高さが低く、他の部分の高さが高くなっている。例えば、図95に示すように、主制御MPU1311は高さが高いので、主制御MPU1311が実装される箇所は主制御基板ボックス1320の高さが高くなっており、主制御MPU1311が実装される箇所の左側の領域は主制御基板ボックス1320の高さが高くなっており、比較的背が高い電解コンデンサ等の部品が搭載される。一方、主制御MPU1311が実装される箇所の右側の領域は主制御基板ボックス1320の高さが低くなっており、背が低いIC等の部品が搭載される(背が高い部品が配置できない)。なお、主制御基板ボックス1320の高さが高く、高さが高い部品を実装可能な領域をハッチングで示す。また、コネクタ13101、13102が取り付けられる領域では、主制御基板ボックス1320は、相手方コネクタが挿抜される面と同程度以下(基
板面と同じ高さとすることが望ましい)の高さに形成し、他の基板と接続するケーブル(コネクタ)の挿抜に支障が生じないようにするとよい。
The main
このように、基板上に搭載される部品の高さに合わせて主制御基板ボックス1320の高さを部分的に変えることによって、主制御基板上の不正な部品(回路)を取り付けるゴト行為を抑制できる。
In this way, by partially changing the height of the main
図95では、主制御基板1310の右上部にベース表示器1317を配置したが、メンテナンスの都合で本体枠4を所定の角度だけ開放しても、遊技者が表示内容を視認困難な位置にベース表示器1317を配置するとよい。例えば、営業中のメンテナンス(補給タンクの遊技球の有無が確認する)ために本体枠4を所定の角度だけ開放したときに、遊技者がベース表示器1317の表示内容を視認できると、遊技者はベース表示器1317の表示の読み方を正しく理解していない場合が多いことから、ベース表示器1317の表示内容について、遊技者から説明を求められることがあり、このような煩雑さを防止するために、遊技者が表示内容を視認困難な位置にベース表示器1317を配置するとよい。また、このようにベース表示器1317を配置すると、遊技者からの問い合わせを抑制できる。すなわち、ベース表示器1317は、最大でアウト球数で52000個の稼動分のベース値を表示するが、当該遊技者による短時間の遊技におけるベース値と異なるため、出球率についてクレームが生じることがある。このようにベース表示器1317を配置すると、遊技者からのクレームを抑制できる。以上のことは、前述した役物比率表示器1317でも同様であり、遊技者が表示内容を視認困難な位置に役物比率表示器1317を配置するとよい。
In FIG. 95, the
図示したように、ベース表示器(7セグメントLED)1317は高さが低いので、主制御基板ボックス1320の高さが低い領域に実装される。
As shown, the base indicator (7-segment LED) 1317 is low in height, so it is mounted in the low height area of the main
図96は、主制御I/Oポート1314の構成を示す図であり、図93(A)に示すように、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とが異なるドライバ回路1334に接続される例の回路図である。本実施例では、機能表示ユニット1400及びベース表示器1317が発光ダイオード(LED)で構成される例を説明するが、ランプ(電球)や他の発光素子で構成されてもよい。主制御I/Oポート1314は、主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317や機能表示ユニット1400との間に配置され、主制御MPU1311から出力された表示データをベース表示器1317や機能表示ユニット1400へ出力する。
FIG. 96 is a diagram showing the configuration of the main control I/
前述したように、主制御I/Oポート1314は、ラッチ回路1333及びドライバ回路1334を含む。
As previously mentioned, main control I/
ラッチ回路1333は、入力されたデータをクロック信号のタイミングで取り込み、次にクロック信号又はクリア信号が入力されるまで保持し、出力する。ドライバ回路1334は、入力された信号に従ってスイッチングトランジスタを動作させ、それぞれ、ドライバ回路1334のVCC端子に入力される電源電圧(+12V)を出力する。
The
具体的には、ラッチ回路1333は、クロック信号CKの立ち上がりタイミングでD1~D8端子に入力されたバスデータを取り込み、それぞれ、Q1~Q8端子からドライバ回路1334に出力する。ドライバ回路1334は、I1~I8端子に入力された信号に従ってスイッチングトランジスタを動作させ、それぞれ、O1~O8端子の電圧を変化させる。ドライバ回路1334の出力O1~O8は、ベース表示器1317を構成する7セグメントLEDのセグメント端子や機能表示ユニット1400の7セグメントLEDに接続される。
Specifically, the
例えば、ベース表示器1317の1桁目の7セグメントLED(7seg1)を点灯させるため、CS1の立ち上がりタイミングで、ラッチ2(1333)に取り込まれたバスデータD1~D8を、ドライバ2(1334)がセグメントデータ(点灯時がLOW)として出力する。また、ベース表示器1317の7セグメントLEDの駆動タイミングはコモン端子に印加される電圧のタイミングによって定まる。すなわち、CS0の立ち上がりタイミングで、ラッチ1(1333)に取り込まれたバスデータD1~D4を、ドライバ1(1334)がコモンデータ(駆動時がHIGH)として出力する。具体的には、CS0の立ち上がりタイミングで、バスデータD1がHIGHであれば、ドライバ1(1334)から出力されるCOM1がHIGHとなり、ベース表示器1317の1桁目の7セグメントLED(7seg1)が駆動される。
For example, in order to light the first digit 7-segment LED (7seg1) of the
また、機能表示ユニット1400の7セグメントLEDを点灯させるため、CS2の立ち上がりタイミングで、ラッチ3(1333)に取り込まれたバスデータD1~D8を、ドライバ3(1334)がセグメントデータ(点灯時がLOW)として出力する。また、機能表示ユニット1400の7セグメントLEDの駆動タイミングはコモン端子(LED-C1)に印加される電圧のタイミングによって定まる。すなわち、CS3の立ち上がりタイミングで、ラッチ4(1333)に取り込まれたバスデータD1~D4を、ドライバ4(1334)がコモンデータ(駆動時がHIGH)として出力する。具体的には、CS3の立ち上がりタイミングで、バスデータD1がHIGHであれば、ドライバ4(1334)のO1端子がHIGHとなり、機能表示ユニット1400の7セグメントLED(LED-C1)が駆動される。
In addition, in order to light the 7-segment LED of the
本実施例では、ベース表示器1317も機能表示ユニット1400も7セグメントLEDはアノードコモン型であるため、7セグメントLEDにはドライバ1からドライバ2への電流が流れる。このため、当該セグメントの点灯時のドライバ1、4の出力はVCC(+12V)であり、ドライバ2、3の出力はGND(0V)となる。
In this embodiment, since the 7-segment LEDs of both the
なお、コモン側のラッチ1、4(1333)は、データバスから入力されたデータをそのままQ1~Q8端子に出力するものであるが、ラッチ1、4(1333)がデコーダ機能を有しデータバスから取得した2進数データに従って、Q1~Q8のいずれかの端子から信号を出力してもよい。
The
次に、図93(A)や図96に示すように、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とを異なるドライバ回路1334に接続した場合の信号の出力タイミングについて説明する。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 93A and 96, the signal output timing when the
ドライバ2(1334)からベース表示器1317に送られるセグメントデータと、ドライバ1(1334)からベース表示器1317に送られるコモンデータとは、同じタイマ割込み処理において出力される。また、ドライバ3(1334)から機能表示ユニット1400に送られるセグメントデータと、ドライバ4(1334)から機能表示ユニット1400に送られるコモンデータも、同じタイマ割込み処理において出力される。すなわち、コモンデータもセグメントデータも別の信号線でベース表示器1317及び機能表示ユニット1400へ送られるので、ベース表示器1317への表示データと、機能表示ユニット1400への表示データとの両方が、一つのタイマ割込み処理において出力される。
The segment data sent from the driver 2 (1334) to the
そして、次のタイマ割込み処理で、次の桁(LEDのグループ)を選択するコモンデータを出力し、コモンデータの出力と同じタイミングで各LEDの点灯を制御するセグメントデータを出力する。 Then, in the next timer interrupt process, common data for selecting the next digit (LED group) is output, and segment data for controlling lighting of each LED is output at the same timing as the output of common data.
ベース表示器1317への表示データと、機能表示ユニット1400への表示データとは、タイマ割込み処理内の別の処理で生成され、タイマ割込み処理内の別のタイミングで出力される。すなわち、主制御MPU1311が遊技制御領域外のベース算出・表示用コード13135を実行することによって、ベース表示器1317への表示データを生成し、出力する。一方、主制御MPU1311が遊技制御領域の遊技制御用コード13131を実行することによって、機能表示ユニット1400への表示データを生成し、出力する。これらのデータは、別のプログラム(コード)によって生成され、別なタイミングで出力されることになる。
The display data for the
次に、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とを異なるドライバ回路1334に接続した場合の信号の出力タイミングの変形例について説明する。
Next, a modification of the signal output timing when the
ドライバ2(1334)からベース表示器1317に送られるセグメントデータと、ドライバ1(1334)からベース表示器1317に送られるコモンデータとは、同じタイマ割込み処理において出力される。同様に、ドライバ3(1334)から機能表示ユニット1400に送られるセグメントデータと、ドライバ4(1334)から機能表示ユニット1400に送られるコモンデータとは、同じタイマ割込み処理において出力される。ベース表示器1317に送るデータを出力するタイマ割込み処理は、機能表示ユニット1400に送るデータを出力するタイマ割込み処理と異なるタイミングで実行され、続いて実行するとよい。
The segment data sent from the driver 2 (1334) to the
機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とに信号を出力する処理は、RAM1312の異なる領域に格納されたプログラム(遊技制御用コード13131、ベース算出・表示用コード13135)に従って実行されるが、同一のタイミングでコモン信号が送信されないように、二つのコードで共通する制御用のデータを使用して、コモン信号の送信タイミングが重複しないように制御するとよい。例えば、遊技制御用コード13131とベース算出・表示用コード13135とが共通に使用するコモンカウンタを設け、例えば、コモンカウンタが0~3の場合に機能表示ユニット1400にコモン信号を出力し、コモンカウンタが4~7の場合にベース表示器1317にコモン信号を出力するように制御する。
The process of outputting signals to the
コモン信号を出力する処理とセグメント信号を出力する処理とを別個又は一つのサブルーチンで構成してもよい。機能表示ユニット1400に送るデータを出力する処理を実行するための遊技制御用コード13131と、ベース表示器1317に送るデータを出力する処理を実行するためのベース算出・表示用コード13135とが、各プログラムで定められたタイミングで当該サブルーチンを呼び出して、機能表示ユニット1400やベース表示器1317に信号を出力するとよい。この場合、機能表示ユニット1400に送るデータの出力と、ベース表示器1317に送るデータを出力とは、同じタイマ割込み処理内では行われない。遊技制御用コード13131及びベース算出・表示用コード13135は、一つのタイマ割込み処理内で実行されるものの、当該サブルーチンは異なるタイマ割込み処理で呼び出される。
The processing of outputting the common signal and the processing of outputting the segment signal may be configured separately or in one subroutine. A
図93(A)や図96に示すように、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とを異なるドライバ回路1334に接続すると、主制御基板1310の外部に設けられた表示器(機能表示ユニット1400)からノイズが混入しても、主制御基板1310の内部の表示器(ベース表示器1317)や主制御基板1310の回路に及ぼす影響を抑制できる。
As shown in FIGS. 93A and 96, when the
図97は、主制御I/Oポート1314の構成を示す図であり、図93(B)に示すよ
うに、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とがコモン側で共通するドライバ回路1334に接続される例の回路図である。主制御I/Oポート1314は、主制御MPU1311とベース表示器1317や機能表示ユニット1400との間に配置され、主制御MPU1311から出力された表示データをベース表示器1317や機能表示ユニット1400へ出力する。
FIG. 97 shows the configuration of the main control I/
前述したように、主制御I/Oポート1314は、ラッチ回路1333及びドライバ回路1334を含む。主制御I/Oポート1314に含まれる回路の構成は、前述した回路構成と同じであるため、以下では図96に示す構成例との違いを説明する。
As previously mentioned, main control I/
図97に示す例では、ベース表示器1317の7セグメントLEDを点灯させるための動作は、図96に示す例と同じであるが、機能表示ユニット1400のコモンがベース表示器1317とでコモン信号が共通である。
In the example shown in FIG. 97, the operation for lighting the 7-segment LED of the
機能表示ユニット1400の7セグメントLEDを点灯させるため、CS2の立ち上がりタイミングで、ラッチ3(1333)に取り込まれたバスデータD1~D8を、ドライバ3(1334)がセグメントデータ(点灯時がLOW)として出力する。また、機能表示ユニット1400の7セグメントLEDの駆動タイミングはコモン端子(LED-C1)に印加される電圧のタイミングによって定まる。すなわち、CS0の立ち上がりタイミングで、ラッチ1(1333)に取り込まれたバスデータD1~D4を、ドライバ1(1334)がコモンデータ(駆動時がHIGH)として出力する。
In order to light the 7-segment LED of the
このように、ベース表示器1317と機能表示ユニット1400とでドライバ回路を共通にすることによって、回路規模を削減できる。部品点数が減ることで、故障率が低下し、基板のサイズも小さくすることができ、基板ユニット(主制御基板1310と主制御基板ボックス1320を含め)を容易に小型化できる。パチンコ機において、主制御基板1310では、内層パターン(3層以上のプリント基板)を使用せず、表面と裏面にのみパターンを有する2層基板を使用する。このため、2層基板で構成した主制御基板1310上に、部品が物理的に配置が可能であっても配線パターンを引き回す領域が確保できず、3層以上の多層基板より基板が大きくならざるを得ないことから、部品点数の削減による小型化が重要となる。
Thus, by sharing the driver circuit between the
図98は、図97に示す主制御I/Oポート1314の構成例におけるタイミング図である。図98において、時間軸と垂直な点線はタイマ割込み処理の区切り(タイマ割込み処理の開始タイミング)を示す。
FIG. 98 is a timing chart for an example configuration of the main control I/
タイマ割込み処理内で、主制御MPU1311は、CS0を出力するタイミングで、桁選択データをデータバスに出力する。CS0で選択されるラッチ1(1333)は、CS0の立ち上がりタイミングで、データバスからD1~D4を取り込み、ドライバ1(1334)は、D1~D4で指示された桁に対応するコモンデータ(駆動時がHIGH)を出力する。
In the timer interrupt process, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、CS2を出力するタイミングで、機能表示ユニット1400で点灯するセグメントのデータをデータバスに出力する。CS2で選択されるラッチ3(1333)は、CS2の立ち上がりタイミングで、データバスからD1~D8を取り込み、ドライバ3(1334)は、D1~D8で指示されたセグメントデータ(点灯時がLOW)を出力し、機能表示ユニット1400の7セグメントLEDを点灯する。
Next, the
その後、主制御MPU1311は、CS1を出力するタイミングで、ベース表示器1317で点灯するセグメントのデータをデータバスに出力する。CS1で選択されるラッチ
2(1333)は、CS1の立ち上がりタイミングで、データバスからD1~D8を取り込み、ドライバ2(1334)は、D1~D8で指示されたセグメントデータ(点灯時がLOW)を出力し、ベース表示器1317の7セグメントLEDを点灯する。
After that, the
最後に、主制御MPU1311は、CS0、CS1、CS2を出力するタイミングで、データバスのデータを全て0に設定する。これによって、ラッチ1(1333)に設定された桁選択データと、ラッチ2、3(1333)に設定された表示データとが消去され、7セグメントLEDが消灯する。
Finally, the
次のタイマ割込み処理において、主制御MPU1311は、CS0を出力するタイミングで、次の桁選択データをデータバスに出力し、前述した処理を繰り返して、桁選択データ及び表示データを出力する。このようにして、ベース表示器1317と機能表示ユニット1400とでコモン側のドライバ回路を共通にして、セグメントデータを時分割して出力し、共通のコモンデータを用いて、ベース表示器1317と機能表示ユニット1400とのLED素子を点灯できる。
In the next timer interrupt processing, the
図93(B)や図97に示すように、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とを共通のドライバ回路1334に接続するので、主制御基板1310の回路規模を小さくでき、高密度実装(例えば、多層基板の採用や部品の近接配置)が不可能な主制御基板1310における部品の実装を容易にできる。
As shown in FIGS. 93(B) and 97, the
また、一つのタイマ割込み処理において機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317との両方を共通のコモンデータによって制御するために、当該コモンデータを出力している期間において、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317とに異なるタイミングでセグメントデータを出力する。このため、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317との両方を共通のコモンデータ線によって制御しつつ、機能表示ユニット1400とベース表示器1317との両方を、一つのタイマ割込み処理内で表示制御できる。
In addition, in order to control both the
図98に示す場合では、機能表示ユニット1400の表示用データを先に出力し、ベース表示器1317の表示用データを後に出力している。各表示用データは、チップセレクト(CS2、CS1)の立ち上がりタイミングでラッチされ、消去データに対応するチップセレクト(CS0)の立ち上がりタイミングで消去される。このため、図示するように、機能表示ユニット1400の表示用データを先に出力し、ベース表示器1317の表示用データを後に出力すると、機能表示ユニット1400の表示時間がベース表示器1317の表示時間より長くなる。これは、パチンコ機1の表面側に配置されている機能表示ユニット1400のLEDの1サイクルにおける点灯時間を長くし、輝度を上げることによって、ホールの照明に直接照らされることによる視認性の低下を防ぐためである。また、ベース表示器1317は、パチンコ機1の表面側より暗い裏面側に配置されているため、LEDを低輝度で発光させても、ベース表示器1317の視認性への影響が小さい。すなわち、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、主制御MPU1311で制御される第1LEDと第2LEDが設けられており、第1LEDの発光輝度を第2LEDの発光輝度より高くしている。
In the case shown in FIG. 98, the display data for the
なお、上記とは逆に、ベース表示器1317の表示用データを先に出力し、機能表示ユニット1400の表示用データを後に出力して、ベース表示器1317の表示時間を機能表示ユニット1400の表示時間より長くしてもよい。
In contrast to the above, the display data for the
図99は、ベース値の計算にかかる状態(区間)の変化を示す図である。 FIG. 99 is a diagram showing changes in states (intervals) involved in base value calculation.
本実施例のパチンコ機1のベース表示器1317には、暫定区間表示と確定区間表示とが所定時間(例えば5秒)間隔で切り替えられて表示される。暫定区間表示では、計測中の区間のベース値を表示する。具体的には、上2桁に「bA.」を表示してベース値Aを表示していることを示し、下2桁に計測中のベース値Aを2桁の百分率で表示する。なお、ベース値Aの百分率の整数部分が99である場合は「99」を表示し、100以上である場合は「99.」を表示し、0である場合は「00」を表示する。このため、ベース表示器1317の表示桁数が2桁でも、ベース値Aが0%か100%かが分かるように表示できる。
On the
また、暫定区間表示では、低確率・非時短アウト球数が所定数(例えば、6000個)未満の場合は上2桁(又は4桁全て)を点滅表示して(例えば、周期0.6秒で、0.3秒点灯と0.3秒消灯を繰り返す)、正確なベース値が計測できていないことを示す。一方、低確率・非時短アウト球数が所定数(例えば、6000個)以上の場合は上2桁を点灯表示して、正確なベース値が計測できていることを示す。 Also, in the provisional section display, if the number of low-probability, non-time-saving out balls is less than a predetermined number (e.g., 6000), the upper two digits (or all four digits) are displayed blinking (e.g., cycle 0.6 seconds (Repeatedly turned on for 0.3 seconds and turned off for 0.3 seconds), indicating that an accurate base value cannot be measured. On the other hand, when the number of low-probability non-time-saving out balls is a predetermined number (for example, 6000) or more, the upper two digits are lit and displayed to indicate that an accurate base value can be measured.
確定区間表示では、一つ前の区間のベース値を表示する。具体的には、上2桁に「bb.」を点灯表示してベース値Bを表示していることを示し、下2桁に一つ前の区間のベース値(一つ前の期間の下2桁の最終値であるベース値B)を2桁の百分率で点灯表示する。なお、ベース値Bの百分率の整数部分が99である場合は「99」を表示し、100以上である場合は「99.」を表示し、0である場合は「00」を表示する。このため、ベース表示器1317の表示桁数が2桁でも、ベース値Bが0%か100%かが分かるように表示できる。
In the fixed interval display, the base value of the previous interval is displayed. Specifically, the upper two digits indicate that the base value B is displayed by lighting up “bb.” The base value B), which is the final value of two digits, is lit and displayed as a percentage of two digits. When the integer part of the percentage of the base value B is 99, "99" is displayed, when it is 100 or more, "99." is displayed, and when it is 0, "00" is displayed. Therefore, even if the number of display digits of the
なお、第1区間においては、一つ前の区間はテスト区間であるため、ベース値が計測されていない。このため、確定区間表示では、上2桁に「bb.」を点滅表示し、下2桁に「--」を点滅表示する。 In the first section, the base value is not measured because the previous section is the test section. For this reason, in the fixed section display, the upper two digits are indicated by blinking "bb." and the lower two digits are indicated by blinking "--".
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、初回電源投入からアウト球数が500個未満の所定数(例えば、256個)はテスト区間として、ベース値を計算しない。これは、パチンコ機1の初回電源投入から所定数の発射においては、確率分布の範囲内で出球がばらつくことがあり、ベース値が安定せず、意味のあるベース値が計測できないからである。このため、テスト区間においては、ベース表示器1317にベース値を表示せずに、ベース値を不定とする。具体的には、暫定区間表示では、上2桁に「bA.」を表示し、下1桁に「--」を表示し、確定区間表示では、上2桁に「bb.」を表示し、下1桁に「--」を表示する。テスト区間においては、ベース表示器1317の全桁数を点滅表示して、正確なベース値が計測できていないことを示す。なお、テスト区間においてもベース値を計算して、計算されたベース値をベース表示器1317に表示せずに、ベース値を不定としてもよい。
In the
ここで、初回電源投入時とは、パチンコ機の1の完成後の初めての電源投入時や、ベース算出用ワークエリアの初期化(図101のS26、図108のS8013)が実行された直後の状態である。また、本明細書で一般的に用いられる電源投入時とは、初回電源投入時以外の電源投入時である。
Here, when the power is turned on for the first time, the power is turned on for the first time after the
また、電源投入後の所定時間や、設定変更モードや設定確認モードの終了後(設定キー971のOFF操作から)所定時間において、ベース表示器1317の全ての桁の全LEDを点滅してもよい。
Further, all the LEDs of all digits of the
なお、後述するベース算出用領域13128のデータの検査において、データに異常が検出され、データが消去された場合、ベース値の計算はテスト区間から再開する。
In addition, in the inspection of the data in the
テスト区間以外の各区間において、全ての遊技状態(大当たり中、通常遊技中、時短中、非時短中、高確率中、低確率中など)の全アウト球数が52000に至ると、次の区間に切り替え、新たにベース値を計測する。なお、1区間のアウト球数は52000個ではなく、予め定めた値であれば他の数でもよい。例えば、パチンコ機1の1日の稼動時間を10時間だと想定すると、1日の稼動(アウト球数)である60000個を1区間のアウト球数に採用してもよい。切りのよい数字である50000個や100000個を採用してもよい。
In each section other than the test section, when the number of all out balls reaches 52000 in all game states (during jackpot, normal game, time saving, non time saving, high probability, low probability, etc.), the next section , and measure a new base value. Note that the number of out balls in one section is not 52,000, and may be any other number as long as it is a predetermined value. For example, assuming that the
なお、1区間のアウト球数を適宜変更可能とする構成にしてもよい。例えば、主制御基板1310に設定用のスイッチ(DIPスイッチ、ロータリースイッチなど)を設け、当該スイッチの設定に応じて1区間のアウト球数が設定されるとよい。当該スイッチは、パチンコ機1の裏面側に設けられる主制御基板1310又は主制御基板1310に接続される他の基板上に設けられる。さらに、当該スイッチの設定を変更すると、RAM1312のベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)を初期化してテスト区間からベース値の計算を再開したり、現在の区間の最初から再開してもよい。パチンコ機は、新台として導入された直後は稼動が多いので、1区間のアウト球数を大きい数に設定し、営業期間が経過すると、1区間のアウト球数を小さい数に設定する。すなわち、本実施例のパチンコ機1ではベース値の計算の単位となる区間の長さを定める稼動が設定可能な設定手段を有し、初回電源投入時には、該設定手段によって設定された稼動に基づいて1区間の長さが設定される。
It should be noted that the configuration may be such that the number of out-balls in one section can be changed as appropriate. For example, a setting switch (DIP switch, rotary switch, etc.) may be provided on the
なお、確定区間表示として、現在測定中の暫定区間の一つ前の区間を表示する例を説明するが、複数の確定区間(例えば、1~3区間前の区間)のベース値を切り替えて表示してもよい。このとき、所定時間毎に暫定区間→確定区間1→確定区間2→確定区間3と切り替えて表示しても、別途設けた表示切替スイッチの操作によって、暫定区間→確定区間1→確定区間2→確定区間3を切り替えて表示してもよい。
An example of displaying the section immediately before the provisional section currently being measured as the final section display will be explained. You may At this time, even if the display is switched from the provisional section → the fixed
この場合、確定区間表示におけるベース表示器1317の上2桁を「bb.」ではなく、「b1」「b2」「b3」のように、表示されている区間が分かるように、各確定区間で異なる表示をするとよい。
In this case, the upper two digits of the
このように、ベース表示器1317に、現在計測中の区間のベース値と、直前の一つ又は複数の区間のベース値とを所定時間毎に切り替えて表示する。また、ベース表示器1317の一部に表示内容を区別可能な表示を行い、他の一部に計測されたベース値を表示する。
In this manner, the
図100は、ベース表示器1317に表示される文字の例を示す図である。
FIG. 100 is a diagram showing an example of characters displayed on the
前述したように、ベース表示器1317は、複数桁(例えば4桁)の7セグメントLEDで構成されており、各桁のセグメントを点灯又は点滅することによって、数字や文字を表示する。数字として0から9を表示でき、文字としてアルファベットのA、b、c、d、E、F、Lや-符号も表示できる。さらに、数字や文字と同時に小数点も表示できる。小数点と同時に数字の6が表示される場合と数字の9が表示される場合を図示した。
As described above, the
図101及び図102は、本実施例のパチンコ機の初期化処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。 101 and 102 are flowcharts showing an example of initialization processing of the pachinko machine of this embodiment.
図101及び図102に示す初期化処理は、図21及び図22で前述した初期化処理と比較し、チェックコード算出処理(ステップS50)及びチェックコード格納処理(ステ
ップS52)が削除される。このため、ベース算出用領域のチェックコードの計算は、タイマ割込み処理のベース算出処理(ステップS8038)で実行される。なお、図21及び図22で前述した初期化処理と同じステップには同じ符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。
The initialization processing shown in FIGS. 101 and 102 is different from the initialization processing described above with reference to FIGS. 21 and 22, except that the check code calculation processing (step S50) and the check code storage processing (step S52) are deleted. Therefore, the calculation of the check code in the base calculation area is executed in the base calculation process (step S8038) of the timer interrupt process. 21 and 22, the same steps as those of the initialization process described above are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
パチンコ機1に電源が投入されると、主制御基板1310の主制御MPU1311が主制御プログラムを実行することによって初期化処理を行う。主制御MPU1311は、まず、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたRAM1312のプロテクトを書き込み許可に設定し、RAM1312への書き込みができる状態にする(ステップS10)。続いて、主制御MPU1311は、内蔵されたウォッチドッグタイマを起動し(ステップS12)、所定のウェイト時間(サブ基板(周辺制御基板1510など)が起動するために必要な時間)が経過したかを判定する(ステップS16)。所定のウェイト時間が経過していれば、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されているかを判定する(ステップS18)。RAMクリアスイッチが操作されている場合、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータのうちベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)以外の領域のデータを消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されていない場合、内蔵RAM1312にバックアップされているデータを消去せず、停電フラグが設定されているかを判定する(ステップS20)。
When the
その結果、停電フラグが設定されていなければ、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータ(ベース算出用領域13128以外)を消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、停電フラグが設定されていれば、停電フラグをクリアし、前回の電源遮断時に計算されたチェックサムを用いて内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータから算出したチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとを比較(検証)する(ステップS22)。
As a result, if the power failure flag is not set, the data in the work area of the built-in
その結果、バックアップデータから算出されたチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとが一致しなければ、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータ(ベース算出用領域13128以外)を消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、バックアップデータから算出されたチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとが一致すれば、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しいので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータを消去せず、ステップS24に進む。
As a result, if the checksum calculated from the backup data does not match the checksum stored in step S48, the data in the work area of the
続いて、チェックコードを用いてベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)が正常かを判定する(ステップS24)。異常であると判定された場合、ベース算出用ワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ベース算出用ワークエリアに格納されているデータを消去する(ステップS26)。 Subsequently, it is determined whether the base calculation work area (base calculation area 13128) is normal using the check code (step S24). If it is determined to be abnormal, the data in the base calculation work area may be incorrect, so the data stored in the base calculation work area is deleted (step S26).
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、RAM1312の少なくとも一部の領域が初期化されるケースとして、RAMクリアスイッチの操作(ステップS18)と、停電フラグがセットされていない停電フラグ異常(ステップS20)と、RAMのチェックサムが一致しないRAM異常(ステップS22)と、ベース算出用ワークの異常(ステップS24)とがある。これらのうち、図示したように、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチの操作が検出された場合、及び停電フラグ異常、RAM異常の場合は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)をクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(ベース算出用ワーク領域とベース算出用スタック領域を含む)はクリアしない。また、ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)をクリアし、遊技制御用領域13126はクリアしない。
In the
なお、図示したものと異なり、停電フラグ異常、RAM異常、ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合は、RAM1312に格納されたデータの正当性が保証されないことから、遊技制御用領域13126及びベース算出用領域13128を含む全RAM領域をクリアしてもよい。ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合に全RAM領域をクリアすると、遊技状態を示すデータが消失して正常な処理が実行不可能になるメモリ構成である場合、ベース算出用ワーク領域とベース算出用スタック領域のみを初期化するとよい。また、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチの操作が検出された場合は、前述と同様に、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)をクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128はクリアしなくてよい。
It should be noted that, unlike the illustrated one, in the case of power failure flag abnormality, RAM abnormality, base calculation work abnormality, since the validity of the data stored in the
なお、ベース算出用領域13128に、1又は複数のバックアップ領域を設ける場合、最初に、チェックコードを用いてメイン領域を判定し、メイン領域が異常であると判定された場合、バックアップ領域1、2、Nの順で判定し、最初に正常であると判定されたバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製するとよい。その後、バックアップ領域のデータは消去しても、そのまま残してもよい。メイン領域が正常であると判定された場合、バックアップ領域のデータは消去しても、そのまま残してもよい。
When one or more backup areas are provided in the
このように、本実施形態のパチンコ機1では、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータを、データの種別毎に(遊技制御用領域13126とベース算出用領域13128とを)異なる条件で消去する。すなわち、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって、バックアップされた遊技制御用領域13126は消去されるが、バックアップされたベース算出用領域13128は消去されない。RAMクリアスイッチの操作によってベース算出用領域13128が消去できると、パチンコ機1が算出したベース値を任意のタイミングで消去できる。このため、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって、バックアップされたベース算出用領域13128が消去されないようにして、遊技場の係員の操作によるベース算出用領域13128の消去を防止し、異常なベース値の隠蔽を防止できる。このため、ベース値が高い状態や低い状態へ改造された遊技機を確実に検出できる。
Thus, in the
主制御MPU1311は、RAM作業領域の復電時設定又はRAM初期化処理が実行されると、主制御MPU1311(CPU13111)の各種設定レジスタに設定するための初期設定処理(ステップS28)、周辺制御基板1510に送信するための電源投入時コマンド設定処理(ステップS32)を実行し、タイマ割込み処理をはじめとする割り込み処理の実行を許可する(ステップS34)。続いて、主制御MPU1311は、停電予告信号を取得し(ステップS36)、停電予告信号がONであるか否かを判定する(ステップS38)。停電予告信号がONでない場合(ステップS38の結果が「No」)、乱数更新処理を実行する(ステップS40)。
When the
一方、停電予告信号を検出した場合には(ステップS38の結果が「Yes」)、主制御MPU1311は、電源断時処理を実行する(電断時設定手段)。電源断時処理では、まず、割込み処理の実行を禁止し(ステップS42)、出力ポートをクリアして、各ポートからの出力によって制御される機器の動作を停止する(ステップS44)。続いて、主制御MPU1311は、バックアップされるワークエリアに格納されたデータが正常に保持されたか否かを判定するためのチェックサムを計算し(ステップS46)、チェックサムの計算結果をRAM1312のチェックサムエリアに格納する(ステップS48)。
On the other hand, when the power failure warning signal is detected (the result of step S38 is "Yes"), the
続いて、ベース算出用ワーク(ベース算出用領域13128)のメイン領域のデータを各バックアップ領域に複製する(ステップS54)。このとき、計算されたチェックコードも複製する。バックアップは、主基板側電源断時処理ではなく、ベース算出処理で適宜
(例えば、データの更新の都度)、実行してもよい。このように、ベース値の算出に使用するデータを、計算された(又は、所定値の)チェックコードと共にバックアップ領域に格納することによって、電源遮断時にもベース算出用のデータや算出されたベース値を保持し、長期間の稼動におけるベース値を算出できる。
Subsequently, the data in the main area of the base calculation work (base calculation area 13128) is copied to each backup area (step S54). At this time, the calculated check code is also duplicated. The backup may be executed as appropriate (for example, each time data is updated) in the base calculation process instead of the main board side power-off process. By storing the data used to calculate the base value in the backup area together with the calculated (or predetermined value) check code in this way, the data for base calculation and the calculated base value can be saved even when the power is shut off. can be stored and the base value for long-term operation can be calculated.
なお、ステップS24でチェックされるチェックコードは、ベース算出処理のステップS8038(図106)で算出される。また、後述する変形例においては、初期化処理のステップS50(図22)で算出される。 Note that the check code checked in step S24 is calculated in step S8038 (FIG. 106) of the base calculation process. Further, in a modified example described later, it is calculated in step S50 (FIG. 22) of the initialization process.
さらに、停電フラグとしてバックアップフラグエリアに正常にバックアップされたことを示す値を格納し(ステップS56)、RAMプロテクトレジスタに書き込み禁止を示す”01H”を出力することでRAM1312の書き込みを禁止し(ステップS58)、停電から復旧するまでの間、待機する(無限ループ)。
Furthermore, a value indicating normal backup is stored in the backup flag area as a power failure flag (step S56), and writing to the
図103は、本実施例のパチンコ機1において、図26(A)に示す役物比率算出用領域が読み替えられるベース算出用領域13128の構成を示す図である。
FIG. 103 is a diagram showing the configuration of the
ベース算出用領域13128は、RAM1312の一部の領域で構成され、前述したように、遊技制御用領域13126とは別に(遊技制御領域外に)設けられる。
The
ベース算出用領域13128は、ベース値A、ベース値B、区間カウンタ、全アウト球数、低確率・非時短アウト球数及び低確率・非時短賞球数の格納領域を含む。
The
ベース値Aの格納領域は、1バイトで構成され、現在計測中の暫定区間のベース値を格納する。ベース値Bの格納領域は、1バイトで構成され、前記暫定区間の一つ前の区間において計測されたベース値を格納する。区間カウンタの格納領域は、1バイトで構成され、現在ベース値を測定中の区間を示す値を格納する。区間カウンタは、区間が切り替えられる毎に更新され、区間によって異なる表示内容を制御するために使用される。なお、区間カウンタは、0、1、2のいずれかの値、すなわち、2より大きくならないように制御するとよい。具体的には、テスト区間では区間カウンタ=0、第1区間では区間カウンタ=1、第2区間以後では区間カウンタ=2である。また、区間カウンタは、0から255の値として、255より大きくならないように制御してもよく、第2区間以後では区間カウンタ=2以上となる。 The base value A storage area consists of 1 byte and stores the base value of the provisional section currently being measured. The storage area for the base value B consists of 1 byte and stores the base value measured in the section immediately before the provisional section. The storage area of the section counter consists of 1 byte and stores a value indicating the section in which the base value is currently being measured. The section counter is updated each time the section is switched, and is used to control different display contents depending on the section. It should be noted that the interval counter should be controlled to be any value of 0, 1, or 2, that is, not to exceed 2. Specifically, the section counter is 0 in the test section, the section counter is 1 in the first section, and the section counter is 2 in the second and subsequent sections. Also, the section counter may be controlled to have a value from 0 to 255 so as not to exceed 255, and the section counter will be 2 or more after the second section.
全アウト球数の格納領域は、2バイトで構成され、遊技状態によらない全てのアウト球数(すなわち、遊技機の稼働を示す値)を格納する。全アウト球数は、ベースの測定単位である区間の切り替えを判定するために使用される。本実施例のパチンコ機では、概ね1日の稼働を一つの区間として、各区間におけるベース値を計測する。このため、2バイト(65536)を全アウト球数の格納領域に割り当てている。全アウト球数は、前述したように、遊技状態によらない全てのアウト球数を区間毎に計数するための記憶領域であり、前述した実施例の総アウト球数(特賞中のアウト球数のパチンコ機1の稼働開始からの合計値)とは異なるものである。 The storage area for the total number of out-balls consists of 2 bytes, and stores all the number of out-balls regardless of the gaming state (that is, a value indicating the operation of the gaming machine). Total out pitches are used to determine interval switching, which is the base unit of measure. In the pachinko machine of the present embodiment, the base value is measured for each section, with the operation of approximately one day as one section. Therefore, 2 bytes (65536) are allocated to the storage area for the number of all-out pitches. As described above, the total number of out balls is a storage area for counting all the number of out balls regardless of the game state for each section. total value from the start of operation of the pachinko machine 1).
低確率・非時短アウト球数の格納領域は、2バイト以上(望ましくは、4バイト)で構成され、ベース値を計算するためのアウト球数(特賞中以外の遊技状態のアウト球数)を格納する。低確率・非時短賞球数の格納領域は、2バイト以上(望ましくは、4バイト)で構成され、ベース値を計算するための賞球数(特賞中以外の遊技状態の賞球数)を格納する。なお、低確率・非時短アウト球数の格納領域と低確率・非時短賞球数の格納領域は2バイト以上の領域であればよいが、ベース値の計算処理を考慮すると、同じバイト数にする方が望ましい。 The storage area for the number of low-probability/non-time-saving out-balls is composed of 2 bytes or more (preferably 4 bytes), and the number of out-balls for calculating the base value (the number of out-balls in the game state other than during the special prize) Store. The storage area for the number of low-probability/non-time-saving prize balls is composed of 2 bytes or more (preferably 4 bytes), and the number of prize balls for calculating the base value (the number of prize balls in the game state other than the special prize) Store. In addition, the storage area for the number of low-probability/non-time-saving out balls and the storage area for the number of low-probability/non-time-saving prize balls may be an area of 2 bytes or more, but considering the calculation process of the base value, the same number of bytes It is preferable to
前述した各格納領域の記憶容量(バイト数)は、前述したものは一例に過ぎず、1区間のアウト球数に応じて定めるとよい。 The storage capacity (number of bytes) of each storage area described above is merely an example, and may be determined according to the number of out balls in one section.
また、ベース算出用領域13128のメイン領域とバックアップ領域とを設ける場合、同じ構成の記憶領域をRAM1312に設ける。
When providing the main area and the backup area of the
図104は、本実施例のパチンコ機のタイマ割込み処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 104 is a flow chart showing an example of timer interrupt processing of the pachinko machine of this embodiment.
図104に示すタイマ割込み処理は、図23で前述したタイマ割込み処理と比較し、ステップS81の役物比率算出用領域更新処理に代えてベース算出処理(ステップS801)が設けられ、ステップS89の役物比率算出・表示処理が削除される。なお、図23で前述したタイマ割込み処理と同じステップには同じ符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。 The timer interrupt process shown in FIG. 104 is different from the timer interrupt process described above in FIG. Object ratio calculation/display processing is deleted. The same steps as those of the timer interrupt processing described above in FIG.
タイマ割込み処理が開始されると、主制御MPU1311は、主制御プログラムを実行することによって、まず、プログラムステータスワードのRBS(レジスタバンク選択フラグ)に1を設定し、レジスタを切り替える(ステップS70)。
When timer interrupt processing is started, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)、タイマ更新処理(ステップS76)、乱数更新処理1(ステップS78)、賞球制御処理を実行する(ステップS80)。
Next, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、現在の遊技状態を参照して、遊技価値として払い出される賞球数を現在の遊技状態に対応した領域に加算して、主制御内蔵RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128(図103参照)を更新し、ベース値を計算する(ステップS801)。ベース算出処理の詳細は、図105及び図106を用いて後述する。ベース算出処理(ステップS801)は、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)の後であれば、どの順序で実行してもよいが、タイマ割込み毎に確実に実行するために、早い順序で実行するとよい。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、枠コマンド受信処理(ステップS82)、不正行為検出処理(ステップS84)、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理(ステップS86)、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理(ステップS88)、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)、周辺制御基板コマンド送信処理(ステップS92)を実行する。
Subsequently, the
最後に、主制御MPU1311は、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットする(ステップS96)。また、最後に、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンクを切り替える(復帰する)。以上の処理が終了すると、タイマ割込み処理を終了し、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。
Finally, the
このように、本実施例のパチンコ機では、タイマ割込み処理でベース値を計測するので、遊技中のベース値をリアルタイムに計測できる。 As described above, in the pachinko machine of the present embodiment, the base value is measured by the timer interrupt process, so the base value during the game can be measured in real time.
図105、図106は、ベース算出処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。 105 and 106 are flowcharts showing an example of base calculation processing.
ベース算出処理(ステップS801)は、タイマ割込み処理から呼び出されて、主制御MPU1311が実行する。
The base calculation process (step S801) is called from the timer interrupt process and executed by the
主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出プログラムを実行することによって、まず、ベース値の計算にエラーがあるかを判定する(ステップS8011)。例えば、前述したように、入賞口センサ(一般入賞口センサ3015、第一始動口センサ2104、第二始動口センサ2551、第一大入賞口センサ2114、第二上大入賞口センサ2554、第二下大入賞口センサ2557など)や排出球センサ(盤側排出球センサ3060A、枠側排出球センサ3060B)に異常がある場合、インターフェイス回路1331から出力された異常信号によって、ベース値を正確に計算できないエラーがあると判定する。また、不正行為が行われていると判定された(例えば、磁気検出センサが磁気を検出した、振動検出センサが振動を検出した、電波検出センサが電波を検出した)場合も、ベース値を正確に計算できないエラーがあると判定する。このエラーがあると判定された場合、ベース表示器1317の表示を消灯してもよい。ステップS8011では、遊技停止を伴うエラー(例えば、磁気、振動、電波エラー等)については、エラーである(YES)と判定し、遊技停止を伴わないエラー(例えば、賞球異常、扉開放等)やベースに算出に直接関係しない故障(補給切れ、満タンエラー等)については、エラーではない(NO)と判定してもよい。つまり、複数種類の異常状態のうち、一部の異常があってもベース算出処理を実行して、他の異常があればベース算出処理を実行しなくてもよい。
The
次に、主制御MPU1311は、アウト球数を取得する(ステップS8014)。アウト球数は、前述したように、発射球センサ1020や排出球センサ3060などによって検出され、ステップS74のスイッチ入力処理で、これらのセンサの検出信号を読み取って、センサの検出信号があればアウト球数=1を取得する。複数の排出球センサ3060でアウト球が検出された場合、各センサで検出された数の合計値をアウト球数として取得する。すなわち、1回のタイマ割込み処理において、複数のアウト球を検出することがある。
Next, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、賞球数を取得する(ステップS8015)。賞球数は、前述したように、ステップS80の賞球制御処理で入力情報に基づいて算出された賞球数を取得する。ベース算出処理で取得する賞球数は、払い出しが決定した賞球数でもよい。また、作成済みの払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。また、送信済の払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。また、主制御基板1310が払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信し、払出制御基板951から受信確認(ACK)を受信した払出コマンドに対応する賞球数でもよい。さらに、主制御基板1310が払出制御基板951に払出コマンドを送信し、払出制御基板951から払出完了の報告を受けた賞球数(払出済み賞球数)でもよい。このバリエーションは図41から図44を用いて説明した通りである。
Next, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、ステップS8014でアウト球が検出されているかを判定する(ステップS8016)。アウト球が検出されていなければ、アウト球に関する処理を実行せずに、ステップS8022に進む。一方、アウト球が検出されていれば、ベース算出用領域13128に格納されている全アウト球数に検出されたアウト球数を加算する(ステップS8017)。
Next, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出用領域13128に格納されている区間カウンタを参照して、現在、テスト区間であるかを判定する(ステップS8018)。テスト区間は、パチンコ機の初回電源投入(又は、ベース算出用領域13128の初期化)からアウト球数が500個未満の所定値である区間であり、区間カウンタの値は初期値である0となっている。このため、区間カウンタ値が0であればテスト区間であると判定できる。テスト区間であれば、ベース値を計算する必要がないので、ステップS8028に進む。一方、テスト区間でなければ、現在の遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS8019)。特賞中であるかの判定は、前述した図39のステップS810と同様に判定できる。遊技状態が特賞中であるとは、大当りにより大入賞口2005、2006が
開放しており、遊技者が多くの賞球を獲得できる時間中であるが、大当り遊技のオープニングやエンディングの時間を含めてもよい。一つの大当り中で大入賞口2005、2006が開放と閉鎖を繰り返す場合、大入賞口の閉鎖から次の開放までの間(閉鎖インターバル)の時間を含んでもよい。すなわち、ステップS810における特賞中は、条件装置作動中を意味し、例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当たり図柄の確定からエンディング終了までである。また、右打ち指示中の全ての時間を含んでもよい。
Next, the
さらに、始動口2002、2004においては、時短中、確変中(ST中)、電サポ中を特賞中に含めてもよい。さらに、時短中、確変中(ST中)、電サポ中以外の遊技状態において、始動口2004の開放から閉鎖後の所定時間(例えば、始動口に入賞した球がアウト球として検出されるまでに必要な数秒)までの間を特賞中に含めてもよい。なお、高確率遊技状態であるが時短中(電サポ中)とならない所謂「潜伏遊技状態」は特賞中に含まずに、通常状態(低確率・非時短状態)と同様に、当該遊技状態における賞球数やアウト球数を使用してベース値を算出してもよい。この場合、通常遊技状態と潜伏遊技状態の各々において、別個にベース値を算出し、何れのベース表示か否かが識別可能にベース値を表示してもよい。
Furthermore, in the starting
潜伏遊技状態は高確率であっても遊技者には高確率状態であることを認識させない遊技状態であるが、潜伏遊技状態をベース値の算出から除外すると、営業中に枠が開放された場合に、遊技者がベース表示器1317を見て、潜伏遊技状態(すなわち、高確率)であることを認識することがある。つまり、枠開放状態で、ホールの従業員が入賞口に球を手入れしたりアウト口に球を流した場合に、遊技者はベース表示が変わるかによって遊技状態を知ることができる。通常遊技状態と潜伏遊技状態とを区別せずにベース値を計算することによって、このような問題を回避できる。
The hidden game state is a game state in which even if the probability is high, the player does not recognize that it is a high probability state. In addition, the player may look at the
一方、ホールの営業上、低確率・非時短状態におけるベース値の管理が必要な場合があり、潜伏遊技状態を含めてベース値を計算すると、ホールの営業形態に応じた管理ができない場合がある。潜伏遊技状態を除外してベース値を計算することによって、このような問題を回避できる。通常遊技状態と潜伏遊技状態とで分けてベース値を計算することによって、同様の問題を回避できる。すなわち、通常遊技状態と潜伏遊技状態とは、そもそも異なる遊技状態であることから、ホールの営業形態によっては、各遊技状態で分けてベース値を管理(検査)したいと考える場合もあるためである。 On the other hand, there are cases where it is necessary to manage the base value in a low-probability/non-time-saving state for the operation of the hall. . Such problems can be avoided by calculating the base value while excluding the latent gaming state. A similar problem can be avoided by calculating the base value separately for the normal game state and the hidden game state. In other words, since the normal game state and the hidden game state are different game states in the first place, depending on the business form of the hall, it may be desired to manage (inspect) the base value separately for each game state. .
なお、通常遊技状態と潜伏遊技状態とを分けてベース値を算出する場合、各遊技状態の専用の計算処理を用いてベース値を算出しても、共通の計算処理を用いてベース値を算出してもよい。共通の計算処理を用いてベース値を算出することによって、CPUの処理負担を軽減でき、プログラム容量を軽減できる。 In addition, when calculating the base value separately for the normal game state and the hidden game state, even if the base value is calculated using the dedicated calculation process for each game state, the base value is calculated using the common calculation process. You may By calculating the base value using common calculation processing, the processing load on the CPU can be reduced, and the program capacity can be reduced.
本実施例のパチンコ機1に設けられる電動作動役物は、ベース値の計算の観点から2種類に分けられる。前述したように、本実施例の遊技機における、大入賞口2005、2006に関する特賞中とは、条件装置作動中(例えば、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当たり図柄の確定からエンディング終了まで)であり、ベース値は特賞中以外の賞球およびアウト球数で計算されるので、大入賞口2005、2006への正常な(いわゆる大当り中の)入賞はベース値の算出に使用されない。一方、開閉部材を有する始動口2004(いわゆる、電動チューリップ)は、特賞中以外(低確率時や非時短時)の入賞球および賞球がベース値の算出に使用される。つまり、電動作動役物のうち、一部の役物(大入賞口2005、2006)は、遊技状態(特賞中か否か)に関係なく、入賞球数および賞球数をベース値の計算に使用せず、他の役物(始動口2004)は、入賞球数および賞球数をベース値の計算に使用するか使用しないかが、遊技状態(特賞中か否か)に応じて切り替えられることになる。
The electrically operated accessories provided in the
また、大入賞口2005、2006は、条件装置が作動しない場合でも(いわゆる小当たりとして)開放するときがある。一般的に小当りは時短中に発生し、短時間開放のため遊技球が入賞する可能性が低いので、ベース値の計算には影響しない。しかし、特賞中以外(通常時)に小当たりを発生させ、遊技球が入賞する可能性が高くなる時間だけ開放してもよい。この場合、特賞中以外に発生した小当りにおける大入賞口2005、2006への入賞球および賞球はベース値の計算に使用してもよい。このようにすると、特賞中以外の小当たりの発生確率を制御することによって、ベース値の期待値(設計値)を変更できる。すなわち、ベース値の規格に対し柔軟に対応できるパチンコ機を提供でき、設計の自由度を向上できる。
Also, the
遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しないアウト球であるため、低確率・非時短アウト球数を更新せずに、ステップS8022に進む。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、ステップS8014で検出されたアウト球数はベースの計算に用いるべきものなので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納されている低確率・非時短アウト球数に検出されたアウト球数を加算する(ステップS8020)。そして、更新フラグを1に設定する(ステップS8021)。更新フラグは、ベース算出処理(タイマ割込み処理)の実行毎に特賞中以外のアウト球や賞球が検出された場合に1に設定され、ベース値を計算すべきタイミングを示す(ステップS8026からS8027参照)。 If the game state is during the special prize, the out-ball is not related to the calculation of the base value, so the process proceeds to step S8022 without updating the number of low-probability/non-time-saving out-balls. On the other hand, if the gaming state is not a special prize, the number of out-balls detected in step S8014 should be used for base calculation. The number of out-balls given is added (step S8020). Then, the update flag is set to 1 (step S8021). The update flag is set to 1 each time the base calculation process (timer interrupt process) is executed, when an out ball or a prize ball other than during a special prize is detected, and indicates the timing at which the base value should be calculated (steps S8026 to S8027). reference).
次に、主制御MPU1311は、ステップS8015で賞球が検出されているかを判定する(ステップS8022)。賞球が検出されていなければ、賞球に関する処理を実行せずに、ステップS8026に進む。一方、賞球が検出されていれば、現在の遊技状態が特賞中であるかを判定する(ステップS8023)。特賞中であるかの判定は、ステップS8019と同じでよい。
Next, the
遊技状態が特賞中であれば、ベース値の計算に関係しない賞球であるため、低確率・非時短賞球数を更新せずに、ステップS8026に進む。一方、遊技状態が特賞中でなければ、ステップS8015で検出された賞球数はベースの計算に用いるべきものなので、ベース算出用領域13128に格納されている低確率・非時短賞球数に検出された賞球数を加算する(ステップS8024)。そして、更新フラグを1に設定する(ステップS8025)。
If the game state is during the special prize, it is a prize ball that is not related to the calculation of the base value, so the process proceeds to step S8026 without updating the number of low-probability/non-time-saving prize balls. On the other hand, if the game state is not in the special prize, the number of prize balls detected in step S8015 should be used for base calculation, so it is detected as the number of low-probability/non-time-saving prize balls stored in the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、更新フラグが1であるかを判定する(ステップS8026)。更新フラグが1である場合、当該ベース算出処理(タイマ割込み処理)において特賞中以外のアウト球又は賞球が検出されているので、低確率・非時短賞球数を低確率・非時短アウト球数で除してベース値を計算し、ベース算出用領域13128のベース値Aの格納領域に格納する(ステップS8027)。
Next, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、区間カウンタを参照して、テスト区間中であるかを判定する(ステップS8028)。そして、区間カウンタ値が0であり、テスト区間であることを示す場合、テスト区間を終了するタイミングであるかを判定する(ステップS8029)。テスト区間は、パチンコ機の初回電源投入(ベース算出用領域13128の初期化を含む)からアウト球数が500個未満の所定値である区間であり、区間カウンタがテスト区間であることを示し、全アウト球数が当該所定値以上であれば、テスト区間を終了するタイミングであると判定できる。
Next, the
その結果、テスト区間を終了するタイミングでなければ、テスト区間を継続するために、ベース算出用領域13128を更新せずに、ステップS8034に進む。一方、テスト区間中でありかつテスト区間を終了するタイミングであれば、テスト区間から第1区間に
移行するため、ステップS8032に進む。具体的には、主制御MPU1311は、区間カウンタに1を加算する(ステップS8032)。区間カウンタは、テスト区間を表す0から第1区間を表す1に変化する。そして、全アウト球数、低確率・非時短アウト球数、及び低確率・非時短賞球数を0に初期化する(ステップS8033)。この処理によって、テスト区間を終了して、第1区間に移行する。
As a result, if it is not the time to end the test section, the process proceeds to step S8034 without updating the
一方、ステップS8028で、区間カウンタ値が0ではなく、テスト区間中ではないと判定された場合、主制御MPU1311は、全アウト球数が52000以上であるかを判定する(ステップS8030)。全アウト球数が52000より小さければ、現在の区間を継続するために、ステップS8034に進む。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S8028 that the section counter value is not 0 and that the game is not in the test section, the
一方、全アウト球数が52000以上であれば、当該区間が終了し、新たな区間を開始するための処理(ステップS8031~S8033)を実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出用領域13128において、ベース値A格納領域からベース値Aを読み出し、ベース値B格納領域に書き込む(ステップS8031)。その後、区間カウンタに1を加算する(ステップS8032)。区間カウンタは、前述したように、0、1、2のいずれかの値、すなわち、2より大きくならないように制御されるので、区間カウンタ値が2の場合に区間カウンタに1を加算しても区間カウンタ値は増加せず、2のままである。そして、全アウト球数、低確率・非時短アウト球数、及び低確率・非時短賞球数を0に初期化し(ステップS8033)、次の区間に移行する。
On the other hand, if the total number of out-balls is 52000 or more, the section ends and a process for starting a new section (steps S8031 to S8033) is executed. Specifically, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、更新フラグが1であるかを判定する(ステップS8034)。更新フラグが1である場合、新しく算出されたベース値を表示するためのデータを生成する(ステップS8035)。ベース表示データ生成処理の詳細は、図107を用いて後述する。その後、主制御MPU1311は、更新フラグを0に設定する(ステップS8036)。
Next, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、表示切替カウンタに1を加算する(ステップS8037)。表示切替カウンタは、図99で説明した暫定区間表示と確定区間表示とを所定時間間隔(例えば5秒)で切り替えて表示するために使用される。暫定区間表示と確定区間表示とを切り替える所定時間は、各区間における低確率・非時短アウト球数が6000個未満である場合の点滅表示(図107のステップS8051で制御される点滅表示)の周期より十分に長い時間にするとよい。これは、点滅と表示切り替えとが同程度の周期だと、点滅表示(すなわち、低確率・非時短アウト球数が6000個未満であるか)が分かりにくくなることから、点滅表示なのか表示の切り替えなのかを分かりやすくするためである。
Next, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出用領域13128のデータからチェックコード(例えば、チェックサム)算出する(ステップS8038)。チェックコードの算出方法は、初期化処理(図22)のステップS50でチェックコードを算出する処理と同じ算出方法を用いる。また、チェックコードを算出することなく固定値とする場合には、チェックコードの隣り合うビット同士が同値とならない複数バイトの値とするとよい(例えば、2バイトであれば、A55AH(1010010101011010B)のようにする)。また、連続
したエリアに固定値を設定するのではなく、分けて配置してもよい。例えば、ベース算出用領域13128の先頭に第1固定値を格納し、中間に第2固定値を格納し、最後に第3固定値を格納する。チェックコードが固定値である場合、チェックサムの算出によるチェックデータより多いバイト数で構成して、RAM異常の判定可能性を向上するとよい。
Next, the
このように、本実施例のベース算出処理によると、タイマ割込み処理ごとにベース値を算出して、表示するので、賞球の発生毎やアウト球の発生毎のタイミングでベース値を遅
滞なく(リアルタイムに)表示でき、ベース値が正常か異常かを遅滞なく判断できる。なお、ベース算出用に使用する記憶領域であるベース算出用領域13128の容量は、遊技制御用領域13126の容量と比較して極めて少ないため、ベース算出処理の実行毎に、その終了時にチェックコードを算出しても、主制御MPU1311の処理負荷に及ぼす影響は少ない。
Thus, according to the base calculation process of this embodiment, the base value is calculated and displayed for each timer interrupt process, so the base value can be calculated without delay ( can be displayed in real time), and it can be judged without delay whether the base value is normal or abnormal. In addition, the capacity of the
また、賞球について、発生した入賞信号に基づく賞球払出予定数を用いてベース値を算出・表示している場合、ベース値として算出・表示されるタイミングと、賞球が払出されるタイミングとが異なる。すなわち、払出装置に異常が生じて、賞球が払い出されない状態(補給切れ、上皿が満タン、賞球通路に設けられた払出数カウントセンサの故障、払出モータの故障などによる払出装置の停止など)になっても、ベース値は算出され、表示される。 Also, regarding the prize balls, if the base value is calculated and displayed using the number of prize balls to be paid out based on the winning signal generated, the timing of calculating and displaying the base value and the timing of the prize balls being paid out will differ. is different. In other words, a state in which an abnormality occurs in the payout device and the prize balls are not paid out (out of supply, top tray is full, failure of the payout count sensor provided in the prize ball passage, failure of the payout motor, etc.) stop, etc.), the base value is calculated and displayed.
なお、前述したベース算出処理では、タイマ割込み処理からベース算出処理が呼び出される毎に当該タイマ割込み処理で検出されたアウト球数及び計算された賞球数を用いてベース値を計算したが、排出球センサ3060がアウト球を検出する毎、及び各種入賞口センサが入賞球を検出する毎にベース値を計算してもよい。すなわち、1回のタイマ割り込み処理において、ベース値計算処理が複数回呼び出され、ベース値が複数回計算される。このようにすると、1回のベース算出処理の中で前述した区間の切り替え(アウト球数が52000個)のタイミングが到来しても、前後のいずれの区間のベース値として計算するかを区別でき、リアルタイムに正確なベース値を表示できる。
In the base calculation process described above, the base value is calculated using the number of out balls detected in the timer interrupt process and the number of prize balls calculated each time the base calculation process is called from the timer interrupt process. The base value may be calculated each time the
また、前述したベース算出用領域更新処理(図46)のステップS815からS817のように、賞球数に異常があるかを判定し、賞球数に異常があれば、異常報知コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知用タイマをリセットしてもよい。さらに、ステップS824からS825のように、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップしたかを判定し、賞球異常報知用タイマがタイムアップすると、賞球異常報知停止コマンドを生成し、賞球異常報知を停止してもよい。 Also, as in steps S815 to S817 of the base calculation area updating process (FIG. 46) described above, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, and if there is an abnormality in the number of prize balls, an abnormality notification command is generated. , You may reset the timer for prize ball abnormality notification. Further, as in steps S824 to S825, it is determined whether the timer for abnormal prize notification has timed up. may be stopped.
図107は、ベース表示データ生成処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 107 is a flowchart illustrating an example of base display data generation processing.
ベース表示データ生成処理は、ベース算出処理のステップS8035から呼び出されて実行される。 The base display data generation process is called from step S8035 of the base calculation process and executed.
主制御MPU1311は、ベース表示データ生成プログラムを実行することによって、まず、表示切替カウンタが1250より小さいかを判定する(ステップS8041)。前述したタイマ割込み処理は4ミリ秒ごとに実行されることから、表示切替カウンタが1250に到達すると、表示切替カウンタが0に初期化されてから5秒の時間が経過している。ステップS8053において、表示切替カウンタは、2499に到達すると0に初期化されるので、表示切替カウンタが0~1249の間はステップS8042~S8045の処理を実行し、表示切替カウンタが1250~2499の間はステップS8046~S8049の処理を実行する。このため、本実施例のベース表示データ生成処理では、5秒ごとにベース表示器1317の表示データを切り替える。
The
表示切替カウンタが1250より小さければ、ベース表示器1317の上2桁に「bA.」を表示するためのデータを生成する(ステップS8042)。その後、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出用領域13128に格納されている区間カウンタを参照して、現在、テスト区間であるかを判定する(ステップS8043)。テスト区間ではベース値が計算されていないので、下2桁に「--」を表示するためのデータを生成する(ステップS8044)。一方、テスト区間でなければ、暫定区間において現在計測中のベース値A
を表示するためのデータを生成する(ステップS8045)。
If the display switching counter is smaller than 1250, data for displaying "bA." After that, the
is generated (step S8045).
ステップS8041において、表示切替カウンタが1250以上であると判定されると、ベース表示器1317の上2桁に「bb.」を表示するためのデータを生成する(ステップS8046)。その後、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出用領域13128に格納されている区間カウンタを参照して、現在、テスト区間又は第1区間であるかを判定する(ステップS8047)。テスト区間又は第1区間では過去の確定区間でベース値が計測されていないので、下2桁に「--」を表示するためのデータを生成する(ステップS8048)。一方、テスト区間及び第1区間のいずれでもなければ、直近の確定区間において計測されたベース値Bを表示するためのデータを生成する(ステップS8049)。
If it is determined in step S8041 that the display switching counter is equal to or greater than 1250, data for displaying "bb." After that, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出用領域13128に格納されている低確率・非時短アウト球数を参照して、低確率・非時短アウト球数が6000より小さいかを判定する(ステップS8050)。そして、低確率・非時短アウト球数が6000より小さければ、当該区間でベース値の計測を開始した後の稼働数(アウト球数)が少ないので、ベース値が安定していないことがあり、ベース表示器1317の表示が点滅するように制御する(ステップS8051)。一方、低確率・非時短アウト球数が6000以上であれば、ベース表示器1317の表示が点滅しないで点灯するように制御する(ステップS8052)。
Next, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、表示切替カウンタが2499以上であるかを判定する(ステップS8053)。表示切替カウンタが2499より小さければ、表示切替カウンタを初期化せず、ステップS8055に進む。一方、表示切替カウンタが2499以上であれば、一つの繰り返しが終了したので、表示切替カウンタを0に初期化する(ステップS8054)。
Next, the
最後、主制御MPU1311は、生成された表示データと点灯態様(点灯又は点滅)が指定された表示パターンを生成する(ステップS8055)。
Finally, the
このように、所定時間毎に実行されるタイマ割込み処理(ベース算出処理)において、定期的に更新される表示切替カウンタを用いてベース表示器1317への表示内容を切り替えることによって、暫定区間において現在計測中のベース値Aと確定区間において過去に計測したベース値Bとを分かりやすく表示できる。
In this way, in the timer interrupt processing (base calculation processing) that is executed at predetermined time intervals, by switching the display content on the
また、各区間においてベース値が安定しない範囲では点滅表示をするので、ベース値が安定した範囲にあるか、安定していない範囲にあるかを、ベース表示器1317の表示によって容易に確認できる。 In addition, since the blinking display is performed in the range in which the base value is not stable in each section, whether the base value is in the stable range or not can be easily confirmed by the display of the base display 1317.例文帳に追加
図108は、ベース算出処理の変形例を示すフローチャートである。図108に示す変形例では、ベース算出用ワークのチェック処理(ステップS8012、S8013)が追加された他は、図105に示すベース算出処理と同じである。なお、図108では、ベース算出処理のうちベース値Aの計算(ステップS8027)までを説明するが、ステップS8028からS8038の処理は、前述した図106と同じである。 FIG. 108 is a flowchart illustrating a modification of base calculation processing. The modified example shown in FIG. 108 is the same as the base calculation process shown in FIG. 105, except for the addition of base calculation work check processing (steps S8012 and S8013). In FIG. 108, the calculation of the base value A (step S8027) in the base calculation processing will be described, but the processing from steps S8028 to S8038 is the same as in FIG. 106 described above.
主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出プログラムを実行することによって、まず、ベース値の計算にエラーがあるかを判定する(ステップS8011)。
The
次に、主制御MPU1311は、チェックコードを用いてベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)が正常かを判定する(ステップS8012)。異常であると判定された場合、ベース算出用ワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ベ
ース算出用ワークエリアに格納されているデータを消去する(ステップS8013)。
Next, the
なお、ベース算出用領域13128に、1又は複数のバックアップ領域を設ける場合、最初に、チェックコードを用いてメイン領域を判定し、メイン領域が異常であると判定された場合、バックアップ領域1、2、Nの順で判定し、最初に正常であると判定されたバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製するとよい。その後、バックアップ領域のデータは消去しても、そのまま残してもよい。メイン領域が正常であると判定された場合、バックアップ領域のデータは消去しても、そのまま残してもよい。
When one or more backup areas are provided in the
図示した例では、ベース値の計算にエラーがあるかを判定(ステップS8011)した後に、ベース算出用領域13128が正常かを判定(ステップS8012)したが、これとは逆に、ベース算出用領域13128が正常かを判定(ステップS8012)して、判定結果に基づく必要な処理を実行した後に、ベース値の計算にエラーがあるかを判定(ステップS8011)してもよい。
In the illustrated example, after determining whether there is an error in the calculation of the base value (step S8011), it is determined whether the
以後の処理(ステップS8014~)は前述した図105及び図106と同じなので、それらの説明は省略する。 The subsequent processing (from step S8014 onwards) is the same as in FIGS. 105 and 106 described above, so description thereof will be omitted.
図108に示すベース算出処理では、タイマ割込み毎(すなわち、4ミリ秒毎)に、ベース算出用領域13128のデータが正常かを判定するので、ベース算出用領域13128の異常が早く検出でき、異常なベース値の表示を抑制できる。
In the base calculation process shown in FIG. 108, it is determined whether the data in the
次に、本実施例のパチンコ機においてベース算出用領域13128の異常判定方法を説明する。ベース値の計算に用いられる値及び計算されたベース値は、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのベース算出用領域13128(図26に示す「役物比率算出用領域13128」は「ベース算出用領域13128」と読み替えられる)に格納されており、所定のタイミングでデータが正常かを判定する。この正常・異常の判定ステップと、チェックコードの計算ステップとを、どの処理(タイミング)で行うかは以下のバリエーションがある。
・図101及び図106:ベース算出処理(タイマ割込み処理)で計算したチェックコードを、電源投入時に判定する。
・図21及び図22:電源遮断時に計算したチェックコードを、電源投入時(初期化処理)に判定する。
・図106及び図108:ベース算出処理(タイマ割込み処理)で計算したチェックコードを、ベース算出処理(タイマ割込み処理)で判定する。
Next, a method for judging abnormality of the
101 and 106: The check code calculated in the base calculation process (timer interrupt process) is determined when the power is turned on.
21 and 22: The check code calculated when the power is turned off is determined when the power is turned on (initialization processing).
106 and 108: The check code calculated by the base calculation process (timer interrupt process) is judged by the base calculation process (timer interrupt process).
(チェックコードをタイマ割込み毎に算出し、電源投入時に判定するケース)
まず、図101及び図106を用いて、ベース算出処理(タイマ割込み処理)で計算したチェックコードを、電源投入時に判定する処理を説明する。
(Case where the check code is calculated for each timer interrupt and judged when the power is turned on)
101 and 106, the process of judging the check code calculated in the base calculation process (timer interrupt process) when the power is turned on will be described.
初期化処理を図101、図102に示すものとし、ベース算出処理を図105、図106に示すものとした場合、ベース算出処理(図105、図106)のステップS8038で、ベース算出用領域13128のデータからチェックコード(例えば、チェックサム)算出する。 101 and 102, and the base calculation processing shown in FIGS. 105 and 106, in step S8038 of the base calculation processing (FIGS. 105 and 106), A check code (for example, a checksum) is calculated from the data.
また、初期化処理(図101、図102)のステップS24で、チェックコードを用いてベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)が正常かを判定する。その結果、異常であると判定された場合、ベース算出用ワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ベース算出用ワークエリアに格納されているデータを消去する(ステップS26)。 Also, in step S24 of the initialization process (FIGS. 101 and 102), it is determined using a check code whether the base calculation work area (base calculation area 13128) is normal. As a result, if it is determined that there is an abnormality, the data stored in the base calculation work area may be incorrect, so the data stored in the base calculation work area is deleted (step S26).
ベース算出用領域13128のデータが消去された場合、ベース値の計算にかかる状態が初期化されるので、計算されたベース値はクリアされ、ベース値の計算はテスト期間から開始される。
When the data in the
なお、ベース算出用領域13128に、1又は複数のバックアップ領域を設ける場合、最初に、チェックコードを用いてメイン領域を判定し、メイン領域が異常であると判定された場合、バックアップ領域1、2、Nの順で判定し、最初に正常であると判定されたバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製して、ベース算出用領域13128のデータを復旧してもよい。その後、バックアップ領域のデータは消去しても、そのまま残してもよい。メイン領域が正常であると判定された場合、バックアップ領域のデータは消去しても、そのまま残してもよい。
When one or more backup areas are provided in the
この場合、チェックコードの判定の頻度が少なく、異常判定にかかる計算リソース(主制御MPU1311)の消費を低減できる。 In this case, the frequency of check code determination is low, and the consumption of computational resources (main control MPU 1311) required for abnormality determination can be reduced.
(チェックコードを電源遮断時に算出し、電源投入時に判定するケース)
次に、図21及び図22を用いて、電源遮断時に計算したチェックコードを、電源投入時(初期化処理)に判定する処理を説明する。
(Case where the check code is calculated when the power is turned off and judged when the power is turned on)
21 and 22, the process of determining the check code calculated when the power is turned off when the power is turned on (initialization process) will be described.
初期化処理を図21、図22に示すものとし、ベース算出処理を図105、図106に示すものとした場合、初期化処理(図21、図22)の電源断時処理のステップS50で、ベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)のデータからチェックコード(例えば、チェックサム)算出する。 Assuming that the initialization processing is shown in FIGS. 21 and 22 and the base calculation processing is shown in FIGS. A check code (eg, checksum) is calculated from the data in the base calculation work area (base calculation area 13128).
また、初期化処理(図21、図22)のステップS24で、チェックコードを用いてベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)が正常かを判定する。その結果、異常であると判定された場合、ベース算出用ワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ベース算出用ワークエリアに格納されているデータを消去する(ステップS26)。 Also, in step S24 of the initialization process (FIGS. 21 and 22), it is determined using a check code whether the base calculation work area (base calculation area 13128) is normal. As a result, if it is determined that there is an abnormality, the data stored in the base calculation work area may be incorrect, so the data stored in the base calculation work area is deleted (step S26).
この場合、ベース算出処理のステップS8038でのチェックコードの算出は省略してよい。 In this case, the calculation of the check code in step S8038 of the base calculation process may be omitted.
この場合、チェックコードの計算及び判定の頻度が少なく、異常判定にかかる計算リソース(主制御MPU1311)の消費を低減できる。 In this case, the frequency of check code calculation and determination is low, and the consumption of computational resources (main control MPU 1311) required for abnormality determination can be reduced.
(チェックコードをタイマ割込み処理で算出し、判定するケース)
次に、図106及び図108を用いて、ベース算出処理(タイマ割込み処理)で計算したチェックコードを、ベース算出処理(タイマ割込み処理)で判定する処理を説明する。
(Case where the check code is calculated and judged by timer interrupt processing)
Next, with reference to FIGS. 106 and 108, the process of determining the check code calculated in the base calculation process (timer interrupt process) in the base calculation process (timer interrupt process) will be described.
ベース算出処理を図108、図106に示すものとした場合、ベース算出処理(図108、図106)のステップS8038で、ベース算出用領域13128のデータからチェックコード(例えば、チェックサム)算出する。
108 and 106, a check code (for example, checksum) is calculated from the data in the
また、ベース算出処理(図108、図106)のステップS8012で、チェックコードを用いてベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)が正常かを判定する。その結果、異常であると判定された場合、ベース算出用ワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ベース算出用ワークエリアに格納されているデータを消去する(ステップS8013)。 Also, in step S8012 of the base calculation process (FIGS. 108 and 106), it is determined using a check code whether the work area for base calculation (base calculation area 13128) is normal. As a result, if it is determined to be abnormal, the data stored in the base calculation work area may be incorrect, so the data stored in the base calculation work area is deleted (step S8013).
この場合、初期化処理を図101、図102に示すものとし、ステップS24、S26のベース算出用ワークエリアが正常かの判定ステップは省略してよい。 In this case, the initialization process is shown in FIGS. 101 and 102, and the step of determining whether the base calculation work area is normal in steps S24 and S26 may be omitted.
この場合、前述した場合と比較して、ベース算出用領域13128の異常を迅速に検出できる。
In this case, abnormalities in the
なお、チェックコードにチェックサムではなく固定値を用いる場合、チェックコードの設定及び判定のタイミングは、チェックサムの算出及び判定のタイミングと同じでよい。また、チェックコードとしてチェックサムと固定値の両方を併用して判定してもよい。 If a fixed value is used instead of the checksum for the check code, the timing for setting and determining the check code may be the same as the timing for calculating and determining the checksum. Also, both the checksum and the fixed value may be used as the check code for determination.
図109は、遊技状態が切り替わるときのベース値の計算を示す図である。 FIG. 109 is a diagram showing calculation of the base value when the game state is switched.
始動口2004(電動チューリップ)の開放中に一つの遊技球が入賞し、その後に所定回数の変動表示ゲームが終了して、時短状態が終了し通常状態に戻った。その後、通常状態において、さらに、開放中の始動口2004に遊技球が入賞した場合を想定する。
One game ball wins while the starting port 2004 (electric tulip) is open, and after that, the variable display game of a predetermined number of times is finished, the time saving state is finished, and the normal state is restored. After that, in the normal state, it is assumed that a game ball has entered the
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、始動口2004への入賞に従って、第二特別図柄表示器に第二特別図柄が変動表示する。すなわち、図示した、始動口2004へのいずれの入賞に関連して第二特別図柄が変動表示する変動表示ゲームが行われる。
In the
また、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、特賞中のアウト球をベース計算に用いないので、始動口2004への一つ目の入賞球は低確率・非時短アウト球数に加算されずに、二つ目の入賞球は低確率・非時短アウト球数に加算される。
Also, in the
前述では、時短状態終了時について説明したが、STによる確変終了時も同様である。 In the above description, the end of the time saving state has been described, but the same applies to the end of the probability variation by ST.
前述した時短状態終了時の他、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの大当り発生時にも同様の現象が生じる。通常状態で、始動口2004(電動チューリップ)の開放中に一つの遊技球が入賞し、その後に大当り状態が開始し、さらに、開放中の始動口2004に遊技球が入賞した場合を想定する。
A similar phenomenon occurs when a big hit occurs in the special symbol variation display game, in addition to the end of the time-saving state described above. In a normal state, it is assumed that one game ball wins while the starting port 2004 (electric tulip) is open, then a big hit state starts, and the game ball wins the starting
この場合も、いずれの始動口2004への入賞に関連して第二特別図柄が変動表示する変動表示ゲームが行われる。一方、特賞中のアウト球をベース計算に用いないので、始動口2004への一つ目の入賞球は低確率・非時短アウト球数に加算されるが、二つ目の入賞球は低確率・非時短アウト球数に加算されない。
Also in this case, a variable display game is performed in which the second special symbol is variable and displayed in relation to the winning of any
さらに、特定のエラー発生時にも同様の現象が生じる。通常状態で、始動口2004(電動チューリップ)の開放中に一つの遊技球が入賞し、その後に特定のエラーが発生し、さらに、開放中の始動口2004に遊技球が入賞した場合を想定する。前述したように、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、特定のエラー発生時(インターフェイス回路1331から出力された異常信号によって、ベース値を正確に計算できないエラーがあると判定される場合)に、アウト球をベース計算に用いない。
Furthermore, a similar phenomenon occurs when a specific error occurs. In a normal state, it is assumed that one game ball wins while opening the starting port 2004 (electric tulip), a specific error occurs after that, and the game ball wins the starting
この場合も、いずれの始動口2004への入賞に関連して第二特別図柄が変動表示する変動表示ゲームが行われる。一方、特定のエラー発生中のアウト球をベース計算に用いないので、始動口2004への一つ目の入賞球は低確率・非時短アウト球数に加算されるが、二つ目の入賞球は低確率・非時短アウト球数に加算されない。
Also in this case, a variable display game is performed in which the second special symbol is variable and displayed in relation to the winning of any
すなわち、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、特定の条件(時短終了時、特別図柄変動表示
ゲームの大当り発生時、特定のエラー発生時など)において、電動役物作動中に入賞した複数の遊技球について、ベース値の算出に用いられる場合とベース算出に用いられない場合があり、何れの入賞においても特図の変動を開始し得るものである。
That is, in the
また、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、保留中の特別図柄変動表示ゲームの先読み演出について、始動口2004へ時短状態で入賞した一つ目の入賞は先読み演出の対象とならず、通常状態で入賞した二つ目の入賞は先読み演出の対象としてもよい。これとは逆に、始動口2004へ時短状態で入賞した一つ目の入賞は先読み演出の対象として、通常状態で入賞した二つ目の入賞は先読み演出の対象としなくてもよい。
In addition, in the
なお、時短状態から通常状態へ変化するタイミングについて説明したが、確変状態(ST)又は電サポ状態から通常状態へ変化するタイミングについても同様である。 In addition, although the timing of changing from the time saving state to the normal state has been described, the same applies to the timing of changing from the variable probability state (ST) or the electric sapo state to the normal state.
[10.遊技制御領域外の処理におけるメモリの切り替え]
次に、遊技制御領域外の処理(例えば、ベース算出処理)において、CPUが使用するメモリの切り替えを説明する。
[10. Memory switching in processing outside the game control area]
Next, switching of memory used by the CPU in processing outside the game control area (for example, base calculation processing) will be described.
図110は、主制御MPU1311の内部構成のうち記憶領域に関する構成を示す図である。
FIG. 110 is a diagram showing the internal configuration of the
主制御MPU1311は、全体として図18に示すように構成されているが、図110では記憶領域に関する構成を詳細に示す。
The
主制御MPU1311内にはデータを格納する記憶領域としてRAM1312とROM1313とCPU内補助記憶部13142とが設けられている。CPU内補助記憶部13142は、専ら、CPU13111によるプログラム実行時のデータ(例えば、演算結果の状態を表すフラグ、プログラムの実行状態、CPU13111に入出力されるデータなど)を一時的に格納する。CPU内補助記憶部13142には、例えば、乱数更新処理(図22のステップS40)において更新される乱数値や、乱数値更新演算における中間的な値を一時的に格納する。また、実行するサブルーチンのアドレスやジャンプ先のアドレスをCPU内補助記憶部13142に一時的に格納し、プロセッサコア13141が当該格納したアドレスに対応した処理を実行するようにする。さらには、主制御基板1310に接続される各種のスイッチからポートに入力された値(例えば、スイッチから入力された信号のエッジ情報を作成する途中の値や、エッジ情報の検出結果)を一時的に格納する。
In the
また、始動口入賞時に乱数を取得して保留記憶領域に記憶する際に、乱数値をCPU内補助記憶部13142に一時的に格納し、一時的に格納された乱数値をRAM1312の保留記憶領域に記憶する。また、始動口入賞時の乱数を取得して当該乱数の値に基づいて先読み判定(始動口入賞時における当落判定)を行う際には、CPU内補助記憶部13142に一時的に格納された乱数値に基づいて、先読み判定を行ってもよいし、保留記憶領域に記憶した乱数値をCPU内補助記憶部13142の何れかの記憶領域に(再度)読み出して先読み判定を行ってもよい。
In addition, when a random number is acquired and stored in the reserved storage area at the time of winning the starting opening, the random number is temporarily stored in the
CPU内補助記憶部13142は、RAM1312及びROM1313によって構成されアドレスで指定されるメモリ空間とは別に設けられ、CPU内補助記憶部13142に含まれる各記憶領域の名称(例えば、Area0)で特定される。CPU内補助記憶部13142は、切替部13143、切替用レジスタ13144及び複数の補助記憶領域13145A~Cを含む。
The intra-CPU
補助記憶領域13145A~Cは、所定のビット数(例えば、1バイトや2バイト)の複数の記憶領域(Area0~6)で構成され、所定数(図では7個)の記憶領域毎にグループが構成され、該グループ毎にプロセッサコア13141からのアクセスが可能となる。すなわち、補助記憶領域13145Aが選択されている場合、プロセッサコア13141は、補助記憶領域13145Aのみにアクセス可能であって、他の補助記憶領域13145B、Cにはアクセスできない。
The
この補助記憶領域13145の選択は、後述するように、一つのCHANGE命令でグループ毎に複数の記憶領域を一括して切り替えることができる。例えば、命令CHANGE 0によって、グループ0の補助記憶領域13145Aが選択され、プロセッサコア13141がアクセス可能な補助記憶領域がグループ0に切り替えられる。
As will be described later, the selection of the auxiliary storage area 13145 can collectively switch a plurality of storage areas for each group with one CHANGE instruction. For example, the
補助記憶領域13145は、図示した例では三つのグループで構成されるが、二つ以上であればいくつでもよい。すなわち、補助記憶領域13145は、同じ構成で少なくとも二つ設けられる。 The auxiliary storage area 13145 is composed of three groups in the illustrated example, but any number of groups of two or more may be used. That is, at least two auxiliary storage areas 13145 are provided with the same configuration.
補助記憶領域13145の記憶領域(Area0~5)は、プログラム実行時のデータを一時的に格納するためにRAM1312とは別に設けられる記憶領域であり、一つ(1バイト=8ビット)でも使用可能であり、複数をセットにしても(例えば、Area0とArea1を組とした2バイト=16ビットでも)使用可能である。このため、記憶領域に余剰の容量を生じさせることなく、8ビットのデータや16ビットのデータを補助記憶領域13145に格納できる。また、記憶領域(Area6)は、他の記憶領域の整数倍(例えば、2バイト)の容量で使用される記憶領域として設定されており、1バイトの記憶領域に分割して使用できない。このように、複数の容量の記憶領域によって補助記憶領域13145を構成し、また任意に組み合わせて使用できる記憶領域を設けたので、演算処理における用途(例えば、データ長)に応じて記憶領域を使い分けることができる。例えば、アドレス空間が16ビットで表される場合、一つの(又は組み合わされた一組の)記憶領域でアドレスを指定できる。このため、命令の引数を少なくでき、少ないクロック数で命令を実行できる。
The storage area (
切替部13143は、切替用レジスタ13144に格納された値に従って、プロセッサコア13141がアクセス可能となる記憶領域のグループを切り替える。
The
切替用レジスタ13144は、アクセス可能な補助記憶領域13145を決定するためのデータを格納する記憶領域であり、補助記憶領域13145の選択によらずにプロセッサコア13141がアクセス可能な領域である。切替用レジスタ13144には、例えば、選択される補助記憶領域13145を識別するためのデータ(例えば、4領域を切り替えるための2ビットのデータ)、切り替えが正常に行われなかったことを示す異常フラグ(異常フラグが設定されると、再度切替命令を実行することになる)、及び、選択されていない補助記憶領域13145の値が変化した異常が生じた場合に設定される不正アクセスフラグが記憶されるとよい。
The
また、切替用レジスタ13144は、演算結果の状態を表すフラグ(例えば、キャリーフラグ、パリティ/オーバーフローフラグ、ゼロフラグ、サインフラグなど)を格納してもよい。
Also, the switching
切替用レジスタ13144の他に、補助記憶領域13145の選択によらずにプロセッサコア13141がアクセス可能な記憶領域を設けてもよい。例えば、プログラムを実行中のアドレスを示すプログラムカウンタ、RAM1312に設けられたスタック領域の先頭アドレスを示すスタックポインタを設けてもよい。
In addition to the
図111は、タイマ割込み処理及びベース算出処理のプログラムの一例を示す図であり、タイマ割込み処理からベース算出処理を呼び出し、ベース算出処理から復帰する部分の具体例を示す。 FIG. 111 is a diagram showing an example of a program for timer interrupt processing and base calculation processing, and shows a specific example of a portion that calls base calculation processing from timer interrupt processing and returns from base calculation processing.
タイマ割込み処理(図104)では、ステップS801においてベース算出処理を呼び出すが、ベース算出処理に移行する前に、DI命令によって割り込みを禁止する。DI命令からEI命令までの間の処理が割り込みによって中断することなくベース算出処理を行うことができる。 In the timer interrupt process (FIG. 104), the base calculation process is called in step S801, but interrupts are prohibited by the DI instruction before proceeding to the base calculation process. The base calculation process can be performed without interrupting the process from the DI instruction to the EI instruction.
その後、PUSH命令によって、切替用レジスタ13144のデータを遊技制御用スタック領域13137(図113参照)に退避する。その後、CALL命令によってベース算出処理の先頭番地xxxxからプログラムが実行される。
Then, by the PUSH instruction, save the data of the
ベース算出処理では、図105~図108に示す処理を開始する前に、CHANGE命令によって、補助記憶領域13145を、呼び出し元のタイマ割込み処理で使用するグループ0から呼び出し先のベース算出処理で使用するグループ1に切り替える。このように、一つのCHANGE命令によって、複数の記憶領域をグループ毎に切り替えることができ、一つの命令(すなわち、少ないステップ)で、複数の記憶領域を一括して切り替えることができる。
In the base calculation process, before starting the processes shown in FIGS. 105 to 108, the CHANGE instruction causes the auxiliary storage area 13145 to be used in the base calculation process of the callee from
また、LD命令によって、タイマ割込み処理で使用中のスタックポインタ値をRAM1312の任意のアドレス(例えば、zzzz)に書き込み、スタックポインタ値を退避する。その後、LD命令によって、ベース算出用スタック領域13138のアドレスyyyyをスタックポインタに書き込み、スタック領域を変更する。
Also, the LD instruction writes the stack pointer value being used in timer interrupt processing to an arbitrary address (for example, zzzz) in the
ベース算出処理を実行する準備が完了した後、図105又は図108のステップS8011から処理を実行する。そして、ベース算出処理が終了した後(図106のステップS8038の後)、LD命令によって、タイマ割込み処理で使用していたスタックポインタ値をRAM1312のアドレスzzzzから復旧する。その後、CHANGE命令によって、補助記憶領域13145を、呼び出し先のベース算出処理で使用するグループ1から呼び出し元のタイマ割込み処理で使用するグループ0に切り替えた後、RET命令によって呼び出し元のタイマ割込み処理に戻る。なお、一般的には、補助記憶領域13145を切り替える命令とスタックに退避されたデータを復帰する命令とは異なる役割を有するが、本実施例では、ベース算出処理からタイマ割込み処理に戻った後に、スタックに退避されたデータを切替用レジスタ13144に戻すことによって、補助記憶領域13145が切り替わる。このため、本実施例では、ベース算出処理が終了した後にCHANGE命令によって、補助記憶領域13145をグループ0に切り替えなくてもよいが、CHANGE命令によって補助記憶領域13145を確実に切り替えてもよい。
After the preparation for executing the base calculation process is completed, the process is executed from step S8011 in FIG. 105 or FIG. After the base calculation process ends (after step S8038 in FIG. 106), the stack pointer value used in the timer interrupt process is restored from the address zzzz of the
このように、CHANGE命令は、引数(オペランド)を変えることによって補助記憶領域13145を切り替えるが、各補助記憶領域13145毎に異なる命令を設けてもよい。 In this way, the CHANGE instruction switches the auxiliary storage area 13145 by changing the argument (operand), but a different instruction may be provided for each auxiliary storage area 13145 .
その後、ベース算出処理から復帰すると、POP命令によって、遊技制御用スタック領域13137に退避した切替用レジスタ13144のデータを切替用レジスタ13144に復旧する。なお、切替用レジスタ13144のデータの退避及び復旧は、スタック操作命令であるPUSHやPOPを使用せず、他の命令(例えば、データ転送命令LD、交換命令EX)を使用してもよい。
After that, when returning from the base calculation process, the data of the
その後、EI命令によって割り込みを許可した後、タイマ割込み処理を続行し、RETIでタイマ割込み処理を終了して、主制御側メイン処理(図21のステップS36~S40)に戻る。 After that, after enabling the interrupt by the EI instruction, the timer interrupt processing is continued, the timer interrupt processing is terminated by RETI, and the main control side main processing (steps S36 to S40 in FIG. 21) is returned to.
なお、タイマ割込み処理の先頭でDI命令によって割り込みを禁止し、タイマ割込み処理の最後にEI命令によって割り込みを許可してもよい。また、DI命令やEI命令によらず、割り込み許可フラグを直接操作することによって、タイマ割込み処理が開始すると割り込みが禁止され、RETI命令の実行タイミングで割り込みを許可してもよい。 It should be noted that interrupts may be inhibited by a DI instruction at the beginning of timer interrupt processing, and interrupts may be permitted by an EI instruction at the end of timer interrupt processing. Alternatively, by directly manipulating the interrupt enable flag without relying on the DI or EI instruction, interrupts may be prohibited when timer interrupt processing starts, and interrupts may be enabled at the timing of execution of the RETI instruction.
また、タイマ割込み処理は、本来、割り込みが禁止された状態で実行されるものであるため、タイマ割込み処理内でさらに割り込みを禁止したり、割り込みを許可する必要はない。図示したプログラム例において、DI命令による割込禁止は、何らかの事情によって割込許可となった状態を割込禁止に設定するためである。この場合、タイマ割込み処理の最後まで割込禁止状態を継続すべきなので、EI命令は、POP命令の直後ではなく、タイマ割込み処理の最後に行うとよい。 In addition, since timer interrupt processing is originally executed in a state in which interrupts are disabled, there is no need to further disable or enable interrupts within timer interrupt processing. In the illustrated program example, the DI instruction disables interrupts in order to disable interrupts when interrupts are enabled for some reason. In this case, since the interrupt disabled state should be continued until the end of the timer interrupt processing, the EI instruction should be executed at the end of the timer interrupt processing, not immediately after the POP instruction.
なお、前述した例では、切替用レジスタ13144の退避は呼び出し元のタイマ割込み処理で実行し、補助記憶領域13145の切り替えとスタック領域の切り替えは、呼び出し先のベース算出処理で実行したが、この三つの処理は、遊技制御領域外に処理が移る際、及び遊技制御領域内に処理が戻る際に呼び出し元又は呼び出し先のいずれかで実行すればよい。呼び出し元のタイマ割り込み処理で補助記憶領域13145を切り替える例を図112で説明する。
In the above example, saving of the
図112は、タイマ割込み処理及びベース算出処理のプログラムの別の一例を示す図であり、タイマ割込み処理からベース算出処理を呼び出し、ベース算出処理から復帰する部分の具体例を示す。 FIG. 112 is a diagram showing another example of a program for timer interrupt processing and base calculation processing, and shows a specific example of a portion that calls base calculation processing from timer interrupt processing and returns from base calculation processing.
タイマ割込み処理(図104)では、ステップS801においてベース算出処理を呼び出すが、ベース算出処理に移行する前に、DI命令によって割り込みを禁止する。DI命令からEI命令までの間に割り込みによって、その間の処理が割り込みによって中断することなくベース算出処理を行うことができる。 In the timer interrupt process (FIG. 104), the base calculation process is called in step S801, but interrupts are prohibited by the DI instruction before proceeding to the base calculation process. By interrupting between the DI instruction and the EI instruction, the base calculation processing can be performed without interrupting the processing during that period.
その後、PUSH命令によって、切替用レジスタ13144のデータを遊技制御用スタック領域13137(図113参照)に退避する。その後、CHANGE命令によって、補助記憶領域13145を、呼び出し元のタイマ割込み処理で使用するグループ0から呼び出し先のベース算出処理で使用するグループ1に切り替える。このように、一つのCHANGE命令によって、複数の記憶領域をグループ毎に切り替えることができ、一つの命令(すなわち、少ないステップ)で、複数の記憶領域を一括して切り替えることができる。
Then, by the PUSH instruction, save the data of the
その後、CALL命令によってベース算出処理の先頭番地xxxxからプログラムが実行される。 After that, the program is executed from the start address xxxx of the base calculation processing by the CALL instruction.
ベース算出処理では、図105~図108に示す処理を開始する前に、LD命令によって、タイマ割込み処理で使用中のスタックポインタ値をRAM1312の任意のアドレス(例えば、zzzz)に書き込み、スタックポインタ値を退避する。その後、LD命令によって、ベース算出用スタック領域13138のアドレスyyyyをスタックポインタに書き込み、スタック領域を変更する。
In the base calculation process, before starting the processes shown in FIGS. 105 to 108, the LD instruction writes the stack pointer value being used in the timer interrupt process to an arbitrary address (for example, zzzz) in the
ベース算出処理を実行する準備が完了した後、図105又は図108のステップS80
11から処理を実行する。そして、ベース算出処理が終了した後(図106のステップS8038の後)、LD命令によって、タイマ割込み処理で使用していたスタックポインタ値をRAM1312のアドレスzzzzから復旧する。
After the preparation for executing the base calculation process is completed, step S80 in FIG. 105 or FIG.
11 is executed. After the base calculation process ends (after step S8038 in FIG. 106), the stack pointer value used in the timer interrupt process is restored from the address zzzz of the
その後、ベース算出処理から復帰すると、CHANGE命令によって、補助記憶領域13145を、呼び出し先のベース算出処理で使用するグループ1から呼び出し元のタイマ割込み処理で使用するグループ0に切り替え、POP命令によって、遊技制御用スタック領域13137に退避した切替用レジスタ13144のデータを切替用レジスタ13144に復旧する。なお、切替用レジスタ13144のデータの退避及び復旧は、スタック操作命令であるPUSHやPOPを使用せず、他の命令(例えば、データ転送命令LD、交換命令EX)を使用してもよい。
After that, when returning from the base calculation process, the CHANGE instruction switches the auxiliary storage area 13145 from the
前述したように、切替用レジスタ13144の復帰によって補助記憶領域13145はベース算出処理を呼び出す前の状態に戻るので、CHANGE命令によって補助記憶領域13145を切り替えなくてもよい。しかし、CHANGE命令によって補助記憶領域13145を確実に切り替えてもよい。
As described above, by restoring the
その後、EI命令によって割り込みを許可した後、タイマ割込み処理を続行し、RETIでタイマ割込み処理を終了して、主制御側メイン処理(図21のステップS36~S40)に戻る。 After that, after enabling the interrupt by the EI instruction, the timer interrupt processing is continued, the timer interrupt processing is terminated by RETI, and the main control side main processing (steps S36 to S40 in FIG. 21) is returned to.
なお、前述と同様に、タイマ割込み処理の先頭でDI命令によって割り込みを禁止し、タイマ割込み処理の最後にEI命令によって割り込みを許可してもよい。また、DI命令やEI命令によらず、割り込み許可フラグを直接操作することによって、タイマ割込み処理が開始すると割り込みが禁止され、RETI命令の実行タイミングで割り込みを許可してもよい。 In the same manner as described above, the DI instruction may be used to inhibit interrupts at the beginning of timer interrupt processing, and the EI instruction may be used to enable interrupts at the end of timer interrupt processing. Alternatively, by directly manipulating the interrupt enable flag without relying on the DI or EI instruction, interrupts may be prohibited when timer interrupt processing starts, and interrupts may be enabled at the timing of execution of the RETI instruction.
また、タイマ割込み処理は、本来、割り込みが禁止された状態で実行されるものであるため、タイマ割込み処理内でさらに割り込みを禁止したり、割り込みを許可する必要はない。図示したプログラム例において、DI命令による割込禁止は、何らかの事情によって割込許可となった状態を割込禁止に設定するためである。この場合、タイマ割込み処理の最後まで割込禁止状態を継続すべきなので、EI命令は、POP命令の直後ではなく、タイマ割込み処理の最後に行うとよい。 In addition, since timer interrupt processing is originally executed in a state in which interrupts are disabled, there is no need to further disable or enable interrupts within timer interrupt processing. In the illustrated program example, the DI instruction disables interrupts in order to disable interrupts when interrupts are enabled for some reason. In this case, since the interrupt disabled state should be continued until the end of the timer interrupt processing, the EI instruction should be executed at the end of the timer interrupt processing, not immediately after the POP instruction.
図111では、タイマ割込み処理とベース算出処理と補助記憶領域13145を切り替える例を説明したが、さらに、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133が実行する検査処理でも補助記憶領域13145を切り替えてもよい。この場合、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の先頭で、CHANGE命令によって補助記憶領域13145を検査処理用の補助記憶領域13145に切り替えるとよい。また、初期化処理(図21のステップS10~図22のステップS34)と、主制御側メイン処理(図21のステップS36~S40)と、電源断時処理(図21のステップS42~S58)と、タイマ割込み処理(図23、図75、図80など)とで補助記憶領域13145を切り替えて、各処理で異なる補助記憶領域13145を使い分けてもよい。
In FIG. 111, an example of switching timer interrupt processing, base calculation processing, and auxiliary storage area 13145 has been described, but inspection processing executed by debugging (inspection function)
さらに、補助記憶領域13145が二つだけ設けられている場合、遊技制御領域内で実行される処理(例えば、主制御側メイン処理、タイマ割込み処理など)と、遊技制御領域外(例えば、デバッグ(検査機能)領域、ベース算出領域など)で実行される処理(例えば、デバッグ処理、ベース算出処理など)とで補助記憶領域13145を切り替えて、遊技制御領域の内外で異なる補助記憶領域13145を使い分けてもよい。 Furthermore, if only two auxiliary storage areas 13145 are provided, the processing executed within the game control area (eg, main control side main processing, timer interrupt processing, etc.) and outside the game control area (eg, debugging ( Inspection function) area, base calculation area, etc.) processing (e.g., debug processing, base calculation processing, etc.) to be executed by switching the auxiliary storage area 13145, and using different auxiliary storage areas 13145 inside and outside the game control area good too.
この場合、主制御側メイン処理とタイマ割込み処理とで同じ補助記憶領域13145を使用することになるが、実行中の主制御側メイン処理を中断してタイマ割込み処理を開始することから、タイマ割込み処理の開始時に(例えば、タイマ割込み処理の先頭で)補助記憶領域13145の値を遊技制御用スタック領域13137に一時的に格納し、タイマ割込み処理の終了時に(例えば、タイマ割込み処理の最後に)遊技制御用スタック領域13137に一時的に格納された値を補助記憶領域13145に戻すとよい。
In this case, the same auxiliary storage area 13145 is used for the main control side main processing and the timer interrupt processing. At the start of processing (eg, at the beginning of timer interrupt processing) temporarily store the value of the auxiliary storage area 13145 in the game
例えば、補助記憶領域13145は複数(バイト)の記憶領域を有することから、一単位(バイト又はワード)ずつスタック領域へ退避すると、退避のための命令数が増える。同様に、スタック領域からデータを復旧するための命令数が増える。また、この場合、スタック領域へのデータ退避とスタック領域からのデータ復旧とで処理の順序を間違えると、異なるデータをスタック領域から読み出してしまうため、以降の処理が正確に行われないことがある。このため、補助記憶領域13145の複数の記憶領域の全てを一括してスタック領域に退避し、補助記憶領域13145の複数の記憶領域の全てを一括してスタック領域から復旧する命令を設けることによって、上記問題を解決できる。 For example, since the auxiliary storage area 13145 has a plurality of (byte) storage areas, saving to the stack area one unit (byte or word) at a time increases the number of instructions for saving. Similarly, the number of instructions for recovering data from the stack area increases. Also, in this case, if the order of processing for saving data to the stack area and restoring data from the stack area is incorrect, different data will be read from the stack area, and subsequent processing may not be performed correctly. . Therefore, by providing an instruction to collectively save the plurality of storage areas of the auxiliary storage area 13145 to the stack area and restore all of the plurality of storage areas of the auxiliary storage area 13145 from the stack area, It can solve the above problem.
さらに、補助記憶領域13145の全ての記憶領域をスタック領域に退避すると、スタック領域がオーバーフローして、スタック領域として予定されている領域外(他の用途のスタック領域など)のデータを書き換える可能性がある。このため、補助記憶領域13145の全ての記憶領域を一括してスタック領域に記憶する命令以外に、補助記憶領域13145のうち任意に指定した複数の記憶領域を一括してスタック領域に退避する命令と、スタック領域に退避した補助記憶領域13145のうちの任意に指定した複数の記憶領域に一括して復旧する命令を設けて、実行するようにしてもよい。 Furthermore, if the entire storage area of the auxiliary storage area 13145 is saved to the stack area, the stack area may overflow and data outside the area reserved for the stack area (stack area for other purposes, etc.) may be rewritten. be. For this reason, in addition to the instruction to store all the storage areas of the auxiliary storage area 13145 to the stack area collectively, there is an instruction to collectively save a plurality of storage areas specified arbitrarily from the auxiliary storage area 13145 to the stack area. Alternatively, an instruction may be provided and executed to collectively restore data to a plurality of arbitrarily designated storage areas among the auxiliary storage areas 13145 saved in the stack area.
このように、遊技制御領域外の処理に移る際に別の補助記憶領域13145に切り替えて、遊技制御領域内の処理に移る際に元の補助記憶領域13145に切り替えるので、補助記憶領域13145に格納されたデータをRAM1312(例えば、スタック領域)に退避させずに処理を進行できる。 In this way, it switches to another auxiliary storage area 13145 when moving to the process outside the game control area, and switches to the original auxiliary storage area 13145 when moving to the process within the game control area, so stored in the auxiliary storage area 13145 The processing can proceed without saving the received data to the RAM 1312 (for example, stack area).
また、遊技制御領域外の処理に移る際に切替用レジスタ13144をRAM1312(例えば、スタック領域)に退避して、遊技制御領域内の処理に移る際に切替用レジスタ13144をRAM1312から回復するので、遊技制御領域内の処理に移る際に補助記憶領域13145を切り替えることができ、補助記憶領域13145のデータをRAM1312から回復することなく、復旧できる。
In addition, when moving to the process outside the game control area, save the
また、遊技制御領域外の処理に移行する際に別のスタック領域に切り替え、遊技制御領域内の処理に移る際に元のスタック領域に切り替えるので、遊技制御領域内の処理で使用するスタック領域が、遊技制御領域外の処理において更新されることなく、遊技制御領域内外の処理を完全に分けることができる。 Also, when moving to the process outside the game control area, switch to another stack area, and when moving to the process within the game control area, switch to the original stack area, so the stack area used in the process within the game control area , The processing inside and outside the game control area can be completely separated without being updated in the processing outside the game control area.
また、遊技制御領域外の処理に移行する際に切替用レジスタ13144に格納された値をRAM1312(例えば、スタック領域)に退避し、遊技制御領域内の処理に移る際に退避した値を切替用レジスタ13144に復旧するので、遊技制御領域内におけるプログラムの実行結果に関する値が、遊技制御領域外の処理において更新されることなく、遊技制御領域内外の処理を完全に分けることができる。
In addition, the value stored in the
図113(A)は、主制御基板1310の主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたROM1313及びRAM1312に格納されたプログラム(コード)及びデータの配置の一例を示す図である。図113に示すメモリ上の配置は、図26で前述したメモリ上の配置では省略したスタック領域をRAM1312内に図示しているが、図26に示すRAM131
2にもスタック領域は設けられている。
FIG. 113A is a diagram showing an example of arrangement of programs (codes) and data stored in the
2 is also provided with a stack area.
ROM1313には、遊技制御用コード13131、遊技制御用データ13132、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133、デバッグ(検査機能)用データ13134、ベース算出・表示用コード13135及びベース算出・表示用データ13136を格納する領域が含まれている。本実施形態のROM1313には、遊技制御用コード13131及び遊技制御用データ13132などのパチンコ機1に関わるプログラムやデータを格納する遊技制御領域(第一記憶領域)と、デバッグ(検査機能)コード13133及びデバッグ(検査機能)データ13134などの、パチンコ機1のデバッグ(検査機能)に必要な信号の出力を目的として使用されるプログラムやデータを格納するデバッグ(検査機能)領域(第二記憶領域)と、ベース算出・表示用コード13135及びベース算出・表示用データ13136などの、ベース値の算出を目的として使用されるプログラムを格納するベース算出領域(第三記憶領域)が割り当てられている。
The
遊技制御用データ13132の最終アドレスと、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の先頭アドレスとの間には16バイト以上の空き領域(未使用空間)が設けられており、ダンプリスト形式で表示した場合に遊技制御領域とデバッグ(検査機能)領域とが容易に区別できるようになっている。同様に、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の最終アドレスと、ベース算出・表示用コード13135の先頭アドレスとの間には所定長の空き領域(未使用空間)が設けられている。この所定長を16バイト以上とすると、ダンプリスト形式で表示した場合にデバッグ(検査機能)領域とベース算出用領域とが容易に区別できるので望ましいが、所定長は16バイトより短くてもよい。なお、空き領域に格納される値は、同一の値である固定値とし、かつ、遊技制御領域、デバッグ領域で設定される値とは異なる値又は頻度が低い値で設定されるとよい。また、空き領域に格納される値は、No OperationコードなどCPUが何もしない命令でもよい。このようにすると、ダンプリスト形式で表示される場合、遊技制御領域、デバッグ(検査機能)領域、ベース算出領域が容易に区別できるようになる。
Between the end address of the
また、デバッグ(検査機能)領域とベース算出領域とを分けずに、デバッグ領域の一部にベース算出・表示用コード13135やベース算出・表示用データ13136を格納してもよい。すなわち、遊技制御領域と他の領域とが明確に区別されていればよい。このように、遊技制御領域と他の領域とを明確に区別することによって、遊技の進行の制御に直接関わらない処理であるデバック領域(デバック(検査機能)用コード、デバック(検査機能)用データ)やベース算出領域(ベース算出・表示用コード13135やベース算出・表示用データ13136)を遊技制御領域と分けて配置して、ベース算出・表示用コード13135の不具合(バグ等)が遊技制御に影響を及ぼす危険性を回避している。
Alternatively, the base calculation/
なお、デバッグ(検査機能)領域には、遊技に直接関連しない目的のプログラムやデータが格納されており、例えば、パチンコ機1の遊技制御以外にパチンコ機1のデバッグ時のみに使用される各種機能検査信号を出力するためのコード13133が格納される。これらデバッグ用(検査機能)コード13133は、デバッグ用(検査機能)信号を出力するためのプログラムである。また、ベース算出領域には、遊技の進行に直接関係しない、ベース値を算出するためのプログラムが格納される。
The debug (inspection function) area stores programs and data for purposes not directly related to the game. A
また、遊技制御用コード13131は、主制御MPU1311によって実行される。また、遊技制御用コード13131は、RAM1312に対して適宜読み書きが可能であるが、遊技制御用コード13131で使用する遊技制御用領域13126に対しては、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133から読み出しのみが実行可能となるように構成されており、当該領域に対する書き込みが実行できないように構成されている。このように、遊技制御用領域13126は、遊技制御用コード13131のみからアクセス可能な、遊
技制御領域を構成する。デバッグ(検査機能)用コードに基づく処理は、遊技制御用コード13131の実行中において、一方的に呼び出して実行することが可能であるが、デバッグ(検査機能)用コードから遊技制御用コード13131を呼び出して実行することができないように構成している。これにより、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の独立性を高められるので、遊技制御用コード13131を変更した場合であってもデバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133の変更を最小限にとどめることができる。
Also, the
また、ベース算出・表示用コード13135は、遊技制御用コード13131から呼び出され(例えば、図23に示すタイマ割込み処理のステップS89)、主制御MPU1311によって実行される。ベース算出・表示用コード13135によって計算されたベース値は、RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128に格納される。ベース算出用領域13128は、図示するように、遊技制御用領域13126とは別に(遊技制御領域外に)設けられる。このように、ベース算出・表示用コード13135を遊技制御用コード13131と別に設計し、別の領域に格納することによって、ベース算出・表示用コード13135の検査と遊技制御用コード13131の検査とを別に行うことができ、パチンコ機1の検査の手間を減少できる。また、ベース算出・表示用コード13135を、機種に依存せず、複数の機種で共通に使用できる。
Also, the base calculation/
RAM1312には、遊技制御用領域13126、デバッグ用領域、ベース算出用領域13128、遊技制御用スタック領域13137、デバッグ用スタック領域、及びベース算出用スタック領域13138が設けられる。
The
遊技制御用領域13126は、遊技制御用コード13131が使用するデータが格納さる領域であり、遊技制御用領域13126からは読み書きが可能である。また、遊技制御用領域13126は、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133及びベース算出・表示用コード13135からデータを書き込めないが、リードアクセスが可能であり、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133及びベース算出・表示用コード13135は遊技制御用領域13126に格納されているデータを参照できる。
The
デバッグ用領域は、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133が使用するデータが格納される領域である。デバック用領域は、遊技制御用コード13131、ベース算出・表示用コード13135からアクセス可能であるが、データの読み出しのみが許可され、データの書き込みが禁止されている。ベース算出用領域13128は、ベース算出・表示用コード13135が使用するデータを格納する領域である。ベース算出用領域13128は、遊技制御用コード13131、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133からアクセス可能であるが、データの読み出しのみが許可され、データの書き込みが禁止されている。
The debug area is an area in which data used by the debug (inspection function)
遊技制御用スタック領域13137は、遊技制御用コード13131が使用するデータが退避される領域である。デバッグ用スタック領域は、デバッグ(検査機能)用コード13133が使用するデータが退避される領域である。ベース算出用スタック領域13138は、ベース算出・表示用コード13135が使用するデータが退避される領域である。各スタック領域は、専ら、CPU内補助記憶部13142に格納されたデータを一時的に退避するために用いられる。各スタック領域は、CPU13111が管理するスタックポインタの値を変更することによって、切り替えることができる。なお、スタックポインタは、スタック領域の開始アドレスを指定する記憶領域である。
The game
図113(B)は、ベース算出用領域13128の詳細を示す図である。ベース算出用領域13128は、ベースの算出結果が格納されるメイン領域の他、メイン領域に格納されたデータの複製が格納されるバックアップ領域1及びバックアップ領域2とを設けてもよい。バックアップ領域は一つでも複数でもよい。各領域には、データの誤りを検出する
ためのチェックコードが付加される。チェックコードは、各領域のデータのチェックサムでも予め定めた値でもよい。チェックコードは、パチンコ機1の電源投入時に初期化処理で設定したり、ベース算出・表示処理においてメイン領域のデータが更新される毎に設定したり、主制御側電源断時処理(図22のステップS50~S54)において設定してもよい。特に、チェックコードが固定値である場合、初期化処理で正常と判定した又はデータを消去した際にチェックコードを初期化し、主制御側電源断時処理(図20のステップS50)において固定値をセットしてもよい。チェックコードは、停電フラグと兼用してもよい。すなわち、メイン領域のチェックコードに所定値が設定されていれば、停電フラグが設定されていると判定してもよい。また、停電フラグに所定値が設定されていれば、各領域のチェックコードが正しい値である(すなわち、各領域のデータが正常である)と判定してもよい。
FIG. 113B is a diagram showing details of the
なお、メイン領域が異常であると判定された場合にバックアップ領域が正常であるかを判定し、正常であると判定されたバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製してもよい(図21のステップS24)。また、主制御側電源断時処理において、メイン領域の値を各バックアップ領域に複製してもよい(図22のステップS54)。また、ベース算出・表示処理において、ベース算出・表示処理の終了時にメイン領域の値をバックアップ領域に複製してもよい。少なくともメイン領域の一部が更新された際に、メイン領域の全部又は更新された値の領域のみをバックアップ領域に複製するものであればよい(図25のステップS168、S170)。 Incidentally, if it is determined that the main area is abnormal, it may be determined whether or not the backup area is normal, and the data in the backup area determined to be normal may be copied to the main area (step in FIG. 21). S24). Also, in the main control side power-off process, the values in the main area may be duplicated in each backup area (step S54 in FIG. 22). Further, in the base calculation/display process, the values in the main area may be copied to the backup area when the base calculation/display process ends. When at least part of the main area is updated, the entire main area or only the updated value area may be copied to the backup area (steps S168 and S170 in FIG. 25).
メイン領域とバックアップ領域1との間、及びバックアップ領域1とバックアップ領域2との間には、未使用空間が設けられる。各領域の間に未使用空間を設けることによって、各領域のアドレスを遠ざけることができ、アドレスの上位桁で各領域を区別できる。
Unused space is provided between the main area and the
[11.遊技履歴の記録]
次に、遊技履歴を記録し、出力するパチンコ機の実施例を説明する。
[11. Recording game history]
Next, an embodiment of a pachinko machine that records and outputs game histories will be described.
[11-1.遊技履歴を記録する遊技機の基本構成]
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、周辺制御部1511は、主制御基板1310から送信される変動パターンコマンドに適合する演出を複数用意された演出の中から決定し、決定された演出をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示する。その際、周辺制御部1511は複数用意された演出のうち特定の演出(例えば、3種類のスーパーリーチのうち2種類の特定の演出)を現出することが決定すると、遊技状態の切り替わりを起点として何回の特別図柄変動表示ゲームが行われて、その特定の演出が現出されたか(換言すると、何回転目に当該演出が出現したか)を、ゲームの進行状況と共にメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示する。
[11-1. Basic configuration of gaming machine that records gaming history]
In the
具体的には、図114に示す遊技履歴に従って、10時25分の34回転目にスーパーリーチ1が現出して、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの結果はハズレとなり、10時54分の127回転目にスーパーリーチ2が現出して、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの結果はハズレとなり、11時30分の428回転目にスーパーリーチ2が出現して、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの結果は確変大当りとなった、という内容が表示される。
Specifically, according to the game history shown in FIG. 114,
大当たり履歴の表示(例えば、15回転目に大当たり、50回転目に大当たりという履歴)は、ホールに備え付けられているデータ表示器で確認できるが、大当たりまでに現出した特定の演出は確認できない。特定の演出が現出する程度からパチンコ機1が好調か不調かを見極める遊技者もいる(例えば、大当たり終了後50回転以内にスーパーリーチ2が出現すると、短時間で大当たりに当選すると考える)。このような遊技者の期待に応えるために、演出の現出の程度を視認可能に表示する。また、遊技者が演出の現出の程度を
確認しているときは遊技球を発射しないことから、複数用意されている演出の全ての現出の程度が分かる表示をすると、遊技者が演出毎の現出の程度を確認する時間がかかり、遊技台の稼働が低下する可能性がある。このため、リーチ演出のうちの特定のリーチ演出(大当たりに対する期待度が高いリーチ演出)のみを表示するとよい。また、所定の操作手段(操作ボタン220Cなど)の操作によって、演出毎の現出の履歴を確認できるようにしてもよい。
The display of the jackpot history (for example, the history of the jackpot on the 15th spin and the jackpot on the 50th spin) can be confirmed with a data display provided in the hall, but the specific performance that appears before the jackpot cannot be confirmed. Some players judge whether the
具体的な処理として、周辺制御部1511は、主制御基板1310から変動パターンコマンドを受信すると、変動回数と現出された演出の情報を記憶する。さらに、周辺制御部1511は、受信した変動パターンコマンドに基づいて、変動回数と現出された演出の情報を更新する。そして、所定の操作手段(操作ボタン220Cなど)が操作されると、現出された全ての演出ではなく、限定された特定の演出が現出するまでに要した変動回数を加算して表示する処理を行えばよい。
As a specific process, when the
また、営業中のパチンコ機1にエラーが発生した場合、パチンコ機1からエラー情報を出力しホールの従業員に報知する。この通知の形態は、図115(A)に示すエラー画面をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示したり、図115(B)に示す詳細エラー画面をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示して、エラーの原因を報知したり、警報音を出力したり、図116に示すエラー信号を外部端子板784から出力する。また、パチンコ機1における代表的なエラーは、図117、図118、図119に示すものがある。パチンコ機1に発生するエラーはホールの従業員がその原因を知ることができるように、パチンコ機1の外に報知される。例えば、エラーの種別毎に定められたコードを、機能表示ユニット1400に含まれる状態表示LEDに表示していてもよい。具体的には、主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951との間のケーブルの接続不良である場合、機能表示ユニット1400に含まれる状態表示LEDに「0」を表示し、扉右中のLEDが青色に点灯する。
Also, when an error occurs in the
しかしながら、エラーは、パチンコ機1の軽微な故障(例えば、コネクタ外れ)によるものや、部品交換が必要な重度の故障によるものや、不正行為に起因するもの等、様々な原因により発生する。 However, errors occur due to various causes, such as a minor failure of the pachinko machine 1 (for example, disconnection of a connector), a serious failure requiring part replacement, or fraudulent activity.
エラーが発生したパチンコ機1は、エラー発生原因を探り、エラーから復旧して稼動させなければならない。エラー発生原因の探求には時間やコストが必要であり、エラーによるパチンコ機1の稼働停止は、売上の低下を招く。従って、ホールは、発生したエラーの詳細な情報を知ることができれば、エラーを早期に解決でき、パチンコ機1の稼動停止時間を短縮できる。
The
より具体的には、ホールは、ホールコンピュータを用いて、外部端子板784から出力された信号によってパチンコ機1の状態を判定する。しかし、エラーの原因の探求には、外部端子板784から出力された信号に加え、望ましくは、「一般入賞口の入賞数」「大入賞口の入賞数」「ゲート通過数」「普通図柄変動数」などの遊技履歴情報が必要である。パチンコ機1の故障であれば、修理や部品交換で解決するので、それほど大きな問題はないが、不正行為によって遊技球が取得された場合、正常な遊技者が利益を得られる機会が減り、ホールの営業を妨害し、最終的には、ホールが経営難となる可能性がある。
More specifically, the hall uses the hall computer to determine the state of the
このような遊技履歴情報を外部端子板784から出力すると、外部端子板784に用いられるコネクタの端子数が増加し、パチンコ機1のコストが増大する。さらに、「一般入賞口への入賞」「大入賞口への入賞」「ゲートの通過」「普通図柄が変動」等のイベントは頻繁に生じるため、パチンコ機1から全てのデータを出力すると、データを解析するために高性能のホールコンピュータが必要となり、ホールの負担が増大する。
When such game history information is output from the external
本実施例のパチンコ機1は、前述した課題を解決するために、外部端子板748からリアルタイムな信号として出力されないデータをパチンコ機1の内部に記憶し、記憶されたデータを後に参照可能とすることによって、エラー発生までの経緯の詳細を確認できるようにした。
In the
さらに、これらエラー発生までの経過において生じたイベント(一般入賞口の入賞数、大入賞口の入賞数、ゲート通過数、普通図柄変動数など)の発生時刻が記録されるので、どれだけの時間にどれだけのイベントが発生したかを把握できる。例えば、一般入賞口の入賞数が1分間に50個だった等の異常が分かる。 In addition, since the time of occurrence of events (number of winnings in general winnings, number of winnings in big winnings, number of gates passed, number of normal symbol fluctuations, etc.) that occurred in the course of the error occurrence is recorded, how long It is possible to know how many events have occurred in For example, an abnormality such as the number of prizes won in a general prize gate being 50 per minute can be detected.
なお、イベント毎に発生日時を記録すると、エラー発生原因の探求に使用するデータ量が多くなり、エラー発生原因の探求に時間がかかる。このため、所定時間(例えば、1分間)に所定数以上のイベントが発生している場合にエラー情報として出力し、報知してもよい。 If the date and time of occurrence are recorded for each event, the amount of data used to search for the cause of the error will increase, and it will take time to search for the cause of the error. Therefore, when a predetermined number or more of events occur within a predetermined time period (for example, one minute), the error information may be output and notified.
例えば、どの遊技状態においても一般入賞口へは入賞可能なので、所定時間に所定数以上の入賞があった場合にエラー情報を出力し報知するとよいが、大入賞口へは大当たり遊技中のみで入賞するので、所定時間を大当たり遊技開始から終了までに設定し、所定時間に所定数以上の大入賞口への入賞があった場合にエラー情報を出力し報知するとよい。 For example, since it is possible to win a prize in a general prize-winning slot in any game state, it is preferable to output and notify error information when a predetermined number or more of prizes are won in a predetermined period of time. Therefore, it is preferable to set a predetermined period of time from the start to the end of the jackpot game, and output and notify error information when a predetermined number or more of prizes are won in the large winning openings within the predetermined period of time.
以下に説明するパチンコ機では、周辺制御部1511が遊技履歴を記録し、所定の形式のデータで出力する。
In the pachinko machine described below, the
図120は、本実施例の周辺制御部電源投入時処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。図120に示す周辺制御部電源投入時処理は、図60を用いて前述した周辺制御部電源投入時処理に遊技履歴記録処理(ステップS1023)が追加されている。 FIG. 120 is a flow chart showing an example of the power-on processing of the peripheral control unit according to the present embodiment. 120 is obtained by adding a game history recording process (step S1023) to the peripheral control unit power-on process described above with reference to FIG.
遊技履歴記録処理は、周辺制御部1511が、主制御基板1310から受信したコマンドの解析結果に基づいて、受信したコマンドが所定のコマンドである場合、遊技履歴をメモリに記録する。遊技履歴は、例えば、図122に示すような形式でイベントの発生日時として記録される。遊技履歴が記録されるメモリは、DRAMでもよいが、電源遮断時にも記憶内容を保持することを考慮しリフレッシュ動作が不要で消費電力が低いSRAMに記録するとよい。
In the game history recording process, the
遊技履歴記録処理(ステップS1023)は、遊技制御に関する処理(ステップS1024~S1032)より前に実行するとよい。遊技履歴記録処理を周辺制御部定常処理の早い段階で実行することによって、遊技制御に関する処理が途中で停止して、一部の演出が実行されなくても、遊技履歴を正確に記録できる。すなわち、一部の演出が実行されなくても(たとえ全ての演出が実行されなくても)、主制御基板1310で既に行われた抽選の結果は変わらず、遊技者に付与される特典も変わらないことから、演出より優先して遊技履歴を記録している。また、遊技履歴記録処理が遊技制御に関する処理に影響されないので、複数の機種のパチンコ機で遊技履歴記録処理を共通化できる。
The game history recording process (step S1023) is preferably executed before the game control process (steps S1024 to S1032). By executing the game history recording process at an early stage of the steady process of the peripheral control part, the game history can be accurately recorded even if the process related to the game control is stopped on the way and part of the performance is not executed. That is, even if some effects are not executed (even if all effects are not executed), the result of the lottery already performed by the
次に、記録される遊技履歴のメモリの容量が上限に達した場合の処理を説明する。記録される遊技履歴のデータ量がメモリの容量の上限に達している場合、遊技履歴記録処理を実行するが、メモリに記録されている遊技履歴を更新しなくてもよい。つまり、メモリに記録されている情報は変化しない。このように、遊技履歴を記録するメモリの容量に空きがなくても遊技履歴記録処理を実行することによって、遊技履歴を記録するメモリの空き状態を確認する必要がなく、周辺制御部1511の毎回の処理を軽減できる。 Next, a description will be given of the processing when the memory capacity of the game history to be recorded reaches the upper limit. When the data amount of the game history to be recorded reaches the upper limit of the capacity of the memory, the game history recording process is executed, but the game history recorded in the memory does not have to be updated. That is, the information recorded in memory does not change. In this way, by executing the game history recording process even if there is no free space in the memory for recording the game history, there is no need to check the free state of the memory for recording the game history. processing can be reduced.
また、記録される遊技履歴のメモリの容量が上限に達している場合、遊技履歴記録処理を実行し、メモリに記録されている遊技履歴を更新してもよい。この場合、複数(例えば10個)の記憶領域を有するリングバッファを周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に設け、最古の遊技履歴を消去して最新の遊技履歴を記録してもよい。この場合でも、遊技履歴を記録するメモリの空き状態を確認する必要がなく、周辺制御部1511の毎回の処理を軽減できる。
Further, when the memory capacity of the game history to be recorded reaches the upper limit, the game history recording process may be executed to update the game history recorded in the memory. In this case, a ring buffer having a plurality of (for example, 10) storage areas may be provided in the game history storage area of the
また、記録される遊技履歴がメモリの容量の上限に達した場合に、ステップS1023をスキップして、遊技履歴記録処理を実行しなくてもよい。記録される遊技履歴がメモリの容量の上限に達した場合に遊技履歴記録処理を実行しないことによって、無駄な処理の実行を防止できるため、周辺制御部1511が行う他の処理(演出制御、ランプ制御、音制御)を確実に実行できるとともに、空いた処理時間を利用して、新たな処理(例えば、処理時間に余裕がないために複数回の周辺制御部定常処理に跨って実行される処理や、毎回実行する必要がないために何回かの周辺制御部定常処理に1回実行される処理(例えば、選択テーブルを切り替える処理))を実行してもよい。 Also, when the game history to be recorded reaches the upper limit of the memory capacity, step S1023 may be skipped and the game history recording process may not be executed. By not executing the game history recording process when the recorded game history reaches the upper limit of the memory capacity, it is possible to prevent unnecessary processing from being executed. control, sound control) can be reliably executed, and at the same time, using the spare processing time, new processing (for example, processing that is executed over multiple times of peripheral control unit steady processing due to lack of processing time) Alternatively, a process (for example, a process of switching the selection table) that is executed once in a number of peripheral control unit steady processes because it is not necessary to be executed each time may be executed.
なお、割り込みタイマ起動処理(ステップS1010)の直後に受信コマンドを解析し(ステップS1022)、遊技履歴記録処理(ステップS1023)を実行してもよい。 Note that the received command may be analyzed (step S1022) immediately after the interrupt timer activation process (step S1010), and the game history recording process (step S1023) may be executed.
図121は、遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブルの構成例を示す図である。 FIG. 121 is a diagram showing a configuration example of a game history recording condition setting table.
遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブルは、周辺制御部1511が主制御基板1310から受信するコマンドのうち、遊技履歴として記録されるコマンドの種別、すなわち、遊技履歴として記録されるイベントを登録する。
The game history recording condition setting table registers the types of commands recorded as game history among the commands received by the
例えば、遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブルには、以下のコマンド種別が登録され、当該コマンドの発生条件や、遊技履歴として記録する目的は以下の通りである。 For example, the following command types are registered in the game history recording condition setting table, and the conditions for generating the commands and the purpose of recording as game history are as follows.
例えば、始動口1入賞時コマンド、始動口2入賞時コマンドは、それぞれ、始動口2002、始動口2004への遊技球の入賞を検出すると主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が各始動口への入賞球数を計数できる。また、特別図柄1図柄種別コマンド、特別図柄2図柄種別コマンドは、それぞれ、特別図柄の変動開始時に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が特別図柄1、2の変動数を計数できる。
For example, when the starting
また、電源投入コマンドは、電源投入時に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511がラムクリア操作などを取得できる。変動開始時状態コマンドは、特別図柄の変動開始時に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が特別図柄の変動開始時の状態を取得できる。変動開始時状態コマンドで区別可能な状態は、低確率・時短、低確率・非時短、高確率・時短、高確率・非時短の4状態であり、状態の変化を取得でき、各状態で開始した変動の数を計数できる。ここで、低確率とは、特別図柄変動表示ゲームに伴う大当たり抽選において大当たりが導出される確率が通常の確率である状態であり、高確率とは、特別図柄変動表示ゲームに伴う大当たり抽選において大当たりが導出される確率が通常より高い状態である。時短は、前述した第二始動口扉部材2549が開放(又は、拡大)状態となる確率が非時短と比べて高確率になったり、普通図柄が変動を開始してから確定するまでの時間が短くなるなど、第二始動口扉部材2549が開放(又は、拡大)状態となる頻度が非時短状態より高い状態である。それに伴い、1回の特別図柄変動表示ゲームの時間が短い演出が選択される確率が高くなる。
Also, the power-on command is transmitted from the
大入賞口1入賞コマンド(入賞毎)、大入賞口2入賞コマンド(入賞毎)は、それぞれ、大入賞口2005、大入賞口2006へ遊技球が入賞すると主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が各大入賞口への入賞球数を計数できる。
A large winning
大入賞口1入賞コマンド(規定入賞以下)、大入賞口2入賞コマンド(規定入賞以下)は、それぞれ、大入賞口2005、大入賞口2006において、ラウンド終了までに規定数以下の遊技球しか入賞しなかった場合、各大入賞口の閉鎖時から所定時間経過時(例えば、1秒後から次回の開放前まで)に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が各大入賞口への1ラウンドにおける入賞の状態を取得できる。大入賞口1入賞コマンド(規定入賞より大きい)、大入賞口2入賞コマンド(規定入賞より大きい)は、それぞれ、大入賞口2005、大入賞口2006において規定数を超える遊技球が入賞してラウンドが終了した場合、各大入賞口の閉鎖時から所定時間経過時(例えば、1秒後から次回の開放前まで)に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が各大入賞口への1ラウンドにおける入賞の状況を取得できる。なお、このコマンドが各大入賞口2005、2006の閉鎖時から所定時間経過時に送信されるのは、1回のラウンドで定める規定数(例えば、10個)の入賞球を検出して大入賞口を閉鎖した時に未検出の遊技球が大入賞口内に存在する可能性もあり、このようなオーバー入賞時にも正確に入賞の状況を把握するためである。
For the big winning
大当たりOPコマンドは、大当たり発生時(すなわち、条件装置作動時又は役物連続作動装置作動)に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が大当たり状態への変化を取得でき、大当たり回数を計数できる。大当たり動作終了時移行先コマンドは、大当たり状態の終了時に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、大当たり状態の終了と、周辺制御部1511が大当たり後の状況を取得できる。
The jackpot OP command is transmitted from the
小当りOPコマンドは、大入賞口の開放が比較的短時間(例えば、1回の開放時間が1.8秒であったり、複数回の開放時間の合計が1.8秒未満)の開放であって、役物連続作動装置が作動しない当たり(いわゆる、小当たり)に、主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が小当り回数を計数できる。
In the small hit OP command, the opening of the big winning opening is relatively short (for example, the opening time of one time is 1.8 seconds, or the total opening time of multiple times is less than 1.8 seconds). A command is transmitted from the
普通図柄停止コマンドは、普通図柄の停止時に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が普通図柄の停止図柄を取得でき、普通図柄の変動数を計数できる。普図ゲート通過コマンドは、遊技球がゲート部2003を通過すると主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511がゲート部2003を通過した遊技球数を取得できる。
The normal symbol stop command is transmitted from the
始動口に入賞したりゲートを通過しても特別図柄や普通図柄の抽選が行われない場合(オーバーフローや記憶がない場合など)でも、主制御基板1310は周辺制御部1511に、始動口1入賞時コマンド、始動口2入賞時コマンドおよび普図ゲート通過コマンドを送信する。このため、周辺制御部1511は始動口への入賞球数とゲート部を通過した球数を計数できる。
Even if the lottery for special symbols or normal symbols is not performed even after winning the starting gate or passing the gate (overflow or no memory, etc.), the
エラー表示コマンドは、エラー発生時に主制御基板1310から周辺制御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511がエラーの発生タイミングを取得でき、エラー発生数を計数できる。
The error display command is transmitted from the
一般入賞口1入賞コマンド、一般入賞口2入賞コマンド、一般入賞口3入賞コマンドは、それぞれ、各一般入賞口2001へ遊技球が入賞すると主制御基板1310から周辺制
御部1511へコマンド送信され、周辺制御部1511が各一般入賞口2001への入賞球数を計数できる。なお、一般入賞口入賞コマンドは、遊技領域5aに設けられる一般入賞口2001の数だけ定められるとよく、前述では三つの一般入賞口2001が設けられている場合を例示している。本実施例のパチンコ機1は図10や図16に示すように、四つの一般入賞口2001が設けられるので、一般入賞口1入賞コマンドから一般入賞口4入賞コマンドの四種類の一般入賞口入賞コマンドが定められるものである。
The general winning
図122は、メモリに記録された遊技履歴の構成例を示す図である。 FIG. 122 is a diagram showing a configuration example of game history recorded in the memory.
遊技履歴は、履歴番号、イベント、及びイベント発生日時を含み、望ましくは、イベント発生時刻順にメモリに記録される。イベント発生日時は、周辺制御部1511が主制御基板1310からコマンドを受信した時刻をイベント発生日時として記録してもよく、主制御基板1310がイベント発生を検出した時刻を周辺制御部1511に通知して、周辺制御部1511は、主制御基板1310から通知されたイベント発生時刻を記録してもよい。図示した遊技履歴では、イベント発生日時は分までの粒度で記録されているが、秒まで記録してもよい。
The game history includes a history number, event, and event occurrence date and time, and is preferably recorded in the memory in order of event occurrence time. As the event occurrence date and time, the time at which the
図122に示す形態の遊技履歴の解析によって、主制御基板1310から送信されたコマンドに関連して発生したイベントの詳細(例えば、遊技状態の変化、変動表示ゲームの結果など)を知ることができる。例えば、履歴番号1の電源投入コマンドは、2016年3月15日の15時30分に発生し、コマンドの内容からRAMクリアが行われて、低確率・非時短状態で遊技が開始したことが分かる。すなわち、ホールが15時30分に営業を開始しパチンコ機1の電源を投入し、遊技者がしばらくして(例えば、煙草に火をつけた後に)打ち始めて、一般入賞口2001に入賞した経緯が分かる。また、履歴番号4の特図1変動開始イベントは、2016年3月15日の15時34分に発生し、受信した特別図柄1図柄種別コマンドの内容(停止図柄の種別)から、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの結果が分かる。履歴番号6の特図1変動開始イベントは、2016年3月15日の15時34分に発生し、受信した特別図柄1図柄種別コマンドの内容(停止図柄の種別)から、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの結果が分かる。なお、図122には特別図柄変動表示ゲームの結果を図示していないが、特別図柄の変動開始時に受信する図柄種別コマンドに含まれる変動表示ゲームの結果を示す数値によって、各特別図柄変動表示ゲームの結果を知ることができ、変動表示ゲームの結果(ハズレ、通常4ラウンド当たり、高確率4ラウンド当たり、高確率16ラウンド当たりなど)を遊技履歴として記録してもよい。
By analyzing the game history in the form shown in FIG. 122, it is possible to know the details of the events that have occurred in relation to the commands sent from the main control board 1310 (for example, changes in the game state, the result of the variable display game, etc.). . For example, the power-on command with
次に、メモリに記録された情報(遊技履歴)をホールが参照する方法を説明する。 Next, a method of referring to the information (game history) recorded in the memory by the hole will be described.
まず、周辺制御部1511からメモリに記録された情報を出力する履歴出力インターフェイス1590を設ける。そして、周辺制御部1511は、主制御基板1310から履歴参照コマンドを受信すると、メモリに記録される遊技履歴を履歴出力インターフェイス1590から出力する。
First, a history output interface 1590 for outputting information recorded in the memory from the
また、パチンコ機1にデータ収集端末を接続し、周辺制御部1511は、該データ収集端末から履歴参照コマンドを受信すると、メモリに記録される遊技履歴を履歴出力インターフェイス1590から出力する。履歴出力インターフェイス1590は、周辺制御部1511に設けた履歴出力端子で構成しても、周辺制御部1511とは別に設けてもよい。データ収集端末は、パチンコ機1のデータ管理用にホールが保有するとよい。
Also, a data collection terminal is connected to the
データ収集端末とパチンコ機1との間の接続は、履歴出力インターフェイス1590を介したケーブルによる接続でも、近距離無線(たとえば、ブルートゥース(登録商標))を介した無線接続でもよい。
The connection between the data collection terminal and the
周辺制御部1511が遊技履歴を出力するトリガとなるコマンドは、遊技履歴出力専用の履歴参照コマンドでも、パチンコ機1に電源が投入されてから通常の遊技を行っているときには送信されないコマンド(図121には定義されていないコマンド)で特別な条件(操作)が行われたときのコマンドを履歴参照コマンドとしてもよい。特別な条件(操作)は、例えば、パチンコ機1に電源が投入されている状態でRAMクリアボタンを操作するなどである。また、通常の遊技を行っているときに送信されるコマンドでも、起こりえない(または、起こりにくい)事象を条件として、履歴参照コマンドを送信してもよい。例えば、1分間に始動口や一般入賞口に50個入賞した場合などである。また、遊技制御に使用するコマンドを通常はあり得ない特殊な順序で受信した場合に遊技履歴を出力してもよい。
The command that triggers the output of the game history by the
なお、パチンコ機1の裏面側(遊技者から見えない場所)に操作パネル(キーボード)及び表示器(液晶表示装置)を設け、遊技履歴を表示してもよい。 An operation panel (keyboard) and a display (liquid crystal display device) may be provided on the back side of the pachinko machine 1 (where the player cannot see) to display the game history.
図123は、周辺制御基板及びその周辺の構成を示すブロック図である。 FIG. 123 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the peripheral control board and its periphery.
周辺制御基板1510は、主制御基板1310からの各種コマンドに基づいて演出制御を行い、かつ、枠周辺中継端子板868を介して、演出表示駆動基板4450と制御コマンドや各種情報(各種データ)をやり取りする周辺制御部1511と、メイン液晶表示装置1600及び扉枠側演出表示装置460の描画制御を行い、かつ、下部スピーカ921及び上部スピーカ573から流れる音楽や効果音等の音制御を行う液晶表示制御部1512と、年月日を特定するカレンダー情報と時分秒を特定する時刻情報とを保持するリアルタイムクロック(以下、「RTC」と記載する。)制御部4165とを有する。
Peripheral control board 1510 performs effect control based on various commands from
演出制御を行う周辺制御部1511は、図123に示すように、マイクロプロセッサとしての周辺制御MPU1511aと、電源投入時に実行される電源投入時処理を制御し、電源投入時から所定時間が経過した後に実行される演出動作を制御するサブ制御プログラムなどの各種制御プログラム、各種データ、各種制御データ及び各種スケジュールデータを記憶する周辺制御ROM1511bと、後述する液晶表示制御部1512の音源内蔵VDP1512aからのVブランク信号が入力されるごとに実行される周辺制御部定常処理をまたいで継続される各種情報(例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600に描画する画面を規定するスケジュールデータや各種LED等の発光態様を規定するスケジュールデータなどを管理するための情報など)を記憶する周辺制御RAM1511cと、日をまたいで継続される各種情報(例えば、大当たり遊技状態が発生した履歴を管理するための情報や特別な演出フラグの管理するための情報など)を記憶する周辺制御SRAM1511dと、周辺制御MPU1511aが正常に動作しているか否かを監視するための周辺制御外部ウォッチドッグタイマ1511e(以下、「周辺制御外部WDT1511e」と記載する。)とを有する。
As shown in FIG. 123, the
周辺制御RAM1511cは、電力が長時間遮断された状態(長時間の電断が発生した場合)ではその内容を失うのに対して、周辺制御SRAM1511dは、電源基板931に設けられた図示しない大容量の電解コンデンサ(以下、「SRAM用電解コンデンサ」と記載する。)によりバックアップ電源が供給されることにより、記憶された内容を50時間程度、保持することができるようになっている。電源基板931にSRAM用電解コンデンサが設けられるので、遊技盤5をパチンコ機1から取り外した場合には、周辺制御SRAM1511dにバックアップ電源が供給されなくなるため、周辺制御SRAM1511dは、記憶された内容を保持することができなくなってその内容を失う。
The
また、周辺制御SRAM1511dの一部の領域は、電源基板931から供給されるバ
ックアップ電源と異なるバックアップ電源1513によって電源が供給される。バックアップ電源1513によって電源が供給される周辺制御SRAM1511dの領域には、遊技履歴が記録され、パチンコ機1の電源が遮断されても、記憶内容を保持できるように構成されている。バックアップ電源1513は、リチウムイオン電池などの二次電池で構成され、数週間から1か月程度の間、周辺制御SRAM1511dの少なくとも一部の領域のデータを保持可能な電源供給能力を有するとよい。
Power is supplied to a part of the
図124は、周辺制御SRAM1511dの周辺の構成を示すブロック図である。
FIG. 124 is a block diagram showing the peripheral configuration of the
周辺制御SRAM1511dのうち、遊技履歴を格納する領域は、周辺制御MPUを含む周辺制御CPUとは別のパッケージで構成されても、周辺制御MPUと共に周辺制御CPUのパッケージ内に構成されてもよい。
The area for storing the game history in the
図124(A)は、周辺制御CPUとは別のパッケージで遊技履歴を格納する領域を構成した周辺制御SRAM1511dの周辺の構成を示す。図示するように、バックアップ電源1513から電源が供給されない演出制御用領域は周辺制御CPUパッケージの外部に設けられ、バックアップ電源1513から電源が供給される遊技履歴格納領域は周辺制御CPUパッケージの外部に設けられる。
FIG. 124(A) shows the peripheral configuration of the
RAMクリアスイッチを操作してパチンコ機1をリセットする場合、周辺制御CPU内の周辺制御SRAM(演出制御用領域)1511dのデータはクリアされるが、周辺制御CPU外の周辺制御SRAM(遊技履歴格納用領域)1511dのデータはクリアされない。
When the RAM clear switch is operated to reset the
図124(B)は、周辺制御CPUのパッケージ内に遊技履歴を格納する領域を構成した周辺制御SRAM1511dの周辺の構成を示す。図示するように、バックアップ電源1513から電源が供給されない演出制御用領域及びバックアップ電源1513から電源が供給される遊技履歴格納領域の両方が周辺制御CPUパッケージ内に設けられる。
FIG. 124(B) shows the peripheral configuration of the
図124(B)に示す構成でも、RAMクリアスイッチを操作してパチンコ機1をリセットする場合、周辺制御CPU内の周辺制御SRAM(演出制御用領域)1511dのデータはクリアされるが、周辺制御CPU外の周辺制御SRAM(遊技履歴格納用領域)1511dのデータはクリアされない。このため、周辺制御SRAM1511dの演出制御用領域と遊技履歴格納領域とは、望ましくは、物理的に分けて構成されているとよい。
Even in the configuration shown in FIG. 124(B), when the RAM clear switch is operated to reset the
なお、周辺制御SRAM1511dのうち、遊技履歴を格納する領域を、SRAMではなく、フラッシュメモリで構成してもよい。フラッシュメモリに遊技履歴を格納することによって、バックアップ電源1513を設けることなく、電源が供給されていないパチンコ機1においても遊技履歴を保持できる。
Note that the area for storing the game history in the
図124(A)、(B)いずれの形態においても、パチンコ機1は、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域のデータを初期化する手段を有する。周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域のデータを初期化する手段は、RAMクリアスイッチを操作しながらパチンコ機1の電源を投入するという通常のデータの初期化方法とは異なる手順の方法であれば何でもよい。例えば、RAMクリアスイッチの他に履歴クリアスイッチを設け、履歴クリアスイッチを操作しながらパチンコ機1の電源を投入すると、記憶された遊技履歴を初期化する。この場合、RAMクリアスイッチと履歴クリアスイッチの両方を操作しながらパチンコ機1の電源を投入すると、記憶された遊技状態の情報と遊技履歴の両方を初期化する。履歴クリアスイッチは、周辺制御基板1510に直接接続されてもよい。
124A and 124B, the
また、RAMクリアスイッチを操作しながらパチンコ機1の電源を投入し、電源投入後も所定時間RAMクリアスイッチを継続して操作した場合に、記憶された遊技状態の情報と遊技履歴の両方を初期化してもよい。
In addition, when the power of the
周辺制御SRAM1511dに記憶された遊技履歴を初期化する場合、主制御基板1310は、通常の電源投入コマンドと異なるコマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
When initializing the game history stored in the
また、主制御基板1310は、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されている間は、周辺制御基板1510に電源投入コマンドを送信し続け、周辺制御基板1510は、所定時間内に所定回数の電源投入コマンドを受信した場合、又は電源投入コマンドを連続して受信した場合周辺制御SRAM(遊技履歴格納用領域)1511dに記憶された遊技履歴を初期化してもよい。このように遊技履歴格納領域のデータを初期化する手段を設けることによって、例えば、遊技機が1年間ホールで稼働し続けても、最新の情報を正確に記録し、解析できる。
Further, while the RAM clear switch is being operated, the
周辺制御外部WDT1511eは、周辺制御MPU1511aのシステムが暴走していないかを監視するためのタイマであり、このタイマがタイマアップすると、ハードウェア的にリセットをかけるようになっている。つまり、周辺制御MPU1511aは、一定期間内(タイマがタイマアップするまで)に周辺制御外部WDT1511eのタイマをクリアするクリア信号を周辺制御外部WDT1511eに出力しないときには、リセットがかかることとなる。周辺制御MPU1511aは、一定期間内にクリア信号を周辺制御外部WDT1511eに出力するときには、周辺制御外部WDT1511eのタイマカウントを再スタートさせるため、リセットがかからない。
The peripheral control external WDT 1511e is a timer for monitoring whether the system of the
周辺制御MPU1511aは、パラレルI/Oポート、シリアルI/Oポート等を複数内蔵しており、主制御基板1310からの各種コマンドを受信すると、この各種コマンドに基づいて、遊技盤5の各装飾基板に設けた複数のLED等への点灯信号、点滅信号又は階調点灯信号を出力するための遊技盤側発光データをランプ駆動基板用シリアルI/Oポートから図示しない周辺制御出力回路を介してランプ駆動基板4170に送信したり、遊技盤5に設けた各種可動体を作動させるモータやソレノイド等の電気的駆動源への駆動信号を出力するための遊技盤側モータ駆動データをモータ駆動基板用シリアルI/Oポートから周辺制御出力回路を介してモータ駆動基板4180に送信したり、扉枠3に設けられた電気的駆動源への駆動信号を出力するための扉側モータ駆動データを枠装飾駆動アンプ基板モータ用シリアルI/Oポートから周辺制御出力回路、枠周辺中継端子板868を介して枠装飾駆動アンプ基板に送信したり、扉枠3の各装飾基板に設けた複数のLED等への点灯信号、点滅信号又は階調点灯信号を出力するための扉側発光データを枠装飾駆動アンプ基板LED用シリアルI/Oポートから周辺制御出力回路、枠周辺中継端子板868を介して枠装飾駆動アンプ基板に送信したりする。
The
主制御基板1310からの各種コマンドは、図示しない周辺制御入力回路を介して、周辺制御MPU1511aの主制御基板用シリアルI/Oポートに入力されている。また、演出操作ユニット220に設けられた、ダイヤル操作部401の回転(回転方向)を検出するための回転検出スイッチからの検出信号、及び押圧操作部405の操作を検出するための押圧検出スイッチからの検出信号は、枠装飾駆動アンプ基板194に設けた図示しない扉側シリアル送信回路でシリアル化され、このシリアル化された演出操作ユニット検出データが扉側シリアル送信回路から、周辺扉中継端子板882、枠周辺中継端子板868、そして周辺制御入力回路を介して、周辺制御MPU1511aの演出操作ユニット検出用シリアルI/Oポートに入力されている。
Various commands from the
遊技盤5に設けた各種可動体の原位置や可動位置等を検出するための各種検出スイッチ(例えば、フォトセンサなど。)からの検出信号は、モータ駆動基板4180に設けた図示しない遊技盤側シリアル送信回路でシリアル化され、このシリアル化された可動体検出データが遊技盤側シリアル送信回路から周辺制御入力回路を介して、周辺制御MPU1511aのモータ駆動基板用シリアルI/Oポートに入力されている。周辺制御MPU1511aは、モータ駆動基板用シリアルI/Oポートの入出力を切り替えることにより周辺制御基板1510とモータ駆動基板4180との基板間における各種データのやり取りを行うようになっている。
Detection signals from various detection switches (for example, photosensors, etc.) for detecting the original positions and movable positions of various movable bodies provided on the
以上に説明したように、本実施例の遊技機では、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510へ送信されるコマンドに従って、遊技中に生じたイベントを遊技履歴として記録するので、遊技中に生じたイベントを後で(例えば、ホールの営業終了後など)解析して、遊技機の性能や故障を把握できる。また、遊技履歴は不揮発性メモリ(バックアップ電源が入力されたSRAM)に格納するので、遊技機を再起動した後でも遊技履歴を確認できる。
As described above, in the gaming machine of this embodiment, according to commands transmitted from the
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、図121、図122等に示すように、様々な情報が発生時刻とともに記録される。また、例えば、始動口1に入賞した場合は、(1)始動口1に入賞した事実、(2)始動口1に入賞した時刻、(3)始動口1に入賞する前に起きたイベントのように、図116に示す外部端子板748から出力される情報よりも多くの情報をパチンコ機1の内部に記憶している。これは、始動口に入賞した場合など、必要最低限の情報(前述の(1)始動口に入賞した事実を示す情報)は外部端子板784から出力し、特別な場合(例えば、エラーの原因を調査するとき)には、パチンコ機1の内部に記憶した情報を確認できるようにしたためである。これは、始動口への入賞時に内部に記憶している情報の全てを外部端子板784から出力すると、パチンコ機1の稼動に関する情報の出力量が多くなり、ホールに負担となる恐れがあるからである。つまり、イベント発生時に、外部端子板784から出力される情報より多くの情報をパチンコ機1の内部に記録しておき、内部に記録される情報の一部を外部端子板784を介してパチンコ機1の外部に出力し、特別な場合にはパチンコ機1の内部に記憶した情報を確認できるようにした。
In the
[11-2.コンパクト案1]
次に、遊技履歴を記録し、出力するパチンコ機の変形例を説明する。なお、以下に説明するいくつかの変形例は、前述した実施例の一部を変更するものであって、当該実施例の一部を成すものである。
[11-2. Compact plan 1]
Next, a modified example of a pachinko machine that records and outputs game history will be described. It should be noted that some of the modified examples described below change a part of the above-described embodiment and constitute a part of the embodiment.
前述した実施例では、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510へ送信されるコマンドのうち、予め定められた所定のコマンドについて、発生したイベント(コマンドの種別)及びイベント発生日時を記録した。しかし、遊技履歴を記録するSRAM1511dの容量は有限であり、遊技中に発生する膨大な量のイベントの全てを長時間にわたり記録することは困難である。このため、変形例1(コンパクト案1)では、パチンコ機1の状態の変化と、当該状態において生じた計数イベントの数を記録するものとした。
In the above-described embodiment, among the commands transmitted from the
図125は、変形例1の遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブルの構成例を示す図である。
125 is a diagram showing a configuration example of a game history recording condition setting table of
変形例1の遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブルでは、遊技履歴として記録されるコマンドが、計数するコマンドと状態変化の契機となるコマンドとに分けて定義されており、両方の属性が設定されているコマンドもある。なお、計数可能な情報の欄と取得可能な状態変化の欄は説明の便宜上設けたものであり、遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブルがパチンコ機1に実装される場合には、コマンド種別欄だけでよい。
In the game history recording condition setting table of
周辺制御部1511は、計数する属性が設定されているコマンドを受信すると、コマンド解析の結果、コマンド発行の契機となったイベントの数を計数する。また、周辺制御部1511は、状態変化の契機となる属性が設定されているコマンドを受信すると、コマンド解析の結果、メモリに記録される遊技履歴の状態を新しくして、イベント数を計数するレコードを追加する。
When the
例えば、電源投入コマンド、変動開始時状態コマンド、大当たりOPコマンド、大当たり動作終了時移行先コマンド、エラー表示コマンドは、状態変化によって発行されるコマンドであり、それぞれ、電源投入、特別図柄変動表示開始、大当たり状態開始、大当たり状態終了、エラー状態発生の状態の切り替わりとして把握できる。 For example, the power-on command, the state command at the start of fluctuation, the jackpot OP command, the transition destination command at the end of the jackpot operation, and the error display command are commands issued by state changes, respectively, power-on, special symbol fluctuation display start, It can be grasped as switching between the start of the jackpot state, the end of the jackpot state, and the occurrence of an error state.
また、計数コマンドを用いて、計数コマンド発行の契機となったイベント数を計数する。具体的には、始動口1入賞時コマンド、始動口2入賞時コマンドでは、各始動口への入賞球数を計数できる。特別図柄1図柄種別コマンド、特別図柄2図柄種別コマンドは、各特別図柄の変動数を計数できる。大入賞口1入賞コマンド(入賞毎)、大入賞口2入賞コマンド(入賞毎)は、各大入賞口への入賞球数を計数できる。大入賞口1入賞コマンド(規定入賞以下)、大入賞口2入賞コマンド(規定入賞以下)は、規定入賞数以下で終了したラウンドの数を計数できる。大入賞口1入賞コマンド(規定入賞より大きい)、大入賞口2入賞コマンド(規定入賞より大きい)は、規定入賞数を超えて(すなわち、オーバー入賞で)終了したラウンドの数を計数できる。
Also, using the count command, the number of events that triggered the issuance of the count command is counted. Specifically, the number of winning balls to each starting port can be counted in the
小当りOPコマンドは、小当り回数を計数できる。普通図柄停止コマンドは、普通図柄の変動数を計数できる。普図ゲート通過コマンドは、ゲート部を通過した遊技球数を取得できる。エラー表示コマンドは、エラー発生数を計数できる。一般入賞口1入賞コマンド、一般入賞口2入賞コマンド、一般入賞口3入賞コマンドは、各一般入賞口への入賞球数を計数できる。
The small hit OP command can count the number of small hits. The normal design stop command can normally count the number of fluctuations in the design. Ordinary figure gate passage command can acquire the number of game balls that have passed through the gate section. The error display command can count the number of error occurrences. The general winning
図126は、変形例1のメモリに記録された遊技履歴を示す図である。
126 is a diagram showing the game history recorded in the memory of
変形例1の遊技履歴は、パチンコ機1の状態変化の契機となった状態変化イベントと、当該状態変化イベント後の状態と、当該状態変化イベントが発生した時刻と、所定の起算点から当該状態の終了まで(次の状態変化イベントまで)に検出された計数イベントの累計数とを含む。遊技履歴として記録される計数イベントの数は、当該状態中(一つ前の状態変化イベントから当該状態変化イベントまでの間)に検出された計数イベントの数でもよい。所定の起算点は、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴記憶領域の初期化時点である。計数イベントが分けて記録される状態は、低確率・非時短状態、低確率・時短状態、高確率・非時短状態、高確率・時短状態、大当たり状態の5状態を想定しているが、この状態を更に細分化してもよい。
The game history of the modified example 1 includes the state change event that triggered the state change of the
次に、変形例1における遊技履歴記録処理の詳細を説明する。図126に示す遊技履歴では、計数イベントとして、始動口1入賞数、始動口2入賞数、特別図柄1変動数、特別図柄2変動数、一般入賞口1入賞数、一般入賞口2入賞数、一般入賞口3入賞数、大入賞口1入賞数、大入賞口2入賞数、ゲート通過数、普通図柄変動数が記録される。なお、図示した以外のイベントの数を計数してもよい。
Next, details of the game history recording process in
各計数イベントの累積数の記憶領域は2バイトあれば十分である。特に、それほど頻繁に派生せず、累積数が大きくならないデータ(例えば、一般入賞口入賞数)は1バイトでもよく、それ以外は2バイトにするとよい。この場合、1バイトのデータと2バイトのデータとを混在させることなく、2バイト、1バイトの順(又は、1バイト、2バイトの順)で並べるとよい。 Two bytes are sufficient for storing the cumulative number of each counting event. In particular, data that is not derived very frequently and does not have a large cumulative number (for example, the number of general winnings) may be 1 byte, and other data may be 2 bytes. In this case, 1-byte data and 2-byte data should be arranged in the order of 2 bytes and 1 byte (or in the order of 1 byte and 2 bytes) without mixing 1-byte data and 2-byte data.
また、状態変化イベントが生じると、状態変化イベントの種別、当該イベント発生後の状態、当該イベントの発生日時が記録され、遊技履歴に新たなレコードが作られる。そして、状態変化後の計数イベントは新たなレコードに記録される。 Also, when a state change event occurs, the type of state change event, the state after the occurrence of the event, and the date and time of occurrence of the event are recorded, and a new record is created in the game history. Then, the counting event after the state change is recorded in a new record.
なお、現在の状態における計数イベントの計数結果は、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録し、状態変化後にSRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に作られた新たなレコードに格納するとよい。なお、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の新たなレコードは状態変化を契機として作成されるが、計数イベントが計数される期間の開始時に新たなレコードを作成してもよい。この場合、計数イベントが計数される間、作成された新たなレコードにデータは格納されていなくても、初期値として0を格納してもよい。また、計数イベントが計数される期間の終了時に新たなレコードを作成してもよい。この場合、新たなレコードを作成した直後に、当該期間の計数イベントの計数結果が新たなレコードに格納される。
The counting result of the counting event in the current state may be recorded in the work area of the
遊技状態が変化して作業領域(周辺制御RAM1511c)に記録されたデータを遊技履歴格納領域(周辺制御SRAM1511d)に格納する場合、遊技履歴格納領域からデータを読み出して、作業領域に記録された計数値を加算して、遊技履歴格納領域に格納する。一方、当該状態中(一つ前の状態変化イベントから当該状態変化イベントまでの間)に検出された計数イベントの数が遊技履歴として記録される場合、計数イベントの計数値を周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に格納する。
When the game state changes and the data recorded in the work area (
すなわち、状態変化イベントが生じる毎に、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の計数値が更新される。このため、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録されている現在の状態における計数結果は、次の状態変化イベントが発生するまで周辺制御RAM1511cに記録されており、停電発生時には記憶内容がバックアップされるが、通常のラムクリア操作によって初期化されることになる。具体的には、例えば、低確率・非時短状態において、始動口1への入賞数が50個が作業領域(周辺制御RAM1511c)に記録されている遊技履歴の情報は、変形例1のパチンコ機1では遊技状態が変化した後に周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に記録される。換言すれば、遊技状態が変化しなければ、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に遊技履歴が記録されない。このため、低確率・非時短状態のまま、電源を遮断してラムクリア操作すると、この50個の入賞数は初期化され0個となる。
That is, every time a state change event occurs, the count value in the game history storage area of the
また、現在の状態における計数イベントの計数結果を、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に書き込んでもよい。すなわち、計数イベントが生じる毎に、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の計数値が更新される。この場合、周辺制御SRAM1511dに記録されている現在の状態における計数結果は、通常のラムクリア操作によっては初期化されないが、前述した遊技履歴初期化操作によって初期化される。
Also, the counting result of the counting event in the current state may be written in the game history storage area of the
また、記録される遊技履歴がメモリの容量の上限に達した場合でも、遊技履歴記録処理を実行するとよい。この場合、現在の状態において遊技履歴の周辺制御RAM1511cへの記録は継続して実行し、計数イベントの累積数を状態変化時に周辺制御RAM1511cから周辺制御SRAM1511d格納しなくてもよい。また、最古の状態における遊技履歴(計数イベントの累積数)を消去して直前の状態における計数イベントの累積数を記録してもよい。この場合、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域にリングバッファを構成するとよい。
Also, even when the game history to be recorded reaches the upper limit of the capacity of the memory, it is preferable to execute the game history recording process. In this case, the game history is continuously recorded in the
遊技履歴を記録するメモリの容量に空きがなくても遊技履歴記録処理を実行することによって、遊技履歴を記録するメモリの空き状態を確認する必要がなく、周辺制御部151
1の毎回の処理を軽減できる。また、現在の状態における計数イベントの累積数は周辺制御RAM1511cに記録されているので、直近の遊技履歴を確認できる。
By executing the game history recording process even if there is no free space in the memory for recording the game history, there is no need to check the free state of the memory for recording the game history, and the peripheral control unit 151
1 can be reduced. Also, since the cumulative number of counting events in the current state is recorded in the
また、記録される遊技履歴がメモリの容量の上限に達した場合に、ステップS1023をスキップして、遊技履歴記録処理を実行しなくてもよい。記録される遊技履歴がメモリの容量の上限に達した場合に遊技履歴記録処理を実行しないことによって、無駄な処理の実行を防止し、周辺制御部1511の処理を軽減できる。
Also, when the game history to be recorded reaches the upper limit of the memory capacity, step S1023 may be skipped and the game history recording process may not be executed. By not executing the game history recording process when the game history to be recorded reaches the upper limit of the memory capacity, it is possible to prevent the execution of unnecessary processes and reduce the processing of the
以上に説明したように、変形例1では、パチンコ機1の状態の切り替わりを記録し、切り替わり間の各状態における計数イベント(各入賞数、変動数など)の数を記録するので、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の容量を大きくせずに、長時間の遊技履歴が記録できる。
As described above, in
また、前述したように、変形例1のパチンコ機1では、外部端子板784から出力される情報よりも多くの情報を内部的に記録しているのも特徴である。
Further, as described above, the
さらに、前述したように、変形例1のパチンコ機1では、遊技履歴に新たなレコードが作られる条件は遊技状態の変化であり、遊技状態が変化しなければ周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に情報(遊技履歴)が書き込まれない。つまり、遊技履歴格納領域に新たなレコードが作られない状態(同じ遊技状態の継続中)において不正が行われると、不正の発見が困難となるおそれがある。前述したように、ホールは、メモリに書き込まれた情報(遊技履歴)を解析するために、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に書き込まれた情報を確認できるものの、変形例1のパチンコ機1では、遊技状態が変化しないかぎり、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に情報が書き込まれないので、周辺制御SRAM1511dから情報を読み出しても、現在の状態の情報(遊技履歴)を確認できない。このような場合にも早期に不正を発見できるチェック機能を設けてもよい。
Furthermore, as described above, in the
具体的には、直近の状態の遊技履歴が記録された第1のレコード(周辺制御SRAM1511dの最新のレコード)と現在の状態の遊技履歴が記録された第2のレコード(周辺制御RAM1511cのレコード)との比較結果が所定の条件を満たした場合、エラーを報知してもよい。
Specifically, the first record (latest record of the
例えば、高確率・時短状態や大当たり遊技状態では遊技領域5aの右側を転動するように遊技球を発射する、いわゆる右打ちを行うパチンコ機1において、高確率・時短状態から大当たり遊技状態へ遷移し、さらに大当たり遊技状態終了後に高確率・時短状態へ遷移した場合、状態が切り替わっても、通常は右打ちを行っているため、遊技領域5aの左側にある一般入賞口に入賞する可能性は極めて低い。この場合、一般入賞口への入賞数を大当たり遊技状態とその後の高確率・時短状態とで比較して、差が検出されると、エラーを報知してもよい。状態間の一般入賞口への入賞球数の差の許容値は1個とし、2個以上の差が生じるとエラーを報知するとよい。これは、発射ハンドルから手を離すと発射勢にムラが生じ遊技領域5aの左側を遊技球が転動する可能性があるからである。
For example, in a so-called right-
エラー報知に代えて、図116に示す外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を送信してもよい。前述した早期不正発見チェック機能は、パチンコ機1の遊技状態から、遊技を予想して(例えば、高確率・時短状態だから右打ちするだろう)エラーを検出しているので、不慣れな遊技者が想定外の打ち方をする場合にエラーを検出する可能性がある。このため、パチンコ機1においてエラーを報知せず、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力するのみとし、遊技客には知らせないようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、ホールの店員がパチンコ機1から離れた場所から、遊技者に気付かれずにエラーの可能性を確
認でき、遊技客とのトラブルも防止できる。
A security signal may be transmitted from the external
このように、パチンコ機1のエラー検出機能は万全ではないため、パチンコ機1の外部で遊技履歴を解析することによって、エラーの原因をチェックできるようにした。
As described above, since the error detection function of the
[11-3.コンパクト案2]
前述した変形例1では、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510へ送信されるコマンドのうち、状態変化イベントでパチンコ機1の状態の切り替わりを記録し、切り替わりの間の各状態における計数イベントの数を記録した。しかし、変化する個々の状態におけるイベントの数は重要ではない場合もあり、繰り返し発生する状態の種別毎のイベントの数が分かれば十分な場合も考えられる。このため、変形例2(コンパクト案2)では、パチンコ機1の状態と、当該状態毎の計数イベントの累計数を記録するものとした。
[11-3. Compact plan 2]
In the above-described
変形例2では、変形例1と同じ遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブル(図125)を用いて、遊技履歴を記録する。
In
図127は、変形例2のメモリに記録された遊技履歴を示す図である。
127 is a diagram showing the game history recorded in the memory of
図127に示すように、変形例2の遊技履歴は、状態イベントの履歴と状態毎の各計数イベントの累計数とで構成される。状態イベントの履歴は、パチンコ機1の状態変化の契機となった状態変化イベントと、当該状態変化イベント後の状態と、当該状態変化イベントが発生した時刻とを含む。変形例2のパチンコ機1では、低確率・非時短状態、低確率・時短状態、高確率・非時短状態、高確率・時短状態、大当たり状態の5状態において、計数イベントの累計数が記録される。変形例2において記録される計数イベント(及び、当該イベントに関連するコマンド)は、始動口1入賞数(始動口1入賞時コマンド)、始動口2入賞数(始動口2入賞時コマンド)、特別図柄1変動数(特別図柄1図柄種別コマンド)、特別図柄2変動数(特別図柄2図柄種別コマンド)、一般入賞口1入賞数(一般入賞口1入賞コマンド)、一般入賞口2入賞数(一般入賞口2入賞コマンド)、一般入賞口3入賞数(一般入賞口3入賞コマンド)、大入賞口1入賞数(大入賞口1入賞コマンド)、大入賞口2入賞数(大入賞口2入賞コマンド)、ゲート通過数(普図ゲート通過コマンド)、普通図柄変動数(普通図柄停止コマンド)である。
As shown in FIG. 127, the game history of
なお、前述した以外の計数イベントの数を計数してもよく、計数イベントが分けて記録される状態を更に細分化してもよい。 Note that the number of count events other than those described above may be counted, and the state in which the count events are separately recorded may be further subdivided.
次に、変形例2における遊技履歴記録処理の詳細を説明する。図127に示す遊技履歴では、状態変化イベントが生じると、状態変化イベントの種別、当該イベント発生後の状態、当該イベントの発生日時が状態イベント履歴に記録される。状態変化イベントによって遊技機の状態の変化が検出されると、変化前の状態において計数された計数イベントの累計数を不揮発性メモリに記録し、変化後の状態に対応して、前述した計数イベントの累計数の記録を開始する。
Next, details of the game history recording process in
なお、現在の状態における計数イベントの計数結果は、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録し、状態変化後にSRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域(当該状態の累積値)を読み出して、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録された値を加算して、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に格納するとよい。すなわち、状態変化イベントが生じる毎に、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の累積値が、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録された当該状態変化前の値を用いて更新される。このため、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録されている現在の状態における計数結果は、停電発生時には記憶内容がバックアップされるが、通常のラムクリア操作によって初期化される
。
The counting result of the counting event in the current state is recorded in the work area of the
また、現在の状態における計数イベントの計数結果を、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に書き込んでもよい。すなわち、計数イベントが生じる毎に、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の累積値が更新される。この場合、SRAM1511dに記録されている現在の状態における計数結果は、通常のラムクリア操作によっては初期化されないが、前述した遊技履歴初期化操作によって初期化される。
Also, the counting result of the counting event in the current state may be written in the game history storage area of the
以上に説明したように、変形例2では、パチンコ機1の状態の切り替わりを記録し、状態の種別毎の計数イベント(各入賞数、変動数など)を記録するので、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の容量を大きくせずに、長時間の遊技履歴が記録できる。
As described above, in
[11-4.コンパクト案3]
前述した変形例2では、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510へ送信されるコマンドのうち、状態変化イベントでパチンコ機1の状態変化を記録し、状態毎の計数イベントの累積数を記録した。しかし、状態が切り替わったタイミングは重要ではない場合もあり、状態の種別毎のイベントの数が分かれば十分な場合も考えられる。このため、変形例3(コンパクト案3)では、パチンコ機1の状態の切り替わりを記録せず、状態毎の計数イベントの累計数を記録するものとした。
[11-4. Compact plan 3]
In the
変形例3では、変形例1と同じ遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブル(図125)を用いて、遊技履歴を記録する。
In
変形例3では、図125に示す遊技履歴記録条件設定テーブルを用いて、変形例1で記録されるイベントと同じイベントを記録する。
In
図128は、変形例3のメモリに記録された遊技履歴を示す図である。
128 is a diagram showing the game history recorded in the memory of
図128に示すように、変形例3の遊技履歴は、各状態における計数イベントの累計数で構成される。さらに、変形例3の遊技履歴は、各状態の累積時間を含む。累積時間を含めたのは、累積時間からイベントの発生回数(例えば、大当たりの発生回数等)をホールが推測できるようにするためである。計数イベントが分けて記録される状態は、低確率・非時短状態、低確率・時短状態、高確率・非時短状態、高確率・時短状態、大当たり状態の5状態であるが、更に細分化して計数イベントを記録してもよい。
As shown in FIG. 128, the game history of
変形例3において記録される計数イベント(及び、当該イベントに関連するコマンド)は、始動口1入賞数(始動口1入賞時コマンド)、始動口2入賞数(始動口2入賞時コマンド)、特別図柄1変動数(特別図柄1図柄種別コマンド)、特別図柄2変動数(特別図柄2図柄種別コマンド)、一般入賞口1入賞数(一般入賞口1入賞コマンド)、一般入賞口2入賞数(一般入賞口2入賞コマンド)、一般入賞口3入賞数(一般入賞口3入賞コマンド)、大入賞口1入賞数(大入賞口1入賞コマンド)、大入賞口2入賞数(大入賞口2入賞コマンド)、ゲート通過数(普図ゲート通過コマンド)、普通図柄変動数(普通図柄停止コマンド)である。なお、前述した以外の計数イベントの数を計数してもよい。
The counting events (and the commands related to the event) recorded in
次に、変形例2における遊技履歴記録処理の詳細を説明する。図128に示す遊技履歴では、状態変化イベントが生じると、当該状態変化イベントによって変化した遊技機の状態に対応して、前述した計数イベントの累計数が記録される。
Next, details of the game history recording process in
なお、現在の状態における計数イベントの計数結果は、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録し、状態変化後にSRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域(当該状態の累積
値)を読み出して、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録された値を加算して、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に格納するとよい。すなわち、状態変化イベントが生じる毎に、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の累積値が更新される。このため、周辺制御RAM1511cの作業領域に記録されている現在の状態における計数結果は、停電発生時には記憶内容がバックアップされるが、通常のラムクリア操作によって初期化される。
The counting result of the counting event in the current state is recorded in the work area of the
また、現在の状態における計数イベントの計数結果を、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に書き込んでもよい。すなわち、計数イベントが生じる毎に、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の累積値が更新される。この場合、SRAM1511dに記録されている現在の状態における計数結果は、通常のラムクリア操作によっては初期化されないが、前述した遊技履歴初期化操作によって初期化される。
Also, the counting result of the counting event in the current state may be written in the game history storage area of the
以上に説明したように、変形例2では、パチンコ機1の状態の切り替わりを記録し、状態の種別毎の計数イベント(各入賞数、変動数など)を記録するので、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域の容量を大きくせずに、長時間の遊技履歴が記録できる。
As described above, in
以上に説明したように、変形例1~3については、遊技履歴記録処理によってイベント発生時に一旦作業領域(周辺制御RAM1511c)に記録し、周辺制御SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に書き込む条件を満たしたときに、作業領域のデータをSRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に書き込む。また、通常のラムクリア操作では、SRAM1511dの遊技履歴格納領域に書き込まれた情報は消去(初期化)しないが、作業領域(周辺制御RAM1511c)に記録した情報は消去(初期化)される。
As described above, in
ここでホールの営業について簡単に触れておく。多くの場合、ホールは営業時間が定められており、例えば開店時間が10:00で閉店時間が23:00である。このため、開店から間もない時間帯や夕方の時間帯などの、多くの遊技客がいる時間帯では、遊技客が不正な遊技をしているかの店員による監視は困難な場合がある。しかしながら、閉店時間が近づくと遊技客も減り、閉店間際において高確率・時短状態のパチンコ機があると、翌日の営業に向けて、高確率・時短状態のパチンコ機を初期化して、低確率・非時短状態にすることがある。この場合、遊技客が少ないことから、高確率・時短状態のパチンコ機を監視できるため、直近の遊技については不正されているかが分かる。つまり、直近の遊技履歴は必要ないパチンコ機もあるという状況を考慮すると、店員が直近の情報を残すかを選択可能にすることで、効率のよい遊技機を提供できる。 Here I will briefly touch on the hall business. In many cases, halls have set business hours, for example, opening at 10:00 and closing at 23:00. For this reason, it is sometimes difficult for staff to monitor whether players are playing illegal games during hours when there are many players, such as hours just after the store opens or in the evening. However, as the closing time approaches, the number of players decreases, and if there is a pachinko machine in a high-probability/short-time state just before closing time, the high-probability/short-time state pachinko machine is initialized for the next day's business, and the low-probability/ It may be in a non-working time state. In this case, since the number of players is small, it is possible to monitor pachinko machines in a high-probability/time-saving state, so it is possible to know whether or not the most recent game has been fraudulent. In other words, considering that some pachinko machines do not require the most recent game history, it is possible to provide an efficient gaming machine by enabling the store clerk to select whether or not to keep the most recent information.
具体的には、ラムクリア操作によるパチンコ機1の初期化によって、直近のイベントの後に発生したイベントに関して作業領域に格納された遊技履歴を消去し、直近のイベントの前に発生したイベントに関して遊技履歴格納領域に格納された遊技履歴は残している。つまり、パチンコ機は外部端子板784から出力されない情報を記録するものの、RAMクリア操作によって消去される作業領域に記録された情報と、RAMクリア操作によって消去されない遊技履歴格納領域に記録された情報とに分けて、遊技履歴を記録している。このようにすることで、作業領域に記録される全てのイベントの記録を残したい場合、店員がパチンコ機の状態変化を引き起こせばよく、作業領域に記録されたイベントの記録を消去したい場合、店員はラムクリア操作を行えばよい。ラムクリア操作によって、全ての遊技履歴を消去せず、直近のイベントの後に発生したイベントに関する作業領域に格納された遊技履歴のみを消去することとしたのは、前述したように、直近のイベントの前までに発生したイベントは店員は見ていない(遊技客が多いため見られない)ためである。
Specifically, by initializing the
前述したように、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、始動口に入賞したという情報の記録だけでなく、抽選と関係ない一般入賞口への入賞も作業領域に一旦は記録するため、特別図
柄(始動口に入賞したことによって変動を開始する図柄で、この図柄の停止態様をもって当落の抽選結果が示される図柄)が変動していなくとも、遊技領域5aに遊技球が打ち出されている間は遊技履歴を収集することを特徴としている。つまり、遊技履歴記録処理は、当落の抽選を契機に実行される処理ではなく、パチンコ機に電源が供給されている間は常に実行される可能性がある処理であると言える。
As described above, in the
また、低確率・非時短状態であれば、いわゆる左打ちやちょろ打ちのように、始動口2002へ遊技球が入賞するように遊技球を発射する。このような場合、始動口2002や一般入賞口2001へは適度に入賞するはずである。しかし、一般入賞口2001への入賞が無い(または、極めて少ない)が、始動口2002に多くの遊技球が入賞している場合や、逆に始動口2002への入賞が無い(または、極めて少ない)が、一般入賞口2001に多くの遊技球が入賞している場合には、不正が行われている可能性がある。そこで、同時期に遊技球が入賞する第1の入賞口と第2の入賞口を監視対象に設定し、第1の入賞口への入賞数が第2の入賞口への入賞数の所定倍率を超えるときに、エラーを報知してもよい。
Moreover, if it is a low-probability and non-time-saving state, it shoots a game ball so that a game ball may win a prize to the
また、エラー報知に代えて、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を送信してもよい。前述の検出方法では、不慣れな遊技者が想定外の打ち方をする場合にエラーを検出する可能性がある。このため、パチンコ機1においてエラーを報知せず、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力するのみとし、遊技客には知らせないようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、ホールの店員がパチンコ機1から離れた場所から、遊技者に気付かれずにエラーの可能性を確認でき、遊技客とのトラブルも防止できる。
Also, a security signal may be transmitted from the external
また、本実施例のパチンコ機1は、複数ゲームで累積した情報を遊技履歴として収集していることも特徴としている。記録可能な遊技履歴のデータ量には上限があるため、1ゲーム(1変動)ごとに記録すると、多くのゲーム(長時間)の記録ができないため、より多くのゲームの記録を保持可能にしている。
The
[12.遊技性能の設定機能]
次に、設定機能を有するパチンコ機の実施例を説明する。本実施例のパチンコ機は、遊技性能として、例えば条件装置の作動割合を変更する設定機能を有する。
[12. Game performance setting function]
Next, an embodiment of a pachinko machine having a setting function will be described. The pachinko machine of this embodiment has, as game performance, a setting function for changing, for example, the operating ratio of the condition device.
[12-1.設定機能を有するパチンコ機の基本構成]
図129は、設定部を有するパチンコ機の制御構成を概略的に示すブロック図であり、図130は、設定部を有するパチンコ機を開扉状態で裏面側から見た斜視図であり、図131は、図130に示すパチンコ機を閉扉状態で裏面側から見た斜視図であり、図132は、図130に示すパチンコ機の設定部を示す図である。
[12-1. Basic configuration of pachinko machine with setting function]
FIG. 129 is a block diagram schematically showing the control configuration of a pachinko machine having a setting section, FIG. 130 is a perspective view of the pachinko machine having a setting section with the door open, viewed from the rear side, and FIG. 130 is a perspective view of the pachinko machine shown in FIG. 130 with the door closed, viewed from the back side, and FIG. 132 is a diagram showing the setting section of the pachinko machine shown in FIG.
図129に示すパチンコ機は、パチンコ機の遊技性能を設定するための設定基板970を有する。設定基板970は、払出制御基板951と接続されており、払出制御部952が各スイッチの操作状態を取得し、設定表示器974の表示を制御する。
The pachinko machine shown in FIG. 129 has a setting
図132(A)の正面図に示すように、設定基板970には、パチンコ機1の動作モードを設定変更モードや設定確認モードに変更するための設定キー971、設定値を変更するための設定変更スイッチ972、変更された設定値を確定入力するための設定確定スイッチ973、及び、設定又は選択された設定値を表示する設定表示器974が設けられる。設定基板970は、設定変更の操作を受け付ける設定変更操作部として機能する。
As shown in the front view of FIG. 132(A), the setting
本実施例では、設定基板970上の設定キー971、設定変更スイッチ972及び設定確定スイッチ973の操作信号は、払出制御部952に取り込まれる。また、設定表示器
974は、払出制御部952によって制御される。確定した設定は、払出制御部952から主制御基板1310に送信される。なお、後述するように、主制御基板1310が設定基板970上の部品を制御してもよい。
In this embodiment, operation signals of the setting
設定キー971は、鍵穴(鍵挿入部)に所定の鍵を挿入して、設定位置に鍵を回す操作によって接点の短絡又は開放状態を維持して、設定変更モードや設定確認モードに変更するための契機となる信号を出力するスイッチである。なお、設定キー971を設けずに、他のスイッチで兼用してもよい。この場合、設定変更スイッチ972を所定時間(例えば5秒)以上操作すること(長押し)によって、設定変更モードや設定確認モードを開始し、設定変更モードや設定確認モード中における設定変更スイッチ972の長押しによって、設定変更モードや設定確認モードを終了してもよい。
The setting
また、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作によって設定変更モードを開始・終了してもよい。例えば、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作しながら電源を投入し、さらにRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を所定時間(例えば5秒)以上継続すること(長押し)によって、設定変更モードを開始する。また、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作しながら電源を投入し、RAMクリアスイッチ954の継続した操作が所定時間未満であれば、RAMクリア処理を実行する。さらに、設定変更モード中におけるRAMクリアスイッチ954の長押しによって、設定変更モードを終了してもよい。
Also, the setting change mode may be started/finished by operating the RAM
このようにすると、設定キー971用の鍵を保有していない従業員でも設定変更が可能なことから、ホールでのパチンコ機1の取り扱いが容易になる。また、設定変更スイッチ972の操作時間を検出することから、設定変更スイッチ972の立ち下がりで操作を検出するとよい。
By doing so, even an employee who does not have a key for the setting key 971 can change the setting, so that the
設定変更スイッチ972は、例えば押しボタンスイッチで構成され、設定値(1~6)を順に切り替えて選択するために操作される。つまり、設定変更スイッチ972が1回押されると、設定値が1増加し、設定値=6の時に設定変更スイッチ972が操作されると設定値=1となる。なお、設定変更スイッチ972を設けずに、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作によって設定値が選択可能でもよい。なお、設定値は、6段階でなく、これより少ない段階(例えば2段階)でも、多い段階(例えば8段階)でもよい。
The setting
また、設定変更スイッチ972を設けず、設定キー971が設定変更スイッチ972を兼ねてもよい。この場合、設定キー971が3段階に操作可能で、中立位置(通常位置)では鍵が挿抜可能で、左に回すと設定変更モードを開始するための操作となり、右に回すと設定すべき設定値を選択するための操作となる(右に回すと設定変更スイッチ972として機能する)。設定キー971は、左位置及び中立位置を保持可能なアルタネイティブ動作をし、右位置が保持されない(鍵から手を離すと中立位置に戻る)モーメンタリ動作をする。
Also, the setting
なお、設定値は条件装置の作動割合(つまり、特別図柄の当り確率)を変更するものであり、設定値=1が当り確率が低く、設定値=6が当り確率が高い。また、設定値によって、確変大当りの割り合い、大当り後の時短(ST)の割り合い、時短回数、大当りのラウンド数やカウント数、普図当り確率、一般入賞口や始動口や大入賞口の賞球数など、遊技に関する様々なパラメータを変更して遊技者が獲得できる賞球の数を変化させてもよい。 In addition, the set value changes the operating ratio of the condition device (that is, the hit probability of the special symbol), and the set value = 1 has a low hit probability, and the set value = 6 has a high hit probability. In addition, depending on the setting value, the ratio of the probability variable jackpot, the ratio of the time saving (ST) after the jackpot, the number of times of saving time, the number of rounds and counts of the jackpot, the probability of the normal drawing, the general winning mouth, the starting mouth and the big winning mouth Various game-related parameters, such as the number of prize balls, may be changed to change the number of prize balls that a player can win.
設定確定スイッチ973は、例えばモーメンタリ型のスイッチで構成され、設定変更スイッチ972の操作によって選択された設定値を確定し、パチンコ機1に入力するためのスイッチである。設定確定スイッチ973は、モーメンタリ型のスイッチであれば、押し
ボタンスイッチでも、モーメンタリ型のトグルスイッチでもよい。設定変更スイッチ972と設定確定スイッチ973とは、両スイッチを間違えて操作しないように、操作方法(操作方向)や形状が異なるスイッチで構成するとよい。例えば、設定変更スイッチ972を押しボタンスイッチで構成し、設定確定スイッチ973をモーメンタリ型のトグルスイッチで構成するとよい。
The setting
なお、設定確定スイッチ973を設けずに、設定キー971を通常位置に戻す操作によって選択された設定を確定してもよい。また、パチンコ機1に設けられた他のスイッチやセンサの動作を契機に選択された設定値を確定してもよい。例えば、ハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504の操作や、ハンドルレバー504に触ったことによる接触検知センサ509による接触検出や、ハンドルユニット500のストップボタンの操作や、操作ボタン220Cの操作や、球貸ボタンの操作や、返却ボタンの操作や、始動口2002、2004への遊技球の入賞検出などによって、選択された設定を確定してもよい。設定確定スイッチ973を代用する操作部は、遊技者が操作可能な(遊技に使用する)スイッチでも、遊技者が操作不可能な(パチンコ機の裏面側に設けられた)スイッチでもよい。
Alternatively, the selected setting may be confirmed by returning the setting key 971 to the normal position without providing the
つまり、図示した例では、パチンコ機1に遊技性能を設定するために、設定基板970に三つのスイッチ(設定キーも含む)を設けたが、設定基板970には、一つ又は二つのスイッチを設ければ足りる。
That is, in the illustrated example, three switches (including setting keys) are provided on the setting
さらに、設定キー971、設定変更スイッチ972及び設定確定スイッチ973のいずれも設けず、RAMクリアスイッチ954のみで設定変更操作を可能としてもよい。例えば、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作しながら電源を投入し、さらにRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を所定時間(例えば5秒)以上継続すること(長押し)によって、設定変更モードを開始する。また、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作しながら電源を投入し、RAMクリアスイッチ954の継続した操作が所定時間未満であれば、RAMクリア処理を実行する。さらに、設定変更スイッチ972に代えて、設定変更モード中におけるRAMクリアスイッチ954の所定時間(例えば5秒)未満の操作によって、設定値を選択可能とし、設定確定スイッチ973に代えて、RAMクリアスイッチ954の所定時間以上の操作(長押し)によって、設定値を確定可能とする。さらに、設定確定後のRAMクリアスイッチ954の長押しによって、設定変更モードを終了してもよい。
Furthermore, the setting change operation may be enabled only by the RAM
設定表示器974は、例えば7セグメントLEDで構成され、設定変更スイッチ972の操作によって選択された設定値を表示し、所定の操作(例えば、設定キー971の操作)によって現在の設定値を表示する。なお、設定表示器974を7セグメントLEDではなく、設定可能な値の数のLEDによって構成してもよい。この場合、設定値に対応するLEDが点灯して、設定値を表示する。
The
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、払出制御基板951に払出エラーの種別を表示する7セグメントLEDによるエラー種別表示器が設けられているが、このエラー種別表示器と設定表示器974を兼用し、選択された設定値や現在の設定値をエラー種別表示器に表示してもよい。この場合、エラー種別の表示と設定値の表示とを区別できるように表示態様を変えるとよい。例えば、エラー種別の表示においてはドットを消灯し、設定値の表示においてはドットを点灯してもよい。また、エラー種別の表示は(点滅しない)点灯表示をし、設定値の表示は点滅表示をしてもよい。
In the
図示した例では、設定基板970が払出制御基板951と接続されているが、電源基板ボックス930内の電源基板(図示省略)と接続されてもよい。設定基板970を電源基板に併設して(又は、電源基板ボックス930の内部に)設けることによって、設定変更
時に操作される設定キー971と電源スイッチ932を近隣に配置して、設定変更の操作性を向上できる。
In the illustrated example, the setting
また、後述するように、設定基板970が主制御基板1310と接続されてもよい。
Also, as will be described later, the setting
さらに別な形態として、設定基板970が独立した基板ではなく、払出制御基板951や電源基板や主制御基板1310の一部でも構成されてもよい。すなわち、払出制御基板951、電源基板又は主制御基板1310のいずれかに、設定キー971、設定変更スイッチ972、設定確定スイッチ973及び設定表示器974が搭載されてもよい。
As another form, the setting
図130に示すように、設定基板970は、パチンコ機1を構成する本体枠4の下部(つまり、遊技盤5ではなく枠側)の右側面に取り付けられており、図131に示すように、本体枠4を外枠2に収容すると設定基板970の少なくとも一部が外枠2の右枠部材40とが対向する。本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では、設定基板970と右枠部材40との間隔は狭いので、この状態で設定基板970上のキーやスイッチの操作は困難となっている。このように、右枠部材40は、設定キー971を隠蔽し、設定キー971の鍵穴への鍵の挿入を阻害し、設定基板970(設定変更操作部)の操作を困難にする設定変更困難化手段として機能する。本実施例のパチンコ機1では、本体枠4を外枠2に収容した状態で、設定基板970の少なくとも一部として設定キー971が外枠2の右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向すればよいが、設定基板970の全部が外枠2の右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向してもよい。この場合、設定基板970の幅が右枠部材40の幅を超えないように、キーやスイッチを縦に並べて配置するとよい。このように、設定基板970の全部が外枠2の右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向すると、パチンコ機1の稼動中に(つまり、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で)設定基板970の操作を困難にして、遊技者がパチンコ機1の設定を変える不正行為を抑制できる。
As shown in FIG. 130, the setting
本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で設定基板970と対向する部材(設定変更困難化手段)は、図示した例では、右枠部材40であるが、他の部材でもよい。例えば、外枠2に設けられるカバーが、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では、設定基板970と狭い間隔で対向する位置に配置されてもよい。また、本体枠4の開閉に連動して移動するカバーを設け、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では、該カバーが設定基板970と狭い間隔で対向する位置に配置されてもよい。
In the illustrated example, the member facing the setting board 970 (means for making setting change difficult) while the
設定基板970と対向して設けられる部材によって構成される設定変更困難化手段は、設定基板970を覆うカバーでもよい。この場合、設定変更モードを開始する契機となる設定キー971を2重のカバーで覆うとよい。例えば、設定基板970を覆う内カバーと、設定基板970を含めた各種制御基板を覆う外カバーとを設ける。また、設定キー971の鍵穴を覆う内カバーと、設定基板970を覆う外カバーとを設けてもよい。より具体的には、設定基板970は設定基板ケースに収容されており、設定基板ケースには設定キー971や各スイッチ972、973(少なくとも設定キー971)の不用意な操作を妨げる第1のカバー体(例えば、操作時に開けることができる扉状の蓋体)を設ける。さらに、設定基板970や主制御基板1310も含めた各種制御基板を覆う第2のカバー体を、外枠2に設ける。なお、第2のカバー体は、本体枠4や遊技盤5に設けて各種制御基板を覆ってもよい。このようにすると、不用意な操作による設定変更モードの開始を防止でき、不正な遊技者がパチンコ機1の設定を変える不正行為を抑制できる。
The setting change making member configured to face the setting
本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で設定基板970が右枠部材40などの部材と対向する距離は、設定キー971の鍵穴に挿入される鍵の頭部(操作時に把持するキーヘッド)の長さより短ければよい。
The distance at which the setting
設定変更時に操作される設定キー971と電源スイッチ932とが近隣に配置されるように、設定基板970を電源スイッチ932の近傍に配置するとよい。このようにすると、設定変更モードを起動する際の操作性を向上できる。
The setting
また、図131に示すように、電源基板ボックス930には、パチンコ機1に通電するための電源スイッチ932が設けられており、払出制御基板ユニット950には、パチンコ機1の主制御RAM1312を初期化するRAMクリアスイッチ954が設けられている。このように、パチンコ機1には、遊技中には操作されず、裏面側から操作可能な複数のスイッチが設けられているが、前述した電源スイッチ932とRAMクリアスイッチ954とは、裏面側から視認及び操作可能な位置に設けられている。一方、設定キー971は(望ましくは、設定変更スイッチ972と設定確定スイッチ973も)、パチンコ機1の稼動中には裏面側から視認及び操作困難な位置に設けられている。これは、電源スイッチ932やRAMクリアスイッチ954は、製造工程で頻繁に操作されることから、パチンコ機1の稼動中に裏面側から操作可能な位置に設けられる。一方、設定キー971は、パチンコ機1の稼動中には操作困難に隠しておくことによって、遊技中に設定基板970を操作して、パチンコ機1の設定を変える不正行為を抑制している。このように本実施例のパチンコ機1では、利便性と不正行為の抑制を両立させるように、パチンコ機1の裏面側のスイッチを配置している。
Further, as shown in FIG. 131, the power
同様に、パチンコ機1の現在の設定値は、遊技客の台の選択に重要な情報であることから、遊技客に知られないことが望ましい。このため、図131に示すように、設定キー971と同様に、設定表示器974も右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向させて表示が見えないようにするとよい。なお、通常は、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態や設定キー971が操作されていない状態では、設定表示器974は消灯して、遊技者に設定値を知られないようにすることが望ましい。このように、右枠部材40は、設定表示器974の表示内容を隠蔽し、設定表示器974(設定状態表示部)の表示内容の視認を困難にする視認困難化手段として機能する。
Similarly, the current set value of the
図132(B)は、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で、設定基板970を上から見た図である。この状態では、設定基板970は右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向しているので、設定キー971の鍵穴に挿入された鍵975の頭部と右枠部材40とが干渉し、設定キー971の鍵穴に鍵975を挿入できない。
FIG. 132B is a top view of the setting
一方、本体枠4が外枠2から開放された状態では、設定キー971の鍵穴の前面に右枠部材40が位置せず、設定キー971の鍵穴に鍵975を挿入可能となる。
On the other hand, when the
また、設定表示器974の表示面は、パチンコ機1の側面を向いており、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では右枠部材40と対向しているので、遊技者による正面からパチンコ機の現在の設定値の確認が困難になっている。
The display surface of the
図133は、設定基板970の変形例を示す図である。
FIG. 133 is a diagram showing a modification of the setting
本変形例でも、前述した例と同様に、設定基板970には、設定キー971、設定変更スイッチ972、設定確定スイッチ973及び設定表示器974が設けられる。しかし、本変形例では、設定キー971が設定基板970に横向きに配置されており、設定基板の側方から鍵975を挿入するようになっている。
In this modified example, a setting
このため、本変形例の設定基板970は、本体枠4の側面側ではなく裏面側に、鍵穴が側面を向くように設置する。そして、図133(B)に示すように、設定基板970を上から見ると、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で、設定基板970の側面(すなわち、
鍵穴)は右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向しているので、設定キー971の鍵穴に挿入された鍵975の頭部と右枠部材40とが干渉し、設定キー971の鍵穴に鍵975を挿入できない。
For this reason, the setting
(keyhole) faces the
図133に示す変形例では、パチンコ機1の基板を他の基板と同じ向きに配置でき、基板配置の困難性を低くしても、パチンコ機1の稼動中に設定基板970を操作して、パチンコ機1の設定を変える不正行為を抑制できる。
In the modification shown in FIG. 133, the board of the
次に、設定部を有するパチンコ機の変形例を説明する。本変形例では、設定基板970が本体枠4ではなく遊技盤5に設けられており、主制御基板1310に接続されている。
Next, a modified example of a pachinko machine having a setting section will be described. In this modified example, the setting
図134は、本変形例のパチンコ機の制御構成を概略的に示すブロック図であり、図135は、設定部を有する遊技盤を後ろから見た斜視図であり、図136は、図135に示す遊技盤を実装したパチンコ機を後ろから見た斜視図である。 FIG. 134 is a block diagram schematically showing the control configuration of the pachinko machine of this modified example, FIG. 1 is a rear perspective view of a pachinko machine mounted with a game board shown; FIG.
設定基板970は、設定キー971、設定変更スイッチ972、設定確定スイッチ973及び設定表示器974が設けられる。設定基板970は、図132(A)に示すものでも図133(A)に示すものでもよい。
A setting
図134に示すパチンコ機1では、パチンコ機の遊技性能を設定するための設定基板970は、主制御基板1310と接続されており、主制御MPU1311が各スイッチの操作状態を取得し、主制御MPU1311が設定表示器974の表示を制御する。
In the
設定基板970や、設定基板上の各部品の機能及び構成は、前述した実施例と同じであり、共通する説明は省略する。
The setting
主制御基板1310には7セグメントLEDで構成されるベース表示器1317が設けられている。このため、ベース表示器1317と設定表示器974を兼用し、選択された設定値や現在の設定値をベース表示器1317に表示してもよい。ベース表示器1317には、通常は、暫定区間(現在計測中の区間)のベース値と確定区間(直線の区間)のベース値とが所定時間間隔で切り替えて表示される。一方、設定変更モード中では、選択された(次に設定される)設定値が表示され、設定確認中(図152参照)では、現在の設定値が表示される。
The
この場合、ベース値の表示と設定値の表示とを区別できるように表示態様を変えるとよい。例えば、ベース値の表示は4桁を使用するが、設定値の表示は所定の1桁(例えば、最右の桁)のみを使用し、「-」を表示してもよい。設定値の表示で使用されない桁には、「-」ではなく、ベース値の表示で使用されないものであれば他の数字、文字、記号を表示してもよい。また、設定値を表示する場合、ベース値の表示で使用されない文字を表示してもよい。例えば、設定値をアルファベットのA、b、C、d、E、Fの6段階で表示する。 In this case, it is preferable to change the display mode so that the display of the base value and the display of the set value can be distinguished from each other. For example, the base value may be displayed using four digits, but the setting value may be displayed using only one predetermined digit (for example, the rightmost digit) and displaying "-". Digits that are not used to display the set value may display other numbers, letters, or symbols instead of "-" as long as they are not used to display the base value. Also, when displaying the setting value, characters that are not used for displaying the base value may be displayed. For example, the setting value is displayed in six stages of alphabetical characters A, b, C, d, E, and F.
さらに、設定変更モードにおいて設定値の選択中は点滅表示し、確定した設定値は点灯表示するとよい。また、現在の設定値は点灯表示するとよい。また、ベース表示において上2桁は表示データの種別を表し、数字が表示されることはない。このため、最上位桁を使用して設定値を表示してもよい。なお、ベース表示器1317と設定表示器974を兼用する場合、設定変更モード及び設定確認中は設定値が優先して表示されるので、ベース値の計算は行われているものの、ベース値が表示されない。その後、設定変更モードや設定値の確認が終了すると、ベース表示器1317は、ベース値の表示を再開する。
Furthermore, in the setting change mode, it is preferable that the setting value is displayed blinking while the setting value is being selected, and the determined setting value is lit. In addition, the current set value should be indicated by lighting. Also, in the base display, the upper two digits represent the type of display data, and numbers are not displayed. Therefore, the most significant digit may be used to display the setting value. When the
また、ベース表示器1317と設定表示器974を兼用する場合、設定表示器974へ表示内容を出力する処理は遊技制御領域内の遊技制御用コード13131によって実行され、ベース表示器1317へ表示内容を出力する処理は遊技制御領域外のベース算出・表示用コード13135で実行される。しかし、ベース算出・表示用コード13135の一部(例えば、表示データをドライバ回路に出力する処理)を遊技制御領域内に設けてもよい。処理の共通化によってプログラムの容量を小さくでき、メモリを節約できる。
Also, when the
一方、設定表示器974へ表示内容を出力する処理は遊技制御領域内の遊技制御用コード13131によって実行され、ベース表示器1317へ表示内容を出力する処理は遊技制御領域外のベース算出・表示用コード13135で実行すると、遊技制御領域内外の処理を完全に分離でき、セキュリティを向上できる。
On the other hand, the process of outputting the display contents to the
また、設定変更や設定確認の処理は、遊技制御領域外で実行してもよい。 In addition, the process of setting change and setting confirmation may be executed outside the game control area.
つまり、設定表示器974が、ベース表示器1317と別に設けられても、ベース表示器1317と兼用されても、いずれの場合も、本明細書に記載された発明の範疇に含まれる。このように、設定変更モードや設定値の確認中において、主制御基板ボックス1320に設けられる複数の表示を紛らわしくないように表示することによって、設定変更時の誤操作や設定値の誤認を防止できる。
That is, whether the
また、ベース表示器1317と設定表示器974を兼用しない場合でも、設定表示器974が設定値を表示中は、ベース表示器1317の表示を消したり、全点灯してもよい。この場合でも、設定変更モードや設定値の確認が終了すると、ベース表示器1317はベース値の表示を再開する。設定変更モードや設定値の確認中において、主制御基板ボックス1320に複数の表示をしないことによって、設定変更時の誤操作や設定値の誤認を防止できる。
Also, even if the
図示した例では、設定基板970が主制御基板1310と接続されているが、設定基板970が独立した基板ではなく、主制御基板1310の一部に形成されてもよい。すなわち、主制御基板1310に、設定キー971、設定変更スイッチ972、設定確定スイッチ973及び設定表示器974が搭載されてもよい。
In the illustrated example, the setting
設定基板970は、主制御基板1310と共に主制御基板ボックス1320に封入されてもよい。設定基板970が主制御基板ボックス1320に封入される場合、主制御基板ボックス1320には、設定基板970上の設定キー971、設定変更スイッチ972及び設定確定スイッチ973を操作するための穴や切り欠きが設けられる。
The
設定基板970を主制御基板ボックス1320に封入する場合、設定基板970上の設定キー971の鍵穴の向きによって主制御基板ボックス1320の構造、つまり開閉方向が異なる。具体的には、鍵975を基板の正面から基板に垂直に挿入する場合、主制御基板ボックス1320は、設定基板970の表面と裏面とで設定基板970に垂直に分離する又は表面側箱体(又はカバー)と裏面側箱体とを1辺を蝶番として開閉可能な構造にするとよい。一方、鍵975を側方から基板が延伸する方向に挿入する場合、主制御基板ボックス1320は、設定基板970の表面側箱体(又はカバー)と裏面側箱体とで設定基板970の延伸方向(鍵975の挿入方向)にスライドして分離する構造にするとよい。
When the setting
本変形例では、設定基板970上の設定キー971、設定変更スイッチ972及び設定確定スイッチ973の操作信号は、主制御MPU1311に取り込まれる。また、設定表示器974は、主制御MPU1311によって制御される。
In this modification, operation signals of setting
図135に示すように、設定基板970は、パチンコ機1を構成する遊技盤5の右側面(図135では左側)に取り付けられており、図136に示すように、遊技盤5が取り付けられた本体枠4を外枠2に収容すると設定基板970の少なくとも一部が外枠2の右枠部材40とが対向する。本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では、設定基板970と右枠部材40との間隔は狭いので、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では、設定基板970上のキーやスイッチの操作は困難となっている。本実施例のパチンコ機1では、本体枠4を外枠2に収容した状態で、設定基板970の少なくとも一部として設定キー971が外枠2の右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向すればよいが、設定基板970の全部が外枠2の右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向してもよい。この場合、設定基板970の幅が右枠部材40の幅を超えないように、キーやスイッチを縦に並べて配置するとよい。このように、設定基板970の全部が外枠2の右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向すると、パチンコ機1の稼動中に(つまり、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で)設定基板970を操作して、パチンコ機1の設定を変える不正行為を抑制できる。
As shown in FIG. 135, the setting
本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で設定基板970と対向する部材(設定変更困難化手段)は、図示した例では、右枠部材40であるが、他の部材でもよい。例えば、外枠2に設けられるカバーが、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では、設定基板970と狭い間隔で対向する位置に配置されてもよい。また、本体枠4の開閉に連動して移動するカバーを設け、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では、該カバーが設定基板970と狭い間隔で対向する位置に配置されてもよい。
In the illustrated example, the member facing the setting board 970 (means for making setting change difficult) while the
本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で設定基板970が右枠部材40などの部材と対向する距離は、設定キー971の鍵穴に挿入される鍵の頭部(操作時に把持するキーヘッド)の長さより短ければよい。
The distance at which the setting
また、図136に示すように、電源基板ボックス930には、パチンコ機1に通電するための電源スイッチ932が設けられており、払出制御基板ユニット950には、パチンコ機1の主制御RAM1312を初期化するRAMクリアスイッチ954が設けられている。このように、パチンコ機1には、遊技中には操作されず、裏面側から操作可能な複数のスイッチが設けられているが、前述した電源スイッチ932とRAMクリアスイッチ954とは、裏面側から視認及び操作可能な位置に設けられている。一方、設定キー971は(望ましくは、設定変更スイッチ972と設定確定スイッチ973も)、パチンコ機1の稼動中には裏面側から視認及び操作困難な位置に設けられている。これは、電源スイッチ932やRAMクリアスイッチ954は、製造工程で頻繁に操作されることから、パチンコ機1の稼動中に裏面側から操作可能な位置に設けられる。一方、設定キー971は、パチンコ機1の稼動中には操作困難に隠しておくことによって、遊技中に設定基板970を操作して、パチンコ機1の設定を変える不正行為を抑制している。このように本実施例のパチンコ機1では、利便性と不正行為の抑制を両立させるように、パチンコ機1の裏面側のスイッチを配置している。
136, the power
同様に、パチンコ機1の現在の設定値は、遊技客の台の選択に重要な情報であることから、遊技客に知られないことが望ましい。このため、図136に示すように、設定キー971と同様に、設定表示器974も右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向させて表示が見えないようにするとよい。なお、通常は、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態や設定キー971が操作されていない状態では、設定表示器974は消灯して、遊技者に設定値を知られないようにすることが望ましい。このように、右枠部材40は、設定表示器974の表示内容を隠蔽し、設定表示器974(設定状態表示部)の表示内容の視認を困難にする視認困難化手段として機能する。
Similarly, the current set value of the
図134に示すパチンコ機1において、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態で、設定基
板970を上から見た図は、図132(B)や図133(B)に示すとおりである。この状態では、設定基板970や設定キー971の鍵穴は右枠部材40と狭い間隔で対向しているので、設定キー971の鍵穴に挿入された鍵975の頭部と右枠部材40とが干渉し、設定キー971の鍵穴に鍵975を挿入できない。
In the
また、設定表示器974の表示面は、パチンコ機1の側面を向いており、本体枠4が外枠2に収容された状態では右枠部材40と対向しているので、遊技者による正面からパチンコ機の現在の設定値を確認できなくなっている。
The display surface of the
次に、設定変更に関する処理を説明する。 Next, processing related to setting change will be described.
図137は、初期化処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。図137に示す初期化処理は、図21で前述した初期化処理と比較し、設定キーが操作されている場合にRAMクリア処理を行う点(ステップS17、ステップS30)及びCPU初期設定処理(ステップS28)内で設定変更処理を行う点が相違する。なお、図21で前述した初期化処理と同じステップには同じ符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。 FIG. 137 is a flowchart illustrating an example of initialization processing. The initialization process shown in FIG. 137 is different from the initialization process described above in FIG. The difference is that the setting change processing is performed in S28). The same steps as in the initialization process described above in FIG. 21 are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
パチンコ機1に電源が投入されると、主制御基板1310の主制御MPU1311が主制御プログラムを実行することによって初期化処理を行う。主制御MPU1311は、まず、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたRAM1312のプロテクトを書き込み許可に設定し、RAM1312への書き込みができる状態にする(ステップS10)。続いて、主制御MPU1311は、内蔵されたウォッチドッグタイマを起動し(ステップS12)、所定のウェイト時間(サブ基板(周辺制御基板1510など)が起動するために必要な時間)が経過したかを判定する(ステップS16)。所定のウェイト時間が経過していれば、設定キー971が操作されており、その出力がオンであるかを判定する(ステップS17)。設定キー971が操作されている場合、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータのうち設定値のデータと遊技状態(例えば、確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータを消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。
When the
一方、設定キー971が操作されていない場合、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されているかを判定する(ステップS18)。RAMクリアスイッチが操作されている場合、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータのうちベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)以外の領域のデータを消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されていない場合、内蔵RAM1312にバックアップされているデータを消去せず、停電フラグが設定されているかを判定する(ステップS20)。
On the other hand, if the setting
その結果、停電フラグが設定されていなければ、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータ(ベース算出用領域13128以外)を消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、停電フラグが設定されていれば、停電フラグをクリアし、前回の電源遮断時に計算されたチェックサムを用いて内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータから算出したチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとを比較(検証)する(ステップS22)。
As a result, if the power failure flag is not set, the data in the work area of the built-in
その結果、バックアップデータから算出されたチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとが一致しなければ、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータ(ベース算出用領域13128以外)を消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、バック
アップデータから算出されたチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとが一致すれば、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しいので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータを消去せず、ステップS24に進む。
As a result, if the checksum calculated from the backup data does not match the checksum stored in step S48, the data in the work area of the
続いて、チェックコードを用いてベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)が正常かを判定する(ステップS24)。異常であると判定された場合、ベース算出用ワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、ベース算出用ワークエリアに格納されているデータを消去する(ステップS26)。 Subsequently, it is determined whether the base calculation work area (base calculation area 13128) is normal using the check code (step S24). If it is determined to be abnormal, the data in the base calculation work area may be incorrect, so the data stored in the base calculation work area is deleted (step S26).
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、RAM1312の少なくとも一部の領域が初期化されるケースとして、設定キー971の操作(ステップS17)と、RAMクリアスイッチの操作(ステップS18)と、停電フラグがセットされていない停電フラグ異常(ステップS20)と、RAMのチェックサムが一致しないRAM異常(ステップS22)と、ベース算出用ワークの異常(ステップS24)とがある。これらのうち、図示したように、電源投入時に設定キー971の操作が検出された場合は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)のうち、設定値と遊技状態(例えば、確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータをクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)はクリアしない。電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチの操作が検出された場合、及び停電フラグ異常、RAM異常の場合は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)をクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(ベース算出用ワーク領域とベース算出用スタック領域を含む)はクリアしない。また、ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)をクリアし、遊技制御用領域13126はクリアしない。
In the
なお、図示したものと異なり、停電フラグ異常、RAM異常、ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合は、RAM1312に格納されたデータの正当性が保証されないことから、遊技制御用領域13126及びベース算出用領域13128を含む全RAM領域をクリアしてもよい。ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合に全RAM領域をクリアすると、遊技状態を示すデータが消失して正常な処理が実行不可能になるメモリ構成である場合、ベース算出用ワーク領域とベース算出用スタック領域のみを初期化するとよい。また、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチの操作が検出された場合は、前述と同様に、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)をクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128はクリアしなくてよい。
It should be noted that, unlike the illustrated one, in the case of power failure flag abnormality, RAM abnormality, base calculation work abnormality, since the validity of the data stored in the
このように、本実施形態のパチンコ機1では、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータを、データの種別毎に(遊技制御用領域13126(設定値、遊技状態のデータ)、ベース算出用領域13128)異なる条件で消去する。すなわち、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって、設定値以外のバックアップされた遊技制御用領域13126は消去され、設定値とベース算出用領域13128は消去されない。RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって設定値が消去されると、RAMクリア操作毎に設定値を再設定する必要があり、ホールのパチンコ機1のメンテナンスが煩雑になるからである。このため、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって、設定値が消去されないようにしている。
Thus, in the
ステップS28より後の処理は、必要に応じて、図22と図102とのいずれかを採用すればよい。図22と図102との違いは、電源遮断時にベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)のデータからチェックコード算出して格納する処理(ステップS50、S52)の有無である。 Either FIG. 22 or FIG. 102 may be employed for the processing after step S28 as required. The difference between FIG. 22 and FIG. 102 is the presence or absence of processing (steps S50 and S52) for calculating and storing a check code from the data in the base calculation work area (base calculation area 13128) when the power is turned off.
図138、図139は、設定変更処理及び設定表示処理の一例を示すフローチャートで
あり、図138は設定基板970が払出制御基板951に接続されている(又は払出制御基板951と一体に構成されている)場合の処理を示し、図139は設定基板970が主制御基板1310に接続されている(又は主制御基板1310と一体に構成されている)場合の処理を示す。
138 and 139 are flowcharts showing an example of setting change processing and setting display processing, and FIG. 139 shows the processing when the setting
まず、図138(A)に示す主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951とが連携した設定変更処理を説明する。
First, the setting change processing in which the
パチンコ機1に電源が投入されると、(1)払出制御部952が、設定キー971がオンに操作されているか、及び、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかを判定する。本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかは、本体枠開放スイッチからの検出信号によって判定できる。なお、設定キー971の配置位置から考えると、設定キー971を操作するためには、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているので、この本体枠4の開放の判定は省略してもよい。
When the
設定キー971がオンに操作されており、かつ、本体枠4が外枠2から開放していれば、払出制御部952は設定変更モードを開始する。このように、払出制御部952は設定変更許容状態発生手段として機能する。前述以外の設定変更モードの開始条件として、ハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504の操作や、ハンドルレバー504に触ったことによる接触検知センサ509による検出や、CRユニットにプリペイドカードが挿入されていたり(プリペイドカードの残高がある)、現金サンドに投入された残高がある場合に設定変更モードを開始しなくてもよい。また、パチンコ機1が何らかの不正行為の可能性(例えば磁気エラー)を検出している場合にも、設定変更モードを開始しない方がよい。これらの条件の判定は、払出制御部952ではなく主制御MPU1311が、設定変更開始コマンドを受信した後に行ってもよい。このような場合、ホールによるパチンコ機1のメンテナンスではないと推定され、不正な遊技者による設定変更操作が行われようとしている可能性があるため、設定変更モードへ移行しない方がよいからである。
If the setting
(2)設定変更モードが開始すると、払出制御部952は、主制御基板1310に設定変更開始コマンドを送信する。
(2) When the setting change mode starts, the
(3)主制御MPU1311は、払出制御部952から設定変更開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更前のRAMクリア処理を実行する。この設定変更前のRAMクリア処理は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)のうち、遊技状態(例えば、確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータをクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)はクリアしない。なお、設定値は、後に手順(6)で初期値に設定されるので、本ステップでクリアしなくてもよい。
(3) When the
(4)その後、主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御部1511に設定変更開始コマンドを送信する。
(4) After that, the
(5)周辺制御部1511は、主制御MPU1311から設定変更開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを報知する。設定変更モード中の報知は、役物の初期動作を行ったり、メイン液晶表示装置1600に所定の表示を行う。なお、周辺制御部1511は、役物の初期動作を行わなくてもよい。例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600に設定変更の手順や状態を表示する場合に、設定変更中に役物の初期動作を行うと、メイン液晶表示装置1600の表示を部分的に隠すことになり、設定変更作業の邪魔をするからである。
(5) When the
また、周辺制御部1511による設定変更モードの報知に合わせて、主制御MPU1311も設定変更モードを報知してもよい。例えば、機能表示ユニット1400の表示を、通常の遊技中には表れない特殊な態様の表示(例えば、特別図柄表示用のLEDを全部消灯又は点灯)をして遊技の進行を停止してもよい。また、主制御MPU1311は、入賞球やアウト球の検出を停止して、遊技の進行を停止することによって、設定変更モードを報知してもよい。その結果、設定変更モードにおいては、ベース値が計算されない。また、主制御MPU1311は、発射許可信号の出力を停止して、発射制御装置によって制御される遊技球の発射を停止して、発射不能化手段として機能することによって、設定変更モードを報知してもよい。設定変更モード中に遊技球の発射を停止する場合、発射停止期間中の遊技球の発射をエラーとして、当該期間中にハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504が操作されるとエラーを検知してもよい。
In addition, the
(6)次に、主制御MPU1311は、設定値を0にリセットする。前述したように、設定値は1~6の間で選択可能で、設定値=0は設定がされていない状態であり、設定値=0では設定変更モードを終了できず、遊技(遊技球の発射、変動表示ゲームなど)が開始しない。
(6) Next, the
(7)その後、遊技者が設定変更スイッチ972を操作する毎に、払出制御部952は選択された設定値を設定表示器974に表示する。
(7) Thereafter, each time the player operates the setting
(8)払出制御部952は、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかを判定する。なお、前述した手順(1)でも本体枠4の開放を判定しているが、設定確定スイッチ973の操作を判定する前に少なくとも1回判定すればよい。このように、払出制御部952は、設定変更の確定前に設定変更の条件が整っているかを判定する設定変更許容状態発生手段として機能する。
(8) The
(9)さらに、払出制御部952は、設定確定スイッチ973が操作されているかを判定する。
(9) Furthermore, the
(10)払出制御部952は、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しており、かつ、設定確定スイッチ973が操作されていれば、選択された設定値を確定し、設定値が確定したことを設定表示器974に表示する。設定値確定表示は、設定値として選択できない値(例えば8)を表示したり、確定した設定値を所定時間点滅表示してもよい。
(10) If the
(11)その後、払出制御部952は、設定キー971のオフに操作されているかを判定する。
(11) After that, the
(12)設定キー971がオフに操作されていれば、設定変更モードを終了するので、払出制御部952は、主制御基板1310に設定変更終了コマンドを送信する。この設定変更終了コマンドによって、確定した設定値が主制御MPU1311に通知される。
(12) If the setting
(13)主制御MPU1311は、払出制御部952から設定変更終了コマンドを受信すると、周辺制御部1511に設定変更終了コマンドを送信する。
(13) When the
(14)周辺制御部1511は、主制御MPU1311から設定変更終了コマンドを受信すると、設定変更中の報知を終了する。これと共に、主制御MPU1311で設定変更中の報知を行っていれば、これも終了する。
(14) When the
なお、設定変更モードが終了すると直ちに報知(遊技停止、発射停止も含む)を解除しても、所定時間経過後に解除してもよい。手順(5)で行う報知を、単なる外部(遊技者
、ホール従業員)への報知と考えれば、設定変更モード終了後、直ちに報知を解除するとよい。しかし、手順(5)で行う報知を不正行為の発見の観点で捕らえると、設定変更モードが終了して所定時間経過後に報知を解除するとよい。これは、設定変更が行われた場合、所定時間だけ所定の表示が行われたり、遊技が停止するので、不正な遊技者が営業時間中に設定を変更したことの発見が容易になるためである。
The notification (including game stop and firing stop) may be canceled immediately after the setting change mode ends, or may be canceled after a predetermined period of time has elapsed. If the notification performed in step (5) is considered merely to be a notification to the outside (players, hall employees), the notification should be canceled immediately after the setting change mode ends. However, if the notification performed in step (5) is taken from the viewpoint of discovery of fraudulent activity, it is preferable to cancel the notification after a predetermined time has elapsed after the setting change mode is terminated. This is because when the setting is changed, a predetermined display is performed for a predetermined period of time or the game is stopped, so that it is easy to discover that an unauthorized player has changed the setting during business hours. be.
設定変更モード終了後の所定期間に遊技球の発射を停止する場合、発射停止期間中の遊技球の発射をエラーとして、当該期間中にハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504が操作されるとエラーを検知してもよい。
When the shooting of game balls is stopped during a predetermined period after the end of the setting change mode, shooting of game balls during the shooting suspension period is treated as an error, and an error is detected when the
(15)その後、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更後のRAMクリア処理を実行する。この設定変更後のRAMクリア処理は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)のうち、設定値と遊技状態(例えば、確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータをクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)はクリアしない。つまり、設定変更後のRAMクリア処理では、設定変更前のRAMクリア処理と異なり、設定値が初期化されない。
(15) After that, the
そして、設定変更モードを終了する。 Then, the setting change mode is terminated.
このように、設定基板970が払出制御基板951に接続されており、払出制御基板951の子基板として機能している(又は、設定基板970が払出制御基板951と一体に構成されている)場合、主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951とが連携して設定変更処理を実行する。
Thus, when the setting
なお、前述した処理では、設定キー971が操作されているかを払出制御部952が判定しているが、主制御MPU1311が判定してもよい。この場合、払出制御部952から主制御基板1310への設定キー971の操作に関する信号は、シリアル通信で送信したり、所定のパルス信号(所定周波数のパルスを所定回数)を送信したり、電源電圧でもグランド電圧でもない中間電位の信号を出力してもよい。これは、設定キー971の端子を短絡して設定変更モードを起動する不正行為を防止するために、端子の短絡では生じ得ない信号によって設定キー971の操作に関する信号を払出制御部952から主制御基板1310に送信することが好ましいからである。
In the processing described above, the
次に、図138(B)に示す主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951とが連携した設定表示処理を説明する。
Next, the setting display processing in which the
パチンコ機1の稼働中(通電中)に設定キー971をオンに操作すると、払出制御部952は、当該設定キー971の操作を検出し、設定表示モードを開始する。
When the setting
(1)設定表示モードでは、払出制御部952は、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかを判定する。なお、設定キー971の配置位置から考えると、設定キー971を操作するためには、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているので、この本体枠4の開放の判定は省略してもよい。
(1) In the setting display mode, the
(2)払出制御部952は、本体枠4が外枠2から開放していると判定されると、主制御基板1310に設定値要求コマンドを送信する。
(2) When the
(3)主制御MPU1311は、払出制御部952から設定値要求コマンドを受信すると、主制御RAM1312に記憶された設定値を読み出し、設定値通知コマンドを払出制
御部952に送信する。
(3) When the
(4)払出制御部952は、主制御MPU1311から設定値通知コマンドで通知された設定値を設定表示器974に表示する。
(4) The
なお、上記では、主制御基板1310(主制御RAM1312)に格納された設定値を設定表示器974に表示したが、払出制御部952が設定値を格納しておき、払出制御部952に格納された設定値を設定表示器974に表示してもよい。
In the above description, the setting values stored in the main control board 1310 (main control RAM 1312) are displayed on the
次に、図139(A)に示す主制御基板1310による設定変更処理を説明する。
Next, setting change processing by the
パチンコ機1に電源が投入されると、(1)主制御MPU1311が、設定キー971がオンに操作されているか、及び、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかを判定する。このように、主制御MPU1311は設定変更許容状態発生手段として機能する。本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかは、本体枠開放スイッチからの検出信号によって判定できる。本体枠開放スイッチの検出信号は、払出制御基板951を経由して主制御基板1310に送信される。払出制御基板951は、受信した本体枠開放検出スイッチの検出信号に基づいて、主制御基板1310に本体枠開放検出コマンドを送信してもよい。また、払出制御基板951は、受信した本体枠開放検出スイッチの検出信号をそのまま主制御基板1310に出力してもよい。なお、設定キー971の配置位置から考えると、設定キー971を操作するためには、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているので、この本体枠4の開放の判定は省略してもよい。
When the
設定キー971がオンに操作されており、かつ、本体枠4が外枠2から開放していれば、主制御MPU1311は設定変更モードを開始する。前述以外の設定変更モードの開始条件として、ハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504の操作や、ハンドルレバー504に触ったことによる接触検知センサ509による検出や、CRユニットにプリペイドカードが挿入されていたり(プリペイドカードの残高がある)、現金サンドに投入された残高がある場合に設定変更モードを開始しなくてもよい。また、パチンコ機1が何らかの不正行為の可能性(例えば磁気エラー)を検出している場合にも、設定変更モードを開始しない方がよい。このような場合、ホールによるパチンコ機1のメンテナンスではないと推定され、不正な遊技者による設定変更操作が行われようとしている可能性があるため、設定変更モードへ移行しない方がよいからである。
If the setting
(3)設定変更モードが開始すると、主制御MPU1311は、払出制御部952から設定変更開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更前のRAMクリア処理を実行する。この設定変更前のRAMクリア処理は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)のうち、遊技状態(例えば、確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータをクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)はクリアしない。なお、設定値は、後に手順(6)で初期値に設定されるので、本ステップでクリアしなくてもよい。
(3) When the setting change mode starts, the
(4)その後、主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御部1511に設定変更開始コマンドを送信する。
(4) After that, the
(5)周辺制御部1511は、主制御MPU1311から設定変更開始コマンドを受信すると、設定変更モード中であることを報知する。設定変更モード中の報知は、役物の初期動作を行ったり、メイン液晶表示装置1600に所定の表示を行う。なお、周辺制御部1511は、役物の初期動作を行わなくてもよい。例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600に設定変更の手順や状態を表示する場合に、設定変更中に役物の初期動作を行うと、メイ
ン液晶表示装置1600の表示を部分的に隠すことになり、設定変更作業の邪魔をするからである。
(5) When the
また、周辺制御部1511による設定変更モードの報知に合わせて、主制御MPU1311も設定変更モードを報知してもよい。例えば、機能表示ユニット1400の表示を、通常の遊技中には表れない特種な態様の表示(例えば、特別図柄表示用のLEDを全部消灯又は点灯)をして遊技の進行を停止してもよい。また、主制御MPU1311は、入賞球やアウト球の検出を停止して、遊技の進行を停止することによって、設定変更モードを報知してもよい。その結果、設定変更モードにおいては、ベース値が計算されない。また、主制御MPU1311は、発射許可信号の出力を停止して、発射制御装置によって制御される遊技球の発射を停止して、発射不能化手段として機能することによって、設定変更モードを報知してもよい。設定変更モード中に遊技球の発射を停止する場合、発射停止期間中の遊技球の発射をエラーとして、当該期間中にハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504が操作されるとエラーを検知してもよい。
In addition, the
(6)次に、主制御MPU1311は、設定値を0にリセットする。前述したように、設定値は1~6の間で選択可能で、設定値=0は設定がされていない状態であり、設定値=0では設定変更モードを終了できず、遊技(遊技球の発射、変動表示ゲームなど)が開始しない。
(6) Next, the
(7)その後、遊技者が設定変更スイッチ972を操作する毎に、主制御MPU1311は選択された設定値を設定表示器974に表示する。
(7) After that, the
(8)主制御MPU1311は、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかを判定する。なお、前述した手順(1)でも本体枠4の開放を判定しているが、設定確定スイッチ973の操作を判定する前に少なくとも1回判定すればよい。このように、払出制御部952は、設定変更の確定前に設定変更の条件が整っているか(特に、払出制御基板951から本体枠開放スイッチの検出信号が入力されているか)を判定する設定変更許容状態発生手段として機能する。
(8) The
(9)さらに、主制御MPU1311は、設定確定スイッチ973が操作されているかを判定する。
(9) Furthermore, the
(10)主制御MPU1311は、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しており、かつ、設定確定スイッチ973が操作されていれば、選択された設定値を確定し、設定値が確定したことを設定表示器974に表示する。設定値確定表示は、設定値として選択できない値(例えば8)を表示したり、確定した設定値を所定時間点滅表示してもよい。
(10) If the
(11)その後、主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971のオフに操作されているかを判定する。
(11) After that, the
(13)設定キー971がオフに操作されていれば、設定変更モードを終了するので、主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御部1511に設定変更終了コマンドを送信する。
(13) If the setting
(14)周辺制御部1511は、主制御MPU1311から設定変更終了コマンドを受信すると、設定変更中の報知を終了する。これと共に、主制御MPU1311で設定変更中の報知を行っていれば、これも終了する。
(14) When the
なお、設定変更モードが終了すると直ちに報知(遊技停止、発射停止も含む)を解除しても、所定時間経過後に解除してもよい。手順(5)で行う報知を、単なる外部(遊技者
、ホール従業員)への報知と考えれば、設定変更モード終了後、直ちに報知を解除するとよい。しかし、手順(5)で行う報知を不正行為の発見の観点で捕らえると、設定変更モードが終了して所定時間経過後に報知を解除するとよい。これは、設定変更が行われた場合、所定時間だけ所定の表示が行われたり、遊技が停止するので、不正な遊技者が営業時間中に設定を変更したことの発見が容易になるためである。
The notification (including game stop and firing stop) may be canceled immediately after the setting change mode ends, or may be canceled after a predetermined period of time has elapsed. If the notification performed in step (5) is considered merely to be a notification to the outside (players, hall employees), the notification should be canceled immediately after the setting change mode ends. However, if the notification performed in step (5) is taken from the viewpoint of discovery of fraudulent activity, it is preferable to cancel the notification after a predetermined time has elapsed after the setting change mode is terminated. This is because when the setting is changed, a predetermined display is performed for a predetermined period of time or the game is stopped, so that it is easy to discover that an unauthorized player has changed the setting during business hours. be.
設定変更モード終了後の所定期間に遊技球の発射を停止する場合、発射停止期間中の遊技球の発射をエラーとして、当該期間中にハンドルユニット500のハンドルレバー504が操作されるとエラーを検知してもよい。
When the shooting of game balls is stopped during a predetermined period after the end of the setting change mode, shooting of game balls during the shooting suspension period is treated as an error, and an error is detected when the
(15)その後、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更後のRAMクリア処理を実行する。この設定変更後のRAMクリア処理は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)のうち、設定値と遊技状態(例えば、確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータをクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)はクリアしない。つまり、設定変更後のRAMクリア処理では、設定変更前のRAMクリア処理と異なり、設定値が初期化されない。
(15) After that, the
そして、設定変更モードを終了する。 Then, the setting change mode is terminated.
このように、設定基板970が主制御基板1310に接続されており、主制御基板1310の子基板として機能している(又は、設定基板970が主制御基板1310と一体に構成されている)場合、主制御基板1310は払出制御基板951から本体枠開放スイッチの検出信号を取得するので、主制御基板1310のみでは設定変更処理を実行できず、主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951とが連携して設定変更処理を実行している。
In this way, the setting
次に、図139(B)に示す設定基板970と払出制御基板951とが連携した設定表示処理を説明する。
Next, the setting display processing in which the setting
パチンコ機1の稼働中(通電中)に設定キー971をオンに操作すると、主制御MPU1311は、当該設定キー971の操作を検出し、設定表示モードを開始する。
When the setting
設定表示モードでは、主制御MPU1311は、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかを判定する。なお、設定キー971の配置位置から考えると、設定キー971を操作するためには、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているので、この本体枠4の開放の判定は省略してもよい。
In the setting display mode, the
主制御MPU1311は、本体枠4が外枠2から開放していると判定されると、主制御RAM1312に記憶された設定値を読み出し、設定表示器974に表示する。
When the
図138(A)及び図139(A)で説明した設定変更処理において、設定変更モード中にパチンコ機1がエラーを検出すると、設定変更モードを無効とし、一旦設定変更モードを停止するとよい。そして、パチンコ機1の電源を遮断し、再度電源を投入することによって、停止した設定変更モードを再開する。設定変更モードの再開は、エラー検出によって停止した段階から行っても、設定変更モードの最初(設定値が選択されていない状態の設定値=0)から行ってもよい。
138(A) and 139(A), when the
設定値の変更は、所定回数履歴を記録するとよい。具体的には、設定を確定した日時及び確定した設定値を主制御RAM1312又は周辺制御部1511のRAMに格納する。設定値の履歴を周辺制御部1511に格納する場合、周辺制御部1511内に設けられた
RTC内のRAMに格納すると、パチンコ機1の電源遮断時にも記憶内容がバックアップされるので好ましい。さらに、記録された設定値の変更の履歴は出力できる。例えば、所定の操作によって、記録された設定値の変更の履歴をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示するとよい。
It is preferable to record a history of changes in set values for a predetermined number of times. Specifically, the date and time when the setting was confirmed and the confirmed setting value are stored in the
設定値が変更された場合にベース値の計測の区間を変えてもよい。すなわち、設定値が変更されると、現在ベース値を計測中の区間の全アウト球数が52000未満でも、当該区間を終了して、次の区間を開始する。設定値によって遊技機の遊技性能が変更されることから、設定値の変更で区間を変えることによって、異なる遊技性能が混在しないベース値を計算でき、設定値の変更によるベース値の推移を把握できる。 The interval for measuring the base value may be changed when the set value is changed. That is, when the set value is changed, even if the total number of out-balls in the section in which the base value is currently being measured is less than 52000, the section is ended and the next section is started. Since the game performance of the game machine changes depending on the setting value, by changing the interval by changing the setting value, it is possible to calculate the base value that does not mix different game performance, and it is possible to grasp the transition of the base value due to the change of the setting value. .
また、設定値が変更された場合にベース値の計測の区間を変えずに、現在ベース値を計測中の区間を継続してもよい。設定値は条件装置の作動割合を変えるものであるところ、設定値の変更によってベース値は大きく変化しない設計も可能である。このような場合には、設定値の変更によって、ベース値の計算の区間を変更する必要がないからである。 Also, when the setting value is changed, the interval in which the base value is currently being measured may be continued without changing the interval for measuring the base value. Since the set value changes the operating ratio of the conditional device, it is possible to design the base value not to change greatly by changing the set value. This is because, in such a case, it is not necessary to change the calculation interval of the base value by changing the set value.
また、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作と設定キー971のオン操作との両方が検出されている場合、設定変更モードを起動してもよい。RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971のオン操作とでは、その操作の方法や操作手段の配置から考えると、設定キー971の操作の方が誤って操作する可能性が低いので、設定変更モードの起動が操作者の意思だと考えられるからである。また、設定変更モードでは、遊技状態とベース値以外の主制御RAM1312の記憶内容がクリアされることから、RAMクリアを希望する場合でも、設定変更モードを起動すれば十分だと考えられるからである。
Also, if both the operation of the RAM
一方、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作と設定キー971のオン操作との両方が検出されている場合に、設定変更モードを起動せず、RAMクリアを行ってもよい。これは、両方が操作されている場合に、操作者は少なくともRAMクリアを望んでいると考えられるからである。また、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作と設定キー971のオン操作との両方が検出されている場合に、設定変更モードの起動もRAMクリアも行わなくてもよい。これは、誤操作に対するファイルセーフの観点からは、操作者の意思が明確ではない操作は受け付けないことが好ましいからである。
On the other hand, if both the operation of the RAM
前述した手順(3)や(15)のRAMクリアにおいて、遊技状態のデータを維持しているが、特別図柄の保留記憶は消去してもよい。設定値は条件装置の作動割合を変えるものであるところ、特別図柄抽選の乱数の判定結果が変わることがある。このため、特別図柄の保留記憶は消去して、新たに抽選を行わせる方が好ましいからである。 In the RAM clearing of the procedures (3) and (15) described above, the game state data is maintained, but the reserved memory of the special symbols may be erased. The setting value changes the operating ratio of the condition device, and the random number determination result of the special symbol lottery may change. For this reason, it is preferable to erase the reserved memory of the special symbols and make a new lottery.
一方、特別図柄の抽選(当たり乱数の抽出)は始動口への遊技球の入賞時に行われるが、抽選結果の判定は変動表示ゲームの開始時に行われることから、設定値の変更後の条件で保留記憶された乱数値を判定すればよい。このため、特別図柄の保留記憶を維持してもよい。 On the other hand, the lottery for special symbols (extraction of winning random numbers) is performed when the game ball enters the starting hole, but the lottery result is determined at the start of the variable display game. It suffices to determine the reserved and stored random value. Therefore, the reserved memory of the special symbol may be maintained.
また、前述した手順(3)や(15)のRAMクリアにおいて、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作に起因して消去される領域と同じ領域で主制御RAM1312を初期化してもよい。すなわち、設定変更モード中のRAMクリア処理において、設定値以外のバックアップされた遊技制御用領域13126は消去され(遊技状態のデータも消去し)、設定値とベース算出用領域13128は消去されない。通常、設定変更は、ホールの閉店から翌日の開店までの間に行われることから、遊技状態のデータ(確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報など)を消去せずに維持する必要はないからである。
Further, in the RAM clearing of the procedures (3) and (15) described above, the
[12-2.設定機能を有するパチンコ機における演出]
[12-2-1.特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理]
以下、主制御MPU1311による処理の詳細を説明する。まず、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理について説明する。図140は、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理の手順の一例を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理は、主制御側タイマ割り込み処理におけるステップS86の処理で実行される。以下、第一始動口2002及び第二始動口2004を総称して始動口とも呼ぶ。また、第一大入賞口2005及び第二大入賞口2006を総称して単に大入賞口とも呼ぶ。また、第一特別図柄と第二特別図柄を総称して単に特別図柄とも呼ぶ。
[12-2. Effect in pachinko machine with setting function]
[12-2-1. Special pattern and special electric accessories control process]
Details of the processing by the
特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理では、始動口への遊技球の受け入れ、すなわち、始動入賞を契機として(始動条件の成立)、この始動条件が成立した始動記憶情報(始動情報)ごとに大当り判定用乱数を取得し、この大当り判定用乱数が主制御内蔵ROMに予め記憶されている大当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定する(抽選手段)。そして、抽選結果に基づいて大当り遊技状態を発生させるか否かを判定し、大当り用乱数値が大当り判定値と一致している(予め定められた当選条件が成立している)場合には通常遊技状態から大当り遊技状態に移行させる。以下、図140に示したフローチャートに沿って特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理の手順を説明する。 In the special symbol and special electric accessory control processing, the acceptance of the game ball into the starting port, that is, the start winning prize (satisfaction of the starting condition), the big hit for each starting memory information (starting information) in which the starting condition is satisfied. A determination random number is acquired, and it is determined whether or not the big hit determination random number matches a big hit determination value preliminarily stored in a main control built-in ROM (lottery means). Then, it is determined whether or not to generate a big win game state based on the lottery result. A game state is shifted to a jackpot game state. Hereinafter, the procedure of special symbol and special electric accessary product control processing will be described along the flowchart shown in FIG.
特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理が開始されると、主制御MPU1311は、まず、大入賞口に遊技球Bが入賞したか否かを判定する(ステップS100)。大入賞口に遊技球Bが入賞した場合には(ステップS100の結果が「yes」)、大入賞口入賞指定コマンドをセットする(ステップS102)。
When the special symbol and special electric role product control process is started, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、始動口に遊技球が入賞したか否かを判定する(ステップS112)。そして、始動口に遊技球が入賞したか否かは、主制御側タイマ割り込み処理におけるスイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)で第一始動口センサ3002又は第二始動口センサ2511からの検出信号の有無を読み取って主制御内蔵RAMの入力情報記憶領域に記憶された入力情報に基づいて行われる。
Subsequently, the
主制御MPU1311は、始動口に遊技球が入賞した場合には(ステップS114の結果が「yes」)、始動口入賞時処理を実行する(ステップS116)。始動口入賞時処理では、始動口に新たに遊技球が入賞した場合に送信される始動口入賞コマンドを設定したり、大当り判定用乱数等を抽出して所定の領域に格納したり、特別図柄先読み演出を実行するための処理等を実行したりする。
The
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、遊技の進行に応じて実行される分岐処理の種類が指定された遊技進行状態変数である特別図柄・電動役物動作番号に基づいて対応する処理を実行する(ステップS124)。遊技進行状態変数は、主制御内蔵RAMの遊技進行状態記憶領域に記憶されており、遊技の進行に応じて実行された各分岐処理において更新される。ステップS124の処理では、遊技進行状態記憶領域に記憶されている遊技進行状態変数の値に基づいて指定された分岐処理に移行し、移行した分岐処理を終えると、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理を終了する。なお、遊技進行状態記憶領域に記憶される遊技進行状態変数の値等は、遊技情報であるため、主制御側電源断時処理においてバックアップされる。
Subsequently, the
ステップS130の処理では、遊技進行状態変数の値に基づいて、分岐処理として、特別図柄変動待ち処理(ステップS130)、特別図柄変動中処理(ステップS132)、特別図柄大当り判定処理(ステップS134)、特別図柄はずれ停止処理(ステップS1
36)、特別図柄大当り停止処理(ステップS138)、大入賞口開放前インターバル処理(ステップS140)、大入賞口開放処理(ステップS142)、大入賞口閉鎖中処理(ステップS144)又は大入賞口開放終了インターバル処理(ステップS146)が実行される。
In the processing of step S130, based on the value of the game progress state variable, as branch processing, special symbol variation waiting processing (step S130), special symbol variation in-process (step S132), special symbol big hit determination processing (step S134), Special symbol deviation stop processing (step S1
36), special symbol jackpot stop processing (step S138), interval processing before large winning opening opening (step S140), large winning opening opening processing (step S142), large winning opening closing process (step S144) or large winning opening opening End interval processing (step S146) is executed.
特別図柄変動待ち処理(ステップS130)では、始動口に遊技球Bが入球したことに基づいて、特別図柄表示器における特別図柄の変動表示を開始させる処理等を行う。 In the special symbol variation waiting process (step S130), when the game ball B enters the starting hole, the special symbol display device starts to display the variation of the special symbol.
特別図柄変動中処理(ステップS132)では、特別図柄の変動表示を制御する処理等を行う。特別図柄大当り判定処理(ステップS134)では、始動口に遊技球が入球したことに基づいて、確定停止した特別図柄が大当り遊技状態を発生させるか否かの判定を行う。 In the special symbol fluctuation process (step S132), a process for controlling the variable display of the special symbol and the like are performed. In the special symbol big hit determination process (step S134), it is determined whether or not the fixed and stopped special symbol generates a big win game state based on the entry of the game ball into the starting hole.
特別図柄はずれ停止処理(ステップS136)では、大当り遊技状態を発生させない場合に特別図柄の変動表示を停止させてその旨を報知する処理等を行う。特別図柄大当り停止処理(ステップS138)では、大当り遊技状態を発生させる場合に特別図柄の変動表示を停止させてその旨を報知する処理等を行う。 In the special symbol deviation stop process (step S136), when the big hit game state is not generated, the process of stopping the variable display of the special symbol and notifying the fact is performed. In the special symbol jackpot stop processing (step S138), when a jackpot game state is to be generated, a process of stopping the variable display of the special symbols and notifying that effect is performed.
大入賞口開放前インターバル処理(ステップS140)では、大当り遊技状態を発生させて大当り動作が開始される旨を報知するための処理等を行う。大入賞口開放処理(ステップS142)では、大入賞口を開状態とすることにより各大入賞口に遊技球が入球容易とする大当り動作に関する処理等を行う。 In the interval process before opening the big winning opening (step S140), a process for generating a big win game state and notifying that a big win operation is started is performed. In the big winning opening opening process (step S142), a process related to a big winning operation for making it easier for a game ball to enter each big winning opening is performed by opening the big winning opening.
大入賞口閉鎖中処理(ステップS144)では、大入賞口を開状態から閉状態とすることにより各大入賞口に遊技球が入球困難とする大当り動作に関する処理等を行う。入賞口開放終了インターバル処理(ステップS146)では、大当り動作が終了しているときにはその旨を報知する処理等を行う。 In the big winning opening closing process (step S144), by closing the big winning opening from the open state, a process related to the big winning operation to make it difficult for the game ball to enter each big winning opening is performed. In the winning opening opening end interval process (step S146), when the jackpot operation is over, a process of notifying that effect is performed.
[12-2-2.特別図柄変動待ち処理]
続いて、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理における特別図柄変動待ち処理(ステップS130)の詳細について説明する。図141は、特別図柄変動待ち処理の手順の一例を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄変動待ち処理では、特別図柄の変動表示が実行されていない状態で実行され、当該変動表示が保留されている場合には、特別図柄の変動表示を開始する準備を行う。
[12-2-2. Special symbol variation waiting process]
Subsequently, the details of the special symbol variation waiting process (step S130) in the special symbol and special electric accessary product control process will be described. FIG. 141 is a flow chart showing an example of the procedure of the special symbol variation waiting process. The special symbol variation waiting process is executed in a state where the special symbol variation display is not performed, and when the variation display is suspended, preparations are made to start the special symbol variation display.
主制御MPU1311は、まず、特別図柄の変動が保留されているか否かを判定する(ステップS420)。具体的には、特別図柄作動保留球数が0でないか否を判定する。なお、特別図柄作動保留球数は、複数の始動口が設けられている場合には始動口ごとに記憶される。特別図柄の変動が保留されていない場合には(ステップS420の結果が「no」)、特別図柄の変動表示を開始しないので本処理を終了する。
The
一方、特別図柄の変動表示が保留されている場合には(ステップS420の結果が「yes」)、主制御MPU1311は、コマンドデータとして保留球数指定コマンドをセットする(ステップS438)。
On the other hand, when the variable display of the special symbols is suspended (the result of step S420 is "yes"), the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、特別図柄・フラグ設定処理を実行する(ステップS442)。特別図柄・フラグ設定処理では、始動口入賞時に取得された大当り判定用の乱数などに基づいて、特別抽選を実行する。
Subsequently, the
さらに、主制御MPU1311は、特別図柄変動パターン設定処理を実行する(ステッ
プS444)。特別図柄変動パターン設定処理では、特別抽選の結果に基づいて、変動パターンを設定する。特別図柄変動パターン設定処理の詳細については、図126にて後述する。
Furthermore, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板1510に送信するための変動パターンコマンドを作成する。具体的には、まず、コマンド値として、特別図柄識別フラグに対応する特図変動パターン基準コマンドの上位バイトを設定する(ステップS452)。さらに、下位のコマンドデータとして、変動パターンエリアに格納された変動パターン値を設定する(ステップS458)。さらに、変動タイプ種別エリアから変動タイプ種別値を取得し(ステップS460)、ステップS452の処理で設定されたコマンド値に変動タイプ種別値を加算することによって変動タイプに応じた変動パターンコマンドの上位バイトを算出する(ステップS462)。このようにして作成された変動パターンコマンドのコマンドデータを所定の領域に格納する。
Next,
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板1510に送信するための図柄種別コマンドを設定する(ステップS466)。さらに、変動時状態指定コマンドをコマンドバッファに設定する(ステップS474)。
Subsequently, the
以上の処理で作成された各コマンドは、コマンドバッファに設定される。コマンドバッファに設定された保留球数指定コマンドは、主制御側タイマ割り込み処理における周辺制御基板コマンド送信処理(ステップS92)によって送信される。 Each command created by the above processing is set in the command buffer. The reserved ball number designation command set in the command buffer is transmitted by the peripheral control board command transmission processing (step S92) in the main control side timer interrupt processing.
[12-2-3.特別図柄変動パターン設定処理]
続いて、特別図柄変動待ち処理における特別図柄変動パターン設定処理(ステップS444)の詳細について説明する。特別図柄変動パターン設定処理では、特別図柄の変動表示における変動パターンを設定するための処理である。図142は、特別図柄変動パターン設定処理の手順の一例を示すフローチャートである。
[12-2-3. Special symbol variation pattern setting process]
Subsequently, the details of the special symbol variation pattern setting process (step S444) in the special symbol variation waiting process will be described. The special symbol variation pattern setting process is a process for setting the variation pattern in the special symbol variation display. FIG. 142 is a flow chart showing an example of the procedure of the special symbol variation pattern setting process.
主制御MPU1311は、まず、特別図柄作動保留球数を取得する(ステップS530)。特別図柄作動保留球数は、特別図柄作動保留球数バッファに格納される。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、大当りフラグエリアから大当りフラグを設定する(ステップS538)。
The
そして、主制御MPU1311は、特別図柄作動保留球数及び大当りフラグに基づいて、特別図柄の変動パターンを選択する変動パターン選択判定処理を実行する(ステップS542)。変動パターン選択判定処理の詳細については、図143にて後述する。
Then, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、変動パターン選択判定処理によって抽出された変動パターン値を取得する(ステップS544)。そして、特別図柄変動時間データから変動パターン値に対応するデータ(変動時間値)を検索する(ステップS546)。
Next, the
さらに、主制御MPU1311は、特別図柄の変動表示における変動パターンに定義された変動タイプを選択するための変動タイプ判定処理を実行する(ステップS548)。変動タイプ判定処理によって取得された変動タイプ種別値を設定する(ステップS550)。
Furthermore, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、変動時間加算値データから変動タイプ種別値に対応する変動時間加算値を検索する(ステップS552)。変動時間加算値は変動タイプに対応する加算時間であり、例えば、疑似連回数に応じた加算時間などに相当する。そして、主制御MPU1311は、ステップS546の処理で検索された基準となる変動時間値に
ステップS552の処理で検索された変動時間加算値を加算し、最終的な変動時間を取得する(ステップS554)。最後に、最終的な変動時間を特別図柄・電動役物動作タイマエリアに格納し(ステップS556)、特別図柄変動パターン設定処理を終了する。
Subsequently, the
[12-2-4.変動パターン選択判定処理]
続いて、変動パターン選択判定処理(ステップS542)の詳細について説明する。図143は、変動パターン選択判定処理の手順の一例を示すフローチャートである。変動パターン選択判定処理は、特別図柄の変動表示における変動パターンを選択するための処理である。
[12-2-4. Fluctuation pattern selection judgment processing]
Next, details of the variation pattern selection determination process (step S542) will be described. FIG. 143 is a flowchart showing an example of the procedure of variation pattern selection determination processing. The variation pattern selection determination process is a process for selecting a variation pattern in the variation display of special symbols.
主制御MPU1311は、まず、変動テーブル番号に基づいて変動情報源テーブルを取得する(ステップS340)。変動テーブル番号は、変動情報源アドレステーブルから変動情報源テーブルを選択(取得)するための値である。変動情報源テーブルは、遊技状態などに応じた、当り(当り変動選択情報状態テーブル)、はずれ(はずれ変動選択情報状態テーブル)、リーチ(リーチ変動選択情報状態テーブル)、リーチ確率(特別図柄リーチ確率テーブル)、変動タイプ(変動タイプ判定データテーブル)を参照するためのテーブル情報が記憶されたデータテーブルである。
The
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、特別抽選の結果を導出するための当り判定値を取得する(ステップS346)。当り判定値が大当り値と一致するか否かを判定することによって大当りに当選したか否かを判定する(ステップS350)。大当りに当選した場合には(ステップS350の結果が「yes」)、大当りフラグ及び大当り図柄種別を取得する(ステップS354)。
Subsequently, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、大当りフラグ及び大当り図柄種別に基づいて、変動情報番号検索処理を実行する(ステップS358)。変動情報番号検索処理では、大当り変動選択情報種別テーブルから当り時変動パターン選択値データテーブルを決定するための変動情報番号を取得する。主制御MPU1311は、取得された変動情報番号に基づいて、大当り変動選択情報種別テーブルから変動パターン用乱数1を取得する(ステップS360)。
Next, the
一方、主制御MPU1311は、大当り若しくは小当りに当選していない場合には(ステップS350の結果が「no」)、始動入賞に対応する変動表示においてリーチを発生させるか否かを判定する(ステップS372)。
On the other hand, when the
主制御MPU1311は、当該変動表示においてリーチを発生させない場合には(ステップS372の結果が「no」)、保留球数に基づいてはずれ変動選択情報保留テーブルから変動パターン用乱数1を取得する(ステップS376)。
The
一方、主制御MPU1311は、当該変動表示においてリーチを発生させる場合には(ステップS372の結果が「yes」)、状態フラグに基づいて、リーチ変動選択情報状態テーブルから変動パターン用乱数1を取得する(ステップS382)。
On the other hand, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、ステップS360、ステップS378又はステップS382の処理で取得された変動パターン用乱数1に基づいて、変動情報番号検索処理を実行する(ステップS388)。そして、変動情報番号検索処理によって変動パターン選択値データテーブルを取得し、変動パターン選択値データテーブルから変動パターン用乱数2を取得する(ステップS392)。さらに、変動パターン用乱数2及び変動パターン選択値データテーブルに基づいて、変動情報番号検索処理を実行する(ステップS394)。変動情報番号検索処理の結果に基づいて変動パターンを選択し(ステップS396)
、本処理を終了する。
Subsequently, the
, the process ends.
本実施形態では、変動パターン用乱数1(ステップS360、S372、S378)及び変動パターン用乱数2(ステップS392)の2種類の乱数によって2段階で変動パターンが選択される。まず、変動パターン用乱数1に基づいて変動パターンの種別(○○系リーチといった変動パターン群)を選択する。さらに、変動パターン用乱数2に基づいて変動パターン用乱数1によって選択した変動パターン群から、最終的に変動表示する変動パターン(変動パターンコマンドに設定される値)が選択される。なお、2段階で抽選する方法に限定されず、3段階以上で抽選する方式でもよいし、一の変動パターン用乱数で直接変動パターンを選択するようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, a variation pattern is selected in two steps by two types of random numbers, variation pattern random number 1 (steps S360, S372, S378) and variation pattern random number 2 (step S392). First, based on the variation pattern
[12-3.設定機能を有するパチンコ機における演出の説明]
以下、設定機能を有するパチンコ機1における演出について説明する。具体的には、現在の設定を示唆する設定示唆演出について説明する。設定機能を有するパチンコ機1においては、例えば、設定が高いほど特別抽選の回数に対する遊技球の払い出し数が多くなる。具体的には、例えば、設定が高いほど非確変状態における大当り当選確率が高い(例えば、設定1:1/300、設定2:1/290、設定3:1/280、設定4:1/270、設定5:1/250、設定6:1/230等)。従って、遊技者はなるべく高い設定のパチンコ機1で遊技を行いたいため、設定示唆演出が搭載されることにより、遊技意欲が高まる。
[12-3. Explanation of production in pachinko machine with setting function]
The effect of the
以下、本章では、説明の便宜のため、主制御MPU1311は、ステップS542の変動パターン選択判定処理において、一の変動パターン用乱数で直接変動パターンを選択するものとする。具体的には、本章では、主制御MPU1311は、ステップS542において以下の処理を実行するものとする。
Hereinafter, in this chapter, for convenience of explanation, the
主制御MPU1311は、ステップS542において、現在の遊技状態(時短状態(時短制御が実行されている状態)であるか、時短状態以外の通常状態であるか)と、特別抽選の結果(大当りに当選したか外れであるか)と、に応じた変動パターンテーブルを選択する。主制御MPU1311は、特別抽選の結果が大当りである場合には、変動パターン用乱数を取得し、取得した変動パターン用乱数と、選択した変動パターンテーブルにおける各変動パターンの振り分けと、に基づいて、選択した変動パターンテーブルから変動パターンを選択するものとする。また、特別抽選の結果が外れである場合にはさらにリーチ発生有無を判定し、変動パターン用乱数を取得し、取得した変動パターン用乱数と、選択した変動パターンテーブルにおける各変動パターンの振り分けと、に基づいて、選択した変動パターンテーブルから変動パターンを選択するものとする。
In step S542, the
図144(A)は、遊技状態が通常状態であり、かつ特別抽選の結果が外れである場合に選択される変動パターンテーブルの一例である。図144(B)は、遊技状態が通常状態であり、かつ特別抽選の結果が大当りである場合に選択される変動パターンテーブルの一例である。 FIG. 144(A) is an example of a variation pattern table selected when the gaming state is the normal state and the result of the special lottery is lost. FIG. 144(B) is an example of a variation pattern table selected when the gaming state is the normal state and the result of the special lottery is a big win.
変動パターンテーブルは、例えば、主制御基板1310のROM1313に格納されている。変動パターンテーブルは、例えば、変動パターン種別欄、変動時間欄、対応する演出内容欄、及び変動パターン決定用乱数振り分け欄を含む。変動パターン種別欄は変動パターンをテーブル内で識別するための種別を特定する情報を格納する。変動時間欄は、対応する変動パターン種別における変動時間を特定する情報を格納する。対応する演出内容欄は、対応する変動パターンにおいて実行される演出内容を特定する情報を格納する。
The variation pattern table is stored in the
変動パターン決定用振り分け乱数欄は、対応する変動パターンが選択される振り分けを
設定ごとに格納する。なお、特別抽選結果が外れである場合に選択される変動パターンテーブル(即ち図144(A)及び後述する図149(A)の変動パターンテーブル)の変動パターン決定用振り分け乱数欄は、リーチ発生時及びリーチ非発生時のそれぞれについて、対応する変動パターンが選択される振り分けを設定ごとに格納する。
The distribution random number column for determining the variation pattern stores the distribution for selecting the corresponding variation pattern for each setting. In addition, the random number column for determining the variation pattern of the variation pattern table selected when the special lottery result is out (that is, the variation pattern table in FIG. 144 (A) and FIG. 149 (A) described later) is when reach occurs. And for each of reach non-occurrence time, the distribution in which the corresponding variation pattern is selected is stored for each setting.
[12-4.特別抽選結果の仮表示後に実行される設定示唆演出]
まず、図144(A)の変動パターンテーブルに格納された、外れ変動パターンにおける設定示唆演出について説明する。まず、外れ変動パターン24~29において実行される演出について、図144も併せて用いながら説明する。
[12-4. Setting Suggestion Effect Executed After Temporary Display of Special Lottery Result]
First, the setting suggestion effect in the deviation variation pattern stored in the variation pattern table of FIG. 144(A) will be described. First, the effect executed in the
図144は、図144(A)の変動パターンテーブルにおける外れ変動パターン20、及び24~29において実行される演出の一例を示す概要図である。外れ変動パターン20の変動では、SPリーチ1が実行された後に特別抽選結果が外れである可能性が高いことを示す仮表示をメイン液晶表示装置1600上に表示した後に、その後特別抽選結果が外れであることを示す確定表示をメイン液晶表示装置1600上に表示する。これに対し、外れ変動パターン25~29の変動では、SPリーチ1が実行された後に特別抽選結果が外れである可能性が高いことを示す仮表示をメイン液晶表示装置1600上に表示した後に、設定示唆演出を実行し、その後特別抽選結果が外れであることを示す確定表示をメイン液晶表示装置1600上に表示する。
FIG. 144 is a schematic diagram showing an example of an effect executed in the
このように、変動パターン25~29において、特別抽選結果が外れである可能性が高いことを示す仮表示を行った後に、設定示唆演出が実行されることにより、当該仮表示が実行されても遊技者は、その後の設定示唆演出の発生を期待し、期待感を維持することができる。また、外れ変動において設定示唆演出が発生した場合には、特別抽選結果が外れであっても、特別抽選の結果による遊技者の落胆を抑制し、ひいては高揚感を高めることができる。
In this way, in the
なお、外れ変動パターン24の変動では、SPリーチ1が実行された後に特別抽選結果が外れである可能性が高いことを示す仮表示をメイン液晶表示装置1600上に表示した後に、設定示唆演出の実行を示唆するガセ演出を実行するものの、設定示唆演出自体を行わずに、特別抽選結果が外れであることを示す確定表示をメイン液晶表示装置1600上に表示する。
In addition, in the variation of the lost
なお、SPリーチとは、特別抽選の結果が大当りである場合に選択される割合が高く、特別抽選の結果が外れである場合に選択される割合が低いリーチ演出である。つまり、SPリーチが実行される変動の大当り期待度は高い。 The SP reach is a ready-to-win effect that is highly selected when the special lottery result is a big hit and is less likely to be selected when the special lottery result is a loss. That is, the degree of expectation for a big hit of variation in which SP reach is executed is high.
以下、外れ変動パターン20、及び24~29において実行される演出について具体的に説明する。なお、各演出においては、以下に説明する内容以外にも、各種スピーカからの音出力、各種ランプからの発光、各種可動体の動作、及び/又はメイン液晶表示装置1600における表示等が同時に実行されてもよい。
Below, the effects executed in the
外れ変動パターン20、及び24~29において、まず、リーチ前演出が実行される。リーチ前演出では、メイン液晶表示装置1600において全ての装飾図柄が変動する。続いて、外れ変動パターン20、及び24~29において、ノーマルリーチ演出に発展する。ノーマルリーチ演出では、メイン液晶表示装置1600において装飾図柄がリーチ状態となる。具体的には、例えば、3つの装飾図柄(例えば、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄)のうち、左図柄と右図柄が同一の図柄で停止し、中図柄が変動中の状態となる。
In the
続いて、外れ変動パターン20、及び24~29において、SPリーチ1に発展し、S
Pリーチ1の前半演出が実行される。SPリーチ1では、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600において1人の主人公キャラクタと1人の敵キャラクタが表示され、じゃんけん勝負をする。外れ変動パターン20、及び24~29におけるSPリーチ1の前半演出では、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、主人公キャラクタが敵キャラクタにじゃんけん勝負で負けてしまう演出が実行される。なお、SPリーチ中において装飾図柄は、例えば、リーチ前演出時及びノーマルリーチ演出時と比較して、小さく、かつメイン液晶表示装置1600の周囲に近い位置に表示されてもよい。
Subsequently, in the
The first half production of P reach 1 is executed. In
続いて、外れ変動パターン20、及び24~29において、SPリーチ1の後半演出に発展する。外れ変動パターン20、及び24~29におけるSPリーチ1の後半演出では、例えば、所謂復活演出が実行され、例えば後半演出の開始時に「まだまだ!」等の主人公の声が各種スピーカから出力され、メイン液晶表示装置1600上において、再度主人公キャラクタと敵キャラクタとのじゃんけん勝負が行われる演出が実行される。外れ変動パターン24~29におけるSPリーチ1の後半演出では、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、主人公キャラクタが敵キャラクタにじゃんけん勝負で再度負けてしまう演出が実行される。
Subsequently, in the
続いて、特別抽選結果が外れである仮表示がメイン液晶表示装置1600上で実行される。具体的には、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、外れ状態の装飾図柄の1つの組み合わせ(例えば、装飾図柄の左図柄と右図柄はリーチ状態で停止した図柄と同一の図柄で、中図柄は当該同一の図柄とは異なる図柄)が、小さい幅で揺れているような態様で表示される。
Subsequently, the main liquid
続いて、外れ変動パターン20においては仮表示後に、他の演出が行われることなく、特別抽選結果が外れであったことを示す確定表示がメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される。外れ変動パターン24においては仮表示後に設定示唆ガセ演出が実行され、その後特別抽選結果が外れであったことを示す確定表示がメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される。これに対して、外れ変動パターン25~29においては仮表示後に設定示唆演出が実行され、その後特別抽選結果が外れであったことを示す確定表示がメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される。確定表示においては、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、仮表示において表示した装飾図柄の組み合わせと同一の組み合わせが、完全に停止した態様で表示される。なお、仮表示及び確定表示においては、装飾図柄は、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600の中央部に、リーチ前演出及びノーマルリーチ演出時と同様の大きさで、表示される。
Subsequently, in the
外れ変動パターン24における設定示唆ガセ演出では、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、主人公キャラクタ1人が敵キャラクタ2人を発見して、当該敵キャラクタを追いかけるものの捕まえることができない演出が実行される。図144(A)における外れ変動パターン24の振り分けのように、設定示唆ガセ演出が実行される変動パターンの振り分けは、全ての設定において均等又はおおよそ均等であることが望ましい。当該振り分けが均等でない場合には、設定示唆ガセ演出が設定を示唆してしまうからである。
In the set-suggestion fake effect in the
また、SPリーチ1が実行される変動の振り分けの合計に占める外れ変動パターン24の振り分けの割合は低い(例えば、20%以下)であることが望ましい。当該振り分けが高いと、SPリーチ1に発展した場合に頻繁に設定示唆ガセ演出が発生することになり、設定示唆演出の発生に対する遊技者の期待感を削ぐおそれがあるからである。
In addition, it is desirable that the proportion of the distribution of the
外れ変動パターン25~29における設定示唆演出では、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、主人公キャラクタ1人が敵キャラクタ2人を発見して、当該敵キャラクタを追いかけて捕まえ、その後3人でじゃんけん勝負をする演出が実行される。
In the setting-suggestion effects in the
外れ変動パターン25における設定示唆演出では、3人でのじゃんけん勝負において3人ともグーを出してあいこになる演出が実行される。また、図144(A)において外れ変動パターン25は、低設定(設定1、2、及び3)においてのみ振り分けられるように定められている。即ち、外れ変動パターン25における設定示唆演出は、低設定が確定する演出である。
In the setting-suggestion effect in the
なお、図144(A)の例では、外れ変動パターン25の振り分けは、高設定(設定4、5、及び6)における外れ変動パターン26等の振り分けと同じ値であるが、低設定確定演出が発生すると、遊技者が遊技を早期に中止する可能性もあるため、外れ変動パターン25の振り分けは、他の設定における他の設定確定演出の振り分けより低く設定されていてもよいし、外れ変動パターン25自体が存在しなくてもよい。
In addition, in the example of FIG. 144 (A), the distribution of the
外れ変動パターン26における設定示唆演出では、3人でのじゃんけん勝負において3人ともチョキを出してあいこになる演出が実行される。また、図144(A)において外れ変動パターン26は高設定(設定4、5、及び6)においてのみ振り分けられるように定められている。即ち、外れ変動パターン26における設定示唆演出は、高設定が確定する演出である。
In the set-suggestion effect in the
外れ変動パターン27における設定示唆演出では、3人でのじゃんけん勝負において3人ともパーを出してあいこになる演出が実行される。また、図144(A)において外れ変動パターン27は偶数設定(設定2、4、及び6)においてのみ振り分けられるように定められている。即ち、外れ変動パターン27における設定示唆演出は、偶数設定が確定する演出である。
In the set-suggestion effect in the
外れ変動パターン28における設定示唆演出では、3人でのじゃんけん勝負において3人とも違う手を出してあいこになる演出が実行される。また、図144(A)において外れ変動パターン28は奇数設定(設定1、3、及び5)においてのみ振り分けられるように定められている。即ち、外れ変動パターン28における設定示唆演出は、奇数設定が確定する演出である。
In the set-suggestion effect in the
なお、例えば、奇数設定と偶数設定とが異なる特性を有する場合には、上述のような奇数設定確定演出又は偶数設定確定演出が搭載されることにより、遊技者の演出に対する興味を惹くことができる。 In addition, for example, when the odd number setting and the even number setting have different characteristics, the player's interest in the effect can be attracted by installing the odd number setting confirmed effect or the even number set confirmed effect as described above. .
具体的には、例えば、設定6、4、2、5、3、1の順に通常状態の大当り当選確率が高く(6が最高、1が最低)、設定5、3、1、6、4、2の順に大当り当選のうちの確変大当りの割合が高く(5が最高、2が最低)、かつ設定6、5、4、3、2、1の順に第一始動口2002及び第二始動口2004への遊技球の入賞個数に対する遊技球払い出し総数の割合が高く(6が最高、1が最低)なるように、各設定における大当り当選確率及び確変割合が定められているとする。
Specifically, for example, in order of setting 6, 4, 2, 5, 3, 1, the probability of winning the jackpot in the normal state is high (6 is the highest, 1 is the lowest), setting 5, 3, 1, 6, 4, In order of 2, the ratio of probability variable jackpots among jackpot winnings is high (5 is the highest, 2 is the lowest), and the
この場合、偶数設定は奇数設定と比較して、通常状態における大当り当選確率が高い代わりに、確変割合が低い、即ち、所謂初当りに当選するために要する遊技球の数は少なくなりやすいものの、初当りからの一度の連荘で得られる遊技球の総量も少なくなりがちである。一方、奇数設定は偶数設定と比較して、通常状態における大当り当選確率が低い代わりに、確変割合が高い、即ち、初当りに当選するために要する遊技球の数は多くなりがちだが、初当りからの一度の連荘で得られる遊技球の総量は多くなりやすい。このよう場合、ある遊技者は偶数設定の出玉傾向を好み、別の遊技者は奇数設定の出玉傾向を好む、という事態が発生する可能性があるため、奇数設定確定演出又は偶数設定確定演出への遊
技者の関心が高くなる。また、偶数設定は奇数設定と比較して、通常状態における大当り当選確率が高い代わりに、ラウンド数の少ない大当りが選択されやすい等の、特徴があってもよい。
In this case, compared to the odd number setting, the even number setting has a higher jackpot winning probability in the normal state, but a lower probability variable ratio, that is, the number of game balls required to win the so-called first hit tends to be smaller. The total amount of game balls that can be obtained in one consecutive game from the beginning tends to be small. On the other hand, compared to the even number setting, the odd number setting has a low jackpot winning probability in the normal state, but a high probability variation ratio, that is, the number of game balls required to win the first win tends to be large, but the first win The total amount of game balls that can be obtained from a single consecutive residence tends to be large. In such a case, there is a possibility that one player prefers an even-numbered ball payout tendency and another player prefers an odd-numbered ball payout tendency. The player's interest in the performance increases. Also, compared to the odd number setting, the even number setting may have a feature such as a higher jackpot winning probability in the normal state, but a larger jackpot with a smaller number of rounds being more likely to be selected.
上述した外れ変動パターン25~29においては、設定示唆演出が開始するまでの演出は同一であるが、設定示唆演出の内容は異なる(3人でのじゃんけん勝負における結果が異なる)。なお、3人でのじゃんけん勝負演出は外れ変動パターン25~29のみで用いられることが望ましい。これにより3人でのじゃんけん勝負演出が開始した時点で、遊技者は設定示唆演出が開始したことを認識することができ、高揚感がより高まる。
In the
なお、例えば、外れ変動パターン25は、高設定が確定する演出が実行される変動パターンであるが、高設定の可能性が高いことを示唆する演出が実行される変動パターンであってもよい。具体的には、例えば、低設定においても変動パターン25の振り分けを有し、かつ当該振り分けが高設定における変動パターン25の振り分けよりも低ければ(例えば、50%以下)、外れ変動パターン25における演出は高設定が確定する演出ではなく、高設定の可能性が高いことを示唆する演出となる。
It should be noted that, for example, the
なお、高設定が確定する演出が実行される変動パターンに加えて上述のような高設定の可能性が高いことを示唆する演出が実行される変動パターンが定められていてもよい。上述したことは、低設定確定演出、奇数設定確定演出、偶数設定確定演出、及び最高設定確定演出等についても同様である。 In addition to the variation pattern in which the effect that the high setting is confirmed is performed, a variation pattern in which the effect suggesting that the possibility of the high setting as described above is performed may be determined. What has been described above is the same for the low setting confirmation effect, the odd setting confirmation effect, the even setting confirmation effect, the highest setting confirmation effect, and the like.
なお、図144(B)の変動パターンテーブル(通常時かつ大当り当選時の変動パターンテーブル)によれば通常状態において特別抽選結果が大当りである場合には、最高設定が確定する当り変動パターン34以外の設定示唆演出は実行されない。また、設定示唆演出が実行されない変動パターンの振り分けが、特別抽選結果が外れである場合と比較して高くなっている。これにより、設定示唆演出は、主として特別抽選結果が外れであるときに実行される演出となり、特別抽選結果が外れである場合においても遊技者は期待感を得ることができる。 According to the variation pattern table of FIG. 144 (B) (variation pattern table at normal time and jackpot winning), when the special lottery result is a jackpot in the normal state, the winning variation pattern other than 34 in which the highest setting is fixed The setting suggestion effect of is not executed. In addition, the distribution of variation patterns in which the setting suggestion effect is not executed is high compared to the case where the special lottery result is a loss. As a result, the setting suggestion performance becomes a performance mainly executed when the special lottery result is a win, and the player can get a sense of expectation even when the special lottery result is a win.
[12-5.短縮変動を用いた設定示唆演出]
以下、外れ変動パターン30について図146も併せて用いて説明する。図146は、図144(A)の変動パターンテーブルにおける外れ変動パターン1、2、及び30において実行される演出の一例を示す概要図である。
[12-5. Setting Suggestion Production Using Shortened Variation]
The
外れ変動パターン1、2、及び30において、短縮変動が実行される。短縮変動とは、例えば、他の変動パターンと比較して、変動時間が短い変動であり、メイン液晶表示装置1600上で装飾図柄の変動を開始した後に、リーチ状態に発展することなく全ての装飾図柄が停止する変動である。通常の変動においては、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、装飾図柄が、例えば左図柄、右図柄、中図柄の順に停止するが、短縮変動においては全ての装飾図柄が一斉に停止してもよい。
For
続いて、外れ変動パターン1、2、及び30において、特別抽選結果が外れである可能性が高いことを示す仮表示を行った後に、特別抽選結果が外れであることを示す確定表示を行う。仮表示、及び確定表示についての説明は上述した説明と同様であるため、省略する。
Subsequently, in
外れ変動パターン30は、外れ変動パターン1、2のような短縮変動が実行される他の全ての変動パターンの変動時間と異なる変動時間を有する。図144(A)の例では、外れ変動パターン1の変動時間は2秒であり、外れ変動パターン2の変動時間は、5秒であ
り、外れ変動パターン30の変動時間は3.5秒である。また、図144(A)において外れ変動パターン30は最高設定(設定6)においてのみ振り分けられるように定められている。即ち、外れ変動パターン30が実行されると、最高設定が確定する。
The
また、短縮変動が実行されかつ設定を示唆する変動パターンである外れ変動パターン30の振り分けは、短縮変動が実行される他の変動パターンの振り分けと比較して、極めて低い(例えば当該他の変動パターンの最小の振り分けの10%以下である)ことが望ましい。また、短縮変動が実行される各変動パターンにおいて、仮表示及び確定表示の実行時間は同じであり、短縮変動の時間のみが異なることが望ましい。また、外れ変動パターン30の変動時間と、他の短縮変動が実行される変動パターンの変動時間と、の差は、遊技者が認識可能な程度(例えば1.5秒以上)であることが望ましい。
In addition, the distribution of the deviating
これにより、短縮変動が実行された時点で遊技者は、振り分けの多い外れ変動パターン1、2のような変動時間を想定するが、外れ変動パターン30が実行された場合には想定した変動時間と異なることを認識することができ、最高設定が確定する演出を楽しむことができる。特に、図144(A)の例では、短縮変動を含む変動パターンは、リーチなし外れ時にしか選択されないため、遊技者は短縮変動が実行されると期待感が削がれ、短縮変動に興味を持てなくなってしまう。しかし、このように短縮変動を用いた設定示唆演出が実行されることにより、遊技者は、リーチなし外れ時にしか選択されない短縮変動に対しても期待感を有することができ、興趣の低下を抑制することができる。
As a result, when the shortened variation is executed, the player assumes a variation time such as the often-distributed
また外れ変動パターン1、2、及び30では、メイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される内容は同一であるものの、短縮変動の時間だけが異なる。これにより、遊技者を、最高設定確定演出を見逃さないように演出に集中させることができる。
Also, in the
なお、外れ変動パターン30は、最高設定が確定し、かつ短縮変動が実行される変動パターンであるが、最高設定以外の各設定についても、当該設定が確定し、かつ短縮変動が実行される変動パターンが存在してもよい。この場合、例えば、当該変動パターンそれぞれの変動時間は、短縮変動が実行される他の外れ変動パターンの変動時間と異なることが望ましい。
Note that the
[12-6.特別抽選結果の仮表示前に実行される設定示唆演出]
以下、外れ変動パターン31、及び当り変動パターン34について図147も併せて用いて説明する。図147は、図144(A)の変動パターンテーブルにおける外れ変動パターン31、及び当り変動パターン34において実行される演出の一例を示す概要図である。図144において外れ変動パターン31、及び当り変動パターン34は最高設定(設定6)においてのみ振り分けられるように定められている。即ち、外れ変動パターン31及び当り変動パターン34が実行されると、最高設定が確定する。
[12-6. Setting Suggestion Effect Executed Before Temporary Display of Special Lottery Result]
The
外れ変動パターン31、及び当り変動パターン34では、例えば、変動開始と同時に、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、スペシャルムービー1が流れる。スペシャルムービー1は、外れ変動パターン31及び当り変動パターン34においてのみ発生する演出であり、つまり最高設定が確定する演出である。
In the
外れ変動パターン31においては、スペシャルムービー1の終了後、特別抽選結果が外れである可能性が高いことを示す仮表示を行った後に、特別抽選結果が外れであることを示す確定表示を行う。当り変動パターン34においては、スペシャルムービー1の終了後、特別抽選結果が当りであることを示す仮表示を行った後に、特別抽選結果が当りであることを示す確定表示を行う。
In the
外れ変動パターン31及び当り変動パターン34は、外れ変動パターン25~30等と異なり、仮表示の前に(具体的には、例えば、変動開始と同時に)設定示唆演出が開始されている。これにより、遊技者は最高設定が確定した状態で、大当り抽選結果の報知を待つ高揚感を得ることができる。また、特にスペシャルムービー1の表示時間が長い(例えば30秒以上)場合には、他の遊技者に対して当該パチンコ機1の設定が最高設定であることをアピールすることができ、ひいては遊技者は当該他の遊技者に対して優越感を感じることができ、ホールにとっても当該他の遊技者に対して最高設定を使用していることをアピールしやすくなる。
Unlike the
[12-7.大当り当選又は高設定が確定する設定示唆演出]
以下、外れ変動パターン32、及び当り変動パターン35について図148も併せて用いて説明する。図148は、図144(A)の変動パターンテーブルにおける外れ変動パターン32、及び当り変動パターン35において実行される演出の一例を示す概要図である。図144(A)において外れ変動パターン32は高設定(設定4、5、6)のみにおいて振り分けられるように定められている。即ち、外れ変動パターン32が実行されると、最高設定が確定する。
[12-7. Setting suggestion production that confirms jackpot winning or high setting]
The
外れ変動パターン32、及び当り変動パターン35では、例えば、変動開始と同時に、メイン液晶表示装置1600において、スペシャルムービー2が流れる。スペシャルムービー2は、外れ変動パターン31及び当り変動パターン34のみで発生する演出である。
In the
外れ変動パターン32においては、スペシャルムービー2の終了後、特別抽選結果が外れである可能性が高いことを示す仮表示を行った後に、特別抽選結果が外れであることを示す確定表示を行う。当り変動パターン35においては、スペシャルムービー2の終了後、特別抽選結果が当りであることを示す仮表示を行った後に、特別抽選結果が当りであることを示す確定表示を行う。
In the
従って、スペシャルムービー2が発生した場合には、高設定又は当該変動における大当りの一方が確定する。つまり、スペシャルムービー2が発生した後に特別抽選結果が外れであった場合には高設定が確定するため、遊技者は特別抽選結果が外れであったことに対する落胆を抑えることができ、ひいては高設定が確定したことにより高揚感を得ることができる。
Therefore, when the
また、特にスペシャルムービー2の表示時間が長い場合には(例えば30秒以上)、遊技者は他の遊技者に対して優越感を感じることができる上に、さらにスペシャルムービー2が発生した上で特別抽選結果が外れである場合には、他の遊技者に対しても高設定を使用していることをホールがアピールしやすくなる。
In addition, when the display time of the
[12-8.時短状態における設定示唆演出]
以下、遊技状態時短状態である場合において選択される変動パターンについて説明する。図149(A)は、遊技状態が時短状態であり、かつ特別抽選の結果が外れである場合に選択される変動パターンテーブルの一例である。図149(B)は、遊技状態が時短状態であり、かつ特別抽選の結果が大当りである場合に選択される変動パターンテーブルの一例である。
[12-8. Setting suggestion production in time saving state]
Hereinafter, the variation pattern selected in the game state time saving state will be described. FIG. 149(A) is an example of a variation pattern table that is selected when the gaming state is the time saving state and the result of the special lottery is out. FIG. 149(B) is an example of a variation pattern table selected when the gaming state is the time saving state and the result of the special lottery is a big hit.
図149(A)の例では、設定が高いほど、リーチなし外れ時における、外れ変動パターン3の振り分けが大きく、かつ外れ変動パターン2の振り分けが小さくなっている。また、外れ変動パターン2の変動時間は、外れ変動パターン3の変動時間より短い。例えば、設定が高いほど大当り当選確率が高い場合には、仮に全ての設定において各変動パターンの振り分けが同一であるとすると、設定が高いほど短時間で大当りに当選しやすくなり
、単位時間あたりの遊技球の払い出し数が増加し、ホールの負担につながるおそれがある。
In the example of FIG. 149(A), the higher the setting, the larger the allocation of the
しかし図149(A)の例のように、設定が高いほど、変動時間の長い変動パターンの振り分けが多いことにより、各設定における単位時間あたりの大当りによる遊技球の払い出し数を均等にすることができる。また、設定が高いほど、短縮変動を含む変動パターンの中では変動時間が長い外れ変動パターン3、の選択率が高くなるため、外れ変動パターン3は高設定を示唆する変動パターンとしても機能することができる。
However, as shown in the example of FIG. 149(A), the higher the setting, the more variation patterns with longer variation times are distributed, so that the number of game balls paid out by the big hit per unit time in each setting can be equalized. can. In addition, the higher the setting, the higher the selection rate of the deviating
また、リーチあり外れ時においても、同様に、設定が高いほど、変動時間の長い外れ変動パターン11の振り分けが大きくなり、かつ変動時間の短い外れ変動パターン12の振り分けが小さくなっている。また、大当り当選時においても、同様に、設定が高いほど、変動時間の長い当り変動パターン2の振り分けが大きくなり、かつ変動時間の短い当り変動パターン3の振り分けが小さくなっている。
Similarly, when the reach is not reached, the higher the setting, the larger the allocation of the
上述したように、例えば、設定が高いほど大当り当選確率が高い場合には、仮に全ての設定において各変動パターンの振り分けが同一であるとすると、設定が高いほど短時間で大当りに当選しやすくなる、換言すれば、設定が低いほど大当りに当選するために長時間を要し、大当りに当選するまでに発射する遊技球の数が多くなる。例えば、設定が低いほど変動時間の長い変動パターンの振り分けが大きくなり、かつ変動時間の短い変動パターンの選択率が小さくなれば、変動中に遊技球の発射を中止する遊技者であれば、各設定における単位時間あたりの遊技球の発射数を均等にすることができる。 As described above, for example, if the higher the setting, the higher the probability of winning a big hit, and if the distribution of each variation pattern is the same for all settings, the higher the setting, the easier it is to win a big win in a short time. In other words, the lower the setting, the longer it takes to win the big win, and the more game balls are shot until the big win is won. For example, the lower the setting, the greater the distribution of variation patterns with a long variation time, and the lower the selection rate of variation patterns with a short variation time. It is possible to equalize the number of shots of game balls per unit time in the setting.
なお、本章で述べた各種設定示唆演出において設定が示唆されるタイミングにおいて、所定の効果音が出力されたり、所定の発光演出が実行されたりしてもよい。なお、当該所定の効果音及び当該所定の発光演出は、設定示唆演出時のみに実行される専用のものであってもよい。また、特に高設定や最高設定が確定する設定示唆演出においては、当該設定示唆演出のみで実行される、所定の効果音の出力や、所定の発光演出が実行されるとよい。 It should be noted that a predetermined sound effect may be output or a predetermined light emission effect may be executed at the timing when the setting is suggested in the various setting suggestion effects described in this chapter. Note that the predetermined sound effect and the predetermined light emission effect may be dedicated ones that are executed only during the setting suggestion effect. In addition, especially in the setting suggestion effect in which the high setting and the maximum setting are confirmed, it is preferable that a predetermined sound effect output and a predetermined light emission effect, which are executed only in the setting suggestion effect, are executed.
なお、高設定や最高設定が確定する、又は可能性が高いことを示唆する演出が実行される変動パターンの振り分けは、他の変動パターンの振り分けと比較して極めて低いことが望ましい。当該変動パターンの振り分けが高いと、遊技者が、少ない遊技時間しか遊技していないにも関わらず、高設定示唆演出や最高設定示唆演出が実行されないと、期待感を失い、ひいては早期に遊技を中止するおそれがあるからである。 It should be noted that it is desirable that the distribution of the variation pattern in which an effect suggesting that the high setting or the highest setting is confirmed or executed with a high possibility is extremely low compared to the distribution of other variation patterns. When the distribution of the variation pattern is high, the player loses expectations and ends up playing the game early if the high setting suggesting effect or the highest setting suggesting effect is not executed even though the player is playing for only a short playing time. This is because there is a risk of discontinuation.
また、低設定や最低設定が確定する、又は可能性が高いことを示唆する演出が実行される変動パターンの振り分けは、他の変動パターンの振り分けと比較して極めて低いことが望ましい。当該変動パターンの振り分けが高いと、低設定示唆演出や最低設定示唆演出が頻繁に実行されてしまうことにより、遊技者が期待感を失い、ひいては早期に遊技を中止するおそれがあるからである。 In addition, it is desirable that the distribution of variation patterns in which an effect suggesting that the low setting or the lowest setting is confirmed or executed with a high possibility is extremely low compared to the distribution of other variation patterns. This is because, if the distribution of the variation pattern is high, the low setting suggesting performance and the minimum setting suggesting performance are frequently executed, so that the player loses his sense of anticipation and eventually stops playing the game at an early stage.
また、高設定、低設定、最高設定、奇数設定、偶数設定等の設定のグループを示唆する設定示唆演出について説明したが、設定示唆演出における設定のグループはこれらに限られない。1以上の設定からなる任意のグループについての設定示唆演出が実行されてもよい。例えば、設定1、2を低設定、設定3、4を中間設定、設定5、6を高設定としてグループ分けされていてもよいし、設定5のみからなるグループがあってもよい。
Also, the setting suggestion effect that suggests a setting group such as high setting, low setting, maximum setting, odd setting, and even setting has been described, but the setting group in the setting suggesting effect is not limited to these. A setting suggestion effect may be executed for any group consisting of one or more settings. For example,
[12-9.設定機能を有するパチンコ機の他の形態]
図150は、主制御基板1310の実装例を示す図である。なお、本図において、主制
御基板ボックス1320の構成を実線で示し、主制御基板ボックス1320内の構成を点線で示す。
[12-9. Other form of pachinko machine with setting function]
FIG. 150 is a diagram showing a mounting example of the
前述した説明では、設定基板970が払出制御基板951と接続されており、払出制御部952が各スイッチの操作状態を取得し、設定表示器974の表示を制御していたが、以後の説明では、設定基板970は主制御基板1310と接続されており、主制御MPU1311が各スイッチの操作状態を取得し、設定表示器974の表示を制御する。
In the above description, the setting
図150(A)は、本実装例の主制御基板ボックス1320を示す。主制御基板ボックス1320は、一度閉めたら破壊せずに開けることができない構造で封印可能に主制御基板1310を収容する透明の樹脂によって構成される。主制御基板ボックス1320には、表示スイッチ1318を操作するための穴1318A、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作するための穴954A、及び設定キー971を操作するための穴971Aが設けられる。
FIG. 150(A) shows the main
図150(B)は、(A)に示す主制御基板ボックス1320に、主制御基板1310及び設定基板970を収容した状態を示す。図150(B)に示す例では、主制御基板1310上には、主制御MPU1311やドライバ回路(図示省略)の他、ベース表示器1317、表示スイッチ1318及びRAMクリアスイッチ954が実装されている。なお、RAMクリアスイッチ954は主制御基板1310に実装されずに、他の制御基板(例えば、払出制御基板951や電源基板)に実装されてもよい。この場合、主制御基板ボックス1320には穴954Aを設けない。
FIG. 150(B) shows a state in which the
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、主制御基板ボックス1320内にRAMクリアの契機となる二つの操作部(RAMクリアスイッチ954、設定キー971)が設けられている。なお、後述するように、RAMクリアスイッチ954のみの操作時と、設定キー971が操作された場合とは、データが消去される主制御RAM1312の記憶領域が異なる。
In the
設定基板970は、主制御基板1310に近接して設けられ、設定基板970と主制御基板1310とは、信号が伝達可能なように電気的に接続される。設定基板970と主制御基板1310との接続は、コネクタによって基板間を直接接続したり、電線によって接続してもよい。設定基板970上には、パチンコ機1の動作モードを設定変更モードや設定確認モードに変更するための設定キー971、及び設定又は選択された設定値を表示する設定表示器974が実装される。なお、設定値を変更するための設定変更スイッチ972及び変更された設定値を確定入力するための設定確定スイッチ973が設定基板970上に実装されてもよい。
The setting
設定基板970に設けられる各種スイッチ971、972、973の出力は、主制御基板1310に送られ、主制御MPU1311のポートに入力される。
Outputs of
また、主制御基板1310と設定基板970とがシリアル通信を行い、設定表示器974のドライバ回路を設定基板970に実装してもよい。
Also, the
主制御基板ボックス1320は、パチンコ機1の裏面側に配置されるので、設定基板970上の設定表示器974はパチンコ機1の裏面側から見ることができる位置に実装される。
Since the main
主制御基板1310は、初期化処理(図21、図22)において設定基板970を認証してもよい。例えば、パチンコ機の製造者毎の認証用コードを設定基板970に設定し、主制御基板1310が設定基板970に設定された認証用コードを読み出して照合する。
そして、設定基板970が認証できなければ、パチンコ機1で遊技を開始できないようにする。つまり、遊技領域5aに向けて遊技球を発射可能であるが、入賞口に入賞しても賞球は払い出されず、変動表示ゲームの実行されない状態となる。認証用コードは、パチンコ機の機種毎に設定してもよいし、パチンコ機毎のシリアル番号を設定してもよい。認証用コードの設定方法は、例えば、設定基板970に設けたDIPスイッチ、ジャンパ線、ジャンパピン、パターンの短絡などで認証用コードを設定したり、認証用コードが設定されたロジック回路(例えば、小容量のFPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array))を
設定基板970に搭載してもよい。
The
If the setting
また、主制御基板ボックス1320内に実装されている基板が、設定基板970なのかダミー基板979なのかを、主制御基板1310(主制御MPU1311)が識別可能としてもよい。例えば、設定基板970とダミー基板979とが異なる信号を主制御基板1310に出力することによって、主制御MPU1311が、接続されている基板が設定基板970とダミー基板979とのいずれであるかを認識する。具体的には、設定基板970は+5Vを出力し、ダミー基板979は0V(グランドレベル)を出力する。設定基板970及びダミー基板979からの信号は、主制御基板1310のインターフェイス回路1331回路の特定のポートに入力される。主制御MPU1311は、該ポートへの入力信号によって、接続されている基板を判定する。
Also, the main control board 1310 (main control MPU 1311) may be able to identify whether the board mounted in the main
このように、製造者毎(機種毎)に設定基板970のコードを変えることによって、誤った設定基板970の主制御基板ボックス1320への実装を防止できる。また、設定基板970上のロジック回路に認証用コードを設定することによって、設定基板970の不正な交換を防止できる。
In this way, by changing the code of the setting
図150(C)は、(A)に示す主制御基板ボックス1320に、主制御基板1310及びダミー基板979を収容した状態を示す。
FIG. 150(C) shows a state in which the
前述したように、近年、パチンコ機1は遊技性能の設定機能を有するものがある。この設定機能は、特別図柄変動表示ゲームにおける大当り確率など遊技者が獲得する賞球に関するパチンコ機の性能を変更でき、設定機能によって、ホールの営業方針に沿ってパチンコ機1の性能を変更できる。一方、設定機能を有さない従来のパチンコ機で十分であり、設定機能が不要だと思うホールもある。このため、パチンコ機の製造者は、設定機能を有さないパチンコ機と、設定機能を有するパチンコ機との両方を設計、生産する必要があり、パチンコ機の仕様を共通化して、二種類のパチンコ機の設計、生産を効率的に行うことが求められている。
As described above, in recent years, some
このため、設定機能を有さないパチンコ機1においては、設定基板970の実装スペースにダミー基板979を実装して、設定基板970が実装されている場合と同様に、パチンコ機1が生産できるようにする。また、設定機能を有さないパチンコ機と、設定機能を有するパチンコ機とで、主制御基板1310を共通化できる。
For this reason, in the
ダミー基板979は、設定基板970上に実装される設定キー971や設定表示器974などのデバイスが実装されていないが、これらのデバイスを実装するためのパターンを有してもよい。すなわち、ダミー基板979上にはデバイスを実装するためのパターンが設けられているが、当該パターン上にデバイスは実装されていない。
ダミー基板979は、プリント基板によって構成されなくても、設定基板970と同じ位置で主制御基板ボックス1320に取り付け可能な部材(例えば、樹脂ケースで構成されたユニット)でもよい。
The
また、設定表示器974のドライバ回路は主制御基板1310に実装されることから、設定表示器974のドライバ回路の出力は、ダミー基板979においては、オープンでもグランドでもなく、ダミー抵抗によって終端されるとよい。これによってドライバ回路の過電流による破損を防止できる。また、主制御基板1310と設定基板970とがシリアル通信を行う場合、ダミー基板979は、主制御基板1310とのシリアル通信を終端するとよい。
Also, since the driver circuit of the setting
ダミー基板979が実装される場合、主制御基板ボックス1320には穴971Aを設けない。なお、穴971Aを塞ぐように移動可能な小扉を、主制御基板ボックス1320の内側からは操作可能で、外側からは操作不可能に主制御基板ボックス1320に設けることによって、設定機能を有さないパチンコ機と、設定機能を有するパチンコ機と、主制御基板ボックス1320を共通化してもよい。
When the
なお、後述するダミー基板979にも、主制御基板1310が認証するための、認証用コードを設定してもよい。また、ダミー基板979は、主制御基板1310による認証を不要とし、認証用コードを設定しなくてもよい。主制御基板1310とダミー基板979とがシリアル通信を行い、主制御基板1310がダミー基板を認証してもよい。
An authentication code for authentication by the
以上に説明した設定基板970に実装される操作手段のバリエーションを纏めると以下の通りとなる。
The variations of the operating means mounted on the setting
(1)設定変更スイッチ972有り、設定確定スイッチ973有り
この場合、設定キー971に鍵975を挿入し、設定位置に回した状態で(さらに、RAMクリアスイッチ954を押した状態で)、パチンコ機1の電源スイッチを操作して電源を投入する。そして、設定変更スイッチ972を操作して設定すべき設定値を選択した後、設定確定スイッチ973を操作する。
(1) With a setting
(2)設定変更スイッチ972有り、設定確定スイッチ973無し
この場合、設定キー971に鍵975を挿入し、設定位置に回した状態で(さらに、RAMクリアスイッチ954を押した状態で)、パチンコ機1の電源スイッチを操作して電源を投入する。そして、設定変更スイッチ972を操作して設定すべき設定値を選択した後、設定キー971を通常位置に戻す。
(2) With the
(3)設定変更スイッチ972無し、設定確定スイッチ973有り
この場合、設定キー971に鍵975を挿入し、設定位置に回した状態で(さらに、RAMクリアスイッチ954を押した状態で)、パチンコ機1の電源スイッチを操作して電源を投入する。そして、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作して設定すべき設定値を選択した後、設定確定スイッチ973を操作する。なお、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作に代えて、設定キー971を右に回して、設定すべき設定値を選択してもよい。
(3) Without setting
(4)設定変更スイッチ972無し、設定確定スイッチ973無し
この場合、設定キー971に鍵975を挿入し、設定位置に回した状態で(さらに、RAMクリアスイッチ954を押した状態で)、パチンコ機1の電源スイッチを操作して電源を投入する。そして、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作して設定すべき設定値を選択した後、設定キー971を通常位置に戻す。なお、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作に代えて、設定キー971を右に回して、設定すべき設定値を選択してもよい。
(4) Without setting
図151、図152は、主制御基板1310の別の実装例を示す図である。なお、本図において、主制御基板ボックス1320の構成を実線で示し、主制御基板ボックス1320内の構成を点線で示す。
151 and 152 are diagrams showing another mounting example of the
図151、図152に示す実装例では、主制御基板ボックス1320に小扉1321が設けられている点が、図150に示す実装例と異なる。
The mounting example shown in FIGS. 151 and 152 differs from the mounting example shown in FIG. 150 in that a main
図151(A)は、本実装例の主制御基板ボックス1320を示す。主制御基板ボックス1320は、前述と同様に、一度閉めたら破壊せずに開けることができない構造で封印可能に主制御基板1310を収容する透明の樹脂によって構成される。主制御基板ボックス1320には、表示スイッチ1318を操作するための穴1318A、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作するための穴954A、及びパチンコ機1の動作モードを設定変更モードに変更するための設定モードスイッチ976を操作するための穴976Aが設けられる。
FIG. 151(A) shows the main
穴976Aは、通常時は、小扉1321によって覆われている。小扉1321には鍵ユニット1322が設けられており、鍵ユニット1322の鍵穴に鍵975を挿入して操作することによって主制御基板ボックス1320から小扉1321を開放し、穴976Aが露出し、設定モードスイッチ976を操作可能となる。
The
図152(A)に示すように、鍵975が挿抜可能な通常状態では、鍵ユニット1322から閂1323が最大突出位置にあり、閂1323が受座1324に挿入されて、閂1323と受座1324とが係合して、小扉1321は閉鎖位置に固定される。一方、図152(B)に示すように、鍵975を鍵穴に挿入して回転操作をすると、閂1323が最大突出位置から後退して、閂1323と受座1324との係合が解除されて、蝶番1325を軸として、小扉1321が開放可能となる。小扉1321が開放状態(図152(B))では、穴976Aが露出して、設定モードスイッチ976が操作可能となる。
As shown in FIG. 152(A), in a normal state in which the
図153は、主制御基板1310のさらに別の実装例を示す図である。図153に示す実装例では、パチンコ機1の裏面側を覆う裏カバー980に鍵ユニット1322が設けられている。すなわち、鍵ユニット1322の鍵穴に鍵975を挿入して操作することによって裏カバー980を本体枠ベース600から開放し、主制御基板ボックス1320(設定基板970に設けられた設定モードスイッチ976)を操作可能となる。
FIG. 153 is a diagram showing yet another mounting example of the
すなわち、鍵975が挿抜可能な通常状態では、裏カバー980が本体枠ベース600の裏面側を閉鎖して固定されており、主制御基板ボックス1320は裏カバー980に収容された状態となる。一方、鍵975を鍵穴に挿入して回転操作をすると、裏カバー980を本体枠ベース600から開放可能となり、裏カバー980の内部に収容されている主制御基板ボックス1320が裏面側に露出し、設定モードスイッチ976が操作可能となる。
That is, in a normal state in which the
裏カバー980に鍵ユニット1322を設ける場合、主制御基板ボックス1320(主制御基板1310)は、図151(C)に示す構成でよい。具体的には、主制御基板ボックス1320は、一度閉めたら破壊せずに開けることができない構造で封印可能に主制御基板1310を収容する透明の樹脂によって構成される。主制御基板ボックス1320には、表示スイッチ1318を操作するための穴1318A、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作するための穴954A及びパチンコ機1の動作モードを設定変更モードに変更するための設定モードスイッチ976を操作するための穴976Aが設けられる。主制御基板ボックス1320には、主制御基板1310及び設定基板970を収容される。主制御基板1310上には、主制御MPUやドライバ回路(図示省略)の他、ベース表示器1317、表示スイッチ1318及びRAMクリアスイッチ954が実装される。なお、RAMクリアスイッチ954は主制御基板1310に実装されずに、他の制御基板(例えば、払出制御基板951や電源基板)に実装されてもよい。この場合、主制御基板ボックス13
20には穴954Aを設けない。
When the
20 is not provided with
設定基板970は、主制御基板1310に近接して設けられ、設定基板970と主制御基板1310とは、信号は伝達可能なように電気的に接続される。設定基板970と主制御基板1310との接続は、コネクタによって基板間を直接接続したり、電線によって接続してもよい。設定基板970上には、パチンコ機1の動作モードを設定変更モードに変更するための設定モードスイッチ976、及び設定又は選択された設定値を表示する設定表示器974が実装される。なお、設定値を変更するための設定変更スイッチ972及び変更された設定値を確定入力するための設定確定スイッチ973が設定基板970上に実装されてもよい。
The
[12-10.設定変更処理の詳細]
図154は、初期化処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。図154に示す初期化処理は、図101で前述した初期化処理と比較し、設定キー971が操作されている場合にRAMクリア処理を行う点(ステップS17、ステップS30)が相違する。なお、図21、図101で前述した初期化処理と同じステップには同じ符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。
[12-10. Details of setting change processing]
FIG. 154 is a flowchart illustrating an example of initialization processing. The initialization process shown in FIG. 154 differs from the initialization process described above with reference to FIG. 101 in that RAM clear processing is performed (steps S17 and S30) when the
パチンコ機1に電源が投入されると、主制御基板1310の主制御MPU1311が主制御プログラムを実行することによって初期化処理を行う。主制御MPU1311は、まず、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたRAM1312のプロテクトを書き込み許可に設定し、RAM1312への書き込みができる状態にする(ステップS10)。続いて、主制御MPU1311は、内蔵されたウォッチドッグタイマを起動し(ステップS12)、所定のウェイト時間(サブ基板(周辺制御基板1510など)が起動するために必要な時間)が経過したかを判定する(ステップS16)。所定のウェイト時間が経過していれば、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されているかを判定する(ステップS18)。
When the
なお、RAMクリアスイッチ954は、電源投入後直ちに(例えばステップS12の前に)検出して、検出結果を所定のレジスタに格納しておき、格納した値をステップS18で判定するとよい。電源投入後、直ぐにRAMクリアスイッチ954を検出することによって、電源投入後短時間しかRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されなくても、確実にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を検出できる。
It should be noted that the RAM
RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されている場合、設定キー971が操作されており、その出力がオンであるかを判定する(ステップS17)。設定キー971が操作されていない場合は、通常のRAMクリア操作なので、ステップS30に進み、内蔵RAM1312の所定領域を初期化する。一方、設定キー971が操作されている場合、すなわち、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954との両方が操作された状態で電源が投入された場合、設定変更モードに移行する。すなわち、設定変更モードを開始するために二つのスイッチの操作と電源スイッチの操作が必要なので、誤って設定変更モードを開始する誤操作を防止できる。
If the RAM
設定変更モードでは、まず、設定値を表示する(ステップS60)。具体的には、主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312から現在の設定値を読み出して設定表示器974に表示するためのデータを生成する。そして、セキュリティ信号を出力する(ステップS61)。具体的には、主制御MPU1311は、セキュリティ信号を出力するためのデータを生成する。セキュリティ信号は、パチンコ機1が異常を検出した場合に外部端子板784から出力される信号であるが、遊技中にパチンコ機1を設定変更モードにすることは極めて希であり、不正行為の可能性があることから、営業時間中に設定変更モードに移行した場合にはホールコンピュータに通知すべきだからである。
In the setting change mode, first, the setting values are displayed (step S60). Specifically, the
セキュリティ信号は、設定変更モードの開始から所定時間だけ出力しても、設定変更モードの開始から終了までの間に出力しても、設定変更モードの開始から設定変更モードの終了後の所定期間まで出力してもよい。設定変更モードの終了後の所定期間までセキュリティ信号を出力することによって、異常を検出できる期間が長くなり、セキュリティ性をより高くできる。 Whether the security signal is output for a predetermined period from the start of the setting change mode, or is output from the start to the end of the setting change mode, or is output from the start of the setting change mode to the predetermined period after the end of the setting change mode. may be output. By outputting the security signal for a predetermined period after the end of the setting change mode, the period during which an abnormality can be detected becomes longer, and the security can be further enhanced.
その後、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更スイッチ972の操作の有無によって、設定変更操作がされたかを判定し(ステップS62)、設定変更スイッチ972の操作に従って設定値を変更して、主制御RAM1312に書き込む(ステップS63)。例えば、設定変更スイッチ972が押しボタンスイッチで構成される場合、設定変更スイッチ972が1回押されると、設定値を1段階変更する。また、設定キー971が設定変更スイッチ972を兼ねる場合、設定キー971が1回右に回されると、設定値を1段階変更する。そして、主制御MPU1311は、変更後の設定値を設定表示器974に表示するためのデータを生成する(ステップS64)。
After that, the
その後、設定変更モードを終了して設定値を確定するかを判定する(ステップS65)。具体的には、主制御MPU1311が設定確定スイッチ973の操作を検出すると、設定変更モードを終了し、ステップS30に進む。また、設定キー971を通常位置に戻す操作によって設定変更モードを終了してもよい。また、パチンコ機1に設けられた他のスイッチやセンサの動作を契機に設定変更モードを終了してもよい。
After that, it is determined whether or not to end the setting change mode and fix the setting value (step S65). Specifically, when the
前述した処理では、設定変更モード終了後、又は、ステップS17で設定キーがオンではないと判定された場合、ステップS30に進んだが、ステップS20に進んでもよい。この場合、設定変更モード終了後に、停電フラグが設定されているかを判定し(ステップS20)、チェックサムが一致したかを判定し(ステップS22)、停電フラグが設定されておらず、かつ、チェックサムが一致しない場合に、内蔵RAM1312の所定領域を初期化する。なお、ステップS17で設定キーがオンではないと判定された場合はステップS30に進む。
In the above-described process, after the setting change mode ends, or when it is determined in step S17 that the setting key is not on, the process proceeds to step S30, but the process may proceed to step S20. In this case, after the setting change mode ends, it is determined whether the power failure flag is set (step S20), whether the checksum matches (step S22), whether the power failure flag is not set, and the check If the sums do not match, a predetermined area of the built-in
設定変更モードの終了後、ステップS30において、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータのうち設定値のデータとベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)と遊技状態(例えば、確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータを消去し、ステップS24に進む。なお、遊技状態のデータは残さずに消去してもよい。この場合、設定変更操作後において消去されるRAM領域によって消去される記憶領域とRAMクリア操作によって消去される記憶領域とは同じになる。
After the setting change mode ends, in step S30, among the data backed up in the work area of the built-in
一方、設定変更モードを終了する操作を検出しなければ、ステップS62に戻り、さらに、設定変更操作を検出する。 On the other hand, if an operation to end the setting change mode is not detected, the process returns to step S62 and further detects a setting change operation.
また、ステップS17において、設定キー971の操作が検出されなければ、ステップS30において、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータのうち設定値のデータとベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータを消去し、ステップS24に進む。
In step S17, if the operation of the setting
また、ステップS18で、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作が検出されなければ、主制御MPU1311は、内蔵RAM1312にバックアップされているデータを消去せず、停電フラグが設定されているかを判定する(ステップS20)。
Also, in step S18, if the operation of the RAM
その結果、停電フラグが設定されていなければ、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、主制御MPU1311は、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータ(ベース算出用領域13128以外)を消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、停電フラグが設定されていれば、主制御MPU1311は、停電フラグをクリアし、前回の電源遮断時に計算されたチェックサムを用いて内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバックアップされているデータから算出したチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとを比較(検証)する(ステップS22)。
As a result, if the power failure flag is not set, the data in the work area of the built-in
その結果、バックアップデータから算出されたチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとが一致しなければ、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、主制御MPU1311は、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータ(ベース算出用領域13128以外)を消去し(ステップS30)、ステップS24に進む。一方、バックアップデータから算出されたチェックサムとステップS48で記憶したチェックサムとが一致すれば、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアのデータは正しいので、ワークエリアにバックアップされているデータを消去せず、ステップS24に進む。
As a result, if the checksum calculated from the backup data does not match the checksum stored in step S48, the data in the work area of the built-in
ステップS24では、主制御MPU1311は、チェックコードを用いてベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)が正常かを判定する。異常であると判定された場合、ベース算出用ワークエリアのデータは正しくない恐れがあるので、主制御MPU1311は、ベース算出用ワークエリアに格納されているデータを消去する(ステップS26)。
In step S24, the
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、RAM1312の少なくとも一部の領域が初期化されるケースとして、設定キー971の操作(ステップS17)と、RAMクリアスイッチのみの操作(ステップS18)と、停電フラグがセットされていない停電フラグ異常(ステップS20)と、RAMのチェックサムが一致しないRAM異常(ステップS22)と、ベース算出用ワークの異常(ステップS24)とがある。これらのうち、図示したように、電源投入時に設定キー971の操作が検出された場合は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)のうち、設定値と遊技状態(例えば、確変状態、時短状態、特別図柄や普通図柄の保留記憶、賞球に関する情報)のデータを残し、それ以外のデータをクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)はクリアしない。電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作が検出されたが、設定キー971の操作が検出されない場合、及び停電フラグ異常、RAM異常の場合は、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)をクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128(ベース算出用ワーク領域とベース算出用スタック領域を含む)はクリアしない。また、ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合、ベース算出用領域13128(遊技制御領域外)をクリアし、遊技制御用領域13126はクリアしない。
In the
なお、図示したものと異なり、停電フラグ異常、RAM異常、ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合は、RAM1312に格納されたデータの正当性が保証されないことから、遊技制御用領域13126及びベース算出用領域13128を含む全RAM領域をクリアしてもよい。ベース算出用ワーク異常の場合に全RAM領域をクリアすると、遊技状態を示すデータが消失して正常な処理が実行不可能になるメモリ構成である場合、ベース算出用ワーク領域とベース算出用スタック領域のみを初期化するとよい。また、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチの操作が検出された場合は、前述と同様に、遊技制御用領域13126(遊技用ワーク領域と遊技用スタック領域を含む)をクリアし、ベース算出用領域13128はクリアしなくてよい。
It should be noted that, unlike the illustrated one, in the case of power failure flag abnormality, RAM abnormality, base calculation work abnormality, since the validity of the data stored in the
このように、本実施形態のパチンコ機1では、内蔵RAM1312のワークエリアにバ
ックアップされているデータを、データの種別毎に(遊技制御用領域13126(設定値、遊技状態のデータ)、ベース算出用領域13128)異なる条件で消去する。すなわち、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって、設定値以外のバックアップされた遊技制御用領域13126は消去され、設定値とベース算出用領域13128は消去されない。RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって設定値が消去されると、RAMクリア操作毎に設定値を再設定する必要があり、ホールのパチンコ機1のメンテナンスが煩雑になるからである。このため、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によって、設定値が消去されないようにしている。
Thus, in the
ステップS28より後の処理は、必要に応じて、図22と図102とのいずれかを採用すればよい。図22と図102との違いは、電源遮断時にベース算出用ワークエリア(ベース算出用領域13128)のデータからチェックコード算出して格納する処理(ステップS50、S52)の有無である。 Either FIG. 22 or FIG. 102 may be employed for the processing after step S28 as required. The difference between FIG. 22 and FIG. 102 is the presence or absence of processing (steps S50 and S52) for calculating and storing a check code from the data in the base calculation work area (base calculation area 13128) when the power is turned off.
以上に説明した初期化処理では設定確認処理を実行せず、後述するタイマ割込み処理から呼び出される設定確認処理で実行するものとしたが(図155、図156)、初期化処理で設定確認処理を実行してもよい。初期化処理で設定確認処理を実行することによって、電源投入時のみに設定確認を許可でき、パチンコ機1の動作中の不用意な操作による設定値の確認を防止できる。
In the initialization process described above, the setting confirmation process is not executed, and is executed in the setting confirmation process called from the timer interrupt process (see FIGS. 155 and 156). may be executed. By executing the setting confirmation process in the initialization process, the setting confirmation can be permitted only when the power is turned on, and the confirmation of the setting value by careless operation during operation of the
この場合、設定キー971とは別に、設定確認用の操作部(例えば、押しボタンスイッチ)を設け(設定変更スイッチ972が設定確認用の操作部の機能を有してもよい)、電源投入時に当該設定確認用操作部が操作されている場合には、主制御RAM1312から現在の設定値を読み出して設定表示器974に表示するためのデータを生成して、設定値を設定表示器974に表示するとよい。この場合も、設定値の表示に伴いセキュリティ信号を出力するとよい。
In this case, an operation unit (for example, a push button switch) for setting confirmation is provided separately from the setting key 971 (the setting
本実施例のパチンコ機1の主制御基板1310は、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されても直ちにRAMクリア処理を実行しない場合があることになる。具体的には、設定キー971をオンに操作した状態で、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作して電源を投入すると、設定変更モードの終了後に主制御RAMがクリアされる(ステップS30)。すなわち、主制御MPU1311がRAMクリア処理を保留して、所定の条件が満たされた(設定変更モードの終了)後にRAMクリア処理を実行する。設定変更モード中は、主制御MPU1311がRAMクリア処理を実行することを記憶するように制御していると言える。一方、設定キー971を操作せずに、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作して電源を投入すると、設定変更モードを開始せずに主制御RAMがクリアされる(ステップS30)。
The
以上、主制御RAM1312のクリア(初期化)について詳しく述べたが、次に払出制御基板951に搭載された払出制御部952のRAMのクリアについて説明する。
The clearing (initialization) of the
設定変更モードの後、ステップS30で主制御RAM1312をクリアするが、これと共に払出制御部のRAMをクリアしてもよい。また、払出制御部952のRAMをクリアしなくてもよい。さらに、操作によって払出制御部のRAMをクリアするかを切り替えてもよい。例えば、設定キー971をオンに操作した状態で、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作しながら電源を投入すると主制御RAM1312と払出制御部952のRAMをクリアし、設定キー971をオンに操作した状態で、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作しないで電源を投入すると主制御RAM1312をクリアし、払出制御部952のRAMをクリアしない。このように、操作方法を変えることによって、主制御RAM1312の一部の領域をクリアし、払出制御部952のRAMはクリアされない処理を実行できる。
After the setting change mode, the
また、主制御RAM1312と払出制御部952のRAMをクリアする場合、設定キー971の操作の有無によって、主制御RAM1312がクリアされるタイミングと払出制御部952のRAMがクリアされるタイミングとにずれが生じることがある。すなわち、設定キー971がオンに操作された状態で、RAMクリアスイッチ954を操作して電源を投入した場合、設定変更モードの終了後に主制御RAM1312がクリアされる(ステップS30)。一方、払出制御部952は、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を検出すると、直ちにRAMをクリアする。このため、条件(操作)によっては、払出制御部952のRAMはクリアされるが、主制御RAM1312がクリアされていない状態が生じ得る。
Also, when clearing the RAM of the
また、RAMクリアスイッチ954を主制御基板1310に設ける場合だけでなく、払出制御基板951や電源基板931に設けたパチンコ機1においても、設定値を変更する際にRAMクリアスイッチ954を操作しながら電源を投入すると払出制御部952のRAMがクリアされるとよい。すなわち、主制御基板1310からのRAMクリアコマンドによって払出制御部952がRAMクリアするのではなく、電源投入時に払出制御部952がRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルを検出して、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されているかを判定し、払出制御部952のRAMをクリアするかを判定する。払出制御基板951にRAMクリアスイッチを設けると、枠側の制御プログラムを変えることなく、多様な機種に対応できる効果がある。
In addition, not only when the RAM
[12-11.設定確認処理の詳細]
図155は、本実施例のパチンコ機のタイマ割込み処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
[12-11. Details of setting confirmation process]
FIG. 155 is a flowchart showing an example of timer interrupt processing of the pachinko machine of this embodiment.
図155に示すタイマ割込み処理は、図23で前述したタイマ割込み処理と比較し、ステップS81の役物比率算出用領域更新処理に代えてベース算出処理(ステップS801)が設けられ、ステップS89の役物比率算出・表示処理が削除される。また、パチンコ機1の遊技性能(例えば、条件装置の作動割合)を示す設定値を表示するための設定確認処理(ステップS802)が追加される。なお、図23や図104で前述したタイマ割込み処理と同じステップには同じ符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。 The timer interrupt process shown in FIG. 155 is different from the timer interrupt process described above with reference to FIG. Object ratio calculation/display processing is deleted. In addition, a setting confirmation process (step S802) for displaying a set value indicating the game performance of the pachinko machine 1 (for example, the operating ratio of the condition device) is added. The same steps as those of the timer interrupt process described above in FIGS. 23 and 104 are denoted by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
タイマ割込み処理が開始されると、主制御MPU1311は、主制御プログラムを実行することによって、まず、プログラムステータスワードのRBS(レジスタバンク選択フラグ)に1を設定し、レジスタを切り替える(ステップS70)。
When timer interrupt processing is started, the
次に、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入力処理(ステップS74)、タイマ更新処理(ステップS76)、乱数更新処理1(ステップS78)、賞球制御処理を実行する(ステップS80)。
Next, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、現在の遊技状態を参照して、遊技価値として払い出される賞球数を現在の遊技状態に対応した領域に加算して、主制御内蔵RAM1312のベース算出用領域13128(図103参照)を更新し、ベース値を計算する(ステップS801、ベース算出処理の詳細は図105及び図106を参照)。ベース算出処理(ステップS801)は、賞球制御処理(ステップS80)の後であれば、どの順序で実行してもよいが、タイマ割込み毎に確実に実行するために、早い順序で実行するとよい。
Subsequently, the
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、枠コマンド受信処理(ステップS82)、不正行為検出処理(ステップS84)、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理(ステップS86)、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理(ステップS88)を実行する。
Subsequently, the
その後、パチンコ機1の遊技性能を示す設定値を表示するための設定確認処理(ステップS802)を実行する。設定確認処理では、ホールの従業員が所定の操作をすることによって、現在の設定値を設定表示器974に表示する。設定確認処理の詳細は図156を用いて後述する。
After that, a setting confirmation process (step S802) for displaying the setting value indicating the game performance of the
続いて、出力データ設定処理(ステップS90)、周辺制御基板コマンド送信処理(ステップS92)を実行する。 Subsequently, output data setting processing (step S90) and peripheral control board command transmission processing (step S92) are executed.
最後に、主制御MPU1311は、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットする(ステップS96)。また、最後に、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンクを切り替える(復帰する)。以上の処理が終了すると、タイマ割込み処理を終了し、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。
Finally, the
図156は、本実施例のパチンコ機の設定確認処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。設定確認処理は、タイマ割込み処理(図155)のステップS802から呼び出されて実行される。 FIG. 156 is a flow chart showing an example of the pachinko machine setting confirmation process of the present embodiment. The setting confirmation process is called from step S802 of the timer interrupt process (FIG. 155) and executed.
設定確認処理では、まず、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認操作中であるかを判定する(ステップS8061)。具体的には、設定キー971が操作されているかを判定する。設定キー971は、電源投入時に操作されていると設定変更モードへの移行の契機となり(図154のステップS17)、動作中に操作されると設定確認操作となり、現在の設定を表示できる。
In the setting confirmation process, first, the
設定キー971の操作を検出しなければ、設定キー971が通常位置に戻されたので、設定値を表示しないためのデータを生成し、設定値を非表示にする(ステップS8065)。
If no operation of the setting
一方、設定キー971の操作を検出すると、設定表示条件を満たすかを判定する(ステップS8062)。
On the other hand, when the operation of the setting
設定表示条件としては、枠開放スイッチの出力によって、本体枠4が外枠2から開放しているかを判定する。設定キー971はパチンコ機1の裏面側に設置されているので、外枠2が開放していなければ設定キー971を操作できない。しかし、外枠2が閉鎖しているのに設定キー971の操作が検出された場合、パチンコ機1に何らかの異常(故障や、不正行為)が生じていることが推定され、この場合には設定を表示しない方がよい。また、設定表示器974はパチンコ機1の裏面側に設置されているので、外枠2が開放していなければ設定表示器974を見ることができず、設定を表示する必要がない。
As a setting display condition, it is determined whether or not the
パチンコ機1の動作中はいつでも設定値を表示してもよい。また、特定の時間において表示可能とする設定表示条件を設けてもよい。例えば、電源投入時から所定時間(例えば、10秒間)だけ設定位置を表示可能としてもよい。この場合、電源投入(又は、ステップS28のCPU初期設定)からの経過時間を計測するタイマを動作させ、当該タイマがタイムアップするまでは設定値の表示を可能とするとよい。
The setting value may be displayed at any time during operation of the
また、特定の遊技状態において設定値を表示可能とする設定表示条件を設けてもよい。例えば、特別図柄の変動表示中や大当たり遊技中には設定表示条件を表示不可能とする。すなわち、特別図柄変動中及び大当たり中以外の期間において設定値を表示可能とする設定表示条件を設ける。なお、前述した以外の遊技状態で設定値を表示不可としてもよい。この場合、特別図柄変動ゲーム中や大当たり遊技中に設定キーが操作された場合、特別図柄変動ゲームや大当たり遊技が終了するタイミングに設定値を表示してもよい。 Also, a setting display condition may be provided to enable the setting value to be displayed in a specific game state. For example, the set display conditions cannot be displayed during variable display of special symbols or during a jackpot game. That is, a setting display condition is provided to enable the setting value to be displayed during a period other than during the special symbol fluctuation and during the jackpot. It should be noted that the display of the setting value may be disabled in game states other than those described above. In this case, when the setting key is operated during the special symbol variation game or the jackpot game, the set value may be displayed at the timing when the special symbol variation game or the jackpot game ends.
設定表示条件を満たすと判定されると、セキュリティ信号を出力する(ステップS8063)。具体的には、主制御MPU1311は、セキュリティ信号を出力するためのデータを生成する。セキュリティ信号は、パチンコ機1が異常を検出した場合に外部端子板784から出力される信号であるが、パチンコ機1が遊技中に設定を確認することは希であり、不正行為の前触れとなることもあるので、営業時間中に設定確認操作がされた場合にはホールコンピュータに通知すべきだからである。
If it is determined that the set display condition is satisfied, a security signal is output (step S8063). Specifically, the
セキュリティ信号は、設定値表示開始から所定時間だけ出力しても、設定値表示開始から終了までの間に出力しても、設定値表示開始から設定値表示終了後の所定期間まで出力してもよい。設定値表示終了後の所定期間までセキュリティ信号を出力することによって、異常を検出できる期間が長くなり、セキュリティ性をより高くできる。 The security signal may be output for a specified period of time from the start of setting value display, from the start of setting value display to the end of setting value display, or from the start of setting value display to a predetermined period after the end of setting value display. good. By outputting the security signal for a predetermined period after the setting value is displayed, the period during which an abnormality can be detected becomes longer, and security can be further enhanced.
図示した設定確認処理では、設定表示条件を満たす場合にセキュリティ信号を送信するが、設定表示条件を満たさない場合でも、設定確認操作(設定キー971の操作)を検出するとセキュリティ信号を送信してもよい。 In the illustrated setting confirmation process, the security signal is transmitted when the setting display condition is satisfied. good.
その後、設定値を表示する(ステップS8064)。具体的には、主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312から現在の設定値を読み出して設定表示器974に表示するためのデータを生成する。
After that, the setting value is displayed (step S8064). Specifically, the
なお、設定表示条件を満たさない場合、設定表示条件を満たすまで条件を確認するが、長時間ループから抜け出せない可能性があるので、所定の時間、連続して設定表示条件を満たさない場合、設定確認処理を終了してもよい。例えば、特別図柄変動表示中であるために設定値を表示しないと判定された後、所定時間内に特別図柄変動表示が終了すると、特別図柄変動表示の終了を契機に設定表示条件を満たすことになり、設定値を表示する。また、設定条件を満たさない場合、設定条件の確認を繰り返さず、直ちに設定確認処理を終了してもよい。 If the set display conditions are not met, the conditions are checked until the set display conditions are met. The confirmation process may end. For example, after it is determined that the set value is not displayed because of the special symbol variation display, when the special symbol variation display ends within a predetermined time, the set display condition is set with the termination of the special symbol variation display as an opportunity. and displays the set value. Also, if the setting condition is not satisfied, the setting confirmation process may be terminated immediately without repeating confirmation of the setting condition.
このとき、設定値を表示中でないことを特別図柄変動表示開始条件に含めてもよい。このようにすると、設定値の表示中は新たな特別図柄変動表示を開始せず、設定値が非表示になった後に新たな特別図柄変動表示を開始する。 At this time, the fact that the set value is not being displayed may be included in the special symbol variation display start condition. In this way, a new special symbol variation display is not started while the set value is being displayed, and a new special symbol variation display is started after the set value is hidden.
以上に説明したように、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、所定のタイミングで設定値を確認できるようにしたので、他の表示を妨げることなく、設定値を確認できる。特にベース表示器1317と設定表示器974を兼用する場合、設定確認中は設定値が優先して表示されるので、ベース値の計算は行われているものの、ベース値が表示されない。短時間に多くの賞球が払い出される遊技状態では、ベース値の変化を確認したい場合がある。このため、ベース値のリアルタイム表示を妨げることなく、設定値を表示できる。
As described above, in the
[12-12.設定変更、設定確認に伴うセキュリティ信号の出力]
図157は、設定変更、設定確認に伴って出力されるセキュリティ信号のタイミング図である。
[12-12. Security signal output accompanying setting change and setting confirmation]
FIG. 157 is a timing chart of security signals output with setting change and setting confirmation.
前述したように、設定変更モード及び設定確認時にセキュリティ信号が出力される(図154のS61、図156のS8063)。 As described above, a security signal is output during the setting change mode and setting confirmation (S61 in FIG. 154, S8063 in FIG. 156).
設定変更モードには、図157(A)に示すように、設定変更モードの開始から所定時間だけ外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号が出力される。セキュリティ信号が出力される所定時間(T秒)は、ホールコンピュータがセキュリティ信号を認識できる時間以上
であればよく、1秒以下でも、数十秒の長さでもよい。
In the setting change mode, as shown in FIG. 157(A), a security signal is output from the external
また、セキュリティ信号は、設定変更モードの開始から所定時間ではなく、設定変更モードの開始から終了までの期間、出力されてもよい。 Also, the security signal may be output for a period from the start to the end of the setting change mode instead of the predetermined time from the start of the setting change mode.
また、設定変更モードには、図157(B)に示すように、設定変更モードに伴って実行されるRAMクリア処理のタイミングで所定時間(T秒)だけセキュリティ信号を出力してもよい。 Further, in the setting change mode, as shown in FIG. 157B, the security signal may be output for a predetermined time (T seconds) at the timing of the RAM clearing process executed in conjunction with the setting change mode.
設定確認時には、図157(C)に示すように、設定確認の開始から所定時間だけ外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号が出力される。セキュリティ信号が出力される所定時間(T秒)は、ホールコンピュータがセキュリティ信号を認識できる時間以上であればよく、1秒以下でも、数十秒の長さでもよい。
At the time of setting confirmation, as shown in FIG. 157(C), a security signal is output from the external
また、セキュリティ信号は、設定確認の開始から所定時間ではなく、設定確認の開始から終了までの期間(設定値が表示されている期間)、出力されてもよい。 Also, the security signal may be output for a period from the start to the end of the setting confirmation (the period during which the setting value is displayed) instead of the predetermined time from the start of the setting confirmation.
パチンコ機1がエラーを検出すると、図157(D)に示すように、エラーの検出から所定時間(T秒)だけ外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号が出力される。設定確認中にパチンコ機1がエラーを検出した場合、図157(E)に示すように、エラーの検出から所定時間だけセキュリティ信号が出力される。すなわち、設定確認に起因するセキュリティ信号と、エラー検出に起因するセキュリティ信号とが連続して、所定時間(T秒)を超えて(エラー検出から所定時間)出力される。なお、設定確認中にエラーが検出された場合でも、セキュリティ信号の出力時間を延長しなくてもよい。すなわち、セキュリティ信号出力中にエラーが検出されても、エラー検出に起因するセキュリティ信号が出力されず、出力中のセキュリティ信号に吸収される。
When the
なお、設定変更モード中は、パチンコ機1がエラーを検出しないので、設定確認に起因するセキュリティ信号と、エラー検出に起因するセキュリティ信号とは重複しない。すなわち、設定変更モード中はエラーが発生してもセキュリティ信号の出力時間が延長しないが、設定確認時にエラーが発生するとセキュリティ信号の出力時間が延長する。
Since the
[12-13.設定確認処理の別例]
以下、設定確認処理の別例について説明する。上記説明では、周辺制御部定常処理におけるタイマ割り込み処理において、設定確認処理が行われる例について主に説明したが、以下では、パチンコ機1への電源投入時の初期化処理において設定確認処理が行わる例について説明する。
[12-13. Another example of setting confirmation processing]
Another example of the setting confirmation process will be described below. In the above description, an example in which the setting confirmation process is performed in the timer interrupt process in the peripheral control unit steady process has been mainly described. example.
具体的には、例えば、パチンコ機1への電源投入時に設定キーがオンである場合に、設定確認処理へ移行する。以下、当該処理の詳細を説明する。なお、本章における周辺制御MPUが実行するタイマ割込み処理は、図23におけるタイマ割込み処理(即ちステップS802における設定確認処理を含まないタイマ割込み処理)であるものとする。
Specifically, for example, when the setting key is on when the
図158は、初期化処理の別例を示すフローチャートである。図154との相違点を説明する。主制御MPU1311は、ステップS18において、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていないと判定した場合(ステップS18:No)、設定キー971が操作されており、その出力がオンであるかを判定する(ステップS29)。
FIG. 158 is a flowchart showing another example of initialization processing. Differences from FIG. 154 will be described. If the
主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971の出力がオンであると判定した場合(ステップS29:Yes)、ステップS807における設定確認処理へと移行し、その後ステッ
プS20へ移行する。ステップS807における設定確認処理については後述する。主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971の出力がオフであると判定した場合(ステップS29:No)、ステップS20へ移行する。
When the
図159は、設定確認処理の別例(ステップS807における設定確認処理)を示すフローチャートである。図156との相違点について説明する。主制御MPU1311は、ステップS8061の処理を行うことなく、設定表示条件を満たすかを判定する(ステップS8062)。主制御MPU1311は、設定表示条件を満たすと判定した場合(ステップS8062:Yes)、セキュリティ信号を出力(ステップS8063)し、設定値を表示する(ステップS8064)。主制御MPU1311は、設定表示条件を満たさないと判定した場合(ステップS8062:No)、ステップS8062の処理を再度実行する。
FIG. 159 is a flowchart showing another example of setting confirmation processing (setting confirmation processing in step S807). Differences from FIG. 156 will be described. The
主制御MPU1311は、ステップS8064の処理に続いて、設定キー971が操作されており、その出力がオフであるかを判定する(ステップS8071)。主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971の出力がオンであると判定した場合(ステップS8071:No)、例えば所定時間経過後に、再度ステップS8071の判定を実行する。主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971の出力がオフであると判定した場合(ステップS8071:Yes)、設定値を非表示にし(ステップS8075)、設定確認処理を終了する。つまり、RAMクリアボタンを押下することなく、設定キー971をオン状態にして電源を立ち上げた場合に設定確認状態に移行する。
Following the processing of step S8064, the
なお、特別図柄変動中にパチンコ機1の電源をオフにした場合、主制御基板1310が管理する保留記憶数や当該特別図柄における残り変動時間等は、そのまま記憶される。その後、次回の電源投入時に設定確認処理が行われた場合(設定キー971がオン状態とされた状態で電源を立ち上げたとき)、設定確認処理終了後(電源をオフ状態にすることなく設定キー971を初期位置に戻した後)に当該特別図柄変動が再開する。このとき、例えば、当該特別図柄変動とともに実行されていた演出(表示装置を用いた演出、ランプを用いた演出、スピーカを用いた音演出、及び可動体を用いた演出等)は、当該特別図柄変動の再開後は一切行われない。
In addition, when the power of the
また、特別図柄変動中にパチンコ機1の電源をオフにして、次回の電源投入時に設定確認処理が行われた場合において、設定確認処理終了後の当該特別図柄変動の再開時に、当該特別図柄変動とともに実行されていた演出を再開してもよい。例えば、中断されていた、表示装置、ランプ、及びスピーカを用いた演出を再開する。また、可動体を用いた演出については、例えば、当該特別図柄変動の再開後又は電源投入時に当該可動体を初期位置に戻した後に、当該演出の演出パターンにおいて可動体を動作させることが定められている場合、当該演出パターンに従って可動体を動作させる。
Further, when the
つまり、可動体が初期位置ではないときに設定確認状態に移行した場合は、電源立ち上げ時又は設定確認処理が終了したときに一度初期位置に戻し、その後、特別図柄変動の変動パターンに基づいて決定された演出の中に可動体を動作(移動)させる演出が含まれているのであれば、可動体を動作(移動)させてもよい。なお、可動体が動作(移動)しているときに設定確認状態に移行した場合は、当該動作(移動)の動作パターンは実行されないものとしてもよいし、当該可動体を一度初期位置に戻してからでも動作可能なパターンであれば可動体を動作させてよい。 In other words, if the movable body is not in the initial position and has shifted to the setting confirmation state, it is returned to the initial position once when the power is turned on or the setting confirmation process is completed, and then based on the fluctuation pattern of the special symbol fluctuation If the determined effects include an effect of moving (moving) the movable body, the movable body may be moved (moved). If the setting confirmation state is entered while the movable body is moving (moving), the action pattern for that movement (moving) may not be executed, or the movable body may be returned to its initial position. The movable body may be operated as long as it is a pattern that allows it to operate even if it is empty.
また、特別図柄変動中にパチンコ機1の電源をオフにして、次回の電源投入時に設定確認処理が行われた場合において、設定確認処理終了後の当該特別図柄変動の再開時に、当該特別図柄変動とともに実行されていた演出のうち表示装置を用いた演出、ランプを用い
た演出、及びスピーカを用いた音演出を再開し、当該特別図柄変動の再開後又は電源投入時に当該可動体を初期位置に戻し、可動体を用いた演出については行わなくてもよい。
Further, when the
また、特別図柄変動中にパチンコ機1の電源をオフにして、次回の電源投入時に設定確認処理が行われた場合において、設定確認処理終了後の当該特別図柄変動の再開時に、メイン液晶表示装置1600に表示されていた装飾図柄の変動を再開(もともと行う予定の演出を再開)するようにしてもよいし、装飾図柄の変動において図柄確定時まで(又は図柄確定時の直前の揺れ変動時まで)装飾図柄を透明にした高速変動を行うようにしてもよいし、図柄確定時まで(又は図柄確定時の直前の揺れ変動時まで)装飾図柄を非表示にしてもよい。また、図柄確定時においては、例えば、電源をオフにする前に予定されていた装飾図柄の組み合わせをメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示する。また、この場合において、再開後の当該特別図柄変動の終了時に、所定の装飾図柄の組み合わせ、初期電源投入時に表示される装飾図柄の組み合わせ、又は通常の特別図柄変動時には表示されない特殊な装飾図柄の組み合わせ(例えば、「×××」等)を、メイン液晶表示装置1600に表示してもよい。
In addition, when the
なお、特別図柄変動中にパチンコ機1の電源をオフにして、次回の電源投入時に設定確認処理が行われ、設定確認処理が終了して通常状態に復帰するときに、設定キー971がオフ状態の電源投入時(つまり、通常に電源を立ち上げたとき)と同様の初期動作(例えば、可動体の所定の動作や、LEDの所定の発光などを確認等の動作)が行われてもよい(この初期動作を行ってから上述した演出等を再開させるようにしてもよい)。
It should be noted that the power of the
また、特別図柄変動中に先読み演出が行われているときにパチンコ機1の電源をオフにして、次回の電源投入時に設定確認処理が行われた場合、例えば、設定確認処理終了後の当該特別図柄変動の再開時に、当該先読み演出、及び電源をオフにする直前に保留されていた特別図柄変動についての先読み演出を実行しない(具体的には、例えば、電源をオフ状態にする前に行われていた特別図柄の変動中に表示していた特別なゾーン(例えば、大当たりの期待が高いことを複数の変動に跨って遊技者に見せる特別なステージで、後述するライバル馬演出から競馬演出へと発展するゾーン(競馬演出は、それ自体の期待度が高めに(例えば後述する台詞演出よりも相対的に期待が高めに)設定されている特別なゾーン))待機中の表示や、当該特別なゾーン中の表示演出を消去したり、保留表示の態様が例えば通常の白色ではなく青色であった場合、通常の白色に戻したりする)。但し、設定確認処理終了後の入賞に対応する特別図柄変動については先読み演出を実行してもよい。
Also, when the power of the
また、特別図柄変動中に先読み演出が行われているときにパチンコ機1の電源をオフにして、次回の電源投入時に設定確認処理が行われた場合、例えば、設定確認処理終了後の当該特別図柄変動の再開時に、当該特別図柄変動中における先読み演出は中止(具体的には、例えば、電源をオフ状態にする前に行われていた特別図柄の変動中に表示していた当該特別なゾーン待機中の表示や、当該特別なゾーン中の表示演出を消去したり、保留表示の態様が例えば通常の白色ではなく青色であった場合、通常の白色に戻したりする)されるが、次の特別図柄変動から先読み演出が再開されてもよい(消去した表示を元に戻したり、変動開始時に先読み演出を昇格させる演出パターンであった場合には昇格後の表示態様にて復帰させたりしてもよい)。この場合、次の特別図柄変動から実行される先読み演出は、例えば、当該特別図柄変動中における先読み演出は中止されなかったものとして再開される。つまり、パチンコ機1の電源をオフにする前に、当該次の特別図柄変動以降において実行される予定だった先読み演出を実行する。また、新たな先読み演出のパターンを設定して、当該次の特別図柄変動から当該新たな先読みパターンの演出が実行されてもよい。
Also, when the power of the
[12-14.設定示唆演出の別例]
以下、設定示唆演出の実行が制限される処理の一例について説明する。なお、以下の説明において、通常時における設定1~設定6の大当り確率が、それぞれ1/240、1/230、1/220、1/210、1/200、1/190であるものとし、確変時における設定1~設定6の大当り確率が、それぞれ1/48、1/46、1/44、1/42、1/40、1/38であるものとする。また、大当り当選時の確変割合が50%であるものとする。
[12-14. Another example of setting suggestion effect]
An example of processing for restricting execution of the setting suggestion effect will be described below. In the following description, the probability of setting 1 to setting 6 in normal times is 1/240, 1/230, 1/220, 1/210, 1/200, 1/190, respectively. Assume that the jackpot probabilities of setting 1 to setting 6 at time are 1/48, 1/46, 1/44, 1/42, 1/40, and 1/38, respectively. In addition, it is assumed that the probability variation rate at the time of winning the jackpot is 50%.
[12-14-1.変動パターンテーブル]
図160は、変動パターンテーブルの別例である。変動パターンテーブルは、例えば、主制御基板1310のROM1313に格納されている。図142等の説明においては、特別抽選結果の当落種別ごとに変動パターンテーブルが存在する例を説明したが、図160の例では、1つの変動パターンテーブルで特別抽選結果の当落種別ごとの変動パターンが定義されている。また、図160の例では、全設定において共通の変動パターンテーブルが使用されるものとする。
[12-14-1. Fluctuation pattern table]
FIG. 160 is another example of the variation pattern table. The variation pattern table is stored in the
図160の変動パターンテーブルは、特別抽選結果の当落種別と、変動パターンの識別子と、当該変動パターンの演出の概要と、選択率と、の対応を示す。上述したように図160の例では、各特別抽選結果の変動パターンの情報が、1つの変動パターンテーブルに格納されている。従って、主制御MPU1311は、入賞に対応する当落種別に対応する変動パターンを、変動パターンテーブルが示す選択率に従って選択する。なお、図144の例のように、変動パターンテーブル内に各変動パターンの変動時間が定義されていてもよい。
The variation pattern table in FIG. 160 shows the correspondence between the winning/losing type of the special lottery result, the identifier of the variation pattern, the outline of the effect of the variation pattern, and the selection rate. As described above, in the example of FIG. 160, the information on the variation pattern of each special lottery result is stored in one variation pattern table. Therefore, the
なお、概要欄に記載されているムービーリーチとは、特別抽選の結果が大当りである場合に選択される割合が高く、特別抽選の結果が外れである場合に選択される割合が極めて低いリーチ演出である。つまり、ムービーリーチが実行される変動の大当り期待度は高い。また、ムービーリーチ発生時には所定のムービーがメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される。
In addition, the movie reach described in the summary column is a reach effect that has a high percentage of selection when the result of the special lottery is a big hit, and an extremely low percentage of selection when the result of the special lottery is a loss. is. In other words, the expectation of a big hit is high for variations in which Movie Reach is executed. Also, a predetermined movie is displayed on the main liquid
また、概要欄に記載されている、当落種別が「はずれ」である場合の「+1図柄」とは、装飾図柄がリーチ状態で停止した後、最後まで変動している装飾図柄が、リーチ状態の装飾図柄を1つ通り過ぎて停止することを示す。具体的には、例えば、装飾図柄「7」でリーチ状態になった後に、最後まで変動していた装飾図柄が「8」で停止する。当落種別が「大当り」である場合の「+1図柄」とは、装飾図柄がリーチ状態で停止した後、最後まで変動している装飾図柄が、リーチ状態の装飾図柄を1つ通り過ぎて一旦停止したように見せかけた後に、当該装飾図柄がリーチ状態の装飾図柄と同一の図柄として停止する。具体的には、例えば、装飾図柄「7」でリーチ状態になった後に、最後まで変動していた装飾図柄が「8」で一旦停止したように見せかけ、その後当該装飾図柄が「7」で停止し、大当りを報知する。 In addition, the "+1 pattern" when the winning type is "lost", which is described in the summary column, means that after the decorative pattern stops in the reach state, the decorative pattern that is fluctuating until the end is in the reach state. Indicates to stop past one decorative symbol. Specifically, for example, after reaching the ready-to-win state with the decorative pattern "7", the decorative pattern that has been fluctuating until the end stops at "8". "+1 pattern" when the win/lose type is "jackpot" means that after the decorative pattern stops in the ready-to-win state, the decorative pattern that is fluctuating to the end passes one decorative pattern in the ready-to-reach state and temporarily stops. After making it look like this, the decorative pattern stops as the same pattern as the decorative pattern in the ready-to-win state. Specifically, for example, after reaching the ready-to-win state at decorative pattern "7", the decorative pattern that has been fluctuating until the end is made to appear to have temporarily stopped at "8", and then the decorative pattern stops at "7". and announce the jackpot.
なお、図161の例における概要欄において、「+1図柄」は当落種別が大当りのうち「大当たり(非確変)」の場合のみ選択されるようになっているが、「大当たり(確変)」の場合のみ選択されてもよいし、「大当り(非確変)」及び「大当たり(確変)」の場合に選択されてもよい。また、「+1図柄」は当落種別が「はずれ」である場合のみ選択されてもよい。 In addition, in the overview column in the example of FIG. 161, "+1 pattern" is selected only when the hit type is "jackpot (non-variable)" among the big hits, but in the case of "jackpot (variable probability)" It may be selected only, or may be selected in the case of "jackpot (non-probability variation)" and "jackpot (probability variation)". In addition, "+1 symbol" may be selected only when the winning/losing type is "lost".
また、概要欄に記載されている「+擬似1」及び「+擬似2」は、それぞれ2連の擬似連続演出、及び3連の擬似連続演出が実行されることを示す。擬似連続演出とは、装飾図柄の変動を行い装飾図柄の変動を終了させる動作を、第一特別図柄表示器又は第二特別図柄表示器の一回の変動中に、複数回実行する演出である。「装飾図柄の変動を終了させる
」とは、例えば、装飾図柄の一部または全部を停止表示させる態様、装飾図柄の変動が一旦終了したように遊技者に認識させるような態様、及び装飾図柄の一部に擬似連図柄(この図柄が停止すれば擬似連が確定する図柄)が停止する態様、などである。なお、当該動作がN回(Nは1以上の自然数)行われる擬似連続演出をN連の擬似連続演出と呼び、N連の擬似連続演出におけるM回目の装飾図柄の変動(Mは1以上N以下の自然数)をM連目の擬似連続演出と呼ぶ。また、第一特別図柄表示器又は第二特別図柄表示器の一回の変動中に、当該動作を再度実行する可能性があることを遊技者に示唆しつつ、実際には当該動作を再度実行しない演出を、「擬似ガセ演出」と呼ぶ。また、以下、擬似連続演出のことを単に「擬似連演出」とも呼ぶ。
Also, "+
擬似連演出が発生又は継続する、即ち、装飾図柄の変動を行い装飾図柄の変動を終了させる動作を、第一特別図柄表示器又は第二特別図柄表示器の一回の変動中に、再度実行することが確定している場合に、周辺制御MPUは、左装飾図柄、中装飾図柄、及び右装飾図柄の少なくとも1つに擬似連図柄を停止させてもよい。以下の例では、周辺制御MPUは、「続く!」のような文字を擬似連図柄として中装飾図柄に停止させる。なお、例えば、特定の装飾図柄の組み合わせ(例えば、左装飾図柄、中装飾図柄、右装飾図柄の全てが奇数又は偶数かつリーチ非発生)を擬似連図柄としてもよい。なお、擬似ガセ演出は、例えば、演出の概要が「通常変動」等のときに実行され得る。また、例えば、「+擬似1」が実行される変動パターンであっても、「+擬似2」における3連目の擬似連の発生を示唆する擬似ガセ演出を実行するようにしてもよい。
Pseudo continuous effect occurs or continues, that is, the operation of changing the decorative pattern and ending the decorative pattern change is executed again during one time fluctuation of the first special symbol display device or the second special symbol display device. When it is decided to do so, the peripheral control MPU may stop the pseudo-continuous design in at least one of the left decorative design, the middle decorative design, and the right decorative design. In the following example, the peripheral control MPU causes a character such as "Continue!" It should be noted that, for example, a combination of specific decorative symbols (for example, all of the left, middle, and right decorative symbols are odd-numbered or even-numbered and reach-free) may be pseudo-continuous symbols. It should be noted that the pseudo fake effect can be executed, for example, when the outline of the effect is "normal variation" or the like. Also, for example, even if the variation pattern is to execute "+
[12-14-2.最終保留色テーブル]
図161は、最終保留色テーブルの一例である。最終保留色テーブルは、例えば、周辺主制御ROMに格納されている。最終保留色テーブルは、例えば、変動パターン(特別抽選結果の当落種別、変動パターンの識別子、及び当該変動パターンの演出の概要)ごとの当該変動終了時の保留表示の表示色(以下、最終保留色とも呼ぶ)の選択率と、を保持する。
[12-14-2. Final reserved color table]
FIG. 161 is an example of the final reserved color table. The final reserved color table is stored, for example, in the peripheral main control ROM. The final pending color table is, for example, the display color of the pending display at the end of the variation for each variation pattern (special lottery result winning/losing type, variation pattern identifier, and outline of the variation pattern production) (hereinafter referred to as the final pending color ) and the selectivity.
なお、メイン液晶表示装置1600は、保留中の第一特別乱数及び第二特別乱数の数を示す保留表示領域を含む。図142のステップS116の始動口入賞時処理では、第一特別乱数及び第二特別乱数の保留数を指定する保留数指定コマンドが周辺制御基板1510に対して送信される。周辺制御MPUは、保留数指定コマンドが示す保留数を示す表示を、保留表示領域に行う。
In addition, the main liquid
具体的には、第一始動口2002又は第二始動口2004に遊技球が入賞(始動条件が成立)したときには、保留数指定コマンドから特定される保留数(保留記憶数)が増加することで、保留表示領域に1つの保留表示を追加して表示する。一方、保留表示に基づいた装飾図柄の変動表示(特別図柄の変動表示)を開始(開始条件が成立)するときには、保留数指定コマンドから特定される保留数(保留記憶数)が減少することで、保留表示領域における当該保留表示を消去する。
Specifically, when the game ball wins the
なお、保留表示には複数の表示態様が存在してもよい。例えば、当該複数の表示態様として、複数の色(白、青、緑、赤、虹)による保留表示の表示態様が存在する。以下、保留表示の色が白、青、緑、赤、虹の順で、当該保留表示に対応する特別抽選結果の大当り期待度が高くなるものとする。特に図161の例では、虹色の保留表示は特別抽選の結果が大当りである場合にのみに選択される。 It should be noted that the hold display may have a plurality of display modes. For example, as the plurality of display modes, there is a display mode of holding display in a plurality of colors (white, blue, green, red, rainbow). Hereafter, it is assumed that the degree of expectation for a big hit in the special lottery result corresponding to the reserved display increases in the order of white, blue, green, red, and rainbow as the colors of the reserved display. In particular, in the example of FIG. 161, the rainbow-colored pending display is selected only when the result of the special lottery is a big win.
つまり、周辺制御MPUは、選択された変動パターンに対応する最終保留色を、最終保留色テーブルが示す選択率に従って選択する。また、周辺制御MPUは、例えば、保留表示領域に保留表示を表示してから当該保留表示が消去されるまでの表示期間中に、保留表
示の表示態様を変化させることで、当該保留表示に対応する装飾図柄の変動表示(特別図柄の変動表示)に対する大当り期待度を示唆する保留予告演出を実行可能としている。
That is, the peripheral control MPU selects the final reserved color corresponding to the selected variation pattern according to the selection rate indicated by the final reserved color table. Further, the peripheral control MPU responds to the pending display by, for example, changing the display mode of the pending display during the display period from when the pending display is displayed in the pending display area to when the pending display is erased. It is possible to execute a holding advance notice performance suggesting the degree of expectation for a big hit with respect to the variable display of decorative patterns (variable display of special patterns).
また、本実施例において、保留表示の表示期間中において、保留表示の表示態様が変化する可能性を示唆する保留変化演出を実行可能としている。なお、保留表示の表示期間中かつ当該保留に対応する変動開始前、における保留変化演出及び保留予告演出を保留先読み演出とも呼ぶ。 Further, in the present embodiment, during the display period of the pending display, a pending change effect suggesting the possibility that the display mode of the pending display may change can be executed. In addition, the suspension change effect and the suspension notice effect during the display period of the suspension display and before the start of the fluctuation corresponding to the suspension are also called a suspension look-ahead effect.
例えば、周辺制御ROMは、保留表示の表示態様の変化タイミングを定義する保留予告テーブル(図示しない)を保持する。具体的には、例えば、保留予告テーブルは、保留表示の表示態様の変化タイミングと、入賞時及び各変化タイミングにおける保留表示の表示態様(表示色)と、を最終保留色ごとに定義する。入賞時以降かつ当該入賞に対応する特別図柄変動以前の特別図柄変動の開始時、変動中、及び終了時等は、当該変化タイミングの一例である。 For example, the peripheral control ROM holds a hold notice table (not shown) that defines the change timing of the display mode of the hold display. Specifically, for example, the pending notice table defines, for each final pending color, the change timing of the display mode of the pending display and the display mode (display color) of the pending display at the time of winning and at each change timing. The start time, during the change, and the end time of the special symbol variation after the winning and before the special symbol variation corresponding to the winning are examples of the change timing.
なお、各変化タイミングにおける保留表示の表示態様は、最終保留色の大当り期待度以下の大当り期待度を有する保留色であることが望ましい。また、各変化タイミングにおいて保留表示が示す大当り期待度が降格しないことが望ましい(例えば、青色の保留表示が白色の保留表示に変化しないことが望ましい)。なお、入賞時の保留記憶数ごとに異なる保留予告テーブルが存在してもよい。 In addition, it is desirable that the display mode of the reservation display at each change timing is a reservation color having a jackpot expectation less than or equal to the jackpot expectation of the final reservation color. Also, it is desirable that the degree of expectation for a big win indicated by the pending display does not drop at each change timing (for example, it is desirable that the blue pending display does not change to the white pending display). It should be noted that there may be a different pending notice table for each pending memory number at the time of winning.
なお、例えば、当該保留表示以前に保留された特別図柄変動の開始時は、上述した保留表示の表示態様の変化タイミングの一例であるまた、例えば、当該保留表示に対応する特別図柄変動中にも、保留表示の表示態様の変化タイミングが設けられていてもよい。 It should be noted that, for example, the start of the special symbol variation suspended before the suspension display is an example of the change timing of the display mode of the suspension display described above, and for example, during the special symbol variation corresponding to the suspension display , a change timing of the display mode of the pending display may be provided.
なお、保留先読み演出を含む先読み演出は、図142のステップS116の始動口入賞時処理において行われる事前判定処理において、主制御MPU1311から周辺制御基板1510へ送信される事前判定コマンドに基づいて実行される。
It should be noted that the look-ahead effect including the pending look-ahead effect is executed based on the pre-determination command transmitted from the
以下、第一特別図柄についての始動口入賞処理における事前判定処理について説明する。なお、第二特別図柄についての始動口入賞処理における事前判定処理についても同様であるため、ここでは第一特別図柄についてのみ説明する。事前判定処理において、主制御MPU1311は、事前判定テーブル(図示しない)と、特別乱数、図柄乱数、リーチ乱数、及び変動乱数とを比較することにより大当りとなるか否か、大当りとなる場合には大当りの種類、大当りとならない場合にはメイン液晶表示装置1600で実行される遊技演出としてリーチ演出を実行するか、実行する遊技演出の態様種別、を特定する。
Hereinafter, the preliminary determination processing in the start opening winning processing for the first special symbol will be described. In addition, since the same applies to the preliminary determination process in the starting opening winning process for the second special symbol, only the first special symbol will be described here. In the pre-determination process, the
そして、特定した事前判定情報(大当りとなるか否か、大当りとなる場合には大当りの種類、大当りとならない場合にはメイン液晶表示装置1600で実行される遊技演出としてリーチ演出を実行するか、実行する遊技演出の態様種別など)と、取得した特別乱数の種別(第一特別乱数)と、取得した特別乱数に対応して記憶される保留記憶数(保留数カウンタの値)と、に応じた事前判定コマンドをセットする。例えば、第一特別図柄に関する演出事前判定処理では、特定した事前判定情報と、第一特別乱数を取得したことと、第一保留記憶数と、に応じた第一特別図柄事前判定コマンドをセットする。
Then, the specified advance determination information (whether or not it will be a big hit, if it will be a big hit, the type of the big win, if it will not be a big hit, whether to execute a ready-to-win effect as a game effect executed on the main liquid
そして、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510に事前判定コマンドが送信されることにより、始動入賞が発生した始動口に対応して記憶される保留記憶数に加え、発生した始動入賞に基づく特別図柄の変動表示の表示結果を大当りとするか否か、大当りとなる場合には大当りの種類、大当りとならない場合にはメイン液晶表示装置1600で実行される遊技演出としてリーチ演出を実行するか、実行する遊技演出の態様種別などの事前
判定情報を、当該始動入賞に応じた変動表示を開始する以前に周辺制御基板1510に搭載される周辺制御IC1510aが把握できるようになる。
Then, by transmitting a pre-determination command from the
図162は、図160の変動パターンテーブルによって変動パターンが決定され、かつ図161の最終保留色テーブルによって最終保留色が決定された場合における、設定1の変動パターンごとの各最終保留色の出現率を示すテーブルの一例である。図163は、同様の場合における、設定3の変動パターンごとの各最終保留色の出現率を示すテーブルの一例である。図164は、同様の場合における、設定5の変動パターンごとの各最終保留色の出現率を示すテーブルの一例である。図162乃至図164によれば、高設定ほど上位の大当り期待度の保留表示の表示態様の出現率が高い。また、各色の大当り期待度は高設定ほど高い。なお、これらの出現率や期待度は、上述した各設定の大当り確率に基づいて算出されたものであり、最終保留色テーブルについては、全ての設定において図161の最終保留色テーブルが用いられているものとしている。
FIG. 162 shows the appearance rate of each final reserved color for each variation pattern of
なお、周辺制御ROMは、設定ごとに異なる最終保留色テーブルを保持してもよい。この場合、例えば、同一の保留表示の表示態様において、高設定になるほど大当り期待度が高くなるように最終保留色の最終保留色テーブルの選択率が設定されている。これにより、例えば、赤色の保留表示に対応する特別図柄変動において大当りに当選した場合、さらに高設定への期待度も高くなるため、遊技者は高揚感を得ることができる。 Note that the peripheral control ROM may hold a different final reserved color table for each setting. In this case, for example, the selection rate of the final reserved color table of the final reserved color is set such that the higher the setting, the higher the expectation of the big win in the same display mode of the reserved display. As a result, for example, when a big win is won in the special symbol variation corresponding to the red pending display, the degree of expectation for the high setting is further increased, so that the player can get an exhilarating feeling.
また、例えば、最も多く選択される白色以外の保留表示の表示態様において、同一の保留表示の表示態様については、低設定になるほど大当り期待度が高くなるように最終保留色テーブルの最終保留色の選択率が設定されていてもよい(具体的には、例えば、保留表示の態様が赤色である場合の大当り期待度が、低設定である設定1では50%、高設定である設定6では30%になるように設定する)。これにより、例えば、赤色の保留表示に対応する特別図柄変動において大当りに当選しなかった場合であっても、高設定への期待度が高くなるため、遊技者の落胆を抑制、遊技の継続を促進することができる。 Further, for example, in the display mode of the pending display other than white, which is most frequently selected, the final pending color of the final pending color table is changed so that the lower the setting, the higher the expectation of the big hit, for the same pending display display mode. A selection rate may be set (specifically, for example, the jackpot expectation when the pending display mode is red is 50% for setting 1, which is a low setting, and 30% for setting 6, which is a high setting. %). As a result, for example, even if a big hit is not won in the special symbol variation corresponding to the red pending display, the degree of expectation for the high setting is high, so that the disappointment of the player is suppressed and the continuation of the game is encouraged. can be promoted.
また、例えば、最も多く選択される白色以外の保留表示の表示態様において、同一の保留表示の表示態様については、全設定で大当り期待度が略共通になるように最終保留色テーブルの最終保留色の選択率が設定されていてもよい。これにより、例えば、最終保留色と特別抽選結果との組み合わせから設定を推定することが困難となり、遊技者は保留表示の表示態様から特別抽選結果に対する期待感のみに集中することができる。また、例えば、赤色の表示態様に対応する特別図柄変動において大当りに当選しなかった場合に、低設定の可能性が高くなるという事態が発生しないようにすることができる。 Further, for example, in the display mode of the pending display other than white, which is most frequently selected, for the display mode of the same pending display, the final pending color of the final pending color table so that the jackpot expectation is substantially common in all settings may be set. As a result, for example, it becomes difficult to estimate the setting from the combination of the final reserved color and the special lottery result, and the player can concentrate only on the expectation for the special lottery result from the display mode of the reserved display. Also, for example, when a big win is not won in the special symbol variation corresponding to the display mode of red, the possibility of low setting can be prevented from occurring.
[12-14-3.予告演出テーブル]
図165は、予告演出テーブルの一例である。予告演出テーブルは、例えば周辺制御ROMに格納されている。予告演出テーブルは、例えば、変動パターン(特別抽選結果の当落種別、変動パターンの識別子、及び当該変動パターンの演出の概要で特定される)ごとの予告演出の選択率を保持する。
[12-14-3. Notice production table]
FIG. 165 is an example of a notice effect table. The advance notice effect table is stored, for example, in the peripheral control ROM. The advance notice effect table holds, for example, the selection rate of the advance notice effect for each variation pattern (specified by the winning/losing type of the special lottery result, the identifier of the variation pattern, and the outline of the effect of the variation pattern).
図165の例では、予告演出として、台詞演出、天候変化演出、及びライバル馬演出がある。台詞演出は、例えば、当該変動において所定のキャラクタがメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示され、台詞を言う演出である。天候変化演出は、例えば、当該変動において、メイン液晶表示装置1600上に表示された装飾図柄の背景における天候が変化する演出である。ライバル馬演出は、当該変動において、メイン液晶表示装置1600に主人公キャラクタが育てる馬のライバル馬が出現する演出である。
In the example of FIG. 165, the notice effects include dialogue effects, weather change effects, and rival horse effects. The dialogue effect is, for example, an effect in which a predetermined character is displayed on the main liquid
なお、予告演出を用いた設定示唆演出の実行が可能であり、予告演出テーブルには、設
定示唆演出の実行有無別の各予告演出の選択率が格納されている。図165の例における「set無し」は設定示唆演出が実行されないことを示し、「set有」は設定示唆演出が実行されることを示す。周辺制御MPUは、変動パターンと予告演出テーブルの選択率とに基づいて、実行する予告演出を決定する。
It should be noted that it is possible to execute setting suggestive effects using advance notice effects, and the advance notice effect table stores the selection rate of each advance notice effect depending on whether or not the setting suggestive effects are executed. "No set" in the example of FIG. 165 indicates that the setting suggesting effect is not executed, and "with set" indicates that the setting suggesting effect is executed. The peripheral control MPU determines the announcement effect to be executed based on the variation pattern and the selection rate of the announcement effect table.
なお、予告演出テーブルの各変動パターンにおける各予告演出において、設定示唆演出有りの選択率より、設定示唆演出無しの選択率の方が十分に高いことが望ましい。設定示唆演出有りの選択率が高いと、設定示唆演出が頻繁に発生する。この状態で高設定を示唆する設定示唆演出の発生頻度が低い場合には、遊技者は短時間で遊技を中止してしまう可能性が高いからである。つまり、低設定であるパチンコ機1の稼働率が著しく低下してしまい、ホールに過大な負担を強いるおそれがある。逆に、例えば、高設定を示唆する設定示唆演出の発生頻度が高い場合には、ホール内の他のパチンコ機1の設定が低いと推測する遊技者が増えて当該他のパチンコ機1の稼働率が低下してしまい、ホールに過大な負担を強いるおそれがある。
Incidentally, in each of the advance notice effects in each variation pattern of the advance notice effect table, it is desirable that the selection rate without the setting suggestion effect is sufficiently higher than the selection rate with the setting suggestion effect. If the selection rate of the presence of the setting suggestion effect is high, the setting suggestion effect occurs frequently. This is because, in this state, if the occurrence frequency of setting suggestion effects suggesting a high setting is low, there is a high possibility that the player will stop playing the game in a short period of time. In other words, the operating rate of the
なお、擬似連回数が多くなるほど大当り期待度が向上するよう、変動パターンテーブルにおける変動パターンの選択率が決定されているが、例えば、設定示唆演出の出現率は擬似連回数によって概ね変化しないように、予告演出テーブルにおける設定示唆演出の実行有無の選択率が決定されている。つまり、例えば、概要が「SPリーチ」、「SPリーチ+擬似1」、「SPリーチ+擬似2」である変動パターンについて、設定示唆演出の出現率が略同一となるように、擬設定示唆演出の実行有無の選択率が決定されている。これにより、擬似連回数が少ない変動パターンについては、大当り期待度は低いものの、設定示唆演出の発生率は擬似連回数が多い変動パターンと比較しても低くないため、遊技者は擬似連回数が少ない変動パターンの変動についても興味を抱くことができる。
In addition, the selection rate of the variation pattern in the variation pattern table is determined so that the higher the number of pseudo-runs, the higher the expectation of a big hit. , the selection rate of execution/non-execution of the setting suggestion effect in the advance notice effect table is determined. That is, for example, for the variation patterns whose outlines are "SP reach", "SP reach +
また、擬似連回数が多くなるほど、設定示唆演出の出現率が高くなるように、予告演出テーブルにおける設定示唆演出の実行有無の選択率が決定されていてもよいし、擬似連回数が少なくなるほど、設定示唆演出の出現率が高くなるように、予告演出テーブルにおける設定示唆演出の実行有無の選択率が決定されていてもよい。なお、擬似連回数が少なくなるほど設定示唆演出の出現率を高くした場合には上述した課題が発生するおそれがあるため、擬似連回数が少なくなるほど設定示唆演出の出現率を高くした場合であっても、ほぼ同等の数値として設定するほうが望ましい(具体的には、例えば、はずれ時における変動パターン5選択時の台詞演出のset有りは15/256、変動パターン6選択時の台詞演出のset有りは16/256、のように設定する)。
Further, the selection rate of whether or not to execute the setting suggesting effect in the advance notice effect table may be determined so that the appearance rate of the setting suggesting effect increases as the number of pseudo repeats increases. The selection rate of execution/non-execution of the setting-suggestion effect in the advance notice effect table may be determined so that the appearance rate of the setting-suggestion effect is high. Note that if the appearance rate of setting-suggestion effects is increased as the number of pseudo-runs decreases, the above-described problem may occur. It is desirable to set the numbers to approximately the same values (specifically, for example, if the dialogue effect is set when
また、大当り期待度の高い変動パターン(又は大当たり期待度の高い変動パターンではないものの、現出された演出の期待度合いが相対的に高い演出(例えば、大当り期待度が所定値以上である演出))ほど、設定示唆演出の出現率が高くなるように、予告演出テーブルにおける設定示唆演出の実行有無の選択率が決定されていてもよい。具体的には、例えば、「通常変動」、「ノーマルリーチ」を含む変動、「SPリーチ」を含む変動、「ムービーリーチ」を含む変動の順で、設定示唆演出の出現率が高くなるように、予告演出テーブルにおける設定示唆演出の実行有無の選択率が決定されていてもよい。 In addition, a variation pattern with a high degree of expectation for a big win (or a variation pattern with a high degree of expectation for a big win, but a performance with a relatively high degree of expectation for the produced performance (for example, a performance with a degree of expectation for a big win equal to or higher than a predetermined value) ), the selection rate of execution/non-execution of the setting suggestion effect in the advance notice effect table may be determined so that the appearance rate of the setting suggestion effect increases. Specifically, for example, in the order of "normal fluctuation", fluctuation including "normal reach", fluctuation including "SP reach", and fluctuation including "movie reach", so that the appearance rate of the setting suggestion effect increases, A selection rate of execution/non-execution of the setting suggestion effect in the advance notice effect table may be determined.
また、図165の例では、全ての予告演出(台詞演出、天候変化演出、及びライバル馬演出)において、設定示唆演出が発生する可能性があるが、例えば、設定示唆演出が発生しない予告演出が存在してもよい。 In addition, in the example of FIG. 165, there is a possibility that the setting suggesting effect will occur in all of the advance notice effects (dialogue effect, weather change effect, and rival horse effect). may exist.
また、変動パターンの概要が同一であれば、特別抽選結果が確変ありの大当りである場合より、特別抽選結果が確変無しの大当りである方が、設定示唆演出の出現率が高くなるように、予告演出テーブルにおける設定示唆演出の実行有無の選択率が決定されていても
よい。これにより、確変無しの大当りに当選した場合において設定示唆演出の出現率が高くなり、確変が付与されなかったことに対する遊技者の落胆を軽減することができる。なお、上述の例において、台詞演出、天候変化演出、及びライバル馬演出の3種類の予告演出について説明したが、3種類に限らないことは言うまでもない。
Also, if the outline of the variation pattern is the same, the special lottery result is a big hit without a probability change than the case where the special lottery result is a big hit with a probability change. A selection rate of execution/non-execution of the setting suggestion effect in the advance notice effect table may be determined. As a result, the appearance rate of the setting suggesting performance is increased in the case of winning a jackpot with no probability variation, and the disappointment of the player due to the fact that the probability variation is not provided can be reduced. In the above example, the three types of advance notice effects, namely, the dialogue effect, the weather change effect, and the rival horse effect, have been described, but it is needless to say that the number of types is not limited to three.
[12-14-4.台詞演出]
以下、予告演出のうち、台詞演出の詳細について説明する。周辺制御MPUは、予告演出として設定示唆演出無しの台詞演出を選択した場合、例えば、当該変動の開始から所定時間経過後(例えば2秒後)に、メイン液晶表示装置1600にキャラAを出現させ、キャラAの台詞として「今日、何日だっけ?」と表示する。そして、周辺制御MPUは、例えば、キャラAの台詞表示から所定時間後(例えば3秒後)に、メイン液晶表示装置1600にキャラBを出現させ、キャラBの台詞として「さあ・・・・」と表示する。なお、例えば、キャラA及びキャラBの台詞は当該変動の大当り期待度を示唆するものであってもよい。
[12-14-4. Dialogue production]
In the following, the details of the dialogue effect will be described among the advance notice effects. When the dialogue effect without setting suggestion effect is selected as the advance notice effect, the peripheral control MPU causes the character A to appear on the main liquid
一方、周辺制御MPUは、予告演出として設定示唆演出有りの台詞演出を選択した場合、後述する台詞演出テーブルからキャラBの台詞(設定を示唆する台詞)を選択する。周辺制御MPUは、例えば、当該変動の開始から所定時間経過後(例えば2秒後、つまり上述の設定示唆演出無しの場合のキャラAが出現するタイミングと同じタイミング)に、メイン液晶表示装置1600にキャラAを出現させ、キャラAの台詞として「今日、何日だっけ?」と表示する。周辺制御MPUは、例えば、キャラAの台詞表示から所定時間後(例えば3秒後)に、メイン液晶表示装置1600にキャラBを出現させ、選択したキャラBの台詞を表示する。なお、キャラAの台詞は、例えば、「今日のこの台の設定って知ってる?」のような設定値を直接表現する台詞であってもよい。
On the other hand, the peripheral control MPU selects the dialogue of the character B (the dialogue suggesting the setting) from a dialogue production table, which will be described later, when the dialogue effect with the setting suggestion effect is selected as the advance notice effect. For example, the peripheral control MPU displays the main liquid
図166は、台詞演出テーブルの一例である。台詞演出テーブルは、例えば周辺制御ROMに格納されている。台詞演出テーブルは、台詞演出の演出種別及びキャラBの台詞の内容の選択率、を設定ごとに保持する。なお、演出種別は、「途中まで一緒のパターン」と「いきなり分岐するパターン」とを含み、当該2つのパターンそれぞれに対して「かもね系」の台詞と「確定系」の台詞とが存在する。 FIG. 166 is an example of a dialogue effect table. The dialogue effect table is stored, for example, in the peripheral control ROM. The dialogue effect table holds the effect type of the dialogue effect and the selection rate of the content of the dialogue of the character B for each setting. Note that the production types include "patterns that are the same until the end" and "patterns that suddenly diverge", and for each of the two patterns, there are "Kamone" lines and "deterministic" lines. .
「途中まで一緒のパターン」に属する各台詞は、途中まで同一の台詞を含み、その後異なる台詞へと分岐する。図166の例では、「途中まで一緒のパターン」に属する台詞は、全て「さあ・・・」で始まり、その後異なる台詞へと分岐する。一方、「いきなり分岐するパターン」に属する台詞は、始めから異なる台詞へと分岐する。なお、「途中まで一緒のパターン」に属する台詞の選択率の方が、「いきなり分岐するパターン」に属する台詞の選択率より高いほうが望ましい。期待感を引っ張るためである。 Each line belonging to the "partially same pattern" contains the same line halfway, and then branches to a different line. In the example of FIG. 166, all of the lines belonging to the "partially same pattern" start with "Come on..." and then branch into different lines. On the other hand, the lines belonging to the "suddenly branching pattern" branch into different lines from the beginning. In addition, it is desirable that the selection rate of the lines belonging to the "partially same pattern" is higher than the selection rate of the lines belonging to the "suddenly branching pattern". This is to create a sense of anticipation.
「かもね系」に属する台詞は、現在の設定を示唆するものの、設定を確定的には告知しない台詞である。例えば、「でも、偶数の日だったような気がする・・・」は、偶数設定を示唆する「かもね系」の台詞である。「でも、偶数の日だったような気がする・・・」は「かもね」系の台詞であるため、奇数設定でも出現する可能性があるように選択率が決定されている。但し、奇数設定での当該台詞の選択率は、偶数設定での当該台詞の選択率より十分に低いものとする。他の「かもね系」の台詞についても同様に、台詞が示唆する設定における当該台詞の選択率は、他の設定における当該台詞の選択率より十分に高いものとする。 Lines belonging to the "Kamone system" are lines that suggest the current setting but do not definitely announce the setting. For example, "But I feel like it was an even-numbered day..." is a "Kamone-type" line suggesting an even-numbered setting. "But I feel like it was an even day..." is a "maybe" type of line, so the selection rate is determined so that it may appear even in odd number settings. However, it is assumed that the selection rate of the line in the odd number setting is sufficiently lower than the selection rate of the line in the even number setting. Similarly, with regard to other "Kamone-type" lines, the selection rate of the line in the setting suggested by the line is sufficiently higher than the selection rate of the line in other settings.
一方「確定系」に属する台詞は、設定を確定的に告知する台詞である。例えば、「あっ!思い出した!偶数の日だ!」は、偶数設定を確定的に告知する「確定系」の台詞である。従って、奇数設定における当該台詞の選択率は0であり、偶数設定においてのみ選択率
が0を超える。
On the other hand, the lines belonging to the "deterministic type" are lines that definitely announce the setting. For example, "Oh! I remember! It's an even number day!" Therefore, the selection rate of the line is 0 in the odd setting, and the selection rate exceeds 0 only in the even setting.
なお、「確定系」に属する台詞の選択率より、「かもね系」に属する台詞の選択率の方が高いことが望ましい。仮に「確定系」に属する台詞の選択率が高いとすると、遊技を開始してから短い時間で確定的に高設定を遊技者に報知する可能性が十分にあり、この場合、ホール内の他のパチンコ機1の設定がよくないと推測する遊技者が一定数存在するため、他の遊技機の稼働を低下させてしまうおそれがあるからである。
In addition, it is desirable that the selection rate of the lines belonging to the "Kamane type" is higher than the selection rate of the lines belonging to the "deterministic type". Assuming that the selection rate of lines belonging to the "deterministic type" is high, there is a good possibility that the high setting will definitely be notified to the player within a short period of time after the start of the game. This is because there is a certain number of players who presume that the setting of the
なお、SPリーチやムービーリーチなどの特定のリーチ演出を実行する場合の台詞演出や、擬似連を行う場合の台詞演出では、キャラクタBの設定示唆を行う台詞を赤文字(大当り期待示唆演出等における通常演出の台詞は白文字)で表示してもよい。これにより、遊技者にとって期待示唆演出の台詞と設定示唆演出の台詞とが区別しやすくなるため、遊技者に不自然さを感じさせることなく2種類の演出(設定示唆演出と期待示唆演出)共存させることができる。なお、期待示唆演出とは、当該特別図柄変動における大当り期待度が所定値であることを示す演出であり、具体的には、1回の変動内で大当たりに対する期待を示唆する予告演出や、複数の変動に跨って大当たりに対する期待を示唆する先読み演出を含む。 In addition, in the dialogue production when executing a specific reach production such as SP reach or movie reach, or in the dialogue production when performing a pseudo-continuation, the dialogue suggesting the setting of character B is written in red Dialogue in normal production may be displayed in white letters). This makes it easier for the player to distinguish between the lines of the expected suggestive effect and the lines of the set suggested effect, so that the two types of effects (the set suggested effect and the expected suggested effect) coexist without making the player feel unnatural. can be made In addition, the expected suggestion production is a production that indicates that the degree of expectation for the big hit in the special symbol fluctuation is a predetermined value. Includes a look-ahead effect that suggests expectations for a big win across fluctuations in
なお、周辺制御MPUは、天候変化演出やライバル馬演出についても、図示はしないが、台詞演出テーブルと同様の抽選テーブルによって設定示唆演出を決定するとよい。例えば、天候変化演出における設定示唆演出において、メイン液晶表示装置1600に雷雲が表示され、雷光によって「246?」等の数字が表示されたり(偶数設定を示唆する「かもね系」の演出)、ライバル馬演出における設定示唆演出において、主人公キャラクタが育てている馬とライバル馬による併せ馬演出がメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示され、例えばライバル馬のゼッケンに「135?」等の数字が表示されたりする(奇数設定を示唆する「かもね系」の演出)。
It should be noted that the peripheral control MPU may also determine setting suggesting effects for the weather change effect and the rival horse effect using a lottery table similar to the dialogue effect table, although not shown. For example, in a setting suggestion effect in a weather change effect, thunderclouds are displayed on the main liquid
上述の例では台詞演出におけるキャラAの台詞として「今日、何日だっけ?」を表示するようにしたが、この台詞の他にも、キャラAが「先週のテスト何点だった?」、キャラBが「66点だよ!(設定6が確定する「確定系」)」や「55点だった気が・・(設定5を示唆する「かもね系」)」のように、一の演出(例えば台詞演出)に対して複数のバリエーションを設けるようにしてもよい。その場合に、A演出(例えば日付を聞く演出)よりもB演出(例えばテストの点数を聞く演出)のほうが設定示唆に対する信憑性を高めるようにするとよい。具体的には、例えば、A演出で「6が付いた日だった気が・・(かもね系)」といわれたときの設定6である期待度は30%に留まるものの、B演出で「66点だった気が・・(かもね系)」といわれたときの設定6である期待度は50%といったようにするとよい。 In the above example, character A's line in the line production is "What day is it today?" Character B is ``66 points! A plurality of variations may be provided for the production (for example, dialogue production). In that case, it is preferable that the B effect (for example, asking for a test score) is more credible than the A effect (for example, asking for a date). Specifically, for example, when A production says, “I feel like it was a day with 6 (maybe)”, the expectation level, which is set to 6, remains at 30%, but B production says “ I feel like it was 66 points (maybe)", the expectation level, which is set at 6, should be 50%.
[12-14-5.予告演出テーブルの別例]
図167は予告演出テーブルの別例である。図167の例では、予告演出テーブル173は各変動パターンについての予告演出の選択率を保持する。図165の例と異なり、図167の予告演出テーブルは、設定示唆演出の実行有無についての情報を保持していない。つまり、周辺制御MPUは、図167の予告演出テーブルの変動パターンに対応する選択率に従って、予告演出の種類のみを選択する。
[12-14-5. Another example of the notice effect table]
FIG. 167 is another example of the notice effect table. In the example of FIG. 167, the notice effect table 173 holds the selection rate of the notice effect for each variation pattern. Unlike the example in FIG. 165, the advance notice effect table in FIG. 167 does not hold information on whether or not the setting suggestion effect is executed. In other words, the peripheral control MPU selects only the type of notice effect according to the selection rate corresponding to the variation pattern of the notice effect table of FIG.
そして、周辺制御MPUは、変動パターンと、選択した予告演出の種類に基づいて、設定示唆演出を実行するか否かを決定する。図168(A)は、変動パターンの概要が「通常変動」であり、かつ予告演出として「台詞演出」が選択された場合の、設定示唆演出実行有無の振り分けを示す設定示唆演出テーブルの一例である。図168(B)は、変動パターンの概要が「ノーマルリーチ+1図柄」であり、かつ予告演出として「台詞演出」が
選択された場合の、設定示唆演出実行有無の振り分けを示す設定示唆演出テーブルの一例である。図168のような、変動パターンと予告演出との全ての組み合わせについての設定示唆演出テーブルが、予め周辺制御ROMに格納されている。
Then, the peripheral control MPU determines whether or not to execute the setting suggestion effect based on the variation pattern and the type of the selected advance notice effect. FIG. 168(A) is an example of a setting suggestion effect table showing the sorting of setting suggestion effect execution presence/absence when the outline of the variation pattern is "normal variation" and "dialogue effect" is selected as the notice effect. be. FIG. 168(B) is an example of a setting suggestion effect table showing the sorting of whether or not to execute a setting suggestion effect when the outline of the variation pattern is "
なお、上述の例では、周辺制御MPUは、予告演出の内容を決定した後に設定示唆演出の実行有無を決定しているが、設定示唆演出の実行有無を決定してから予告演出の内容を決定してもよい。このような手法を用いることで、図165のようなテーブルよりもデータ量が多くなるものの、演出の出現率や信頼度を詳細に設定することができる。また、図165に示すテーブルと本別例で示す処理とを複合させてもよい。 In the above example, the peripheral control MPU determines whether or not to execute the setting suggestion effect after determining the content of the advance notice effect. You may By using such a method, although the amount of data is larger than that of the table shown in FIG. 165, it is possible to set the appearance rate and reliability of effects in detail. Also, the table shown in FIG. 165 and the processing shown in this example may be combined.
[12-14-6.設定示唆演出の具体例]
図169は、設定示唆演出の概要の一例を示す説明図である。図169(A)、(B)、(C)の順に進行する演出は、台詞演出において、キャラBの台詞として「4か5か6が付く日だよ!」が選択された場合における設定示唆演出の概要である。
[12-14-6. Concrete example of setting suggestion effect]
FIG. 169 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of an outline of setting suggestion effect. 169A, 169B, and 169C are shown in the order of the dialogue production, and are suggested settings when "It's a day with 4, 5, or 6!" is selected as the dialogue of character B. This is an overview of the production.
図169(A)において、特別図柄変動が開始する。図169(B)において、当該特別図柄変動の開始後に、メイン液晶表示装置1600にキャラBの台詞「4か5か6が付く日だよ!」が表示される。図169(C)において、特別図柄変動の終了時まで、当該台詞がメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示される。
In FIG. 169(A), the special symbol variation starts. In FIG. 169(B), after the start of the special symbol variation, the main liquid
図169(A)、(D)、(E)の順に進行する演出は、台詞演出において、キャラBの台詞として「6が付く日だよ!」が選択された場合における設定示唆演出の概要である。図169(A)、(D)、(E)の順に進行する演出において、設定示唆演出は特別図柄変動の開始時から開始しつつ、設定示唆演出において示唆される設定が特別図柄変動終了中に変更されている。具体的には、図169(D)において、当該特別図柄変動の開始後に、メイン液晶表示装置1600にキャラBの台詞「4か5か6が付く日だよ!」が表示される。図169(E)において、特別図柄変動の終了時に、キャラBの台詞「6が付く日だよ!」が表示される。つまり、キャラBの台詞が示唆する設定が昇格している。
169A, 169D, and 169E are outlines of setting suggestion effects when "It's a day with 6!" be. 169 (A), (D), (E) in the order of production, while setting suggestion production is started from the start of the special symbol variation, the setting suggested in the setting suggestion production is during the end of the special symbol variation has been edited. Specifically, in FIG. 169(D), after the start of the special symbol variation, the main liquid
具体的には、例えば、台詞演出テーブルにおける台詞(最終的に表示される台詞)それぞれについて、台詞変更のタイミングと各タイミングにおける台詞とを示す1以上のシナリオ、及び各シナリオの選択率が、設定ごとに定義されていてもよい。周辺制御MPUは、選択したシナリオに従って、台詞変更のタイミングにおいて当該タイミングにおける台詞を表示する。 Specifically, for example, for each line in the line production table (line to be finally displayed), one or more scenarios indicating the timing of line change and the line at each timing, and the selection rate of each scenario are set. may be defined for each The peripheral control MPU displays the dialogue at the timing of the dialogue change according to the selected scenario.
なお、この場合、台詞演出テーブルは、示唆する設定が降格する可能性があるシナリオを保持しないことが望ましい。具体的には、例えば、台詞演出テーブルは、「4か5か6が付く日だよ!」という台詞の後に、「偶数の日だよ!」という台詞が表示されるシナリオを保持しないことが望ましい。 In this case, it is desirable that the dialogue rendering table does not hold a scenario in which suggested settings may be demoted. Specifically, for example, the dialogue production table may not hold a scenario in which the dialogue "It's a day with 4, 5 or 6!" desirable.
また、図169の例では、特別図柄変動において設定示唆演出のみが行われているが、他の演出(例えば大当り期待度を示唆する演出等)が並行して実行されてもよい。なお、特別図柄変動の終了時にキャラBの台詞が昇格する例を示したが、これに限らず、特別図柄変動の終了前に昇格させるようにしてもよい。なお、キャラBの台詞の前にキャラAが出現し、キャラAがキャラBに話しかける演出を行うが、図面では割愛している。 In addition, in the example of FIG. 169, only the setting suggestion effect is performed in the special symbol variation, but other effects (for example, the effect of suggesting the degree of expectation for a big hit, etc.) may be performed in parallel. Although the example in which the dialogue of character B is promoted at the end of the special symbol variation has been shown, this is not the only option, and the promotion may be performed before the special symbol variation is terminated. Character A appears before character B's dialogue, and an effect is performed in which character A speaks to character B, but this is omitted in the drawing.
図170は、先読み演出としての設定示唆演出の概要の一例を示す説明図である。図170(A)において、特別図柄変動の保留がない状態での特別図柄変動中に、第一始動口2002に遊技球Bが入賞している。続いて、図170(B)において、第一始動口2002への遊技球Bの入賞直後に、メイン液晶表示装置1600にキャラBの台詞「4か5
か6が付く日だよ!」が表示される。この場合、既に変動している特別図柄の残り時間が不定となるため、キャラAを表示することなくキャラBを即座に表示してもよいし、入賞から所定時間経過後にキャラBを表示してもよいし、キャラAを表示してからキャラBを表示するようにしてもよい。また、図170(B)において保留表示領域内の表示が示す保留数が1つ増えている。
FIG. 170 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of an overview of the setting suggestion effect as the look-ahead effect. In FIG. 170(A), the game ball B has won the
It's a day with a 6! ” is displayed. In this case, since the remaining time of the special symbols that have already changed is indefinite, the character B may be displayed immediately without displaying the character A, or the character B may be displayed after a predetermined time has passed since the prize was won. Alternatively, the character B may be displayed after the character A is displayed. Also, in FIG. 170(B), the number of reservations indicated by the display in the reservation display area is increased by one.
続いて、図170(C)において、全ての装飾図柄が停止し、当該特別図柄変動が終了する。また、メイン液晶表示装置1600にキャラBの台詞「4か5か6が付く日だよ!」が表示されたままである。続いて、図170(D)において、当該入賞に対応する特別図柄変動が開始する。また、当該特別図柄変動の開始と同時に、メイン液晶表示装置1600に表示されるキャラBの台詞が「5か6が付く日だよ!」に変化する。つまり、キャラBの台詞が示す設定が昇格している。
Subsequently, in FIG. 170(C), all decorative symbols are stopped, and the special symbol variation ends. In addition, the main liquid
続いて図170(E)において、全ての装飾図柄が停止し、当該入賞に対応する特別図柄変動が終了する。当該入賞に対応する特別図柄変動の終了時に、メイン液晶表示装置1600に表示されるキャラBの台詞が「6が付く日だよ!」に変化する。つまり、キャラBの台詞が示す設定が昇格している。
Subsequently, in FIG. 170(E), all decorative symbols are stopped, and the special symbol variation corresponding to the winning is terminated. At the end of the special symbol variation corresponding to the winning prize, the dialogue of character B displayed on the main liquid
なお、例えば、周辺制御ROMは、キャラBの台詞及び台詞の変化タイミングを定義する台詞先読み演出テーブル(図示しない)を保持する。具体的には、例えば、台詞先読み演出テーブルは、キャラBの台詞の変化タイミングと、入賞時及び各変化タイミングにおけるキャラBの台詞と、を定義する。入賞時以降かつ当該入賞に対応する特別図柄変動以前の特別図柄変動の開始時、変動中、及び終了時等は、当該変化タイミングの一例である。なお、各変化タイミングにおいて台詞が示唆する設定が降格しないことが望ましい。なお、入賞時の保留記憶数ごとに異なる台詞先読み演出テーブルが存在してもよい。周辺制御MPUは、事前判定コマンドに基づいて先読み演出を実行すると決定した場合に、例えば、所定の割合で、台詞先読み演出テーブルを参照して台詞先読み演出を実行する。また、昇格する場合において図170では1段階ずつ昇格させている(「4か5か6が付く日だよ!」、「5か6が付く日だよ!」、「6が付く日だよ!」の順に昇格)が、一気に複数段階昇格させるようにしてもよい。具体的には、例えば、図170において、(D)の台詞を表示することなく(E)の台詞を表示してもよい。 It should be noted that, for example, the peripheral control ROM holds a dialogue look-ahead effect table (not shown) that defines the dialogue of character B and the timing at which the dialogue changes. Specifically, for example, the dialogue look-ahead effect table defines the change timings of character B's dialogue and the dialogue of character B at the time of winning and at each change timing. The start time, during the change, and the end time of the special symbol variation after the winning and before the special symbol variation corresponding to the winning are examples of the change timing. It is desirable that the settings suggested by the dialogue are not downgraded at each change timing. It should be noted that there may be a different speech prefetch effect table for each number of pending memories at the time of winning. When the peripheral control MPU determines to execute the look-ahead effect based on the advance determination command, for example, at a predetermined rate, it executes the look-ahead effect with reference to the look-ahead effect table. In addition, in the case of promotion, promotion is performed one step at a time in FIG. !”) may be promoted in multiple stages at once. Specifically, for example, in FIG. 170, the dialogue (E) may be displayed without displaying the dialogue (D).
なお、設定示唆演出は、上記した以外の特定の状況下で実行されてもよい。例えば、保留連の条件を満たした場合に、設定示唆演出が実行されてもよい。保留連とは、大当り遊技の終了までに保留された特別乱数によって次回の大当りが実現されることである。この場合、例えば、当該保留が行われた後、かつ当該大当り遊技終了前に、設定示唆演出が実行される。また、例えば、特定の変動パターンが所定回数連続した場合において、当該所定回数目の特別図柄変動において、設定示唆演出が実行されてもよい。 Note that the setting suggestion effect may be executed under specific circumstances other than those described above. For example, when the condition of the pending series is satisfied, the setting suggesting effect may be executed. The reserved series means that the next big hit is realized by the special random numbers reserved until the end of the big win game. In this case, for example, after the suspension is performed and before the big win game ends, the setting suggestion effect is executed. Further, for example, when a specific variation pattern continues for a predetermined number of times, the setting suggestion effect may be executed in the special symbol variation of the predetermined number of times.
[12-15.設定示唆演出の制限]
以下、特定の条件下における設定示唆演出の制限について説明する。
[12-15. Restrictions on setting suggestion effects]
Restrictions on setting suggestion effects under specific conditions will be described below.
[12-15-1.特殊状態以降時における設定示唆演出の制限]
まず、特殊状態以降時における設定示唆演出の制限について説明する。以下、設定確認モード中とエラー発生中は、いずれも特殊状態の一例である。なお、設定確認モードとは、設定確認処理において、設定表示条件を満たすと判定された場合(ステップS8062:Yes)に開始する、設定値を表示するためのモードである。
[12-15-1. Restriction of setting suggestion production after special state]
First, the limitation of the setting suggestion effect after the special state will be described. Below, both the setting confirmation mode and the occurrence of an error are examples of special states. Note that the setting confirmation mode is a mode for displaying setting values that is started when it is determined in the setting confirmation process that the setting display condition is satisfied (step S8062: Yes).
図171(A)は、設定確認モード時演出制限テーブルの一例である。図171(B)は、エラー発生時演出制限テーブルの一例である。設定確認モード時演出制限テーブル及
びエラー発生時演出制限テーブルは、例えば、周辺制御ROMに格納されている。
FIG. 171(A) is an example of an effect limit table for the setting confirmation mode. FIG. 171(B) is an example of an effect limit table when an error occurs. The effect limit table at the time of setting confirmation mode and the effect limit table at the time of error occurrence are stored, for example, in the peripheral control ROM.
[12-15-1-1.設定確認モード以降時における設定示唆演出の制限]
まず、設定確認モード時演出制限テーブルについて説明する。設定確認モード時演出制限テーブルは、設定示唆演出を実行すると決定された変動(以下、本章において設定示唆変動と呼ぶ)の実行中又は保留中に、設定確認モードが開始した場合における、当該変動の設定示唆演出を制限するか否かを示す制限フラグを格納する。
[12-15-1-1. Restriction of setting suggestion effect after setting confirmation mode]
First, the setting confirmation mode effect limit table will be described. The setting confirmation mode effect restriction table is a setting confirmation mode when the setting confirmation mode starts during the execution or suspension of the variation determined to execute the setting suggestion effect (hereinafter referred to as setting suggestion variation in this chapter). Stores a restriction flag indicating whether or not to restrict setting suggestion rendering.
設定確認モード時演出制限テーブルは、設定示唆演出の開始前(つまり、設定示唆演出を行うと判定されたにも関わらず設定示唆にかかわる演出が実行(表示)されていないとき)に設定確認モードが開始した場合における制限フラグを格納するレコード1701と、設定示唆変動における設定示唆演出の開始後(つまり、設定示唆演出を行うと判定され設定示唆にかかわる演出が実行(表示)されたとき)に設定確認モードが開始した場合における制限フラグを格納するレコード1702と、を含む。
The setting confirmation mode effect limit table is set in the setting confirmation mode before the start of the setting suggestion effect (that is, when the effect related to the setting suggestion is not executed (displayed) even though it is determined to perform the setting suggestion effect) A
図159に示す設定確認処理が行われる場合には、設定確認モード開始時に遊技が停止しており、図156に示す設定確認処理が行われる場合には、設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行する。従って、設定確認モード時演出制限テーブルは、設定確認モード開始時に遊技が停止している場合における制限フラグを格納するカラム1703と、設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行する場合における制限フラグを格納するカラム1704と、を含む。
When the setting confirmation process shown in FIG. 159 is performed, the game is stopped at the start of the setting confirmation mode, and when the setting confirmation process shown in FIG. 156 is performed, the game progresses even during the setting confirmation mode. . Therefore, the effect restriction table in the setting confirmation mode stores a
また、設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行する場合には、設定確認モード中に始動口に遊技球が入賞することにより、新たな設定示唆変動を保留する可能性がある。従って、カラム1704は、設定確認モード中の始動口への入賞に対応する新たな設定示唆変動における制限フラグを格納するカラム1705を含む。なお、設定確認モード時演出制限テーブル中の各制限フラグは、例えば、パチンコ機1の製造時又はホール等において、パチンコ機1に備え付けられた操作媒体(遊技者が操作できない操作媒体でも遊技者が操作できる操作媒体でも構わない)によって、設定可能である。なお、設定確認モード中に、始動口に遊技球が入球した場合に、当該入球に対しては抽選情報の取得及び賞球が実施されなくてもよい。但し、このような場合においても、既に保留されている特別図柄変動においては、設定確認モード中又は設定変更モード終了後に実行される。
In addition, when the game progresses even during the setting confirmation mode, there is a possibility that a new setting suggestion variation may be suspended by winning a game ball in the starting hole during the setting confirmation mode. Accordingly,
設定確認モード開始時に遊技が停止する場合においては、フィールド1706及びフィールド1707の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1708~1711の値が0であり、フィールド1712及びフィールド1713の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1714~1717の値が0である。
When the game stops at the start of the setting confirmation mode, the value of one of the
また、設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行する場合においては、フィールド1706及びフィールド1707の値が0であり、フィールド1708及びフィールド1709の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1710及びフィールド1711の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1712及びフィールド1713の値が0であり、フィールド1714及びフィールド1715の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1716又はフィールド1717の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0である。
In addition, when the game progresses even during the setting confirmation mode, the values of the
周辺制御MPUは、設定確認モード開始時演出制限テーブルやエラー発生時演出制限テーブルに定義された各状態における制限フラグに従って、設定示唆演出の制限パターンを実行する。以下、これらの制限パターンについて説明する。 A peripheral control MPU executes a setting suggestion effect limit pattern according to a limit flag in each state defined in the effect limit table at the time of setting confirmation mode start and the effect limit table at the time of error occurrence. These restriction patterns are described below.
(1)設定示唆演出の開始前に設定確認モードが開始し、かつ設定確認モード開始時に遊
技が停止する場合について。
(1) Regarding the case where the setting confirmation mode starts before the setting suggestion effect starts and the game stops when the setting confirmation mode starts.
(1-1)遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を実行する(フィールド1706の値が1かつフィールド1707の値が0)。設定示唆演出が実行されることで、設定変更処理が実行される設定変更モードではなく設定確認モードが実行されたことを遊技者に知らせることができ、遊技の結果に影響がないという安心感を与えることができる。
(1-1) After restarting the game, the setting suggestion effect is executed (the value of the
(1-2)遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を実行しない(フィールド1706の値が0かつフィールド1707の値が1)。例えば、設定確認モード中に、設定確認中であることを示す音声や画像が各種スピーカ及びメイン液晶表示装置1600に出力される場合、このように設定示唆演出を実行しないことで、設定確認モード中でありながら高設定に変更されたかもしれないという期待感を、遊技者に提供することができる。
(1-2) The setting suggestion effect is not executed after the game is restarted (the value of the
(2)設定示唆演出の開始前に設定確認モードが開始し、かつ設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行する場合における、当該設定示唆変動の設定示唆演出について。 (2) Regarding the setting suggestion effect of the setting suggestion variation when the setting confirmation mode is started before the setting suggestion effect is started and the game progresses even during the setting confirmation mode.
(2-1)設定示唆演出を実行する(フィールド1708の値が1かつフィールド1709の値が0)。設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行するため、稼働を落とすことがない。なお、設定確認モード中であることを示す音声及び画像が、各種スピーカ及びメイン液晶表示装置1600に出力される場合には、これらの音声及び画像を、設定示唆演出における音声及び画像に優先して出力する。このとき、遊技者に対して不快感を与えないために、設定示唆演出の一部又は全部が表示されるように、設定確認モード中であることを示す画像をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示する。また、「設定示唆演出がいつ表示されたのか」、「高設定を示唆する設定示唆演出が表示されたかもしれない」、という期待感を遊技者に提供するために、設定示唆演出の全てを隠すようにして、設定確認モード中であることを示す画像をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示してもよい。
(2-1) Execute setting suggestion rendering (the value of
(2-2)設定示唆演出を実行しない(フィールド1708の値が0かつフィールド1709の値が1)。例えば、設定値を遊技者が確認した場合において、設定示唆演出による設定示唆と実際の設定とが相違すると(例えば、設定値が1であるときに「高設定かも?」のような高設定を示唆する演出が発生すると)、遊技者が遊技機に対して不信感を抱く可能性があり、設定示唆演出を実行しないことにより、このような事態を回避することができる。
(2-2) Do not execute the setting suggestion effect (the value of the
(2’)設定示唆演出の開始前に設定確認モードが開始し、かつ設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行する場合における、設定確認モード中の始動口への入賞に対応する新たな設定示唆変動の設定示唆演出について。 (2′) New setting suggestion variation corresponding to winning in the starting hole during the setting confirmation mode when the setting confirmation mode starts before the setting suggestion effect starts and the game progresses even during the setting confirmation mode. About the setting suggestion production.
(2’-1)設定示唆演出を実行する(フィールド1710の値が1かつフィールド1711の値が0)。設定示唆演出が実行されることで、設定変更モードではなく設定確認モードが実行されたことを遊技者に知らせることができ、遊技の結果に影響がないという安心感を与えることができる。
(2'-1) Execute setting suggestion effect (the value of
(2’-2)設定示唆演出を実行しない(フィールド1710の値が0かつフィールド1711の値が1)。例えば、ホールが設定値に疑問を感じているために設定確認モードに移行させた場合には、その後設定値を変更する可能性がある。このような場合において当該設定示唆演出が実行されると、当該設定示唆演出と実際の設定とが異なる(例えば、当該設定示唆演出において偶数設定が確定する表示がされながら、異なる設定に変更された後の当該設定示唆演出において奇数設定が確定する表示がされる)可能性があるため、ホールと遊技者との間でトラブルが発生しかねない。設定示唆演出を実行しないことによ
り、このような事態の発生を回避することができる。
(2'-2) The setting suggestion effect is not executed (the value of
なお、上述した設定確認状態であること示す画像、音、及び光などについては、上述したフィールドの値に問わず現出させるようにしたほうが望ましい。また、設定確認状態に移行したら遊技を停止させる場合にも新たな入賞を有効とする場合も想定されるため、その場合には遊技を進行させる処理と同様の処理を行えばよい。 It is desirable that the image, sound, light, etc., indicating the setting confirmation state described above should appear regardless of the field values described above. Also, when the game is stopped after shifting to the setting confirmation state, it is assumed that a new winning prize may be validated.
(3)設定示唆変動中かつ設定示唆演出の開始後(設定示唆演出を表示しているとき、及び設定示唆演出を表示し該設定示唆演出の表示を終了した後)に設定確認モードが開始し、かつ設定確認モード開始時に遊技が停止する場合について。 (3) The setting confirmation mode starts during the setting suggestion change and after the setting suggestion effect is started (when the setting suggestion effect is displayed, and after the setting suggestion effect is displayed and the setting suggestion effect is finished displaying). And about the case where the game stops when the setting confirmation mode starts.
(3-1)遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を再開する(フィールド1712の値が1かつフィールド1713の値が0)。開始済みの設定示唆演出が中止されると、遊技者は設定が変更されたのではないかと不信感を抱いてしまう可能性があり、遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を再開することにより、このような事態の発生を回避することができる。
(3-1) After restarting the game, the setting suggestion effect is restarted (the value of the
(3-2)遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を再開しない(フィールド1712の値が0かつフィールド1713の値が1)。例えば、設定確認モード中に、設定確認中であることを示す音声や画像が各種スピーカ及びメイン液晶表示装置1600に出力される場合、このように設定示唆演出を実行しないことで、設定確認モード中でありながら高設定に変更されたかもしれないという期待感を、遊技者に提供することができる。
(3-2) Do not restart the setting suggestion effect after restarting the game (the value of the
(4)設定示唆変動中かつ設定示唆演出の開始後(設定示唆演出を表示しているとき、及び設定示唆演出を表示し該設定示唆演出の表示を終了した後)に設定確認モードが開始し、かつ設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行する場合における、当該設定示唆変動の設定示唆演出について。 (4) The setting confirmation mode starts during the setting suggestion change and after the setting suggestion effect is started (when the setting suggestion effect is displayed, and after the setting suggestion effect is displayed and the setting suggestion effect is finished displaying). And regarding the setting suggestion effect of the setting suggestion change when the game progresses even during the setting confirmation mode.
(4-1)設定示唆演出を継続する(フィールド1714の値が1かつフィールド1715の値が0)。設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行するため、稼働を落とすことがない。なお、設定確認モード中であることを示す音声及び画像が、各種スピーカ及びメイン液晶表示装置1600に出力される場合には、これらの音声及び画像を、設定示唆演出における音声及び画像に優先して出力する。このとき、遊技者に対して不快感を与えないために、設定示唆演出の一部又は全部が表示されるように、設定確認モード中であることを示す画像をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示する(設定示唆演出にかかる画像と設定確認モードを示す画像とが重ならない、又は設定示唆演出にかかる画像と「設定確認モード中」のように設定確認モードを示す文字とが重ならないように表示する)。なお、この表示等については、後述するエラー発生時でも同様の処理とすることができる。なお、ここでいう「重ならない」とは、実際にRAMに設定されている画像データではなく、遊技者からの見た目が重ならないことを示す。
(4-1) Continue setting suggestion rendering (the value of
また、「設定示唆演出がいつ表示されたのか」、「高設定を示唆する設定示唆演出が表示されたかもしれない」、という期待感を遊技者に提供するために、設定示唆演出の全てを隠すようにして、設定確認モード中であることを示す画像をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示してもよい。
In addition, in order to provide the player with a sense of expectation such as "When was the setting suggesting effect displayed?" An image indicating the setting confirmation mode may be displayed on the main liquid
(4-2)設定示唆演出を中止する(フィールド1714の値が0かつフィールド1715の値が1)。例えば、設定値を遊技者が確認した場合において、設定示唆演出による設定示唆と実際の設定とが相違すると(例えば、設定値が1であるときに「高設定かも?」のような高設定を示唆する演出が発生すると)、遊技者が遊技機に対して不信感を抱く可能性があり、設定示唆演出を実行しないことにより、このような事態を回避することが
できる。
(4-2) Stop the setting suggestion effect (the value of the
(4’)設定示唆変動中かつ設定示唆演出の開始後に設定確認モードが開始し、かつ設定確認モード中にも遊技が進行する場合における、設定確認モード中の始動口への入賞に対応する新たな設定示唆変動の設定示唆演出について。 (4') A new game corresponding to winning at the starting port during the setting confirmation mode when the setting confirmation mode is started after the setting suggestion change is started and the setting confirmation mode is started, and the game is progressing even during the setting confirmation mode. About setting suggestion production of setting suggestion change.
(4’-1)設定示唆演出を実行する(フィールド1716の値が1かつフィールド1717の値が0)。設定示唆演出が実行されることで、設定変更モードではなく設定確認モードが実行されたことを遊技者に知らせることができ、遊技の結果に影響がないという安心感を与えることができる。
(4'-1) Execute setting suggestion effect (the value of
(4’-2)設定示唆演出を実行しない(フィールド1716の値が0かつフィールド1717の値が1)。例えば、ホールが設定値に疑問を感じているために設定確認モードに移行させた場合には、その後設定値を変更する可能性がある。このような場合において当該設定示唆演出が実行されると、当該設定示唆演出と実際の設定とが異なる(例えば、当該設定示唆演出において偶数設定が確定する表示がされながら、異なる設定に変更された後の設定示唆演出において奇数設定が確定する表示がされる)ため、ホールと遊技者との間でトラブルが発生しかねない。設定示唆演出を実行しないことにより、このような事態の発生を回避することができる。
(4'-2) The setting suggestion effect is not executed (the value of
なお、設定確認モードにおいても遊技が進行する場合において、設定確認モードが複数の変動に跨った場合、例えば、周辺制御MPUは、例えば、主制御MPU1311からの通知に基づいて、設定確認モード開始後の最初の図柄確定時又は次の変動開始時に、設定確認モードか否かの判定を行う。周辺制御MPUは、設定確認モードである判定した場合、新たに入賞した保留が設定示唆変動であれば当該保留に対応する変動とともに設定示唆演出を行う。設定示唆演出が実行されることで、設定変更処理が実行される設定変更モードではなく設定確認モードが実行されたことを遊技者に知らせることができ、遊技の結果に影響がないという安心感を与えることができる。
In addition, when the game progresses even in the setting confirmation mode, if the setting confirmation mode straddles a plurality of fluctuations, for example, the peripheral control MPU, for example, based on the notification from the
また、周辺制御MPUは、この場合に設定示唆演出を実行しないようにしてもよい。設定値を遊技者が確認した場合において、設定示唆演出による設定示唆と実際の設定とが相違すると(例えば、設定値が1であるときに「高設定かも?」のような高設定を示唆する演出が発生すると)、遊技者が遊技機に対して不信感を抱く可能性があり、設定示唆演出を実行しないことにより、このような事態を回避することができる。 Also, the peripheral control MPU may not execute the setting suggestion effect in this case. When the player confirms the setting value, if the setting suggestion by the setting suggestion effect and the actual setting are different (for example, when the setting value is 1, a high setting is suggested such as "Maybe high setting?") When the effect occurs), the player may have a sense of distrust toward the gaming machine, and such a situation can be avoided by not executing the setting suggesting effect.
このように、設定示唆演出を行う場合、及び設定示唆演出を行わない場合において、双方に効果が発揮されるため、設定示唆演出に対する演出制限等をホール等が設定可能にすることで、ホール等の営業スタイルのニーズに合わせた遊技機を提供することができる。 In this way, both when the setting suggestion effect is performed and when the setting suggestion effect is not performed, the effect is exhibited in both cases. It is possible to provide amusement machines that meet the needs of each business style.
[12-15-1-2.エラー発生時における設定示唆演出の制限]
続いて、図171(B)を用いて、エラー発生時演出制限テーブルについて説明する。エラー発生時演出制限テーブルは、設定示唆演出を実行すると決定された変動(以下、本章において設定示唆変動と呼ぶ)の実行中又は保留中に、エラーが発生した場合における、当該変動の設定示唆演出を制限するか否かを示す制限フラグを格納する。
[12-15-1-2. Restriction of setting suggestion effect when error occurs]
Next, with reference to FIG. 171(B), the effect restriction table at the time of error occurrence will be described. The effect limit table at the time of error occurrence is a setting suggestion effect of the variation when an error occurs during the execution or suspension of the variation determined to execute the setting suggestion effect (hereinafter referred to as setting suggestion change in this chapter) stores a restriction flag indicating whether or not to restrict
エラー発生時演出制限テーブルは、設定示唆演出の開始前にエラーが発生した場合における制限フラグを格納するレコード1801と、設定示唆変動の変動中かつ設定示唆変動における設定示唆演出の開始後にエラーが発生した場合における制限フラグを格納するレコード1802と、を含む。
The effect limit table at the time of error occurrence includes a
なお、エラーには、遊技を停止させて報知される強エラーと、遊技が進行したまま報知される弱エラーと、がある。発射球センサ1020及び遊技領域5a内における不正な磁気を検知したエラーは、強エラーの一例である。満タンエラー(満タン検知センサ535からの検出信号に基づいてファールカバーユニット520内に貯留された遊技球で満タンであることを示すエラー)は、弱エラーの一例である。
Errors include a strong error that is reported after the game is stopped and a weak error that is reported while the game is in progress. An error that detects illegal magnetism in the
従って、エラー発生時演出制限テーブル、遊技が停止して報知されるエラーに対応する制限フラグを格納するカラム1803と、遊技が進行したまま報知されるエラーに対応する制限フラグを格納するカラム1804と、を含む。
Therefore, a
また、エラー発生中にも遊技が進行する場合には、エラー発生中に始動口に遊技球が入賞することにより、新たな設定示唆変動を保留する可能性がある。従って、カラム1804は、エラー発生中の始動口への入賞に対応する新たな設定示唆変動における制限フラグを格納するカラム1805を含む。
In addition, if the game progresses even during the occurrence of an error, there is a possibility that new setting suggestion fluctuations will be suspended due to the game ball entering the starting hole during the occurrence of the error. Therefore,
なお、エラー発生時演出制限テーブル中の制限フラグは、例えば、パチンコ機1の製造時又はホール等において、パチンコ機1に備え付けられた操作媒体(遊技者が操作できない操作媒体でも遊技者が操作できる操作媒体でも構わない)によって、設定可能である。
In addition, the restriction flag in the effect restriction table at the time of error occurrence can be set, for example, at the time of manufacture of the
なお、エラー発生時演出制限テーブルにおいて、フィールド1806及びフィールド1807の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1808及びフィールド1809の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1810及びフィールド1811の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1812及びフィールド1813の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1814及びフィールド1815の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0であり、フィールド1816及びフィールド1817の一方の値が1かつ他方の値が0である。
In the effect restriction table when an error occurs, the value of one of the
周辺制御MPUは、エラー発生時演出制限テーブルに定義された各ケースの制限フラグに従って、設定示唆演出の制限パターンを実行する。以下、これらの制限パターンについて説明する。 The peripheral control MPU executes the restriction pattern of the setting suggestion rendering in accordance with the restriction flag for each case defined in the rendering restriction table when an error occurs. These restriction patterns are described below.
(1)設定示唆演出の開始前にエラーが開始し、かつ当該エラー発生時に遊技が停止する(強エラー)場合について。 (1) Regarding the case where an error starts before the setting suggestion effect starts and the game stops when the error occurs (strong error).
(1-1)遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を実行する(フィールド1806の値が1かつフィールド1807の値が0)。設定示唆演出が実行されることで、ホール店員によってエラーが解除された際に設定が変更されていないことを遊技者に知らせることができ、遊技の結果に影響がないという安心感を与えることができる。
(1-1) After restarting the game, a setting suggestion effect is executed (the value of the
(1-2)遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を実行しない(フィールド1806の値が0かつフィールド1807の値が1)。これにより、エラーが発生した場合には、設定示唆演出が実行されなくなるという遊技者にとって不利となる事態が発生し得るため、遊技者はエラーを発生させないように遊技を進行させるようになり、遊技が円滑に進行し、かつホールの負担を軽減することができる。
(1-2) The setting suggestion effect is not executed after the game is restarted (the value of the
(2)設定示唆演出の開始前にエラーが発生し、かつ当該エラー発生始後も遊技が進行する(弱エラー)場合における、当該設定示唆変動の設定示唆演出について。 (2) Regarding the setting suggestion effect of the setting suggestion change when an error occurs before the setting suggestion effect starts and the game progresses even after the error occurrence (weak error).
(2-1)設定示唆演出を実行する(フィールド1808の値が1かつフィールド1809の値が0)。これにより、エラー発生中にも遊技が進行するため、遊技機の稼働を落
とすことがない。また、エラー発生中にも設定示唆演出が発生するため、遊技者の興趣を向上させることができる。なお、エラー発生中であることを示す音声及び画像が、各種スピーカ及びメイン液晶表示装置1600に出力される場合には、これらの音声及び画像を、設定示唆演出における音声及び画像に優先して出力する。このとき、遊技者に対して不快感を与えないために、設定示唆演出の一部又は全部が表示されるように、エラー発生中であることを示す画像をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示する。また、「設定示唆演出がいつ表示されたのか」、「高設定を示唆する設定示唆演出が表示されたかもしれない」、という期待感を遊技者に提供するために、設定示唆演出の全てを隠すようにして、エラー発生中であることを示す画像をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示してもよい。
(2-1) Execute setting suggestion rendering (the value of
(2-2)設定示唆演出を実行しない(フィールド1808の値が0かつフィールド1809の値が1)。これにより、エラーが発生した場合には、設定示唆演出が実行されなくなるという遊技者にとって不利となる事態が発生し得るため、遊技者はエラーを発生させないように遊技を進行させるようになり、遊技が円滑に進行し、かつホールの負担を軽減することができる。
(2-2) Do not execute setting suggestion rendering (the value of
(2’)設定示唆演出の開始前にエラーが発生し、かつ当該エラー発生中も遊技が進行する(弱エラー)場合における、当該エラー発生中の始動口への入賞に対応する新たな設定示唆変動の設定示唆演出について。 (2′) In the case where an error occurs before the setting suggestion effect starts and the game progresses even during the occurrence of the error (weak error), a new setting suggestion corresponding to the winning of the starting hole during the error occurrence. About setting suggestion production of variation.
(2’-1)設定示唆演出を実行する(フィールド1810の値が1かつフィールド1811の値が0)。これにより、エラー発生中にも遊技が進行するため、遊技機の稼働を落とすことがない。また、エラー発生中にも設定示唆演出が発生するため、遊技者の興趣を向上させることができる。
(2'-1) Execute setting suggestion effect (the value of
(2’-2)設定示唆演出を実行しない(フィールド1810の値が0かつフィールド1811の値が1)。これにより、エラー発生中の入賞については設定示唆演出が実行されないため、遊技者は遊技球の打ち出しを中止して、早期にエラー解除をするようになる。
(2'-2) The setting suggestion effect is not executed (the value of
(3)設定示唆変動中かつ設定示唆演出の開始後にエラーが発生し、かつ当該エラー発生時に遊技が停止する(強エラー)場合について。 (3) Regarding the case where an error occurs during the setting suggestion change and after the setting suggestion effect is started, and the game stops when the error occurs (strong error).
(3-1)遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を再開する(フィールド1812の値が1かつフィールド1813の値が0)。開始済みの設定示唆演出が中止されると、遊技者は設定が変更されたのではないかと不信感を抱いてしまう可能性があり、遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を再開することにより、このような事態の発生を回避することができる。
(3-1) After restarting the game, the setting suggestion effect is restarted (the value of the
(3-2)遊技再開後に設定示唆演出を再開しない(フィールド1812の値が0かつフィールド1813の値が1)。これにより、エラーが発生した場合には、設定示唆演出が中止されるという遊技者にとって不利となる事態が発生し得るため、遊技者はエラーを発生させないように遊技を進行させるようになり、遊技が円滑に進行し、かつホールの負担を軽減することができる。
(3-2) Do not restart the setting suggestion effect after restarting the game (the value of the
(4)設定示唆変動中かつ設定示唆演出の開始後にエラーが発生し、かつ当該エラー発生中にも遊技が進行する(弱エラー)場合における、当該設定示唆変動の設定示唆演出について。 (4) Regarding the setting suggestion effect of the setting suggestion change when an error occurs during the setting suggestion change and after the setting suggestion effect is started, and the game progresses even during the occurrence of the error (weak error).
(4-1)設定示唆演出を継続する(フィールド1814の値が1かつフィールド1815の値が0)。これにより、エラー発生中にも遊技が進行するため、遊技機の稼働を落
とすことがない。また、エラー発生中にも設定示唆演出が発生するため、遊技者の興趣を向上させることができる。なお、エラー発生中であることを示す音声及び画像が、各種スピーカ及びメイン液晶表示装置1600に出力される場合には、これらの音声及び画像を、設定示唆演出における音声及び画像に優先して出力する。このとき、遊技者に対して不快感を与えないために、設定示唆演出の一部又は全部が表示されるように、エラー発生中であることを示す画像をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示する。また、「設定示唆演出がいつ表示されたのか」、「高設定を示唆する設定示唆演出が表示されたのか」、という期待感を遊技者に提供するために、設定示唆演出の全てを隠すようにして、エラー発生中であることを示す画像をメイン液晶表示装置1600に表示してもよい。
(4-1) Continue setting suggestion rendering (the value of
(4-2)設定示唆演出を中止する(フィールド1814の値が0かつフィールド1815の値が1)。これにより、エラーが発生した場合には、設定示唆演出が中止するという遊技者にとって不利となる事態が発生し得るため、遊技者はエラーを発生させないように遊技を進行させるようになり、遊技が円滑に進行し、かつホールの負担を軽減することができる。
(4-2) Stop the setting suggestion effect (the value of the
(4’)設定示唆変動中かつ設定示唆演出の開始後にエラーが発生し、かつ当該エラー発生中も遊技が進行する(弱エラー)場合における、エラー発生中の始動口への入賞に対応する新たな設定示唆変動の設定示唆演出について。 (4') In the case where an error occurs during the setting suggestion change and after the setting suggestion effect is started, and the game progresses even during the occurrence of the error (weak error), a new prize corresponding to the winning at the start port during the error occurrence About setting suggestion production of setting suggestion change.
(4’-1)設定示唆演出を実行する(フィールド1816の値が1かつフィールド1817の値が0)。これにより、エラー発生中にも遊技が進行するため、遊技機の稼働を落とすことがない。また、エラー発生中にも設定示唆演出が発生するため、遊技者の興趣を向上させることができる。
(4'-1) Execute setting suggestion effect (the value of
(4’-2)設定示唆演出を実行しない(フィールド1816の値が0かつフィールド1817の値が1)。これにより、エラー発生中の入賞については設定示唆演出が実行されないため、遊技者は遊技球の打ち出しを中止して、早期にエラー解除をするようになる。
(4'-2) The setting suggestion effect is not executed (the value of
このように、設定示唆演出を行う場合、及び設定示唆演出を行わない場合において、双方に効果が発揮されるため、設定示唆演出に対する演出制限等をホール等が設定可能にすることで、ホール等の営業スタイルのニーズに合わせた遊技機を提供することができる。 In this way, both when the setting suggestion effect is performed and when the setting suggestion effect is not performed, the effect is exhibited in both cases. It is possible to provide amusement machines that meet the needs of each business style.
[12-15-2.新たな始動入賞における演出の制限]
以下、特別図柄変動中かつ新たな変動を保留可能な状態での新たな始動入賞、に対応する変動における演出の制限について説明する。図172は、新始動入賞演出制限テーブルの一例である。新始動入賞演出制限テーブルは、例えば、周辺制御ROMに格納されている。
[12-15-2. Restrictions on production in new start winning prizes]
Hereinafter, the limitation of the effect in the variation corresponding to the new start winning prize during the special symbol variation and in the state where the new variation can be reserved will be described. FIG. 172 is an example of a new start prize effect limit table. The new start prize effect limit table is stored in, for example, the peripheral control ROM.
新始動入賞演出制限テーブルは、例えば、条件欄と、参照処理テーブル欄と、フラグ欄と、を含む。条件欄の条件は、前変動の演出についての仮定と、当該仮定における新たな始動入賞における演出における演出制限と、によって定義されている。なお、本章における前変動とは、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の直前の変動である。前変動の演出の条件として、当該変動に対応する特別抽選結果が大当りであるかの期待示唆演出のみが行われる場合と、期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が行われる場合と、がある。 The new start prize effect limit table includes, for example, a condition column, a reference processing table column, and a flag column. The conditions in the condition column are defined by the assumptions about the performance of the previous variation and the restrictions on the performances in the new starting winnings under the assumptions. It should be noted that the previous change in this chapter is the change immediately before the change corresponding to the new start winning. As a condition for the performance of the previous variation, there are a case where only an expectation suggesting performance is performed as to whether or not the special lottery result corresponding to the variation is a big hit, and a case where both the expectation suggesting performance and the set suggesting performance are performed.
また、新たな始動入賞における先読み演出の演出制限として、先読み演出における設定示唆演出のみを制限(つまり設定示唆演出を実行しない)、先読み演出における設定示唆演出と期待示唆演出の両方を制限(つまり設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出を実行しない)
、及び先読み演出における設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出のいずれも制限しない(つまり設定示唆演出及び先読み演出を実行する)、がある。
In addition, as a production restriction for the pre-reading production in the new start prize, only the setting suggestion production in the pre-reading production is restricted (that is, the setting suggestion production is not executed), and both the setting suggestion production and the expected suggestion production in the pre-reading production are restricted (that is, the setting Suggestion production and expected suggestion production are not executed)
, and neither the setting suggestion effect nor the expected suggestion effect in the look-ahead effect is restricted (that is, the setting suggestion effect and the look-ahead effect are executed).
参照処理テーブル欄は、対応する条件に含まれる、新たな始動入賞における先読み演出制限を実行する場合に参照する処理テーブルの識別子を格納する。フラグ欄は、どの条件を実行し、かつどの処理テーブルを用いて新たな始動入賞における先読み演出に対する処理を決定するかを示すフラグを格納する。 The reference process table column stores the identifier of the process table to be referred to when executing the look-ahead effect restriction in the new start winning, which is included in the corresponding condition. The flag column stores flags indicating which conditions are to be executed and which processing table is used to determine the processing for the look-ahead effect in the new start winning.
なお、処理テーブル1~3のいずれか1つに対応するフラグ欄に1が格納され、処理テーブル1~3の他の2つに対応するフラグ欄には0が格納される。また、処理テーブル4~6のいずれか1つに対応するフラグ欄に1が格納され、処理テーブル4~6の他の2つに対応するフラグ欄には0が格納される。新始動入賞演出制限テーブル中のフラグは、例えば、パチンコ機1の製造時又はホール等において、パチンコ機1に備え付けられた操作媒体(遊技者が操作できない操作媒体でも遊技者が操作できる操作媒体でも構わない)によって、設定可能である。
1 is stored in the flag column corresponding to one of the processing tables 1-3, and 0 is stored in the flag column corresponding to the other two of the processing tables 1-3. Also, 1 is stored in the flag column corresponding to one of the processing tables 4-6, and 0 is stored in the flag column corresponding to the other two of the processing tables 4-6. The flags in the new startup prize effect restriction table are, for example, the operation media installed in the
周辺制御MPUは、特別図柄変動中かつ新たな変動を保留可能な状態での新たな始動入賞があり、かつ前変動において期待示唆演出のみが実行されると判定した場合、新始動入賞演出制限テーブルの「前変動の演出」欄の値が「期待示唆のみ」に対応するフラグ欄であって、値として1を格納するフラグ欄、に対応する、条件欄が示す条件を実行する。さらに、周辺制御MPUは、当該フラグ欄に対応する処理テーブルを参照して、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動における先読み演出の内容を決定する。 When the peripheral control MPU determines that there is a new start winning during the special symbol variation and in a state where the new variation can be suspended, and that only the expected suggestive performance is executed in the previous variation, the new start winning performance restriction table The condition indicated by the condition column corresponding to the flag column storing 1 as the value is executed. Further, the peripheral control MPU refers to the processing table corresponding to the flag column, and determines the content of the look-ahead effect in the variation corresponding to the new start winning.
同様に、周辺制御MPUは、特別図柄変動中かつ新たな変動を保留可能な状態での新たな始動入賞があり、かつ前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が実行される場合、新始動入賞演出制限テーブルの「前変動の演出」欄の値が「期待示唆+設定示唆」に対応するフラグ欄であって、値として1を格納するフラグ欄、に対応する処理テーブルを参照して、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動における先読み演出の内容を決定する。 Similarly, the peripheral control MPU, when there is a new start winning during the special symbol variation and in a state where the new variation can be suspended, and when the expected suggestive effect and the set suggestive effect are executed in the previous change, the new start win By referring to the processing table corresponding to the flag column in which the value of the "previous variation effect" column of the effect restriction table corresponds to "expectation suggestion + setting suggestion" and which stores 1 as a value, a new Determine the contents of the look-ahead effect in the variation corresponding to the start winning prize.
以下、条件欄が示す各条件について説明する。第1の条件(処理テーブル1が選択される条件)は、前変動において期待示唆演出のみが実行される場合に、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出のみが制限されることである。第1の条件において、前変動において期待示唆演出が行われるため、遊技者は大当りに対する期待による高揚感が高まっている。このような状態で当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出として設定示唆演出が実行されると、遊技者の意識が当該設定示唆演出に対しても向けられることにより、前変動の演出における高揚感が低下するおそれがある。また、遊技者が当該設定示唆演出を当該期待示唆演出と混同して、遊技者をぬか喜びさせてしまうおそれがある。従って、第1の条件が実行されることにより、これらの事態の発生を抑制することができる。 Each condition indicated by the condition column will be described below. The first condition (the condition for selecting the processing table 1) is that when only the expected suggestive effect is executed in the previous change, only the setting suggestive effect is restricted as the prefetch effect restriction of the change corresponding to the new start winning. It is to be done. In the first condition, since the expectation-suggesting effect is performed in the previous variation, the player's feeling of excitement due to the expectation of the big win is heightened. In such a state, when the setting suggestion effect is executed as a variable prefetch effect corresponding to the new start winning, the player's consciousness is also directed to the setting suggestion effect, so that the previous variation effect There is a risk that the feeling of exaltation will decrease. In addition, the player may confuse the setting suggestive effect with the expected suggestive effect, which may make the player feel uneasy. Therefore, the occurrence of these situations can be suppressed by executing the first condition.
また、第1の条件において、前変動において期待示唆演出が行われるが、この状態でさらに当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出として設定示唆演出が実行された場合には、遊技者は、前変動ではずれることを想定した場合であっても、まだ当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動にも期待ができるため、遊技者に安心感を提供することができる。 In addition, in the first condition, the expected suggestive effect is performed in the previous variation, but in this state, if the set suggested effect is performed as the prefetch effect of the variation corresponding to the new start winning, the player , even if it is assumed that the previous fluctuation will be off, since the fluctuation corresponding to the new start prize can still be expected, it is possible to provide the player with a sense of security.
例えば、例えば図165の予告演出テーブルによって演出を選択する場合、周辺制御MPUは、当該テーブルによって演出を決定し、その後に設定示唆演出を制限することを示す条件欄のフラグが1であるか否か(制限するか否か)を判定し、1(制限する)であればset有りが選択されたとしてもset無しに書き換えて表示するような処理を行うことで、設定示唆演出の制限を実施する。つまり、周辺制御MPUは、演出を決定した後に
、判定処理を実施することで、図165に示した予告演出テーブルを用いて、設定示唆演出の制限を実行することができる。即ち、パチンコ機1は演出の制限種別ごとの演出テーブルを保持する必要がないため、データ量を削減することができる。なお、後述する期待示唆演出も同様に、周辺制御MPUは、図161の最終保留色テーブルを用いて先読み保留表示が白以外を選択した場合であっても、期待示唆演出を制限した場合には選択した保留表示を白に書き換えて表示する。
For example, when an effect is selected from the advance notice effect table of FIG. 165, the peripheral control MPU decides the effect from the table, and then determines whether the flag in the condition column indicating that the setting suggestion effect is restricted is 1 or not. (whether or not to restrict), and if it is 1 (restrict), even if set is selected, the setting suggestion effect is restricted by performing processing to rewrite and display without set. do. That is, the peripheral control MPU can limit the setting suggestion effect using the advance notice effect table shown in FIG. 165 by executing the determination process after determining the effect. That is, since the
第2の条件(処理テーブル2が選択される条件)は、前変動において期待示唆演出のみが実行される場合に、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出の双方を制限することである。第2の条件において、前変動において期待示唆演出が行われるため、遊技者は大当りに対する期待による高揚感が高まっている。このような状態で当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出として、設定示唆演出及び期態度示唆演出が実行されると、遊技者の意識がこれらの演出に対しても向けられることにより、前変動の演出における高揚感が低下するおそれがある。従って、第2の条件が実行されることにより、これらの事態の発生を抑制することができる。 The second condition (the condition for selecting the processing table 2) is that when only the expected suggestion effect is executed in the previous variation, the setting suggestion effect and the expected suggestion are set as the prefetch effect restriction of the change corresponding to the new start winning. It is to limit both sides of the production. In the second condition, the expectation-suggesting effect is performed in the previous variation, so that the player has a heightened sense of exhilaration due to the expectation of the big win. In such a state, when the setting suggesting effect and the attitude suggesting effect are executed as the variable anticipatory effect corresponding to the new start winning, the player's attention is directed to these effects as well. There is a possibility that the exhilaration in the presentation of the previous variation may be reduced. Therefore, the occurrence of these situations can be suppressed by executing the second condition.
第3の条件(処理テーブル3が選択される条件)は、前変動において期待示唆演出のみが実行される場合に、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出のいずれも制限しないことである。第3の条件において、前変動において期待示唆演出が行われるため、遊技者は大当りに対する期待による高揚感が高まっている。このような状態で、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出として設定示唆演出が実行されることにより、大当りに対する高揚感に加え、設定示唆演出に対する高揚感(特に、高設定確定示唆演出又は高設定確定演出等が実行された場合)を遊技者に与えることができる。 The third condition (the condition for selecting the processing table 3) is that when only the expected suggestive effect is executed in the previous change, the setting suggested effect and the expected suggested effect are set as the prefetch effect restriction of the change corresponding to the new start winning. Do not limit any of the renditions. In the third condition, since the expectation-suggesting effect is performed in the previous variation, the player has an increased sense of exhilaration due to the expectation of the big win. In such a state, the setting suggestion effect is executed as a variable look-ahead effect corresponding to the new start winning, so that in addition to the uplifting feeling for the big hit, the feeling of exhilaration for the setting suggesting effect (especially, the high setting fixed suggesting effect Or when a high setting confirmation effect etc. is executed) can be given to the player.
第4の条件(処理テーブル4が選択される条件)は、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が実行される場合に、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出のみが制限されることである。第4の条件において、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が行われるため、遊技者は前変動で大当りに当選するかもしれないという高揚感と、(特に高設定示唆演出又は高設定確定演出が実行された場合)設定示唆による高揚感と、を感じている。このような状態で、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出として設定示唆演出が実行されると、前変動の保留における大当りに対する期待への高揚感が低下する事態が発生するおそれがある。 The fourth condition (the condition for selecting the processing table 4) is that when the expected suggestive effect and the set suggestive effect are executed in the previous change, the set suggestive effect is set as the prefetch effect limit of the change corresponding to the new start winning. The only limitation is In the fourth condition, since the expected suggestive effect and the setting suggestive effect are performed in the previous fluctuation, the player has an exhilarating feeling that he may win a big hit in the previous fluctuation (especially high setting suggestive effect or high setting fixed effect is executed), and feel a sense of elation due to setting suggestions. In such a state, if the setting suggestion effect is executed as the look-ahead effect of the variation corresponding to the new start winning, there is a possibility that the excitement of the expectation for the big win in the suspension of the previous variation may be lowered. .
具体的には、例えば、前変動の設定示唆演出において設定4以上が確定し、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出としての設定示唆演出で設定5以上が確定する場合、前変動における設定示唆演出は不正確な情報を多く含んでいる(本来は設定5以上であるにも関わらず、設定4である可能性も示唆している)。このような場合には、遊技者は、前変動における設定示唆演出だけでなく期待示唆演出についても、不正確な情報を多く含んでいると推測する(具体的には、例えば、表示態様が赤色である保留についても大当り期待度が高くないと推測する)可能性があり、当該期待示唆演出に対する高揚感が低下するおそれがある。第4の条件が実行されることにより、このような事態の発生を抑制することができる。 Specifically, for example, when setting 4 or more is confirmed in the setting suggestion effect of the previous change, and setting 5 or more is confirmed in the setting suggestion effect as the prefetch effect of the change corresponding to the new start winning, in the previous change The setting suggesting effect contains a lot of inaccurate information (although originally the setting is 5 or higher, it also suggests the possibility of setting 4). In such a case, the player presumes that not only the setting suggestion effect in the previous fluctuation but also the expected suggestion effect contains a lot of inaccurate information (specifically, for example, the display mode is red There is a possibility that the degree of expectation for a big hit is not high for the reservation that is ), and there is a possibility that the feeling of exhilaration for the expected suggestive performance will decrease. By executing the fourth condition, the occurrence of such a situation can be suppressed.
第5の条件(処理テーブル5が選択される条件)は、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が実行される場合に、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出の双方を制限することである。第5の条件において、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が行われるため、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出で設定示唆演出が行われると、短期間で複数回の設定示唆演出が行われることになり、遊技者が設定値を高精度に推測してしまうおそれがある(例えば、奇数設
定示唆演出と高設定示唆演出が行われた場合、設定5である可能性が高い)。このような状態で遊技者に低設定だと判断された場合には、当該パチンコ機1での遊技を中止するおそれがあり、高設定だと判断された場合には、ホール内の他のパチンコ機1の稼働が低下するおそれがある。第5の条件が実行されることにより、このような事態の発生を抑制することができる。
The fifth condition (the condition for selecting the processing table 5) is that when the expected suggestive effect and the set suggestive effect are executed in the previous change, the set suggestive effect is set as the prefetch effect limit of the change corresponding to the new start winning prize. and the expected suggestive performance. In the fifth condition, since the expected suggesting effect and the setting suggesting effect are performed in the previous change, when the setting suggesting effect is performed in the look-ahead effect corresponding to the new start winning, the setting suggesting effect is performed multiple times in a short period of time. There is a risk that the player will guess the setting value with high accuracy (for example, if the odd number setting suggesting effect and the high setting suggesting effect are performed, there is a high possibility that the setting is 5). In such a state, if the player determines that the setting is low, there is a risk of stopping the game with the
また特に、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が行われ、かつ新たな始動入賞に対応する変動でも先読み演出として期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が行われると、短期間に多くの演出が発生し、遊技者が混乱するおそれがある。第5の条件が実行されることにより、このような事態の発生を抑制することができる。 In particular, if the expected suggestive effect and setting suggestive effect are performed in the previous change, and the expected suggestive effect and setting suggestive effect are performed as the prefetch effect even in the change corresponding to the new start winning, many effects occur in a short period of time. This may confuse the player. By executing the fifth condition, the occurrence of such a situation can be suppressed.
第6の条件(処理テーブル6が選択される条件)は、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が実行される場合に、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出のいずれも制限しないことである。第6の条件において、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が行われるため、遊技者は当該設定示唆演出で示唆された設定における、当該期待示唆演出の期待度を想定している。この状態で、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動において、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出が行われることにより、これら2つの期待示唆演出による期待度が挙がる可能性がある。 The sixth condition (the condition for selecting the processing table 6) is that when the expected suggestion effect and the set suggestion effect are executed in the previous variation, the set suggestion effect is set as the prefetch effect restriction of the variation corresponding to the new start winning prize. and expected suggestive renditions. In the sixth condition, since the expected suggestive effect and the setting suggestive effect are performed in the previous variation, the player assumes the degree of expectation of the expected suggestive effect in the settings suggested by the set suggestive effect. In this state, the setting suggestion effect and the expected suggestion effect are performed in the variation corresponding to the new start winning, and there is a possibility that the degree of expectation is raised by these two expected suggestion effects.
具体的には、例えば、前変動において設定4以上を示唆する設定示唆演出が実行され、かつ新たな始動入賞における先読み演出として設定5以上を示唆する設定示唆演出が実行された場合、遊技者は前変動における期待示唆演出について設定4以上における期待度を想定している。しかし、その後、新たな始動入賞における先読み演出としての設定示唆演出によって設定5以上が示唆されるため、当該期待示唆演出についての期待度が設定5以上の期待度を想定するようになり、遊技者の高揚感が増す。 Specifically, for example, when a setting suggestion effect suggesting a setting of 4 or more is executed in the previous variation, and a setting suggestion effect suggesting a setting of 5 or more is executed as a look-ahead effect in the new start winning, the player Expectations are assumed at a setting of 4 or higher for the expected suggestive performance in the previous fluctuation. However, after that, since the setting suggestion effect as the look-ahead effect in the new start winning suggests a setting of 5 or more, the expectation level for the expected suggestion effect comes to assume an expectation level of 5 or more, and the player The feeling of exhilaration increases.
このように、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出制限内容それぞれについて、効果が発揮されるため、このような先読み演出制限内容をホール等が設定可能にすることで、ホール等の営業スタイルのニーズに合わせた遊技機を提供することができる。 In this way, since the effect is exhibited for each of the prefetching effect restriction contents corresponding to the new start winning, the hall etc. can set such prefetching effect restriction contents, so that the needs of the sales style of the hall etc. It is possible to provide a game machine that meets the needs.
以下、各処理テーブル、及び各処理テーブルを参照して実行される先読み演出について説明する。なお、各処理テーブルは、例えば、周辺制御ROMに格納されている。 Each processing table and the look-ahead effect executed with reference to each processing table will be described below. Each processing table is stored, for example, in a peripheral control ROM.
図173は、処理テーブル1の一例である。まず、各処理テーブルについて共通の内容について説明する。各処理テーブルは、前変動の特別抽選結果における当選種別と、当該当選種別に対応する新たな始動入賞に係る処理内容と、当該処理内容の識別子である処理番号と、を格納する。 173 is an example of the processing table 1. FIG. First, contents common to each processing table will be described. Each processing table stores the type of winning in the special lottery result of the previous change, the processing content related to the new start winning corresponding to the type of winning, and the processing number as the identifier of the processing content.
なお、各処理テーブルが保持する処理内容は、制限対象でない先読み演出についての処理内容が定義されている。具体的には、例えば、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出のみを制限する場合に参照されるテーブルである処理テーブル1の処理内容には、期待示唆演出についての処理内容が定義されている。同様に、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出の双方を制限する場合に参照されるテーブルである処理テーブル3の処理内容には、期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出についての処理内容が定義されている。 It should be noted that the processing content held by each processing table defines the processing content for the look-ahead effect that is not subject to restriction. Specifically, for example, the processing contents of the processing table 1, which is a table to be referred to when restricting only the setting suggestive effect as the variable prefetch effect restriction corresponding to the new start winning, includes the expected suggestive effect. Processing content is defined. Similarly, the processing contents of the processing table 3, which is a table referred to when restricting both the expected suggestive effect and the setting suggested effect, as the variable prefetch effect restriction corresponding to the new start winning, include the expected suggestive effect and the set suggestive effect. The processing content for the setting suggestion effect is defined.
従って、周辺制御MPUは、新始動入賞演出制限テーブルのフラグに基づいて、新たな始動入賞における制限対象の先読み演出、及び参照する処理テーブルを決定し、当該処理テーブルに基づいて、制限対象ではない先読み演出に対する処理を決定する。 Therefore, the peripheral control MPU determines the restricted target look-ahead effect in the new start winning effect and the processing table to be referred to based on the flag of the new start winning effect restriction table, and based on the processing table, determines that the target is not restricted. Determines the processing for the look-ahead effect.
なお、後述する処理テーブル3及び処理テーブル6は、新たな始動入賞に係る処理内容を複数の処理内容から選択するためのフラグを格納する。なお、処理テーブル中のフラグは、例えば、パチンコ機1の製造時又はホール等において、パチンコ機1に備え付けられた操作媒体(遊技者が操作できない操作媒体でも遊技者が操作できる操作媒体でも構わない)によって、設定可能である。
Note that the processing table 3 and the processing table 6, which will be described later, store flags for selecting the processing content related to the new starting prize from a plurality of processing content. Note that the flags in the processing table may be operation media provided in the
以下、処理テーブル1が定義する新たな始動入賞に係る処理内容について説明する。処理テーブル1は、前変動において期待示唆演出のみが実行され、かつ新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出のみを制限する場合に参照されるテーブルである。以下、期待示唆を行う先読み演出として保留先読みが行われる例について記載する。 Hereinafter, the processing contents related to the new start prize defined by the processing table 1 will be described. A processing table 1 is a table referred to when only the expected suggesting performance is executed in the previous variation and only the set suggesting performance is restricted as the pre-reading performance restriction of the variation corresponding to the new start winning. Hereinafter, an example in which pending prefetching is performed as a prefetching effect for suggesting expectations will be described.
処理番号1の処理は、前変動の当選種別が時短ありの大当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号1の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様が、大当り期待度が高い特定の態様(例えば、青、緑、赤等の保留表示態様)である場合、例えば、前変動で当選した大当りのオープニング画面の開始時に、新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様をデフォルト(図161の最終保留色テーブルにおける白色の表示態様)に戻す。但し、大当りのオープニング画面の開始時に、保留表示領域において保留が表示されなくなる場合には、当該特定の態様の保留表示を、他の保留表示と同様に消去する。また、周辺制御MPUは、当該大当り終了後の時短移行時に、当該新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様を、当該特定の表示態様に戻さない(即ちデフォルト表示のままにする)。なお、周辺制御MPUは、当該時短終了時に当該新たな入賞の保留が消化されていない場合であっても、当該新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様を、当該特定の表示態様に戻さない(即ちデフォルト表示のままにする)。
The process of
処理番号2の処理は、前変動の当選種別が時短なしの大当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号2の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様が、大当り期待度が高い特定の態様である場合、例えば、前変動で当選した大当りのオープニング画面の開始時に、新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様をデフォルトに戻す。但し、大当りのオープニング画面の開始時に、保留表示領域において保留が表示されなくなる場合には、当該特定の態様の保留表示を、他の保留表示と同様に消去する。また、当該大当り遊技が終了した後に制御される通常状態移行時も、当該新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様を、当該特定の表示態様に戻さない(即ちデフォルト表示のままにする)。
The process of
処理番号3の処理は、前変動の当選種別が小当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号3の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様を変更しない(つまり、当該保留表示を継続、具体的には、例えば、青色の保留表示態様であれば、青色の保留表示態様を継続して表示する)。また、周辺制御MPUは、前変動で当選した小当りのオープニング画面の開始時に、新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様をデフォルトに戻してもよい。但し、小当りのオープニング画面の開始時に、保留表示領域において保留が表示されなくなる場合には、当該特定の態様の保留表示を、他の保留表示と同様に消去する。
The process of
処理番号4の処理は、前変動の当選種別がはずれである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号4の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、新たな始動入賞の保留表示の態様を変更しない(つまり、当該保留表示を継続、具体的には、例えば、青色の保留表示態様であれば、青色の保留表示態様を継続して表示する)。
The process of
図174は、処理テーブル2の一例である。処理テーブル2は、前変動において期待示
唆演出のみが実行され、かつ新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出の双方を制限する場合に参照されるテーブルである。処理テーブル2は、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出の双方を制限する場合に参照されるテーブルであるため、前変動の大当り種別に関わらず、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動における先読み演出に対して特別な処理が実行されないことが定義されている。
174 is an example of the processing table 2. FIG. The processing table 2 is a table that is referred to when only the expected suggesting effect is executed in the previous variation and both the set suggesting effect and the expected suggesting effect are restricted as the pre-reading effect restriction of the variation corresponding to the new start winning. be. Since the processing table 2 is a table to be referred to when restricting both the setting suggesting effect and the expected suggesting effect as the fluctuation predictive effect restriction corresponding to the new start winning, regardless of the big hit type of the previous change, It is defined that no special processing is executed for the look-ahead effect in the variation corresponding to the new start winning.
図175は、処理テーブル3の一例である。処理テーブル3は、前変動において期待示唆演出のみが実行され、かつ新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出のいずれも制限しない場合に参照されるテーブルである。 175 is an example of the processing table 3. FIG. The processing table 3 is a table referred to when only the expected suggestive effect is executed in the previous variation and neither the set suggestive effect nor the expected suggestive effect is limited as the prefetch effect restriction of the variation corresponding to the new start winning. be.
処理番号5~6の処理は、前変動の当選種別が時短ありの大当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号5~6の処理のうちの1つをフラグによって選択可能である。処理番号5~6の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号1の処理と同様である。
The processing of
処理番号5の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した大当り遊技中、又は前変動で当選した大当りに付随する時短中の第二特別図柄の保留の消化中等である。処理番号5の処理により、前変動の開始前等に設定示唆演出が開始したことを遊技者が認識している場合に、設定示唆演出が行われることを遊技者が忘れないようにすることができる。
In the process of
処理番号6の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。なお、前変動において時短付きの大当りに当選しているため、当該新たな入賞に対応する変動は当該時短の終了後に開始する可能性が高い(時短中には第二始動口2004に遊技球が高頻度で入賞し、かつ第一特別図柄変動及び第二特別図柄変動の保留がある場合には、第一特別図柄変動に優先して第二特別図柄変動が実行されるため)。従って、処理番号6の処理により、時短終了後に設定示唆演出が実行されるため、時短が終了してしまったことによる遊技者の落胆を軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号7~8の処理は、前変動の当選種別が時短無しの大当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号7~8の処理のうちの1つをフラグによって選択可能である。処理番号7~8の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号2の処理と同様である。
The processing of
処理番号7の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した大当り遊技中等である。遊技者は、大当りに当選したものの時短に当選しなかったことに対して落胆を感じるものの、処理番号7の処理により、遅くとも大当り遊技中には設定示唆演出が開始する場合には、当該落胆を軽減した状態で大当り遊技を楽しむことができる。
In the process of
処理番号8の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号8の処理により、大当り終了後にすぐに設定示唆演出が開始するため、時短が付与されなかったことに対する遊技者の落胆を軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号9~10の処理は、前変動の当選種別が小当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞
に係る処理である。処理番号9~10の処理のうちの1つをフラグによって選択可能である。処理番号9~10の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号3の処理と同様である。
The processing of
処理番号9の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した小当りのオープニング中、又は当該小当り中等である。小当りでは、遊技者に対して小さな特典が付与されるだけであるため、遊技者は落胆する可能性があるが、処理番号9の処理により、早いタイミングで設定示唆演出が開始することで落胆を軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号10の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。小当りに係る一連の消化時間は大当りに係る一連の消化時間よりも短いため、前変動の開始前等に設定示唆演出が開始したことを遊技者が認識している場合に、当該設定示唆演出を実行しないと遊技者は不信感を感じる可能性がある。処理番号10の処理により、遊技者に対してこのような不信感を与えないようにすることができる。
In the process of
処理番号11~13の処理は、前変動の当選種別がはずれである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号11~13の処理のうちの1つをフラグによって選択可能である。処理番号11~13の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号4の処理と同様である。
The processes of
処理番号11の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。
In the process of
処理番号12の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の保留先読み演出における保留表示の態様が大当たり期待度の高い特定の態様(例えば、緑又は赤)である場合に限って、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に、当該新たな始動入賞における先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。なお、当該設定示唆演出の実行タイミングについては、変更しない、即ち特別な処理を行わないが、設定示唆演出の実行タイミングを異なるように制御(例えば、キャラBによる設定を示唆する台詞が現出するタイミングを通常よりも所定秒数(例えば2秒)遅らせたり、所定秒数(例えば2秒)早めたりなど)してもよい。処理番号12の処理により、前変動において大当り期待度が高い保留表示の態様が出現したにも関わらずはずれたことに対する落胆を感じている遊技者に対して、このような落胆を軽減することができる。なお、図175及び後述する図178における、旧保留とは前変動に対応する保留であり、新保留とは当該新たな始動入賞に対応する保留である。
In the process of
処理番号13の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、保留表示の態様が大当たり期待度の高い特定の態様(例えば、緑又は赤)である場合には、当該新たな始動入賞における先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行しない。処理番号13の処理により、前変動において大当り期待度が高い保留表示の態様が出現したにも関わらずはずれ、さらに当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動でも先読み演出としての設定示唆演出も出現しないため、遊技者の遊技に対するのめりこみを抑止することができる。
In the process of
図176は、処理テーブル4の一例である。処理テーブル4は、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が実行され、かつ新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出のみが制限される場合に参照されるテーブルである。 176 is an example of the processing table 4. FIG. The processing table 4 is a table referred to when the expected suggesting effect and the setting suggesting effect are executed in the previous variation and only the setting suggesting effect is limited as the prefetch effect restriction of the variation corresponding to the new start winning. .
処理番号14の処理は、前変動の当選種別が時短有りの大当りである場合の、新たな始
動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号14の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号1の処理と同様である。
The process of
処理番号15の処理は、前変動の当選種別が時短無しの大当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号15の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号2の処理と同様である。
The process of
処理番号16の処理は、前変動の当選種別が小当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号16の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号3の処理と同様である。
The process of
処理番号17の処理は、前変動の当選種別がはずれである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号16の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号4の処理と同様である。
The process of
なお、処理テーブル4は、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出のみを制限する場合に参照されるテーブルであるため、前変動の大当り種別に関わらず、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動における設定示唆演出に対して特別な処理が実行されないことが定義されている。 In addition, since the processing table 4 is a table that is referred to when limiting only the setting suggestion effect as the variable prefetch effect restriction corresponding to the new start winning, regardless of the big hit type of the previous change, the new start It is defined that special processing is not executed for setting suggestion effects in variations corresponding to winning.
図177は、処理テーブル5の一例である。処理テーブル5は、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が実行され、かつ新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出の双方が制限される場合に参照されるテーブルである。処理テーブル5は、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出の双方を制限する場合に参照されるテーブルであるため、前変動の大当り種別に関わらず、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動における先読み演出に対して特別な処理が実行されないことが定義されている。 177 is an example of the processing table 5. FIG. The processing table 5 is referred to when both the expected suggesting effect and the set suggesting effect are executed in the previous variation, and both the set suggesting effect and the expected suggesting effect are restricted as the pre-reading effect restriction of the variation corresponding to the new start winning. It is a table where Since the processing table 5 is a table that is referred to when limiting both the set suggesting effect and the expected suggesting effect as the variable prefetch effect restriction corresponding to the new start winning, regardless of the type of the previous variation jackpot, It is defined that no special processing is executed for the look-ahead effect in the variation corresponding to the new start winning.
図178は、処理テーブル6の一例である。処理テーブル6は、前変動において期待示唆演出及び設定示唆演出が実行され、かつ新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出及び期待示唆演出のいずれも制限されない場合に参照されるテーブルである。 178 is an example of the processing table 6. FIG. The processing table 6 is referred to when the expected suggesting effect and the set suggesting effect are executed in the previous variation and neither the set suggesting effect nor the expected suggesting effect are restricted as the prefetch effect restriction of the variation corresponding to the new start winning. table.
処理番号18~21の処理は、前変動の当選種別が時短ありの大当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号18~21の処理のうちの1つをフラグによって選択可能である。処理番号18~21の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号1の処理と同様である。
The processing of
処理番号18の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した大当り遊技中、又は前変動で当選した大当りに付随する時短中の第二特別図柄の保留の消化中等である。処理番号18の処理により、前変動の開始前等に設定示唆演出が開始したことを遊技者が認識している場合に、設定示唆演出が行われることを遊技者が忘れないようにすることができる。
In the process of
処理番号19の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好な場合(具体的には、例えば、前変動の設定示唆演出において設定4以上が確定することが報知され、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する
変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において設定5以上が確定することが報知される場合)にのみ、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した大当り遊技中、又は前変動で当選した大当りに付随する時短中の第二特別図柄の保留の消化中等である。
In the processing of
処理番号19の処理により、遊技者は、遅くとも時短付き大当り中には高設定示唆演出を見ることができるため、時短付き大当りと高設定示唆とによる二重の高揚感を得ることができる。また、例えば、前変動の設定示唆演出において設定5以上が確定することが報知され、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において設定4以上が確定することが報知されるような場合は、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出は遊技者に対して新たな情報を提供していない無駄な演出であり、処理番号19の処理によりこのような無駄な演出を省略することができる。逆に、例えば、前変動の設定示唆演出において設定4以上が確定することが報知された場合には、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において設定5以上が確定することが報知されなくても遊技者は遊技を続行する可能性が高いため、当該設定示唆演出は無駄な演出になる可能性が高く、処理番号19の処理によりこのような無駄な演出を省略することができる。
By the processing of the
処理番号20の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号20の処理により、時短終了後にすぐに設定示唆演出が開始することが多いため、時短状態が終了したことに対する遊技者の落胆を軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号21の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好な場合にのみ、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号21の処理により、処理番号19の処理において説明したような無駄な設定示唆演出を省略したり、時短状態が終了したことに対する遊技者の落胆を軽減したりすることができる。
In the processing of
処理番号22~25の処理は、前変動の当選種別が時短なしの大当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号22~25の処理のうちの1つをフラグによって選択可能である。処理番号22~25の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号2の処理と同様である。
The processing of
処理番号22の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した大当り遊技中等である。遊技者は、大当りに当選したものの時短に当選しなかったことに対して落胆を感じるものの、処理番号22の処理により、遅くとも大当り遊技中には設定示唆演出が開始する場合には、当該落胆を軽減した状態で大当り遊技を楽しむことができる。
In the process of
処理番号23の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好な場合にのみ、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した大当り遊技中等である。処理番号23の処理により、遅くとも大当り遊技中には設定示唆演出が開始する場合には、当該落胆を軽減した状態で大当り遊技を楽しむことができる。
In the process of
処理番号24の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号24の処理により、大当り終了後にすぐに設定示唆演出が開始するため、時短に突入しなかったことに対する遊技者の落胆を軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号25の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好な場合にのみ、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号21の処理により、処理番号19の処理において説明したような無駄な設定示唆演出を省略したり、時短に突入しなかったことに対する遊技者の落胆を軽減したりすることができる。また、仮に、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好でない場合に、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行すると、時短に突入しないことに落胆している遊技者にさらに無駄な設定示唆演出を見せることになり、遊技者を逆なでするおそれがある。
In the processing of
処理番号26~29の処理は、前変動の当選種別が小当りである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号26~29の処理のうちの1つをフラグによって選択可能である。処理番号26~29の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号3の処理と同様である。
Processing of
処理番号26の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した小当りのオープニング中、又は当該小当り中等である。小当りでは、遊技者に対して小さな特典が付与されるだけであるため、遊技者は落胆する可能性があるが、処理番号26の処理により、早いタイミングで設定示唆演出が開始することで落胆を軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号27の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好な場合にのみ、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前とは、具体的には、例えば、前変動の変動中、前変動で当選した小当りのオープニング中、又は当該小当り中等である。処理番号27の処理により、処理番号19の処理において説明したような無駄な設定示唆演出を省略したり、小当りにおいて小さなメリットしか付与されないことによる遊技者の落胆を軽減したりすることができる。
In the processing of
処理番号28の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。小当りに係る一連の消化時間は大当りに係る一連の消化時間よりも短いため、前変動の開始前等に設定示唆演出が開始したことを遊技者が認識している場合に、当該設定示唆演出を実行しないと遊技者は不信感を感じる可能性がある。処理番号28の処理により、遊技者に対してこのような不信感を与えないようにすることができる。
In the process of
処理番号29の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好な場合にのみ、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号29の処理により、処理番号19の処理に
おいて説明したような無駄な設定示唆演出を省略したり、小当りにおいて小さなメリットしか付与されないことに対する遊技者の落胆を軽減したりすることができる。また、仮に、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好でない場合に、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行すると、小当りにおいて小さなメリットしか付与されないことに対して落胆している遊技者にさらに無駄な設定示唆演出を見せることになり、遊技者を逆なでするおそれがある。
In the processing of
処理番号30~34の処理は、前変動の当選種別がはずれである場合の、新たな始動入賞に係る処理である。処理番号30~34の処理のうちの1つをフラグによって選択可能である。処理番号30~34の処理における、新たな始動入賞に対応する先読み演出としての期待示唆演出についての処理は、処理番号4の処理と同様である。
The processes of
処理番号30の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号30の処理により、前変動がはずれたことによる遊技者の落胆を軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号31の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の保留先読み演出における保留表示の態様が大当たり期待度の高い特定の態様(例えば、緑又は赤)である場合に限って、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に、当該新たな始動入賞における先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。なお、当該設定示唆演出の実行タイミングについては、変更しない、即ち特別な処理を行わないが、設定示唆演出の実行タイミングを異なるように制御(例えば、キャラBによる設定を示唆する台詞が現出するタイミングを通常よりも所定秒数(例えば2秒)遅らせたり、所定秒数(例えば2秒)早めたりなど)してもよい。処理番号31の処理により、前変動において大当り期待度が高い保留表示の態様が出現したにも関わらずはずれたことに対する落胆を感じている遊技者に対して、このような落胆を軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号32の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の保留先読み演出における保留表示の態様が大当たり期待度の高い特定の態様(例えば、緑又は赤)である場合であって、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好な場合、に限って、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に、当該新たな始動入賞における先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号32の処理により、大当り期待度の高い保留表示の態様であった前変動がはずれであったことに対する遊技者の落胆を、設定示唆演出によって軽減することができる。
In the process of
処理番号33の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、前変動の保留先読み演出における保留表示の態様が大当たり期待度の高い特定の態様(例えば、緑又は赤)でない場合に限って、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に、当該新たな始動入賞における先読み演出としての設定示唆演出を実行する。処理番号33の処理によって、前変動の保留先読み演出では大当りに対する期待度を得られず落胆が続いていた遊技者に対して、設定示唆演出によってこのような落胆を軽減することができる。
In the processing of
処理番号34の処理において、周辺制御MPUは、保留表示の態様が大当たり期待度の高い特定の態様(例えば、緑又は赤)ではない場合であって、前変動の設定示唆演出において示唆される設定より、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の開始前に先読み演出としての設定示唆演出において示唆される設定の方が良好な場合、に限って、当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動中に、当該新たな始動入賞における先読み演出としての設定示唆演出
を実行する。処理番号34の処理により、前変動の保留表示の態様が低期待度かつ当該新たな始動入賞に対応する変動における設定示唆演出において低設定を示唆する、という遊技者の苛立ちを増幅させるような事態の発生を抑制することができる。
In the processing of
なお、上述した処理において、新たな始動入賞に対応する変動の先読み演出制限として、設定示唆演出が制限されない状況下であっても、以下のような場合には、周辺制御MPUは、当該設定示唆演出を実行しなくてもよい。例えば、当該新たな始動入賞が大当り中に行われた場合には、周辺制御MPUは、当該設定示唆演出を実行しなくてもよい。大当り遊技の直後においては、設定示唆演出によるインセンティブを与えなくても遊技者は遊技を続行する可能性が高いためである。 It should be noted that, in the above-described processing, even under circumstances where setting suggestion effects are not limited as changes in anticipation effects corresponding to new start winnings, in the following cases, the peripheral control MPU will not limit the setting suggestions. You don't have to perform the performance. For example, when the new start winning is performed during the big win, the peripheral control MPU does not need to execute the setting suggestion effect. This is because there is a high possibility that the player will continue the game immediately after the jackpot game without giving an incentive by the setting suggestion effect.
処理テーブル3及び処理テーブル6の例のように、各処理番号が定める新たな始動入賞に係る処理それぞれにおいて効果が発揮されるため、新たな始動入賞に係る処理をホール等が設定可能にすることで、ホール等の営業スタイルのニーズに合わせた遊技機を提供することができる。 As in the examples of the processing table 3 and the processing table 6, each processing related to the new starting prize determined by each processing number is effective, so that the processing related to the new starting winning can be set by the hall or the like. This enables us to provide gaming machines that meet the needs of halls and other business styles.
また、例えば、当該新たな始動入賞がST状態(大当りに当選する又は所定回数の特別図柄変動が実行するまで継続する確変状態)の終了間際(具体的には、例えば、ST状態終了までの特別図柄の残り変動数が、特別図柄の最大保留数である4以下である状態、又はST状態終了までの特別図柄の残り変動数が、メイン液晶表示装置1600に表示されている状態等)に行われた場合には、周辺制御MPUは、当該設定示唆演出を実行しなくてもよい。ST状態終了直前においては、遊技者の最大の関心事は当該STにおいて大当りに当選するか否かである。このような状態で新たな始動入賞に係る先読み演出として設定示唆演出が開始すると、遊技者は当該設定示唆演出を咄嗟に大当り期待度の高い演出と勘違いし、遊技者をぬか喜びさせる事態が発生するおそれがある。上述した処理により、このような事態の発生を抑制することができる。 Also, for example, the new start winning prize is just before the end of the ST state (a probability variable state that continues until the jackpot is won or a predetermined number of special symbol variations are executed) (specifically, for example, a special until the end of the ST state The number of remaining variations in the symbol is 4 or less, which is the maximum number of reserved special symbols, or the number of remaining variations in the special symbol until the end of the ST state is displayed on the main liquid crystal display device 1600). If so, the peripheral control MPU does not need to execute the setting suggestion effect. Immediately before the end of the ST state, the player's greatest concern is whether or not the player wins the jackpot in the relevant ST. In such a state, when the setting suggesting effect is started as a look-ahead effect related to the new start winning, the player immediately misunderstands the setting suggesting effect as a performance with a high expectation of a big hit, and a situation occurs in which the player is overjoyed. There is a risk of Occurrence of such a situation can be suppressed by the above-described processing.
また、例えば、ST状態が終了して通常状態に移行してから所定回数の特別図柄変動(具体的には、例えば、特別図柄の最大保留数である4回の特別図柄変動、又はST状態から通常状態に移行した直後には第二始動口2004が開放している場合もあり、それを考慮して所定回数(例えば5回)の特別図柄変動)が行われるまでの間に、当該新たな始動入賞が行われた場合には、周辺制御MPUは、当該設定示唆演出を実行しなくてもよい。ST状態終了直後においては、遊技者の最大の関心事はすぐに大当りに当選するか否かである。特にST状態終了直後には、遊技者にとってメリットの大きい種別の大当りに当選しやすい第二特別図柄の保留に対応する変動が実行される可能性が高い。このような状態で新たな始動入賞に係る先読み演出として設定示唆演出が開始すると、遊技者は当該設定示唆演出を咄嗟に大当り期待度の高い演出と勘違いし、遊技者をぬか喜びさせる事態が発生するおそれがある。上述した処理により、このような事態の発生を抑制することができる。
Also, for example, after the ST state ends and shifts to the normal state, a predetermined number of special symbol variations (specifically, for example, 4 special symbol variations, which is the maximum number of special symbols reserved, or from the ST state Immediately after the transition to the normal state, the
また、複数の保留において、それぞれ単独で完結する設定示唆演出が実行されると決定された場合、当該複数の保留に対応する変動に跨る1つの設定示唆演出が実行されるように、前変動における設定示唆演出を変更してもよい。 In addition, in a plurality of holds, when it is determined that a setting suggestion effect that is completed independently is executed, so that one setting suggestion effect is executed across the fluctuations corresponding to the plurality of holds, In the previous fluctuation You may change setting suggestion production.
[12-16.設定変更・確認処理の別例1]
以下、設定変更機能を有するパチンコ機の別な実施例について説明する。以下に説明する実施例では、設定変更スイッチ972を設けずに、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作によって設定値が選択できるものであるが、RAMクリアスイッチ954の本来の主制御RAM1312の初期化機能と、設定変更機能とを区別して記載するために、設定値の変更にかかる操作については設定変更スイッチ972として説明することがある。
[12-16. Another example of setting change/confirmation process 1]
Another embodiment of a pachinko machine having a setting change function will be described below. In the embodiment described below, the setting value can be selected by operating the RAM
図179、図180は、電源投入時に主制御MPU1311が実行する電源投入時処理のフローチャートである。図179、図180に示す電源投入時処理は、図21のステップS10から図22のステップS34の別例である。
179 and 180 are flowcharts of power-on processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、RAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベル及び設定キー971の信号のレベルを入力ポートから取り込み、取り込んだレベルのデータをレジスタに格納する(ステップS201)。なお、RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971が操作されているか否かの判定は、周辺制御基板1510が確実に起動した後のステップS212、S214で主制御MPU1311が行う。このため、周辺制御基板1510が起動するまでの待機中に、ホールの従業員がRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作を誤って中断すると、ホールの従業員が意図していない状態でRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971が判定されてしまう。このため、電源投入時処理開始後の早い段階でRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の入力状態(レベル)をレジスタ等の一時的な記憶手段に格納し、周辺制御基板1510の待機状態の終了後にレジスタ等の一時的な記憶手段に格納したRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の状態を判定することによって、ホールの従業員が電源投入後の早い段階でキー操作を誤って中断しても、電源投入操作時のRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作を確実に検出する。
First, the
なお、RAMクリアスイッチ954のONレベルと設定キー971のONレベルとを異ならせてもよい。例えば、RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971とで論理の正負を変えて、RAMクリアスイッチ954はHighレベルでON、設定キー971はLowレベルのときONとしてもよい。また、RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971とでONと判定する電圧を変えてもよい。このようにすることによって、パチンコ機1への電波の照射によって信号レベルを変化させて、設定変更モードを起動する不正行為を困難にできる。また、後述するように、設定変更モードや設定確認モードにおいて、不正検出用のセンサの信号のレベルを監視する必要がなくなる。
The ON level of the RAM
そして、設定値が所定の範囲内であるかを判定する(ステップS202)。例えば、設定が1~6までの段階で選択可能なパチンコ機1において、設定値が格納されるワークの値が0~5に対応している(設定1のとき=0、設定6のとき=5)場合には、5以下の値が格納されていれば、所定の範囲内であると判定される。
Then, it is determined whether the set value is within a predetermined range (step S202). For example, in a
設定値が所定の範囲内でなければ、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)を記録し、パチンコ機1のリセット信号による初期化を待つ(ステップS203)。設定値は、チェックサムが計算される範囲ではなく、RAMクリア操作によって消去されないので、異常な設定値は修正されない。このため、電源投入時に設定値に異常がないかを判定して、異常があれば特図や普図等の通常遊技に関する処理を実行しないようにしている。
If the setting value is not within the predetermined range, a value (08H) indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, and initialization by the reset signal of the
なお、設定値は、電源投入時に判定するだけでなく、始動口への入賞時や、変動表示ゲームの開始時や、遊技状態が切り替わるとき(通常状態から大当り状態、低確率状態から高確率状態、非時短状態から時短状態など)等の所定の条件が成立したときにも判定する。これによって、設定値に誤って異常な値となっても、誤った設定値に基づいて、抽選が行われることを防止している。 In addition, the set value is determined not only when the power is turned on, but also when winning a prize at the start gate, starting a variable display game, and when the game state changes (normal state to big hit state, low probability state to high probability state). , from a non-time-saving state to a time-saving state, etc.) is also determined when a predetermined condition is satisfied. This prevents the lottery from being performed based on the erroneous set value even if the set value is erroneously abnormal.
設定値が異常と判定された場合には、遊技が停止し、電源を再投入するか、又は、設定値の変更操作がされるまでは、設定値異常(RAM異常)の状態が維持される。設定値が異常と判定された場合には、予め定められた値を設定するとよい。予め定められた値とし
ては、最高設定を示す設定6に対応した値や、最低設定を示す設定1に対応した値を用いて、設定値の格納エリアを更新するとよい。
If the set value is determined to be abnormal, the game is stopped and the set value abnormality (RAM abnormality) state is maintained until the power is turned on again or the setting value is changed. . If the set value is determined to be abnormal, a predetermined value may be set. As the predetermined value, a value corresponding to setting 6 indicating the highest setting or a value corresponding to setting 1 indicating the lowest setting may be used to update the setting value storage area.
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、設定変更モードを経由してのみRAM異常を解消でき、電源の再投入のみではRAM異常が解消しないようになっている。これは、RAM異常は不具合の他、不正によって発生する場合があり、不正により発生したRAM異常を電源再投入操作で解消できると、RAM異常を簡単に解消できることになる。これに対して、設定変更モードを経由しないとRAM異常を解消できないようにすれば、電源スイッチ932、設定キー971、RAMクリアスイッチ954の三つを操作しないとRAM異常を解消できず、さらに、鍵を有するホールの従業員しか操作し得ない設定キー971の操作を含むので、不正行為に対するセキュリティ性能を高めることができる。
In the
なお、不正に設定値を不定な値に変更するゴト行為に対応するため、設定値が異常と判定された場合には、最低設定を示す設定1に対応した値に更新すると、遊技機のセキュリティ性を向上できて、有効である。 In addition, in order to cope with fraudulent acts of changing the set value to an indeterminate value, if the set value is determined to be abnormal, updating it to the value corresponding to setting 1, which indicates the lowest setting, will prevent the security of the game machine. It is effective because it can improve performance.
設定状態管理エリアは、図201(B)に示すように、パチンコ機1の動作モードが記録される記憶領域であり、例えば、通常遊技状態(遊技開始可能状態)、設定確認モード、設定変更モード、主制御RAM1312の異常が記録される。
The setting state management area, as shown in FIG. 201(B), is a storage area in which the operation mode of the
一方、設定値が所定の範囲内であれば、周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ(ステップS204)。 On the other hand, if the set value is within the predetermined range, it waits for the activation of the peripheral control board 1510 (step S204).
そして、前回の電源遮断時に主制御RAM1312にバックアップされているデータから算出したチェックサムと、前回の電源遮断時に計算されてステップS48で記憶されたチェックサムとを比較(検証)する。なお、チェックサムではなく、固定値のチェックコードを用いてもよい。さらに、バックアップフラグエリアの値が正常であるかを判定する。正常にバックアップされたことを示す停電フラグの値がバックアップフラグエリアに格納されていれば、停電発生時にRAMのデータが正常にバックアップされている(ステップS205)。
Then, the checksum calculated from the data backed up in the
判定の結果、チェックサム又はバックアップフラグエリアの値のいずれかが異常であれば、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)を記録し(ステップS206)、主制御RAM1312の全領域(設定値が格納されている領域も含む)を初期化して(ステップS207)、ステップS216に進む。なお、主制御RAM1312の全領域又は所定の領域に格納されたデータの消去を「初期化」と称するが、「RAMクリア」も同じ意味で使用される。
As a result of the determination, if either the checksum or the value of the backup flag area is abnormal, a value (08H) indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area (step S206), and all areas of the main control RAM 1312 (setting (including areas where values are stored) are initialized (step S207), and the process proceeds to step S216. Erasure of data stored in the entire area or a predetermined area of the
一方、チェックサム及びバックアップフラグエリアの値が正常であれば、レジスタに格納された設定キーの値(内容)に基づいて設定変更操作(RAMクリアスイッチ954がON、設定キー971がON)がされているかを判定する。設定変更操作ではない(RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の両方もしくは、いずれかがOFF)場合には、電源投入前に状態が設定変更中であったかを判定するために、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更中を示す値(02H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS208)。
On the other hand, if the checksum and backup flag area values are normal, the setting change operation (the RAM
その結果、設定変更操作がされていることがレジスタに格納されていれば、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954及び設定キー971で設定変更モードにする操作がされており、設定変更動作を開始すべき状態であると判定できる。また、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更中を示す値(02H)が記録されていれば、設定変更動作中に停電した後の電源投入であると判定できる。レジスタに格納された値又は設定状態管理エリアに記憶された
値に基づいて、設定変更モードに移行すると判定されたときには、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更状態を示す値(02H)を記録し(ステップS209)、RAM正常時に初期化すべき主制御RAM1312のクリア領域を初期化して(ステップS210)、ステップS216に進む。
As a result, if it is stored in the register that a setting change operation has been performed, it means that the RAM
なお、ステップS208において、設定状態管理エリアに記憶された値に基づいて設定変更モードに移行するときに、ステップS209において設定状態管理エリアに設定変更状態(02H)を示す値を記録するが、この際、同じ値(設定変更状態(02H))を再度設定する必要はないため、設定状態管理エリアに記憶された値に基づいて設定変更モードに移行すると判定したときには、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更状態を示す値(02H)を記録しなくてもよい。 In step S208, when shifting to the setting change mode based on the value stored in the setting state management area, the value indicating the setting change state (02H) is recorded in the setting state management area in step S209. In this case, since it is not necessary to set the same value (setting change state (02H)) again, when it is determined to shift to the setting change mode based on the value stored in the setting state management area, the setting change is performed in the setting state management area. The value (02H) indicating the state may not be recorded.
一方、レジスタに設定変更操作が設定されておらず、かつ、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更中を示す値(02H)が記録されていなければ、設定変更動作を開始すべきでないため、電源投入前の状態がRAM異常中であったかを判定するために、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS211)。 On the other hand, if the setting change operation is not set in the register and the value (02H) indicating that the setting is being changed is not recorded in the setting state management area, the setting change operation should not be started. In order to determine whether the state of is during RAM abnormality, it is determined whether a value (08H) indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area (step S211).
その結果、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていれば、電源投入前の状態がRAM異常中(主制御RAM1312が異常)と判定し、ステップS216に進む。一方、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていなければ、電源投入前の状態がRAM異常中(主制御RAM1312が異常)ではないため、レジスタにRAMクリアスイッチ954のONレベルが格納されているかを判定する(ステップS212)。
As a result, if a value indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, it is determined that the state before power-on is RAM abnormality (
その結果、レジスタにRAMクリアスイッチ954のONレベルが格納されていれば、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されているので、設定値や設定状態管理エリアを除く遊技制御領域内のRAM領域(RAM正常時のクリア領域)を初期化するために、ステップS210に進む。
As a result, if the ON level of the RAM
一方、レジスタにRAMクリアスイッチ954のON操作のレベルが格納されていなければ、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていないので、電源投入時状態バッファを設定する(ステップS213)。電源投入時状態バッファに設定された内容は、電源復帰時に主制御MPU1311で管理している遊技状態を通知するための電源投入時状態コマンドとして主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510に送信される。
On the other hand, if the ON operation level of the RAM
その後、レジスタに設定キー971のONレベルが格納されているかを判定する(ステップS214)。その結果、レジスタに設定キー971のONレベルが格納されていれば、電源投入時に設定キー971が操作されており設定確認動作を開始すべきであるため、設定状態管理エリアに設定確認モードを示す値(01H)を記録する(ステップS215)。
After that, it is determined whether or not the ON level of the setting
その後、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されているデバイスの初期設定を行い(ステップS216)、電源投入時の各部の動作を通知する電源投入時動作コマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信する(ステップS217)。電源投入時動作コマンドは、図22のステップS32で説明した電源投入時コマンドの一つである。そして、主制御RAM1312を電源投入時の状態に初期設定する(ステップS218)。
After that, the device built in the
その後、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS219)。設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値が記録されていれば、通常遊技が開始可能なので、ステップS220に進み、初期設定を続
ける。一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値が記録されていなければ、通常遊技が開始できないので、初期設定を終了し、ステップS224に進む。
After that, it is determined whether or not a value (00H) indicating a game-startable state is recorded in the setting state management area (step S219). If a value indicating a game-startable state is recorded in the setting state management area, the normal game can be started, so the process proceeds to step S220 to continue initial setting. On the other hand, if the setting state management area does not record a value indicating a game-startable state, the normal game cannot be started.
ステップS220では、遊技開始時の初期設定又は停電復帰時の初期設定を行う。その後、電源投入時の各部の状態を通知する電源投入時状態コマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信する(ステップS221)。そして、停電復帰時に特別図柄の状態を通知する電源投入時復帰先コマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信するためにバッファに格納する(ステップS222)。電源投入時状態コマンドや電源投入時復帰先コマンドは、図22のステップS32で説明した電源投入時コマンドの一つである。なお、バッファに格納された各種コマンドは、タイマ割込み処理において送信される。 In step S220, the initial setting at the time of game start or the initial setting at the time of power failure recovery is performed. After that, a power-on state command for notifying the state of each unit when the power is turned on is transmitted to the peripheral control board 1510 (step S221). Then, it stores in the buffer in order to transmit to the peripheral control board 1510 a power-on recovery destination command for notifying the state of the special symbol at the time of power failure recovery (step S222). The power-on state command and the power-on recovery destination command are one of the power-on commands described in step S32 of FIG. Various commands stored in the buffer are transmitted in timer interrupt processing.
さらに、設定値を通知する設定値コマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信し(ステップS223)、割り込みを許可して(ステップS224)、通常のメインループ(例えば、図22のステップS36)に進む。 Further, a set value command for notifying the set value is transmitted to the peripheral control board 1510 (step S223), interrupts are permitted (step S224), and the routine proceeds to a normal main loop (eg, step S36 in FIG. 22).
図181、図182は、主制御MPU1311が実行するタイマ割込み処理のフローチャートである。図181、図182に示すタイマ割込み処理は、図24、図75、図80、図104、図155で示すタイマ割込み処理とは異なり、タイマ割込み処理内で設定変更の処理を実行する。
181 and 182 are flowcharts of timer interrupt processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、LEDコモンカウンタ(LED_CT)を更新する(ステップS230)。LEDコモンカウンタは、ベース表示器1317のどのコモン端子をオンにするか、すなわち表示する桁を定めるカウンタである。なお、本実施例では、ベース表示器1317と設定表示器974を兼用する例を説明するが、ベース表示器1317と設定表示器974とは、別に設けてもよい。この場合、表示器の数だけLEDコモンカウンタが設けられるとよい。
First, the
その後、スイッチ入力処理を実行する(ステップS231)。スイッチ入力処理は、図23のステップS74と同じである。 Thereafter, switch input processing is executed (step S231). The switch input process is the same as step S74 in FIG.
次に、設定状態管理エリアに初期値(遊技開始可能状態を示す値)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS232)。設定状態管理エリアに初期値(遊技開始可能状態を示す値)が記録されていれば、タイマ割込み処理で設定変更/確認処理(ステップS234以後)を実行する必要がないので、通常のタイマ割込み処理(例えば、図23のステップS76以後)を実行する(ステップS233)。ステップS233の通常のタイマ割込み処理では、後述する性能表示処理(図183)が実行される。一方、設定状態管理エリアに初期値(遊技開始可能状態を示す値)が記録されていなければ、タイマ割込み処理で通常の遊技処理を実行せず、設定変更/確認処理を実行する。 Next, it is determined whether or not an initial value (a value indicating a game-startable state) is recorded in the setting state management area (step S232). If the initial value (the value indicating the game-startable state) is recorded in the setting state management area, there is no need to execute the setting change/confirmation processing (after step S234) in the timer interrupt processing, so normal timer interrupt processing is performed. (for example, after step S76 in FIG. 23) are executed (step S233). In normal timer interrupt processing in step S233, performance display processing (FIG. 183), which will be described later, is executed. On the other hand, if the initial value (the value indicating the game-startable state) is not recorded in the setting state management area, the normal game processing is not executed in the timer interrupt processing, but the setting change/confirmation processing is executed.
設定変更/確認処理では、まず、LEDコモンポートからOFFを出力し、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力し、遊技中断信号をONに設定する(ステップS234)。タイマ割込み処理の早い段階でLEDコモン信号をOFFにすることによって、LEDコモン信号がオンになるまでの時間、すなわちLEDの消灯時間を確保し、LEDの表示切替前後の表示が混ざって見えるゴースト現象を抑制し、LEDのちらつきを防止している。
In the setting change/confirmation process, first, OFF is output from the LED common port, the security signal is output from the external
その後、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS235)。設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていれば、設定値を変更/確認する処理を実行することなく、ステップS245に進む。一方、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていなければ、設定値を変更/確
認する操作がされているかを判定する(ステップS236、S237)。具体的には、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更を示す値(02H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS236)。
Thereafter, it is determined whether a value (08H) indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area (step S235). If a value indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, the process proceeds to step S245 without executing the process of changing/confirming the setting value. On the other hand, if a value indicating RAM abnormality is not recorded in the setting state management area, it is determined whether an operation to change/confirm the setting value has been performed (steps S236 and S237). Specifically, it is determined whether a value (02H) indicating a setting change is recorded in the setting state management area (step S236).
そして、設定変更スイッチ972が操作されていれば、設定値を1加算して(ステップS238)、ステップS245に進む。なお、設定値を加算した結果上限値を超えていれば初期値に戻す。一方、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更を示す値が記録されていない(設定状態管理エリアに設定確認を示す値が記録されている)、又は、設定変更スイッチ972が操作されていなければ、設定キー971の出力レベルのOFFエッジが検出されたかを判定する(ステップS239)。設定キー971の出力レベルのOFFエッジが検出されると、設定キー971が通常位置へ操作されたので、設定変更/確認モード終了処理を実行する(ステップS240~S244)。一方、設定キー971の出力レベルのOFFエッジが検出されていなければ、設定変更/確認モードを終了せず、ステップS245に進む。
Then, if the setting
設定変更/確認モード終了処理では、図182に示すように、設定状態管理エリアに初期値(遊技開始可能状態を示す値)を記録し(ステップS240)、遊技開始時の初期設定又は停電復帰時の初期設定を行い(ステップS241)、電源投入時の各部の状態(低確率/高確率、時短/非時短等の遊技状態)を通知する電源投入時状態コマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信するためにバッファに格納する(ステップS242)。そして、停電後の復帰時に特別図柄の状態を通知する電源投入時復帰先コマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信するためにバッファに格納する(ステップS243)。具体的には、特別図柄/特別電動役物に関する処理状態(特別図柄/特別電動役物に関する各処理(待機中、変動中、判定、大当り中等)の状態)を示すカウンタ値をコマンドとして送信する。これにより、周辺制御基板1510は、電源復帰時に特別図柄に関する遊技状態や特別電動役物の動作状態を判定できる。そして、設定値を通知する設定値コマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信するためにバッファに格納して(ステップS244)、ステップS245に進む。 In the setting change/confirmation mode ending process, as shown in FIG. (step S241), to send a power-on state command to the peripheral control board 1510 to notify the state of each part at the time of power-on (game state such as low probability / high probability, time saving / non-time saving, etc.) is stored in the buffer (step S242). Then, it stores in the buffer in order to transmit to the peripheral control board 1510 a power-on recovery destination command for notifying the state of the special symbol at the time of recovery after the power failure (step S243). Specifically, a counter value indicating the processing state of the special symbol/special electric accessory (the state of each process (waiting, fluctuating, judging, jackpot, etc.) regarding the special symbol/special electric accessory is transmitted as a command. . As a result, the peripheral control board 1510 can determine the game state related to the special symbols and the operation state of the special electric accessory when the power is restored. Then, a setting value command for notifying the setting value is stored in the buffer for transmission to the peripheral control board 1510 (step S244), and the process proceeds to step S245.
なお、設定値を通知するコマンドは、電源投入時の設定変更/確認モード終了処理だけでなく、変動開始時や遊技状態の切り替わり時にも送信するとよい。そのとき、電源投入時に送信する設定値のコマンドと変動開始時等の通常遊技中で送信するコマンドとは同じコマンドでも、異なるコマンド(例えば、上位バイトの値が異なる等)でもよい。 It should be noted that the command for notifying the setting value may be sent not only at the time of power-on, but also at the start of fluctuation or when the game state is switched. At that time, the setting value command transmitted when the power is turned on and the command transmitted during the normal game such as when the fluctuation starts may be the same command or different commands (for example, different upper byte values).
電源投入時と通常遊技時とで設定値コマンドを異ならせた場合、周辺制御基板1510は、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの開始時に、設定値を含む一連のコマンド(変動パターンコマンド、図柄コマンド等)を受信すると、コマンドが欠落していないかを判定する。コマンドが送信されるタイミング(電源投入時、通常遊技中など)でコマンドの内容を異ならせることによって、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時に正しく受信した設定値なのか、変動開始時に設定値以外の変動パターンコマンドや図柄コマンドが欠落したのかを判定できる。 When the set value command is different between when the power is turned on and when the normal game is played, the peripheral control board 1510 sends a series of commands (variation pattern command, symbol command, etc.) including the set value at the start of the special symbol variation display game. When received, determine if the command is missing. By changing the content of the command depending on the timing at which the command is sent (when the power is turned on, during a normal game, etc.), the peripheral control board 1510 can determine whether the set value is correctly received when the power is turned on, or when the variation starts. It can be determined whether the variation pattern command or the design command is missing.
ステップS245では、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)が記憶されているかを判定する。設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていれば、ベース表示器1317(別体の場合は設定表示器974)にエラー表示をするための設定を行う(ステップS246)。一方、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていなければ、現在の設定値をベース表示器1317(別体の場合は設定表示器974)に表示をするための設定を行う(ステップS247)。
In step S245, it is determined whether a value (08H) indicating RAM abnormality is stored in the setting state management area. If a value indicating a RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, settings are made to display an error on the base indicator 1317 (or the
その後、ベース表示器1317のLEDのコモン端子にONを出力し、ステップS24
6又はS247における設定に従って出力されるセグメント信号によってベース表示器1317を点灯させる(ステップS248)。このように、タイマ割込み処理の開始後に、設定値変更操作を判定し(ステップS237)、その後、タイマ割り込み毎にLEDのコモン端子にONを出力して、設定値を表示する(設定値の表示を切り替える)。設定操作をトリガとしないで、設定値が表示されることになる。具体的には、設定変更/確認に関する処理を電源投入時の処理として行うのではなく、通常の遊技が開始されたときと同じタイマ割込み処理内で行うことによって、設定変更/確認処理の実行中に停電し、設定キー971が元の状態に戻された後に電源が復帰した場合でも、設定キー971や設定変更スイッチ972を停電発生時と同じ位置に操作しなくても、停電発生時の設定変更/確認処理の状態に戻すことができるようにしている。さらに、設定変更/確認処理において、コマンド送信処理、LEDのダイナミック点灯の制御等、通常の遊技処理でも実行される処理を共通化できる。
After that, ON is output to the common terminal of the LED of the
6 or the segment signal output according to the setting in S247 causes the
そして、周辺制御基板1510にコマンドを送信し(ステップS249)、タイマ割込み処理を終了する。すなわち、ステップS249では、ステップS242、S243、S244等においてバッファに格納されたコマンドが、実際に主制御基板1310からシリアルデータとして出力される。
Then, the command is transmitted to the peripheral control board 1510 (step S249), and the timer interrupt processing ends. That is, in step S249, the commands stored in the buffer in steps S242, S243, S244, etc. are actually output from the
以上で説明したタイマ割込み処理では、通常遊技を実行するか、設定変更モード(又は設定確認モード)を実行するかで処理を分岐しているが(図181のステップS232)、複数のタイマ割込み処理を設け、通常遊技状態と設定変更モード及び/設定変更モードとで、異なるタイマ割込み処理を起動してもよい。この複数のタイマ割込み処理は、一部に共通の処理を含んでも(例えば、各タイマ割込み処理で共通のサブルーチンが呼び出されても)、すべてが異なるルーチンで構成されてもよい。つまり、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードではタイマ割込み処理1(設定変更/確認用)が呼び出され、通常遊技状態ではタイマ割込み2(通常遊技用)が呼び出され、この二つのタイマ割込み処理で共通に実行される処理(モジュール)と、一方のタイマ割込み処理のみで実行される専用の処理(モジュール)とを有することになる。共通に実行される処理には、例えば、入賞口センサなど各種検出スイッチの出力を取り込むスイッチ入力処理や周辺制御基板1510にコマンドを送信する周辺基板コマンド処理などがある。 In the timer interrupt processing described above, the processing is branched depending on whether the normal game is executed or the setting change mode (or setting confirmation mode) is executed (step S232 in FIG. 181). may be provided, and different timer interrupt processes may be activated in the normal game state and the setting change mode and/or setting change mode. The plurality of timer interrupt processes may include some common processes (for example, a common subroutine may be called in each timer interrupt process), or all may consist of different routines. That is, timer interrupt processing 1 (for setting change/confirmation) is called in the setting change mode and setting confirmation mode, and timer interrupt 2 (for normal game) is called in the normal game state. It has a process (module) that is executed and a dedicated process (module) that is executed only in one timer interrupt process. Commonly executed processes include, for example, a switch input process for capturing outputs from various detection switches such as a winning hole sensor, a peripheral board command process for transmitting a command to the peripheral control board 1510, and the like.
また、通常遊技で実行される処理と設定変更モードで実行される処理とでレジスタバンクを共通してもよい。主制御側メイン処理でバンク0を使用する場合には、二つのタイマ割込み処理では共にバンク1を使用する。二つのタイマ割込み処理は同時に起動することがないため、一つのレジスタバンクを共用できる。すなわち、本実施例のパチンコ機では、主制御MPU1311は、バンクによって切り替え可能な2以上のレジスタを有しており、繰り返し実行される主制御側メイン処理と、周期的に実行されるタイマ割込み処理1(通常遊技中)と周期的に実行されるタイマ割込み処理2(設定変更モード)とを有し、主制御側メイン処理とタイマ割込み処理1とタイマ割込み処理2のうち少なくとも二つの処理では共通のバンクのレジスタを使用する。
Further, the processing executed in the normal game and the processing executed in the setting change mode may share a register bank. When
通常遊技で実行されるタイマ割込み処理と設定変更モードで実行されるタイマ割込み処理とでは、その実行周期は同じにするとよいが、異なる周期で実行してもよい。設定変更時モードで実行されるタイマ割込み処理におけるスイッチのサンプリングはRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971だけなので、通常遊技状態のタイマ割込み処理の実行周期が4msであるところ、設定変更モードで実行されるタイマ割込み処理の実行周期が早かったり(例えば2ms)、遅かったり(例8ms)してもよい。なお、設定変更モードで実行されるタイマ割込み処理の実行周期を遅くすると、設定値を表示するLEDのダイナミック点灯制御の周期が遅くなり、設定値の表示態様が通常遊技中のベース表示と異なることになる。LEDのコモンが8本ある場合、タイマ割込み処理の実行周期が8msで
あると、表示周期は64ms(表示ONが8ms、OFFが56ms)となり、タイマ割込み処理の実行周期が4msであると、表示周期は32ms(表示ONが4ms、OFFが20ms)となり、タイマ割込み処理の実行周期に比例してOFF時間が長くなり、LEDの点灯ちらつきが大きくなることにより通常遊技中のベース表示との表示態様とが異なって認識することが可能となる。
The timer interrupt processing executed in the normal game and the timer interrupt processing executed in the setting change mode may have the same execution cycle, but may be executed in different cycles. Since only the RAM
また、電源起動時に設定変更モード又は設定確認モードを起動するときには、設定変更/確認用のタイマ割込み処理1を許可し、通常遊技用のタイマ割込み処理2を禁止する。一方、電源起動時に通常遊技状態で起動する(設定変更/確認モードに移行しない)ときには、設定変更/確認用のタイマ割込み処理1を禁止、通常遊技用のタイマ割込み処理2を許可する。そして、設定変更モード又は設定確認モードの終了時には、設定変更/確認用のタイマ割込み処理1を禁止し、通常遊技用のタイマ割込み処理2を許可する。
Also, when starting the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode at the time of power activation, the timer interrupt
図183は、主制御MPU1311が実行する性能表示処理のフローチャートである。性能表示処理では、ベース表示器1317にパチンコ機1の性能(例えばベース値)を表示する。
FIG. 183 is a flowchart of performance display processing executed by the
性能表示処理は、前述した通常遊技状態のタイマ割込みにおいて実行される。具体的には、図181に示すタイマ割込み処理のステップS233の通常の割り込み処理や、図191に示すタイマ割込み処理のステップS2087のベース表示器出力処理で実行される。 The performance display process is executed in the above-described normal game state timer interrupt. Specifically, it is executed in the normal interrupt processing in step S233 of the timer interrupt processing shown in FIG. 181 and the base display unit output processing in step S2087 of the timer interrupt processing shown in FIG.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、遊技制御領域内のスタックアドレスを退避し、遊技制御領域外スタックアドレスを設定し(ステップS260)、レジスタ退避用バッファに遊技制御領域内で使用するレジスタを退避する(ステップS261)。ステップS261における、遊技制御領域内で使用されるレジスタの退避先は、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のワークエリアであるとよい。なお、遊技制御領域内で使用されるレジスタの退避先は、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のスタックエリアでもよい。
First, the
その後、初回電源投入フラグが正常かを判定する(ステップS262)。初回電源投入フラグは、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の領域が初期化されているか(すなわち、最初の電源投入か)を示すフラグであり、遊技制御領域外の領域を初期化すると5AHが設定される。すなわち、初回電源投入フラグの値が5AHであれば、初回の電源投入時における主制御RAM1312が初期化(すなわち、遊技制御領域外の領域も初期化)されていると判定できる。
After that, it is determined whether the initial power-on flag is normal (step S262). The first power-on flag is a flag indicating whether the area outside the game control area of the
そして、ベース値の表示に使用されるパラメータの値は所定の範囲内であるかを判定する(ステップS263)。例えば、ベース表示器1317の表示桁を切り替えるためのLEDコモンカウンタの値が0~3以外であると、パラメータの値が異常であると判定し、ステップS264で遊技制御領域外の主制御RAM1312を初期化する。
Then, it is determined whether the value of the parameter used for displaying the base value is within a predetermined range (step S263). For example, if the value of the LED common counter for switching the display digits of the
停電フラグが正常ではなく、又は、各パラメータの値は所定の範囲内でなければ、遊技制御領域外の主制御RAM1312を初期化し、停電フラグ5AHに設定し(ステップS264)、ステップS265に進む。一方、停電フラグが正常であり、かつ、各パラメータの値は所定の範囲内であれば、各種入賞口センサ3015、2114、2554、2557及び排出球センサ3060を検出し、ベース値を計算する(ステップS265)。
If the power failure flag is not normal, or the value of each parameter is not within a predetermined range, the
そして、ベース値計算の区間の切替時間であるかを判定し(ステップS266)、切替時間が到来していれば、表示モードを切り替える(ステップS267)。そして、表示モードに従って表示データを作成し、バッファに格納する(ステップS268)。そして、
区間毎に表示を制御する。例えば、区間毎の表示制御には、アウト球数500個未満のテスト区間の表示や、低確率・非時短アウト球数が所定数(例えば、6000個)未満の場合の点滅表示などがある(ステップS269)。
Then, it is determined whether or not it is the switching time of the section for base value calculation (step S266), and if the switching time has come, the display mode is switched (step S267). Display data is created according to the display mode and stored in the buffer (step S268). and,
Control the display for each section. For example, the display control for each section includes display of test sections with less than 500 out-balls, and flashing display when the number of low-probability/non-time-saving out-balls is less than a predetermined number (e.g., 6000) ( step S269).
その後、レジスタ退避用バッファからレジスタの値を元に戻し(ステップS270)、遊技制御領域内のスタックアドレスを元に戻して(ステップS271)、性能表示処理を終了する。 After that, restore the value of the register from the register saving buffer (step S270), restore the stack address in the game control area (step S271), and end the performance display process.
次に、図184を参照して、本実施例のパチンコ機1の報知態様について説明する。前述したように、本実施例のパチンコ機では、電源投入時に主制御RAM1312が異常である場合や、設定変更モード中や、設定確認モード中に報知をして、ホールの従業員にパチンコ機の状態を分かりやすく知らせる。
Next, with reference to FIG. 184, the notification mode of the
なお、以下に説明する報知態様(例えば、機能表示ユニット1400の表示態様)は、設定変更モードや設定確認モードの中で選択された態様で出力される。これらの報知は、タイマ割込み処理(図181)のステップS246、S247でベース表示器1317への表示設定と合わせて、報知パターンを選択して報知を制御する。具体的には、図190に示すタイマ割込み処理のステップS2069の設定表示処理で実行される。なお、パチンコ機1の動作モードを表示するための専用モジュールを設けて処理を実行してもよい。
Note that the notification mode (for example, the display mode of the function display unit 1400) described below is output in the mode selected in the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode. These notifications are controlled by selecting a notification pattern together with display settings on the
まず、主制御RAM1312が異常である場合、タイマ割込み処理(図181)のステップS249で周辺制御基板1510に送信されるコマンドで制御される。なお、主制御RAM1312の異常は、他の異常や状態の報知より優先して報知される。
機能表示ユニット1400 全消灯、又は、全LEDを同一周期で高速点滅
メイン液晶表示装置1600 「RAMエラー」の文字を表示
音(効果音) RAM異常報知音を出力(RAM異常報知音は、設定変更モードや設定確認モード以外の報知音と同じでもよい)
音(音声) 「RAMエラーです」の音声を出力
音量 周辺制御基板ボックス1520のボリュームや遊技者による音量設定に依存しない最大音量
枠装飾LED 扉枠3に設けられた所定の枠ランプ(トップランプを含み、球切れやストック報知LEDを除く)を赤色で点滅表示
パネル装飾LED 全消灯
外部出力(セキュリティ信号) 出力
試験信号(遊技機エラー信号) 出力
再報知 する
解除条件 主制御基板1310で設定変更によりRAMクリアされた、又は、周辺制御基板1510に電源が再投入された
First, if the
Sound (Voice) Output volume for the voice “RAM error” Maximum volume that does not depend on the volume of the peripheral
次に、主制御RAM1312が設定変更モードで起動した場合の設定変更報知を説明する。設定変更報知は、タイマ割込み処理(図181)のステップS249で周辺制御基板1510に送信されるコマンドで制御される。
機能表示ユニット1400 全点灯、又は、全LEDを同一周期で中速点滅
メイン液晶表示装置1600 「設定変更中」の文字を表示
音(効果音) 設定変更モードの報知音を出力
音(音声) 「設定変更中です」の音声を所定回数(例えば16回)出力
音量 周辺制御基板ボックス1520のボリュームや遊技者による音量設定に依存しない最大音量
枠装飾LED 扉枠3に設けられた所定の枠ランプ(トップランプを含み、球切れやストック報知LEDを除く)を白色で点滅表示
パネル装飾LED 全消灯
外部出力(セキュリティ信号) 出力
試験信号(遊技機エラー信号) 出力
再報知 する
解除条件 周辺制御基板1510が電源投入時動作コマンドとして「A001H」を受信した
Next, setting change notification when the
次に、主制御RAM1312が設定確認モードで起動した場合の設定確認報知を説明する。設定確認報知は、タイマ割込み処理(図181)のステップS249で周辺制御基板1510に送信されるコマンドで制御される。
機能表示ユニット1400 全点灯、又は、全LEDを同一周期で低速点滅
メイン液晶表示装置1600 「設定確認中」の文字を表示
音(効果音) 設定確認モードの報知音を出力(設定確認モードの報知音は、設定変更モードの報知音と同じでもよい)
音(音声) 「設定確認中です」の音声を所定回数(例えば16回)出力
音量 周辺制御基板ボックス1520のボリュームや遊技者による音量設定に依存しない最大音量
枠装飾LED 扉枠3に設けられた所定の枠ランプ(トップランプを含み、球切れやストック報知LEDを除く)を白色で点滅表示
パネル装飾LED 全消灯
外部出力(セキュリティ信号) 出力
試験信号(遊技機エラー信号) 出力
再報知 する
解除条件 周辺制御基板1510が電源投入時動作コマンドとして「A001H」を受信して所定時間(例えば30秒)が経過
Next, setting confirmation notification when the
Sound (Voice) Outputs the voice “Settings are being checked” a predetermined number of times (for example, 16 times). Predetermined frame lamps (including top lamps, excluding out-of-ball and stock notification LEDs) blinking in white Display panel decorative LEDs All off External output (security signal) Output test signal (gaming machine error signal) Cancellation condition for re-notification of output A predetermined time (for example, 30 seconds) has elapsed since the peripheral control board 1510 received "A001H" as the power-on operation command.
前述した三つの状態の報知は、主制御RAM1312の異常が最優先で報知され、設定変更モード、設定確認モードの順に優先して報知が行われるとよい。より具体的には、図185に示す順序で優先度を定めるとよい。なお、優先度1が報知の優先度が高く、優先度9が報知の優先度が低い。すなわち、複数の報知をすべき場合には、優先度が高い(数字が小さい)報知が行われる。また、優先度が同じ複数の報知の条件が成立したて、報知が競合する場合、競合する複数の報知を切り替えて報知しても、先に成立した報知を行い、当該報知が解除された後に競合する報知が条件を満たしていれば当該競合する報知を行ってもよい。具体的には、優先度3において、RAMクリア報知と設定確認報知とは同時に発生しないので報知は競合しない。優先度4において、賞球過多異常報知と普通電動役物入賞異常報知は同時に発生して、二つの報知が競合することがある。
優先度1:RAMの異常が検出された場合のRAMエラー報知
優先度2:設定変更モードにおける設定変更報知
優先度3:RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作により主制御RAMが初期化された場合のRAMクリア報知(設定変更によるRAMクリアは除く)
優先度3:設定確認モードにおける設定確認報知
優先度4:賞球が所定数以上多く払いだされた場合の賞球過多異常報知
優先度4:普通電動役物非作動時に所定数以上連続して入賞を検出した場合、又は、一回の普通電動焼役物作動時に所定以上の入賞を検出した場合の普通電動役物入賞異常報知
優先度5:大入賞口の入賞数と排出数との差が所定数以上となった場合の排出異常報知
優先度6:振動を検知した場合の振動センサ異常報知
優先度7:扉枠3又は本体枠4の開放を検出した場合の扉開放異常報知
優先度8:磁気センサが磁気を検知した場合の磁気センサ異常報知
優先度9:大入賞口の非作動時に所定数以上連続して入賞を検出した場合、又は、一回の大当り時に所定以上の入賞を検出した場合の大入賞口入賞異常報知
It is preferable that the notification of the three states described above is performed with the highest priority given to the abnormality of the
Priority 1: RAM error notification when a RAM abnormality is detected Priority 2: Setting change notification priority in the setting change mode 3: RAM clear when the main control RAM is initialized by operating the RAM
Priority 3: Setting confirmation notification in setting confirmation mode Priority 4: Prize ball excess abnormality notification when more than a predetermined number of prize balls are paid out When a prize is detected, or when more than a predetermined number of prizes are detected during a single operation of the normal electric accessory, the normal electric accessory winning abnormality notification priority 5: the difference between the number of prizes won and the number of discharges of the large winning opening is equal to or greater than a predetermined number 6: Vibration sensor abnormality notification priority when vibration is detected 7: Door open abnormality notification priority when opening of
次に、前述した電源投入時処理(図179、図180)の詳細を説明する。図186、図187は、電源投入時に主制御MPU1311が実行する電源投入時処理のフローチャートである。
Next, the details of the above-described power-on process (FIGS. 179 and 180) will be described. 186 and 187 are flowcharts of power-on processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、電源の投入により、リセット信号が解除されるとプログラムコードの開始番地である8000番地の処理から開始する。主制御RAM1312のプロテクト無効及び禁止領域無効をRAMプロテクトレジスタに設定する(ステップS2000)。主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の使用領域を指定することによって、指定領域以外の禁止領域へアクセスがあった場合には、異常と判定してリセットする機能を有する。主制御RAM1312の禁止領域へのアクセスによるリセット機能を解除するために、禁止領域を無効に設定することで主制御RAM1312の全領域へのアクセスを可能とする。なお、主制御RAM1312のうち未使用領域を禁止領域に指定して、禁止領域を有効にして、指定された禁止領域にアクセスを検出した場合には、主制御MPU1311がリセットされるようにしてもよい。
First, the
次に、所定時間の単純クリアモードタイマをウォッチドッグタイマに設定し(ステップS2001)、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアする(ステップS2002)。その後、停電クリア信号をONに設定し(ステップS2003)、停電クリア信号をOFFに設定する(ステップS2004)。一旦、停電クリア信号をONに設定してから、OFFに設定することによって、ラッチに記憶された停電信号を正常な値に設定できる。 Next, a simple clear mode timer of a predetermined time is set in the watchdog timer (step S2001), and the watchdog timer is cleared (step S2002). After that, the power failure clear signal is set to ON (step S2003), and the power failure clear signal is set to OFF (step S2004). By once setting the power failure clear signal to ON and then setting it to OFF, the power failure signal stored in the latch can be set to a normal value.
次に、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをPFポートから読み出し、レジスタに記憶する(ステップS2005)。RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971が操作されているか否かの判定は、周辺制御基板1510が確実に起動した後に主制御MPU1311が行うため、周辺制御基板1510が起動するまでの待機中に、ホールの従業員がRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作を誤って中断すると、ホールの従業員が意図していない状態でRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971が判定されてしまう。このため、電源投入時処理開始後の早い段階でRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の入力状態(レベル)を一時的な記憶手段であるレジスタ等に格納し、周辺制御基板1510の待機状態の終了後に一時的な記憶手段であるレジスタ等に格納したRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の状態を判定することによって、ホールの従業員が電源投入後の早い段階でキー操作を誤って中断しても、電源投入操作時のRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作を確実に検出する。
Next, the signal levels of the setting
その後、停電予告信号が停電中であるかを判定する(ステップS2006)。停電予告信号が検出されていれば、パチンコ機の電源電圧が正常ではないので、ステップS2006で電源電圧が安定するまで待機する。 After that, it is determined whether or not the power failure warning signal indicates power failure (step S2006). If the power failure warning signal has been detected, the power supply voltage of the pachinko machine is not normal, so the system waits until the power supply voltage stabilizes in step S2006.
その後、設定値が所定の範囲内であるかを判定する(ステップS2007)。例えば、設定が1~6までの段階で選択可能なパチンコ機1において、設定値が格納されるワークの値が0~5に対応している(設定1のとき=0、設定6のとき=5)場合には、5以下の値が格納されていれば、所定の範囲内であると判定される。
After that, it is determined whether the set value is within a predetermined range (step S2007). For example, in a
設定値が所定の範囲内でなければ、設定値を0に初期化し(ステップS2023)、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)を記録し(ステップS2024)、パチンコ機1のリセット信号による初期化を待つ。設定値は、チェックサムが計算される範囲ではなく、RAMクリア操作によって消去されないので、設定値が異常な値となっていても修正されない。このため、電源投入時に設定値に異常がないかを判定して、異常があれば通常遊技を起動しないようにしている。パチンコ機が設置されているホールでは、設
定値を維持したまま遊技状態を初期化したい(例えば、潜伏確変(高確率非時短)をクリアして、低確率時短である通常の状態に戻したい)場合に、RAMクリア操作をすることがある。営業中のRAMクリア操作によって設定値が初期化されると、設定値を再設定して営業を継続するために電源を遮断して設定変更モードを起動して、元の設定値を設定し直す必要がある。このような手間を発生させないために、RAMクリア操作によって、設定値をクリアせずに維持している。
If the setting value is not within the predetermined range, the setting value is initialized to 0 (step S2023), a value (08H) indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2024), and a reset signal for the
一方、設定値が所定の範囲内であれば、サブ起動待ちタイマ(例えば約2秒)を開始し、当該タイマがタイムアップするまでの間ウォッチドッグタイマを継続的にクリアし、周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ(ステップS2008)。周辺制御基板1510の起動待ちは、設定値を判定した後でなくても、電源投入後から周辺制御基板1510に最初にコマンドを送信するまでの期間であればいつでもよい。 On the other hand, if the set value is within a predetermined range, a sub-activation wait timer (for example, about 2 seconds) is started, and the watchdog timer is continuously cleared until the timer expires. is activated (step S2008). Waiting for activation of the peripheral control board 1510 may be any period from when the power is turned on until the first command is sent to the peripheral control board 1510, even if it is not after the setting value is determined.
その後、停電予告信号が停電中であるかを再度判定する(ステップS2009)。停電予告信号が検出されていれば、パチンコ機1の電源電圧が異常なので、ステップS2009で待機する。
After that, it is determined again whether the power failure warning signal indicates power failure (step S2009). If the power failure warning signal is detected, the power supply voltage of the
また、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域に異常があるかを判定し、判定結果をレジスタに格納する(ステップS2010)。具体的には、前回の電源遮断時に内蔵RAM1312にバックアップされている領域のうち遊技制御領域として使用されているデータ(スタックに退避されたデータは除く)から算出して記憶されたチェックサムと、同じ領域を使用して算出されたチェックサムとを比較し、両者が異なれば、主制御RAM1312に異常があると判定する。また、正常にバックアップされた(電源断時処理が正常に実行された)ことを示す停電フラグの値がバックアップフラグエリアに格納されていなければ、停電発生時に主制御RAM1312のデータが正常にバックアップされておらず(電源断時処理が正常に実行されておらず)、主制御RAM1312に異常があると判定する。
Also, it determines whether there is an abnormality in the game control area of the
そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域に異常があれば、設定状態管理エリアの情報を退避し(ステップS2011)、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)を仮に記録する(ステップS2012)。
Then, if there is an abnormality in the game control area of the
そして、PFポートの値が記録されたレジスタ値のうち、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954のビットをマスクする(ステップS2013)。その後、電源投入時に設定キー971がONに操作されており、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2014)。そして、設定キー971がONに操作されており、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていれば、設定変更操作がされていると判定し、図187のステップS2030に進む。
Then, the bits of the setting
一方、設定キー971が操作されておらず、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていなければ、停電発生時に設定変更モードであったかを判定する(ステップS2015)。例えば、S2011で退避した設定状態管理エリアの値が設定変更モード(02H)のときに、設定変更モード中に停電が発生したと判定する。
On the other hand, if the setting
そして、設定変更モード中に停電が発生したと判定したときには図187のステップS2030に進む。 Then, when it is determined that a power failure has occurred during the setting change mode, the process proceeds to step S2030 in FIG.
一方、設定変更モード中に停電が発生していないと判定したときには、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域に異常があるかを判定する(ステップS2016)。具体的には、前述したステップS2010でレジスタに格納された判定結果を用いて判定できる。その
結果、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域に異常があれば、図187のステップS2031に進む。
On the other hand, when it is determined that a power failure has not occurred during the setting change mode, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the game control area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2016). Specifically, determination can be made using the determination result stored in the register in step S2010 described above. As a result, if there is an abnormality in the game control area of the
一方、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域に異常がなければ、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したかを判定する(ステップS2017)。例えば、退避した設定状態管理エリアの値がRAM異常を示す値(08H)のときに、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したと判定する。
On the other hand, if there is no abnormality in the game control area of the
そして、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したと判定したときには、図187のステップS2036に進む。一方、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生していないと判定したときには、設定状態管理エリアに通常遊技状態を示す値(00H)を記録する(ステップS2018)。ステップS2018で設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録することによって、ステップS2012で設定状態管理エリアに仮に記録されたRAM異常を示す値(08H)を、正常な状態に戻している。また、ステップS2018で設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録することによって、ステップS2016とS2019とからステップS2031にジャンプした際の設定状態管理エリアの値が異なることから、両者でプログラムを共通にでき、プログラムサイズを小さくできる。 Then, when it is determined that a power failure has occurred during the RAM abnormality processing, the process proceeds to step S2036 in FIG. On the other hand, when it is determined that a power failure has not occurred during the RAM abnormality processing, the value (00H) indicating the normal game state is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2018). By recording 00H in the setting state management area in step S2018, the value (08H) temporarily recorded in the setting state management area in step S2012 indicating a RAM abnormality is returned to a normal state. By recording 00H in the setting state management area in step S2018, the values in the setting state management area differ when jumping from steps S2016 and S2019 to step S2031. size can be reduced.
その後、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2019)。そして、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていれば、RAMクリア操作がされていると判定し、図187のステップS2031に進む。
Thereafter, it is determined using the value stored in the register whether or not the RAM
本実施例のパチンコ機では、RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の操作と、設定状態管理エリアに記録された値とに基づいて、処理を振り分ける。例えば、主制御RAM1312が異常であると判定されると、設定状態管理エリアには08Hが記録され、電源が遮断されるまでに08Hが維持されるため、通常遊技処理を実行できない。このとき、一旦電源を遮断した後に設定変更操作をして電源を投入すると、RAM異常を解除できる。すなわち、ステップS2014で設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954の両方が操作されている(設定変更操作)と判定されると、設定状態管理エリアがRAM異常を示す値(08H)から設定変更を示す値(02H)に更新され(ステップS2030)、RAM異常状態が終了する。このように、RAM異常からの復帰は、必ず設定変更を経由することになっている。換言すると、停電発生時の状態がRAM異常かを判定する前に、設定変更操作がされているかを判定するので、RAM異常は設定値の変更を契機としてのみ解消できる。
In the pachinko machine of this embodiment, processing is distributed based on the operation of the RAM
一方、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていなければ、停電発生前の状態に復旧するために、停電発生時点での遊技状態の情報を電源投入時状態バッファに記憶する(ステップS2020)。
On the other hand, if the RAM
その後、電源投入時に設定キー971がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2021)。そして、設定キー971がONに操作されていれば、設定確認操作がされていると判定し、設定状態管理エリアに設定確認モードを示す値(01H)を記録し(ステップS2022)、図187のステップS2036に進む。すなわち、停電発生時の状態が設定確認中かにかかわらず、設定キー971のみが操作されていれば(RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていなければ)、設定確認モードに移行する。
Thereafter, it is determined using the value stored in the register whether or not the setting
ステップS2018からS2022は、RAMクリアスイッチ954か設定キー971の少なくとも一つが操作されていない場合に実行される処理であることから、RAMクリ
アスイッチ954の操作の判定(ステップS2019)と、設定キー971の操作の判定(ステップS2021)とのいずれを先に行ってもよい。すなわち、図示したように、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を判定(ステップS2019)した後に設定キー971の操作を判定(ステップS2021)してもよく、設定キー971の操作を判定(ステップS2021)した後にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を判定(ステップS2019)してもよい。
Steps S2018 to S2022 are processes executed when at least one of the RAM
次に、電源投入時処理(図186)の続きである図187を説明する。 Next, FIG. 187, which is a continuation of the power-on processing (FIG. 186), will be described.
ステップS2014または、ステップS2015でYESと判定されると、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更モードを示す値(02H)を記録する(ステップS2030)。そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内の設定値及び設定状態管理エリア以外の領域と遊技制御領域内のスタック領域とを初期化する(ステップS2031)。その後、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域に異常があるかを判定する(ステップS2032)。具体的には、前述したステップS2010での判定結果がレジスタに記憶されているので、ステップS2032では、レジスタに格納された判定結果を用いてに基づいて判定できる。
If YES is determined in step S2014 or step S2015, a value (02H) indicating the setting change mode is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2030). Then, the area other than the setting value and setting state management area in the game control area of the
主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域に異常があると判定されたときには、フラグレジスタを遊技制御領域内スタック領域に退避し(ステップS2033)、RAM異常時初期化処理によって、主制御RAM1312のうち遊技制御領域外で使用されるRAM(ワークエリアとスタック領域)を初期化する(ステップS2034)。RAM異常時初期化処理の詳細は図189で後述する。そして、遊技制御領域内スタック領域に退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2035)。
When it is determined that there is an abnormality in the game control area of the
その後、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたデバイス(CTC、SIO等)の機能を初期設定し(ステップS2036)、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたハードウェア乱数(例えば当落乱数)を起動する(ステップS2037)。そして、電源投入時設定処理を実行する(ステップS2038)。電源投入時設定処理の詳細は図194で後述する。
After that, the function of the device (CTC, SIO, etc.) built in the
最後にタイマ割込みを許可に設定し(ステップS2039)、主制御側メイン処理(図188)に進む。 Finally, the timer interrupt is enabled (step S2039), and the process proceeds to main control side main processing (FIG. 188).
図188は、主制御MPU1311が実行する主制御側メイン処理のフローチャートである。主制御側メイン処理は、電源投入時処理(図187)のステップS2039の後に実行される。
FIG. 188 is a flow chart of main control side main processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、停電予告信号を取得し、停電予告信号がONであるかによって停電が発生しているかを判定する(ステップS2040)。停電予告信号がONでない場合、正常に電源が供給されているので、乱数更新処理2を実行する(ステップ2041)。乱数更新処理2の詳細は図195で後述する。乱数更新処理2では、主として特別抽選や普通抽選において当選判定を行うための乱数以外の乱数を更新する。
First, the
一方、停電予告信号を検出した場合、電源断時処理(ステップS2042~S2046)を実行する。電源断時処理では、停電発生前の状態に復帰させるためのデータをバックアップする処理を実行する。具体的には、まず、割込みを禁止する(ステップS2042)。これにより後述するタイマ割込み処理が行われなくなり、主制御内蔵RAM1312へのデータの書き込みを禁止し、遊技情報の書き換えを保護する。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、出力ポートをクリアして、各ポートからの出力によって制御される機器の動作を停止する(ステップS2043)。具体的には、ソレノイド・停電クリア・ACK出
力ポートに停電クリア信号OFFビットデータを出力する。なお、全ての出力ポートがクリアされなくてもよく、例えば、電力消費が大きいソレノイドやモータを制御するための出力ポートをクリアしてもよい。これらの出力ポートをクリアすることによって、主基板側電源断時処理が終了するまでの消費電力を低減し、主基板側電源断時処理を確実に終了できるようにする。
On the other hand, when the power failure warning signal is detected, power failure processing (steps S2042 to S2046) is executed. In the power failure process, a process of backing up data for returning to the state before the power failure occurred is executed. Specifically, first, the interrupt is prohibited (step S2042). As a result, timer interrupt processing, which will be described later, is not performed, prohibits writing data to the main control built-in
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、バックアップされるワークエリアに格納されたデータが正常に保持されたか否かを判定するためのチェックサムを計算し、主制御RAM1312の所定のチェックサム格納エリアに記憶する(ステップS2044)。このチェックサムはワークエリアにバックアップされたデータが正常かの判定に使用される。なお、チェックサムが算出される対象の領域は、遊技制御領域内のワークエリアのうち、電源投入後主制御側メイン処理の実行までの間に変更される可能性がある設定状態管理(設定値と設定状態管理エリアの値)や、バックアップフラグや、チェックサムエリアの値を除外するとよい。
Subsequently, the
さらに、停電フラグとしてバックアップフラグエリアに正常に電源断時処理が実行されたことを示す値(5AH)を格納する(ステップS2045)。これにより、遊技バックアップ情報の記憶が完了する。最後に、RAMプロテクト有効(書き込み禁止)、禁止領域の無効をRAMプロテクトレジスタに書き込み、主制御RAM1312の所定の領域への書き込みを禁止し(ステップS2046)、停電から復旧するまでの間、待機する(無限ループ)。主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の使用領域を指定することによって、指定領域以外の禁止領域へアクセスがあった場合には、異常と判定してリセットする機能を有する。主制御RAM1312の禁止領域へのアクセスによるリセット機能を解除するために、禁止領域をとして無効に設定することで主制御RAM1312の全領域へのアクセスを可能としている。なお、主制御RAM1312のうち未使用領域を禁止領域に指定して、禁止領域を有効にして、指定された禁止領域にアクセスを検出した場合には、主制御MPU1311がリセットされるようにしてもよい。
Further, a value (5AH) indicating that the power failure processing has been normally executed is stored in the backup flag area as a power failure flag (step S2045). This completes the storage of the game backup information. Finally, write RAM protection valid (write prohibited) and prohibited area invalid to the RAM protect register, prohibit writing to a predetermined area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2046), and wait until recovery from the power failure. (infinite loop). The
図189は、主制御MPU1311が実行するRAM異常時初期化処理のフローチャートである。RAM異常時初期化処理は、電源投入時処理(図187)のステップS2034において実行される。
FIG. 189 is a flow chart of RAM abnormality initialization processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、スタックポインタの値を遊技制御領域外のSP退避用バッファに格納し(ステップS2050)、遊技制御領域外スタックポインタ値をスタックポインタに設定し(ステップS2051)、全てのレジスタ値を遊技制御領域外のレジスタ退避用バッファに格納する(ステップS2052)。 First, the main control MPU1311 stores the value of the stack pointer in the SP saving buffer outside the game control area (step S2050), sets the stack pointer value outside the game control area to the stack pointer (step S2051), all registers The value is stored in the register saving buffer outside the game control area (step S2052).
その後、最初の電源投入時における初期化かを電源投入時の初回電源投入フラグの値にもとづいて判定する(ステップS2053)。最初の電源投入時とは、パチンコ機として最初に電源が投入されるとき、及び、バックアップ電源が途絶して主制御RAM1312にバックアップされたデータが消去した状態からの電源投入時を意味する。例えば、主制御基板1310とバックアップ電源(例えば、本体枠4に設置)との接続線を外すと、主制御RAM1312へのバックアップ電源の供給が絶たれ、主制御RAM1312のデータが保持できなくなる。
After that, it is determined whether the initialization is performed when the power is turned on for the first time, based on the value of the first power-on flag when the power is turned on (step S2053). When the power is turned on for the first time means when the power is first turned on as a pachinko machine, and when the power is turned on after the backup power supply is interrupted and the data backed up in the
最初の電源投入時における初期化であれば、ステップS2056に進む。一方、最初の電源投入時における初期化でなければ、ベース算出対象の排出球が所定の範囲外かを判定する(ステップS2054)。ベース算出対象の排出球が所定の範囲外であれば、ステップS2056に進む。一方、ベース算出対象の排出球が所定の範囲内であれば、性能表示モニタの表示用パラメータが正常範囲内かを判定する(ステップS2055)。そして、
性能表示モニタの表示用パラメータが正常範囲内であれば、RAM異常時初期化処理を終了し、呼出元の処理に戻る。
If it is initialization at the time of the first power-on, the process proceeds to step S2056. On the other hand, if the initialization is not performed when the power is turned on for the first time, it is determined whether or not the discharge ball for base calculation is outside the predetermined range (step S2054). If the discharged ball for base calculation is out of the predetermined range, the process proceeds to step S2056. On the other hand, if the discharged ball for base calculation is within the predetermined range, it is determined whether the display parameters of the performance display monitor are within the normal range (step S2055). and,
If the display parameters of the performance display monitor are within the normal range, the RAM abnormality initialization process is terminated, and the caller process is returned to.
一方、性能表示モニタの表示モードが正常範囲外であれば、主制御RAM1312の使用領域外の全てのワークエリアに00Hを書き込んで初期化し(ステップS2056)、使用領域外の全てのスタック領域に00Hを書き込んで初期化し(ステップS2057)、電源投入時の初期化フラグに所定値(例えば、5AH)を設定して(ステップS2058)、呼出元の処理に戻る。
On the other hand, if the display mode of the performance display monitor is out of the normal range, 00H is written to all work areas outside the use area of the
図190、図191は、主制御MPU1311が実行するタイマ割込み処理のフローチャートである。
190 and 191 are flowcharts of timer interrupt processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンク選択フラグを1に設定し、レジスタのバンクを切り替える(ステップS2060)。なお、主制御MPU1311は、演算に使用するレジスタ群を二つ有し、一つはバンク0のレジスタ群として使用し、他はバンク1のレジスタ群として使用可能とされており、バンク切換を行わずに、両方のバンクのレジスタを使用できないように構成されている。主制御側メイン処理ではレジスタバンク0が使用され、タイマ割込み処理ではレジスタバンク1が使用される。このため、タイマ割込み処理の開始時にはバンクを1に切り替える命令を実行するが、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にはバンクを0切り替える命令を実行する必要がない。これは、主制御MPU1311は、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタ(例えば、Zフラグ、Cフラグがセットされているレジスタ)に記憶しており、フラグレジスタは、割込開始時にスタック領域に退避され、RET命令の実行によってスタック領域から復帰する。このため、RET命令を実行することでフラグレジスタに記憶したレジスタのバンクフラグも元に戻る。なお、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタに記憶しない構成を採用した場合、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にバンク切替命令を実行して、バンク0に戻す。
First, the
なお、フラグレジスタには、割込可否を制御するフラグも記憶されているため、割り込み許可に設定してからRET命令を実行しなくてもよい。なお、割込可否を制御するフラグは、タイマ割込み処理の開始時に、フラグレジスタをスタックした後に割込禁止状態に設定される。このため、タイマ割込処理中に割込を許可(EI命令など)するか、RETI命令を実行しない限り、割込み許可状態にはならない。 Since the flag register also stores a flag for controlling whether or not to enable interrupts, it is not necessary to execute the RET instruction after enabling interrupts. It should be noted that the flag that controls whether or not to allow interrupts is set to the interrupt disabled state after the flag register is stacked at the start of timer interrupt processing. Therefore, unless an interrupt is permitted (EI instruction, etc.) or a RETI instruction is executed during timer interrupt processing, the interrupt enabled state is not entered.
次に、LEDコモンカウンタを+1更新する。なお、LEDコモンカウンタ値が上限を超える場合は0にする(ステップS2061)。 Next, the LED common counter is updated by +1. If the LED common counter value exceeds the upper limit, it is set to 0 (step S2061).
次に、スイッチ入力処理1を実行する(ステップS2062)。スイッチ入力処理1では、主制御MPU1311の各種入力ポートの入力端子に入力されている各種信号を読み取り、ONエッジを作成し、入力情報として主制御RAM1312の入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。
Next, switch
なお、ステップS2062のスイッチ入力処理1は入賞信号に関する処理であり、後述するステップS2080のスイッチ入力処理2は不正検出センサ(磁石センサ、電波センサ、振動センサ等)の入力に関する処理である。このため、設定変更モードや設定確認モードで実行されるタイマ割込み処理では、ステップS2604においてNOと判定されるので、入賞検出は行われるが、不正は検出されない。なお、入賞が検出されても、賞球の払出しや変動表示等は実行されない。設定変更操作や設定確認操作はホールの従業員が行うものであり、設定変更モードや設定確認モードでは不正が行われず、不正を検出しない方が望ましいと考えられるからである。
Note that
なお、設定変更モードや設定確認モードでも、一部の不正検出センサ(例えば電波センサ)はスイッチ入力処理1で検出し、特定の種類の不正を監視してもよい。このようにすると、不正行為を行おうとする者(ゴト師)が電波を照射する等によって強制的に設定変更モードを起動する不正を検出できる。
Note that even in the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, some fraud detection sensors (for example, radio wave sensors) may detect in the
続いて、乱数更新処理1を実行する(ステップS2063)。乱数更新処理1では、大当り判定用乱数、大当り図柄用乱数、及び小当り図柄用乱数を更新する。またこれらの乱数に加えて、図188に示した主制御側メイン処理の乱数更新処理2で更新される大当り図柄決定用乱数及び小当り図柄決定用乱数の初期値を変更するための、それぞれの初期値決定用乱数を更新する。
Subsequently, random
その後、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2064)。設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていれば、図191のステップS2080に進む。一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていなければ、LEDコモンポートをOFFにする(ステップS2065)。タイマ割込み処理の早い段階でLEDコモン信号をOFFにすることによって、LEDコモン信号がオンになるまでの時間、すなわちLEDの消灯時間を確保し、LEDの表示切替前後の表示が混ざって見えるゴースト現象を抑制し、LEDのちらつきを防止している。 After that, it is determined whether a value (00H) indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2064). If a value indicating game start is recorded in the setting state management area, the process proceeds to step S2080 in FIG. On the other hand, if the value indicating the start of the game is not recorded in the setting state management area, the LED common port is turned off (step S2065). By turning off the LED common signal at an early stage of the timer interrupt processing, the time until the LED common signal turns on, that is, the LED extinguishing time is secured, and the ghost phenomenon in which the display before and after the LED display switching appears mixed. to prevent flickering of the LED.
その後、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力し(ステップS2066)、試験信号を出力する(ステップS2067)。ステップS2067では、遊技状態エラー信号のみONし、それ以外はOFFにするとよい。 Thereafter, a security signal is output from the external terminal board 784 (step S2066), and a test signal is output (step S2067). At step S2067, only the game state error signal is turned ON, and other signals are turned OFF.
そして、設定処理を実行する(ステップS2068)。設定処理の詳細は図192で後述する。 Then, setting processing is executed (step S2068). Details of the setting process will be described later with reference to FIG.
その後、設定表示処理を実行する(ステップS2069)。設定表示処理の詳細は図193で後述する。 Thereafter, setting display processing is executed (step S2069). Details of the setting display processing will be described later with reference to FIG.
さらに、送信情報記憶領域の値をシリアル通信回路に出力する周辺基板コマンド送信処理を実行する(ステップS2070)。送信情報記憶領域は、生成された送信コマンドを一時的に格納する記憶領域である。送信情報記憶領域に格納された値(コマンド)は、ステップ2070で読み出されてシリアル通信回路(SIO)の送信情報記憶領域に格納される。シリアル通信回路は、複数バイトのFIFO形式の送信バッファである送信情報記憶領域を有し、送信情報記憶領域に格納された値を、順次、周辺制御基板1510に送信する。 Further, peripheral board command transmission processing for outputting the value of the transmission information storage area to the serial communication circuit is executed (step S2070). The transmission information storage area is a storage area that temporarily stores the generated transmission command. The value (command) stored in the transmission information storage area is read at step 2070 and stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit (SIO). The serial communication circuit has a transmission information storage area, which is a transmission buffer in the FIFO format of multiple bytes, and sequentially transmits the values stored in the transmission information storage area to the peripheral control board 1510 .
その後、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットして、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアする(ステップS2071)。なお、ウォッチドッグタイマは、単純クリアモードを使用しているので、1ワードをセットすることによってウォッチドッグタイマがクリアされる。その後、復帰命令(例えばRETI)によって、レジスタのバンクを切り替え(ステップS2072)、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。 Thereafter, a predetermined value (18H) is set in the watchdog timer clear register WCL to clear the watchdog timer (step S2071). Note that the watchdog timer uses a simple clear mode, so setting one word clears the watchdog timer. Thereafter, a return instruction (for example, RETI) switches the bank of the register (step S2072), and returns to the processing before the interrupt.
続いて図191を説明する。図190のステップS2064において設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていると判定されると、主制御MPU1311は、不正検出のためのセンサ(スイッチ)の状態を検出するスイッチ入力処理2を実行する(ステップS2080)。具体的には、磁石を用いた不正行為を検出する磁気検出スイッチ3024からの検出信号などを読み取り、所定のレベル(ONレベル又はOFFレベル)が所定時間継続している場合、入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。スイッチ入力処理2で生成され
た各不正検出センサの検出状態に基づいて、ステップS2084の不正行為検出処理で不正が検出されたか否かを判定する。なお、不正行為検出処理(ステップS2084)では、不正検出センサによる不正検出の他に、大入賞口、普通電動役物の入賞過多等の入賞異常も判定する。
Next, FIG. 191 will be explained. When it is determined in step S2064 in FIG. 190 that a value indicating the start of a game is recorded in the setting state management area, the
その後、タイマ更新処理を実行する(ステップS2081)。タイマ更新処理では、例えば、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理で決定される変動表示パターンに従って特別図柄表示器1185が点灯する時間、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理で決定される普通図柄変動表示パターンに従って普通図柄表示器1189が点灯する時間のほかに、主制御基板1310(主制御MPU1311)が送信した各種コマンドを払出制御基板951が正常に受信した旨を伝える払主ACK信号が入力されているか否かを判定する際にその判定条件として設定されているACK信号入力判定時間等の時間管理を行う。具体的には、変動表示パターン又は普通図柄変動表示パターンの変動時間が5秒間であるときには、タイマ割り込み周期が4msに設定されているので、このタイマ減算処理を行うごとに変動時間を4msずつ減算し、その減算結果が値0になることで変動表示パターン又は普通図柄変動表示パターンの変動時間を正確に計測している。
Thereafter, timer update processing is executed (step S2081). In the timer update process, for example, the time during which the special symbol indicator 1185 lights up according to the variation display pattern determined by the special symbol and special electric auditors control process, the normal symbol fluctuation determined by the normal symbol and normal electric auditors control process In addition to the time during which the normal symbol display 1189 lights up according to the display pattern, a
続いて、賞球制御処理を実行する(ステップS2082)。賞球制御処理では、入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、読み出した入力情報に基づいて払い出される遊技球(賞球)の数を計算し、主制御RAM1312に書き込む。また、賞球数の計算結果に基づいて、遊技球を払い出すための賞球コマンドを作成したり、主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951との基板間の接続状態を確認するためのセルフチェックコマンドを作成したりする。主制御MPU1311は、作成した賞球コマンドやセルフチェックコマンドを主払シリアルデータとして払出制御基板951に送信する。
Subsequently, prize ball control processing is executed (step S2082). In the prize ball control process, input information is read from the input information storage area, the number of game balls (prize balls) to be paid out is calculated based on the read input information, and the calculated number is written in the
続いて、枠コマンド受信処理を実行する(ステップS2083)。払出制御基板951では、払出制御プログラムによって、状態表示に区分される1バイト(8ビット)の各種コマンド(例えば、枠状態1コマンド、エラー解除ナビコマンド、及び枠状態2コマンド)を送信する。一方、後述するように、払出制御プログラムによって、払出動作にエラーが発生した場合にエラー発生コマンドを出力したり、操作スイッチの検出信号に基づいてエラー解除報知コマンドを出力する。枠コマンド受信処理では、各種コマンドを払主シリアルデータとして正常に受信すると、その旨を払出制御基板951に伝える情報を主制御内蔵RAM1312の出力情報記憶領域に記憶する。また、主制御MPU1311は、払主シリアルデータとして正常に受信したコマンドを2バイト(16ビット)のコマンドに整形し(例えば、枠状態表示コマンド、エラー解除報知コマンドなど)、上述した送信情報記憶領域に記憶する。具体的には、枠コマンド受信処理では、払出制御基板951から受信したコマンドに対応した報知を行うために、払出制御基板951から受信したコマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信するコマンドの体系に適合するように修正して、他の生成したコマンドと同様にシリアル通信回路(SIO)の送信情報記憶領域に格納する。また、払出制御基板951からのコマンドを正常に受信した場合には、主ACK信号の出力を制御するための信号を生成する。主ACK信号は、シリアル通信回路ではなく、出力ポートから払出制御基板951に直接出力される。
Subsequently, frame command reception processing is executed (step S2083). The
続いて、不正行為検出処理を実行する(ステップS2084)。不正行為検出処理では、不正に関連した異常状態(磁気、振動、入賞異常等)を確認する。例えば、上述した入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、大当り遊技状態でない場合にカウントスイッチによって大入賞口2005、2006に遊技球が入球していると検知されたとき等には、主制御プログラムは、異常状態として報知表示に区分される入賞異常表示コマンドを作成し、送信情報として上述した送信情報記憶領域に記憶する。
Subsequently, fraud detection processing is executed (step S2084). In the fraudulent activity detection process, an abnormal state (magnetism, vibration, winning anomaly, etc.) related to fraud is confirmed. For example, when the input information is read out from the above-described input information storage area, and when it is detected that the game ball is entering the
続いて、入賞スイッチや始動口スイッチに関する各種スイッチの通過検出時に対応するコマンドを作成し送信情報記憶領域にセットするスイッチ通過時コマンド出力処理を実行する(ステップS2085)。 Subsequently, a switch-passing command output process is executed to create a command corresponding to the detection of the passage of various switches relating to the winning switch and the starting switch and set it in the transmission information storage area (step S2085).
そして、フラグレジスタを遊技制御領域内のスタック領域に退避し(ステップS2086)、ベース表示器出力処理を実行する(ステップS2087)。ベース表示器出力処理は、他の処理と異なり、遊技制御領域外の第2領域を使用して実行される処理であり、パチンコ機1の仕様に影響を受けない共通の処理である。このため、ベース表示器出力処理の独立性を担保するために、ベース表示器出力処理の実行前後に、フラグレジスタなどの所定のデータを遊技制御領域内のスタック領域に退避して、ベース表示器出力処理で更新されないようにしている。その後、遊技制御領域内のスタック領域に退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2088)。
Then, the flag register is saved in the stack area within the game control area (step S2086), and the base display output process is executed (step S2087). The base display output process is a process executed using the second area outside the game control area, unlike other processes, and is a common process that is not affected by the specifications of the
続いて、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理を実行する(ステップS2089)。特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理では、大当り用乱数値が主制御内蔵ROMに予め記憶されている当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定し、大当り図柄乱数値に基づいて確率変動状態に移行するか否かを判定する。そして、大当り用乱数値が当り判定値と一致している場合には、大入賞口2005、2006を開閉動作させるか否かを決定する。この決定により大入賞口2005、2006を開閉動作させる場合、大入賞口2005、2006が開放(又は、拡大)状態となることで大入賞口2005、2006に遊技球が受け入れ可能となる遊技状態となって遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態に移行する。また、確変移行条件が成立している場合には、その後、確率変動状態に移行する一方、確変移行条件が成立していない場合には当該確率変動状態以外の遊技状態に移行する。ここで、「確率変動状態」とは、上述した特別抽選の当選確率が通常遊技状態(低確率状態)と比較して相対的に高く設定された状態(高確率状態)をいう。
Subsequently, a special symbol and special electric accessary product control process is executed (step S2089). In the special symbol and special electric accessory control processing, it is determined whether or not the big hit random number value matches the hit determination value pre-stored in the main control built-in ROM, and the probability fluctuation state is established based on the big hit symbol random number value. Determine whether to migrate. Then, when the big win random number value matches the hit determination value, it is determined whether or not to open and close the
続いて、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理を実行する(ステップS2090)。普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理では、上述した入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、ゲートスイッチ2352からの検出信号が入力端子に入力されていたか否かを判定する。検出信号が入力端子に入力されていた場合には、普通図柄当り判定用乱数を抽出し、主制御内蔵ROMに予め記憶されている普通図柄当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定する(「普通抽選」という)。そして、普通抽選による抽選結果に応じて第二始動口扉部材2549を開閉動作させるか否かを決定する。この決定により開閉動作をさせる場合、第二始動口扉部材2549が開放(又は、拡大)状態となることで始動口2004に遊技球が受け入れ可能となる遊技状態となって遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態に移行する。
Subsequently, normal symbol and normal electric accessary product control processing is executed (step S2090). In the normal symbol and normal electric accessory control process, the input information is read from the above-described input information storage area, and it is determined whether or not the detection signal from the gate switch 2352 is input to the input terminal. When the detection signal is input to the input terminal, the random number for normal symbol per determination is extracted, and it is determined whether or not it matches the normal per symbol determination value stored in advance in the main control built-in ROM (" “General Lottery”). Then, it is determined whether or not to open and close the second starting
続いて、出力データ設定処理を実行する(ステップS2091)。出力データ設定処理では、主制御MPU1311の各種出力ポートの出力端子から各種信号を出力する。例えば、出力情報に基づいて主制御MPU1311の所定の出力ポートの出力端子から、払出制御基板951からの各種コマンドを正常に受信したときには主払ACK信号を払出制御基板951に出力したり、大当り遊技状態であるときには大入賞口2005、2006の開閉部材2107の開閉動作を行うアタッカソレノイド(第一アタッカソレノイド2113、第二上アタッカソレノイド2553、第二下アタッカソレノイド2556)に駆動信号を出力したり、始動口(第二始動口扉部材2549)の開閉動作を行う始動口ソレノイド2550に駆動信号を出力したりするほかに、ホールコンピュータへの出力情報として、確率変動中情報出力信号、特別図柄表示情報出力信号、普通図柄表示情報出力信号、時短中情報出力情報、始動口入賞情報出力信号等の遊技に関する各種情報(遊技情報)信号及びセキュリティ信号を外部端子板784に出力する。
Subsequently, output data setting processing is executed (step S2091). In the output data setting process, various signals are output from output terminals of various output ports of the
また、出力データ設定処理では、スイッチ入力処理2(ステップS2080)で計数さ
れたアウト球数に対応する信号を外部端子板784から出力する。例えば、所定のアウト球数(10個など)毎に外部端子板784から所定長のパルス信号を出力してもよい。
Also, in the output data setting process, a signal corresponding to the number of out balls counted in the switch input process 2 (step S2080) is output from the external
また、出力データ設定処理では、パチンコ機1に接続された検査装置に出力するための試験信号を設定する。試験信号には、例えば、遊技状態を示す信号や普通図柄、特別図柄の停止図柄を示す信号が含まれる。
Also, in the output data setting process, a test signal to be output to the inspection device connected to the
その後、図190のステップS2070に進む。 After that, the process proceeds to step S2070 in FIG.
図192は、設定処理のフローチャートである。設定処理は、設定状態管理エリアが通常遊技状態を示す値(00H)ではない場合に、タイマ割込み処理のステップS2068において実行され、主に設定値を変更する処理を実行する。 FIG. 192 is a flowchart of setting processing. The setting process is executed in step S2068 of the timer interrupt process when the setting state management area does not indicate the normal game state (00H), and mainly executes the process of changing the set value.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2100)。設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていれば、設定処理を実行することなく、呼出元の処理に戻る。
First, the
RAM異常と判定されると設定処理を繰り返し実行することになるため、特別図柄や普通図柄に関する処理が実行されず、遊技が全くできない状態になる。このRAM異常は、一旦電源を遮断して停電処理を実行後、電源を再投入する際に、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954とで設定変更モードを起動する操作をすることによって、設定変更状態となりRAM異常が解消される。そして、設定キー971を元に戻す操作によって設定変更モードが終了して通常遊技が開始可能となる。
When it is determined that the RAM is abnormal, the setting process is repeatedly executed, so that the process related to the special design and the normal design is not executed, and the game cannot be played at all. This RAM abnormality can be corrected by turning off the power once, executing power failure processing, and then, when turning on the power again, by operating the setting
また、電源を再投入する際に、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954とで設定変更モードを起動する以外の操作をした場合、設定状態管理エリアのRAM異常を示す値(08H)は維持され、RAM異常状態が継続し、通常遊技を開始できない。つまり、RAM異常を解消して通常遊技状態にするためには、必ず、設定変更モードを経由する必要がある。
When the power is turned on again, if an operation other than starting the setting change mode is performed with the setting
一方、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていなければ、設定キー971がOFF位置に戻ったかを判定する(ステップS2101)。具体的には、設定キー971のONからOFFへのエッジ、又は、ONからOFFへ変化してから所定期間経過したかを検出する。
On the other hand, if no value indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, it is determined whether the setting
設定キー971がOFF位置に戻ったと判定されると、セキュリティ信号出力タイマに出力時間を設定し(ステップS2102)、設定状態管理エリアを初期化して(ステップS2103)、電源投入時設定処理を実行し(ステップS2104)、呼出元の処理に戻る。
When it is determined that the setting
設定変更モードを終了する操作(設定キー971をOFF)がされた場合、セキュリティ信号出力タイマに出力時間値を設定することによって、設定変更モードの終了後セキュリティ信号がOFFになるまでの遅延時間を設ける。このため、設定変更モードや設定確認モードが短時間(例えば、一度のタイマ割込み処理内)で終了しても、セキュリティ信号の最短の出力信号をセキュリティ信号出力タイマに出力時間値として設定した分だけ確保でき、ホールコンピュータが確実にセキュリティ信号を検出できる。 When an operation to terminate the setting change mode (turning off the setting key 971) is performed, by setting an output time value in the security signal output timer, the delay time until the security signal is turned off after the setting change mode is terminated can be set. prepare. Therefore, even if the setting change mode or setting confirmation mode ends in a short time (for example, within one timer interrupt process), the shortest output signal of the security signal is set to the security signal output timer as the output time value. This ensures that the hall computer can reliably detect the security signal.
また、セキュリティ信号がOFFになるまでの遅延時間中に不正を検出した場合、セキュリティ信号を維持したまま、新たに検出した不正に対応した期間又は時間分、セキュリティ信号を出力するとよい。 Further, when fraud is detected during the delay time until the security signal is turned off, it is preferable to output the security signal for a period or time corresponding to the newly detected fraud while maintaining the security signal.
さらに、セキュリティ信号がOFFになるまでの遅延時間中に停電が発生した場合、電源復帰時に通常遊技状態でホットスタートすると、残時間分のセキュリティ信号を出力し、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によるRAMクリア時又はRAM異常によるRAMクリア時には、残時間分のセキュリティ信号を出力しない。これは、主制御RAM1312の初期化によって、セキュリティ信号出力タイマ値がリセットされ、セキュリティ信号の出力が停止するためである。
In addition, if a power failure occurs during the delay time until the security signal turns OFF, when the hot start is performed in the normal game state when the power is restored, the security signal for the remaining time is output, and when the RAM is cleared by operating the RAM clear switch Alternatively, when the RAM is cleared due to a RAM abnormality, the security signal for the remaining time is not output. This is because the initialization of the
セキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後に電源が投入されたときには、ホットスタート、RAMクリア、設定変更モード、設定確認モード、RAM異常状態継続の5パターンのいずれかになる。 When the power is turned on after a power failure occurs while the security signal is being output, one of five patterns of hot start, RAM clear, setting change mode, setting confirmation mode, and RAM abnormal state continuation occurs.
設定変更モード及び設定確認モードに移行した場合、起動されたモードが終了し、遅延時間が経過するまでセキュリティ信号が出力される。RAM異常状態が継続する場合、電源が復帰しても設定変更操作がされていないので、継続するRAM異常によるセキュリティ信号が出力される。ホットスタートの場合、残余時間分だけセキュリティ信号が出力される。 When shifting to the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, the activated mode ends and the security signal is output until the delay time elapses. If the RAM abnormality continues, a security signal is output due to the continued RAM abnormality because the setting change operation has not been performed even after the power is restored. In the case of hot start, the security signal is output for the remaining time.
セキュリティ信号を継続して出力する場合でも、電源投入時のパワーオンリセット信号によってセキュリティ信号の出力が停止し、所定時間(例えば、周辺制御基板1510の起動待ち時間中)の経過後にタイマ割込み処理に移行してからセキュリティ信号の出力が再開する。つまり、以下の場合においてセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後にセキュリティ信号を継続して出力するときでも、電源復帰後の所定の期間はセキュリティ信号の出力を停止する期間を設けている。
・不正検出などによるセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後、ホットスタートで電源が復帰する場合
・RAM異常によるセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後、電源が復帰して、RAM異常が継続する場合
・設定変更モードによるセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後、電源が復帰して、設定変更モードが継続する場合
・設定確認モードによるセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後、電源が復帰して、設定確認モードが継続する場合
Even if the security signal is continuously output, the output of the security signal is stopped by the power-on reset signal when the power is turned on, and after a predetermined time (for example, during the startup wait time of the peripheral control board 1510), the timer interrupt process starts. After the transition, output of the security signal resumes. That is, in the following cases, even when the security signal is continuously output after a power failure occurs while the security signal is being output, there is provided a period during which the output of the security signal is stopped for a predetermined period after the power is restored.
・When the power is restored by hot start after a power failure occurs while security signals are being output due to fraud detection, etc. ・After a power failure occurs while security signals are being output due to a RAM error, the power is restored and the RAM error continues. - After a power failure occurs while security signals are being output in setting change mode, the power is restored and the setting change mode continues. and the setting confirmation mode continues
このように、セキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後にセキュリティ信号を継続して出力するときでも、電源復帰後の所定の期間はセキュリティ信号の出力を停止することによって、ホールコンピュータ側でセキュリティ信号に異常があったのか、セキュリティ信号の出力に伴う状態が解除されたのかを判別できる。 In this way, even when the security signal is continuously output after a power failure occurs while the security signal is being output, the hall computer can respond to the security signal by stopping the output of the security signal for a predetermined period after the power is restored. It is possible to determine whether there is an abnormality or whether the state accompanying the output of the security signal has been released.
また、設定キー971のみが操作された設定確認モードでは、セキュリティ信号が出力される残時間にかかわらず、設定確認モードが終了するまでセキュリティ信号を出力し、設定確認モードが終了して遅延時間が経過した後にセキュリティ信号の出力を停止する。また、設定キー971及びRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作された設定変更モードでも設定確認モードと同様の処理を行うとよい。
In the setting confirmation mode in which only the setting
一方、設定キー971がOFF位置に戻っていないと判定されると、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更を示す値(02H)が記録されているかを判定し(ステップS2105)、設定変更スイッチ972が操作されたかを判定する(ステップS2106)。なお、設定変更スイッチ972は、RAMクリアスイッチ954と兼用される構成でもよい。その結果、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更を示す値が記録されており、かつ、設定変更スイッチ972が操作されたと判定されると、設定値を+1更新する。なお、設定値が上限6を超
える場合は1にする(ステップS2107)。その後、呼出元の処理に戻る。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the setting
一方、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更を示す値が記録されておらず(つまり、設定確認モードであり)、又は、設定変更スイッチ972が操作されていないと判定されると、設定値を更新せずに、呼出元の処理に戻る。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the value indicating the setting change is not recorded in the setting state management area (that is, the setting confirmation mode is set) or the setting
なお、設定変更スイッチ972の操作を判定する際(直前又は直後に)、設定キー971がONに操作されているかを判定してもよい。このように、設定変更スイッチ972の操作時に設定キー971の操作を判定すると、停電発生時に設定変更モードであり、停電復帰時に設定キー971がONに操作されていなくても、設定変更スイッチ972の操作によって設定変更が可能となることを防止できる。
When determining whether the setting
図193は、設定表示処理のフローチャートである。設定表示処理は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS2069において実行される。 FIG. 193 is a flowchart of setting display processing. The setting display process is executed in step S2069 of the timer interrupt process.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2110)。設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていなければ、現在の設定値がベース表示器1317に表示されるようにLEDのセグメント端子の出力を設定する(ステップS2111)。一方、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていれば、エラーがベース表示器1317に表示されるように、LEDのセグメント端子の出力を設定する(ステップS2112)。
First, the
その後、LEDコモンカウンタに対応したLEDコモン信号を出力し(ステップS2113)、設定値又はエラー表示に対応する表示データ(セグメント信号)をベース表示器1317に出力するようドライバを駆動し(ステップS2114)、呼出元の処理に戻る。 After that, an LED common signal corresponding to the LED common counter is output (step S2113), and the driver is driven to output display data (segment signal) corresponding to the set value or error display to the base display 1317 (step S2114). , return to the calling process.
図194は、電源投入時設定処理のフローチャートである。電源投入時設定処理は、サブルーチン化されており、電源投入時処理(図187)のステップS2038と設定処理のS2104で呼び出されて実行される。 FIG. 194 is a flowchart of power-on setting processing. The power-on setting process is a subroutine, and is called and executed in step S2038 of the power-on process (FIG. 187) and S2104 of the setting process.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、電源投入時動作コマンドを作成し、作成したコマンドを送信情報記憶領域にセットする(ステップS2120)。電源投入時動作コマンドは、図202(A)に示すように、設定状態管理エリアの記録内容を通知するコマンドである。
First, the
次に、入力レベルデータ2領域の設定キー971に対応するビットと設定変更スイッチ972に対応するビットとを初期値である1に設定する。なお、他のビットは0を設定するとよい(ステップS2121)。入力レベルデータ2エリアの設定キー971に対応するビットと設定変更スイッチ972に対応するビットを1に設定するのは、次のタイマ割込み時に当該スイッチのビットを1で検知して、ONエッジが誤って作られないようにするためである。
Next, the bit corresponding to the setting
その後、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2122)。設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値が記録されていなければ、設定変更モードであるか設定確認モードであるかRAM異常のいずれかなので、電源投入時設定処理を終了し、呼出元の処理に戻る。 After that, it is determined whether or not a value (00H) indicating a game-startable state is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2122). If no value indicating a game-startable state is recorded in the setting state management area, it means that it is either the setting change mode, the setting confirmation mode, or the RAM is abnormal. Return to processing.
一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値(00H)が記録されていれば
、通常遊技を開始できる状態なので、主制御RAM1312を初期化したか否かに応じて遊技制御領域内ワークエリアを初期設定する(ステップS2123)。
On the other hand, if a value (00H) indicating a game-startable state is recorded in the setting state management area, it is a state in which a normal game can be started. The area is initialized (step S2123).
その後、電源投入時状態コマンドを作成し、作成したコマンドを送信情報記憶領域に格納する(ステップS2124)。電源投入時状態コマンドは、図202(B)に示すように、設定状態管理エリアの記録内容に基づいて、通常遊技開始可能状態であるかを通知するコマンドである。 Thereafter, a power-on state command is created, and the created command is stored in the transmission information storage area (step S2124). As shown in FIG. 202B, the power-on state command is a command for notifying whether or not the normal game can be started based on the contents recorded in the setting state management area.
そして、電源投入時復帰先コマンドを作成し、作成したコマンドを送信情報記憶領域にセットする(ステップS2125)。電源投入時復帰先コマンドは、図202(C)に示すように、特別図柄に関する遊技状態を通知するコマンドである。 Then, a power-on recovery destination command is created, and the created command is set in the transmission information storage area (step S2125). The return destination command at power-on is, as shown in FIG.
さらに、設定値コマンドを作成し、作成したコマンドを送信情報記憶領域にセットする(ステップS2126)。設定値コマンドは、図202(D)に示すように、設定値を通知するコマンドである。 Further, a set value command is created, and the created command is set in the transmission information storage area (step S2126). The setting value command is a command for notifying a setting value, as shown in FIG. 202(D).
なお、電源投入時状態コマンド、電源投入時復帰先コマンド、設定値コマンドと共に、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの保留数を示す特別図柄保留数コマンドを送信して、機能表示ユニット1400やメイン液晶表示装置1600において保留数表示を停電発生前の状態に復旧させてもよい。なお、特別図柄保留数コマンドを送信順序は、電源投入時状態コマンド、電源投入時復帰先コマンド及び設定値コマンドの送信後でも、これらのコマンドの送信前でも、これらのコマンドの送信途中に送信してもよい。
In addition to the power-on state command, the power-on return destination command, and the setting value command, a special symbol reserve number command indicating the number of reservations of the special symbol variation display game is transmitted, and the
その後、呼出元の処理に戻る。 After that, it returns to the calling process.
電源投入時設定処理は、停電復帰時に設定変更モードでも設定確認モードでもない場合や、設定変更モードの終了時や設定確認モードの終了時に実行されるので、前述した各コマンド(電源投入時動作コマンド、電源投入時状態コマンド、電源投入時復帰先コマンド、設定値コマンド)は、設定変更モードでも設定確認モードでもない停電復帰時や設定変更モードの終了時や設定確認モードの終了時に送信される。 The power-on setting process is executed when the setting change mode is not in the setting confirmation mode when the power failure is restored, or when the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode ends. , power-on status command, power-on recovery destination command, and set value command) are sent at the time of recovery from a power failure in neither the setting change mode nor the setting confirmation mode, at the end of the setting change mode, or at the end of the setting confirmation mode.
図195は、乱数更新処理2のフローチャートである。乱数更新処理2は、メイン処理(図188)のステップS2041において実行され、主として特別抽選や普通抽選において当選判定を行うための乱数以外の乱数を更新する。
195 is a flowchart of random
まず、主制御MPU1311は、割込み禁止を設定し(ステップS2131)、初期値乱数を更新し(ステップS2132)、割込み許可を設定する(ステップS2133)。初期値乱数は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS2063の乱数更新処理1でも更新されるため、タイマ割込み処理によって初期値乱数更新処理が中断しないように、初期値乱数更新処理の前に割込みを禁止し、初期値乱数更新処理の後に割込みを許可している。初期値乱数は、特別図柄の大当りを抽選するための大当り判定用乱数、普通図柄の当りを抽選する当り乱数、特別図柄の大当り時の図柄の種別(低確率/高確率/時短/非時短等)を決定する乱数などの一周期ごとの初期値を変更するための乱数である。
First, the
その後、当落乱数以外の乱数(初期値乱数を除く)を更新し(ステップS2134)、呼出元の処理に戻る。 After that, the random numbers (excluding the initial value random numbers) other than the winning random numbers are updated (step S2134), and the process returns to the calling source.
図196は、主制御MPU1311が実行するタイマ割込み処理の別例のフローチャートである。なお、図181、図182で前述したタイマ割込み処理と同じ処理ステップには同じ符号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。
FIG. 196 is a flowchart of another example of timer interrupt processing executed by the
以下に説明する別例1においては、設定確認モードにおいても設定変更モードと同様に、主制御RAM1312が初期化されるとよい。この別例1において、電源復帰時に設定キー971の操作が検出されると、設定変更モードでも設定確認モードでも主制御RAM1312が初期化されることから、RAMクリアスイッチ954は、設定変更モードか設定確認モードかを切り替えるものではなく、設定値を変更する操作としての機能のみを有することになる。
In another example 1 described below, it is preferable that the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンク選択フラグを1に設定し、レジスタのバンクを切り替え(ステップS2060)、スイッチ入力処理3を実行し(ステップS2141)、スイッチ入力処理3の詳細は図197で後述する。なお、ステップS2141では、図197で説明するスイッチ入力処理3ではなく、S2062のスイッチ入力処理1を適用してもよい。
First, the
そして、乱数更新処理1を実行し(ステップS2063)、設定変更/確認処理を実行する(ステップS2142)。設定変更/確認処理の詳細は図200で後述する。
Then, random
続いて、スイッチ入力処理2を実行し(ステップS2080)、タイマ更新処理を実行し(ステップS2081)、賞球制御処理を実行する(ステップS2082)。続いて、枠コマンド受信処理を実行し(ステップS2083)、不正行為検出処理を実行し(ステップS2084)、スイッチ通過時コマンド出力処理を実行する(ステップS2085)。
Subsequently, switch
そして、フラグレジスタを遊技制御領域内のスタック領域に退避し(ステップS2086)、ベース表示器出力処理を実行し(ステップS2087)、遊技制御領域内のスタック領域に退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2088)。続いて、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理を実行し(ステップS2089)、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理を実行し(ステップS2090)、出力データ設定処理を実行する(ステップS2091)。さらに、周辺基板コマンド送信処理を実行し(ステップS2070)、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアし(ステップS2071)、復帰命令(例えばRETI)によって、レジスタのバンクを切り替え(ステップS2072)、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。 Then, the flag register is saved in the stack area within the game control area (step S2086), the base display output process is executed (step S2087), and the flag register saved in the stack area within the game control area is restored (step S2088). Subsequently, a special symbol and special electric auditors product control process is executed (step S2089), a normal symbol and normal electric auditors product control process is executed (step S2090), and an output data setting process is executed (step S2091). Further, peripheral board command transmission processing is executed (step S2070), the watchdog timer is cleared (step S2071), the bank of the register is switched by a return instruction (for example, RETI) (step S2072), and the processing before the interrupt is restored. do.
図197は、スイッチ入力処理3のフローチャートである。スイッチ入力処理3は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS2141において実行され、主制御MPU1311の各種入力ポートの入力端子に入力されている各種信号を読み取り、ONエッジを作成し、入力情報として主制御RAM1312の入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。
197 is a flowchart of
まず、主制御MPU1311は、スイッチ入賞情報データの先頭アドレスを設定し(ステップS2160)、スイッチ入賞情報データから処理の繰り返し回数を取得する(ステップS2161)。処理の繰り返し回数は、スイッチ入賞情報データテーブルのブロックの数nである。そして、スイッチ入賞情報データで指定された入力ポートアドレスを取得し(ステップS2162)、スイッチ入賞情報データで指定された入力レベルデータエリアアドレスを取得する(ステップS2163)。さらに、取得した入力ポートアドレスから入力情報を読み込み(ステップS2164)、読み込んだ入力情報をスイッチ入賞情報データで指定された論理補正値を用いて補正する(ステップS2165)。
First, the
その後、設定状態管理エリアに記録された値を参照して、設定変更モードである又は設定確認モードであるかを判定する(ステップS2166)。そして、設定変更モード又は設定確認モードでなければ、補正値をスイッチ入賞情報データに指定された通常遊技中の
マスク値でマスクする(ステップS2167)。このマスクによって、入力ポートのうち通常遊技中に使用するビットを取得できる。
Thereafter, referring to the value recorded in the setting state management area, it is determined whether the mode is the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode (step S2166). Then, if it is not the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode, the correction value is masked with the mask value during the normal game specified in the switch winning information data (step S2167). With this mask, you can get the bits of the input port that are used during normal play.
一方、設定変更モード又は設定確認モードであれば、補正値をスイッチ入賞情報データに指定された設定変更/確認中のマスク値でマスクする(ステップS2168)。このマスクによって、入力ポートのうち設定変更モード又は設定確認モードにおいて使用するビットのみを取得できる。 On the other hand, if it is the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode, the correction value is masked with the mask value during setting change/confirmation specified in the switch winning prize information data (step S2168). With this mask, only the bits used in the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode can be obtained from the input ports.
その後、マスク処理で取得したビットから入力レベルデータを生成し、スイッチ入賞情報データで指定された入力レベルデータエリアを更新する(ステップS2169)。 After that, the input level data is generated from the bits acquired by the mask processing, and the input level data area specified by the switch winning prize information data is updated (step S2169).
そして、OFFからONへの変化のエッジデータを入力レベルデータから生成して、スイッチ入賞情報データで指定された入力エッジデータエリアを更新する(ステップS2170)。 Then, the edge data of the change from OFF to ON is generated from the input level data, and the input edge data area specified by the switch winning information data is updated (step S2170).
その後、スイッチ入賞情報データとして次のブロックに設定し(ステップS2171)、全スイッチ入力ポートの処理が終了しているかを判定する(ステップS2172)。全スイッチ入力ポートの処理が終了していないと判定したときには、ステップS2162に戻り、次の入力ポートを処理する。一方、全スイッチ入力ポートの処理が終了したと判定したときには、スイッチ入力処理3を終了し、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。
After that, it is set in the next block as switch winning prize information data (step S2171), and it is determined whether the processing of all switch input ports is completed (step S2172). When it is determined that the processing of all switch input ports has not been completed, the process returns to step S2162 to process the next input port. On the other hand, when it is determined that the processing of all switch input ports has been completed, the
図198(A)は、スイッチ入賞情報データテーブルの構成例を示す図である。 FIG. 198(A) is a diagram showing a configuration example of a switch winning prize information data table.
図198(A)に示すスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルはn個のブロック毎に分かれて構成されており(nは処理の繰り返し回数)、各ブロックには入力ポートアドレス、論理補正値、通常遊技中マスク値、設定変更/確認中マスク値、及び入力レベルデータエリアのアドレスが含まれる。 The switch winning prize information data table shown in FIG. 198(A) is divided into n blocks (where n is the number of repetitions of processing), and each block contains an input port address, a logic correction value, and a normal game mask. value, mask value during setting change/confirmation, and address of the input level data area.
図198(B)は、スイッチ入力レベル/エッジデータエリアの構成例を示す図である。 FIG. 198B is a diagram showing a configuration example of the switch input level/edge data area.
スイッチ入力レベル/エッジデータエリアは、入力レベルデータエリアのアドレスと入力エッジデータエリアのアドレスとの組がn個含まれる。 The switch input level/edge data area includes n pairs of the address of the input level data area and the address of the input edge data area.
入力エッジデータエリアのアドレスは、図示するように、入力レベルデータエリアの次のアドレスに設定されているので、スイッチ入賞情報データには指定されない。入力レベルデータエリアと入力エッジデータエリアとを連続して配置しない場合には、同テーブルに入力レベルデータエリアとともに入力エッジデータエリアのアドレスを設定することになる。なお、入力レベルデータエリアや入力エッジデータエリアのアドレスは、16ビット(2バイト)の値であるが、スイッチ入賞情報データテーブルに設定される入力レベルデータエリアや入力エッジデータエリアのアドレスとして設定される値は、下位の8ビット(1バイト)の値であってもよい。すなわち、アドレスの上位バイトは入力レベルデータエリアや入力エッジデータエリアの値で変化しない固定値なので、上位バイトはRAM領域のアドレスの上位バイトであり、下位バイトだけ設定すればよいことから、データ容量を削減できる。 Since the address of the input edge data area is set to the next address of the input level data area, it is not designated as the switch winning information data. If the input level data area and the input edge data area are not arranged continuously, the address of the input edge data area is set in the same table together with the input level data area. Although the addresses of the input level data area and the input edge data area are 16-bit (2-byte) values, they are set as the addresses of the input level data area and the input edge data area set in the switch winning information data table. The value may be the lower 8-bit (1 byte) value. That is, since the upper byte of the address is a fixed value that does not change with the values of the input level data area and the input edge data area, the upper byte is the upper byte of the address in the RAM area, and only the lower byte needs to be set. can be reduced.
図199は、スイッチ入賞情報データテーブルの別な構成例を示す図であり、図199(A)は、通常遊技状態で使用されるスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルの構成例を示し、図199(B)は、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードで使用されるスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルの構成例を示す。 Fig. 199 shows another configuration example of the switch winning information data table, Fig. 199(A) shows a configuration example of the switching winning information data table used in the normal game state, and Fig. 199(B). shows a configuration example of a switch winning information data table used in the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode.
図199に示すスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルは、いずれも、n個のブロック毎に分かれて構成されており(nは処理の繰り返し回数)、各ブロックには入力ポートアドレス、論理補正値、マスク値、及び入力レベルデータエリアのアドレスを含む。通常遊技状態で使用されるスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルと、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードで使用されるスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルとでは、論理補正値とマスク値とが異なるポートが含まれる。つまり、図198(A)に示すスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルでは、設定変更モード(及び設定確認モード)と通常遊技状態とでマスク値を異なる値にしているが、図199に示すスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルでは、設定変更モード(及び設定確認モード)と通常遊技状態とで異なるスイッチ入賞情報データテーブルを使用し、異なるスイッチ入賞情報データを取得可能としている。 The switch winning prize information data table shown in FIG. 199 is divided into n blocks (where n is the number of repetitions of processing), and each block contains an input port address, a logical correction value, a mask value, and the address of the input level data area. The switch winning information data table used in the normal game state and the switching winning information data table used in the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode include ports with different logic correction values and mask values. That is, in the switch winning prize information data table shown in FIG. 198(A), the mask values are different between the setting change mode (and setting confirmation mode) and the normal game state, but the switch winning prize information data table shown in FIG. uses different switch winning information data tables in the setting change mode (and setting confirmation mode) and in the normal game state, making it possible to acquire different switch winning information data.
このような構成に対応するため、スイッチ入力処理3(図197)を以下のように変更する。例えば、ステップS2160において、設定変更モード(又は設定確認モード)であるか通常遊技状態であるかを判定し、該判定結果に応じたスイッチ入賞情報データの先頭アドレスを設定する。そして、ステップS2166で、設定変更モードである又は設定確認モードであるかを判定することなく、ステップS2167において、補正値をスイッチ入賞情報データに指定されたマスク値でマスクする。 In order to accommodate such a configuration, switch input processing 3 (FIG. 197) is changed as follows. For example, in step S2160, it is determined whether it is the setting change mode (or setting confirmation mode) or the normal game state, and the start address of the switch winning information data is set according to the determination result. Then, in step S2166, the correction value is masked with the mask value specified in the switch winning information data without determining whether it is the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode in step S2167.
図200は、設定変更/確認処理のフローチャートである。設定変更/確認処理は、タイマ割込み処理のステップS2142において実行される。図200に示す設定変更/確認処理において、図181、図182で前述したタイマ割込み処理と同じ処理ステップには同じ符号を付し、その詳細の説明は省略する。 FIG. 200 is a flowchart of setting change/confirmation processing. The setting change/confirmation process is executed in step S2142 of the timer interrupt process. In the setting change/confirmation process shown in FIG. 200, the same processing steps as those in the timer interrupt process described above with reference to FIGS.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2064)。設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていれば、設定変更/確認処理を終了し、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていなければ、LEDコモンポートをOFFにし(ステップS2065)、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力し(ステップS2066)、試験信号を出力する(ステップS2067)。そして、設定処理(図192)を実行し(ステップS2068)、設定表示処理(図193)を実行する(ステップS2069)。
First, the
図201(A)は、スイッチ入力ポート2の構成例を示す図である。
FIG. 201A is a diagram showing a configuration example of the
スイッチ入力ポート2は、各種スイッチやセンサの出力が入力されるポート群の一つであり、8ビットで構成される。図示する例では、ビット7では、レベル1で払出制御基板951からの受信確認信号(ACK)が検出される。ビット6では、レベル0で停電監視回路からの停電予告信号が検出される。ビット5では、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されると、信号レベルが1になる。ビット4では、設定キー971がONに操作されると、信号レベルが0になる。ビット3では、扉開放センサが扉枠3の開を検出すると、信号レベルが1になる。ビット2では、磁気検出スイッチ(磁気検出センサ)が磁気を検出するとレベルが0になる。ビット1、0は使用されていない。
A
図201(B)は、設定状態管理エリアの構成例を示す図である。 FIG. 201B is a diagram showing a configuration example of the setting state management area.
設定状態管理エリアは、図201(B)に示すように、パチンコ機1の動作モードが記録される1バイトの記憶領域であり、例えば下位の4ビットが使用され、上位の4ビットは定義されていない。具体的には、通常遊技状態では00H、設定確認モードでは01H、設定変更モードでは02H、主制御RAM1312に異常があれば08Hが記録される
。
The setting state management area, as shown in FIG. 201(B), is a 1-byte storage area in which the operation mode of the
設定状態管理エリアは、RAMクリアスイッチ954のみの操作によるRAMクリア処理では00Hに更新されず、現在の値が維持される。また、設定確認モードの終了時には01Hから00Hに更新され、設定変更モードの終了時には02Hから00Hに更新される。さらに、主制御RAM1312が異常である場合、次の電源投入時の設定変更操作によって設定変更モードになると08Hから02Hに更新され、設定変更モードの終了時に02Hから00Hに更新される。
The setting state management area is not updated to 00H by the RAM clearing process by operating only the RAM
図202(A)は、電源投入時動作コマンドの構成例を示す図である。電源投入時動作コマンドは、設定状態管理エリアの記録内容を通知するコマンドである。例えば、電源投入時動作コマンドは2バイトで構成され、上位バイトがA0Hで、下位バイトが設定状態管理エリアの記録内容を示す。下位バイトの値は設定状態管理エリアの値に1を加算した値を格納している。これは、通常遊技中のときに設定状態管理エリアの値は00Hとなるため、コマンドとして送信される値が00Hであると、出力が0となるハードウェア異常と区別できないので、いずれかのビットが1にセットされるようにしている。 FIG. 202A is a diagram showing a configuration example of a power-on operation command. The power-on operation command is a command for notifying the contents recorded in the setting state management area. For example, the power-on operation command consists of 2 bytes, the upper byte being A0H, and the lower byte indicating the content recorded in the setting state management area. The value of the lower byte stores the value obtained by adding 1 to the value of the setting state management area. This is because the value of the setting state management area is 00H during a normal game, so if the value sent as a command is 00H, it cannot be distinguished from a hardware error in which the output is 0. is set to 1.
なお、電源投入時動作コマンドは、電源投入時処理で少なくとも1度作られる。具体的には、ホットスタート、RAMクリア及びRAM異常のときには1度作られ、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードでは、電源投入時処理と設定変更/確認終了時との2度作られる。 Note that the power-on operation command is generated at least once in the power-on processing. Specifically, it is generated once at hot start, RAM clear, and RAM failure, and is generated twice in the setting change mode and setting confirmation mode, at power-on processing and at the end of setting change/confirmation.
周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時動作コマンドを受信すると、設定確認モード、設定変更モード、RAM異常の状態に応じて、前述した態様で報知を行う(図184参照)。 Upon receipt of the power-on operation command, the peripheral control board 1510 performs notification in the manner described above according to the setting confirmation mode, setting change mode, and RAM abnormality state (see FIG. 184).
周辺制御基板1510が、電源投入時動作コマンドでA001Hを受信することなく、通常遊技中の遊技コマンドを受信した場合、遊技状態が不整合となっている可能性があるため、受信した遊技コマンドを無効と判定し、当該遊技コマンドに対する遊技動作(演出など)を開始しない。但し、所定条件を満たした(例えば、通常遊技中の遊技コマンドが連続して所定回数送信された)場合、周辺制御基板1510が電源投入時動作コマンド(A001H)を取りこぼした可能性があるため、受信した遊技コマンドの無効化を解除し、遊技コマンドに対応する演出を行うとよい。 If the peripheral control board 1510 receives a game command during a normal game without receiving A001H as the power-on operation command, the game state may be inconsistent. It is determined to be invalid, and the game action (effect etc.) corresponding to the game command is not started. However, if a predetermined condition is met (for example, a game command during a normal game is continuously transmitted a predetermined number of times), there is a possibility that the peripheral control board 1510 has missed the power-on operation command (A001H). It is preferable to release the invalidation of the received game command and perform an effect corresponding to the game command.
なお、遊技コマンドが無効化されている状態で、受信した遊技コマンドのうち、所定条件を満たす演出を行い(例えば、図柄の動作、ランプ、可動体、音声等については受信したコマンドに対応する演出を行い)、表示装置の背景や所定のランプを用いて、遊技状態の不整合が発生している旨を報知してもよい。また、遊技状態の不整合が発生している旨を小さな音量で報知してもよい。これは、所定条件となるまで、何の演出も行わないと、遊技状態の不整合が発生していることを理解できない遊技者は、始動口に入賞しても特別図柄変動表示ゲームが開始しないようなパチンコ機1の故障だと思い、ホールで発生する可能性があるトラブルを防止するためである。なお、周辺制御基板1510が遊技コマンドを無効化していても、主制御基板1310は通常の遊技処理を実行しているので、機能表示ユニット1400における特別図柄や普通図柄などの機能表示は正常に表示される。
In addition, in a state where the game commands are invalidated, an effect that satisfies a predetermined condition among the received game commands is performed (for example, the effect corresponding to the received command is performed for symbol movements, lamps, movable bodies, sounds, etc.). ), and the background of the display device or a predetermined lamp may be used to notify the occurrence of an inconsistency in the game state. Also, the fact that the game state is inconsistent may be notified with a low volume. If no effect is performed until a predetermined condition is met, the player who cannot understand that the game state is inconsistent will not start the special symbol variation display game even if he/she wins the starting gate. This is to prevent troubles that may occur in the pachinko hall due to the
図202(B)は、電源投入時状態コマンドの構成例を示す図である。電源投入時状態コマンドは、設定状態管理エリアの記録内容に基づいて、通常遊技開始可能状態であるかを通知するコマンドである。例えば、電源投入時状態コマンドは2バイトで構成され、上位バイトが30Hで、下位バイトが01Hであれば、通常遊技開始可能状態であることを示す。電源投入時状態コマンドの下位バイトを用いて、パチンコ機の機種毎のシリーズコ
ードを通知してもよい。例えば、ビット6~4を使用すると8種類のシリーズを識別できる。なお、電源投入時状態コマンドは、図220(C)に示す別例でもよい。図220(C)に示す電源投入時状態コマンドを使用すると、電源投入時バッファに記録された情報(停電前の遊技状態)を周辺制御基板1510に通知できる。
FIG. 202B is a diagram showing a configuration example of a power-on status command. The power-on state command is a command for notifying whether or not a normal game can be started based on the contents recorded in the setting state management area. For example, when the power-on status command is composed of 2 bytes, and the upper byte is 30H and the lower byte is 01H, it indicates that the normal game can be started. The series code for each pachinko machine model may be notified using the lower byte of the power-on state command. For example, bits 6-4 can be used to identify eight different series. Note that the power-on state command may be another example shown in FIG. 220(C). By using the power-on state command shown in FIG. 220(C), the peripheral control board 1510 can be notified of the information recorded in the power-on buffer (game state before power failure).
図202(C)は、電源投入時復帰先コマンドの構成例を示す図である。電源投入時復帰先コマンドは、特別図柄に関する遊技状態を通知するコマンドであり、例えば、電源投入時復帰先コマンドは2バイトで構成され、上位バイトが31Hで、下位バイトが特別図柄に関する遊技状態を示す。電源投入時復帰先コマンドは、停電発生時の特別図柄の状態及び特別電動役物の動作状態を通知する。電源投入時復帰先コマンドは、電源投入時に1回送信される。 FIG. 202C is a diagram showing a configuration example of a power-on recovery destination command. The power-on return destination command is a command for notifying the game state related to special symbols. show. The power-on return destination command notifies the state of the special symbol and the operating state of the special electric accessory at the time of power failure. The power-on recovery destination command is sent once when the power is turned on.
図202(D)は、設定値コマンドの構成例を示す図である。設定値コマンドは、設定値を通知するコマンドであり、例えば、設定値コマンドは2バイトで構成され、上位バイトがA1Hで、下位バイトが設定値を示す。設定値コマンドは、設定変更モードでも設定確認モードでもない停電復帰時や設定変更モードの終了時や設定確認モードの終了時に送信される。また、特別図柄変動開始時や、遊技状態の変化時(大当り、確変、時短などの開始及び終了時)に送信する。これにより、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時に送信される設定値コマンドを取りこぼしても、その後の遊技において(例えば、特別図柄の変動開始)により、正しい設定値に変更されるため、誤った設定値に基づいて演出が行われないようになっている。設定値に基づく演出とは、表示器、ランプ、音声、可動体等の演出装置を用いて設定値を示唆する演出であり、通常時には発生し難い(又は発生しない)演出態様を所定の確率で発生させることによって設定値を示唆するものである。この設定値示唆演出は、以下に例示する演出の他の態様の演出も考えられ、ガセも含んでもよい。設定値示唆演出として、表示器の一例であるメイン液晶表示装置1600では、設定値に対応した予告等の演出を表示したり、図柄の変動態様を通常時と変える(例えば、左右中図柄の変動開始や確定のタイミングが通常時と違うタイミングになる(通常時は各図柄が同時に変動を開始し、高設定の場合には、左、中、右の順で変動を開始する等))、音声を用いると、始動口入賞時に設定値に対応した報知音が所定の確率で発生させたり、演出中の音声を通常時とは異なる音声を発生する(通常時が男性の声、高設定時には女性の声など)、などを行う。
FIG. 202D is a diagram showing a configuration example of a setting value command. The setting value command is a command for notifying a setting value. For example, the setting value command is composed of 2 bytes, where the upper byte indicates A1H and the lower byte indicates the setting value. The set value command is sent at the time of recovery from a power failure in neither the setting change mode nor the setting confirmation mode, at the end of the setting change mode, or at the end of the setting confirmation mode. In addition, it is transmitted at the time of the start of special symbol fluctuation, or at the time of change in the game state (at the time of start and end of big hit, probability variation, time reduction, etc.). As a result, even if the peripheral control board 1510 misses the setting value command transmitted when the power is turned on, the setting value is changed to the correct setting value in the subsequent game (for example, the start of fluctuation of the special symbol), so that the setting value is incorrect. Rendering is not performed based on the value. Effects based on set values are effects that suggest set values using effects devices such as display devices, lamps, sounds, and movable bodies. It suggests a set value by generating it. This set value suggesting effect may be effected in other aspects than the effect illustrated below, and may include a fake. As a set value suggesting effect, the main liquid
図203は、様々な状態において、主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510へ送信されるコマンドを示す図である。以下の説明において、nは特別図柄/特別電動役物に関する処理状態を示すカウンタ値、mは設定値に応じた値である。
FIG. 203 shows commands sent from the
図示するように、通常遊技状態が起動するホットスタートでは、電源投入時動作コマンド(A001H)→電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)→電源投入時復帰先コマンド(310nH)→設定値コマンド(A10mH)の順に送信される。 As shown in the figure, in the hot start where the normal game state is started, the operation command at power on (A001H) → state command at power on (3001H) → return destination command at power on (310nH) → set value command (A10mH) sent in order.
また、RAMクリアスイッチ954のみの操作による主制御RAM1312の初期化時には、電源投入時動作コマンド(A001H)→電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)→電源投入時復帰先コマンド(3101H)→設定値コマンド(A10mH)の順に送信される。
Further, when the
また、設定変更モードでは、まず、電源投入時動作コマンド(A003H)が送信された後、設定変更モードで設定値が変更されて、設定キー971を通常位置に戻す操作の後、電源投入時動作コマンド(A001H)→電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)→電源投入時復帰先コマンド(3101H)→設定値コマンド(A10mH)の順に送信される。
In the setting change mode, first, after the power-on operation command (A003H) is transmitted, the setting value is changed in the setting change mode, and after the setting
また、設定確認モードでは、まず、電源投入時動作コマンド(A002H)が送信された後、設定値を確認して、設定キー971を通常位置に戻す操作の後、電源投入時動作コマンド(A001H)→電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)→電源投入時復帰先コマンド(310nH)→設定値コマンド(A10mH)の順に送信される。
In the setting confirmation mode, first, after the power-on operation command (A002H) is transmitted, the setting value is confirmed, and after the setting
また、RAM異常時には、まず、電源投入時動作コマンド(A009H)が送信され、電源遮断後の電源復帰時に設定変更操作(設定キー971及びRAMクリアスイッチ954がオン)によって設定変更モードが起動し、電源投入時動作コマンド(A003H)が送信される。その後、設定キー971を通常位置に戻す操作の後、電源投入時動作コマンド(A001H)→電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)→電源投入時復帰先コマンド(3101H)→設定値コマンド(A10mH)の順に送信される。
In addition, when the RAM is abnormal, the operation command (A009H) at power-on is first transmitted, and the setting change mode is activated by the setting change operation (the setting
なお、RAM異常時には、まず、電源投入時動作コマンド(A009H)が送信され、電源遮断後の電源復帰時に設定変更操作がされていなければ、RAM異常状態が継続し、電源投入時動作コマンド(A009H)が送信される。その後、設定キー971を通常位置に戻す操作の後、電源投入時動作コマンド(A001H)→電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)→電源投入時復帰先コマンド(3101H)→設定値コマンド(A10mH)の順に送信される。 When the RAM is abnormal, the power-on operation command (A009H) is first transmitted. ) is sent. After that, after the operation of returning the setting key 971 to the normal position, the operation command at power-on (A001H)→state command at power-on (3001H)→return destination command at power-on (3101H)→setting value command (A10mH) in this order. sent.
以上に説明したように、通常の遊技状態で主制御基板1310が起動する場合には、複数のコマンドが電源の復帰を示すコマンド群(所定順序の複数のコマンドの組み合わせ)が所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信される。このため、A001H~A10mHまでの一連のコマンドの全ての受信が完了した後に通常遊技状態を開始可能であると判定し、当該一連のコマンドの一部のコマンドの受信ができない(取りこぼした)ときには、通常遊技状態を開始できないと判定して、通常遊技状態の開始不可を報知する。
As described above, when the
すなわち、前述した遊技コマンドが無効化されている状態の演出と同様に、受信した遊技コマンドのうち、所定条件を満たす演出を行い(例えば、図柄の動作、ランプ、可動体、音声等については受信したコマンドに対応する演出を行い)、表示装置の背景や所定のランプを用いて、遊技状態の不整合が発生している旨を報知してもよい。 That is, in the same way as the above-described effect when the game command is disabled, an effect that satisfies a predetermined condition among the received game commands is performed (for example, symbol movements, lamps, movable bodies, voices, etc. are received.) The effect corresponding to the given command may be performed), and the occurrence of inconsistency in the game state may be notified using the background of the display device or a predetermined lamp.
なお、周辺制御基板1510は、設定値コマンドを受信しなかった場合、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの開始時に送信される設定値コマンドによって、電源投入時に取りこぼした設定値コマンドを補って、通常遊技を開始してもよい。 In addition, when the peripheral control board 1510 does not receive the set value command, the set value command transmitted at the start of the special symbol variation display game compensates for the set value command that was missed when the power was turned on, and the normal game is started. You may
また、周辺制御基板1510は、設定値コマンドを受信しなかった場合、周辺制御基板1510の電源投入時に所定の初期値(例えば、設定1)を設定値として、設定値コマンドを受信すると、受信したコマンドに対応する設定値に更新してもよい。 Further, when the peripheral control board 1510 does not receive the setting value command, when the power of the peripheral control board 1510 is turned on, the setting value command is set to a predetermined initial value (for example, setting 1) as the setting value. It may be updated to the setting value corresponding to the command.
なお、電源投入時動作コマンド(A0001H)と電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)とは、共に通常遊技開始可能状態を通知するものであり、通常は続けて送信されることから、いずれかを主制御基板に送信すれば足りる。 Note that both the power-on operation command (A0001H) and the power-on state command (3001H) notify the normal game start-ready state, and are normally transmitted in succession. Sending to the board is sufficient.
図204は、設定状態管理エリアの電源遮断前の状態から電源復旧後に設定される値の状態遷移を示す図である。 FIG. 204 is a diagram showing state transition of values set after power restoration from the state before power shutdown in the setting state management area.
設定機能を有するパチンコ機の電源投入時の動作は、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されているか、また、設定キー971が操作されているかによって異なり、不正防止対策と利用者(ホールの従業員)の利便性を考慮した複数のパターンがある。
The operation of a pachinko machine having a setting function when the power is turned on differs depending on whether the RAM
<パターン1>
図204(A)に示す、直前の電源遮断時に通常遊技状態(VALID_PLAY=00H)であり、かつ、停電復帰時に主制御RAM1312が正常である場合の動作例を説明する。まず、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されており、かつ、設定キー971がONに操作されている場合、主制御RAM1312は設定値とベース値以外の全領域スタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化する。また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードで起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は02Hに更新される。また、ベース表示器1317は、設定変更に伴う設定値を表示する。
<
An operation example in which the normal game state (VALID_PLAY=00H) is in effect at the time of power interruption immediately before and the
電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されておらず(OFF)、かつ、設定キー971がONに操作されている場合、主制御RAM1312の記憶内容は初期化されない。また、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認モードで起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は01Hに更新される。また、ベース表示器1317は、設定確認のために現在の設定値を表示する。
If the RAM
電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されており、かつ、設定キー971が操作されていない(OFF)場合、主制御RAM1312は設定値とベース値以外の全領域スタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化する。また、主制御MPU1311は、通常遊技状態で起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は00Hに維持される。また、ベース表示器1317は、電源投入時の初期表示として性能表示に切り替えられたことを示す表示(例えば、5秒の全点滅)をした後にパチンコ機の性能を表すベース値を表示する。
If the RAM
電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されておらず(OFF)、かつ、設定キー971が操作されていない(OFF)場合、主制御RAM1312の記憶内容は停電前の状態が維持される。なお、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内の全ての記憶内容が維持されなくても、少なくとも、停電前の遊技状態に戻すための情報が記憶されている領域(遊技に関する情報が格納されている記憶領域(特別図柄、普通図柄に関する領域、賞球に関する領域、プログラムで生成される乱数(変動パターン乱数、初期値乱数など)))が維持されればよく、停電前の遊技状態に戻すために必要でない情報が記憶されている領域は電源復帰後に停電前と異なる状態となってもよい。また、主制御MPU1311は、通常遊技状態で起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は00Hが維持される。なお、元の値にかかわらず、同じ値(00H)を設定してもよい。また、ベース表示器1317は、電源投入時の初期表示として性能表示に切り替えられたことを示す表示(例えば、5秒の全点滅)をした後にパチンコ機の性能を表すベース値を表示する。
If the RAM
<パターン2-1>
図204(B)に示すように、直前の電源遮断時に設定変更モードであり、かつ、停電復帰時に主制御RAM1312が正常である場合の動作例1では、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作の有無や、設定キー971の操作の有無にかかわらず、主制御RAM1312は設定値とベース値以外のスタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化する。また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードで起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は02Hが維持される。なお、元の値にかかわらず、同じ値(02H)を設定してもよい。また、ベース表示器1317は、設定変更に伴う設定値を表示する。
<Pattern 2-1>
As shown in FIG. 204(B), in an operation example 1 in which the setting change mode is set at the time of power interruption immediately before and the
パターン2-1における主制御RAM1312の初期化は、停電発生時に既に実行された初期化処理で初期化された記憶領域とあわせてスタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化すればよい。例えば、主制御RAM1312の初期化処理中に電
源が遮断した場合、初期化処理が終わっていない残りの記憶領域を初期化すればよい。一方、停電時における初期化処理の進捗にかかわらず、電源復帰後に主制御RAM1312のスタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化してもよい。
Initialization of the
初期化処理中に停電が発生した場合、主制御RAM1312の初期化処理中であるかを記憶する領域(例えば、RAMクリア処理中フラグ)を設け、RAMクリア処理中フラグが設定されている間は初期化処理の対象となる記憶領域へのデータの書き込みを禁止するとよい。
If a power failure occurs during the initialization process, an area (for example, a RAM clearing flag) is provided to store whether the
また、設定変更モードや設定確認モードで停電を監視する処理を繰り返し実行してもよい。このため、メインループ(図22のステップS36からS40)の他、例えば、タイマ割り込みで停電予告信号を監視してもよい。 Further, the process of monitoring power failure may be repeatedly executed in the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode. Therefore, in addition to the main loop (steps S36 to S40 in FIG. 22), for example, a timer interrupt may be used to monitor the power failure warning signal.
停電監視処理及び電源断時処理は、設定変更モードと設定確認モードと通常遊技状態との何れにおいても共通の処理で実行しても、別個の処理で実行しても、設定変更モードと設定確認モードでは共通の処理で実行し、通常遊技状態では別の処理で実行してもよい。すなわち、パチンコ機の動作における三つ以上の状態(動作モード)のうち、少なくとも二つの状態で停電監視処理及び電源断時処理を共通にしてもよい。 Whether the power failure monitoring process and the power failure process are executed as common processing in any of the setting change mode, the setting confirmation mode, and the normal game state, or executed as separate processing, the setting change mode and the setting confirmation are performed. Common processing may be executed in the mode, and different processing may be executed in the normal game state. That is, out of three or more states (operation modes) in the operation of the pachinko machine, at least two states may share the power failure monitoring process and the power failure process.
以上に説明したように、設定変更モードにおいて電源が遮断し、停電復帰時に主制御RAM1312が正常である場合のパターン2-1では、設定キー971やRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作にかかわらず、常に設定変更モードで起動する。例えば、ホールで設定変更作業中に停電が発生すると、電源復帰時にも設定変更モードが起動するとよい。しかし、電源復帰時に設定変更モードを起動するための設定キー971やRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作がされていないことがある。このため、パターン2-1のように制御することによって、電源復帰時に意図しない(設定変更モードとは異なる)状態になることを防止できる。
As described above, in the pattern 2-1 when the power is interrupted in the setting change mode and the
例えば、電源復帰時に設定キー971のみが操作されている(RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていない)と、設定変更モードではなく設定確認モードで起動したり、RAMクリアスイッチ954のみが操作されている(設定キー971が操作されていない)と、主制御RAM1312を初期化して通常の遊技状態が起動したり、何れのスイッチも操作されていないと、通常の遊技状態が起動することになる。しかし、パターン2-1のように制御すると、設定キー971やRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作にかかわらず、常に設定変更モードで起動する。
For example, if only the setting
<パターン2-2>
直前の電源遮断時に設定変更モードであり、かつ、停電復帰時に主制御RAM1312が正常である場合には、パターン2-1とは異なり、図204(C)に示す別のパターンで動作してもよい。電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されており、かつ、設定キー971がONに操作されている場合、主制御RAM1312は設定値とベース値以外のスタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化する。また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードで起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は02Hが維持される。なお、元の値にかかわらず、同じ値(02H)を設定してもよい。また、ベース表示器1317は、設定変更に伴う設定値を表示する。
<Pattern 2-2>
If the setting change mode is set at the time of the last power interruption and the
電源投入時のRAMクリアスイッチ954及び設定キー971の操作が上記以外の場合、電源投入時に、少なくともRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971のいずれかが操作されていない(OFF)場合では、主制御RAM1312の記憶内容は変化しない。また、主制御MPU1311は、遊技停止状態で起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は主制
御RAM1312の異常を示す08Hに更新される。また、ベース表示器1317は、エラー(例えば、エラーコード)を表示する。遊技停止状態は、主制御MPU1311に無限ループを実行することによる遊技停止でも、通常遊技処理を実行しないことによる遊技停止でもよい。
If the operation of the RAM
すなわち、パターン2-1では、電源復旧後に設定キーとRAMクリアスイッチが何れの状態であったとしても無条件に設定変更モードに移行するものであるが、パターン2-2では、電源復帰時に設定キー971及びRAMクリアスイッチ954で設定変更モードを起動する操作がされているときには設定変更モードを起動し、設定キー971及びRAMクリアスイッチ954が他の状態では、遊技を実行できない状態(RAM異常)とする。すなわち、パターン2-2では、電源復帰時の設定キー971及びRAMクリアスイッチ954の少なくとも一つが操作されていたとしても、RAM異常状態として通常遊技を開始せず、設定変更モードを経由した後に通常遊技を開始する。このため、設定変更モードを起動する操作がされていないとき、RAM異常などの設定変更モードや設定確認モードとは別の状態で通常遊技を実行せず、遊技中止状態を報知することによって、ホールの従業員に設定変更モードを起動する操作を促してもよい。
That is, in pattern 2-1, regardless of the state of the setting key or the RAM clear switch after power is restored, the transition to the setting change mode is made unconditionally. When the key 971 and the RAM
設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)が記録されている場合、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域と遊技制御領域内スタック領域を初期化することなく、次に設定変更操作がされるまで遊技停止状態で待機する。遊技停止状態は、主制御MPU1311に無限ループを実行することによる遊技停止でも、通常遊技処理を実行しないことによる遊技停止でもよい。その後、一旦電源を遮断し、設定キーとRAMクリアスイッチとを設定変更モードに操作し、電源を投入することで、設定状態管理エリアの値は02Hに更新され、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域と遊技制御領域内スタック領域をクリアし、設定変更モードを開始する。
If the value (08H) indicating the RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, without initializing the game control area and the stack area in the game control area of the
<パターン3-1、3-2>
図204(D)に示す、直前の電源遮断時に設定確認モードであり、かつ、停電復帰時に主制御RAM1312が正常である場合の動作例を説明する。まず、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されており、かつ、設定キー971がONに操作されている場合、主制御RAM1312は設定値とベース値以外のスタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化する。また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードで起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は02Hに更新される。また、ベース表示器1317は、設定変更に伴う設定値を表示する。
<Pattern 3-1, 3-2>
204(D), an operation example will be described in which the setting confirmation mode is set at the time of power interruption immediately before and the
電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されておらず(OFF)、かつ、設定キー971がONに操作されている場合、主制御RAM1312の記憶内容は変化しない。また、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認モードで起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は01Hに維持される。なお、元の値にかかわらず、同じ値(01H)を設定してもよい。また、ベース表示器1317は、設定確認のために現在の設定値を表示する。
When the RAM
電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されており、かつ、設定キー971が操作されていない(OFF)場合、主制御RAM1312は設定値とベース値以外のスタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化する。また、主制御MPU1311は、通常遊技状態で起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は00Hに更新される。また、ベース表示器1317は、電源投入時の初期表示として性能表示に切り替えられたことを示す表示(例えば、5秒の全点滅)をした後にパチンコ機の性能を表すベース値を表示する。
When the RAM
電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されておらず(OFF)、かつ、設定
キー971が操作されていない(OFF)場合、主制御RAM1312の記憶内容は変化しない。また、主制御MPU1311は、通常遊技状態で起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は00Hに更新される。また、ベース表示器1317は、電源投入時の初期表示として性能表示に切り替えられたことを示す表示(例えば、5秒の全点滅)をした後にパチンコ機の性能を表すベース値を表示する。なお、この場合、図204(E)に示すパターン3-2のように、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認モードで起動してもよく、設定状態管理エリアの値は01Hに維持され(元の値にかかわらず同じ値(01H)を設定してもよい)、ベース表示器1317は、設定確認のために現在の設定値を表示してもよい。
If the RAM
<パターン4>
図204(F)に示すように、停電復帰時に主制御RAM1312に異常がある場合の動作例を説明する。まず、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されており、かつ、設定キー971がONに操作されている場合、主制御RAM1312は設定値とベース値以外の全領域スタック領域を含む遊技制御領域として使用される領域を初期化する。また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードで起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は02Hとなる。また、ベース表示器1317は、設定変更のための表示をする。
<
As shown in FIG. 204(F), an operation example when there is an abnormality in the
電源投入時のRAMクリアスイッチ954及び設定キー971の操作が上記以外の場合、すなわち、電源投入時に、少なくともRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971のいずれかが操作されていない(OFF)場合では、主制御RAM1312の記憶内容は変化しない。また、主制御MPU1311は、遊技停止状態で起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は08Hが維持される。なお、元の値にかかわらず、同じ値(08H)を設定してもよい。また、ベース表示器1317は、エラー(例えば、エラーコード)を表示する。
When the operation of the RAM
なお、直前の電源遮断時に主制御RAM1312に異常がある場合には、電源遮断前に主制御RAM1312が初期化されていれば、停電復帰時に主制御RAM1312を再度初期化せずに、(1)主制御MPU1311に内蔵されているデバイスの初期設定を行う。(2)ハードウェア乱数を再起動する。(3)割り込み許可を設定するの少なくとも一つを実行後にメインループを実行するとよい。
If there is an abnormality in the
また、直前の電源遮断時に主制御RAM1312に異常があっても、電源投入時には、停電前の状態がRAM異常かの判定(図179のステップS211)の前に、RAMクリアスイッチ954及び設定キー971の操作の有無を判定する。そして、電源投入時に設定変更操作(RAMクリアスイッチ954及び設定キー971がオン)が検出されると設定変更モードを起動するが、電源投入時に設定変更操作がされていない場合でも(設定確認モードを起動する操作がされている、RAMクリアスイッチ954のみが操作されている、何れも操作されていないの何れの場合でも)、RAM異常の状態を維持する。すなわち、通常は、設定変更モードの起動時と設定確認モードの起動時とは、タイマ割り込み処理内で設定変更モードの処理や設定確認モードの処理を実行するが、RAM異常状態から電源が再投入された場合には、設定変更モードと設定確認モードでは異なる処理を実行する。換言すると、RAM異常状態から電源が再投入されて復帰する場合、設定変更モードで起動するときは、通常と同様にタイマ割り込み処理内で設定変更モードの処理を実行するが、設定確認モードで起動するときは、タイマ割り込み処理内では通常と異なる処理を実行する。
Also, even if there is an abnormality in the
このように、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(08H)が記録されると、電源を再投入しても遊技が開始できない状態となる。ただし、主制御RAM1312は既に初期化されているので、再度主制御RAM1312を初期化しなくてもよい。
Thus, when the value (08H) indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, the game cannot be started even if the power is turned on again. However, since the
次に、タイムチャートを用いてパチンコ機1の動作及びそのバリエーションを説明する
。以下に説明するタイムチャートの概要は以下のとおりである。
・通常の設定変更に関するタイムチャート(図205)
・通常の設定確認に関するタイムチャート(図206)
・停電時に設定変更モードで、電源復帰後に設定キー971がOFFかつRAMクリアスイッチ954がOFFの状態で設定変更モードに移行する場合のタイムチャート(図207)
・停電時に設定変更モードで、電源復帰後に設定キー971がONかつRAMクリアスイッチ954がOFFの状態で設定変更モードに移行する場合のタイムチャート(図208)
・停電時に設定確認モードで、電源復帰後に設定キー971がOFFかつRAMクリアスイッチ954がOFFの状態で設定確認モードに移行する場合のタイムチャート(図209)
Next, the operation of the
・Time chart for normal setting changes (Fig. 205)
・Time chart for normal setting confirmation (Fig. 206)
・Time chart when transitioning to the setting change mode at power failure with the setting key 971 turned off and the RAM
・Time chart when transitioning to the setting change mode at power failure with the setting key 971 ON and the RAM
・Time chart when transitioning to the setting confirmation mode at the time of power failure with the setting key 971 turned off and the RAM
図205は、設定変更モードの開始から終了のタイムチャートである。 FIG. 205 is a time chart from the start to the end of the setting change mode.
図205に示すタイムチャートでは、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されており、かつ、設定キー971がONに操作されているので、主制御MPU1311は設定変更モードで起動する。
In the time chart shown in FIG. 205, since the RAM
まず、主制御基板1310に電源が供給され、5V電源が立ち上がると(T1)、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が出力され、主制御MPU1311が起動する(T2)。
First, when power is supplied to the
主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号によってプログラムコードの先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311はセキュリティチェック実行し、タイミングT3で主制御プログラムを開始する。その後、タイミングT4で設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタに記憶し、タイミングT5まで周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ。
The
周辺制御基板1510は、通電の開始によって起動すると、客待ち演出を開始する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、主制御基板1310からのコマンドを受信した後に客待ち演出を開始してもよい。
When the peripheral control board 1510 is activated by the start of energization, the customer waiting effect is started. Note that the peripheral control board 1510 may start the customer waiting effect after receiving the command from the
主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT5において、設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタから読み出し、設定状態管理エリアに02Hを記録して設定変更モードに移行する。また、主制御MPU1311は、機能表示ユニット1400の全LEDを点灯させる。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、セキュリティ信号の出力を開始する。なお、機能表示ユニットの表示態様については前述の図184に記載した通りである。
The
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードに移行することを示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A003H)を作成し、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
Also, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時コマンドに従って、前述の図184に示した設定変更モードにおける演出(報知)を実行する。 Peripheral control board 1510 executes the effect (notification) in the setting change mode shown in FIG. 184 described above according to the power-on command received.
設定変更モード中において、RAMクリアスイッチ954(設定変更スイッチ972兼用)が操作されると、主制御MPU1311はRAMクリアスイッチ954のONを検出し、設定値をNからN+1に更新し、ベース表示器1317は更新後の設定値N+1を表
示する(T6)。さらに、RAMクリアスイッチ954(設定変更スイッチ972兼用)の2回目の操作によって、主制御MPU1311はRAMクリアスイッチ954のONを検出し、設定値をN+1からN+2に更新し、ベース表示器1317は更新後の設定値N+2を表示する(T7)。すなわち、設定変更モードでは、RAMクリアスイッチ954(設定変更スイッチ972兼用)が操作される毎に設定値が1~6の範囲で変更され、設定値が6を超えた場合には1に更新される。
During the setting change mode, when the RAM clear switch 954 (also used as the setting change switch 972) is operated, the
ホールの従業員は、設定値の変更が終わると設定キー971をOFF位置に操作する。主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971のOFFエッジを検出すると、設定変更モードを終了し、設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録し、電源投入時動作コマンド(A0001H)を作成して、通常遊技状態に移行する(T8)。作成された電源投入時動作コマンド(A0001H)は、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信される。設定状態管理エリアに00Hが記録されることによって、タイマ割込み処理において通常遊技中の処理を実行可能となる。また、主制御MPU1311は、機能表示ユニット1400の全点灯を終了し、通常遊技状態における表示を開始する。さらに、ベース表示器1317は、所定時間(例えば5秒)全LEDを点滅表示した後、通常遊技状態におけるベース値を表示する。このように、通常遊技状態の開始時にベース表示器1317を所定の態様で表示することによって、設定変更モードの終了が明確に分かり、設定変更モード終了時の操作ミスを低減できる。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)と電源投入時復帰先コマンド(3101H)と設定値コマンド(A10mH)を周辺制御基板1510に送信する。設定変更モードでは主制御RAM1312が初期化されるため、電源投入時復帰先コマンドの下位バイトは01Hになる。設定値コマンド(A10mH)のmは、図202(D)に示すように設定値に応じた1から6の数値である。なお、電源投入時動作コマンド(A0001H)と電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)とは共に通常遊技開始可能状態を通知するものであり、通常は続けて送信されることから、いずれかを主制御基板に送信すれば足りる。
The hall employee operates the setting key 971 to the OFF position after finishing changing the set values. When the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知り、通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を実行する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知ってから所定の遅延時間が経過した後に、設定変更中の報知演出を中止し通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を開始するように演出を切り替えてもよい。なお、所定の遅延時間中は、一部の演出装置によって設定変更中の報知演出を行うとよい、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600や音は通常遊技状態の演出に戻り、装飾ランプは設定変更中の報知演出を継続する。また、装飾ランプによる報知演出の継続は、一部の装飾ランプ(例えば、枠側)は報知演出を継続し、他の装飾ランプ(例えば、パネル側)はは通常遊技状態の演出に戻ってもよい。 The peripheral control board 1510 learns from the received power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and executes an effect in the normal game state (for example, a customer waiting effect). It should be noted that the peripheral control board 1510 stops the notification effect during the setting change after a predetermined delay time has passed since it is known by the power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and the effect in the normal game state ( For example, the production may be switched so as to start a customer waiting production. It should be noted that during the predetermined delay time, it is preferable to perform a notification effect that the setting is being changed by some effect devices. continue the notification production. In addition, the continuation of the notification effect by the decorative lamps is that some of the decorative lamps (eg, the frame side) continue the notification effect, and the other decorative lamps (eg, the panel side) return to the normal game state effect. good.
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードの終了から所定時間(例えば、50ミリ秒)遅延した後、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止する(T9)。これは、設定変更モードが極めて短時間で終了して、セキュリティ信号が全く又は短時間しか出力されないと、ホールコンピュータで設定変更モードへの移行を把握できないため、セキュリティ信号の最低限の出力時間を確保するためである。
Also, the
図206は、設定確認モードの開始から終了のタイムチャートである。 FIG. 206 is a time chart from the start to the end of the setting confirmation mode.
図206に示すタイムチャートでは、直前の電源遮断時に通常遊技状態又は設定確認モードであり、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されておらず、かつ、設定キー971がONに操作されているので、主制御MPU1311は設定確認モードで起動する。
In the time chart shown in FIG. 206, when the power was cut off just before, the normal game state or setting confirmation mode was in effect, and when the power was turned on, the RAM
まず、主制御基板1310に電源が供給され、5V電源が立ち上がると(T1)、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が出力され、主制御MPU1311が起動する(T2)。
First, when power is supplied to the
主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号によってプログラムコードの先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311はセキュリティチェック実行し、タイミングT3で主制御プログラムを開始する。その後、タイミングT4で設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタに記憶し、タイミングT5まで周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ。
The
周辺制御基板1510は、通電の開始によって起動すると、客待ち演出を開始する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、主制御基板1310からのコマンドを受信した後に客待ち演出を開始してもよい。
When the peripheral control board 1510 is activated by the start of energization, the customer waiting effect is started. Note that the peripheral control board 1510 may start the customer waiting effect after receiving the command from the
主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT5において、設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタから読み出し、設定状態管理エリアに01Hを記録して設定確認モードに移行する。また、主制御MPU1311は、機能表示ユニット1400の全LEDを点灯させる。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、セキュリティ信号の出力を開始する。
The
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認モードに移行することを示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A002H)を作成し、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
In addition, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時コマンドに従って、設定確認モードにおける演出を実行する。 Peripheral control board 1510 executes an effect in the setting confirmation mode according to the received power-on command.
ホールの従業員は、設定値の確認が終わると設定キー971をOFF位置に操作する。主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971のOFFエッジを検出すると、設定変更モードを終了し、設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録し、通常遊技状態に移行する(T6)。設定状態管理エリアの値が00Hとなることによって、タイマ割込み処理において通常遊技中の処理を実行可能となる。また、ベース表示器1317は、所定時間(例えば5秒)全LEDを点滅表示した後、通常遊技状態におけるベース値を表示する。
After confirming the setting values, the hall employee operates the setting key 971 to the OFF position. When the
さらに、主制御MPU1311は、電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)と電源投入時復帰先コマンド(310nH)と設定値コマンド(A10mH)を周辺制御基板1510に送信する。設定値コマンド(A10mH)のmは、図202(D)に示すように設定値に応じた1から6の数値である。設定確認モードでは、原則として主制御RAM1312は初期化されないため、電源投入時復帰先コマンドの下位バイトとしては、停電前の状態が送信される。
Further, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知り、通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を実行する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知ってから所定の遅延時間が経過した後に、設定変更中の報知演出を中止し通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を開始するように演出を切り替えてもよい。なお、所定の遅延時間中は、一部の演出装置によって設定変更中の報知演出を行うとよい、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600や音は通常遊技状態の演出に戻り、装飾ランプは設定変更中の報知演出を継続する。また、装飾ランプによる報知演出の継続は、一部の装飾ラン
プ(例えば、枠側)は報知演出を継続し、他の装飾ランプ(例えば、パネル側)はは通常遊技状態の演出に戻ってもよい。
The peripheral control board 1510 learns from the received power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and executes an effect in the normal game state (for example, a customer waiting effect). It should be noted that the peripheral control board 1510 stops the notification effect during the setting change after a predetermined delay time has passed since it is known by the power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and the effect in the normal game state ( For example, the production may be switched so as to start a customer waiting production. It should be noted that during the predetermined delay time, it is preferable to perform a notification effect that the setting is being changed by some effect devices. continue the notification production. In addition, the continuation of the notification effect by the decorative lamps is that some of the decorative lamps (eg, the frame side) continue the notification effect, and the other decorative lamps (eg, the panel side) return to the normal game state effect. good.
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認モードの終了から所定時間(例えば、50ミリ秒)遅延した後、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止する(T7)。
In addition, the
図207は、設定変更モードの開始から終了の別なタイムチャートである。 FIG. 207 is another time chart from the start to the end of the setting change mode.
図207に示すタイムチャートでは、直前の電源遮断時に設定変更モードであるので、主制御MPU1311は設定変更モードで起動する。なお、図204(B)に示すように、直前の電源遮断時に設定変更モードであれば、電源投入時のRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作によらず、主制御MPU1311は設定変更モードで起動する場合を示している。
In the time chart shown in FIG. 207, the
まず、主制御基板1310に電源が供給され、5V電源が立ち上がると(T1)、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が出力され、主制御MPU1311が起動する(T2)。
First, when power is supplied to the
主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号によってプログラムコードの先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311はセキュリティチェック実行し、タイミングT3で主制御プログラムを開始する。その後、タイミングT4で設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタに記憶し、タイミングT5まで周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ。
The
周辺制御基板1510は、通電の開始によって起動すると、客待ち演出を開始する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、主制御基板1310からのコマンドを受信した後に客待ち演出を開始してもよい。
When the peripheral control board 1510 is activated by the start of energization, the customer waiting effect is started. Note that the peripheral control board 1510 may start the customer waiting effect after receiving the command from the
主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT5において、設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタから読み出し、設定状態管理エリアに02Hを記録して設定変更モードに移行する。また、主制御MPU1311は、機能表示ユニット1400の全LEDを点灯させる。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、セキュリティ信号の出力を開始する。
The
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードに移行することを示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A003H)を作成し、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
Also, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時コマンドに従って、設定変更モードにおける演出を実行する。周辺制御基板1510は、電源の遮断によって動作状態がリセットされ初期状態に戻るので、電源復帰時に主制御基板1310送信した電源投入時動作コマンドを受信して、設定変更状態を継続する。
Peripheral control board 1510 executes effects in the setting change mode according to the received power-on command. Since the peripheral control board 1510 is reset to the initial state by power interruption, it receives the power-on operation command transmitted by the
設定変更モード中において、RAMクリアスイッチ954(設定変更スイッチ972兼用)が操作されると、主制御MPU1311はRAMクリアスイッチ954のONを検出し、設定値をNからN+1に更新し、ベース表示器1317は更新後の設定値N+1を表示する(T6)。
During the setting change mode, when the RAM clear switch 954 (also used as the setting change switch 972) is operated, the
その後、主制御基板への電源供給が停止すると、主制御MPU1311は停電を検出し電源断時処理を実行する(T7)。そして、リセット回路1335からリセット信号の出
力が停止し、ベース表示器1317による設定値の表示が消え、セキュリティ信号の出力が停止する(T8)。なお、電源断時処理において、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止し、ベース表示器1317を消灯してもよい。例えば、電源断時処理のプログラムによってセキュリティ信号の出力ポートやベース表示器1317への出力ポートをOFFすることによって、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止し、ベース表示器1317を消灯できる。
After that, when the power supply to the main control board is stopped, the
電源断時処理で出力ポートをOFFすることによって、電源断時処理中の消費電力低減し、電源断時処理の完了前に電源(5V)が低下することによるリセットを防止できる。例えば、電源断時処理におけるチェックサムの算出前に、出力ポートをOFFすると効果的である。なお、大入賞口2005、2006や第二始動口2004等の開閉を制御するソレノイドへの信号の出力ポートもOFFしてソレノイドの駆動信号を停止するとよい。
By turning off the output port in the power-off processing, the power consumption during the power-off processing can be reduced, and a reset due to the power supply (5V) dropping before the power-off processing is completed can be prevented. For example, it is effective to turn off the output port before calculating the checksum in the power-off process. In addition, it is preferable to turn OFF the output port of the signal to the solenoid for controlling the opening and closing of the
その後、主制御基板1310に電源が供給され、5V電源が立ち上がると(T9)、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が出力され、主制御MPU1311が起動する(T10)。
Thereafter, power is supplied to the
主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号によってプログラムコードの先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311はセキュリティチェック実行し、タイミングT11で主制御プログラムを開始し、その後、タイミングT12で設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタに記憶し、タイミングT13まで周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ。
The
主制御MPU1311は、設定状態管理エリアの値を参照する。図207に示す例では、設定状態管理エリアに02Hが記録されているので、設定キー971やRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作にかかわらず、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT13において、設定変更モードに移行する。設定変更モードに移行する際、通常の設定変更モードへの移行と同様に、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域と遊技制御領域内のスタック領域を再度初期化する。なお、主制御RAM1312の初期化が完了してから停電を監視し、その後停電処理を実行するため、RAMクリア処理が電源断時処理により中断されることはないため、停電時に設定変更モードである場合には、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域は既に初期化されているので、停電復帰時にRAMクリア処理を実行して遊技制御領域を初期化しないようにしてもよい。再度初期化した後に、主制御MPU1311は、機能表示ユニット1400の全LEDを点灯させ、セキュリティ信号の出力を開始する。
The
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードに移行することを示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A003H)を作成し、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
Also, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時コマンドに従って、設定変更モードにおける演出を実行する。周辺制御基板1510は、電源の遮断によって動作状態がリセットされ初期状態に戻るので、電源復帰時に主制御基板1310から送信される電源投入時動作コマンドを受信して、設定変更状態を継続する。
Peripheral control board 1510 executes effects in the setting change mode according to the received power-on command. Since the operation state of the peripheral control board 1510 is reset and returns to the initial state when the power is turned off, the peripheral control board 1510 receives the power-on operation command transmitted from the
設定変更モード中において、RAMクリアスイッチ954(設定変更スイッチ972兼用)が操作されると、主制御MPU1311はRAMクリアスイッチ954のONを検出し、設定値を更新し、更新後の設定値をベース表示器1317に表示する。
During the setting change mode, when the RAM clear switch 954 (also used as the setting change switch 972) is operated, the
ホールの従業員は、設定値の変更が終わると設定キー971をOFF位置に操作する。主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971のOFFエッジを検出すると、設定変更モード
を終了し、設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録し、通常遊技状態に移行する(T14)。設定状態管理エリアに00Hが記録されることによって、タイマ割込み処理において処理が通常遊技中の処理を実行可能となる。また、ベース表示器1317は、所定時間(例えば5秒)全LEDを点滅表示した後、通常遊技状態におけるベース値を表示する。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)と電源投入時復帰先コマンド(3101H)と設定値コマンド(A10mH)を周辺制御基板1510に送信する。設定値コマンド(A10mH)のmは、図202(D)に示すように設定値に応じた1から6の数値である。
The hall employee operates the setting key 971 to the OFF position after finishing changing the set value. When the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知り、通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を実行する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知ってから所定の遅延時間が経過した後に、設定変更中の報知演出を中止し通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を開始するように演出を切り替えてもよい。なお、所定の遅延時間中は、一部の演出装置によって設定変更中の報知演出を行うとよい、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600や音は通常遊技状態の演出に戻り、装飾ランプは設定変更中の報知演出を継続する。また、装飾ランプによる報知演出の継続は、一部の装飾ランプ(例えば、枠側)は報知演出を継続し、他の装飾ランプ(例えば、パネル側)はは通常遊技状態の演出に戻ってもよい。 The peripheral control board 1510 learns from the received power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and executes an effect in the normal game state (for example, a customer waiting effect). It should be noted that the peripheral control board 1510 stops the notification effect during the setting change after a predetermined delay time has passed since it is known by the power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and the effect in the normal game state ( For example, the production may be switched so as to start a customer waiting production. It should be noted that during the predetermined delay time, it is preferable to perform a notification effect that the setting is being changed by some effect devices. continue the notification production. In addition, the continuation of the notification effect by the decorative lamps is that some of the decorative lamps (eg, the frame side) continue the notification effect, and the other decorative lamps (eg, the panel side) return to the normal game state effect. good.
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードの終了から所定時間(例えば、50ミリ秒)遅延した後、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止する(T15)。これは、設定変更モードが極めて短時間で終了して、セキュリティ信号が全く又は短時間しか出力されないことが生じると、設定変更モードへの移行をホールコンピュータで把握できないため、セキュリティ信号の最低限の出力時間を確保するためである。
Also, the
図208は、設定変更モードの開始から終了の別なタイムチャートである。 FIG. 208 is another time chart from the start to the end of the setting change mode.
図208に示すタイムチャートでは、直前の電源遮断時に設定変更モードである場合でも、主制御MPU1311は、電源投入時のRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作によって異なる動作モードで起動する。
In the time chart shown in FIG. 208, even if the
まず、主制御基板1310に電源が供給され、5V電源が立ち上がると(T1)、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が出力され、主制御MPU1311が起動する(T2)。
First, when power is supplied to the
主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号によってプログラムコードの先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311はセキュリティチェック実行し、タイミングT3で主制御プログラムを開始する。その後、タイミングT4で設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタに記憶し、タイミングT5まで周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ。
The
周辺制御基板1510は、通電の開始によって起動すると、客待ち演出を開始する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、主制御基板1310からのコマンドを受信した後に客待ち演出を開始してもよい。
When the peripheral control board 1510 is activated by the start of energization, the customer waiting effect is started. Note that the peripheral control board 1510 may start the customer waiting effect after receiving the command from the
主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT5において、設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタから読み出し、設定状態管理エリアに02Hを記録して設定変更モードに移行する。また、主制御MPU1311は、セキュリティ信号の出力を開始する。
The
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードに移行することを示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A003H)を作成し、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
Also, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時コマンドに従って、設定変更モードにおける演出を実行する。周辺制御基板1510は、電源の遮断によって動作状態がリセットされ初期状態に戻るので、電源復帰時に主制御基板1310送信した電源投入時動作コマンドを受信して、設定変更状態を継続する。
Peripheral control board 1510 executes effects in the setting change mode according to the received power-on command. Since the peripheral control board 1510 is reset to the initial state by power interruption, it receives the power-on operation command transmitted by the
設定変更モード中において、RAMクリアスイッチ954(設定変更スイッチ972兼用)が操作されると、主制御MPU1311はRAMクリアスイッチ954のONを検出し、設定値をNからN+1に更新し、ベース表示器1317は更新後の設定値N+1を表示する(T6)。
During the setting change mode, when the RAM clear switch 954 (also used as the setting change switch 972) is operated, the
その後、主制御基板への電源供給が停止すると、主制御MPU1311は停電を検出し電源断時処理を実行する(T7)。そして、リセット回路1335からリセット信号の出力が停止し、ベース表示器1317による設定値の表示が消え、セキュリティ信号の出力が停止する(T8)。なお、電源断時処理において、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止し、ベース表示器1317を消灯してもよい。例えば、電源断時処理のプログラムによってセキュリティ信号の出力ポートやベース表示器1317への出力ポートをOFFすることによって、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止し、ベース表示器1317を消灯できる。
After that, when the power supply to the main control board is stopped, the
電源断時処理で出力ポートをOFFすることによって、電源断時処理中の消費電力低減し、電源断時処理の完了前に電源(5V)が低下することによるリセットを防止できる。例えば、電源断時処理におけるチェックサムの算出前に、出力ポートをOFFすると効果的である。なお、大入賞口2005、2006や第二始動口2004等の開閉を制御するソレノイドへの信号の出力ポートもOFFしてソレノイドの駆動信号を停止するとよい。
By turning off the output port in the power-off processing, the power consumption during the power-off processing can be reduced, and a reset due to the power supply (5V) dropping before the power-off processing is completed can be prevented. For example, it is effective to turn off the output port before calculating the checksum in the power-off process. In addition, it is preferable to turn OFF the output port of the signal to the solenoid for controlling the opening and closing of the
その後、主制御基板1310に電源が供給され、5V電源が立ち上がると(T9)、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が出力され、主制御MPU1311が起動する(T10)。
Thereafter, power is supplied to the
主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号によってプログラムコードの先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311はセキュリティチェック実行し、タイミングT11で主制御プログラムを開始し、その後、タイミングT12で設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタに記憶し、タイミングT13まで周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ。
The
主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT13において、設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタから読み出し、設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルとによって動作モードを変える。図208に示す例では、電源再投入時に設定確認モードとなるようにRAMクリアスイッチ954がOFFで設定キー971がONに操作されているが、設定状態管理エリアに記録された停電前の状態が設定変更を示す値(02H)となっているために、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT13において、主制御MPU1311は設定変更モードで再起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は02Hが維持される。なお、元の値にかかわらず、同じ値(02H)を設定してもよい。設定変更モードに移行する際、通常の設定変更モードへの移行と同様に、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域と遊技制御領域内のスタック領域を再度初期化する。なお、主制御
RAM1312の初期化が完了してから停電を監視し、その後停電処理を実行するため、RAMクリア処理が電源断時処理により中断されることはないため、停電時に設定変更モードである場合には、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域は既に初期化されているので、停電復帰時にRAMクリア処理を実行して遊技制御領域を初期化しないようにしてもよい。例えば、前述した図186では、停電前の状態が設定変更中であればステップS2015でYESとなり、RESET_P_5A(図187のステップS2030)に分岐してRAM異常時初期化処理(ステップS2034)を実行するが、RESET_P_7(図187のS203
6)に分岐すれば、RAM異常時初期化処理ステップS2034を実行することなく、電源遮断前の状態を継続することになる。再度初期化した後に、主制御MPU1311は、機能表示ユニット1400の全LEDを点灯させ、セキュリティ信号の出力を開始する。つまり、図208に示すタイムチャートでは、設定キー971がONに操作されていなくても設定変更モードが起動可能となっている。換言すると、設定変更モードについては、電源投入時に設定キー971及びRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていることによって設定変更モードが起動し、さらに、電源投入時に設定キー971やRAMクリアスイッチ954がONでなくても設定変更モードの起動が可能となっている。
The
If the process branches to 6), the state before the power shutdown is continued without executing the RAM abnormality initialization processing step S2034. After re-initialization, the
なお、タイミングT12の箇所に破線で示すが、電源再投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がOFFで設定キー971がOFFに操作されている場合は、図207に示すタイムチャートと異なり、設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録して、設定変更モードに戻すことなく通常遊技が実行できない状態(例えばRAM異常)で再起動してもよい。つまり、図208に示す動作パターンでは、停電時に設定変更モードであっても、電源復帰時に設定変更操作がされていなければ、RAM異常の状態で再起動する。つまり、設定変更モード中に電源が遮断されると、いずれかの時点で設定変更モードを正常に終了しないと通常遊技を開始できない。
As indicated by a broken line at timing T12, when the RAM
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードに移行することを示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A003H)を作成し、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
Also, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時コマンドに従って、設定変更モードにおける演出を実行する。周辺制御基板1510は、電源の遮断によって動作状態がリセットされ初期状態に戻るので、電源復帰時に主制御基板1310送信した電源投入時動作コマンドを受信して、設定変更状態を継続する。
Peripheral control board 1510 executes effects in the setting change mode according to the received power-on command. Since the peripheral control board 1510 is reset to the initial state by power interruption, it receives the power-on operation command transmitted by the
設定変更モード中において、RAMクリアスイッチ954(設定変更スイッチ972兼用)が操作されると、主制御MPU1311はRAMクリアスイッチ954のONを検出し、設定値を更新し、更新後の設定値をベース表示器1317に表示する(T14)。
During the setting change mode, when the RAM clear switch 954 (also used as the setting change switch 972) is operated, the
ホールの従業員は、設定値の変更が終わると設定キー971をOFF位置に操作する。主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971のOFFエッジを検出すると、設定変更モードを終了し、設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録し、通常遊技状態に移行する(T15)。設定状態管理エリアに00Hが記録されることによって、タイマ割込み処理において処理が通常遊技中の処理を実行可能となる。また、ベース表示器1317は、所定時間(例えば5秒)全LEDを点滅表示した後、通常遊技状態におけるベース値を表示する。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)と電源投入時復帰先コマンド(3101H)と設定値コマンド(A10mH)を周辺制御基板1510に送信する。設定変更モードでは主制御RAM1312が初期化されるため、電源投入時復帰先コマンドの下位バイトは01Hになる。設定値コマンド(A10mH)のmは、図202(D)に示すように設定値に応じた1から6の数値である。なお、電源投入時動作コマンド(A0001H)と電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)とは、共に通常遊技開始可
能状態を通知するものであり、通常は続けて送信されることから、いずれかを主制御基板に送信すれば足りる。
The hall employee operates the setting key 971 to the OFF position after finishing changing the set value. When the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知り、通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を実行する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知ってから所定の遅延時間が経過した後に、設定変更中の報知演出を中止し通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を開始するように演出を切り替えてもよい。なお、所定の遅延時間中は、一部の演出装置によって設定変更中の報知演出を行うとよい、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600や音は通常遊技状態の演出に戻り、装飾ランプは設定変更中の報知演出を継続する。また、装飾ランプによる報知演出の継続は、一部の装飾ランプ(例えば、枠側)は報知演出を継続し、他の装飾ランプ(例えば、パネル側)はは通常遊技状態の演出に戻ってもよい。 The peripheral control board 1510 learns from the received power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and executes an effect in the normal game state (for example, a customer waiting effect). It should be noted that the peripheral control board 1510 stops the notification effect during the setting change after a predetermined delay time has passed since it is known by the power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and the effect in the normal game state ( For example, the production may be switched so as to start a customer waiting production. It should be noted that during the predetermined delay time, it is preferable to perform a notification effect that the setting is being changed by some effect devices. continue the notification production. In addition, the continuation of the notification effect by the decorative lamps is that some of the decorative lamps (eg, the frame side) continue the notification effect, and the other decorative lamps (eg, the panel side) return to the normal game state effect. good.
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更モードの終了から所定時間(例えば、50ミリ秒)遅延した後、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止する(T16)。これは、設定変更モードが極めて短時間で終了して、セキュリティ信号が全く又は短時間しか出力されないことが生じると、設定変更モードへの移行をホールコンピュータで把握できないため、セキュリティ信号の最低限の出力時間を確保するためである。
Further, the
図209は、設定確認モードの開始から終了の別なタイムチャートである。 FIG. 209 is another time chart from the start to the end of the setting confirmation mode.
図209に示すタイムチャートでは、直前の電源遮断時に設定確認モードであれば、電源投入時のRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作によらず、主制御MPU1311は設定確認モードで起動する。
In the time chart shown in FIG. 209, if the setting confirmation mode is set at the time of the last power-off, the
まず、主制御基板1310に電源が供給され、5V電源が立ち上がると(T1)、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が出力され、主制御MPU1311が起動する(T2)。
First, when power is supplied to the
主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号によってプログラムコードの先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311はセキュリティチェック実行し、タイミングT3で主制御プログラムを開始する。その後、タイミングT4で設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタに記憶し、タイミングT5まで周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ。
The
周辺制御基板1510は、通電の開始によって起動すると、客待ち演出を開始する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、主制御基板1310からのコマンドを受信した後に客待ち演出を開始してもよい。
When the peripheral control board 1510 is activated by the start of energization, the customer waiting effect is started. Note that the peripheral control board 1510 may start the customer waiting effect after receiving the command from the
主制御MPU1311は、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT5において、設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタから読み出し、設定状態管理エリアに02Hを記録して設定変更モードに移行する。また、主制御MPU1311は、セキュリティ信号の出力を開始する。
The
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認モードに移行することを示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A002H)を作成し、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
In addition, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時動作コマンドに従って、設定確認モード
における演出を実行する。
Peripheral control board 1510 executes an effect in the setting confirmation mode according to the received power-on operation command.
その後、主制御基板への電源供給が停止すると、主制御MPU1311は停電を検出し電源断時処理を実行し、主制御MPU1311は動作を停止する(T7)。そして、リセット回路1335からリセット信号の出力が停止し、ベース表示器1317による設定値の表示が消え、セキュリティ信号の出力が停止する(T8)。なお、電源断時処理において、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止し、ベース表示器1317を消灯してもよい。例えば、電源断時処理のプログラムによってセキュリティ信号の出力ポートやベース表示器1317への出力ポートをOFFすることによって、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止し、ベース表示器1317を消灯できる。
After that, when the power supply to the main control board is stopped, the
電源断時処理で出力ポートをOFFすることによって、電源断時処理中の消費電力低減し、電源断時処理の完了前に電源(5V)が低下することによるリセットを防止できる。例えば、電源断時処理におけるチェックサムの算出前に、出力ポートをOFFすると効果的である。なお、大入賞口2005、2006や第二始動口2004等の開閉を制御するソレノイドへの信号の出力ポートもOFFしてソレノイドの駆動信号を停止するとよい。
By turning off the output port in the power-off processing, the power consumption during the power-off processing can be reduced, and a reset due to the power supply (5V) dropping before the power-off processing is completed can be prevented. For example, it is effective to turn off the output port before calculating the checksum in the power-off processing. In addition, it is preferable to turn OFF the output port of the signal to the solenoid for controlling the opening and closing of the
その後、主制御基板1310に電源が供給され、5V電源が立ち上がると(T9)、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が出力され、主制御MPU1311が起動する(T10)。
Thereafter, power is supplied to the
主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号によってプログラムコードの先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。具体的には、主制御MPU1311はセキュリティチェック実行し、タイミングT11で主制御プログラムを開始し、その後、タイミングT12で設定キー971の信号のレベルとRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをレジスタに記憶し、タイミングT13まで周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ。
The
主制御MPU1311は、設定状態管理エリアの値を参照する。図209に示す例では、電源再投入時に設定確認モードとなるようにRAMクリアスイッチ954がOFFで設定キー971がONに操作されているが、設定状態管理エリアに記録された停電前の状態が設定確認を示す値(01H)となっているために、周辺制御基板起動待ち時間が経過したタイミングT13において、設定確認モードで再起動し、設定状態管理エリアの値は01Hが維持される。なお、元の値にかかわらず、同じ値(01H)を設定してもよい。その後、主制御MPU1311は、セキュリティ信号の出力を開始する。つまり、図209に示すタイムチャートでは、設定キー971がONに操作されていなくても設定確認モードが起動可能となっている。換言すると、電源投入時に設定キー971がONに操作されており及びRAMクリアスイッチ954がOFFに操作されていることによって設定確認モードが起動し、さらに、電源投入時に設定キー971がONでなくても設定確認モードの起動が可能となっている。
The
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認モードに移行することを示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A002H)を作成し、所定のタイミングで周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
In addition, the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時コマンドに従って、設定確認モードにおける演出を実行する。 Peripheral control board 1510 executes an effect in the setting confirmation mode according to the received power-on command.
設定確認モード中において、RAMクリアスイッチ954(設定変更スイッチ972兼用)が操作され、主制御MPU1311はRAMクリアスイッチ954のONを検出しても、設定値を更新することなく設定値をベース表示器1317に継続して表示する。
During the setting confirmation mode, the RAM clear switch 954 (also used as the setting change switch 972) is operated, and even if the
ホールの従業員は、設定値の確認が終わると設定キー971をOFF位置に操作する。主制御MPU1311は、設定キー971のOFFエッジを検出すると、設定確認モードを終了し、設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録し、通常遊技状態に移行する(T15)。設定状態管理エリアに00Hが記録されることによって、タイマ割込み処理において処理が通常遊技中の処理を実行可能となる。また、ベース表示器1317は、所定時間(例えば5秒)全LEDを点滅表示した後、通常遊技状態におけるベース値を表示する。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、電源投入時状態コマンド(3001H)と電源投入時復帰先コマンド(310nH)と設定値コマンド(A10mH)を周辺制御基板1510に送信する。
After confirming the setting values, the hall employee operates the setting key 971 to the OFF position. When the
周辺制御基板1510は、受信した電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知り、通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を実行する。なお、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知ってから所定の遅延時間が経過した後に、通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を開始してもよい。また、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時状態コマンドで通常遊技開始可能状態であることを知ってから所定の遅延時間が経過した後に、設定変更中の報知演出を中止し通常遊技状態における演出(例えば、客待ち演出)を開始するように演出を切り替えてもよい。なお、所定の遅延時間中は、一部の演出装置によって設定変更中の報知演出を行うとよい、例えば、メイン液晶表示装置1600や音は通常遊技状態の演出に戻り、装飾ランプは設定変更中の報知演出を継続する。また、装飾ランプによる報知演出の継続は、一部の装飾ランプ(例えば、枠側)は報知演出を継続し、他の装飾ランプ(例えば、パネル側)はは通常遊技状態の演出に戻ってもよい。 The peripheral control board 1510 learns from the received power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and executes an effect in the normal game state (for example, a customer waiting effect). It should be noted that the peripheral control board 1510 starts an effect in the normal game state (for example, a customer waiting effect) after a predetermined delay time has passed since it was known by the power-on state command that the normal game can be started. may In addition, the peripheral control board 1510 cancels the notification effect during the setting change after a predetermined delay time has passed since it is known by the power-on state command that the normal game can be started, and the effect in the normal game state ( For example, the production may be switched so as to start a customer waiting production. It should be noted that during the predetermined delay time, it is preferable to perform a notification effect that the setting is being changed by some effect devices. continue the notification production. In addition, the continuation of the notification effect by the decorative lamps is that some of the decorative lamps (eg, the frame side) continue the notification effect, and the other decorative lamps (eg, the panel side) return to the normal game state effect. good.
また、主制御MPU1311は、設定確認モードの終了から所定時間(例えば、50ミリ秒)遅延した後、セキュリティ信号の出力を停止する(T16)。これは、設定変更モードが極めて短時間で終了して、セキュリティ信号が全く又は短時間しか出力されないことが生じると、設定変更モードへの移行をホールコンピュータで把握できないため、セキュリティ信号の最低限の出力時間を確保するためである。
Also, the
図210から図212は、大当り判定閾値テーブルの構成例を示す図である。大当り判定閾値テーブルは、特別図柄の大当りを抽選するための大当り判定用乱数値の当たり判定用閾値が格納される。 210 to 212 are diagrams showing configuration examples of the big hit determination threshold table. The big-hit determination threshold value table stores the hit-determination threshold value of the big-hit determination random number value for lottery for the big win of the special symbol.
図210に示す大当り閾値判定テーブルは、設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブル及び各設定値用判定閾値テーブルで構成される。図210に示す大当り判定閾値テーブルは、大当り判定用乱数値がテーブルに定義される閾値より大きい場合に大当りと判定する例である。 The big hit threshold determination table shown in FIG. 210 is composed of a set value table selection address table and each set value determination threshold table. The big-hit determination threshold table shown in FIG. 210 is an example of judging a big-hit when the random number value for big-hit determination is larger than the threshold value defined in the table.
設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブルには、各設定値において選択される判定閾値テーブルのポインタアドレスが定義されており、各データは2バイトの値として構成するとよい。なお、上位バイトが固定値であれば、下位バイトのみを定義してもよい。各設定値用判定閾値テーブルは、低確率(通常状態)時の閾値と高確率(確変状態)時の閾値を格納する。 In the set value table selection address table, the pointer address of the determination threshold table selected for each set value is defined, and each data may be configured as a 2-byte value. Note that if the upper byte is a fixed value, only the lower byte may be defined. Each setting value determination threshold table stores a threshold for low probability (normal state) and a threshold for high probability (variable probability state).
大当り判定時に、設定値テーブル選択用のアドレステーブルに定義されているポインタアドレスを取得し、この値をオフセットとして現在の設定値の閾値判定用テーブルを選択する。そして、確変状態フラグ(0:低確率、1:高確率)をオフセットとして、選択された閾値判定用テーブルから大当り判定用の閾値を取得する。そして、始動口の入賞時に取得した大当り判定用乱数値が、取得した閾値以上である場合に大当りと判定し、閾値未
満である場合にはずれと判定する。
When judging a big hit, a pointer address defined in an address table for selecting a set value table is acquired, and this value is used as an offset to select a threshold judgment table for the current set value. Then, using the variable probability state flag (0: low probability, 1: high probability) as an offset, the threshold value for big hit determination is acquired from the selected threshold value determination table. When the random number value for judging a big hit acquired at the time of winning of the start opening is equal to or greater than the acquired threshold value, it is determined as a big win, and when it is less than the threshold value, it is determined as a deviation.
図211に示す大当り判定閾値テーブルは、設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブル及び各設定値用判定閾値テーブルで構成される。図211に示す大当り判定閾値テーブルは、大当り判定用乱数値が、テーブルに定義される下限から上限までの範囲である場合に大当りと判定する例である。 The big hit determination threshold table shown in FIG. 211 is composed of a set value table selection address table and each set value determination threshold table. The big-hit determination threshold table shown in FIG. 211 is an example of judging a big-hit when the random number value for big-hit determination is within the range from the lower limit to the upper limit defined in the table.
設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブルには、各設定値において選択される判定閾値テーブルのポインタアドレスが定義されており、各データは2バイトの値として構成するとよい。なお、上位バイトが固定値であれば、下位バイトのみを定義してもよい。各設定値用判定閾値テーブルは、低確率(通常状態)時の下限閾値と低確率(通常状態)時の上限閾値と高確率(確変状態)時の下限閾値と高確率(確変状態)時の上限閾値を格納する。 In the set value table selection address table, the pointer address of the determination threshold table selected for each set value is defined, and each data may be configured as a 2-byte value. Note that if the upper byte is a fixed value, only the lower byte may be defined. The judgment threshold table for each setting value is the lower threshold at low probability (normal state), the upper threshold at low probability (normal state), the lower threshold at high probability (variable state), and the lower threshold at high probability (variable state). Stores the upper threshold.
大当り判定時に、設定値テーブル選択用のアドレステーブルに定義されているポインタアドレスを取得し、この値をオフセットとして現在の設定値の閾値判定用テーブルを選択する。そして、確変状態フラグ(0:低確率、1:高確率)をオフセットとして、選択された閾値判定用テーブルの低確率のブロックか高確率のブロックかを決定し、大当り判定用の下限閾値と上限閾値を取得する。そして、始動口の入賞時に取得した大当り判定用乱数値が、取得した下限閾値以上かつ上限閾値以下の場合に大当りと判定し、下限閾値から上限閾値の範囲外の場合にはずれと判定する。 When judging a big hit, a pointer address defined in an address table for selecting a set value table is acquired, and this value is used as an offset to select a threshold judgment table for the current set value. Then, by using the variable probability state flag (0: low probability, 1: high probability) as an offset, it is determined whether the block is a low probability block or a high probability block in the selected threshold value determination table, and the lower limit threshold and upper limit for big hit determination Get the threshold. When the random number value for judging a big win acquired at the time of winning the starter is equal to or more than the acquired lower limit threshold and equal to or less than the upper threshold, it is judged as a big win, and when it is out of the range from the lower limit threshold to the upper limit threshold, it is judged as a deviation.
図212に示す大当り判定閾値テーブルは、低確率用設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブル、低確率用の各設定値用判定閾値テーブル、高確率用設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブル及び高確率用の各設定値用判定閾値テーブルで構成される。図211に示す大当り判定閾値テーブルは、低確率用のテーブルと高確率のテーブルが一体に構成されているが、図212に示す大当り判定閾値テーブルは、低確率用のテーブルと高確率のテーブルが別に構成されている。 The big hit determination threshold table shown in FIG. 212 includes an address table for low probability setting value table selection, a determination threshold table for each setting value for low probability, an address table for high probability setting value table selection, and each setting for high probability. It consists of a value judgment threshold table. The jackpot determination threshold table shown in FIG. 211 is composed of a low probability table and a high probability table, but the jackpot determination threshold table shown in FIG. 212 has a low probability table and a high probability table. configured separately.
低確率用設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブルには、低確率(通常状態)の各設定値において選択される判定閾値テーブルのポインタアドレスが定義されており、高確率用設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブルには、高確率(確変状態)の各設定値において選択される判定閾値テーブルのポインタアドレスが定義されている。各設定値テーブル選択用アドレステーブルに定義されるデータは2バイトの値として構成するとよい。なお、上位バイトが固定値であれば、下位バイトのみを定義してもよい。低確率用の各設定値用判定閾値テーブルは、低確率(通常状態)時の下限閾値と低確率(通常状態)時の上限閾値を格納する。高確率用の各設定値用判定閾値テーブルは、高確率(通常状態)時の下限閾値と高確率(通常状態)時の上限閾値を格納する。 The low-probability setting value table selection address table defines the pointer address of the judgment threshold table selected for each low-probability (normal state) setting value. defines the pointer address of the determination threshold table selected for each set value of high probability (probability variable state). The data defined in each set value table selection address table may be configured as a 2-byte value. Note that if the upper byte is a fixed value, only the lower byte may be defined. The determination threshold value table for each set value for low probability stores a lower limit threshold for a low probability (normal state) and an upper limit threshold for a low probability (normal state). The determination threshold value table for each set value for high probability stores a lower threshold value for a high probability (normal state) and an upper threshold value for a high probability (normal state).
大当り判定時に、確変状態フラグ(0:低確率、1:高確率)により低確率用設定値テーブル選択用のアドレステーブルか高確率用設定値テーブル選択用のアドレステーブルかを決定し、決定された設定値テーブル選択用のアドレステーブルから設定値をオフセットとして取得し、取得したオフセットによって現在の設定値に対応した判定閾値テーブルを選択する。そして、始動口の入賞時に取得した大当り判定用乱数値が、取得した下限閾値以上かつ上限閾値以下の場合に大当りと判定し、下限閾値から上限閾値の範囲外の場合にはずれと判定する。 At the time of jackpot determination, the address table for selecting the setting value table for low probability or the address table for selecting the setting value table for high probability is determined by the probability variable state flag (0: low probability, 1: high probability). A set value is acquired as an offset from the address table for selecting the set value table, and the judgment threshold table corresponding to the current set value is selected by the acquired offset. When the random number value for judging a big win acquired at the time of winning the starter is equal to or more than the acquired lower limit threshold and equal to or less than the upper threshold, it is judged as a big win, and when it is out of the range from the lower limit threshold to the upper limit threshold, it is judged as a deviation.
[12-17.設定変更・確認処理の別例2]
次に、設定変更機能を有するパチンコ機の別な実施例について説明する。以下に説明する実施例では、設定変更スイッチ972を設けずに、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作によって設定値が選択できるものであるが、RAMクリアスイッチ954の本来の主制御
RAM1312の初期化機能と、設定変更機能とを区別して記載するために、設定値の変更にかかる操作については設定変更スイッチ972として説明することがある。
[12-17. Example 2 of setting change/confirmation process]
Next, another embodiment of a pachinko machine having a setting change function will be described. In the embodiment described below, the setting value can be selected by operating the RAM
図213、図214は、電源投入時に主制御MPU1311が実行する電源投入時処理のフローチャートである。
213 and 214 are flowcharts of power-on processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、電源の投入により、リセット信号が解除されるとプログラムコードの開始番地である8000番地の処理から開始する。主制御RAM1312のプロテクト無効及び禁止領域無効をRAMプロテクトレジスタに設定する(ステップS2200)。主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の使用領域を指定することによって、指定領域以外の禁止領域へアクセスがあった場合には、異常と判定してリセットする機能を有する。主制御RAM1312の禁止領域へのアクセスによるリセット機能を解除するために、禁止領域を無効に設定することで主制御RAM1312の全領域へのアクセスを可能としている。なお、主制御RAM1312のうち未使用領域を禁止領域に指定して、禁止領域を有効にして、指定された禁止領域にアクセスを検出した場合には、主制御MPU1311がリセットされるようにしてもよい。
First, the
次に、所定時間の単純クリアモードタイマをウォッチドッグタイマに設定し(ステップS2201)、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアする(ステップS2202)。その後、停電クリア信号をONに設定し(ステップS2203)、停電クリア信号をOFFに設定する(ステップS2204)。一旦、停電クリア信号をONに設定してから、OFFに設定することによって、ラッチに記憶された停電信号を正常な値に設定できる。 Next, a simple clear mode timer of a predetermined time is set in the watchdog timer (step S2201), and the watchdog timer is cleared (step S2202). After that, the power failure clear signal is set to ON (step S2203), and the power failure clear signal is set to OFF (step S2204). By once setting the power failure clear signal to ON and then setting it to OFF, the power failure signal stored in the latch can be set to a normal value.
次に、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをPFポートから読み出し、レジスタに記憶する(ステップS2205)。レジスタは、主制御MPU1311に予め設けられた複数の汎用レジスタ(処理の演算で演算に係る情報を一時的に記憶する記憶手段)の何れかを利用すればよい。汎用レジスタは、バンク0とバンク1とに分かれており、ステップS2205ではバンク0のレジスタが使用される。レジスタは、主制御RAM1312に設けられ、停電時に情報が保持されることなく消去されるものであり、停電時に情報がバックアップされるRAMの領域とは異なる。RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971が操作されているか否かの判定は、周辺制御基板1510が確実に起動した後に主制御MPU1311が行うため、周辺制御基板1510が起動するまでの待機中に、ホールの従業員がRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作を誤って中断すると、ホールの従業員が意図していない状態でRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971が判定されてしまう。このため、電源投入時処理開始後の早い段階でRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の入力状態(レベル)を一時的な記憶手段であるレジスタ等に格納し、周辺制御基板1510の待機状態の終了後に一時的な記憶手段であるレジスタ等に格納したRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の状態を判定することによって、ホールの従業員が電源投入後の早い段階でキー操作を誤って中断しても、電源投入操作時のRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作を確実に検出する。
Next, the signal levels of the setting
その後、停電予告信号が停電中であるかを判定する(ステップS2206)。停電予告信号が検出されていれば、パチンコ機の電源電圧が正常ではないので、ステップS2206で電源電圧が安定するまで待機する。 After that, it is determined whether or not the power failure warning signal indicates power failure (step S2206). If the power failure warning signal is detected, the power supply voltage of the pachinko machine is not normal, so the system waits until the power supply voltage stabilizes in step S2206.
その後、サブ起動待ちタイマ(例えば約2秒)を開始し、当該タイマがタイムアップするまでの間ウォッチドッグタイマを継続的にクリアし、周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ(ステップS2207)。周辺制御基板1510の起動待ちは、電源投入後から周辺制御基板1510に最初にコマンドを送信するまでの期間であればいつでもよい。 Thereafter, a sub activation wait timer (for example, about 2 seconds) is started, and the watchdog timer is continuously cleared until the timer expires to wait for activation of the peripheral control board 1510 (step S2207). Waiting for activation of the peripheral control board 1510 may be any period from power-on to transmission of the first command to the peripheral control board 1510 .
その後、停電予告信号が停電中であるかを再度判定する(ステップS2208)。停電予告信号が検出されていれば、パチンコ機1の電源電圧が異常なので、ステップS2208で待機する。
After that, it is determined again whether the power failure warning signal indicates power failure (step S2208). If the power failure warning signal is detected, the power supply voltage of the
その後、設定値確認処理を実行して、設定値が正常範囲内かを判定し、設定状態管理エリアの値が正常範囲内かを判定する(ステップS2209)。設定値確認処理の詳細は図215で後述する。 After that, setting value confirmation processing is executed to determine whether the setting value is within the normal range, and whether the value in the setting state management area is within the normal range (step S2209). Details of the setting value confirmation processing will be described later with reference to FIG.
その後、フラグレジスタを遊技制御領域内スタックエリアに退避する(ステップS2210)。これは、遊技制御領域外の処理と遊技制御領域内の処理との独立性を確保するために、一方の処理で使用した情報を他方の処理に影響させないためである。その後、電源投入時遊技領域外RAM確認処理を実行して、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の異常を判定する(ステップS2211)。電源投入時遊技領域外RAM確認処理の詳細は図216で後述する。そして、遊技制御領域内スタックエリアに退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2212)。 After that, the flag register is saved in the stack area within the game control area (step S2210). This is because the information used in one process does not affect the other process in order to ensure the independence of the process outside the game control area and the process within the game control area. After that, when the power is turned on, a RAM confirmation process outside the game area is executed to determine an abnormality outside the game control area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2211). The details of the outside-game-area RAM checking process at power-on will be described later with reference to FIG. Then, the flag register saved in the stack area within the game control area is restored (step S2212).
その後、RAM異常判定結果値をCレジスタに仮設定し(ステップS2213)、設定状態管理エリアにおけるRAM異常値(03H)をBレジスタに仮設定する(ステップS2214)。ステップS2213及びS2214で使用されるBレジスタ及びCレジスタは汎用レジスタである。なお、電源投入時の処理ではバンク0の汎用レジスタが使用される。
Thereafter, the RAM abnormality determination result value is temporarily set in the C register (step S2213), and the RAM abnormality value (03H) in the setting state management area is temporarily set in the B register (step S2214). The B and C registers used in steps S2213 and S2214 are general purpose registers. Note that the general-purpose registers of
別例2において設定状態管理エリアに設定される値は、前述した実施例において図201(B)に示したものと異なり、図220(A)に示すように、主制御RAM1312に異常があれば03Hが記録される。すなわち、別例2の設定状態管理エリアは、パチンコ機1の動作モードが記録される1バイトの記憶領域であり、例えば下位の4ビットが使用され、上位の4ビットは定義されていない。具体的には、通常遊技状態では00H、設定確認モードでは01H、設定変更モードでは02H、主制御RAM1312に異常があれば03Hが記録される。
The value set in the setting state management area in Example 2 is different from that shown in FIG. 03H is recorded. That is, the setting state management area of example 2 is a 1-byte storage area in which the operation mode of the
設定状態管理エリアは、RAMクリアスイッチ954のみの操作によるRAMクリア処理では00Hに更新されず、現在の値が維持される。また、設定確認モードの終了時には01Hから00Hに更新され、設定変更モードの終了時には02Hから00Hに更新される。さらに、主制御RAM1312が異常である場合、次の電源投入時の設定変更操作によって設定変更モードになると03Hから02Hに更新され、設定変更モードの終了時に02Hから00Hに更新される。
The setting state management area is not updated to 00H by the RAM clearing process by operating only the RAM
さらに、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域に異常があるかを判定し、判定結果をCレジスタに格納し(ステップS2215、S2216)、ステップ2219に進む。具体的には、前回の電源遮断時に内蔵RAM1312にバックアップされている領域のうち遊技制御領域として使用されているデータ(スタックに退避されたデータは除く)から算出して記憶されたチェックサムと、同じ領域を使用して算出されたチェックサムとを比較し、両者が異なれば、主制御RAM1312に異常があると判定する。また、正常にバックアップされた(電源断時処理が正常に実行された)ことを示す停電フラグの値がバックアップフラグエリアに格納されていなければ、停電発生時に主制御RAM1312のデータが正常にバックアップされておらず(電源断時処理が正常に実行されておらず)、主制御RAM1312に異常があると判定する。
Further, it determines whether there is an abnormality in the game control area of the
そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外のいずれにも異常
がなければ、RAM正常判定結果値をCレジスタに仮設定し(ステップS2217)、設定状態管理エリアの情報をBレジスタに設定して(ステップS2218)、ステップ2219に進む。
Then, if there is no abnormality in the game control area and outside the game control area of the
その後、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(03H)を仮に記録する(ステップS2219)。 After that, a value (03H) indicating RAM abnormality is temporarily recorded in the setting state management area (step S2219).
そして、PFポートの値が記録されたレジスタ値のうち、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954のビットをマスクする(ステップS2220)。PFポートの値が記憶されるレジスタは汎用レジスタのうちS2213、S2214で仮設定されるレジスタとは異なるものを使用する。その後、電源投入時に設定キー971がONに操作されており、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2221)。そして、設定キー971がONに操作されており、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていれば、設定変更操作がされていると判定し、ステップS2230に進む。
Then, among the register values in which the values of the PF ports are recorded, the bits of the setting
一方、設定キー971が操作されておらず、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていなければ、停電発生時に設定変更モードであったかを判定する(ステップS2222)。例えば、設定状態管理エリアの値が設定変更モード(02H)のときに、設定変更モード中に停電が発生したと判定する。
On the other hand, if the setting
そして、設定変更モード中に停電が発生したと判定したときには、ステップS2230に進む。 Then, when it is determined that a power failure has occurred during the setting change mode, the process proceeds to step S2230.
一方、設定変更モード中に停電が発生していないと判定したときは、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外に異常があるかを判定する(ステップS2223)。例えば、前述したステップS2213、S2217でCレジスタに格納された判定結果を用いて、遊技制御領域内の異常を判定できる。その結果、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外のいずれかに異常があれば、ステップS2236に進む。
On the other hand, when it is determined that a power failure has not occurred during the setting change mode, it is determined whether there is an abnormality within the game control area and outside the game control area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2223). For example, using the determination results stored in the C register in steps S2213 and S2217 described above, an abnormality in the game control area can be determined. As a result, if there is an abnormality either inside the game control area of the
一方、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外のいずれにも異常がなければ、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したかを判定する(ステップS2224)。例えば、退避した設定状態管理エリアの値がRAM異常を示す値(03H)であれば、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したと判定する。
On the other hand, if there is no abnormality in the game control area and outside the game control area of the
そして、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したと判定したときには、ステップS2236に進む。一方、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生していないと判定したときには、設定状態管理エリアに通常遊技状態を示す値(00H)を記録する(ステップS2225)。ステップS2225で設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録することによって、ステップS2214で設定状態管理エリアに仮に記録されたRAM異常を示す値(03H)を、正常な状態に戻している。また、ステップS2225で設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録することによって、ステップS2226とS2231とからステップS2235にジャンプした際の設定状態管理エリアの値が異なる。このように、通常のRAMクリア処理と設定変更処理に伴うRAMクリア処理とで設定状態管理エリアの値が異なることから、両方のRAMクリア処理のためのプログラムを共通にしても呼出元を区別でき、別個にプログラムを設ける必要がなく、プログラムサイズのサイズを小さくできる。 Then, when it is determined that a power failure has occurred during the RAM abnormality processing, the process proceeds to step S2236. On the other hand, when it is determined that a power failure has not occurred during the RAM abnormality processing, a value (00H) indicating the normal game state is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2225). By recording 00H in the setting state management area in step S2225, the value (03H) indicating RAM abnormality temporarily recorded in the setting state management area in step S2214 is returned to the normal state. Also, by recording 00H in the setting state management area in step S2225, the values in the setting state management area differ when jumping from steps S2226 and S2231 to step S2235. In this way, since the values in the setting state management area are different between the normal RAM clearing process and the RAM clearing process associated with the setting change process, even if the programs for both RAM clearing processes are shared, the caller can be distinguished. , there is no need to provide a separate program, and the size of the program can be reduced.
その後、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2226)。そして、RAMクリアス
イッチ954がONに操作されていれば、ステップS2235に進む。
Thereafter, it is determined using the value stored in the register whether the RAM
本実施例のパチンコ機では、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作と設定キー971の操作と設定状態管理エリアに記録された値とに基づいて、処理を振り分ける。例えば、主制御RAM1312が異常であると判定されると、設定状態管理エリアには03Hが記録され、電源が遮断されるまで03Hが維持されるため、通常遊技処理を実行できない。このとき、一旦電源を遮断した後に設定変更操作をして電源を投入すると、RAM異常を解除できる。すなわち、ステップS2221で設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954の両方が操作されている(設定変更操作)と判定されると、設定状態管理エリアがRAM異常を示す値(03H)から設定変更を示す値(02H)に更新され(ステップS2230)、RAM異常状態が終了する。このように、RAM異常からの復帰は、必ず設定変更を経由することになっている。換言すると、停電発生時の状態がRAM異常かを判定する前に、設定変更操作がされているかを判定するので、設定値の変更を契機としてのみRAM異常を解消できる。
In the pachinko machine of this embodiment, processing is distributed based on the operation of the RAM
一方、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていなければ、停電発生前の状態に復旧すために、停電発生時点での遊技状態の情報を電源投入時状態バッファに記憶する(ステップS2227)。
On the other hand, if the RAM
その後、電源投入時に設定キー971がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2228)。そして、設定キー971がONに操作されていれば、設定確認操作がされていると判定し、設定状態管理エリアに設定確認モードを示す値(01H)を記録し(ステップS2229)、S2236に進む。すなわち、停電発生時の状態が設定確認モードであっても、電源投入時に設定キー971が操作されていない場合には通常遊技状態となる。なお、停電発生時の状態が設定確認モードで、電源投入時に設定キー971が操作されていない場合に、通常遊技状態ではなく、停電発生前と同じ停電確認モードに移行してもよい。
After that, it is determined using the value stored in the register whether the setting
ステップS2225からS2229は、RAMクリアスイッチ954か設定キー971の少なくとも一つが操作されていない場合に実行される処理であることから、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作の判定(ステップS2226)と、設定キー971の操作の判定(ステップS2228)とのいずれを先に行ってもよい。すなわち、図示したように、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を判定(ステップS2226)した後に設定キー971の操作を判定(ステップS2228)してもよく、設定キー971の操作を判定(ステップS2228)した後にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を判定(ステップS2226)してもよい。
Steps S2225 to S2229 are processes executed when at least one of the RAM
ステップS2221又はステップS2222でYESと判定されると、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更モードを示す値(02H)を記録する(ステップS2230)。そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外に異常があるかを判定する(ステップS2231)。例えば、前述したステップS2266で遊技領域外RAM異常判別エリアに設定されたRAM異常判定結果に基づいて、遊技制御領域外の異常を判定できる。その結果、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外に異常がなければ、ステップS2235に進む。
If YES is determined in step S2221 or step S2222, a value (02H) indicating the setting change mode is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2230). Then, it is determined whether there is an abnormality outside the game control area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2231). For example, based on the RAM abnormality determination result set in the RAM abnormality determination area outside the game area in step S2266 described above, it is possible to determine the abnormality outside the game control area. As a result, if there is no abnormality outside the game control area of the
一方、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外に異常があれば、遊技制御領域外のRAMクリア処理を実行する。すなわち、フラグレジスタを遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避し(ステップS2232)、遊技領域外RAM異常時処理を実行する(ステップS2233)。遊技領域外RAM異常時処理の詳細は図217で後述する。その後、ステップS2232で遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2234)。
On the other hand, if there is an abnormality outside the game control area of the
そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内の設定値と設定状態管理エリア以外の領域と遊技制御領域内のスタックエリアとを初期化する(ステップS2235)。つまり、遊技制御領域外のRAMクリア処理は、設定変更を経由しないと実行されないことになる。遊技制御領域外のRAM異常時には、遊技制御領域内のRAM異常時と同様に、設定状態管理エリアに03Hが記録されており、遊技が停止するため、設定変更を経由しないとRAM異常状態から復帰できないようになっている。但し、遊技制御領域外のRAMクリアの条件は設定変更のみであるのに対し、遊技制御領域内のRAMクリアの条件は設定変更及びRAMクリアスイッチ954操作(RAM異常が発生していないにも場合に従業員の操作によって強制的にRAMクリアする場合)の二つになる。
Then, the setting value in the game control area of the
ステップS2235の遊技領域内のRAMクリア処理において、設定値と設定状態管理エリアを除外するのは、遊技者による不正なRAMクリア操作によって設定値が高設定になる場合にホール側に損害が発生すること、高設定で遊技中に不具合(RAM異常)が生じて遊技が停止すると、RAMクリア操作によって高設定から低設定となり、遊技者に損害が発生するためである。 In the RAM clearing process in the game area in step S2235, the setting value and the setting state management area are excluded because if the setting value becomes high due to an illegal RAM clearing operation by the player, damage will occur on the hall side. This is because if a problem (RAM abnormality) occurs during a game with high settings and the game is stopped, the high settings are changed to low settings by the RAM clearing operation, which causes damage to the player.
その後、全コマンドバッファを初期化する(ステップS2236)。これは、コマンドバッファにコマンドが記憶された状態で電源が遮断された後にRAMクリアせずに電源を復帰すると、コマンドバッファに格納された未送信のコマンドが送信される。例えば、変動コマンドの送信中に電源が遮断されることによって、図柄コマンドは送信したが、後続する変動パターンコマンドが未送信となることがある。そして、電源投入時に、変動パターンコマンドだけが送信されると、周辺制御基板1510が異常と判定することがある。さらに、設定変更に関する処理における未送信のコマンドがコマンドバッファに格納されている場合、電源復帰後に設定処理中に未送信となったコマンドが送信されることによって、周辺制御基板1510が当該コマンドに基づいて遊技状態を設定して、誤動作する可能性がある。このような異常の発生を防止するために、ステップS2236において、コマンドバッファを初期化している。 After that, all command buffers are initialized (step S2236). When the power is turned off while commands are stored in the command buffer and the power is turned back on without clearing the RAM, the unsent commands stored in the command buffer are sent. For example, when the power supply is interrupted during the transmission of the variation command, the symbol command is transmitted, but the subsequent variation pattern command may not be transmitted. Then, when only the variation pattern command is transmitted when the power is turned on, the peripheral control board 1510 may be determined to be abnormal. Furthermore, if a command that has not been transmitted during the setting change process is stored in the command buffer, the command that has not been transmitted during the setting process is transmitted after the power is restored, so that the peripheral control board 1510 There is a possibility of malfunction by setting the game state by In order to prevent such an abnormality from occurring, the command buffer is initialized in step S2236.
なお、ステップS2236でコマンドバッファを初期化しているが、設定変更処理を開始するとき及び設定確認処理を開始するときにのみ、コマンドバッファをクリアしてもよい。なお、設定変更処理においては、主制御RAM1312の初期化に伴ってコマンドバッファがクリアされるので、別途コマンドバッファをクリアしなくてもよいが、設定確認モードにおいては、主制御RAM1312が初期化されないことから、設定確認モードに移行するときに、コマンドバッファをクリアするとよい。
Although the command buffer is initialized in step S2236, the command buffer may be cleared only when starting the setting change process and when starting the setting confirmation process. In the setting change process, the command buffer is cleared along with the initialization of the
その後、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたデバイス(CTC、SIO等)の機能を初期設定し(ステップS2237)、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたハードウェア乱数(例えば当落乱数)を起動する(ステップS2238)。ステップS2238でハードウェア乱数を起動することによって、設定変更モードや設定確認モードにおいてもハードウェア乱数が更新されるようにしているが、設定変更モードや設定確認モードの終了時にハードウェア乱数を起動してもよい。そして、電源投入時設定処理を実行する(ステップS2239)。電源投入時設定処理の詳細は図219で後述する。
After that, the function of the device (CTC, SIO, etc.) built in the
最後にタイマ割込みを許可に設定し(ステップS2240)、主制御側メイン処理(図221)に進む。 Finally, the timer interrupt is enabled (step S2240), and the process proceeds to main control side main processing (FIG. 221).
図215は、設定値確認処理のフローチャートである。設定値確認処理は、電源投入時処理(図213)のステップS2209において実行され、設定状態管理エリアの設定値が正常範囲内かを判定し、設定状態管理エリアの値が正常範囲内かを判定する。なお、設
定値確認処理は、電源投入時の他、設定変更モードの終了時や設定確認モードの終了時に実行してもよい。また、特別図柄変動開始時や、遊技状態の変化時(大当り、確変、時短などの開始及び終了時)に実行してもよい。
FIG. 215 is a flowchart of setting value confirmation processing. The setting value confirmation process is executed in step S2209 of the power-on process (FIG. 213) to determine whether the setting value in the setting state management area is within the normal range, and whether the value in the setting state management area is within the normal range. do. Note that the setting value confirmation process may be executed when the setting change mode or the setting confirmation mode is finished, in addition to when the power is turned on. Also, it may be executed at the start of special symbol variation, or at the time of change in the game state (at the start and end of a big hit, probability variation, time reduction, etc.).
設定値確認処理では、まず、主制御MPU1311は、設定状態管理エリアに本来記録される値以外の値が設定されているかを判定する(ステップS2250)。設定状態管理エリアは、図220(A)に示すように、00H~03Hが記録されるので、04H以上の値が設定されていれば異常であり、ステップS2252に進む。
In the setting value confirmation process, first, the
一方、設定状態管理エリアに正常な値(03H以下)が設定されていれば、設定値が所定の範囲内であるかを判定する(ステップS2251)。例えば、設定が1~6までの段階で選択可能なパチンコ機1において、設定値が格納されるワークの値が0~5に対応している(設定1のとき=0、設定6のとき=5)場合には、6以上の値が格納されていれば、所定の範囲外であると判定される。
On the other hand, if a normal value (03H or less) is set in the setting state management area, it is determined whether the set value is within a predetermined range (step S2251). For example, in a
設定値が所定の範囲外であれば、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(03H)を記録し(ステップS2252)、設定値を0に初期化し(ステップS2253)、電源投入時処理に戻る。一方、設定値が所定の範囲内であれば、電源投入時処理に戻る。 If the set value is out of the predetermined range, a value (03H) indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2252), the set value is initialized to 0 (step S2253), and the process returns to power-on processing. . On the other hand, if the set value is within the predetermined range, the process returns to power-on processing.
設定状態管理エリアに記録される値及び設定値に関しては、主制御RAM1312が異常であるかが遊技の進行中(変動開始毎、遊技状態の切り替え時など)にも判定される。このため、遊技中に設定状態管理エリア及び設定値に関するRAM異常と判定される条件と、電源投入時にRAM異常(設定状態管理エリア及び設定値を除く遊技領域内のワークエリアと、遊技領域外のワークRAMの異常)と判定される条件の二つの条件は異なっている。なお、この二つのRAM異常判定条件は、一部が同じでもよい。例えば、電源投入時も設定状態管理エリア及び設定値が異常であるかを判定すると、二つの判定条件は一部が同じであるといえる。
Regarding the values and setting values recorded in the setting state management area, whether or not the
このように、RAM異常の判定条件が異なるのは、設定値に関するRAM異常の判定を電源投入時のみに行うとすると、不正行為やノイズ等による誤動作によって設定値が変更された場合、ホールや遊技者に不利益が生じることから、早期に異常を検出して、不利益が生じる期間を短くすることが望ましいからである。 The reason why the RAM abnormality determination conditions are different is that if the RAM abnormality determination regarding the setting value is performed only when the power is turned on, if the setting value is changed due to fraud or malfunction due to noise, etc. This is because it is desirable to detect the abnormality at an early stage and shorten the period during which the disadvantage occurs.
また、遊技中に設定状態管理エリアと設定値に関するRAM異常判定処理をサブルーチン化することによって、遊技の進行中に必要に応じて当該サブルーチンを呼び出してRAM異常を判定することによって、同じプログラムを複数箇所に設けることなく、プログラムのサイズを小さくできる。 In addition, by subroutineing the RAM abnormality determination processing related to the setting state management area and the set value during the game, the same program can be used in a plurality of ways by calling the subroutine and determining the RAM abnormality as necessary during the game progress. It is possible to reduce the size of the program without providing it in place.
また、設定状態管理エリアは、電源投入時のRAM異常判定対象外としているが、RAM異常判定対象として、主制御RAM1312の他の領域と同様に取り扱ってもよい。設定状態管理エリアを電源投入時のRAM異常判定対象とすることによって、停電前に設定変更モードであり、電源復帰時にRAM異常と判定された場合には、RAM異常が優先される。このため、設定状態管理エリアの値に異常(すなわち、RAM異常)が生じれば、設定状態管理エリアに記録された値を初期化することが望ましいからである。なお、この場合、主制御RAM1312のうち設定値が格納された記憶領域は、電源投入時のRAM異常判定対象としても、RAM異常判定対象外としてもよい。
Also, the setting state management area is not subject to RAM abnormality determination at power-on, but may be handled in the same manner as other areas of the
なお、電源投入時の判定における優先順は、RAM異常が最も優先度が高く、通常遊技状態になることが最も優先度が低くなっている。さらに、設定変更モードになることは、設定確認モードになることやRAMクリア操作によってRAMクリア処理を実行すること
より優先度が高くなっている。このように、導出される状態の優先度の順に判定処理を実行することによって、電源復帰後に複数の条件が成立している場合にも、優先度が高い状態を的確に導出することができる。
In addition, regarding the order of priority in the determination at the time of turning on the power, the RAM abnormality has the highest priority, and the normal game state has the lowest priority. Furthermore, entering the setting change mode has a higher priority than entering the setting confirmation mode and executing RAM clear processing by a RAM clear operation. By executing the determination process in the order of priority of the derived states in this way, it is possible to accurately derive the state with the highest priority even when a plurality of conditions are satisfied after the power is restored.
図216は、電源投入時遊技領域外RAM確認処理のフローチャートである。電源投入時遊技領域外RAM確認処理は、電源投入時処理(図213)のステップS2211において実行され、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の異常を判定する。
FIG. 216 is a flow chart of the outside-game-area RAM checking process when the power is turned on. When the power is turned on, the outside game area RAM confirmation process is executed in step S2211 of the power on process (FIG. 213), and the abnormality outside the game control area of the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のSP退避用バッファにスタックポインタの値を格納し(ステップS2260)、遊技領域値外スタックポインタ値をスタックポインタに設定し(ステップS2261)、呼出元の処理で使用されているバンク(バンク0又はバンク1)の全てのレジスタ値を遊技領域外のレジスタ退避用バッファに格納する(ステップS2262)。なお、遊技制御領域外で実行される処理において全レジスタを格納する退避用バッファとして遊技制御領域外のスタックエリアを使用してもよい。
First, the
そして、既に初回の電源投入等で主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外が初期化されているか否かを判定する(ステップS2263)。具体的には、パワーダウンチェックエリア(EX_PDIND)の値が5AHであれば、初回の電源投入等で主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外が初期化されていると判定できる。
Then, it is determined whether or not the area outside the game control area of the
初回の電源投入等で主制御RAM1312が初期化されていなければ、ステップS2264~S2265を実行することなく、ステップS2266に進む。一方、初回の電源投入等で主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外が初期化済みであれば、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のチェックサムを算出し(ステップS2264)、算出したチェックサムが正常かを判定する(ステップS2265)。
If the
算出したチェックサムが正常であれば、ステップS2267に進む。一方、算出したチェックサムが異常であれば、遊技領域外RAM異常判別エリアにRAM異常判定結果値(01H)を設定し(ステップS2266)、ステップS2271に進む。なお、S2266で遊技領域外RAM異常判別エリアに設定した値に基づいて、S2231で遊技制御領域外のRAM異常が判定される。 If the calculated checksum is normal, the process proceeds to step S2267. On the other hand, if the calculated checksum is abnormal, the RAM abnormality determination result value (01H) is set in the RAM abnormality determination area outside the game area (step S2266), and the process proceeds to step S2271. In addition, RAM abnormality outside the game control area is determined at S2231 based on the value set in the RAM abnormality determination area outside the game area at S2266.
一方、ステップS2265で算出したチェックサムが正常であると判定されると、LEDチェックタイマに5秒を設定し、LEDチェックタイマを起動し(ステップS2267)、LED点滅周期タイマに点滅周期値(600ミリ秒)を設定し(ステップS2268)、モード切替時間タイマにモード切替時間(5秒)を設定する(ステップS2269)。LED点滅周期タイマは、ベース表示器1317の上2桁(又は4桁全て)を点滅表示するためのタイマであり、LED点滅周期タイマのタイムアップで一つの点滅周期になる。モード切替時間タイマは、ベース表示器1317におけるモード切り替えを制御するためのタイマであり、モード切替時間タイマがタイムアップすることで、ベース表示のモードに切り替わる。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the checksum calculated in step S2265 is normal, the LED check timer is set to 5 seconds, the LED check timer is activated (step S2267), and the LED blink cycle timer is set to the blink cycle value (600 milliseconds) is set (step S2268), and the mode switching time (5 seconds) is set in the mode switching time timer (step S2269). The LED blinking cycle timer is a timer for blinking the upper two digits (or all four digits) of the
その後、性能表示モニタ表示管理エリアに0を設定して初期化し(ステップS2270)、ステップS2271に進む。 Thereafter, the performance display monitor display management area is initialized by setting 0 (step S2270), and the process proceeds to step S2271.
その後、パワーダウンチェックエリアを00Hに初期化する(ステップS2271)。 After that, the power down check area is initialized to 00H (step S2271).
そして、遊技領域外のレジスタ退避用バッファに退避した、呼出元の処理で使用するバンク(バンク0又はバンク1)の全レジスタ値を復帰し(ステップS2272)、遊技領
域外のSP退避用バッファに退避したスタックポインタ値を復帰し(ステップS2273)、電源投入時処理に戻る。
Then, all the register values of the bank (
図217は、遊技領域外RAM異常時処理のフローチャートである。遊技領域外RAM異常時処理は、電源投入時処理(図214)のステップS2233において実行され、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の領域を初期化する。
FIG. 217 is a flow chart of the out-of-game area RAM abnormality processing. The RAM abnormality time process outside the game area is executed in step S2233 of the power-on process (FIG. 214), and the area outside the game control area of the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のSP退避用バッファにスタックポインタの値を格納し(ステップS2280)、遊技領域外スタックポインタ値をスタックポインタに設定し(ステップS2281)、呼出元の処理で使用されているバンク(バンク0又はバンク1)の全てのレジスタ値を遊技領域外のレジスタ退避用バッファに格納する(ステップS2282)。なお、遊技制御領域外で実行される処理において全レジスタを格納する退避用バッファとして遊技制御領域外のスタックエリアを使用してもよい。
First, the
そして、使用領域外RWM初期化処理を実行して、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の領域を初期化する(ステップS2283)。使用領域外RWM初期化処理の詳細は図218で後述する。 Then, the RWM initialization process outside the use area is executed to initialize the area outside the game control area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2283). Details of the out-of-use area RWM initialization process will be described later with reference to FIG.
その後、主制御RAM1312の遊技領域外RAM異常判別エリア(EX_RWMERROR)にRAM正常判別値(00H)を設定する(ステップS2284)。ステップS2284で遊技領域外RAM異常判別エリアに設定した値に基づいて、次の電源投入時にステップS2231で主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外が異常か否かが判定される。
Thereafter, the RAM normality determination value (00H) is set in the outside game area RAM abnormality determination area (EX_RWMERROR) of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2284). Based on the value set in the RAM abnormality determination area outside the game area in step S2284, it is determined whether or not the outside of the game control area of the
そして、LEDチェックタイマに5秒を設定し、LEDチェックタイマを起動し(ステップS2285)、LED点滅周期タイマに点滅周期値(600ミリ秒)を設定し(ステップS2286)、モード切替時間タイマにモード切替時間(5秒)を設定する(ステップS2287)。これらのタイマ値は、ベース表示器1317にベース値を表示するための初期設定である。
Then, the LED check timer is set to 5 seconds, the LED check timer is activated (step S2285), the blinking cycle value (600 milliseconds) is set to the LED blinking cycle timer (step S2286), and the mode switching timer is set to the mode switching time timer. A switching time (5 seconds) is set (step S2287). These timer values are initial settings for displaying base values on
そして、遊技領域外のレジスタ退避用バッファに退避した全レジスタ値(ステップS2262で退避した呼出元の処理で使用されていたバンク(バンク0又はバンク1)のレジスタ値)を復帰し(ステップS2288)、遊技領域外のSP退避用バッファに退避したスタックポインタ値を復帰し(ステップS2289)、呼び出し元の電源投入時処理に戻る。
Then, all the register values saved in the register save buffer outside the game area (the register values of the bank (
図218は、使用領域外RWM初期化処理のフローチャートである。使用領域外RWM初期化処理は、遊技領域外RAM異常時処理のステップS2283において実行され、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の領域を初期化する。
FIG. 218 is a flow chart of RWM initialization processing outside the used area. The RWM initialization process outside the use area is executed in step S2283 of the outside game area RAM abnormality processing, and initializes the area outside the game control area of the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のワークエリアに00Hを書き込んで初期化する(ステップS2290)。そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のスタックエリアに00Hを書き込んで初期化する(ステップS2291)。その後、遊技領域外RAM異常時処理に戻る。
First, the
図219は、電源投入時設定処理のフローチャートである。電源投入時設定処理は、サブルーチン化されており、電源投入時処理(図214)のステップS2239で実行され、電源投入時の初期設定を実行する。 FIG. 219 is a flowchart of power-on setting processing. The power-on setting process is a subroutine and is executed in step S2239 of the power-on process (FIG. 214) to perform initial settings when power is turned on.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、電源投入時動作コマンドを作成し、作成したコマンドを送信情報記憶領域にセットする(ステップS2300)。電源投入時動作コマンドは、図220(B)で後述するように、設定状態管理エリアの記録内容を通知する、2バイトで構成されるコマンドであり、上位バイトがA0Hで下位バイトが設定状態管理エリアの値に1を加算した値となっている。
First, the
次に、入力レベルデータ2領域の設定キー971に対応するビットと設定変更スイッチ972に対応するビットとを初期値である1に設定する。なお、他のビットは0を設定するとよい(ステップS2301)。入力レベルデータ2エリアの設定キー971に対応するビットと設定変更スイッチ972に対応するビットを1に設定するのは、次のタイマ割込み時に当該スイッチのビットを1で検知して、ONエッジが誤って作られないようにするためである。
Next, the bit corresponding to the setting
次に、バックアップフラグをクリアする(ステップS2302)。 Next, the backup flag is cleared (step S2302).
その後、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2303)。設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値が記録されていなければ、設定変更モードであるか設定確認モードであるかRAM異常のいずれかなので、電源投入時設定処理を終了し、呼出元の処理に戻る。 After that, it is determined whether or not a value (00H) indicating a game-startable state is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2303). If no value indicating a game-startable state is recorded in the setting state management area, it means that it is either the setting change mode, the setting confirmation mode, or the RAM is abnormal. Return to processing.
一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始可能状態を示す値(00H)が記録されていれば、通常遊技を開始できる状態なので、主制御RAM1312を初期化したか否かに応じて遊技制御領域内ワークエリアを初期設定する(ステップS2304)。 On the other hand, if a value (00H) indicating a game-startable state is recorded in the setting state management area, it is a state in which a normal game can be started. The area is initialized (step S2304).
その後、電源投入時状態コマンドを作成し、作成したコマンドを送信情報記憶領域に格納する(ステップS2305)。電源投入時状態コマンドは、図220(C)に示すように、、2バイトで構成されるコマンドであり、上位バイトが30Hで下位バイトが停電前の状態を示す。 Thereafter, a power-on state command is created, and the created command is stored in the transmission information storage area (step S2305). As shown in FIG. 220(C), the power-on state command is a command composed of 2 bytes, where the upper byte is 30H and the lower byte indicates the state before the power failure.
そして、電源投入時復帰先コマンドを作成し、作成したコマンドを送信情報記憶領域にセットする(ステップS2306)。電源投入時復帰先コマンドは、図202(C)に示すように、特別図柄に関する遊技状態を通知する、2バイトで構成されるコマンドであり、上位バイトが31Hで下位バイトが停電発生時の特別図柄の状態及び特別電動役物の動作状態を示す。電源投入時復帰先コマンドは、電源投入時に1回送信される。 Then, a power-on recovery destination command is created, and the created command is set in the transmission information storage area (step S2306). As shown in FIG. 202(C), the power-on return destination command is a 2-byte command that notifies the game state related to special symbols. The state of the pattern and the operation state of the special electric accessory are shown. The power-on recovery destination command is sent once when the power is turned on.
さらに、設定値コマンドを作成し、作成したコマンドを送信情報記憶領域にセットする(ステップS2307)。設定値コマンドは、図202(D)に示すように、設定値を通知する、2バイトで構成されるコマンドであり、上位バイトがA1Hで、下位バイトが設定値を示す。 Further, a setting value command is created, and the created command is set in the transmission information storage area (step S2307). The setting value command, as shown in FIG. 202(D), is a 2-byte command for notifying a setting value, where the upper byte indicates A1H and the lower byte indicates the setting value.
なお、電源投入時状態コマンド、電源投入時復帰先コマンド、設定値コマンドと共に、特別図柄変動表示ゲームの保留数を示す特別図柄保留数コマンドを送信して、メイン液晶表示装置1600において保留数表示を停電発生前の状態に復旧させてもよい。なお、特別図柄保留数コマンドの送信順序は、電源投入時状態コマンド、電源投入時復帰先コマンド及び設定値コマンドの送信後でも、これらのコマンドの送信前でも、これらのコマンドの送信途中に送信してもよい。
In addition to the power-on state command, the power-on return destination command, and the setting value command, a special symbol reserve number command indicating the number of reservations of the special symbol variation display game is transmitted, and the number of reservations is displayed on the main liquid
その後、呼出元の処理に戻る。 After that, it returns to the calling process.
電源投入時設定処理は、設定変更モードであるかにかかわらず必ず実行される。また、
電源投入時設定処理は、設定キー971のOFFを検出して、設定変更/確認処理を終了する際に設定処理(図224)から呼び出される。このとき、設定状態管理エリアには00Hが記録されているので、S2300~S2307までの全ての処理が実行される。
The power-on setting process is always executed regardless of whether the mode is the setting change mode. again,
The power-on setting process is called from the setting process (FIG. 224) when it detects that the setting
なお、設定変更/確認処理を実行する場合、電源投入時設定処理が電源投入処理のステップS2239及び設定処理のステップS2355から呼び出されるので、電源投入時動作コマンドが2回送信される。一方、設定変更/確認処理を実行しない場合、電源投入処理のステップS2239から呼び出された電源投入時設定処理のみで、電源投入時動作コマンドが1回送信される。電源投入時動作コマンドは、主制御基板1310の状態(設定変更モード、設定確認モード、RAM異常など)を周辺制御基板1510で識別するために送信される。周辺制御基板1510は、当該コマンドを受信することによって、設定変更モード、設定確認モード、RAM異常時などの状態に対応した報知を行なう。 When executing the setting change/confirmation process, the power-on setting process is called from step S2239 of the power-on process and step S2355 of the setting process, so the power-on operation command is transmitted twice. On the other hand, if the setting change/confirmation process is not executed, the power-on operation command is transmitted once only by the power-on setting process called from step S2239 of the power-on process. The power-on operation command is sent to allow the peripheral control board 1510 to identify the state of the main control board 1310 (setting change mode, setting confirmation mode, RAM error, etc.). Peripheral control board 1510, upon receiving the command, performs notification corresponding to a setting change mode, a setting confirmation mode, a RAM abnormality, and the like.
なお、設定/確認変更モードでは、遊技者による設定調整機能(例えば、扉枠3に設けられたボタンの操作による音量や輝度の調整)を停止し、ホールの従業員による調整(周辺基板ボックス1520に設けられたボリュームによる音量や輝度の調整)は有効としてもよい。具体的には、通常遊技状態を示す電源投入時動作コマンドを受信するまでは、遊技者による設定調整機能を停止するとよい。
In the setting/confirmation change mode, the setting adjustment function by the player (for example, the adjustment of the volume and brightness by operating the button provided on the door frame 3) is stopped, and the adjustment by the hall employee (
また、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードのいずれにおいても、メイン液晶表示装置1600の全画面を用いて、設定変更モードであるか設定確認モードであるかRAM異常状態であるかを表示してもよい。この場合、設定変更モードであるか設定確認モードであるかの音声メッセージを出力してもよい。さらに、一部又のランプ又は全てのランプ(扉枠3に設けられたランプを含めてもよい)を使用して報知してもよい。
In addition, in both the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, the entire screen of the main liquid
図220(B)は、電源投入時動作コマンドの構成例を示す図である。電源投入時動作コマンドは、設定状態管理エリアの記録内容を通知するコマンドであり、下位バイトの値は設定状態管理エリアの値に1を加算した値を格納しているため、前述した実施例において図202(A)に示したものと異なり、別例2ではRAM異常発生時は下位バイトが04Hとなる。 FIG. 220B is a diagram showing a configuration example of a power-on operation command. The power-on operation command is a command for notifying the recorded contents of the setting state management area. Unlike the example shown in FIG. 202A, in Example 2, the lower byte becomes 04H when a RAM error occurs.
具体的には、電源投入時動作コマンドは2バイトで構成され、上位バイトがA0Hで、下位バイトが設定状態管理エリアの記録内容を示す。下位バイトの値は設定状態管理エリアの値に1を加算した値を格納している。これは、通常遊技中のときに設定状態管理エリアの値は00Hとなるため、コマンドとして送信される値が00Hであると、出力が0となるハードウェア異常と区別できないので、いずれかのビットが1にセットされるようにしている。 Specifically, the power-on operation command consists of 2 bytes, the upper byte being A0H, and the lower byte indicating the content recorded in the setting state management area. The value of the lower byte stores the value obtained by adding 1 to the value of the setting state management area. This is because the value of the setting state management area is 00H during a normal game, so if the value sent as a command is 00H, it cannot be distinguished from a hardware error in which the output is 0. is set to 1.
なお、電源投入時動作コマンドは、電源投入時処理で少なくとも1度作られる。具体的には、ホットスタート、RAMクリア及びRAM異常のときに対応してA001H又はA004Hのコマンドが一度作られ、設定変更モード及び設定確認モードでは、電源投入時処理でA002H又はA003Hのコマンドが作られ、その後、設定変更/確認終了時とでA001Hのコマンドとして2度作られる。 Note that the power-on operation command is generated at least once in the power-on processing. Specifically, a command A001H or A004H is created once in response to a hot start, RAM clear, or RAM abnormality, and a command A002H or A003H is created in power-on processing in the setting change mode and setting confirmation mode. After that, it is generated twice as the A001H command, once upon completion of setting change/confirmation.
周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時動作コマンドを受信すると、通常遊技開始可能状態(A001H)、設定確認モード(A002H)、設定変更モード(A003H)、RAM異常の状態(A004H)に応じて、前述した態様で報知を行う(図184参照)。なお、通常遊技開始可能状態の報知は、図184に示していないが、デモ画面を表示したり、遊技内容を説明する待機状態の演出を行う。 When the peripheral control board 1510 receives the power-on operation command, the above-mentioned Notification is performed in the manner in which the information is displayed (see FIG. 184). Although not shown in FIG. 184, the notification of the state in which the normal game can be started is performed by displaying a demo screen or performing a standby state to explain the contents of the game.
周辺制御基板1510が、電源投入時動作コマンドでA001Hを受信することなく、通常遊技中の遊技コマンドを受信した場合、遊技状態が不整合となっている可能性があるため、受信した遊技コマンドを無効と判定し、当該遊技コマンドに対する遊技動作(演出など)を開始しない。但し、所定条件を満たした(例えば、通常遊技中の遊技コマンドが連続して所定回数送信された)場合、周辺制御基板1510が電源投入時動作コマンド(A001H)を取りこぼした可能性があるため、受信した遊技コマンドの無効化を解除し、遊技コマンドに対応する演出を行うとよい。 If the peripheral control board 1510 receives a game command during a normal game without receiving A001H as the power-on operation command, the game state may be inconsistent. It is determined to be invalid, and the game action (effect etc.) corresponding to the game command is not started. However, if a predetermined condition is met (for example, a game command during a normal game is continuously transmitted a predetermined number of times), there is a possibility that the peripheral control board 1510 has missed the power-on operation command (A001H). It is preferable to release the invalidation of the received game command and perform an effect corresponding to the game command.
なお、遊技コマンドが無効化されている状態で、受信した遊技コマンドのうち、所定条件を満たす演出を行い(例えば、図柄の動作、ランプ、可動体、音声等については受信したコマンドに対応する演出を行い)、表示装置の背景や所定のランプを用いて、遊技状態の不整合が発生している旨を報知してもよい。また、遊技状態の不整合が発生している旨を小さな音量で報知してもよい。これは、所定条件となるまで、何の演出も行わないと、遊技状態の不整合が発生していることを理解できない遊技者は、始動口に入賞しても特別図柄変動表示ゲームが開始しないようなパチンコ機1の故障だと思い、ホールで発生する可能性があるトラブルを防止するためである。なお、周辺制御基板1510が遊技コマンドを無効化していても、主制御基板1310は通常の遊技処理を実行しているので、機能表示ユニット1400における特別図柄や普通図柄などの機能表示は正常に表示される。
In addition, in a state where the game commands are invalidated, an effect that satisfies a predetermined condition among the received game commands is performed (for example, the effect corresponding to the received command is performed for symbol movements, lamps, movable bodies, sounds, etc.). ), and the background of the display device or a predetermined lamp may be used to notify the occurrence of an inconsistency in the game state. Also, the fact that the game state is inconsistent may be notified with a low volume. If no effect is performed until a predetermined condition is met, the player who cannot understand that the game state is inconsistent will not start the special symbol variation display game even if he/she wins the starting gate. This is to prevent troubles that may occur in the pachinko hall due to the
図220(C)は、電源投入時状態コマンドの構成例を示す図である。前述した実施例において図202(B)に示したものと異なり、別例2の電源投入時状態コマンドは、01H、02H、03H、04Hの4状態が定義される。すなわち、電源投入時状態コマンドは、電源投入時状態バッファの記録内容に基づいて、通常遊技開始可能状態であるかを通知し、さらに、停電前の状態を通知するコマンドである。例えば、電源投入時状態コマンドは2バイトで構成され、上位バイトが30Hで、下位バイトが01Hであれば、RAMクリアを報知するために主制御RAM1312が初期化された状態であることを示す。また、下位バイトが02Hであれば、停電前の状態が低確率・非時短状態であり、主制御RAM1312が初期化されずに復帰し、通常遊技開始可能状態であることを示す。また、下位バイトが03Hであれば、停電前の状態が高確率・時短状態であり、主制御RAM1312が初期化されずに復帰し、通常遊技開始可能状態であることを示す。また、下位バイトが04Hであれば、停電前の状態が低確率・時短状態であり、主制御RAM1312が初期化されずに復帰し、通常遊技開始可能状態であることを示す。
FIG. 220C is a diagram showing a configuration example of a power-on status command. Unlike the example shown in FIG. 202B in the above-described embodiment, the power-on state command of example 2 defines four states of 01H, 02H, 03H, and 04H. That is, the power-on state command is a command for notifying whether or not a normal game can be started based on the contents recorded in the power-on state buffer, and for notifying the state before the power failure. For example, the power-on status command consists of 2 bytes. If the upper byte is 30H and the lower byte is 01H, it indicates that the
また、電源投入時状態バッファは、前述したように、停電発生前の状態に復旧するために、停電発生時点での遊技状態の情報を記憶する記憶領域であるが、電源投入時状態コマンドには、電源投入時状態バッファの値に1を加算した値が格納される。例えば、低確率非時短では、電源投入時状態バッファには1が記憶されており、この値に1を加算した2が電源投入時状態コマンドに格納される。また、主制御RAM1312が初期化された場合、電源投入時状態バッファが0となっているので、電源投入時状態コマンドには1が格納され、主制御RAM1312が初期化されたことを通知できる。
As described above, the power-on state buffer is a storage area for storing information on the game state at the time of the power failure in order to restore the state before the power failure occurred. , the value obtained by adding 1 to the value of the power-on state buffer is stored. For example, in the low-probability non-shortening of working hours, 1 is stored in the power-on state buffer, and 2 obtained by adding 1 to this value is stored in the power-on state command. Also, when the
図221は、主制御MPU1311が実行する主制御側メイン処理のフローチャートである。主制御側メイン処理は、電源投入時処理(図214)のステップS2240の後に実行される。
FIG. 221 is a flow chart of main control side main processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、停電予告信号を取得し、停電予告信号がONであるかによって停電が発生しているかを判定する(ステップS2310)。別例2では、メイン処理において停電を監視しているが、タイマ割込み処理で停電を監視して、停電発生が検出された場合に停電処理を実行してもよい。例えば、タイマ割込みの開始及び終了時の少なくとも一方で停電予告信号がONであるかを判定し、停電予告信号が継続的に出力され
ている期間をカウントし、カウント結果が所定値となった場合に停電が発生していると判定してもよい。
First, the
停電予告信号がONでない場合、正常に電源が供給されているので、乱数更新処理2を実行する(ステップS2311)。乱数更新処理2は、図195で説明したものと同じでよく、主として特別抽選や普通抽選において当選判定を行うための乱数以外の乱数を更新する。
If the power failure warning signal is not ON, the power is normally supplied, so random
一方、停電予告信号を検出した場合、電源断時処理(ステップS2312~S2319)を実行する。電源断時処理では、停電発生前の状態に復帰させるためのデータをバックアップする処理を実行する。具体的には、まず、割込みを禁止する(ステップS2312)。これにより後述するタイマ割込み処理が行われなくなる。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、出力ポートをクリアして、各ポートからの出力によって制御される機器の動作を停止する(ステップS2313)。具体的には、ソレノイド・停電クリア・ACK出力ポートに停電クリア信号OFFビットデータを出力する。なお、全ての出力ポートがクリアされなくてもよく、例えば、電力消費が大きいソレノイドやモータを制御するための出力ポートをクリアしてもよい。これらの出力ポートをクリアすることによって、主基板側電源断時処理が終了するまでの消費電力を低減し、主基板側電源断時処理を確実に終了できるようにする。
On the other hand, when a power failure warning signal is detected, power failure processing (steps S2312 to S2319) is executed. In the power failure process, a process of backing up data for returning to the state before the power failure occurred is executed. Specifically, first, the interrupt is prohibited (step S2312). As a result, timer interrupt processing, which will be described later, is not performed. Furthermore, the
その後、フラグレジスタを遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避し(ステップS2314)、電源OFF時処理を実行して、電源が遮断される前に必要な処理を実行する(ステップS2315)。電源OFF時処理の詳細は図222で後述する。そして、遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2316)。 After that, the flag register is saved in the stack area within the game area (step S2314), the power OFF processing is executed, and necessary processing is executed before the power is cut off (step S2315). The details of the power-off processing will be described later with reference to FIG. Then, the flag register saved in the game area stack area is restored (step S2316).
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、バックアップされるワークエリアに格納されたデータが正常に保持されたか否かを判定するための、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内のワークエリアのチェックサムを計算し、主制御RAM1312の所定のチェックサム格納エリアに記憶する(ステップS2317)。このチェックサムはワークエリアにバックアップされたデータが正常かの判定に使用される。なお、チェックサムが算出される対象の領域は、遊技制御領域内のワークエリアのうち、電源投入後主制御側メイン処理の実行までの間に変更される可能性がある設定状態管理(設定値と設定状態管理エリアの値)や、バックアップフラグや、チェックサムエリアの値を除外するとよい。
Subsequently, the
さらに、停電フラグとしてバックアップフラグエリアに正常に電源断時処理が実行されたことを示す値(5AH)を格納する(ステップS2318)。これにより、遊技バックアップ情報の記憶が完了する。最後に、RAMプロテクト有効(書き込み禁止)、禁止領域の無効をRAMプロテクトレジスタに書き込み、主制御RAM1312の所定の領域への書き込みを禁止し(ステップS2319)、停電から復旧するまでの間、待機する(無限ループ)。主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の使用領域を指定することによって、指定領域以外の禁止領域へアクセスがあった場合には、異常と判定してリセットする機能を有する。このため、RAMプロテクトレジスタの禁止領域を無効に設定することで主制御RAM1312へのアクセスによるリセット機能が解除される(リセットされない)ようにして、全領域へのアクセスを可能とする。なお、主制御RAM1312のうち未使用領域を禁止領域に指定して、禁止領域を有効にして、指定された禁止領域にアクセスを検出した場合には、主制御MPU1311がリセットされるようにしてもよい。
Further, a value (5AH) indicating that the power failure processing has been normally executed is stored in the backup flag area as a power failure flag (step S2318). This completes the storage of the game backup information. Finally, write RAM protection valid (write prohibited) and prohibited area invalid to the RAM protect register, prohibit writing to a predetermined area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2319), and wait until recovery from power failure. (infinite loop). The
図222は、電源OFF時処理のフローチャートである。電源OFF時処理は、主制御側メイン処理(図221)のステップS2315において実行され、電源が遮断される前に必要な処理を実行する。 FIG. 222 is a flowchart of processing when the power is turned off. The power-off processing is executed in step S2315 of the main control-side main processing (FIG. 221), and executes necessary processing before the power is turned off.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のSP退避用バッファにスタックポインタの値を格納し(ステップS2320)、遊技領域外スタックポインタ値をスタックポインタに設定し(ステップS2321)、全てのレジスタ値を遊技領域外のレジスタ退避用バッファに格納する(ステップS2322)。
First, the
続いて、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のチェックサムを算出し、主制御RAM1312の遊技領域外チェックサム格納エリアに格納する(ステップS2323)。その後、パワーダウンチェックエリア(EX_PDIND)に5AHを設定し、主制御RAM1312のうち遊技領域外のRAMエリアが初期化済みであることを記録する(ステップS2324)。パワーダウンチェックエリアに5AHが記録されている場合、停電処理が正常に実行されている。この意味において、パワーダウンチェックエリアと遊技制御領域内のRAMのバックアップフラグとは実質的に同じである。停電処理が正常に実行されているので、既に主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の領域については正常であると判定されており、結果としてパワーダウンチェックエリアに5AHが設定されていれば、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の領域の初期化が完了している。
Subsequently, the checksum outside the game control area of the
このように、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、停電処理が正常に実行されたことを示す二種類のフラグが、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内と遊技制御領域外の各々に設けられている。これは、遊技制御領域内と遊技制御領域外とで二重に判定するためであり、また、遊技制御領域内と遊技制御領域外とで一つの記憶領域を共有していないことから、独立に処理することが望ましいからである。例えば、停電処理が正常に実行されたことを示すフラグが一つであると、誤って当該フラグに5AHがセットされて、停電処理を行なうことなく復帰すると、停電処理が正常に実行されたと誤って判定される。このように二重で判定することによって、誤判定の可能性を低減している。
Thus, in the
さらに、二つのフラグは、領域として離れた領域(例えば、アドレスの下位バイト(**00H~**FFH)又は上位バイト(00**H又は01**H)が重ならない領域)に設けることによって、ノイズなどの不具合によってデータが書き換えられても正しく復帰できるようになっている。 Furthermore, the two flags should be provided in separate areas (for example, areas where the lower bytes (**00H to **FFH) or the upper bytes (00**H or 01**H) of addresses do not overlap). Even if the data is rewritten due to a problem such as noise, it can be restored correctly.
そして、遊技領域外のレジスタ退避用バッファに退避した、呼出元の処理で使用するバンク(バンク0又はバンク1)の全レジスタ値を復帰し(ステップS2325)、遊技領域外のSP退避用バッファに退避したスタックポインタ値を復帰し(ステップS2326)、呼び出し元に戻る。
Then, all the register values of the bank (
図223は、主制御MPU1311が実行するタイマ割込み処理のフローチャートである。
FIG. 223 is a flowchart of timer interrupt processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンク選択フラグを1に設定し、レジスタのバンクを切り替える(ステップS2330)。なお、主制御MPU1311は、演算に使用するレジスタ群を二つ有し、一つはバンク0のレジスタ群として使用し、他はバンク1のレジスタ群として使用可能とされており、バンク切換を行わずに、両方のバンクのレジスタを使用できないように構成されている。主制御側メイン処理ではレジスタバンク0が使用され、タイマ割込み処理ではレジスタバンク1が使用される。このため、タイマ割込み処理の開始時にはバンクを1に切り替える命令を実行するが、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にはバンクを0切り替える命令を実行する必要がない。これは、主制御MPU1311は、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタ(例えば、Zフラグ、Cフラグがセットされているレジスタ)に記憶しており、フラグレジスタは、割込開始時にスタックエリアに退避され、RET命令の実行によってスタックエリアから復帰する。このため、RET命令を実行す
ることでフラグレジスタに記憶したレジスタのバンクフラグも元に戻る。なお、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタに記憶しない構成を採用した場合、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にバンク切替命令を実行して、バンク0に戻す。
First, the
なお、フラグレジスタには、割込可否を制御するフラグも記憶されているため、割り込み許可に設定してからRET命令を実行しなくてもよい。なお、割込可否を制御するフラグは、タイマ割込み処理の開始時に、フラグレジスタをスタックした後に割込禁止状態に設定される。このため、タイマ割込処理中に割込を許可(EI命令など)するか、RETI命令を実行しない限り、割込み許可状態にはならない。 Since the flag register also stores a flag for controlling whether or not to enable interrupts, it is not necessary to execute the RET instruction after enabling interrupts. It should be noted that the flag that controls whether or not to allow interrupts is set to the interrupt disabled state after the flag register is stacked at the start of timer interrupt processing. Therefore, unless an interrupt is permitted (EI instruction, etc.) or a RETI instruction is executed during timer interrupt processing, the interrupt enabled state is not entered.
次に、LEDコモンカウンタを+1更新する。なお、LEDコモンカウンタ値が上限を超える場合は0にする(ステップS2331)。 Next, the LED common counter is updated by +1. If the LED common counter value exceeds the upper limit, it is set to 0 (step S2331).
次に、スイッチ入力処理1を実行する(ステップS2332)。スイッチ入力処理1では、主制御MPU1311の各種入力ポートの入力端子に入力されている各種信号を読み取り、ONエッジを作成し、入力情報として主制御RAM1312の入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。
Next, switch
なお、ステップS2332のスイッチ入力処理1は入賞信号に関する処理であり、図191のステップS2080のスイッチ入力処理2は不正検出センサ(磁石センサ、電波センサ、振動センサ等)の入力に関する処理である。このため、設定変更モードや設定確認モードで実行されるタイマ割込み処理では、ステップS2335においてNOと判定されるので、入賞検出は行われるが、不正検出センサによる不正は検出されない。なお、入賞が検出されても、賞球の払出しや変動表示等は実行されない。設定変更操作や設定確認操作はホールの従業員が行うものであり、設定変更モードや設定確認モードでは不正が行われず、不正を検出しない方が望ましいと考えられるからである。例えば、設定変更や設定確認の操作は扉が開放された状態で行われるため、ヒンジ部材によって外枠2と接続された扉枠3及び本体枠4が揺れやすい状態となることから、振動センサが振動を誤検知する可能性がある。このため、設定変更モードや設定確認モードにおいて不正検出センサによる不正の検出を止めることによって、このような誤報知を防止できる。また、ホールの従業員が床に落ちている球を回収するための磁石を所持しており、設定変更や設定確認の操作時の従業員が保持している磁石の誤報知を防止できる。すなわち、本実施例のパチンコ機1は、不正検出を無効化(又は、制限、規制、抑制など)する手段を有し、通常の遊技処理に移行した後(例えば、電源投入時の初期設定処理の終了後)に、不正検出を有効化し、特定の遊技状態(例えば、設定処理中)においては、前記手段により不正検出を無効化(又は、制限、規制、抑制など)する。
Note that
なお、設定変更モードや設定確認モードでも、一部の不正検出センサ(例えば電波センサ)はスイッチ入力処理1で検出し、特定の種類の不正を監視してもよい。このようにすると、不正行為を行おうとする者(ゴト師)が電波を照射する等によって強制的に設定変更モードを起動する不正を検出できる。
Note that even in the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, some fraud detection sensors (for example, radio wave sensors) may detect in the
続いて、乱数更新処理1を実行する(ステップS2333)。乱数更新処理1では、大当り判定用乱数、大当り図柄用乱数、及び小当り図柄用乱数を更新する。またこれらの乱数に加えて、図221に示した主制御側メイン処理の乱数更新処理2で更新される大当り図柄決定用乱数及び小当り図柄決定用乱数の初期値を変更するための、それぞれの初期値決定用乱数を更新する。図223に示すタイマ割込み処理では、設定値を変更するための設定処理を実行する場合でも乱数を更新する。これは、当落を判定するハードウェア乱数は、設定変更や設定確認の処理中かにかかわらず更新されるため、ソフトウェアで生成する乱数も、ハードウェア乱数の起動と同じタイミングで更新する、すなわち、設定変更や
設定確認の処理中も更新することによって、ハードウェア乱数とソフトウェア乱数との不整合が生じにくく、遊技における演出の期待値や、特定の演出時に大当りが導出される期待値の設計値からの乖離を抑制できる。
Subsequently, random
その後、設定値確認処理(図215)を実行して、設定値が正常範囲内かを判定する(ステップS2334)。なお、設定値確認処理は、タイマ割込み処理において定期的に実行されるが、タイマ割込み処理において設定値確認処理を実行しなくても、変動開始時、遊技状態の切替時(例えば、大当り確率の切替時、大当り遊技の開始時や終了時、時短状態の開始時や終了時)、不正検出時(例えば、扉開放時、磁気検知時)などの特定の条件の成立を契機に行なうとよい。タイマ割込み処理の実行時のように短周期で定期的に判定しなくても、特定条件の成立時に判定すれば、主制御MPU1311のリソースの消費を抑制できる。
Thereafter, the set value confirmation process (FIG. 215) is executed to determine whether the set value is within the normal range (step S2334). The set value confirmation process is periodically executed in the timer interrupt process. When switching, at the start or end of a jackpot game, at the start or end of a time-saving state), at the time of fraud detection (for example, when the door is opened, when magnetism is detected). Even if the determination is not performed regularly in a short period as in the execution of timer interrupt processing, the resource consumption of the
そして、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2335)。設定値確認処理(ステップS2334、図215)の後に設定状態管理エリアの値を確認することによって、設定値が異常と判定されたときに、直後の設定状態管理エリアの値を確認(S2335)で通常遊技処理が実行されないように制御している。設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていれば、図191のステップS2080に進む。一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていなければ、LEDコモンポートをOFFにする(ステップS2336)。タイマ割込み処理の早い段階でLEDコモン信号をOFFにすることによって、LEDコモン信号がオンになるまでの時間、すなわちLEDの消灯時間を確保し、LEDの表示切替前後の表示が混ざって見えるゴースト現象を抑制し、LEDのちらつきを防止している。 Then, it is determined whether or not a value (00H) indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2335). By checking the value of the setting status management area after the setting value checking process (step S2334, FIG. 215), if the setting value is determined to be abnormal, the value of the setting status management area can be checked immediately after (S2335). It is controlled so that normal game processing is not executed. If a value indicating game start is recorded in the setting state management area, the process proceeds to step S2080 in FIG. On the other hand, if the value indicating the game start is not recorded in the setting state management area, the LED common port is turned off (step S2336). By turning off the LED common signal at an early stage of the timer interrupt processing, the time until the LED common signal turns on, that is, the LED extinguishing time is secured, and the ghost phenomenon in which the display before and after the LED display switching appears mixed. to prevent flickering of the LED.
その後、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力し(ステップS2337)、フラグレジスタを遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避する(ステップS2338)。そして、試験信号出力処理を実行して、試験信号を出力する(ステップS2339)。そして、フラグレジスタを遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避する(ステップS2340)。試験信号を出力するための処理の実行の開始前後において、他の遊技領域外処理と同様にスタックポインタ、レジスタを退避し、処理終了後に復帰している。試験信号処理は、遊技の進行を制御するものではないことから、遊技制御領域外の処理として実行している。なお、試験信号処理を、遊技制御領域内の処理として実行しても遊技に影響を及ぼさなければ、遊技制御領域内の処理として実行してもよい。試験信号処理を遊技制御領域内の処理として実行する場合、試験信号出力処理(ステップS2339)の前後で実行されるフラグレジスタの退避及び復帰(ステップS2337、S2340)が不要となる。 Thereafter, a security signal is output from the external terminal board 784 (step S2337), and the flag register is saved in the stack area within the game area (step S2338). Then, the test signal output process is executed to output the test signal (step S2339). Then, the flag register is saved in the game area stack area (step S2340). Before and after the execution of the processing for outputting the test signal is started, the stack pointer and the register are saved in the same manner as other processing outside the game area, and are restored after the processing is completed. Since the test signal processing does not control the progress of the game, it is executed as processing outside the game control area. In addition, if the test signal processing is executed as processing within the game control area and does not affect the game, it may be executed as processing within the game control area. When the test signal processing is executed as processing within the game control area, saving and restoring the flag register (steps S2337, S2340) executed before and after the test signal output processing (step S2339) becomes unnecessary.
そして、設定処理を実行する(ステップS2341)。設定処理の詳細は図224で後述する。 Then, setting processing is executed (step S2341). Details of the setting process will be described later with reference to FIG.
その後、設定表示処理を実行する(ステップS2342)。設定表示処理の詳細は図225で後述する。 Thereafter, setting display processing is executed (step S2342). Details of the setting display processing will be described later with reference to FIG.
さらに、送信情報記憶領域の値をシリアル通信回路に出力する周辺基板コマンド送信処理を実行する(ステップS2343)。送信情報記憶領域は、生成された送信コマンドを一時的に格納する記憶領域である。送信情報記憶領域に格納された値(コマンド)は、ステップ2070で読み出されてシリアル通信回路(SIO)の送信情報記憶領域に格納される。シリアル通信回路は、複数バイトのFIFO形式の送信情報記憶領域を有する。この送信情報記憶領域には、コマンド生成毎に生成されたコマンドが格納され、送信情報記憶領域に格納された値(コマンド)を、順次、周辺制御基板1510に送信する。なお、コマンド生成毎に、シリアル通信回路のFIFO形式の送信情報記憶領域に、生成された
コマンドを直接格納してもよい。
Further, peripheral board command transmission processing for outputting the value of the transmission information storage area to the serial communication circuit is executed (step S2343). The transmission information storage area is a storage area that temporarily stores the generated transmission command. The value (command) stored in the transmission information storage area is read at step 2070 and stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit (SIO). The serial communication circuit has a multi-byte FIFO format transmission information storage area. This transmission information storage area stores a command generated each time a command is generated, and the values (commands) stored in the transmission information storage area are sequentially transmitted to the peripheral control board 1510 . It should be noted that each time a command is generated, the generated command may be directly stored in the FIFO format transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit.
その後、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットして、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアする(ステップS2344)。なお、ウォッチドッグタイマは、単純クリアモードを使用しているので、1ワードをセットすることによってウォッチドッグタイマがクリアされる。その後、復帰命令(例えばRETI)によって、レジスタのバンクを切り替え(ステップS2345)、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。 Thereafter, a predetermined value (18H) is set in the watchdog timer clear register WCL to clear the watchdog timer (step S2344). Note that the watchdog timer uses a simple clear mode, so setting one word clears the watchdog timer. Thereafter, a return instruction (for example, RETI) switches the bank of the register (step S2345), and returns to the processing before the interrupt.
ステップS2335で設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていると判定された後の処理は、図191で前述した処理と同じである。ステップS2091で、出力データ設定処理を実行した後、図223のステップS2343に進む。 The processing after it is determined in step S2335 that the value indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area is the same as the processing described above with reference to FIG. After executing the output data setting process in step S2091, the process proceeds to step S2343 in FIG.
図224は、設定処理のフローチャートである。設定処理は、設定状態管理エリアが通常遊技状態を示す値(00H)ではない場合に、タイマ割込み処理(図223)のステップS2341において実行され、主に設定値を変更する処理を実行する。 FIG. 224 is a flowchart of setting processing. The setting process is executed in step S2341 of the timer interrupt process (FIG. 223) when the setting state management area does not indicate the normal game state (00H), and mainly executes the process of changing the set value.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(03H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2350)。設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていれば、電源投入時コマンドを作成し(ステップS2351)、呼出元の処理に戻る。
First, the
これにより、RAM異常の場合、RAM異常が解除されるまでRAM異常を示す電源投入時動作コマンド(A004H)がタイマ割込み毎に送信される。これは、RAM異常を示す電源投入時動作コマンドを1回しか送らないと、コマンドが欠落した場合にRAM異常再通知がされないことから、周辺制御基板1510が遊技機の状態を知ることができないためである。また、機能表示ユニット1400が全消灯なので、周辺制御基板1510が遊技機の状態を知らないと、異常報知が行われなくなるため、遊技機の状態を外部から確認できなくなることを防ぐためである。また、RAM異常時には、遊技が行われないために、当該電源投入時動作コマンド以外のコマンドが周辺制御基板1510に送信されないために、RAM異常状態が継続する限り、電源投入時動作コマンドを繰り返し送信している。
As a result, in the case of a RAM abnormality, the power-on operation command (A004H) indicating the RAM abnormality is transmitted at each timer interrupt until the RAM abnormality is cleared. This is because if the power-on operation command indicating the RAM abnormality is sent only once, the RAM abnormality notification will not be sent again if the command is missing, so the peripheral control board 1510 cannot know the state of the gaming machine. is. Also, since the
すなわち、本実施例のパチンコ機は、同一系統のコマンド(例えば、電源投入時動作コマンド)において、所定の周期毎に実行される定期処理(タイマ割込み処理)の実行を契機として、所定回数(例えば、1回、2、3回などの少ない回数の複数回)だけ送信する第1のケースと、パチンコ機の動作中において、回数を制限することなく、所定の周期毎に繰り返し送信される第2のケースとを含み、前記第2のケースでは、周辺制御基板1510が正しく受信したか否かに関わらず、同一のコマンドが繰り返し送信され、通常遊技の停止時に他の遊技関連コマンドが送信されない状態でも送信されるコマンドである。 That is, the pachinko machine of the present embodiment is triggered by execution of regular processing (timer interrupt processing) that is executed every predetermined period in commands of the same system (for example, operation command at power-on), and executes a predetermined number of times (for example, , 1, 2, 3, etc.), and the second case, in which the number of times is not limited during operation of the pachinko machine and is repeatedly transmitted in a predetermined cycle. In the second case, the same command is repeatedly transmitted regardless of whether the peripheral control board 1510 has received it correctly, and other game-related commands are not transmitted when the normal game is stopped. is the command to be sent.
周辺制御基板1510は、RAM異常に関するコマンドを受信すると、RAM異常に関する報知を行なう。なお、RAM異常報知中に再度同じコマンドを受信しても、受信したRAM異常に関するコマンドを無効として、現在行われている報知を継続するとよい。後続するコマンドを無効とすることによって、例えば、音声による報知を最初から繰り返すことを防止でき、正常な報知ができる。 When peripheral control board 1510 receives a command regarding RAM abnormality, it notifies about RAM abnormality. Even if the same command is received again during the RAM abnormality notification, it is preferable to invalidate the received command regarding the RAM abnormality and continue the current notification. By invalidating the subsequent command, for example, it is possible to prevent the voice notification from being repeated from the beginning, and the normal notification can be performed.
RAM異常に関するコマンドは、常に同じでもよいが、送信されるタイミングによって異なってもよい。送信されるタイミングによってRAM異常に関するコマンドを変えることによって、コマンドの整合性を判定してもよい。例えば、電源投入時にRAM異常であるときに送信される電源投入時動作コマンド(A004H)と、通常のタイマ割込み時に
RAM異常であるときに送信される電源投入時動作コマンド(A005H)とすることによって、周辺制御基板1510は、電源投入時コマンド(A004H)の後に電源投入時コマンド(A005H)を受信すると、電源投入時のRAM異常が継続していると判定できる。一方、電源投入時コマンド(A004H)を受信せずに電源投入時コマンド(A005H)を受信すると、電源復帰後(例えば、通常遊技中)に主制御RAM1312に記録された設定値や設定状態管理エリアが異常になったと判定できる。このようにすると、判定される二つの状態の各々で、報知態様を異ならせることができる。例えば、電源投入時のRAM異常が継続している場合はRAM異常と報知し、電源復帰後にRAM異常が発生した場合は設定値異常と報知する等が可能となる。
Commands related to RAM abnormality may always be the same, but may differ depending on the timing of transmission. Command consistency may be determined by changing a command related to a RAM abnormality depending on the timing of transmission. For example, by setting the power-on operation command (A004H) that is transmitted when the RAM is abnormal when the power is turned on and the power-on operation command (A005H) that is transmitted when the RAM is abnormal during a normal timer interrupt. When the peripheral control board 1510 receives the power-on command (A005H) after the power-on command (A004H), it can determine that the RAM abnormality at power-on continues. On the other hand, when the power-on command (A005H) is received without receiving the power-on command (A004H), after the power is restored (for example, during normal play), the setting values recorded in the
なお、RAM異常報知中では、遊技者による設定調整機能(例えば、扉枠3に設けられたボタンの操作による音量や輝度の調整)を停止してもよい。これは、RAM異常報知中の遊技者による設定調整操作は、誤操作だと考えられるからである。具体的には、通常遊技状態を示す電源投入時動作コマンドを受信するまでは、遊技者による設定調整機能を停止するとよい。 It should be noted that while the RAM abnormality is being notified, the player's setting adjustment function (for example, adjustment of volume and brightness by operating buttons provided on the door frame 3) may be stopped. This is because the setting adjustment operation by the player during the RAM abnormality notification is considered to be an erroneous operation. Specifically, the setting adjustment function by the player may be stopped until the power-on operation command indicating the normal game state is received.
RAM異常と判定されると設定処理を繰り返し実行することになるため、特別図柄や普通図柄に関する処理が実行されず、遊技が全くできない状態になる。このRAM異常は、一旦電源を遮断して停電処理を実行後、電源を再投入する際に、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954とで設定変更モードを起動する操作をすることによって、設定変更状態となりRAM異常が解消される。そして、設定キー971を元に戻す操作によって設定変更モードが終了して通常遊技が開始可能となる。
When it is determined that the RAM is abnormal, the setting process is repeatedly executed, so that the process related to the special design and the normal design is not executed, and the game cannot be played at all. This RAM abnormality can be corrected by turning off the power once, executing power failure processing, and then, when turning on the power again, by operating the setting
また、電源を再投入する際に、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954とで設定変更モードを起動する以外の操作をした場合、設定状態管理エリアのRAM異常を示す値(03H)は維持され、RAM異常状態が継続し、通常遊技を開始できない。つまり、RAM異常を解消して通常遊技状態にするためには、必ず、設定変更モードを経由する必要がある。
When the power is turned on again, if an operation other than starting the setting change mode is performed with the setting
一方、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていなければ、設定キー971がOFF位置に戻ったかを判定する(ステップS2352)。具体的には、設定キー971のONからOFFへのエッジ、又は、ONからOFFへ変化してから所定期間経過したかを検出する。
On the other hand, if no value indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, it is determined whether the setting
設定キー971がOFF位置に戻ったと判定(設定変更又は設定確認の終了と判定)されると、セキュリティ信号出力タイマに出力時間を設定し(ステップS2353)、設定状態管理エリアを初期化して(ステップS2354)、図219に示す電源投入時設定処理を実行し(ステップS2355)、呼出元の処理に戻る。
When it is determined that the setting
設定変更モードを終了する操作(設定キー971をOFF)がされた場合、セキュリティ信号出力タイマに出力時間値を設定することによって、設定変更モードの終了後セキュリティ信号がOFFになるまでの遅延時間を設ける。このため、設定変更モードや設定確認モードが短時間(例えば、一度のタイマ割込み処理内)で終了しても、セキュリティ信号の最短の出力信号をセキュリティ信号出力タイマに出力時間値として設定した分だけ確保でき、ホールコンピュータが確実にセキュリティ信号を検出できる。 When an operation to terminate the setting change mode (turning off the setting key 971) is performed, by setting an output time value in the security signal output timer, the delay time until the security signal is turned off after the setting change mode is terminated can be set. prepare. Therefore, even if the setting change mode or setting confirmation mode ends in a short time (for example, within one timer interrupt process), the shortest output signal of the security signal is set to the security signal output timer as the output time value. This ensures that the hall computer can reliably detect the security signal.
また、セキュリティ信号がOFFになるまでの遅延時間中に不正を検出した場合、セキュリティ信号を維持したまま、新たに検出した不正に対応した期間又は時間分、セキュリティ信号を出力するとよい。 Further, when fraud is detected during the delay time until the security signal is turned off, it is preferable to output the security signal for a period or time corresponding to the newly detected fraud while maintaining the security signal.
さらに、セキュリティ信号がOFFになるまでの遅延時間中に停電が発生した場合、電源復帰時に通常遊技状態でホットスタートすると、残時間分のセキュリティ信号を出力し、RAMクリアスイッチの操作によるRAMクリア時又は設定変更によるRAMクリア時には、残時間分のセキュリティ信号を出力しない。これは、主制御RAM1312の初期化によって、セキュリティ信号出力タイマ値がリセットされ、当該主制御RAM1312の初期化に伴うセキュリティ信号の出力が開始するためである。
In addition, if a power failure occurs during the delay time until the security signal turns OFF, when the hot start is performed in the normal game state when the power is restored, the security signal for the remaining time is output, and when the RAM is cleared by operating the RAM clear switch Alternatively, when the RAM is cleared by setting change, the security signal for the remaining time is not output. This is because the security signal output timer value is reset by the initialization of the
セキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後に電源が投入されたときには、ホットスタート、RAMクリア、設定変更モード、設定確認モード、RAM異常状態継続の5パターンのいずれかになる。 When the power is turned on after a power failure occurs while the security signal is being output, one of five patterns of hot start, RAM clear, setting change mode, setting confirmation mode, and RAM abnormal state continuation occurs.
設定変更モード及び設定確認モードに移行した場合、起動されたモードが終了し、遅延時間が経過するまでセキュリティ信号が出力される。RAM異常状態が継続する場合、電源が復帰しても設定変更操作がされていないので、継続するRAM異常によるセキュリティ信号が出力される。設定変更モードまたは設定確認モードが終了し、遅延時間が経過する前に停電した場合、電源の復旧後にホットスタートの場合、残余時間分だけセキュリティ信号が出力される。 When shifting to the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, the activated mode ends and the security signal is output until the delay time elapses. If the RAM abnormality continues, a security signal is output due to the continued RAM abnormality because the setting change operation has not been performed even after the power is restored. If the setting change mode or setting confirmation mode ends and power failure occurs before the delay time elapses, or in the case of a hot start after the power is restored, the security signal is output for the remaining time.
セキュリティ信号を継続して出力する場合でも、電源投入時のパワーオンリセット信号によってセキュリティ信号の出力が停止し、所定時間(例えば、周辺制御基板1510の起動待ち時間中)の経過後にタイマ割込み処理に移行してからセキュリティ信号の出力が再開する。つまり、以下の場合においてセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後にセキュリティ信号を継続して出力するときでも、電源復帰後の所定の期間はセキュリティ信号の出力を停止する期間を設けている。
・不正検出などによるセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後、ホットスタートで電源が復帰する場合
・RAM異常によるセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後、電源が復帰して、RAM異常が継続する場合
・設定変更モードによるセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後、電源が復帰して、設定変更モードが継続する場合
・設定確認モードによるセキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後、電源が復帰して、設定確認モードが継続する場合
Even if the security signal is continuously output, the output of the security signal is stopped by the power-on reset signal when the power is turned on, and after a predetermined time (for example, during the startup wait time of the peripheral control board 1510), the timer interrupt process starts. After the transition, output of the security signal resumes. That is, in the following cases, even when the security signal is continuously output after a power failure occurs while the security signal is being output, there is provided a period during which the output of the security signal is stopped for a predetermined period after the power is restored.
・When the power is restored by hot start after a power failure occurs while security signals are being output due to fraud detection, etc. ・After a power failure occurs while security signals are being output due to a RAM error, the power is restored and the RAM error continues. - After a power failure occurs while security signals are being output in setting change mode, the power is restored and the setting change mode continues. and the setting confirmation mode continues
このように、セキュリティ信号出力中に停電が発生した後にセキュリティ信号を継続して出力するときでも、電源復帰後の所定の期間はセキュリティ信号の出力を停止することによって、ホールコンピュータ側でセキュリティ信号に異常があったのか、セキュリティ信号の出力に伴う状態が解除されたのかを判別できる。 In this way, even when the security signal is continuously output after a power failure occurs while the security signal is being output, the hall computer can respond to the security signal by stopping the output of the security signal for a predetermined period after the power is restored. It is possible to determine whether there is an abnormality or whether the state accompanying the output of the security signal has been released.
また、設定キー971のみが操作された設定確認モードでは、セキュリティ信号が出力される残時間にかかわらず、設定確認モードが終了するまでセキュリティ信号を出力し、設定確認モードが終了して遅延時間が経過した後にセキュリティ信号の出力を停止する。また、設定キー971及びRAMクリアスイッチ954が操作された設定変更モードでも設定確認モードと同様の処理を行うとよい。
In the setting confirmation mode in which only the setting
一方、ステップS2352で、設定キー971がOFF位置に戻っていないと判定されると、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更を示す値(02H)が記録されているかを判定し(ステップS2356)、設定変更モードであると判定された場合には、設定変更スイッチ972が操作されたかを判定する(ステップS2357)。なお、設定変更スイッチ972は、RAMクリアスイッチ954と兼用される構成でもよい。その結果、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更を示す値が記録されており、かつ、設定変更スイッチ972が操作され
たと判定されると、設定値を+1更新する(ステップS2358)。なお、設定値が上限6を超える場合は0にする(ステップS2359、S2360)。その後、呼出元の処理に戻る。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S2352 that the setting
一方、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更を示す値が記録されておらず(つまり、設定確認モードであり)、又は、設定変更スイッチ972が操作されていないと判定されると、設定値を更新せずに、呼出元の処理に戻る。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the value indicating the setting change is not recorded in the setting state management area (that is, the setting confirmation mode is set) or the setting
なお、設定変更スイッチ972の操作を判定する際(直前又は直後に)、設定キー971がONに操作されているかを判定してもよい。このように、設定変更スイッチ972の操作時に設定キー971の操作を判定すると、停電発生時に設定変更モードであり、停電復帰時に設定キー971がONに操作されていなくても、設定変更スイッチ972の操作によって設定変更が可能となることを防止できる。
When determining whether the setting
図225は、主制御MPU1311が実行する設定表示処理のフローチャートである。設定表示処理は、設定状態管理エリアが通常遊技状態を示す値(00H)ではない場合に、タイマ割込み処理(図223)のステップS2342において実行され、設定値を表示する処理を実行する。
FIG. 225 is a flowchart of setting display processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、LEDセグメントポートをクリアする(ステップS2370)。
First, the
そして設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(03H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2371)。設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていなければ、現在の設定値がベース表示器1317に表示されるようにLEDのセグメント端子の出力を設定する(ステップS2372)。一方、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値が記録されていれば、エラーがベース表示器1317に表示されるように、LEDのセグメント端子の出力を設定する(ステップS2373)。 Then, it is determined whether a value (03H) indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2371). If no value indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, the output of the segment terminal of the LED is set so that the current setting value is displayed on the base display 1317 (step S2372). On the other hand, if a value indicating RAM abnormality is recorded in the setting state management area, the output of the segment terminal of the LED is set so that the error is displayed on the base display 1317 (step S2373).
その後、LEDコモンカウンタに対応したLEDコモン信号を出力し(ステップS2374)、設定値又はエラー表示に対応する表示データ(セグメント信号)をベース表示器1317に出力するようドライバを駆動し(ステップS2375)、呼出元の処理に戻る。 After that, an LED common signal corresponding to the LED common counter is output (step S2374), and the driver is driven to output display data (segment signal) corresponding to the set value or error display to the base display 1317 (step S2375). , return to the calling process.
[12-18.設定変更・確認処理の別例3]
次に、設定変更機能を有するパチンコ機の別な実施例について説明する。以下に説明する別例3では、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理が通常遊技用のタイマ割込み処理と別に設けられている点が、前述した別例2との主な相違点である。以下に説明する以外の処理は、前述した別例2と同じである。
[12-18. Another example 3 of setting change/confirmation process]
Next, another embodiment of a pachinko machine having a setting change function will be described. In another example 3 described below, the main difference from the above-described example 2 is that timer interrupt processing for setting change processing is provided separately from timer interrupt processing for normal games. Processes other than those described below are the same as those of Example 2 described above.
なお、別例3では、別例2と同様に、設定変更スイッチ972を設けずに、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作によって設定値が選択できるものであるが、RAMクリアスイッチ954の本来の主制御RAM1312の初期化機能と、設定変更機能とを区別して記載するために、設定値の変更にかかる操作については設定変更スイッチ972として説明することがある。
In addition, in Example 3, as in Example 2, the setting value can be selected by operating the RAM
図226、図227は、電源投入時に主制御MPU1311が実行する電源投入時処理のフローチャートである。
226 and 227 are flowcharts of power-on processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、電源の投入により、リセット信号が解除されるとプロ
グラムコードの開始番地である8000番地から処理を開始する。主制御RAM1312のプロテクト無効及び禁止領域無効をRAMプロテクトレジスタに設定する(ステップS2400)。主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の使用領域を指定することによって、指定領域以外の禁止領域へアクセスがあった場合には、異常と判定してリセットする機能を有する。本別例3においては、主制御RAM1312の禁止領域へのアクセスによるリセット機能を解除するために、禁止領域を無効に設定することで主制御RAM1312の全領域へのアクセスを可能としている。なお、主制御RAM1312のうち未使用領域を禁止領域に指定して、禁止領域を有効にして、指定された禁止領域にアクセスを検出した場合には、主制御MPU1311がリセットされるようにしてもよい。
First, the
すなわち、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作された状態で電源が投入された場合には、直ちに主制御RAM1312の所定の領域を初期化している。しかし、チェックサムが不一致の場合や、バックアップフラグが正常に設定されていない場合には、RAM異常として遊技機の機能を停止して、遊技ができない状態にした後に、設定変更操作が行なわれないと、主制御RAM1312は初期化されず、遊技も実行されないように制御している。
That is, in the
このため、RAMプロテクトレジスタの禁止領域を有効に設定した場合、誤動作や不具合などによるRAMの禁止領域への誤ったアクセスによってリセットが発生し、主制御MPU1311が電源投入時処理を実行した際に、停電処理が実行されておらず、チェックサムが計算されず、バックアップフラグが設定されていないために、RAM異常と判定される。RAM異常と判定されるとRAMクリア処理によって遊技が初期化されるだけでなく、ホールの従業員によるRAM異常解除操作(設定変更操作)がされない限り、遊技を再開できないため、RAMプロテクトレジスタの禁止領域の設定としては「無効」とするのが望ましい。 Therefore, if the prohibited area of the RAM protection register is set to valid, a reset occurs due to erroneous access to the prohibited area of the RAM due to a malfunction or defect. Since the power failure process has not been executed, the checksum has not been calculated, and the backup flag has not been set, it is determined that the RAM is abnormal. If it is determined that there is a RAM abnormality, not only is the game initialized by RAM clearing processing, but the game cannot be restarted unless the hall employee performs a RAM abnormality cancellation operation (setting change operation), so the RAM protect register is prohibited. It is desirable to set the area to "disabled".
なお、禁止領域を有効に設定してもよい。禁止領域を有効に設定することによって、不正等で主制御RAM1312の禁止領域へのアクセスがあった場合に、ホールの店員によるRAM異常解除操作(設定変更操作)がされない限り、遊技を再開できないことから、、不正行為に対する耐性を向上できる。
Note that the prohibited area may be set valid. By setting the prohibited area to valid, if the prohibited area of the
次に、所定時間の単純クリアモードタイマをウォッチドッグタイマに設定し(ステップS2401)、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアする(ステップS2402)。その後、停電クリア信号をONに設定し(ステップS2403)、停電クリア信号をOFFに設定する(ステップS2404)。これは、停電クリア信号をONに設定してから、OFFに設定することによって、ラッチに記憶された停電予告信号を正常な状態(停電ではない状態)に設定できる。 Next, a simple clear mode timer of a predetermined time is set in the watchdog timer (step S2401), and the watchdog timer is cleared (step S2402). After that, the power failure clear signal is set to ON (step S2403), and the power failure clear signal is set to OFF (step S2404). By setting the power failure clear signal to ON and then to OFF, the power failure warning signal stored in the latch can be set to a normal state (not a power failure state).
次に、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954の信号のレベルをPFポートから読み出し、レジスタに記憶する(ステップS2405)。RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971が操作されているか否かの判定は、周辺制御基板1510が確実に起動した後に主制御MPU1311が行うため、周辺制御基板1510が起動するまでの待機中に、ホールの従業員がRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作を誤って中断すると、ホールの従業員が意図していない状態でRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971が判定されてしまう。このため、電源投入時処理開始後の早い段階でRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の入力状態(レベル)を一時的な記憶手段であるレジスタ等に格納し、周辺制御基板1510の待機状態の終了後に一時的な記憶手段であるレジスタ等に格納したRAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971の状態を判定することによって、ホールの従業員が電源投入後の早い段階でキー操作を誤って中断しても、電源投入操作時のRAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971の操作を確実に検出する。
Next, the signal levels of the setting
その後、停電予告信号が停電中であるかを判定する(ステップS2406)。停電予告信号が検出されていれば、パチンコ機の電源電圧が正常ではないので、ステップS2406で電源電圧が安定するまで待機する。ステップS2406のループでは、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアしないため、停電が解除されなければウォッチドッグタイマがリセットを発生する。このウォッチドッグタイマによるリセットでは、システムリセットのようにセキュリティチェックを実行することなく直ちにスタートアドレスからプログラムを開始し、電源投入時処理が実行される。このため、ステップS2406のループにおいて停電予告信号が解除されない限り、ループから抜け出さない。 After that, it is determined whether or not the power failure warning signal indicates power failure (step S2406). If the power failure warning signal is detected, the power supply voltage of the pachinko machine is not normal, so the system waits until the power supply voltage stabilizes in step S2406. Since the watchdog timer is not cleared in the loop of step S2406, the watchdog timer is reset unless the power failure is canceled. This reset by the watchdog timer immediately starts the program from the start address without executing a security check like the system reset, and executes the power-on processing. Therefore, the loop of step S2406 is not exited unless the blackout warning signal is canceled.
このように、停電予告信号を検出する停電判定処理が、一つ目は電源投入時処理中のステップS2406、S2408で、二つ目は通常遊技中の主制御側メイン処理のステップS2450で、2箇所で実行している。後者(ステップS2450)では、停電を検出することでステップS2462以後の停電処理を実行するが、前者(ステップS2406、2408)では、停電を検出しても停電処理を実行しない。なお、ループの期間は、チェックサムの値とバックアップフラグの値が維持されるために、停電処理を実行しなくても、停電発生時の状態に正しく復帰できる。 In this way, the power failure determination process for detecting the power failure warning signal is performed in steps S2406 and S2408 during the power-on process, and in step S2450 of the main control side main process during the normal game. running in place. In the latter (step S2450), power failure processing is executed after step S2462 by detecting a power failure, but in the former (steps S2406 and 2408), power failure processing is not performed even if a power failure is detected. Since the checksum value and the backup flag value are maintained during the loop period, the state at the time of the power failure can be restored correctly without executing power failure processing.
なお、本実施例のパチンコ機1におけるリセットは、リセット回路によって発生するシステムリセットと、ウォッチドッグタイマや遊技制御RAM1312の指定領域外のアクセスによって発生するユーザリセットがある。システムリセットでは、数百ミリ秒のセキュリティチェックが実行された後にプログラムが起動するが、ユーザリセットでは、リセットの解除時にセキュリティチェックを実行することなく直ちにプログラムを起動する。
The reset in the
このため、例えば、通常の遊技処理中にウォッチドッグタイマによりリセットが発生すると、停電処理が実行されず、チェックサムが計算されず、かつバックアップフラグが設定されていないために、RAM異常と判定される。RAM異常と判定されるとRAMクリア処理によって遊技状態が初期化され、ホールの店員によるRAM異常解除操作(設定変更操作)が行われない限り遊技を再開できない。一方、電源投入時処理中のステップS2406、S2408において、ウォッチドッグタイマによってリセットが発生しても、ホールの店員によるRAM異常解除操作(設定変更操作)が行われずに、停電発生時の状態に正しく復帰できる。 Therefore, for example, if a watchdog timer resets during normal game processing, the power failure processing is not executed, the checksum is not calculated, and the backup flag is not set, so it is determined that the RAM is abnormal. be. When it is determined that the RAM is abnormal, the game state is initialized by RAM clear processing, and the game cannot be restarted unless the hall clerk performs a RAM abnormality release operation (setting change operation). On the other hand, in steps S2406 and S2408 during power-on processing, even if a reset occurs due to the watchdog timer, the hall clerk does not perform the RAM abnormality cancellation operation (setting change operation), and the state at the time of the power failure is correctly restored. can return.
このように、ウォッチドッグタイマにより発生したリセットについて、パチンコ機1を再起動するためにRAM異常を解除するための設定変更操作を必要とする場合と必要とない場合とを設けたのは、通常時遊技中にウォッチドッグタイマによるリセットの発生は、ソフト的な不具合が発生したときであり、主制御RAM1312に格納されたデータが破壊されており、停電発生時の遊技状態と違う内容が記憶されている可能性が高いため、主制御RAM1312を初期化することが望ましい。一方、電源投入時処理でウォッチドッグタイマによるリセットの発生は、ハード的な不具合が発生したときであり、主制御RAM1312に格納されたデータが破壊される可能性は低いため、主制御RAM1312を初期化する必要性が低いからである。
Thus, regarding the reset generated by the watchdog timer, the setting change operation for canceling the RAM abnormality is required in order to restart the
以上にウォッチドッグタイマにより発生するリセットについて説明したが、ウォッチドッグタイマにより発生するリセットの他の種類のユーザリセットでも同様な処理が行われる。すなわち、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、複数のリセットの要因があり、そのうちの一つのリセット要因に伴って発生するリセット(例えば、ウォッチドッグタイマによるユーザーリセット)によって前述した処理が実行され得る。
Although the reset generated by the watchdog timer has been described above, similar processing is performed for other types of user resets than the reset generated by the watchdog timer. That is, the
その後、サブ起動待ちタイマ(例えば約2秒)を開始し、当該タイマがタイムアップす
るまでの間ウォッチドッグタイマを継続的にクリアし、周辺制御基板1510の起動を待つ(ステップS2407)。周辺制御基板1510の起動待ちは、設定値を判定した後でなくても、電源投入後から周辺制御基板1510に最初にコマンドを送信するまでの期間であればいつでもよい。
Thereafter, a sub activation wait timer (for example, about 2 seconds) is started, the watchdog timer is continuously cleared until the timer times out, and activation of the peripheral control board 1510 is waited for (step S2407). Waiting for activation of the peripheral control board 1510 may be any period from when the power is turned on until the first command is sent to the peripheral control board 1510, even if it is not after the setting value is determined.
その後、停電予告信号が停電中であるかを再度判定する(ステップS2408)。停電予告信号が検出されていれば、パチンコ機1の電源電圧が異常なので、ステップS2408で待機する。なお、停電予告信号が停電中であるかの判定は、ステップS2406とS2408の両方で判定しなくても、いずれか一方で判定してもよい。
After that, it is determined again whether the power failure warning signal indicates power failure (step S2408). If the power failure warning signal is detected, the power supply voltage of the
その後、図215に示す設定値確認処理を実行して、設定値が正常範囲内かを判定する(ステップS2409)。 After that, the setting value confirmation process shown in FIG. 215 is executed to determine whether the setting value is within the normal range (step S2409).
その後、フラグレジスタを遊技制御領域内スタックエリアに退避し(ステップS2410)、図216に示す電源投入時遊技領域外RAM確認処理を実行して、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外の異常を判定する(ステップS2411)。そして、遊技制御領域内スタックエリアに退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2412)。 Thereafter, the flag register is saved in the stack area within the game control area (step S2410), and the power-on time RAM confirmation process outside the game area shown in FIG. (Step S2411). Then, the flag register saved in the stack area within the game control area is restored (step S2412).
その後、RAM異常判定結果値をCレジスタに仮設定し(ステップS2413)、設定状態管理エリアにおけるRAM異常値(03H)をBレジスタに仮設定する(ステップS2414)。 Thereafter, the RAM abnormality determination result value is temporarily set in the C register (step S2413), and the RAM abnormality value (03H) in the setting state management area is temporarily set in the B register (step S2414).
別例3において設定状態管理エリアに設定される値は、前述した実施例において図201(B)に示したものと異なり、図220(A)に示すように、主制御RAM1312に異常があれば03Hが記録される。すなわち、別例3の設定状態管理エリアは、パチンコ機1の動作モードが記録される1バイトの記憶領域であり、例えば下位の4ビットが使用され、上位の4ビットは定義されていない。具体的には、通常遊技状態では00H、設定確認モードでは01H、設定変更モードでは02H、主制御RAM1312に異常があれば03Hが記録される。
The value set in the setting state management area in Example 3 differs from that shown in FIG. 201(B) in the above-described embodiment. 03H is recorded. That is, the setting state management area of example 3 is a 1-byte storage area in which the operation mode of the
設定状態管理エリアは、RAMクリアスイッチ954のみの操作によるRAMクリア処理では00Hに更新されず、現在の値が維持される。また、設定確認モードの終了時には01Hから00Hに更新され、設定変更モードの終了時には02Hから00Hに更新される。さらに、主制御RAM1312が異常である場合、次の電源投入時の設定変更操作によって設定変更モードになると03Hから02Hに更新され、設定変更モードの終了時に02Hから00Hに更新される。
The setting state management area is not updated to 00H by the RAM clearing process by operating only the RAM
さらに、主制御RAM1312に異常があるかを判定する(ステップS2415、S2416)。具体的には、前回の電源遮断時に内蔵RAM1312にバックアップされている領域のうち遊技制御領域として使用されているデータ(スタックに退避されたデータは除く)から算出して記憶されたチェックサムと、同じ領域を使用して算出されたチェックサムとを比較し、両者が異なれば、主制御RAM1312に異常があると判定する。また、正常にバックアップされた(電源断時処理が正常に実行された)ことを示す停電フラグの値がバックアップフラグエリアに格納されていなければ、停電発生時に主制御RAM1312のデータが正常にバックアップされておらず(電源断時処理が正常に実行されておらず)、主制御RAM1312に異常があると判定する。
Further, it is determined whether or not there is an abnormality in the main control RAM 1312 (steps S2415 and S2416). Specifically, the checksum calculated and stored from the data used as the game control area (excluding the data saved in the stack) among the areas backed up in the built-in
そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外のいずれかに異常があれば、ステップS2419に進む。一方、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外のいずれにも異常がなければ、RAM正常判定結果値をCレジスタに仮
設定し(ステップS2417)、設定状態管理エリアの情報をBレジスタに設定して(ステップS2418)、ステップ2219に進む。これにより、Cレジスタには、主制御RAM1312が異常か否かの判定結果が設定されるため、以降の処理で「RAM異常」「電断前の遊技状態」の判定として、RAM異常を判定する処理(チェックサム、バックアップフラグの一致を判定する処理)を再度実行する必要がなく、プログラムのサイズを小さくできる。
Then, if there is an abnormality in either the game control area of the
また、Bレジスタには、停電発生時の設定状態管理エリアの値又は電源復帰時の主制御RAM1312の判定結果(RAM異常値)が設定され、ステップS2419で設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常値を仮設定することで、不要な処理を削除でき、プログラムのサイズを小さくできる。例えば、ステップS2419で設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常値を仮設定しなければ、ステップS2423やS2424の各判定でYESと判定されたとき、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常値を設定して、ステップS2436へのJUMP命令を実行する必要がある。しかし、ステップS2419で既に設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常値が仮設定されているため、ステップS2423の判定時にJUMP先としてS2436を指定することによって、以下に例示するソースコード例に示すように、JUMP命令を減少できる。
In addition, in the B register, the value of the setting state management area at the time of power failure or the determination result (RAM abnormal value) of the
ステップS2419でRAM異常値を仮設定しない場合のソースコード例
AND A,30H ;S2420
CP A,30H ;S2421(bit5:設定キー,bit4:RAMクリアSWとした場合)
JR Z,RESET_P_6 ;
CP B,02H ;S2422
JR Z,RESET_P_6 ;
CP C,00H ;S2423
JR Z,$111 ;
$000:
LD W,03H ;S2419相当
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
JR S2436 ;S2436へのジャンプ命令
$111:
CP B,03H ;S2424
JR Z,$000 ;
XOR W,W ;S2425
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
Source code example when RAM abnormal value is not temporarily set in step S2419
AND A,30H ;S2420
CP A,30H ;S2421 (bit5: setting key, bit4: RAM clear SW)
JR Z, RESET_P_6 ;
CP B,02H ;S2422
JR Z, RESET_P_6 ;
CP C,00H ;S2423
JR Z,$111 ;
$000:
LD W,03H ;Equivalent to S2419
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
JR S2436 ;Jump instruction to S2436
$111:
CP B,03H ;S2424
JR Z,$000 ;
XOR W,W ;S2425
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
ステップS2419でRAM異常値を仮設定する場合のソースコード例
LD W,03H ;S2419
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
AND A,30H ;S2420
CP A,30H ;S2421
JR Z,RESET_P_6 ;
CP B,02H ;S2422
JR Z,RESET_P_6 ;
CP C,00H ;S2423
JR NZ,S2436 ;
CP B,03H ;S2424
JR Z,S2436 ;
XOR W,W ;S2425
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
Example of source code when temporary setting of RAM abnormal value in step S2419
LD W,03H ;S2419
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
AND A,30H ;S2420
CP A,30H ;S2421
JR Z, RESET_P_6 ;
CP B,02H ;S2422
JR Z, RESET_P_6 ;
CP C,00H ;S2423
JR NZ,S2436 ;
CP B,03H ;S2424
JR Z,S2436 ;
XOR W,W ;S2425
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
その後、ステップS2419では、設定状態管理エリアにRAM異常を示す値(03H)を仮に記録する(ステップS2419)。 Thereafter, in step S2419, a value (03H) indicating RAM abnormality is temporarily recorded in the setting state management area (step S2419).
そして、PFポートの値が記録されたレジスタ値のうち、設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954のビットをマスクする(ステップS2420)。その後、電源投入時に設定キー971がONに操作されており、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2421)。そして、設定キー971がONに操作されており、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていれば、設定変更操作がされていると判定し、ステップS2430に進む。
Then, among the register values in which the values of the PF ports are recorded, the bits of the setting
一方、設定キー971が操作されておらず、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていなければ、停電発生時に設定変更モードであったかを判定する(ステップS2422)。例えば、ステップS2418で設定されたBレジスタの値が設定変更モード(02H)であるときに、設定変更モード中に停電が発生したと判定する。
On the other hand, if the setting
そして、設定変更モード中に停電が発生したと判定したときには、ステップS2430に進む。 Then, when it is determined that a power failure has occurred during the setting change mode, the process proceeds to step S2430.
一方、設定変更モード中に停電が発生していないと判定したときは、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外に異常があるかを判定する(ステップS2423)。例えば、前述したステップS2413でCレジスタに格納された判定結果を用いて、遊技制御領域内の異常を判定できる。その結果、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外のいずれかに異常があれば、ステップS2436に進む。 On the other hand, when it is determined that a power failure has not occurred during the setting change mode, it is determined whether there is an abnormality within the game control area and outside the game control area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2423). For example, using the determination result stored in the C register in step S2413 described above, it is possible to determine an abnormality in the game control area. As a result, if there is an abnormality either inside the game control area of the main control RAM 1312 or outside the game control area, the process proceeds to step S2436.
一方、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内及び遊技制御領域外のいずれにも異常がなければ、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したかを判定する(ステップS2424)。例えば、S2418でBレジスタに設定された設定状態管理エリアの値がRAM異常を示す値(03H)であれば、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したと判定する。
On the other hand, if there is no abnormality in the game control area and outside the game control area of the
そして、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生したと判定したときには、ステップS2436に進む。一方、RAM異常処理中に停電が発生していないと判定したときには、設定状態管理エリアに通常遊技状態を示す値(00H)を記録する(ステップS2425)。ステップS2425で設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録することによって、ステップS2419で設定状態管理エリアに仮に記録されたRAM異常を示す値(03H)から、仮設定値として00Hに再設定される。また、ステップS2425で設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録することによって、ステップS2426とS2431とからステップS2435にジャンプした際の設定状態管理エリアの値が異なる。このため、通常のRAMクリア処理と設定変更処理に伴うRAMクリア処理とで設定状態管理エリアの値が異なることから、両方のRAMクリア処理のためのプログラムを共通にしても、呼出元を区別でき、別個にプログラムを設ける必要がなく、プログラムサイズを小さくできる。 Then, when it is determined that a power failure has occurred during the RAM abnormality processing, the process proceeds to step S2436. On the other hand, when it is determined that a power failure has not occurred during the RAM abnormality processing, a value (00H) indicating the normal game state is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2425). By recording 00H in the setting state management area in step S2425, the value (03H) indicating the RAM abnormality temporarily recorded in the setting state management area in step S2419 is reset to 00H as a temporary setting value. Also, by recording 00H in the setting state management area in step S2425, the values in the setting state management area differ when jumping from steps S2426 and S2431 to step S2435. Therefore, since the values in the setting state management area are different between the normal RAM clearing process and the RAM clearing process associated with the setting change process, even if the same program is used for both RAM clearing processes, the calling source cannot be distinguished. , there is no need to provide a separate program, and the program size can be reduced.
以下に例示するソースコード例に示すように、ステップS2425のタイミングでは、設定状態管理エリアに01H又は00Hのいずれが記録されるかが決定していない。設定状態管理エリアには、決定時点で、決定した値を設定すべきだが、そうすると、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていると判定されたときのRAMクリア処理後に設定状態管理エリアに00Hを記録する処理が必要になる。このため、電源投入時処理と設定変更時のRAMクリア処理とで処理内容が異なるため、主制御RAM1312を初期化する処理以外の部分で、それぞれで専用の処理が必要になる。このため、主制御RAM1312を初期化する処理を設定変更時とRAMクリアスイッチ954のみが操作された時とで共通化するため、ステップS2425にて00Hを仮設定している。
As shown in the source code example exemplified below, at the timing of step S2425, it is not determined whether 01H or 00H is recorded in the setting state management area. The determined value should be set in the setting state management area at the time of determination, but in that case, 00H is set in the setting state management area after the RAM clearing process when it is determined that the RAM
ステップS2425で設定状態管理エリアに00Hを仮設定しない場合のソースコード例
CP A,10H ;S2426(AレジスタにPFポートの情報が記憶されている)
JR NZ,$000 ;(bit5:設定キー bit4:RAMクリアSW)
LD A,(JOTAI_BF) ;S2427
LD (POWER_BF),A ;
CP A,20H ;S2428
JR NZ,$111 ;
LD W,01H ;S2429
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
JR S2436 ;
$000:
XOR W,W ;S2425に相当
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
JR S2435 ;増加分
$111:
XOR W,W ;増加分
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;増加分
JR S2436 ;増加分
S2430:
LD W,02H ;S2430
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
・・・・・
S2435:
[RAMクリア処理] ;S2435
S2436:
[全コマンドバッファ初期化] ;S2436
Source code example when 00H is not provisionally set in the setting state management area in step S2425
CP A,10H ;S2426 (PF port information is stored in A register)
JR NZ,$000 ;(bit5: setting key bit4: RAM clear SW)
LD A,(JOTAI_BF) ;S2427
LD (POWER_BF),A ;
CP A,20H ;S2428
JR NZ,$111 ;
LD W,01H ;S2429
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
JR S2436;
$000:
XOR W,W ;Equivalent to S2425
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
JR S2435 ;increase
$111:
XOR W,W ;increment
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;increase
JR S2436 ;increase
S2430:
LD W,02H ;S2430
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
・・・・
S2435:
[RAM clear processing] ;S2435
S2436:
[Initialize all command buffers] ;S2436
ステップS2425で設定状態管理エリアに00Hを仮設定する場合のソースコード例
XOR W,W ;S2425
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
CP A,10H ;S2426
JR NZ,S2435 ;
LD A,(JOTAI_BF) ;S2427
LD (POWER_BF),A ;
CP A,20H ;S2428
JR Z,S2436 ;
LD W,01H ;
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
JR S2436 ;
S2430:
LD W,02H ;S2430
LD (VALID_PALY),W ;
・・・・・
S2435:
[RAMクリア処理] ;S2435
S2436:
[全コマンドバッファ初期化] ;S2436
Source code example when 00H is provisionally set in the setting state management area in step S2425
XOR W,W ;S2425
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
CP A,10H ;S2426
JR NZ,S2435 ;
LD A,(JOTAI_BF) ;S2427
LD (POWER_BF),A ;
CP A,20H ;S2428
JR Z,S2436 ;
LD W,01H ;
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
JR S2436;
S2430:
LD W,02H ;S2430
LD (VALID_PALY), W ;
・・・・
S2435:
[RAM clear processing] ;S2435
S2436:
[Initialize all command buffers] ;S2436
その後、電源投入時にRAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2426)。そして、RAMクリアスイッチ954がONに操作されていれば、ステップS2435に進む。
Thereafter, it is determined using the value stored in the register whether the RAM
本実施例のパチンコ機では、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作と設定キー971の操作と設定状態管理エリアに記録された値とに基づいて、処理を振り分ける。例えば、主制御RAM1312が異常であると判定されると、設定状態管理エリアには03Hが記録され、電源が遮断されるまで03Hが維持されるため、通常遊技処理を実行できない。このとき、一旦電源を遮断した後に設定変更操作をして電源を投入すると、RAM異常を解除できる。すなわち、ステップS2421で設定キー971とRAMクリアスイッチ954の両方が操作されている(設定変更操作)と判定されると、設定状態管理エリアがRAM異常を示す値(03H)から設定変更を示す値(02H)に更新され(ステップS2430)、RAM異常状態が終了する。このように、RAM異常からの復帰は、必ず設定変更を経由することになっている。換言すると、停電発生時の状態がRAM異常かを判定する前に、設定変更操作がされているかを判定するので、設定値の変更を契機としてのみRAM異常を解消できる。
In the pachinko machine of this embodiment, processing is distributed based on the operation of the RAM
なお、RAM異常と判定された場合に、遊技制御領域内の領域及び遊技制御領域外の領域のワークエリアとスタックエリアを初期化して遊技処理を開始してもよい。このようにすると、主制御RAM1312が異常であると判定されても自動的に通常遊技状態に復帰できる。
In addition, when it is determined that the RAM is abnormal, the work area and the stack area in the area within the game control area and the area outside the game control area may be initialized and the game process may be started. In this way, even if it is determined that the
また、RAM異常と判定された場合に、遊技を停止し、電源遮断後、電源復帰時に遊技制御領域内の領域及び遊技制御領域外の領域のワークエリアが正常であると判定されたときに、遊技制御領域内の領域及び遊技制御領域外の領域のワークエリアとスタックエリアを初期化して遊技処理を開始してもよい。このようにすると、電源スイッチのON/OFFの操作によって通常遊技状態に復帰できる。 Also, when it is determined that the RAM is abnormal, the game is stopped, and after the power is cut off, when the work area of the area within the game control area and the area outside the game control area is determined to be normal when the power is restored, The game processing may be started by initializing the work area and the stack area of the area within the game control area and the area outside the game control area. In this way, the normal game state can be restored by turning the power switch ON/OFF.
また、RAM異常と判定された場合に遊技を停止し、電源遮断後、電源復帰時に遊技制御領域内の領域及び遊技制御領域外の領域のワークエリアが正常であると判定され、かつ、RAMクリアスイッチが操作されているときに、遊技制御領域内の領域及び遊技制御領
域外の領域のワークエリアとスタックエリアを初期化して遊技処理を開始してもよい。このようにすると、電源遮断後のRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作によって通常遊技状態に復帰できる。
In addition, when it is determined that the RAM is abnormal, the game is stopped, and after the power is cut off, when the power is restored, it is determined that the work area in the area within the game control area and the area outside the game control area is normal, and the RAM is cleared. When the switch is operated, the work area and the stack area in the area inside the game control area and the area outside the game control area may be initialized and the game process may be started. By doing so, it is possible to return to the normal game state by operating the RAM
また、RAM異常と判定された場合に、遊技を停止し、電源遮断後、電源復帰時に遊技制御領域内の領域及び遊技制御領域外の領域のワークエリアが正常であると判定され、かつ、設定キー971が操作されているときに、遊技制御領域内の領域及び遊技制御領域外の領域のワークエリアとスタックエリアを初期化して遊技処理を開始してもよい。このようにすると、電源遮断後の設定キー971の操作によって通常遊技状態に復帰できる。 In addition, when it is determined that the RAM is abnormal, the game is stopped, and after the power is cut off, when the power is restored, it is determined that the work area in the area within the game control area and the area outside the game control area is normal, and the setting When the key 971 is operated, the work area and the stack area of the area inside the game control area and the area outside the game control area may be initialized and the game process may be started. By doing so, it is possible to return to the normal game state by operating the setting key 971 after the power is turned off.
一方、RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていなければ、停電発生前の遊技状態に復旧するために、停電発生時点での遊技状態の情報を電源投入時状態バッファに記憶する(ステップS2427)。このようにすると、周辺制御基板1510側の、各遊技状態(例えば、低確率状態か高確率状態か、時短状態か非時短状態か)に対応した演出(背景、装飾図柄の態様(低確率時と高確率時とで異なる態様の装飾図柄を使用する)を元に戻すための準備が行われる。ステップS2439で実行される電源投入時設定処理(INITIAL_SET)のステップS2300において、電源投入時動作コマンドを作成する際に使用され
る。
On the other hand, if the RAM
その後、電源投入時に設定キー971がONに操作されていたかを、レジスタに記憶された値を用いて判定する(ステップS2428)。そして、設定キー971がONに操作されていれば、設定確認操作がされていると判定し、設定状態管理エリアに設定確認モードを示す値(01H)を記録し(ステップS2429)、S2436に進む。すなわち、停電発生時の状態が設定確認モードかにかかわらず、設定キー971のみが操作されていれば(RAMクリアスイッチ954が操作されていなければ)、設定確認モードに移行する。
After that, it is determined using the value stored in the register whether the setting
ステップS2425からS2429は、RAMクリアスイッチ954か設定キー971の少なくとも一つが操作されていない場合に実行される処理であることから、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作の判定(ステップS2426)と、設定キー971の操作の判定(ステップS2428)とのいずれを先に行ってもよい。すなわち、図示したように、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を判定(ステップS2426)した後に設定キー971の操作を判定(ステップS2428)してもよく、設定キー971の操作を判定(ステップS2428)した後にRAMクリアスイッチ954の操作を判定(ステップS2426)してもよい。
Steps S2425 to S2429 are processes executed when at least one of the RAM
ステップS2421又はステップS2422でYESと判定されると、設定状態管理エリアに設定変更モードを示す値(02H)を記録する(ステップS2430)。そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外のワークエリアに異常があるかを判定する(ステップS2431)。例えば、前述したステップS2413でCレジスタに格納された判定結果を用いて、遊技制御領域外の異常を判定できる。その結果、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外に異常がなければ、ステップS2435に進む。
If YES is determined in step S2421 or step S2422, a value (02H) indicating the setting change mode is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2430). Then, it is determined whether there is an abnormality in the work area outside the game control area of the main control RAM 1312 (step S2431). For example, using the determination result stored in the C register in step S2413 described above, it is possible to determine an abnormality outside the game control area. As a result, if there is no abnormality outside the game control area of the
一方、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域外に異常があれば、フラグレジスタを
遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避し(ステップS2432)、図217に示す遊技領域外RAM異常時処理を実行する(S2433)。その後、ステップS2432で遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2434)。
On the other hand, if there is an abnormality outside the game control area of the
そして、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内の設定値及び設定状態管理エリア以外のワークエリアと遊技制御領域内のスタックエリアとを初期化する(ステップS2435
)。なお、ワークエリアとスタックエリアの間に設けられる未使用領域をあわせて初期化してもよい。
Then, the work area other than the setting value and setting state management area in the game control area of the
). An unused area provided between the work area and the stack area may be initialized together.
その後、全コマンドバッファを初期化する(ステップS2436)。これは、コマンドバッファアにコマンドが記憶された状態で電源が遮断された後にRAMクリアをせずに電源を復帰すると、コマンドバッファに格納された未送信のコマンドが送信される。例えば、変動コマンドの送信中に電源が遮断されることによって、図柄コマンドは送信したが、後続する変動パターンコマンドが未送信となることがある。そして、電源投入時に、変動パターンコマンドだけが送信されると、周辺制御基板1510が異常と判定することがある。さらに、設定変更に関する処理における未送信のコマンドがコマンドバッファに格納されている場合、電源復帰後に設定処理中に未送信となったコマンドが送信されることによって、周辺制御基板1510が当該コマンドに基づいて遊技状態を設定して、誤動作する可能性がある。このような異常の発生を防止するために、ステップS2436において、コマンドバッファを初期化している。 After that, all command buffers are initialized (step S2436). When the power is turned off without clearing the RAM after the power is turned off while commands are stored in the command buffer, the unsent commands stored in the command buffer are transmitted. For example, when the power supply is interrupted during the transmission of the variation command, the symbol command is transmitted, but the subsequent variation pattern command may not be transmitted. Then, when only the variation pattern command is transmitted when the power is turned on, the peripheral control board 1510 may be determined to be abnormal. Furthermore, if a command that has not been transmitted during the setting change process is stored in the command buffer, the command that has not been transmitted during the setting process is transmitted after the power is restored, so that the peripheral control board 1510 There is a possibility of malfunction by setting the game state by In order to prevent such an abnormality from occurring, the command buffer is initialized in step S2436.
なお、ステップS2436でコマンドバッファを初期化しているが、設定変更処理を開始するとき又は設定確認処理を開始するときに、コマンドバッファをクリアしてもよい。なお、設定変更処理においては、主制御RAM1312の初期化に伴ってコマンドバッファがクリアされるので、別途コマンドバッファをクリアする必要はないが、設定確認時処理においては、主制御RAM1312が初期化されないことから、設定確認に移行するときに、コマンドバッファをクリアするとよい。
Although the command buffer is initialized in step S2436, the command buffer may be cleared when starting the setting change process or when starting the setting confirmation process. In the setting change process, the command buffer is cleared along with the initialization of the
その後、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたデバイス(CTC、SIO等)の機能を初期設定する(ステップS2437)。具体的には、設定変更処理用のCTC0にタイマ割込み周期時間を設定し、CTC0を割込み許可に設定する。なお、通常遊技状態におけるタイマ割込み処理を制御するCTC1の時間は設定せず、通常遊技用のCTC1の割込みは禁止に設定されたままとなっている。
After that, the functions of the devices (CTC, SIO, etc.) built in the
そして、主制御MPU1311に内蔵されたハードウェア乱数(例えば当落乱数)を起動し(ステップS2438)てハード乱数の更新を開始し、図219に示す電源投入時設定処理を実行する(ステップS2439)。
Then, the hardware random number (for example, win-lose random number) built in the
最後にタイマ割込みを許可に設定し(ステップS2440)、主制御側メイン処理(図228)に進む。 Finally, the timer interrupt is enabled (step S2440), and the process proceeds to main control side main processing (FIG. 228).
図228は、主制御MPU1311が実行する主制御側メイン処理のフローチャートである。主制御側メイン処理は、電源投入時処理(図227)のステップS2440の後に実行される。
FIG. 228 is a flow chart of main control side main processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、設定変更処理用の第1メインループ処理(ステップS2450~S2453)を実行する。第1メインループ処理では、まず、主制御MPU1311は、停電予告信号を取得し、停電予告信号がONであるかによって停電が発生しているかを判定する(ステップS2450)。別例3では、メイン処理において停電を監視しているが、タイマ割込み処理で停電を監視して、停電発生が検出された場合に停電処理を実行してもよい。例えば、タイマ割込みの開始及び終了時の少なくとも一方で停電予告信号がONであるかを判定し、停電予告信号が継続的に出力されている期間をカウントし、カウント結果が所定値となった場合に停電が発生していると判定してもよい。別例3では、設定処理用のタイマ割込み処理と通常遊技処理用のタイマ割込み処理とが別に設けられているため、何れのタイマ割込み処理で停電を監視してもよく、両方のタイマ割込み処理で停電を監視してもよい。このため、停電監視処理と停電処理をサブルーチン化して、
二つのタイマ割込み処理の各々でこれらのサブルーチン(停電監視処理、停電処理)を実行することによって、停電監視処理と停電処理の同じプログラム(コード)を各タイマ割込み処理に組み込む必要がなく、プログラムのサイズを小さくできる。
First, the
By executing these subroutines (power failure monitoring process, power failure process) in each of the two timer interrupt processes, there is no need to incorporate the same program (code) for power failure monitoring process and power failure process into each timer interrupt process. size can be reduced.
停電予告信号を検出した場合、電源断時処理(ステップS2462~S2469)を実行する。 When the power failure warning signal is detected, power failure processing (steps S2462 to S2469) is executed.
一方、停電予告信号がONでない場合、正常に電源が供給されているので、割込みを禁止に設定し(ステップS2451)、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2452)。設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていれば、通常遊技を開始するためにステップS2454に進む。一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていなければ、割込を許可に設定し(ステップS2453)、ステップS2450に戻る、設定変更処理用の第1メインループ処理を繰り返し実行する。 On the other hand, if the power failure warning signal is not ON, the power is normally supplied, so interrupts are set to be prohibited (step S2451), and it is checked whether a value (00H) indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area. Determine (step S2452). If a value indicating game start is recorded in the setting state management area, the process proceeds to step S2454 to start the normal game. On the other hand, if the value indicating the game start is not recorded in the setting state management area, the interrupt is set to be permitted (step S2453), the process returns to step S2450, and the first main loop process for setting change process is repeatedly executed. .
ステップS2452で設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていると判定されると、割込みタイマを通常遊技用に切り替えた後、通常遊技用の第2メインループ処理(ステップS2457~S2458)を実行する。第2メインループ処理を実行する前に、まず、通常遊技用のCTC1にタイマ割込み周期時間を設定し(ステップS2454)、CTC0の割込み(設定処理用のタイマ割込み)を停止し、CTC1の割込み(通常遊技処理用のタイマ割込み)を起動して(ステップS2455)、割込み許可に設定する(ステップS2456)。 When it is determined in step S2452 that the value indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area, after switching the interrupt timer to the normal game, the second main loop processing for the normal game (steps S2457 to S2458) to run. Before executing the second main loop process, first, set the timer interrupt cycle time in CTC1 for normal game (step S2454), stop the interrupt of CTC0 (timer interrupt for setting process), interrupt the CTC1 ( Timer interrupt for normal game processing) is activated (step S2455), and interrupt permission is set (step S2456).
その後、停電予告信号を取得し、停電予告信号がONであるかによって停電が発生しているかを判定する(ステップS2457)。停電予告信号を検出した場合、電源断時処理(ステップS2462~S2469)を実行する。一方、停電予告信号がONでない場合、正常に電源が供給されているので、乱数更新処理2を実行する(ステップS2458)。乱数更新処理2は、図195で説明したものと同じでよく、主として特別抽選や普通抽選において当選判定を行うための乱数以外の乱数を更新する。その後、ステップS2457に戻り、通常遊技用の第2メインループ処理を繰り返し実行する。
After that, a power failure warning signal is obtained, and it is determined whether or not a power failure has occurred depending on whether the power failure warning signal is ON (step S2457). When the power failure warning signal is detected, power failure processing (steps S2462 to S2469) is executed. On the other hand, if the power failure warning signal is not ON, the power is normally supplied, so random
ステップS2450、S2457で停電予告信号を検出した場合、電源断時処理(ステップS2462~S2469)を実行する。図228に示す主制御側メイン処理では、
電源断時処理では、停電発生前の状態に復帰させるためのデータをバックアップする処理を実行する。具体的には、まず、割込みを禁止する(ステップS2462)。これにより後述するタイマ割込み処理が行われなくなる。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、出力ポートをクリアして、各ポートからの出力によって制御される機器の動作を停止する(ステップS2463)。具体的には、ソレノイド・停電クリア・ACK出力ポートに停電クリア信号OFFビットデータを出力する。なお、全ての出力ポートがクリアされなくてもよく、例えば、電力消費が大きいソレノイドやモータを制御するための出力ポートをクリアしてもよい。これらの出力ポートをクリアすることによって、主基板側電源断時処理が終了するまでの消費電力を低減し、主基板側電源断時処理を確実に終了できるようにする。
When the power failure warning signal is detected in steps S2450 and S2457, power failure processing (steps S2462 to S2469) is executed. In the main control side main processing shown in FIG.
In the power failure process, a process of backing up data for returning to the state before the power failure occurred is executed. Specifically, first, the interrupt is prohibited (step S2462). As a result, timer interrupt processing, which will be described later, is not performed. Furthermore, the
その後、フラグレジスタを遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避し(ステップS2464)、電源OFF時処理を実行して、遊技領域外のワークエリアについて電源が遮断される前に必要な処理を実行する(ステップS2465)。電源OFF時処理の詳細は図222の通りである。そして、遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2466)。 After that, the flag register is saved in the stack area within the game area (step S2464), the power OFF processing is executed, and necessary processing is executed before the power is cut off for the work area outside the game area (step S2465). ). The details of the power-off processing are as shown in FIG. Then, the flag register saved in the game area stack area is restored (step S2466).
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、バックアップされるワークエリアに格納されたデータが正常に保持されたか否かを判定するための、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内のワークエリアのチェックサムを計算し、主制御RAM1312の所定のチェックサム格納エリアに記憶する(ステップS2467)。このチェックサムはワークエリアにバックアップされたデータが正常かの判定に使用される。なお、チェックサムが算出される対象の領域は、遊技制御領域内のワークエリアのうち、電源投入後主制御側メイン処理の実行までの間に変更される可能性がある設定状態管理(設定値と設定状態管理エリアの値)や、バックアップフラグや、チェックサムエリアの値を除外するとよい。
Subsequently, the
さらに、停電フラグとしてバックアップフラグエリアに正常に電源断時処理が実行されたことを示す値(5AH)を格納する(ステップS2468)。これにより、遊技バックアップ情報の記憶が完了する。最後に、RAMプロテクト有効(書き込み禁止)、禁止領域の無効とする設定値をRAMプロテクトレジスタに書き込み、主制御RAM1312の書き込みを禁止し(ステップS2469)、停電から復旧するまでの間、待機する(無限ループ)。主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の使用領域を指定することによって、指定領域以外の禁止領域へアクセスがあった場合には、異常と判定してリセットする機能を有する。本実施例では、この禁止領域へのアクセスによるリセット機能を解除して、全領域へのアクセスを可能としている。なお、主制御RAM1312のうち未使用領域を禁止領域に指定して、RAMプロテクトレジスタに禁止領域を有効として設定することで、指定された禁止領域にアクセスを検出した場合には、主制御MPU1311がリセットされるようにしてもよい。
Further, a value (5AH) indicating that the power failure processing has been normally executed is stored in the backup flag area as a power failure flag (step S2468). This completes the storage of the game backup information. Finally, write a setting value for validating RAM protection (writing prohibited) and invalidating the prohibited area to the RAM protection register, prohibiting writing to the main control RAM 1312 (step S2469), and waiting until recovery from the power failure ( infinite loop). The
なお、前述した処理では、出力ポートのクリア(ステップS2463)、電源OFF時処理(ステップS2465)、チェックサムの算出(ステップS2467)、バックアップフラグの設定(ステップS2468)の順に処理を実行しているが、この四つの処理の実行順は、図示したものに限定されず、他の順序でもよい。 In the above-described processing, the processing is executed in the order of clearing the output port (step S2463), processing when the power is turned off (step S2465), calculating the checksum (step S2467), and setting the backup flag (step S2468). However, the execution order of these four processes is not limited to the illustrated one, and other orders may be used.
なお、別例3では、主制御側メイン処理で停電の発生を監視しているが、タイマ割込み処理で停電の発生を監視し、監視結果に基づいて停電処理を実行してもよい。例えば、二つのメインループの各々において、開始時及び終了時の少なくとも一方で停電信号を確認し、停電信号が継続的に出力されている期間を測定し、測定結果が所定値となった場合に停電の発生を検知するとよい。 In example 3, the occurrence of a power failure is monitored by the main processing on the main control side, but the occurrence of a power failure may be monitored by the timer interrupt processing, and the power failure processing may be executed based on the monitoring result. For example, in each of the two main loops, check the power failure signal at least at the start and end, measure the period during which the power failure signal is continuously output, and if the measurement result reaches a predetermined value It is preferable to detect the occurrence of a power failure.
図228に示す主制御側メイン処理では、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理と通常遊技用タイマ割込みとの各々に対応して二つのメインループが設けられており、必ず一回は設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理の実行契機がある。また、この実行契機において、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理が実行されないこともある(例えば、ステップS2454でYESに分岐する場合)。このようにメインループを二つ設けることによって、通常遊技用のメインループ(タイマ割込み処理)でベース値を計算する処理を実行し、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理では不要なベース値を計算する処理を実行ししないように、ベース値を計算する処理を実行するかを切り替えることができる。別例3では、設定処理用のタイマ割込み処理と通常遊技処理用のタイマ割込み処理とが別に設けられているため、何れのタイマ割込み処理で停電を監視してもよく、両方のタイマ割込み処理で停電を監視してもよい。このため、停電監視処理と停電処理をサブルーチン化して、二つのタイマ割込み処理の各々でこれらのサブルーチン(停電監視処理、停電処理)を実行することによって、停電監視処理と停電処理の同じプログラム(コード)を各タイマ割込み処理に組み込む必要がなく、プログラムのサイズを小さくできる。 In the main control side main processing shown in FIG. 228, two main loops are provided corresponding to each of the timer interrupt processing for setting change processing and the timer interrupt for normal game. There is an opportunity to execute the timer interrupt processing of Also, in this execution opportunity, timer interrupt processing for setting change processing may not be executed (for example, when branching to YES in step S2454). By providing two main loops in this way, the main loop for normal games (timer interrupt processing) executes processing for calculating the base value, and the timer interrupt processing for setting change processing calculates unnecessary base values. It is possible to switch between executing the processing for calculating the base value and not executing the processing. In another example 3, timer interrupt processing for setting processing and timer interrupt processing for normal game processing are separately provided, so power failure may be monitored by either timer interrupt processing, and both timer interrupt processing Power outages may be monitored. For this reason, the same program (code ) into each timer interrupt process, the size of the program can be reduced.
図229は、主制御MPU1311が実行する設定処理用のタイマ割込み処理のフローチャートである。
FIG. 229 is a flowchart of timer interrupt processing for setting processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンク選択フラグを1に設定し、レジスタのバンクを切り替える(ステップS2470)。なお、主制御MPU1311は、演算に使用するレジスタ群を二つ有し、一つはバンク0のレジスタ群として使用し、他はバンク1のレジスタ群として使用可能とされており、バンクを切り換えることによって、いずれかのバンクが使用できるように構成されている。本実施例では、主制御側メイン処理ではレジスタバンク0が使用され、設定処理用または通常遊技用のタイマ割込み処理ではレジスタバンク1が使用される。このため、タイマ割込み処理の開始時にはバンク1に切り替える命令を実行するが、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にはバンク0に切り替える命令を実行する必要がない。これは、主制御MPU1311は、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタ(例えば、Zフラグ、Cフラグがセットされているレジスタ)に記憶しており、フラグレジスタは、割込開始時にスタックエリアに退避され、RET命令の実行によってスタックエリアから復帰する。このため、RET命令を実行することでフラグレジスタに記憶したレジスタのバンクフラグも元に戻るように構成しているためである。なお、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタに記憶しない構成を採用した場合、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にバンク切替命令を実行して、バンク0に戻す必要がある。
First, the
なお、フラグレジスタには、割込可否を制御するフラグも記憶されているため、割り込み許可に設定してからRET命令を実行しなくてもよい。なお、割込可否を制御するフラグは、タイマ割込み処理の開始時に、フラグレジスタをスタックした後に割込禁止状態に設定される。このため、タイマ割込処理中に割込を許可(EI命令など)するか、RETI命令を実行しない限り、割込み許可状態にはならない。 Since the flag register also stores a flag for controlling whether or not to enable interrupts, it is not necessary to execute the RET instruction after enabling interrupts. It should be noted that the flag that controls whether or not to allow interrupts is set to the interrupt disabled state after the flag register is stacked at the start of timer interrupt processing. Therefore, unless an interrupt is permitted (EI instruction, etc.) or a RETI instruction is executed during timer interrupt processing, the interrupt enabled state is not entered.
次に、LEDコモンカウンタを+1更新する。なお、LEDコモンカウンタ値が上限を超える場合は0にする(ステップS2471)。 Next, the LED common counter is updated by +1. If the LED common counter value exceeds the upper limit, it is set to 0 (step S2471).
次に、スイッチ入力処理1を実行する(ステップS2472)。スイッチ入力処理1では、主制御MPU1311の各種入力ポートの入力端子に入力されている各種信号を読み取り、ONエッジを作成し、入力情報として主制御RAM1312の入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。
Next, switch
なお、ステップS2472のスイッチ入力処理1は入賞信号に関する処理であるため、設定変更モードや設定確認モードで実行されるタイマ割込み処理では、ステップS2473においてNOと判定されるので、入賞検出は行われるが、不正は検出されない。なお、入賞が検出されても、賞球の払出しや変動表示等は実行されない。設定変更操作や設定確認操作はホールの従業員が行うものであり、設定変更モードや設定確認モードでは不正が行われず、不正を検出しない方が望ましいと考えられるからである。
Since the
なお、設定変更モードや設定確認モードでも、一部の不正検出センサ(例えば電波センサ)はスイッチ入力処理1で検出し、特定の種類の不正を監視してもよい。このようにすると、不正行為を行おうとする者(ゴト師)が電波を照射する等によって強制的に設定変更モードを起動する不正を検出できる。例えば、ホールの従業員が設定変更や設定確認の操作をしている間は、扉が開放されており、扉に取り付けられたセンサが隣のパチンコ機に近づく位置になる。このため、設定変更操作や設定確認を行っている間は、隣のパチンコ機における電波等によるゴト行為を検出できるようになっている。
Note that even in the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, some fraud detection sensors (for example, radio wave sensors) may detect in the
そして、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2473)。なお、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理において、通常であれば遊技状態管理エリアの値は、00H以外(01H~03H)となっているため、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定しなくても
よいが、通常遊技中に、不正に設定変更モードに移行するような不正行為防止するために、あえて判定を行なっている。
Then, it is determined whether a value (00H) indicating game start is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2473). In the timer interrupt process for the setting change process, the value of the game state management area is usually other than 00H (01H to 03H), so the value (00H) indicating the start of the game is displayed in the setting state management area. Although it is not necessary to determine whether or not is recorded, determination is purposely made in order to prevent fraudulent acts such as illegally shifting to the setting change mode during the normal game.
設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていれば、設定値の変更、設定表示に関する処理(ステップS2474~S2478)を実行せず、ステップS2479に進む。一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていなければ、特定の出力ポートをクリアする(ステップS2474)、例えば、ステップ2474で特定の出力ポートとしてクリアされる信号は、停電クリア信号、大入賞口・電チュー等のソレノイド信号、払出制御基板951へのコマンド受信時の応答信号(ACK)がある。その後、LEDコモンポートをOFFにする(ステップS2475)。タイマ割込み処理の早い段階でLEDコモン信号をOFFにすることによって、LEDコモン信号がオンになるまでの時間、すなわちLEDの消灯時間を確保し、LEDの表示切替前後の表示が混ざって見えるゴースト現象を抑制し、LEDのちらつきを防止している。
If a value indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area, the process for changing the setting value and setting display (steps S2474 to S2478) is not executed, and the process proceeds to step S2479. On the other hand, if the value indicating the start of the game is not recorded in the setting state management area, the specific output port is cleared (step S2474). , a solenoid signal such as a large winning opening and an electric chew, and a response signal (ACK) at the time of command reception to the
その後、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力し(ステップS2476)、図224に示した設定処理を実行する(ステップS2477)。その後、図225に示した設定表示処理を実行する(ステップS2478)。 After that, a security signal is output from the external terminal board 784 (step S2476), and the setting process shown in FIG. 224 is executed (step S2477). After that, the setting display process shown in FIG. 225 is executed (step S2478).
さらに、送信情報記憶領域の値をシリアル通信回路に出力する周辺基板コマンド送信処理を実行する(ステップS2479)。送信情報記憶領域は、生成された送信コマンドを一時的に格納する記憶領域である。送信情報記憶領域に格納された値(コマンド)が読み出されてシリアル通信回路(SIO)の送信情報記憶領域に格納される。シリアル通信回路は、複数バイトのFIFO形式の送信バッファである送信情報記憶領域を有し、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納された値を、順次、周辺制御基板1510に送信する。なお、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域の容量は有限であるため、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に未送信のコマンドが残っており、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域が満状態又は満状態に近い場合には、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域の空き状態に応じて、コマンドをシリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納するかを制御するとよい。例えば、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納するコマンドの大きさ(バイト数)よりもシリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域の空き容量が大きいかを判定し、空き容量の方が大きければコマンドをシリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納してもよい。また、1回の周辺制御基板1510へのコマンド送信処理の実行毎に、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納するコマンドの大きさに所定の上限を設け、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域の空き容量を判定することなく、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納するコマンドの大きさが所定の上限を超える場合には、全てのコマンドをシリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納できなくても、次のタイマ割込み処理で実行される周辺基板コマンド送信処理において、残りのコマンドをシリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納して、周辺制御基板1510に送信するとよい。 Further, peripheral board command transmission processing for outputting the value of the transmission information storage area to the serial communication circuit is executed (step S2479). The transmission information storage area is a storage area that temporarily stores the generated transmission command. A value (command) stored in the transmission information storage area is read and stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit (SIO). The serial communication circuit has a transmission information storage area which is a transmission buffer in the FIFO format of multiple bytes, and sequentially transmits the values stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit to the peripheral control board 1510 . Since the capacity of the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit is finite, unsent commands remain in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit, and the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit is full or full. , it is preferable to control whether the command is stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit according to the free state of the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit. For example, it determines whether the free space in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit is larger than the size (number of bytes) of the command to be stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit. It may be stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit. Also, each time the command transmission process to the peripheral control board 1510 is executed, a predetermined upper limit is set for the size of the command to be stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit. If the size of commands to be stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit exceeds a predetermined upper limit without judging the free space, all the commands cannot be stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit. Also, in the peripheral board command transmission process executed in the next timer interrupt process, the remaining commands should be stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit and transmitted to the peripheral control board 1510 .
なお、上限数は、1回のタイマ割込み周期でシリアル通信回路(SIO)が送信可能なデータ量と同じか、少ない量に設定するとよい。例えば、シリアル通信回路の通信速度20kbpsであり、タイマ割込み周期が4m秒である場合、一回のタイマ割込み周期で約80ビットのシリアル通信が可能となる。一つのコマンドが20ビットで構成されている場合、80÷20=4となるので4コマンドを上限とするとよい。なお、実質的には、一つ多い5コマンドを上限に設定してもよい。これは、コマンドの最大長を20ビットと仮定したが、最大長より短いコマンドも多くあるからである。 It should be noted that the upper limit number should be set equal to or less than the amount of data that can be transmitted by the serial communication circuit (SIO) in one timer interrupt cycle. For example, if the communication speed of the serial communication circuit is 20 kbps and the timer interrupt period is 4 ms, serial communication of approximately 80 bits is possible in one timer interrupt period. If one command consists of 20 bits, 80/20=4, so the upper limit should be 4 commands. In practice, the upper limit may be set to 5 commands, which is one more command. This is because although the maximum command length was assumed to be 20 bits, there are many commands shorter than the maximum length.
なお、1回のコマンド送信処理において送信情報記憶領域に格納されるコマンドのデータ量に所定の上限を設けるかにかかわらず、送信情報記憶領域が満状態にならないように、送信情報記憶領域に格納前のコマンドが格納される記憶領域の容量を送信情報記憶領域
の容量より小さいか、同じにするとよい。
Regardless of whether a predetermined upper limit is set for the amount of command data stored in the transmission information storage area in one command transmission process, data is stored in the transmission information storage area so that the transmission information storage area does not become full. It is preferable that the capacity of the storage area in which the previous command is stored be smaller than or equal to the capacity of the transmission information storage area.
その後、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットして、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアする(ステップS2480)。なお、ウォッチドッグタイマは、単純クリアモードを使用しているので、1ワードをセットすることによってウォッチドッグタイマがクリアされる。その後、復帰命令(例えばRETI)によって、レジスタのバンクを切り替え(ステップS2481)、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。 Thereafter, a predetermined value (18H) is set in the watchdog timer clear register WCL to clear the watchdog timer (step S2480). Note that the watchdog timer uses a simple clear mode, so setting one word clears the watchdog timer. Thereafter, a return instruction (for example, RETI) switches the bank of the register (step S2481), and returns to the processing before the interrupt.
図229に示す設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理では、他のタイマ割込み処理と異なり、乱数更新処理(R_ATART_K)を実行しないようにしているが、S2438でハード乱数を起動済みであるために、ハード乱数と同様に設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理において乱数更新処理を実行してもよい。 Unlike the other timer interrupt processes, the timer interrupt process for the setting change process shown in FIG. 229 does not execute the random number update process (R_ATART_K). As with the random number, the random number update process may be executed in the timer interrupt process for the setting change process.
なお、別例3では、試験信号出力処理は、通常遊技用のタイマ割込み処理(例えば、図230の出力データ設定処理S2505)で実行しても、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理内で呼び出してもよい。 In another example 3, the test signal output process is called in the timer interrupt process for the setting change process even if it is executed in the timer interrupt process for the normal game (for example, the output data setting process S2505 in FIG. 230). good too.
図230は、主制御MPU1311が実行する通常遊技用のタイマ割込み処理のフローチャートである。
FIG. 230 is a flow chart of the normal game timer interrupt process executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンク選択フラグを1に設定し、レジスタのバンクを切り替える(ステップS2490)。なお、主制御MPU1311は、演算に使用する二つのレジスタ群を有し、一つはバンク0のレジスタ群として使用し、他はバンク1のレジスタ群として使用可能とされており、バンクを切り換えることにより、いずれかのバンクが使用できるように構成されている。本実施例では、主制御側メイン処理ではレジスタバンク0が使用され、設定処理又は通常遊技用のタイマ割込み処理ではレジスタバンク1が使用される。このため、タイマ割込み処理の開始時にはバンク1に切り替える命令を実行するが、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にはバンク0に切り替える命令を実行する必要がない。これは、主制御MPU1311は、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタ(例えば、Zフラグ、Cフラグがセットされているレジスタ)に記憶しており、フラグレジスタは、割込開始時にスタックエリアに退避され、RET命令の実行によってスタックエリアから復帰する。このため、RET命令を実行することでフラグレジスタに記憶したレジスタのバンクフラグも元に戻るように構成しているためである。なお、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタに記憶しない構成を採用した場合、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にバンク切替命令を実行して、バンク0に戻す必要がある。
First, the
なお、フラグレジスタには、割込可否を制御するフラグも記憶されているため、割り込み許可に設定してからRET命令を実行しなくてもよい。なお、割込可否を制御するフラグは、タイマ割込み処理の開始時に、フラグレジスタをスタックした後に割込禁止状態に設定される。このため、タイマ割込処理中に割込を許可(EI命令など)するか、RETI命令を実行しない限り、割込み許可状態にはならない。 Since the flag register also stores a flag for controlling whether or not to enable interrupts, it is not necessary to execute the RET instruction after enabling interrupts. It should be noted that the flag that controls whether or not to allow interrupts is set to the interrupt disabled state after the flag register is stacked at the start of timer interrupt processing. Therefore, unless an interrupt is permitted (EI instruction, etc.) or a RETI instruction is executed during timer interrupt processing, the interrupt enabled state is not entered.
次に、LEDコモンカウンタを+1更新する。なお、LEDコモンカウンタ値が上限を超える場合は0にする(ステップS2491)。 Next, the LED common counter is updated by +1. If the LED common counter value exceeds the upper limit, it is set to 0 (step S2491).
次に、スイッチ入力処理1を実行する(ステップS2492)。スイッチ入力処理1では、主制御MPU1311の各種入力ポートの入力端子に入力されている各種信号を読み取り、ONエッジを作成し、入力情報として主制御RAM1312の入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。
Next, switch
続いて、乱数更新処理1を実行する(ステップS2493)。乱数更新処理1では、大当り判定用乱数、大当り図柄用乱数、及び小当り図柄用乱数を更新する。またこれらの乱数に加えて、図221に示した主制御側メイン処理の乱数更新処理2で更新される大当り図柄決定用乱数及び小当り図柄決定用乱数の初期値を変更するための、それぞれの初期値決定用乱数を更新する。
Subsequently, random
その後、スイッチ入力特殊処理を実行する(ステップS2494)。 Thereafter, switch input special processing is executed (step S2494).
その後、タイマ更新処理を実行する(ステップS2495)。タイマ更新処理では、例えば、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理で決定される変動表示パターンに従って特別図柄表示器1185が点灯する時間、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理で決定される普通図柄変動表示パターンに従って普通図柄表示器1189が点灯する時間のほかに、主制御基板1310(主制御MPU1311)が送信した各種コマンドを払出制御基板951が正常に受信した旨を伝える払主ACK信号が入力されているか否かを判定する際にその判定条件として設定されているACK信号入力判定時間等の時間管理を行う。具体的には、変動表示パターン又は普通図柄変動表示パターンの変動時間が5秒間であるときには、タイマ割り込み周期が4msに設定されているので、このタイマ減算処理を行うごとに変動時間を4msずつ減算し、その減算結果が値0になることで変動表示パターン又は普通図柄変動表示パターンの変動時間を正確に計測している。
Thereafter, timer update processing is executed (step S2495). In the timer update process, for example, the time during which the special symbol indicator 1185 lights up according to the variation display pattern determined by the special symbol and special electric auditors control process, the normal symbol fluctuation determined by the normal symbol and normal electric auditors control process In addition to the time during which the normal symbol display 1189 lights up according to the display pattern, a
続いて、賞球制御処理を実行する(ステップS2496)。賞球制御処理では、入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、読み出した入力情報に基づいて払い出される遊技球(賞球)の数を計算し、主制御RAM1312に書き込む。また、賞球数の計算結果に基づいて、遊技球を払い出すための賞球コマンドを作成したり、主制御基板1310と払出制御基板951との基板間の接続状態を確認するためのセルフチェックコマンドを作成したりする。主制御MPU1311は、作成した賞球コマンドやセルフチェックコマンドを主払シリアルデータとして払出制御基板951に送信する。主制御MPU1311は、2チャネルの出力用のシリアル通信回路を有しており、1チャネルで周辺制御基板1510へコマンドを送信し、他の1チャネルで払出制御基板951へコマンドを送信している。シリアル通信の転送レート(ボーレート)は、チャネルごとに設定可能となっており、例えば、ステップS2437において、シリアル通信回路の転送レートを設定する。例えば、転送レートは、払出制御基板951側の転送レートを、周辺制御基板1510側の転送データより低く設定するとよい。これは、払出制御基板951が制御する賞球は遊技価値を伴うために、ノイズ等の影響を受けづらく、コマンド化けや欠落等により、異常な賞球コマンドにならないように低速で転送するが、周辺制御基板1510側では、遊技価値を伴わない演出用のコマンドが送信されるため、次のコマンドで演出が復帰すればよく、さらに、多数のコマンドが送信され、レスポンスよく演出を行って、遊技者に違和感を与えないために、周辺制御基板1510に早くコマンドを送信することが望ましい。なお、演出のレスポンスが悪い(例えば、始動入賞口に遊技球が入賞し、機能表示ユニット1400の特別図柄表示が変動を開始しても、メイン液晶表示装置1600において装飾図柄が変動を開始しない)と、遊技者は、故障ではないかと不安を感じるためである。
Subsequently, prize ball control processing is executed (step S2496). In the prize ball control process, input information is read from the input information storage area, the number of game balls (prize balls) to be paid out is calculated based on the read input information, and the calculated number is written in the
続いて、枠コマンド受信処理を実行する(ステップS2497)。払出制御基板951では、払出制御プログラムによって、状態表示に区分される1バイト(8ビット)の各種コマンド(例えば、枠状態1コマンド、エラー解除ナビコマンド、及び枠状態2コマンド)を送信する。一方、後述するように、払出制御プログラムによって、払出動作にエラーが発生した場合にエラー発生コマンドを出力したり、操作スイッチの検出信号に基づいてエラー解除報知コマンドを出力する。枠コマンド受信処理では、各種コマンドを払主シリアルデータとして正常に受信すると、その旨を払出制御基板951に伝える情報を主制御内蔵RAM1312の出力情報記憶領域に記憶する。また、主制御MPU1311は、払
主シリアルデータとして正常に受信したコマンドを2バイト(16ビット)のコマンドに整形し(例えば、枠状態表示コマンド、エラー解除報知コマンドなど)、上述した送信情報記憶領域に記憶する。具体的には、枠コマンド受信処理では、払出制御基板951から受信したコマンドに対応した報知を行うために、払出制御基板951から受信したコマンドを周辺制御基板1510に送信するコマンドの体系に適合するように修正して、他の生成したコマンドと同様にシリアル通信回路(SIO)の送信情報記憶領域に格納する。また、払出制御基板951からのコマンドを正常に受信した場合には、主ACK信号の出力を制御するための信号を生成する。主ACK信号は、シリアル通信回路ではなく、出力ポートから払出制御基板951に直接出力される。なお、主ACK信号は、シリアル通信回路からコマンドとして出力してもよい。
Subsequently, frame command reception processing is executed (step S2497). The
続いて、不正行為検出処理を実行する(ステップS2498)。不正行為検出処理では、不正に関連した異常状態(磁気、振動、入賞異常等)を確認する。例えば、上述した入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、大当り遊技状態でない場合にカウントスイッチによって大入賞口2005、2006に遊技球が入球していると検知されたとき等には、主制御プログラムは、異常状態として報知表示に区分される入賞異常表示コマンドを作成し、送信情報として上述した送信情報記憶領域に記憶する。
Subsequently, fraud detection processing is executed (step S2498). In the fraudulent activity detection process, an abnormal state (magnetism, vibration, winning anomaly, etc.) related to fraud is confirmed. For example, when the input information is read out from the above-described input information storage area, and when it is detected that the game ball is entering the
続いて、入賞スイッチや始動口スイッチに関する各種スイッチの通過検出時に対応するコマンドを作成し送信情報記憶領域にセットするスイッチ通過時コマンド出力処理を実行する(ステップS2499)。 Subsequently, a switch-passing command output process is executed to create a command corresponding to the detection of the passage of various switches relating to the winning switch and the starting switch and set it in the transmission information storage area (step S2499).
そして、フラグレジスタを遊技制御領域内のスタックエリアに退避し(ステップS2500)、ベース表示器出力処理を実行する(ステップS2501)。ベース表示器出力処理は、他の処理と異なり、遊技制御領域外の第2領域を使用して実行される処理であり、パチンコ機1の仕様に影響を受けない共通の処理である。このため、ベース表示器出力処理の独立性を担保するために、ベース表示器出力処理の実行前後に、フラグレジスタなどの所定のデータを遊技制御領域内のスタックエリアに退避して、ベース表示器出力処理で更新されないようにしている。その後、遊技制御領域内のスタックエリアに退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2502)。
Then, the flag register is saved in the stack area in the game control area (step S2500), and the base display output process is executed (step S2501). The base display output process is a process executed using the second area outside the game control area, unlike other processes, and is a common process that is not affected by the specifications of the
続いて、特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理を実行する(ステップS2503)。特別図柄及び特別電動役物制御処理では、大当り用乱数値が主制御内蔵ROMに予め記憶されている当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定し、大当り図柄乱数値に基づいて確率変動状態に移行するか否かを判定する。そして、大当り用乱数値が当り判定値と一致している場合には、大入賞口2005、2006を開閉動作させるか否かを決定する。この決定により大入賞口2005、2006を開閉動作させる場合、大入賞口2005、2006が開放(又は、拡大)状態となることで大入賞口2005、2006に遊技球が受け入れ可能となる遊技状態となって遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態に移行する。また、確変移行条件が成立している場合には、その後、確率変動状態に移行する一方、確変移行条件が成立していない場合には当該確率変動状態以外の遊技状態に移行する。ここで、「確率変動状態」とは、上述した特別抽選の当選確率が通常遊技状態(低確率状態)と比較して相対的に高く設定された状態(高確率状態)をいう。
Subsequently, a special symbol and special electric accessary product control process is executed (step S2503). In the special symbol and special electric accessory control processing, it is determined whether or not the big hit random number value matches the hit determination value pre-stored in the main control built-in ROM, and the probability fluctuation state is established based on the big hit symbol random number value. Determine whether to migrate. Then, when the big win random number value matches the hit determination value, it is determined whether or not to open and close the
続いて、普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理を実行する(ステップS504)。普通図柄及び普通電動役物制御処理では、上述した入力情報記憶領域から入力情報を読み出し、ゲートスイッチ2352からの検出信号が入力端子に入力されていたか否かを判定する。検出信号が入力端子に入力されていた場合には、普通図柄当り判定用乱数を抽出し、主制御内蔵ROMに予め記憶されている普通図柄当り判定値と一致するか否かを判定する(「普通抽選」という)。そして、普通抽選による抽選結果に応じて第二始動口扉部材254
9を開閉動作させるか否かを決定する。この決定により開閉動作をさせる場合、第二始動口扉部材2549が開放(又は、拡大)状態となることで始動口2004に遊技球が受け入れ可能となる遊技状態となって遊技者にとって有利な遊技状態に移行する。
Subsequently, normal symbol and normal electric accessory control processing is executed (step S504). In the normal symbol and normal electric accessory control process, the input information is read from the above-described input information storage area, and it is determined whether or not the detection signal from the gate switch 2352 is input to the input terminal. When the detection signal is input to the input terminal, the random number for normal symbol per determination is extracted, and it is determined whether or not it matches the normal per symbol determination value stored in advance in the main control built-in ROM (" “General Lottery”). Then, according to the lottery result of the ordinary lottery, the second start opening door member 254
9 is to be opened or closed. When the opening and closing operation is performed by this determination, the second starting
続いて、出力データ設定処理を実行する(ステップS2505)。出力データ設定処理では、主制御MPU1311の各種出力ポートの出力端子から各種信号を出力する。例えば、出力情報に基づいて主制御MPU1311の所定の出力ポートの出力端子から、払出制御基板951からの各種コマンドを正常に受信したときには主払ACK信号を払出制御基板951に出力したり、大当り遊技状態であるときには大入賞口2005、2006の開閉部材2107の開閉動作を行うアタッカソレノイド(第一アタッカソレノイド2113、第二上アタッカソレノイド2553、第二下アタッカソレノイド2556)に駆動信号を出力したり、始動口(第二始動口扉部材2549)の開閉動作を行う始動口ソレノイド2550に駆動信号を出力したりするほかに、ホールコンピュータへの出力情報として、確率変動中情報出力信号、特別図柄表示情報出力信号、普通図柄表示情報出力信号、時短中情報出力情報、始動口入賞情報出力信号等の遊技に関する各種情報(遊技情報)信号及びセキュリティ信号を外部端子板784に出力する。また、出力データ設定処理では、試験信号出力処理を実行して、試験信号を出力してもよい。
Subsequently, output data setting processing is executed (step S2505). In the output data setting process, various signals are output from output terminals of various output ports of the
また、出力データ設定処理では、スイッチ入力特殊処理(ステップS2494)で計数されたアウト球数に対応する信号を外部端子板784から出力する。例えば、所定のアウト球数(10個など)毎に外部端子板784から所定長のパルス信号を出力してもよい。
Also, in the output data setting process, a signal corresponding to the number of out balls counted in the switch input special process (step S2494) is output from the external
また、出力データ設定処理では、パチンコ機1に接続された検査装置に出力するための試験信号を設定する。試験信号には、例えば、遊技状態を示す信号や普通図柄、特別図柄の停止図柄を示す信号が含まれる。
Also, in the output data setting process, a test signal to be output to the inspection device connected to the
さらに、送信情報記憶領域の値をシリアル通信回路に出力する周辺基板コマンド送信処理を実行する(ステップS2506)。送信情報記憶領域は、生成された送信コマンドを一時的に格納する記憶領域である。送信情報記憶領域に格納された値(コマンド)は、ステップ2070で読み出されてシリアル通信回路(SIO)の送信情報記憶領域に格納される。シリアル通信回路は、複数バイトのFIFO形式の送信バッファである送信情報記憶領域を有し、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納された値を、順次、周辺制御基板1510に送信する。 Further, peripheral board command transmission processing for outputting the value of the transmission information storage area to the serial communication circuit is executed (step S2506). The transmission information storage area is a storage area that temporarily stores the generated transmission command. The value (command) stored in the transmission information storage area is read at step 2070 and stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit (SIO). The serial communication circuit has a transmission information storage area which is a transmission buffer in the FIFO format of multiple bytes, and sequentially transmits the values stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit to the peripheral control board 1510 .
その後、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットして、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアする(ステップS2507)。なお、ウォッチドッグタイマは、単純クリアモードを使用しているので、1ワードをセットすることによってウォッチドッグタイマがクリアされる。その後、復帰命令(例えばRETI)によって、レジスタのバンクを切り替え(ステップS2508)、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。 Thereafter, a predetermined value (18H) is set in the watchdog timer clear register WCL to clear the watchdog timer (step S2507). Note that the watchdog timer uses a simple clear mode, so setting one word clears the watchdog timer. Thereafter, a return instruction (for example, RETI) switches the bank of the register (step S2508), and returns to the processing before the interrupt.
[12-18.設定変更・確認処理の別例4]
次に、設定変更機能を有するパチンコ機の別な実施例について説明する。以下に説明する別例4では、タイマ割込み処理ではなく主制御側メイン処理で設定変更に関する処理を実行する。以下に説明する以外の処理は、前述した別例3と同じである。
[12-18. Another example 4 of setting change/confirmation process]
Next, another embodiment of a pachinko machine having a setting change function will be described. In another example 4 described below, processing related to setting change is executed in main processing on the main control side instead of timer interrupt processing. Processes other than those described below are the same as those of Example 3 described above.
なお、別例4では、別例2と同様に、設定変更スイッチ972を設けずに、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作によって設定値が選択できるものであるが、RAMクリアスイッチ954の本来の主制御RAM1312の初期化機能と、設定変更機能とを区別して記載するために、設定値の変更にかかる操作については設定変更スイッチ972として説明することがある。
In addition, in Example 4, as in Example 2, the setting value can be selected by operating the RAM
図231は、主制御MPU1311が実行する主制御側メイン処理のフローチャートである。主制御側メイン処理は、電源投入時処理(図227)のステップS2440の後に実行される。別例4の主制御側メイン処理は、別例3の主制御側メイン処理(図228)のステップS2452に代えて、ステップS2481~S2484を実行する。主制御側メイン処理で設定変更や設定確認の処理を実行するのは、別例4のように設定処理用のタイマ割込み処理と通常遊技処理用のタイマ割込み処理とを別に設ける場合だけでなく、別例1や別例2にも適用可能である。例えば、図231に示す主制御メイン処理は、設定処理用の第1メインループ処理(ステップS2450~S2453)と通常遊技用の第2メインループ処理(ステップS2457~S2458)とを含むところ、いずれのメインループ処理でも、一つのタイマ割込み処理(別例1の図196、別例2の図223)が実行される、タイマ割込み処理の中で設定処理(図190のステップ2068、図223のステップS2341)と通常遊技処理とが実行される。この場合、メインループで実行されるタイマ割込み処理が一つであるため、後述するステップS2454、S2455のCTCの切り替えは不要となる。
FIG. 231 is a flow chart of main control side main processing executed by the
図231に示す主制御側メイン処理では、別例3の主制御側メイン処理(図228)と同じ処理には同じ符号を付す。 In the main-control-side main process shown in FIG. 231, the same processes as those of the main-control-side main process (FIG. 228) of Example 3 are given the same reference numerals.
まず、主制御MPU1311は、設定処理用の第1メインループ処理(ステップS2450~S2453)を実行する。第1メインループ処理では、まず、主制御MPU1311は、停電予告信号を取得し、停電予告信号がONであるかによって停電が発生しているかを判定する(ステップS2450)。別例4では、メイン処理において停電を監視しているが、タイマ割込み処理で停電を監視して、停電発生が検出された場合に停電処理を実行してもよい。例えば、タイマ割込みの開始及び終了時の少なくとも一方で停電予告信号がONであるかを判定し、停電予告信号が継続的に出力されている期間をカウントし、カウント結果が所定値となった場合に停電が発生していると判定してもよい。別例4では、設定処理用のタイマ割込み処理と通常遊技処理用のタイマ割込み処理とが別に設けられているため、何れのタイマ割込み処理で停電を監視してもよく、両方のタイマ割込み処理で停電を監視してもよい。このため、停電監視処理と停電処理をサブルーチン化して、二つのタイマ割込み処理の各々でこれらのサブルーチン(停電監視処理、停電処理)を実行することによって、停電監視処理と停電処理の同じプログラム(コード)を各タイマ割込み処理に組み込む必要がなく、プログラムのサイズを小さくできる。
First, the
停電予告信号を検出した場合、電源断時処理(ステップS2462~S2469)を実行する。 When the power failure warning signal is detected, power failure processing (steps S2462 to S2469) is executed.
一方、停電予告信号がONでない場合、正常に電源が供給されているので、割込みを禁止に設定し(ステップS2451)、図224に示した設定処理を実行する(ステップS2482)。その後、図225に示した設定表示処理を実行する(ステップS2483)。 On the other hand, if the power failure warning signal is not ON, the power is normally supplied, so interrupt is disabled (step S2451), and the setting process shown in FIG. 224 is executed (step S2482). After that, the setting display process shown in FIG. 225 is executed (step S2483).
その後、設定キー971がOFF位置に戻ったかによって、設定変更・設定確認の処理が終了したかを判定する(ステップS2484)。具体的には、設定キー971のONからOFFへのエッジ、又は、ONからOFFへ変化してから所定期間経過したかを検出する。設定変更・設定確認の処理を終了する操作がされていれば、通常遊技を開始するためにステップS2454に進む。一方、設定変更・設定確認の処理が終了していなければ、RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971のエッジ情報をクリアする(ステップS2485)。エッジ情報のクリアによって、1回の操作で複数回の設定値の変更を防止する。これは、RAMクリアスイッチ954や設定キー971のエッジを検出するタイマ割込
み処理が1回実行される間に、第1のメインループ処理が複数回実行されることがあるため、1回設定変更した後に実行される第1のメインループ処理において、前回と同じエッジ情報を使って設定変更しないようにするためである。なお、設定キー971のエッジ情報をクリアせず、RAMクリアスイッチ954のエッジ情報だけをクリアしてもよい。その後、割込を許可に設定し(ステップS2453)、ステップS2450に戻る、設定変更処理用の第1メインループ処理を繰り返し実行する。S2482~S2485までの処理において割込み禁止に設定しているのは、設定変更処理や設定確認処理がタイマ割込みで中断されることを防止するためである。
After that, it is determined whether or not the setting change/setting confirmation process is completed depending on whether the setting
なお、設定処理用の第1メインループ処理(ステップS2450~S2453)では、RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971のエッジ情報をクリアし続けており、通常遊技に移行すると(第2メインループ処理の実行中は)、RAMクリアスイッチ954と設定キー971のエッジ情報を参照されないようになっている。
In addition, in the first main loop processing (steps S2450 to S2453) for the setting processing, the edge information of the RAM
ステップS2484で設定変更・設定確認の処理が終了したと判定されると、通常遊技用の第2メインループ処理(ステップS2457~S2458)を実行する。第2メインループ処理を実行する際は、まず、通常遊技用のCTC1にタイマ割込み周期時間を設定し(ステップS2454)、CTC0の割込みを停止し、CTC1の割込みを起動して(ステップS2455)、CTC1を割込み許可に設定する(ステップS2456)。 When it is determined in step S2484 that the setting change/setting confirmation process is completed, the second main loop process for normal game (steps S2457 to S2458) is executed. When executing the second main loop process, first, the timer interrupt cycle time is set in CTC1 for normal game (step S2454), the interrupt of CTC0 is stopped, and the interrupt of CTC1 is started (step S2455), CTC1 is set to allow interrupts (step S2456).
その後、停電予告信号を取得し、停電予告信号がONであるかによって停電が発生しているかを判定する(ステップS2457)。停電予告信号を検出した場合、電源断時処理(ステップS2462~S2469)を実行する。一方、停電予告信号がONでない場合、正常に電源が供給されているので、乱数更新処理2を実行する(ステップS2458)。乱数更新処理2は、図195で説明したものと同じでよく、主として特別抽選や普通抽選において当選判定を行うための乱数以外の乱数を更新する。その後、ステップS2457に戻り、通常遊技用の第2メインループ処理を繰り返し実行する。なお、通常遊技中(第2メインループに入った後)に設定キー971がONに操作されていることを検出した場合、主制御MPU1311は、その旨を報知するコマンドを生成して、周辺制御基板1510が表示装置に報知演出を行なってもよい。この報知演出は通常遊技中に行われるものであることから、通常遊技の進行に邪魔にならない程度の態様が望ましく、例えば、特定のLEDのみ点灯表示したり、メイン液晶表示装置1600の狭い領域に文字や特定の記号などを表示したり、設定キー971がONに操作されていることを示す特定のキャラクタを遊技の進行に合わせて表示してもよい。
After that, a power failure warning signal is obtained, and it is determined whether or not a power failure has occurred depending on whether the power failure warning signal is ON (step S2457). When the power failure warning signal is detected, power failure processing (steps S2462 to S2469) is executed. On the other hand, if the power failure warning signal is not ON, the power is normally supplied, so random
ステップS2450、S2457で停電予告信号を検出した場合、電源断時処理(ステップS2462~S2469)を実行する。 When the power failure warning signal is detected in steps S2450 and S2457, power failure processing (steps S2462 to S2469) is executed.
電源断時処理では、停電発生前の状態に復帰させるためのデータをバックアップする処理を実行する。具体的には、まず、割込みを禁止する(ステップS2462)。これにより後述するタイマ割込み処理が行われなくなる。さらに、主制御MPU1311は、出力ポートをクリアして、各ポートからの出力によって制御される機器の動作を停止する(ステップS2463)。具体的には、ソレノイド・停電クリア・ACK出力ポートに停電クリア信号OFFビットデータを出力する。なお、全ての出力ポートがクリアされなくてもよく、例えば、電力消費が大きいソレノイドやモータを制御するための出力ポートをクリアしてもよい。これらの出力ポートをクリアすることによって、主基板側電源断時処理が終了するまでの消費電力を低減し、主基板側電源断時処理を確実に終了できるようにする。
In the power failure process, a process of backing up data for returning to the state before the power failure occurred is executed. Specifically, first, the interrupt is prohibited (step S2462). As a result, timer interrupt processing, which will be described later, is not performed. Furthermore, the
その後、フラグレジスタを遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避し(ステップS2464)
、電源OFF時処理を実行して、遊技領域外のワークエリアについて電源が遮断される前に必要な処理を実行する(ステップS2465)。電源OFF時処理の詳細は図222の通りである。そして、遊技領域内スタックエリアに退避したフラグレジスタを復帰する(ステップS2466)。
After that, the flag register is saved in the game area stack area (step S2464)
, the power-off processing is executed, and necessary processing is executed before the power is turned off for the work area outside the game area (step S2465). The details of the power-off processing are as shown in FIG. Then, the flag register saved in the game area stack area is restored (step S2466).
続いて、主制御MPU1311は、バックアップされるワークエリアに格納されたデータが正常に保持されたか否かを判定するための、主制御RAM1312の遊技制御領域内のワークエリアのチェックサムを計算し、主制御RAM1312の所定のチェックサム格納エリアに記憶する(ステップS2467)。このチェックサムはワークエリアにバックアップされたデータが正常かの判定に使用される。なお、チェックサムが算出される対象の領域は、遊技制御領域内のワークエリアのうち、電源投入後主制御側メイン処理の実行までの間に変更される可能性がある設定状態管理(設定値と設定状態管理エリアの値)や、バックアップフラグや、チェックサムエリアの値を除外するとよい。
Subsequently, the
さらに、停電フラグとしてバックアップフラグエリアに正常に電源断時処理が実行されたことを示す値(5AH)を格納する(ステップS2468)。これにより、遊技バックアップ情報の記憶が完了する。最後に、RAMプロテクト有効(書き込み禁止)、禁止領域の無効とする設定値をRAMプロテクトレジスタに書き込み、主制御RAM1312の書き込みを禁止し(ステップS2469)、停電から復旧するまでの間、待機する(無限ループ)。主制御MPU1311は、主制御RAM1312の使用領域を指定することによって、指定領域以外の禁止領域へアクセスがあった場合には、異常と判定してリセットする機能を有する。本実施例では、この禁止領域へのアクセスによるリセット機能を解除して、全領域へのアクセスを可能としている。なお、主制御RAM1312のうち未使用領域を禁止領域に指定して、RAMプロテクトレジスタに禁止領域を有効として設定することで、指定された禁止領域にアクセスを検出した場合には、主制御MPU1311がリセットされるようにしてもよい。
Further, a value (5AH) indicating that the power failure processing has been normally executed is stored in the backup flag area as a power failure flag (step S2468). This completes the storage of the game backup information. Finally, write a setting value for validating RAM protection (writing prohibited) and invalidating the prohibited area to the RAM protection register, prohibiting writing to the main control RAM 1312 (step S2469), and waiting until recovery from the power failure ( infinite loop). The
なお、前述した処理では、出力ポートのクリア(ステップS2463)、電源OFF時処理(ステップS2465)、チェックサムの算出(ステップS2467)、バックアップフラグの設定(ステップS2468)の順に処理を実行しているが、この四つの処理の実行順は、図示したものに限定されず、他の順序でもよい。 In the above-described processing, the processing is executed in the order of clearing the output port (step S2463), processing when the power is turned off (step S2465), calculating the checksum (step S2467), and setting the backup flag (step S2468). However, the execution order of these four processes is not limited to the illustrated one, and other orders may be used.
なお、別例4では、主制御側メイン処理で停電の発生を監視しているが、タイマ割込み処理で停電の発生を監視し、監視結果に基づいて停電処理を実行してもよい。例えば、二つのメインループの各々において、開始時及び終了時の少なくとも一方で停電信号を確認し、停電信号が継続的に出力されている期間を測定し、測定結果が所定値となった場合に停電の発生を検知するとよい。別例4では、設定処理用のタイマ割込み処理と通常遊技処理用のタイマ割込み処理とが別に設けられているため、何れのタイマ割込み処理で停電を監視してもよく、両方のタイマ割込み処理で停電を監視してもよい。このため、停電監視処理と停電処理をサブルーチン化して、二つのタイマ割込み処理の各々でこれらのサブルーチン(停電監視処理、停電処理)を実行することによって、停電監視処理と停電処理の同じプログラム(コード)を各タイマ割込み処理に組み込む必要がなく、プログラムのサイズを小さくできる。 In Example 4, the occurrence of a power failure is monitored by the main processing on the main control side, but the occurrence of a power failure may be monitored by the timer interrupt processing, and power failure processing may be executed based on the monitoring result. For example, in each of the two main loops, check the power failure signal at least at the start and end, measure the period during which the power failure signal is continuously output, and if the measurement result reaches a predetermined value It is preferable to detect the occurrence of a power failure. In another example 4, timer interrupt processing for setting processing and timer interrupt processing for normal game processing are provided separately, so power failure may be monitored by either timer interrupt processing, and both timer interrupt processing Power outages may be monitored. For this reason, the same program (code ) into each timer interrupt process, the size of the program can be reduced.
図231に示す主制御側メイン処理では、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理と通常遊技用タイマ割込みとの各々に対応して二つのメインループが設けられており、必ず一回は設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理の実行契機がある。また、この実行契機において、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理が実行されないこともある(例えば、ステップS2454でYESに分岐する場合)。このようにメインループを二つ設けることによって、通常遊技用のメインループ(タイマ割込み処理)でベース値を計算する処理を実行し、設定変
更処理用のタイマ割込み処理では不要なベース値を計算する処理を実行しないように、ベース値を計算する処理を実行するかを切り替えることができる。
In the main control side main processing shown in FIG. 231, two main loops are provided corresponding to each of the timer interrupt processing for setting change processing and the timer interrupt for normal game. There is an opportunity to execute the timer interrupt processing of Also, in this execution opportunity, timer interrupt processing for setting change processing may not be executed (for example, when branching to YES in step S2454). By providing two main loops in this way, the main loop for normal games (timer interrupt processing) executes processing for calculating the base value, and the timer interrupt processing for setting change processing calculates unnecessary base values. It is possible to switch between executing the processing for calculating the base value and not executing the processing.
図232は、主制御MPU1311が実行する設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理のフローチャートである。別例4では、設定変更・設定確認の処理は、設定処理用のメインループで繰り返し実行される。このため、別例4における設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理は、別例3における設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理(図229)の設定変更・設定確認の処理(ステップS2477~S2478)が削除されたものである。
232 is a flowchart of timer interrupt processing for setting change processing executed by the
まず、主制御MPU1311は、レジスタバンク選択フラグを1に設定し、レジスタのバンクを切り替える(ステップS2470)。なお、主制御MPU1311は、演算に使用するレジスタ群を二つ有し、一つはバンク0のレジスタ群として使用し、他はバンク1のレジスタ群として使用可能とされており、バンク切換を行わずに、両方のバンクのレジスタを使用できないように構成されている。主制御側メイン処理ではレジスタバンク0が使用され、タイマ割込み処理ではレジスタバンク1が使用される。このため、タイマ割込み処理の開始時にはバンクを1に切り替える命令を実行するが、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にはバンクを0切り替える命令を実行する必要がない。これは、主制御MPU1311は、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタ(例えば、Zフラグ、Cフラグがセットされているレジスタ)に記憶しており、フラグレジスタは、割込開始時にスタックエリアに退避され、RET命令の実行によってスタックエリアから復帰する。このため、RET命令を実行することでフラグレジスタに記憶したレジスタのバンクフラグも元に戻る。なお、バンクの状態をフラグレジスタに記憶しない構成を採用した場合、タイマ割込み処理の終了時にバンク切替命令を実行して、バンク0に戻す。
First, the
なお、フラグレジスタには、割込可否を制御するフラグも記憶されているため、割り込み許可に設定してからRET命令を実行しなくてもよい。なお、割込可否を制御するフラグは、タイマ割込み処理の開始時に、フラグレジスタをスタックした後に割込禁止状態に設定される。このため、タイマ割込処理中に割込を許可(EI命令など)するか、RETI命令を実行しない限り、割込み許可状態にはならない。 Since the flag register also stores a flag for controlling whether or not to enable interrupts, it is not necessary to execute the RET instruction after enabling interrupts. It should be noted that the flag that controls whether or not to allow interrupts is set to the interrupt disabled state after the flag register is stacked at the start of timer interrupt processing. Therefore, unless an interrupt is permitted (EI instruction, etc.) or a RETI instruction is executed during timer interrupt processing, the interrupt enabled state is not entered.
次に、LEDコモンカウンタを+1更新する。なお、LEDコモンカウンタ値が上限を超える場合は0にする(ステップS2471)。 Next, the LED common counter is updated by +1. If the LED common counter value exceeds the upper limit, it is set to 0 (step S2471).
次に、スイッチ入力処理1を実行する(ステップS2472)。スイッチ入力処理1では、主制御MPU1311の各種入力ポートの入力端子に入力されている各種信号を読み取り、ONエッジを作成し、入力情報として主制御RAM1312の入力情報記憶領域に記憶する。
Next, switch
なお、ステップS2472のスイッチ入力処理1は入賞信号に関する処理であるため、設定変更モードや設定確認モードで実行されるタイマ割込み処理では、入賞が検出されても、賞球の払出しや特別図柄、普通図柄の変動表示等の遊技の進行にかかる処理が実行されない。また、遊技の進行に関する入賞検出は行われるが、磁石や衝撃(振動)等の不正に関する検出は実行しないようになっている。これは、設定変更操作や設定確認操作はホールの従業員が行なうものであり、設定変更モードや設定確認モードでは、磁石や衝撃(振動)等の不正が行われず、磁気や振動等による不正を検出しない方が望ましいと考えられるためである。
In addition, since the
なお、設定変更モードや設定確認モードでも、一部の不正検出センサ(例えば電波センサ)はスイッチ入力処理1で検出し、特定の種類の不正を監視してもよい。このようにすると、不正行為を行おうとする者(ゴト師)が電波を照射する等によって強制的に設定変
更モードを起動する不正を検出できる。
Note that even in the setting change mode and the setting confirmation mode, some fraud detection sensors (for example, radio wave sensors) may detect in the
そして、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値(00H)が記録されているかを判定する(ステップS2473)。なお、設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理において、遊技状態管理エリアの値を判定しなくてもよい。これは、不正に設定変更処理に移行する不正行為へ対応するためである。また、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値(00H)が記録されているかの判定はスイッチ入力処理1(ステップS2472)の前に判定し、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていれば、周辺基板コマンド送信処理(ステップS2479)の後に進んでもよい。 Then, it is determined whether a value (00H) indicating game start is recorded in the setting state management area (step S2473). It should be noted that the value of the gaming state management area may not be determined in the timer interrupt process for the setting change process. This is to deal with the fraudulent act of illegally shifting to the setting change process. Further, whether or not the value (00H) indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area is determined before the switch input process 1 (step S2472), and the value indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area. If so, the process may proceed after the peripheral board command transmission process (step S2479).
設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていれば、設定値の変更、表示に関する処理(ステップS2474~S2476)を実行せず、ステップS2479に進む。なお、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されている場合、異常なタイマ割込み処理が実行されていることを報知する異常報知用コマンドを生成してもよい。設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されている場合、図232に示す設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理が実行されることはなく、何らかの異常が発生しているからである。この異常報知の態様は、磁石、電波、振動等の報知のように液晶やランプや音を使う報知や、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力してもよい。これらの報知態様の一つ以上を採用して、一つ又は組合せで報知してもよい。
If a value indicating the start of the game is recorded in the setting state management area, the processing (steps S2474 to S2476) related to changing and displaying the setting value is not executed, and the process proceeds to step S2479. Incidentally, when a value indicating the start of a game is recorded in the setting state management area, an abnormality notification command for notifying that an abnormal timer interrupt process is being executed may be generated. This is because when a value indicating the start of a game is recorded in the setting state management area, the timer interrupt processing for the setting change processing shown in FIG. 232 is not executed, and some kind of abnormality has occurred. This anomaly notification mode may be notification using a liquid crystal, lamp, or sound, such as magnet, radio wave, or vibration notification, or a security signal may be output from the external
一方、設定状態管理エリアに遊技開始を示す値が記録されていなければ、特定の出力ポートをクリアする(ステップS2474)、例えば、ステップ2474で特定の出力ポートとしてクリアされる信号は、停電クリア信号、大入賞口・電チュー等のソレノイド信号、払出制御基板951へのコマンド受信時の応答信号(ACK)がある。その後、LEDコモンポートをOFFにする(ステップS2475)。タイマ割込み処理の早い段階でLEDコモン信号をOFFにすることによって、LEDコモン信号がオンになるまでの時間、すなわちLEDの消灯時間を確保し、LEDの表示切替前後の表示が混ざって見えるゴースト現象を抑制し、LEDのちらつきを防止している。
On the other hand, if the value indicating the start of the game is not recorded in the setting state management area, the specific output port is cleared (step S2474). , a solenoid signal such as a large winning opening and an electric chew, and a response signal (ACK) at the time of command reception to the
その後、外部端子板784からセキュリティ信号を出力する(ステップS2476)。なお、セキュリティ信号を出力する処理も、設定変更・設定確認の処理と同様に、図231に示す主制御側メイン処理の設定変更処理用のメインループで実行してもよい。 Thereafter, a security signal is output from the external terminal board 784 (step S2476). The process of outputting the security signal may also be executed in the main loop for the setting change process of the main control side main process shown in FIG. 231, similarly to the setting change/setting confirmation process.
さらに、送信情報記憶領域の値をシリアル通信回路に出力する周辺基板コマンド送信処理を実行する(ステップS2479)。送信情報記憶領域は、生成された送信コマンドを一時的に格納する記憶領域である。送信情報記憶領域に格納された値(コマンド)は、ステップ2070で読み出されてシリアル通信回路(SIO)の送信情報記憶領域に格納される。シリアル通信回路は、複数バイトのFIFO形式の送信バッファである送信情報記憶領域を有し、シリアル通信回路の送信情報記憶領域に格納された値を、順次、周辺制御基板1510に送信する。周辺基板コマンド送信処理を、タイマ割込み処理ではなく、メイン処理のS2480又はS2481の処理の終了後に実行してもよい。 Further, peripheral board command transmission processing for outputting the value of the transmission information storage area to the serial communication circuit is executed (step S2479). The transmission information storage area is a storage area that temporarily stores the generated transmission command. The value (command) stored in the transmission information storage area is read at step 2070 and stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit (SIO). The serial communication circuit has a transmission information storage area which is a transmission buffer in the FIFO format of multiple bytes, and sequentially transmits the values stored in the transmission information storage area of the serial communication circuit to the peripheral control board 1510 . The peripheral board command transmission process may be executed after the process of S2480 or S2481 of the main process is completed instead of the timer interrupt process.
その後、ウォッチドッグタイマクリアレジスタWCLに所定値(18H)をセットして、ウォッチドッグタイマをクリアする(ステップS2480)。なお、ウォッチドッグタイマは、単純クリアモードを使用しているので、1ワードをセットすることによってウォッチドッグタイマがクリアされる。その後、復帰命令(例えばRETI)によって、レジスタのバンクを切り替え(ステップS2481)、割り込み前の処理に復帰する。 Thereafter, a predetermined value (18H) is set in the watchdog timer clear register WCL to clear the watchdog timer (step S2480). Note that the watchdog timer uses a simple clear mode, so setting one word clears the watchdog timer. Thereafter, a return instruction (for example, RETI) switches the bank of the register (step S2481), and returns to the processing before the interrupt.
図232に示す設定変更処理用のタイマ割込み処理では、他のタイマ割込み処理と異なり、乱数更新処理(R_ATART_K)を実行しない。これは、RAM異常時にソフト
ウェアで生成される乱数を更新する必要がないためであるが、乱数更新処理を実行してもよい。
In timer interrupt processing for setting change processing shown in FIG. 232, unlike other timer interrupt processing, random number update processing (R_ATART_K) is not executed. This is because there is no need to update random numbers generated by software when a RAM abnormality occurs, but random number update processing may be executed.
[13.導光板を備えるパチンコ機]
次に、導光板を備えるパチンコ機の実施例を説明する。近年のパチンコ機は、照光によって発光する導光板をメイン液晶表示装置1600の前面側に備え、メイン液晶表示装置1600と共に特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出を行っている。この種のパチンコ機では、液晶表示装置と導光板を用いて、例えば画像を重畳させることによって、複雑な演出が可能である。また、導光板は、液晶表示装置の前面に設けられているので、液晶表示装置に表示される画像と合わせて、立体感がある演出を表示している。また、左右眼の視差を利用した立体視が可能な導光板があり、さらに大きな立体感がある演出を表示している。
[13. Pachinko machine with light guide plate]
Next, an embodiment of a pachinko machine having a light guide plate will be described. A recent pachinko machine has a light guide plate that emits light by illumination on the front side of the main liquid
しかし、導光板を用いた演出がマンネリ化しており、新たな発光演出による興趣の向上が必要となっている。さらに、1枚で複数の絵柄を表示できる導光板があり、さらに多様な絵柄を表示して、興趣の高い演出が求められている。 However, the performance using the light guide plate has become boring, and it is necessary to improve the interest by a new light emission performance. Furthermore, there is a light guide plate that can display a plurality of patterns on a single plate, and there is a demand for more interesting effects by displaying a wider variety of patterns.
[13-1.構造]
図233は、遊技盤5の表ユニット2000のセンター役物2500と表演出ユニット2600とを分解して前から見た分解斜視図である。図234は、表演出ユニットにおいて第一絵柄を発光表示した状態を示す正面図である。図235は、表演出ユニットにおいて第二絵柄を発光表示した状態を示す正面図である。
[13-1. structure]
FIG. 233 is an exploded perspective view of the
表ユニット2000の表演出ユニット2600は、枠状のセンター役物2500の枠内を閉鎖するように、センター役物2500に取付けられている。表演出ユニット2600は、センター役物2500の後側に取付けられている。表演出ユニット2600は、センター役物2500の枠内を閉鎖する透明な平板状の導光板2610と、センター役物2500の後側に取付けられている第一絵柄用基板2611及び第二絵柄用基板2612とを有する。第一絵柄用基板2611には、導光板2610の右側面に光を照射可能な複数の導光板用LED2613が実装されており、第二絵柄用基板2612には、導光板2610の上側面に光を照射可能な複数の導光板用LED2614が実装されている。
The
第一絵柄用基板2611及び第二絵柄用基板2612は、導光板2610の側面に光を照射可能なように、導光板2610と垂直に配置されている。このため、パチンコ機1の正面側からは、第一絵柄用基板2611及び第二絵柄用基板2612の側面しか見えず、第一絵柄用基板2611及び第二絵柄用基板2612が遊技者側から見え辛くなっており、遊技領域5a内の見栄えを良くしている。
The
なお、本実施例では、導光板(表導光板)2610について説明するが、導光板2610と液晶表示装置1600との間に他の裏導光板を設けてもよい。
Although the light guide plate (front light guide plate) 2610 will be described in this embodiment, another back light guide plate may be provided between the
導光板2610は、上方向からの光を前面側へ反射させる凹凸状の無数の第一反射部により形成されている第一絵柄2621(図234を参照)と、横方向からの光を前面側へ反射させる凹凸状の無数の第二反射部により形成されている第二絵柄2622(図235を参照)とを有している。つまり、表演出ユニット2600は、第一絵柄用基板2611の導光板用LEDを2613発光させると、導光板2610に第一絵柄2621を発光表示でき、第二絵柄用基板2612の導光板用LED2614を発光させると、導光板2610に第二絵柄2622を発光表示する。第一絵柄用基板2611及び第二絵柄用基板2612に実装されている複数のLED2613、2614は、望ましくはフルカラーLEDであり、狭い範囲に光を照射する指向性が強い発光源(レンズ付きLED)が望ましい。フルカラーLEDを用いることによって、任意の単一色や複数色(例えば、7色のレイ
ンボーカラー)によって第一絵柄2621や第二絵柄2622を導光板2610に写すことができる。
The
導光板2610には、第一絵柄2621を写すための複数の第一反射部を構成する凹凸、第二絵柄2622を写すための複数の第二反射部を構成する凹凸が微細に形成されており、第一絵柄用基板2611の導光板用LED2613や第二絵柄用基板2612の導光板用LED2614が発光していない状態では、導光板2610が光を透過して、後側に配置されている裏ユニット3000の各種の装飾体や演出表示装置1600に表示されている演出画像等を良好に視認できる。導光板2610には、導光板用LED2613、2614が発光状態でも、裏面側に設けられた液晶表示装置1600が透過して見える透過領域と、導光板2610に照射された光を反射せず、磨りガラス状の加工がされたマット領域と、導光板2610内の光の進行方向によらずに、透過する光を反射する反射パターンが形成されているラメ領域と、導光板用LED2613の発光箇所(すなわち、導光板2610内の光の進行方向)によって発光するかが変わるように反射パターンが形成されているムービング領域とが設けられる。
On the
図234に示すように、第一絵柄2621は、後述するように液晶表示装置1600に表示される画像と共に特別図柄変動表示ゲームの演出の一部となる。第一絵柄2621は、ムービング領域2621a、2621cと、ラメ領域2621b、2621dと、マット領域2621eとによって構成される。第一絵柄2621の外側は透過領域2621fとなっている。ムービング領域2621a、2621cは、第一絵柄用基板2611の導光板用LED2613の一部を点灯させ、点灯箇所を切り替えることによって、ムービング領域2621aが発光したり、ムービング領域2621cが発光したりする。このため、導光板用LED2613を点滅させることによって、第一絵柄2621の大きさが変わるように見せることができる。
As shown in FIG. 234, the
図234に示す第一絵柄2621では、ムービング領域とラメ領域とが2回繰り返されて配置されているが、繰り返しは何回でもよい。ムービング領域とラメ領域とが複数回繰り返されて第一絵柄2621を構成することによって、第一絵柄2621によって複雑な動きを表すことができる。また、図234に示す第一絵柄2621では、ムービング領域とラメ領域とが交互に繰り返されているが、ムービング領域の間にラメ領域を挟まずに、特性(すなわち、当該ムービング領域が発光するための光の入射位置)が異なるムービング領域を隣接して配置してもよい。
In the
導光板用LED2613によって発光色が変わるように導光板用LED2613を発光させることによって、ムービング領域2621a毎に色を変えて光らせることができる。そして、導光板用LED2613の発光色を順次変える(例えば、赤→橙→黄→緑→青→藍→紫→赤、と繰り返す)ことによって、色の変化に伴って絵柄が移動するように見せることができる。
By causing the light
図235に示すように、第二絵柄2622は、複数の光の筋が斜め下方へ延びている絵柄である。第二絵柄2622は、斜めに延びた光の筋が、第二絵柄用基板2612に実装されている導光板用LED2614の位置と対応するように、形成されている。つまり、一つの導光板用LED2614を発光させると、導光板2610の上辺の、発光した導光板用LED2614の部位を起点として、導光板2610の下方向へ斜めに延びた光の筋が発光する。
As shown in FIG. 235, the
この第二絵柄2622は、導光板2610の下方向へ向かうほど、導光板用LED2614から遠くなるため、光の筋の明るさは、導光板2610の下方向へ向かうに従って暗くなる。これにより、第二絵柄2622を前方(遊技者側)から見ると、導光板2610
の下方向へ向かうほど、光の筋が後方へ延びているように見え、光が立体的に放射されているように錯覚させることができ、導光板2610による発光演出を楽しませることができる。
The
As it goes downward, the lines of light appear to extend backward, giving the illusion that the light is emitted three-dimensionally, and the light emission performance by the
さらに、左右眼の視差による立体視が可能なように反射部を配置するとよい。例えば、第二絵柄2622を構成する1本の光の筋に着目すると、当該光の筋を遊技者の網膜に結像させる光を発する第二反射部を、左右眼で、導光板2610の異なる位置に配置することによって、遊技者の左右眼の視差を生じさせることができ、奥行きを持った第二絵柄を見せることができる。
Furthermore, it is preferable to arrange the reflectors so that stereoscopic viewing is possible due to parallax between the left and right eyes. For example, focusing on one light streak that constitutes the
本実施例の導光板2610は、図234に示すように、一方向からの光の照射によって映し出される第一絵柄2621を、照射された光を反射しないマット領域2621eや、光の進行方向によらずに、透過する光を反射する反射パターンが形成されているラメ領域2621b、2621dや、特定の進行方向の光を反射する反射パターンが形成されているムービング領域2621a、2621c、2622aによって構成するので、第一絵柄を動いて見えるムービング絵柄領域(動的な絵柄)と静止して見える静止絵柄領域(静的な絵柄)とで構成できる。
As shown in FIG. 234, the
また、1枚の導光板2610で、照光方向の違いによって、図234に示す第一絵柄2621と、図235に示す第二絵柄2622とを映し出すことができる。このため、横方向から単一色(例えば、単一波長の赤色や複数波長の光が混在している白色)の光を照射し、上方向から複数色の光を照射(例えば、隣接するLED群2614が異なる波長で発光)することによって、1枚の導光板2610で、7色に輝くレインボー絵柄(レインボービーム)と単一色の絵柄とによる演出を行うことができる。
234 and the
本実施例の導光板2610において、横方向からの光の照射によって、第一絵柄2621のマット領域2621eやラメ領域2621b、2621dで静止絵柄、及びムービング領域2621a、2621c、2622aで動いて見えるムービング絵柄を映している。すなわち、横方向からの光の照射による第一絵柄2621によって、静止絵柄とムービング絵柄の両方による導光板演出が行われる。この場合、第一絵柄2621による静止絵柄とムービング絵柄とは同時に映し出されることになる。
In the
前述とは異なり、第一絵柄2621をマット領域及びラメ領域によって構成し、第一絵柄2621にはムービング絵柄を含めなくてもよい。この場合、横方向からの光の照射による第一絵柄2621による静止絵柄と、上方向からの光の照射による第二絵柄2622とで導光板演出が行われる。この場合、第一絵柄2621による静止絵柄と第二絵柄2622によるムービング絵柄とは異なるタイミングで映し出すことができる。すなわち、静止絵柄を映した後にムービング絵柄を映してもよく、ムービング絵柄を映した後に静止絵柄を映してもよい。このように、静止絵柄とムービング絵柄とを異なるタイミングで映すことによって、多様な演出を行うことができる。特に、レインボー絵柄をムービング絵柄として表示した後に静止絵柄で特定のキャラクタを表示することによって、当該キャラクタが降臨するような演出を行うことができる。一方、静止絵柄で背景を表示した後にムービング絵柄でキャラクタを表示することによって、特定の場所でキャラクタが移動するような演出を行うことができる。
Unlike the above, the
本実施例の導光板2610において、第一絵柄2621と第二絵柄2622とを重畳させて配置してもよい。横方向と上方向とから光を照射した場合、導光板2610上で二つの絵柄が重畳している領域では、二つの絵柄の反射パターンが混在して設けられるので、二つの絵柄が共に認識できる。しかし、第一絵柄2621が平面視される絵柄であり、第二絵柄2622が立体視される絵柄である場合、二つの絵柄が混在する領域では立体視が
困難になる場合がある、このため、第一絵柄2621の反射パターンが設けられず、裏面側(液晶表示装置1600)が透過して見える透過領域2621fを設け、第二絵柄2622の反射パターンによる絵柄を映し出すと、第二絵柄2622を遊技者に容易に立体視させることができる。
In the
本実施例の導光板2610において、第一絵柄2621と第二絵柄2622とを重畳させずに、別領域に配置してもよい。第一絵柄2621が平面視される絵柄であり、第二絵柄2622が立体視される絵柄である場合、二つの絵柄が混在する領域では立体視が困難になる場合がある、このため、第一絵柄2621の反射パターンが設けられる領域と、第二絵柄2622の反射パターンが設けられる領域とを分けて、第二絵柄2622の反射パターンによる絵柄を映し出すと、第二絵柄を遊技者に容易に立体視させることができる。
In the
[13-2.導光板の構成]
次に、反射部の具体的な構成を説明する。図236は、導光板2610の構造(特に、反射部の配置)を示す図である。
[13-2. Configuration of Light Guide Plate]
Next, a specific configuration of the reflector will be described. FIG. 236 is a diagram showing the structure of the light guide plate 2610 (especially the arrangement of the reflectors).
前述したように、導光板2610には、裏面側(液晶表示装置1600)が透過して見える透過領域2621fと、照射された光を反射しないマット領域2621eと、光の進行方向によらずに、透過する光を反射する反射パターンが形成されているラメ領域2621b、2621dと、特定の進行方向の光を反射する反射パターンが形成されているムービング領域2621a、2621c、2622aとが設けられる。
As described above, the
図237は、反射部の構造を示す図である。 FIG. 237 is a diagram showing the structure of the reflector.
反射部は導光板2610の裏面側に設けられた凹部で形成され、境界面(反射面2651)における光の反射によって、導光板2610の内部を進行する光を、導光板2610の前面側に反射して、導光板2610の絵柄部分を発光させ、遊技者に絵柄を視認させる。導光板2610の内部では導光板用LED2614から入射した光は、ある程度の広がり(例えば±30度)で導光板2610の内部を進行する。第二絵柄2622を構成する光の筋は、当該光の筋の方向に進行する光が、以下に説明する反射部2650で反射することによって見える。
The reflecting portion is formed by a concave portion provided on the back side of the
図237(A)に示すムービング領域2622aの反射部は、光の筋に沿って複数の反射部2650が配置されている。なお、反射部2650の大きさは、望ましくは数百マイクロメートルから数ミリメートルであり、導光板2610上に表れる光の筋より極めて小さい大きさであるが、図では大きく図示している。
In the reflecting portion of the moving
反射部2650は、光を反射する反射面2651と、反射面2651の裏側の傾斜面2652と、曲面によって形成された側面2653とによって構成される。反射面2651は、導光板2610の表面に対して略45度の角度で、かつ、反射面2651の垂線と反射する光の入射方向とが略45度になるように配置される。このため、導光板2610の内部を進行し、反射部2650の反射面2651に当たった光は、図237(B)に示すように、導光板2610の前面側に反射する。
The reflecting
また、ムービング領域2622aに表れる光の筋に垂直な方向、すなわち、反射面2651に沿って反射面2651と平行に進行する光は反射面2651に当たらず、反射部2650で反射して導光板2610の表面から出射しない。同様に、ムービング領域2622aに表れる光の筋と角度を持った(特に、鋭角となる)方向に進行する光は反射面2651に当たる量が少なく、反射部2650では少しの光しか反射せず、導光板2610の表面からは弱い光しか出射しない。このため、多く到達する波長の光が遊技者の目には見
え、特定位置で発光する導光板用LED2614の色で絵柄を見せることができる。
In addition, the direction perpendicular to the streak of light appearing in the moving
このとき、反射面2651を少し傾けることによって、反射光の出射方向を導光板2610に垂直方向から左右に少しずらしてもよい。本実施例の導光板2601を照射する光源は指向性が強い光を照射するので、反射部2650からの反射光も指向性を持った光のビームとして遊技者に到達する。このため、遊技者の左右眼の視差を生じさせることができ、奥行きを持った第二絵柄を見せることができる。すなわち、右眼へ到達する光を反射する反射部2650と左眼へ到達する光を反射する反射部2650とが異なる位置にあるため、右眼へ到達する光と左眼へ到達する光との仮想的な交点は導光板2610上にはない。つまり、右眼へ到達する光と左眼へ到達する光との仮想的な交点が導光板2610より後方にあれば、絵柄が奥まった位置に見え、右眼へ到達する光と左眼へ到達する光との仮想的な交点が導光板2610より前方にあれば、絵柄が手前の位置に見える。
At this time, by tilting the reflecting surface 2651 a little, the emission direction of the reflected light may be slightly shifted left and right from the direction perpendicular to the
反射面2651の反対側に設けられる傾斜面2652は、反射面2651と同様に導光板2610の表面に対して略45度の角度で設けられてもよいし、導光板2610の内部を進行する光を導光板2610の前面側に反射しない角度で(例えば、導光板2610の表面と垂直に)形成してもよい。
The
側面2653は、曲面に加工されている。側面2653を、平面ではなく、曲面に加工することによって、一方向から入射した光を強く反射することなく、特定の方向以外から到来する光によって絵柄が表示されることを防止できる。
The
図238に示すラメ領域2621b、2621dの反射部2660は、導光板2610の裏面側に設けられた球面状の凹部によって構成されており、導光板2610内を進行し、複数の方向から(すなわち、複数の経路で)反射部2660に到来する光を反射し、導光板2610の前面側に出射する。ラメ領域の反射部2660は、複数の導光板用LED2614からの光を反射するので、導光板用LED2614の各々が異なるタイミングで点滅すると、ラメ領域2621bは、キラキラ光ることになる。また、導光板用LED2614が異なる色で発光すると、ラメ領域2621bは、複数色が混ざって光ることになる。さらに、導光板用LED2614が異なる色で点滅すると、ラメ領域2621bは、複数色が混ざってキラキラ光ることになる。
Reflecting
なお、マット領域2621eには、反射部が設けられておらず、すりガラス状に不定形の凹凸に加工されており、導光板2610内を進行する光を前面側に反射しない。
The
ここまで第一絵柄と第二絵柄とを表す導光板2610を説明したが、次に、異なる絵柄を表す導光板の実施例を説明する。図239は、図240から図242に示す絵柄を構成する導光板におけるLEDと反射部との関係を模式的に示す図である。
So far, the
図239に示す導光板2610は、その裏面に形成されており、導光板2610の上側面の複数の特定入光部2630の何れかから入射した光を反射し、導光板2610の前面側へ出射する微細な複数の反射部2670を有している。導光板2610の複数の特定入光部2630は、複数の位置から導光板2610内を光が進行するように、光を導入するものである。複数の特定入光部2630は、第一特定入光部2630a、第二特定入光部2630b、第三特定入光部2630c、第四特定入光部2630dの四つを図示したが、第一特定入光部2630aから第七特定入光部までが設けられている。これは、導光板を七色に発光させるレインボー演出のために七つの特定入光部2630(LED群2614)を繰り返し設けるものであり、発光色の種類によって特定入光部の数を決めるとよい。第一特定入光部2630aから第七特定入光部(図示省略)は、導光板2610の上側面を長手方向(図において左右方向)で左から右へ順番に繰り返し(第七特定入光部の次
は初めに戻って第一特定入光部2630aとなる順で)配置されている。
The
反射部2670は、対応している特定入光部2630と結んだ直線(特定入光部2630から入射した光が導光板2610内を進行する方向)に対して、直角方向へ延びていると共に導光板2610の後面に対して45度傾斜している境界面を有している。反射部2670は、ペントルーフ状の三角形に凹んでいる。反射部2670は、対応している特定入光部2630から入射した光を反射して、導光板2610の前面に対して略垂直な方向へ出射する。また、反射部2670は、対応していない特定入光部2630から入射した光を反射し、導光板2610の前面の垂直線に対して傾斜している方向へ出射する。
The reflecting portion 2670 extends in a direction perpendicular to a straight line connecting the corresponding specific light entrance portion 2630 (the direction in which the light incident from the specific
これにより、図239において破線で示すように、対応している特定入光部2630から入射した光はと、反射部2670により導光板2610の前面側の正面(紙面に対して垂直方向)へ反射し、パチンコ機1の正面に着座している遊技者からは当該反射部2670が発光して見える。これに対して、図239において一点鎖線で示すように、対応していない特定入光部2630から入射した光は、反射部2670により導光板2610の前方正面以外の方向へ反射し、パチンコ機1の正面に着座している遊技者からは当該反射部2670が発光していないように見える。
As a result, as indicated by broken lines in FIG. 239, the light incident from the corresponding specific
なお、本実施例では、反射部2670として、三角形に凹んだ状態で、対応している特定入光部2630と結んだ直線に対して直角方向へ延びている形態のものを示したが、これに限定するものではなく、対応する特定入光部2630と結んだ直線に対して直角方向へ延びているものであればよい。
In this embodiment, the reflecting portion 2670 is recessed in a triangular shape and extends in the direction perpendicular to the straight line connecting the corresponding specific
複数の反射部2670は、複数の特定入光部2630の何れかに対応しており、第一特定入光部2630aに対応している複数の第一反射部2670a、第二特定入光部2630bに対応している複数の第二反射部2670b、第三特定入光部2630cに対応している複数の第三反射部2670c、第四特定入光部2630dに対応している複数の第四反射部2670dなどを含む。
The plurality of reflecting portions 2670 correspond to any of the plurality of specific
また、導光板2610は、複数の反射部2670のうちの特定の反射部2670が前方へ光を反射させることにより、互いに異なる態様に発光表示可能な複数の絵柄2623を表示可能となっている。複数の絵柄2623は、複数の第一反射部2670aからなる絵柄2623aと、複数の第二反射部2670bからなる絵柄2623bと、複数の第三反射部2670cからなる絵柄2623cと、複数の第四反射部2670dからなる絵柄2623dなどを含む。
Further, the
絵柄は、図240から図242に示すように、中心から外側へ順番に且つ巡回するように配置されている。 As shown in FIGS. 240 to 242, the patterns are arranged in order from the center to the outside in a circulating manner.
第二絵柄用基板2612は、左右に延びた帯板状で、各特定入光部2630に対応する位置にLED2614が実装されている。複数のLED2614は、第一特定入光部2630aと対応している第一LED群2614aと、第二特定入光部2630bと対応している第二LED群2614bと、第三特定入光部2630cと対応している第三LED群2614cと、第四特定入光部2630dと対応している第四LED群2614dと、第五特定入光部(図示省略)と対応している第五LED群(図示省略)と、第六特定入光部(図示省略)と対応している第六LED群(図示省略)と、第七特定入光部(図示省略)と対応している第七LED群(図示省略)とから構成されている。なお、図239には、第一LED群2614aから第四LED群2614dを図示し、第五LED群から第七LED群の図示は省略した。各LED群は、第二絵柄用基板2612上で長手方向(図において左右方向)に列設されている複数のLED2614を、第二絵柄用基板2612の左
右方向で分割し、左から右へ順番に繰り返し(第七LED群の次は初めに戻って第一LED群2614aとなる順で)配置されている。本実施例では、各LED群は、夫々6個ずつLED2614を有している。
The
次に、本実施形態の表演出ユニット2600による発光演出について、詳細に説明する。第二絵柄用基板2612の第一LED群2614aを発光させると、導光板2610内に第一特定入光部2630aから光が入射し、第一反射部2670aでは導光板2610の正面へ反射し、他の第二反射部2670b、第三反射部2670c、第四反射部2670d等では正面以外へ反射するため、パチンコ機1の正面に着座した遊技者からは第一反射部2670aのみが光って見えることとなり、複数の第一反射部2670aから構成されている絵柄を発光させることができる。
Next, the lighting effect by the
第二絵柄用基板2612の第二LED群2614bを発光させると、導光板2610内に第二特定入光部2630bから光が入射し、第二反射部2670bでは導光板2610の正面へ反射し、他の第一反射部2670a、第三反射部2670c、第四反射部2670d等では正面以外へ反射するため、パチンコ機1の正面に着座した遊技者からは第二反射部2670bのみが光って見えることとなり、複数の第二反射部2670bから構成されている絵柄を発光させることができる。
When the
第二絵柄用基板2612の第三LED群2614cを発光させると、導光板2610内に第三特定入光部2630cから光が入射し、第三反射部2670cでは導光板2610の正面へ反射し、他の第一反射部2670a、第二反射部2670b、第四反射部2670d等では正面以外へ反射するため、パチンコ機1の正面に着座した遊技者からは第三反射部2670cのみが光って見えることとなり、複数の第三反射部2670cから構成されている絵柄を発光させることができる。
When the
第二絵柄用基板2612の第四LED群2614dを発光させると、導光板2610内に第四特定入光部2630dから光が入射し、第四反射部2670dでは導光板2610の正面へ反射し、他の第一反射部2670a、第二反射部2670b、第三反射部2670c等では正面以外へ反射するため、パチンコ機1の正面に着座した遊技者からは第四反射部2670dのみが光って見えることとなり、複数の第四反射部2670dから構成されている絵柄を発光させることができる。
When the
第五LED群から第七LED群2614も同様に、各LED群を発光させると、対応する特定入光部2630から導光板2610内に光が入射し、対応する反射部2670で導光板2610の正面へ反射し、他の反射部2670では正面以外へ反射し、パチンコ機1の正面に着座した遊技者からは対応する反射部2670のみが光って見えることとなり、対応する反射部2670から構成されている絵柄を発光させることができる。
Similarly, when each LED group is caused to emit light from the fifth LED group to the
前述したように、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、LED群を切り替えて発光させることによって、複数の絵柄2623を夫々発光させることができ、複数の絵柄を順に発光させて、動きのあるアニメーションのような発光演出を行うことができる。特に、図240に示すように、相似形の絵柄を重畳させた導光板2610においては、中心から外側へ広がる、又は外側から中心へ縮むような動きがあるアニメーションのように絵柄を発光させるムービング演出ができる。
As described above, in the
図240は、導光板によるムービング演出で表示される絵柄の例を示す図である。図240に示す例では、発光するLED群の位置を時間の経過と共に切り替えることによって、絵柄の大きさが変化するムービング演出を行う。 FIG. 240 is a diagram showing an example of a pattern displayed in a moving effect by the light guide plate. In the example shown in FIG. 240, by switching the position of the group of LEDs that emit light with the lapse of time, a moving effect is performed in which the size of the pattern changes.
前述したように、導光板2610には、第一特定入光部2630aから第七特定入光部2630gが設けられており、各特定入光部2630a~2630gに対応して第一LED群2614aから第七LED群2614gが配置されている。なお、図240では、各特定入光部に対応する位置を符号の最後の一文字のアルファベットによって表す。
As described above, the
図240(A)に示すように、第六LED群2614f及び第七LED群2614gが点灯し、第六特定入光部2630f及び第七特定入光部2630gから光が入射すると、導光板2610に入射した光を第六反射部2670f及び第七反射部2670gが反射し、第六反射部2670f及び第七反射部2670gが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。
As shown in FIG. 240(A), when the sixth LED group 2614f and the seventh LED group 2614g are turned on and light enters from the sixth specific light entrance portion 2630f and the seventh specific light entrance portion 2630g, the
その後、第五LED群2614e及び第六LED群2614fが点灯し、第五特定入光部2630e及び第六特定入光部2630fから光が入射すると、導光板2610に入射した光を第五反射部2670e及び第六反射部2670fが反射し、第五反射部2670e及び第六反射部2670fが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。
After that, when the fifth LED group 2614e and the sixth LED group 2614f are turned on and the light enters from the fifth specific light entering portion 2630e and the sixth specific light entering portion 2630f, the light entering the
さらに、図240(B)に示すように、第四LED群2614d及び第五LED群2614eが点灯し、第四特定入光部2630d及び第五特定入光部2630eから光が入射すると、導光板2610に入射した光を第四反射部2670d及び第五反射部2670eが反射し、第四反射部2670d及び第五反射部2670eが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 240(B), when the
その後、第三LED群2614c及び第四LED群2614dが点灯し、第三特定入光部2630c及び第四特定入光部2630dから光が入射すると、導光板2610に入射した光を第三反射部2670c及び第四反射部2670dが反射し、第三反射部2670cd及び第四反射部2670dが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。
After that, when the
さらに、図240(C)に示すように、第二LED群2614b及び第三LED群2614cが点灯し、第二特定入光部2630b及び第三特定入光部2630cから光が入射すると、導光板2610に入射した光を第二反射部2670b及び第三反射部2670cが反射し、第二反射部2670b及び第三反射部2670cが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 240(C), when the
このように、発光させるLED群(LED素子)の数を変えずに、位置を変えることによって、絵柄の大きさを変化させ、中心から外側へ動くように絵柄を発光させるムービング演出ができる。このとき、LED群は単一色で発光しても、各群で(すなわち、位置によって)異なる色で発光してもよい。 In this way, by changing the position of the group of LEDs (LED elements) to emit light without changing the number thereof, the size of the pattern can be changed, and a moving effect can be achieved in which the pattern emits light so as to move from the center to the outside. At this time, the LED groups may emit a single color, or each group may emit a different color (ie, depending on the position).
図241は、導光板による別のムービング演出で表示される絵柄の例を示す図である。図241に示す例では、発光するLED群の数を時間の経過と共に変えることによって、絵柄の大きさが変化するムービング演出を行う。 FIG. 241 is a diagram showing an example of a pattern displayed in another moving effect by the light guide plate. In the example shown in FIG. 241, by changing the number of light-emitting LED groups with the lapse of time, a moving effect is performed in which the size of the pattern changes.
前述したように、導光板2610には、第一特定入光部2630aから第七特定入光部2630gが設けられており、各特定入光部2630a~2630gに対応して第一LED群2614aから第七LED群2614gが配置されている。なお、図241では、各特定入光部に対応する位置を符号の最後の一文字のアルファベットによって表す。
As described above, the
図241(A)に示すように、第二LED群2614b~第七LED群2614gが点灯し、第二特定入光部2630b~第七特定入光部2630gから入射した光を第二反射部2670b~第七反射部2670gが反射し、第二反射部2670b~第七反射部26
70gが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。
As shown in FIG. 241(A), the
The pattern in which 70g is arranged emits light and can be recognized by the player.
その後、第三LED群2614c~第七LED群2614gが点灯し、第三特定入光部2630c~第七特定入光部2630gから入射した光を第三反射部2670c~第七反射部2670gが反射し、第三反射部2670c~第七反射部2670gが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。
After that, the
さらに、図241(B)に示すように、第四LED群2614d~第七LED群2614gが点灯し、第四特定入光部2630d~第七特定入光部2630gから入射した光を第四反射部2670d~第七反射部2670gが反射し、第四反射部2670d~第七反射部2670gが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 241(B), the
その後、第五LED群2614e~第七LED群2614gが点灯し、第五特定入光部2630e~第七特定入光部2630gから入射した光を第五反射部2670e~第七反射部2670gが反射し、第五反射部2670e~第七反射部2670gが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。 After that, the fifth LED group 2614e to the seventh LED group 2614g are turned on, and the light incident from the fifth specific light entrance portion 2630e to the seventh specific light entrance portion 2630g is reflected by the fifth reflection portion 2670e to the seventh reflection portion 2670g. Then, the pattern in which the fifth reflecting portion 2670e to the seventh reflecting portion 2670g are arranged emits light and can be recognized by the player.
さらに、図241(C)に示すように、第六LED群2614f~第七LED群2614gが点灯し、第六特定入光部2630f~第七特定入光部2630gから入射した光を第六反射部2670f~第七反射部2670gが反射し、第六反射部2670f~第七反射部2670gが配置された絵柄が発光し、遊技者が認識できる。 Further, as shown in FIG. 241(C), the sixth LED group 2614f to the seventh LED group 2614g are turned on, and light incident from the sixth specific light entrance portion 2630f to the seventh specific light entrance portion 2630g is reflected in the sixth direction. The part 2670f to the seventh reflecting part 2670g reflect, and the pattern in which the sixth reflecting part 2670f to the seventh reflecting part 2670g are arranged emits light, which the player can recognize.
このように、発光させるLED群(LED素子)の数を変えることによって、絵柄の大きさ(発光範囲)を変化させ、縮むように絵柄を発光させるムービング演出ができる。このとき、LED群は単一色で発光しても、各群で(すなわち、位置によって)異なる色で発光してもよい。 In this way, by changing the number of LED groups (LED elements) that emit light, it is possible to change the size of the pattern (light emission range) and perform a moving effect in which the pattern emits light in a shrinking manner. At this time, the LED groups may emit a single color, or each group may emit a different color (ie, depending on the position).
図242は、導光板による別のムービング演出で表示される絵柄の例を示す図である。図242に示す例では、LED群の発光色を時間の経過と共に変えることによって、絵柄の色が変化するムービング演出を行う。 FIG. 242 is a diagram showing an example of a pattern displayed in another moving effect by the light guide plate. In the example shown in FIG. 242, by changing the emission color of the LED group with the lapse of time, a moving effect is performed in which the color of the pattern changes.
前述したように、導光板2610には、第一特定入光部2630aから第七特定入光部2630gが設けられており、各特定入光部2630a~2630gに対応して第一LED群2614aから第七LED群2614gが配置されている。第一LED群2614aから第七LED群2614gは、フルカラーLEDによって構成されており、多色で発光できる。なお、図242では、各特定入光部に対応する位置を符号の最後の一文字のアルファベットによって表す。
As described above, the
図242(A)に示すように、第一LED群2614aが赤色で点灯し、第一特定入光部2630aから入射した赤色光が第一反射部2670aで反射し、第一反射部2670aが配置された絵柄が赤色で発光し、遊技者は赤色の絵柄を認識する。同様に、第二LED群2614bが橙色で点灯し、第二特定入光部2630bから入射した橙色光が第二反射部2670bで反射して絵柄が橙色で発光する。また、第三LED群2614cが黄色で点灯し、第三特定入光部2630cから入射した黄色光が第三反射部2670cで反射して絵柄が黄色で発光する。また、第四LED群2614dが緑色で点灯し、第四特定入光部2630dから入射した緑色光が第四反射部2670dで反射して絵柄が緑色で発光する。また、第五LED群2614eが青色で点灯し、第五特定入光部2630eから入射した青色光が第五反射部2670eで反射して絵柄が青色で発光する。また、第六LED群2614fが藍色で点灯し、第六特定入光部2630fから入射した藍色光が第六反射部2670fで反射して絵柄が藍色で発光する。また、第七LED群2614gが紫色
で点灯し、第七特定入光部2630gから入射した紫色光を第七反射部2670gが反射して絵柄が紫色で発光する。
As shown in FIG. 242(A), the
その後、図242(B)に示すように、第一LED群2614a~第七LED群2614gが、それぞれ紫色、赤色、橙色、黄色、緑色、青色、藍色で点灯し、絵柄の色が変わる。さらに時間が経過すると、図242(C)に示すように、第一LED群2614a~第七LED群2614gが、それぞれ藍色、紫色、赤色、橙色、黄色、緑色、青色で点灯し、絵柄の色が変わる。
After that, as shown in FIG. 242(B), the
このように、LED群を構成するLEDの発光色を変化させ、絵柄の色を順次(例えば0.5秒ごとに)変えていく。人間の目は、同じ色で発光する絵柄を注視するので、内側に動くように絵柄を発光させるムービング演出ができる。 In this way, the colors of the LEDs forming the group of LEDs are changed, and the color of the pattern is changed sequentially (for example, every 0.5 seconds). Since the human eye pays close attention to patterns that emit light in the same color, it is possible to create a moving effect in which the patterns emit light as if they move inward.
図243は、導光板2610上の絵柄の配置とLED群2614の配置を示す図である。
FIG. 243 is a diagram showing the arrangement of patterns on the
本実施例では、複数のLED群2614が一つの絵柄を構成する反射部2670に対応しており、当該複数のLED群2614が所定のパターンで発光して一つの絵柄の表示している。具体的には、7個のLED群を繰り返し単位として、LED群2614(特定入光部2630)の発光パターンが繰り返されるように制御している。また、LEDは指向性を持って発光し、LEDの正面から所定の角度範囲を照光するように構成されている。
In this embodiment, a plurality of
つまり、図243に示すように、同じパターンで発光する(一つの絵柄を構成する光の発光源である)LEDの照光範囲は、図中の扇形で示す範囲となり、第二絵柄用基板2612の近傍では、LEDからの光が到達しない範囲が生じる。 That is, as shown in FIG. 243, the illumination range of the LEDs emitting light in the same pattern (which is the light emitting source of the light forming one picture) is the range shown by the fan shape in the drawing. In the vicinity, there is a range where the light from the LED does not reach.
このため、導光板2610に光が入射する端部から所定の距離だけ離した位置に絵柄を設ける。例えば、LEDの照光範囲が60度(半値全角θ=±30度)である場合、LEDからの光が到達しない範囲は正三角形となることから、LED群の繰り返し単位の長さ(同じパターンで発光するLEDの間隔)αの0.87倍の長さだけ導光板2610の端部から絵柄を離して設ける。
For this reason, a pattern is provided at a position separated by a predetermined distance from the edge of the
一般化すると、LED群の繰り返し単位の長さα、LEDの照光角度をθ、導光板2610の端部から絵柄を離す距離をLとすると、以下の関係となる。
L=tanθ×α/2
To generalize, the following relationship is established where α is the length of the repeating unit of the LED group, θ is the illumination angle of the LED, and L is the distance separating the pattern from the edge of the
L=tan θ×α/2
このように、動いて見えるムービング絵柄が複数のLED群からの光で構成される場合、導光板2610の端部から所定の距離だけ離れた位置にムービング絵柄を配置しなければならない。すなわち、動いて見える絵柄を映し出すムービング絵柄領域は、静止している絵柄を映し出す静止絵柄領域より小さくなる。導光板2610を液晶表示装置1600の表示領域と同じ大きさとした場合、液晶表示装置1600の表示領域より狭い領域で導光板2610によるムービング演出が可能となる。このため、変動表示ゲームの演出において、通常は液晶表示装置1600の表示領域の端部近くに表示される特別図柄の視認を阻害せず、変動表示ゲームの進行を遊技者に認識させることができる。また、遊技者が注視する液晶表示装置1600の中央部でムービング演出を行うことによって、ムービング演出による遊技者のワクワク感によって、興趣の低下を抑制できる。
In this way, when a moving picture that appears to move is composed of light from a plurality of LED groups, the moving picture must be placed at a position a predetermined distance away from the edge of the
前述した実施例では、表ユニット2000のセンター役物2500導光板2610が取り付けられている例を説明したが、この場合、センター役物2500の内枠(パチンコ機1の前側に位置する遊技者から視認可能な開口窓部)の中に、導光板2610の端部から
所定の距離以内のムービング演出が不可能な領域ができてしまい、ムービング演出が不可能な領域が遊技者に視認できる。また、ムービング演出が可能な領域が狭くなり、演出効果が減少する。
In the above-described embodiment, an example in which the
このため、前述とは異なり、導光板2610を裏ユニット3000に取り付けてもよい。この場合、導光板2610をセンター役物2500の内枠より大きくできるので、ムービング演出が不可能な領域をセンター役物2500で隠し、ムービング演出が不可能な領域をメイン液晶表示装置1600の表示領域の外側に配置し、センター役物2500の内枠の全て(又は、大部分)の領域でムービング演出が可能となる。つまり、パチンコ機1を正面から見た場合、導光板2610の端部はメイン液晶表示装置1600の周縁やセンター役物2500の外周から外側に離れたところに位置することとなる。
Therefore, unlike the above, the
裏ユニット3000は各種装飾体(装飾ユニット3050、可動演出ユニット3100、3200、3300、3400、3500等)を備えているため、これらの装飾体の背後に導光板2610の端部が位置するように導光板2610を配置し、装飾体の後方に発光装置(第一絵柄用基板2611、第二絵柄用基板2612)を位置させることができる。これにより、光源となる基板を遊技者が見えない位置に配置でき、装飾性を担保できる。
Since the
さらに、導光板2610用のLED(導光板用LED2613、2614)と装飾体を発光させるLEDとを一つの基板に実装してもよい。
Furthermore, the LEDs for the light guide plate 2610 (
このように、導光板2610を裏ユニット3000に取り付けると、メイン液晶表示装置1600の表示領域の全部をムービング演出が可能な領域にでき、ムービング演出領域の制限による不自然さを遊技者に気付かせないようにできる。
In this way, when the
図244は、導光板による別のムービング演出で表示される絵柄の例を示す図である。図244に示す例では、LED群の発光色を時間の経過と共に変えることによって、絵柄の色が変化するムービング演出を行う。 FIG. 244 is a diagram showing an example of a pattern displayed in another moving effect by the light guide plate. In the example shown in FIG. 244, by changing the emission color of the LED group with the lapse of time, a moving effect is performed in which the color of the pattern changes.
前述したように、導光板2610には、第一特定入光部2630aから第七特定入光部2630gが設けられており、各特定入光部に対応して第一LED群2614aから第七LED群2614gが配置されている。第一LED群2614aから第七LED群2614gは、フルカラーLEDによって構成されており、多色で発光できる。なお、図244では、各特定入光部に対応する位置を符号の最後の一文字のアルファベットによって表す。
As described above, the
図示するように、第一LED群2614aが赤色で点灯し、第一特定入光部2630aから入射した赤色光を第一反射部2670aが反射し、第一反射部2670aが配置された絵柄が赤色で発光し、遊技者は赤色の絵柄を認識する。同様に、第二LED群2614bが橙色で点灯し、第二特定入光部2630bから入射した橙色光を第二反射部2670bが反射して絵柄が橙色で発光する。また、第三LED群2614cが黄色で点灯し、第三特定入光部2630cから入射した黄色光を第三反射部2670cが反射して絵柄が黄色で発光する。また、第四LED群2614dが緑色で点灯し、第四特定入光部2630dから入射した緑色光を第四反射部2670dが反射して絵柄が緑色で発光する。また、第五LED群2614eが青色で点灯し、第五特定入光部2630eから入射した青色光を第五反射部2670eが反射して絵柄が青色で発光する。また、第六LED群2614fが藍色で点灯し、第六特定入光部2630fから入射した藍色光を第六反射部2670fが反射して絵柄が藍色で発光する。また、第七LED群2614gが紫色で点灯し、第七特定入光部2630gから入射した紫色光を第七反射部2670gが反射して絵柄が紫
色で発光する。
As illustrated, the
その後、第一LED群2614a~第七LED群2614gのそれぞれが、紫色、赤色、橙色、黄色、緑色、青色、藍色で点灯し、絵柄の色が変わる。さらに時間が経過すると、第一LED群2614a~第七LED群2614gのそれぞれが、藍色、紫色、赤色、橙色、黄色、緑色、青色で点灯し、絵柄の色が変わる。
After that, each of the
このように、LED群を構成するLEDの発光色を変化させ、絵柄の色を順次(例えば0.5秒ごとに)変えていく。人間の目は、同じ色で発光する絵柄を注視するので、七色の光の筋が流れるように絵柄を発光させるムービング演出ができる。 In this way, the colors of the LEDs forming the group of LEDs are changed, and the color of the pattern is changed sequentially (for example, every 0.5 seconds). Since the human eye pays close attention to patterns that emit light in the same color, it is possible to create a moving effect in which the pattern emits light as if streaks of light in seven colors flow.
詳しい説明は省略するが、図235に示す2本の光の筋が交差するような絵柄を有する導光板2610でも、図244で説明したと同様に各LED群2614の発光色を変えることによって、絵柄(光の筋)の色が変わり、七色の光の筋が流れるように絵柄を発光させるムービング演出ができる。また、左右眼視差を用いて、光の筋が光源から離れるに従って奥まって又は手前側に見えるようにすると、立体感がある絵柄を表示できる。
Although the detailed description is omitted, even with the
次に、導光板2610による立体視絵柄と平面視絵柄とを説明する。
Next, a stereoscopic pattern and a planar pattern by the
図245は、導光板2610によって平面視される絵柄が表示される様子を表す図である。
FIG. 245 is a diagram showing how the
図245(B)に示すように、導光板2610の裏面に設けられた反射部2660は、反射面が曲面となっているので、導光板2610内を進行する光は、複数の方向に反射し、遊技者の右眼10R及び左眼10Lに到達する。また、反射部2660は、導光板2610内を進行し、複数の方向から(すなわち、複数の経路で)反射部2660に到来する光を反射し、導光板2610の前面側に出射する。このため、図245(A)に示すように、反射部2660によって構成される絵柄2621には左右眼の視差が生じないため、遊技者は絵柄2621を導光板2610の位置にある平面的な絵柄として見ることとなる。
As shown in FIG. 245B, since the reflecting surface of the reflecting
図246は、導光板2610によって平面視される絵柄が表示される様子を表す図である。
FIG. 246 is a diagram showing how the
図246(B)に示すように、導光板2610の裏面に設けられた反射部2650Lは、導光板2610内を進行する光を遊技者の左眼10Lの方向に反射し、反射部2650Rは、導光板2610内を進行する光を遊技者の右眼10Rの方向に反射する。しかし、反射部2650Lと反射部2650Rとは近接して(例えば、1mm以下で)配置されているので、図246(A)に示すように、反射部2650L、Rによって構成される絵柄2621の左右眼の視差は小さく、反射部2650Lによって構成される左眼用絵柄と、反射部2650Rによって構成される右眼用絵柄とは同じ位置に配置されていると言える。このため、遊技者は絵柄2621を導光板2610の位置にある平面的な絵柄として見ることとなる。
As shown in FIG. 246(B), the reflecting
図247は、導光板2610によって立体視可能な絵柄が表示される様子を表す図である。
FIG. 247 is a diagram showing how a stereoscopic pattern is displayed by the
図247(B)に示すように、導光板2610の裏面に設けられた反射部2650Lの反射面2651は導光板2610内を進行する光を遊技者の左眼10Lの方向に反射する角度に設定されており、反射部2650Rの反射面2651は導光板2610内を進行す
る光を遊技者の右眼10Rの方向に反射する角度に設定されている。このため、図247(A)に示すように、導光板2610上では反射部2650Lと反射部2650Rとの距離だけ左眼画像2621Lと右眼画像2621Rとがズレた位置となり、遊技者は左右眼視差がある右眼画像と左眼画像とを認識する。図247に示す状態では、遊技者の左眼10Lへ到達する光と右眼10Rへ到達する光とは導光板2610の裏面側の点2621Cで交差する。このため、遊技者は反射部2650L、Rによって構成される絵柄2621を導光板2610の後方位置にある立体的な絵柄として見ることとなる。
As shown in FIG. 247(B), the reflecting
図248は、導光板2610によって立体視可能な絵柄が表示される様子を表す図である。
FIG. 248 is a diagram showing how a stereoscopic pattern is displayed by the
図248(B)に示すように、導光板2610の裏面に設けられた反射部2650Lの反射面2651は導光板2610内を進行する光を遊技者の左眼10Lの方向に反射する角度に設定されており、反射部2650Rの反射面2651は導光板2610内を進行する光を遊技者の右眼10Rの方向に反射する角度に設定されている。このため、図248(A)に示すように、導光板2610上では反射部2650Lと反射部2650Rとの距離だけ左眼画像2621Lと右眼画像2621Rとがズレた位置となり、遊技者は左右眼視差がある右眼画像と左眼画像とを認識する。図248に示す状態では、遊技者の左眼10Lへ到達する光と右眼10Rへ到達する光とは導光板2610の表面側の点2621Cで交差する。このため、遊技者は反射部2650L、Rによって構成される絵柄2621を導光板2610の手前にある立体的な絵柄として見ることとなる。
As shown in FIG. 248(B), the reflecting
このように、表演出ユニット2600によれば、一枚の導光板2610により、複数の異なる絵柄を発光させることができるため、アニメーション表示等をさせるために絵柄毎に複数の導光板を備える必要がなく、表演出ユニット2600の前後方向の厚さを可及的に薄くできる。また、導光板2610をセンター役物2500に取付けているため、導光板2610を遊技者側へ可及的に近付けた位置とすることができ、導光板2610の後側に広いスペースを確保し易くできる。従って、導光板2610の後側に広いスペースを確保できるため、導光板2610の後側に、下部可動演出ユニット3100、上部後可動演出ユニット3200、及び上部前可動演出ユニット3300等を配置でき、それらにより遊技領域5a内の見栄えを良くして遊技者に対する訴求力の高いパチンコ機1にできると共に、絵柄2623の発光表示による演出に加えて、下部可動演出ユニット3100、上部後可動演出ユニット3200、及び上部前可動演出ユニット3300等による可動演出を行うことで遊技者に多彩な演出を提供することができ、遊技者を楽しませて興趣の低下を抑制できる。
As described above, according to the
また、演出ユニットや装飾体、演出表示装置1600の前方に導光板2610を配置することによって、複数の反射部2670の発光による半透明な複数の絵柄が浮かびあがってアニメーションのよう動く発光装飾を見せることができるため、従来の導光板を用いた発光演出に見慣れた遊技者に対して強いインパクトを与えることができ、遊技者を驚かせて楽しませることができると共に、遊技者に対して何か良いことがあるのではないかと思わせることができ、遊技者の遊技に対する期待感を高めさせて興趣の低下を抑制できる。
In addition, by arranging the
また、パチンコ機1の前方正面に着座している遊技者のみが導光板2610による絵柄の発光表示を良好に見ることができるため、正面から離れている他の遊技者からは絵柄2623の発光表示が見辛くなり、他の遊技者に対して、導光板2610を用いた演出が行われていることを気付かせ難くでき、他の遊技者が注目するのを抑制することができると共に、他の遊技者に気兼ねすことなく遊技ができ、遊技を楽しませて興趣の低下を抑制できる。
In addition, since only the player sitting in front of the
更に、正面視遊技領域5a内の中央にセンター役物2500を取り付けられているセンター役物2500の枠内に導光板2610を取付けているため、LED2613、2614により絵柄2621、2622を発光表示しても、発光表示されている絵柄が遊技領域5a内での遊技の妨げとなることはなく、実際に遊技が行われる領域を遊技者側から良好な状態で視認でき、遊技が見え辛くなることで遊技者に不信感を与えるのを防止して良好な状態で遊技を楽しませることができる。
Furthermore, since the
また、枠状のセンター役物2500に導光板2610を取り付けていることから、導光板2610の周縁とセンター役物2500の枠とを一致させることで、導光板2610の周縁(第一絵柄用基板2611、第二絵柄用基板2612)を遊技者側から見え難くでき、遊技者に対して導光板2610の存在に気付かせ難くできるため、絵柄を発光表示させた時に、導光板2610が存在していないと思っていた遊技者に対して強いインパクトを与えて驚かせることができ、導光板2610による複数の絵柄の発光表示を楽しませて興趣の低下を抑制できる。
In addition, since the
更に、導光板2610の後方に演出画像を表示可能な演出表示装置1600を備えていることから、導光板2610による互いに異なる複数の絵柄の発光表示と、演出表示装置1600による演出画像とを合わせた演出を遊技者に見せることができるため、それらを適宜組み合わせることで多様な演出ができ、遊技者を飽きさせ難くできると共に、導光板2610と演出表示装置1600とによる演出によって遊技者を楽しませることができ、遊技者の遊技に対する興趣の低下を抑制できる。
Further, since the
また、導光板2610の後方に演出表示装置1600を配置していることから、パチンコ機1の前方に着座した遊技者からの導光板2610までの距離と、演出表示装置1600までの距離とが異なっているため、導光板2610で発光表示される複数の絵柄2623と関連した演出画像を表示して、発光表示されている絵柄2623に奥行き感や立体感を付与させることが可能となり、遊技者の関心を強く引付けさせることが可能な演出(表示演出)を遊技者に見せることができ、遊技者を楽しませて遊技に対する興趣の低下を抑制できる。
In addition, since the
また、LED2613、2614は、単色LEDでもよいし、フルカラーLEDでもよい。また、絵柄の数、形状、大きさに合わせて、特定入光部、反射部、及びLED群の数を適宜選択できる。
Also, the
[13-3.演出例]
次に、特別図柄変動表示ゲームにおける導光板を用いた演出表示の例を説明する。図249から図254は、導光板を用いた演出例を示す図である。
[13-3. Production example]
Next, an example of effect display using the light guide plate in the special symbol variation display game will be described. 249 to 254 are diagrams showing examples of effects using a light guide plate.
図249に示す演出表示では、導光板2610に所定の絵柄が映るように導光板2610を発光させ、該所定の画像に向かって画像を移動させる移動演出を液晶表示装置1600に表示する。この演出表示は、特定の特別図柄変動表示ゲーム(例えば、特定のリーチ演出や予告演出として)で実行されてもよい。
In the effect display shown in FIG. 249, the
具体的には、まず、図249(A)に示すように、液晶表示装置1600に何も表示されず、画面が全て黒色に暗転(ブラックアウト)する。このブラックアウトによって、遊技者を液晶表示装置1600に注視させる。
Specifically, first, as shown in FIG. 249A, nothing is displayed on the liquid
その後、図249(B)に示すように、第一絵柄用基板2611に実装されているLED2613を点灯し、導光板2610に第一絵柄2621を映す。これによって、遊技者を第一絵柄2621に注視させる。そして、図249(C)に示すように、第一絵柄26
21に向かって移動する画像を液晶表示装置1600に表示する移動演出を行う。また、図249(D)に示すように、移動演出は、液晶表示装置1600の複数箇所(すなわち複数方向)から第一絵柄2621に向かって画像1611を移動させてもよい。液晶表示装置1600に移動して表示される画像1611は、第一絵柄2621と同じ色でも異なる色でもよい。また、液晶表示装置1600に移動して表示される画像1611は、図249に示すように、第一絵柄2621と同じ形状(相似形)でも、図250に示すように、異なる形状でもよい。また、移動して表示される画像1611と第一絵柄2621とは、同じキャラクタの画像(ポーズや顔が同じでも異なってもよい)や、同じ文字(例えば、キャラクタの称呼)で字体や色が同じでも異なってもよい。本実施例のパチンコ機1では、液晶表示装置1600の前面側に導光板2610が配置されているので、図249(D)に示すように導光板2610上に映された第一絵柄2621の裏にも液晶表示装置1600によって画像が表示されるとよい。
After that, as shown in FIG. 249(B), the
21 is displayed on the liquid
その後、図249(E)に示すように、移動演出において、第一絵柄2621に向かって移動する画像1611の数や、当該移動画像1611が液晶表示装置1600の表示領域において占める割合を時間の経過に伴って変化させてもよい。
After that, as shown in FIG. 249(E), in the moving effect, the number of
移動演出の間、導光板2610に映される第一絵柄2621の態様を変えてもよい。例えば、図251に示すように、導光板2610に映される第一絵柄2621の色や明るさを、移動演出の間に変更してもよい。第一絵柄2621の色や明るさは、連続的に(徐々に)変えても、段階的に(ステップ的に)変えてもよい。
The aspect of the
また、図252に示すように、導光板2610に映される第一絵柄2621の大きさを、移動演出の間、変えてもよい。この場合、複数の導光板を設け、他の導光板を用いて大きさが違う絵柄を映すとよい。また、導光板2610は、異なる方向からの光の照射によって複数の異なる絵柄を映すことができるので、初期の大きさの第一絵柄2621を映すための照射方向(横方向)と異なる方向(例えば、斜め方向)からの光の照射によって、異なる大きさの(大きな又は小さな)第一絵柄2621を映してもよい。
Also, as shown in FIG. 252, the size of the
所定の時間、移動演出を行った後、図249(F)に示すように、第一絵柄用基板2611に実装されているLED2613を消灯し、導光板2610から第一絵柄2621を消す。さらに、液晶表示装置1600に表示されている画像も消して、画面が全て黒色に暗転(ブラックアウト)する。このブラックアウトによって、遊技者を液晶表示装置1600に注視させ、次の演出への期待感を向上させるための間を作る。
After performing the moving effect for a predetermined time, the
その後、図249(G)に示すように、第一絵柄2621や移動表示された画像と異なる画像1612(例えば、当りの信頼度が高いキャラクタ)を液晶表示装置1600に表示する。さらに、図249(H)に示すように、キャラクタ画像1612の大きさを変更する。例えば、キャラクタ画像1612の大きさを大きくすると、遊技者の当りへの期待感が高まるが、キャラクタ画像1612の大きさを小さくすると、遊技者の当りへの期待感が低くなる。なお、キャラクタ画像1612の色や表情を変えてもよい。また、キャラクタ画像1612は第一絵柄2621の表示領域と重なる領域に表示するとよい。さらに、キャラクタ画像1612の表示と共に、導光板2610を上方向から照射して、レインボー絵柄を映してもよい(図235参照)。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 249(G), an
なお、このキャラクタ画像を導光板2610に映してもよい。前述したように、導光板2610は、異なる方向からの光の照射によって複数の異なる絵柄を映すことができるので、第一絵柄2621を映すための照射方向(横方向)と異なる方向(例えば、斜め方向)からの光の照射によって、キャラクタ画像を映してもよい。また、複数の導光板を設け、他の導光板でキャラクタ画像を映してもよい。導光板2610の他に設けた導光板で、
大きさや表情が異なるキャラクタ画像を映すと、平面的な液晶表示装置1600と異なり、奥行き感がある演出表示が可能となる。
Note that this character image may be projected on the
When character images with different sizes and facial expressions are displayed, an effect display with a sense of depth is possible, unlike the planar liquid
以上説明した、第一絵柄2621に向かって画像が移動する移動演出は、第一絵柄2621が映された後に、液晶表示装置1600上の画像が移動するが、液晶表示装置1600上の画像が移動を開始した後、第一絵柄2621が映されてもよい。具体的には、図253に示すように、ブラックアウト(図253(A))の後、図253(B)に示すように、第一絵柄2621が映される前に、第一絵柄2621が映される位置に向かって移動する画像を液晶表示装置1600に表示する移動演出を開始する。その後、図253(C)に示すように、第一絵柄用基板2611に実装されているLED2613を点灯し、導光板2610に第一絵柄2621を映す。その後、図253(D)に示すように、第一絵柄2621に向かって画像が移動する移動演出を継続する。
As described above, in the moving effect in which the image moves toward the
このように、第一絵柄2621が映される時間(導光板演出の時間)と、画像1611が移動する演出時間(液晶表示装置1600に移動画像が表示される時間)とは、第一絵柄2621が映される導光板演出が、画像1611が移動する演出より先に開始しても、後に開始してもよい。また、第一絵柄2621が映される導光板演出の時間が、画像1611が移動する演出時間より長くても、短くてもよい。
In this way, the time during which the
また、図254に示すように、画像が集まる先の絵柄が動いて見えるムービング絵柄と動かないように見える静止絵柄とを切り替えて変動表示ゲームの演出を行ってもよい。 Further, as shown in FIG. 254, a variable display game effect may be performed by switching between a moving pattern in which the patterns at which the images gather appear to move and a static pattern in which the patterns appear not to move.
図254に示す導光板演出では、ムービング絵柄が登場すると大当りへの期待が高く、静止絵柄が登場しただけだと大当りへの期待が低い演出を行う。具体的には、図254(A)に示すように、変動表示ゲームの進行に応じて、導光板2610に静止絵柄2621を表示し、図254(B)に示すように、表示された静止絵柄2621に向かって移動する画像1611を液晶表示装置1600に表示する移動演出を行う。また、変動表示ゲームの進行に伴って、図254(C)に示すように、静止絵柄2621をムービング絵柄に切り替える。さらに、図254(D)に示すように、液晶表示装置1600の複数箇所(すなわち複数方向)から第一絵柄2621に向かって画像1611を移動させる移動演出を行ってもよい。
In the light guide plate presentation shown in FIG. 254, when a moving picture appears, the expectation for a big win is high, and when a static picture only appears, the expectation for a big win is low. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 254(A), a
一方、図254(E)に示すように、変動表示ゲームの進行に応じて、導光板2610に静止絵柄2621を表示し、図254(F)に示すように、表示された静止絵柄2621に向かって移動する画像1611を液晶表示装置1600に表示する移動演出を行う。また、変動表示ゲームの進行に伴って、図254(G)に示すように、液晶表示装置1600の複数箇所(すなわち複数方向)から絵柄1613に向かって画像1611を移動させる移動演出を行ってもよい。その後、図254(H)に示すように、静止絵柄2621をムービング絵柄に切り替えることなく、変動表示ゲームがハズレで終了する。
On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 254(E), a
図254に示す演出では、特別図柄変動表示ゲームにおいて特定の表示演出(例えば、特定のリーチ演出、擬似連演出、特定の先読み演出)が選択された場合に、上記特定の表示演出において表示される特定の画像1611が第一絵柄2621によるムービング演出と一体に演出を行い、その他の場合には第一絵柄はムービング演出を行わなくてもよい。
In the effect shown in FIG. 254, when a specific display effect (for example, a specific ready-to-win effect, a pseudo-continuous effect, or a specific look-ahead effect) is selected in the special symbol variation display game, the specific display effect is displayed. The
このように、図254に示す変動表示ゲームの演出において、導光板2610による静止絵柄とムービング絵柄とが選択的に表示される演出を行うので、変動表示ゲームの発展に遊技者が期待感を持ち、遊技興趣の低下を抑制できる。
As described above, in the effect of the variable display game shown in FIG. 254, the static pattern and the moving pattern are selectively displayed by the
次に、特別図柄変動表示ゲームにおける導光板を用いた演出表示に、稼動体による演出
を加えた演出の例を説明する。
Next, an example of an effect in which an effect using an operating object is added to the effect display using the light guide plate in the special symbol variation display game will be described.
図255、図256は、導光板2610と可動体3601を用いた演出例を示す図である。
255 and 256 are diagrams showing examples of effects using the
図255に示す演出では、導光板2610に表示される絵柄と、液晶表示装置1600の前面に登場する可動体3601とで一つの絵柄を構成する。具体的には、図255(A)に示すように、変動表示ゲームの進行に応じて、液晶表示装置1600の表示画面の上部から可動体3601の一部が現れたり、隠れたりを短周期で繰り返し、遊技者に大当りへの期待を高める。そして、図255(B)に示すように、可動体3601の全部が液晶表示装置1600の表示画面の前面に出現する。
In the rendering shown in FIG. 255, the pattern displayed on the
その後、図255(C)に示すように、可動体に重畳する絵柄2621を導光板2610の発光によって表示し、可動体3601に向かって移動する画像1611を液晶表示装置1600に表示する移動演出を行う。また、変動表示ゲームの進行に伴って、図255(D)に示すように、液晶表示装置1600の複数箇所(すなわち複数方向)から絵柄2621に向かって画像を移動させる移動演出を行ってもよい。
After that, as shown in FIG. 255(C), a
この移動演出が開始するタイミング、又は移動演出の途中で、可動体3601を発光させてもよい。可動体3601の発光態様(発光色や発光タイミング)は、導光板2610の発光態様と同じでも、異なってもよい。
The
図249に示す可動体3601が登場しない演出表示と、図255に示す可動体3601が登場する演出表示とのいずれかを選択的に行うことによって、変動表示ゲームの発展についての遊技者の期待を高めることができ、興趣が高いパチンコ機とすることができる。
Players' expectations for the development of the variable display game can be increased by selectively performing either the effect display in which the
前述した例では、画像が集まる先の絵柄に代えて可動体3601を出現させたが、一つのキャラクタを導光板2610と可動体3601とによって構成してもよい。例えば、可動体3601で胴体を表し、導光板2610によって顔を表すと、導光板2610に表示される絵柄を切り替えることによって、顔の表情を変えることができる。このように、液晶表示装置1600による演出に加えて、導光板2610による多様な演出を実現できる。
In the above example, the
図256に示す演出では、可動体3601の出現を示唆する演出として導光板2610を用いる。具体的には、図256(A)に示すように、変動表示ゲームの進行に応じて、導光板2610の発光によって絵柄2621を表示し、図256(B)に示すように、導光板2610によって表示された絵柄に向かって移動する画像1611を液晶表示装置1600に表示する移動演出を行う。また、変動表示ゲームの進行に伴って、図256(C)に示すように、液晶表示装置1600の複数箇所(すなわち複数方向)から第一絵柄2621に向かって画像1611を移動させる移動演出を行ってもよい。その後、図256(D)に示すように、液晶表示装置1600の表示画面の上部から可動体3601が現れ、導光板2610の絵柄2621と重なる位置で停止する。
In the effect shown in FIG. 256, a
一方、図256(E)に示すように、変動表示ゲームの進行に応じて、液晶表示装置1600に絵柄1613を表示し、図256(F)に示すように、表示された絵柄1613に向かって移動する画像1611を液晶表示装置1600に表示する移動演出を行う。また、変動表示ゲームの進行に伴って、図256(G)に示すように、液晶表示装置1600の複数箇所(すなわち複数方向)から絵柄1613に向かって画像1611を移動させる移動演出を行ってもよい。その後、図256(H)に示すように、可動体は表れずに変
動表示ゲームがハズレで終了する。
On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 256(E), according to the progress of the variable display game, a
このように、図256に示す演出では、可動体が出てくることを示唆する演出を、導光板を用いて行うことができる。 In this manner, in the effect shown in FIG. 256, the effect suggesting that the movable body is coming out can be performed using the light guide plate.
[14.シリアル通信機能を有する主制御MPUを用いたパチンコ機]
本実施例のパチンコ機1の主制御MPU1311は、従来の8ビットのパラレルバスによる通信機能の他に同期シリアル通信機能を有する。
[14. Pachinko machine using main control MPU with serial communication function]
The
従来のパチンコ機では、主制御基板1310内における主制御MPU1311の入出力信号は、一つの信号が1本の信号線で伝送されるパラレルポートや、8ビットバスを用いて伝送されていることから、主制御MPU1311から出力されるデータを読み取ったり、主制御MPU1311に不正な信号を入力して不正行為が行われることがあった。このため、主制御MPU1311の入出力信号を外部から検出困難な構成が求められており、1本の信号線で所定のタイミングで連続しでデータを伝送するシリアル通信機能を用いると、当該シリアル通信線のタイミングに合わせてデータを読み取ったり、データを入力することは困難となる。
In the conventional pachinko machine, the input/output signals of the
また、主制御基板1310は、検査機関がパチンコ機を検査する際に信号をモニタする目的で試験用信号出力回路を搭載している。例えば、特別電動役物の動作を検査する場合、特別電動役物を開閉動作させるソレノイドの出力信号をモニタするため、ソレノイド駆動用ドライバ(トランジスタ)へ入力される信号(例えば、5Vのオン・オフ信号)を分岐して、検査用の信号としていた。前述した主制御基板1310内で伝送されるシリアル信号を検査用信号として出力すると、検査機関はシリアル信号を解析する装置が必要になることから、該シリアル信号を検査用の信号に用いることは困難である。このため、主制御基板1310内でシリアル通信で信号を伝送するパチンコ機においては、検査用信号の出力に工夫が必要である。このため、本実施例のパチンコ機では、並列に接続された二つのシリアル・パラレル変換回路に一つのシリアル信号を入力することによって、ソレノイド駆動用の信号と同じタイミングでレベルを変化させる検査用信号を生成するものとした。シリアル・パラレル変換回路の出力トランジスタオープンコレクタ(又は、オープンドレイン)で構成すると、並列に接続された二つのシリアル・パラレル変換回路に印加する電圧(5Vと12V)を変えることによって、電圧レベルが異なる二つの同期した信号を生成できる。
In addition, the
さらに、シリアル通信による入力を検出するためのプログラムのステップ数を減らしソフト的な負荷を低減する必要がある。本実施例のパチンコ機では、主制御MPU1311へ入力される信号の一部をパラレル・シリアル変換回路に入力し、一部を主制御MPU1311の汎用ポートに直接入力する構成としたので、どのポートで入力信号を受け入れるかに工夫が必要である。例えば、電源投入直後に入力レベルを判定する必要がある信号はパラレル・シリアル変換回路に入力せず、主制御MPU1311の汎用ポートに直接入力するとよい。これは、割り込み処理を実行する前でも、主制御MPUI1311の汎用ポートに入力された信号のレベルを検出できることから、電源投入直後などのタイマ割り込み処理以外でも信号レベルを検出できるからである。
Furthermore, it is necessary to reduce the number of steps of the program for detecting the input by serial communication and reduce the software load. In the pachinko machine of this embodiment, part of the signal input to the
特に、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、主制御MPU1311に直接入力される信号の数によっては、チップセレクトを使用した拡張I/Oを使用しなくてよく、主制御MPUI1311の汎用ポートに入力された信号のレベルをクロック毎にbit単位で取り込むことができ、シリアル信号の受信を待たずに信号レベルをリアルタイムで検出できる。
In particular, in the
図257は、主制御基板1310の同期シリアルインターフェイスの周辺のブロック図
であり、図258は、シリアル・パラレル変換回路とLEDとの接続を示す回路図であり、図261は、主制御MPU1311及び周辺部品の主制御基板1310上の配置を示す図である。なお、図257、図258及び図261において、太線はパラレル信号の伝送ラインを示し、細線はシリアル信号の伝送ラインを示す。
257 is a block diagram around the synchronous serial interface of the
本実施例の主制御MPU1311は、他の基板(周辺制御基板1510、払出制御基板951など)との間で通信するための非同期シリアル通信ポート(非同期シリアル通信機能)と、主制御基板1310内のインターフェイス回路と通信するための同期シリアル通信ポート(同期シリアル通信機能)と、他の装置(ソレノイドなど)の制御信号を出力したり、振動検出センサ、磁気検出センサなどの異常検出センサから出力される信号が入力される汎用ポートを有する。
The
主制御MPU1311の同期シリアル通信機能は、複数の送受信ポートと、複数の送信ポートとを有する。送受信ポートの通信相手は、主制御MPU1311から出力されるチップセレクト信号によって選択される。
The synchronous serial communication function of the
送受信ポートは、シリアル信号送信端子(SERTX)、受信信号入力端子(SERRX)、チップセレクト出力端子(SERS0~SERS3)、同期信号出力端子(SERCK)から構成される。また、送信ポートは、シリアル信号送信端子(SERTXT)、チップセレクト出力端子(SERST)、同期信号出力端子(SERCKT)から構成される。 The transmission/reception port includes a serial signal transmission terminal (SERTX), a reception signal input terminal (SERRX), chip select output terminals (SERS0 to SERS3), and a synchronization signal output terminal (SERCK). A transmission port is composed of a serial signal transmission terminal (SERTXT), a chip select output terminal (SERST), and a synchronization signal output terminal (SERCKT).
図257に示すように、送受信ポートには一つのパラレル・シリアル変換回路1341と、二つのシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343が接続される。送受信ポートに接続されるパラレル・シリアル変換回路の数は、図示したものに限られない。
As shown in FIG. 257, one parallel/
なお、チップセレクト端子を使用せずに、パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341のような接続をすることによって、更に多くのシリアル・パラレル変換回路を接続してもよい。この場合、シリアル・パラレル変換回路から出力される信号の種類は増加しない。
A larger number of serial/parallel conversion circuits may be connected by connecting like the parallel/
送受信ポートに接続されるパラレル・シリアル変換回路1341は、CLEAR/LOAD(負論理)が0レベルの時に入力されたパラレルデータを取り込み、CLEAR/LOAD(負論理)が1に立ち上がった後に所定のクロックのタイミングでシリアルポートからデータを出力する。パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341には、遊技球検出スイッチ(始動入賞口、大入賞口カウントスイッチ、普通入賞口、特定領域スイッチ、普通図柄ゲートスイッチ、遊技板排出スイッチ)やフォトセンサなどの信号が入力されており、主に遊技領域5aを流下する遊技球を検出する。パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341は、16ビットの入力ポートを有する構成であるが、8ビットの入力ポートを有する集積回路を並列に接続して、16ビット構成としてもよい。
A parallel-to-
具体的には、パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341のCLEAR/LOAD(負論理)には、シリアル信号送信端子(SERTX)が接続されているので、主制御MPU1311が出力するシリアル送信信号が0レベルの時に入力された遊技球検出スイッチの出力信号を取り込み、シリアル送信信号(SERTX)が1に立ち上がった後に所定のクロックのタイミングでシリアルポートから、遊技球検出スイッチのレベルに応じたシリアルデータを出力する。このように、パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341は、SERTX信号をトリガにして遊技球検出スイッチの出力信号を取り込むので、任意のタイミングで球検出センサのデータを取り込むことができる。
Specifically, since the serial signal transmission terminal (SERTX) is connected to the CLEAR/LOAD (negative logic) of the parallel/
また、送受信ポートに接続されるシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342及びシリアル・
パラレル変換回路1343は、いずれも、LED(機能表示ユニット1400、ベース表示器1317)を点灯するための信号を出力するものであり、主制御MPU1311からのチップセレクト信号によって、データの送信先が選択される。シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343は、チップセレクト(CS)信号が0レベルの時に入力されたシリアルデータを所定のクロック信号に従って取り込み、チップセレクト信号が1に立ち上がったタイミングでパラレルポートから信号を出力する。パラレルポートからの出力レベルは、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343内でラッチされており、チップセレクト信号が次回に1に立ち上がるタイミングまで維持される。
Also, a serial/
The
具体的には、図258に示すように、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342はLEDのセグメント側に接続され、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1343はLEDのコモン側に接続される、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342及びシリアル・パラレル変換回路1343が所定のタイミングで信号を出力することによって、LEDをダイナミック点灯する。シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343は、16ビットの出力ポートを有する構成であるが、8ビットの出力ポートを有する集積回路を並列に接続して、16ビット構成としてもよい。
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 258, a serial/
主制御MPU1311は、チップセレクト端子(SERS0)から0を出力するタイミングでコモン信号を出力し、ベース表示器1317の7セグメントLEDの表示桁を設定し、チップセレクト端子(SERS1)から0を出力するタイミングでセグメント信号を出力して、LEDを点灯させる。
The
なお、本実施例では、LEDのアノード側がコモン端子となっている7セグメントLEDをベース表示器1317に使用しており、LEDの点灯時にはアノード側のコモン端子からカソード側のセグメント端子に駆動電流が流れる。しかし、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342及びシリアル・パラレル変換回路1343に同じ構成の集積回路を用いているので、各変換回路1342、1343内のドライバ回路が出力する電流の向き(ドライバ回路の出力トランジスタの極性)は同じになる。このため、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1343の後段にドライバ回路1344を設け、アノード側のコモン端子に電流を供給できるようにしている。すなわち、ドライバ回路1344はLEDを点灯するための駆動電流を出力する機能を有し、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1343はLEDを点灯するための駆動電流を吸い込む機能を有する。
In this embodiment, a 7-segment LED having a common terminal on the anode side of the LED is used for the
換言すると、LED(機能表示ユニット1400、ベース表示器1317)のコモン側には、信号の方向を規制する信号方向規制手段として機能するシリアル・パラレル変換回路1343及びドライバ回路1344が接続されている。すなわち、LEDのコモン側には、2段階の信号方向規制手段が設けられている。一方、LEDのセグメント側には、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342が設けられており、1段階の信号方向規制手段が設けられている。
In other words, the common side of the LEDs (
パラレル・シリアル変換回路と1341とシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343とは、それぞれ、パラレル・シリアル変換機能のみを有する集積回路と、シリアル・パラレル変換機能のみを有する集積回路を使用してもよく、また、シリアル信号とパラレル信号とを相互に変換可能な集積回路でパラレル・シリアル変換機能とシリアル・パラレル変換機能とを切り替えて使用してもよい。
The parallel-to-
また、主制御MPU1311の送信ポートには、二つのシリアル・パラレル変換回路1345及び1346が接続されている。シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345、1346は、前述したシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343と同様に、チップセレクト(CS)が0レベルの時に入力されたシリアルデータを所定のクロック信号に従って取り
込み、CSが1に立ち上がったタイミングでパラレルポートから出力する。パラレルポートの出力にはドライバ用のトランジスタが備わっており、ドライバ用トランジスタに印加された電圧をスイッチングして、出力信号を生成する。すなわち、ドライバ用トランジスタに印加する電圧によって、様々な電圧の出力信号を生成できる。
Two serial/
シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345のチャネルAの出力ポート(PA0~PA7)には、外部端子板784が接続されており、外部端子板784から出力する信号(例えば、セキュリティ信号や、球払出信号など)が出力される。また、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345のチャネルBの出力ポート(PB0~PB7)には、各種ソレノイドが接続されており、各種ソレノイドの駆動信号が出力される。また、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346のチャネルBの出力ポート(PB0~PB7)には、検査用端子1348が接続されており、検査用端子1348から出力する信号(例えば、特別電動役物開放信号、普通電動役物開放信号など)が出力される。また、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346のチャネルAの出力ポートには、何も接続されていない。
An external
主制御MPU1311の送信ポートは、1チャネル(16ビット)しか制御できず、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345及びシリアル・パラレル変換回路1346には、チップセレクトも含めて分岐された同じ信号が入力されているので、パラレル側には同じ信号が出力される。このため、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345及びシリアル・パラレル変換回路1346は、一つのシリアル信号から同じタイミングで変化するパラレル信号の組を生成している。つまり、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345のチャネルBの出力ポート(PB0~PB7)から出力されるソレノイド駆動信号と、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346のチャネルBの出力ポート(PB0~PB7)出力される検査用信号とは、同じタイミングで変化する。このため、ソレノイドの動きを正確に検査用端子1348から出力できる。なお、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345には+12Vを印加して、12Vでソレノイドを駆動し、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346には+5Vを印加して、5Vの検査用信号を出力する。このように、異なる電圧が印加された二つのシリアル・パラレル変換回路を用いることによって、電圧レベルが異なる同期した信号を生成できる。
The transmission port of the
シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345及びシリアル・パラレル変換回路1346から出力のうち、比較的大きな電流が流れるソレノイド駆動信号の出力側のパターンは太くし、比較的小さな電流しか流れない検査用信号の出力側のパターンは細くてもよい。なお、パターンを太くしなくても、パターンの抵抗を減少すればよく、表裏の両面にパターンを形成して実質的な断面積を増加したり、内層パターンを形成して実質的な断面積を増加してもよい。
Among the outputs from the serial/
また、二つのシリアル・パラレル変換回路1345及び1346は独立して動作するので、一方の変換回路の負荷が大きくなっても、他方の変換回路の出力信号の波形が乱れることなく、出力信号に影響が生じない。すなわち、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346は、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345に接続されたソレノイドの動作によらず、ソレノイドの駆動信号の本来の波形と同じ波形の検査信号を出力でき、正確な検査に役立つ。
In addition, since the two serial/
主制御MPU1311には、リセット回路1335からリセット信号が入力される。リセット回路1335から出力されたリセット信号は、バッファ回路1336の二つのインバータ・バッファを経由して主制御MPU1311に入力される。主制御MPU1311は、リセット信号を受けると、動作がリセットされ、先頭アドレスからプログラムを実行する。
A reset signal is input from the
また、リセット信号は、リセット回路1335からバッファ回路1336の二つのイン
バータ・バッファを経由して各シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343にも入力される。各シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343は、リセット信号を受けると、動作がリセットされ、機能表示ユニット1400やベース表示器1317の表示内容を初期状態に戻す(例えば、表示を消去する)。
The reset signal is also input to each of the serial/
バッファ回路1336は、少なくとも4個のインバータ・バッファを有しており、リセット回路1335と主制御MPU1311との間に二つのインバータ・バッファが配置され、リセット回路1335とシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343との間に二つのインバータ・バッファが配置されている。リセット回路1335から主制御MPU1311までの経路と、リセット回路1335からシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343までの経路とに同じ特性のインバータ・バッファを配置したのは、リセット回路1335から二つの経路で出力されるリセット信号の波形やタイミングをできるだけ同じにするためである。
The
このバッファ回路1336のインバータ・バッファは、一方向のみに信号を通過させる信号方向規制手段として機能する。リセット回路1335からシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343までの経路で信号方向を規制することによって、外部より侵入するノイズの主制御MPU1311への到達を抑制できる。しかしながら、リセット回路1335とシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343とを直結すると、リセット回路1335から主制御MPU1311に入力されるリセット信号とは異なるタイミングで、リセット信号がシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343に入力されることになる。すなわち、リセット回路1335から主制御MPU1311への経路に設けられた2段のインバータ・バッファの分シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343には、リセット信号の伝達が早くなり、主制御MPU1311に制御されるシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343に先にリセット指令が到達することになる。
The inverter buffer of this
このため、本実施例では、リセット回路1335から制御MPU1311への経路と、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343への経路とに、主に2段のインバータ・バッファを設け、主制御MPU1311とシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343とに同じタイミングでリセット信号が伝達され、同じタイミングで各回路がリセットされるようにしている。このように、リセット回路1335から主制御MPU1311までの経路に配置したインバータ・バッファは、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343への経路に入力されるリセット信号の伝達タイミングと限りなく一致させており、一見すると、二つの経路に設けられる回路は同じように見えるが、異なる機能を果たしている。
For this reason, in this embodiment, two stages of inverter buffers are mainly provided in the path from the
なお、一般的にリセット回路から出力されるリセット信号を伝達する経路には、特別な回路を配置する必要はないが、本件のように、リセット信号のタイミングを揃える観点からはバッファ(タイミング調整手段)の配置が必要となる。 In general, it is not necessary to place a special circuit in the path for transmitting the reset signal output from the reset circuit. ) is required.
また、信号のタイミングを合わせる(信号を遅延させる)ためには、前述したインバータ・バッファに限らず、タイミングを一致させる他の種類の回路でもよい。本実施例では、図259、図260に示すように、6個のインバータ・バッファを収容するICを採用したが、パッケージされたICには、6個のインバータ・バッファが1個の集積化された半導体チップ上に形成されている。半導体チップは、単結晶シリコン(インゴット)から切り出されたシリコンウェハ上にいくつかの処理を経て複数組の回路が形成される。これをダイシングして回路を切り離し、チップ状にした回路をパッケージしてICとなる。それゆえ、同じシリコンウェハ上に形成された複数の回路の各々の特性のバラツキは小さい。本件では、このようなことも加味して、一つのICに収容されているインバータ・バッファを、二つの経路に配置して、経路上の信号伝達特性を同じにしている。 Further, in order to match the signal timing (to delay the signal), other types of circuits for matching the timing may be used instead of the inverter buffer described above. In this embodiment, as shown in FIGS. 259 and 260, an IC accommodating six inverter buffers is used, but six inverter buffers are integrated into one packaged IC. It is formed on a semiconductor chip with a A semiconductor chip is formed by several sets of circuits on a silicon wafer cut out from single crystal silicon (ingot) through several processes. This is diced to separate the circuit, and the chip-shaped circuit is packaged to form an IC. Therefore, variations in the characteristics of each of a plurality of circuits formed on the same silicon wafer are small. In this case, in consideration of this, the inverter buffer housed in one IC is arranged in two paths to make the signal transmission characteristics on the paths the same.
また、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、枠が開閉するためのヒンジ側に、機能表示ユニット1400が配置されており、ヒンジ側には賞球払出機構も配置されている。パチンコ機が設置される島設備から供給される遊技球は、帯電した状態で賞球払出機構内を移動する。遊技球は、賞球払出機構を構成する樹脂部材との摩擦によって、さらに帯電する。そして、帯電した遊技球が静電気を放電すると電磁ノイズが発生し、これが直接又は信号経路(ハーネスを構成する電線)を伝って電子回路に侵入してくる。
Further, in the
前述したように、本実施例の主制御基板は、一定周期の割り込み処理で遊技制御を実行している(前述の初期化処理~タイマ割り込み処理:図21~図23)。このため、周辺制御装置1510は、仮に情報がリセットされても、主制御MPU1311が正常に動作していれば、次の割り込み周期(本件では4ms後)には新たな情報(表示データ)が主制御MPU1311から指令されて、正常動作に復帰する。
As described above, the main control board of the present embodiment executes game control by interrupt processing of a constant cycle (initialization processing to timer interrupt processing described above: FIGS. 21 to 23). Therefore, even if the information is reset, the peripheral control device 1510 will receive new information (display data) in the next interrupt period (after 4 ms in this case) as long as the
しかしながら、主制御MPU1311がリセットされると、メイン液晶表示装置1600を制御する周辺制御基板1510の初期化処理のために必要な時間をウェイトすることから、機能表示ユニット1400への指令が途絶えて、機能表示ユニット1400の表示が消えて、遊技者は遊技が継続して行えるのかを不安に思うことになる。このため、主制御MPU1311をリセットさせないことが望ましい。
However, when the
次に、インバータ・バッファのICパッケージ内の配置及び端子の接続を説明する。図259、図260は、インバータ・バッファを収容するICの端子の接続例を説明する図である。 Next, the arrangement of the inverter/buffer in the IC package and the connection of the terminals will be described. 259 and 260 are diagrams for explaining connection examples of terminals of an IC that accommodates an inverter buffer.
図259、図260に示すICは、ICパッケージの両側に並んで端子が(すなわち2列に)配置される形状(例えば、挿入実装型のDual In-line Packageや、表面実装型のSmall Outline Package)であり、6個のインバータ・バッファを有し、各インバータ・バッファの入力及び出力の端子番号が1-2、3-4、5-6、9-8、11-10、13-12となっている。 The IC shown in FIGS. 259 and 260 has a shape in which terminals are arranged (that is, in two rows) on both sides of the IC package (for example, an insertion mounting type Dual In-line Package or a surface mounting type Small Outline Package). ), which has six inverter buffers, and the input and output terminal numbers of each inverter buffer are 1-2, 3-4, 5-6, 9-8, 11-10, and 13-12. It's becoming
各インバータ・バッファは、単なるインバータ・バッファではなく、ヒステリシス特性を有するシュミットトリガ型のインバータ・バッファであるとよい。インバータ・バッファにヒステリシス特性を持たせることによって、リセット信号の波形を確実に整形でき、ノイズへの耐性を向上できる。また、シュミットトリガ型のバッファを用いることによって、入力信号の立ち上がりが遅い波形にも対応できる。すなわち、CMOSでは、入力信号のレベルが長時間スレッショルド付近にあることによって、ゲート内で大電流が流れ、ラッチアップを引き起こすことがあるが、シュミットトリガ型のバッファを用いることによって、入力信号の立ち上がりが遅い波形でもラッチアップが抑制できる。 Each inverter buffer is preferably not a simple inverter buffer but a Schmitt trigger type inverter buffer having a hysteresis characteristic. By giving the inverter buffer a hysteresis characteristic, the waveform of the reset signal can be reliably shaped, and the resistance to noise can be improved. Also, by using a Schmitt trigger type buffer, it is possible to cope with waveforms of input signals whose rise is slow. That is, in CMOS, when the level of the input signal is near the threshold for a long time, a large current flows in the gate, causing latch-up. Latch-up can be suppressed even with slow waveforms.
図259に示す接続例では、リセット回路1335から出力されるリセット信号は端子3及び端子11に入力される、端子3に入力されたリセット信号は、インバータ・バッファを経由して端子4から出力され、端子5に入力され、さらにインバータ・バッファを経由して端子6から出力され、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343に入力される。一方、端子11に入力されたリセット信号は、インバータ・バッファを経由して端子10から出力され、端子9に入力され、さらにインバータ・バッファを経由して端子8から出力され、主制御MPU1311に入力される。
In the connection example shown in FIG. 259, the reset signal output from the
このように図259に示す接続例では、両側に並んで端子が(すなわち2列に)配置されたICパッケージの片側の端子にシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343へ送られるリセット信号を通し、もう他方の側の端子に主制御MPU1311へ送られるリセ
ット信号を通すので、2系統のリセット信号が交錯せず、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343への信号線に誘起したノイズの主制御MPU1311への入力を抑制できる。
In the example of connection shown in FIG. Since the reset signal sent to the
一方、図260に示す接続例では、リセット回路1335から出力されるリセット信号は端子1及び端子3に入力される、端子1に入力されたリセット信号は、インバータ・バッファを経由して端子2から出力され、端子13に入力され、さらにインバータ・バッファを経由して端子12から出力され、主制御MPU1311に入力される。一方、端子3に入力されたリセット信号は、インバータ・バッファを経由して端子4から出力され、端子11に入力され、さらにインバータ・バッファを経由して端子10から出力され、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343に入力される。
On the other hand, in the connection example shown in FIG. 260, the reset signal output from the
このように図260に示す接続例では、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343へ送られるリセット信号をICの一部に集めて通し、主制御MPU1311へ送られるリセット信号を他の一部に集めて通すので、2系統のリセット信号が交錯せず、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343への信号線に誘起したノイズの主制御MPU1311への入力を抑制できる。
Thus, in the connection example shown in FIG. 260, the reset signals sent to the serial/
次に、図261を参照して、主制御MPU1311及び周辺部品の主制御基板1310上での配置を説明する。
Next, with reference to FIG. 261, the arrangement of the
図261に示すように、主制御基板1310上には主制御MPU1311が搭載されており、その周辺に各種インターフェイス回路が配置されている。また、主制御基板1310上には、検査用回路配置エリアが設けられており、該検査用回路配置エリアには、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346とインターフェイス回路1347と検査用端子1348が設けられる。検査用回路配置エリアに設けられる回路部品(シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346、インターフェイス回路1347、検査用端子1348など)は、検査機関による検査を受けるパチンコ機1にのみ搭載され、一般に市販されるパチンコ機1には搭載されない(部品搭載用のパターンは設けられている)。すなわち、一般に市販されるパチンコ機1には、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1345からソレノイドに出力される信号を中継するコネクタは実装されているが、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346から出力される検査用信号を中継する検査用端子1348は実装されていない。このため、市販されるパチンコ機1では、検査用信号が不正行為者に検出されて不正行為に利用されることがない構成となっている。
As shown in FIG. 261, a
前述したように、市販用のパチンコ機1では、検査用回路配置エリアには部品が搭載されないがプリントパターン(例えば、インターフイス回路1347に繋がるデータバス)が設けられている。このため、ノイズがデータバスに誘起し誤動作を引き起こす可能性があることから、検査用回路配置エリアの配線(プリントパターン)を抵抗を介して電源(+5V)へプルアップして(又は、GNDへプルダウンして)、ノイズの影響を低減するとよい。
As described above, in the commercially
さらに、不正改造防止の観点から、市販されるパチンコ機1には表面実装部品は使用していないが、検査用回路配置エリアに設けられる回路部品は市販されるパチンコ機1には搭載されないので、表面実装部品を使用できる。このため、検査用回路の部品を小型化でき、検査用回路配置エリアを小さくでき、ひいては、主制御基板1310を小型化できる。同様に不正改造防止の観点から、市販されるパチンコ機1には主制御基板1310の裏面側には部品を搭載していないが、検査用回路配置エリアに設けられる回路部品は市販されるパチンコ機1には搭載されないので、主制御基板1310の裏面側には部品を搭載できる。
Furthermore, from the viewpoint of preventing unauthorized modification, the
なお、検査用回路の部品のうち、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346及び検査用端子1348を、主制御基板1310の近傍に配置される別基板に設けてもよい。この別基板は、検査機関による検査を受けるパチンコ機1にのみ実装され、一般に市販されるパチンコ機1には実装されない。この場合も、一般に市販されるパチンコ機1からは、検査用信号が出力されない。
Of the parts of the inspection circuit, the serial/
このように、パチンコ機1の検査に用いる回路部品を検査用回路配置エリアに集約して配置することによって、市販用のパチンコ機1における部品の欠落を発見しやすく、不正のための付加部品の取り付けを発見しやすい。また、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1346及びインターフェイス回路1347を検査用端子1348の近くに配置でき、ノイズ耐性が高い主制御基板1310を構成できる。
By arranging the circuit parts used for inspection of the
さらに、図261に示すように、検査用回路配置エリアに配置される回路部品は、主制御基板1310の他の場所に配置される同種の回路部品と異なる向き(例えば、図示するように180度回転した方向)に配置するとよい。このように、検査用回路配置エリアと主制御基板1310の他の場所とで回路部品を異なる向きに配置することによって、通常遊技に用いる部品と検査用の部品を容易に区別できるようになり、市販されるパチンコ機1の製造工程において、検査用回路配置エリアに誤って部品を配置する誤実装を防止できる。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 261, the circuit components placed in the inspection circuit placement area are oriented differently from the same type of circuit components placed elsewhere on the main control board 1310 (for example, 180 degrees as shown). rotated direction). In this way, by arranging the circuit parts in different directions in the inspection circuit layout area and other places on the
また、主制御基板1310上には、搭載されている回路部品の記号や番号(又はその組み合わせ)が例えばシルク印刷で表示されているが、検査用回路配置エリアに配置される回路部品の記号や番号は、遊技制御に使用される回路部品の記号や番号に後続する記号や番号で纏めて付けるとよい。例えば、遊技制御用の集積回路はIC1~IC11とし、検査用回路配置エリアに配置される集積回路はIC12以後の記号を付す。このようにすると、市販されるパチンコ機1に実装される遊技制御用の回路部品に飛びがない記号や番号を付すことができ、回路部品を主制御基板1310に搭載した後のチェックを簡易にできる。
Also, on the
さらに、検査用端子の記号や番号は、遊技制御用の部品と接続されるコネクタの記号や番号とは別系統にすると、遊技制御用の部品と接続されるコネクタと検査用端子とを容易に区別でき、ケーブルを誤って接続する誤配線を防止できる。特に、検査用端子の記号や番号を相手方の検査用装置の接続先の記号や番号と同じにすると、検査時のケーブルの接続に便利であり、接続ミスを低減できる。 Furthermore, if the symbols and numbers of the inspection terminals are in a separate system from the symbols and numbers of the connectors connected to the game control parts, the connectors and inspection terminals connected to the game control parts can be easily identified. It is possible to distinguish between them and prevent miswiring of incorrectly connecting cables. In particular, if the symbols and numbers of the inspection terminals are the same as the symbols and numbers of the connection destinations of the inspection device of the other party, it is convenient for cable connection during inspection, and connection errors can be reduced.
また、主制御MPU1311の汎用ポートの一部は使用されていない空きポートとなっており、主制御MPU1311の隣接した端子に集約するように空きポートを配置するとよい。すなわち、未使用ポートのポート番号が連続かにかかわらず、空きポートの端子が集約した位置に配置されるとよい。空き端子を集約して配置することによって、主制御基板1310上のプリントパターンが設けられていない領域が集約されており、部品の欠落を発見しやすく、不正のための付加部品の取り付けを発見しやすくなっている。
In addition, some of the general-purpose ports of the
また、空きポートの端子は、コネクタとの位置関係において、比較的大きな電流が流れる(例えば、ソレノイドが接続される)コネクタに近い位置に配置している。すなわち、主制御MPU1311の長手方向において、空きポートの端子がある側の左右(図では上下)に遊技制御用の信号を入出力するコネクタを配置している。このため、パチンコ機1に追加の機能を付加する場合に、長いパターンを引き回すことなく、主制御基板1310を容易に設計変更できる。
In addition, the terminal of the empty port is arranged at a position close to the connector through which a relatively large current flows (for example, a solenoid is connected) in terms of the positional relationship with the connector. That is, in the longitudinal direction of the
以上に説明したように、主制御基板1310内の信号伝送にシリアル通信を使用することによって、データバスの配線を減らすことができ、不正のための付加部品の取り付けを発見しやすくなる。すなわち、複数のパラレルインターフェイス回路に接続される多数本のデータバスがなくなり、制御線も含めて何本かの信号線になることによって、多数本のデータバスの回路パターンが複雑に配置された配線から、すっきりした回路パターンとなる。また、データ線の引き回し距離が短くなることによって、ノイズに強い主制御基板1310を構成できる。
As described above, by using serial communication for signal transmission within the
また、データ線の数が減るので、データ線の引き回しに影響されずに回路を配置できることから、I/O用IC(パラレルインターフェイス回路、シリアルインターフェイス回路)を主制御MPU1311の近くに配置できる。 In addition, since the number of data lines is reduced, the circuits can be arranged without being affected by the routing of the data lines.
また、回路パターンが減少することによって、主制御基板1310の面積を変えずにグランドパターンを増やすことができ、よりノイズに強い主制御基板1310を構成できる。
Further, by reducing the number of circuit patterns, the number of ground patterns can be increased without changing the area of the
図262は、主制御MPU1311におけるポートの配置を示す図である。
FIG. 262 is a diagram showing the arrangement of ports in the
アドレスD2(チップセレクトSERS0)のパラレル出力ポートはシリアル・パラレル変換回路1343であり、図258に示すように、チャネルAの出力ポートPA0~PA3が機能表示ユニット1400のコモン側(LEDのアノード端子)に接続されており、出力ポートPA4~PA7がベース表示器1317のコモン側(7セグメントLEDのアノード端子)に接続されている。シリアル・パラレル変換回路1343のチャネルBの出力ポートPB0~PB7は使用されていない。
The parallel output port of address D2 (chip select SERS0) is the serial/
また、アドレスD3(チップセレクトSERS1)のパラレル出力ポートはシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342であり、図258に示すように、チャネルAの出力ポートPA0~PA7が機能表示ユニット1400のセグメント側(LEDのカソード端子)に接続されており、チャネルBの出力ポートPB0~PB7がベース表示器1317のセグメント側(7セグメントLEDのカソード端子)に接続されている。
Also, the parallel output port of address D3 (chip select SERS1) is the serial/
LEDのコモン側(LEDのアノード端子)は一定周期(例えば、4ms毎の割り込み)でONにする出力ポートを切り替えている。チャネルAの出力ポートに注目した場合、タイマ割込み処理でPA0だけをON、次のタイマ割込み処理(4ms後)でPA1だけをON、・・・、次のタイマ割込み処理(4ms後)でPA7だけをONを一定周期(4ms×ポートの数)で繰り返している。すなわち、8ポートを繰り返して切り替える場合、各ポートは32ms毎にONになる。もしくは、チャネルAの出力ポートPA0~PA3とPA4~PA7をそれぞれグループとして、チャネルAの出力ポートに注目した場合、タイマ割込み処理でPA0とPA4だけをON、次のタイマ割り込み処理(4ms後)でPA1とPA5だけをON、・・・、次のタイマ割込み処理(4ms後)でPA3とPA7だけをONを一定周期(4ms×ポートの数)で繰り返してもよい。この一定周期の動作をシリアル通信とすることで、主制御MPU1311の動作タイミングの察知を困難にできる。
On the common side of the LED (anode terminal of the LED), the output port to be turned on is switched at a constant cycle (for example, interrupt every 4 ms). When focusing on the output port of channel A, only PA0 is turned on in the timer interrupt processing, only PA1 is turned on in the next timer interrupt processing (after 4 ms), and only PA7 is turned on in the next timer interrupt processing (after 4 ms). is repeatedly turned on at a constant cycle (4 ms×the number of ports). That is, when repeatedly switching 8 ports, each port is turned ON every 32 ms. Alternatively, if the channel A output ports PA0 to PA3 and PA4 to PA7 are grouped respectively and attention is focused on the channel A output port, only PA0 and PA4 are turned ON in the timer interrupt processing, and in the next timer interrupt processing (4 ms later) Only PA1 and PA5 are turned ON, . . . , and only PA3 and PA7 are turned ON in the next timer interrupt process (after 4 ms). By using serial communication for this constant cycle operation, it is possible to make it difficult to perceive the operation timing of the
また、アドレスD5のパラレル入力ポートはパラレル・シリアル変換回路1341であり、入力PA1~PA7及びPB0~PB7に遊技球を検出するためのスイッチ(球検出センサ)が接続されている。これらの球検出センサの出力はシリアル信号として主制御MPU1311に入力され、アドレスD5の信号として読み取られる。
The parallel input port of address D5 is parallel/
さらに、主制御MPU1311に備わる汎用入力ポートINP0~INP4には、設定
キー971の操作情報、RAMクリアスイッチ954の操作情報、停電予告信号、主払ACK信号、枠開放検出スイッチの検出信号が入力されている。これらの信号はリアルタイム(プログラムが要求した時点)での監視が必要であったり、タイマ割込み処理外(例えば、電源投入直後)に監視が必要なため、パラレル・シリアル変換回路を介さずに主制御MPU1311に直接入力される。
Furthermore, general-purpose input ports INP0 to INP4 provided in the
さらに、主制御MPU1311に備わる汎用入出力ポート(入出力兼用)IOP0~IOP3には、電波検出センサの検出信号、振動検出センサの検出信号、磁気検出スイッチの検出信号、近接エラースイッチの検出信号が入力されている。これらの信号はパチンコ機1に異常(不正行為や故障など)が生じている時に出力される信号であり、リアルタイム(プログラムが要求した時点)での監視が必要なため、パラレル・シリアル変換回路を介さずに主制御MPU1311に直接入力されている。また、これらのセンサやスイッチの検出信号によって、メイン液晶表示装置1600や音声で異常が報知される。この異常報知によって、ホールの従業員がパチンコ機の状態を確認に来るので、実質的に遊技が停止することになる。この異常報知が誤報知であれば、遊技者に不快な思いをさせることから、誤検出を抑制する必要がある。このため、これらの信号を汎用入出力ポートに入力して、短時間で複数回検出して(いわゆる2度読みをして)ノイズの影響による誤検出を抑制するとよい。
Furthermore, the general-purpose input/output ports (both input/output) IOP0 to IOP3 provided in the
この2度読みの処理は、1回のタイマ割込み処理において、読み込み命令を連続して実行して汎用入出力ポート(又は汎用入力ポート)に入力される信号レベルを短い時間間隔で判定したり、数個の命令を挟んだ複数の読み込み命令を実行して汎用入出力ポート(又は汎用入力ポート)に入力される信号レベルを短い時間間隔で判定したり、数クロックのウェイトを挟んだ複数の読み込み命令を実行して汎用入出力ポート(又は汎用入力ポート)に入力される信号レベルを短い時間間隔で判定することによって行われる。このため、パラレル・シリアル変換回路を介してポートのレベルを続けて判定する場合は数十マイクロ秒間隔でしかレベルを検出できないのに対し、汎用ポートのレベルを続けて判定する場合は1マイクロ秒以下の間隔でレベルを検出でき、信号レベルを短い周期で検出できる。 In this double read process, in one timer interrupt process, read instructions are continuously executed to determine the signal level input to a general-purpose input/output port (or general-purpose input port) at short time intervals. Execute multiple read instructions with several instructions in between to determine the signal level input to the general-purpose input/output port (or general-purpose input port) at short time intervals, or perform multiple read operations with a wait of several clocks in between. This is done by executing an instruction to determine the signal level input to a general purpose input/output port (or general purpose input port) at short time intervals. Therefore, when the port level is continuously determined via the parallel/serial conversion circuit, the level can be detected only at intervals of several tens of microseconds. The level can be detected at the following intervals, and the signal level can be detected in a short period.
このように、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、チップセレクトを使用した拡張I/Oを使用せずに、リアルタイム性が必要な各種スイッチやセンサの信号を汎用入力ポート及び汎用出力ポートに直接入力でき、汎用入出力ポート(入出力兼用)に入力された信号のレベルをクロック毎にbit単位で取り込むので、シリアル信号の受信を待たずに信号レベルをリアルタイムで検出できる。
In this way, in the
なお、汎用入出力ポート(入出力兼用)IOP4~IOP7は使用されていないが、パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341を介して入力される信号の一部を汎用入出力ポート(入出力兼用)IOP4~IOP7に入力してもよい。
Although the general-purpose input/output ports (both input/output) IOP4 to IOP7 are not used, part of the signals input via the parallel/
また、図示を省略したが、主制御MPU1311は、汎用出力ポートを有してもよい。
Although not shown, the
なお、汎用入力ポートが空き端子である場合、抵抗を介して5Vへプルアップするか、GNDへプルダウンして、端子が中間電位になることを防止し、電源ラインに誘起されるノイズの影響を低減するとよい。また、汎用出力ポートが空き端子である場合、オープンとしてもよいが、ダミー抵抗を介して5Vへプルアップするか、GNDへプルダウンして、出力ポートのレベル変化がノイズとならないようにするとよい。 If the general-purpose input port is a vacant terminal, it is pulled up to 5 V via a resistor or pulled down to GND to prevent the terminal from going to an intermediate potential and reduce the effects of noise induced in the power supply line. should be reduced. Also, if the general-purpose output port is a free terminal, it may be left open, but it should be pulled up to 5V or pulled down to GND via a dummy resistor so that the level change of the output port does not become noise.
以上に説明したように、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、検査用信号は主制御MPU1311の汎用ポートから出力し、遊技制御に用いる信号はシリアル・パラレル変換回路を介して出力する。このため、入賞球検出信号は一つのポートに集約されて入力され、遊技制
御プログラムで取り扱いやすくなる。
As described above, in the
また、主制御MPU1311に入力される信号のうち、短時間で複数回検出する(いわゆる2度読みをする)必要がある信号を汎用ポートに入力し、2度読みする必要がない信号をシリアル・パラレル変換回路を介して主制御MPU1311に入力する。汎用ポートはリアルタイムに信号レベルを確認できるので、信号レベルを短時間に複数回検出して、ノイズによる影響を排除して判定ができる。汎用入力ポートが空いていれば、2度読みする必要がない信号が汎用ポートに入力されるように、ポートを割り当ててもよい。
In addition, among the signals input to the
汎用入力ポートには主制御MPU1311に入力される信号を割り当て可能であるが、汎用入出力ポート(入出力兼用)には主制御MPU1311に入力される信号と主制御MPU1311から出力される信号とのいずれも割り当て可能であるので、汎用入出力ポートは、仕様の変更に対する汎用性が高い。このため、新機能の追加のために予備として残しておくポートは汎用入出力ポート(入出力兼用)が望ましく、汎用入力ポートを優先して割り当てることが望ましい。
A signal to be input to the
次に、図263を用いて、同期シリアル信号によるデータの出力と取り込みのタイミングを説明する。 Next, with reference to FIG. 263, the timing of data output and capture by synchronous serial signals will be described.
主制御MPU1311が、チップセレクト端子SERS0から0(LOW)を出力すると、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1343が選択され、主制御MPU1311が、ベース表示器1317のコモン側の選択信号を出力する。図では、PA7~PA4においてPA7(COM4)が選択されている。その後、主制御MPU1311が、シリアル信号送信端子SERTXから機能表示ユニット1400のコモン側の選択信号を出力する。図では、PA3~PA0においてPA3(LED-C4)が選択されている。
When the
シリアル・パラレル変換回路1343のBチャネルポートには出力が割り当てられていないので、本来PB7~PB0のデータ取り込みタイミングには何も出力せず、1(HIGH)を維持する。しかし、本実施例のパチンコ機では、主制御MPU1311から出力されるシリアル送信信号SERTXは、パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341のデータ取り込みタイミングを定めるCLR/LOAD端子に接続されており、この信号が0(LOW)のときにPA0からPB7からデータが取り込まれる。このため、PB7~PB0のいずれかのタイミングでシリアル送信信号SERTXを0(LOW)にして、パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341のPA0~PB7からデータを取り込む。
Since no output is assigned to the B channel port of the serial/
パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341は、データを取り込み、シリアル送信信号SERTXが1(HIGH)に立ち上がった後、クロック信号に従ってシリアル信号出力端子(Q8C)からシリアルデータを出力する。なお、この間、シリアル送信信号SERTXが1(HIGH)を維持して、新たなデータを取り込まないように制御する。
The parallel/
このように、本実施例のパチンコ機では、遊技球検出センサの出力を取り込むトリガに空いている出力ポートの送信信号を使用するので、任意のタイミングで球検出センサのデータを取り込むことができる。 As described above, the pachinko machine of this embodiment uses the transmission signal of the open output port as a trigger to capture the output of the game ball detection sensor, so the data of the ball detection sensor can be captured at any timing.
次に、図264、図265を用いて、主制御基板ボックス1320における主制御基板1310の別の配置を説明する。
Next, another arrangement of the
主制御基板1310は、再設計をせずに複数の機種で共通に使用することが望ましい。しかし、主制御基板1310の入出力信号は機種や仕様によって異なることがある。このため、本実施例では、機種によって異なる主制御基板1310の入出力インターフェイス
を別基板(入出力基板1351)に実装し、各機種で共通となる主制御MPU1311の周辺は主制御基板1310に実装する構成とする。主制御基板1310を複数機種で共通にする、すなわち、基板サイズ、回路設計、プリント基板のアートワーク、部品配置などを同じにすることによって、性能(例えば、耐ノイズ性能)が評価されており設計品質が安定している主制御基板1310を再設計をせずに複数の機種で共通に使用できる。
It is desirable to use the
また、主制御基板1310の入出力インターフェイスを別の入出力基板1351に実装する場合に、どこで回路を分けるかが問題となる。一つは、シリアル信号線で別ける方法であり、二つ目はシリアル信号を変換したパラレル信号で別ける方法である。前者の場合、後者より基板間の配線の数を減少でき望ましい。また、シリアル信号は、信号自体が取得されても、データが送信される順序を知ることが困難であり、どのタイミングでどのデータが送信されているかが不明である。さらに、シリアル信号用のクロックに同期した速度で出力され、この同期クロックは、主制御MPU1311の動作クロックと異なってもよく、変更可能である。このため、外部からデータレートを推測され難く、シリアル信号を取得しても、伝送されているデータの内容を知ることは困難である。このため、主制御基板1310と入出力基板1351との間はシリアル信号線で接続すると好ましい。
Also, when the input/output interface of the
図264に示すように、主制御基板1310に附属する入出力基板1351が設けられ、主制御基板1310及び入出力基板1351は、主制御基板ボックス1320内に取り付けられる。主制御基板ボックス1320は、一度閉めたら破壊せずに開けることができない構造で封印可能に主制御基板1310及び入出力基板1351を収容する透明の樹脂によって構成される。入出力基板1351には、パラレル・シリアル変換回路1341及びシリアル・パラレル変換回路1345が設けられる。主制御基板1310と入出力基板1351(主制御MPU1311とパラレル・シリアル変換回路1341及びシリアル・パラレル変換回路1345)との間は、シリアル通信線で接続されており、パラレルバスや汎用ポートで接続するより少ない本数で基板間を接続できる。シリアル信号線は、電線で接続しても、基板間コネクタで接続してもよい。
As shown in FIG. 264, an input/output board 1351 attached to the
また、基板間をシリアル通信にすれば、その信号を取得されても、データの解析が困難であることから、伝送されているデータの内容を不正行為者に知られる可能性を低減できる。また、遊技制御のための信号を入出力する入出力基板1351を主制御基板1310から分離して構成し、機種によって変わる入出力信号を入出力基板1351に設定するので、主制御基板1310を改造することなく適用できる機種が増え、主制御基板1310の汎用性を向上できる。
In addition, if serial communication is used between boards, it is difficult to analyze the data even if the signal is acquired. In addition, the input/output board 1351 for inputting/outputting signals for game control is configured separately from the
さらに、主制御基板1310及び入出力基板1351を一つの主制御基板ボックス1320内に収容することによってシリアル通信の信号線を短くできる。
Furthermore, by housing the
また、他の機種に主制御基板1310を使用するときには、入出力基板1351を設計変更すればよく、主制御基板1310のコネクタと主制御MPU1311との関係は機種によって変わることがないので、パチンコ機の設計が容易になり、性能(例えば、耐ノイズ性能)が評価されており設計品質が安定している主制御基板1310を使用できる。また、入出力基板1351の大きさや取付穴の位置を変えなければ主制御基板ボックス1320を設計し直さなくても、従来の主制御基板ボックス1320を流用できる。また、機種毎に変化するノイズ対策は、主制御基板1310ではなく、入出力基板1351で行えばよい。
Also, when the
ベース表示器1317の駆動信号を出力するシリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343は、主制御基板1310上に配置するとよい。なお、ベース表示器1317を入出力基板1351上に配置する場合は、シリアル・パラレル変換回路1342、1343を
入出力基板1351上に配置し、機能表示ユニット1400を駆動するための信号を入出力基板1351から出力するとよい。
Serial/
また、検査用信号を生成するシリアル・パラレル変換回路1346は、主制御基板1310上に配置するとよい。すなわち、検査用回路配置エリア及び検査用端子1348は主制御基板1310に設けるちとよい。これは、検査用端子1348から出力される信号の一部は、主制御MPU1311からパラレルバスによって出力されることから、入出力基板1351上に検査用端子1348を配置すると主制御基板1310と入出力基板1351との間の接続線が増えるからである。
Also, the serial/
また、図265に示すように、主制御基板1310を主制御基板ボックス1320内に収容し、入出力基板1351を主制御基板ボックス1320の外に取り付けてもよい。
Also, as shown in FIG. 265, the
図265に示す形態では、主制御基板ボックス1320の外に入出力基板1351を設けるので、主制御基板ボックス1320の大きさが変わっても、主制御基板ボックス1320を共通で使用できる。また、入出力基板1351と主制御基板1310とを別な基板ボックスに収容するので、基板の配置の自由度が向上する。また、主制御基板1310が収容される主制御基板ボックス1320と入出力基板1351が収容される入出力基板ボックス1350を別体に設けると、各基板ボックスが小さくなり、基板設置位置が自由になる。さらに、主制御基板1310はベース表示器1317やエラーコードを表示するLEDや設定キー971が設けられているので、パチンコ機1の裏面側に表れている必要があるが、入出力基板1351はパチンコ機1の裏面側から視認できなくてもよいので、基板設置位置が自由になる。このように、図265に示す形態では、設計の自由度を向上できる。
In the form shown in FIG. 265, since the input/output board 1351 is provided outside the main
なお、図265に示す形態では、主制御MPU1311から出力されるシリアル信号が主制御基板ボックス1320の外部に出力されることになる。主制御MPU1311は、シリアル信号の他にデータバスからデータを出力する。パチンコ機においては、不正行為者にパチンコ機の動作を察知されないようにするために、封印されている主制御基板ボックス1320の外部には主制御MPU1311から出力されるデータバスを出力しないのが望ましい。しかし、主制御MPU1311から出力されるシリアル信号は主制御基板ボックス1320の外部に出力されても、不正行為者にパチンコ機の動作状況を察知される可能性は低い。これは、データバスは主制御MPU1311の動作クロックに従ってデータが出力されて、データレートが一定であることから、外部からデータレートを推測されやすく、その結果、データバスで伝送される信号を取得されることがある。しかし、シリアル信号は、シリアル信号用のクロックに同期した速度で出力され、この同期クロックの速度は、主制御MPU1311の動作クロックと異なってもよく、変更可能である。このため、外部からデータレートを推測され難く、シリアル信号を取得しても、伝送されているデータの内容を知ることは困難である。
265, the serial signal output from the
以上に、主制御基板1310と別体に入出力基板1351を設け、機種依存性がある信号の入出力機能を入出力基板1351に搭載する例を説明したが、他に主制御基板1310外に配置しても不正やノイズへの耐性が低下しない部分があれば、入出力基板1351に搭載してもよい。例えば、遊技盤5に取り付けられるソレノイドやモータなどの駆動電流を必要する信号の出力や、機能表示ユニット1400の駆動信号の出力や、各種センサ(入賞球検出、電波センサ、磁気センサ、振動センサ)の信号の入力は、入出力基板1351に搭載してもよい機能である。また、払出制御基板951との通信、外部端子板784から出力する信号の出力、停電検知、設定キー971の入力(設定キー971自体は主制御基板1310外に設けてもよい)、ベース表示器1317への出力は、主制御基板に1310に搭載するとよい機能である。
As described above, the input/output board 1351 is provided separately from the
また、入出力基板1351に搭載されるパラレル・シリアル変換回路1341及びシリアル・パラレル変換回路1345は、空き入力端子にダミー信号(0V又は5V)を入力
するか、空き出力端子にダミー抵抗を接続するとよい。これは、空き端子に何も接続しないと、ノイズを取り込んで、回路が誤動作することがあるからである。
Also, the parallel/
特に、不正行為者が取得しようとする複数の信号のうち一部の信号をパラレルバスや汎用ポートで伝送し、他の信号をシリアル信号で伝送すると、シリアル信号の解析が困難であることから、不正行為者は主制御基板1310と入出力基板1351とを含む複数箇所から信号を取得する必要があり、不正に対する抑止力を高められる。
In particular, it is difficult to analyze the serial signals if some of the multiple signals that the fraudster attempts to obtain are transmitted via a parallel bus or general-purpose port, and other signals are transmitted as serial signals. A fraudulent person needs to obtain signals from a plurality of locations including the
[15.パチンコ機内部の電源供給経路に関する実施例]
次に、パチンコ機内部の電源供給経路における過電流保護に関する実施例を説明する。
[15. Example of Power Supply Path Inside Pachinko Machine]
Next, an embodiment relating to overcurrent protection in the power supply path inside the pachinko machine will be described.
パチンコ機1には交流24Vの電源が供給されている。電源基板931は、パチンコ機1に供給された交流24Vの電源から、パチンコ機1内部で使用する様々な直流(例えば5V、12V、24V、35V)の電源を作成する電源作成回路933を有している。
The
電源基板931から出力される電源は、パチンコ機1の演出や装飾のための役物やランプ(LED)を駆動するために、これらの演出部材や制御装置などに供給される。このような演出部材への駆動電源を供給する電線は一般的に固定されているものの、役物の駆動部分の可動部では、役物によって電線が引っ張られないように、余裕を持った長さで配線されている。このため、役物の動作によって、電線が役物を構成する部材に擦れたり、役物の駆動部分の可動部に挟まったりして、電線の被覆が破損するおそれがある。このような状況下で電源線とグランド線とが近接している場合においては、短絡して大きな電流が流れることになる。
The power output from the power supply board 931 is supplied to the performance members, the control device, and the like in order to drive accessories and lamps (LEDs) for performance and decoration of the
しかし、電源基板931に近い箇所で短絡した場合には大きな電流が流れ、電源基板931に実装された過電流保護機能(ヒューズ)が動作して、電源を遮断する。 However, if a short circuit occurs near the power supply board 931, a large current flows, and an overcurrent protection function (fuse) mounted on the power supply board 931 operates to cut off the power.
ところが、前述したように、電源基板931から遠い箇所で短絡すると過電流保護機能(ヒューズ)が動作する程度の大きさの電流は流れず、不具合が顕在化しない。これは、配線された電線が負荷となることにある。例えば、電線のインピーダンスが1Ω程度になる場所で短絡すると、演出部材に供給される駆動電源が12Vだとすると、12Aの電流が流れるも、電源基板931の過電流保護機能(例えば、15Aヒューズ)が動作しない。全ての電源線に、正常状態で流れる電流を考慮した適切な容量の過電流保護デバイス(ヒューズ)を取り付ければよいが、部品コスト及び組み立てコストの上昇を招く。 However, as described above, if a short circuit occurs at a location far from the power supply substrate 931, a current large enough to operate the overcurrent protection function (fuse) does not flow, and the problem does not occur. This is because the wired electric wire becomes a load. For example, if there is a short circuit at a place where the wire impedance is about 1Ω, and the driving power supplied to the production member is 12V, a current of 12A will flow, but the overcurrent protection function (eg, 15A fuse) of the power supply board 931 will operate. do not do. An overcurrent protection device (fuse) having an appropriate capacity considering the current flowing in a normal state should be attached to all the power lines, but this leads to an increase in parts cost and assembly cost.
そこで、特に可動部分の近くを通る電線で電源線とグランド線とが近接して配置される場合は、当該電線が接続される基板に、電源に実際に流れる電流の2~3倍で動作する過電流保護デバイス(ヒューズ)を配置して、短絡時に、大きな電流が流れることを防止する。 Therefore, especially when the power line and the ground line are arranged close to each other with the electric wire passing near the movable part, the board to which the electric wire is connected operates at 2 to 3 times the current actually flowing in the power supply. Overcurrent protection devices (fuses) are placed to prevent large currents from flowing in the event of a short circuit.
ここで、駆動装置の一例として、図16の上部可動ユニット3400について説明する。
Here, the upper
本実施例のパチンコ機1では、図16に示すように遊技盤5を正面から見た上部には、麻雀の点棒をモチーフに形どられた意匠からなり、可動する点棒役物(可動体)3410が配置されている。点棒役物3410は、非演出状態では上部位置に待機し、演出状態においては下方の遊技盤中央位置まで移動可能であって、遊技盤中央位置では中央装飾ランプ3412aを中心に回転動作をするものである。
In the
図示されていないが、遊技盤を正面から見て遊技領域に重なる右側裏面には、ユニットベース体が設けられており、点棒役物3410は、ユニットベース体に旋回可能に従動軸に軸支され、点棒役物3411からユニットベース体へと延びる役物ベース体と、役物ベース体の旋回動作を規制、アシスト(点棒役物3410の上下方向の移動を規制、アシスト)し、点棒役物3410の役物ベースに設けたブッシュを挿入させて摺動させるためのスリットを有し、ユニットベース体に可動可能に従動軸に軸支されるアーム体とによって支えられている。
Although not shown, a unit base body is provided on the back side of the right side overlapping the game area when viewed from the front of the game board, and the
ユニットベース体には、その他、点棒役物3410を下方の遊技盤中央位置まで移動させるための移動用のステッピングモータMAや移動検知センサ等が取り付けられている。また、役物ベース体にも回転させるための回転用のステッピングモータMBや回転検知センサ、および中央装飾ランプ3412aのLEDが実装されたLED基板(4250A)やその他、左右装飾ランプ3411のLEDが実装されたLED基板(4250Bなど)が備えられている。
The unit base body is also provided with a moving stepping motor MA for moving the
そして、これら回転用のステッピングモータMBや回転検知センサ、およびLEDを駆動するための駆動信号線や検出信号線が、役物ベース体から電源線やグランド線とともに引き回されて、中継基板(3044A、3044B、3044Cなど)を介して、あるいは直接、演出駆動基板3043へと延び接続されている。なお、各種電線は、上部可動ユニット3400の点棒役物3410の待機位置と演出位置との間で定まり、ある程度の遊びを持った線長とされ、束ねられたバラの電線を用いているがフラットケーブルを用いて配線してもよい。また、中継基板や演出駆動基板は、上部可動ユニット3400に設けているが、外部に設けられていてもよい。
Then, the stepping motor MB for rotation, the rotation detection sensor, and the drive signal line and detection signal line for driving the LED are routed from the accessory base body together with the power line and the ground line, and the relay board (3044A , 3044B, 3044C, etc.) or directly to the
図266は、前記した駆動装置である上部可動ユニット3400について、各種基板や駆動源等の電気的な接続関係を示すブロック図である。
FIG. 266 is a block diagram showing the electrical connections of various substrates, drive sources, etc. in the upper
電源基板931には、パチンコ機1の外部から供給された交流24Vの電源が入力されている。電源基板931は電源作成回路933を有しており、電源作成回路933には、交流24Vの電源が、過電流保護デバイス(過電流保護手段)としてのヒューズ934を経由して入力される。
24V AC power supplied from the outside of the
電源作成回路933は、24Vの交流から、パチンコ機1内部で使用する様々な直流(おもにステッピングモータやソレノイド、およびLED、あるいは各種センサ等に使用される12V、24V、35Vや、おもにCPUなど電子回路の制御電源として使用される5Vなど(別途制御基板上で他の直流電源から降圧して作成してもよい))の電源を作成する。
The
本実施例では12Vで動作するステッピングモータ、および12V電源を使用して点灯、点滅させるLED(基板)を例に挙げて説明するため、図266では12V電源の系統についてのみ太線で示し、その他の系統については省略している。また、その他、後述する各種制御線や駆動線については細線で示している。なお、各基板はコネクタおよびハーネス(電線)で接続されているものとする。 In this embodiment, a stepping motor that operates at 12V and an LED (substrate) that is lit and blinked using a 12V power supply are used as examples for explanation. Therefore, in FIG. Systems are omitted. In addition, various control lines and drive lines, which will be described later, are indicated by thin lines. It is assumed that each board is connected by a connector and a harness (electric wire).
電源基板931から出力された12V電源は、払出制御基板951を経由して主制御基板1310から周辺制御基板1510を経て、演出駆動基板3043を介して各種ステッピングモータ(MA、MB)や各種LED基板(4250A、4250B)に供給される。
The 12V power supply output from the power supply board 931 passes through the
図示するように、演出駆動基板3043と移動用ステッピングモータMAおよび回転用ステッピングモータMBとの間には、それぞれ中継基板3044Bおよび中継基板3044Cが設けられている。同様に演出駆動基板3043と中央装飾ランプLED基板4250Aとの間にも中継基板3044Aが設けられている。なお、左右装飾ランプ基板4250Bについては、演出駆動基板3043と直接接続されている。
As shown, a
次に、各種ステッピングモータ(MA、MB)や各種LED基板(4250A、4250B)には、各種ステッピングモータを駆動する駆動信号や各種LEDを点灯、点滅させる制御信号が入力されている。 Next, various stepping motors (MA, MB) and various LED boards (4250A, 4250B) are supplied with driving signals for driving various stepping motors and control signals for lighting and blinking various LEDs.
主制御基板1310に接続されている、第一始動入口2002や第二始動口2004の第一始動口センサ2014および第二始動口センサ2551によって、球の入球が検出されると、主制御基板1310は、払出制御基板951とをつなぐ制御線を使って、払出装置830を動作させて球の払い出しを実行するためのコマンドを送信し、周辺制御基板1510とをつなぐ制御線を使って、入球が検出されたことにより抽選された結果に基づく演出表示をメイン液晶表示装置1600にて実行するためのコマンドが送信される。
When the entrance of the ball is detected by the first starting inlet sensor 2014 and the second
そして、演出表示の実行にともない各種ステッピングモータ(MA、MB)や各種LED基板(4250A、4250B)を備える駆動装置が駆動されることになるが、各種ステッピングモータ(MA、MB)については、各種ステッピングモータ(MA、MB)とをつなぐ駆動線を使って、周辺制御基板1510から出力される制御信号(駆動信号)が演出駆動基板3043に設けたステッピングモータドライバに入力されて、さらに駆動信号として演出駆動基板から出力される駆動信号を受けて駆動する。
Various stepping motors (MA, MB) and driving devices including various LED boards (4250A, 4250B) are driven along with the execution of the effect display. The control signal (drive signal) output from the peripheral control board 1510 is input to the stepping motor driver provided on the
また、各種LED基板に実装されたLEDについては、各種LED基板とをつなぐ制御線を使って、周辺制御基板1510から出力される制御信号を一旦LEDドライバで受けて、さらに基板上で駆動信号として出力される駆動信号を受けて点灯、点滅する。 Also, for the LEDs mounted on various LED boards, the control signal output from the peripheral control board 1510 is once received by the LED driver using the control line connecting the various LED boards, and is further processed as a drive signal on the board. Lights up or blinks in response to the output drive signal.
ここで、駆動信号とは、ステッピングモータの場合は、各コイル(各相)に与える所謂励磁信号のことを示し、LEDの場合は、LEDが点灯、点滅するためにLEDに流れる電流を供給、遮断するための信号を示す。 Here, in the case of a stepping motor, the drive signal means a so-called excitation signal given to each coil (each phase). Indicates a signal for blocking.
なお、演出駆動基板3043に実装されたステッピングモータドライバは、シリアル/パラレル変換機能を有しデイジーチェーン接続されて周辺制御基板1510からシリアル出力されるそれぞれのステッピングモータの制御信号を、駆動信号としてステッピングモータに出力するものであり、12V電源が供給されてデバイス内部でデバイス内部の回路電源を作成して動作するデバイスである。
The stepping motor driver mounted on the
ヒューズ934は、パチンコ機1が通常遊技状態において消費する全消費電力から定まる定格電流のものを使用しており、遮断電流は定格電流より大きな値となっている。
本実施例では、パチンコ機1で通常使用時に消費される電源の総消費電流でも遮断動作しないように定格15A、遮断電流37.5A(定格の2.5倍)のものを採用している。
The
In this embodiment, a rated current of 15 A and a breaking current of 37.5 A (2.5 times the rating) are used so as not to cut off even the total current consumption of the power supply during normal use of the
また、演出駆動基板3043および各種中継基板(3044A、3044C)にもそれぞれ、電流遮断用のチップヒューズ3071、3072、3074、3075が実装されている。これらヒューズの役割等について続けて説明する。
In addition, chip fuses 3071, 3072, 3074, 3075 for current interruption are mounted on the
[15-1.役物やLED装飾を実装した駆動装置の保護]
演出駆動基板3043は、LED基板4250A、4250Bに接続されて、LEDを点灯、点滅させるための電源と、LEDドライバの制御信号とを出力する。
[15-1. Protection of the driving device that implements accessories and LED decorations]
The
また、LED基板4250A、4250Bへ出力される電源線には、過電流保護デバイスとしてのヒューズ3074、3075が設けられている。これは、役物の動作によって、電線が駆動装置を構成する部材に擦れたり、役物の駆動部分などの可動部に挟まったりして、電線の被覆が破損するおそれがあるが、このような状況下で電源線とグランド線とが近接している場合において短絡すると、電源線に大きな電流が流れる。このため、電源線が焼損しないようヒューズ3074、3075を動作させ、電源線の焼損により役物が溶けたり焦げるといった、駆動装置を構成する役物の損傷を防止する。
Further, fuses 3074 and 3075 as overcurrent protection devices are provided on the power lines output to the
各ヒューズ3074、3075の定格電流は、一緒に束ねられて配置されている電線の間に生じる電位差と、当該電線の引き回し長(インピーダンス)によって定めることができる。最大の電位差はグランド(0V)と電源電圧(例えば12V)との間で生じことになるが、電線が破損して内部の導電体が露出してグランド線と短絡する場合、当該露出箇所と電源供給源である電源基板931との間の電線のインピーダンスと、この最大電位差から、オームの法則を用いて求められる電流を遮断電流にする。
The rated current of each
12V電源が総消費電流15Aの見積もりのうち通常時でも2Aを消費する負荷であるとした場合には、LED基板4250Aまでの電線のインピーダンスが仮に2Ωであれば、短絡時には6Aの電流が流れることとなるので、例えばヒューズ3075については定格2Aで遮断電流5A(定格の2.5倍)のものを採用すればよい。
Assuming that the 12V power supply is a load that consumes 2A of the estimated total current consumption of 15A even at normal times, if the impedance of the wire to the
また、ヒューズ3074についても、点灯、点滅させるLEDがLED基板4250Aに採用するものと同等品、かつ同じ個数のLEDが実装されている場合においては、LED基板4250Bまでの電線のインピーダンスが仮に1.5Ωであるなら、短絡時には8Aの電流が流れることとなるので、ヒューズ3074についても定格2Aで遮断電流5Aのものを採用してもよいことになる。
As for the
本来、どこであろうと電線が短絡をおこしようものなら、すみやかに電源基板931に設けられたヒューズ934を遮断するような大きな遮断電流が流れてヒューズ934が遮断するはずだが、実際のところ負荷に供給するための電線すらも負荷(電線のインピーダンス)とみなされてしまっていたため、本実施例では、電源基板から遠く短絡要因がある個所においては、引き回される電線のインピーダンスを考慮して別途ヒューズ(3071など)を設けて短絡時に備え、遮断するようにしている。
Originally, if a wire were to short-circuit anywhere, a large breaking current would immediately flow to break the
また、駆動装置を遊技盤側のみならず、扉側に配置する場合には、ホール店員による扉の開閉によって駆動装置を駆動するための電線が引っ張られないように、余裕を持った長さで配線されているが、逆に扉の開閉によって、電線が配線される経路に近い部材に擦れたり、電線が扉の開閉部分(ヒンジなど)などの可動部に挟まったりして、電線の被覆が破損するおそれがある。このような状況下で電源線とグランド線とが近接している場合においては、短絡して大きな電流が流れることになる。 Also, when the driving device is placed not only on the game board side but also on the door side, the length should be sufficient so that the electric wire for driving the driving device is not pulled when the door is opened or closed by the hall clerk. Wires are wired, but conversely, when the door is opened and closed, the wires rub against members near the wiring path, or the wires get caught in the opening and closing parts of the door (hinges, etc.) and other moving parts, causing the wires to be covered. There is a risk of damage. Under such circumstances, if the power supply line and the ground line are close to each other, they will be short-circuited and a large amount of current will flow.
あるいは、ホール店員による遊技盤の着脱作業時に、やむなく電線をヒンジ側や開閉側に配線せざるをえない場合においては、電線が擦れたり、本体枠との間に挟まったりして、電線の被覆が破損するおそれがある。このような状況下で電源線とグランド線とが近接している場合においても。短絡して大きな電流が流れることになる。 Alternatively, when a hall clerk attaches and detaches the game board, if it is unavoidable to wire the wires on the hinge side or the opening/closing side, the wires may rub or get caught between the main frame and the wire coating. may be damaged. Even if the power line and the ground line are close to each other under such circumstances. A short circuit will cause a large current to flow.
このように摺動部の人的動作によるものであったり、あるいは、人的な物損による場合においても、本願発明を適用することができる。ヒューズは適切な位置に適切な容量のものを配置するのがよいが、特に扉側に駆動装置を配置する場合は、要因となる扉の開閉部分の下流近傍に、ヒューズを実装した中継基板を配置するとよい。 In this way, the present invention can be applied even in the case of human operation of the sliding portion or in the case of human property damage. A fuse with an appropriate capacity should be placed in an appropriate position, but especially when arranging a drive unit on the door side, a relay board with a fuse mounted should be placed near the downstream of the opening/closing part of the door, which is a factor. should be placed.
ここまで、特に第2の過電流保護デバイスとしてヒューズ3074,3075を例に説明したが、これに代えて、大電流が流れると遮断するも、所定の時間経過後に導通が復帰する自己復帰型のデバイス、例えばサーミスタなどを用いてもよい。
So far, the
本実施形態において、第2の過電流保護デバイスであるヒューズ3071には駆動装置の大きさを考慮し表面実装形のチップヒューズを使用しているが、チップヒューズは管ヒューズと比べ小型である利点があるものの、電気的な導通の可否は外観からは分からない。このような場合、電線や電線が接続される負荷(駆動源)から、可動体を駆動するための演出駆動基板3043、およびヒューズが実装された中継基板3044Aもセットで交換が必要となる。
In this embodiment, a surface-mounted chip fuse is used for the
サーミスタは、大電流による発熱によって自身の温度が変化して、内部抵抗を上昇させて電流を遮断する機能を有する。自身の温度が再び低温に戻ることで内部抵抗を低下させて再利用可能に復帰する。つまり、ヒューズに代えて、表面実装型サーミスタに置き換えれば、少なくともサーミスタが実装される基板(例えば中継基板)については、交換の必要がなく引き続き使用できる利点がある。 A thermistor has the function of increasing internal resistance and cutting off current when its temperature changes due to heat generated by a large current. When its temperature returns to a low temperature again, the internal resistance is lowered and it becomes reusable. That is, if the fuse is replaced with a surface-mounted thermistor, there is an advantage that at least the board (for example, relay board) on which the thermistor is mounted does not need to be replaced and can be used continuously.
なお、第1の過電流保護デバイスとしてのヒューズ934について、本実施の形態では管ヒューズを採用しているが、管ヒューズの場合、大きな電流が流れることによりヒューズエレメントが溶断するため、チップヒューズのように電気的な導通の可否が外観から分からなくはないが、管ヒューズのヒューズエレメント自体は細く、灰色に近い金属色であるため、一般的な緑色のレジスト基板上では溶断状況が判り難い。そこで、より溶断していることを判り易くするために、ヒューズが実装される領域内のレジスト上に、金属色のヒューズエレメントを目立たせ視認性を上げるために、白色や黄色といった明色のべたシルクを印刷しておくとよい。
Regarding the
また、異なる定格のものであったり、同じ定格容量でも特に注意が必要な過電流保護デバイスについて、識別を目的、特別な印(例えば星印)などをデバイスの近傍にシルク印刷するなり、シルクの色を異ならせたり、あるいはデバイスの配置方向を基板に対し縦置き、横置き、斜め置きなどして区別できるようにしてもよい。
[15-2.ステッピングモータドライバの保護]
In addition, for overcurrent protection devices that have different ratings or that require special attention even if they have the same rated capacity, for the purpose of identification, a special mark (such as an asterisk) is silk-printed near the device. Different colors may be used, or the orientation of the devices may be set vertically, horizontally, or obliquely with respect to the substrate for distinction.
[15-2. Protection of Stepping Motor Driver]
演出駆動基板3043には、ステッピングモータドライバと、過電流保護デバイスとしてのヒューズ3071や3072が設けられている。図266では、二つのステッピングモータドライバを示したが、パチンコ機1に使用されるステッピングモータの数に応じて複数のステッピングモータドライバが実装される。
The
ステッピングモータドライバは、電源基板931から供給された電源を周辺制御基板1510からの制御信号に従ってスイッチングして駆動信号を生成する。この駆動信号によって、役物に組み込まれたステッピングモータを駆動して、役物が動作する。なお、図示した例では、12Vがステッピングモータドライバやステッピングモータに供給されているが、駆動するステッピングモータドライバやステッピングモータの仕様に応じて必要な電源を選定すればよい。 The stepping motor driver switches the power supplied from the power supply board 931 according to the control signal from the peripheral control board 1510 to generate a drive signal. This drive signal drives a stepping motor incorporated in the accessory to operate the accessory. Although 12 V is supplied to the stepping motor driver and the stepping motor in the illustrated example, a necessary power supply may be selected according to the specifications of the stepping motor driver and stepping motor to be driven.
図266に示す例では、二つのステッピングモータの12Vの電源線にそれぞれヒューズを設けているが、さらにデイジーチェーン接続する場合においては、他のステッピングモータドライバの電源線にもヒューズを設けるとよい。 In the example shown in FIG. 266, fuses are provided in the 12V power supply lines of the two stepping motors, but in the case of daisy chain connection, fuses may also be provided in the power supply lines of the other stepping motor drivers.
デイジーチェーン接続された各ステッピングモータの電源線に接続される各ヒューズ3071や3072は、いずれかの電源線に大きな電流が流れることにより、他のステッピングモータドライバにも飛び火し、損傷することを防止している。すなわち、ステッピングモータは規定温度を超える高温の状態で駆動し続けた場合、コイルの抵抗値が下がりステッピングモータドライバに大きな電流が流れ込むおそれがある。その場合デイジーチェーン接続されている他のステッピングモータドライバにもまた大きな電流が流れ込むことになるが、これを防止している。
The
また、コイルの抵抗値が下がるとステッピングモータ自体も発熱することとなるが、そのさい絶縁を担保する電線(コイル)の被覆が破損する事態になると、ステッピングモータ内で短絡が生じることになる。このような事態に備え、ステッピングモータドライバの損傷に加え、ステッピングモータ内での短絡が原因となり役物が溶けたり焦げるといった、駆動装置を構成する役物の損傷を防止するためにも、別途ヒューズを設けるとよい。 In addition, when the resistance value of the coil decreases, the stepping motor itself heats up, and if the coating of the wire (coil) that ensures insulation is damaged, a short circuit will occur within the stepping motor. In preparation for such a situation, in addition to damage to the stepping motor driver, a separate fuse is also provided to prevent damage to the components that make up the drive device, such as melting or burning of components caused by a short circuit in the stepping motor. should be provided.
なお、本実施の形態で採用するヒューズの遮断電流についても、中継基板に実装するか演出駆動基板に実装するかにおいては、同様に、配線のインピーダンスを考慮して決定するればよい。 Regarding the breaking current of the fuse employed in the present embodiment, whether to mount the fuse on the relay board or on the effect drive board may be similarly determined in consideration of the wiring impedance.
このように、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、電源作成装置(電源作成回路933)へ交流電源を供給する経路に配置されて、電源作成装置が供給する電流に応じて電源作成装置を過電流状態から保護する第1の過電流保護手段(ヒューズ934)と、駆動源(ステッピングモータMAやLED基板4250AのLED等)へ直流電源を供給する経路に配置されて、電源作成装置が供給する電流に応じて電源作成装置を過電流状態から保護する第2の過電流保護手段(ヒューズ3075等)とを備え、第2の過電流保護手段は、電源作成手段が作成した直流電源が駆動制御基板(演出駆動基板3043)に分配された後段であって、第1の過電流保護手段より駆動源に近い位置に配置され、第1の過電流保護手段よりも電源作成装置を過電流状態から保護するための電流が小さいため、役物等演出部品や電線の破損を効果的に防止できる。
In this way, the
また、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、遊技における演出を制御する周辺制御基板1510と、周辺制御基板から送信された駆動データに基づいて、演出部材(点棒役物(可動体)3410や中央装飾ランプ3412a等)を駆動する駆動源(ステッピングモータMAやLED基板4250AのLED等)を備える駆動装置(上部可動ユニット3400)に駆動信号を出力する駆動制御基板(演出駆動基板3043)と、駆動源に供給される直流電源を作成する電源作成装置(電源作成回路933)と、電源作成装置へ交流電源を供給する経路に配置されて、電源作成装置が供給する電流に応じて当該電源作成装置を保護する電源作成装置保護手段(ヒューズ934)と、駆動源へ直流電源を供給する経路に配置されて、電源作成装置が供給する電流に応じて前記駆動装置を保護する駆動装置保護手段(ヒューズ3075等)と、を備えるため、役物等演出部品や電線の破損を効果的に防止できる。
In addition, in the
また、本実施例のパチンコ機1では、例えば、中継基板3044Aの上流側又は下流側に接続され、駆動信号を伝送する電線を含む二以上の電線は、互いに電位差を有しており、第2保護手段(ヒューズ3075)は、当該電位差を有する電線が短絡したときに流れる電流で遮断動作をする。この遮断動作の電流は、当該電線の電位差とインピーダンスから、オームの法則を用いて求められるものである。このため、電源作成装置(電源作成回路933)へ交流電源を供給する経路に配置される第1の過電流保護手段(ヒューズ934)が作動しなくても、第2保護手段によって部品や電線の破損を効果的に防止できる。
Further, in the
[16.スロットマシン]
ここまでパチンコ機のROMに記憶されるプログラム及びデータの配置について説明したが、続いて、スロットマシン(回胴式遊技機)のRAM及びROMに記憶されるプログラム及びデータの配置について説明する。なお、パチンコ機については、図26にて概略を説明したが、以降説明するスロットマシン4000の場合と同様にRAM及びROMにプログラム及びデータが配置されている。
[16. slot machine]
The arrangement of the programs and data stored in the ROM of the pachinko machine has been described so far, and the arrangement of the programs and data stored in the RAM and ROM of the slot machine (rotary game machine) will now be described. Although the outline of the pachinko machine has been described with reference to FIG. 26, programs and data are arranged in the RAM and ROM in the same manner as the
[16-1.構造]
まず、本実施形態におけるスロットマシン4000の構造について説明する。図267は、スロットマシン4000の斜視図であり、図268は、前面部材4200を開いた状態のスロットマシン4000の斜視図である。
[16-1. structure]
First, the structure of the
図267及び図268に示すように、本実施形態のスロットマシン4000は、前面が開放した箱形の筐体4100の内部に各種の機器が設けられるとともに、この筐体4100の前面に、前面部材4200が片開き形式に開閉可能に設けられている。前面部材4200の上部には、遊技の進行状況に応じて表示による演出や情報表示を行う画像表示体4500、音による演出を行うスピーカ等が設けられている。画像表示体4500は、例えば液晶表示パネルで構成され、遊技に関する演出表示のほか、様々な情報を表示する。そして、画像表示体4500における各種演出表示や履歴情報表示は、演出制御基板4700によって制御される。すなわち、画像表示体4500が、ゲームの進行に応じた演出を表示することが可能な演出表示手段をなし、演出制御基板4700が、演出表示手段の表示制御を行うことが可能な表示制御手段をなす。
As shown in FIGS. 267 and 268, the
前面部材4200の中央部には、後方を視認できないようにするとともに装飾のための絵柄等が描かれた前面パネルが配され、前面パネルの中央部には後方を視認可能な(例えば、透明の)図柄表示窓4401が形成されている。なお、前面パネルを表示装置で構成しても良く、図柄表示窓4401の部分に画像を表示しない状態ではリール4301を視認可能とし、主に図柄表示窓4401の周囲において遊技を演出する画像を表示する。この場合、図柄表示窓4401の部分に遊技を演出する画像を表示することも可能である。
At the center of the
図柄表示窓4401(窓部)を透して、筐体内に配設されたリール4301の回転により変動表示される図柄を視認可能となっている。リール4301は、円筒形の左リール4301a、中リール4301b、右リール4301cが水平方向に並設されて構成されている。これらのリール4301a,4301b,4301cの外周面には、長手方向に沿って複数の図柄が描画された短冊状のシートが巻き付けられることで、所定の配列に従って複数の図柄が配されている。
Through the symbol display window 4401 (window portion), the symbols that are variably displayed by the rotation of the reels 4301 arranged in the housing can be visually recognized. The reel 4301 is configured by horizontally arranging a
各リール4301a,4301b,4301cには、それぞれステッピングモータであるリール駆動モータ4341a,4341b,4341c(図269参照)が設けられており、各リール4301a,4301b,4301cを独立して回転駆動及び回転停止することが可能となっている。すなわち、リール駆動モータ4341a,4341b,4341cが各リール4301a,4301b,4301cの駆動源をなしている。さらに、リール駆動モータ4341a,4341b,4341cは、前述したパチンコ機1の払出モータ839と同様に、2相励磁方式によって制御することにより、駆動トルクと静止トルクとを大きくしている。これにより、駆動源に小型のモータを採用することが可能となり、コストを削減することができる。
なお、以下では必要に応じて、リール4301a,4301b,4301cをそれぞれ左リール4301a,中リール4301b,右リール4301cとする。そして、これに対応するそれぞれのリール停止ボタン4211a,4211b,4211cを左リール停止ボタン4211a,中リール停止ボタン4211b,右リール停止ボタン4211cとする。さらに、各リールに対応するリール駆動モータ4341を左リール駆動モータ4341a,中リール駆動モータ4341b,右リール駆動モータ4341cとする。
In the following description, the
また、リール駆動モータ4341によりリール4301を回転させることによって、図柄表示窓4401から視認される複数種類の図柄を、例えば上から下へと循環するように変動させる(変動表示)。一方、リール4301が停止している状態では、各リール4301a,4301b,4301cについて、連続する所定数(例えば、3つ)の図柄、つまり3×3の計9つの図柄が図柄表示窓4401を介して視認可能となっている。すなわち、図柄表示窓4401を透して、ゲームの停止結果を導出表示するためのリール4301a,4301b,4301cの有効表示部を視認可能となっている。
In addition, by rotating the reel 4301 by the reel drive motor 4341, the plurality of types of symbols viewed from the
図柄表示窓4401から視認される3×3の図柄行列に対しては、所定の有効化可能ラインが設定される。本実施形態では各リール4301a,4301b,4301c中段の図柄を横切るライン(中段ライン)、左リール4301a下段-中リール4301b中段-右リール4301c上段にかけて各リール4301a,4301b,4301cを斜めに横切るライン(右上がりライン)、左リール4301a上段-中リール4301b中段-右リール4301c下段にかけて各リール4301a,4301b,4301cを斜めに横切るライン(右下がりライン)が有効化可能ラインとなっている。そして、遊技者によるメダルの投入又はクレジットからの入力(以下「賭操作」という。)によって有効化可能ラインが有効化され、この有効ライン上に形成された図柄組合せ態様(出目)に基づいて入賞(役)の成立/不成立が判断される。
A predetermined activatable line is set for the 3×3 symbol matrix visually recognized from the
入賞が成立する場合には、有効ライン上に所定の図柄が3つ並ぶ場合の他、見た目上で他のラインで所定の図柄が3つ並ぶ場合もある。このようなラインとしては、各リール4301a,4301b,4301c上段の図柄を横切るライン(上段ライン)がある。なお、各リール4301a,4301b,4301c下段の図柄を横切るライン(下段ライン)や、上記以外の各リール4301a,4301b,4301cの図柄表示窓4401に臨む前面部(視認可能な部分)を横切るように位置する仮想的なラインに見た目上図柄が並ぶようにしても良い。以下、有効化可能ライン(中段、右上がり、右下がりライン)や、入賞時に見た目上図柄が整列可能なライン(上段ライン)、その他のライン(下段ライン等)をまとめて図柄停止ライン(図柄整列ライン)と称する。
When a prize is established, there are cases where three predetermined patterns are lined up on the activated line, and there are cases where three predetermined patterns are lined up on another line visually. As such a line, there is a line (upper line) that crosses the upper pattern of each
上段、中段、下段、右上がり及び右下がりラインを有効化可能ラインとして、賭数に応じて所定の有効化可能ラインを有効化し、この有効ライン上に形成された図柄組合せ態様に基づいて入賞(役)の成立/不成立を判断する。例えば、賭数1では中段ラインを有効ラインとし、賭数2では中段ラインに加え、上下段ラインを有効ラインとし、賭数3では上中下段ラインに加え、右上がり、右下がりラインを有効ラインとする。また、賭数には無関係に(賭数が1または2であっても)すべてのラインを有効としてもよいし、3枚がけ専用としてもよい。 The upper, middle, lower, right-up and right-down lines are set as activatable lines, and predetermined activatable lines are activated according to the number of bets. role) is established/not established. For example, if the number of bets is 1, the middle line is the valid line, if the number of bets is 2, in addition to the middle line, the upper and lower lines are valid lines. and Also, regardless of the number of bets (whether the number of bets is 1 or 2), all lines may be valid, or may be dedicated to 3-coin stakes.
図柄表示窓4401の周辺(例えば、下方)には、ゲームによって払い出されるメダルの枚数を表示する払出枚数表示LED4562が設けられる。スロットマシン4000内に貯留されたメダルの枚数を表示するクレジット表示器や、特賞中の残りのゲーム数を表示するカウント表示器が設けられてもよい。
Around (for example, below) the
図柄表示窓4401の下方には、前側に突出する段部が形成されており、この段部の上面は前面側下方に向かって傾斜する操作部4202となっている。操作部4202には、メダル投入口4203と、ゲームを進行させるための進行操作部としての1枚投入ボタン4205、マックスベットボタン4206が設けられている。
Below the
メダル投入口4203は、操作部4202における当該スロットマシン4000の前面側から見て右側に配設されている。遊技者がこのメダル投入口4203にメダルを投入して賭操作を行うことにより、ゲームが実行可能となる。メダル投入口4203から投入されたメダルが通過する経路には、メダルの通過を検出する投入センサ4207bが設けられており、投入センサ4207bによる検出情報をもとにメダルの投入枚数がカウントされる。
The
1枚投入ボタン4205及びマックスベットボタン4206は、操作部4202における当該スロットマシン4000の前面側から見て左側に配設されている。1枚投入ボタン4205は、押圧操作を一度行うことでクレジットから1枚ずつ入力できる。マックスベットボタン4206は、押圧操作を一度行うことでクレジットから賭数の上限数(例えば、3枚)まで入力できるが、クレジット数が上限数に満たない場合にはクレジット数を賭数として入力するようになっている。
A
操作部4202の下方には、払戻ボタン4209、始動レバー4210、返却ボタン4208、リール停止ボタン4211、鍵装置4215等が設けられている。払戻ボタン4209は、メダル投入口4203から投入されたメダルや1枚投入ボタン4205、マックスベットボタン4206により賭数として入力されたメダル(賭メダル)又は入賞が成立することにより払い出されクレジットとして記憶されているメダル(貯留メダル)をメダル用受け皿4201に返却させる指令を与える際に用いられる。なお、再遊技入賞(リプレイ入賞)の成立に基づく自動賭操作の後にメダル投入口4203からメダルが投入された場合や、クレジットとして記憶可能な所定数を超えるメダルもメダルセレクタ4207を介してメダル用受け皿4201に返却される。
Below the
始動レバー4210は、一区切りのゲームを開始させるための操作レバーである。鍵装置4215は、前面部材4200を開く際、或いは当該スロットマシン4000のエラー(例えば、ホッパーエラー)状態をリセットする際に鍵を差し込むためのものである。返却ボタン4208は、メダル投入口4203から投入されてメダルセレクタ4207の内部に詰まったメダルをメダル用受け皿4201に返却させる際に用いられる。
The
リール停止ボタン4211は、左リール4301a、中リール4301b及び右リール4301cとそれぞれ1対1で対応付けられて設けられた、左リール停止ボタン4211a、中リール停止ボタン4211b及び右リール停止ボタン4211cで構成され、停止操作に応じて対応するリール4301a,4301b,4301cの回転をそれぞれ停止させるためのものである。
The reel stop button 4211 is composed of a left
また、これらの操作ボタン類が設けられた部分の下方には、前面部材4200の下部領域を構成する装飾板(化粧パネル)が設けられている。さらに、装飾板の下方であって前面部材4200の最下部には、メダルを貯留するためのメダル用受け皿4201、メダル払出口、音声を出力するためのスピーカ4512等が設けられている。
A decorative plate (decorative panel) forming the lower region of the
筐体内部の上部には、スロットマシン4000全体を制御するメイン基板(遊技制御装置)4600(図269参照)が配設されている。メイン基板4600上には役物比率表示器1317及び表示スイッチ1318が設けられる。役物比率表示器1317は、前述したパチンコ機と同様に、例えば、4桁の7セグメントLEDによって構成される。メイン基板4600上に設けられた液晶表示装置によって役物比率表示器1317を構成してもよい。
A main board (game control device) 4600 (see FIG. 269) that controls the
役物比率表示器1317を、メイン基板4600上に設けず、スロットマシン4000の正面に設けられた他の表示器(例えば、払出枚数表示LED4562や画像表示体4500)と兼用し、払出枚数表示LED4562や画像表示体4500に役物比率を表示してもよい。
The
表示スイッチ1318を操作すると、役物比率表示器1317に役物比率を表示する。表示スイッチ1318の近傍のプリント基板上又は筐体4100に、役物比率の表示を操作するためのスイッチであることを表示(印刷、刻印、シールなど)するとよい。なお、表示スイッチ1318は、役物比率表示器1317の付近に設けることが望ましいが、主制御ユニット1300ではなくても、操作が容易な場所であれば、他の基板(例えば、演出制御基板4700、電源装置4112)や筐体4100や前面部材4200に設けられてもよい。また、後述するように、表示スイッチ1318はRAMクリアスイッチと兼用してもよい。表示スイッチ1318を遊技者が操作できない位置に設けることで、遊技者が誤って操作することを防止できる。
When the
また、筐体内部のほぼ中央には、図柄変動表示装置4300が設けられ、回転可能なリール4301a,4301b,4301cが載置されている。また、当該スロットマシン4000の筐体内部にはメイン基板4600から外部の装置へ信号を出力するための外部中継端子板4131が設けられている。
In addition, a pattern
さらに、筐体内部の下部には、メダル払出装置(ホッパー)4110が配設されている。メダル払出装置4110は、メダル投入口4203から投入されてメダルセレクタ4207により誘導されたメダルを受け入れて貯留するとともに、有効ライン上に所定の図柄組合せ態様が形成され入賞が成立した場合に、この入賞に対応する枚数のメダル(払出メダル)又は入賞成立に伴う加算によりクレジットの上限を超えた分のメダルをメダル用受け皿4201に払い出す。クレジット分のメダルは払戻ボタン4209を操作することによりメダル払出装置4110によってメダル用受け皿4201に払い出される。また、メダル払出装置4110の右方には、メダル払出装置4110からオーバーフローして流入してくるメダルを貯留したり、流入してきたメダルを当該スロットマシン4000が設置される設置島のメダル回収機構へ誘導したりするためのオーバーフロータンクが設けられている。
Furthermore, a medal payout device (hopper) 4110 is arranged in the lower part inside the housing. The
[16-2.スロットマシンの内部構成]
図269は、スロットマシン4000に備えられた各種の機構要素や電子機器類、操作部材等の構成を示すブロック図である。スロットマシン4000は遊技の進行を統括的に制御するためのメイン基板4600を有しており、メイン基板4600にはCPU4601をはじめ、ROM4602、RAM4603、入出力インターフェイス4604等が実装されている。
[16-2. Internal configuration of the slot machine]
FIG. 269 is a block diagram showing the configuration of various mechanical elements, electronic devices, operating members, etc. provided in the
また、前述したように、メイン基板4600には、CPU4601が計算した役物比率を表示する役物比率表示器1317及び役物比率表示器1317の表示を切り替える表示スイッチ1318が設けられる。表示スイッチ1318は、モーメンタリ動作をする押ボタンスイッチで構成するとよいが、他の形式のスイッチでもよい。表示スイッチ1318を操作すると、役物比率表示器1317に役物比率を表示してもよい。
Further, as described above, the
前述した1枚投入ボタン4205、マックスベットボタン4206、始動レバー4210、リール停止ボタン4211a,4211b,4211c、払戻ボタン4209等はいずれもメイン基板4600に接続されており、これら操作ボタン類は図示しないセンサを用いて遊技者による操作をし、検出された操作信号をメイン基板4600に出力する。具体的には、始動レバー4210が操作されると前述した図柄変動表示装置4300を始動させる(リール4301a,4301b,4301cの回転を開始させる)操作信号がメイン基板4600に出力され、リール停止ボタン4211a,4211b,4211cが操作されると、リール4301a,4301b,4301cをそれぞれ停止させる操作信号がメイン基板4600に出力される。
All of the above-mentioned
また、スロットマシン4000にはメイン基板4600とともにその他の機器類が収容されており、これら機器類からメイン基板4600に各種の信号が入力されている。機器類には、図柄変動表示装置4300のほか、メダル払出装置4110等がある。
Further, the
図柄変動表示装置4300は、前述のように、リール4301a,4301b,4301cをそれぞれ回転させるためのリール駆動モータ4341a,4341b,4341cを備えている(左リール駆動モータ4341a、中リール駆動モータ4341b、右リール駆動モータ4341c)。リール駆動モータ4341はステッピングモータからなり、それぞれのリール4301a,4301b,4301cは独立して回転、停止することが可能となっており、その回転時には図柄表示窓4401にて複数種類の図柄が上から下へ連続的に変化しつつ表示される。
As described above, the variable
また、各リール4301a,4301b,4301cの回転に関する基準位置を検出するための位置センサ4331a,4331b,4331cを有しており、各リール4301a,4301b,4301cにはそれぞれ位置センサ4331a,4331b,4331cがリール内に対応して設けられている(左リール位置センサ4331a、中リール位置センサ4331b、右リール位置センサ4331c)。これら位置センサからの検出信号(インデックス信号)がメイン基板4600に入力されることで、メイン基板4600では各リールの停止位置情報を得ることができる。
メダルセレクタ4207内には、前述したソレノイド4207aや投入センサ4207bが設置されている。投入センサ4207bは、メダル投入口4203から投入されたメダルを検出し、メダルの検出信号をメイン基板4600に出力する。ソレノイド4207aがOFFの状態のとき、投入されたメダルは投入センサ4207bで検出される。逆にソレノイド4207aがONの状態のときは、メダルセレクタ4207内で投入センサ4207bに到達する通路がロックアウトされてメダルの投入が受け付けられなくなり、遊技者がメダルを投入しても、メダルセレクタ4207を通って返却樋に流れたメダルはメダル用受け皿4201に戻る。このとき合わせて投入センサ4207bの機能が無効化されるので、メダル投入によるベット又はメダルの貯留のいずれも行われなくなる。
Inside the
メダル払出装置4110は、払い出されたメダルを1枚ずつ検出する払出センサ4110eを放出口内に有しており、払出センサ4110eからメダル1枚ごとの払出メダル信号がメイン基板4600に入力されている。また、遊技メダル用補助収納箱にはメダル満タンセンサ4111aが設けられており、内部に貯留されたメダルの貯留数が所定数量を超えた場合、メダルが所定数量を超えた検出信号をメイン基板4600に出力する。このとき、画像表示体4500、エラーランプ4554等によりメダル貯留の異常を知らせるエラー表示が行われ、遊技者やホール従業員等に異常が発生したことが報知される。
The medal pay-out
一方、メイン基板4600からは、図柄変動表示装置4300やメダル払出装置4110に対して制御信号が出力される。すなわち、前述した各リール駆動モータ4341a,4341b,4341cの起動及び停止を制御するための駆動パルス信号がメイン基板4600から出力される。また、メダル払出装置4110には、有効ライン上に停止した図柄の組合せの種類に応じてメイン基板4600から駆動信号が入力され、これを受けてメダル払出装置4110はメダルの払い出し動作を行う。このとき、メダル払出装置4110内に払い出しに必要な枚数のメダルが不足しているか、あるいはメダルが全く無い状態であった場合、払出センサ4110eによる枚数検出が滞ることとなる。そして所定時間(例えば3秒間)が経過すると、払出センサ4110eより払い出しメダルの異常信号がメイン基板4600へ出力され、これを受けてメイン基板4600は、メダルの払い出しに異常が発生したことを知らせる内容をエラーランプ4554や画像表示体4500等に表示させて遊技者やホール従業員等に異常が発生したことを報知する。
On the other hand, the
スロットマシン4000は、メイン基板4600の他に演出制御基板4700を備えており、この演出制御基板4700にはCPU4701やROM4702、RAM4703、入出力インターフェイス4707、VDP(Video Display Processor)4704、AMP(オーディオアンプ)4705、音源IC4706等が実装されている。演出制御基板4700はメイン基板4600から各種の指令信号を受け、画像表示体4500の表示や照明装置4502等の発光(または点灯、点滅、消灯等)及びスピーカ4512の作動を制御している。
The
さらに、外部中継端子板4131を設け、スロットマシン4000は外部中継端子板4131を介して遊技場のホールコンピュータ4800に接続される。外部中継端子板4131はメイン基板4600から送信される各種信号(投入メダル信号や払出メダル信号、遊技ステータス等)をホールコンピュータ4800に中継する役割を担っている。
Furthermore, an external
電源装置4112は、島設備から供給される交流24ボルト(AC24V)の電源から、複数種類の直流電源を作成する。例えば、直流+5V(以下、「+5V」)、直流+12V(以下、「+12V」)、及び直流+24V(以下、「+24V」)の3種類の電源が作成される。電源装置4112で作成された+5V、+12V、及び+24Vの3種類の電源は、スロットマシン4000に含まれる各構成に供給され、例えば、+5V及び+12Vの2種類の電源がリール4301及びリール駆動モータ4341を備える図柄変動表示装置4300に供給される。
The
その他、電源装置4112には、設定変更キースイッチ4112tやリセットスイッチ4112u、電源スイッチ4112v等が付属している。これらスイッチ類はいずれもスロットマシン4000の外側に露出しておらず、前面部材4200を開けることではじめて操作可能となる。電源スイッチ4112vは、スロットマシン4000への電力供給をON-OFFするためのものであり、設定変更キースイッチ4112tはスロットマシン4000の設定(例えば設定1~6)を変更するためのものである。また、リセットスイッチ4112uはスロットマシン4000で発生したエラーを解除するためのものであり、更には設定変更キースイッチ4112tとともに設定を変更する際にも操作される。
In addition, the
また、メイン基板4600には、リール駆動モータ電圧切替回路4605を設けられている。リール駆動モータ4341の出力軸を回転駆動してリール4301を回転させるための駆動トルクを得る場合には、CPU4601が電圧切替信号の論理(例えば、HI)に設定してリール駆動モータ電圧切替回路4605に出力することでモータ駆動電圧として+12Vをリール駆動モータ4341に供給する制御を行う。一方、リール駆動モータ4341の出力軸を停止させた状態を維持するための静止トルクを得る場合には、CPU4601が電圧切替信号の論理(例えば、LOW)に設定してリール駆動モータ電圧切替回路4605に出力することでモータ駆動電圧として+5Vをリール駆動モータ4341に供給する制御を行うようになっている。
Further, the
以上がスロットマシン4000の構成例である。スロットマシン4000によるゲームは、遊技者がメダルの掛け数を決定した状態で始動レバー4210を操作すると各リール4301a,4301b,4301cが回転し、この後、遊技者がリール停止ボタン4211a,4211b,4211cを操作すると、対応する各リール4301a,4301b,4301cが停止制御され、そして、全てのリール4301a,4301b,4301cが停止すると、有効ライン上での図柄の組合せ態様からゲーム結果を判断し、必要に応じて該当する当選役に対応する規定数のメダルが付与される。
The configuration example of the
前述したとおり、各リール4301a,4301b,4301cには、それぞれ図柄が描かれたリール帯が付されている。そして、全てのリール4301a,4301b,4301cを停止させた際に図柄表示窓4401内に表示される表示内容(有効ライン上に表示された図柄の組合せ態様)から所定の当選役に対応する図柄の組合せ態様(図柄組合せ)が表示されたか否かが判断される。具体的には、図柄表示窓4401内で前述の有効ラインに所定の当選役に対応する図柄の組合せ態様が表示されているか否かが判断される。なお、複数の有効ラインの各々で当選役に対応する図柄組合せが表示されているか否かが判断される。その結果、複数の当選役の図柄組合せが表示されていると判断された場合には、表示された各当選役に対応する払出数を合算した数量のメダルの払い出しが行われる。
As described above, each of the
[16-3.記憶領域の構成]
続いて、メイン基板4600に備えられたROM4602及びRAM4603などによって提供される記憶領域について説明する。なお、パチンコ機の記憶領域については、図24にて概略を説明したが、図270から図273に示したスロットマシン4000の場合と同様に構成されている。図270は、本実施形態におけるスロットマシン4000の遊技制御におけるアクセス領域と、ROM4602に対応する記憶領域であるROM領域5100の詳細を示す図である。
[16-3. Storage area configuration]
Next, storage areas provided by the
本実施形態における記憶領域は、ROM4602、RAM4603などの媒体によって提供されており、”0000H”から”FFFFH”までのアドレスが付与された一のアクセス領域として提供されている。また、本実施形態のアクセス領域は、当該アクセス領域を提供する媒体に対応した所定の領域に分割されており、ROM領域5100、RAM領域5200、I/O領域5300、パラメータ情報設定領域5400が含まれている。なお、各領域は、必ずしもアクセス領域を提供する媒体に対応する必要はなく、複数の媒体で一の領域を提供してもよいし、一の媒体で複数の領域を提供してもよい。
The storage area in this embodiment is provided by media such as the
本実施形態のアクセス領域が以上のように構成されていることによって、CPU4601がアドレスを指定することで実際にアクセス領域を提供する媒体を意識せずにプログラムやデータにアクセスすることができる。以下、アクセス領域の詳細について説明する。
Since the access area of this embodiment is configured as described above, the
[16-3-1.ROM領域]
まず、ROM領域5100の構成について説明する。ROM領域5100は、ROM4602によって提供される記憶領域に対応する。ROM4602はパチンコ機1の電源が切断された場合であっても記憶内容が保持される不揮発性の記憶媒体であり、記憶されたデータを読み出すことは可能であるが、更新したり削除したりすることはできないようになっている。なお、ROM4602は不揮発性の記憶媒体であれば良く、ROM領域5100に記憶されるデータを更新可能としてもよい。
[16-3-1. ROM area]
First, the configuration of the
ROM領域5100は、”0000H”から”1FFFH”までのアドレスが付与されている。CPU4601がアドレス”0000H”から”1FFFH”を指定することでROM4602に記憶されたデータにアクセスすることができる。
The
ROM領域5100は、第一制御領域、第一隔離領域、第一データ領域、第二制御領域、第二隔離領域、第二データ領域、第三制御領域、第三隔離領域及び第四隔離領域が含まれる。各領域には、開始アドレスと終了アドレスが設定されている。
The
第一制御領域は、遊技制御領域であり、遊技制御を行うためのプログラムなどが記憶されている。また、第一データ領域は、遊技制御を行うために必要なデータが記憶されている遊技データ領域である。すなわち、第一制御領域に記憶されたプログラムを実行し、第一データ領域に記憶されたデータを参照しながら遊技制御を行う。なお、遊技制御に使用される領域(第一制御領域、第一データ領域)を遊技制御用領域(第一記憶領域)とする。 The first control area is a game control area, and stores programs and the like for performing game control. The first data area is a game data area in which data necessary for game control are stored. That is, the program stored in the first control area is executed, and game control is performed while referring to the data stored in the first data area. In addition, let the area|region (1st control area, 1st data area) used for game control be the area|region for game control (1st storage area).
第二制御領域は、制御プログラムのデバッグ(機能検査)を行うためのプログラムなどが記憶されている。また、第二データ領域は、デバッグ(機能検査)を行うためのデータを記憶するための領域である。なお、第二データ領域は必ずしも必要ではなく、第二制御領域にデバッグ用のデータを格納するようにしてもよい。なお、遊技制御に使用されずに遊技制御プログラムのデバッグ(機能検査)を行うためのプログラムやデータが格納される領域(第二制御領域、第二データ領域)をデバッグ(検査機能)用領域(第二記憶領域)とする。 The second control area stores a program for debugging (functional inspection) of the control program. The second data area is an area for storing data for debugging (function test). The second data area is not necessarily required, and debugging data may be stored in the second control area. In addition, the area (second control area, second data area) where the program and data for debugging (function inspection) of the game control program without being used for game control are stored is the area for debugging (inspection function) ( second storage area).
第三制御領域は、役物比率を算出及び表示するためのプログラムなどが記憶されている。第三制御領域には、役物比率算出用のデータも格納される。役物比率算出用のデータを格納する第三データ領域を設けてもよい。なお、遊技制御に使用されずに役物比率を算出するためのプログラムやデータが格納される領域(第三制御領域)を役物比率算出用領域(第三記憶領域)とする。このように、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135を遊技制御用コード13131と別に設計し、別の領域に格納することによって、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135の検査と遊技制御用コード13131の検査とを別に行うことができ、スロットマシン4000の検査の手間を減少できる。また、役物比率算出・表示用コード13135を、機種に依存せず、複数の機種で共通に使用できる。
The third control area stores a program for calculating and displaying the character product ratio. The third control area also stores data for character product ratio calculation. A third data area may be provided for storing data for character product ratio calculation. An area (third control area) in which a program and data for calculating the role product ratio without being used for game control are stored is defined as a role product ratio calculation area (third storage area). Thus, by designing the role product ratio calculation/
第一隔離領域、第二隔離領域、第三隔離領域及び第四隔離領域は、制御領域及びデータ領域の間に割り当てられた領域であり、アクセスが禁止された領域である。CPU4601による処理において、隔離領域にアクセスされた場合には、強制的にリセット処理を実行するように構成されている。第一隔離領域、第二隔離領域第三隔離領域及び第四隔離領域は、前後の領域と連続する領域であり、例えば、第一隔離領域の開始アドレスは、第一制御領域の終了アドレスの次のアドレス(”0A00H”)となり、第一隔離領域の終了アドレスは、第一データ領域の一つ前のアドレス(”0AFFH”)となる。また、第三隔離領域は、遊技制御用領域及びデバッグ(機能検査)用領域の間に配置されており、図30では遊技制御用領域として扱うようにしているが、デバッグ(機能検査)用領域として扱うようにしてもよい。同様に、第四隔離領域は、デバッグ(機能検査)用領域及び役物比率算出用領域の間に配置されており、図270ではデバッグ(機能検査)用領域として扱うようにしているが、役物比率算出用領域として扱うようにしてもよい。
The first isolation area, the second isolation area, the third isolation area, and the fourth isolation area are areas allocated between the control area and the data area, and access is prohibited. In the processing by the
[16-3-2.RAM領域]
続いて、RAM領域5200の構成について説明する。図271は、本実施形態におけるRAM領域5200の詳細を示す図である。RAM領域5200は、RAM4603によって提供される記憶領域に対応する。RAM4603はパチンコ機1の電源を切断すると、記憶内容が消去される揮発性の記憶媒体であり、記憶されたデータの読み書きが可能となっている。RAM領域5200は、ROM領域5100に記憶されたプログラムやデータを一時的に記憶したり、プログラムの実行によって導出されたデータを記憶する。なお、RAM4603はデータが読み書き可能であればよく、不揮発性の記憶媒体であってもよい。また、停電発生時には、バックアップ電源によってRAM4603に記憶されたデータは所定期間保持することが可能となっている。
[16-3-2. RAM area]
Next, the configuration of the
RAM領域5200は、”3000H”から”31FFH”までのアドレスが付与されている。CPU4601がアドレス”3000H”から”31FFH”を指定することでRAM4603に記憶されたデータにアクセスすることができる。
The
RAM領域5200は、遊技制御用ワーク領域、デバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域、退避領域及び隔離領域を含む。各領域には、開始アドレスと終了アドレスが設定されている。
The
遊技制御用ワーク領域は、遊技制御(第一制御)を実行する際に使用するワークエリア(一時領域)である。デバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域は、プログラムのデバッグ制御(第二制御)を実行する際に使用するワークエリアである。役物比率算出用ワーク領域は、役物比率を算出するためのデータや算出された役物比率(役物比率、連続役物比率、有利区間役物比率など)を格納する領域である。なお、デバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域や役物比率算出用ワーク領域は、必ずしも専用のワークエリアを確保する必要はなく、遊技制御用ワーク領域を使用するようにしてもよいし、遊技制御用ワーク領域に、デバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域や役物比率算出用ワーク領域を割り当ててもよい。この場合、遊技制御領域とデバッグ(検査機能)用制御領域と役物比率算出用ワーク領域との独立性は低下することになる。ただし、デバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域や役物比率算出用ワーク領域を使用しないようなプログラム構成とすれば必ずしもデバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域や役物比率算出用ワーク領域を使用しなくてもよい。 The work area for game control is a work area (temporary area) used when executing game control (first control). The debug (inspection function) work area is a work area used when executing program debug control (second control). The role product ratio calculation work area is an area for storing data for calculating the role product ratio and the calculated role product ratio (character product ratio, continuous accessory ratio, advantageous section accessory ratio, etc.). It should be noted that the work area for debugging (inspection function) and the work area for calculating the character ratio do not necessarily need to secure a dedicated work area. A work area for debugging (inspection function) or a work area for calculating the character ratio may be assigned to the work area. In this case, the independence of the game control area, the control area for debugging (inspection function), and the work area for calculating the character ratio is reduced. However, if the program configuration does not use the work area for debugging (inspection function) or the work area for calculating the character ratio, it is not necessary to use the work area for debugging (inspection function) or the work area for calculating the character ratio. good too.
退避領域は、遊技制御またはデバック(検査機能)制御または役物比率算出において使用されるデータを退避させるために一時的に記憶する領域である。例えば、割り込みが発生して所定の処理を実行する場合に、当該所定の処理を実行する前にCPUの各種レジスタ(演算用レジスタ、フラグレジスタ、スタックポインタ等)の値を退避領域にコピーし、処理終了後にコピーされた値をCPUの各種レジスタに戻す。なお、退避領域は、遊技制御とデバック(検査機能)と役物比率算出とで共通に使用してもよいが、ワーク領域と同様に、遊技制御用とデバック(検査機能)用と役物比率算出とで個別に分けてもよい。それにより、遊技制御とデバック(検査機能)制御と役物比率算出とで、より独立性を保つことができる。 The withdrawal area is an area for temporarily storing in order to save data used in game control or debug (inspection function) control or character product ratio calculation. For example, when an interrupt occurs and a predetermined process is executed, the values of various CPU registers (calculation registers, flag registers, stack pointers, etc.) are copied to a save area before executing the predetermined process, After the processing is completed, the copied values are returned to various registers of the CPU. The retreat area may be used in common for game control, debugging (inspection function), and character ratio calculation. Calculation may be divided separately. Thereby, independence can be maintained more by game control, debug (inspection function) control, and role product ratio calculation.
隔離領域は、遊技制御用ワーク領域とデバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域と役物比率算出用ワーク領域との間、デバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域と退避領域と役物比率算出用退避領域との間に割り当てられており、各領域(前後の領域)と連続する領域となっている。例えば、遊技制御用ワーク領域とデバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域との間の隔離領域の開始アドレスは、遊技制御用ワーク領域の終了アドレスの次のアドレス(”3076H”)となり、終了アドレスは、デバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域の一つ前のアドレス(”307FH”)となる。また、隔離領域は、アクセスが禁止された領域となっており、CPU4601による処理においてアクセスされた場合には、強制的にリセット処理を実行するように構成されている。
The isolated area is between the work area for game control, the work area for debugging (inspection function), and the work area for calculating the character ratio, and the work area for debugging (inspection function), the save area, and the save area for calculating the character ratio. , and is a continuous area with each area (areas before and after). For example, the start address of the isolated area between the work area for game control and the work area for debugging (inspection function) is the next address ("3076H") after the end address of the work area for game control, and the end address is It becomes the previous address ("307FH") of the work area for debugging (inspection function). The isolated area is an area to which access is prohibited, and is configured to forcibly execute reset processing when accessed during processing by the
図271は、その右側に役物比率算出用ワーク領域の詳細を示す。役物比率算出用ワーク領域は、役物比率の算出結果が格納されるメイン領域の他、メイン領域に格納されたデータの複製が格納されるバックアップ領域1及びバックアップ領域2とを設けてもよい。バックアップ領域は一つでも複数でもよい。各領域には、データの誤りを検出するためのチェックコードが付加される。チェックコードは、各領域のデータのチェックサムでも予め定めた値でもよい。チェックコードは、スロットマシン4000の電源投入時に初期化処理で設定したり、役物比率算出・表示処理においてメイン領域のデータが更新される毎に設定したり、初期化処理(図274のステップS1020)において設定してもよい。特に、チェックコードが固定値である場合、初期化処理で正常と判定した又はデータを消去した際にチェックコードを初期化し、初期化処理(図274のステップS1020)において固定値をセットしてもよい。チェックコードは、電断フラグと兼用してもよい。すなわち、メイン領域のチェックコードに所定値が設定されていれば、電断フラグが設定されていると判定してもよい。また、電断フラグに所定値が設定されていれば、各領域のチェックコードが正しい値である(すなわち、各領域のデータが正常である)と判定してもよい。
FIG. 271 shows the details of the role product ratio calculation work area on the right side thereof. The role product ratio calculation work area may include a main area for storing the calculation result of the role product ratio, and a
なお、初期化処理(図274のステップS1020)において、バックアップ領域のデータが正常か否かが判定され、正常であると判定されたバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製するとよい。また、電源遮断時に実行される電源断時処理において、メイン領域の値を各バックアップ領域に複製してもよい。 In the initialization process (step S1020 in FIG. 274), it is determined whether or not the data in the backup area is normal, and the data in the backup area determined to be normal should be copied to the main area. Also, in the power-off processing executed when the power is turned off, the values in the main area may be copied to each backup area.
メイン領域とバックアップ領域1との間、及びバックアップ領域1とバックアップ領域2との間には、未使用空間が設けられる。各領域の間に未使用空間を設けることによって、各領域のアドレスを遠ざけることができ、アドレスの上位桁で各領域を区別できる。
Unused space is provided between the main area and the
図272は、役物比率算出用ワーク領域における各データを格納するためのワークエリアの具体的な構造を示す図である。 FIG. 272 is a diagram showing a specific structure of a work area for storing each data in the role product ratio calculation work area.
図272(A)は、最も簡単な方法のワークエリアの構造を示す。図272(A)に示すワークエリアの構造では、役物払出数、連続役物払出数、総払出数、役物比率、連続役物比率、有利区間遊技数、非有利区間遊技数及び有利区間割合を格納する。役物払出数は、役物作動中(例えば、レギュラーボーナス中)に払い出されるメダルの数である。連続役物獲得球数は、連続役物作動中(例えば、ビッグボーナス中)に払い出されるメダルの数である。総払出数は、ゲームによって払い出された全てのメダルの数である。役物比率は、役物払出数÷総払出数で計算できる。連続役物比率は、連続役物払出数÷総獲払出数で計算できる。有利区間遊技数は、遊技者に有利な遊技状態(例えば、ART(アシスト・リプレイ・タイム)などの手持ちのメダルが減りにくい遊技状態)で実行されたゲーム数であり、非有利区間遊技数は、有利区間以外の遊技状態で実行されたゲーム数である。有利区間割合は、有利区間遊技数÷(有利区間遊技数+非有利区間遊技数)で計算できる。 FIG. 272(A) shows the structure of the work area of the simplest method. In the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 272(A), the number of payouts, the number of consecutive payouts, the total number of payouts, the ratio of prizes, the ratio of consecutive prizes, the number of advantageous section games, the number of non-advantageous section games, and the advantageous section Stores a percentage. The number of prizes paid out is the number of medals paid out while the prize is in operation (for example, during a regular bonus). The number of consecutive award winning balls is the number of medals paid out during continuous award operation (for example, during big bonus). The total number of payouts is the total number of medals paid out in the game. The role ratio can be calculated by dividing the number of payouts by the total number of payouts. The continuous accessory ratio can be calculated by dividing the number of continuous accessory payouts divided by the total number of wins and payouts. The number of games played in an advantageous interval is the number of games played in a game state that is advantageous to the player (for example, a game state in which the number of medals in hand is less likely to decrease, such as ART (Assist Replay Time)), and the number of games played in a non-advantageous interval. , is the number of games executed in a game state other than the advantageous section. The advantageous section ratio can be calculated by dividing the number of games in the advantageous section by (the number of games in the advantageous section + the number of games in the non-advantageous section).
図272(A)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、役物払出数、連続役物払出数、総払出数、有利区間遊技数及び非有利区間遊技数は、後述する図272(B)の総累計に相当し、各々3又は4バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215又は4294967295までの数値を記憶できる。これらのデータはデータに異常が生じない限り消去されないことから、長期間のデータを格納できるように大きな記憶領域を用意している。また、役物比率、連続役物比率及び有利区間割合は、1バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で255までの数値を記憶できる。 Among the structure of the work area shown in FIG. It corresponds to the cumulative total and is a storage area of 3 or 4 bytes each, and can store numerical values up to 16777215 or 4294967295 in decimal. Since these data will not be erased unless an abnormality occurs in the data, a large storage area is provided so that long-term data can be stored. Also, the role product ratio, continuous role product ratio, and advantageous section ratio are storage areas of 1 byte, and can store numerical values up to 255 in decimal.
役物払出数、連続役物払出数、総払出数、有利区間遊技数、及び非有利区間遊技数は、役物比率算出用領域更新処理(図274のステップS1038)で更新され、役物比率、連続役物比率、及び有利区間割合は、役物比率算出・表示処理(図275のステップS1119)で計算され、格納される。 The number of bonus payouts, the number of continuous bonus payouts, the total number of payouts, the number of advantageous zone games, and the number of non-advantageous zone games are updated in the zone update process for calculating the role ratio (step S1038 in FIG. 274), and the role ratio , the continuous role ratio, and the advantageous section ratio are calculated and stored in the role ratio calculation/display process (step S1119 in FIG. 275).
図272(B)は、リングバッファを用いたワークエリアの構造を示す。図272(B)に示すワークエリアの構造では、再遊技回数、入賞払出数、役物払出数、連続役物払出数、遊技回数、役物比率、連続役物比率、有利区間遊技数、非有利区間遊技数及び有利区間割合を格納する。また、各データの記憶領域は、所定数のゲーム毎にn個の記憶領域(例えば、400ゲーム毎に15個の記憶領域)を持つリングバッファによって構成されており、実行されたゲーム数が所定数(400回)になると全てのデータの書き込みポインタが移動して、データが更新される記憶領域が変わる。そして、n番目の記憶領域に所定数の遊技回数のデータが格納された後、書き込みポインタは1番目の記憶領域に移動し、1番目の記憶領域にデータを格納する。 FIG. 272B shows the structure of a work area using a ring buffer. In the structure of the work area shown in FIG. Stores the number of games played in the advantageous section and the ratio of the advantageous section. Each data storage area is configured by a ring buffer having n storage areas for each predetermined number of games (for example, 15 storage areas for every 400 games). When the number (400) is reached, the write pointers for all data are moved, and the storage area where the data is updated changes. Then, after the data of the predetermined number of games is stored in the n-th storage area, the write pointer moves to the first storage area and stores the data in the first storage area.
なお、リングバッファの書き込みポインタ及び読み出しポインタは全てのデータに共通であり、所定の賞球数毎に全てのデータの書き込みポインタが移動する。また、書き込みポインタの移動に伴い、読み出しポインタも移動する。読み出しポインタは、書き込みポインタより一つ遅れた記憶領域を指す。これは400ゲーム分のデータを用いて役物比率を計算するためである。 The write pointer and read pointer of the ring buffer are common to all data, and the write pointers for all data are moved for each predetermined number of winning balls. Further, the read pointer also moves along with the movement of the write pointer. The read pointer points to a storage area one behind the write pointer. This is for calculating the character ratio using data for 400 games.
各データの累計は、リングバッファのn個の記憶領域に格納されているデータの累計値であり、役物比率、連続役物比率の累計の値は各データの累計値から算出された値であり、リングバッファが一巡して、新たなデータを書き込むためにリングバッファの一つの記憶領域にクリアされると、当該クリアされた領域のデータを除外して累計値が計算される。各データの総累計は、過去に収集したデータの累計値であり、役物比率、連続役物比率の累計の値は各データの累計値から算出された値であり、リングバッファが一巡して、新たなデータを書き込むためにリングバッファの一つの記憶領域にクリアされても、当該クリアされた領域のデータを含めて総累計値が計算される。 The cumulative total of each data is the cumulative value of the data stored in the n storage areas of the ring buffer. When the ring buffer is cycled and one storage area of the ring buffer is cleared for writing new data, the cumulative value is calculated excluding the data in the cleared area. The total cumulative value of each data is the cumulative value of the data collected in the past, and the cumulative value of the character ratio and the continuous component ratio is the value calculated from the cumulative value of each data. Even if one storage area of the ring buffer is cleared for writing new data, the total cumulative value is calculated including the data in the cleared area.
図272(B)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、リングバッファ内の再遊技回数、入賞払出数、役物払出数、連続役物払出数及び遊技回数は、各々2バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で65535までの数値を記憶できる。再遊技回数、入賞払出数、役物払出数、連続役物払出数及び遊技回数の累計は、各々3バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215までの数値を記憶できる。累計は例えば400ゲーム×n(n=15の場合は6000ゲーム)分のデータの合計であることから、大きな記憶領域を用意している。再遊技回数、入賞払出数、役物払出数、連続役物払出数及び遊技回数の総累計は、各々3又は4バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215又は4294967295までの数値を記憶できる。総累計はデータに異常が生じない限り消去されないことから、長期間のデータを格納できるように、さらに大きな記憶領域を用意している。また、役物比率及び連続役物比率の累計及び総累計は、各々1バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で255までの数値を記憶できる。有利区間遊技数及び非有利区間遊技数は、各々3バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で16777215までの数値を記憶できる。有利区間割合は、1バイトの記憶領域であり、10進数で255までの数値を記憶できる。 Of the structure of the work area shown in FIG. 272(B), the number of replays, the number of prize payouts, the number of award payouts, the number of continuous award payouts, and the number of games in the ring buffer are each a 2-byte storage area. Numerical values up to 65535 in decimal can be stored. The number of replays, the number of winning prizes, the number of payouts, the number of consecutive payouts, and the total number of games are storage areas of 3 bytes each, and can store values up to 16,777,215 in decimal. A large storage area is provided because the cumulative total is, for example, the sum of data for 400 games×n (6000 games when n=15). The number of replays, the number of prize payouts, the number of payouts of the award, the number of consecutive payouts of the award, and the cumulative total of the number of games are each a storage area of 3 or 4 bytes, and can store numerical values up to 16777215 or 4294967295 in decimal. Since the total cumulative total is not deleted unless an abnormality occurs in the data, a larger storage area is provided so that long-term data can be stored. Also, the sum total and total sum of the role ratio and the continuous role ratio are each a storage area of 1 byte, and can store numerical values up to 255 in decimal. The number of games played in an advantageous section and the number of games played in a non-advantageous section are each a 3-byte storage area, and can store numerical values up to 16777215 in decimal. The advantageous interval ratio is a 1-byte storage area, and can store numerical values up to 255 in decimal.
なお、リングバッファを構成する各記憶領域に格納されるデータに対応するゲーム数を多くする(例えば、600ゲーム)にすることによって、時系列のデータを格納するための連続する記憶領域の数(n)を10に減らしても、累計で同じ6000ゲーム分のデータを格納できる。このため、リングバッファとして使用する記憶領域のサイズを小さくできる。 By increasing the number of games corresponding to the data stored in each storage area constituting the ring buffer (for example, 600 games), the number of continuous storage areas for storing time-series data ( Even if n) is reduced to 10, the data for the same 6000 games in total can be stored. Therefore, the size of the storage area used as the ring buffer can be reduced.
図272(B)に示すワークエリアの構造のうち、役物払出数、連続役物払出数、役物比率、連続役物比率、有利区間遊技数、非有利区間遊技数、有利区間割合は、図272(A)における説明と同じである。再遊技回数は、リプレイとなったゲームの数である。入賞払出数は、ゲームによって払い出された全てのメダルの数である。遊技回数は、実行されたゲームの回数であり、この値が所定数になると書き込みポインタが移動する。 Among the structure of the work area shown in FIG. The description is the same as in FIG. 272(A). The number of replays is the number of games that have been replayed. The winning payout number is the total number of medals paid out in the game. The number of games played is the number of games played, and when this value reaches a predetermined number, the write pointer moves.
再遊技回数、入賞払出数、役物払出数、連続役物払出数、総払出数、有利区間遊技数、及び非有利区間遊技数は、役物比率算出用領域更新処理(図274のステップS1038)で更新され、役物比率、連続役物比率、及び有利区間割合は、役物比率算出・表示処理(図275のステップS1119)で計算され、格納される。 The number of replays, the number of prize payouts, the number of accessory payouts, the number of continuous accessory payouts, the total number of payouts, the number of advantageous section games, and the number of non-advantageous section games are updated in the area update process for calculating the role ratio (step S1038 in FIG. 274). ), and the role ratio, continuous role ratio, and advantageous section ratio are calculated and stored in the role ratio calculation/display process (step S1119 in FIG. 275).
図272(A)に示すデータ構造では、格納されている値が異常であると判定された場合に、初期化処理(図274のステップS1020)で役物比率算出用ワーク領域のデータが消去されるが、他の契機でデータは消去されない。このため、所定期間(例えば、1日、1週間、1月など)毎に役物比率算出用ワーク領域のデータを消去してもよい。同様に、図272(B)の総累計を所定期間毎に消去してもよい。 In the data structure shown in FIG. 272(A), when it is determined that the stored value is abnormal, the data in the role product ratio calculation work area is deleted in the initialization process (step S1020 in FIG. 274). data is not erased by other triggers. For this reason, the data in the work area for calculating the role product ratio may be erased every predetermined period (for example, one day, one week, one month, etc.). Similarly, the total accumulation in FIG. 272(B) may be erased every predetermined period.
また、役物比率算出用ワーク領域のデータや、算出された役物比率が異常値である(例えば、役物比率が100%超、役物比率の算出結果が前回の算出値から大きく変化した、役物払出数>総払出数など)場合、当該異常値を消去してもよい。当該異常値だけでなく、役物比率算出用ワーク領域の全データを消去してもよい。また、役物比率算出用ワーク領域のデータや、算出された役物比率が異常値である場合、異常であることを報知してもよい。また、チェックコードを用いてバックアップ領域のデータを検査し、正常なバックアップ領域のデータをメイン領域に複製後に、再度役物比率を計算してもよい。 Also, the data in the work area for calculating the character ratio or the calculated character ratio is an abnormal value (for example, the character ratio is over 100%, or the calculation result of the character ratio has changed significantly from the previous calculation value. , number of payouts>total number of payouts, etc.), the abnormal value may be deleted. Not only the abnormal value but also all the data in the work area for calculating the role product ratio may be deleted. Further, if the data in the work area for calculating the role product ratio or the calculated role product ratio is an abnormal value, it may be notified that there is an abnormality. Also, the data in the backup area may be inspected using the check code, and after duplicating the normal data in the backup area to the main area, the character product ratio may be calculated again.
[16-3-3.I/O領域の構成]
続いて、I/O領域5300について説明する。I/O領域5300には入出力ポートが対応しており、CPU4601がI/O領域5300にアクセスすることによって各入出力ポートにアクセスすることができる。入出力ポートは、例えば、スイッチ等の入力に関するポートや、大入賞口ソレノイド、LED駆動信号等の出力に関するポートが該当する。入出力ポートの設定(入力設定や出力設定等の使用/未使用に関する設定)は、パラメータ情報設定領域5400の設定値に基づいて設定される。
[16-3-3. Configuration of I/O Area]
Next, the I/
[16-3-4.パラメータ情報設定領域]
続いて、パラメータ情報設定領域5400について説明する。図273は、本実施形態のパラメータ情報設定領域5400の詳細を示す図である。パラメータ情報設定領域5400は各種設定が可能な領域である。例えば、各種設定には、図273に示すように、各制御領域、データ領域の開始/終了アドレスが含まれる。なお、図273では、第三制御領域、役物比率算出用ワーク領域、役物比率算出用退避領域の各領域の開始アドレス及び終了アドレスの定義について図示を省略したが、第三制御領域開始設定及び第三制御領域終了設定は他の制御領域の開始及び終了設定と同様に定義され、役物比率算出用ワーク領域開始設定及び役物比率算出用ワーク領域終了設定は他のワーク領域の開始及び終了設定と同様に定義され、役物比率算出用退避領域開始設定及び役物比率算出用退避領域終了設定は他の退避領域の開始及び終了設定と同様に定義さる。ここで設定された領域以外の領域が未使用(未設定)領域とされる。これにより、未使用領域にCPU4601がアクセスした場合には、強制的にリセット信号がCPU4601に入力されるように構成している。なお、図273には連続した領域に設定しているが、設定領域として連続している必要はなく、例えば、パラメータをグループ化して所定間隔で配置してもよい。
[16-3-4. Parameter information setting area]
Next, the parameter
また、本実施形態では、設定領域以外の領域(ROM5100の第一~四隔離領域、RAM5200の隔離領域)にアクセスした場合には、強制的にリセットを発生させる構成となっている。そこで、意図的に隔離領域にアクセスすることによってリセットが発生することでプログラムの初期起動を行うことが可能となる。スロットマシンではシーケンシャルに処理を実行するため、最後のゲーム処理が完了した後に隔離領域にアクセスすることによって起動処理からプログラムを実行させて再度初期設定を実行することができる。これにより、遊技中に初期設定の機能がノイズ等で設定値とは異なる値に設定されたとしても初期設定が再度実行されることで正常な値を再設定することが可能となる。さらに、初期設定処理では、電断フラグによりRAMクリアを判定するようになっているが、電断フラグをセットすることなく隔離領域にアクセスさせることで強制的にRAMクリアを発生させることが可能となる。一方、前述したパチンコ機では並行して遊技が行われるため、遊技自体が初期化されてしまうと遊技を継続することができなくなってしまうが、スロットマシンの場合にはゲーム終了後に不要となったRAMの情報を初期化する必要があるため、隔離領域にアクセスさせることによってRAMの情報を初期化するための処理を不要にすることができる。
Further, in this embodiment, when an area other than the setting area (the first to fourth isolated areas of the
パラメータ情報設定領域5400に設定される値は、CPU4601の初期設定などのユーザープログラム処理で順次設定するものではなく、ROM4602にパラメータ領域のアドレスと設定値とをプログラムとは別に設定しておくことによって、CPU4601が起動時に制御プログラムを開始する前に、ROM4602に設定されたパラメータ情報をCPUの各機能設定レジスタに順次設定するようになっている。これにより、パチンコ機1の電源投入とともに各種パラメータを設定することができる。各種パラメータの設定値はユーザー側で管理(決定)する情報のため、遊技制御プログラムが記憶されたROM4602に設定されている。
The values set in the parameter
[16-4.遊技制御]
[16-4-1.システムリセット起動処理]
続いて、本実施形態のスロットマシンの制御について説明する。図274は、スロットマシン4000がリセットされた場合に実行されるシステムリセット起動処理の手順を説明するフローチャートである。システムリセット起動処理は、スロットマシン4000の電源投入時や停電発生時などに実行される処理であり、CPU4601にリセット信号が入力された場合に起動する処理である。
[16-4. Game control]
[16-4-1. System reset startup process]
Next, control of the slot machine of this embodiment will be described. FIG. 274 is a flow chart for explaining the procedure of system reset activation processing executed when the
CPU4601は、システムリセット起動処理が開始されると、まず、遊技の実行に必要な各種パラメータを設定するパラメータ設定処理を実行する(ステップS1010)。具体的には、記憶領域に含まれるパラメータ情報設定領域5400に格納された設定値をCPU4601の各機能設定レジスタに設定したり、アクセス領域に割り当てられた各領域のアドレスを設定値として設定する。各領域のアドレスを設定値として設定することにより、例えば、RAM領域5200にワーク領域や退避領域を使用領域として割り当て、使用領域として割り当てられていない領域(図271の隔離領域)は未使用領域として割り当てられる。また、ワーク領域及び退避領域は、それぞれ遊技制御用とデバッグ(検査機能)用(又はその他の用途)に切り分けられている。また、ROM領域5100は、RAM領域5200と同様に、プログラムやデータを格納する領域を使用領域として割り当て、使用領域として割り当てられていない領域は未使用領域として割り当てられる。
When the system reset activation process is started, the
次に、CPU4601は、セキュリティチェック処理を実行する(ステップS1012)。セキュリティチェック処理は、ROM4602に記憶されたデータが正常なデータであるか否かを判定する処理である。ROM4602に記憶されたデータが正常なデータでない場合には、例えば、ROM4602が不正なROMに交換されているおそれがあるので、スロットマシン4000の起動を中止する。さらに、CPU4601は、セキュリティチェックに要する時間が経過するまで待機する(ステップS1014)。
Next, the
なお、スロットマシンの電源投入からセキュリティチェックが終了するまでの処理(ステップS1014までの処理)は、ユーザープログラムによって定義された処理ではなく、開発者が変更できないCPU内のハードウェアで構成される処理となっている。 It should be noted that the processing from power-on of the slot machine to the end of the security check (processing up to step S1014) is not defined by the user program, but is configured by hardware inside the CPU that cannot be changed by the developer. It has become.
続いて、CPU4601は、初期化を行うためのデバイス初期化設定処理を実行する(ステップS1016)。デバイス初期化設定処理では、定期的に所定の処理を実行する定期処理(図275、タイマ割込み処理)の起動設定などの処理を実行する。本実施形態では、乱数機能の設定など遊技の抽選に関する設定をセキュリティチェック後にユーザープログラムによって書き換えることができないようにする機能などをパラメータ設定処理で実行し、これらの機能以外についてはデバイス初期化設定処理で実行している。このようにCPU4601の初期化をパラメータ設定処理とデバイス初期化設定処理とに分けることによって、遊技制御の自由度を高めるとともに遊技において不正が行われにくくしている。
Subsequently, the
さらに、CPU4601は、RAM4603の初期化を実行するか否かを判定する(ステップS1018)。ステップS1018の処理では、RAM4603を初期化するコールドスタートを行うか、バックアップされたRAM4603の内容で遊技に復帰するホットスタートを行うかを判定する。
Furthermore, the
CPU4601は、RAM4603を初期化するコールドスタートを行う場合には(ステップS1018の結果が「Yes」)、RAM4603の初期化を実行する初期化処理を実行する(ステップS1020)。コールドスタートは、パチンコ機1の設定変更操作した場合、RAM4603の内容に異常が発生した場合、電断フラグが設定されていない場合などに行われる。
When performing a cold start to initialize the RAM 4603 (result of step S1018 is "Yes"), the
一方、CPU4601は、RAM4603の内容に基づいて遊技に復帰させるホットスタートを行う場合には(ステップS1018の結果が「No」)、バックアップされたRAM4603の内容に基づいて遊技を復帰させる処理を実行する(ステップS1022)。このとき、復帰処理によって、電断時に中断した処理に復帰する。具体的には、後述するシステムリセット起動処理のステップS1024からステップS1042又は定期処理(図275)のステップS1110からステップS1130までのいずれかの処理で、電断時に中断した処理に復帰させる。
On the other hand, the
なお、本実施形態におけるスロットマシン4000では、停電発生時及び復帰処理実行時にRAM4603に記憶された情報に基づいてチェックサムを算出する。このとき、チェックサムの算出対象をワークとして使用(遊技制御用ワーク領域とデバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域)する全領域のうちデバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域を除いた遊技制御用ワーク領域のみとしてもよい。遊技制御用ワーク領域のみでチェックサムを算出するのは、デバッグ(検査機能)処理は遊技制御処理とは独立性を維持するように作られており、かつ、遊技の結果に影響を与えることのない処理であることから、不十分な検証により多少バグが残ることも考えられ、この場合、そのような処理を実行することで得られた情報が保持されるデバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域をチェックサムの算出対象とすることは、電断から正常に復帰する信頼性を損ねる可能性がある。一方、遊技制御処理は遊技に直接関わるため、バグ等が残ったまま製品に搭載されると、市場で大きなトラブルとなる。場合によっては、販売が中止され、製品の回収が必要とする可能性が考えられ、この場合には製造メーカ及びホールに対して費用面等で甚大な損害をもたらす可能性が極めて高いことから徹底的に検証が行われるために、遊技制御用ワーク領域はデバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域と比較して信頼性が高いためである。
Note that the
CPU4601は、初期化処理が終了すると、又は、一連のゲームが終了すると、新たにゲームを開始するために、遊技初期設定処理を実行する(ステップS1024)。遊技初期設定処理では、一連の遊技制御を行う上で不要となったRAM4603の情報を一旦初期設定状態に戻す処理を実行する。
When the initialization process ends, or when a series of games ends, the
CPU4601は、遊技初期設定処理が終了すると、遊技開始時におけるデバック(検査機能)信号を出力するための情報信号1出力処理を実行する(ステップS1026)。情報信号1出力処理では、デバック用(検査機能)信号を初期状態に設定するなどの処理を行っている。なお、情報信号出力処理は、情報信号1~N出力処理が定義されており、情報信号を出力するタイミングで必要なモジュールが呼び出される。例えば、ゲーム開始時処理内でゲーム開始にともなうデバック(検査機能)信号(リールの回転開始、スタートレバーのON、当選役に関する情報)の出力時、図柄停止処理内で各リールの停止に関するデバック(検査機能)信号(停止操作信号、停止した図柄情報等)の出力時、入賞判定処理内で確定役に関するデバック(検査機能)信号(各リール上で停止表示された確定役、確定役に伴う払出枚数情報、払出時の払出数に関する出力信号の情報(払出メダル数)等)の出力時に、当該処理に必要な「情報信号N出力処理」モジュールが適宜呼び出されて実行される。
After completing the game initial setting process, the
続いて、CPU4601は、遊技者が始動レバー4210を操作する前段階の処理を行う待機処理を実行する(ステップS1028)。始動レバー4210を操作する前段階には、例えば、再遊技(リプレイ)の実行指示がなされたか否か、メダルが投入されたか否か、メダル清算が行われたか否かなどを判定し、さらに、ゲームの設定値の確認等が行われる。
Subsequently, the
始動レバー4210が操作されると、CPU4601は、ゲームを開始させるゲーム開始処理を実行する(ステップS1030)。ゲーム開始処理では、遊技の抽選を行うための乱数値を取得し、入賞役等の判定を行うとともに、リール4301の回転を開始させる。その後、CPU4601は、リール4301が正常な回転速度に到達するまで待機するためのWait処理を実行する(ステップS1032)。
When the starting
CPU4601は、リール4301が正常な回転速度に到達すると、リール停止ボタン4211の入力を受付可能とし、すべてのリール4301が停止するまでの処理を行う図柄停止処理を実行する(ステップS1034)。
When the reels 4301 reach the normal rotational speed, the
さらに、すべてのリール4301が停止すると、CPU4601は、停止した図柄に基づく入賞役を判定する入賞判定処理を実行する(ステップS1036)。入賞判定処理では、入賞役を判定するとともに、入賞と判定された場合には入賞役に対応した設定を行い、入賞役に対応した払出処理を実行するための設定を行う。
Furthermore, when all the reels 4301 are stopped, the
続いて、CPU4601は、現在の遊技状態を判定し、遊技価値として払い出される賞メダルの数を現在の遊技状態に対応した領域に加算して、RAM領域5200の役物比率算出用ワーク領域(図271、図272参照)を更新する(ステップS1038)。ステップS1038の処理は、ステップS1036で払い出されるべき賞メダルがない場合にはスキップでき、CPU4601の負荷を軽減できる。
Subsequently, the
なお、スロットマシン4000が不正を検出して遊技を中止した場合でも、役物比率算出用領域更新処理(ステップS1038)を実行する。不正が検出されたか否かにかかわらず、これらの処理を実行することによって、不正報知中でも役物比率計算用のデータを収集できる。
Note that even when the
最後に、CPU4601は、ゲーム終了時の処理を行うゲーム終了処理を実行する(ステップS1042)。ゲーム終了処理では、入賞役に対応した払出処理を実行し、入賞していない場合、又は、払い出しのない入賞の場合には、当該処理をスキップする。ゲーム終了処理が終了すると、遊技初期設定処理に戻り、ステップS1024からステップS1038までのメインループ処理を実行する。
Finally, the
[16-4-2.定期処理]
続いて、システムリセット初期起動処理のメインループ処理が実行されている間に、あらかじめ定められた周期で起動される割り込み処理である定期処理について説明する。図275は、定期処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[16-4-2. Periodic processing]
Next, periodic processing, which is interrupt processing that is activated at predetermined intervals while the main loop processing of the system reset initial activation processing is being executed, will be described. FIG. 275 is a flowchart showing the procedure of regular processing.
CPU4601は、定期処理が実行されると、まず、全レジスタに格納されている値を退避する(ステップS1110)。このとき、退避されるデータは、図271に示した遊技制御用退避領域に格納される。前述のように、定期処理はメインループ処理が実行されている間に起動される割り込み処理であるため、メインループ処理で使用しているCPUのレジスタを退避することによって復帰後に処理を継続できるようにする必要がある。
When the regular processing is executed, the
続いて、CPU4601は、CPUに内蔵されたウォッチドッグタイマをリセットする(ステップS1112)。これにより、ウォッチドッグタイマを定期的にクリアすることができる。
Subsequently, the
次に、CPU4601は、各種スイッチからの入力信号をサンプリングするスイッチ入力処理を実行する(ステップS1114)。さらに、遊技状態チェック処理を実行する(ステップS1116)。遊技状態チェック処理では、リール4301を回転させる駆動体(ステッピングモータ)の駆動制御に関する処理を行う。具体的には、ステッピングモータのパルス出力、原点位置の検出等を行う。
Next, the
続いて、CPU4601は、遊技制御で使用される各種タイマの更新を行うタイマ計測処理を実行する(ステップS1118)。定期処理は周期的に実行されるため、設定時間は定期処理の実行間隔×設定回数となる。
Subsequently, the
続いて、CPU4601は、表示スイッチ1318が操作されているかを判定し、表示スイッチ1318が操作されていれば、役物比率算出・表示処理を呼び出し、役物比率算出用ワーク領域に格納されたメダルの払出数を参照して役物比率を算出する。そして、算出された役物比率を役物比率表示器1317に表示する(ステップS1119)。役物比率算出・表示処理は、パチンコ機1の実施例で説明した役物比率算出・表示処理(図24、図25)と同じである。また、役物比率の具体的な計算方法、及び役物比率の具体的な表示方法は、パチンコ機1の実施例で説明した方法と同じである。このように、タイマ割込み処理において役物比率算出・表示処理を呼び出して、役物比率を算出することによって、直近のデータによる役物比率(スロットマシン4000の射幸性)を確認できる。
Subsequently, the
なお、表示スイッチ1318が操作されている場合に、全ての種類の値(役物比率、連続役物比率、累計、総累計)を計算してもよいが、表示スイッチ1318の操作毎に、表示される値のみを計算してもよい。また、表示スイッチ1318が操作されているかにかかわらず役物比率を計算し、算出された役物比率を表示スイッチ1318の操作を契機に役物比率表示器1317に表示してもよい。
In addition, when the
続いて、CPU4601は、LEDの制御を行うためのLED出力処理を実行する(ステップS1120)。制御対象のLEDはメイン基板4600で制御されるものが対象であり、例えば、払出枚数表示LED4562である。また、役物比率をLEDに表示するためのデータを出力する。
Subsequently, the
CPU4601は、外部中継端子板4131に信号を出力する情報出力処理を実行する(ステップS1122)。出力された信号は、外部中継端子板4131を介してホールコンピュータ4800に送信される。さらに、CPU4601は、コマンドバッファに記憶されたコマンドを演出制御基板4700に出力する(ステップS1124)。
CPU4601は、遊技に用いられる乱数を更新する乱数更新処理を実行する(ステップS1126)。乱数更新処理では、ソフト処理で生成するための乱数の更新を実行する。ここでは、ソフトウェアのみで生成する乱数の他に、CPUに内蔵されたソフト乱数の更新処理を実行する。CPU内蔵のソフト乱数では、カウント自体はハードウェアで実行するものの、更新の契機を本処理で決定する。このように構成することによって、乱数更新に係るプログラム処理を削減することが可能となる。
The
乱数更新処理が終了すると、CPU4601は、割り込まれた処理(メインループ処理)に復帰するための処理を行う。具体的には、ステップS1110の処理で退避したレジスタの値を復帰させる(ステップS1128)。さらに、割り込みの実行を許可する(ステップS1130)。定期処理(タイマ割込み処理)の実行中は、新たなタイマ割込みが発生したとしても、新たなタイマ割込みはペンディングされ、直前に実行されたタイマ割込み処理が正常に終了して割り込みが許可されてから実行されるようになっている。このため、定期処理(タイマ割込み処理)が多重に実行されることがないように構成されている。
When the random number update process ends, the
[16-4-3.情報信号出力処理]
続いて、システムリセット起動処理などで実行される情報信号出力処理について説明する。情報信号出力処理は、出力信号の機能毎(1~N)に応じて設けられており、複数のモジュールによって構成されている。例えば、「条件装置出力信号用(条件装置作動に係る信号出力)」「抽選判定処理(抽選に係る信号出力)」などがある。出力する信号は異なるものの、各情報出力処理の構成は基本的には同じであるため、それぞれのフローについては説明を割愛する。図276は、本実施形態の情報信号出力処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。
[16-4-3. Information signal output processing]
Next, information signal output processing executed in system reset start-up processing and the like will be described. The information signal output processing is provided according to each output signal function (1 to N), and is composed of a plurality of modules. For example, there are "conditional device output signal (signal output related to conditional device operation)" and "lottery determination processing (signal output related to lottery)". Although the signals to be output are different, the configuration of each information output process is basically the same, so the explanation of each flow is omitted. FIG. 276 is a flow chart showing the procedure of information signal output processing of this embodiment.
CPU4601は、情報信号出力処理が開始されると、まず、CPUの全レジスタの値を退避させる(ステップS1210)。これは、情報信号出力処理を実行することによってレジスタに設定された値が破壊されることを防止するため(破壊しても確実に復帰させるため)であり、全レジスタの値をスタック領域に退避させるようになっている。また、このとき使用されるスタック領域は、デバッグ(検査機能)用退避領域に割り当てられており、遊技制御用退避領域とは切り分けられた異なる領域に割り当てられる。
When the information signal output process is started, the
続いて、CPU4601は、出力する情報信号(デバック用(検査機能)信号)を選択(ON/OFF)するために参照する情報をRAM4603から取得する(ステップS1212)。各情報信号出力処理では、RAM4603に記憶された情報を参照するのみで、当該処理内でRAM4603にデータを書き込むことはなく、書き込みが必要な場合にはデバッグ(検査機能)用ワーク領域に情報出力専用のワークを設け、当該ワークは、情報信号出力処理以外の処理で使用(参照含む)しないように構成する。これにより、情報信号出力処理を実行するプログラムを他の遊技制御プログラムと別の場所に配置しても共通の領域を使用せずに、他の遊技制御プログラムとの独立性を担保することができる。
Subsequently, the
次に、CPU4601は、ステップS1212の処理で取得された情報に基づいて、出力する情報信号を生成し(ステップS1214)、生成した信号を対応するポートに出力する(ステップS1216)。さらに、出力した信号を維持するための時間である情報信号出力時間が経過するまで待機する(ステップS1218)。情報信号出力時間は、あらかじめ決められており、十分な時間を設定することでデバック用(検査機能)信号を送信先に確実に伝達することができる。その後、ステップS1210の処理で退避した全レジスタの値を復帰させ(ステップS1220)、本処理を終了する。
Next, the
以上のように、ステップS1210からステップS1220までの処理で情報信号(デバック用(検査機能)信号)を生成及び出力する。そして、出力するデバック用(検査機能)信号の分だけ、ステップS1210からステップS1220までの処理を実行する。出力信号の機能毎(1~N)に異なる種類及び数の信号を出力する。なお、本実施形態では、機能ごとに複数種類の情報信号出力処理が定義されているように構成されているが、機能に対応する出力信号を定義したテーブルをデバッグ(検査機能)用領域の第二データ領域に用意し、呼び出し元から指定された機能に対応する信号を選択し、出力するように構成することによって、情報信号出力処理を共通化するようにしてもよい。 As described above, the information signal (debugging (inspection function) signal) is generated and output by the processing from step S1210 to step S1220. Then, the processing from step S1210 to step S1220 is executed for the debug (inspection function) signals to be output. Different types and numbers of signals are output for each output signal function (1 to N). In this embodiment, a plurality of types of information signal output processing are defined for each function. Information signal output processing may be made common by preparing two data areas and selecting and outputting a signal corresponding to a function designated by a caller.
以上のように、本実施形態では、遊技制御プログラムを格納する領域(遊技制御用領域)とは明確に区別された領域に、情報信号出力処理などを実行するプログラム(信号出力プログラム)を格納する領域(デバッグ(検査機能)用領域)を設けることによって、パチンコ機1のデバッグ(検査機能)を目的とするプログラムを独立して配置することができる。信号出力プログラムは、パチンコ機1のデバッグ(検査機能)を目的として使用され、遊技の結果に影響を与えることのない処理であって、遊技の公正を害さないものとなっている。また、これ以外の目的(例えば、遊技制御用のプログラムや汎用的なプログラムを配置し、遊技制御用領域の容量の不足を補うため)では、デバッグ(検査機能)用領域にプログラムが配置されないようになっている。
As described above, in the present embodiment, a program (signal output program) for executing information signal output processing etc. is stored in an area clearly distinguished from the area for storing the game control program (game control area). By providing an area (debugging (inspection function) area), a program for debugging (inspection function) of the
信号出力プログラムは、遊技制御プログラムから静的に呼び出された上で実行され、この際、呼び出し先のアドレスが明示されている。さらに、信号出力プログラムは、機能ごとにモジュール化されており、呼び出された際には遊技制御用領域で利用している全レジスタを保護する。また、前述したように、遊技制御用領域のプログラム処理を実行している場合にはデバック(検査機能)用ワーク領域へのアクセスを禁止し、デバッグ(検査機能)用領域のプログラム処理を実行している場合には、遊技制御用ワーク領域の参照のみを許可し、書込を禁止するように構成されている。さらに、デバッグ(検査機能)用領域から遊技制御用領域に配置されたモジュール(サブルーチンを含む)を呼び出すことも禁止するように構成されている。信号出力プログラムを含むデバッグ(検査機能)用領域に配置されたプログラムは、必ずサブルーチン形式で呼び出され、サブルーチン終了後は復帰命令により呼び出し直後に戻る。なお、デバッグ(検査機能)用領域に格納されるモジュールは目的ごとに構成されている。このように構成することによって、信号出力プログラム(デバッグ(検査機能)用領域に配置されたプログラム)の実行により、遊技制御プログラムの実行が影響されないように構成されている。 The signal output program is executed after being statically called from the game control program, and at this time, the address of the call destination is specified. Furthermore, the signal output program is modularized for each function, and protects all registers used in the game control area when called. Also, as mentioned above, when executing the program processing of the game control area, access to the debug (inspection function) work area is prohibited, and the program processing of the debug (inspection function) area is executed. If it is, it is configured to permit only reference to the work area for game control and prohibit writing. Furthermore, it is configured to prohibit calling modules (including subroutines) placed in the game control area from the debug (inspection function) area. The program placed in the debug (inspection function) area including the signal output program is always called in the form of a subroutine, and after the subroutine ends, the return instruction returns immediately after the call. The modules stored in the debug (inspection function) area are configured for each purpose. By configuring in this way, the execution of the game control program is not affected by the execution of the signal output program (the program placed in the debug (inspection function) area).
スロットマシン4000の実施例において、RAM(遊技制御用ワーク領域、役物比率算出用ワーク領域)の消去タイミングは、パチンコ機1の実施例の図21のステップS18~S26と同様でよい。なお、スロットマシン4000は、RAMクリアスイッチを有さず、設定変更キースイッチ4112tが操作されていると、遊技状態のバックアップデータを消去する。
In the embodiment of the
以上のように、本実施形態によれば、前述したパチンコ機の実施例で説明した効果の他、稼働中のスロットマシンの役物比率を正確に計算でき、稼働中の遊技機の射幸性を確認できる。 As described above, according to the present embodiment, in addition to the effects described in the embodiment of the pachinko machine described above, it is possible to accurately calculate the role ratio of the slot machine in operation, and to enhance the gambling nature of the gaming machine in operation. I can confirm.
1 パチンコ機(遊技機)
2 外枠
3 扉枠
4 本体枠
5 遊技盤
5a 遊技領域
930 電源基板ボックス
951 払出制御基板
1300 主制御ユニット
1310 主制御基板
1311 主制御MPU(CPU)
1312 RAM
13121 演算回路
1313 ROM
1314 主制御I/Oポート
1317 役物比率表示器(ベース表示器)
1510 周辺制御基板
1600 メイン液晶表示装置
2002 第一始動口
2004 第二始動口
4000 スロットマシン(遊技機)
4210 始動レバー
4211 リール停止ボタン
4300 図柄変動表示装置
4301 リール
4341 リール駆動モータ
4500 画像表示体
4600 メイン基板(遊技制御装置)
4601 CPU
4602 ROM
4603 RAM
4700 演出制御基板
5100 ROM領域
5200 RAM領域
5300 I/O領域
5400 パラメータ情報設定領域
1 Pachinko machine (game machine)
2
1312 RAM
13121
1314 Main control I/
1510
4210 starting lever 4211
4601 CPU
4602 ROMs
4603 RAM
4700
Claims (1)
前記主制御手段に制御されて遊技に関する情報を表示する表示装置と、
前記表示装置に表示信号を出力する表示信号出力手段と、
リセット信号を出力する初期化手段とを備える遊技機であって、
前記リセット信号は、前記主制御手段と前記表示信号出力手段とへ出力され、
前記初期化手段から前記主制御手段と前記表示信号出力手段に向けて出力される前記リセット信号の経路から分岐した経路であって、前記表示信号出力手段に向かう経路上に信号方向を規制可能に構成された第2の信号方向規制手段を設け、
前記初期化手段から前記主制御手段への前記リセット信号の経路上に前記第2の信号方向規制手段に入力されて前記表示信号出力手段に出力されるリセット信号に同期して前記主制御手段にリセット信号が出力可能に構成された第1の信号方向規制手段を設け、
前記第1の信号方向規制手段は、前記第2の信号方向規制手段と同じようにバッファ回路が複数直列に接続された回路であり、
前記第1の信号方向規制手段と前記第2の信号方向規制手段は、複数のバッファ回路と該バッファ回路の入力と出力に電気的に接続された複数の接続端子を有する同一のワンチップの集積回路である
ことを特徴とする遊技機。 Main control means for performing lottery control and controlling the progress of the game based on the lottery result ;
a display device controlled by the main control means to display information about a game;
display signal output means for outputting a display signal to the display device;
A gaming machine comprising initialization means for outputting a reset signal,
the reset signal is output to the main control means and the display signal output means;
A path branched from a path of the reset signal output from the initialization means to the main control means and the display signal output means, the signal direction being able to be regulated on the path toward the display signal output means. a configured second signal direction regulating means;
In synchronism with the reset signal input to the second signal direction regulating means on the path of the reset signal from the initialization means to the main control means and output to the display signal output means, providing first signal direction regulation means configured to output a reset signal;
The first signal direction regulating means is a circuit in which a plurality of buffer circuits are connected in series like the second signal direction regulating means,
Said first signal direction regulating means and said second signal direction regulating means are integrated on the same one chip having a plurality of buffer circuits and a plurality of connection terminals electrically connected to the inputs and outputs of said buffer circuits. is a circuit
A gaming machine characterized by:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018161494A JP7188738B2 (en) | 2018-08-30 | 2018-08-30 | game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018161494A JP7188738B2 (en) | 2018-08-30 | 2018-08-30 | game machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020031909A JP2020031909A (en) | 2020-03-05 |
| JP2020031909A5 JP2020031909A5 (en) | 2022-03-16 |
| JP7188738B2 true JP7188738B2 (en) | 2022-12-13 |
Family
ID=69666197
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018161494A Active JP7188738B2 (en) | 2018-08-30 | 2018-08-30 | game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7188738B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7185653B2 (en) * | 2020-03-16 | 2022-12-07 | 株式会社平和 | game machine |
| JP7169565B2 (en) * | 2020-04-03 | 2022-11-11 | 株式会社藤商事 | game machine |
| JP7144686B2 (en) * | 2020-04-03 | 2022-09-30 | 株式会社藤商事 | game machine |
| JP7144685B2 (en) * | 2020-04-03 | 2022-09-30 | 株式会社藤商事 | game machine |
| JP7169566B2 (en) * | 2020-04-03 | 2022-11-11 | 株式会社藤商事 | game machine |
| JP7169567B2 (en) * | 2020-04-03 | 2022-11-11 | 株式会社藤商事 | game machine |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002204877A (en) | 2000-11-09 | 2002-07-23 | Taiyo Elec Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2003135778A (en) | 2001-10-31 | 2003-05-13 | Sankyo Kk | Game machine |
| JP2011125625A (en) | 2009-12-21 | 2011-06-30 | Toyomaru Industry Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2011200368A (en) | 2010-03-25 | 2011-10-13 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
| JP2015047375A (en) | 2013-09-03 | 2015-03-16 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
-
2018
- 2018-08-30 JP JP2018161494A patent/JP7188738B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002204877A (en) | 2000-11-09 | 2002-07-23 | Taiyo Elec Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2003135778A (en) | 2001-10-31 | 2003-05-13 | Sankyo Kk | Game machine |
| JP2011125625A (en) | 2009-12-21 | 2011-06-30 | Toyomaru Industry Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2011200368A (en) | 2010-03-25 | 2011-10-13 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
| JP2015047375A (en) | 2013-09-03 | 2015-03-16 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020031909A (en) | 2020-03-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7120596B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7307486B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7307483B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7307488B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7188738B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023026678A (en) | game machine | |
| JP7301371B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP2020000657A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP7178079B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7251695B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP2022190098A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2022190099A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2022179766A (en) | game machine | |
| JP7139044B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023026677A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2022179765A (en) | game machine | |
| JP7120595B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7202017B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7127093B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7301370B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023014303A (en) | game machine | |
| JP7176751B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7120594B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7120593B2 (en) | game machine | |
| JP7307465B2 (en) | game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210823 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220308 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220614 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220809 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20221025 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20221124 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 7188738 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |